JP7466383B2 - System and program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment - Google Patents
System and program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipmentDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7466383B2 JP7466383B2JP2020099535AJP2020099535AJP7466383B2JP 7466383 B2JP7466383 B2JP 7466383B2JP 2020099535 AJP2020099535 AJP 2020099535AJP 2020099535 AJP2020099535 AJP 2020099535AJP 7466383 B2JP7466383 B2JP 7466383B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- amount
- water heater
- value
- abnormal operation
- smart meter
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Remote Monitoring And Control Of Power-Distribution Networks (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、電気機器の異常運転を推定するシステムである電気機器の異常運転推定システム、及び電気機器の異常運転を推定するプログラムである電気機器の異常運転推定プログラムに関する。The present invention relates to an electrical equipment abnormal operation estimation system, which is a system for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment, and an electrical equipment abnormal operation estimation program, which is a program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment.
家電機器の運転管理装置として、特開2018-207500号公報(特許文献1)に記載されたものが知られている。
この装置は、家電機器(例えば誘導加熱調理器)から異常に関する情報(例えば左誘導加熱源電源緊急オフ)を受信すると、その家電機器の主電源をオフにする。 A known example of an operation management device for home appliances is described in Japanese Patent Laid-Open Publication No. 2018-207500 (Patent Document 1).
When this device receives information about a malfunction (eg, emergency power off of the left induction heating source) from a home appliance (eg, an induction heating cooker), it turns off the main power supply of the home appliance.
上記の装置では、家電機器において自ら把握可能な異常を管理することができるものの、機器において自ら把握されない異常を管理することはできない。The above device can manage abnormalities that the home appliance can detect by itself, but cannot manage abnormalities that the appliance cannot detect by itself.
そこで、本発明の主な目的は、電気機器における自ら把握されない異常な運転を推定可能である電気機器の異常運転推定システム,プログラムを提供することである。The main objective of the present invention is to provide a system and program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment that can estimate abnormal operation of electrical equipment that is not detected by the equipment itself.
請求項1に記載の発明は、電気機器の異常運転を推定する電気機器の異常運転推定システムであって、サーバコンピュータを備えており、前記サーバコンピュータは、制御手段と、通信手段と、を備えており、前記通信手段は、通信可能な電力計であるスマートメーターの値が集計される集計サーバコンピュータ、外気温を送信可能な外気温サーバコンピュータ、日射量を送信可能な日射量サーバコンピュータ、及び風速を送信可能な風速サーバコンピュータの少なくとも何れかと通信可能であり、前記制御手段は、前記通信手段を制御して、前記スマートメーターの値、前記外気温、前記日射量、及び前記風速の少なくとも何れかを得ると共に、前記スマートメーターの値、前記外気温、前記日射量、及び前記風速の少なくとも何れかに基づいて、前記電気機器の消費電力量及び発電電力量の少なくとも一方又はこれに関連する値である関連値を算出し、更に、前記消費電力量及び前記発電電力量の少なくとも一方又は前記関連値について、統計的な外れ値を抽出し、
前記外れ値に基づいて、前記電気機器の異常運転を推定することを特徴とするものである。
請求項2に記載の発明は、上記発明において、前記電気機器は、ヒートポンプ式給湯機であり、前記制御手段は、前記通信手段を制御して、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機の水温又は製造年を取得し、且つ、前記スマートメーターの値、及び前記外気温を得ると共に、前記スマートメーターの値、前記外気温、並びに、前記水温又は前記製造年に基づいて、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機の前記消費電力量を算出し、更に、前記消費電力量についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機の水漏れを推定することを特徴とするものである。
請求項3に記載の発明は、上記発明において、前記電気機器は、ヒートポンプ式給湯機であり、前記制御手段は、前記通信手段を制御して、前記スマートメーターの値、及び前記外気温を得ると共に、前記スマートメーターの値、及び前記外気温に基づいて、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機の前記消費電力量の深夜率であるヒートポンプ式給湯機深夜率を算出し、更に、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機深夜率についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機のタイマーずれを推定することを特徴とするものである。 The invention described in
The method is characterized in that abnormal operation of the electrical equipment is estimated based on the outlier value.
The invention described in
The invention described in
請求項4に記載の発明は、上記発明において、前記電気機器は、電気温水器であり、前記制御手段は、前記通信手段を制御して、特定の時間帯に係る前記スマートメーターの値を得ると共に、前記スマートメーターの値に基づいて、前記電気温水器の前記消費電力量を算出し、更に、前記消費電力量についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記電気温水器の水漏れを推定することを特徴とするものである。
請求項5に記載の発明は、上記発明において、前記電気機器は、電気温水器であり、前記制御手段は、前記通信手段を制御して、特定の時間帯を含む全時間帯に係る前記スマートメーターの値を得ると共に、前記スマートメーターの値に基づいて、前記電気温水器の前記消費電力量の深夜率である電気温水器深夜率を算出し、更に、前記電気温水器深夜率についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記電気温水器のタイマーずれを推定することを特徴とするものである。
請求項6に記載の発明は、上記発明において、前記電気機器は、全量買取に係る太陽光パネルであり、前記制御手段は、前記通信手段を制御して、前記太陽光パネルの発電容量を取得し、且つ、前記スマートメーターの値、前記外気温、前記日射量、及び前記風速を得ると共に、前記外気温、前記日射量、及び前記風速、並びに前記発電容量に基づいて、前記太陽光パネルの発電電力量を算出して、前記関連値として前記発電電力量から前記スマートメーターの値を減じた値を算出し、更に、前記発電電力量から前記スマートメーターの値を減じた値についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定することを特徴とするものである。
請求項7に記載の発明は、上記発明において、前記電気機器は、余剰買取に係る太陽光パネルであり、前記制御手段は、前記通信手段を制御して、曇天時を含む前記スマートメーターの値、及び前記外気温を得ると共に、曇天時の前記スマートメーターの値から前記外気温の関数としての使用電力量の推定式を作成し、当該推定式に前記外気温を当てはめて前記使用電力量を推定し、前記スマートメーターの値から前記使用電力量を減じて前記発電電力量を算出して、前記関連値として前記発電電力量から前記スマートメーターの値を減じた値を算出し、更に、前記発電電力量から前記スマートメーターの値を減じた値についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定することを特徴とするものである。 The invention described in
The invention described in
The invention described in
The invention described in
請求項8に記載の発明は、上記発明において、前記外れ値は、箱ひげ図に係るものであることを特徴とするものである。
請求項9に記載の発明は、上記発明において、前記外れ値は、予測区間に係るものであることを特徴とするものである。
請求項10に記載の発明は、上記発明において、更に、前記サーバコンピュータと通信可能な端末を備えており、前記端末は、端末表示手段を有すると共に、前記電気機器と接続される前記スマートメーターを区別するIDと関連付けられており、前記サーバコンピュータは、前記電気機器の異常運転が推定されると、前記電気機器に係る前記IDと関連付けられた前記端末に、前記電気機器の異常運転が推定された旨の情報である異常運転情報を送信し、前記異常運転情報を受信した前記端末は、前記異常運転情報に基づく表示を、前記端末表示手段において行うことを特徴とするものである。 The invention described in
The invention described in
The invention described in
請求項11に記載の発明は、電気機器の異常運転推定プログラムにおいて、サーバコンピュータに読み取られることにより、前サーバ記コンピュータに、上記発明の前記通信手段及び前記制御手段が形成されるものであることを特徴とする。The invention described in claim 11 is characterized in that, in an abnormal operation estimation program for electrical equipment, the communication means and the control means of the invention are formed in the server computer by being read by the server computer.
本発明の主な効果は、電気機器における自ら把握されない異常な運転を推定可能である電気機器の異常運転推定システム,プログラムが提供されることである。The main advantage of the present invention is that it provides a system and program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment that can estimate abnormal operation of electrical equipment that is not detected by the equipment itself.
以下、本発明に係る実施の形態の例が、その変更例と共に、適宜図面に基づいて説明される。
尚、当該形態は、下記の例及び変更例に限定されない。 DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described together with modified examples with reference to the accompanying drawings.
It should be noted that the embodiment is not limited to the following examples and modified examples.
≪外的構成等≫
図1は、本発明に係る推定システムE1(電気機器の異常運転推定システム)及び関連する要素の全体ブロック図である。
推定システムE1では、電気機器の異常運転推定プログラム(推定プログラム)を読み取って実行可能なサーバ1(サーバコンピュータ)が用いられる。尚、サーバ1は、パーソナルコンピュータ及び携帯端末の少なくとも一方であっても良いし、複数台が適宜ネットワークを介して組み合わせられたものであっても良い。<External Composition, etc.>
FIG. 1 is an overall block diagram of an estimation system E1 (electrical equipment abnormal operation estimation system) according to the present invention and related elements.
The estimation system E1 uses a server 1 (server computer) that can read and execute an abnormal operation estimation program for an electrical device (estimation program). The
サーバ1は、電力会社(子会社等の関連団体を含む)に設置されている。
サーバ1は、情報等を表示する表示手段2と、情報等の入力を受け付ける入力手段4と、情報等を記憶する記憶手段6と、専用線EL及びインターネットINに接続可能な通信手段7と、これらを制御する制御手段8と、を有する。例えば、表示手段2はモニタであり、入力手段4は、キーボード及びポインティングデバイスの少なくとも一方であり、記憶手段6はメモリ及びハードディスクの少なくとも一方であり、通信手段7は専用線EL及びインターネットINに接続可能な通信ユニットであり、制御手段8はCPUである。
尚、通信手段7は、専用線ELの接続部とインターネットINの接続部とで分離していても良い。又、専用線EL及びインターネットINの何れか一方が使用されない場合、その使用されない部分が省略されても良い。 The
The
The communication means 7 may be separated into a connection part for the dedicated line EL and a connection part for the Internet IN. When either the dedicated line EL or the Internet IN is not used, the unused part may be omitted.
通信手段7は、専用線ELを介して、上記電力会社に設置された集計サーバCC(集計サーバコンピュータ)と接続されている。尚、集計サーバCCは、他の場所あるいは団体に設置されていても良い。又、サーバ1は、集計サーバCCと、インターネットIN等を介して接続されていても良い。
集計サーバCCには、複数のスマートメーターSMが接続されている。スマートメーターSMは、通信可能な電力計である。ここでは、各スマートメーターSMは、集計サーバCCと、無線通信網等を介して接続されている。尚、各スマートメーターSMは、集計サーバCCと、インターネットINを介して接続されていても良いし、携帯電話網等を介して接続されていても良い。
各スマートメーターSMは、電力を消費する世帯(電力供給契約を締結した世帯)に設置され、当該世帯の消費電力量を計測可能な電力計であり、更に所定の時間帯(ここでは30分間の時間帯であり1日当たり48個の時間帯)毎の消費電力量を積算した時間帯別消費電力量を算出して、世帯ID(世帯識別情報)を付して集計サーバCCに送信可能である。世帯ID付きの各時間帯別消費電力量は、いわゆるAルート値である。尚、二世帯住宅のような場合に、1つの建物に複数のスマートメーターSMが設置されていても良い。
各世帯は、電気機器に属する家電機器の使用により、電力を消費する。家電機器として、例えば、HP式給湯機(ヒートポンプ式給湯機)、電気温水器(ヒーター式給湯器)、及び世帯に設置される太陽光パネル(太陽光発電設備)の少なくとも何れかが挙げられる。家電機器は、世帯毎に、スマートメーターSMに接続されている。
又、太陽光パネルは、発電事業所に設置されても良い。この場合、太陽光パネルは、電気機器である。スマートメーターSMは、電力を発電し又消費する発電事業所に設置され、当該発電事業所の消費電力量を計測可能な電力計であり、世帯のスマートメーターSMと同様に成る。発電事業所に対しては、世帯IDと同様である事業者IDが付与される。以下、特に断らない限り、発電事業所のスマートメーターSMの説明は、世帯のスマートメーターSMの説明に含まれるものとして適宜省略される。又、事業所IDの説明は、同様に適宜世帯IDの説明に含まれる。更に、発電事業所の太陽光パネル(電気機器)の説明は、同様に適宜世帯の太陽光パネル(家電機器)の説明に含まれる。加えて、事業所の説明は、同様に適宜世帯の説明に含まれる。
集計サーバCCは、世帯IDと、時間帯の種類(時間帯に係る日時)と、時間帯別消費電力量とを対応付けた消費電力量データベースを有している。 The communication means 7 is connected to a tallying server CC (tallying server computer) installed in the electric power company via a dedicated line EL. The tallying server CC may be installed in another place or organization. The
A plurality of smart meters SM are connected to the tallying server CC. The smart meters SM are power meters capable of communication. Here, each smart meter SM is connected to the tallying server CC via a wireless communication network or the like. Note that each smart meter SM may be connected to the tallying server CC via the Internet IN, or via a mobile phone network or the like.
Each smart meter SM is installed in a household that consumes electricity (a household that has concluded an electricity supply contract) and is a power meter that can measure the amount of power consumed by that household, and can further calculate the amount of power consumed by each time period by accumulating the amount of power consumed for each specific time period (here, 30-minute time periods, i.e., 48 time periods per day), and can transmit this amount of power consumed by each time period to the aggregation server CC with a household ID (household identification information). The amount of power consumed by each time period with the household ID attached is the so-called A route value. Note that in cases such as a two-family home, multiple smart meters SM may be installed in one building.
Each household consumes electricity by using home appliances belonging to the electrical equipment. Examples of the home appliances include at least one of a HP water heater (heat pump water heater), an electric water heater (heater water heater), and a solar panel (photovoltaic power generation equipment) installed in the household. The home appliances are connected to a smart meter SM for each household.
The solar panels may also be installed at a power generation facility. In this case, the solar panels are electrical equipment. The smart meter SM is installed at a power generation facility that generates and consumes electricity, and is a power meter capable of measuring the amount of power consumed by the power generation facility, and is similar to the smart meter SM of a household. A business ID, which is similar to a household ID, is assigned to the power generation facility. Hereinafter, unless otherwise specified, the explanation of the smart meter SM of the power generation facility will be omitted as appropriate as it is included in the explanation of the smart meter SM of the household. Furthermore, the explanation of the business ID will similarly be included in the explanation of the household ID as appropriate. Furthermore, the explanation of the solar panels (electrical equipment) of the power generation facility will similarly be included in the explanation of the solar panels (home appliances) of the household as appropriate. In addition, the explanation of the business facility will similarly be included in the explanation of the household as appropriate.
The tallying server CC has an energy consumption database in which household IDs, types of time periods (dates and times related to the time periods), and energy consumption amounts for each time period are associated with each other.
又、通信手段7は、インターネットINを介して、外気温サーバTC(外気温サーバコンピュータ)と、風速サーバWS(風速サーバコンピュータ)と、日射量サーバLC(日射量サーバコンピュータ)と、にそれぞれ接続されている。
外気温サーバTCは、例えば気象観測団体が設置しているサーバコンピュータであり、地域及び日付を指定して問い合わせると、当該地域及び日付において観測された日平均の外気温が送信される。尚、外気温は、最低気温あるいは最高気温等であっても良いし、これらの組合せであっても良いし、週間平均気温等であっても良い。
風速サーバWSは、例えば外気温サーバTCと同じ団体あるいは異なる団体が設置しているサーバコンピュータであり、地域及び日付を指定して問い合わせると、当該地域及び日付における風速が送信される。ここでは、風速は、当該日付の日の入りの時刻から翌朝の日の出の時刻までの時間である。尚、風速は、当該日付の前日の日の入りの時刻から当該日付の日の出の時刻までの時間等の他の夜間を示す時間であっても良い。又、風速は、地域及び日付に応じて制御手段8で演算されても良いし、記憶手段6において風速データベースとして記憶されていても良い。
日射量サーバLCは、例えば他のサーバと同じ団体あるいは異なる団体が設置しているサーバコンピュータであり、地域及び日付並びに斜面の角度を指定して問い合わせると、当該地域及び日付における全天日射量並びに当該角度における斜面日射量が送信される。尚、斜面日射量及び全天日射量の少なくとも一方は、地域及び日付あるいは更に斜面の角度に応じて制御手段8で演算されても良いし、記憶手段6において日射量データベースとして記憶されていても良い。又、外気温サーバTC、風速サーバWS、日射量サーバLC及び集計サーバCCの少なくとも何れか2つは、共通のサーバであっても良い。 In addition, the communication means 7 is connected to an outside air temperature server TC (outside air temperature server computer), a wind speed server WS (wind speed server computer), and a solar radiation server LC (solar radiation server computer) via the Internet IN.
The outdoor temperature server TC is a server computer installed by, for example, a meteorological observation organization, and when an inquiry is made by specifying a region and date, the daily average outdoor temperature observed in the specified region and date is transmitted. Note that the outdoor temperature may be the minimum temperature, the maximum temperature, or a combination of these, or may be the weekly average temperature, etc.
The wind speed server WS is a server computer installed, for example, by the same organization as the outdoor air temperature server TC or by a different organization, and when an inquiry is made by specifying a region and date, the wind speed for that region and date is transmitted. Here, the wind speed is the time from sunset on that date to sunrise the next morning. The wind speed may be a time indicating another nighttime period, such as the time from sunset on the day before that date to sunrise on that date. The wind speed may be calculated by the control means 8 according to the region and date, or may be stored as a wind speed database in the storage means 6.
The solar radiation server LC is a server computer installed by the same organization as the other servers or by a different organization, and when an inquiry is made by specifying a region, date, and slope angle, the global solar radiation for the region and date and the slope solar radiation at the angle are transmitted. At least one of the slope solar radiation and the global solar radiation may be calculated by the control means 8 according to the region, date, and/or slope angle, or may be stored as a solar radiation database in the storage means 6. At least two of the outside air temperature server TC, the wind speed server WS, the solar radiation server LC, and the aggregation server CC may be a common server.
更に、通信手段7は、インターネットINを介して、端末Tと接続されている。
端末Tは、ここでは携帯端末であり、サーバ1と同様に、情報等を表示する端末表示手段12と、情報等の入力を受け付ける端末入力手段14と、情報等を記憶する端末記憶手段16と、端末通信手段17と、これらを制御する端末制御手段18と、を有する。端末表示手段12及び端末入力手段14は、例えばタッチセンサ付きディスプレイであり、端末記憶手段16は、例えばメモリであり、端末通信手段17は、例えば携帯電話網に対しデータ通信可能に接続される通信ユニットであり、端末制御手段18はCPUである。
端末Tの端末記憶手段16には、サーバ1の推定プログラムと連携する推定アプリケーション(推定アプリ,端末側推定プログラム)が記憶されており、端末制御手段18は推定アプリを実行可能である。推定アプリは、ユーザの世帯(当該世帯のスマートメーターSM)と対応付けられており、世帯IDを保持している。尚、端末Tにおける世帯IDとサーバ1における世帯IDとが異なるものとされ、サーバ1等にこれらの対応表が記憶されていても良い。
尚、外気温サーバTC、風速サーバWS、日射量サーバLC及び端末Tの少なくとも何れかは、サーバ1と、専用線ELあるいは構内通信等のインターネットIN以外の経路で接続されていても良い。各種の通信の経路は、有線を含んでいても良いし、無線を含んでいていても良い。又、端末Tは、ユーザの世帯等に置かれたPC(パーソナルコンピュータ)であっても良い。 Furthermore, the communication means 7 is connected to a terminal T via the Internet IN.
The terminal T is a mobile terminal in this embodiment, and similar to the
The terminal storage means 16 of the terminal T stores an estimation application (estimation app, terminal-side estimation program) that cooperates with the estimation program of the
At least one of the outside air temperature server TC, the wind speed server WS, the solar radiation server LC, and the terminal T may be connected to the
推定プログラムは、記憶手段6に記憶され、制御手段8により実行される。
推定プログラムは、複数の機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムと、太陽光パネルの場合の発電電力量等算出プログラムと、複数の機器別推定プログラムと、を含む。
推定アプリは、サーバ1に対する各種の情報の送受信を主に行い、適宜推定プログラムと連携して動作する。
各機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムは、取得された対象世帯における対応する機器の消費電力量を算出する機能を有している。ここでは、各機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムは、世帯の状況に応じ、HP式給湯機、電気温水器、及び太陽光パネルの各消費電力量を算出する。各機器の消費電力量は、世帯の全消費電力量の関数として算出されても良いし、世帯の全消費電力量から用途別の消費電力量として分解して割り出されても良い(ディスアグリゲーション)。機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムには、ここでは、HP式給湯機消費電力量算出プログラム、電気温水器消費電力量算出プログラム、及び太陽光パネル消費電力量算出プログラムが含まれる。
発電電力量等算出プログラムは、太陽光パネルの発電電力量等(太陽光パネルの異常運転推定に必要な要素)を算出する機能を有している。発電電力量等算出プログラムは、スマートメーターSM及び集計サーバCCからは直接得ることができない発電電力量を、所定の基準に基づいて推定により算出する。当該所定の基準として、例えば、日射量,外気温,風速の少なくとも何れかの関数が挙げられ、あるいは、予測された全消費電力量から、スマートメーターSMで実測された余剰電力量(+)又は不足電力量(-)を減算したものが挙げられる。
機器別推定プログラムは、当該電気機器に係る異常運転の発生の有無についての推定を行う機能を有している。機器別推定プログラムは、推定において、適宜機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムで算出された電気機器別であり更に時間帯別である各消費電力量を用いる。機器別推定プログラムには、ここでは、HP式給湯機推定プログラム、電気温水器推定プログラム、及び太陽光パネル推定プログラムが含まれる。
尚、他の電気機器に係る機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムあるいは機器別推定プログラムが追加されても良いし、何れかの機器別推定プログラムが省略されても良い。太陽光パネルのみが電力を消費する発電事業所を対象とする場合等において、機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムが省略されても良い。 The estimation program is stored in the storage means 6 and executed by the control means 8 .
The estimation program includes a program for calculating power consumption, etc., for each of a plurality of devices, a program for calculating generated power, etc., in the case of a solar panel, and a program for estimating the amount of power consumed, etc., for each of a plurality of devices.
The estimation application mainly transmits and receives various information to and from the
The program for calculating the power consumption, etc., for each device has a function of calculating the power consumption of the corresponding device in the acquired target household. Here, the program for calculating the power consumption, etc., for each device calculates the power consumption of each HP water heater, electric water heater, and solar panel according to the household situation. The power consumption of each device may be calculated as a function of the total power consumption of the household, or may be calculated by breaking down the total power consumption of the household into power consumption by purpose (disaggregation). Here, the program for calculating the power consumption, etc., for each device includes a program for calculating the power consumption of an HP water heater, a program for calculating the power consumption of an electric water heater, and a program for calculating the power consumption of a solar panel.
The program for calculating the amount of generated power, etc. has a function of calculating the amount of generated power, etc. of the solar panel (elements necessary for estimating abnormal operation of the solar panel). The program for calculating the amount of generated power, etc., estimates the amount of generated power that cannot be obtained directly from the smart meter SM and the aggregation server CC based on a predetermined criterion. The predetermined criterion may be, for example, at least one function of the amount of solar radiation, the outside temperature, or the wind speed, or may be a function obtained by subtracting the amount of surplus power (+) or the amount of shortage power (-) actually measured by the smart meter SM from the predicted total power consumption.
The device-specific estimation program has a function of estimating whether or not abnormal operation has occurred for the electrical device. In the estimation, the device-specific estimation program uses the power consumption of each electrical device and for each time period calculated by the device-specific power consumption calculation program as appropriate. The device-specific estimation programs here include an HP water heater estimation program, an electric water heater estimation program, and a solar panel estimation program.
In addition, a device-specific power consumption calculation program or a device-specific estimation program for other electrical devices may be added, or any of the device-specific estimation programs may be omitted. In the case of a power generation facility where only solar panels consume power, the device-specific power consumption calculation program may be omitted.
≪内的構成及び動作例等≫
[推定プログラムの処理開始等]
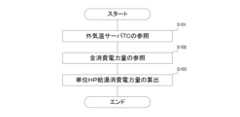
図2は、実行により推定システムE1における電気機器の異常運転推定の動作がなされる、推定プログラム及び推定アプリのフローチャートである。
端末Tにおける推定アプリの実行により、端末制御手段18は初期設定の処理を行う(ステップS1)。初期設定が済んでいる場合、サーバ1の制御手段8は、ステップS1に基づく推定プログラムにおける初期設定関連処理を飛ばしてステップS2に移行する。
ステップS1において、端末制御手段18は、ユーザ(世帯)が保有する電気式給湯器の有無及び種類(ここではHP式給湯機又は電気温水器の2種)、HP式給湯機が含まれる場合の製造年及び深夜帯の種類の少なくとも一方、電気温水器が含まれる場合の世帯人数,貯湯量及びヒーター出力のうちの少なくとも何れか、に係る各情報の入力を受け付ける。当該入力は、例えば端末表示手段12に表示されたプルダウンリストの端末入力手段14による選択によって行われる。ユーザによりこれら全ての情報の入力がなされると(例えば全てのプルダウンリストにおいて選択が行われた状態で入力完了ボタンが押されると)、端末制御手段18は、端末記憶手段16に、初期設定に係る各情報(初期情報)を記憶させる。<Internal configuration and operation examples, etc.>
[Start of estimation program processing, etc.]
FIG. 2 is a flowchart of an estimation program and an estimation application that, when executed, causes the estimation system E1 to perform an operation of estimating abnormal operation of an electric device.
By executing the estimation application in the terminal T, the terminal control means 18 performs an initial setting process (step S1). If the initial setting has been completed, the control means 8 of the
In step S1, the terminal control means 18 accepts input of each piece of information related to the presence or absence and type of electric water heater owned by the user (household) (here, two types: HP water heater or electric water heater), at least one of the year of manufacture and the type of late-night time zone if an HP water heater is included, and at least one of the number of people in the household, hot water storage amount, and heater output if an electric water heater is included. The input is performed, for example, by selecting from a pull-down list displayed on the terminal display means 12 using the terminal input means 14. When the user has input all of this information (for example, when the input completion button is pressed with selections made in all pull-down lists), the terminal control means 18 stores each piece of information related to the initial settings (initial information) in the terminal storage means 16.
次いで、ステップS2として、推定実行ボタンが表示され、ユーザが、端末Tの端末入力手段14により推定実行ボタンを押すと、端末制御手段18は、端末通信手段17を介してサーバ1へ、世帯IDと共に推定プログラムの実行指令を発信する。初期設定(ステップS1)がなされた場合、初期情報も、サーバ1へ送信される。Next, in step S2, an estimation execution button is displayed, and when the user presses the estimation execution button using the terminal input means 14 of the terminal T, the terminal control means 18 transmits an execution command for the estimation program together with the household ID to the
サーバ1の制御手段8は、推定プログラムの実行指令を受信すると、世帯IDに係る世帯を推定の対象である対象世帯として、推定プログラムを実行する。制御手段8は、初期設定の各情報を受信した場合、世帯IDに対応付けて記憶手段6に記憶させる。
制御手段8は、推定プログラムの実行によって、大要、各機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムにより各家電機器の消費電力量(用途別消費電力量)等を算出し、あるいは発電電力量等算出プログラムにより太陽光パネルの太陽光発電量及び発電電力量を算出し、算出された各消費電力量、太陽光発電量及び発電電力量の少なくとも何れか等に基づいて、対応する機器別推定プログラムにより当該家電機器の異常運転を推定する。各機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムは、対応する機器の異常運転推定に必要な要素を用意するプログラムである。尚、機器別推定プログラムにおいて、機器別の全消費電力量又は発電量若しくは発電電力量が用いられない場合がある。又、機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムと機器別推定プログラムとの区分は便宜上のものであり、例えば、推定に必要な要素は、機器別推定プログラムにおいて算出されても良い。
以下、説明の便宜のため、世帯の全消費電力量の算出、HP式給湯機の用途別消費電力量の算出、HP式給湯機の異常運転推定、電気温水器の用途別消費電力量の算出、電気温水器の異常運転推定、全量買取における太陽光パネルの発電電力量の算出、全量買取における太陽光パネルの異常運転推定、余剰買取における太陽光パネルの発電電力量の算出、余剰買取における太陽光パネルの異常運転推定が、この記載順で説明される。
又、推定プログラムにおける処理は、所定期間毎に繰り返し行われる。即ち、推定プログラムにおける処理は、所定期間を単位として行われる。ここでは、所定期間は、1日である。
尚、サーバ1は、端末Tにおける推定実行ボタンへの入力に基づかず、初期情報の受信のみに基づいて、推定プログラムを実行しても良い。又、サーバ1は、推定プログラムにおいて、上記説明の順番とは異なる順序で処理を実行しても良く、例えば、全消費電力量等から全家電機器の消費電力量等(各機器の異常運転推定に必要な要素)をまとめて算出した後、各家電機器の異常運転推定を行っても良い。サーバ1は、各家電機器の消費電力量の算出において、異常運転推定を行わない他の家電機器の消費電力量を算出しても良い。又、所定期間は、端末T等において指定されても良い。機器別消費電力量等算出プログラムの繰り返しの期間と、機器別推定プログラムの繰り返しの期間とが、互いに相違していても良い。あるいは、推定プログラムは、特定期間(例えば1か月)にわたり1回のみ実行されるものであっても良い。 When the control means 8 of the
The control means 8 executes the estimation program to calculate the power consumption (power consumption by application) of each home appliance by the power consumption calculation program for each appliance, or calculates the solar power generation and power generation of the solar panel by the power generation calculation program, and estimates abnormal operation of the home appliance by the corresponding estimation program for each appliance based on at least one of the calculated power consumption, solar power generation, and power generation. The power consumption calculation program for each appliance is a program that prepares elements necessary for estimating abnormal operation of the corresponding appliance. Note that the total power consumption or power generation or power generation amount for each appliance may not be used in the estimation program for each appliance. The distinction between the power consumption calculation program for each appliance and the estimation program for each appliance is for convenience, and for example, the elements necessary for estimation may be calculated in the estimation program for each appliance.
For ease of explanation, the following will be explained in the following order: calculation of total electricity consumption for a household, calculation of electricity consumption by use of an HP water heater, estimation of abnormal operation of an HP water heater, calculation of electricity consumption by use of an electric water heater, estimation of abnormal operation of an electric water heater, calculation of the amount of electricity generated by solar panels when purchasing the entire amount, estimation of abnormal operation of solar panels when purchasing the entire amount, calculation of the amount of electricity generated by solar panels when purchasing surplus electricity, and estimation of abnormal operation of solar panels when purchasing surplus electricity.
The process of the estimation program is repeated every predetermined period. That is, the process of the estimation program is performed in units of a predetermined period. In this example, the predetermined period is one day.
The
[全消費電力量の算出等]
制御手段8は、まず、集計サーバCCに対し、対象世帯の世帯IDにおける、1日(前日)の全ての時間帯別消費電力量の送信を要求する。集計サーバCCは、消費電力量データベースから要求に係る時間帯別消費電力量を見出し、サーバ1に送信する。サーバ1の制御手段8は、通信手段7において受信した当該時間帯別消費電力量を、記憶手段6において記憶させる(ステップS3)。例えば、2020年1月1日分であれば、制御手段8は、同年1月1日第1時間帯(0時~0時30分)から同日第48時間帯(23時30分~24時)までの各時間帯別消費電力量を取得する。
そして、制御手段8は、全ての時間帯別消費電力量を合算して、対象世帯における1日の全体の消費電力量である全消費電力量を得、これを日毎に記憶させる(ステップS4)。[Calculation of total power consumption, etc.]
The control means 8 first requests the tallying server CC to transmit all time-slot-specific power consumption for the household ID of the target household on the first day (the previous day). The tallying server CC finds the requested time-slot-specific power consumption from the power consumption database and transmits it to the
The control means 8 then sums up all the time-zone-specific power consumption amounts to obtain the total power consumption amount, which is the total power consumption amount for the target household in one day, and stores this for each day (step S4).
[HP式給湯機の用途別消費電力量の算出等]
次いで、制御手段8は、HP式給湯機の用途別消費電力量に係る単位HP給湯消費電力量を1日毎に算出する(ステップS5)。
制御手段8は、初期情報によって当該世帯にHP式給湯機がないことを把握している場合、ステップS5~S7をスキップすることができる。又、制御手段8は、初期情報によって当該世帯に複数台のHP式給湯機が存在することを把握している場合、各HP式給湯機についてステップS5~S7を行っても良い。[Calculation of power consumption by application of HP water heaters, etc.]
Next, the control means 8 calculates the unit HP hot water supply power consumption amount relating to the power consumption amount by application of the HP water heater for each day (step S5).
When the control means 8 knows from the initial information that the household does not have an HP water heater, it can skip steps S5 to S7. Also, when the control means 8 knows from the initial information that the household has multiple HP water heaters, it may perform steps S5 to S7 for each HP water heater.
制御手段8は、次の式(1A),(2)あるいは(1B),(2)により、単位HP給湯消費電力量を算出する。HP式給湯機消費電力量等算出プログラムには、次の式(1A)~(2)が含まれている。
式(1A),(1B)は、1日の全消費電力量に対するHP式給湯機の消費電力量の割合(HP式給湯機割合)の推定式である。式(1A)は、初期情報としてHP式給湯機の製造年が得られている場合のものである。式(1B)は、HP式給湯機の製造年が得られていない場合のものである。
式(2)は、HP式給湯機割合から単位HP給湯消費電力量を得る式である。 The control means 8 calculates the unit HP hot water power consumption by the following formulas (1A) and (2) or (1B) and (2). The HP hot water heater power consumption calculation program includes the following formulas (1A) to (2).
Equations (1A) and (1B) are equations for estimating the ratio of the power consumption of an HP water heater to the total power consumption in a day (HP water heater ratio). Equation (1A) is used when the manufacturing year of the HP water heater is obtained as initial information. Equation (1B) is used when the manufacturing year of the HP water heater is not obtained.
Equation (2) is used to obtain the unit HP hot water power consumption from the HP water heater ratio.
HP式給湯機割合=-0.0003×外気温2+0.0025×外気温
-0.0384×製造年+77.4307 (1A)
HP式給湯機割合=-0.0003×外気温2+0.0055×外気温
-0.0024×水温+0.2875 (1B)
単位HP給湯消費電力量=全消費電力量×HP式給湯機割合 (2)HP water heater ratio = -0.0003 x outside temperature2 + 0.0025 x outside temperature
-0.0384 x year of manufacture +77.4307 (1A)
HP water heater ratio = -0.0003 x outside temperature2 + 0.0055 x outside temperature
-0.0024 x water temperature +0.2875 (1B)
Unit HP hot water power consumption = total power consumption x HP water heater ratio (2)
式(1A),(1B)は、HP式給湯機を有する150以上のサンプル世帯について分析した結果に基づいている。尚、HP式給湯機割合が式(1A),(1B)で示されると仮定することについて、単位HP給湯消費電力量と外気温との相関係数0.7以上の世帯が全体の85%となっており、よってこの仮定は相当の妥当性を有する。
式(1B)中、水温は、HP式給湯機に供給される水温であり、ここでは文献値を用いている。尚、初期情報が水温を含み、その水温が式(1B)で用いられても良い。 Formulas (1A) and (1B) are based on the results of an analysis of more than 150 sample households with HP water heaters. Assuming that the proportion of HP water heaters is as shown in formulas (1A) and (1B), 85% of the households have a correlation coefficient of 0.7 or more between unit HP hot water power consumption and outdoor temperature, so this assumption has considerable validity.
In formula (1B), the water temperature is the temperature of water supplied to the HP water heater, and a literature value is used here. Note that the initial information may include the water temperature, and the water temperature may be used in formula (1B).
図3は、ステップS5の詳細を示すフローチャートである。
HP式給湯機消費電力量等算出プログラムを実行する制御手段8は、外気温サーバTCから、当該1日の外気温を取得して、式(1A),(1B)に当てはめてHP式給湯機割合を算出し(ステップS101)、算出済みの当該1日の全消費電力量を参照し(ステップS102)、式(2)に当てはめ、当該1日の単位HP給湯消費電力量を算出する(ステップS103)。尚、全消費電力量は、予め算出されず、ステップS102において算出されても良い。
制御手段8は、算出された単位HP給湯消費電力量を、日毎に、記憶手段6に記憶させる。制御手段8は、日々の単位HP給湯消費電力量を、その日の外気温に応じて統計処理可能とするため、各単位HP給湯消費電力量を、その日の外気温と共に記憶手段6に記憶させる。制御手段8は、外気温を外気温サーバTCから得る。尚、以下の機器別消費電力量及び発電電力量等について、適宜同様に外気温が対応付けられて記憶される。 FIG. 3 is a flow chart showing the details of step S5.
The control means 8, which executes the HP water heater power consumption calculation program, acquires the outdoor air temperature for that day from the outdoor air temperature server TC, applies it to formulas (1A) and (1B) to calculate the HP water heater ratio (step S101), refers to the calculated total power consumption for that day (step S102), applies it to formula (2), and calculates the unit HP hot water power consumption for that day (step S103). Note that the total power consumption does not need to be calculated in advance, and may be calculated in step S102.
The control means 8 stores the calculated unit HP hot water power consumption for each day in the storage means 6. To enable statistical processing of the daily unit HP hot water power consumption according to the outdoor temperature of the day, the control means 8 stores each unit HP hot water power consumption together with the outdoor temperature of the day in the storage means 6. The control means 8 obtains the outdoor temperature from the outdoor temperature server TC. The outdoor temperature is also associated with the following device-specific power consumption and power generation amount, etc., and stored accordingly.
[HP式給湯機の異常運転推定等]
続いて、制御手段8は、HP式給湯機推定プログラムの実行により、HP式給湯機の異常運転を推定する(ステップS6,S7)。
HP式給湯機の異常運転は、ここでは、水漏れ(ステップS6)、及びタイマーずれ(ステップS7)である。
HP式給湯機の水漏れは、HP式給湯機の消費電力量を通常より増加させる異常運転であり、具体的には、貯湯タンクの湯が、各種配管及び弁の少なくとも一方から漏れること、並びにHPユニットから貯湯タンクに供給される配管部で湯が漏れること、の少なくとも一方である。
HP式給湯機のタイマーずれは、HP式給湯機が通常運転される時間帯(夜間)からずれた時間(昼間)に運転される異常運転であり、具体的には、停電等の異常事象の発生によりHP式給湯機のタイマーがずれたり、人為的な設定ミスによりタイマーがずれたりすることである。又、HP式給湯機が故障し、通常運転される時間帯に運転されなくなった場合も、タイマーずれ(異常運転)として推定可能である。
尚、推定対象であるHP式給湯機の異常運転は、水漏れ及びタイマーずれに限られない。又、水漏れ及びタイマーずれの推定の順番は、上記のものと逆であっても良い。[Estimation of abnormal operation of HP water heater, etc.]
Next, the control means 8 executes the HP water heater estimation program to estimate abnormal operation of the HP water heater (steps S6, S7).
The abnormal operation of the HP water heater here is a water leak (step S6) and a timer deviation (step S7).
A water leak from an HP water heater is an abnormal operation that increases the amount of power consumed by the HP water heater more than normal, and specifically, is at least one of the following: hot water leaking from the hot water storage tank from various pipes and valves, and hot water leaking from the piping that supplies water from the HP unit to the hot water storage tank.
A timer deviation in an HP water heater is an abnormal operation in which the HP water heater is operated at a time (daytime) different from the normal operating time (nighttime), specifically, the timer of the HP water heater is shifted due to an abnormal event such as a power outage, or the timer is shifted due to an artificial setting error. Also, if the HP water heater breaks down and no longer operates during the normal operating time, this can be estimated as a timer deviation (abnormal operation).
The abnormal operation of the HP water heater to be estimated is not limited to water leakage and timer deviation. Also, the order of estimation of water leakage and timer deviation may be reversed from that described above.
HP式給湯機の水漏れ(ステップS6)に関し、図4に示されるように、制御手段8は、単位HP給湯消費電力量について大きい側の外れ値を抽出する処理を行う(ステップS201)と共に、直近の所定日数の単位HP給湯消費電力量が、過去の単位HP給湯消費電力量に対して、何れも統計的に大きい側の外れ値となると(ステップS202でYes)、HP式給湯機が水漏れを起こしており、異常運転しているものと推定する(ステップS203)。
所定日数は、ここでは5日である。即ち、制御手段8は、単位HP給湯消費電力量が5日連続で大きい側の外れ値となると、HP式給湯機の水漏れを推定する。
制御手段8は、HP式給湯機における水漏れの発生を推定すると、その旨の情報である水漏れ情報(異常運転情報)を、世帯IDに係る端末Tに送信し、端末Tは、推定アプリにより、受信した水漏れ情報に基づく表示を行う。ユーザは、当該表示により、HP式給湯機に水漏れが発生していることを認識することができ、HP式給湯機の点検等の処置を行うことができる。このような端末Tに対する処理は、以下の場合でも同様に行われ得る。端末Tは、推定アプリにおいて世帯IDの入力を受け付け、世帯IDを端末記憶手段16に記憶することで、スマートメーターSMを他のスマートメーターSMと区別するIDである世帯IDと関連付けられている。尚、水漏れ情報(異常運転情報)は、電子メールによって端末Tに送信されても良いし、端末Tによる専用のウェブサイトへのアクセスにより表示されても良い。当該電子メールのアドレスは、初期情報に含められても良い。又、このような端末Tに対する処理は、省略されても良い。
尚、所定日数は、1日を含む4日以下であっても良いし、6日以上であっても良い。又、制御手段8は、直近の7日間中5日以上において外れ値となったときといったように、特定期間中の特定日数以上の外れ値の出現によって、水漏れを推定しても良い。異常運転情報としての水漏れ情報及びこれに基づく表示の少なくとも一方は、HP式給湯機の単位HP給湯消費電力量が統計的に上昇していることを示すものであっても良い。これらの所定日数、特定期間、及び異常運転情報に関する変更例は、以下の場合でも同様に具備され得る。 Regarding water leakage from the HP water heater (step S6), as shown in FIG. 4, the control means 8 performs a process of extracting outliers on the larger side for the unit HP hot water power consumption (step S201), and if the unit HP hot water power consumption for the most recent specified number of days is a statistically larger outlier compared to the past unit HP hot water power consumption (Yes in step S202), it is estimated that the HP water heater is leaking water and operating abnormally (step S203).
The predetermined number of days is 5 in this example. That is, when the unit HP hot water supply power consumption is an outlier on the larger side for 5 consecutive days, the control means 8 estimates that the HP hot water heater has a water leak.
When the control means 8 estimates the occurrence of a water leak in the HP water heater, it transmits water leak information (abnormal operation information) to the terminal T associated with the household ID, and the terminal T performs a display based on the received water leak information using the estimation app. The user can recognize that a water leak has occurred in the HP water heater from the display, and can take measures such as inspecting the HP water heater. Such processing for the terminal T can be performed in the same manner in the following cases. The terminal T accepts input of a household ID in the estimation app and stores the household ID in the terminal storage means 16, thereby associating the smart meter SM with the household ID, which is an ID for distinguishing the smart meter SM from other smart meters SM. The water leak information (abnormal operation information) may be transmitted to the terminal T by email, or may be displayed by the terminal T accessing a dedicated website. The email address may be included in the initial information. Moreover, such processing for the terminal T may be omitted.
The specified number of days may be four days or less including one day, or six days or more. The control means 8 may also estimate a water leak when outliers appear for a specified number of days or more during a specific period, such as when outliers appear on five or more days out of the most recent seven days. At least one of the water leakage information as abnormal operation information and the display based thereon may indicate that the unit HP hot water power consumption of the HP water heater is statistically increasing. These modified examples of the specified number of days, the specific period, and the abnormal operation information may also be provided in the following cases.
ステップS201において、統計的な外れ値は、どのように抽出されても良いところ、以下、2つの例が挙げられる。制御手段8は、少なくとも何れか一方を用いて、外れ値を見出す。In step S201, statistical outliers may be extracted in any manner, but the following two examples are given. The control means 8 uses at least one of them to find the outliers.
1つ目は、図5に示されるような箱ひげ図の作成によるものである。尚、制御手段8は、実際に箱ひげ図を描画する必要はなく、統計的に同等な処理がなされれば足りる。あるいは、制御手段8は、箱ひげ図を表示手段2において表示しても良い。
HP式給湯機は、湯の時間帯毎の使用量の傾向等により世帯毎に異なるため、制御手段8は、世帯毎に箱ひげ図を作成する。又、一般に、HP式給湯機は、外気温によって消費電力量が変わるため、箱ひげ図の横軸は、外気温(図では平均気温[℃])とされ、縦軸は、単位HP給湯消費電力量(図では推定値[kWh](キロワット時))とされる。
制御手段8は、外気温サーバTCから取得した外気温に応じて、単位HP給湯消費電力量を記憶させる。
制御手段8は、外気温毎に、単位HP給湯消費電力量に係る第1四分位数及び第3四分位数を把握し、第3四分位数から、第1四分位数から第3四分位数までの単位HP給湯消費電力量の幅(箱の大きさ)の1.5倍を超えて大きい値となっている(箱の大きさの1.5倍のひげの外側にある)単位HP給湯消費電力量は、大きい側の外れ値とみなされる。尚、当該1.5倍の値は、1.5より小さくても良いし、1.5より大きくても良い。又、第1四分位数及び第3四分位数の少なくとも一方は、第1八分位数あるいは第7八分位数等とされても良い。
このように、外気温毎に単位HP給湯消費電力量が統計的に処理されるため、単位HP給湯消費電力量のある程度の蓄積が必要となり、実質的には、推定の開始は、数週間あるいは数か月後となる。
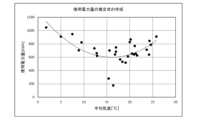
尚、制御手段8は、外気温毎の処理として、図5のような1℃幅の処理に代えて、0.5℃幅あるいは5℃幅の処理、又は温度帯により幅の異なる不等幅の処理等を行っても良い。又、制御手段8は、初期情報等に応じ、類似するHP式給湯機における単位HP給湯消費電力量の分布を取得して、当該世帯における過去の単位HP給湯消費電力量とみなして処理しても良い。これらの変更例は、以下の場合でも同様に具備され得る。 The first method is to create a box plot as shown in Fig. 5. It is not necessary for the control means 8 to actually draw the box plot, and it is sufficient that a statistically equivalent process is performed. Alternatively, the control means 8 may display the box plot on the display means 2.
Since HP water heaters vary from household to household depending on trends in hot water usage per time period, the control means 8 creates a box-and-whisker plot for each household. Generally, the power consumption of HP water heaters varies depending on the outside temperature, so the horizontal axis of the box-and-whisker plot is the outside temperature (average temperature [°C] in the figure), and the vertical axis is the unit HP hot water power consumption (estimated value [kWh] (kilowatt-hours) in the figure).
The control means 8 stores the unit HP hot water power consumption amount according to the outside air temperature acquired from the outside air temperature server TC.
The control means 8 grasps the first and third quartiles of the unit HP hot water power consumption for each outdoor air temperature, and a value larger than 1.5 times the range (box size) of the unit HP hot water power consumption from the third quartile to the third quartile (outside the whiskers of 1.5 times the box size) is regarded as an outlier on the larger side. Note that the value of 1.5 times may be smaller than 1.5 or may be larger than 1.5. Also, at least one of the first and third quartiles may be the first octile or the seventh octile, etc.
In this way, since the unit HP hot water power consumption is statistically processed for each outside temperature, a certain amount of data on the unit HP hot water power consumption is required, and in practice, estimation begins several weeks or months later.
Incidentally, the control means 8 may process for each outside air temperature in 0.5°C or 5°C increments, or in unequal increments that vary depending on the temperature zone, instead of in 1°C increments as shown in Fig. 5. Furthermore, the control means 8 may obtain the distribution of unit HP hot water energy consumption in similar HP water heaters according to the initial information, etc., and process it as the past unit HP hot water energy consumption in the household. These modified examples may also be provided in the following cases.
2つ目は、図6に示されるような予測区間のグラフによるものである。尚、制御手段8は、実際にグラフを描画する必要はなく、統計的に同等な処理がなされれば足りる。あるいは、制御手段8は、予測区間のグラフを表示手段2において表示しても良い。
制御手段8は、横軸が外気温(図では平均気温[℃])とされ、縦軸が単位HP給湯消費電力量(図では推定値[kWh])とされた世帯毎の平面に対して、日毎に単位HP給湯消費電力量をプロットしていく。
そして、制御手段8は、そのグラフ上で、予測区間を決定する。予測区間は、ある確率で、個々の単位HP給湯消費電力量があると考えられる区間で、ここでは、95%の確率に係る区間と、99%の確率に係る区間とが図示されている。制御手段8は、何れか一方の区間を予測区間として用いれば良い。あるいは、その他の確率に係る予測区間が用いられても良い。
制御手段8は、予測区間の上側より上方に出ている単位HP給湯消費電力量を、大きい側の外れ値とする。
図6において、上から1番目の右下がりの直線が、99%予測区間の上側の境界線であり、上から2番目の右下がりの直線が、95%予測区間の上側の境界線であり、上から3番目の右下がりの直線が、95%予測区間の下側の境界線であり、上から4番目の右下がりの直線が、99%予測区間の下側の境界線である。
尚、参考のため、95%予測区間の上側の境界線が、次の式(3)で示され、95%予測区間の下側の境界線が、次の式(4)で示される。式(3),(4)中、t値はt検定に係るものであり、nはサンプル数(単位HP給湯消費電力量の個数)である。 The second method is to use a graph of the prediction interval as shown in Fig. 6. It is not necessary for the control means 8 to actually draw a graph, and it is sufficient that a statistically equivalent process is performed. Alternatively, the control means 8 may display the graph of the prediction interval on the display means 2.
The control means 8 plots the unit HP hot water power consumption for each day on a plane for each household, with the horizontal axis being the outside air temperature (average air temperature [°C] in the figure) and the vertical axis being the unit HP hot water power consumption (estimated value [kWh] in the figure).
Then, the control means 8 determines a prediction interval on the graph. The prediction interval is an interval in which each unit HP hot water power consumption is considered to exist with a certain probability, and here, an interval with a 95% probability and an interval with a 99% probability are illustrated. The control means 8 may use either one of the intervals as the prediction interval. Alternatively, a prediction interval with another probability may be used.
The control means 8 determines a unit HP hot water supply power consumption amount that is above the upper side of the prediction interval as an outlier on the large side.
In Figure 6, the first line sloping downward to the right from the top is the upper boundary of the 99% prediction interval, the second line sloping downward to the right from the top is the upper boundary of the 95% prediction interval, the third line sloping downward to the right from the top is the lower boundary of the 95% prediction interval, and the fourth line sloping downward to the right from the top is the lower boundary of the 99% prediction interval.
For reference, the upper boundary of the 95% prediction interval is shown by the following formula (3), and the lower boundary of the 95% prediction interval is shown by the following formula (4). In formulas (3) and (4), the t value is related to the t-test, and n is the number of samples (the number of unit HP hot water power consumption).
予測区間の上側=平均値+95%t値×標準偏差×√(1+1/n) (3)
予測区間の下側=平均値-95%t値×標準偏差×√(1+1/n) (4)Upper part of prediction interval = mean + 95% t-value × standard deviation × √(1 + 1/n) (3)
Lower prediction interval = mean - 95% t-value x standard deviation x √(1 + 1/n) (4)
他方、HP式給湯機のタイマーずれ(ステップS7)に関し、図7に示されるように、制御手段8は、単位HP給湯消費電力量の深夜率(HP式給湯機深夜率,ヒートポンプ式給湯器深夜率)について算出し(ステップS301)、HP式給湯機深夜率について小さい側の外れ値を抽出する処理を行う(ステップS302)と共に、直近の所定日数のHP式給湯機深夜率が、過去のHP式給湯機深夜率に対して、何れも統計的に小さい側の外れ値となると(ステップS303でYes)、HP式給湯機がタイマーずれを起こしており、異常運転しているものと推定する(ステップS304)。
所定日数は、ここでは3日である。即ち、制御手段8は、HP式給湯機深夜率が3日連続で小さい側の外れ値となると、HP式給湯機のタイマーずれを推定する。
HP式給湯機深夜率が大幅に小さくなれば、通常深夜帯に稼働されるように設定されているHP式給湯機が深夜帯以外でも稼働されている蓋然性が高く、HP式給湯機のタイマーがずれている蓋然性が高いこととなる。 On the other hand, with regard to the HP type water heater's timer deviation (step S7), as shown in FIG. 7, the control means 8 calculates the night-time rate of unit HP hot water power consumption (HP type water heater night-time rate, heat pump type water heater night-time rate) (step S301), and performs a process of extracting smaller outliers for the HP type water heater night-time rate (step S302). If the HP type water heater night-time rate for the most recent specified number of days is a statistically smaller outlier compared to the past HP type water heater night-time rate (Yes in step S303), it is estimated that the HP type water heater has a timer deviation and is operating abnormally (step S304).
Here, the predetermined number of days is 3. That is, when the HP water heater midnight rate is an outlier on the small side for three consecutive days, the control means 8 estimates a timer deviation of the HP water heater.
If the HP water heater late-night rate becomes significantly smaller, there is a high probability that an HP water heater that is normally set to operate during the late night hours is also being operated outside of the late night hours, and there is a high probability that the timer of the HP water heater is out of sync.
HP式給湯機の消費電力量に関連する関連値であるHP式給湯機深夜率は、次の式(5A),(5B)で算出される。式(5A),(5B)は、深夜帯の種類に応じて選択される。当該世帯における深夜帯の種類は、初期情報で示される。HP式給湯機推定プログラムは、式(5A),(5B)を含む。尚、制御手段8は、当該世帯における過去の全消費電力量あるいは単位HP給湯消費電力量の状況により、深夜帯の種類を判別しても良い。例えば、制御手段8は、22時の時間帯から全消費電力量が顕著に増加する世帯の場合、式(5A)に係る深夜帯であると判別しても良い。
式(5A)は、深夜帯が22時から翌8時までである場合に用いられる。当該深夜帯は、例えば、世帯に対する比較的に新しい電力供給契約において、深夜電力割引がなされる時間帯である。
式(5B)は、深夜帯が23時から翌7時までである場合に用いられる。当該深夜帯は、例えば、世帯に対する比較的に古い電力供給契約において、深夜電力割引がなされる時間帯である。
式(5A),(5B)における全消費電力量の深夜率[%]は、次の式(6)で表される。
式(5A),(5B)は、HP式給湯機を有する150以上のサンプル世帯(上述のサンプル世帯とは別の世帯)について分析した結果に基づいている。尚、HP式給湯機深夜率が式(5A),(5B)で示されると仮定することについて、単位HP給湯消費電力量と外気温との相関係数0.7以上の世帯が全体の85%となっており、よってこの仮定は相当の妥当性を有する。
尚、制御手段8は、HP式給湯機深夜率の算出(ステップS301)及び全消費電力量の深夜率の少なくとも一方について、単位HP給湯消費電力量の算出時(ステップS5)に行っても良い。この場合、式(5A)~(6)は、HP式給湯機消費電力量等算出プログラムに含まれ得る。 The HP water heater midnight rate, which is a related value related to the power consumption of the HP water heater, is calculated by the following formulas (5A) and (5B). Formulas (5A) and (5B) are selected according to the type of midnight period. The type of midnight period for the household is indicated in the initial information. The HP water heater estimation program includes formulas (5A) and (5B). The control means 8 may determine the type of midnight period based on the past total power consumption or unit HP hot water power consumption of the household. For example, in the case of a household in which the total power consumption increases significantly from the 10 p.m. time slot, the control means 8 may determine that the midnight period is related to formula (5A).
Formula (5A) is used when the late night period is from 10 p.m. to 8 a.m. The late night period is, for example, a time period during which a late night power discount is applied in a relatively new power supply contract for a household.
Formula (5B) is used when the late night period is from 11pm to 7am the following morning. The late night period is, for example, a time period during which a late night power discount is applied in a relatively old power supply contract for a household.
The midnight rate [%] of the total power consumption in the formulas (5A) and (5B) is expressed by the following formula (6).
Formulas (5A) and (5B) are based on the results of an analysis of more than 150 sample households (households different from the sample households mentioned above) that have HP water heaters. Assuming that the HP water heater midnight rate is expressed by formulas (5A) and (5B), 85% of the households have a correlation coefficient of 0.7 or more between the unit HP hot water power consumption and the outdoor temperature, and therefore this assumption has considerable validity.
The control means 8 may calculate at least one of the HP water heater midnight rate (step S301) and the midnight rate of the total power consumption when calculating the unit HP hot water power consumption (step S5). In this case, the formulas (5A) to (6) may be included in the HP water heater power consumption calculation program.
HP式給湯機深夜率[%]=0.0049×外気温
-0.00000084×全消費電力量
+0.6095×全消費電力量の深夜率[%]+0.6061 (5A)
HP式給湯機深夜率[%]=0.0062×外気温
-0.00000078×全消費電力量
+0.8446×全消費電力量の深夜率[%]+0.5207 (5B)
全消費電力量の深夜率[%]=当該深夜帯に属する各時間帯の消費電力量の合計
/全消費電力量×100 (6)HP water heater midnight rate [%] = 0.0049 x outside temperature
-0.00000084 x total power consumption
+ 0.6095 x nighttime rate of total power consumption [%] + 0.6061 (5A)
HP water heater nighttime rate [%] = 0.0062 x outside temperature
-0.00000078 x total power consumption
+ 0.8446 x nighttime rate of total power consumption [%] + 0.5207 (5B)
Nighttime rate [%] of total power consumption = Sum of power consumption for each time period belonging to the nighttime period
/Total power consumption x 100 (6)
制御手段8は、外気温サーバTCから、当該1日の外気温を取得すると共に、当該世帯IDに係るスマートメーターSMの当該1日における深夜帯の消費電力量を取得して、深夜帯の合計(深夜帯の消費電力量)を算出し、更に全消費電力量を参照して、式(5A),(5B)~(6)にそれぞれ当てはめることでHP式給湯機深夜率を算出して、日毎に記憶させる(ステップS301)。尚、制御手段8は、ステップS301において全消費電力量を算出しても良い。
そして、制御手段8は、HP式給湯機の水漏れ推定と同様に、HP式給湯機深夜率の外れ値の抽出処理(ステップS302)を行う。
当該抽出処理は、図8に示されるように、箱ひげ図によっても良いし、図9に示されるように、予測区間によっても良い。
尚、抽出されるHP式給湯機深夜率の外れ値は、小さい側の外れ値であるから、図8では、外れ値を考慮した第1四分位数、即ち箱の長さの1.5倍の長さを有する下ひげの下端よりより下方にある外れ値である。又、図9において、予測区間の境界の各直線は、何れも右上がりとなり、95%予測区間の下側の境界(下から2番目の直線)あるいは99%予測区間の下側の境界(下から1番目の直線)より下方に位置するものが、HP式給湯機深夜率の外れ値となる。 The control means 8 acquires the outdoor temperature of the day from the outdoor temperature server TC, acquires the power consumption of the smart meter SM related to the household ID during the late night hours of the day, calculates the total power consumption during the late night hours (power consumption during the late night hours), and further calculates the HP water heater late night rate by referring to the total power consumption and applying it to each of the formulas (5A), (5B) to (6), and stores it for each day (step S301). Note that the control means 8 may calculate the total power consumption in step S301.
Then, the control means 8 performs a process of extracting outliers of the HP water heater midnight rate (step S302), similar to the case of estimating water leakage from the HP water heater.
The extraction process may be performed using a box plot as shown in FIG. 8, or using a prediction interval as shown in FIG.
In addition, the outliers of the HP water heater midnight rate extracted are smaller outliers, and therefore in Fig. 8, they are the first quartile taking the outliers into consideration, that is, the outliers below the lower end of the lower whisker having a length 1.5 times the length of the box. In Fig. 9, each line of the boundary of the prediction interval rises to the right, and the outliers of the HP water heater midnight rate are those that are below the lower boundary of the 95% prediction interval (the second line from the bottom) or the lower boundary of the 99% prediction interval (the first line from the bottom).
[電気温水器の用途別消費電力量の算出等]
続いて、制御手段8は、電気温水器の用途別消費電力量に係る単位電気温水器消費電力量を算出する(ステップS8)。[Calculation of power consumption by use of electric water heaters, etc.]
Next, the control means 8 calculates the unit electric water heater power consumption amount related to the power consumption amount by application of the electric water heater (step S8).
図10は、ステップS8の詳細を示すフローチャートである。
電気温水器は、ヒーター出力が4.5kWのものと5.5kWのものが普及している。かような出力は、電気温水器が設置された典型的なサンプル世帯における時間帯別消費電力量(30分間)の1日の推移(夏季及び冬季)を示す図11にも示されるように、他の電気機器に比べて十分に大きく、時間帯別消費電力量が4.5/2=2.25kWhあるいは5.5/2=2.75kWhを超えていれば、電気温水器が作動しているといえる。
よって、電気温水器消費電力量等算出プログラムを実行する制御手段8は、初期情報として得られた電気温水器のヒーター出力,貯湯量及び世帯人数のうちの少なくとも何れかに従い(ステップS401)、対象期間内の日において時間帯別消費電力量が2.25kWhあるいは2.75kWhを超えている時間帯数をカウントし、得られた時間帯数に2.25kWhあるいは2.75kWhを乗じて、単位電気温水器消費電力量を算出する(ステップS402)。初期情報としてヒーター出力が得られた場合、制御手段8は、当該ヒーター出力の値によりそのまま4.5kWのものと5.5kWのものとの区別を行い、初期情報として貯湯量が得られた場合、制御手段8は、貯湯量が370リットルであればヒーター出力4.5kWのものに対応させ、貯湯量が460リットルであればヒーター出力5.5kWのもの対応させ、初期情報として世帯人数が得られた場合、制御手段8は、所定人数(4人)以下であるとヒーター出力4.5kWのものに対応させ、当該所定人数を超えるとヒーター出力5.5kWのものに対応させる。時間帯別消費電力量が2.25kWhあるいは2.75kWhを超えている時間帯は、電気温水器の消費電力量の算出に係る特定の時間帯である。
尚、制御手段8は、時間帯別消費電力量が2.25kWh以上2.75kWh未満に収まっているか、あるいは2.75kWh以上となる時間帯が存在するかを判別することにより、電気温水器のヒーター出力につき初期情報を参照することなく判定しても良い。この場合、初期設定時のヒーター出力の取得を省略することができる。又、制御手段8は、電気温水器が典型的に深夜に作動することに基づき、時間帯別消費電力量のカウント等を行う時間帯を制限しても良い。この場合、初期情報として、対象世帯において電気温水器が深夜電力により作動するか否かの情報が含まれていても良い。又、新たなヒーター出力に係る電気温水器が普及した場合等において、ヒーター出力の値が変更されても良い。電気温水器の消費電力量に対する感度に余裕を持たせるため、電気温水器作動時の時間帯別消費電力量が計算上2.25kWhあるいは2.75kWhであっても、その計算上の値より小さい値(例えば2.0kWh)以上である時間帯をカウントしても良い。更に、HP式給湯機の場合と同様に、ステップS8がスキップされても良いし、複数台の電気温水器への対応がなされていても良い。 FIG. 10 is a flow chart showing the details of step S8.
Electric water heaters with heater outputs of 4.5 kW and 5.5 kW are widely available. As shown in Fig. 11, which shows the daily trends (summer and winter) of power consumption by time period (30 minutes) in a typical sample household with an electric water heater installed, such outputs are sufficiently large compared to other electric appliances, and if the power consumption by time period exceeds 4.5/2 = 2.25 kWh or 5.5/2 = 2.75 kWh, it can be said that the electric water heater is operating.
Therefore, the control means 8 executing the electric water heater power consumption calculation program, etc., counts the number of time periods in which the power consumption by time period exceeds 2.25 kWh or 2.75 kWh on days within the target period based on at least one of the heater output of the electric water heater, the hot water storage capacity, and the number of people in the household obtained as initial information (step S401), and multiplies the obtained number of time periods by 2.25 kWh or 2.75 kWh to calculate the unit power consumption of the electric water heater (step S402). When heater output is obtained as initial information, the control means 8 distinguishes between 4.5 kW and 5.5 kW based on the heater output value, when the amount of stored hot water is obtained as initial information, the control means 8 corresponds the amount of stored hot water to 370 liters with a heater output of 4.5 kW, and corresponds the amount of stored hot water to 460 liters with a heater output of 5.5 kW, when the number of people in the household is obtained as initial information, the control means 8 corresponds the amount of heater output to 4.5 kW if the number of people is a predetermined number (4 people) or less, and corresponds the amount of heater output to 5.5 kW if the number of people exceeds the predetermined number. The time periods when the power consumption by time period exceeds 2.25 kWh or 2.75 kWh are specific time periods related to the calculation of the power consumption of the electric hot water heater.
The
[電気温水器の異常運転推定等]
続いて、制御手段8は、電気温水器推定プログラムの実行により、電気温水器の異常運転を推定する(ステップS9,S10)。
電気温水器の異常運転は、ここでは、水漏れ(ステップS9)、及びタイマーずれ(ステップS10)である。
電気温水器の水漏れは、電気温水器の消費電力量を通常より増加させる異常運転であり、具体的には、貯湯タンクの湯が、各種配管及び弁の少なくとも一方から漏れること、並びに温水ユニットから貯湯タンクに供給される配管部で湯が漏れること、の少なくとも一方である。
電気温水器のタイマーずれは、電気温水器が通常運転される時間帯(夜間)からずれた時間(昼間)に運転される異常運転であり、具体的には、停電等の異常事象の発生により電気温水器のタイマーがずれたり、人為的な設定ミスによりタイマーがずれたりすることである。又、電気温水器が故障し、通常運転される時間帯に運転されなくなった場合も、タイマーずれ(異常運転)として推定可能である。
尚、推定対象である電気温水器の異常運転は、水漏れ及びタイマーずれに限られない。又、水漏れ及びタイマーずれの推定の順番は、上記のものと逆であっても良い。[Estimation of abnormal operation of electric water heater, etc.]
Next, the control means 8 executes an electric water heater estimation program to estimate abnormal operation of the electric water heater (steps S9 and S10).
The abnormal operation of the electric water heater here is a water leak (step S9) and a timer deviation (step S10).
A water leak from an electric water heater is an abnormal operation that increases the amount of power consumed by the electric water heater more than usual, and specifically, is at least one of the following: hot water leaking from the hot water storage tank from various pipes and valves, and hot water leaking from the piping that supplies water from the hot water unit to the hot water storage tank.
A timer deviation in an electric water heater is an abnormal operation in which the electric water heater is operated at a time (daytime) different from the normal operating time (nighttime), specifically, when the timer of the electric water heater is shifted due to an abnormal event such as a power outage, or when the timer is shifted due to a human error in setting. Also, if the electric water heater breaks down and no longer operates during the normal operating time, this can be estimated as a timer deviation (abnormal operation).
The abnormal operation of the electric water heater to be estimated is not limited to water leakage and timer deviation. Also, the order of estimation of water leakage and timer deviation may be reversed from that described above.
電気温水器の水漏れ(ステップS9)に関し、図12に示されるように、制御手段8は、単位電気温水器消費電力量について大きい側の外れ値を抽出する処理を行う(ステップS501)と共に、直近の所定日数の単位電気温水器消費電力量が、過去の単位電気温水器消費電力量に対して、何れも統計的に大きい側の外れ値となると(ステップS502でYes)、電気温水器が水漏れを起こしており、異常運転しているものと推定する(ステップS503)。
所定日数は、ここでは3日である。即ち、制御手段8は、単位電気温水器消費電力量が3日連続で大きい側の外れ値となると、電気温水器の水漏れを推定する。 Regarding water leakage from the electric water heater (step S9), as shown in FIG. 12, the control means 8 performs a process of extracting outliers on the larger side for the unit electric water heater power consumption (step S501), and if the unit electric water heater power consumption for the most recent specified number of days is a statistically larger outlier compared to the past unit electric water heater power consumption (Yes in step S502), it is estimated that the electric water heater is leaking water and operating abnormally (step S503).
The predetermined number of days is 3 in this example. That is, when the unit electric water heater power consumption amount is an outlier on the larger side for three consecutive days, the control means 8 estimates that the electric water heater is leaking water.
制御手段8は、HP式給湯機の水漏れ推定と同様に、単位電気温水器消費電力量の外れ値の抽出処理(ステップS501)を行う。
当該抽出処理は、図13に示されるように箱ひげ図によっても良いし、あるいは予測区間によっても良い。 The control means 8 performs a process of extracting outliers of the unit electric water heater power consumption (step S501), similar to the case of estimating water leakage from an HP water heater.
The extraction process may be performed using a box plot as shown in FIG. 13, or using a prediction interval.
他方、電気温水器のタイマーずれ(ステップS10)に関し、図14に示されるように、制御手段8は、単位HP給湯消費電力量の関連値である深夜率(電気温水器深夜率)について算出し(ステップS601)、電気温水器深夜率について小さい側の外れ値を抽出する処理を行う(ステップS602)と共に、直近の所定日数の電気温水器深夜率が、過去の電気温水器深夜率に対して、何れも統計的に小さい側の外れ値となると(ステップS603でYes)、電気温水器がタイマーずれを起こしており、異常運転しているものと推定する(ステップS604)。
所定日数は、ここでは2日である。即ち、制御手段8は、電気温水器深夜率が2日連続で小さい側の外れ値となると、電気温水器のタイマーずれを推定する。
電気温水器深夜率が大幅に小さくなれば、通常深夜帯に稼働されるように設定されている電気温水器が深夜帯以外でも稼働されている蓋然性が高く、電気温水器のタイマーがずれている蓋然性が高いこととなる。
電気温水器深夜率は、次の式(7)で算出される。式(7)は、電気温水器推定プログラムに含まれる。尚、電気温水器深夜率の算出は、電気温水器消費電力量等算出プログラム(ステップS8)において行われても良い。 On the other hand, with regard to the electric water heater timer deviation (step S10), as shown in FIG. 14, the control means 8 calculates the midnight rate (electric water heater midnight rate), which is a related value of the unit HP hot water power consumption (step S601), and performs a process to extract an outlier on the smaller side for the electric water heater midnight rate (step S602). If the electric water heater midnight rate for the most recent specified number of days is a statistically smaller outlier compared to the past electric water heater midnight rates (Yes in step S603), it is estimated that the electric water heater has a timer deviation and is operating abnormally (step S604).
Here, the predetermined number of days is 2. That is, when the electric water heater midnight rate is an outlier on the small side for two consecutive days, the
If the electric water heater night-time rate is significantly reduced, there is a high probability that an electric water heater that is normally set to operate during the night hours is also operating outside of the night hours, and there is a high probability that the timer of the electric water heater is out of sync.
The electric water heater midnight rate is calculated by the following formula (7). Formula (7) is included in the electric water heater estimation program. The electric water heater midnight rate may be calculated in the electric water heater power consumption calculation program (step S8).
電気温水器深夜率[%]=単位電気温水器消費電力量/全消費電力量 (7)Electric hot water heater nighttime rate [%] = unit electric hot water heater power consumption / total power consumption (7)
制御手段8は、HP式給湯機のタイマーずれ推定と同様に、電気温水器深夜率の外れ値の抽出処理(ステップS601)を行う。
当該抽出処理は、図15に示されるように箱ひげ図によっても良いし、予測区間によっても良い。 The control means 8 performs a process of extracting outliers of the electric water heater midnight rate (step S601) in the same manner as in estimating the timer deviation of the HP water heater.
The extraction process may be performed using a box plot as shown in FIG. 15 or a prediction interval.
[全量買取における太陽光パネルの発電電力量の算出等]
太陽光パネルを具備する世帯に対しては、2種類の契約が存在する。即ち、全量買取と、余剰買取である。
全量買取は、太陽光パネルにより生み出された発電電力が電力会社により全量買い取られる契約である。全量買取では、全消費電力量は使用する分だけ電力会社から売ってもらうため、全消費電力量については基本的に太陽光パネルのない世帯と同様の処理が可能である。
余剰買取は、太陽光パネルで発電された発電電力を自家消費して、余剰電力を電力会社に買い取ってもらい(余剰買取)、不足電力を電力会社に売ってもらう契約である。この場合、スマートメーターSMでは、時間帯別の余剰電力量(電力会社が買い取るため買電電力量とも呼ばれる)及び不足電力量(同様に売電電力量とも呼ばれる)が取得される。
制御手段8は、当該世帯が全量買取である場合、全量買取での太陽光パネルの発電電力量の算出(ステップS11)、及び全量買取での太陽光パネルの異常運転推定(ステップS12)を行い、当該世帯が余剰買取である場合、余剰買取での太陽光パネルの発電電力量の算出(ステップS13)、及び余剰買取での太陽光パネルの異常運転推定(ステップS14)を行う。
制御手段8は、太陽光パネルが複数種類存在する場合、ステップS11,12又はステップS13,14の処理を、それら種類分繰り返す。又、制御手段8は、当該世帯に太陽光パネルがない場合、ステップS11~14の処理をスキップする。
尚、全量買取は、まれである。全量買取か余剰買取かの買取態様を示す情報(買取態様情報)は、全量買取がまれであることに鑑み得なくても良いし、初期情報として得ても良いし、スマートメーターSMあるいは集計サーバCCに保持されたものを参照しても良い。[Calculation of the amount of electricity generated by solar panels for full purchase, etc.]
There are two types of contracts available for households with solar panels: full purchase and surplus purchase.
A full-amount purchase is a contract in which the electric power company purchases all of the electricity generated by solar panels. With a full-amount purchase, the electric power company sells all of the electricity consumed to the household only for the amount used, so the total amount of electricity consumed can basically be handled in the same way as a household without solar panels.
Surplus purchase is a contract whereby electricity generated by solar panels is consumed by the customer, the surplus electricity is purchased by the electric power company (surplus purchase), and the shortage electricity is sold to the electric power company. In this case, the smart meter SM acquires the amount of surplus electricity (also called the amount of purchased electricity because it is purchased by the electric power company) and the amount of shortage electricity (also called the amount of sold electricity) by time period.
If the household is subject to full purchase, the control means 8 calculates the amount of electricity generated by the solar panels when the full amount is purchased (step S11) and estimates abnormal operation of the solar panels when the full amount is purchased (step S12).If the household is subject to surplus purchase, the control means 8 calculates the amount of electricity generated by the solar panels when the surplus amount is purchased (step S13) and estimates abnormal operation of the solar panels when the surplus amount is purchased (step S14).
If there are multiple types of solar panels, the control means 8 repeats the processing of steps S11, 12 or steps S13, 14 for each type. Also, if the household does not have solar panels, the control means 8 skips the processing of steps S11 to 14.
In addition, the entire amount is rarely purchased. In view of the fact that the entire amount is rarely purchased, information indicating the purchase mode (purchase mode information) whether the entire amount is purchased or surplus purchase may not be obtained, and may be obtained as initial information or may refer to information stored in the smart meter SM or the aggregation server CC.
太陽光パネルの異常運転の推定は、過去の発電電力量に対する発電電力量の統計的な低下に基づき、発電に関する機能が異常となっているものとしてなされる。よって、太陽光パネルの日々の発電電力量の算出が必要になる。
全量買取の場合、発電電力量は、次の式(8),(9)によって計算される。式(8),(9)は、発電電力量等算出プログラムに含まれる。
尚、式(8)に代えて、式(8)’が用いられても良い。 Abnormal operation of solar panels is estimated based on a statistical drop in the amount of generated power compared to the amount of power generated in the past, and it is assumed that the power generation function is abnormal. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the daily amount of power generated by solar panels.
In the case of full purchase, the amount of generated power is calculated by the following formulas (8) and (9). Formulas (8) and (9) are included in the program for calculating the amount of generated power, etc.
Incidentally, instead of formula (8), formula (8)' may be used.
太陽光発電量[kWh/kW]=
0.8813×日射量[kWh/m2]-0.0168×外気温
+0.2173×風速-0.2656 (8)
太陽光発電量[kWh/kW]=
0.8944×日射量[kWh/m2]-0.01670×外気温
+0.0154 (8)’
発電電力量=太陽光発電量×発電容量 (9)Solar power generation amount [kWh/kW] =
0.8813 x solar radiation [kWh/m2 ] - 0.0168 x outside temperature
+0.2173 × wind speed -0.2656 (8)
Solar power generation amount [kWh/kW] =
0.8944 x solar radiation [kWh/m2 ] - 0.01670 x outside temperature
+0.0154 (8)'
Amount of generated electricity = Amount of solar power generation x Power generation capacity (9)
式(8)における日射量は、年月日及び太陽光パネルが設置された地域を日射量サーバLCに送信してその応答として日射量サーバLCから得られるものであり、ここでは当該年月日及び地域(に属する代表地点)における水平面全天日射量を、方位角0°傾斜角30°に補正した値である。制御手段8は、日射量サーバLCから直接傾斜角30°に補正した値を得ても良いし、日射量サーバLCから得た水平面全天日射量を演算して傾斜角30°に補正した値を得ても良い。尚、日射量として、他の方位角及び傾斜角の少なくとも一方に係るものとする等、他のものが用いられても良い。又、太陽光パネルが設置された地域に代えて、太陽光パネルが設置された場所(世帯)の緯経度等が送信されても良い。
式(8)における外気温は、上述の通り外気温サーバTCから得られるものであり、ここでは1日の平均気温である。尚、HP式給湯機の異常運転推定の場合における外気温の変更例と同様に、日平均気温以外の気温が用いられても良い。
式(8)における風速は、風速サーバWSから得られるものであり、ここでは1日の平均風速である。尚、風速として、1日の最高風速等が用いられても良い。
式(8)’における日射量及び外気温は、式(8)と同様である。式(8)’において、風速は用いられない。
式(9)における発電容量は、当該太陽光パネルにおける発電の容量であり、初期情報として取得される。尚、発電容量は、スマートメーターSMにおける発電電力等から算出されても良い。 The amount of solar radiation in formula (8) is obtained from the solar radiation server LC in response to the date and the area where the solar panel is installed, and is a value obtained by correcting the horizontal plane total solar radiation on the date and area (a representative point belonging to the date and area) to an azimuth angle of 0° and an inclination angle of 30°. The control means 8 may obtain a value corrected to an inclination angle of 30° directly from the solar radiation server LC, or may calculate the horizontal plane total solar radiation obtained from the solar radiation server LC to obtain a value corrected to an inclination angle of 30°. Note that other values may be used as the amount of solar radiation, such as those relating to at least one of another azimuth angle and inclination angle. Also, instead of the area where the solar panel is installed, the latitude and longitude of the place (household) where the solar panel is installed may be transmitted.
The outdoor temperature in formula (8) is obtained from the outdoor temperature server TC as described above, and is the average temperature in one day. Note that, similar to the example of changing the outdoor temperature in the case of estimating abnormal operation of the HP water heater, a temperature other than the average temperature in one day may be used.
The wind speed in formula (8) is obtained from the wind speed server WS and is the average wind speed for one day here. Note that the maximum wind speed for one day, etc. may also be used as the wind speed.
The solar radiation and the outside air temperature in formula (8)' are the same as those in formula (8). The wind speed is not used in formula (8)'.
The power generation capacity in formula (9) is the capacity of power generation in the solar panel and is acquired as initial information. Note that the power generation capacity may be calculated from the power generation power in the smart meter SM.
式(8),(9)は、全量買取に係る150以上のサンプル世帯(上述のサンプル世帯とは別)について分析した結果に基づいている。尚、全量買取での発電電力量が式(8),(9)で示されると仮定することについて、当該地域の日射量データを用いれば、重相関係数0.92となっており、よってこの仮定は相当の妥当性を有する。
式(8)’については、式(8)と同様である。 Equations (8) and (9) are based on the results of an analysis of more than 150 sample households (separate from the sample households mentioned above) involved in the full-amount purchase. Assuming that the amount of generated electricity in the full-amount purchase is shown in equations (8) and (9), if the solar radiation data for the area is used, the multiple correlation coefficient is 0.92, and therefore this assumption has considerable validity.
Equation (8)' is the same as equation (8).
図16は、全量買取での太陽光パネルの発電電力量の算出(ステップS11)の詳細に係るフローチャートである。
発電電力量等算出プログラムを実行する制御手段8は、日射量サーバLCから当該1日の日射量を取得すると共に(ステップS701)、外気温サーバTCから当該1日の外気温を取得し(ステップS702)、更に風速サーバWSから当該1日の風速を所得して(ステップS703)、式(8),(9)に当てはめて、全量買取における太陽光パネルの発電電力量(推定値)を算出する(ステップS704)。尚、ステップS701~S703の順序は変更されても良いし、ステップS701~S703は並列して同時に行われても良い。
制御手段8は、算出された全量買取での太陽光パネルの発電電力量を、日毎に、記憶手段6に記憶させる。 FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing the details of the calculation of the amount of power generated by the solar panels in the case of full purchase (step S11).
The control means 8, which executes the program for calculating the amount of generated power, etc., obtains the amount of solar radiation for that day from the solar radiation server LC (step S701), obtains the outside air temperature for that day from the outside air temperature server TC (step S702), and further obtains the wind speed for that day from the wind speed server WS (step S703), and applies these to equations (8) and (9) to calculate the amount of generated power (estimated value) of the solar panels in the case of full purchase (step S704). Note that the order of steps S701 to S703 may be changed, and steps S701 to S703 may be performed in parallel at the same time.
The control means 8 stores the calculated amount of electricity generated by the solar panels at the full purchase price in the storage means 6 for each day.
[全量買取における太陽光パネルの異常運転推定等]
続いて、制御手段8は、全量買取での太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定する(ステップS12)。
上述の通り、推定される太陽光パネルの異常運転は、発電に関する機能の低下である。
尚、推定対象である全量買取時の太陽光パネルの異常運転は、発電に関する機能の低下に限られない。これは、余剰買取においても、同様である。[Estimation of abnormal operation of solar panels in the case of full purchase]
Next, the control means 8 estimates abnormal operation of the solar panels when the entire amount is purchased (step S12).
As mentioned above, the suspected abnormal operation of solar panels is a decrease in their power generation function.
In addition, the abnormal operation of solar panels during the full purchase, which is the subject of the estimation, is not limited to a decrease in the power generation function. This also applies to surplus purchase.
図17は、ステップS12の詳細に係るフローチャートである。
全量買取時の太陽光パネルの異常運転の推定において、太陽光パネル推定プログラムを実行する制御手段8は、まず、発電電力量からその日の売電量を差し引いた値について大きい側の外れ値を抽出する処理を行う(ステップS801)。制御手段8は、売電量を、集計サーバCCから取得する。発電電力量から売電量を差し引いた値は、発電電力量が日射量、外気温、風速及び発電容量から算出された理想的なものであることから、大きいほど太陽光パネルの実際の発電電力量に相当する売電量が理想から遠いこととなり、発電機能が低下していることになる。尚、発電電力量から売電量を差し引いた値は、ステップS704において、発電電力量と合わせて算出されても良い。
次いで、制御手段8は、直近の所定日数に係る発電電力量から売電量を差し引いた値が、過去のものに対して、何れも統計的に大きい側の外れ値となると(ステップS802でYes)、全量買取における太陽光パネルが異常運転しているものと推定する(ステップS803)。
所定日数は、ここでは5日である。即ち、制御手段8は、発電電力量から売電量を差し引いた値が5日連続で大きい側の外れ値となると、全量買取での太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定する。 FIG. 17 is a flowchart showing details of step S12.
In estimating abnormal operation of the solar panel during full purchase, the control means 8 executing the solar panel estimation program first performs a process of extracting the larger outlier of the value obtained by subtracting the amount of power sold on that day from the amount of power generated (step S801). The control means 8 acquires the amount of power sold from the aggregation server CC. Since the value obtained by subtracting the amount of power sold from the amount of power generated is an ideal value calculated from the amount of solar radiation, outside temperature, wind speed, and power generation capacity, the larger the value, the further the amount of power sold that corresponds to the actual amount of power generated by the solar panel is from the ideal, and the more degraded the power generation function is. Note that the value obtained by subtracting the amount of power sold from the amount of power generated may be calculated together with the amount of power generated in step S704.
Next, if the value obtained by subtracting the amount of electricity sold from the amount of electricity generated for the most recent specified number of days is a statistically larger outlier compared to past values (Yes in step S802), the control means 8 estimates that the solar panels that are being purchased in full are operating abnormally (step S803).
Here, the predetermined number of days is 5. That is, when the value obtained by subtracting the amount of electricity sold from the amount of generated electricity is an outlier on the larger side for 5 consecutive days, the
制御手段8は、HP式給湯機の水漏れ推定と同様に、発電電力量から売電量を差し引いた値の外れ値の抽出処理(ステップS801)を行う。
当該抽出処理は、図18に示されるように箱ひげ図によっても良いし、あるいは図19に示されるように予測区間によっても良い。これらの図は、何れも、横軸を外気温として作成される。
図18,図19において、発電電力量から売電量を差し引いた値は、推定値-売電量[kWh/m2]と表され、外気温は平均気温[℃]と表されている。 The control means 8 performs an outlier extraction process (step S801) of the value obtained by subtracting the amount of electricity sold from the amount of electricity generated, similar to the water leakage estimation of the HP water heater.
The extraction process may be performed using a box plot as shown in Fig. 18, or a prediction interval as shown in Fig. 19. Both of these graphs are created with the outside air temperature on the horizontal axis.
18 and 19, the value obtained by subtracting the amount of power sold from the amount of generated power is expressed as estimated value-amount of power sold [kWh/m2 ], and the outside air temperature is expressed as average air temperature [° C.].
[余剰買取における太陽光パネルの発電電力量の算出等]
上述の通り、太陽光パネルの異常運転の推定は、過去の発電電力量に対する発電電力量の統計的な低下に基づいてなされる。
余剰買取の場合、発電電力量は、次の式(10),(11)によって計算される。式(10),(11)は、発電電力量等算出プログラムに含まれる。[Calculation of the amount of electricity generated by solar panels for surplus purchases, etc.]
As described above, the estimation of abnormal operation of the solar panels is based on a statistical decrease in the amount of generated power compared to the amount of power generated in the past.
In the case of surplus purchase, the amount of generated power is calculated by the following formulas (10) and (11). The formulas (10) and (11) are included in the program for calculating the amount of generated power, etc.
使用電力量[kWh]=a1×外気温2+a2×外気温+b (10)
発電電力量[kWh]=使用電力量-スマートメーターSMの値 (11)Power consumption [kWh] =a1 × outside temperature2 +a2 × outside temperature + b (10)
Amount of generated electricity [kWh] = Amount of electricity used - Value of smart meter SM (11)
式(10)における外気温は、上述の通り外気温サーバTCから得られたものであり、1日の平均気温である。尚、HP式給湯機の異常運転推定の場合における外気温の変更例と同様に、平均気温以外の気温が用いられても良い。
式(11)におけるスマートメーターSMの値は、余剰電力量の場合プラスであり、不足電力量の場合マイナスである。 The outdoor temperature in formula (10) is obtained from the outdoor temperature server TC as described above, and is the average temperature for one day. Note that, similar to the example of changing the outdoor temperature in the case of estimating abnormal operation of the HP water heater, a temperature other than the average temperature may be used.
The value of the smart meter SM in equation (11) is positive in the case of surplus energy and negative in the case of deficit energy.
式(10),(11)は、余剰買取に係る150以上のサンプル世帯(上述のサンプル世帯とは別)について分析した結果に基づいている。尚、余剰買取での発電電力量が式(10),(11)で示されると仮定することについて、重相関係数0.8となっており、よってこの仮定は相当の妥当性を有する。Equations (10) and (11) are based on the results of an analysis of more than 150 sample households (separate from the sample households mentioned above) involved in surplus purchases. In addition, the multiple correlation coefficient for assuming that the amount of electricity generated through surplus purchases is shown in equations (10) and (11) is 0.8, and therefore this assumption is quite valid.
図20は、余剰買取での太陽光パネルの発電電力量の算出(ステップS13)の詳細に係るフローチャートである。
発電電力量等算出プログラムを実行する制御手段8は、まず、使用電力量の推定式(10)の作成(ステップS902)を行うため、ステップS902に先立ち、曇天時の全消費電力量の算出を行う(ステップS901)。ここでは、制御手段8は、ステップS4での全消費電力量の算出時に、曇天時であることの印(フラグ)及び外気温サーバTCから得た当該日の外気温を付すことで、ステップS901を行う。制御手段8は、曇天時であるか否かの判別を、日射量サーバLCから得た日射量が所定値以下である場合に曇天時であるとすることで行う。又、制御手段8は、ステップS901において、式(11)のため、その日のスマートメーターSMの値を、曇天時の全消費電力量と対応付けて記憶させる。
尚、制御手段8は、曇天時の全消費電力量及び外気温を、記憶手段6中の曇天時全消費電力量テーブルに記憶させることで、ステップS901を行っても良い。更に、ステップS901において、発電事業所の休業日に係る消費電力量は、曇天時であっても全消費電力量の算出から除外されても良い。又、制御手段8は、曇天時であるか否かの判別を、気象種別サーバへの問い合わせにより行っても良い。気象種別サーバは、地域及び日付を指定した問い合わせに応じ、気象種別(晴天,曇天等)を問い合わせ元等に送信するものである。尚、気象種別サーバは、日射量サーバLCと同様の変更例を有する。 FIG. 20 is a flowchart showing details of the calculation of the amount of generated electricity by the solar panels in surplus purchase (step S13).
The control means 8 that executes the program for calculating the amount of generated power, etc., first calculates the total amount of power consumed on a cloudy day (step S901) prior to step S902 in order to create an estimation equation (10) for the amount of power consumed (step S902). Here, the control means 8 performs step S901 by adding a mark (flag) indicating that the day is cloudy and the outdoor air temperature of the day obtained from the outdoor air temperature server TC when calculating the total amount of power consumed in step S4. The control means 8 determines whether the day is cloudy or not by determining that the day is cloudy when the amount of solar radiation obtained from the solar radiation server LC is equal to or less than a predetermined value. In addition, in step S901, the control means 8 stores the value of the smart meter SM of that day in association with the total amount of power consumed on a cloudy day for the purpose of equation (11).
The control means 8 may perform step S901 by storing the total power consumption on cloudy days and the outside temperature in a cloudy day total power consumption table in the storage means 6. Furthermore, in step S901, the power consumption on days when the power generation facility is closed may be excluded from the calculation of the total power consumption even if the day is cloudy. The control means 8 may determine whether or not the day is cloudy by making an inquiry to a weather type server. The weather type server transmits the weather type (sunny, cloudy, etc.) to the source of the inquiry in response to an inquiry that specifies a region and date. The weather type server has the same modifications as the solar radiation server LC.
次に、制御手段8は、使用電力量の推定式(10)の作成を行う(ステップS902)。ステップS902では、単位HP給湯消費電力量等と同様に、曇天時の全消費電力量のある程度の蓄積が必要になる。
制御手段8は、曇天時の全消費電力量を、当該世帯の使用電力量とみなして、ステップS902を実行する。一般に、曇天時には、太陽光パネルは発電せず、発電電力量はゼロであるため、曇天時の全消費電力量を使用電力量とみなすことは合理的である。尚、制御手段8は、曇天時の全消費電力量を例えば所定の関数等により演算して、使用電力量を得ても良い。
図21は、ある世帯における外気温(平均気温[℃],横軸)と使用電力量([kWh],縦軸)との関係に係るグラフである。何れの世帯においても、図21の点線及び式(10)のように、使用電力量は外気温の二次関数に近似され、使用電力量の推定式(10)は二次関数となる。
制御手段8は、ステップS902において、外気温と使用電力量との関係が示されるグラフにおいて各1日におけるものをプロットすると共に、これらプロットに係る近似式を最小自乗法等により求め、当該近似式を使用電力量の推定式とし、即ち式(10)の各係数(各定数)a1,a2,bを算出する。
尚、使用電力量は、各1日におけるものに代えて、各日の昼間の時間帯に係る値のみで、即ち太陽光パネルが発電し得ない夜間の使用電力量を考慮しない状態で推定されても良い。昼間の時間帯は、日射量が所定値以上(例えば0を超えた値)である時間帯とする等、日射量から決定されても良いし、日の出の時刻及び日の入りの時刻から決定されても良い。日の出の時刻及び日の入りの時刻は、日射量サーバLCから取得されても良いし、他のサーバ等から取得されても良い。 Next, the
The control means 8 executes step S902 by regarding the total amount of power consumption on a cloudy day as the amount of power used by the household. Generally, on a cloudy day, the solar panel does not generate power and the amount of power generated is zero, so it is reasonable to regard the total amount of power consumption on a cloudy day as the amount of power used. The control means 8 may obtain the amount of power used by calculating the total amount of power consumption on a cloudy day using, for example, a predetermined function.
Fig. 21 is a graph showing the relationship between the outside temperature (average temperature [°C], horizontal axis) and the amount of electricity used ([kWh], vertical axis) in a certain household. In each household, the amount of electricity used is approximated to a quadratic function of the outside temperature, as shown by the dotted line in Fig. 21 and equation (10), and the estimation equation (10) for the amount of electricity used is a quadratic function.
In step S902, the control means 8 plots the relationship between the outside air temperature and the amount of electricity used for each day on a graph, and obtains an approximation equation relating to these plots using the least squares method or the like, and uses the approximation equation as an estimation equation for the amount of electricity used, i.e., calculates each of the coefficients (each of the constants)a1 ,a2 , and b in equation (10).
The amount of power usage may be estimated based only on values related to the daytime hours of each day, i.e., without considering the amount of power usage at night when the solar panel cannot generate power. The daytime hours may be determined from the amount of solar radiation, such as a time period when the amount of solar radiation is equal to or greater than a predetermined value (e.g., a value exceeding 0), or may be determined from the time of sunrise and sunset. The time of sunrise and sunset may be obtained from the solar radiation server LC or from another server, etc.
続いて、制御手段8は、ステップS902で使用電力量の推定式(10)が得られていれば、集計サーバCCから当該世帯における本日のスマートメーターSMの値を得ると共に外気温サーバTCからから当該世帯における本日の外気温を得て(ステップS903)、式(10),(11)に当てはめ、余剰買取における太陽光パネルの発電電力量(推定値)を算出する(ステップS904)。尚、ステップS901~S904の順序は変更されても良い。
制御手段8は、算出された余剰買取での太陽光パネルの発電電力量を、日毎に、記憶手段6に記憶させる。
尚、制御手段8は、当該世帯の使用電力量の推定式が一旦算出された時、あるいはその後所定期間を経た時等において、曇天時の全消費電力量の算出及び使用電力量の推定式の算出(ステップS901~S902)を停止し、ステップS903~S904のみを行うようにしても良い。 Next, if the estimation formula (10) for the amount of power usage has been obtained in step S902, the control means 8 obtains the value of the smart meter SM for the household for today from the tallying server CC and the outdoor air temperature for the household for today from the outdoor air temperature server TC (step S903), and applies them to the formulas (10) and (11) to calculate the amount of power generated by the solar panels for surplus purchase (estimated value) (step S904). Note that the order of steps S901 to S904 may be changed.
The control means 8 stores the calculated amount of electricity generated by the solar panels at the surplus purchase price in the storage means 6 for each day.
In addition, once the estimation formula for the amount of electricity used by the household has been calculated, or after a predetermined period of time has elapsed, the control means 8 may stop calculating the total electricity consumption on cloudy days and the estimation formula for the amount of electricity used (steps S901 to S902), and may perform only steps S903 to S904.
[余剰買取における太陽光パネルの異常運転推定等]
続いて、制御手段8は、余剰買取での太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定する(ステップS14)。
上述の通り、推定される太陽光パネルの異常運転は、発電に関する機能の低下である。[Estimation of abnormal operation of solar panels in surplus purchase]
Next, the control means 8 estimates abnormal operation of the solar panels in the surplus purchase (step S14).
As mentioned above, the suspected abnormal operation of solar panels is a decrease in their power generation function.
余剰買取時の太陽光パネルの異常運転の推定において、太陽光パネル推定プログラムを実行する制御手段8は、全量買取時と同様に処理を行う。
但し、外れ値に係る所定日数は、ここでは一般住宅(発電事業所ではない世帯)において3日であり、発電事業所において2日である。即ち、制御手段8は、発電電力量から売電量を差し引いた値が、一般住宅において3日連続で、又発電事業所において2日連続で大きい側の外れ値となると、余剰買取での太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定する。
発電事業所において外れ値に係る所定日数が一般住宅より少ないものとされることは、発電事業所においては負荷が安定しており全消費電力量の変動幅が一般住宅より小さいことから、合理性を有する。
尚、全量買取時において、外れ値に係る所定日数が一般住宅より少ないものとされても良い。又、余剰買取時において、外れ値に係る所定日数が一般住宅と発電事業所とで一致していても良い。 When estimating abnormal operation of a solar panel during surplus purchase, the control means 8 executing the solar panel estimation program performs processing in the same manner as when the entire amount is purchased.
However, the specified number of days related to the outlier is 3 days for a general residence (a household that is not a power generation facility) and 2 days for a power generation facility. That is, when the value obtained by subtracting the amount of electricity sold from the amount of electricity generated is an outlier on the larger side for 3 consecutive days for a general residence or for 2 consecutive days for a power generation facility, the control means 8 estimates abnormal operation of the solar panels in the surplus purchase.
The fact that the specified number of days related to outliers at power generation facilities is less than that at general residential buildings is reasonable because the load at power generation facilities is stable and the range of fluctuation in total power consumption is smaller than that at general residential buildings.
In addition, when purchasing the entire amount, the predetermined number of days related to the outlier may be less than that for general residential buildings. Also, when purchasing surplus electricity, the predetermined number of days related to the outlier may be the same for general residential buildings and power generation facilities.
制御手段8は、全量買取の場合と同様に、発電電力量から売電量を差し引いた値の外れ値の抽出処理(ステップS801)を行う。
当該抽出処理は、全量買取の場合と同様に、箱ひげ図によっても良いし、あるいは予測区間によっても良い。 The control means 8 performs an extraction process (step S801) of outliers obtained by subtracting the amount of electricity sold from the amount of electricity generated, in the same manner as in the case of full purchase.
The extraction process may be performed using a box plot or a prediction interval, as in the case of purchasing the entire amount.
≪作用効果等≫
以上の推定システムE1は、次のような作用効果を奏する。
即ち、推定システムE1は、電気機器の異常運転を推定するものであって、サーバ1を備えており、サーバ1は、制御手段8と、通信手段7と、を備えており、通信手段7は、通信可能な電力計であるスマートメーターSMの値が集計される集計サーバCC、外気温を送信可能な外気温サーバTC、日射量を送信可能な日射量サーバLC、及び風速を送信可能な風速サーバWSと通信可能であり、制御手段8は、通信手段7を制御して、スマートメーターSMの値、外気温、日射量、及び風速を適宜得ると共に、スマートメーターSMの値、外気温、日射量、及び風速の少なくとも何れかに基づいて、電気機器の消費電力量及び発電電力量の少なくとも一方又はこれに関連する値である関連値を算出し、更に、消費電力量及び発電電力量の少なくとも一方又は関連値について、統計的な外れ値を抽出し、外れ値に基づいて、電気機器の異常運転を推定する。
よって、電気機器の異常運転が、目視の発見が困難なものであったとしても、適切に推定される。又、電気機器の異常運転の推定に際し、世帯を見て回る巡視が不要となる。更に、電気機器自身が異常を把握しなくても、電気機器の異常運転が推定される。加えて、電気機器の異常運転の推定が、低コストで行える。異常運転が推定された電気機器に対して処置が施されれば、省エネルギーとなり、大規模な故障が未然に防止される。<Actions, Effects, etc.>
The above estimation system E1 provides the following advantages.
That is, the estimation system E1 estimates abnormal operation of an electrical appliance and includes a
Therefore, even if the abnormal operation of an electrical appliance is difficult to detect by visual inspection, it can be appropriately estimated. Furthermore, when estimating the abnormal operation of an electrical appliance, it is not necessary to patrol the household. Furthermore, the abnormal operation of an electrical appliance can be estimated even if the electrical appliance itself does not recognize the abnormality. In addition, the estimation of the abnormal operation of an electrical appliance can be performed at low cost. If measures are taken for an electrical appliance suspected to be operating abnormally, energy can be saved and large-scale breakdowns can be prevented.
又、電気機器は、HP式給湯機であり、制御手段8は、通信手段7を制御して、HP式給湯機の水温(文献値)又は製造年(ユーザが分かる場合の初期情報)を取得し、且つ、スマートメーターSMの値、及び外気温を得ると共に、スマートメーターSMの値、外気温、並びに、水温又は製造年に基づいて、HP式給湯機の消費電力量を算出し、更に、HP式給湯機の消費電力量についての外れ値に基づいて、HP式給湯機の水漏れを推定する。よって、目視で発見し難いHP式給湯機の水漏れが、巡視不要で適切に推定される。
更に、電気機器は、HP式給湯機であり、制御手段8は、通信手段7を制御して、スマートメーターSMの値、及び外気温を得ると共に、スマートメーターSMの値、及び外気温に基づいて、HP式給湯機の消費電力量の深夜率であるHP式給湯機深夜率を算出し、更に、HP式給湯機深夜率についての外れ値に基づいて、HP式給湯機のタイマーずれを推定する。よって、目視で発見し難いHP式給湯機のタイマーずれが、巡視不要で適切に推定される。 Furthermore, the electrical equipment is an HP water heater, and the control means 8 controls the communication means 7 to obtain the water temperature (literature value) or manufacturing year (initial information when known by the user) of the HP water heater, and also obtains the value of the smart meter SM and the outside air temperature, and calculates the power consumption of the HP water heater based on the value of the smart meter SM, the outside air temperature, and the water temperature or the manufacturing year, and further estimates a water leak from the HP water heater based on an outlier value for the power consumption of the HP water heater. Thus, a water leak from the HP water heater, which is difficult to detect visually, can be appropriately estimated without the need for patrol.
Furthermore, the electrical equipment is an HP water heater, and the control means 8 controls the communication means 7 to obtain the value of the smart meter SM and the outside air temperature, calculates an HP water heater night-time rate, which is the night-time rate of the power consumption of the HP water heater, based on the value of the smart meter SM and the outside air temperature, and further estimates a timer deviation of the HP water heater based on an outlier value for the HP water heater night-time rate. Thus, a timer deviation of the HP water heater, which is difficult to detect visually, can be appropriately estimated without the need for patrol.
又、電気機器は、電気温水器であり、制御手段8は、通信手段7を制御して、特定の時間帯(深夜帯)に係るスマートメーターSMの値を得ると共に、スマートメーターSMの値に基づいて、電気温水器の消費電力量を算出し、更に、消費電力量についての外れ値に基づいて、電気温水器の水漏れを推定する。よって、目視で発見し難い電気温水器の水漏れが、巡視不要で適切に推定される。
更に、電気機器は、電気温水器であり、制御手段8は、通信手段7を制御して、特定の時間帯(深夜帯)を含む全時間帯に係るスマートメーターSMの値を得ると共に、スマートメーターSMの値に基づいて、電気温水器の消費電力量の深夜率である電気温水器深夜率を算出し、更に、電気温水器深夜率についての外れ値に基づいて、電気温水器のタイマーずれを推定する。よって、目視で発見し難い電気温水器のタイマーずれが、巡視不要で適切に推定される。 The electric appliance is an electric water heater, and the control means 8 controls the communication means 7 to obtain the value of the smart meter SM for a specific time period (late night), calculates the power consumption of the electric water heater based on the value of the smart meter SM, and estimates water leakage from the electric water heater based on an outlier value for the power consumption. Thus, water leakage from the electric water heater, which is difficult to detect visually, can be appropriately estimated without the need for inspection.
Furthermore, the electric appliance is an electric water heater, and the control means 8 controls the communication means 7 to obtain the values of the smart meter SM for all time periods including the specific time period (midnight), calculates an electric water heater midnight rate which is the midnight rate of the power consumption of the electric water heater based on the value of the smart meter SM, and estimates the timer deviation of the electric water heater based on the outlier value of the electric water heater midnight rate. Thus, the timer deviation of the electric water heater, which is difficult to detect visually, can be appropriately estimated without the need for patrol.
又、電気機器は、全量買取に係る太陽光パネルであり、制御手段8は、通信手段7を制御して、太陽光パネルの発電容量を取得し、且つ、スマートメーターSMの値、外気温、日射量、及び風速を得ると共に、外気温、日射量、及び風速、並びに発電容量に基づいて、太陽光パネルの発電電力量を算出して、関連値として発電電力量からスマートメーターSMの値を減じた値を算出し、更に、発電電力量からスマートメーターSMの値を減じた値についての外れ値に基づいて、太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定する。よって、目視で発見し難い全量買取の太陽光パネルの異常運転が、巡視不要で適切に推定される。
更に、電気機器は、余剰買取に係る太陽光パネルであり、制御手段8は、通信手段7を制御して、曇天時を含むスマートメーターSMの値、及び外気温を得ると共に、曇天時のスマートメーターSMの値から外気温の関数としての使用電力量の推定式を作成し、当該推定式に外気温を当てはめて使用電力量を推定し、スマートメーターSMの値から使用電力量を減じて発電電力量を算出して、関連値として発電電力量からスマートメーターSMの値を減じた値を算出し、更に、発電電力量からスマートメーターSMの値を減じた値についての外れ値に基づいて、太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定する。よって、目視で発見し難い余剰買取の太陽光パネルの異常運転が、巡視不要で適切に推定される。 The electrical equipment is a solar panel related to full purchase, and the control means 8 controls the communication means 7 to obtain the power generation capacity of the solar panel, and also obtains the value of the smart meter SM, the outside temperature, the amount of solar radiation, and the wind speed, and calculates the amount of power generated by the solar panel based on the outside temperature, the amount of solar radiation, the wind speed, and the power generation capacity, and calculates a value obtained by subtracting the value of the smart meter SM from the amount of power generated as a related value, and further estimates abnormal operation of the solar panel based on an outlier for the value obtained by subtracting the value of the smart meter SM from the amount of power generated. Thus, abnormal operation of solar panels related to full purchase, which is difficult to detect visually, can be appropriately estimated without the need for patrol.
Furthermore, the electrical equipment is a solar panel related to surplus purchase, and the control means 8 controls the communication means 7 to obtain the value of the smart meter SM including on cloudy days and the outside temperature, creates an estimation formula for the amount of electricity used as a function of the outside temperature from the value of the smart meter SM on cloudy days, estimates the amount of electricity used by applying the outside temperature to the estimation formula, calculates the amount of electricity generated by subtracting the amount of electricity used from the value of the smart meter SM, calculates a value obtained by subtracting the value of the smart meter SM from the amount of electricity generated as a related value, and further estimates abnormal operation of the solar panel based on an outlier for the value obtained by subtracting the value of the smart meter SM from the amount of electricity generated. Thus, abnormal operation of solar panels related to surplus purchase, which is difficult to detect visually, can be appropriately estimated without the need for patrols.
加えて、外れ値は、箱ひげ図に係るものであり、あるいは、外れ値は、予測区間に係るものである。
よって、外れ値が統計的に簡単且つ正確に抽出され、電気機器の異常運転の推定精度がより一層向上する。 Additionally, outliers are associated with box plots, or outliers are associated with prediction intervals.
Therefore, outliers can be extracted statistically simply and accurately, and the accuracy of estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment is further improved.
更に、サーバ1と通信可能な端末Tを備えており、端末Tは、端末表示手段12を有すると共に、電気機器と接続されるスマートメーターSMを区別するIDと関連付けられており、サーバ1は、電気機器の異常運転が推定されると、電気機器に係るIDと関連付けられた端末Tに、電気機器の異常運転が推定された旨の情報である異常運転情報を送信し、異常運転情報を受信した端末Tは、異常運転情報に基づく表示を、端末表示手段12において行う。
よって、電気機器の異常運転が推定された場合に、端末Tを所持するユーザは、簡単、迅速にその旨を知ることができる。 Furthermore, the terminal T is equipped with a terminal T capable of communicating with the
Therefore, when an abnormal operation of an electrical appliance is suspected, a user who owns the terminal T can easily and quickly know the fact.
そして、推定プログラムにより、サーバ1に読み取られることで通信手段7及び制御手段8が形成されるから、推定システムE1が簡単に構築可能である。The estimation program is read by the
E1・・推定システム(電気機器の異常運転推定システム)、1・・サーバ(サーバコンピュータ)、7・・通信手段、8・・制御手段、CC・・集計サーバ(集計サーバコンピュータ)、LC・・日射量サーバ(日射量サーバコンピュータ)、SM・・スマートメーター、T・・端末、TC・・外気温サーバ(外気温サーバコンピュータ)、WS・・風速サーバ(風速サーバコンピュータ)。E1: Estimation system (electrical equipment abnormal operation estimation system), 1: Server (server computer), 7: Communication means, 8: Control means, CC: Aggregation server (aggregation server computer), LC: Solar radiation server (solar radiation server computer), SM: Smart meter, T: Terminal, TC: Outdoor temperature server (outdoor temperature server computer), WS: Wind speed server (wind speed server computer).
Claims (11)
Translated fromJapaneseサーバコンピュータを備えており、
前記サーバコンピュータは、制御手段と、通信手段と、を備えており、
前記通信手段は、通信可能な電力計であるスマートメーターの値が集計される集計サーバコンピュータ、外気温を送信可能な外気温サーバコンピュータ、日射量を送信可能な日射量サーバコンピュータ、及び風速を送信可能な風速サーバコンピュータの少なくとも何れかと通信可能であり、
前記制御手段は、
前記通信手段を制御して、前記スマートメーターの値、前記外気温、前記日射量、及び前記風速の少なくとも何れかを得ると共に、
前記スマートメーターの値、前記外気温、前記日射量、及び前記風速の少なくとも何れかに基づいて、前記電気機器の消費電力量及び発電電力量の少なくとも一方又はこれに関連する値である関連値を算出し、
更に、前記消費電力量及び前記発電電力量の少なくとも一方又は前記関連値について、統計的な外れ値を抽出し、
前記外れ値に基づいて、前記電気機器の異常運転を推定する
ことを特徴とする電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 An abnormal operation estimation system for an electric appliance that estimates an abnormal operation of an electric appliance,
A server computer is provided.
The server computer includes a control means and a communication means,
the communication means is capable of communicating with at least one of an aggregation server computer that aggregates values of a smart meter, which is a power meter capable of communication, an outdoor air temperature server computer that can transmit outdoor air temperature, a solar radiation amount server computer that can transmit solar radiation amount, and a wind speed server computer that can transmit wind speed;
The control means
Controlling the communication means to obtain at least one of the smart meter value, the outside air temperature, the amount of solar radiation, and the wind speed;
Calculating at least one of the amount of power consumed and the amount of power generated by the electrical appliance or a related value that is a value related thereto, based on at least one of the value of the smart meter, the outside air temperature, the amount of solar radiation, and the wind speed;
Further, a statistical outlier is extracted for at least one of the power consumption amount and the power generation amount or the related value;
An electrical equipment abnormal operation inference system, comprising: a processor for inferring abnormal operation of the electrical equipment based on the outlier.
前記制御手段は、
前記通信手段を制御して、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機の水温又は製造年を取得し、且つ、前記スマートメーターの値、及び前記外気温を得ると共に、
前記スマートメーターの値、前記外気温、並びに、前記水温又は前記製造年に基づいて、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機の前記消費電力量を算出し、
更に、前記消費電力量についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機の水漏れを推定する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 The electrical equipment is a heat pump water heater,
The control means
Controlling the communication means to obtain the water temperature or the manufacturing year of the heat pump water heater, and obtaining the value of the smart meter and the outside air temperature,
Calculating the power consumption of the heat pump water heater based on the value of the smart meter, the outside air temperature, and the water temperature or the year of manufacture;
The system for estimating abnormal operation of an electrical device according to claim 1 , further comprising: estimating a water leak from the heat pump water heater based on the outlier value for the amount of power consumption.
前記制御手段は、
前記通信手段を制御して、前記スマートメーターの値、及び前記外気温を得ると共に、
前記スマートメーターの値、及び前記外気温に基づいて、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機の前記消費電力量の深夜率であるヒートポンプ式給湯機深夜率を算出し、
更に、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機深夜率についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記ヒートポンプ式給湯機のタイマーずれを推定する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 The electrical equipment is a heat pump water heater,
The control means
Controlling the communication means to obtain the smart meter value and the outside air temperature,
Calculating a heat pump water heater nighttime rate, which is a nighttime rate of the power consumption of the heat pump water heater, based on the value of the smart meter and the outside air temperature;
The abnormal operation estimation system for electrical equipment according to claim 1 , further comprising: estimating a timer deviation of the heat pump water heater based on the outlier value for the heat pump water heater midnight rate.
前記制御手段は、
前記通信手段を制御して、特定の時間帯に係る前記スマートメーターの値を得ると共に、
前記スマートメーターの値に基づいて、前記電気温水器の前記消費電力量を算出し、
更に、前記消費電力量についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記電気温水器の水漏れを推定する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 The electrical appliance is an electric water heater,
The control means
Controlling the communication means to obtain values of the smart meter relating to a specific time period;
Calculating the power consumption of the electric water heater based on the value of the smart meter;
The system for inferring abnormal operation of an electrical device according to claim 1 , further comprising: estimating a water leak from the electric water heater based on the outlier value for the amount of power consumption.
前記制御手段は、
前記通信手段を制御して、特定の時間帯を含む全時間帯に係る前記スマートメーターの値を得ると共に、
前記スマートメーターの値に基づいて、前記電気温水器の前記消費電力量の深夜率である電気温水器深夜率を算出し、
更に、前記電気温水器深夜率についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記電気温水器のタイマーずれを推定する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 The electrical appliance is an electric water heater,
The control means
Controlling the communication means to obtain values of the smart meter for all time periods including a specific time period;
Calculating an electric water heater midnight rate, which is a midnight rate of the power consumption of the electric water heater, based on the value of the smart meter;
The system for estimating abnormal operation of an electric device according to claim 1 , further comprising: estimating a timer deviation of the electric water heater based on the outlier value for the electric water heater midnight rate.
前記制御手段は、
前記通信手段を制御して、前記太陽光パネルの発電容量を取得し、且つ、前記スマートメーターの値、前記外気温、前記日射量、及び前記風速を得ると共に、
前記外気温、前記日射量、及び前記風速、並びに前記発電容量に基づいて、前記太陽光パネルの発電電力量を算出して、前記関連値として前記発電電力量から前記スマートメーターの値を減じた値を算出し、
更に、前記発電電力量から前記スマートメーターの値を減じた値についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 The electrical equipment is a solar panel that is subject to full purchase,
The control means
Controlling the communication means to acquire the power generation capacity of the solar panel, and acquiring the value of the smart meter, the outside temperature, the amount of solar radiation, and the wind speed,
Calculating the amount of power generated by the solar panel based on the outside temperature, the amount of solar radiation, the wind speed, and the power generation capacity, and calculating a value obtained by subtracting the value of the smart meter from the amount of power generated as the related value;
The abnormal operation estimation system for electrical equipment according to claim 1, further comprising: estimating abnormal operation of the solar panel based on the outlier for the value obtained by subtracting the value of the smart meter from the amount of generated power.
前記制御手段は、
前記通信手段を制御して、曇天時を含む前記スマートメーターの値、及び前記外気温を得ると共に、
曇天時の前記スマートメーターの値から前記外気温の関数としての使用電力量の推定式を作成し、当該推定式に前記外気温を当てはめて前記使用電力量を推定し、前記スマートメーターの値から前記使用電力量を減じて前記発電電力量を算出して、前記関連値として前記発電電力量から前記スマートメーターの値を減じた値を算出し、
更に、前記発電電力量から前記スマートメーターの値を減じた値についての前記外れ値に基づいて、前記太陽光パネルの異常運転を推定する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 The electrical equipment is a solar panel related to surplus purchase,
The control means
Controlling the communication means to obtain the smart meter value including the cloudy day and the outside air temperature,
creating an estimation formula for the amount of power usage as a function of the outside air temperature from the value of the smart meter on a cloudy day, applying the outside air temperature to the estimation formula to estimate the amount of power usage, subtracting the amount of power usage from the value of the smart meter to calculate the amount of power generation, and calculating a value obtained by subtracting the value of the smart meter from the amount of power generation as the related value;
The abnormal operation estimation system for electrical equipment according to claim 1, further comprising: estimating abnormal operation of the solar panel based on the outlier for the value obtained by subtracting the value of the smart meter from the amount of generated power.
ことを特徴とする請求項1ないし請求項7の何れかに記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 8. The system for estimating abnormal operation of an electrical device according to claim 1, wherein the outliers relate to a box plot.
ことを特徴とする請求項1ないし請求項7の何れかに記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 8. The system for estimating abnormal operation of an electrical device according to claim 1, wherein the outlier is related to a prediction interval.
前記端末は、端末表示手段を有すると共に、前記電気機器と接続される前記スマートメーターを区別するIDと関連付けられており、
前記サーバコンピュータは、前記電気機器の異常運転が推定されると、前記電気機器に係る前記IDと関連付けられた前記端末に、前記電気機器の異常運転が推定された旨の情報である異常運転情報を送信し、
前記異常運転情報を受信した前記端末は、前記異常運転情報に基づく表示を、前記端末表示手段において行う
ことを特徴とする請求項1ないし請求項9の何れかに記載の電気機器の異常運転推定システム。 Further, a terminal capable of communicating with the server computer is provided,
the terminal has a terminal display means and is associated with an ID that identifies the smart meter connected to the electrical device;
When an abnormal operation of the electric appliance is estimated, the server computer transmits abnormal operation information, which is information indicating that an abnormal operation of the electric appliance is estimated, to the terminal associated with the ID related to the electric appliance;
10. The abnormal operation inference system for an electrical device according to claim 1, wherein the terminal that has received the abnormal operation information displays a display based on the abnormal operation information on the terminal display means.
ことを特徴とする電気機器の異常運転推定プログラム。 11. An abnormal operation estimation program for an electrical device, comprising: a server computer configured to form the communication means and the control means according to claim 1 in response to reading the program by the server computer.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020099535AJP7466383B2 (en) | 2020-06-08 | 2020-06-08 | System and program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020099535AJP7466383B2 (en) | 2020-06-08 | 2020-06-08 | System and program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021193863A JP2021193863A (en) | 2021-12-23 |
| JP7466383B2true JP7466383B2 (en) | 2024-04-12 |
Family
ID=79168892
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020099535AActiveJP7466383B2 (en) | 2020-06-08 | 2020-06-08 | System and program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7466383B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2025158847A1 (en)* | 2024-01-26 | 2025-07-31 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Information processing system, information processing method, and program |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002058158A (en) | 2000-08-04 | 2002-02-22 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Power load facilities that support power supply contracts |
| US20100324962A1 (en) | 2009-06-22 | 2010-12-23 | Johnson Controls Technology Company | Smart building manager |
| JP2013031271A (en) | 2011-07-27 | 2013-02-07 | Solar Energy Solutions Inc | Electric power input and output management system, and server and power distribution panel for the same |
| JP2014147235A (en) | 2013-01-29 | 2014-08-14 | Solar Energy Solutions Inc | Photovoltaic power generation monitoring method |
| JP2018185581A (en) | 2017-04-24 | 2018-11-22 | トヨタホーム株式会社 | Equipment abnormality management system |
| JP2019133412A (en) | 2018-01-31 | 2019-08-08 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Maintenance planning device and maintenance planning method |
| JP2020530752A (en) | 2017-08-04 | 2020-10-22 | スンチャン カンパニー,リミテッド | Crowd solar tracker control methods and systems |
- 2020
- 2020-06-08JPJP2020099535Apatent/JP7466383B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002058158A (en) | 2000-08-04 | 2002-02-22 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Power load facilities that support power supply contracts |
| US20100324962A1 (en) | 2009-06-22 | 2010-12-23 | Johnson Controls Technology Company | Smart building manager |
| JP2013031271A (en) | 2011-07-27 | 2013-02-07 | Solar Energy Solutions Inc | Electric power input and output management system, and server and power distribution panel for the same |
| JP2014147235A (en) | 2013-01-29 | 2014-08-14 | Solar Energy Solutions Inc | Photovoltaic power generation monitoring method |
| JP2018185581A (en) | 2017-04-24 | 2018-11-22 | トヨタホーム株式会社 | Equipment abnormality management system |
| JP2020530752A (en) | 2017-08-04 | 2020-10-22 | スンチャン カンパニー,リミテッド | Crowd solar tracker control methods and systems |
| JP2019133412A (en) | 2018-01-31 | 2019-08-08 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Maintenance planning device and maintenance planning method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021193863A (en) | 2021-12-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Birt et al. | Disaggregating categories of electrical energy end-use from whole-house hourly data | |
| US20160266594A1 (en) | System and method for residential utility monitoring and improvement of energy efficiency | |
| US10811902B2 (en) | Energy planning system and energy planning method considering a timing of a change in a total number of residents in a home | |
| US8660813B2 (en) | Method and system for disaggregating heating and cooling energy use from other building energy use | |
| CN107851994B (en) | Power supply and demand prediction system, method, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| EP3389162A1 (en) | Power control device, operation plan planning method, and program | |
| JP4938750B2 (en) | Power consumption prediction apparatus, power consumption prediction method, and program | |
| JP6786814B2 (en) | Information processing equipment, information processing methods, and programs | |
| JP6676477B2 (en) | Building power consumption prediction system, power storage device control system, and power storage device control method | |
| KR101355978B1 (en) | Electric management system and method for electric consumption prediction | |
| JP6928164B2 (en) | Hot water supply system, cloud server, boiling schedule creation method and program | |
| US20230418346A1 (en) | Methods, systems, and media for automatic and continuous control of energy-consuming devices | |
| JP2017169289A (en) | Power prediction system, power prediction method, and program | |
| Kröger et al. | The price of natural gas dependency: price shocks, inequality, and public policy | |
| JP7390811B2 (en) | Hot water supply control device, cloud server, hot water system, hot water supply control method and program | |
| JP7466383B2 (en) | System and program for estimating abnormal operation of electrical equipment | |
| Stafford | Long-term monitoring and performance of ground source heat pumps | |
| JP6437139B2 (en) | Power management apparatus, server, power management system, power management method, and program | |
| JP2011159236A (en) | Display system and display method for housing history information | |
| JP5924626B2 (en) | Energy diagnosis system and energy diagnosis program | |
| JP2014155389A (en) | Power supply/demand management device and power supply/demand management method | |
| JP6841231B2 (en) | Information processing device, its information processing method, and program | |
| JP7554027B2 (en) | Abnormal operation estimation system and program | |
| JP6292515B2 (en) | Demand forecasting device, program | |
| JP2016093098A (en) | Power use amount management device and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20230411 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20240221 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20240305 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20240402 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:7466383 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |