JP7467554B2 - An Autonomous Job Queuing System for Hardware Accelerators - Google Patents
An Autonomous Job Queuing System for Hardware AcceleratorsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7467554B2 JP7467554B2JP2022146968AJP2022146968AJP7467554B2JP 7467554 B2JP7467554 B2JP 7467554B2JP 2022146968 AJP2022146968 AJP 2022146968AJP 2022146968 AJP2022146968 AJP 2022146968AJP 7467554 B2JP7467554 B2JP 7467554B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- tcb
- queue
- tcbs
- processor
- priority level
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/48—Program initiating; Program switching, e.g. by interrupt
- G06F9/4806—Task transfer initiation or dispatching
- G06F9/4843—Task transfer initiation or dispatching by program, e.g. task dispatcher, supervisor, operating system
- G06F9/4881—Scheduling strategies for dispatcher, e.g. round robin, multi-level priority queues
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Advance Control (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese関連出願の相互参照
本出願は、2019年7月27日に出願されたインド特許出願201941030394の利益を主張し、その主題は、参照によりその全体が本明細書に組み込まれる。CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application claims the benefit of Indian Patent Application No. 201941030394, filed on July 27, 2019, the subject matter of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
本開示は、概して、コンピューティングの分野に関し、より具体的には、コンピューティングデバイスにおけるジョブキューイングのためのシステムおよび方法に関するが、これに限定されない。The present disclosure relates generally to the field of computing, and more specifically, but not by way of limitation, to systems and methods for job queuing in a computing device.
ハードウェアアクセラレータは、有限インパルス応答(FIR)、無限インパルス応答(IIR)、高速フーリエ変換(FFT)などのような、ほとんどの一般的なデジタル信号プロセッサ(DSP)ルーチンをオフロードするために、DSPにおいてユビキタスである。計算能力を大幅に増強するという考えであり得るとしても、データフローを設定し、実行を追跡し管理しなければならない命令処理コアの必要性により、それらの有効使用には高い障害が存在することが多い。しばしば、このようなコア駆動型の管理は、同様にかなりの命令サイクルを必要とする。これにより、コアとアクセラレータが処理負荷を効率的に分担しなければならないDSPを通るデータフローにそれらをシームレスに統合することは非常に困難である。その結果、コア実行時間およびオーバーヘッドを組み合わせた場合と比較して、アクセラレータがコンピューティングタスクを何倍も速く完了することができる場合を除き、アクセラレータは未使用のままであり得る。Hardware accelerators are ubiquitous in digital signal processors (DSPs) to offload most common DSP routines, such as finite impulse response (FIR), infinite impulse response (IIR), fast Fourier transform (FFT), etc. Even though it may be an idea to greatly increase computational power, there are often high obstacles to their effective use due to the need for instruction processing cores that must set up the data flow and track and manage execution. Often, such core-driven management requires significant instruction cycles as well. This makes it very difficult to seamlessly integrate them into the data flow through the DSP, where cores and accelerators must efficiently share the processing load. As a result, accelerators may remain unused unless they can complete a computing task many times faster compared to the combined core execution time and overhead.
実施形態は、ハードウェアアクセラレータと通信可能に結合されたプロセッサを含む電子デバイスに関し得る。プロセッサは、TCBにおける優先順位レベルの指標に基づいて、TCBがTCBのキュー内に挿入されるべき位置を識別するように構成されてもよい。ハードウェアアクセラレータは、TCBsのキューに関連するジョブを、キュー内のTCBsの順序に関連する順序で行い得る。Embodiments may relate to an electronic device that includes a processor communicatively coupled to a hardware accelerator. The processor may be configured to identify a location in a queue of TCBs where the TCB should be inserted based on an indication of a priority level in the TCB. The hardware accelerator may perform jobs associated with the queue of TCBs in an order related to the order of the TCBs in the queue.
一実施形態は、プロセッサであって、TCBにおいて、TCBの優先順位レベルの指標を識別し、優先順位レベルの指標に基づいて、複数のTCBsのキュー内の位置を識別し、かつ識別された位置でキューにTCBを挿入する、プロセッサと、プロセッサと通信可能に結合されたハードウェアアクセラレータであって、複数のTCBのキュー内のTCBに関連するジョブを行い、複数のTCBのキュー内のTCBの順序に従ってTCBに関連するジョブを行うハードウェアアクセラレータと、を備える、コンピューティングデバイスに関し得る。One embodiment may relate to a computing device including a processor that identifies, in the TCB, an indication of a priority level of the TCB, identifies a position in a queue of multiple TCBs based on the priority level indication, and inserts the TCB into the queue at the identified position; and a hardware accelerator communicatively coupled to the processor that performs a job associated with the TCB in the queue of multiple TCBs and that performs the job associated with the TCB according to an order of the TCBs in the queue of multiple TCBs.
別の実施形態は、ハードウェアアクセラレータと通信するための通信インターフェースと、通信インターフェースと結合された論理であって、TCBにおいて、TCBの優先順位レベルの指標を識別し、優先順位レベルの指標に基づいて、複数のTCBsのキュー内の位置にTCBを挿入し、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、キュー内のそれらの位置に基づいて、複数のTCBのそれぞれを実行する、論理と、を備える、プロセッサに関し得る。Another embodiment may relate to a processor comprising a communications interface for communicating with a hardware accelerator, and logic coupled to the communications interface for identifying, in the TCB, an indication of a priority level of the TCB, inserting the TCB into a position in a queue of multiple TCBs based on the priority level indication, and the hardware accelerator executing each of the multiple TCBs based on their position in the queue.
別の実施形態は、命令を含む1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体であって、命令は、電子デバイスによって実行されると、電子デバイスのプロセッサに、複数のTCBのキューを識別することであって、複数のTCBのそれぞれのTCBが、キュー内のそれぞれのTCBの優先順位レベルの指標を含み、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、TCBの優先順位レベルに従ってそれぞれのTCBに関連するジョブを行う、識別することと、キューに関連するアプリケーションプログラミングインターフェース(API)を実行することと、APIの実行に基づいてキューを改変することと、を行わせる、非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体に関し得る。Another embodiment may relate to one or more non-transitory computer-readable media including instructions that, when executed by an electronic device, cause a processor of the electronic device to: identify a queue of a plurality of TCBs, each TCB of the plurality of TCBs including an indication of a priority level of each TCB in the queue, and a hardware accelerator to perform a job associated with each TCB according to the priority level of the TCB; execute an application programming interface (API) associated with the queue; and modify the queue based on execution of the API.
次の詳細な説明では、同様の番号が全体を通して同様の部品を指定し、本開示の主題が実施され得る例示的な実施形態として示される、本明細書の一部を形成する添付の図面を参照する。本開示の範囲から逸脱することなく、他の実施形態を利用してもよく、構造的または論理的な変更を加えてもよいことを理解されたい。したがって、次の詳細な説明は限定的な意味でとるべきではない。In the following detailed description, references are made to the accompanying drawings, which form a part hereof, in which like numerals designate like parts throughout and which show as exemplary embodiments in which the subject matter of the present disclosure may be practiced. It is to be understood that other embodiments may be utilized and structural or logical changes may be made without departing from the scope of the present disclosure. Therefore, the following detailed description is not to be taken in a limiting sense.
本開示の目的上、「AまたはB」という句は、(A)、(B)、または(AおよびB)を意味する。本開示の目的上、「A、B、またはC」という句は、(A)、(B)、(C)、(AおよびB)、(AおよびC)、(BおよびC)、または(A、B、およびC)を意味する。For purposes of this disclosure, the phrase "A or B" means (A), (B), or (A and B). For purposes of this disclosure, the phrase "A, B, or C" means (A), (B), (C), (A and B), (A and C), (B and C), or (A, B, and C).
説明は、「一実施形態において」または「実施形態において」という句を使用する場合があり、それは、同じまたは異なる実施形態のうちの1つ以上を各々指すことができる。さらに、本開示の実施形態に関して使用されるとき、「備える」、「含む」、「有する」などの用語は同義である。The description may use the phrase "in one embodiment" or "in an embodiment," which may each refer to one or more of the same or different embodiments. Additionally, when used with respect to embodiments of the present disclosure, terms such as "comprising," "including," and "having" are synonymous.
「と結合された」という用語は、その派生語とともに、本明細書で使用され得る。「結合された」とは、次のうちの1つ以上を意味する場合がある。「結合された」とは、2つ以上の要素が直接物理的または電気的に接触していることを意味し得る。しかしながら、「結合された」はまた、2つ以上の要素が互いに間接的に接触するが、それでも互いに協力または相互作用することを意味し得、1つ以上の他の要素が互いに結合されると言われる要素間で結合または接続されることを意味し得る。「直接結合された」という用語は、2つまたは要素が直接接触していることを意味し得る。いくつかの実施形態では、「結合された」とは、2つの要素が物理的に互いの近傍に配置され、それらの間に排他的かつ非常に高速なアクセスを有することを指すことができる。The term "coupled with," along with its derivatives, may be used herein. "Coupled" may mean one or more of the following: "Coupled" may mean that two or more elements are in direct physical or electrical contact. However, "coupled" may also mean that two or more elements are in indirect contact with each other but still cooperate or interact with each other, and may mean that one or more other elements are coupled or connected between the elements that are said to be coupled to each other. The term "directly coupled" may mean that two or elements are in direct contact. In some embodiments, "coupled" may refer to two elements being physically located near each other and having exclusive and very fast access between them.
様々な動作は、特許請求される主題を理解するのに最も役立つ方法で、順番に複数の個別の動作として記載され得る。しかしながら、説明の順序は、これらの動作が必ずしも順序に依存することを暗示するものとして解釈されるべきではない。Various operations may be described as multiple separate operations in a sequence that is most helpful in understanding the claimed subject matter. However, the order of description should not be construed as to imply that these operations are necessarily order dependent.
本明細書で使用されるように、「モジュール」という用語は、1つ以上のソフトウェアまたはファームウェアプログラムを実行する特定用途向け集積回路(ASIC)、電子回路、プロセッサ(共有、専用、もしくはグループ)、もしくはメモリ(共有、専用、もしくはグループ)、組み合わせ論理回路、または記載された機能性を提供する他の好適な構成要素を指してもよく、その一部でもよく、または含んでいてもよい。As used herein, the term "module" may refer to, be a part of, or include an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), electronic circuitry, processor (shared, dedicated, or group), or memory (shared, dedicated, or group), combinatorial logic circuitry, or other suitable components that execute one or more software or firmware programs to provide the described functionality.
上述したように、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、様々な理由で未使用になる場合がある。しかしながら、コアが一定のDSPタスクを専用のハードウェアアクセラレータに効率的にオフロードし、その後タスクが完了するとハードウェアアクセラレータによって通知され得る、管理システムが有用な場合がある。管理システムが、現在のジョブの完了を待たずに、コアがプール内のタスクを提出することを可能にする場合、そのようなシステムの実用性は増加し得る。As mentioned above, hardware accelerators may go unused for a variety of reasons. However, a management system may be useful whereby a core can efficiently offload certain DSP tasks to a dedicated hardware accelerator and then be notified by the hardware accelerator when the task is complete. The utility of such a system may be increased if the management system allows a core to submit a task in the pool without waiting for the current job to complete.
本明細書の実施形態は、様々な利点を提供し得る。例えば、そのような管理システムによって支配されるハードウェアアクセラレータは、プロセッサまたはプロセッサコアが、1つ以上のDSPタスクをハードウェアアクセラレータに効率的にオフロードすることを可能にし得る。加えて、アクセラレータのためのハードウェアベースのキューイングシステムは、例えば、ソフトウェアベースの管理システムよりも有益であり得るが、これは、プロセッサがタスクプールを管理し、現在のタスクが終了すると次のタスクにアクセラレータを割り当てなければならないので、完全にソフトウェアベースの管理システムは計算またはメモリ集約的であり得るためである。Embodiments herein may provide various advantages. For example, a hardware accelerator governed by such a management system may enable a processor or processor core to efficiently offload one or more DSP tasks to the hardware accelerator. In addition, a hardware-based queuing system for an accelerator may be more beneficial than, for example, a software-based management system, since a fully software-based management system may be computationally or memory intensive, since the processor must manage a pool of tasks and assign the accelerator to the next task once the current task is finished.
一般に、本明細書の実施形態は、ハードウェアベースの自律ジョブキュー管理構造に関する。実施形態は、管理構造を実装するために使用され得るいくらかの要素を含んでもよい。そのような要素の1つは、ハードウェアアクセラレータを管理するために使用され得る連鎖DMAインフラストラクチャに関し得る。別のそのような要素は、管理構造内の新しいジョブ提出に関し得る。具体的には、新しいジョブの提出は、DMAチェーンに新しいエントリを作成することによって行われてもよい。DMAチェーンは、例えば、TCBのリンクされたリストであり得る。一般に、TCBは、ハードウェアアクセラレータによって実行される具体的なジョブに関連する要素であると見なされ得る。各TCBは、ジョブの遂行においてハードウェアアクセラレータによって使用される具体的な構成データを含み得る1つ以上のデータ要素またはサブフィールドを含み得る。ここでは、TCBは「タスク制御ブロック」と呼ばれるが、他の実施形態では、TCBは「転送制御ブロック」などの別の名前で呼ばれ得ることが理解されるであろう。In general, embodiments herein relate to a hardware-based autonomous job queue management structure. The embodiments may include several elements that may be used to implement the management structure. One such element may relate to a chained DMA infrastructure that may be used to manage the hardware accelerator. Another such element may relate to new job submission within the management structure. Specifically, the submission of a new job may be done by creating a new entry in the DMA chain. The DMA chain may be, for example, a linked list of TCBs. In general, the TCB may be considered to be an element related to a specific job to be executed by the hardware accelerator. Each TCB may include one or more data elements or subfields that may include specific configuration data used by the hardware accelerator in fulfilling the job. Here, the TCB is referred to as a "task control block," but it will be understood that in other embodiments, the TCB may be referred to by other names, such as a "transfer control block."
様々なTCBまたはそのフィールドは、キューイングメカニズムを支援するために使用され得る情報を含むように改変されてもよい。例えば、TCBは、入力(I/P)バッファへのポインタを含み得る。TCBはまた、出力(O/P)バッファへのポインタを含み得る。TCBはまた、DMAチェーン内の先行または後続のTCBを参照し得る「先の」または「次の」記述子へのポインタを含んでもよい。TCBはまた、そのTCBに関連するシステムアドレスを格納するために使用され得るプレースホルダを含んでもよい。TCBはまた、ハードウェアアクセラレータのジョブ専用計算構成を含んでもよい。TCBは、完了状況を格納するためのプレースホルダを含み、転用し、または再利用することもできる。Various TCBs or fields thereof may be modified to contain information that may be used to assist in queuing mechanisms. For example, the TCB may contain a pointer to an input (I/P) buffer. The TCB may also contain a pointer to an output (O/P) buffer. The TCB may also contain pointers to "previous" or "next" descriptors that may reference preceding or succeeding TCBs in a DMA chain. The TCB may also contain placeholders that may be used to store system addresses associated with that TCB. The TCB may also contain job-specific computational configurations for hardware accelerators. The TCB may also contain placeholders for storing completion status, and may be repurposed or reused.
いくつかの実施形態では、1つ以上のAPIを使用して、新しいジョブの作成または提出、既存のジョブの状況の識別、ジョブの削除などのキュー管理タスクを行ってもよい。APIは、(例えば、所与の優先順位グループの最後のジョブまたはTCBの識別に関連する情報を使用することによって)TCBのリンクされたリストを横断し、様々なTCBまたはそのフィールドを読み取りまたは改変し、リンクされたリストからエントリを導入または除去することなどによって、これらのタスクを達成し得る。In some embodiments, one or more APIs may be used to perform queue management tasks such as creating or submitting new jobs, identifying the status of existing jobs, deleting jobs, etc. The APIs may accomplish these tasks by traversing a linked list of TCBs (e.g., by using information related to the identification of the last job or TCB of a given priority group), reading or modifying various TCBs or fields thereof, introducing or removing entries from the linked list, etc.
次いで、ジョブは、TCBのリンクされたリストに現れる順序で実行され得る。一般に、TCBのリンクされたリストは、提出されたジョブの異なる優先順位に基づいて別個のセクションを有し得る。ハイレベルな例として、TCBの高優先順位セクションは、TCBのリンクされたリストの上位にあり得、それらのTCBに関連するジョブは、最初に実行され得る。TCBの中優先順位セクションは、TCBの高優先順位セクションに続く場合がある。これらの中優先順位TCBに関連するジョブは、高優先順位TCBに関連するジョブの実行後に実行され得る。高優先順位フラグの新しいジョブが受信された場合、それは、TCBのリンクされたリストの高優先順位セクションの末端に挿入され得る。リンクされたリストの高優先順位セクションが終了した場合、高優先順位TCBは、中優先順位セクションのTCBに関連する現在走行中のジョブの直後に挿入され得る。The jobs may then be executed in the order in which they appear in the linked list of TCBs. In general, the linked list of TCBs may have separate sections based on the different priorities of the submitted jobs. As a high level example, the high priority section of the TCB may be at the top of the linked list of TCBs and the jobs associated with those TCBs may be executed first. The medium priority section of the TCB may follow the high priority section of the TCB. The jobs associated with these medium priority TCBs may be executed after the execution of the jobs associated with the high priority TCBs. If a new job with a high priority flag is received, it may be inserted at the end of the high priority section of the linked list of TCBs. If the high priority section of the linked list is finished, the high priority TCB may be inserted immediately after the currently running job associated with the TCB in the medium priority section.
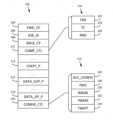
図1は、実行のためにハードウェアアクセラレータに提供され得る例示的なTCB105を示す。わかるように、TCB105は、いくらかのフィールドを含んでもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、TCB105の様々なフィールドは、「語」と呼ばれてもよく、TCB105は、最大16個のフィールドを含んでもよい。FIG. 1 illustrates an exemplary TCB 105 that may be provided to a hardware accelerator for execution. As can be seen, the TCB 105 may include a number of fields. In some embodiments, the various fields of the
別のそのようなフィールドは、チェーンポインタ104であってもよく、チェーンポインタ104は、例えば、前方チェーンポインタであることを示すために「FWD_CP」と呼ばれてもよい。チェーンポインタ104は、TCBのリンクされたリスト内の後続のTCBのアドレスを含み得る。ハードウェアアクセラレータがTCB105に関連するジョブを完了した後、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、チェーンポインタ104内のアドレスを読み取り、チェーンポインタ104によって識別される次のTCBに移動し得る。いくつかの実施形態では、後続のジョブの識別子は、後続のTCBのシステムアドレスであり得る「TCBSYS_ADDR」識別子であってもよい。Another such field may be a
別のそのようなフィールドは、JOB_IDフィールド106であり得る。一般に、JOB_IDフィールド106は、TCB105またはTCB105が関連付けられているジョブに関する識別情報を格納するために使用され得るプレースホルダであってもよい。TCBによって記載された各ジョブは、フィールド106の値によって一意に識別される。このような情報は、例えば、TCB105に関連するジョブの状況を識別するために、プロセッサまたはハードウェアアクセラレータによって使用されてもよい。識別情報は、例えば、TCBSYS_ADDR識別子であり得るか、またはそれを含み得る。Another such field may be the
別のそのようなフィールドは、BACK_CPフィールド108であり得る。BACK_CPフィールド108は、先のTCBの識別子をTCBのリンクされたリストに格納することができるので、後方チェーンポインタと呼ばれることがある。先のTCBの識別子は、例えば、JOB_IDフィールド106に関して上記された識別子であり得る。リンクされたリスト内の各TCBが、先のジョブを識別するBACK_CPフィールド108、および後続のジョブを識別するチェーンポインタを含む場合、それぞれのTCBは、先または後続のTCBを指し示すことによってリンクされたリストを形成し得る。これらのフィールドは、組み合わせて、以下でさらに詳細に記載されるように、リンクされたリストの優先順位ベースの改変に有用であり得るTCBのリンクされたリストを横断するためにAPIによって使用され得る。Another such field may be the
別のこのようなフィールドは、COMP_CTLフィールド112であり得る。COMP_CTLフィールド112は、ジョブ専用計算構成をサポートし得るいくらかのサブフィールド110を含み得る。ここでは「サブフィールド」という用語が使用されるが、他の実施形態では、サブフィールドは「フラグ」または「データ要素」と呼ばれることがある。Another such field may be the
このようなサブフィールドの1つは、FXDサブフィールド122であり得る。FXDサブフィールド122は、ジョブが、固定小数点演算または浮動小数点演算、何らかの他の種類の演算を使用すべきかどうかを示し得る。利用可能なオプションは、例えば、いくつのビットがFXDサブフィールド122に使用されるかに依存し得る。別のこのようなサブフィールドは、TCサブフィールド124であり得る。TCサブフィールド124を使用して、それが動作するデータの種類、またはジョブの実行中にハードウェアアクセラレータによって使用される計算の種類をアクセラレータに示すために使用され得る。別のこのようなサブフィールドは、TCB105に関連付けられたジョブの完了中に使用される丸めモードを示し得るRNDサブフィールド126であり得る。One such subfield may be the
TCB105の別のフィールドは、COEFF_Pフィールド114であり得る。COEFF_Pフィールド114は、TCB105に関連付けられたジョブの遂行中にハードウェアアクセラレータによって使用され得る係数テーブルへの参照を含み得る。例えば、いくつかの実施形態では、COEFF_Pフィールド114に関連付けられた複数のデータワードが存在し得る。データワードは、係数テーブルがシステムメモリにどのようにレイアウトされ得るかを指定してもよい。Another field of the
TCB105の別のフィールドは、DATA_O/P_Pフィールド116であり得る。DATA_O/P_Pフィールド116は、O/Pバッファへのポインタであってもよく、またはそれを含んでもよい。O/Pバッファは、例えば、ハードウェアアクセラレータのバッファ、またはハードウェアアクセラレータがその一部であるか、もしくはハードウェアアクセラレータが通信可能に結合される電子デバイスのバッファであり得る。O/Pバッファは、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、TCB105が関連付けられているジョブの遂行または完了に関連するデータを格納する所であってもよい。Another field of the
TCB105の別のフィールドは、DATA_I/P_Pフィールド118であり得る。DATA_I/P_Pフィールド118は、I/Pバッファへのポインタを含み得る。I/Pバッファは、例えば、ハードウェアアクセラレータのバッファ、またはハードウェアアクセラレータがその一部であるか、もしくはハードウェアアクセラレータが通信可能に結合される電子デバイスのバッファであり得る。I/Pバッファは、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、TCB105が関連付けられているジョブの遂行に関連するデータを受信する場所であり得る。Another field of the
TCB105の別のそのようなフィールドは、CONFIG_CTLフィールド120を含み得る。CONFIG_CTLフィールド120は、本明細書に記載される優先順位ベースのハードウェア加速スキームを実装するために使用され得る追加のサブフィールド115を含んでもよい。そのようなサブフィールドの1つは、ACC_CONFIGサブフィールド102を含んでもよい。ACC_CONFIGサブフィールド102は、TCBに関連するジョブを行うためにハードウェアアクセラレータによって使用され得る技術に関連する情報を含み得る。例えば、ACC_CONFIGサブフィールド102は、ハードウェアアクセラレータに、有限インパルスフィルタ(FIR)、具体的な順序の四次無限インパルスフィルタ(IIR)、ジョブ遂行に関連する具体的な時間ウィンドウであって、ウィンドウ長さが、生成される出力サンプルの数に関連し得る時間ウィンドウ、または使用され得るサンプルレート変換を実装するように指図し得る。しかしながら、これらは、ACC_CONFIGサブフィールド102が含み得る例であり、他の実施形態は、追加またはより少ない要素を含み得ることが理解されるであろう。Another such field of the
別のこのようなサブフィールドは、PRIOサブフィールド128を含んでもよい。PRIOサブフィールド128は、TCBのリンクされたリスト内のTCB105の優先順位レベルを示し得るいくらかのビットを含み得る。例えば、PRIOサブフィールド128は、TCB105が「高い」または「低い」優先順位であるかどうかを示し得る1ビットインジケータであってもよい。代替的に、PRIOサブフィールド128は、TCB105が「非常に高い」、「高い」、「中」、または「低い」優先順位にあるかどうかを示し得る2ビットインジケータであってもよい。Another such subfield may include the
別のこのようなサブフィールドは、IMASKサブフィールド130を含んでもよい。IMASKサブフィールド130は、TCB105が関連付けられるジョブの完了時に割り込みがプロセッサに送信されるかどうかを示し得る。一般に、各ジョブの完了時に割り込みをプロセッサに送信することは望ましくない場合があるので、このサブフィールドは、割り込みが所望されるかどうかを示すフラグとして機能し得る。Another such subfield may include the
別のこのようなサブフィールドは、TMASKサブフィールド132を含んでもよい。IMASKサブフィールド130と同様に、TMASKサブフィールド132は、TCB105が関連付けられるジョブの完了時に、トリガがプロセッササブシステムに送信されるかどうかを示し得る。一般に、各ジョブの完了時にトリガをプロセッササブシステムに送信することは望ましくない場合があるので、このサブフィールドは、トリガが所望されるかどうかを示すフラグとして機能し得る。Another such subfield may include the
別のこのようサブフィールドは、TWAITサブフィールド134を含んでもよい。一般に、プロセッサが、リンクされたリストへの追加として新しいTCBをジョブプールに提出することができる前に、1つ以上の係数(その位置はCOEFF_Pフィールド114によって示され得る)を収容するデータバッファ、および入力データバッファ(これは、DATA_I/P_Pフィールド118によって示されるI/Pバッファ内のデータであり得る)の両方が必要とされ得る。一般に、係数は静的であり得るが、入力データは動的であり得る。入力データが利用できない場合、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、TCB105によって示されるジョブの遂行中に古いまたは破損したデータを処理し得る。次いで、TCB105にTWAITサブフィールドが設定される場合、ハードウェアアクセラレータがそのTCBに関連するジョブを実行しているとき、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、バッファの準備に関与し得るDMAなどのプロセッササブシステムの構成要素のいずれかから受信したトリガの形態でI/Pバッファ完了の指標を待つことができる。トリガがプロセッサから受信されると、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、入力DMAを開始して、データをその内部バッファに転送し、関連したジョブを実行し得る。その結果、TCBは、対応する入力データが、プロセッサによる提出時にI/Pバッファで利用可能でない場合でも、プロセッサによって、リンクされたリストに提出され得る。Another such subfield may include the
一般に、TCB105および関連したフィールド/サブフィールド/などは、このようなフィールド/サブフィールドの例として本明細書に示され、考察されており、他の実施形態は、示されているものと異なり得ることが理解されるであろう。例えば、いくつかのTCBは、示されるフィールドよりも追加の、または少ないフィールドを有し得る。いくつかの実施形態では、記載されるフィールドは、記載された厳密なパラメータとは異なってもよい。具体的な例として、いくつかの実施形態では、PRIOサブフィールド128は、記載された1ビットまたは2ビットの配設よりも多くまたは少ないビットを含んでもよい。加えて、この例で与えられた具体的な名前は、一実施形態で使用され得る名前であることが認識されるであろうが、記載した機能性を行いながら、他の実施形態では、他の名前が具体的なフィールドまたはサブフィールドに使用され得る。他の実施形態では、他の変形例が存在してもよい。In general, it will be appreciated that the
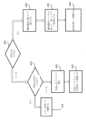
図2は、様々な実施形態による、ジョブキューイングの高レベルな例を示す。具体的には、図2は、新たに導入されたTCBをTCBのリンクされたリストにキューイングする高レベルな例を示す。考察されたTCBの各々は、PRIOサブフィールド128に関して考察されたような優先順位レベルを有し得る。この特定の例では、異なる濃淡に基づいて、図2にグラフィカルに示される3つの異なる優先順位レベルが存在する。3つの異なる優先順位レベルは、高優先順位202、中優先順位204、および低優先順位206である。一般に、高優先順位レベルのTCBは、中または低優先順位レベルのTCBの実行の前に実行される。同様に、中優先順位レベルのTCBは、低優先順位レベルのTCBの実行の前に実行される。2 illustrates a high level example of job queuing, according to various embodiments. Specifically, FIG. 2 illustrates a high level example of queuing a newly introduced TCB to a linked list of TCBs. Each of the considered TCBs may have a priority level as discussed with respect to the
このシステムは、システムバス203によってハードウェアアクセラレータ205と通信可能に結合されるプロセッサ210を含み得る。システムバス203は、電子デバイスの1つ以上の要素が、互いにデータ信号を送受信することを可能にする通信結合であってもよい。プロセッサ210は、例えば、中央処理ユニット(CPU)、マルチもしくはシングルコアプロセッサ、マルチコアプロセッサのコア、または何らかの他の種類のプロセッサであり得る。同様に、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205は、一定の機能もしくは機能のセットを行うように構成されたハードウェア論理ブロック、CPU、マルチコアもしくはシングルコアプロセッサ、マルチコアプロセッサのコア、または何らかの他の種類のプロセッサなどの処理ユニットであってもよい。プロセッサ210は、1つ以上のコンピュータ実行可能命令を実行するための論理、1つ以上の数学的処理または計算を行うための論理などをさらに含んでもよい。The system may include a processor 210 communicatively coupled to the hardware accelerator 205 by a system bus 203. The system bus 203 may be a communication coupling that allows one or more elements of an electronic device to send and receive data signals to each other. The processor 210 may be, for example, a central processing unit (CPU), a multi- or single-core processor, a core of a multi-core processor, or some other type of processor. Similarly, the hardware accelerator 205 may be a processing unit, such as a hardware logic block, a CPU, a multi- or single-core processor, a core of a multi-core processor, or some other type of processor, configured to perform a certain function or set of functions. The processor 210 may further include logic for executing one or more computer-executable instructions, logic for performing one or more mathematical operations or calculations, etc.
システムは、メモリ201をさらに含み得る。メモリ201は、ダブルデータレート(DDR)メモリ、フラッシュメモリ、ランダムアクセスメモリ(RAM)、または何らかの他の種類のメモリなどの揮発性もしくは不揮発性メモリであってもよい。より具体的には、メモリ201は、上記で考察したI/Pバッファ、O/Pバッファ、またはCOEFFバッファなどの1つ以上のバッファを含み得る。加えて、メモリ201は、本明細書に記載された様々な実施形態による、1つ以上のTCBをTCBのリンクされたリストに格納するように構成されてもよい。メモリ201は、システムバス203によってプロセッサ210およびハードウェアアクセラレータ205と通信可能に結合され得る。The system may further include memory 201. Memory 201 may be a volatile or non-volatile memory, such as double data rate (DDR) memory, flash memory, random access memory (RAM), or some other type of memory. More specifically, memory 201 may include one or more buffers, such as an I/P buffer, an O/P buffer, or a COEFF buffer, as discussed above. Additionally, memory 201 may be configured to store one or more TCBs in a linked list of TCBs according to various embodiments described herein. Memory 201 may be communicatively coupled to processor 210 and hardware accelerator 205 by system bus 203.
プロセッサ210、メモリ201、およびハードウェアアクセラレータ205のうちの1つ以上は、システムオンチップ(SoC)、システムインパッケージ(SiP)、または何らかの他の構成として構成されてもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、プロセッサ210、メモリ201、およびハードウェアアクセラレータ205のうちの2つ以上は、同じ基板の要素、例えば、インターポーザまたはプリント回路基板(PCB)の要素であってもよく、一方、他の実施形態では、プロセッサ210、メモリ201、およびハードウェアアクセラレータ205の各々は、異なる基板上にあってもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、メモリ201、プロセッサ210、およびハードウェアアクセラレータ205のうちの2つ以上は、単一の半導体または単一のチップ内の論理的または物理的な区画であってもよく、一方、他の実施形態では、メモリ201、プロセッサ210、およびハードウェアアクセラレータ205のそれぞれは物理的に互いに分離されてもよい。One or more of the processor 210, memory 201, and hardware accelerator 205 may be configured as a system on chip (SoC), a system in package (SiP), or some other configuration. In some embodiments, two or more of the processor 210, memory 201, and hardware accelerator 205 may be elements of the same substrate, e.g., an interposer or printed circuit board (PCB), while in other embodiments, each of the processor 210, memory 201, and hardware accelerator 205 may be on a different substrate. In some embodiments, two or more of the memory 201, processor 210, and hardware accelerator 205 may be logical or physical partitions within a single semiconductor or single chip, while in other embodiments, each of the memory 201, processor 210, and hardware accelerator 205 may be physically separated from one another.
ハードウェアアクセラレータ205は、メモリ201に格納されたTCBのリンクされたリスト内のいくつらのTCBに関連するジョブを実行するように構成され得る。TCBのリンクされたリストのそれぞれのTCBは、例えば、TCB105と類似していてもよい。TCBのリンクされたリストは、図2に、先に実行されたTCB214、現在実行中のTCB218、および実行されるTCB220を含むように示されている。Hardware accelerator 205 may be configured to execute jobs associated with any number of TCBs in a linked list of TCBs stored in memory 201. Each TCB in the linked list of TCBs may be similar to
TCB212は、プロセッサ210によって識別または生成され得る。プロセッサ210は、TCBがTCBのリンクされたリストに挿入されることを識別し得る。次いで、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205へのTCB212の供給には、プロセッサとハードウェアアクセラレータ205との間で交換されるいくらかのメッセージが含まれ得る。具体的には、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205が現在、キュー内のTCBに関連するジョブを実行している場合、プロセッサ210およびハードウェアアクセラレータ205の両方によるTCBの改変は整合性の問題を生じ得るため、キューにTCBを追加することが望ましくない場合がある。プロセッサ210は、236で停止コマンドをハードウェアアクセラレータ205に送信し得る。停止コマンドは、例えば、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205のレジスタにビットを書き込むことを含み得る。236における停止コマンドは、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205が、実用的であればすぐに処理を一時停止することをハードウェアアクセラレータ205に示し得る。いくつかの実施形態では、停止は、イベントでいくらかのサイクルを必要とする場合があり、例えば、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205は、メモリアクセス動作を開始し得、その後、メモリアクセス動作の完了を待っている。236での停止コマンドに応答して、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205は、238で停止確認を送信し得る。238での停止確認は、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205が動作を停止し、プロセッサ210からのさらなる命令を待っていることを示し得る。次いで、プロセッサ210は、TCB212をメモリ201内のTCBのキューに挿入し得る。TCBを他のTCBに対してキュー内の指定された場所に配置することは、例えば、TCBのリンクされたリスト内のTCBのうちの1つ以上のFWD_CP104およびBACK_CP106フィールドを改変することを含み得る。The TCB 212 may be identified or generated by the processor 210. The processor 210 may identify that the TCB is to be inserted into a linked list of TCBs. The provision of the TCB 212 to the hardware accelerator 205 may then involve some messages exchanged between the processor and the hardware accelerator 205. Specifically, if the hardware accelerator 205 is currently executing a job associated with the TCB in the queue, it may not be desirable to add the TCB to the queue because modification of the TCB by both the processor 210 and the hardware accelerator 205 may create integrity issues. The processor 210 may send a stop command at 236 to the hardware accelerator 205. The stop command may include, for example, writing a bit to a register of the hardware accelerator 205. The stop command at 236 may indicate to the hardware accelerator 205 that the hardware accelerator 205 should suspend processing as soon as practical. In some embodiments, the stop may require several cycles in the event, for example, the hardware accelerator 205 may initiate a memory access operation and then wait for the completion of the memory access operation. In response to the stop command at 236, the hardware accelerator 205 may send a stop acknowledgement at 238. The stop acknowledgement at 238 may indicate that the hardware accelerator 205 has stopped operation and is waiting for further instructions from the processor 210. The processor 210 may then insert the TCB 212 into a queue of TCBs in memory 201. Placing the TCB in a specified location in the queue relative to other TCBs may include, for example, modifying the
TCBのキューを参照すると、先に実行されたTCB214がいくらか存在することがわかる。先に実行されたTCB214は、2つの高優先順位TCB208(すなわち、「高」優先順位に従って実行されることを示すPRIOサブフィールドを有するTCB)を含んでもよい。先に実行されたTCB214はまた、中間の優先順位TCB216(すなわち、高優先順位TCB後の「中」優先順位に従って実行されることを示すPRIOサブフィールドを有するTCB)を含んでもよい。さらに、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205は、別の中優先順位TCB218に関連するジョブを実行してもよい。実行されるTCB220は、中優先順位TCB224および低優先順位TCB228(すなわち、高優先順位TCBおよび中優先順位TCB後の「低」優先順位に従って実行されることを示すPRIOサブフィールドを有するTCB)を含んでもよい。Looking at the queue of TCBs, it can be seen that there are some previously executed TCBs 214. The previously executed TCBs 214 may include two high priority TCBs 208 (i.e., TCBs with a PRIO subfield indicating that they will be executed according to "high" priority). The previously executed TCBs 214 may also include a medium priority TCB 216 (i.e., a TCB with a PRIO subfield indicating that they will be executed according to "medium" priority after the high priority TCBs). In addition, the hardware accelerator 205 may execute a job associated with another medium priority TCB 218. The executed TCBs 220 may include a medium priority TCB 224 and a low priority TCB 228 (i.e., a TCB with a PRIO subfield indicating that they will be executed according to "low" priority after the high priority TCBs and the medium priority TCBs).
破線アウトラインを有するTCBは、その優先順位に従って、TCB212をキュー内に配置することができる異なる位置を示す。述べたように、現在実行中のTCBに関連するジョブを停止することはできない。したがって、TCB212が高優先順位TCBである場合、TCB222によって示される位置に配置される。したがって、それは、TCB224のような中優先順位TCBに関連する任意の他のジョブの実行の前に処理され、それに関連する任意のジョブが実行されるように、キュー内に配置される。言い換えれば、現在実行中のTCB218は中優先順位TCBであるため、高優先順位TCB212がキュー内の次となる。The TCBs with dashed outlines indicate the different positions in the queue where TCB 212 can be placed, according to its priority. As stated, the job associated with a currently executing TCB cannot be stopped. Thus, if TCB 212 is a high priority TCB, it will be placed in the position indicated by TCB 222. It will therefore be placed in the queue such that it will be processed before the execution of any other jobs associated with a medium priority TCB, such as TCB 224, and any jobs associated with it will be executed. In other words, since the currently executing TCB 218 is a medium priority TCB, high priority TCB 212 will be next in the queue.
しかしながら、TCB212が中優先順位TCBである場合、TCB226によって示されるキュー内の位置に配置されることになる。この位置は、中優先順位TCBの末端にあるが、任意の低優先順位TCBの前にある。最後に、TCB212が低優先順位TCBである場合、TCB230によって示されるキュー内の位置に配置される。この位置は、低優先順位TCBの末端にある。However, if TCB 212 is a medium priority TCB, it will be placed in the position in the queue indicated by TCB 226, which is at the end of the medium priority TCBs but before any low priority TCBs. Finally, if TCB 212 is a low priority TCB, it will be placed in the position in the queue indicated by TCB 230, which is at the end of the low priority TCBs.
次の表、表1は、3つの優先順位レベル(高、中、および低)を有する実施形態において、優先順位ベースのタスク挿入がどのように達成され得るかの様々な例を提供する。しかしながら、この表は、高レベルな例として意図されており、他の実施形態は、この表の変形例を含んでもよいことが理解されるであろう。The following table, Table 1, provides various examples of how priority-based task insertion may be accomplished in an embodiment having three priority levels (high, medium, and low). However, it will be understood that this table is intended as a high-level example and other embodiments may include variations of this table.
この図2の例は、優先順位ベースのキュー管理の1つの簡略化された例として意図されており、他の実施形態は、示された例と異なり得ることが理解されるであろう。例えば、いくつかの実施形態は、図2に考察しまたは示されるよりも多い、または少ない優先順位レベルを有し得る。優先順位レベルの数は、上記で考察したPRIOサブフィールド128に依存し得る。加えて、様々な優先順位レベルのTCBの数は、異なるユースケースにおいて異なってもよい。It will be understood that this example of FIG. 2 is intended as one simplified example of priority-based queue management, and other embodiments may differ from the example shown. For example, some embodiments may have more or fewer priority levels than discussed or shown in FIG. 2. The number of priority levels may depend on the
加えて、図2のユースケースは、TCB212をキューに導入するように記載されている。しかしながら、キューの他の改変が可能であり得ることが理解されるであろう。このような改変は、キューからのTCBの削除、キューのTCBに関連するジョブの状況のクエリ、キュー内のTCBの改変などを含んでよい。一般に、キューの管理は、キューを管理するためにプロセッサ210によって使用され得る様々なAPIに基づいて行われ得る。図3~図7は、キューの管理に使用され得る様々なAPIを示す。プロセッサ210によるこのようなキューの管理は、次の、「ジョブ」の作成(例えば、メモリ内のTCBの位置決め)、ジョブのキューへの提出、他の既存のTCBに対するキュー内の示された場所でのジョブの挿入、ジョブのキューからの削除、ジョブの完了状況の判定などのうちの1つ以上を含んでよい。これらの管理タスクを行うために、プロセッサ210は、キュー内の最初のTCBのメモリ参照、所与の優先順位レベルのキュー内の最初のTCB、キュー内の最後のTCB、所与の優先順位レベルのキュー内の最後のTCB、またはこれらの何らかの組み合わせなどの一定のキュー関連情報を格納することを必要とし、各TCB内の2つのチェーンポインタフィールド(例えば、チェーンポインタフィールド104およびバック_cpフィールド108)の助けを借りてTCBのリンクされたリストを横断することが可能であり得る。In addition, the use case of FIG. 2 is described as introducing a TCB 212 into a queue. However, it will be understood that other modifications of a queue may be possible. Such modifications may include removing a TCB from a queue, querying the status of a job associated with a TCB in a queue, modifying a TCB in a queue, and the like. In general, management of a queue may be performed based on various APIs that may be used by the processor 210 to manage the queue. FIGS. 3-7 illustrate various APIs that may be used to manage a queue. Such management of a queue by the processor 210 may include one or more of the following: creating a "job" (e.g., locating a TCB in memory), submitting the job to the queue, inserting the job at an indicated location in the queue relative to other existing TCBs, removing the job from the queue, determining the completion status of the job, and the like. To perform these management tasks, the processor 210 needs to store certain queue-related information, such as a memory reference of the first TCB in the queue, the first TCB in the queue at a given priority level, the last TCB in the queue, the last TCB in the queue at a given priority level, or some combination of these, and may be able to traverse the linked list of TCBs with the help of two chain pointer fields in each TCB (e.g., the
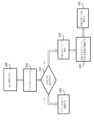
一般に、図3は、ジョブをキューに提出するために使用され得るAPIを記載する。図3のAPIは、例えば、プロセッサ210によって行われ得る。APIに関連する提出コマンドの構文は、submit_job(ACC_TCB TCB_x、ACC_TCB TCB_n)であり得る。「ACC_TCB TCB_x」は、キューに挿入されるTCBを指す情報を含み得る。TCBは、「TCB_x」と呼ばれることがある。情報は、TCB_xを指すポインタであってもよく、またはTCBの全部または部分であってもよい。同様に、「ACC_TCB TCB_n」は、キュー内のTCBを指す情報を含んでもよく、それに続いてTCB_xがキューに配置される。情報は、TCB_nを指すポインタであってもよく、またはTCBの全部または部分であってもよい。In general, FIG. 3 describes an API that may be used to submit a job to a queue. The API of FIG. 3 may be performed by the processor 210, for example. The syntax of a submission command associated with the API may be submit_job(ACC_TCB TCB_x, ACC_TCB TCB_n). The "ACC_TCB TCB_x" may contain information pointing to a TCB to be inserted into the queue. The TCB may be referred to as "TCB_x". The information may be a pointer to TCB_x or may be all or a portion of the TCB. Similarly, the "ACC_TCB TCB_n" may contain information pointing to a TCB in the queue, following which TCB_x is placed in the queue. The information may be a pointer to TCB_n or may be all or a portion of the TCB.
初めに、APIは、305において、ハードウェアアクセラレータ(例えば、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205)が有効であるかどうかをチェックすることを含んでよい。本明細書で使用されるように、「有効」とは、ハードウェアアクセラレータがTCBを受け入れるように構成されているか/TCBに関連するジョブを行うように構成されているかを指し得る。ハードウェアアクセラレータが有効にされていない場合、プロセッサは、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205に、TCBのリンクされたリストで処理される最初のTCBの指標を提供し得る。具体的には、プロセッサは、ハードウェアアクセラレータ内のチェーンポインタレジスタCPを、キュー内の最初のTCBのアドレスで更新し得る。次に、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、TCBを処理し、TCBが関連付けられているジョブを行うように、315で有効にされてもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、305で示されるTCB提出APIは、次いで再開されてもよい。Initially, the API may include checking whether the hardware accelerator (e.g., hardware accelerator 205) is enabled at 305. As used herein, "enabled" may refer to whether the hardware accelerator is configured to accept the TCB/perform the job associated with the TCB. If the hardware accelerator is not enabled, the processor may provide the hardware accelerator 205 with an indication of the first TCB to be processed in the linked list of TCBs. Specifically, the processor may update a chain pointer register CP in the hardware accelerator with the address of the first TCB in the queue. The hardware accelerator may then be enabled at 315 to process the TCB and perform the job with which the TCB is associated. In some embodiments, the TCB submission API shown at 305 may then be resumed.
しかしながら、ハードウェアアクセラレータが有効であると305で識別される場合、次いで、プロセッサは、320でハードウェアアクセラレータを停止することが望ましい場合がある。ハードウェアアクセラレータを停止することは、例えば、図2の要素236に関して考察された停止メッセージを送信することを含み得る。プロセッサは、要素238に関して上記した停止確認のために監視することによって、アクセラレータが停止したことの確認を待ってもよい。次いで、プロセッサは、325において、ハードウェアアクセラレータがアイドルであるかどうかを判定し得る。本明細書で使用されるように、「アイドル」とは、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、TCBの既存のキュー内のすべてのTCBの処理を終了したかを指し得る。ハードウェアアクセラレータが325においてアイドルであると325において判定される場合、次いで、ハードウェアアクセラレータ内の構成レジスタ内の1つ以上のビットフィールドにプロセッサが書き込むによって、330においてハードウェアアクセラレータが無効になり得る。この無効化は、ハードウェアアクセラレータの「リセット」として機能し得る。ハードウェアアクセラレータ内のチェーンポインタレジスタCPは、プロセッサによって335でTCBのアドレスで更新されてもよく、次いで、ハードウェアアクセラレータは340で再有効化されてもよい。ハードウェアアクセラレータの再有効化は、例えば、要素236に関して上記したように、ハードウェアアクセラレータが停止すべきであることを示すレジスタ内のビットを変更することを含み得る。ハードウェアアクセラレータが340で再有効化されると、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、その機能を再開してもよく、加えて、プロセッサは、本明細書に記載のAPI、それ以外のAPI、またはそれ以外の処理機能に関連するアプリケーションコードを実行することを再開してもよい。However, if the hardware accelerator is identified as enabled at 305, then it may be desirable for the processor to stop the hardware accelerator at 320. Stopping the hardware accelerator may include, for example, sending a stop message as discussed with respect to element 236 of FIG. 2. The processor may wait for confirmation that the accelerator has stopped by monitoring for a stop confirmation as described above with respect to element 238. The processor may then determine whether the hardware accelerator is idle at 325. As used herein, "idle" may refer to whether the hardware accelerator has finished processing all TCBs in an existing queue of TCBs. If the hardware accelerator is determined to be idle at 325, then the hardware accelerator may be disabled at 330 by the processor writing to one or more bit fields in a configuration register within the hardware accelerator. This disabling may act as a "reset" of the hardware accelerator. A chain pointer register CP in the hardware accelerator may be updated by the processor with the address of the TCB at 335, and the hardware accelerator may then be re-enabled at 340. Re-enabling the hardware accelerator may include, for example, changing a bit in a register indicating that the hardware accelerator should be stopped, as described above with respect to element 236. Once the hardware accelerator is re-enabled at 340, the hardware accelerator may resume its functionality, and in addition, the processor may resume executing application code associated with the APIs described herein, other APIs, or other processing functions.
しかしながら、ハードウェアアクセラレータが325でアイドルでないと判定される場合、プロセッサは、TCBのキューへのTCBの挿入に関連するAPIを345で行い得る。APIに関連する挿入コマンドの構文は、insert_job(ACC_TCB TCB_x、ACC_TCB TCB_n)であり得る。「ACC_TCB TCB_x」および「ACC_TCB TCB_n」は、図3に関して上記したものと類似していてもよい。図4は、挿入APIの例を示す。他の実施形態では、insert_job APIは、図3のAPIとは別個に行われ得ることが理解されるであろう。However, if the hardware accelerator is determined not to be idle at 325, the processor may perform an API at 345 associated with inserting a TCB into the queue of TCBs. The syntax of the insert command associated with the API may be insert_job(ACC_TCB TCB_x, ACC_TCB TCB_n). "ACC_TCB TCB_x" and "ACC_TCB TCB_n" may be similar to those described above with respect to FIG. 3. FIG. 4 shows an example of an insert API. It will be appreciated that in other embodiments, the insert_job API may be performed separately from the API of FIG. 3.
初めに、APIは、405において、insert_job API内のTCB_nへのポインタがヌル(0)値であるかどうかを識別することを含んでよい。TCB_nがヌル値でない場合、APIは次いで、TCB_nが完了したかどうかを410で識別することを含んでよい。より具体的には、APIは、410において、TCB_nに関連するジョブが完了したか、またはTCB_nが、214で記載された先に実行されたTCBのリストにあるかを識別することを含んでよい。そうである場合、次いで、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、415でエラー指標をプロセッサに提供し得る。エラー指標は、処理が完了したTCBの後に挿入されたTCBが、ハードウェアアクセラレータによってアクセスされないため、関連付けられたジョブが決して実行され得ない事実が原因であり得る。ハードウェアアクセラレータまたはプロセッサは、上記のように動作を再開し得る。Initially, the API may include identifying, at 405, whether the pointer to the TCB_n in the insert_job API is a null (0) value. If the TCB_n is not a null value, the API may then include identifying, at 410, whether the TCB_n is completed. More specifically, the API may include identifying, at 410, whether the job associated with the TCB_n is completed or whether the TCB_n is in the list of previously executed TCBs described at 214. If so, then the hardware accelerator may provide an error indication to the processor at 415. The error indication may be due to the fact that the associated job may never be executed because the TCB inserted after the TCB whose processing has completed is not accessed by the hardware accelerator. The hardware accelerator or processor may resume operation as described above.
しかしながら、TCB_nが410において完了したとして識別されない場合、次いで、プロセッサは、420においてTCB_nをTCBのリスト内で探し得る。具体的には、プロセッサは、TCB_nが識別されるまで、TCBのリスト内の1つ以上のTCBをクエリし得る。次いで、プロセッサは、425でTCBリンクチェーンを更新し得る。リンクチェーンを更新することは、例えば、挿入されるTCBのチェーンポインタを更新すること、チェーン内の1つ以上のTCBのチェーンポインタを更新すること、ハードウェアアクセラレータのバッファを更新すること、プロセッサを更新することなどを含み得る。更新は、TCB_nを正しく識別する目的のためであってもよい。次いで、プロセッサおよびハードウェアアクセラレータは、上記のように動作を再開し得る。However, if TCB_n is not identified as completed at 410, then the processor may look for TCB_n in the list of TCBs at 420. Specifically, the processor may query one or more TCBs in the list of TCBs until TCB_n is identified. The processor may then update the TCB link chain at 425. Updating the link chain may include, for example, updating the chain pointer of the TCB being inserted, updating the chain pointer of one or more TCBs in the chain, updating buffers of the hardware accelerator, updating the processor, etc. The updates may be for the purpose of correctly identifying TCB_n. The processor and hardware accelerator may then resume operation as described above.
APIにおける値TCB_nへのポインタが、405におけるヌル値である場合、これは、TBC_xが、TCB構造105のPRIOフィールド128に示されるように、その優先順位に基づいてキューに挿入されることを示し得る。結果として、プロセッサは次いで、430でTCBの優先順位ベースの挿入を行い得る。優先順位ベースの挿入は、所与の優先順位セクションまたは一般的なキュー内の最初または最後のTCBに関する情報を使用して、TCBが挿入されるべき位置を識別することを含み得る。一例として、優先順位ベースの挿入は、435において、新しいジョブまたは新しいTCBをTCBのリストに挿入するために優先順位テーブルを横断することを含み得る。例えば、プロセッサは、各TCBの優先順位レベルを示すTCBのリストに関連するテーブル、または所与の優先順位セクションの最初もしくは最後のTCBの指標を有してもよく、またはアクセスしてもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、プロセッサは、所与の優先順位レベルで最後のTCBを示すインジケータまたはフラグを有することができるか、またはアクセスすることができる。これらのフラグまたはインジケータは、TCB管理が行われている間、システムまたはハードウェアアクセラレータが停止される時間を短縮するのに役立ち得る。代替的に、プロセッサ210は、TCBのチェーンポインタフィールド104または108の助けを借りて、キュー内の最初のTCB、現在実行中のTCB、またはそれ以外のTCBから開始し、図2のメモリ201内のTCBのチェーンを横断し得る。横断は、例えば、所与の優先順位セクションの最後のTCBを識別するためであり得る。TCBのPRIOフィールド128を読み取ることによって、各TCBの優先順位レベルを判定し得る。優先順位テーブルが本明細書に記載されているが、他の実施形態では、TCBの優先順位ベースの編成に関連するデータ構造は異なり得ることが理解されるであろう。If the pointer to value TCB_n in the API is a null value at 405, this may indicate that TBC_x is to be inserted into the queue based on its priority as indicated in the
次に、APIは、440で戻し、再開してもよい。一般に、APIは、プロセッサ上で実行される、より高いレベルのアプリケーションによって呼び出され得る。APIが戻すと、プロセッサは、アプリケーションコードの残りの部分の実行を「再開」し得る。また、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、上記のように、その機能形態を「停止」状態に再開し得る。The API may then return and resume at 440. In general, the API may be called by a higher level application running on the processor. When the API returns, the processor may "resume" execution of the remainder of the application code. Also, the hardware accelerator may resume its functional form to a "stopped" state, as described above.
プロセッサ210は、(例えば、所与の優先順位セクションの最後のTCBに関する情報を使用することによって、またはそれ以外の技術によって)リンクされたリストを横断して、TCB_xが図2に関して上記されるように配置されるべき位置を識別し得る。位置が識別されると、TCBは、TCBのリストに挿入され得る。次いで、APIは、TCBがTCBのリストに正常に挿入されたことを、例えば、TCBを要求または引き起こし得るより高いレベルのアプリケーションにSUCCESSインジケータを戻すことによって示し、より高いレベルのアプリケーションの他の機能の実行を再開してもよい。The processor 210 may traverse the linked list (e.g., by using information about the last TCB in a given priority section, or by other techniques) to identify the location where TCB_x should be placed as described above with respect to FIG. 2. Once the location is identified, the TCB may be inserted into the list of TCBs. The API may then indicate that the TCB was successfully inserted into the list of TCBs, e.g., by returning a SUCCESS indicator to a higher level application that may have requested or evoked the TCB, and may resume execution of other functions of the higher level application.
いくつかの実施形態では、既存のジョブまたはTCBを改変することが望ましい場合がある。改変は、例えば、TCBのリスト内の既存のTCBを、異なる係数、異なる入力バッファへのポインタなどを含む別のTCBに置き換えることを含み得る。図5は、ジョブまたはTCB改変コマンドに使用され得る例示的なAPIを示す。APIは、プロセッサによって行われてもよい。APIに関連する改変コマンドの構文は、modify_job(ACC_TCB TCB_n、ACC_TCB TCB_o)であり得る。「ACC_TCB TCB_n」は、キューに挿入される新しいTCB(「TCB_n」)を指す情報を含み得る。「ACC_TCB TCB_o」は、キューから除去されるTCB(「TCB_o」)を指す情報を含み得る。具体的には、TCB_nは、TCB_oの代わりにキューに挿入されるTCBであり得る。このようにして、既存のTCB(TCB_o)は、そのTCBを、更新情報を含む新しいTCB(TCB_n)に置き換えることによって改変され得る。In some embodiments, it may be desirable to modify an existing job or TCB. Modification may include, for example, replacing an existing TCB in the list of TCBs with another TCB that includes a different coefficient, a pointer to a different input buffer, etc. FIG. 5 illustrates an example API that may be used for a job or TCB modification command. The API may be performed by a processor. The syntax of the modify command associated with the API may be modify_job(ACC_TCB TCB_n, ACC_TCB TCB_o). "ACC_TCB TCB_n" may include information pointing to a new TCB ("TCB_n") to be inserted into the queue. "ACC_TCB TCB_o" may include information pointing to a TCB ("TCB_o") to be removed from the queue. Specifically, TCB_n may be a TCB to be inserted into the queue in place of TCB_o. In this way, an existing TCB (TCB_o) can be modified by replacing it with a new TCB (TCB_n) that contains the updated information.
APIは、505において、ハードウェアアクセラレータを停止することを含んでもよい。停止は、要素236に関して上記された停止コマンドなどの停止コマンドに応答し得る。次いで、APIは、所与のジョブの状況を510でクエリすることを含み得る。具体的には、プロセッサ210は、保留中、完了中、走行中などのジョブかを510で識別し得る。いくつかの実施形態では、510でのクエリには、クエリAPIを走行することを含んでもよく、これは、図7に関して以下でさらに詳細に考察される。The API may include stopping the hardware accelerator at 505. The stopping may be in response to a stop command, such as the stop command described above with respect to element 236. The API may then include querying the status of a given job at 510. In particular, the processor 210 may identify at 510 whether the job is pending, completing, running, etc. In some embodiments, the query at 510 may include running a query API, which is discussed in more detail below with respect to FIG. 7.
APIは次いで、515において、510におけるクエリの結果は、TCB_oが保留中であることを示すかを判定することを含んでよい。「保留中」TCBは、将来の実行/処理のためにキュー内にあるTCBを指してもよく、そのTCBに関連するそのようなジョブは、現在ハードウェアアクセラレータによって行われていないか、またはまだ行われていない。言い換えれば、保留中のTCBは、図2に関して記載されたように、220で実行されるTCBのキュー内にあり得る。TCB_oが保留中でない場合、APIは520でエラーを戻し得る。エラー条件は、TCB_oが保留中でない場合、そのジョブは既に行われている場合があるため、TCB_oに関連するジョブを改変するか、またはTCB_nとの置換で置き換えることができない場合があるためであり得る。エラー条件が識別されて戻された後、例えば、TCBキュー内の次のTCBを処理することによって、ハードウェアアクセラレータの動作を再開してもよい。The API may then include, at 515, determining whether the results of the query at 510 indicate that TCB_o is pending. A "pending" TCB may refer to a TCB that is in a queue for future execution/processing, where such job associated with the TCB is not currently being performed or has not yet been performed by the hardware accelerator. In other words, a pending TCB may be in a queue of TCBs to be executed at 220, as described with respect to FIG. 2. If TCB_o is not pending, the API may return an error at 520. The error condition may be because if TCB_o is not pending, the job associated with TCB_o may not be able to be modified or replaced with a replacement for TCB_n, since the job may already have been performed. After the error condition is identified and returned, the operation of the hardware accelerator may be resumed, for example, by processing the next TCB in the TCB queue.
しかしながら、510でのクエリが、TCB_oは保留中であることを515で戻す場合、APIは、保留中のTCBのリスト内のTCB_oを525で探すことを含んでよい。例えば、プロセッサ210は、実行されるTCB220におけるTCB_oの位置またはアドレスを識別し得る。TCB_oが見つかると、プロセッサ210は、TCB_oをデリンクし、TCB_nを530でその場所に配置し得る。このようなデリンク動作は、例えば、キュー内のTCB_oに先行するTCBのチェーンポインタFWD_CPフィールドを変えることと、TCB_nのメモリアドレスでこのフィールドを更新することとを含み得る。デリンク動作は、TCB_nのBACK_CPフィールドをTCB_oのBACK_CPフィールド内の同じ値で更新することをさらに含み得る。デリンク動作はまた、TCB_nのFWD_CPフィールドをTCB_oのFWD_CPフィールドの同じ値で更新することと、TCB_nのFWD_CPによって参照されるTCBのBACK_CPフィールドをTCB_nのメモリアドレスで更新することとを含んでもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、APIはまた、TCB_oを格納するために使用されるメモリをフリーにし、メモリをフリーのメモリブロックのプールに戻し得る。最後に、APIは、TCB_oがTCB_nに置き替えられた状況インジケータを535で戻すことを含んでもよく、ハードウェアアクセラレータの動作を再開してもよい。例えば、インジケータが、ハードウェアアクセラレータの別の論理もしくは処理要素、またはプロセッサに送信され、置換が完了したことを示し、次いで、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、TCBのリンクされたリスト内のTCBの処理を再開し得る。要素535の戻しおよび再開機能は、例えば、要素440の戻しおよび再開機能と同様であってもよい。However, if the query at 510 returns at 515 that TCB_o is pending, the API may include looking for TCB_o in a list of pending TCBs at 525. For example, processor 210 may identify a location or address of TCB_o in TCB 220 to be executed. Once TCB_o is found, processor 210 may delink TCB_o and place TCB_n in its place at 530. Such a delink operation may include, for example, altering the chain pointer FWD_CP field of the TCB preceding TCB_o in the queue and updating this field with the memory address of TCB_n. The delink operation may further include updating the BACK_CP field of TCB_n with the same value in the BACK_CP field of TCB_o. The delink operation may also include updating the FWD_CP field of TCB_n with the same value of the FWD_CP field of TCB_o, and updating the BACK_CP field of the TCB referenced by the FWD_CP of TCB_n with the memory address of TCB_n. In some embodiments, the API may also free the memory used to store TCB_o and return the memory to a pool of free memory blocks. Finally, the API may include returning a status indicator at 535 that TCB_o has been replaced with TCB_n, and may resume operation of the hardware accelerator. For example, an indicator may be sent to another logic or processing element of the hardware accelerator, or a processor, to indicate that the replacement is complete, and the hardware accelerator may then resume processing of the TCBs in the linked list of TCBs. The return and resume functions of
いくつかの実施形態では、TCBのリンクされたリスト内のTCBを置き換えるのではなく、除去することが望ましい場合がある。図6は、実行されるTCB220のリストからTCBを除去するためにプロセッサ210などの電子デバイスの構成要素によって使用され得るAPIを示す。APIの構文は、delete_job(ACC_TCB TCB_d)であり得、TCB_dは破棄されるTCBであり得、「ACC_TCB TCB_d」は、TCB_dを参照する情報を含み得る。In some embodiments, it may be desirable to remove, rather than replace, a TCB in a linked list of TCBs. FIG. 6 illustrates an API that may be used by a component of an electronic device, such as the processor 210, to remove a TCB from the list of TCBs 220 to be executed. The syntax of the API may be delete_job(ACC_TCB TCB_d), where TCB_d may be the TCB to be destroyed, and "ACC_TCB TCB_d" may include information referencing TCB_d.
図6のAPIは、図5の要素と類似し得る1つ以上の要素を含み得、1つ以上の特性を図5の要素と共有し得る。具体的には、要素605、610、615、620、625、および635はそれぞれ、図5の要素505、510、515、520、525、および535と類似していてもよく、1つ以上の特性を共有してもよい。これらの要素の詳細は、冗長化を回避するために再反復されない。The API of FIG. 6 may include one or more elements that may be similar to and share one or more characteristics with the elements of FIG. 5. Specifically,
しかしながら、わかるように、TCB_dが、実行されるTCB220のリストに見出された後、図6のAPIは、TCB_dを630でデリンクすること、およびTCB_dの前後にあったリスト内のTCBを接続することを含んでよい。具体的には、TCB_dに先行するTCBのFWD_CPフィールドは、TCB_dに続くTCBを指し示すように変えられてもよい。同様に、TCB_dに続くTCBのBACK_CPフィールドは、TCB_dに先行するTCBを指し示すように変えられてもよい。このようにして、TCB_dは、220で実行されるTCBのリストから効果的に除去され得る。いくつかの実施形態では、APIはまた、TCB_dを格納するために使用されるメモリをフリーにし、メモリをフリーのメモリブロックのプールに戻し得る。However, as can be seen, after TCB_d is found in the list of TCBs to be executed 220, the API of FIG. 6 may include delinking TCB_d at 630 and connecting the TCBs in the list that preceded and followed TCB_d. Specifically, the FWD_CP field of the TCB preceding TCB_d may be changed to point to the TCB following TCB_d. Similarly, the BACK_CP field of the TCB following TCB_d may be changed to point to the TCB preceding TCB_d. In this way, TCB_d may be effectively removed from the list of TCBs to be executed at 220. In some embodiments, the API may also free the memory used to store TCB_d, returning the memory to a pool of free memory blocks.
述べたように、いくつかの実施形態では、TCBのリンクされたリスト内のTCBの状況をクエリすることが望ましい場合がある。例えば、プロセッサ210上で走行中のアプリケーションコードは、特定のTCBまたは特定のジョブの状況更新をハードウェアアクセラレータから要求し得る。別の例として、図5または図6のAPIは、要素510または610でクエリを発行し得る。図7は、このようなクエリに応答して使用され得る例示的なAPIを示す。図7のAPIは、プロセッサ210によって行われてもよい。クエリの構文は、例えば、query_job(ACC_TCB TCB_q)であり得る。「ACC_TCB TCB_q」は、TCB(「TCB_q」)を指す、ポインタおよびアドレスなどの情報を含んでよい。As mentioned, in some embodiments, it may be desirable to query the status of a TCB in the linked list of TCBs. For example, application code running on processor 210 may request a status update from the hardware accelerator for a particular TCB or a particular job. As another example, the API of FIG. 5 or FIG. 6 may issue a query at
いくつかの実施形態では、図3~図6のうちの1つ以上のAPIは、所与の優先順位レベルで最後のTCBに影響を及ぼし得ることに留意されたい。例えば、「高」優先順位を有する新しいTCBは、「高」優先順位を有する既存の最後のTCBの後に挿入され得る。代替的に、所与の優先順位を有する最後のTCBは、置き換えられるか、または除去され得る。この情勢において、その優先順位レベルの更新された「最後のTCB」を正確に反映するために、様々なチェーンポインタ、TCBのリンクされたリストなどに対する様々な更新が行われ得る。Note that in some embodiments, one or more of the APIs in Figures 3-6 may affect the last TCB at a given priority level. For example, a new TCB with "high" priority may be inserted after an existing last TCB with "high" priority. Alternatively, the last TCB with a given priority may be replaced or removed. In this situation, various updates to various chain pointers, linked lists of TCBs, etc. may be made to accurately reflect the updated "last TCB" for that priority level.
APIは、705において、ハードウェアアクセラレータを停止させることを含んでもよい。ハードウェアアクセラレータを停止させることは、要素320、505、605などに関して記載された停止と同様であり得る。次いで、APIは、TCB_qが存在するかを710において識別することを含んでよい。言い換えれば、APIは、TCB_qがTCBのリンクされたリストに位置することができるかを識別し得る。TCB_qが存在しないことが710において見出された場合、APIは、715においてエラーを戻すことと、例えば、上記の要素440と同様であり得る動作を再開することとを含み得る。The API may include, at 705, stopping the hardware accelerator. Stopping the hardware accelerator may be similar to the stopping described with respect to
TCB_qが710で識別される場合、APIは次いで、TCB_qが完了したかを720で識別することを含んでよい。言い換えれば、APIは、TCB_qが先に実行されたTCB214内にあるかを識別することを含んでよい。加えて、または代替的に、TCB_qが完了しているかを識別することは、TCB_qに関連するか、またはTCB_qの一部である完了フラグをチェックすることを含み得る。他の実施形態は、TCBの完了に関連する他のインジケータを含み得る。そうであれば、APIは、725において、TCB_qが完了したという指標を戻すことと、例えば、要素440に関して上記のように動作を再開することと、を含んでよい。If TCB_q is identified at 710, the API may then include identifying at 720 whether TCB_q is completed. In other words, the API may include identifying whether TCB_q is within a previously executed TCB 214. Additionally or alternatively, identifying whether TCB_q is completed may include checking a completion flag associated with or part of TCB_q. Other embodiments may include other indicators related to the completion of the TCB. If so, the API may include returning an indication that TCB_q is completed at 725 and resuming operation as described above with respect to
TCB_qが720において完了していないと識別される場合、APIは、730において、TCB_qが走行中であるかを識別することを含んでよい。本明細書で使用されるように、「走行中」は、TCBが処理されているアクティブ状態にあったか、またはTCBが参照するジョブは、ハードウェアアクセラレータが停止される前にハードウェアアクセラレータによって実行されているかを示し得る。TCB_qが730で走行中と識別される場合、次いで、APIは、TCB_qが735で走行中であるという指標を戻すことと、例えば、要素440に関して上記したように動作を再開することとを含み得る。しかしながら、TCB_qが730において走行中と識別されない場合、次いで、APIは、例えば、要素440に関して上記したように、TCB_qが、再開動作として740で保留中であるという指標を戻すことを含むことができる。If TCB_q is identified as not complete at 720, the API may include identifying whether TCB_q is running at 730. As used herein, "running" may indicate that the TCB was in an active state being processed or that the job referenced by the TCB was being executed by the hardware accelerator before the hardware accelerator was stopped. If TCB_q is identified as running at 730, then the API may include returning an indication that TCB_q is running at 735 and resuming the operation, e.g., as described above with respect to
上記APIは、一実施形態の例として意図されており、他の実施形態は、記載されているものとは異なり得ることが理解されるであろう。例えば、他の実施形態は、より多くまたはより少ない要素、異なる構文などを有し得る。いくつかの実施形態では、一定の要素は、図3~図7に示されるものとは異なる順序で行われてもよい。加えて、一定のAPIまたはその要素は、ハードウェアアクセラレータまたはプロセッサによって行われると記載され得るが、いくつかの実施形態では、ハードウェアアクセラレータによって行われると記載されている1つ以上のAPIまたはその要素は、プロセッサによって行われる場合もあれば、その逆の場合もある。他の実施形態では、他の変形例が存在してもよい。The above APIs are intended as examples of one embodiment, and it will be understood that other embodiments may differ from those described. For example, other embodiments may have more or fewer elements, different syntax, etc. In some embodiments, certain elements may be performed in a different order than that shown in Figures 3-7. Additionally, while certain APIs or elements thereof may be described as being performed by a hardware accelerator or a processor, in some embodiments, one or more APIs or elements thereof that are described as being performed by a hardware accelerator may be performed by a processor, or vice versa. In other embodiments, other variations may exist.
図8は、本明細書に開示された実施形態のいずれかに従って、1つ以上のハードウェアアクセラレータを含み得る例示的な電気デバイス1800のブロック図である。いくらかの構成要素は、電気デバイス1800に含まれるように図8に例示されるが、これらの構成要素のうちの任意の1つ以上は、用途に好適なように省略または複製され得る。いくつかの実施形態では、電気デバイス1800に含まれる構成要素のいくつかまたはすべては、1つ以上のマザーボードに取り付けられてもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、これらの構成要素のいくつかまたはすべては、単一のSoCダイ上に製造される。FIG. 8 is a block diagram of an example
加えて、様々な実施形態において、電気デバイス1800は、図8に例示された1つ以上の構成要素を含まない場合があるが、電気デバイス1800は、1つ以上の構成要素に結合するためのインターフェース回路を含んでもよい。例えば、電気デバイス1800は、ディスプレイデバイス1806を含まなくてもよいが、ディスプレイデバイス1806が結合されてもよいディスプレイデバイスインターフェース回路(例えば、コネクタおよびドライバ回路)を含んでもよい。別の一組の例では、電気デバイス1800は、オーディオ入力デバイス1824またはオーディオ出力デバイス1808を含まなくてもよいが、オーディオ入力デバイス1824またはオーディオ出力デバイス1808が結合されてもよいオーディオ入力または出力デバイスインターフェース回路(例えば、コネクタおよび支持回路)を含んでもよい。Additionally, in various embodiments, the
電気デバイス1800は、処理デバイス1802(例えば、1つ以上の処理デバイス)を含んでもよい。本明細書で使用されるように、「処理デバイス」または「プロセッサ」という用語は、レジスタおよび/またはメモリからの電子データを処理して、その電子データをレジスタおよび/またはメモリに格納され得る他の電子データに変換する任意のデバイスまたはデバイスの一部を指し得る。処理デバイス1802は、1つ以上のDSP、ASIC、CPU、グラフィックス処理ユニット(GPU)、暗号プロセッサ(ハードウェア内の暗号アルゴリズムを実行する専門プロセッサ)、サーバプロセッサ、または任意の他の好適な処理デバイスを含んでもよい。電気デバイス1800は、揮発性メモリ(例えば、ダイナミックランダムアクセスメモリ(DRAM))、不揮発性メモリ(例えば、読み取り専用メモリ(ROM))、フラッシュメモリ、ソリッドステートメモリ、および/またはハードドライブなどの1つ以上のメモリデバイスをそれ自体が含み得るメモリ1804を含んでもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、メモリ1804は、処理デバイス1802とダイを共有するメモリを含んでもよい。このメモリは、キャッシュメモリとして使用され得、埋め込まれた動的ランダムアクセスメモリ(eDRAM)またはスピン転送トルク磁気ランダムアクセスメモリ(STT-MRAM)を含み得る。処理デバイス1802は、例えば、プロセッサ210と同様であり得、ハードウェアアクセラレータ205などのハードウェアアクセラレータと結合され得る。The
いくつかの実施形態では、電気デバイス1800は、通信チップ1812(例えば、1つ以上の通信チップ)を含んでもよい。例えば、通信チップ1812は、電気デバイス1800へのデータの転送および電気デバイス1800からのデータの転送のためのワイヤレス通信を管理するように構成され得る。「ワイヤレス」という用語およびその派生語は、非固体媒体を通じて変調された電磁放射を使用してデータを通信することができる回路、デバイス、システム、方法、技法、通信チャネルなどを説明するために使用され得る。この用語は、関連付けられたデバイスが任意のワイヤを収容しないことを暗示するものではないが、いくつかの実施形態では、それらを含まない場合がある。In some embodiments, the
通信チップ1812は、Wi-Fi(IEEE802.11ファミリー)、IEEE802.16規格(例えば、IEEE802.16-2005改正)、長期進化(LTE)プロジェクトを、任意の改正、更新、および/または改訂(例えば、高度なLTEプロジェクト、超モバイルブロードバンド(UMB)プロジェクト(「3GPP2」とも呼ばれる)など)とともに含む電気電子技術者協会(IEEE)規格を含むが、これらに限定されない、いくらかのワイヤレス規格またはプロトコルのいずれかを実装し得る。IEEE 802.16互換ブロードバンドワイヤレスアクセス(BWA)ネットワークは、一般に、IEEE 802.16規格の適合性および相互運用性試験に合格した製品の認証マークである、マイクロウェーブアクセスのワールドワイド相互運用性を表す頭文字、WiMAXネットワークと呼ばれる。通信チップ1812は、グローバルモバイル通信システム(GSM)、一般パケット無線サービス(GPRS)、ユニバーサルモバイル電気通信システム(UMTS)、高速パケットアクセス(HSPA)、進化HSPA(E-HSPA)、またはLTEネットワークに従って動作してもよい。通信チップ1812は、GSM進化高速データ(EDGE)、GSM EDGE無線アクセスネットワーク(GERAN)、ユニバーサル地上無線アクセスネットワーク(UTRAN)、または進化型UTRAN(E-UTRAN)に従って動作してもよい。通信チップ1812は、コード分割多重アクセス(CDMA)、時間分割多重アクセス(TDMA)、デジタル強化コードレス電気通信(DECT)、進化データ最適化(EV-DO)、およびそれらの派生物、ならびに3G、4G、5G、およびそれ以上に指定される任意の他のワイヤレスプロトコルに従って動作し得る。通信チップ1812は、他の実施形態では、他のワイヤレスプロトコルに従って動作し得る。電気デバイス1800は、ワイヤレス通信を容易にするため、および/または他のワイヤレス通信(AMまたはFM無線伝送など)を受信するためのアンテナ1822を含み得る。The
いくつかの実施形態では、通信チップ1812は、電気的、光学的、または任意の他の好適な通信プロトコル(例えば、イーサネット)などの有線通信を管理し得る。上述したように、通信チップ1812は、複数の通信チップを含んでもよい。例えば、第1の通信チップ1812は、Wi-FiまたはBluetoothなどの短距離ワイヤレス通信に専用であってもよく、第2の通信チップ1812は、全地球測位システム(GPS)、EDGE、GPRS、CDMA、WiMAX、LTE、EV-DOなどの長距離無線通信に専用であってもよい。いくつかの実施形態では、第1の通信チップ1812は、ワイヤレス通信に専用であり得、第2の通信チップ1812は、有線通信に専用であり得る。In some embodiments, the
電気デバイス1800は、バッテリー/電源回路1814を含み得る。バッテリー/電源回路1814は、電気デバイス1800の構成要素を電気デバイス1800とは別個のエネルギー源(例えばACライン電源)に結合するための1つ以上のエネルギー貯蔵デバイス(例えば、バッテリーまたはコンデンサ)および/または回路を含み得る。The
電気デバイス1800は、ディスプレイデバイス1806(または上記で考察したように対応するインターフェース回路)を含んでもよい。ディスプレイデバイス1806は、ヘッドアップディスプレイ、コンピュータモニタ、プロジェクタ、タッチスクリーンディスプレイ、液晶ディスプレイ(LCD)、発光ダイオードディスプレイ、またはフラットパネルディスプレイなど、任意の視覚インジケータを含んでもよい。
電気デバイス1800は、オーディオ出力デバイス1808(または上記で考察したような対応するインターフェース回路)を含み得る。オーディオ出力デバイス1808は、スピーカ、ヘッドセット、またはイヤホンなどの可聴インジケータを生成する任意のデバイスを含み得る。The
電気デバイス1800は、オーディオ入力デバイス1824(または上記で考察したような対応するインターフェース回路)を含み得る。オーディオ入力デバイス1824は、マイク、マイクアレイ、またはデジタル楽器(例えば、楽器デジタルインターフェース(MIDI)出力を有する楽器)などの音を表す信号を生成する任意のデバイスを含み得る。The
電気デバイス1800は、GPSデバイス1818(または上記で考察したような対応するインターフェース回路)を含んでもよい。GPSデバイス1818は、衛星ベースのシステムと通信でき、当該技術分野で知られているように、電気デバイス1800の位置を受信し得る。The
電気デバイス1800は、別の出力デバイス1810(または上記で考察したような対応するインターフェース回路)を含み得る。他の出力デバイス1810の例は、オーディオコーデック、ビデオコーデック、プリンタ、他のデバイスに情報を提供するための有線もしくはワイヤレス送信機、または追加の記憶デバイスを含み得る。The
電気デバイス1800は、別の入力デバイス1820(または上記で考察したような対応するインターフェース回路)を含み得る。他の入力デバイス1820の例には、加速度計、ジャイロスコープ、コンパス、画像キャプチャデバイス、キーボード、マウスなどのカーソル制御デバイス、スタイラス、タッチパッド、バーコードリーダ、クイックレスポンス(QR)コードリーダ、任意のセンサ、または無線周波数識別(RFID)リーダが含まれ得る。The
電気デバイス1800は、ハンドヘルドもしくはモバイル電気デバイス(例えば、携帯電話、スマートフォン、モバイルインターネットデバイス、音楽プレーヤー、タブレットコンピュータ、ラップトップコンピュータ、ネットブックコンピュータ、ウルトラブックコンピュータ、携帯情報端末(PDA)、ウルトラモバイルパーソナルコンピュータなど)、デスクトップ電気デバイス、サーバデバイスもしくは他のネットワークコンピューティングコンポーネント、プリンタ、スキャナ、モニタ、セットトップボックス、エンターテイメント制御ユニット、車両制御ユニット、デジタルカメラ、デジタルビデオレコーダ、または着用可能な電気デバイスなどの任意の所望の形態要因を有し得る。いくつかの実施形態では、電気デバイス1800は、データを処理する任意の他の電子デバイスであり得る。The
様々な実施形態の例
例1は、コンピューティングデバイスの構成要素によって、構成要素により行われるジョブに関連するTCBを識別することと、TCBに基づいてジョブの優先順位レベルを識別することと、識別された優先順位レベルに基づいて行われるジョブのキューにジョブを挿入することと、識別された優先順位レベルに基づいてジョブを行うことと、を含む方法を含む。Examples of Various Embodiments Example 1 includes a method including identifying, by a component of a computing device, a TCB associated with a job to be performed by the component, identifying a priority level of the job based on the TCB, inserting the job into a queue of jobs to be performed based on the identified priority level, and performing the job based on the identified priority level.
例2は、例1、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の方法を含み、構成要素は、コンピューティングデバイスのコアまたはハードウェアアクセラレータである。Example 2 includes the method of Example 1 or any other example herein, where the component is a core or a hardware accelerator of a computing device.
例3は、例1、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の方法を含み、ジョブはDMA要求に関連するジョブである。Example 3 includes the method of example 1 or any other example herein, where the job is a job associated with a DMA request.
例4は、例1~3のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の方法を含み、ジョブが、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブであり、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブをキューに挿入することは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブを、より低い優先順位でのジョブの実行の前に実行されるキューに挿入することを含む。Example 4 includes a method as described in any of Examples 1-3 or any other example herein, where the job is a job of a higher priority level, and inserting the job of the higher priority level into the queue includes inserting the job of the higher priority level into the queue to be executed before execution of the job at the lower priority.
例5は、例4、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の方法を含み、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブは、TCBの識別の前にコンピューティングデバイスの構成要素によって識別されている。Example 5 includes the method of example 4 or any other example herein, wherein the lower priority level job is identified by a component of the computing device prior to identification of the TCB.
例6は、例4、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の方法を含み、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブの挿入の前にキューに挿入されている。Example 6 includes the method of example 4 or any other example herein, wherein a job of a lower priority level is inserted into the queue before the insertion of a job of a higher priority level.
例7は、例1~3のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の方法を含み、行われるジョブのキューにジョブを挿入することは、ジョブに関連するAPIの遂行に基づく。Example 7 includes a method as described in any of Examples 1-3 or any other example herein, where inserting a job into a queue of jobs to be performed is based on execution of an API associated with the job.
例8は、例1~3のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の方法を含み、行われるジョブのキューは、4つの優先順位レベルを有するキューを含む。Example 8 includes the method of any of Examples 1-3 or any other example herein, wherein the queue of jobs to be performed includes a queue having four priority levels.
例9は、命令を含む1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、命令は、コンピューティングデバイスの1つ以上の要素による命令の実行時に、コンピューティングデバイスの構成要素に、構成要素によって行われるジョブに関連するTCBを識別させ、TCBに基づいてジョブの優先順位レベルを識別させ、識別された優先順位レベルに基づいて、行われるジョブのキューにジョブを挿入させ、識別された優先順位レベルに基づいてジョブを行わせる。Example 9 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media containing instructions that, upon execution of the instructions by one or more elements of a computing device, cause a component of the computing device to identify a TCB associated with a job to be performed by the component, identify a priority level for the job based on the TCB, insert the job into a queue of jobs to be performed based on the identified priority level, and perform the job based on the identified priority level.
例10は、例9、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、構成要素は、コンピューティングデバイスのコアまたはハードウェアアクセラレータである。Example 10 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in Example 9 or any other example herein, where the component is a core or hardware accelerator of a computing device.
例11は、例9、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、ジョブはDMA要求に関連するジョブである。Example 11 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in Example 9 or any other example herein, where the job is a job associated with a DMA request.
例12は、例9~11のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、ジョブは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブであり、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブをキューに挿入することは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブを、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブの実行の前に実行されるキューに挿入することを含む。Example 12 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in any of Examples 9-11 or any other example herein, where the job is a job of a higher priority level, and inserting the job of the higher priority level into the queue includes inserting the job of the higher priority level into the queue to be executed before execution of the job of the lower priority level.
例13は、例12、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブは、TCBの識別の前にコンピューティングデバイスの構成要素によって識別されている。Example 13 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in Example 12 or any other example herein, wherein the lower priority level job is identified by a component of the computing device prior to identification of the TCB.
例14は、例12、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブの挿入の前にキューに挿入されている。Example 14 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in Example 12 or any other example herein, wherein a job of a lower priority level is inserted into the queue before the insertion of a job of a higher priority level.
例15は、例9~11のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、行われるジョブのキューにジョブを挿入することは、ジョブに関連するAPIの遂行に基づく。Example 15 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in any of Examples 9-11 or any other example herein, wherein inserting a job into a queue of jobs to be performed is based on execution of an API associated with the job.
例16は、例9~11のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、行われるジョブのキューは、4つの優先順位レベルを有するキューを含む。Example 16 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in any of Examples 9-11 or any other example herein, wherein the queue of jobs to be performed includes a queue having four priority levels.
例17は、構成要素によって行われるジョブに関連するTCBを識別する手段と、TCBに基づいてジョブの優先順位レベルを識別する手段と、識別された優先順位レベルに基づいて、行われるジョブのキューにジョブを挿入する手段と、識別された優先順位レベルに基づいてジョブを行う手段と、を含む装置を含む。Example 17 includes an apparatus including means for identifying a TCB associated with a job to be performed by a component, means for identifying a priority level of the job based on the TCB, means for inserting the job into a queue of jobs to be performed based on the identified priority level, and means for performing the job based on the identified priority level.
例18は、例17、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、構成要素は、コンピューティングデバイスのコアまたはハードウェアアクセラレータである。Example 18 includes the apparatus of Example 17 or any other example herein, where the component is a core or a hardware accelerator of a computing device.
例19は、例17、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、ジョブはDMA要求に関連するジョブである。Example 19 includes the apparatus of Example 17 or any other example herein, wherein the job is a job associated with a DMA request.
例20は、例17~19のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、ジョブは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブであり、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブをキューに挿入する手段は、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブを、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブの実行の前に実行されるキューに挿入する手段を含む。Example 20 includes the apparatus of any of Examples 17-19 or any other example herein, wherein the job is a higher priority level job, and the means for inserting the higher priority level job into the queue includes means for inserting the higher priority level job into the queue to be executed before execution of the lower priority level job.
例21は、例20、または本明細書における何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブは、TCBの識別前にコンピューティングデバイスの構成要素によって識別されている。Example 21 includes the apparatus of Example 20 or any other example herein, wherein the lower priority level job is identified by a component of the computing device prior to identifying the TCB.
例22は、例20、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブの挿入の前にキューに挿入されている。Example 22 includes the apparatus of Example 20 or any other example herein, wherein a job of a lower priority level is inserted into the queue before the insertion of a job of a higher priority level.
例23は、例17~19のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、行われるジョブのキューにジョブを挿入することは、ジョブに関連するAPIの遂行に基づく。Example 23 includes an apparatus as described in any of Examples 17-19 or any other example herein, wherein inserting a job into a queue of jobs to be performed is based on execution of an API associated with the job.
例24は、例17~19のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、行われるジョブのキューは、4つの優先順位レベルを有するキューを含む。Example 24 includes the apparatus of any of Examples 17-19 or any other example herein, wherein the queue of jobs to be performed includes a queue having four priority levels.
例25は、メモリと、メモリと通信可能に結合された構成要素と、を備える装置を含み、構成要素は、構成要素によって行われるジョブに関連するTCBを識別し、TCBに基づいてジョブの優先順位レベルを識別し、識別された優先順位レベルに基づいて、行われるジョブのキューにジョブを挿入し、識別された優先順位レベルに基づいてジョブを行う。Example 25 includes an apparatus comprising a memory and a component communicatively coupled to the memory, the component identifying a TCB associated with a job to be performed by the component, identifying a priority level for the job based on the TCB, inserting the job into a queue of jobs to be performed based on the identified priority level, and performing the job based on the identified priority level.
例26は、例25、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、構成要素は、コンピューティングデバイスのコアまたはハードウェアアクセラレータである。Example 26 includes the apparatus of Example 25 or any other example herein, where the component is a core or a hardware accelerator of a computing device.
例27は、例25、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、ジョブはDMA要求に関連するジョブである。Example 27 includes the apparatus of example 25 or any other example herein, where the job is a job associated with a DMA request.
例28は、例25~27のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、ジョブは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブであり、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブをキューに挿入することは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブを、より低い優先順位のジョブの実行の前に実行されるキューに挿入することを含む。Example 28 includes the apparatus of any of Examples 25-27 or any other example herein, wherein the job is a higher priority level job, and inserting the higher priority level job into the queue includes inserting the higher priority level job into the queue to be executed before execution of the lower priority job.
例29は、例28、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブは、TCBの識別の前にコンピューティングデバイスの構成要素によって識別されている。Example 29 includes the apparatus of Example 28 or any other example herein, wherein the lower priority level job is identified by a component of the computing device prior to identification of the TCB.
例30は、例28、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、より低い優先順位レベルのジョブは、より高い優先順位レベルのジョブの挿入の前にキューに挿入されている。Example 30 includes the apparatus of example 28 or any other example herein, wherein a job of a lower priority level is inserted into the queue before the insertion of a job of a higher priority level.
例31は、例25 ~27のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、行われるジョブのキューにジョブを挿入することは、ジョブに関連するAPIの遂行に基づく。Example 31 includes an apparatus as described in any of Examples 25-27 or any other example herein, wherein inserting a job into a queue of jobs to be performed is based on execution of an API associated with the job.
例32は、例25~27のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の装置を含み、行われるジョブのキューは、4つの優先順位レベルを有するキューを含む。Example 32 includes the apparatus of any of Examples 25-27 or any other example herein, wherein the queue of jobs to be performed includes a queue having four priority levels.
例33は、プロセッサであって、TCBにおいて、TCBの優先順位レベルの指標を識別し、優先順位レベルの指標に基づいて、複数のTCBのキュー内の位置を識別し、かつ識別された位置でキューにTCBを挿入する、プロセッサと、プロセッサと通信可能に結合されたハードウェアアクセラレータであって、複数のTCBのキュー内のTCBに関連するジョブを行い、複数のTCBのキュー内のTCBの順序に従ってTCBに関連するジョブを行うハードウェアアクセラレータと、を備える、コンピューティングデバイスを含む。Example 33 includes a computing device including a processor that identifies, in the TCB, an indication of a priority level of the TCB, identifies a position in a queue of multiple TCBs based on the priority level indication, and inserts the TCB into the queue at the identified position; and a hardware accelerator communicatively coupled to the processor that performs a job associated with the TCB in the queue of multiple TCBs and that performs the job associated with the TCB according to an order of the TCBs in the queue of multiple TCBs.
例34は、例33、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のコンピューティングデバイスを含み、優先順位レベルの指標は、TCBにおける2ビットインジケータである。Example 34 includes the computing device of Example 33 or any other example herein, wherein the indication of the priority level is a two-bit indicator in the TCB.
例35は、例33、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のコンピューティングデバイスを含み、プロセッサは、TCBの伝送の前に停止要求をさらに送信する。Example 35 includes the computing device of Example 33 or any other example herein, wherein the processor further transmits a stop request prior to transmitting the TCB.
例36は、例33~35のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のコンピューティングデバイスを含み、キューは、第1の優先順位レベルのTCBの第1のサブ部分と、第1の優先順位レベルよりも低い第2の優先順位レベルのTCBの第2のサブ部分とを含み、ハードウェアアクセラレータは、TCBの第2のサブ部分に関連するジョブを行う前に、TCBの第1のサブ部分に関連するジョブを行う。Example 36 includes a computing device as described in any of Examples 33-35 or any other example herein, wherein the queue includes a first sub-portion of the TCB at a first priority level and a second sub-portion of the TCB at a second priority level lower than the first priority level, and the hardware accelerator performs a job associated with the first sub-portion of the TCB before performing a job associated with the second sub-portion of the TCB.
例37は、例36、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のコンピューティングデバイスを含み、TCBは、第1の優先順位レベルであり、プロセッサはさらに、現在実行中のTCBの優先順位レベルを識別し、現在実行中のTCBの優先順位レベルに基づいて、キュー内の位置を識別する。Example 37 includes the computing device of Example 36 or any other example herein, wherein the TCB is a first priority level, and the processor further identifies a priority level of a currently executing TCB and identifies a position in the queue based on the priority level of the currently executing TCB.
例38は、例37、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のコンピューティングデバイスを含み、現在実行中のTCBの優先順位レベルは、第1の優先順位レベルであり、位置は、TCBの第1のサブ部分の末端にある。Example 38 includes the computing device of Example 37 or any other example herein, wherein the priority level of the currently executing TCB is a first priority level and the location is at the end of the first subportion of the TCB.
例39は、例37、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のコンピューティングデバイスを含み、現在実行中のTCBの優先順位レベルは、第2の優先順位レベルであり、位置は、現在実行中のTCBの後であり、かつTCBの第2のサブ部分の他のTCBの前である。Example 39 includes the computing device of Example 37 or any other example herein, wherein the priority level of the currently executing TCB is a second priority level and the location is after the currently executing TCB and before other TCBs in the second sub-portion of the TCBs.
例40は、ハードウェアアクセラレータと通信するための通信インターフェースと、通信インターフェースと結合された論理であって、TCBにおいて、TCBの優先順位レベルの指標を識別し、優先順位レベルの指標に基づいて、複数のTCBのキュー内の位置にTCBを挿入し、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、キュー内のそれらの位置に基づいて、複数のTCBのそれぞれを実行する、論理と、を備えるプロセッサを含む。Example 40 includes a processor having a communications interface for communicating with a hardware accelerator, and logic coupled to the communications interface for identifying, in the TCB, an indication of a priority level of the TCB, inserting the TCB into a position in a queue of multiple TCBs based on the indication of the priority level, and executing each of the multiple TCBs based on their position in the queue by the hardware accelerator.
例41は、例40、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のプロセッサを含み、優先順位レベルの指標は、TCBにおける2ビットインジケータである。Example 41 includes the processor of example 40 or any other example herein, wherein the indication of the priority level is a two-bit indicator in the TCB.
例42は、例40、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のプロセッサを含み、優先順位レベルの指標は、TCBが、複数の可能な優先順位レベルのうちの1つにあることを示す。Example 42 includes the processor of Example 40 or any other example herein, where the priority level indication indicates that the TCB is at one of a plurality of possible priority levels.
例43は、例40~42、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のプロセッサを含み、ここで、TCBは、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、TCBを処理する前にプロセッサからトリガを受信するのを待つという指標、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、TCBの完了に関連してプロセッサに割り込みを送信するという指標、またはハードウェアアクセラレータが、TCBの完了に関連してプロセッサにトリガを送信するという指標をさらに含む。Example 43 includes the processor of Examples 40-42 or any other example herein, where the TCB further includes an indication that the hardware accelerator waits to receive a trigger from the processor before processing the TCB, an indication that the hardware accelerator sends an interrupt to the processor in association with completion of the TCB, or an indication that the hardware accelerator sends a trigger to the processor in association with completion of the TCB.
例44は、例40~42のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のプロセッサを含み、TCBは、TCBに関連するジョブを行うために使用される計算の種類の指標をさらに含む。Example 44 includes a processor as described in any of Examples 40-42 or any other example herein, wherein the TCB further includes an indication of a type of computation used to perform a job associated with the TCB.
例45は、例40~42のいずれか、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載のプロセッサを含み、TCBは、複数のTCBのキューにおける先のTCBの指標をさらに含む。Example 45 includes the processor of any of Examples 40-42 or any other example herein, wherein the TCB further includes an index of a previous TCB in a queue of multiple TCBs.
例46は、命令を含む1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、命令は、電子デバイスによって実行されると、電子デバイスのプロセッサに、複数のTCBのキューを識別することであって、複数のTCBのそれぞれのTCBが、キュー内のそれぞれのTCBの優先順位レベルの指標を含み、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、TCBの優先順位レベルに従ってそれぞれのTCBに関連するジョブを行う、識別することと、キューに関連するアプリケーションプログラミングインターフェース(API)を実行すること、APIの実行に基づいてキューを改変することと、を行わせる。Example 46 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media including instructions that, when executed by an electronic device, cause a processor of the electronic device to: identify a queue of a plurality of TCBs, each TCB of the plurality of TCBs including an indication of a priority level of each TCB in the queue, and a hardware accelerator to perform a job associated with each TCB according to the priority level of the TCB; execute an application programming interface (API) associated with the queue; and modify the queue based on execution of the API.
例47は、例46、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、APIは、TCBの優先順位レベルの指標に基づいて複数のTCBのキュー内へのTCBの挿入に関連する。Example 47 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in Example 46 or any other example herein, wherein the API is associated with inserting a TCB into a queue of multiple TCBs based on an indication of a priority level of the TCB.
例48は、例47、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、TCBの挿入は、優先順位レベルでの最後のTCBを示すフラグに関連する。Example 48 includes one or more of the non-transitory computer-readable media of Example 47 or any other example herein, wherein the insertion of the TCB is associated with a flag indicating the last TCB at a priority level.
例49は、例46、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、APIは、キューからのTCBの削除に関連する。Example 49 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in Example 46 or any other example herein, wherein the API is associated with removing a TCB from a queue.
例50は、例46、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、APIは、キューのTCBの改変に関連する。Example 50 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in Example 46 or any other example herein, wherein the API is associated with modifying the TCB of the queue.
例51は、例46、または本明細書の何らかの他の例に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、APIは、キュー内のTCBの実行状況の識別に関連する。Example 51 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in Example 46 or any other example herein, wherein the API is associated with identifying the execution status of the TCB in the queue.
例52は、例46に記載の1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、APIは、ハードウェアアクセラレータのリセットに関連する。Example 52 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media as described in example 46, wherein the API relates to resetting the hardware accelerator.
例53は、例1~52のいずれか、またはそれらのどれかのサブセットもしくは組み合わせの主題を行う方法を含む。Example 53 includes a method of performing the subject matter of any of Examples 1-52, or any subset or combination thereof.
例56は、命令を含む1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体を含み、命令は、コンピューティングデバイスの1つ以上の要素による命令の実行時に、コンピューティングデバイスの構成要素に、例1~52のいずれか、またはそれらのどれかのサブセットもしくは組み合わせに記載の主題を行わせる。Example 56 includes one or more non-transitory computer-readable media containing instructions that, upon execution by one or more elements of a computing device, cause components of the computing device to perform the subject matter described in any of Examples 1-52, or any subset or combination thereof.
例55は、例1~52のいずれか、またはそれらのどれかのサブセットもしくは組み合わせに記載の主題を行うか、または行わせる回路を含む装置を含む。Example 55 includes an apparatus including circuitry that performs or causes to be performed the subject matter described in any of Examples 1-52, or any subset or combination thereof.
例56は、例1~52のいずれか、またはそれらのどれかのサブセットもしくは組み合わせに記載の主題を行うか、または行わせる手段を備える装置を含む。Example 56 includes an apparatus having means for performing or causing to be performed the subject matter described in any of Examples 1-52, or any subset or combination thereof.
様々な実施形態は、上記の(および)連結形態で記載される実施形態の代替的(または)実施形態を含む、上記の実施形態の任意の好適な組み合わせを含んでもよい(例えば、「および」は、「および/または」であってもよい)。さらに、いくつかの実施形態は、実行されると、上記の実施形態のいずれかのアクションをもたらす、そこに格納された命令を有する1つ以上の製造品(例えば、非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体)を含み得る。さらに、いくつかの実施形態は、上記の実施形態の様々な動作を成し遂げる任意の好適な手段を有する装置またはシステムを含んでもよい。Various embodiments may include any suitable combination of the above embodiments, including alternative (or) embodiments of the embodiments described in the above (and) conjunctive form (e.g., "and" may be "and/or"). Additionally, some embodiments may include one or more articles of manufacture (e.g., non-transitory computer-readable media) having instructions stored thereon that, when executed, result in the actions of any of the above embodiments. Additionally, some embodiments may include devices or systems having any suitable means for accomplishing the various operations of the above embodiments.
例示された実施形態の上記の説明は、本要約に記載されるものを含むが、開示された精密な形態に関して網羅的または限定的であることを意図しない。様々な実施形態または概念の具体的な実施態様および例は、例示的な目的のために本明細書に記載されるが、関連する技術分野の当業者が認識するように、様々な等価な改変が可能であり得る。これらの改変は、上記の詳細な説明、要約、図面、または特許請求の範囲に照らしてなされ得る。The above description of illustrated embodiments, including those described in this Summary, is not intended to be exhaustive or limiting as to the precise forms disclosed. Specific implementations and examples of various embodiments or concepts are described herein for illustrative purposes, but various equivalent modifications may be possible, as one of ordinary skill in the relevant art will recognize. These modifications may be made in light of the above detailed description, abstract, drawings, or claims.
202 高優先順位
204 中優先順位
206 低優先順位
201 メモリ
203 システムバス
205 ハードウェアアクセラレータ
210 プロセッサ
212 TCB
214 先に実行されたTCB
218 現在実行中のTCB
220 実行されるTCB
236,238 要素 202 High priority 204 Medium priority 206 Low priority 201 Memory 203 System bus 205 Hardware accelerator 210 Processor 212 TCB
214 Previously executed TCB
218 Currently Executing TCB
220 TCB to be executed
236,238 elements
Claims (20)
Translated fromJapaneseプロセッサであって、
タスク制御ブロック(TCB)において、前記TCBの優先順位レベルの指示を識別し、
前記優先順位レベルの指示に基づいて、複数のTCBのキュー内の位置を識別し、前記複数のTCBのキューの各々のTCBが前記各々のTCBに関するジョブの実行のためのハードウェアアクセラレータに割り当てられ、かつ
前記識別された位置で前記キューに前記TCBを挿入し、前記挿入されたTCBが、前記挿入されたTCBに関連付けられた各々のジョブの完了時に前記プロセッサをシグナルする前記ハードウェアアクセラレータのための、ジョブ完了シグナリングメカニズムの指示を更に含むものである、プロセッサと、
前記プロセッサと通信可能に結合された前記ハードウェアアクセラレータであって、前記複数のTCBの前記キュー内のTCBに関連するジョブを行い、前記複数のTCBの前記キュー内の前記TCBの順序に従ってTCBに関連するジョブを行う、前記ハードウェアアクセラレータと、を備える、コンピューティングデバイス。 1. A computing device comprising:
1. A processor comprising:
identifying in a task control block (TCB) an indication of the priority level of said TCB;
a processor, further comprising: a processor that identifies a location in a queue of a plurality of TCBs based on the indication of priority level, each TCB in the queue of the plurality of TCBs being assigned to a hardware accelerator for execution of a job associated with the respective TCB; and an indication of a job completion signaling mechanism for the hardware accelerator that inserts the TCB into the queue at the identified location, the inserted TCB signaling the processor upon completion of each job associated with the inserted TCB;
a hardware accelerator communicatively coupled to the processor, the hardware accelerator performing jobs associated withTCBs in the queue of the plurality of TCBs and performing jobs associated with TCBs according to an order of the TCBs in the queue of the plurality of TCBs.
現在実行中のTCBの優先順位レベルを識別し、
前記現在実行中のTCBの前記優先順位レベルに基づいて、前記キュー内の前記位置を識別する、請求項4に記載のコンピューティングデバイス。 the TCB is at the first priority level, and the processor
Identifying the priority level of the currently executing TCB;
The computing device of claim 4 , further comprising: a processor configured to: identify the position within the queue based on the priority level of the currently executing TCB.
前記通信インターフェースと結合されたロジックを備えるプロセッサであって、
前記ロジックが、
タスク制御ブロック(TCB)において、前記TCBの優先順位レベルの指示を識別し、
前記優先順位レベルの指示に基づいて、複数のTCBのキュー内の位置に前記TCBを挿入するものであり、
前記ハードウェアアクセラレータが、前記キュー内のそれらの位置に基づいて、前記複数のTCBの各々を実行し、
前記挿入されたTCBが、前記挿入されたTCBに関連付けられた各々のジョブの完了時に前記プロセッサをシグナルする前記ハードウェアアクセラレータのための、ジョブ完了シグナリングメカニズムの指示を更に含むものである、
プロセッサ。 a communications interface for communicating with the hardware accelerator;
A processor comprising logic coupled to the communications interface,
The logic comprises:
identifying in a task control block (TCB) an indication of the priority level of said TCB;
inserting the TCB into a position within a queue of a plurality of TCBs based on the indication of the priority level;
the hardware accelerator executes each of the plurality of TCBs based on their position in the queue;
the inserted TCB further includes an indication of a job completion signaling mechanism for the hardware accelerator that signals the processor upon completion of each job associated with the inserted TCB.
Processor.
前記優先順位レベルの指標は、前記TCBが複数の優先順位レベルのうちの1つであることを示す、請求項8に記載のプロセッサ。 the indication of priority level is a two-bit indicator in the TCB;
9. The processor of claim 8, wherein the priority level indication indicates that the TCB is one of a plurality of priority levels.
前記ハードウェアアクセラレータが、前記挿入されたTCBの完了に関連して前記プロセッサにトリガを送信するか否かを示す指示をさらに含むものである、
請求項8に記載のプロセッサ。 the inserted TCB including an indication of the job completion signaling mechanism,
and further comprising an indication of whetherthe hardware accelerator is to send a trigger to the processor in connection with completion of the inserted TCB.
The processor of claim 8.
複数のタスク制御ブロック(TCB)のキューを識別することであって、前記複数のTCBの各々のTCBが、前記キュー内の前記各々のTCBの優先順位レベルの指示を含み、ハードウェアアクセラレータが、前記TCBの前記優先順位レベルに従って各々のTCBに関連するジョブを行う、識別することであって、前記複数のTCBのうちの少なくとも第1のTCBが、前記第1のTCBに関連付けられた各々のジョブの完了時に前記プロセッサをシグナルする前記ハードウェアアクセラレータのための、ジョブ完了シグナリングメカニズムの指示を更に含むものである、ことと、
前記キューに関連するアプリケーションプログラミングインターフェース(API)を実行することと、
前記APIの実行に基づいて前記キューを改変することであって、前記キューを改変することが、前記キューからのTCBの削除、前記キューのTCBに関するジョブの状況のクエリ、前記キュー内のTCBの改変のうちの少なくとも1つを含む、ことと、
を行わせる、1つ以上の非一時的なコンピュータ可読媒体。 One or more non-transitory computer-readable media containing instructions that, when executed by an electronic device, cause a processor of the electronic device to:
identifying a queue of a plurality of task control blocks (TCBs), each TCB of the plurality of TCBs including an indication of a priority level of each TCB in the queue, and a hardware accelerator performing a job associated with each TCB according to the priority level of the TCB, wherein at least a first TCB of the plurality of TCBs further includes an indication of a job completion signaling mechanism for the hardware accelerator to signal the processor upon completion of each job associated with the first TCB;
Executing an application programming interface (API) associated with the queue;
modifying the queue based on execution of the API, the modifying the queue including at least one of removing TCBs from the queue, querying the status of jobs on TCBs in the queue, and modifying TCBs in the queue;
One or more non-transitory computer-readable media that cause
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN201941030394 | 2019-07-27 | ||
| IN201941030394 | 2019-07-27 | ||
| US16/661,819US11397612B2 (en) | 2019-07-27 | 2019-10-23 | Autonomous job queueing system for hardware accelerators |
| US16/661,819 | 2019-10-23 | ||
| JP2020125332AJP2021022379A (en) | 2019-07-27 | 2020-07-22 | Autonomous job queueing system for hardware accelerators |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020125332ADivisionJP2021022379A (en) | 2019-07-27 | 2020-07-22 | Autonomous job queueing system for hardware accelerators |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2022188077A JP2022188077A (en) | 2022-12-20 |
| JP7467554B2true JP7467554B2 (en) | 2024-04-15 |
Family
ID=74098971
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022146968AActiveJP7467554B2 (en) | 2019-07-27 | 2022-09-15 | An Autonomous Job Queuing System for Hardware Accelerators |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7467554B2 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE102020117505B4 (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004272894A (en) | 2003-02-18 | 2004-09-30 | Microsoft Corp | Multithread kernel of graphics processing unit |
| WO2017163441A1 (en) | 2016-03-24 | 2017-09-28 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Image processing device, image processing method, and image processing program |
| US20180144435A1 (en) | 2016-11-23 | 2018-05-24 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Low power and low latency gpu coprocessor for persistent computing |
| WO2019044340A1 (en) | 2017-08-30 | 2019-03-07 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4658351A (en)* | 1984-10-09 | 1987-04-14 | Wang Laboratories, Inc. | Task control means for a multi-tasking data processing system |
| JPH04308939A (en)* | 1991-04-05 | 1992-10-30 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Queue inserting method |
| JP3760035B2 (en)* | 1996-08-27 | 2006-03-29 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | Multi-thread processor that processes multiple instruction streams independently and flexibly controls processing performance in units of instruction streams |
| KR100500002B1 (en)* | 1996-08-27 | 2005-09-08 | 마츠시타 덴끼 산교 가부시키가이샤 | Multithreaded processor for processing multiple instruction streams independently of each other by flexibly controlling throughput in each instruction stream |
| US7448036B2 (en)* | 2002-05-02 | 2008-11-04 | International Business Machines Corporation | System and method for thread scheduling with weak preemption policy |
- 2020
- 2020-07-02DEDE102020117505.1Apatent/DE102020117505B4/enactiveActive
- 2022
- 2022-09-15JPJP2022146968Apatent/JP7467554B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004272894A (en) | 2003-02-18 | 2004-09-30 | Microsoft Corp | Multithread kernel of graphics processing unit |
| WO2017163441A1 (en) | 2016-03-24 | 2017-09-28 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Image processing device, image processing method, and image processing program |
| US20180144435A1 (en) | 2016-11-23 | 2018-05-24 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Low power and low latency gpu coprocessor for persistent computing |
| WO2019044340A1 (en) | 2017-08-30 | 2019-03-07 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE102020117505A1 (en) | 2021-01-28 |
| DE102020117505B4 (en) | 2025-06-18 |
| JP2022188077A (en) | 2022-12-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102245247B1 (en) | GPU remote communication using triggered actions | |
| CN111737564B (en) | Information query method, device, equipment and medium | |
| US11397612B2 (en) | Autonomous job queueing system for hardware accelerators | |
| US10831481B2 (en) | Handling unaligned load operations in a multi-slice computer processor | |
| CN111208933B (en) | Method, device, equipment and storage medium for data access | |
| US7844752B2 (en) | Method, apparatus and program storage device for enabling multiple asynchronous direct memory access task executions | |
| US10198378B2 (en) | Faster data transfer with simultaneous alternative remote direct memory access communications | |
| US9378163B2 (en) | Method to accelerate message signaled interrupt processing | |
| JP7467554B2 (en) | An Autonomous Job Queuing System for Hardware Accelerators | |
| US8803900B2 (en) | Synchronization with semaphores in a multi-engine GPU | |
| US8706923B2 (en) | Methods and systems for direct memory access (DMA) in-flight status | |
| CN118069665A (en) | Data processing method, apparatus, storage medium, and program product | |
| US10284501B2 (en) | Technologies for multi-core wireless network data transmission | |
| CN116756138A (en) | Data access method and device and electronic equipment | |
| CN104932947A (en) | Barrier synchronization method and device | |
| TW202242645A (en) | Host system and a method thereof | |
| CN113609041A (en) | Data transmission method and system | |
| CN105183668A (en) | Cache refreshing method and device | |
| US20120047285A1 (en) | Interrupt-based command processing | |
| CN117608468B (en) | Data moving method, device, equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN117785767B (en) | Message synchronization method, system and related device | |
| US20180307640A1 (en) | Data transfer apparatus, data transfer method, and computer-readable medium | |
| CN108984450B (en) | Data transmission method, device and equipment | |
| WO2024188112A1 (en) | Task processing method and chip | |
| CN116701021A (en) | Control word output feedback control method based on queue |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20221024 | |
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20221024 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20230727 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20230904 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20231201 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20240304 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20240403 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:7467554 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |