JP7089979B2 - Actuator - Google Patents
ActuatorDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7089979B2 JP7089979B2JP2018148287AJP2018148287AJP7089979B2JP 7089979 B2JP7089979 B2JP 7089979B2JP 2018148287 AJP2018148287 AJP 2018148287AJP 2018148287 AJP2018148287 AJP 2018148287AJP 7089979 B2JP7089979 B2JP 7089979B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- electrode
- actuator
- dielectric elastomer
- drive
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- General Electrical Machinery Utilizing Piezoelectricity, Electrostriction Or Magnetostriction (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、アクチュエーターに関する。 The present invention relates to an actuator.
電気的入力を機械的出力に変換するデバイスの一つとして、誘電エラストマーアクチュエーターが検討されている。かかるアクチュエーターは、一対の電極層によりエラストマー層が狭持された構造を有し、電極に電圧が印加された場合に、エラストマー層の拡がる方向に伸縮する。このような誘電エラストマーアクチュエーターでは、電極間に生じるクーロン力が駆動原理の一つとなっている。 Dielectric elastomer actuators are being studied as one of the devices that convert electrical inputs into mechanical outputs. Such an actuator has a structure in which an elastomer layer is sandwiched by a pair of electrode layers, and when a voltage is applied to the electrodes, the actuator expands and contracts in the direction in which the elastomer layer expands. In such a dielectric elastomer actuator, the Coulomb force generated between the electrodes is one of the driving principles.
例えば、特許文献1には、一対の電極間に誘電エラストマーを狭持したアクチュエーターが開示されている。同文献では、絶縁破壊強度の向上及びアクチュエーターの変位量の向上のために、誘電エラストマーを二次元方向にあらかじめ延伸して電極で狭持することを試みている。 For example,
本発明に係る課題の一つは、誘電エラストマーの変形性能を十分に引き出した変位量の大きいアクチュエーターを提供することにある。 One of the problems according to the present invention is to provide an actuator having a large displacement amount that sufficiently brings out the deformation performance of the dielectric elastomer.
本発明は上述の課題の少なくとも一部を解決するためになされたものであり、以下の態様又は適用例として実現することができる。 The present invention has been made to solve at least a part of the above-mentioned problems, and can be realized as the following aspects or application examples.
本発明に係るアクチュエーターの一態様は、
中間層と、前記中間層を挟んで対向して配置される第1駆動層及び第2駆動層と、を含み、
前記第1駆動層及び前記第2駆動層は、それぞれ第1電極、第1方向に延伸された誘電エラストマー層及び第2電極を含み、
前記中間層は、抑制部材を含み、
前記抑制部材は、前記第1駆動層に接着する第1接着部と、前記第2駆動層に接着する第2接着部と、を含み、
前記第1方向において隣り合う前記第1接着部が互いに第1間隔を隔てて配置され、
前記第1方向において隣り合う前記第2接着部が互いに第2間隔を隔てて配置され、
前記抑制部材は、前記第1間隔及び前記第2間隔が、前記誘電エラストマー層の復元力によって前記第1方向に狭まることを制限する。One aspect of the actuator according to the present invention is
It includes an intermediate layer and a first drive layer and a second drive layer arranged so as to face each other with the intermediate layer interposed therebetween.
The first drive layer and the second drive layer include a first electrode, a dielectric elastomer layer stretched in the first direction, and a second electrode, respectively.
The intermediate layer contains a restraining member and contains a restraining member.
The restraining member includes a first adhesive portion that adheres to the first drive layer and a second adhesive portion that adheres to the second drive layer.
The first adhesive portions adjacent to each other in the first direction are arranged at a distance of a first distance from each other.
The second adhesive portions adjacent to each other in the first direction are arranged at a distance of a second distance from each other.
The restraining member limits the first spacing and the second spacing from narrowing in the first direction due to the restoring force of the dielectric elastomer layer.
本発明に係るアクチュエーターの一態様は、
中間層と、前記中間層を挟んで対向して配置される駆動層及び第1方向に延伸されたエラストマー層と、を含み、
前記駆動層は、第1電極、誘電エラストマー層及び第2電極を含み、
前記中間層は、抑制部材を含み、
前記抑制部材は、前記駆動層に接着する第1接着部と、前記エラストマー層に接着する
第2接着部と、を含み、
前記第1方向において隣り合う前記第1接着部が互いに第1間隔を隔てて配置され、
前記第1方向において隣り合う前記第2接着部が互いに第2間隔を隔てて配置され、
前記抑制部材は、前記第1間隔及び前記第2間隔が、前記エラストマー層の復元力によって前記第1方向に狭まることを制限する。One aspect of the actuator according to the present invention is
It includes an intermediate layer, a drive layer arranged so as to face each other across the intermediate layer, and an elastomer layer stretched in a first direction.
The drive layer includes a first electrode, a dielectric elastomer layer and a second electrode.
The intermediate layer contains a restraining member and contains a restraining member.
The restraining member includes a first adhesive portion that adheres to the drive layer and a second adhesive portion that adheres to the elastomer layer.
The first adhesive portions adjacent to each other in the first direction are arranged at a distance of a first distance from each other.
The second adhesive portions adjacent to each other in the first direction are arranged at a distance of a second distance from each other.
The restraining member limits the first spacing and the second spacing from narrowing in the first direction due to the restoring force of the elastomer layer.
本発明に係るアクチュエーターにおいて、
前記第1接着部は、前記第1方向に直交する第2方向に沿う直線上にあり、
前記第2接着部は、前記第2方向に沿う直線上にあってもよい。In the actuator according to the present invention
The first adhesive portion is on a straight line along a second direction orthogonal to the first direction.
The second adhesive portion may be on a straight line along the second direction.
本発明に係るアクチュエーターにおいて、
前記抑制部材は、前記第1方向に直交する第2方向に延びる棒部材を複数含み、
前記棒部材の前記第2方向に垂直な断面の外形が円形であり、
隣り合う前記棒部材が、互いに接触する状態で前記第1方向に配置され、
前記第1接着部及び前記第2接着部が、それぞれ前記棒部材の外周面の一部であってもよい。In the actuator according to the present invention
The restraining member includes a plurality of rod members extending in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction.
The outer shape of the cross section of the rod member perpendicular to the second direction is circular, and the outer shape is circular.
Adjacent rod members are arranged in the first direction in a state of being in contact with each other.
The first adhesive portion and the second adhesive portion may be a part of the outer peripheral surface of the rod member, respectively.
本発明に係るアクチュエーターにおいて、
前記抑制部材は、前記第1方向に延びる連結部と、
前記連結部から、前記第1方向と前記第1方向に直交する第2方向とに直交する第3方向に延びて前記第1接着部を形成する複数の第1支持部と、
前記連結部から、前記第3方向に延びて前記第2接着部を形成する複数の第2支持部と、
を含んでもよい。In the actuator according to the present invention
The restraining member includes a connecting portion extending in the first direction and a connecting portion.
A plurality of first support portions extending from the connecting portion in a third direction orthogonal to the first direction and the second direction orthogonal to the first direction to form the first adhesive portion.
A plurality of second support portions extending from the connecting portion in the third direction to form the second adhesive portion,
May include.
本発明に係るアクチュエーターは、誘電エラストマーの変形と、エラストマーの復元力を利用することにより、大きく変位させることができる。 The actuator according to the present invention can be greatly displaced by utilizing the deformation of the dielectric elastomer and the restoring force of the elastomer.
以下に本発明のいくつかの実施形態について説明する。以下に説明する実施形態は、本発明の一例を説明するものである。本発明は以下の実施形態になんら限定されるものではなく、本発明の要旨を変更しない範囲において実施される各種の変形形態も含む。なお以下で説明される構成の全てが本発明の必須の構成であるとは限らない。 Hereinafter, some embodiments of the present invention will be described. The embodiments described below describe an example of the present invention. The present invention is not limited to the following embodiments, and includes various modifications implemented without changing the gist of the present invention. Not all of the configurations described below are essential configurations of the present invention.
1.第1実施形態
1.1.アクチュエーターの構造
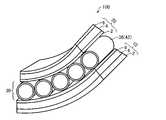
図1は、本実施形態に係るアクチュエーター100を模式的に示す斜視図である。図2は、本実施形態に係るアクチュエーター100の縦断面の模式図である。1. 1. First Embodiment 1.1. Structure of Actuator FIG. 1 is a perspective view schematically showing an
本実施形態のアクチュエーター100は、中間層30と、中間層30を挟んで対向して配置される第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20と、を含む。本実施形態に係るアクチュエーター100は、図1及び図2に示すように、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の2つの駆動層によって中間層30が狭持されており、第1駆動層10、中間層30及び第2駆動層20が、順に積層された構造となっている。 The
1.1.1.第1駆動層
第1駆動層10は、第1電極2、誘電エラストマー層4及び第2電極6を含む。第1電極2、誘電エラストマー層4及び第2電極6は順次積層されており、第1電極2及び第2電極6の間に誘電エラストマー層4が配置された構造となっている。1.1.1. First Drive Layer The
第1電極2は、第2電極6と対になって誘電エラストマー層4に対して電圧(電界)を印加する一方の電極である。第1電極2は、電圧を印加する機能を発揮でき、かつ誘電エラストマー層4の変形に追従できればよく、形状、材質、電気抵抗等は限定されない。第1電極2の形状としては、例えば、平板状、フィルム状、塗膜状等である。第1電極2には1つ以上の孔が開いていてもよく、例えば、平面的に見てスリット等が形成されてもよい。また、例えば、第1電極2は、平面的に見て櫛形、網目等の形状となっていてもよい。 The
第1電極2が第2電極6とともに狭持する誘電エラストマー層4の領域は、誘電エラストマー層4の全体であってもよいし、誘電エラストマー層4の一部であってもよい。第1電極2と誘電エラストマー層4とは、直接接していてもよいし、例えば、接着層等の他の層を介して接していてもよい。 The region of the
第1電極2の材質としては、導電性を有する材質であって、例えば、アルミニウム、銅、金等の金属、各種金属の合金、カーボン、導電性酸化物、導電性ポリマー、導電性ペースト等を例示できる。 The material of the
また、第1電極2は、誘電エラストマー層4の変形に対して追従できるような材質であることがより好ましい。また、第1電極2の材質として、例えば、導電性ポリマーやカーボンペースト、銀ペースト等を採用することにより、誘電エラストマー層4の変形に追従して変形し易くできる。 Further, it is more preferable that the
第1電極2の厚さは、材質に依存するが、例えば、導電性の塗膜である場合には、1μm以上500μm以下であり、好ましくは5μm以上300μm以下、より好ましくは10μm以上200μm以下である。 The thickness of the
第2電極6は、第1電極2と対になって誘電エラストマー層4に対して電圧(電界)を印加する他方の電極である。第2電極6は、電圧を印加する機能を発揮でき、かつ、誘電エラストマー層4の変形に追従できればよく、形状、材質等は限定されない。第2電極6の形状は、上記の第1電極2と同様である。また、第2電極6が第1電極2とともに狭持する誘電エラストマー層4の領域、第2電極6の材質及び厚さについても上記の第1電極2と同様である。 The
誘電エラストマー層4は、第1電極2及び第2電極6に狭持される。誘電エラストマー層4は、第1電極2及び第2電極6に電圧が印加されたときに、第1電極2と第2電極6とがクーロン力によって引き合うことにより、厚さ方向に圧縮される。これにより、誘電エラストマー層4の厚さ方向に直交する方向に、第1駆動層10が伸びることができる。本実施形態においては、厚さ方向はz軸に沿う方向である。 The
誘電エラストマー層4は、あらかじめ第1方向に延伸された状態で第1電極2及び第2電極6に狭持される。又は、誘電エラストマー層4は、延伸される前に第1電極2及び第2電極6と積層されて第1駆動層10となった後、第1駆動層10が第1方向に延伸されて第1電極2及び第2電極6に狭持される。これらのいずれの場合においても、アクチュエーター100が形成された時点において、誘電エラストマー層4は、あらかじめ第1方向に延伸された状態で中間層30に固定されることとなる。第1駆動層10は、誘電エラストマー層4が第1方向に延伸された状態であるので、第1方向に収縮しようとする復元力を有している。 The
ここで「第1方向」とは、誘電エラストマー層4の厚さ方向に直交する方向である。また、第1方向は、誘電エラストマー層4の第1電極2又は第2電極6との境界面に沿う方向である。本実施形態においては、第1方向はx軸に沿った正又は負の方向である。 Here, the "first direction" is a direction orthogonal to the thickness direction of the
誘電エラストマー層4は、第1方向に延伸された状態でアクチュエーター100の一部材となっているが、第1方向に交差する方向(誘電エラストマー層4の第1電極2又は第2電極6との境界面に沿う方向)に延伸された状態であってもよい。例えば、誘電エラストマー層4は、第1方向に直交する第2方向に延伸されていてもよい。 The
ここで「第2方向」とは、誘電エラストマー層4の第1電極2又は第2電極6との境界面に沿う方向であって、第1方向に直交する方向である。本実施形態においては、第2方向は、y軸に沿った正又は負の方向である。 Here, the "second direction" is a direction along the boundary surface of the
誘電エラストマー層4は、延伸された状態でアクチュエーター100を構成するが、当該延伸は一軸又は多軸の延伸であってよく、収縮しようとする復元力が第1方向の成分を含んでいればよい。 The
誘電エラストマー層4が延伸された状態で第1駆動層10が中間層30に固定されることによって、誘電エラストマー層4の厚さが小さくなり、第1電極2と第2電極6とに電場を印加した際に生じるクーロン力をより大きくすることができる。そのため、延伸しない場合と比較して、第1方向の変形をより大きくすることができる。また、誘電エラストマー層4が延伸されて中間層30に固定されることによって、誘電エラストマー層4のヤング率が低く曲げやすい伸張領域での動作を利用しやすくなり、アクチュエーター100の動作における早い応答性及び小さい電力による大きな変形を得やすくなる。 By fixing the
誘電エラストマー層4の延伸率が低すぎると、アクチュエーター100の動作時のゴム弾性による復元力が低くなることで変形量が低下し、誘電エラストマー層4の延伸率が高すぎると、アクチュエーター100の動作時に破断伸びに近い領域で動作することとなるので、動作中に破断してしまうおそれがある。そのため、採用する材料や厚さに応じて適宜の延伸率とすることが好ましい。 If the stretch ratio of the
誘電エラストマー層4の厚さは、10μm以上1mm以下、好ましくは10μm以上800μm以下、より好ましくは50μm以上500μm以下、さらに好ましくは100μm以上500μm以下である。誘電エラストマー層4の厚さが薄過ぎると、アクチュエーター100の組立工程において誘電エラストマー層4が破れやすくなる場合がある。また、誘電エラストマー層4の厚さが厚過ぎると、誘電エラストマー層4の弾性が大きくなり、2軸の延伸が困難となる場合がある。さらに、アクチュエーター100の動作時の電極間の距離が大きくなるため印加電圧に対する応答性が低下する傾向がある。 The thickness of the
誘電エラストマー層4の材質としては、絶縁性を有し、ゴム弾性を有するものであれば特に限定されず、例えば、天然ゴム、イソプレンゴム、スチレン-ブタジエンゴム(SB
R)、ニトリルゴム(NBR)、エチレン・プロピレン・ジエンゴム(EPDM)、アクリルゴム、シリコーンゴム、ウレタンゴム、アクリル系エラストマー等が挙げられる。これらの中でも、誘電エラストマー層4に用いる材料としては、シリコーンゴムやウレタンゴム、アクリル系エラストマーなどがより好適である。The material of the
R), nitrile rubber (NBR), ethylene / propylene / diene rubber (EPDM), acrylic rubber, silicone rubber, urethane rubber, acrylic elastomer and the like can be mentioned. Among these, as the material used for the
また、誘電エラストマー層4に用いる材料は、剛性が低くかつ高伸びを有した材料が好適である。具体的には、誘電エラストマー層4に用いる材料の機械的物性としては、JIS K6251に基づく引っ張り試験における600%伸張時のモジュラスが0.03MPa以上1.0MPa以下、好ましくは0.03MPa以上0.5MPa以下、より好ましくは0.05MPa以上0.3MPa以下の範囲、かつ、破断伸びが800%以上、好ましくは1000%以上である材料がさらに適している。 Further, as the material used for the
第1駆動層10は、誘電エラストマー層4が第1方向に延伸された状態となっているので、第1方向に収縮しようとする復元力を有している。すなわち、アクチュエーター100が形成されたとき、第1駆動層10は、常にゴム弾性によって元の形状に戻ろうとしている状態となる。本実施形態のアクチュエーター100では、第1方向に収縮しようとする復元力を有する第1駆動層10を中間層30に固定化し、後述の第2駆動層20とともに中間層30を挟んで両側で復元力が釣り合った状態で延伸状態が維持されるように固定される。 Since the
1.1.2.第2駆動層
第2駆動層20は、中間層30を挟んで第1駆動層10と対向して配置されている。第2駆動層20は、本実施形態では第1駆動層10と同様に第1電極2、誘電エラストマー層4及び第2電極6を含む。第1電極2、誘電エラストマー層4及び第2電極6の形状、機能、材質、物性等は、上述した第1駆動層10と同様である。11.2. Second Drive Layer The
第2駆動層20においても、誘電エラストマー層4が、延伸されることによって、誘電エラストマー層4の厚さが小さくなり、第1電極2と第2電極6とに電場を印加した際に生じるクーロン力をより大きくすることができる。そのため、延伸しない場合と比較して、より大きく第1方向に第2駆動層20を変形させることができる。また、誘電エラストマー層4が、延伸されることによって、誘電エラストマー層4のヤング率が低く曲げやすい伸張領域での動作を利用しやすくなり、早い応答性及び小さい電力による大きな変形を得やすくなる。 Also in the
第2駆動層20は、アクチュエーター100を構成した場合には、上述の第1駆動層10と同様に、第1方向に延伸された状態であるので、第1方向に収縮しようとする復元力を有している。すなわち、アクチュエーター100を構成した場合、第2駆動層20も、常にゴム弾性によって元の形状に戻ろうとしている状態となっている。この第1方向に収縮しようとする復元力を有する第2駆動層20を中間層30に固定化し、上述の第1駆動層10とともに中間層30を挟んで両側で、第1駆動層10の復元力と第2駆動層20の復元力が、釣り合った状態で延伸状態が維持されるように固定される。 When the
なお、アクチュエーター100では、図1に示すように、第1駆動層10の第2電極6が中間層30側に配置されており、第2駆動層20の第1電極2が中間層30側に配置されている。しかし第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の第1電極2及び第2電極6は、いずれが中間層30側に配置されてもよい。 In the
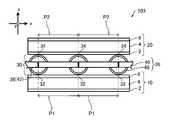
1.1.3.中間層
中間層30は、抑制部材36を含む。抑制部材36は、第1駆動層10に接着する第1接着部32と、第2駆動層20に接着する第2接着部34とを有する。11.3. Intermediate layer The
第1接着部32は、抑制部材36の第1駆動層10に接着する部分である。第1接着部32は複数設けられる。また第1接着部32は、第1駆動層10の第2電極6に接着していてもよいし、例えば、第2電極6に孔が存在する場合には、当該孔の内側で誘電エラストマー層4に接着していてもよい。 The first
第1接着部32は、第1方向において隣り合う第1接着部32が互いに第1間隔P1を隔てて配置される。図示の例では複数存在する第1間隔P1は、互いに等しい間隔であるが、抑制部材36の形状によっては、複数の第1間隔P1の全てが互いに同じでも異なってもよい。 In the first
第1接着部32は、中間層30が展開する面における第1方向に交差する第2方向に沿う直線上にあるように配置されている。各駆動層と抑制部材36とは、第2方向に沿って連続的に接着されてもよいし、不連続に接着されてもよい。図1及び図2の例では、第1接着部32は、第1方向(x)に直交する第2方向(y)に沿って、直線状に形成されている。 The first
第2接着部34は、抑制部材36の第2駆動層20に接着する部分である。第2接着部34の数、第2駆動層20との接着の態様については第1接着部32と同様である。第2接着部34は、第1接着部32と同様に第1方向(x)に直交する第2方向(y)に沿って、直線上に形成されている。 The second
第2接着部34は、第1方向において隣り合う第2接着部34が互いに第2間隔P2を隔てて配置される。図示の例では、第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2は、等しくなっている。また図示において複数存在する第2間隔P2は、互いに等しい間隔であるが、複数の第2間隔P2は互いに同じでも異なってもよい。 In the second
第1接着部32及び第2接着部34には、接着剤を用いることができる。接着剤は、電極層や誘電エラストマー層4の材質に合わせて相溶性の高い材質のものを選ぶことが好ましい。例えば、抑制部材36が誘電エラストマー層4と接着される場合であって誘電エラストマー層4がシリコーンゴムである場合、シリコーン系の接着剤を用いることが好ましい。また電極層が導電性ペーストに接着剤成分が含まれている場合などには、接着剤を用いることなく抑制部材36を電極層と該導電性ペーストによって接着することも可能である。 An adhesive can be used for the first
抑制部材36は、第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が、誘電エラストマー層4(第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20)の復元力によって第1方向に狭まることを制限する。なお、第1電極2及び第2電極6に電圧が印加されて、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20のいずれかが動作した場合には、第1間隔P1又は第2間隔P2の間隔が狭まることが許容される。 The restraining
抑制部材36は、図1及び図2の例では、第1方向に直交する第2方向に延びる棒部材42を複数含み、棒部材42の第2方向に垂直な断面の外形が円形であり、隣り合う前記棒部材42が、互いに接触する状態で第1方向に配置され、第1接着部32及び第2接着部34が、それぞれ棒部材42の外周面の一部となっている。また図示の例では第1接着部32及び第2接着部34は、棒部材42の中心軸を挟んで対向した位置にある。 In the examples of FIGS. 1 and 2, the restraining
抑制部材36と電極層及び/又は誘電エラストマー層4との接着面積(各接着部の面積)はより小さい方が好ましい。接着部の面積が大きくなるにつれ、誘電エラストマー層4の第1方向への伸長変形を拘束しやすくなり、アクチュエーターの変位量が低下する傾向
がある。It is preferable that the bonding area (area of each bonded portion) between the suppressing
また、図示の例では、棒部材42は、中空の円筒状であるが、中実の円柱状であってもよい。また、隣り合う棒部材42の間は、接着されずに接触している。隣り合う棒部材42の間が接触していれば、第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の復元力によって第1方向に狭まることを制限できる。また、隣り合う棒部材42の間が接着されていないことにより、アクチュエーター100をより変形しやすくできる。すなわち隣り合う棒部材42の間が接着されていないので、隣り合う棒部材42が回転しながら相対的な位置の変化を容易に行うことができる構造となる。 Further, in the illustrated example, the
棒部材42の材質としては、金属、セラミックス、樹脂材料などが適用できる。特に、隣り合う棒部材42の間が接着されず接触しているので、結晶性が高く低摩擦係数かつ高ヤング率、を示す材質が好ましい。そのような材質としては、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン、ポリイミドなどのエンジニアリングプラスチック材料が挙げられる。また、棒部材42と第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20との間(中間層30の抑制部材36以外の部分)には、厚さ方向への中間層30の変形を抑制しない弾性体を満たしてもよい。弾性体としては、天然ゴム、イソプレンゴム、スチレン-ブタジエンゴム(SBR)、ニトリルゴム(NBR)、エチレン・プロピレン・ジエンゴム(EPDM)、アクリルゴム、シリコーンゴム、ウレタンゴム等のゴム、スチレン系、オレフィン/アルケン系、塩化ビニル系、ウレタン系、アミド系の熱可塑性樹脂、及びその発泡体などの柔軟な材料を用いることができる。 As the material of the
なお本実施形態では、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の2つの駆動層によって中間層30が狭持されている例を説明したが、これに限らず、駆動層と中間層30の間に他の層を有してもよいし、駆動層の中まで中間層30の一部が入り込んでもよい。 In the present embodiment, an example in which the
1.2.アクチュエーターの動作
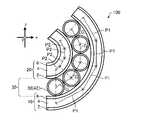
図3は、本実施形態のアクチュエーター100の動作を模式的に示す斜視図である。図4は、本実施形態に係るアクチュエーター100が動作した場合の縦断面の模式図である。1.2. Actuator Operation FIG. 3 is a perspective view schematically showing the operation of the
図3及び図4の例は、本実施形態のアクチュエーター100の第1駆動層10の第1電極2と第2電極6との間に電圧が印加され、両電極間にクーロン力が生じた場合を示している。第1駆動層10の第1電極2と第2電極6との間に電圧が印加された場合、第1駆動層10の第1方向への伸びが発生する。 In the examples of FIGS. 3 and 4, a voltage is applied between the
第1駆動層10が第1方向に伸びると、アクチュエーター100は、第1駆動層10の伸びに基づく屈曲変形と、第2駆動層20の復元力による屈曲変形とが生じる。すなわち、本実施形態のアクチュエーター100では、第1駆動層10の伸びによって第1駆動層10の復元力と第2駆動層20の復元力の釣り合いが崩れ、伸びに基づく屈曲変形及び復元力に基づく屈曲変形の2つの機構によって屈曲変形を起こす。このように誘電エラストマー層4を第1方向に延伸して用いることにより、アクチュエーター100の変位量を非常に大きくできる。 When the
アクチュエーター100の第1駆動層10が第1方向に伸びる場合の屈曲変形は、x軸のプラス側に向かう方向がz軸のプラス側向かう方向に屈曲するような変形である。図示の例では、z軸のマイナス側に第1駆動層10が存在しており、第1駆動層10の伸長により、第2駆動層20が内側となるように湾曲する。すなわち、x-y平面に展開するアクチュエーター100が、z軸に沿った方向(厚さ方向)に屈曲する。このとき棒部材42は、隣り合う棒部材42の外周に沿って移動する。なお、本実施形態において、誘電エ
ラストマー層4の厚さ方向を第3方向ということがあり、第3方向は、x軸及びy軸に直交するz軸に沿った正又は負の方向である。The bending deformation when the
また、アクチュエーター100は、y軸のプラス側に向かう方向がz軸のプラス側向かう方向となるような屈曲は、ほとんど又は全く生じない。これは棒部材42が第2方向に延在し、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の第2方向への変形を拘束していることによる。 Further, the
第1駆動層10の第1電極2と第2電極6とに、互いに異なる極性の電位を印加すれば、第1駆動層10を第1方向に伸ばすことができる。また、第1電極2及び第2電極6のいずれかを接地電位としてもよい。このような電位は、例えば、公知の電圧発生装置(電池、電圧印加回路等)により印加することができる。 If potentials having different polarities are applied to the
図2及び図4を用いて、本実施形態のアクチュエーター100の屈曲構造における棒部材42の力学的モデルを説明する。図2の状態では、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20が駆動しておらず、棒部材42は、隣接する棒部材42と接触している。これにより第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が、棒部材42によって一定に維持されている。また図2の状態では、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20における誘電エラストマー層4の復元力は、第1方向において釣り合っており、アクチュエーター100が屈曲せず平面的な形状となっている。 A mechanical model of the
ここで第1駆動層10の第1電極2及び第2電極6に電圧が印加されると、図4に示す状態となる。図4の状態では、第1駆動層10が第1方向に伸びて第1間隔P1のそれぞれが拡がる。また図2の状態で第1方向において第1駆動層10の復元力と釣り合っていた第2駆動層20が、自身の復元力により収縮することにより、第2間隔P2のそれぞれが狭まる。またこのとき隣り合う棒部材42同士が接触しながら移動することで、図示のように、第2駆動層20を内側とした屈曲変形が生じる。 Here, when a voltage is applied to the
また、図4に示すように、棒部材42は円筒状であるので、隣り合う棒部材42の中心軸間の距離Gは、屈曲した状態でも常に一定となる。このとき第1駆動層10の第2方向の変形は、第1接着部32を介して接着された棒部材42によって拘束される。 Further, as shown in FIG. 4, since the
また、図示しないが、アクチュエーター100の第2駆動層20の第1電極2と第2電極6との間に電圧が印加され、両電極間にクーロン力が生じた場合では、屈曲が反対となるように動作する。 Further, although not shown, when a voltage is applied between the
1.3.駆動層のバリエーション
本実施形態のアクチュエーター100では、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20は、それぞれ第1電極2、誘電エラストマー層4及び第2電極6の3層の組となっており、その組が単層で構成され、誘電エラストマー層4は1層ずつ配置されている。しかし、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20は、いずれも誘電エラストマー層4を2層以上有してもよい。1.3. Variation of Drive Layer In the
例えば、第1駆動層10が誘電エラストマー層4を2層有する態様としては、第1電極2、誘電エラストマー層4、第2電極6、誘電エラストマー層4及び第1電極2の順で積層された構造としてもよい。また例えば、第1駆動層10が誘電エラストマー層4を2層有する態様としては、第1電極2、誘電エラストマー層4、第2電極6、絶縁層、第1電極2、誘電エラストマー層4及び第1電極2の順で積層された構造としてもよい。このようにすることにより、第1駆動層10の変形する力を強めることができる場合がある。第2駆動層20についても同様の構成とすることができる。なお、このような場合には、誘
電エラストマー層4の両側に電極層が存在するように構成され、1つの誘電エラストマー層4の両側の電極層には互いに極性の異なる電圧が互い違いに印加されることにより駆動する。For example, in the embodiment in which the
また、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20は、各層の厚さや積層数等において、同じである必要はない。例えば、中間層30の両側で第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20のゴム弾性による復元力が釣り合っていれば、両側で誘電エラストマー層4の枚数が異なっていてもよい。 Further, the
1.4.抑制部材のバリエーション
抑制部材36は、第1接着部32と第2接着部34とを有し、第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が、誘電エラストマー層4の復元力によって第1方向に狭まることを制限することができ、かつ、厚さ方向の屈曲を許容できれば、任意の形態とすることができる。1.4. Variation of restraining member The restraining
図5、図6及び図7は、変形例の抑制部材36を有するアクチュエーターの縦断面の模式図である。図5に示すアクチュエーター101では、抑制部材36は、第1方向に延びる連結部43と、連結部43から、第1方向と第1方向に直交する第2方向とに直交する第3方向に延びて第1接着部32を形成する複数の第1支持部44と、連結部43から、第3方向に延びて第2接着部34を形成する複数の第2支持部45と、から構成されている。また、連結部43、第1支持部44及び第2支持部45は、一体的に形成されている。 5, 6 and 7 are schematic cross-sectional views of a vertical cross section of an actuator having a modified
アクチュエーター101では、アクチュエーター101の動作を阻害しないようにするため、第1方向に並ぶ複数の第1支持部44の間の間隔(第1間隔P1)は、第1支持部44の第1方向の幅よりも広い間隔で配置することがより好ましい。第2支持部45においても、第1方向に並ぶ複数の第2支持部45の間の間隔(第2間隔P2)は、第2支持部45の第1方向の幅よりも広い間隔で配置することがより好ましい。 In the
また、アクチュエーター101では、第1支持部44及び第2支持部45は、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の第2方向への収縮を抑制している。また、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20が駆動していない状態で、連結部43が第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が狭まらないようにする機能を担っている。 Further, in the
アクチュエーター101の抑制部材36の構造の利点の一つとしては、中間層30と各駆動層との接着部である第1接着部32及び第2接着部34が点接触ではなく面接触となるため、接着面積を確保しやすく、かつ第1支持部44及び第2支持部45の寸法や間隔を調節しやすいことが挙げられる。これにより第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の変形の形態を調整しやすくなる。 One of the advantages of the structure of the restraining
また、連結部43の機能としては、第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が狭まらないようにすることが挙げられるが、アクチュエーター101が屈曲する動作を妨げない程度のz軸方向(第1方向及び第2方向に直交する方向)の柔軟さを有することが好ましい。すなわち、連結部43の材質は、誘電エラストマー層4よりもヤング率(曲げ剛性)が低い材料が適している。 Further, the function of the connecting
連結部43、第1支持部44及び第2支持部45の材質としては、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、ポリ塩化ビニル、ポリ(メタ)アクリル酸などの汎用プラスチック、ポリカーボネート、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン、ポリイミドなどのエンジニアリングプラスチックなどを例示することができる。 Materials for the connecting
なお、アクチュエーター101の例では、第1支持部44及び第2支持部45が連結部43に対して対称に配置されているが、これに限定されず、第1支持部44及び第2支持部45が断面視において連結部43を挟んでずれて(例えば千鳥状に)配置されてもよい。 In the example of the
図6に示す変形例の抑制部材36を有するアクチュエーター102において、抑制部材36は、第1方向に延びる連結部43と、連結部43から、第3方向に延びて第1接着部32を形成する複数の第1蛇腹部材46と、連結部43から、第3方向に延びて第2接着部34を形成する複数の第2蛇腹部材47と、から構成されている。また、連結部43、第1蛇腹部材46及び第2蛇腹部材47は、一体的に形成されている。 In the
アクチュエーター102では、第1蛇腹部材46及び第2蛇腹部材47が、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の第2方向への収縮を抑制している。また、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20が駆動していない状態で、連結部43が第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が狭まらないようにする機能を担っている。 In the
また、アクチュエーター102では、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20は、第1蛇腹部材46及び第2蛇腹部材47の頂点部分と接着され、第1接着部32及び第2接着部34を形成しているが、第1蛇腹部材46及び第2蛇腹部材47の頂点を滑らかあるいは平坦にして、当該接着面積を増大させてもよい。連結部43と、第1蛇腹部材46及び第2蛇腹部材47との接着部分についても同様である。 Further, in the
アクチュエーター102の抑制部材36の構造の利点の一つとしては、アクチュエーター101の抑制部材36の構造における応力集中箇所となり得る連結部43と第1支持部44及び第2支持部45の接着端部を、第1蛇腹部材46及び第2蛇腹部材47によって解消した構造になっている点が挙げられる。 One of the advantages of the structure of the restraining
第1蛇腹部材46及び第2蛇腹部材47の材質としては、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、ポリ塩化ビニル、ポリ(メタ)アクリル酸などの汎用プラスチック、ポリカーボネート、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン、ポリイミドなどのエンジニアリングプラスチックなどを例示することができる。 Examples of the material of the
図7に示す変形例の抑制部材36を有するアクチュエーター103において、抑制部材36は、第2方向に直交する断面が円環の複数の円筒部材48を含み、隣り合う円筒部材48が、互いに離間する状態で第1方向に並べて配置され、隣り合う円筒部材48のそれぞれの内部を貫通する環状のリング部材49によって、隣り合う円筒部材48が連結されて構成されている。アクチュエーター103では、リング部材49が互いに干渉(接触)することにより、第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が狭まることを抑制する。 In the
アクチュエーター103では、円筒部材48は、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20の第2方向への収縮を抑制している。また、第1駆動層10及び第2駆動層20が駆動していない状態で、リング部材49が第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2が狭まらないようにしている。円筒部材48の材質には、金属、セラミックス、樹脂材料などが適用でき、リング部材49の材質には、汎用プラスチック、エンジニアリングプラスチック等を適用できる。 In the
アクチュエーター103の抑制部材36の構造の利点の一つとしては、あらかじめ中空を有した円筒部材48同士を、リング部材49によって連結した状態で固定できるため、組み立て工程において第1間隔P1及び第2間隔P2のずれを少なくきる点が挙げられる。 One of the advantages of the structure of the restraining
1.5.アクチュエーターの製造方法
本実施形態のアクチュエーターの製造方法の一例として、上述のアクチュエーター100の製造方法について説明する。1.5. Actuator Manufacturing Method As an example of the actuator manufacturing method of the present embodiment, the above-mentioned
まず、誘電エラストマー層4を2軸同時に延伸可能な治具に設置し、第1方向及び第2方向に同時に延伸する。次に誘電エラストマー層4に第1電極2及び第2電極6を組み付ける。第1電極2及び第2電極6はその形状によって組み付け方法が異なるが、誘電エラストマー層4を予め延伸した状態で組み付ける点は共通である。抑制部材36と誘電エラストマー層4を直接接着させる場合には、あらかじめ誘電エラストマー層4にマスキングを行って第1電極2及び第2電極6を組み付けてもよい。なお、第1電極2及び第2電極6は、カーボンを塗布して形成してもよいし、蒸着等の方法で形成されてもよい。 First, the
抑制部材36は外部に枠を設けて動かないように固定して組み立てる。その後第1電極2及び第2電極6及び誘電エラストマー層4と接着させる箇所に接着剤を塗布し、延伸された状態で第1電極2及び第2電極6を組み付けた誘電エラストマー層4と貼り合せて接着する。使用する接着剤の種類によっては、誘電エラストマー層4との貼り合わせの後に熱や光などで処理してもよい。 The restraining
例えば以上の工程により、上述のアクチュエーター100を製造することができる。 For example, the
2.第2実施形態
上述の第1実施形態のアクチュエーター100は、2つの駆動層を有していたが、駆動層は1つであってもよい。すなわち本実施形態に係るアクチュエーター200は、中間層30と、中間層30を挟んで対向して配置される駆動層10及び第1方向に延伸されたエラストマー層50と、を含む。2. 2. Second Embodiment The
図8は、本実施形態に係るアクチュエーター200の縦断面を示す模式図である。本実施形態のアクチュエーター200の中間層30及び駆動層10は、それぞれ第1実施形態で述べた中間層30及び第1駆動層10と同様であり、同様の符号を付して詳細な説明は省略する。ただし、アクチュエーター200においては、駆動層10では、誘電エラストマー層4は、第1方向に延伸されていても延伸されていなくてもよい。 FIG. 8 is a schematic view showing a vertical cross section of the
アクチュエーター200は、エラストマー層50を有している。エラストマー層50は、駆動層10に対して、中間層30を介して積層して配置されている。エラストマー層50は、アクチュエーター200において第1方向に延伸された状態であるので、第1方向に収縮しようとする復元力を有している。 The
エラストマー層50は、あらかじめ第1方向に延伸された状態で中間層30に固定される。本実施形態においても、第1方向は、エラストマー層50の厚さ方向に直交する方向であり、中間層30の抑制部材36が並ぶ方向である。 The
エラストマー層50は、第1方向に延伸された状態でアクチュエーター200の一部材となっているが、第1方向に交差する方向に延伸された状態であってもよい。例えば、エラストマー層50は、第1方向に直交する第2方向に延伸されていてもよい。ここで第2方向は、図示において「y」方向である。また、換言すると、エラストマー層50は、延伸された状態でアクチュエーター200を構成するが、当該延伸は一軸又は多軸の延伸であってよく、延伸の方向が第1方向の成分を含んでいればよい。 The
エラストマー層50の材質としては、絶縁性を有し、ゴム弾性を有するものであれば特
に限定されず、例えば、天然ゴム、イソプレンゴム、スチレン-ブタジエンゴム(SBR)、ニトリルゴム(NBR)、エチレン・プロピレン・ジエンゴム(EPDM)、アクリルゴム、シリコーンゴム、ウレタンゴム、アクリル系エラストマー等が挙げられる。The material of the
アクチュエーター200は、中間層30に対して片側にのみ、第1駆動層10を有している。そのため、アクチュエーター200は、エラストマー層50を内側として屈曲する動作をする。 The
アクチュエーター200において、誘電エラストマー層4は延伸していなくてもよい。その場合、中間層30及び第1駆動層10の複合体は、エラストマー層50の復元力に抗することができる程度に曲げ剛性を高くしてもよい。このようにすれば、アクチュエーター200が駆動しない状態において平面的な形状を維持できる。なお、図示しないが、アクチュエーター200は、駆動しない状態においてエラストマー層50を内側として屈曲していてもよい。 In the
エラストマー層50の材質は、誘電エラストマー層4と同じ材料を適用してもよいし、異なる材料を適用してもよい。具体的には工業的に利用されているゴム弾性を示す材料などがあげられる。例えば、天然ゴム、イソプレンゴム、スチレンブタジエンゴム、ブタジエンゴム、アクリロニトリルブダジエンゴム、エピクロロヒドリンゴム、クロロプレンゴム、ブチルゴム、エチレン・プロピレン・ジエンゴム、シリコーンゴム、ウレタンゴムなどが挙げられる。 As the material of the
エラストマー層50の延伸率は、誘電エラストマー層4の延伸率と同様に、適宜に設定される。 The stretch ratio of the
アクチュエーター200では、誘電エラストマー層4は、あらかじめ例えば第1方向にのみ延伸しておいてもよい。あらかじめ延伸された誘電エラストマー層4とする場合には、上述の第1実施形態のアクチュエーター100と同様に、エラストマー層50の復元力と、駆動層10の復元力とが、中間層30を挟んで釣り合うように設定すれば、平面形状を維持できる。この場合、抑制部材36には厚さ方向と第1方向とのヤング率の異方性の高い材料だけでなく、ヤング率が等方性を示す材料を用いることができる。 In the
3.実験例
以下、本発明を実験例によってさらに具体的に説明するが、本発明はこれらの実験例に限定されるものではない。3. 3. Experimental Examples Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail by means of experimental examples, but the present invention is not limited to these experimental examples.
図9に誘電エラストマーの一例であるシリコーンゴムA、B及びCの引張試験によって得られたS-S線図(応力-ひずみ曲線)を示す。シリコーンゴムA、B及びCは、それぞれ架橋剤の量を変量して架橋密度を調整したものである。引張試験は、JIS 1号ダンベルを23℃±2℃、引張速度0.5mm/minで、JIS K6251に準拠して行った。 FIG. 9 shows an SS diagram (stress-strain curve) obtained by a tensile test of silicone rubbers A, B, and C, which are examples of dielectric elastomers. Silicone rubbers A, B and C are obtained by varying the amount of the cross-linking agent to adjust the cross-linking density. The tensile test was performed on a JIS No. 1 dumbbell at 23 ° C. ± 2 ° C. and a tensile speed of 0.5 mm / min in accordance with JIS K6251.
シリコーンゴムAは、100%伸張時のモジュラスが高く、2軸による延伸が困難であった。 Silicone rubber A has a high modulus at the time of 100% stretching, and it is difficult to stretch it by two axes.
シリコーンゴムBは、適度なモジュラスを示す伸張領域が広く、アクチュエーター動作時の変形量も良好であった。 Silicone rubber B has a wide extension region showing appropriate modulus, and the amount of deformation during actuator operation is also good.
シリコーンゴムCは、低伸張領域におけるモジュラスが低すぎるため、延伸した状態での取り扱いが困難であった。 Since the modulus of the silicone rubber C in the low stretch region is too low, it is difficult to handle the silicone rubber C in the stretched state.
これらの結果より、アクチュエーターに用いる誘電エラストマー層に用いる材料としては、低ヤング率かつ高伸びを有した材料が好適であることが分かった。具体的には、誘電エラストマー層に用いる材質としては、600%伸張時のモジュラスが0.03MPa以上1.0MPa以下の範囲かつ破断伸びが800%以上であるような材料が適していることが分かった。 From these results, it was found that a material having a low Young's modulus and a high elongation is suitable as a material used for the dielectric elastomer layer used for the actuator. Specifically, as the material used for the dielectric elastomer layer, it was found that a material having a modulus in the range of 0.03 MPa or more and 1.0 MPa or less at 600% elongation and a breaking elongation of 800% or more is suitable. rice field.
また、シリコーンゴムBを用いて誘電エラストマー層を予め延伸させて用いる場合、図9における、50%以上500%以下の変位の領域で延伸することが好ましいことが分かった。 Further, when the dielectric elastomer layer was previously stretched using the silicone rubber B, it was found that it is preferable to stretch the dielectric elastomer layer in the displacement region of 50% or more and 500% or less in FIG.
さらに、延伸率が50%未満であると、アクチュエーターの動作時のゴム弾性による復元力が低くなることで、変形量が低下すると考えられる。一方、延伸率が500%を超えると、破断伸びに近い領域でアクチュエーターが動作することとなり、耐久性の点で好ましくない。 Further, when the draw ratio is less than 50%, it is considered that the amount of deformation is reduced because the restoring force due to the rubber elasticity during the operation of the actuator is lowered. On the other hand, if the stretching ratio exceeds 500%, the actuator operates in a region close to the breaking elongation, which is not preferable in terms of durability.
本発明は、上述した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、種々の変形が可能である。例えば、本発明は、実施形態で説明した構成と実質的に同一の構成(例えば、機能、方法及び結果が同一の構成、あるいは目的及び効果が同一の構成)を含む。また、本発明は、実施形態で説明した構成の本質的でない部分を置き換えた構成を含む。また、本発明は、実施形態で説明した構成と同一の作用効果を奏する構成又は同一の目的を達成することができる構成を含む。また、本発明は、実施形態で説明した構成に公知技術を付加した構成を含む。 The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications are possible. For example, the present invention includes substantially the same configurations as those described in the embodiments (eg, configurations with the same function, method and result, or configurations with the same purpose and effect). The present invention also includes a configuration in which a non-essential part of the configuration described in the embodiment is replaced. Further, the present invention includes a configuration having the same action and effect as the configuration described in the embodiment or a configuration capable of achieving the same object. Further, the present invention includes a configuration in which a known technique is added to the configuration described in the embodiment.
2…第1電極、4…誘電エラストマー層、6…第2電極、10…第1駆動層、20…第2駆動層、30…中間層、32…第1接着部、34…第2接着部、36…抑制部材、42…棒部材、43…連結部、44…第1支持部、45…第2支持部、46…第1蛇腹部材、47…第2蛇腹部材、48…円筒部材、49…リング部材、50…エラストマー層、100,101,102,103,200…アクチュエーター、P1…第1間隔、P2…第2間隔、G…距離2 ... 1st electrode, 4 ... Dielectric elastomer layer, 6 ... 2nd electrode, 10 ... 1st drive layer, 20 ... 2nd drive layer, 30 ... Intermediate layer, 32 ... 1st adhesive part, 34 ... 2nd adhesive part , 36 ... restraining member, 42 ... rod member, 43 ... connecting part, 44 ... first support part, 45 ... second support part, 46 ... first bellows member, 47 ... second bellows member, 48 ... cylindrical member, 49. ... Ring member, 50 ... Elastomer layer, 100, 101, 102, 103, 200 ... Actuator, P1 ... First interval, P2 ... Second interval, G ... Distance
Claims (5)
Translated fromJapanese前記第1駆動層及び前記第2駆動層は、それぞれ第1電極、第1方向に延伸された誘電エラストマー層及び第2電極を含み、
前記中間層は、抑制部材を含み、
前記抑制部材は、前記第1駆動層に接着する第1接着部と、前記第2駆動層に接着する第2接着部と、を含み、
前記第1方向において隣り合う前記第1接着部が互いに第1間隔を隔てて配置され、
前記第1方向において隣り合う前記第2接着部が互いに第2間隔を隔てて配置され、
前記抑制部材は、前記第1間隔及び前記第2間隔が、前記誘電エラストマー層の復元力によって前記第1方向に狭まることを制限する、アクチュエーター。It includes an intermediate layer and a first drive layer and a second drive layer arranged so as to face each other with the intermediate layer interposed therebetween.
The first drive layer and the second drive layer include a first electrode, a dielectric elastomer layer stretched in the first direction, and a second electrode, respectively.
The intermediate layer contains a restraining member and contains a restraining member.
The restraining member includes a first adhesive portion that adheres to the first drive layer and a second adhesive portion that adheres to the second drive layer.
The first adhesive portions adjacent to each other in the first direction are arranged at a distance of a first distance from each other.
The second adhesive portions adjacent to each other in the first direction are arranged at a distance of a second distance from each other.
The restraining member is an actuator that limits the first interval and the second interval from being narrowed in the first direction by the restoring force of the dielectric elastomer layer.
前記駆動層は、第1電極、誘電エラストマー層及び第2電極を含み、
前記中間層は、抑制部材を含み、
前記抑制部材は、前記駆動層に接着する第1接着部と、前記エラストマー層に接着する第2接着部と、を含み、
前記第1方向において隣り合う前記第1接着部が互いに第1間隔を隔てて配置され、
前記第1方向において隣り合う前記第2接着部が互いに第2間隔を隔てて配置され、
前記抑制部材は、前記第1間隔及び前記第2間隔が、前記エラストマー層の復元力によって前記第1方向に狭まることを制限する、アクチュエーター。It includes an intermediate layer, a drive layer arranged so as to face each other across the intermediate layer, and an elastomer layer stretched in a first direction.
The drive layer includes a first electrode, a dielectric elastomer layer and a second electrode.
The intermediate layer contains a restraining member and contains a restraining member.
The restraining member includes a first adhesive portion that adheres to the drive layer and a second adhesive portion that adheres to the elastomer layer.
The first adhesive portions adjacent to each other in the first direction are arranged at a distance of a first distance from each other.
The second adhesive portions adjacent to each other in the first direction are arranged at a distance of a second distance from each other.
The restraining member is an actuator that limits the first interval and the second interval from being narrowed in the first direction by the restoring force of the elastomer layer.
前記第1接着部は、前記第1方向に直交する第2方向に沿う直線上にあり、
前記第2接着部は、前記第2方向に沿う直線上にある、アクチュエーター。In claim 1 or 2,
The first adhesive portion is on a straight line along a second direction orthogonal to the first direction.
The second adhesive portion is an actuator on a straight line along the second direction.
前記抑制部材は、前記第1方向に直交する第2方向に延びる棒部材を複数含み、
前記棒部材の前記第2方向に垂直な断面の外形が円形であり、
隣り合う前記棒部材が、互いに接触する状態で前記第1方向に配置され、
前記第1接着部及び前記第2接着部が、それぞれ前記棒部材の外周面の一部である、アクチュエーター。In any one of claims 1 to 3,
The restraining member includes a plurality of rod members extending in a second direction orthogonal to the first direction.
The outer shape of the cross section of the rod member perpendicular to the second direction is circular, and the outer shape is circular.
Adjacent rod members are arranged in the first direction in a state of being in contact with each other.
An actuator in which the first adhesive portion and the second adhesive portion are each a part of the outer peripheral surface of the rod member.
前記抑制部材は、前記第1方向に延びる連結部と、
前記連結部から、前記第1方向と前記第1方向に直交する第2方向とに直交する第3方向に延びて前記第1接着部を形成する複数の第1支持部と、
前記連結部から、前記第3方向に延びて前記第2接着部を形成する複数の第2支持部と、
を含む、アクチュエーター。In any one of claims 1 to 3,
The restraining member includes a connecting portion extending in the first direction and a connecting portion.
A plurality of first support portions extending from the connecting portion in a third direction orthogonal to the first direction and the second direction orthogonal to the first direction to form the first adhesive portion.
A plurality of second support portions extending from the connecting portion in the third direction to form the second adhesive portion,
Including actuators.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018148287AJP7089979B2 (en) | 2018-08-07 | 2018-08-07 | Actuator |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018148287AJP7089979B2 (en) | 2018-08-07 | 2018-08-07 | Actuator |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020025392A JP2020025392A (en) | 2020-02-13 |
| JP7089979B2true JP7089979B2 (en) | 2022-06-23 |
Family
ID=69619120
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018148287AActiveJP7089979B2 (en) | 2018-08-07 | 2018-08-07 | Actuator |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7089979B2 (en) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018516039A (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2018-06-14 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェKoninklijke Philips N.V. | Actuators or sensor devices based on electroactive polymers |
| WO2018124308A1 (en) | 2016-12-29 | 2018-07-05 | ソニー株式会社 | Actuator and manufacturing method therefor |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07107763A (en)* | 1991-06-03 | 1995-04-21 | Polytec Design:Kk | Actuator |
| JPH05328762A (en)* | 1992-05-18 | 1993-12-10 | Fukoku Co Ltd | Actuator |
- 2018
- 2018-08-07JPJP2018148287Apatent/JP7089979B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018516039A (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2018-06-14 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェKoninklijke Philips N.V. | Actuators or sensor devices based on electroactive polymers |
| WO2018124308A1 (en) | 2016-12-29 | 2018-07-05 | ソニー株式会社 | Actuator and manufacturing method therefor |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020025392A (en) | 2020-02-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7400080B2 (en) | Elastomer actuator and a method of making an actuator | |
| JP5186160B2 (en) | Flexible electrode and actuator using the same | |
| US9761790B2 (en) | Stretch frame for stretching process | |
| WO2018124308A1 (en) | Actuator and manufacturing method therefor | |
| US11433425B2 (en) | Actuator, driving member, tactile sense presenting device, and driving device | |
| CN105229809A (en) | For the production of the method for multilayer electromechanical transducer | |
| JP6939819B2 (en) | Tactile presentation device | |
| JP2011083122A (en) | Actuator | |
| US7719164B2 (en) | Patterned dielectric elastomer actuator and method of fabricating the same | |
| JP7549356B2 (en) | Multi-layered electrostatic actuator | |
| JP5772221B2 (en) | Electrostrictive actuator and method of using the same | |
| JP7089979B2 (en) | Actuator | |
| JP5530585B2 (en) | Method for producing dielectric elastomer film for electrostrictive actuator | |
| KR101594432B1 (en) | Electrostatic force based actuator including poly-imide organic dielectric layer | |
| KR101797398B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing monolithic stack type dielectric elastomer actuator and monolithic stack type dielectric elastomer actuator | |
| JP5129998B2 (en) | Electrostrictive element | |
| KR102353298B1 (en) | Mechanism for variable stiffness using electro-stiction force | |
| KR102135089B1 (en) | An electro active fiber | |
| JP4063300B2 (en) | Electrostrictive polymer actuator | |
| JP2011176962A (en) | Driver | |
| US10217928B2 (en) | Curved piezoelectric device | |
| EP3268222B1 (en) | Electroactive polymers, methods of manufacture, and structures formed thereof | |
| JP5751044B2 (en) | Electrostrictive actuator | |
| JP2008198811A (en) | Electrostrictive actuator | |
| US10193053B2 (en) | Insulating base material with conductive pattern |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20210706 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20220518 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20220531 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20220613 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:7089979 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |