JP7123203B2 - Autonomous driving propriety determination method, automatic driving propriety determination device, and automatic driving propriety determination system - Google Patents
Autonomous driving propriety determination method, automatic driving propriety determination device, and automatic driving propriety determination systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7123203B2 JP7123203B2JP2021015160AJP2021015160AJP7123203B2JP 7123203 B2JP7123203 B2JP 7123203B2JP 2021015160 AJP2021015160 AJP 2021015160AJP 2021015160 AJP2021015160 AJP 2021015160AJP 7123203 B2JP7123203 B2JP 7123203B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- automatic driving
- map data
- identification information
- road
- area
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Instructional Devices (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、自動運転の技術に関する。 The present invention relates to technology for automatic driving.
従来から、車両の走行を自動制御する所謂自動運転の技術が知られている。自動運転を実行する場合には、例えば、カメラなどの外界センサを用いて、白線や前方車両などの自車両周辺の情報を認識することや、加速度センサやジャイロ等の内界センサを用いて車両の姿勢や状態を把握する必要がある。特許文献1には、車両に設置されたカメラの画像等に基づいて走行中の車線や静止物標を認識する技術が開示されている。また、特許文献2には、自動運転に関する技術が開示されている。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, so-called automatic driving technology for automatically controlling the running of a vehicle has been known. When performing automatic driving, for example, using an external sensor such as a camera, recognizing information around the own vehicle such as white lines and vehicles ahead, and using an internal sensor such as an acceleration sensor and a gyro to recognize the vehicle It is necessary to grasp the posture and state of
一般的に、自動運転の実行の可否は、参照する地図データの精度にも依存する。例えば、低精度の地図データを参照する場合には、当該地図データよりも高精度の地図データを参照する場合と比べて、外界センサによる周辺環境の認識精度をより高精度にする必要があると考えられる。このように、自動運転の実行可否を正確に判定するには、参照する地図データの精度を勘案する必要がある。 In general, whether or not automatic driving can be executed also depends on the accuracy of map data to be referred to. For example, when referring to low-precision map data, it is necessary to increase the accuracy of recognition of the surrounding environment by the external sensor, compared to when referring to map data with higher precision than the map data. Conceivable. Thus, in order to accurately determine whether automatic driving can be executed, it is necessary to consider the accuracy of the map data to be referred to.
本発明は、例えば、上記のような課題を解決するためになされたものであり、自動運転の実行可否を好適に判定することが可能な地図データ構造、及び当該地図データ構造の地図データを用いた送信装置及び地図表示装置を提供することを主な目的とする。 The present invention has been made, for example, to solve the problems described above. A main object of the present invention is to provide a transmission device and a map display device.
請求項1に記載の発明は、
制御部及び記憶部を備える運転支援装置に用いられ、前記記憶部に記憶される地図データのデータ構造である地図データ構造であって、
前記地図データのエリアごと、又は前記地図データの道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法の識別情報が含まれ、
前記識別情報は、前記制御部が前記地図データに基づき移動体の自動運転を行う場合に、前記移動体が移動する対象の道路又はエリアにおいて前記自動運転を実行するために必要なセンサの認識を、前記識別情報ごとに前記自動運転に必要なセンサの情報を記憶した自動運転判定情報に基づき行うことで、前記自動運転の可否判定を行う前記制御部が前記認識を行う処理に用いられる、地図データ構造
であることを特徴とする。The invention according to
A map data structure that is used in a driving support device that includes a control unit and a storage unit and is a data structure of map data stored in the storage unit,
identification information of a method of generating data related to the area or road is included for each area of the map data or each road of the map data;
When the control unit automatically drives a mobile object based on the map data, the identification information is used for recognizing a sensor necessary for executing the automatic operation on a target road or area on which the mobile object moves. , by performing based on the automatic driving determination information that stores the information of the sensor necessary for the automatic driving for each of the identification information, the control unit that determines whether the automatic driving is possible is used for the recognition process, map It is characterized by being a data structure.
請求項4に記載の発明は、
請求項1~3のいずれか一項に記載の地図データ構造を有する地図データを記憶する記憶部と、
前記地図データを、車両または端末に送信する送信部と、
を備える送信装置
であることを特徴とする。The invention according to claim 4,
a storage unit for storing map data having the map data structure according to any one of
a transmission unit that transmits the map data to a vehicle or a terminal;
characterized by being a transmitting device comprising:
請求項5に記載の発明は、
請求項1~3のいずれか一項に記載の地図データ構造を有する地図データを取得する取得部と、
前記地図データに基づき地図を表示する表示部と、を備え、
前記表示部は、前記地図データに含まれる識別情報に基づき、前記地図中のエリア又は道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法を識別する表示を行う地図表示装置
であることを特徴とする。The invention according to claim 5,
an acquisition unit for acquiring map data having the map data structure according to any one of
a display unit that displays a map based on the map data,
The display unit is a map display device that displays, for each area or road in the map, a method of generating data relating to the area or road based on identification information included in the map data. do.
本発明の好適な実施形態によれば、地図データ構造は、地図を示す地図データ構造であって、前記地図のエリアごと、又は前記地図の道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法の識別情報が含まれる。 According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the map data structure is a map data structure showing a map, wherein for each area of said map or each road of said map, a method for generating data relating to said area or road is described. Contains identifying information.
上記地図データ構造には、地図のエリアごと、又は地図の道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法の識別情報が含まれる。一般に、生成される地図データの精度は、当該地図データの生成方法に依存する。よって、この態様によれば、上記地図データ構造を有する地図データを参照することで、対象とする道路又はエリアに関する地図データの精度を好適に推定して自動運転の実行可否の判定などに用いることが可能となる。 The map data structure includes, for each area of the map or each road of the map, identification information of the method of generating data regarding the area or road. In general, the accuracy of generated map data depends on the method of generating the map data. Therefore, according to this aspect, by referring to the map data having the above map data structure, the accuracy of the map data regarding the target road or area can be estimated appropriately and used for determining whether automatic driving can be executed. becomes possible.
上記地図データ構造の一態様では、前記識別情報は、少なくとも、前記エリア又は道路を通行した際の外界センサの出力に基づき前記データが生成されたか、又は/及び、航空写真に基づき前記データが生成されたかを識別する情報である。一般に、道路を実際に走行した際の外界センサの出力に基づき生成された地図データは、航空写真により生成された地図データよりも精度が高く、かつ、高さ方向の情報を含む立体的なデータとなることが推定される。よって、この態様では、データの生成方法の識別情報を参照することで、地図データの精度等を好適に推定して自動運転の実行可否の判定などに用いることが可能となる。 In one aspect of the map data structure, the identification information is at least generated based on the output of an external sensor when passing through the area or road, or/and the data is generated based on an aerial photograph. This is information that identifies whether or not the In general, map data generated based on the output of external sensors when actually driving on a road is more accurate than map data generated from aerial photographs, and is three-dimensional data that includes information in the height direction. It is estimated that Therefore, in this aspect, by referring to the identification information of the data generation method, it is possible to suitably estimate the accuracy of the map data and use it to determine whether automatic driving can be executed.
上記地図データ構造の一態様では、前記識別情報は、前記データが前記外界センサの出力に基づき生成されたことを示す場合に、前記外界センサの種別又は性能を示す情報をさらに含む。一般に、地図データを生成する際に用いる外界センサの種別や性能によって、生成される地図データの精度等は異なる。よって、この態様では、データの生成方法の識別情報により、当該データの生成に用いた外界センサの種別や性能を好適に識別可能とし、自動運転の実行可否の判定等をより正確に実行させることが可能となる。 In one aspect of the map data structure, the identification information further includes information indicating the type or performance of the external sensor when the data indicates that the data is generated based on the output of the external sensor. In general, the accuracy of generated map data differs depending on the type and performance of an external sensor used when generating map data. Therefore, in this aspect, the type and performance of the external sensor used to generate the data can be preferably identified by the identification information of the data generation method, and the determination of whether automatic driving can be executed or the like can be performed more accurately. becomes possible.
本発明の他の好適な実施形態によれば、送信装置は、上記いずれか記載の地図データ構造を有する地図データを記憶する記憶部と、前記地図データを、車両または端末に送信する送信部と、を備える。ここで、「端末」は、送信装置から地図データを受信可能な装置であって、車両内に存在する車載機であってもよく、車載機が読取り可能な記憶媒体に地図データを書き込み可能な家庭用のパーソナルコンピュータであってもよい。この態様によれば、送信装置は、データの生成方法の識別情報を含む地図データを好適に車両や端末に配信し、当該地図データを自動運転等に活用させることができる。 According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, a transmission device includes a storage unit that stores map data having the map data structure described above, and a transmission unit that transmits the map data to a vehicle or a terminal. , provided. Here, the "terminal" is a device capable of receiving map data from a transmission device, and may be an on-vehicle device present in a vehicle, which can write map data to a storage medium readable by the on-vehicle device. It may be a personal computer for home use. According to this aspect, the transmitting device can suitably distribute the map data including the identification information of the data generation method to the vehicle or the terminal, and utilize the map data for automatic driving or the like.
本発明の他の好適な実施形態によれば、地図表示装置は、上記いずれか記載の地図データ構造を有する地図データを取得する取得部と、前記地図データに基づき地図を表示する表示部と、を備え、前記表示部は、前記地図データに含まれる識別情報に基づき、前記地図中のエリア又は道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法を識別する表示を行う。この態様によれば、地図表示装置は、データの生成方法の識別情報を含む地図データを参照し、データの生成方法を識別可能に表示された地図を好適に表示することができる。 According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, a map display device includes an acquisition unit that acquires map data having the map data structure described above; a display unit that displays a map based on the map data; The display unit displays, for each area or road in the map, a method of generating data relating to the area or road based on the identification information included in the map data. According to this aspect, the map display device can refer to the map data including the identification information of the data generation method, and preferably display the map in which the data generation method is identifiable.
上記地図表示装置の一態様では、地図表示装置は、外界センサと、自動運転の可否を判定する判定部と、をさらに備え、前記記憶部は、エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法の識別情報ごとに、自動運転に必要な外界センサの情報を記憶した自動運転判定情報を記憶し、前記判定部は、前記自動運転判定情報に基づき、対象のエリア又は道路に対する自動運転の可否を判定する。この態様により、地図表示装置は、対象のエリア又は道路に対する自動運転の可否を好適に判定することができる。 In one aspect of the map display device, the map display device further includes an external sensor and a determination unit that determines whether or not automatic driving is possible. , stores automatic driving judgment information that stores information of the external sensor necessary for automatic driving, and the judgment unit judges whether automatic driving is possible for the target area or road based on the automatic driving judgment information. With this aspect, the map display device can suitably determine whether automatic driving is possible for the target area or road.
以下、図面を参照して本発明の好適な実施例について説明する。 Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
[自動運転システムの概要]
図1は、本実施例に係る自動運転システムの概略構成である。自動運転システムは、地図データの配信を行うサーバ装置1と、車両と共に移動する運転支援装置2とを備える。[Overview of automated driving system]
FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration of an automatic driving system according to this embodiment. The automatic driving system includes a
サーバ装置1は、配信地図DB10を記憶し、運転支援装置2からの要求に応じて、地図データ「D1」を配信地図DB10から抽出して送信する。地図データD1は、運転支援装置2の自車位置周辺の部分的な地図データであってもよく、運転支援装置2の地図DB20を最新情報に更新するための差分情報であってもよい。ここで、配信地図DB10には、道路ごと又は所定の規則により区切られたエリアごとに、当該道路又はエリアに対応するデータの生成方法に関する識別情報(「データ生成識別情報IG」とも呼ぶ。)が含まれている。サーバ装置1は、本発明における「送信装置」の一例であり、データ生成識別情報IGは、本発明における「識別情報」の一例である。 The
運転支援装置2は、据置型の運転支援装置又はスマートフォンなどの携帯端末であって、データ生成識別情報IGを含んだ地図データD1をサーバ装置1から受信して地図DB20に記憶する。そして、運転支援装置2は、地図DB20を参照し、ユーザが設定した目的地への経路探索や、設定された経路に基づく案内等を行う。また、運転支援装置2は、カメラやライダなどの外界センサの出力に基づき、一部又は全部の運転操作を半自動又は全自動で行う自動運転を行う。この場合、運転支援装置2は、地図DB20に記憶されたデータ生成識別情報IGを参照し、運転支援装置2が備える外界センサにより自動運転が可能か否かの判定を行う。自動運転の実行可否判定の詳細については後述する。運転支援装置2は、本発明における「地図表示装置」の一例である。 The
[サーバ装置の構成]
図2(A)は、サーバ装置1の概略構成を示す。図2(A)に示すように、サーバ装置1は、通信部11と、記憶部12と、制御部15とを有する。通信部11、記憶部12、及び制御部15は、バスラインを介して相互に接続されている。[Configuration of server device]
FIG. 2A shows a schematic configuration of the
通信部11は、制御部15の制御に基づき、運転支援装置2と各種データの通信を行う。本実施例では、通信部11は、運転支援装置2から地図データD1の取得要求を受信した場合に、制御部15が配信地図DB10から抽出した地図データD1を運転支援装置2へ送信する。通信部11は、本発明における「送信部」の一例である。 The
記憶部12は、サーバ装置1の動作を制御するためのプログラムを保存したり、サーバ装置1の動作に必要な情報を保持したりする。また、記憶部12は、データ生成識別情報IGを含んだ配信地図DB10を記憶する。 The
制御部15は、図示しないCPU、ROM及びRAMなどを備え、サーバ装置1内の各構成要素に対して種々の制御を行う。本実施例では、制御部15は、運転支援装置2からの地図データD1の取得要求を通信部11が受信した場合に、配信地図DB10から地図データD1を抽出し、通信部11により運転支援装置2へ送信する。この場合、例えば、地図データD1の取得要求には、運転支援装置2の自車位置情報又は/及び地図DB20の最新の更新日時情報などが含まれ、制御部15は、これらの情報に基づき、配信地図DB10から配信すべき地図データD1を抽出する。 The
[運転支援装置の構成]
図2(B)は、運転支援装置2の機能的構成を表すブロック図を示す。図2(B)に示すように、運転支援装置2は、主に、通信部21と、記憶部22と、センサ部23と、入力部24と、制御部25と、出力部26とを有する。通信部21、記憶部22、センサ部23、入力部24、制御部25及び出力部26は、バスラインを介して相互に接続されている。[Configuration of Driving Support Device]
FIG. 2B shows a block diagram showing the functional configuration of the driving
通信部21は、制御部25の制御に基づき、サーバ装置1から地図データD1を取得する。また、通信部21は、車両を制御するための信号を車両に送信したり、車両の状態に関する信号を車両から受信したりする。 The
記憶部22は、制御部25が実行するプログラムや、制御部25が所定の処理を実行する為に必要な情報を記憶する。本実施例では、記憶部22は、データ生成識別情報IGを含む地図DB20と、自動運転判定テーブルTJとを記憶する。自動運転判定テーブルTJは、道路ごと又はエリアごとに関連付けられたデータ生成識別情報IGから当該道路又はエリアにおける自動運転の実行可否を判定するためのテーブルである。自動運転判定テーブルTJの具体例については後述する。また、記憶部22は、後述する外界センサ31の種別又は性能に関する情報を記憶してもよい。 The
センサ部23は、車両の周辺環境を認識するための1又は複数の外界センサ31と、GPS受信機32と、ジャイロセンサ33及び速度センサ34などの自立測位装置とを含む。外界センサ31は、例えば、カメラ(3Dカメラも含む)、ライダ(LIDAR:Laser Illuminated Detection and Ranging、Laser Imaging Detection and Ranging または LiDAR:Light Detection and Ranging)などが該当する。センサ部23は、生成した出力信号を、制御部25へ供給する。 The
入力部24は、ユーザが操作するためのボタン、タッチパネル、リモートコントローラ、音声入力装置等であり、経路探索のための目的地を指定する入力、自動運転のオン及びオフを指定する入力などを受け付け、生成した入力信号を制御部25へ供給する。 The
出力部26は、例えば、制御部25の制御に基づき出力を行うディスプレイやスピーカ等である。本実施例では、出力部26は、地図DB20に基づく現在位置周辺の地図を表示する場合に、制御部25の制御に基づき、道路ごと又はエリアごとの地図データの生成方法を明示した画面(「生成識別画面」とも呼ぶ。)の表示を行う。 The
制御部25は、プログラムを実行するCPUなどを含み、運転支援装置2の全体を制御する。例えば、制御部25は、通信部21が取得した地図データD1に基づき地図DB20を更新する。また、制御部25は、入力部24により入力された目的地までの経路探索を行い、自動運転や経路案内のための経路を設定する。また、制御部25は、自動運転の経路探索などにおいて、自動運転判定テーブルTJを参照し、特定の道路又はエリアが自動運転により走行可能であるか否かを判定する処理(「自動運転判定処理」とも呼ぶ。)を実行する。そして、制御部25は、自動運転が実行可能な経路が設定された場合に、センサ部23の出力信号及び地図DB20に基づき、設定された経路に即した自動運転を行う。また、制御部25は、入力部24により所定のユーザ入力を検知した場合に、地図DB20を参照し、生成識別画面を出力部26に表示させる。制御部25は、本発明における「取得部」、「表示部」及び「判定部」の一例である。 The
[データ構造]
図3は、配信地図DB10及び地図DB20の概略的なデータ構造の一例を示す。[data structure]
FIG. 3 shows an example of a schematic data structure of the
図3の例では、配信地図DB10及び地図DB20は、施設に関する施設情報と、道路に関する道路データとを含む。さらに、道路データは、各道路をリンクとノードで表した場合のリンクに関するデータであるリンクデータと、ノードに関するデータであるノードデータとを含む。そして、各リンクに対応するリンクデータには、対象となるリンクの始点及び終点等を示す座標データ及び車線に関する車線情報等と共に、データ生成識別情報IGが含まれている。なお、データ生成識別情報IGは、リンクごとに異なる値となってもよく、所定のエリアごとに異なる値となってもよい。後者の場合、道路データとは別に、各エリアに対応するデータ生成識別情報IGの情報が配信地図DB10及び地図DB20に含まれていてもよい。 In the example of FIG. 3, the
図4(A)は、自動運転判定テーブルTJとして記憶する情報を概略的に示したテーブルの一例である。図4(A)に示すテーブルは、「データ生成識別情報」の項目と、「自動運転に必要なセンサ」の項目とを有する。 FIG. 4A is an example of a table schematically showing information stored as the automatic driving determination table TJ. The table shown in FIG. 4A has an item of "data generation identification information" and an item of "sensors necessary for automatic driving".
ここで、「データ生成識別情報」の項目には、タイプX~タイプZの3つに分類されたデータ生成識別情報IGが登録されている。ここで、「タイプX」は、外界センサを搭載した車両が実際に道路上を走行したときの外界センサの出力に基づき配信地図DB10に登録するデータが生成された道路又はエリアを示す。「タイプY」は、配信地図DB10に登録するデータが航空写真により生成された道路又はエリアを示す。「タイプZ」は、外界センサ及び航空写真を併用して配信地図DB10に登録するデータが生成された道路又はエリアを示す。 Here, data generation identification information IG classified into three types of type X to type Z is registered in the item "data generation identification information". Here, "type X" indicates a road or area where data to be registered in the
また、「自動運転に必要なセンサ」の項目には、外界センサの識別情報(ここでは「A」~「D」)が登録されている。「自動運転に必要なセンサ」の項目に登録される外界センサの識別情報は、ライダやカメラなどの外界センサの種別を識別するための情報であってもよく、外界センサの種別と性能の両方を識別するための情報であってもよい。後者の場合、例えば、角度分解能が所定値以上のライダと角度分解能が所定値未満のライダとで別の識別情報が割り当てられてもよい。 Further, the identification information of the external sensors (here, "A" to "D") is registered in the item "sensors necessary for automatic driving". The identification information of the external sensor registered in the "sensors necessary for automated driving" item may be information for identifying the type of the external sensor such as a lidar or a camera. may be information for identifying the In the latter case, for example, different identification information may be assigned to a lidar whose angular resolution is greater than or equal to a predetermined value and to a lidar whose angular resolution is less than a predetermined value.
そして、図4(A)では、タイプXの道路又はエリアに対して自動運転に必要なセンサは、「A」~「D」のいずれかであることが示されている。同様に、図4(A)では、タイプYの道路又はエリアに対して自動運転に必要なセンサは「A」であり、タイプZの道路又はエリアに対して自動運転に必要なセンサは「A」又は「B」のいずれかであることが示されている。このように、図4(A)の例では、道路を実際に走行した際の外界センサの出力に基づき生成された地図データは、航空写真により生成された地図データよりも精度が高く、かつ、高さ方向の情報を含む立体的なデータとなることを勘案し、自動運転に対応可能な外界センサの種別等が多くなっている。一方、航空写真により生成された地図データは、高さ方向の情報を含まない平面的なデータとなることを勘案し、自動運転に対応可能な外界センサの種別等が限られている。 FIG. 4A shows that sensors necessary for automatic driving for type X roads or areas are any of "A" to "D". Similarly, in FIG. 4A, the sensors necessary for automatic driving for type Y roads or areas are "A", and the sensors necessary for automatic driving for type Z roads or areas are "A". ” or “B”. Thus, in the example of FIG. 4A, the map data generated based on the output of the external sensor when actually traveling on the road is more accurate than the map data generated from the aerial photograph, and Considering that the data will be three-dimensional data including information in the height direction, there are many types of external sensors that are compatible with automatic driving. On the other hand, map data generated from aerial photographs is planar data that does not include height direction information.
なお、データ生成識別情報IGは、タイプX、タイプY、タイプZの3つに限らず、タイプX、タイプY、タイプZをさらに詳細に分類したものであってもよい。図4(B)は、タイプXをデータ生成に使用した外界センサの種別又は/及び性能に応じてさらに分類した例を示す。図4(B)の例では、タイプXが外界センサの種別又は/及び性能に応じて「タイプX-1」と「タイプX-2」とに分類されている。タイプX-1は、データの生成に使用した外界センサが「A」である場合を示し、タイプX-2は、データの生成に使用した外界センサが「B」である場合を示す。そして、図4(B)の例では、タイプX-1、タイプX-2のそれぞれに対し、自動運転に必要なセンサが関連付けられている。 Note that the data generation identification information IG is not limited to the three types of type X, type Y, and type Z, and may be classified into type X, type Y, and type Z in more detail. FIG. 4B shows an example in which type X is further classified according to the type and/or performance of the external sensor used for data generation. In the example of FIG. 4B, type X is classified into "type X-1" and "type X-2" according to the type and/or performance of the external sensor. Type X-1 indicates the case where the external sensor used for data generation is "A", and type X-2 indicates the case where the external sensor used for data generation is "B". In the example of FIG. 4B, sensors required for automatic driving are associated with each of type X-1 and type X-2.
[自動運転判定処理]
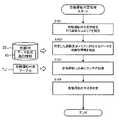
次に、運転支援装置2が実行する自動運転判定処理について説明する。図5は、自動運転判定処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。運転支援装置2は、例えば、図5に示すフローチャートの処理を、自動運転の経路探索時又は生成識別画面の表示を行う際に、繰り返し実行する。[Automatic driving judgment processing]
Next, automatic driving determination processing executed by the driving
まず、運転支援装置2は、自動運転の可否判定を行う道路又はエリアを特定する(ステップS101)。そして、運転支援装置2は、ステップS101で特定した道路又はエリアに対応するデータ生成識別情報IGを地図DB20から抽出する(ステップS102)。そして、運転支援装置2は、ステップS102で抽出したデータ生成識別情報IGに基づき自動運転判定テーブルTJを参照し、対象の道路又はエリアにおいて自動運転を実行する為に必要なセンサを認識する(ステップS103)。そして、運転支援装置2は、ステップS103で認識した自動運転に必要なセンサと、運転支援装置2が備える外界センサ31の種別又は/及び性能とを比較することで、対象の道路又はエリアでの自動運転の実行可否を判定する(ステップS104)。この場合、運転支援装置2は、記憶部22に予め記憶された外界センサ31の種別又は/及び性能の情報を参照してもよく、外界センサ31から当該外界センサ31の種別又は/及び性能の情報を直接取得してもよい。 First, the driving
このように、運転支援装置2は、地図DB20に記憶されたデータ生成識別情報IGを参照することで、道路又はエリアごとに自動運転の実行可否を好適に判定することができる。 In this way, the driving
[生成識別画面]
図6は、データ生成識別情報IGに基づく線分(「生成識別線Ln」とも呼ぶ。)を道路ごとに表示させた生成識別画面の表示例である。ここでは、地図の表示範囲内には、道路81~88が存在している。なお、マーク70は、車両の現在位置を示す。図6の例では、地図DB20には、道路ごとにデータ生成識別情報IGが対応付けられている。[Generation identification screen]
FIG. 6 is a display example of a generated identification screen in which line segments (also referred to as "generated identification lines Ln") based on the data generated identification information IG are displayed for each road. Here,
図6の例では、運転支援装置2は、生成識別線Lnを道路81~88上に表示している。ここで、運転支援装置2は、道路81~88に表示する生成識別線Lnの線種を、道路81~88に対応付けられたデータ生成識別情報IG(ここではタイプX~Z)に応じて決定している。図6では、運転支援装置2は、データ生成識別情報IGが「タイプX」である道路区間に対応する道路81、82を、実線の生成識別線Lnにより重ね、データ生成識別情報IGが「タイプY」である道路区間に対応する道路85~88を、一点鎖線の生成識別線Lnにより重ね、データ生成識別情報IGが「タイプZ」である道路区間に対応する道路83、84を、点線の生成識別線Lnにより重ねて表示している。なお、運転支援装置2は、線種に代えて、線幅又は/及び線色を(又は表示する道路そのものの色を)、対象の道路に対応付けられたデータ生成識別情報IGに応じて変えてもよい。 In the example of FIG. 6, the driving
図7は、エリアごとにデータ生成識別情報IGに基づく色分けを行った生成識別画面の表示例である。図7の例では、地図DB20には、エリアごとにデータ生成識別情報IGが対応付けられている。 FIG. 7 is a display example of a generation identification screen in which areas are color-coded based on the data generation identification information IG. In the example of FIG. 7, data generation identification information IG is associated with each area in the
この場合、運転支援装置2は、まず、現在位置の周辺エリアを表示対象範囲として認識し、表示対象範囲内の各エリアに対応付けられたデータ生成識別情報IGを、地図DB20を参照して特定する。そして、運転支援装置2は、データ生成識別情報IGが対応付けられたエリアのそれぞれを、特定したデータ生成識別情報IGに応じた色で表示する。このように表示することで、利用者は自車位置周辺のエリアの地図データの生成方法を好適に識別することができる。 In this case, the driving
以上説明したように、本実施例に係るサーバ装置1は、配信地図DB10を有する。配信地図DB10には、地図のエリアごと、又は地図の道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法に関するデータ生成識別情報IGが含まれる。そして、サーバ装置1は、配信地図DB10に基づく地図データD1を、車両と共に移動する運転支援装置2に送信する。このようにすることで、サーバ装置1は、データ生成識別情報IGに基づく自動運転の実行可否判定やデータ生成識別情報IGに基づく表示等を好適に運転支援装置2に実行させることができる。 As described above, the
[変形例]
次に、実施例に好適な変形例について説明する。以下の変形例は、任意に組み合わせて上述の実施例に適用してもよい。[Modification]
Next, a modification suitable for the embodiment will be described. The following modifications may be applied to the above embodiments in any combination.
(変形例1)
サーバ装置1は、運転支援装置2に代えて、図5に示す自動運転判定処理を実行してもよい。(Modification 1)
The
例えば、サーバ装置1は、運転支援装置2に代えて自動運転が可能な経路探索を行う場合に、現在位置情報、目的地情報、外界センサ31の情報等を運転支援装置2から受信し、運転支援装置2の現在位置から指定された目的地までの経路探索を行う。この場合、サーバ装置1は、予め記憶部12に記憶させた自動運転判定テーブルTJと配信地図DB10とを参照し、目的地までの経路上の各道路の自動運転の実行可否を、図5のフローチャートを実行することで判定する。そして、サーバ装置1は、探索した経路の情報を、運転支援装置2へ送信する。この態様によっても、運転支援装置2は、自動運転が可能な経路を好適に取得することができる。 For example, the
(変形例2)
運転支援装置2は、運転支援装置2が備える外界センサ31の種別等が予め既知である場合には、自動運転判定テーブルTJを記憶する代わりに、各データ生成識別情報IGに対する自動運転の実行可否の情報を予め記憶してもよい。(Modification 2)
When the type of the
この場合、例えば、運転支援装置2は、データ生成識別情報IGごとに自動運転に必要なセンサと、運転支援装置2が備える外界センサ31の情報とに基づき、データ生成識別情報IGごとの自動運転の実行可否の情報を記憶部22に予め記憶しておく。そして、運転支援装置2は、道路又はエリアの自動運転の可否を判定する場合に、対象の道路又はエリアに対応付けられたデータ生成識別情報IGに基づき、上述の自動運転の実行可否の情報を参照することで、対象の道路又はエリアの自動運転の可否を判定する。この態様によっても、運転支援装置は、対象の道路又はエリアの自動運転の可否を好適に判定することができる。 In this case, for example, the driving
(変形例3)
図4(A)、(B)の例では、自動運転判定テーブルTJには、データ生成識別情報IGごとに、自動運転に必要なセンサの情報が記憶されていた。これに代えて、実行可能な自動運転がレベル分けされている場合には、自動運転判定テーブルTJには、データ生成識別情報IGごとに、自動運転の各レベルを実行するのに必要なセンサの情報が記憶されていてもよい。この態様によれば、運転支援装置2は、自動運転判定テーブルTJを参照することで、対象の道路又はエリアにおいて実行可能な自動運転のレベルを好適に判定することができる。(Modification 3)
In the examples of FIGS. 4A and 4B, the automatic driving determination table TJ stores sensor information necessary for automatic driving for each piece of data generation identification information IG. Alternatively, when executable automatic driving is divided into levels, the automatic driving determination table TJ includes sensors required to execute each level of automatic driving for each data generation identification information IG. Information may be stored. According to this aspect, the driving
1 サーバ装置
2 運転支援装置
10 配信地図DB
11、21 通信部
12、22 記憶部
15、25 制御部
20 地図DB
23 センサ部
24 入力部
26 出力部1
11, 21
23
Claims (7)
Translated fromJapanese前記記憶部は、地図データと自動運転判定情報とを記憶し、
前記地図データは、前記地図データのエリアごと、又は前記地図データの道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法の識別情報を含み、
前記自動運転判定情報は、前記識別情報ごとに前記自動運転に必要なセンサの情報を含み、
前記制御部は、移動体が移動する対象の道路又はエリアにおいて前記自動運転を実行するために必要なセンサの認識を、前記識別情報に応じた前記自動運転判定情報に基づき行うことで、前記自動運転の可否判定を行うことを特徴とする自動運転の可否判定方法。A method for determining whether automatic driving is possible in a driving support device including a control unit and a storage unit,
The storage unitstores map dataand automatic driving determination information ,
the map data includes, for each area of the map data or each road of the map data, identification informationof a method of generating data relating to the area or road;
The automatic driving determination information includes sensor information necessary for the automatic driving for each of the identification information,
The control unit recognizes a sensor necessary for executing the automatic driving on a target road or area on whichthe mobile object moves, based on the automatic driving determination informationcorresponding to the identification information.A method for determining whether automatic driving is possible or not, characterized by determining whether or not automatic driving is possible.
移動体の自動運転の可否を判定する制御部と、を備え、 A control unit that determines whether automatic operation of the mobile object is possible,
前記地図データは、前記地図データのエリアごと、又は前記地図データの道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法の識別情報を含み、 the map data includes, for each area of the map data or each road of the map data, identification information of a method of generating data relating to the area or road;
前記自動運転判定情報は、前記識別情報ごとに前記自動運転に必要なセンサの情報を含み、 The automatic driving determination information includes sensor information necessary for the automatic driving for each of the identification information,
前記制御部は、前記移動体が移動する対象の道路又はエリアにおいて前記自動運転を実行するために必要なセンサの認識を、前記識別情報に応じた前記自動運転判定情報に基づき行うことで、前記自動運転の可否判定を行うことを特徴とする自動運転の可否判定装置。 The control unit recognizes a sensor necessary for executing the automatic driving on a target road or area on which the moving object moves, based on the automatic driving determination information corresponding to the identification information, An automatic operation propriety determination device characterized by performing an automatic operation propriety determination.
前記地図データに基づき地図を表示する表示部と、を備え、
前記表示部は、前記地図データに含まれる前記識別情報に基づき、前記地図中のエリア又は道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法を識別する表示を行う請求項2~5のいずれか一項に記載の自動運転の可否判定装置。an acquisition unit that acquiresthe map data;
a display unit that displays a map based on the map data,
6. The display unit accordingto any one of claims 2 to 5 , wherein, based onthe identification information included in the map data, for each area or road in the map, the display identifies a method of generating data relating to the area or road.1. The device for determining whether automatic driving is possible according to the first item .
地図データを記憶し、前記可否判定装置と通信可能なサーバ装置と、を備え、 a server device that stores map data and can communicate with the availability determination device;
前記地図データは、前記地図データのエリアごと、又は前記地図データの道路ごとに、当該エリア又は道路に関するデータの生成方法の識別情報を含み、 the map data includes, for each area of the map data or each road of the map data, identification information of a method of generating data relating to the area or road;
前記可否判定装置は、 The propriety determination device is
前記識別情報ごとに前記自動運転に必要なセンサの情報を含む自動運転判定情報を記憶する記憶部と、 A storage unit that stores automatic driving determination information including sensor information necessary for automatic driving for each of the identification information;
前記サーバ装置から前記地図データを取得する通信部と、 a communication unit that acquires the map data from the server device;
前記移動体が移動する対象の道路又はエリアにおいて前記自動運転を実行するために必要なセンサの認識を、前記識別情報に応じた前記自動運転判定情報に基づき行うことで、前記自動運転の可否判定を行う制御部と、を備えることを特徴とする自動運転の可否判定システム。 By recognizing the sensor necessary for executing the automatic driving on the target road or area where the moving object moves, based on the automatic driving determination information according to the identification information, the determination of whether the automatic driving is possible and a control unit that performs automatic operation determination system.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021015160AJP7123203B2 (en) | 2021-02-02 | 2021-02-02 | Autonomous driving propriety determination method, automatic driving propriety determination device, and automatic driving propriety determination system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021015160AJP7123203B2 (en) | 2021-02-02 | 2021-02-02 | Autonomous driving propriety determination method, automatic driving propriety determination device, and automatic driving propriety determination system |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016209407ADivisionJP2018072069A (en) | 2016-10-26 | 2016-10-26 | Map data structure, transmission device, and map display device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021092793A JP2021092793A (en) | 2021-06-17 |
| JP7123203B2true JP7123203B2 (en) | 2022-08-22 |
Family
ID=76313262
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021015160AActiveJP7123203B2 (en) | 2021-02-02 | 2021-02-02 | Autonomous driving propriety determination method, automatic driving propriety determination device, and automatic driving propriety determination system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7123203B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9443876B2 (en)* | 2014-02-05 | 2016-09-13 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device, display device including the semiconductor device, display module including the display device, and electronic device including the semiconductor device, the display device, and the display module |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007101580A (en) | 2005-09-30 | 2007-04-19 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | Map database generation system |
| JP2015206655A (en) | 2014-04-18 | 2015-11-19 | 株式会社デンソー | Automatic driving plan display device and program for automatic driving plan display device |
| WO2016152873A1 (en) | 2015-03-24 | 2016-09-29 | パイオニア株式会社 | Automatic driving assistance device, control method, program, and storage medium |
- 2021
- 2021-02-02JPJP2021015160Apatent/JP7123203B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007101580A (en) | 2005-09-30 | 2007-04-19 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | Map database generation system |
| JP2015206655A (en) | 2014-04-18 | 2015-11-19 | 株式会社デンソー | Automatic driving plan display device and program for automatic driving plan display device |
| WO2016152873A1 (en) | 2015-03-24 | 2016-09-29 | パイオニア株式会社 | Automatic driving assistance device, control method, program, and storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2021092793A (en) | 2021-06-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2024127917A (en) | Autonomous driving assistance device, control method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP2019145175A (en) | Output device, map information storage device, automatic driving control device, output method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP4910510B2 (en) | Control information storage device and program | |
| JP2007278765A (en) | Navigation device and map data updating method | |
| JP6478864B2 (en) | Electronic device, route guidance program, and route guidance system | |
| JP2019168271A (en) | Data structure, information processing device, data communication method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP2018072069A (en) | Map data structure, transmission device, and map display device | |
| JP2013036930A (en) | Navigation device and navigation system comprising the same | |
| CN111273652A (en) | Autopilot | |
| JP5203747B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP7123203B2 (en) | Autonomous driving propriety determination method, automatic driving propriety determination device, and automatic driving propriety determination system | |
| US11959767B2 (en) | Map information assessment device, storage medium storing computer program for map information assessment, and map information assessment method | |
| JP7686854B2 (en) | Information transmission device, control method, program, and storage medium | |
| KR20130041698A (en) | Device for creating traveling information of unmanned ground vehicle, unmanned ground vehicle having the same and control method thereof | |
| JP2020008490A (en) | Driving support system and driving support program | |
| JP6923304B2 (en) | Information processing device, terminal device, travel control device, control method, program and storage medium | |
| JP6432312B2 (en) | Navigation system, navigation method, and navigation program | |
| US11898861B2 (en) | Road zone assessment device, medium storing computer program for road zone assessment, and road zone assessment method | |
| JP2006337114A (en) | Navigation system, matching method, route search server, and navigation terminal device | |
| JP7456967B2 (en) | Map information determination device and computer program for map information determination | |
| US9689689B2 (en) | Navigation device and program for performing route guidance along a route using, as a recognized road, an extension road not actually traveled which extends straight from and is continuous with a road actually traveled | |
| WO2019181844A1 (en) | Data structure, information processing device, data communication method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP2019168998A (en) | Data structure, terminal device, data communication method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP7284851B2 (en) | Information processing equipment | |
| JP5317469B2 (en) | Navigation device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20210202 | |
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date:20210903 | |
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date:20210916 | |
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date:20210827 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20211126 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20211217 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20220208 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20220408 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20220802 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20220809 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:7123203 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |