JP7499428B1 - Conductor crimping structure with connection terminal - Google Patents
Conductor crimping structure with connection terminalDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7499428B1 JP7499428B1JP2024038979AJP2024038979AJP7499428B1JP 7499428 B1JP7499428 B1JP 7499428B1JP 2024038979 AJP2024038979 AJP 2024038979AJP 2024038979 AJP2024038979 AJP 2024038979AJP 7499428 B1JP7499428 B1JP 7499428B1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- conductor
- crimping
- layer plate
- inner layer
- connection terminal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Connections Effected By Soldering, Adhesion, Or Permanent Deformation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、例えばコネクタハウジングに内装し、相手側コネクタの接続端子と嵌合する小型の接続端子による導体圧着構造に関するものである。The present invention relates to a conductor crimping structure using small connection terminals that are fitted inside a connector housing and engage with the connection terminals of a mating connector.
電気関係部品の小型化、軽量化、集積化に伴い、回路の接続に使用される接続端子には、より小型のものが常に要求されている。このことから、細線化された電線の導体に対応して、特許文献1に係る圧着接続端子が開示されている。As electrical components become smaller, lighter, and more integrated, there is a constant demand for smaller connection terminals used to connect circuits. For this reason, the crimp connection terminal in
この特許文献1に係る圧着接続端子は、圧着片を二層構造とし、この二層構造の圧着片間に空隙部を形成し、細径の導体に対して加締め力を過大に加えて過度の変形等を与えることなく、この空隙部を維持する適度の弾発性を有する加締め力による加締めて固定することにより、撚線から成る細径の導体を確実に圧着接続することを可能としている。The crimp connection terminal according to
従来においては、使用する導体は複数本の芯線を撚り合わせた撚線を用いるが合が殆どであって、導体自体が或る程度の柔軟性、可塑性を有している。従って、特許文献1のように空隙部を設けた圧着接続端子を用いて、適度の弾発性を有する加締め力により導体を圧着すれば、導体が細線であっても不自然に変形することがなく、また導電性等の電気的特性や引き抜き等の機械的特性を悪化させることはない。Conventionally, the conductors used are almost always twisted wires made by twisting together multiple core wires, and the conductors themselves have a certain degree of flexibility and plasticity. Therefore, if a crimp connection terminal with a gap is used as in
しかし、近年においては、主に経済性の観点から、接続端子に接続する信号電線には、導体として単体の銅合金等の金属線の使用が試みられ、その直径も0.25~0.6mm程度の超細線とされている。However, in recent years, mainly from the perspective of economy, attempts have been made to use metal wires such as simple copper alloys as conductors for the signal wires that connect to the connection terminals, with the diameter being made into ultra-fine wires of around 0.25 to 0.6 mm.
このような単体から成る細線導体を従来の端子圧着片により接続する場合は、一般的には断面が図12に示すような単体の導体aを圧着片bにより全体を包み込む圧着構造になる。しかし、芯線を撚り合わせた導体とは異なり、単体の導体aは柔軟性、可塑性に乏しく剛体に近く、特に細線の導体aにあっては、圧着片bが導体aの周囲を均等な加締め力で加締めているとは限らず、必ずしも十分な機械固定力、電気導電性が得られない。When connecting such a thin conductor consisting of a single unit using a conventional terminal crimping piece, the crimping structure generally has a cross section as shown in Figure 12, in which the single conductor a is entirely wrapped by the crimping piece b. However, unlike a conductor made of twisted core wires, the single conductor a has little flexibility or plasticity and is close to a rigid body. In particular, in the case of a thin conductor a, the crimping piece b does not necessarily crimp the periphery of the conductor a with an even crimping force, and sufficient mechanical fixing force and electrical conductivity are not necessarily obtained.
しかも、単体から成る細径の導体を使用した場合には、特許文献1のような空隙部を有する圧着接続端子を用いても、なお導体を良好に圧着できないことが多く、機械的、電気的な問題が生じ易い。一方、通常の導体に対しては、導体の表面に発生し電気的障害となる酸化物や硫化物は圧着時に破壊されて除去し易いが、単体から成る細径の導体ではこの酸化物や硫化物の除去が極めて難しいという問題がある。Moreover, when using a thin conductor made of a single piece, even if a crimp connection terminal with a gap as in
本発明の目的は、上述の課題を解決し、単線から成る導体であっても、導体を確実に加締めて良好な固定力と導電性とを実現できる接続端子による導体圧着構造を提供することにある。The object of the present invention is to solve the above problems and provide a conductor crimping structure using a connection terminal that can reliably crimp the conductor and achieve good fixing force and conductivity, even if the conductor is made of a single wire.
上記目的を達成するための本発明に係る接続端子による導体圧着構造は、導電金属板を打抜き、折曲して導体圧着部を形成し、該導体圧着部の底部からU字状に立ち上げた一対の圧着片を有する圧着接続端子を用いて、前記圧着片により単体の金属線から成る断面円形の導体を加締めて固定した接続端子による導体圧着構造であって、前記各圧着片は、外層板と、該外層板の上端部の折り返し部から内側に折り返して前記外層板に積層した内層板とから成る二層構造であり、前記底部に対して上方左右に位置し、前記外層板と前記内層板との間の前記折り返し部の内側に、それぞれ空隙部を設け、前記内層板と前記導体との間には、前記底部及び一対の前記空隙部から前記導体の中心に向けて集中する3方向の押圧力によって前記内層板に対して変形を与えて形成される3個所の押圧部と、これらの押圧部同士の間に形成される3個所の非押圧部と備えることを特徴とする。The conductor crimping structure using a connection terminal according to the present invention, which is intended to achieve the above object, is a conductor crimping structure using a connection terminal in which a conductor crimping portion is formed by punching and bending a conductive metal plate, and a crimping connection terminal having a pair of crimping pieces that are raised in a U-shape from the bottom of the conductor crimping portion is used to crimp and fix a conductor having a circular cross section made of a single metal wire, and each of the crimping pieces has a two-layer structure consisting of an outer layer plate and an inner layer plate that is folded inward from the folded portion at the upper end of the outer layer plate and laminated on the outer layer plate, and is located on the left and right above the bottom, and has a gap portion on the inside of the folded portion between the outer layer plate and the inner layer plate, and between the inner layer plate and the conductor, three pressing portions are formed by deforming the inner layer plate by pressing forces in three directions that are concentrated from the bottom and the pair of gap portions toward the center of the conductor, and three non-pressing portions are formed between these pressing portions.
本発明に係る接続端子による導体圧着構造によれば、二層構造の圧着片に設けた空隙部を用いて導体を加締めると共に、導体に対し局部的に強い押圧力を集中する押圧部を3個所に設けると共に、これらの押圧部に隣接する3個所の圧着片と導体との間に非押圧部を設けることにより、導体に対する確実な加締めによる固定が可能で、機械的、電気的な信頼性を確保し得る。The conductor crimping structure of the connection terminal according to the present invention uses a gap provided in the two-layered crimping piece to crimp the conductor, and provides three pressure sections that locally concentrate a strong pressure force on the conductor. In addition, non-pressing sections are provided between the conductor and the three crimping pieces adjacent to these pressure sections, allowing the conductor to be securely crimped and fixed, ensuring mechanical and electrical reliability.
本発明を図1~図11に図示の実施例に基づいて詳細に説明する。
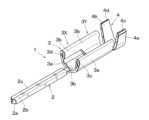
図1は本発明に係る接続端子による導体圧着構造で使用する実施例の圧着接続端子1の斜視図である。この圧着接続端子1は例えば厚さ0.1mmの薄肉の黄銅製であり、予め両表面に銅メッキ、スズメッキ等を施した1枚の導電金属板を打抜き、接続部、圧着部等が折曲により形成されている。 The present invention will be described in detail based on the embodiments shown in FIGS.
1 is a perspective view of a
圧着接続端子1の前方側には、相手側コネクタの接続端子と接続する例えば雄型挿入部である接続部2が形成され、後方側に導体圧着部3、被覆圧着部4が順次に配列されている。また、導体圧着部3は、長手方向に沿って前方から圧着前部3Xと圧着後部3Yとに区分されている。実際の圧着接続端子1には、コネクタハウジング内での姿勢を安定させるためのスタビライザや、コネクタハウジングに対する前後方向への抜け出しを防止するための係止部等が付設されることもあるが、これらの公知の機構の図示は省略している。The front side of the
図2は圧着接続端子1に成型する前の導電金属板5の打抜いた状態の平面図であり、接続部2、導体圧着部3、被覆圧着部4が素材として平面状に区画化されている。被覆圧着部4の更に後方には、打抜いた状態の圧着接続端子同士1を連結するための送り片5aが設けられており、各圧着接続端子1の後端の被覆圧着部4が連結片5bを介して送り片5aに接続されている。なお、送り片5aにはパイロット孔5cが設けられ、圧着接続端子1のその後の成型工程において、導電金属板5を間欠的に搬送するために使用される。Figure 2 is a plan view of the
このように打抜かれた導電金属板5は、例えば必要に応じて面取りや表面処理が行われた後に、送り片5aにより搬送されながら、フォーミングプレスによる各成型工程において、接続部2、導体圧着部3、被覆圧着部4が順次に折曲され、図1に示す圧着接続端子1に成型される。そして、成型後に連結片5bは切断され、各圧着接続端子1は個々に分離される。The
接続部2においては、図1、図2に示すように、導電金属板5の下板とする底板2aの両側から上板となる折返片2b、2cが、点線に沿って上側に折り返され、更に折返片2b、2cの両縁同士が突き合わされた二層構造の雄型挿込端とされている。なお、接続部2は他の雄型形状や、或いは雌型の受用接続部とする場合もある。As shown in Figures 1 and 2, in the
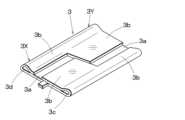
図2に示す導電金属板5では、圧着前部3X、圧着前部3Xはそれぞれ、中央に配置された外層板3aと、この外層板3aの両側から幅方向に延在され、幅方向の長さが異なる2枚の内層板3bとから構成されている。導体圧着部3の2本の長手方向の点線は、後述する折曲工程で外層板3aから内層板3bを内側に折り返す位置を示している。In the
図3は折曲工程の1工程における導体圧着部3の斜視図である。圧着前部3X、圧着後部3Yでは、内層板3bが外層板3aの上端部からそれぞれ折り返し部において内側に折り返されて積層した二層構造とされている。そして、圧着前部3Xの片側の内層板3bの幅が長く延在され、圧着後部3Yでは他側の内層板3bの幅が長くされている。更に、圧着前部3X、圧着後部3Yの折り返し部の内層板3bと外層板3aの間のそれぞれには、断面が例えば水滴形状、風船形状、円形状、楕円形状等の空隙部3c、3dが形成されている。なお、圧着前部3Xの空隙部3cと圧着後部3Yの空隙部3dとは長手方向に連通し、圧着前部3Xの空隙部3dと圧着後部3Yの空隙部3cとは長手方向に連通している。Figure 3 is a perspective view of the
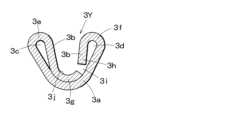
次の折曲工程において、圧着前部3X及び圧着後部3Yでは、両側の外層板3a、内層板3bをそれぞれ図4及び図5に示すように、第1、第2圧着片3e、3fとして、斜め上方に向けてU字状に立ち上げている。この状態において、圧着前部3Xと圧着後部3Yとは左右対称とされている。圧着前部3Xの第1圧着片3e側の内層板3bは外層板3aの上端部の折り返し部から下方に向けられ端縁部3gは外層板3aによる底部を覆い、更に第2圧着片3fの立ち上がり部の略中間位置にまで外層板3aに沿って長く延在されている。一方、第2圧着片3f側の内層板3bは外層板3aの上端部の折り返し部から下方に向けられ、端縁部3hは第2圧着片3fの立ち上がり部の略中間位置までと短く延在されている。そして、内層板3bの端縁部3g、端縁部3h同士との間には、外層板3a上に沿った隙間3iが形成されている。In the next folding process, the
このように、圧着前部3Xと圧着後部3Yとを左右対称としているのは、導体圧着部3の長さを大きくした場合に、後述する圧着工程において、導体に対する圧着力が左右不均衡となり易く、圧着接続端子1が捩れることを防止し、圧着力を左右均等に加えるためである。The reason why the front crimping
単体の導体6を圧着接続端子1により圧着接続するに際しては、先ず図6に示すように、絶縁被覆部が剥離された状態の、例えば直径0.32mmの例えば銅合金である金属線から成る導体6を、圧着接続端子1の長手方向に沿って圧着前部3Xの第1、第2圧着片3e、3fの間に挿入し、内層板3bの底部3j上に載置する。なお、圧着後部3Yにおいても、導体6に対する圧着は同時にかつ同様になされるので、以後の圧着工程は圧着前部3Xについてのみ説明する。When crimping a
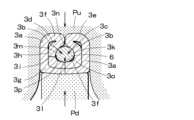
導体圧着装置による導体6に対する圧着工程では、プレス上型Puとプレス下型Pdとの間に第1、第2圧着片3e、3fを配置した状態で、プレス上型Puの下降、プレス下型Pdの上昇を相対的に行う。なお、このプレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdは、圧着前部3Xと圧着後部3Yとを区別することなく一体に作動するようにされている。In the process of crimping the
プレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdとの作動により、図7に示すように、第1、第2圧着片3e、3fはプレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdの形状に従って導体6を包み込むように変形する。この過程で、第1、第2圧着片3e、3fへの加締めにより、内層板3bの端縁部3g、3h間の隙間3iは縮小され、空隙部3c、3dの大きさも縮小され、外層板3aの側面はプレス上型Puにより立ち上げられ、外層板3a、内層板3bによる底部は、プレス下型Pdに沿ってU字形から偏平状に変形する。By the operation of the press upper die Pu and press lower die Pd, the first and
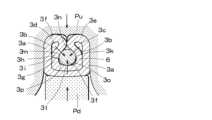
更に、図8に示すようにプレス上型Puとプレス下型Pdの作動により、強い加締め力が第1、第2圧着片3e、3fに加えることにより、第1、第2圧着片3e、3fは更に導体6を包み込むように変形する。このとき、導体6には主に矢印で示す3方向からの押圧力、つまり、底部3jから導体6の中心に向う導体6への上方向の押圧力、及び底部3jに対して上方左右に位置する空隙部3c、3dから導体6の中心に向う導体6への斜め下方向の押圧力が加えられる。そして、これらの導体6の中心に向けて集中して掛かる押圧力の3方向の角度は、約120度間隔とされている。Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 8, by operating the press upper die Pu and press lower die Pd, a strong crimping force is applied to the first and
更なる加締めにより、図9に示すように、第1、第2圧着片3e、3fでは、加締め過程で外層板3a、内層板3bの厚みが増加すると共に、空隙部3c、3dの大きさは更に縮小される。この加締め過程で、プレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdによる押圧力を特に前述の3方向から局部的に集中させ、この押圧力を集中させた3個所において、内層板3dが導体6に接する押圧部3k、3l、3mを設けると共に、これらの押圧部3k、3l、3m同士の間の導体6に沿った3個所においては、内層板3dから導体6に対して押圧力を加えることがなく、この部分における内層板3dと導体6の間に3個所の非押圧部3n、3o、3pを設ける。As a result of further crimping, as shown in Figure 9, the thickness of the
即ち、導体6の外周面に対して導体6を固定する押圧力を3個所に集中させることにより、押圧部3k、3l、3mにおいて導体6のこの部分の酸化物や硫化物から成る被膜を破壊しこれを除去して、内層板3dとの間における電気的接続の信頼性を高めることができる。In other words, by concentrating the pressing force that fixes the
プレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdによる押圧によって、内層板3bと導体6との間に、押圧部3k、3l、3mと非押圧部3n、3o、3pとが形成されるまでの間には、概ね次のような現象が発生している。By the time the pressing by the upper press die Pu and the lower press die Pd forms the pressed
外層板3aは、プレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdによる押圧力を受けて変形し、降伏点を超えると塑性変形する。従って、プレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdによる押圧を解除しても、外層板3aは元の形状に戻ることはない。これに対し、内層板3bは、プレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdによる押圧力を、外層板3aを介して受けている。内層板3bのうち、外層板3aに沿って延在する部分においては、外層板3aに沿った形状に塑性変形する。The
なお、内層板3bのうち、空隙部3c、3dに沿って延在する部分においては、外層板3aを介して内層板3bに掛かる押圧力は、内層板3bの端縁部3g、3h間の隙間3iを縮小させることに費やされた後に、空隙部3c、3dを縮小させることに使われることになる。このため、外層板3aにかかる押圧力が外層板3aの降伏点を超えたからといって、直ちに内層板3bにかかる押圧力も内層板3bの降伏点を超えるものとはならない。そこで、このような外層板3aと内層板3bとの間に存在する押圧力の掛かり方の違いを利用することによって、内層板3bに生ずる変形において、その全部を塑性変形へと至らしめることなく、弾性変形に留まる部分を残すことができる。In the portion of the
従って、プレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdによる押圧を解除すると、内層板3bにおいて、弾性変形により縮小した空隙部3c、3dが元の大きさへと拡大しようとする弾性復元力が生ずる。この弾性復元力は、内層板3bのうち、空隙部3c、3dに沿って延在する部分を外層板3aから離間させる方向に、つまり内方へと押し戻そうとする。このとき、内方へと押し戻されようとする内層板3bは、導体6と接して導体6を押圧し、内層板3bは導体6に対して付勢力を伴って接し、導体6が内層板3bの間に圧着されることになる。Therefore, when the pressure from the upper press die Pu and the lower press die Pd is released, an elastic restoring force is generated in the
そして、本実施例はこのような加締めを可能とする第1、第2圧着片3e、3fと、単体から成る導体6とを組み合わせることによって、次のような作用効果が得られることになる。In this embodiment, by combining the first and second crimping
導体が複数本の芯線を撚り合わせて成る場合においては、各芯線の間に隙間が存在するため、導体が内層板3bによって押圧されると、各芯線は互いの間の隙間を埋めるようにして移動する。その結果、導体の全体としての形状は、内層板3bに囲まれた空間の形状に沿う形状へと変化する。このため、内層板3bからの押圧力は各芯線を移動させることに使われるため、各芯線が内層板3bから受ける押圧力は、導体が単線のものから成る場合に比較して小さい。このことに応じて、各芯線の表面を覆う酸化物等の被膜が破壊される程度もまた小さいものとなる。When a conductor is made of multiple twisted core wires, there are gaps between each core wire, so when the conductor is pressed by the
これに対し、導体6が単体である場合においては、導体が撚線の場合のように芯線の移動を伴わないことから、内層板3bからの押圧力は導体6の3個所に集中して掛かり続けることとなる。その結果として、導体6と内層板3bとの接触面積は小さくなるものの、導体6と内層板3bとが接する3個所の押圧部3k、3l、3mにおいて、大きな付勢力を伴う接触を可能とし、十分な機械的性能、電気的性能が得られ、更には酸化物等から成る被膜の破壊除去をも可能とする。In contrast, when the
上述の作用効果は、導体として撚線を採用した場合からは、予見することができず、単体の導体6を使用する本発明において新たに見出されたものである。即ち、導体として複数本の芯線を撚り合わせて成るものを採用した場合には、断面において周面で接触するに対し、導体として単線を採用した場合には複数の点で接触することにおいて、両者の発想は互いに異なる。The above-mentioned effects could not be predicted when a twisted wire is used as the conductor, but were newly discovered in the present invention, which uses a
このように、空隙部3c、3dに加えて、導体6の上方及び下方両側と内層板3bとの間に、3個所の非押圧部3n、3o、3pを設けて、外層板3a、内層板3bにより導体6を加締めることにより、図10に示すように、空隙部3c、3d、非押圧部3n、3o、3pが更に縮小された接続端子による導体圧着構造が得られる。この構造により、導体6への加締めは、弾力性を保持しながら確実になされ、電気的、機械的な信頼性が確保されることになる。In this way, in addition to the
なお図10においては、3個所の押圧部3n、3o、3pに空隙が生じているように図示しており、導体6に対して3個所の押圧部3k、3l、3mによる3方向からの付勢力を伴う接触がなされている。導体6を押圧部3k、3l、3mにより加締めて圧着固定した際に、非押圧部3n、3o、3pが形成されるが、これらの非押圧部3o、3pについては、非押圧状態で内層板3bと導体6とを接触させて空隙が生じないようにしてもよい。In FIG. 10, the three
つまり、底部3jからの押圧力の上方向と空隙部3cからの押圧力の左下斜め方向との間に形成される非押圧部3oと、底部3jからの押圧力の上方向と空隙部3dからの右下斜め方向との間に形成される非押圧部3pに対しては、内層板3bと導体6とを接触させて空隙が生じないようにし、空隙部3cからの押圧力の左下斜め方向と空隙部3dからの右下斜め方向との間に形成される非押圧部3nのみに空隙が生ずるようにしてもよい。更には、非押圧部3n、3o、3pの全てが、非押圧状態で内層板3bと導体6とを接触させて空隙が生じないようにすることもできる。In other words, the
このようにして、プレス上型Pu、プレス下型Pdによる押圧によって、内層板3bと導体6との間には、底部3j及び空隙部3c、3dが存在する3方向から導体6の中心に向けて押圧力を集中する。これにより、内層板3bに対して変形を与えて形成される3個所の押圧部3k、3l、3mと、これらの押圧部3k、3l、3mの形成に伴い押圧部3k、3l、3m同士の間に形成される3個所の非押圧部3n、3o、3pとが存在することになる。In this way, by pressing with the upper press die Pu and the lower press die Pd, pressing forces are concentrated between the
また、被覆圧着部4においては、導体圧着装置と連動する被覆圧着装置によって、絶縁被覆部7の外側を被覆圧着部4の一対の被覆圧着片4a、4bにより加締めることにより、辺部4c、4dが絶縁被覆部7に喰い込むようにして圧着される。これにより、被覆圧着部4により絶縁被覆部7を固定し、電線に作用する引抜力に対抗することができる。In addition, in the
図11は導体6を導体圧着部3の圧着前部3X、圧着後部3Yにより圧着接続し、被覆圧着部4では被覆圧着片4a、4bにより絶縁被覆部7を圧着固定した状態を示している。Figure 11 shows the state in which the
なお、実施例においては、導体圧着部3は前後に圧着前部3Xと圧着後部3Yに分けて設けたが、このように分けることなく、導体圧着部3の全体をこれらの何れか一方のみの形状とすることもできる。また、内層板3bの長さは左右均等な長さとし、左右対称形としてもよい。In the embodiment, the
更に、実施例においては、空隙部3c、3dを圧着接続端子1に予め形成しておいたが、導体圧着工程時において、プレス上型Puの形状によって、外層板3aと内層板3bとの間に空隙部3c、3dを形成することもできる。Furthermore, in the embodiment, the
1 圧着接続端子
2 接続部
3 導体圧着部
3X 圧着前部
3Y 圧着後部
3a 外層板
3b 内層板
3c、3d 空隙部
3e、3f 圧着片
3k、3l、3m 押圧部
3n、3o、3p 非押圧部
4 被覆圧着部
5 導電金属板
6 導体
7 絶縁被覆部 REFERENCE SIGNS
Claims (4)
Translated fromJapanese前記各圧着片は、外層板と、該外層板の上端部の折り返し部から内側に折り返して前記外層板に積層した内層板とから成る二層構造であり、
前記底部に対して上方左右に位置し、前記外層板と前記内層板との間の前記折り返し部の内側に、それぞれ空隙部を設け、
前記内層板と前記導体との間には、前記底部及び一対の前記空隙部から前記導体の中心に向けて集中する3方向の押圧力によって前記内層板に対して変形を与えて形成される3個所の押圧部と、これらの押圧部同士の間に形成される3個所の非押圧部と備えることを特徴とする接続端子による導体圧着構造。 A conductor crimping structure using a connection terminal, in which a conductor crimping portion is formed by punching and bending a conductive metal plate, and a crimping connection terminal having a pair of crimping pieces standing up in a U-shape from a bottom of the conductor crimping portion is used to crimp and fix a conductor having a circular cross section made of a single metal wire by the crimping pieces,
Each of the pressure-bonding pieces has a two-layer structure including an outer layer plate and an inner layer plate folded inward from a folded-back portion at an upper end of the outer layer plate and laminated on the outer layer plate,
A gap is provided on the left and right sides of the bottom and on the inside of the folded portion between the outer layer board and the inner layer board,
A conductor crimping structure using a connection terminal, characterized in that between the inner layer plate and the conductor, there are three pressed portions formed by deforming the inner layer plate by three-directional pressing forces concentrated from the bottom and a pair of the void portions toward the center of the conductor, and three non-pressed portions formed between these pressed portions.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2024038979AJP7499428B1 (en) | 2024-03-13 | 2024-03-13 | Conductor crimping structure with connection terminal |
| EP24207170.2AEP4560838A1 (en) | 2023-11-24 | 2024-10-17 | Conductor crimp structure using connection terminal |
| CN202411636763.5ACN120049216A (en) | 2023-11-24 | 2024-11-15 | Conductor press-connection structure for connecting terminal |
| US18/950,180US20250174916A1 (en) | 2023-11-24 | 2024-11-18 | Conductor crimp structure using connection terminal |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2024038979AJP7499428B1 (en) | 2024-03-13 | 2024-03-13 | Conductor crimping structure with connection terminal |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP7499428B1true JP7499428B1 (en) | 2024-06-13 |
| JP2025139896A JP2025139896A (en) | 2025-09-29 |
Family
ID=91377593
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2024038979AActiveJP7499428B1 (en) | 2023-11-24 | 2024-03-13 | Conductor crimping structure with connection terminal |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7499428B1 (en) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6506877B1 (en) | 2018-10-29 | 2019-04-24 | 株式会社デルタプラス | Crimp connection terminal |
| JP2021144898A (en) | 2020-03-13 | 2021-09-24 | 株式会社デルタプラス | Method for terminal crimp to wire conductor and crimp connection terminal used for the method |
- 2024
- 2024-03-13JPJP2024038979Apatent/JP7499428B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6506877B1 (en) | 2018-10-29 | 2019-04-24 | 株式会社デルタプラス | Crimp connection terminal |
| JP2021144898A (en) | 2020-03-13 | 2021-09-24 | 株式会社デルタプラス | Method for terminal crimp to wire conductor and crimp connection terminal used for the method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2025139896A (en) | 2025-09-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101100950B1 (en) | Wire with terminal connector and terminal connector | |
| JP5603521B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing connection structure, connection structure, wire harness, crimping member, and crimping apparatus | |
| CN111106454B (en) | Crimp connection terminal | |
| JP2009152110A (en) | Crimping structure and crimping method | |
| EP3425735B1 (en) | Crimp connection terminal and production method therefor | |
| JP2018147828A (en) | Crimp connection terminal and method of connecting the crimp connection terminal | |
| JP2009123622A (en) | Crimp terminal for aluminum wire | |
| JP2009245695A (en) | Crimp terminal | |
| JP6744975B1 (en) | Crimp connection terminal | |
| JP7499428B1 (en) | Conductor crimping structure with connection terminal | |
| JP6858896B1 (en) | Crimping connection terminal | |
| JP7504336B1 (en) | Conductor crimping structure with connection terminal | |
| JP2010067478A (en) | Terminal fitting, and electric wire with terminal fitting | |
| EP4560838A1 (en) | Conductor crimp structure using connection terminal | |
| JP2933929B2 (en) | Electrical connector | |
| JP2020071908A (en) | Crimp connection terminal | |
| JP6770659B1 (en) | Wire conductor crimping method for connection terminals | |
| EP1662615A2 (en) | Electric connector | |
| WO2017150644A1 (en) | Crimp connection terminal and production method therefor | |
| JP7467516B2 (en) | Crimp Terminal | |
| JP5195191B2 (en) | Terminal fittings and electric wires with terminal fittings | |
| JP2019057392A (en) | Crimp terminal, terminal with electric wire, and manufacturing method thereof | |
| EP3968473B1 (en) | Method of manufacturing female terminal | |
| JP2010118238A (en) | Connection structure of terminal metal fitting to electric wire | |
| JP2009193889A (en) | Terminal fitting and wire harness |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20240313 | |
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date:20240313 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20240409 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20240419 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20240507 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20240603 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:7499428 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |