JP6277746B2 - Article discrimination system and article discrimination program - Google Patents
Article discrimination system and article discrimination programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6277746B2 JP6277746B2JP2014017167AJP2014017167AJP6277746B2JP 6277746 B2JP6277746 B2JP 6277746B2JP 2014017167 AJP2014017167 AJP 2014017167AJP 2014017167 AJP2014017167 AJP 2014017167AJP 6277746 B2JP6277746 B2JP 6277746B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- article
- control command
- determination
- type
- determination condition
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、医療などの分野においてカルテなどの書面と各種器具とを管理するシステムに関する。 The present invention relates to a system for managing a document such as a medical record and various instruments in the field of medical treatment and the like.
バーコードやRFタグなどを用いて薬品などを管理するシステムが知られている。例えば特許文献1は、カルテ、処方箋、薬袋あるいは診察券などに処方情報が書き込まれた第1ICタグを付与し、薬品の収容部には薬品情報が書き込まれた第2ICタグを付与し、それらのICタグから読み取った情報に基づいて薬品が一致するか否かを判定する薬管理システムを記載している。 A system for managing chemicals using a bar code, an RF tag, or the like is known. For example, Patent Document 1 gives a first IC tag in which prescription information is written in a medical record, prescription, medicine bag or examination ticket, and gives a second IC tag in which medicine information is written in a medicine container. A medicine management system that determines whether medicines match based on information read from an IC tag is described.
しかし、特許文献1のようなシステムでは、ICタグの読み込み作業やICタグから読み取った情報の比較作業の際に、いちいち作業者の入力・設定などが必要となる。例えば、第1ICタグと第2ICタグの情報を比較する場合には、まず作業者がシステムを第1ICタグの読み取りモードに設定してから第1ICタグを読み取り、次に作業者がシステムを第2ICタグの読み取りモード設定してから第2ICタグを読み取り、さらに作業者が比較の指示を入力してそれらの読み取り情報を比較することになる。よって、ICタグの読み取りや比較処理のたびに作業者の設定・入力などが必要となり作業が煩雑となる。 However, in a system such as Patent Document 1, it is necessary to input and set an operator each time when reading an IC tag or comparing information read from an IC tag. For example, when comparing the information of the first IC tag and the second IC tag, the operator first sets the system to the reading mode of the first IC tag and then reads the first IC tag, and then the operator configures the system to the second IC tag. After the tag reading mode is set, the second IC tag is read, and the operator inputs a comparison instruction to compare the read information. Therefore, each time an IC tag is read or a comparison process is performed, an operator's setting and input are required, and the work becomes complicated.
本発明は、医療その他の分野で利用される書面や各種器具などの物品が、同一の対象者に正しく対応しているかを簡便に確認することが可能な物品判別システムを提供することを目的とする。 It is an object of the present invention to provide an article discrimination system capable of easily confirming whether articles such as documents and various instruments used in medical and other fields correctly correspond to the same subject. To do.
本発明の1つの観点では、物品に付与された物品IDに基づいて同一の対象者に対応する物品を判別する物品判別システムは、物品から物品IDを読み取る読取手段と、物品種別IDと制御命令との対応を記憶する制御命令データベース、及び、物品種別IDと判定条件との対応を記憶する判定条件データベースを記憶する記憶部と、前記読取手段が読み取った物品IDに基づいて、対応する物品種別ID及び対象者IDを取得する第1の取得手段と、前記物品種別IDに基づいて、前記制御命令データベースから制御命令を取得する第2の取得手段と、前記第2の取得手段が取得した制御命令を実行する制御命令実行手段と、を備え、前記制御命令実行手段は、前記制御命令が判定条件設定命令である場合に、物品種別IDに基づいて前記判定条件データベースから判定条件を取得して設定し、前記制御命令が判定実行命令である場合に、物品種別ID及び/又は対象者IDが現在設定されている判定条件を満足するか否かを判定し、満足する場合に適正であることを示す判定結果を出力し、満足しない場合には不適正であることを示す判定結果を出力する。 In one aspect of the present invention, an article discrimination system that discriminates articles corresponding to the same target person based on an article ID assigned to an article includes a reading unit that reads an article ID from an article, an article type ID, and a control command A control command database that stores the correspondence between the storage unit, a storage unit that stores a determination condition database that stores the correspondence between the item type ID and the determination condition, and a corresponding article type based on the article ID read by the reading unit A first acquisition unit that acquires an ID and a target person ID; a second acquisition unit that acquires a control command from the control command database based on the article type ID; and a control acquired by the second acquisition unit. Control instruction execution means for executing an instruction, and the control instruction execution means, when the control instruction is a determination condition setting instruction, based on the article type ID Determination conditions are acquired from the constant condition database and set, and when the control command is a determination execution command, it is determined whether the item type ID and / or the target person ID satisfy the currently set determination condition When satisfied, a determination result indicating that it is appropriate is output, and when not satisfied, a determination result indicating that it is inappropriate is output.
上記の物品判別システムは、物品に付与された物品IDに基づいて、複数の物品が同一の対象者に対応するか否かを判定する。記憶部には、物品IDと対象者IDとの対応を記憶する対象者データベースと、物品種別IDと制御命令との対応を記憶する制御命令データベースと、物品種別IDと判定条件との対応を記憶する判定条件データベースと、が記憶されている。読取手段により物品から物品IDが読み取られ、物品IDに基づいて、物品種別IDと対象者IDとが取得される。また、物品種別IDに基づいて制御命令が取得される。制御命令が判定条件設定命令である場合、物品種別IDに基づいて前記判定条件データベースから判定条件が取得されて設定される。一方、制御命令が判定実行命令である場合、物品種別ID及び/又は対象者IDが現在設定されている判定条件を満足するか否かが判定される。判定条件が満足された場合には適正であること、即ち、物品が同一の対象者に対応することを示す判定結果が出力される。一方、判定条件が満足されない場合には不適正であること、即ち、物品が同一の対象者に対応しないことを示す判定結果が出力される。物品種別IDに対応付けられて制御命令が用意されているので、作業者が物品から物品IDを読み込むだけで判定条件が設定され、判定条件に従って判定が実行される。よって、複数の物品が同一の対象者に対応するか否かを簡便にチェックすることが可能となる。なお、「判定結果を出力する」とは、例えば判定結果が適正であるか不適正であるかを、端末装置の表示部に表示すること、音声により出力すること、判定結果を示すデータを他の端末装置などに送信することなどを含む。 The article discrimination system determines whether or not a plurality of articles correspond to the same target person based on the article ID assigned to the article. The storage unit stores a target person database that stores the correspondence between the article ID and the target person ID, a control instruction database that stores the correspondence between the article type ID and the control instruction, and a correspondence between the article type ID and the determination condition. And a determination condition database to be stored. The article ID is read from the article by the reading unit, and the article type ID and the target person ID are acquired based on the article ID. Further, a control command is acquired based on the article type ID. When the control command is a determination condition setting command, the determination condition is acquired and set from the determination condition database based on the article type ID. On the other hand, when the control command is a determination execution command, it is determined whether or not the article type ID and / or the target person ID satisfy the currently set determination condition. When the determination condition is satisfied, a determination result indicating that the determination is appropriate, that is, the article corresponds to the same subject, is output. On the other hand, when the determination condition is not satisfied, a determination result indicating that the determination is inappropriate, that is, the article does not correspond to the same subject is output. Since the control command is prepared in association with the article type ID, the determination condition is set only by the operator reading the article ID from the article, and the determination is executed according to the determination condition. Therefore, it is possible to easily check whether or not a plurality of articles correspond to the same target person. Note that “output the determination result” means, for example, displaying whether the determination result is appropriate or inappropriate on the display unit of the terminal device, outputting by voice, and other data indicating the determination result. Transmission to a terminal device or the like.
上記の物品判定システムの一態様では、前記記憶部は、物品IDと物品種別IDとの対応を記憶する物品種別データベースを記憶しており、前記第1の取得手段は、前記読取手段が読み取った物品IDに基づいて、前記物品種別データベースから物品種別IDを取得する。この態様では、物品には物品IDが一意に付与されており、物品種別データベースを参照することにより、物品種別IDが取得される。 In one aspect of the article determination system, the storage unit stores an article type database that stores correspondence between an article ID and an article type ID, and the first acquisition unit is read by the reading unit. Based on the item ID, the item type ID is acquired from the item type database. In this aspect, the article ID is uniquely assigned to the article, and the article type ID is acquired by referring to the article type database.
上記の物品判定システムの他の一態様では、前記判定条件データベースは1つの物品種別IDに対して複数の判定条件を記憶しており、前記制御命令実行手段は、1つの物品種別IDに対応する複数の判定条件が設定されている場合には、設定されている複数の判定条件の全てが満足されたときに適正であることを示す判定結果を出力し、満足されないときには不適正であることを示す判定結果を出力する。この態様では、詳細な判定条件を設定して物品の判定を行うことができる。 In another aspect of the article determination system, the determination condition database stores a plurality of determination conditions for one article type ID, and the control command execution unit corresponds to one article type ID. If multiple judgment conditions are set, output a judgment result indicating that it is appropriate when all of the set judgment conditions are satisfied, and if it is not satisfied, The judgment result shown is output. In this aspect, the article can be determined by setting detailed determination conditions.
上記の物品判定システムの他の一態様では、同一の物品について複数の工程が設定されており、前記判定条件データベースは複数の工程ごとに判定条件を記憶しており、前記制御命令実行手段は、前記制御命令が判定条件設定命令である場合に、現在の工程に対応する判定条件を前記判定条件データベースから取得して設定する。この態様では、複数の工程ごとに判定条件を設定しておき、現在の工程に対応する判定条件によって判定を行うことができる。 In another aspect of the article determination system, a plurality of processes are set for the same article, the determination condition database stores determination conditions for each of the plurality of processes, and the control command execution unit includes: When the control command is a determination condition setting command, the determination condition corresponding to the current process is acquired from the determination condition database and set. In this aspect, determination conditions can be set for each of a plurality of processes, and determination can be performed based on the determination conditions corresponding to the current process.
本発明の他の観点では、コンピュータと、物品種別IDと制御命令との対応を記憶する制御命令データベース、及び、物品種別IDと判定条件との対応を記憶する判定条件データベースを記憶する記憶部と、を備え、物品に付与された物品IDに基づいて同一の対象者に対応する物品を判別するシステムにおいて実行される物品判別プログラムは、物品から物品IDを読み取る読取手段、前記読取手段が読み取った物品IDに基づいて、対応する物品種別ID及び対象者IDを取得する第1の取得手段、前記物品種別IDに基づいて、前記制御命令データベースから制御命令を取得する第2の取得手段、前記第2の取得手段が取得した制御命令を実行する制御命令実行手段、として前記コンピュータを機能させ、前記制御命令実行手段は、前記制御命令が判定条件設定命令である場合に、物品種別IDに基づいて前記判定条件データベースから判定条件を取得して設定し、前記制御命令が判定実行命令である場合に、物品種別ID及び/又は対象者IDが現在設定されている判定条件を満足するか否かを判定し、満足する場合に適正であることを示す判定結果を出力し、満足しない場合には不適正であることを示す判定結果を出力する。このプログラムをコンピュータで実行することにより、物品判別システムを実現することができる。 In another aspect of the present invention, a computer, a control command database that stores the correspondence between the article type ID and the control command, and a storage unit that stores a determination condition database that stores the correspondence between the article type ID and the determination condition , And an article discrimination program executed in a system for discriminating an article corresponding to the same target person based on an article ID given to the article is a reading unit that reads the article ID from the article, and the reading unit reads First acquisition means for acquiring a corresponding article type ID and subject ID based on the article ID; second acquisition means for acquiring a control command from the control command database based on the article type ID; The control function execution means for executing the control instruction acquired by the acquisition means of 2 When the control instruction is a determination condition setting instruction, the determination condition is acquired and set from the determination condition database based on the article type ID, and when the control instruction is a determination execution instruction, the article type ID and / or It is determined whether or not the target person ID satisfies the currently set determination condition, and if it is satisfied, a determination result indicating that it is appropriate is output, and if not satisfied, it is determined that it is inappropriate. Output the result. By executing this program on a computer, an article discrimination system can be realized.
以下、図面を参照しながら、本発明の好適な実施形態について説明する。なお、以下の実施形態では、不妊治療分野において、受精卵などを観察したり、培養容器間で移動したりする際に、作業指示書(以下、単に「指示書」とする。)と、受精卵を入れた容器(シャーレ)とが同一の患者のものであることを確認するケースを想定している。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the following embodiments, when observing a fertilized egg or moving between culture vessels in the fertility treatment field, a work instruction (hereinafter simply referred to as “instruction”) and fertilization are performed. A case is assumed in which it is confirmed that the container (petri dish) containing the eggs belongs to the same patient.
[第1実施形態]
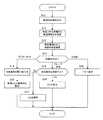
図1は、本実施形態の物品判別システムの概略構成を示す。物品判別システムは、患者用の指示書と器具とが同一の患者に対応するか否かを判別するものである。具体的には、図1に示すように、指示書10及び器具(シャーレ)20には、それぞれバーコード11が付与されている。作業者は、光学的なリーダ30を用いて、指示書10及び器具20のバーコードをそれぞれ読み取る。リーダ30は端末装置40に接続されている。[First Embodiment]
FIG. 1 shows a schematic configuration of an article discrimination system according to the present embodiment. The article discrimination system discriminates whether or not patient instructions and instruments correspond to the same patient. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 1, a
例えば、作業として受精卵の観察作業を行う場合を想定する。器具20には受精卵などの作業対象物が入っており、これを観察する場合、まず作業者は特定の患者用の指示書10と器具20とを用意する。そして、作業者は、リーダ30を用いて指示書10のバーコード11を読み取り、次に器具20のバーコード11を読み取る。指示書10と器具20とが正しく対応している場合、即ち、同一の患者のものである場合、端末装置40の表示画面には適正であることを示す「OK」の表示がなされる。一方、指示書10と器具20とが正しく対応していない場合、即ち、同一の患者のものでない場合、端末装置40の表示画面には不適正であることを示す「NG」の表示がなされる。 For example, it is assumed that a fertilized egg is observed as a work. The
指示書10は、作業者が特定の作業を行う際に参照する書面であり、作業者が行うべき作業の手順が記載されていたり、その作業により得られた情報を記入する記入欄が設けられていたりする。なお、「作業指示書」は一例であり、「工程表」、「カルテ」などの各種の名称の書面が指示書として使用される。器具20は、作業対象物を収納するものであり、シャーレ以外にも各種の器具が使用される。 The
指示書10のバーコード11には指示書10に一意に付与された物品IDが記録されている。一方、器具20のバーコード11には器具20に一意に付与された物品IDが記録されている。 An article ID uniquely assigned to the
図2は、端末装置40の構成を示すブロック図である。端末装置40は、一般的なPCなどにより構成することができ、端末装置40とリーダ30とを接続するためのI/F42と、制御部43と、ROM44と、RAM45と記憶部46とが共通のバス41に接続されてなる。 FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the
I/F42は、バーコード11からリーダ30が読み取ったIDなどの読取情報を制御部43へ供給する。また、端末装置40はI/F42を通じて制御信号を送ることにより、リーダ30による読み取りを制御する。ROM44は、後述する作業書や器具などの対応をチェックする比較処理を実行するためのプログラムを記憶している。RAM45は、リーダ30からの読取情報を一時的に記憶したりする際のワークメモリとして機能する。 The I /
制御部43は、CPUなどにより構成され、端末装置40全体を制御する。制御部43は、ROM44に記憶されている管理プログラムを実行することにより、後述の比較処理を行う。 The
記憶部46は、指示書10と器具20の対応をチェックするために必要な情報を記憶している。具体的に、記憶部46は、物品種別データベース(以下、「データベース」を「DB」と記す。)と、患者DBと、制御命令DBと、比較条件DBとを記憶している。 The
物品種別DBの例を図3(a)に示す。物品種別DBは、指示書10や器具20に一意に付与された物品IDと、その物品の種別を示す物品種別IDとを対応付けて記憶している。図3(a)の例では、物品ID「001」の物品は指示書であり、物品ID「001」に対応する物品種別IDは「指示書01」となっている。また、物品ID「002」の物品は容器であり、物品ID「002」に対応する物品種別IDは「容器01」となっている。 An example of the article type DB is shown in FIG. The article type DB stores an article ID uniquely assigned to the
患者DBの例を図3(b)に示す。患者DBは、指示書10や器具20に一意に付与された物品IDと、その物品に対応する患者を示す患者IDとを対応付けて記憶している。図3(b)の例では、物品ID「001」の物品は患者ID「9001」の患者に対応しており、物品ID「003」の物品は患者ID「9999」の患者に対応している。なお、患者は本発明における対象者の一例であり、患者IDは対象者IDの一例であり、患者DBは対象者DBの一例である。 An example of the patient DB is shown in FIG. The patient DB stores an article ID uniquely assigned to the
制御命令DBの例を図3(c)に示す。制御命令DBは、物品の種別を示す物品種別IDと、その物品の種別に対応して用意された制御命令とを対応付けて記憶している。「制御命令」とは、複数の物品が同一の患者に対応するか否かをチェックする際の処理を指示する命令である。図3(c)の例では、物品種別ID「指示書01」に対応する制御命令は「マスターセット」であり、物品種別ID「容器01」に対応する制御命令は「スレーブ比較」となっている。ここで、「マスター」とは比較を行う際に元になるもの(比較基準物、比較元)を指し、「マスターセット」とは比較基準物を設定する処理を指す。一方、「スレーブ」とは、比較を行う際の相手(比較対象物)を指し、「スレーブ比較」とはスレーブ(比較対象物)を比較条件に従って比較する処理を指す。例えば、いま、ある物品「B」が物品「A」に対応するか否かを判定するために両者を比較するものとする。この場合、まず、制御命令「マスターセット」を実行し、比較条件として物品「A」をマスター(比較基準物)に設定する。次に、物品「B」に対して制御命令「スレーブ比較」を実行して、スレーブ(比較対象物)である物品「B」がマスター(比較基準物)である物品「A」に対応するか否かを判定する。このように、本実施形態では、物品種別IDに制御命令を対応付けて記憶する。 An example of the control command DB is shown in FIG. The control instruction DB stores an article type ID indicating the article type and a control instruction prepared in correspondence with the article type in association with each other. The “control command” is a command for instructing processing when checking whether or not a plurality of articles correspond to the same patient. In the example of FIG. 3C, the control command corresponding to the item type ID “instruction 01” is “master set”, and the control command corresponding to the item type ID “container 01” is “slave comparison”. Yes. Here, “master” refers to a source (comparison reference object, comparison source) when performing comparison, and “master set” refers to processing for setting a comparison reference object. On the other hand, “slave” refers to a partner (comparison target) at the time of comparison, and “slave comparison” refers to processing for comparing slaves (comparison target) according to comparison conditions. For example, it is assumed that a certain item “B” is compared to determine whether or not an item “B” corresponds to the item “A”. In this case, first, the control command “master set” is executed, and the article “A” is set as a master (comparison reference object) as a comparison condition. Next, the control command “slave comparison” is executed for the article “B”, and the article “B” as the slave (comparison object) corresponds to the article “A” as the master (comparison reference object). Determine whether or not. Thus, in this embodiment, a control command is stored in association with an article type ID.
比較条件DBの例を図4(a)に示す。比較条件DBは、物品種別IDに対応付けて比較条件を記憶する。この場合の比較条件は、その物品種別IDに対応付けて制御命令DBに記憶されている制御命令を実行する際に設定される条件である。例えば、図3(c)に示すように、物品種別ID「指示書01」が付与されている物品に対しては、制御命令「マスターセット」が対応付けられている。よって、制御命令「マスターセット」が実行される際に、そのときの比較条件として図4(a)に示すように「患者ID=9001」が設定される。これにより、その後に制御命令「スレーブ比較」が実行される際の比較条件として、「患者ID=9001」が使用されることになる。なお、比較条件DBは本発明の判定条件DBの一例であり、制御命令「マスターセット」は本発明の判定条件設定命令の一例であり、制御命令「スレーブ比較」は本発明の判定実行命令の一例である。 An example of the comparison condition DB is shown in FIG. The comparison condition DB stores the comparison condition in association with the article type ID. The comparison condition in this case is a condition set when executing a control command stored in the control command DB in association with the article type ID. For example, as shown in FIG. 3C, a control command “master set” is associated with an article to which an article type ID “instruction 01” is assigned. Therefore, when the control command “master set” is executed, “patient ID = 9001” is set as a comparison condition at that time, as shown in FIG. Thus, “patient ID = 9001” is used as a comparison condition when the control command “slave comparison” is subsequently executed. The comparison condition DB is an example of the determination condition DB of the present invention, the control instruction “master set” is an example of the determination condition setting instruction of the present invention, and the control instruction “slave comparison” is the determination execution instruction of the present invention. It is an example.
このように、本実施形態では、指示書10、器具20などの物品に対して物品IDが一意に付与されている。また、物品IDに対しては、図3(a)に示すように物品種別IDが対応付けられるとともに、図3(b)に示すように患者IDが対応付けられている。さらに、物品種別IDに対しては、図3(c)に示すように制御命令が対応付けられているとともに、図4(a)に示すように比較条件が対応付けられている。 As described above, in the present embodiment, the article ID is uniquely assigned to the article such as the
上記の構成において、リーダ30は本発明の読取手段の一例であり、制御部43は本発明の第1の取得手段、第2の取得手段、及び、制御命令実行手段の一例である。 In the above configuration, the
次に、指示書10や器具20の対応をチェックするための比較処理について説明する。図5は、第1実施形態による比較処理のフローチャートである。この処理は、端末装置40の制御部43が予め用意されたプログラムを実行することにより実現される。また、この処理は、作業者が物品のバーコード11を読み取るたびに実行される。 Next, a comparison process for checking the correspondence between the
まず、作業者が指示書10や器具20などの物品に付されたバーコード11をリーダ30で読み取り、制御部43はリーダ30を通じて物品IDを読み込む(ステップS10)。 First, the operator reads the
次に、制御部43は、図3(b)に例示する患者DBを参照して物品IDに対応する患者IDを取得するとともに、図3(a)に例示する物品種別DBを参照して物品IDに対応する物品種別IDを取得する(ステップS11)。さらに、制御部43は、図3(c)に例示する制御命令DBを参照して、ステップS11で取得した物品種別IDに対応する制御命令を取得する(ステップS12)。 Next, the
次に、制御部43は、取得した制御命令が「マスターセット」であるか、「スレーブ比較」であるか、それら以外であるかを判定する(ステップS13)。制御命令が「マスターセット」である場合、制御部43は図4(a)に例示する比較条件DBを参照して、物品種別IDに対応する比較条件を問い合わせ(ステップS14)、取得した比較条件を設定する(ステップS15)。 Next, the
一方、制御命令が「スレーブ比較」である場合、制御部43は、その際に設定されている比較条件が満足されているか否かを判定する(ステップS16)。比較条件が満足されていない場合(ステップS16:No)、制御部43は端末装置40に「NG」を表示する(ステップS17)。一方、比較条件が満足されている場合(ステップS16:Yes)、物品が正しく対応していること、即ち同一の患者のものであることが確認されたので、制御部43は端末装置40に「OK」を表示する(ステップS18)。 On the other hand, when the control command is “slave comparison”, the
また、制御命令が「マスターセット」、「スレーブ比較」のいずれでもない場合、制御部43は端末装置40にエラー表示を行う(ステップS19)。 If the control command is neither “master set” nor “slave comparison”, the
次に、上記の比較処理の実行例を説明する。いま、作業者がリーダ30により指示書10のバーコード11を読み取ったとし、指示書10の物品IDが「001」であるとする。制御部43は、物品ID「001」を取得し(ステップS10)、患者DB及び物品種別DBから物品ID「001」に対応する患者ID「9001」及び物品種別ID「指示書01」をそれぞれ取得する(ステップS11)。さらに、制御部43は、制御命令DBから物品種別ID「指示書01」に対応する制御命令「マスターセット」を取得する(ステップS12)。 Next, an execution example of the above comparison process will be described. Now, assume that the operator reads the
ステップS13で制御命令が「マスターセット」であるので、制御部43は、比較条件DBから物品種別ID「指示書01」に対応する比較条件「患者ID=9001」を取得し、設定する(ステップS14、S15)。こうして、指示書10のバーコード11の読み取りにより、制御命令「マスターセット」が実行される。 Since the control command is “master set” in step S13, the
次に、作業者がリーダ30により器具20のバーコードを読み取ったとし、器具20の物品IDが「002」であるとする。制御部43は、物品ID「002」を取得し(ステップS10)、患者DB及び物品種別DBから物品ID「002」に対応する患者ID「9001」及び物品種別ID「容器01」をそれぞれ取得する(ステップS11)。さらに、制御部43は、制御命令DBから物品種別ID「容器01」に対応する制御命令「スレーブ比較」を取得する(ステップS12)。 Next, it is assumed that the operator reads the barcode of the
ステップS13で制御命令が「スレーブ比較」であるので、制御部43は、そのときに設定されている比較条件「患者ID=9001」が満足されているか否かを判定する(ステップS16)。この例では、患者IDは「9001」であるので、制御部43は端末装置40に「OK」を表示し(ステップS18)、処理を終了する。こうして、物品ID「001」である指示書10と、物品ID「002」である器具20とが正しく対応すること、即ち同一の患者のものであることが確認される。 Since the control command is “slave comparison” in step S13, the
いま、上記と同様に作業者が指示書10のバーコード11を読み取って比較条件「患者ID=001」が設定された状態で、仮に作業者が読み込んだ器具20の物品IDが「003」であったとする。この場合、制御部43は物品ID「003」に対応する患者ID「9999」と物品種別ID「容器02」を取得し(ステップS11)、さらに物品種別ID「容器02」に対応する制御命令「スレーブ比較」を取得する(ステップS12)。制御命令が「スレーブ比較」なので制御部43はステップS16へ進むが、患者ID「9999」はこのときの比較条件「患者ID=9001」を満足しないので(ステップS16:No)、制御部43は端末装置40に「NG」を表示する(ステップS17)。こうして、同一の患者のものでない指示書10と器具20とが誤って作業に使用されることが防止される。 Now, in the same manner as described above, the operator reads the
なお、上記のように作業書10と器具20の対応をチェックする比較処理を実行する場合、好ましくは作業者にルールとして「まず最初に作業書を読み込む」ことを知らせておくとよい。これにより、上記のようにまず作業書10が読み込まれてマスターセットが実行され、次に器具20が読み込まれてスレーブ比較が行われるので、チェックが円滑に進行する。 Note that when the comparison process for checking the correspondence between the
ただし、本実施形態では、作業者が器具20を先に読み込んでも問題はない。例えば、作業書10が読み込まれていない状態では「マスターセット」が実行されておらず、比較条件も設定されていない。よって、この状態で先に器具が読み込まれても、比較条件は満足されないので、ステップS17で「NG」が表示される。なお、マスターセットが行われておらず比較条件が未設定である場合には「マスターが読み込まれていません」などのエラーメッセージを表示するようにしてもよい。 However, in this embodiment, there is no problem even if the operator reads the
また、仮に、比較処理が連続して行われている場合には、1つ前の患者に対応する指示書10の読み込みによりマスターセットが行われ、その患者の比較条件が残ったままになっている可能性がある。この場合に作業者が作業書10を読み込む前に器具20を読み込むと、比較条件に設定されている患者IDと今回読み込んだ器具20の患者IDは一致しないので、やはりステップS17で「NG」が表示される。これにより、作業者は誤りであることに気づき、作業書10の読み取りから作業をやり直すことができる。 In addition, if the comparison process is continuously performed, the master set is performed by reading the
上記の例では、制御命令が「マスターセット」、「スレーブ比較」以外である場合、ステップS19でエラー表示がなされることとしたが、これは単なる一例であり、制御命令DBの構造によって各種の処理方法が考えられる。例えば、「マスターセット」、「スレーブ比較」以外の場合には、制御命令DBに制御命令を記憶しないこととしてもよい。この場合には、制御部43はステップS12で制御命令なし(取得不能)とし、ステップS13で制御命令なしと判定してステップS19でエラー表示をしてもよい。その代わりに、「マスターセット」、「スレーブ比較」以外の場合には、制御命令「エラー表示」を用意して制御命令DBに記憶しておいてもよい。この場合には、制御部43は、ステップS13で制御命令が「エラー表示」の場合にステップS19へ進めばよい。 In the above example, when the control command is other than “master set” and “slave comparison”, an error display is made in step S19. However, this is merely an example, and various control commands are used depending on the structure of the control command DB. A processing method can be considered. For example, in cases other than “master set” and “slave comparison”, the control command may not be stored in the control command DB. In this case, the
以上のように、本実施形態では、特定の物品について、物品が正しく対応しているか否か、即ち同一の患者の物品であるか否かをチェックするための制御命令が用意されている。そして、物品IDの読み込みに応じて、対応する制御命令が取得され、実行されて患者IDの比較が行われる。よって、作業者は、単に物品に付されたバーコードを順に読み込むだけで、複数の物品が同一の患者のものであるかを簡便にチェックすることができる。この点、従来の手法では、例えば指示書と器具が同一の患者のものであるかをチェックする場合、作業者はまず端末装置などを操作して指示書の読み込みモードに設定してからリーダで指示書のバーコードを読み込み、次に端末装置などを操作して器具の読み込みモードに設定してからリーダで器具のバーコードを読み込み、さらに場合によっては端末装置などに両者を比較する指示を入力する必要があった。これに対して、本実施形態では、作業者は端末装置40を操作する必要なく、指示書や器具のバーコードを次々と読み取るだけで、それらが同一の患者のものであるか否かを容易にチェックすることが可能となる。 As described above, in this embodiment, a control command for checking whether or not an article corresponds correctly, that is, whether or not the article is the same patient is prepared. And according to reading of article | item ID, the corresponding control command is acquired and executed, and patient ID is compared. Therefore, the operator can simply check whether the plurality of articles belong to the same patient by simply reading the barcodes attached to the articles in order. In this regard, in the conventional method, for example, when checking whether the instruction sheet and the instrument belong to the same patient, the operator first sets the instruction sheet reading mode by operating the terminal device, etc. Read the barcode of the instruction book, then operate the terminal device etc. to set the instrument reading mode, then read the barcode of the instrument with a reader, and in some cases input the instruction to compare both to the terminal device etc. There was a need to do. On the other hand, in this embodiment, the operator does not need to operate the
[第2実施形態]
第1実施形態では、比較条件として1つの患者IDの一致を規定していた。第2実施形態では、比較条件を細かく設定した例を示す。なお、この点以外は、第2実施形態は基本的に第1実施形態と同様である。[Second Embodiment]
In 1st Embodiment, the agreement of one patient ID was prescribed | regulated as a comparison condition. The second embodiment shows an example in which the comparison conditions are set finely. Except for this point, the second embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment.
図4(b)〜(d)は、第2実施形態による比較条件の例を示す。図4(b)の例では、比較条件として患者ID及び容器IDの一致が要求される。即ち、患者IDが「9001」であり、かつ、容器IDが「容器01」である器具のみが正しい器具と判定される。 4B to 4D show examples of comparison conditions according to the second embodiment. In the example of FIG. 4B, matching of the patient ID and the container ID is required as a comparison condition. That is, only an instrument having a patient ID “9001” and a container ID “container 01” is determined to be a correct instrument.
図4(c)の例は、1つの指示書10に対して、2つの器具20が用意される作業についての比較条件の例を示している。例えば、作業対象物を1つの容器からもう1つの容器に移し替える作業などを行う場合に相当する。この例では、患者IDが「9001」であり、かつ、容器IDが「容器01」である器具が2つ揃ったときに比較条件が満足したと判定される。 The example of FIG. 4C shows an example of comparison conditions for the work of preparing two
図4(d)の例は、患者ID及び容器IDが異なる2つの器具が用意される作業についての比較条件の例を示している。例えば、ある作業対象物について父親用の容器と母親用の容器を使用して作業を行うような場合に相当する。この例では、患者IDが「9001」(父親に対応)かつ容器IDが「容器01」である1つの器具と、患者IDが「9002」(母親に対応)かつ容器IDが「容器02」であるもう1つの器具とが揃ったときに比較条件が満足したと判定される。 The example of FIG. 4D shows an example of comparison conditions for an operation in which two instruments having different patient IDs and container IDs are prepared. For example, this corresponds to a case where a certain work target is operated using a container for a father and a container for a mother. In this example, the patient ID is “9001” (corresponding to the father) and the container ID is “container 01”, the patient ID is “9002” (corresponding to the mother), and the container ID is “container 02”. It is determined that the comparison condition is satisfied when a certain other instrument is assembled.
図6は第2実施形態による比較処理のフローチャートを示す。この処理も、端末装置40の制御部43が予め用意されたプログラムを実行することにより実現される。また、この処理は、作業者が物品のバーコード11を読み取るたびに実行される。 FIG. 6 shows a flowchart of the comparison process according to the second embodiment. This process is also realized by the
図6のフローチャートにおいて、ステップS20〜S25は図5に示す第1実施形態のステップS10〜S15と同様であり、ステップS31は第1実施形態のステップS19と同様であるので、説明を省略する。なお、ステップS24、S25においては、図4(b)〜(d)に例示するような複数のIDや器具の比較を含む比較条件が取得され、設定される。 In the flowchart of FIG. 6, steps S20 to S25 are the same as steps S10 to S15 of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 5, and step S31 is the same as step S19 of the first embodiment, and thus description thereof is omitted. In steps S24 and S25, comparison conditions including a comparison of a plurality of IDs and instruments as exemplified in FIGS. 4B to 4D are acquired and set.
ステップS23で制御命令が「スレーブ比較」であった場合、制御部43は、取得した物品の患者IDや物品種別IDが、そのとき設定されている比較条件に含まれているが否かを判定する(ステップS26)。含まれていない場合(ステップS26:No)、その物品は正しい対応関係に無いので、制御部43は「NG」を表示する(ステップS27)。 When the control command is “slave comparison” in step S23, the
一方、取得した物品の患者IDや物品種別IDがそのときの比較条件に含まれている場合(ステップS26:Yes)、制御部43はその物品ですべての比較条件が満足されたか否かを判定する(ステップS28)。すべての比較条件が満足されていない場合(ステップS28:No)、制御部43は「部分OK」を表示する(ステップS29)。「部分OK」は、その物品は正しい対応関係にあるが、対応する他の物品が未だ存在することを作業者に知らせる意味を持つ。これにより、作業者は他の物品の比較処理を続行することになる。一方、すべての比較条件が満足された場合(ステップS28:Yes)、制御部43は「OK」を表示する(ステップS30)。 On the other hand, when the acquired patient ID and article type ID are included in the comparison condition at that time (step S26: Yes), the
[第3実施形態]
第3実施形態では、作業者が複数の工程からなる一連の作業を実施する場合を想定し、工程ごとに比較条件が用意される例を示す。なお、この点以外は、第3実施形態は基本的に第1実施形態と同様である。[Third Embodiment]
In 3rd Embodiment, the case where an operator implements a series of operation | work which consists of a some process is assumed, and the example by which a comparison condition is prepared for every process is shown. Except for this point, the third embodiment is basically the same as the first embodiment.
図7(a)は、作業工程DBの例を示す。作業工程DBは端末装置40の記憶部46に記憶されており、物品IDごとに作業工程を対応付けて記憶している。図7(a)の例では、物品ID「001」の物品は「工程02」で使用され、物品ID「010」の物品は「工程01」で使用されることが示されている。 FIG. 7A shows an example of the work process DB. The work process DB is stored in the
図7(b)は、第3実施形態による比較条件の例を示す。物品種別IDと工程IDに対応付けて比較条件が設定されている。この例は、「工程02」において物品種別IDが「指示書01」である物品が読み込まれた場合に設定される比較条件を示している。 FIG. 7B shows an example of comparison conditions according to the third embodiment. Comparison conditions are set in association with the item type ID and the process ID. This example shows a comparison condition that is set when an article having an article type ID “instruction 01” is read in “Step 02”.
図7(c)は、第3実施形態による他の比較条件の例を示す。物品種別IDと工程IDに対応付けて比較条件が設定されている。この例は、「工程02」において物品種別IDが「指示書01」である物品が読み込まれた場合に設定される比較条件を示している。なお、図7(c)の例では、第2実施形態のように比較条件として複数の器具が設定されている。 FIG. 7C shows another example of comparison conditions according to the third embodiment. Comparison conditions are set in association with the item type ID and the process ID. This example shows a comparison condition that is set when an article having an article type ID “instruction 01” is read in “Step 02”. In the example of FIG. 7C, a plurality of instruments are set as comparison conditions as in the second embodiment.
また、第3実施形態では、端末装置40のRAM45又は記憶部46は、物品IDに対応付けて現在の工程を示す工程IDを記憶している。制御部43は、物品IDに基づいて、現在の工程がどの工程であるかを取得することができる。 In the third embodiment, the
図8は第3実施形態による比較処理のフローチャートを示す。この処理も、端末装置40の制御部43が予め用意されたプログラムを実行することにより実現される。また、この処理は、作業者が物品のバーコード11を読み取るたびに実行される。 FIG. 8 shows a flowchart of the comparison process according to the third embodiment. This process is also realized by the
図8のフローチャートにおいて、ステップS40〜S43は図5に示す第1実施形態のステップS10〜S13と同様であり、ステップS47〜52は図6に示す第2実施形態のステップS26〜S31と同様であるので、説明を省略する。 In the flowchart of FIG. 8, steps S40 to S43 are the same as steps S10 to S13 of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 5, and steps S47 to S52 are the same as steps S26 to S31 of the second embodiment shown in FIG. Since there is, description is abbreviate | omitted.
ステップS23で制御命令が「マスターセット」であった場合、制御部43は、現在の工程IDを取得する(ステップS44)。次に、制御部43は、現在の工程IDと、物品種別IDとに基づいて比較条件を問い合わせ(ステップS45)、取得した比較条件を設定する(ステップS46)。 When the control command is “master set” in step S23, the
このように、第3実施形態では、工程ごとに比較条件が設定されているので、現在の工程IDを取得して比較条件を取得、設定することにより比較処理が行われる。これにより、複数の工程からなる一連の作業について、工程ごとに細かく比較条件を設定することができる。 Thus, in the third embodiment, since the comparison condition is set for each process, the comparison process is performed by acquiring the current process ID and acquiring and setting the comparison condition. Thereby, about a series of work which consists of a plurality of processes, a comparison condition can be set up finely for every process.
[変形例]
(1)上記の例では、指示書、器具などの物品に対して一意に物品IDが付与されるともに、物品種別DBにおいて物品IDと物品種別IDとを対応付けている。その代わりに、物品IDの一部に物品種別IDが含まれるように物品IDを設定することとしてもよい。この場合には、物品種別DBは不要となり、制御部43は物品IDを取得することにより、その一部から物品種別IDを知ることができる。同様に、物品IDの一部に患者ID(対象者ID)が含まれるように物品IDを設定することとしてもよい。さらには、物品IDに物品種別IDと患者IDとの両方が含まれるように物品IDを構成してもよい。例えば、物品種別IDと患者IDを繋げたものを物品IDとしてもよい。[Modification]
(1) In the above example, an article ID is uniquely assigned to an article such as an instruction sheet or an instrument, and the article ID and the article type ID are associated with each other in the article type DB. Instead, the article ID may be set so that the article type ID is included in a part of the article ID. In this case, the article type DB becomes unnecessary, and the
(2)上記の例においては、物品種別DB、患者DB、制御命令DB、比較条件DBを端末装置40の記憶部46に設けているが、本発明の適用はこれには限られない。例えば、端末装置40がネットワークを通じて病院などのセンターサーバと接続されている場合には、これらのDBをセンターサーバ上に設置し、必要なときに端末装置40からアクセスして必要な情報を取得することとしてもよい。 (2) In the above example, the article type DB, the patient DB, the control command DB, and the comparison condition DB are provided in the
(3)上記の例では、1次元のバーコードを利用して患者IDを付与しているが、これ以外に2次元バーコード(いわゆるQRコード(登録商標)など)やICタグなど、各種の機械読み取り可能な標識を利用することができる。また、バーコードのようなコードパターンではなく、数字や文字によるIDを付与し、カメラによる撮影画像からOCR処理によりIDを取得して比較を行うこととしてもよい。 (3) In the above example, a patient ID is assigned using a one-dimensional barcode, but in addition to this, various other types such as a two-dimensional barcode (so-called QR code (registered trademark)), an IC tag, etc. Machine readable signs can be utilized. Also, instead of a code pattern such as a bar code, IDs with numbers or characters may be assigned, and IDs may be obtained from images captured by a camera by OCR processing for comparison.
また、バーコードなどの標識を器具に付与する位置は上記の例のように器具の側面には限られず、器具や容器の底面、蓋などでもよい。また、標識をシールにより器具に貼付する場合にはシールの印刷は通常印刷でも鏡面印刷でもよい。 Further, the position where a label such as a barcode is applied to the instrument is not limited to the side surface of the instrument as in the above example, but may be the bottom surface of the instrument or container, a lid, or the like. In addition, when the sign is affixed to the instrument with a seal, the seal may be printed by normal printing or mirror printing.
(4)比較条件として、作業者IDを追加してもよい。例えば、比較処理の開始時に作業者の社員証などから作業者IDを読み取り、比較条件に作業者IDの条件を含める。これにより、作業の重要度などに応じて、作業者を限定することができる。例えば、特定の作業(受精卵の観察指示における確認)は、特定の作業者(培養士EさんとFさんのみ)が行えるようにしてもよい。このように作業者IDを比較条件に加えることにより、物品の組み合わせのみならず、作業者が適正な人物であるか否かを同時にチェックすることが可能となる。 (4) An operator ID may be added as a comparison condition. For example, the worker ID is read from the employee ID card of the worker at the start of the comparison process, and the condition of the worker ID is included in the comparison condition. Thereby, an operator can be limited according to the importance etc. of work. For example, a specific worker (confirmation in the observation instruction of a fertilized egg) may be performed by a specific worker (only the incubators E and F). In this way, by adding the worker ID to the comparison condition, it is possible to simultaneously check whether the worker is an appropriate person as well as a combination of articles.
(5)上記の実施形態では、制御部43は、比較条件が満足されている場合に端末装置40に「OK」を表示し、比較条件が満足されていない場合に端末装置40に「NG」を表示している。しかし、本発明では、比較処理の結果の出力方法はこれには限られない。例えば、端末装置40への表示の代わりに、又は、表示に加えて、比較結果を音声出力してもよい。また、比較結果を示すデータを他の端末やサーバなどに送信してもよい。 (5) In the above embodiment, the
(6)上記の実施形態では、不妊治療分野における卵子や受精卵の観察、移動作業に対して本発明を適用した例を示しているが、そのほかに再生医療分野における細胞の管理や、病理検査分野における細胞の管理などにも本発明の適用が可能である。 (6) In the above-described embodiment, an example in which the present invention is applied to the observation and movement of eggs and fertilized eggs in the infertility treatment field is shown, but in addition, cell management and pathological examination in the field of regenerative medicine The present invention can also be applied to cell management in the field.
10 指示書
11 バーコード
20 器具
30 リーダ
40 端末装置
43 制御部
46 記憶部DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (5)
Translated fromJapanese物品から物品IDを読み取る読取手段と、
物品種別IDと制御命令との対応を記憶する制御命令データベース、及び、物品種別IDと判定条件との対応を記憶する判定条件データベースを記憶する記憶部と、
前記読取手段が読み取った物品IDに基づいて、対応する物品種別ID及び対象者IDを取得する第1の取得手段と、
前記物品種別IDに基づいて、前記制御命令データベースから制御命令を取得する第2の取得手段と、
前記第2の取得手段が取得した制御命令を実行する制御命令実行手段と、
を備え、
前記制御命令実行手段は、前記制御命令が判定条件設定命令である場合に、物品種別IDに基づいて前記判定条件データベースから判定条件を取得して設定し、前記制御命令が判定実行命令である場合に、物品種別ID及び/又は対象者IDが現在設定されている判定条件を満足するか否かを判定し、満足する場合に適正であることを示す判定結果を出力し、満足しない場合には不適正であることを示す判定結果を出力することを特徴とする物品判別システム。An article discrimination system that discriminates articles corresponding to the same target person based on an article ID assigned to an article,
Reading means for reading the article ID from the article;
A control command database for storing the correspondence between the article type ID and the control command, and a storage unit for storing a determination condition database for storing the correspondence between the article type ID and the determination condition;
First acquisition means for acquiring a corresponding article type ID and subject ID based on the article ID read by the reading means;
Second acquisition means for acquiring a control command from the control command database based on the article type ID;
Control instruction execution means for executing the control instruction acquired by the second acquisition means;
With
When the control command is a determination condition setting command, the control command execution means acquires and sets the determination condition from the determination condition database based on an article type ID, and the control command is a determination execution command To determine whether the item type ID and / or the subject person ID satisfy the currently set determination condition, and output a determination result indicating that the item type ID and / or the subject person ID are appropriate if satisfied. An article discrimination system that outputs a judgment result indicating improperness.
前記第1の取得手段は、前記読取手段が読み取った物品IDに基づいて、前記物品種別データベースから物品種別IDを取得することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の物品判別システム。The storage unit stores an article type database that stores correspondence between article IDs and article type IDs,
The article determination system according to claim 1, wherein the first acquisition unit acquires an article type ID from the article type database based on the article ID read by the reading unit.
前記制御命令実行手段は、1つの物品種別IDに対応する複数の判定条件が設定されている場合には、設定されている複数の判定条件の全てが満足されたときに適正であることを示す判定結果を出力し、満足されないときには不適正であることを示す判定結果を出力することを特徴とする請求項1又は2に記載の物品判別システム。The determination condition database stores a plurality of determination conditions for one article type ID,
When a plurality of determination conditions corresponding to one article type ID are set, the control command execution means indicates that the control instruction execution means is appropriate when all of the set determination conditions are satisfied. 3. The article determination system according to claim 1, wherein a determination result is output, and a determination result indicating that the determination result is inappropriate is output when the determination result is not satisfied.
前記判定条件データベースは複数の工程ごとに判定条件を記憶しており、
前記制御命令実行手段は、前記制御命令が判定条件設定命令である場合に、現在の工程に対応する判定条件を前記判定条件データベースから取得して設定することを特徴とする請求項1乃至3のいずれか一項に記載の物品判別システム。Multiple processes are set for the same article,
The determination condition database stores determination conditions for each of a plurality of steps,
The control command execution means acquires and sets a determination condition corresponding to a current process from the determination condition database when the control instruction is a determination condition setting instruction. The article discrimination system according to any one of claims.
物品から物品IDを読み取る読取手段、
前記読取手段が読み取った物品IDに基づいて、対応する物品種別ID及び対象者IDを取得する第1の取得手段、
前記物品種別IDに基づいて、前記制御命令データベースから制御命令を取得する第2の取得手段、
前記第2の取得手段が取得した制御命令を実行する制御命令実行手段、
として前記コンピュータを機能させ、
前記制御命令実行手段は、前記制御命令が判定条件設定命令である場合に、物品種別IDに基づいて前記判定条件データベースから判定条件を取得して設定し、前記制御命令が判定実行命令である場合に、物品種別ID及び/又は対象者IDが現在設定されている判定条件を満足するか否かを判定し、満足する場合に適正であることを示す判定結果を出力し、満足しない場合には不適正であることを示す判定結果を出力することを特徴とする物品判別プログラム。A computer, a control command database for storing correspondence between the article type ID and the control command, and a storage unit for storing a determination condition database for storing the correspondence between the article type ID and the determination condition, and are provided to the article. An article discrimination program executed in a system for discriminating articles corresponding to the same target person based on the article ID,
Reading means for reading the article ID from the article;
First acquisition means for acquiring a corresponding article type ID and subject ID based on the article ID read by the reading means;
Second acquisition means for acquiring a control command from the control command database based on the article type ID;
Control command execution means for executing the control command acquired by the second acquisition means;
Function the computer as
When the control command is a determination condition setting command, the control command execution means acquires and sets the determination condition from the determination condition database based on an article type ID, and the control command is a determination execution command To determine whether the item type ID and / or the subject person ID satisfy the currently set determination condition, and output a determination result indicating that the item type ID and / or the subject person ID are appropriate if satisfied. An article determination program characterized by outputting a determination result indicating improperness.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014017167AJP6277746B2 (en) | 2014-01-31 | 2014-01-31 | Article discrimination system and article discrimination program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014017167AJP6277746B2 (en) | 2014-01-31 | 2014-01-31 | Article discrimination system and article discrimination program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015143935A JP2015143935A (en) | 2015-08-06 |
| JP6277746B2true JP6277746B2 (en) | 2018-02-14 |
Family
ID=53888930
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014017167AExpired - Fee RelatedJP6277746B2 (en) | 2014-01-31 | 2014-01-31 | Article discrimination system and article discrimination program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6277746B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102169066B1 (en)* | 2019-01-02 | 2020-10-22 | 나이스평가정보 주식회사 | A system for monitoring financial risk based on technology information and a method for the same |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001044412A (en)* | 1999-07-30 | 2001-02-16 | Sony Corp | Semiconductor simulation apparatus |
| JP2002117144A (en)* | 2000-07-31 | 2002-04-19 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | System for managing administration of medicine or the like |
| JP2002092182A (en)* | 2000-09-13 | 2002-03-29 | Techno Medica Co Ltd | Method for preparing medicine for injection and confirmation device for preparing medicine for injection |
| JP2002207958A (en)* | 2001-01-12 | 2002-07-26 | Toshiba Corp | Identifier interpreting apparatus, computer-readable recording medium recording program, and method of executing processing by computer system |
| JP2003030323A (en)* | 2001-07-17 | 2003-01-31 | Moroo Co Ltd | Nursing support system |
| JP2005063085A (en)* | 2003-08-11 | 2005-03-10 | Nec Soft Ltd | System, method and program for providing point |
| JP2005279194A (en)* | 2004-03-31 | 2005-10-13 | Techno Medica Co Ltd | Patient collating device |
| JP2006092388A (en)* | 2004-09-27 | 2006-04-06 | Keyence Corp | Data collator |
- 2014
- 2014-01-31JPJP2014017167Apatent/JP6277746B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015143935A (en) | 2015-08-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2021232819B2 (en) | Method and system for patient and biological sample identification and tracking | |
| US7438216B2 (en) | Medical information access and processing system | |
| US20180342317A1 (en) | Barcode database and software update system | |
| JP5098056B2 (en) | Medical management apparatus, medical management method, and medical management program | |
| CN104854591A (en) | Apparatus and methods for storage and transfer of patient information using biological sample cards with short range communications | |
| ITMI20111795A1 (en) | A SYSTEM FOR MANAGEMENT OF RACKS AND TUBES POSITION FOR CLINICAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORIES | |
| JP2019040624A (en) | Research information management system | |
| US12119109B2 (en) | Method and devices for tracking laboratory resources | |
| JP5134938B2 (en) | Assembly work support method and assembly work support system | |
| JP6277746B2 (en) | Article discrimination system and article discrimination program | |
| US20140337056A1 (en) | Sampling method for performing sampling in an unmistakeable manner | |
| US12002577B2 (en) | Apparatus, system and methods for management of medical supplies | |
| US12093776B2 (en) | Method for capturing computer-readable codes, reading device and reading system | |
| JP6295570B2 (en) | Management system, management program, container, and kit comprising container and identification tag | |
| JP2010250597A (en) | Agreement management system | |
| JP6387612B2 (en) | Management system and management program | |
| Florentino et al. | Hospital automation system RFID-based: technology embedded in smart devices (cards, tags and bracelets) | |
| US20090327348A1 (en) | Job support system and its method | |
| US11967417B2 (en) | System with a smart filtration and/or diffusion device | |
| JP2010108332A (en) | Inspection request system terminal unit | |
| JP6958378B2 (en) | Programs and processing equipment | |
| Rao et al. | Implementation of bar coded wristbands in a large academic medical center: impact on point of care error rates | |
| JP2024152840A (en) | Medical information linking system, medical information linking method, and computer program for medical information linking | |
| JP2023180417A (en) | System, processor, and method for supporting part replacement operation in production facility | |
| JP2006119856A (en) | Mobile terminal device and medical practice management method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20161125 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20171122 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20171219 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20180101 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:6277746 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |