JP7438808B2 - Needs matching equipment and programs - Google Patents
Needs matching equipment and programsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7438808B2 JP7438808B2JP2020055392AJP2020055392AJP7438808B2JP 7438808 B2JP7438808 B2JP 7438808B2JP 2020055392 AJP2020055392 AJP 2020055392AJP 2020055392 AJP2020055392 AJP 2020055392AJP 7438808 B2JP7438808 B2JP 7438808B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- needs
- vector
- registered
- need
- inquiry
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、ニーズマッチングの技術に関する。 The present invention relates to needs matching technology.
企業における事業は、他の企業との取引や協力によって成り立っている。そのため、企業は、新しい取引先や協力相手を探していることが多い。その企業にとって好適な相手が見つかれば、事業活動が円滑に進む。 A company's business is based on transactions and cooperation with other companies. Therefore, companies are often looking for new business partners and cooperation partners. If a company finds a suitable partner, business activities will proceed smoothly.
新しい取引先や協力相手は、人的な紹介などによって見つかることもあるが、人間関係に頼らずに効率よく出会える機会があればなお良い。 New business partners and cooperation partners can sometimes be found through personal introductions, but it would be even better if there were opportunities to meet them efficiently without relying on personal relationships.
双方の事業に関するニーズが満たされるときに、取引や協力関係が成立するという点で、新しい取引先や協力相手を探すということは、企業同士のニーズのマッチングがキーとなると言える。たとえば、ある企業がある商品を売りたいというニーズを持っており、別の企業がその商品を買いたいというニーズを持っていれば、それらのニーズはマッチしており、取引関係へ発展する可能性が高い。 Business transactions and cooperative relationships are established when the business needs of both parties are met, so it can be said that matching the needs of two companies is the key to finding new business partners and cooperation partners. For example, if one company has a need to sell a certain product and another company has a need to buy that product, these needs match and there is a possibility that a business relationship will develop. is high.
特許文献1にビジネスマッチングを支援するシステムが開示されている。特許文献1は、様々の企業に関する情報をデータベース化して、相手企業を探し出そうとする技術の一種である。企業に関する情報はテキストで表現されており、ユーザが設定したキーワードと一致する情報を検索するという手法が基礎となっている。つまり、テキストの比較によって適合する情報を探し出す。 Patent Document 1 discloses a system that supports business matching. Patent Document 1 is a type of technology that attempts to find a partner company by creating a database of information regarding various companies. Information about companies is expressed in text, and the basic method is to search for information that matches keywords set by the user. In other words, matching information is found by comparing texts.
しかし、従来の手法では、必ずしも所望の企業情報にたどり着くとは限らない。表現的に合致していないように見えても、実質的にはニーズに適合する企業情報が見逃されることがある。企業に関する情報は膨大であって、人がニーズの実質的な適合性を判断することは、時間的にも労力的にも負荷が大きい。 However, conventional methods do not always lead to desired corporate information. Corporate information that may not seem to match in terms of expression, but that actually meets the needs, may be overlooked. There is a huge amount of information about companies, and it takes a lot of time and effort for people to judge whether the company is actually compatible with their needs.
本発明は、上記課題認識に基づいて完成された発明であり、その主たる目的は、あるニーズに適合する他のニーズを効率的に見つけられるようにすることである。 The present invention was completed based on the recognition of the above problem, and its main purpose is to enable efficient finding of other needs that match one need.
本発明のある態様におけるニーズマッチング装置は、複数の登録ニーズの内容文をニーズ区分に紐づけて管理するデータベースに関して、各登録ニーズの内容文に含まれる各単語を表すベクトルと、ニーズ区分のタイトルに含まれる各単語を表すベクトルとに基づいて、当該登録ニーズを表す登録ニーズベクトルを算出する算出部と、照会ニーズの内容文を受け付ける第1受付部と、照会ニーズの内容文に含まれる各単語を表すベクトルに基づいて、照会ニーズを表す照会ニーズベクトルを算出し、算出された当該照会ニーズベクトルと類似する登録ニーズベクトルを探索する探索部と、探索された登録ニーズベクトルで表される登録ニーズの少なくとも内容文を出力する出力部と、を備える。 A needs matching device in an aspect of the present invention relates to a database that manages content sentences of a plurality of registered needs by linking them to need categories, and includes a vector representing each word included in the content sentences of each registered need, and a title of the need category. a calculation unit that calculates a registered needs vector representing the registered need based on the vector representing each word included in the registration need; a first reception unit that receives the content sentence of the inquiry need; a search unit that calculates an inquiry needs vector representing an inquiry need based on a vector representing a word, and searches for a registered needs vector similar to the calculated inquiry needs vector; and an output unit that outputs at least a content sentence of the needs.
本発明によれば、あるニーズに適合する他のニーズを効率的に見つけられる。 According to the present invention, other needs matching a certain need can be efficiently found.
企業間の取引や協力関係は、企業同士のニーズが適合したときに成り立つ。ある企業がある商品を売りたいというニーズを持っており、別の企業がその商品を買いたいというニーズを持っていれば、それらのニーズはマッチしており、取引関係へ発展する可能性が高い。他にも、ある企業がある技術を開発したいというニーズを持っており、別の企業がその技術に関連する技術を提供したいというニーズを持っていれば、それらのニーズはマッチしており、研究や開発のパートナーになり得る。また、ある企業があるサービスを受けたいというニーズを持っており、別の企業がそのサービスを提供したいというニーズを持っていれば、それらのニーズはマッチしており、その企業のサービスが利用されるかも知れない。本実施形態では、このような企業間のニーズマッチングを支援するシステムを提案する。 Transactions and cooperative relationships between companies are established when the needs of the companies are compatible. If one company has a need to sell a certain product and another company has a need to buy that product, these needs match and there is a high possibility that a business relationship will develop. . In addition, if one company has a need to develop a certain technology and another company has a need to provide technology related to that technology, these needs are matched, and research and development partners. In addition, if one company has a need to receive a certain service and another company has a need to provide that service, those needs match, and that company's service will be used. Maybe. This embodiment proposes a system that supports such needs matching between companies.
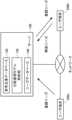
図1は、本実施形態におけるニーズマッチングシステムのネットワーク構成図である。ニーズマッチングシステムにおいて、好適なニーズ同士を引き合わせるためのニーズマッチングを行う。ただし、テキスト検索ではなくて、分散表現モデルを使ったベクトルの類似判定による探索を行う。 FIG. 1 is a network configuration diagram of the needs matching system in this embodiment. In the needs matching system, needs matching is performed to match suitable needs. However, rather than a text search, the search is performed by determining the similarity of vectors using a distributed representation model.
本実施形態におけるニーズマッチングシステムは、サーバ100、ユーザ端末200aおよびユーザ端末200bを含む。この例で、ユーザ端末200aは、たとえばある企業の担当者が自社のニーズを登録するために使用する。登録されたニーズは他社から探索される対象となる。このように探索対象として登録されるニーズを、「登録ニーズ」という。ユーザ端末200bは、たとえば別の企業の担当者が登録ニーズの中から自社のニーズに適合するニーズを探し出すときに使用される。このように好適な登録ニーズを見つけるために提示するニーズを、「照会ニーズ」という。 The needs matching system in this embodiment includes a
ユーザ端末200aおよびユーザ端末200bは、ネットワーク(たとえば、インターネット、LANや専用線など)を介してサーバ100と接続する。この図では、2つのユーザ端末200を示しているが、実際にはより多数のユーザ端末200が使用される。
サーバ100は、分散表現モデルを有している。分散表現モデルは、分散表現モデル記憶部130に格納されている。以下、分散表現モデルについて説明する。
分散表現モデルでは、多数の単語を高い次元の実数ベクトルで表す。分散表現モデルは、自然言語の文章を構造化し大規模に集積したコーパスとよばれるデータベースに基づく学習処理によって得られる。この技術は、自然言語処理の分野においてよく知られている。分散表現モデルとして得られる単語の実数ベクトルを、「単語ベクトル」という。なお、分散表現のベクトルであるという点で、「分散ベクトル」ということもある。また、テキストの意味を数値化しているという点で、「意味ベクトル」ということもある。 In the distributed representation model, many words are represented by high-dimensional real vectors. Distributed representation models are obtained through learning processing based on a database called a corpus, which is a large-scale collection of structured natural language sentences. This technique is well known in the field of natural language processing. A real vector of words obtained as a distributed representation model is called a "word vector." Note that it is also called a "distributed vector" in that it is a vector of distributed representation. It is also sometimes called a "semantic vector" because it digitizes the meaning of the text.
代表的な分散表現の技術として、たとえばWord2vecが知られている。Word2vecでは、「近傍に出現する単語が似ている単語同士は意味的に近い」という前提に立ち、文において対象単語の近傍(たとえば前後5単語あるいは前後10単語)に出現する別の単語を探索するという問題を解く。ここでいう前後5単語とは、対象単語の5個前の単語から1個前までの単語と対象単語の1個後の単語から5個後までの単語の計10の単語の範囲のことである。学習手段としては、ニューラルネットワークが用いられる。大きなコーパスを用いた学習の過程で、近傍に出現する単語が似ている単語同士の単語ベクトルは、似た値を示すように変化する。 For example, Word2vec is known as a typical distributed representation technology. Word2vec searches for other words that appear in the vicinity of the target word (for example, 5 words before or after or 10 words before and after) in a sentence based on the premise that words that appear similar in the vicinity are semantically similar. Solve the problem of. The 5 words before and after the target word refer to a total of 10 words, including the word from 5 words before the target word to the word before the target word, and the word from the word after the target word to the word 5 words after the target word. be. A neural network is used as the learning means. In the process of learning using a large corpus, the word vectors of similar words that appear nearby change to show similar values.
分散表現モデルでは、単語ベクトルによって単語同士の類似関係を示すだけでなく、句、節、文や文章などの類似関係も示すことができる。複数の単語を含む文等において、これらの単語の単語ベクトルからその文等の分散ベクトル(「文ベクトル」等ということがある)を生成することが行われている。ある文の文ベクトルと別の文の文ベクトルが近似する場合、これらの文は内容が近しいことを示している。 In the distributed representation model, word vectors can indicate not only similar relationships between words, but also similar relationships between phrases, clauses, sentences, sentences, etc. BACKGROUND ART In a sentence or the like that includes a plurality of words, a distributed vector (sometimes referred to as a "sentence vector" or the like) of the sentence or the like is generated from the word vectors of these words. When the sentence vector of one sentence and the sentence vector of another sentence are similar, this indicates that these sentences are similar in content.
本実施形態では、分散表現モデルを用いて、ユーザ端末200aから受けた登録ニーズをベクトル化しておく。また、同様に、ユーザ端末200bから受けた照合ニーズもベクトル化する。ニーズ同士の適合性は、これらのベクトルの類似度によって求められる。類似度は、たとえばコサイン類似度である。詳しくは後述するが、本実施形態では、登録ニーズに関してニーズ区分も加味してベクトルを求める。 In this embodiment, registration needs received from the
どのような由来の分散表現モデルを使用するかは任意であるが、ここでは既存の企業情報のデータベースを利用する。企業情報のデータベースからコーパスを生成して、そのコーパスに基づく分散表現モデルを使用するものとする。ニーズマッチングを行う企業は、このデータベースに登録されている必要はない。このデータベースに載っている企業の情報は参考にすぎないので、「参考企業データベース」という。参考企業データベース120は、参考とする企業情報が格納されている参考企業テーブルを有している。 The origin of the distributed representation model to be used is arbitrary, but here an existing corporate information database will be used. A corpus is generated from a database of corporate information, and a distributed representation model based on the corpus is used. Companies that perform needs matching do not need to be registered in this database. Since the information on companies listed in this database is for reference only, it is called the ``reference company database.'' The reference company database 120 has a reference company table in which reference company information is stored.
図2は、参考企業テーブルのデータ構造図である。
参考企業テーブルは、分散表現モデルの生成に利用されるだけで、直接的にニーズマッチングにはかかわらない。企業テーブルは、企業毎のレコードを有する。企業テーブルのレコードには、参考企業ID、参考企業名および事業内容が含まれる。事業内容のフィールドには、一文のみが設定されてもよいし、複数の文が設定されてもよい。あるいは、単語や句を列挙したテキストなどでもよい。 FIG. 2 is a data structure diagram of the reference company table.
The reference company table is only used to generate a distributed representation model and is not directly involved in needs matching. The company table has records for each company. Records in the company table include a reference company ID, a reference company name, and business details. Only one sentence or multiple sentences may be set in the business content field. Alternatively, it may be a text listing words or phrases.
図3は、単語テーブルのデータ構成図である。
分散表現モデルの実体は、たとえば単語テーブルのデータ形式をとる。単語テーブルは、単語毎のレコードを有する。単語テーブルのレコードには、単語および単語ベクトルが設定される。 FIG. 3 is a data configuration diagram of the word table.
The entity of the distributed representation model takes the data format of a word table, for example. The word table has a record for each word. Words and word vectors are set in the records of the word table.
図4は、登録ニーズ受付画面の図である。
登録ニーズ受付画面は、ユーザ端末200aからログインされたサーバ100で生成されて、ユーザ端末200aに送信される。そして、ユーザ端末200aに表示された画面で、ユーザから登録ニーズの情報を受け付ける。登録企業の表示領域300には、ニーズを登録する企業の名前が表示される。ログインされた段階で、企業名、所在地、アカウント情報、担当者氏名、メールアドレスや電話番号などを管理する企業テーブル(図示せず)を参照して、企業名が特定されるものとする。登録ニーズ内容の入力領域302には、登録ニーズの内容がテキストで入力される。ニーズ区分の選択領域304では、ニーズ区分が選択される。この例では、予め設定されているニーズ区分の候補の中からプルダウンメニュー方式で選択する。登録ボタン306がタッチされると、登録企業名、登録ニーズ内容およびニーズ区分IDを含む登録ニーズのデータ(以下、「登録ニーズデータ」という)が、サーバ100へ送信される。取消ボタン308がタッチされると、登録ニーズデータを送信せずに、登録ニーズ受付画面が閉じられる。 FIG. 4 is a diagram of the registration needs reception screen.
The registration needs reception screen is generated by the
図5は、登録ニーズテーブルのデータ構成図である。
サーバ100へ送信された登録ニーズデータは、登録ニーズテーブルに格納される。登録ニーズテーブルは、登録ニーズ毎のレコードを有する。サーバ100において登録ニーズデータを受信すると、新たなレコードが追加される。登録ニーズテーブルのレコードには、登録企業名、登録ニーズ内容およびニーズ区分IDが設定される。 FIG. 5 is a data configuration diagram of the registered needs table.
The registered needs data sent to the
図6は、ニーズ区分テーブルのデータ構成図である。
ニーズ区分テーブルは、ニーズデータベース140に予め用意されている。ニーズ区分テーブルは、ニーズ区分毎のレコードを有する。ニーズ区分テーブルのレコードには、ニーズ区分IDおよびニーズ区分タイトルが設定されている。ニーズ区分タイトルは、上述したニーズ区分の選択領域304のプルダウンメニューで表示される。 FIG. 6 is a data configuration diagram of the needs classification table.
The needs classification table is prepared in advance in the
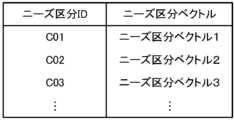
図7は、ニーズ区分ベクトル記憶部のデータ構成図である。
ニーズ区分ベクトル記憶部もニーズ区分テーブルに合わせて、予めニーズデータベース140に用意されている。ニーズ区分ベクトル記憶部は、ニーズ区分ごとのレコードを有する。ニーズ区分ベクトル記憶部のレコードには、ニーズ区分IDとニーズ区分ベクトルが対応付けて設定される。ニーズ区分ベクトルは、ニーズ区分タイトルの分散ベクトルに相当する。つまり、ニーズ区分ベクトルは、ニーズ区分タイトルに含まれる各単語の単語ベクトルから生成される。この例では、ニーズ区分タイトルに含まれる各単語の単語ベクトルの平均化によって生成される。例えば、タイトル「研究開発協力」のニーズ区分ベクトルは、「研究」の単語ベクトル、「開発」の単語ベクトルおよび「協力」の単語ベクトルの平均ベクトルである。したがって、「研究開発協力」のニーズ区分ベクトルには、「研究」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「開発」の単語ベクトルの特徴および「協力」の単語ベクトルの特徴が反映されている。 FIG. 7 is a data configuration diagram of the needs classification vector storage unit.
A needs classification vector storage unit is also prepared in advance in the
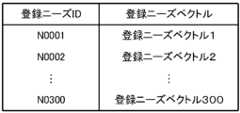
図8は、登録ニーズベクトル記憶部のデータ構成図である。
登録ニーズベクトルは、サーバ100において登録ニーズデータを受信してから生成される。登録ニーズベクトル記憶部は、登録ニーズに対応するレコードを有し、そのレコードには、登録ニーズIDと登録ニーズベクトルが対応付けて設定される。登録ニーズベクトルは、登録ニーズの分散ベクトルに相当する。ただし、登録ニーズ内容のみならず、ニーズ区分も加味して生成される。具体的には、登録ニーズ内容の分散ベクトル(以下、「ニーズ内容ベクトル」という)とニーズ区分ベクトルから生成される。この例では、ニーズ内容ベクトルとニーズ区分ベクトルの加重平均によって登録ニーズベクトルが算出される。重みの比率は一定であるものとする。たとえば、ニーズ内容ベクトルの重みが7で、ニーズ区分ベクトルの重みが3であるとすれば、ベクトルの各成分について、ニーズ内容ベクトルの値に7を乗じ、ニーズ区分ベクトルの値に3を乗じ、それらの合計を10で割ることによって、登録ニーズベクトルの値が算出される。 FIG. 8 is a data configuration diagram of the registered needs vector storage unit.
The registered needs vector is generated after receiving the registered needs data at the
たとえば、図5の登録ニーズID:N0300の登録ニーズベクトルは、「静音モータの応用分野を増やしたい」のニーズ内容ベクトルと「研究開発協力」のニーズ区分ベクトルの7:3の荷重平均によって求められる。「静音モータの応用分野を増やしたい」のニーズ内容ベクトルは、「静音」の単語ベクトル、「モータ」の単語ベクトル、「応用」の単語ベクトル、「分野」の単語ベクトル、「増やす」の単語ベクトルおよび「したい」の単語ベクトルの平均ベクトルである。ここでは、助詞を無視するものとする。また、「研究開発協力」のニーズ区分ベクトルは、「研究」の単語ベクトル、「開発」の単語ベクトルおよび「協力」の単語ベクトルの平均ベクトルである。したがって、登録ニーズID:N0300の登録ニーズベクトルには、「静音」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「モータ」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「応用」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「分野」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「増やす」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「したい」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「研究」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「開発」の単語ベクトルの特徴および「協力」の単語ベクトルの特徴が反映されている。なお、加重平均に代えて、単純平均を用いてもよい。 For example, the registered needs vector of registered needs ID: N0300 in Figure 5 is determined by the weighted average of the needs content vector of "I want to increase the application fields of silent motors" and the needs classification vector of "Research and development cooperation" at a ratio of 7:3. . The need content vector for "I want to increase the application fields of silent motors" is the word vector "quiet", the word vector "motor", the word vector "application", the word vector "field", and the word vector "increase". and the average vector of the word vectors of “I want to”. Here, particles are ignored. Further, the needs category vector of “research and development cooperation” is the average vector of the word vector of “research”, the word vector of “development”, and the word vector of “cooperation”. Therefore, the registered needs vector with registered needs ID: N0300 includes the word vector feature of "quiet", the word vector feature of "motor", the word vector feature of "application", the word vector feature of "field", The characteristics of the word vector ``increase'', the characteristics of the word vector ``want to'', the characteristics of the word vector ``research'', the characteristics of the word vector ``development'', and the characteristics of the word vector ``cooperation'' are reflected. Note that a simple average may be used instead of the weighted average.
図9は、照会ニーズ受付画面の図である。
照会ニーズ受付画面は、ユーザ端末200bからログインされたサーバ100で生成されて、ユーザ端末200bに送信される。そして、ユーザ端末200bに表示された画面で、ユーザから照会ニーズの情報を受け付ける。照会ニーズ内容の入力領域310には、照会ニーズの内容がテキストで入力される。実行ボタン312がタッチされると、照会ニーズ内容が照会ニーズのデータ(以下、「照会ニーズデータ」という)としてサーバ100へ送られる。取消ボタン314がタッチされると、照会ニーズデータを送信せずに、照会ニーズ受付画面が閉じられる。 FIG. 9 is a diagram of the inquiry needs reception screen.
The inquiry needs reception screen is generated by the
サーバ100は、照会ニーズデータを受信すると、照会ニーズ内容のテキストに基づいて、照会ニーズベクトルを生成する。つまり、照会ニーズベクトルは、照会ニーズの分散ベクトルに相当する。具体的には、照会ニーズ内容に含まれる単語の単語ベクトルから生成される。この例では、それらの単語ベクトルの平均が、照会ニーズベクトルとなる。 Upon receiving the inquiry needs data, the
たとえば、「静かな掃除機の開発を手伝って欲しい」の照会ニーズベクトルは、「静か」の単語ベクトル、「掃除機」の単語ベクトル、「開発」の単語ベクトル、「手伝う」の単語ベクトルおよび「欲しい」の単語ベクトルから生成される。したがって、「静かな掃除機の開発を手伝って欲しい」の照会ニーズベクトルには、「静か」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「掃除機」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「開発」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「手伝う」の単語ベクトルの特徴および「欲しい」の単語ベクトルの特徴が反映されている。 For example, a query needs vector for "I want help developing a quiet vacuum cleaner" includes a word vector for "quiet," a word vector for "vacuum cleaner," a word vector for "development," a word vector for "help," and a word vector for "quiet." It is generated from the word vector "I want". Therefore, the query needs vector for "I want help developing a quiet vacuum cleaner" includes features of the word vector "quiet", features of the word vector "vacuum cleaner", features of the word vector "development", and features of the word vector "quiet". The characteristics of the word vector ``help'' and the word vector ``want'' are reflected.
図10は、マッチング結果画面の図である。
マッチング結果画面では、照会ニーズにマッチした登録ニーズを一覧形式で表示する。マッチング結果画面は、照会ニーズデータの送信元であるユーザ端末200bへ返信される。各登録ニーズの行には、登録ニーズ内容の表示領域320、ニーズ区分の表示領域322、登録企業の表示領域324および詳細ボタン326が含まれる。詳細ボタン326にタッチすると、登録企業に関する詳細な情報(企業名、所在地、担当者氏名、メールアドレスや電話番号など)が表示される。 FIG. 10 is a diagram of the matching result screen.
The matching result screen displays registered needs that match the inquiry needs in a list format. The matching result screen is returned to the
第1行に表示された登録ニーズについて説明する。図8に関連して説明したとおり、ニーズ内容ベクトル「静音モータの応用分野を増やしたい」とニーズ区分ベクトル「研究開発協力」から生成された登録ニーズベクトルには、「静音」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「モータ」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「応用」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「分野」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「増やす」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「したい」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「研究」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「開発」の単語ベクトルの特徴および「協力」の単語ベクトルの特徴が反映されている。一方、図9に関連して説明したとおり、「静かな掃除機の開発を手伝って欲しい」の照会ニーズベクトルには、「静か」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「掃除機」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「開発」の単語ベクトルの特徴、「手伝う」の単語ベクトルの特徴および「欲しい」の単語ベクトルの特徴が反映されている。 The registration needs displayed in the first line will be explained. As explained in relation to Figure 8, the registered needs vector generated from the needs content vector "I want to increase the application fields of quiet motors" and the needs classification vector "Research and development cooperation" has the characteristics of the word vector "quiet". , features of the word vector of "motor", features of the word vector of "application", features of the word vector of "field", features of the word vector of "increase", features of the word vector of "want to", features of the word vector of "research". The characteristics of the word vector, the characteristics of the word vector "development" and the characteristics of the word vector "cooperation" are reflected. On the other hand, as explained in relation to FIG. 9, the inquiry needs vector for "I want help developing a quiet vacuum cleaner" includes features of the word vector "quiet", features of the word vector "vacuum cleaner", The characteristics of the word vector ``development'', the characteristics of the word vector ``help'', and the characteristics of the word vector ``want'' are reflected.
両者を比較すると、登録ニーズベクトルの「静音」の単語ベクトルの特徴は、照会ニーズベクトルの「静か」の単語ベクトルの特徴に近しい。登録ニーズベクトルの「モータ」の単語ベクトルの特徴は、照会ニーズベクトルの「掃除機」の単語ベクトルの特徴と関連がある。登録ニーズベクトルの「開発」の単語ベクトルの特徴は、照会ニーズベクトルと共通する。登録ニーズベクトルの「協力」の単語ベクトルの特徴は、照会ニーズベクトルの「手伝う」の単語ベクトルの特徴に近しい。登録ニーズベクトルの「したい」の単語ベクトルの特徴は、照会ニーズベクトルの「欲しい」の単語ベクトルの特徴に近しい。よって、第1行目に関する登録ニーズベクトルは、全体として「静かな掃除機の開発を手伝って欲しい」の照会ニーズベクトルと近しく、高い類似度を示すことになる。特に、「静音モータの応用分野を増やしたい」のニーズ内容ベクトルにはない「開発」の単語ベクトルの特徴と「協力」の単語ベクトルの特徴が、ニーズ区分ベクトルによって補足されている点で、実効性が高まっている。 Comparing the two, the features of the word vector "quiet" in the registered needs vector are close to the features of the word vector "quiet" in the inquiry needs vector. The features of the word vector "motor" in the registered needs vector are related to the features of the word vector "vacuum cleaner" in the inquiry needs vector. The characteristics of the word vector “development” in the registered needs vector are common to those in the inquiry needs vector. The characteristics of the word vector "cooperation" in the registered needs vector are close to the characteristics of the word vector "help" in the inquiry needs vector. The characteristics of the word vector "I want" in the registered needs vector are close to the characteristics of the word vector "I want" in the inquiry needs vector. Therefore, the registered needs vector related to the first row is generally close to the inquiry needs vector of "I want your help in developing a quiet vacuum cleaner" and shows a high degree of similarity. In particular, the characteristics of the word vector ``development'' and the word vector ``cooperation'' that are not found in the need content vector of ``I want to increase the application fields of silent motors'' are supplemented by the needs category vector, making it effective. sexuality is increasing.
図11は、サーバ100の機能ブロック図である。
サーバ100の各構成要素は、CPU(Central Processing Unit)および各種コプロセッサなどの演算器、メモリやストレージといった記憶装置、それらを連結する有線または無線の通信線を含むハードウェアと、記憶装置に格納され、演算器に処理命令を供給するソフトウェアによって実現される。コンピュータプログラムは、デバイスドライバ、オペレーティングシステム、それらの上位層に位置する各種アプリケーションプログラム、また、これらのプログラムに共通機能を提供するライブラリによって構成されてもよい。図示した各ブロックは、ハードウェア単位の構成ではなく、機能単位のブロックを示している。 FIG. 11 is a functional block diagram of the
Each component of the
サーバ100は、データ格納部110、データ処理部150および通信部190を含む。通信部190は、ネットワークを介した通信処理を担当する。データ格納部110は各種データを格納する。データ処理部150は、通信部190により取得されたデータおよびデータ格納部110に格納されているデータに基づいて各種処理を実行する。データ処理部150は、通信部190およびデータ格納部110のインタフェースとしても機能する。
通信部190は、データを送信する送信部180とデータを受信する受信部170を含む。
送信部180は、各種画面データを送信する画面データ送信部182を含む。受信部170は、登録ニーズデータを受信する登録ニーズデータ受信部172および照会ニーズデータを受信する照会ニーズデータ受信部174を含む。 The
The
データ処理部150は、モデル生成部152、登録ニーズベクトル算出部154、画面データ生成部160および探索部162を含む。
モデル生成部152は、分散表現モデル生成処理を実行する。登録ニーズベクトル算出部154は、登録ニーズベクトルを算出する。画面データ生成部160は、各種画面データを生成する。探索部162は、照会ニーズに適合する登録ニーズの探索を行う。 The
The
データ格納部110は、参考企業データベース120、分散表現モデル格納部130およびニーズデータベース140を含む。参考企業データベース120は、図2に示した参考企業テーブルを格納する。分散表現モデル格納部130は、図3に示した単語テーブルを格納する。ニーズデータベース140は、登録ニーズテーブル格納部142、ニーズ区分テーブル格納部144、ニーズ区分ベクトル記憶部146および登録ニーズベクトル記憶部148を有する。登録ニーズテーブル格納部142は、登録ニーズテーブル(図5参照)を格納する。ニーズ区分テーブル格納部144は、ニーズ区分テーブル(図6参照)を格納する。ニーズ区分ベクトル記憶部146については、図7に関連して上述した。登録ニーズベクトル記憶部148については、図8に関連して上述した。 The
図12は、分散表現モデル生成処理の過程を示すフローチャート図である。
モデル生成部152は、参考企業テーブル(図2)からコーパスを生成する(S10)。コーパスとは、自然言語の文章を構造化した大規模データである。コーパスは、データ格納部110に保持される。具体的には、モデル生成部152は、各企業の事業内容から抽出される文ごとに、形態素解析を行って分かち書き形式に変換する。分かち書きとは、単語の間を余白で空けて区切る文字列である。分かち書き形式のデータが、コーパスに含められる。 FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing the process of distributed representation model generation processing.
The
モデル生成部152は、コーパスを用いて単語ベクトルを生成する(S12)。具体的には、モデル生成部152は、たとえばWord2vecの学習処理によって、コーパスに含まれる各単語に関する単語ベクトルを求める。生成された単語ベクトルは、分散表現モデル格納部130に単語テーブル(図3)の形式で格納される。 The
図13は、登録ニーズ追加処理の過程を示すフローチャート図である。
登録ニーズデータ受信部172は、ユーザ端末200から登録ニーズデータを受信すると(S20)、登録ニーズテーブルを更新する(S22)。具体的には、登録ニーズデータ受信部172は、登録ニーズテーブルに新たなレコードを設けて、登録ニーズデータに含まれる登録企業名、登録ニーズ内容およびニーズ区分IDをそのレコードに設定する。 FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing the process of adding registered needs.
When the registered needs data receiving unit 172 receives the registered needs data from the user terminal 200 (S20), it updates the registered needs table (S22). Specifically, the registered needs data receiving unit 172 creates a new record in the registered needs table, and sets the registered company name, registered needs content, and need classification ID included in the registered needs data in the record.
登録ニーズベクトル算出部154は、登録ニーズ内容に含まれる各文の文ベクトルを算出する(S24)。文に含まれる単語の単語ベクトルから、文ベクトルが生成される。生成方法は、例えば平均化である。つまり、文ベクトルは、単語ベクトルの平均ベクトルである。 The registered needs
登録ニーズベクトル算出部154は、登録ニーズ内容に含まれる各文の文ベクトルの平均を算出して、算出された平均ベクトルをニーズ内容ベクトルとする(S26)。登録ニーズベクトル算出部154は、平均化以外の方法で、文ベクトルからニーズ内容ベクトルを生成してもよい。 The registered needs
登録ニーズベクトル算出部154は、上述のとおり、ニーズ内容ベクトルとニーズ区分ベクトルの荷重平均によって、登録ニーズベクトルを算出する(S28)。登録ニーズベクトルは、登録ニーズIDに対応づけて登録ニーズベクトル記憶部148に記憶される。加重平均に代えて、単純平均を用いてもよい。 As described above, the registered needs
図14は、ニーズマッチング処理の過程を示すフローチャート図である。
照会ニーズデータ受信部174がサーバ100から照会ニーズデータを受信すると(S30)、探索部162は、照会ニーズベクトルを算出する(S32)。具体的には、照会ニーズ内容が句、節や文である場合には、形態素解析によって単語を抽出する。照会ニーズ内容が、複数の単語がスペースや読点などで区切られている場合には、それらの単語を用いる。照会ニーズ内容に含まれる単語の単語ベクトルから、照会ニーズベクトルが生成される。生成方法は、例えば平均化である。つまり、照会ニーズベクトルは、単語ベクトルの平均ベクトルである。 FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing the process of needs matching processing.
When the inquiry needs data receiving unit 174 receives inquiry needs data from the server 100 (S30), the searching
探索部162は、照会ニーズベクトルと類似する登録ニーズベクトルを探索する(S34)。具体的には、探索部162は、登録ニーズベクトル記憶部148に記憶されている各登録ニーズベクトルと照会ニーズベクトルとの類似度を算出する。そして、探索部162は、基準値以上の類似度を有する登録ニーズベクトルに対応する登録ニーズ内容、ニーズ区分IDおよび登録企業名を抽出する。 The
画面データ生成部160は、抽出された登録ニーズ内容、ニーズ区分IDおよび登録企業名を一覧表示するマッチング結果画面を生成し、画面データ送信部182は、生成されたマッチング結果画面のデータをユーザ端末200へ送信する(S36)。このとき、類似度の降順に登録ニーズの行がソートされてもよい。また、各登録ニーズに関する類似度が表示されてもよい。 The screen
本実施形態では、登録ニーズベクトル算出部154が、各登録ニーズの内容文に含まれる各単語を表す単語ベクトルからニーズ内容ベクトルを算出し、さらにニーズ区分のタイトルに含まれる各単語を表す単語ベクトルからニーズ区分ベクトルを算出し、そして、ニーズ内容ベクトルの重みとニーズ区分ベクトルの重みの比を一定とした加重平均によって、各登録ニーズベクトルを算出する例を示した。 In this embodiment, the registered needs
[変形例]
変形例として、登録ニーズベクトル算出部154は、各登録ニーズの内容文に含まれる各単語を表す単語ベクトルの第1重みを一定とし、ニーズ区分のタイトルに含まれる各単語を表す単語ベクトルの第2重みを一定とした加重平均によって、各登録ニーズベクトルを算出してもよい。[Modified example]
As a modified example, the registered needs
たとえば、第1重みが7で、第2重みが3であるとすれば、図5の登録ニーズID:N0300の登録ニーズベクトルにおける各要素の値は、「静音」の単語ベクトルの値、「モータ」の単語ベクトルの値、「応用」の単語ベクトルの値、「分野」の単語ベクトルの値、「増やす」の単語ベクトルの値および「したい」の単語ベクトルの値にそれぞれ7を乗じ、「研究」の単語ベクトルの値、「開発」の単語ベクトルの値および「協力」の単語ベクトルの値にそれぞれ3を乗じて、それらの合計を51(=7×6+3×3)で割ることによって算出される。加重平均に代えて、単純平均を用いてもよい。 For example, if the first weight is 7 and the second weight is 3, the values of each element in the registered needs vector of registered needs ID: N0300 in FIG. ”, the value of the word vector of “application”, the value of the word vector of “field”, the value of the word vector of “increase”, and the value of the word vector of “desire” are each multiplied by 7, and the value of the word vector of “research” is multiplied by 7. It is calculated by multiplying the value of the word vector ``, the value of the word vector ``development,'' and the value of the word vector ``cooperation'' by 3, respectively, and dividing the sum by 51 (=7 x 6 + 3 x 3). Ru. A simple average may be used instead of a weighted average.
また、照会ニーズの入力によってニーズマッチングを行った後に、再びその照会ニーズによるニーズマッチングを行うようにしてもよい。そのようにすれば、後に追加された登録ニーズとの適合性もチェックできる。たとえば、新しい登録ニーズが追加された時点で、それまでに受け付けた照合ニーズとの類似を検証してもよいし、周期的に過去の照合ニーズとの類似を検証してもよい。 Further, after performing needs matching by inputting inquiry needs, needs matching may be performed again based on the inquiry needs. In this way, compatibility with registration needs added later can also be checked. For example, when a new registration need is added, it may be verified that it is similar to verification needs that have been accepted up to that point, or it may be periodically verified that it is similar to past verification needs.
そのため、登録ニーズデータ受信部172は、新たな登録ニーズに関する内容文とニーズ区分とを受信すると、受信した登録ニーズをニーズデータベース140に追加する。登録ニーズベクトル154は、追加された登録ニーズを表す登録ニーズベクトルを算出する。探索部162は、追加された登録ニーズの登録ニーズベクトルが、過去に受信した照会ニーズベクトルと近似するか否かを判定する。追加された登録ニーズの登録ニーズベクトルが照会ニーズベクトルと近似する場合に、通知部(不図示)は、追加された登録ニーズの情報を、照会ニーズベクトルを送ったユーザのメールアドレス宛のメールにて送信する。あるいは、過去の照会ニーズに適合する登録ニーズが追加された旨だけをメールで送信してもよい。また、このメールを受け取ったユーザが、ユーザ端末200bからログインして、追加された登録ニーズの情報を確認できるようにしてもよい。 Therefore, when the registration needs data receiving unit 172 receives the content text and the need classification regarding a new registration need, it adds the received registration need to the
ベクトルの平均化において、例えばTF-IDF(Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency)のような評価指標を用いて、元となる単語ベクトル毎、句ベクトル毎あるいは文ベクトル毎などに重みづけを行ってもよい。 In vector averaging, weighting may be performed for each source word vector, phrase vector, or sentence vector using an evaluation index such as TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency). .
また、照会ニーズ受付画面(図9)においてニーズ区分を受け付け、照会ニーズデータにニーズ区分IDを含めてもよい。探索部162は、受け付けたニーズ区分に合致する登録ニーズを登録ニーズテーブル(図5)から抽出し、抽出された登録ニーズについて、反対ニーズのマッチングを行うようにしてもよい。たとえば、「〇〇を買いたい」の反対ニーズは、「〇〇を売りたい」である。つまり、探索部162は、照会ニーズ内容に含まれる「買いたい」を反対語の「売りたい」に置き換えてから、その照会ニーズ内容によって照会ニーズベクトルを算出し、その照会ニーズベクトルと類似する登録ニーズベクトルの探索を行うようにする。 Further, the needs category may be accepted on the inquiry needs reception screen (FIG. 9), and the needs category ID may be included in the inquiry needs data. The
実施形態では、登録ニーズベクトルおよび照会ニーズベクトルを算術平均によって求める例を示したが、他の方法で算出してもよい。たとえば、マッチングに対するフィードバックとして評価や実績を受け付けて、その評価や実績を教師データとする機械学習によって、最終的な登録ニーズベクトルまたは/および最終的な照会ニーズベクトルを算出するようにしてもよい。たとえば、相手と連絡が取れた場合や商談が成立した場合に、評価値を高くするようにしてもよい。相手と連絡が取れた回数や商談が成立した回数を、実績値としてもよい。 In the embodiment, an example has been shown in which the registered needs vector and the inquiry needs vector are calculated by arithmetic averaging, but they may be calculated using other methods. For example, the final registration needs vector and/or final inquiry needs vector may be calculated by accepting evaluations and achievements as feedback for matching, and by machine learning using the evaluations and achievements as training data. For example, the evaluation value may be increased when a contact is made with the other party or when a business negotiation is concluded. The actual value may be the number of times the contact was made with the other party or the number of business negotiations concluded.
照会ニーズ入力の際に、ニーズ区分を指定できるようにしてもよい。また、ニーズ区分に、予め反対ニーズを対応付けて定義しておいてもよい。ニーズマッチングの際には、照会ニーズ内容と、照会ニーズ区分の反対ニーズとに基づいて、照会ニーズベクトルを生成してもよい。そして、その照会ニーズベクトルを用いて登録ニーズベクトルとの類似度を算出するようにしてもよい。 It may also be possible to specify a needs category when inputting inquiry needs. Further, opposite needs may be defined in advance in association with the need categories. During needs matching, an inquiry needs vector may be generated based on the contents of the inquiry needs and the opposite needs of the inquiry needs classification. Then, the query needs vector may be used to calculate the degree of similarity with the registered needs vector.
なお、本発明は上記実施形態や変形例に限定されるものではなく、要旨を逸脱しない範囲で構成要素を変形して具体化することができる。上記実施形態や変形例に開示されている複数の構成要素を適宜組み合わせることにより種々の発明を形成してもよい。また、上記実施形態や変形例に示される全構成要素からいくつかの構成要素を削除してもよい。 It should be noted that the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments and modified examples, and can be embodied by modifying the constituent elements without departing from the scope of the invention. Various inventions may be formed by appropriately combining a plurality of components disclosed in the above embodiments and modified examples. Furthermore, some components may be deleted from all the components shown in the above embodiments and modified examples.
100 サーバ、110 データ格納部、120 参考企業データベース、130 分散表現モデル格納部、140 ニーズデータベース、142 登録ニーズテーブル格納部、144 ニーズ区分テーブル格納部、146 ニーズ区分ベクトル記憶部、148 登録ニーズベクトル記憶部、150 データ処理部、152 モデル生成部、154 登録ニーズベクトル算出部、160 画面データ生成部、162 探索部、170 受信部、172 登録ニーズデータ受信部、174 照会ニーズデータ受信部、180 送信部、182 画面データ送信部、190 通信部、200 ユーザ端末、300 表示領域、302 入力領域、304 選択領域、306 登録ボタン、308 取消ボタン、310 入力領域、312 実行ボタン、314 取消ボタン、320 表示領域、322 表示領域、324 表示領域、326 詳細ボタン100 server, 110 data storage unit, 120 reference company database, 130 distributed representation model storage unit, 140 needs database, 142 registered needs table storage unit, 144 needs classification table storage unit, 146 needs classification vector storage unit, 148 registered needs vector storage unit, 150 data processing unit, 152 model generation unit, 154 registered needs vector calculation unit, 160 screen data generation unit, 162 search unit, 170 reception unit, 172 registered needs data reception unit, 174 inquiry needs data reception unit, 180 transmission unit , 182 screen data transmission section, 190 communication section, 200 user terminal, 300 display area, 302 input area, 304 selection area, 306 registration button, 308 cancel button, 310 input area, 312 execution button, 314 cancel button, 320 display area , 322 display area, 324 display area, 326 details button
Claims (5)
Translated fromJapanese照会ニーズの内容文を受け付ける第1受付部と、
前記照会ニーズの前記内容文に含まれる各単語を表すベクトルに基づいて、前記照会ニーズを表す照会ニーズベクトルを算出し、算出された当該照会ニーズベクトルと類似する登録ニーズベクトルを探索する探索部と、
探索された前記登録ニーズベクトルで表される登録ニーズの少なくとも前記内容文を出力する出力部と、を備えることを特徴とするニーズマッチング装置。 Regarding a database that manages content sentences of multiple registered needs by linking them to need categories, a vector representing each word included in the content sentence of each registered need, and a vector representing each word included in the title of the need category. a calculation unit that calculates a registration needs vector representing the registration needs based on the registration needs;
A first reception department that accepts the content of inquiry needs,
a search unit that calculates an inquiry needs vector representing the inquiry need based on a vector representing each word included in the content sentence of the inquiry need, and searches for a registered needs vector similar to the calculated inquiry needs vector; ,
A needs matching device comprising: an output unit that outputs at least the content sentence of the registered need represented by the searched registered needs vector.
前記算出部は、追加された前記登録ニーズを表す登録ニーズベクトルを算出し、
前記探索部は、追加された前記登録ニーズの前記登録ニーズベクトルが、前記照会ニーズベクトルと近似するか否かを判定し、
前記出力部は、追加された前記登録ニーズの前記登録ニーズベクトルが前記照会ニーズベクトルと近似する場合に、追加された前記登録ニーズの少なくとも前記内容文を出力することを特徴とする請求項1に記載のニーズマッチング装置。 a second reception unit that receives a content statement and a needs category regarding new registration needs and adds the received registration needs to the database;
The calculation unit calculates a registered needs vector representing the added registered needs,
The search unit determines whether the registered needs vector of the added registered need approximates the inquiry needs vector,
2. The output unit outputs at least the content sentence of the added registered need when the registered needs vector of the added registered need approximates the inquiry needs vector. The needs matching device described.
照会ニーズの内容文を受け付ける機能と、
前記照会ニーズの前記内容文に含まれる各単語を表すベクトルに基づいて、前記照会ニーズを表す照会ニーズベクトルを算出し、算出された当該照会ニーズベクトルと類似する登録ニーズベクトルを探索する機能と、
探索された前記登録ニーズベクトルで表される登録ニーズの少なくとも前記内容文を出力する機能と、を情報処理装置に発揮させることを特徴とするプログラム。 Regarding a database that manages content sentences of multiple registered needs by linking them to need categories, a vector representing each word included in the content sentence of each registered need, and a vector representing each word included in the title of the need category. a function of calculating a registration needs vector representing the registration needs based on the registration needs;
A function that accepts the content of inquiry needs,
A function of calculating an inquiry needs vector representing the inquiry need based on a vector representing each word included in the content sentence of the inquiry need, and searching for a registered needs vector similar to the calculated inquiry needs vector;
A program that causes an information processing device to perform a function of outputting at least the content sentence of the registered need represented by the searched registered needs vector.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020055392AJP7438808B2 (en) | 2020-03-26 | 2020-03-26 | Needs matching equipment and programs |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020055392AJP7438808B2 (en) | 2020-03-26 | 2020-03-26 | Needs matching equipment and programs |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021157363A JP2021157363A (en) | 2021-10-07 |
| JP7438808B2true JP7438808B2 (en) | 2024-02-27 |
Family
ID=77918390
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020055392AActiveJP7438808B2 (en) | 2020-03-26 | 2020-03-26 | Needs matching equipment and programs |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7438808B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023074457A1 (en)* | 2021-10-26 | 2023-05-04 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Matching system, matching method, program, and trained model |
| CN118505237A (en)* | 2024-05-27 | 2024-08-16 | 江苏思行达信息技术股份有限公司 | Intelligent customer service system of electric power business hall based on domestic large model and use method |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002251412A (en) | 2001-02-22 | 2002-09-06 | Canon Inc | Document search apparatus and method, and storage medium |
| JP2014167722A (en) | 2013-02-28 | 2014-09-11 | Nihon Unisys Ltd | Merchandise information providing system and program for providing merchandise information |
| JP2015121878A (en) | 2013-12-20 | 2015-07-02 | 株式会社 Icsコンベンションデザイン | Interview reservation support device and interview reservation support method |
| JP2018142131A (en) | 2017-02-27 | 2018-09-13 | 日本放送協会 | Information determination model learning device, information determination device and program therefor |
| CN110909247A (en) | 2019-12-03 | 2020-03-24 | 掌阅科技股份有限公司 | Text information pushing method, electronic equipment and computer storage medium |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH1031677A (en)* | 1996-07-15 | 1998-02-03 | Sharp Corp | Document search device |
| JPH11134359A (en)* | 1997-10-31 | 1999-05-21 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Document similarity calculation method, document similarity calculation device, and recording medium storing document similarity calculation program |
- 2020
- 2020-03-26JPJP2020055392Apatent/JP7438808B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002251412A (en) | 2001-02-22 | 2002-09-06 | Canon Inc | Document search apparatus and method, and storage medium |
| JP2014167722A (en) | 2013-02-28 | 2014-09-11 | Nihon Unisys Ltd | Merchandise information providing system and program for providing merchandise information |
| JP2015121878A (en) | 2013-12-20 | 2015-07-02 | 株式会社 Icsコンベンションデザイン | Interview reservation support device and interview reservation support method |
| JP2018142131A (en) | 2017-02-27 | 2018-09-13 | 日本放送協会 | Information determination model learning device, information determination device and program therefor |
| CN110909247A (en) | 2019-12-03 | 2020-03-24 | 掌阅科技股份有限公司 | Text information pushing method, electronic equipment and computer storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021157363A (en) | 2021-10-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US12197486B2 (en) | Automatic labeling of text data | |
| US9576313B2 (en) | Recommendation systems and methods using interest correlation | |
| US20240370484A1 (en) | Automatic labeling of text data | |
| US20080294622A1 (en) | Ontology based recommendation systems and methods | |
| US20110055186A1 (en) | Method for personalizing information retrieval in a communication network | |
| US20050283473A1 (en) | Apparatus, method and system of artificial intelligence for data searching applications | |
| KR20150016973A (en) | Generating search results | |
| CN114840671A (en) | Dialogue generation method, model training method, device, equipment and medium | |
| CN102222081A (en) | Applying a model of a persona to search results | |
| US12259896B1 (en) | Search and semantic similarity domain determination | |
| TWI851259B (en) | A system of semantic analysis-based trademark class recommendation and the method thereof | |
| CN113821588A (en) | Text processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113868387A (en) | Word2vec medical similar problem retrieval method based on improved tf-idf weighting | |
| JP7438808B2 (en) | Needs matching equipment and programs | |
| JP4743766B2 (en) | Impression determination system, advertisement article generation system, impression determination method, advertisement article generation method, impression determination program, and advertisement article generation program | |
| CN117609612A (en) | Resource recommendation methods, devices, storage media and electronic equipment | |
| TW201933269A (en) | Intellectual property system, intellectual property support method and intellectual property support program | |
| CN101072194B (en) | Method and system for searching information utilizing instant messaging system | |
| JP6537211B1 (en) | Search device and program | |
| CN114840760A (en) | Article recommendation method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| Ding et al. | RAG-VR: Leveraging Retrieval-Augmented Generation for 3D Question Answering in VR Environments | |
| TWM633789U (en) | Matching system | |
| JP2002215642A (en) | Feedback type internet retrieval method, and system and program recording medium for carrying out the method | |
| JP7382590B1 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method and program | |
| CN115422485A (en) | Information sending method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20230302 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20240201 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20240213 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20240214 | |
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration | Ref document number:7438808 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |