JP6232774B2 - Morphological analyzer, morphological analysis method, and morphological analysis program - Google Patents
Morphological analyzer, morphological analysis method, and morphological analysis programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6232774B2 JP6232774B2JP2013133481AJP2013133481AJP6232774B2JP 6232774 B2JP6232774 B2JP 6232774B2JP 2013133481 AJP2013133481 AJP 2013133481AJP 2013133481 AJP2013133481 AJP 2013133481AJP 6232774 B2JP6232774 B2JP 6232774B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- word
- morpheme
- analysis
- words
- compound
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Machine Translation (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、単語辞書を用いる、形態素解析装置、形態素解析方法、及び、形態素解析プログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to a morpheme analyzer, a morpheme analysis method, and a morpheme analysis program using a word dictionary.
「形態素解析装置」とは、入力文字列を、入力文字列を構成する形態素の列に分割する処理である「形態素解析」を行う装置である。ここで、「形態素」とは、ある言語で書かれた、入力された、又は、話された文を、それ以上分割したら意味をなさなくなるところまで分割して抽出された、言語で意味を持つ最小単位の文字列(文字コード等の列)であり、品詞種別が特定された単語である。尚、複数の品詞種別を持ちうる文字列は、文字列としては一つであっても、品詞種別毎に異なる形態素として扱われる(文字列及び品詞種別の組毎に辞書中で与えられたコード等で表現される。)。又、入力された、又は、話された文の場合には、形態素は、文字列ではなく、入力や音素等を表現するコード等の列として扱われることもある。 The “morpheme analyzer” is a device that performs “morpheme analysis”, which is a process of dividing an input character string into morpheme strings that constitute the input character string. Here, a “morpheme” has a meaning in a language that has been extracted and extracted to the point where it does not make sense to divide a sentence that has been written, entered, or spoken in a certain language and further divided It is a character string (character code or the like) in the smallest unit, and is a word with a specified part of speech type. A character string that can have a plurality of part of speech types is treated as a different morpheme for each part of speech type even if there is only one character string (a code given in the dictionary for each set of character string and part of speech types) Etc.). In the case of a sentence that has been input or spoken, the morpheme may not be a character string, but may be treated as a string of codes or the like representing input or phonemes.
形態素解析の手法には、さまざまな方法がある。例えば、形態素の列全体でコストの総和が最小になる形態素の列を最適な分割結果として選択する方法がある。この方法では、入力文字列は、複数の形態素を含む「形態素列」に分割される。このとき、入力文字列中の分割位置を変えることにより、複数の形態素列が作成される。 There are various methods for morphological analysis. For example, there is a method of selecting a morpheme column that minimizes the total cost of the entire morpheme column as an optimal division result. In this method, the input character string is divided into “morpheme strings” including a plurality of morphemes. At this time, a plurality of morpheme strings are created by changing the division position in the input character string.
それぞれの形態素列に含まれる2個の形態素間の接続に対しては、コスト(「接続コスト」ともいう。)が定義される。「コスト」とは、複数の形態素列の中から最も適切なものを選択するために用いられる指標である。そして、複数の形態素列の中から、コストの総和が最小となる形態素列が選択される。 A cost (also referred to as “connection cost”) is defined for the connection between two morphemes included in each morpheme string. “Cost” is an index used to select the most appropriate one from a plurality of morpheme strings. Then, the morpheme string that minimizes the total cost is selected from the plurality of morpheme strings.
形態素解析装置の一例が、特許文献1に開示されている。特許文献1の形態素解析装置は、形態素解析手段と、単語辞書と、接続表と、学習辞書と、解析誤り修正手段とを含む。形態素解析手段は、単語コストを保持した単語辞書と接続コストを保持した接続表とに基づいて(解析候補における単語コストと接続コストの総和を解析候補の尤もらしさの尺度とした最小コスト法に基づいて)、ユーザにより指示された文字列(入力文字列)の文節(形態素列)候補を生成する。解析誤り修正手段は、文節候補結果からユーザにより選択された正しい文節候補に基づき、学習辞書を作成する。形態素解析装置は、次回の形態素解析の際には、学習辞書を参照し、登録されている単語、又は2個の単語の連接(隣接する単語の並び)が含まれる解析結果の優先度を高めることで、学習結果を反映する。具体的には、形態素解析装置は、形態素解析のコスト計算の際に、学習辞書に登録されている単語、又は2個の単語の連接の部分のコストを強制的に”0”にすることによって、学習単位を含む解析結果の優先度を高める。 An example of a morphological analyzer is disclosed in
上記の動作の結果、特許文献1の形態素解析装置では、学習辞書に登録されている単語、又は2個の単語の連接を含む形態素解析候補が、形態素解析の結果として選択される可能性が高まる。 As a result of the above operation, in the morphological analyzer of
特許文献2には、特許文献1の形態素解析装置のような「低速形態素解析装置」による解析結果を学習用データとして用いる「高速形態素解析装置」が開示されている。「低速形態素解析」とは、形態素(単語)辞書を用いる形態素解析である。「高速形態素解析」とは、文字をベースとした確率モデル(統計データベース)を利用した形態素解析である。「高速形態素解析」は、「低速形態素解析」より高速に動作することが多い。特許文献2の形態素解析装置は、低速形態素解析の結果を高速形態素解析の学習データに自動的に変換する。特許文献2の形態素解析装置は、学習データの学習後に、入力文を高速形態素解析により解析する。特許文献2の形態素解析装置は、大量の正確な学習データを学習した後には、低速形態素解析による形態素解析とほぼ同じ精度で形態素解析を実行する。
特許文献1の形態素解析装置では、学習辞書に登録されている単語、又は2個の単語の連接の部分のコストが強制的に優先される。そこで、特許文献1の形態素解析装置では、学習辞書に登録されている単語、又は2個の単語の連接の部分を含み、かつ、学習辞書に登録されている単語、又は2個の単語の連接に基づく形態素解析が不適当な文に対して、不適当な形態素解析結果を出力する可能性が高い。つまり、特許文献1の形態素解析装置では、高精度な形態素解析を実現することが困難であるという問題がある。 In the morphological analysis device of
特許文献2の形態素解析装置では、「低速形態素解析」による形態素解析とほぼ同じ精度で形態素解析を実行するためには、学習データとして大量の正確な「低速形態素解析」による形態素解析結果が必要である。つまり、特許文献2の形態素解析装置では、「低速形態素解析」による高精度な形態素解析結果を効率的に取得する必要があるという問題がある。
(発明の目的)
本発明の目的は、単語辞書を用いる形態素解析において、単語辞書に登録された情報を効率的に修正して、高精度な解析を実現することができる、形態素解析装置、形態素解析方法、及び、形態素解析プログラムを提供することにある。In the morpheme analyzer of
(Object of invention)
An object of the present invention is to efficiently correct information registered in a word dictionary in a morpheme analysis using a word dictionary and realize a highly accurate analysis, a morpheme analysis device, a morpheme analysis method, and To provide a morphological analysis program.
本発明の形態素解析装置は、単語、所定の単語の並びである複合語、及び複合語における所定の単語に分割する位置に関する語切り情報が登録された単語辞書に基づいて、複合語を1つの単語として文章の形態素解析を実行する形態素解析手段と、単語辞書に基づいて、形態素解析の結果に含まれる複合語を所定の単語に分割する形態素細分割手段と、を備えることを特徴とする。 The morpheme analyzer of the present invention provides a compound word based on a word dictionary in which words, compound words that are a sequence of predetermined words, and word-cutting information related to positions at which the compound words are divided into predetermined words are registered. It comprises morpheme analysis means for executing morphological analysis of sentences as words, and morpheme subdivision means for dividing a compound word included in the result of morpheme analysis into predetermined words based on a word dictionary.
本発明の形態素解析方法は、単語、所定の単語の並びである複合語、及び複合語における所定の単語に分割する位置に関する語切り情報が登録された単語辞書に基づいて、複合語を1つの単語として文章の形態素解析を実行し、単語辞書に基づいて、形態素解析の結果に含まれる複合語を所定の単語に分割することを特徴とする。 The morpheme analysis method of the present invention is based on a word dictionary in which word words, compound words that are sequences of predetermined words, and word dictionary information about positions to be divided into predetermined words in the compound words are registered. A morphological analysis of a sentence is executed as a word, and a compound word included in a result of the morphological analysis is divided into predetermined words based on a word dictionary.
本発明の形態素解析プログラムは、単語、所定の単語の並びである複合語、及び複合語における所定の単語に分割する位置に関する語切り情報が登録された単語辞書を備える形態素解析装置の備えるコンピュータを、単語辞書に基づいて、複合語を1つの単語として文章の形態素解析を実行する形態素解析手段と、単語辞書に基づいて、形態素解析の結果に含まれる複合語を所定の単語に分割する形態素細分割手段として機能させることを特徴とする。 A morpheme analysis program according to the present invention is a computer provided in a morpheme analyzer including a word, a compound word that is a sequence of predetermined words, and a word dictionary in which word-cutting information related to positions to be divided into predetermined words in the compound word is registered. Morphological analysis means for executing a morphological analysis of a sentence with a compound word as one word based on a word dictionary, and a morpheme detail for dividing a compound word included in the result of the morphological analysis into predetermined words based on the word dictionary It functions as a dividing means.
本発明によれば、単語辞書を用いる形態素解析において、単語辞書に登録された情報を効率的に修正して、高精度な解析を実現することができるという効果がある。 According to the present invention, in the morphological analysis using the word dictionary, there is an effect that the information registered in the word dictionary can be efficiently corrected and a highly accurate analysis can be realized.
以下、本発明の実施形態について図面を参照して詳細に説明する。尚、すべての図面において、同等の構成要素には同じ符号を付し、適宜説明を省略する。
(第1の実施形態)
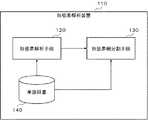
図1は、本実施形態における形態素解析装置の構成の一例を示すブロック図である。Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In all the drawings, equivalent components are denoted by the same reference numerals, and description thereof will be omitted as appropriate.
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a block diagram illustrating an example of the configuration of the morphological analyzer according to the present embodiment.
形態素解析装置110は、入力文字列を形態素(以下、「単語」ともいう。)の列に分割する。入力文字列は、ある言語で書かれた、入力された、又は、話された、文又は文の一部である。入力された、又は、話された、文又は文の一部の場合には、形態素は、文字列ではなく、入力や音素等を表現するコード等の列であってよい。以下、形態素の列を単に「入力文字列」、「文」又は「文章」ともいう。 The
形態素解析装置110は、形態素解析手段120と、形態素細分割手段130と、単語辞書140とを備える。 The
単語辞書140は、登録された単語の情報を保持する。単語辞書140に登録される単語には、任意の品詞に属する形態素である単語(以下、単に「単語」という。)に加え、単語の並び(以下、「複合語」という。)が含まれる。単語辞書140に複合語が登録される場合、単語辞書140には、複合語を複合語に含まれる単語に分割する位置に関する情報(以下、「語切り情報」という。)が含まれる。「語切り情報」は、複合語に対応付けられて登録される。尚、複合語に含まれる単語は、単語辞書に登録されなくてもよい。 The
形態素解析手段120は、複合語を1つの単語として、単語辞書に基づいて、文章の形態素解析を実行する。つまり、形態素解析手段120は、複合語を単語として選択するときは、複合語を更に複合語に含まれる単語に分割することはしない。 The
形態素解析手段120が形態素解析を実行する方法は、単語辞書140に基づいて実行される方法であればよい。形態素解析手段120は、例えば、単語辞書中に定義された単語間の接続コストに基づき、文内の単語間の接続コストの総和が最小になる単語の並びを、形態素解析の結果としてもよい。形態素解析手段120が、単語辞書中に定義された単語間の接続コストに基づき形態素解析を実行する場合、形態素解析手段120は、単語間の接続コストの定義を保持する。 The method by which the
形態素細分割手段130は、単語辞書130に含まれる「語切り情報」等に基づいて、形態素解析手段120による中間的な形態素解析の結果に含まれる複合語を単語に分割する。以下、複合語を単語に分割することを「細分割」という。 The
尚、形態素解析装置110の機能は、形態素解析手段120の機能と形態素細分割手段130の機能とに分離されて、2台の装置に配置されてもよい。 The function of the
図2は、本実施形態における形態素解析装置のハードウェア構成の一例を示すブロック図である。 FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating an example of a hardware configuration of the morphological analyzer according to the present embodiment.
形態素解析装置101は、記憶装置102と、CPU(Central Processing Unit)103と、キーボード104と、モニタ105と、I/O(Input/Output)108とを備え、これらが内部バス106で接続されている。記憶装置102は、形態素細分割手段130等のCPU103の動作プログラムを格納する。CPU103は、形態素解析装置101全体を制御し、記憶装置102に格納された動作プログラムを実行し、I/O108を介して形態素細分割手段130等のプログラムの実行やデータの送受信を行なう。なお、上記の形態素解析装置101の内部構成は一例である。形態素解析装置101は、CPU103のみを備え、外部に備えられた、記憶装置102、キーボード104、モニタ105、及びI/O108を用いて動作してもよい。 The
次に、本実施形態の動作を説明する。 Next, the operation of this embodiment will be described.
図3は、本実施形態における形態素解析装置の動作を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing the operation of the morphological analyzer according to this embodiment.
形態素解析装置110の形態素解析手段120は、複合語を1つの単語として、単語辞書に基づいて、文章の形態素解析を実行する(ステップS11)。 The
形態素解析装置110の形態素細分割手段130は、単語辞書130に含まれる「語切り情報」等に基づいて、形態素解析手段120による中間的な形態素解析の結果に含まれる複合語を単語に分割する(ステップS12)。 The
図4は、本実施形態における形態素解析装置の処理手順の具体例を説明するための図である。 FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining a specific example of the processing procedure of the morphological analyzer according to the present embodiment.
単語辞書140には、予め7個の単語(番号1−7):「そう(副詞)」、「する(動詞)」、「つもり(名詞)」、「つもり(助動詞)」、「で(助詞)」、「でいる(助動詞)」、「いる(動詞)」及び1個の複合語(番号10):「つもりでいる(助動詞)」が登録される。尚、括弧内に示された品詞種別は説明の便宜であり、単語辞書140の内容には含まれなくてもよい。単語辞書140には、品詞が異なるものであれば同じ文字列からなる複数の単語が含まれてもよい。例えば、「つもり(名詞)」(番号3)と「つもり(助動詞)」(番号4)は同じ文字列からなるが、品詞が異なる。 The
単語辞書140には、「語切り情報」として、複合語(番号10):「つもりでいる(助動詞)」を複合語に含まれる単語に分割する位置に関する情報が含まれる。図4の「語切り情報」は、複合語「つもりでいる(助動詞)」(番号10)が、2つの単語「つもり(助動詞)」(番号4)と「でいる(助動詞)」(番号6)とに、単語の間(「/」の位置)で分割されることを示している。単語間の区切り記号「/」は一例であり、別の区切り記号が用いられてもよい。あるいは、区切り記号を用いる代わりに、単に単語の識別子の列(例えば、番号4、番号6の列)が用いられてもよい。あるいは、「語切り情報」は、複合語内で区切られた単語の開始位置を示す数字として保持されてもよい。例えば、「つもりでいる」の場合であれば、先頭の文字から3文字で分割されるとの意味で、語切り情報を”3”としてもよい。 The
形態素解析手段120は、単語辞書140に基づいて、与えられた原文121「そうするつもりでいる」の形態素解析を実行する(ステップS11)。 Based on the
形態素解析手段120は、単語辞書140に基づいて、可能な5つの形態素所解析の候補122(候補1−5)から、例えば、形態素所解析の結果として、中間結果123「/そう(1)/する(2)/つもりでいる(10)」を選択する。 Based on the
形態素細分割手段130は、単語辞書130に含まれる「語切り情報」に基づいて、形態素解析手段120による中間結果123「/そう(1)/する(2)/つもりでいる(10)」に含まれる複合語「つもりでいる(10)」を、単語「つもり(4)」と「でいる(6)」とに分割する(ステップS12)。 The
図5は、本実施形態における形態素解析装置におけるコスト計算の具体例を説明するための表である。 FIG. 5 is a table for explaining a specific example of cost calculation in the morphological analyzer according to the present embodiment.
形態素解析手段120が、定義された単語間の接続コストに基づき形態素解析を実行する場合の詳細について説明する。 Details when the
図5の上側の表は、形態素解析手段120が保持する単語間の接続コストが定義された接続コストテーブルの一例である。接続コストテーブルには、9つの接続コスト(番号1―9)が定義さている。例えば、先頭のルール(番号1)は、「そう(1)」に「する(2)」が続く場合の接続コストが”10”であることを示す。 The upper table in FIG. 5 is an example of a connection cost table in which connection costs between words held by the
図5の下側の表は、図4に示された可能な5つの形態素所解析の候補122(候補1−5)毎の接続コストの総和の一例である。例えば、先頭の候補(候補1)は、「そう(1)」と「する(2)」の接続に対して先頭のルール(番号1)が適用された結果コスト”10”が、「する(2)」と「つもりでいる(10)」の接続に対して4番目のルール(番号4)が適用された結果コスト”10”が加算され、接続コストの総和が”20”であることを示す。可能な5つの形態素所解析の候補122(候補1−5)毎の接続コストの総和が計算された結果、先頭の候補(候補1)の接続コストの総和が最も小さいので、先頭の候補(候補1)が形態素解析の結果(中間結果)として選択される。 The lower table of FIG. 5 is an example of the sum of connection costs for each of the five possible morphological analysis candidates 122 (candidates 1-5) shown in FIG. For example, the top candidate (candidate 1) has the cost “10” as a result of applying the top rule (number 1) to the connection of “Yes (1)” and “Yes (2)”. 2) "and" I'm going to be (10) "connection, the result of applying the fourth rule (number 4), the cost" 10 "is added, and the total connection cost is" 20 " Show. As a result of calculating the sum of the connection costs for each of the five possible morphological analysis candidates 122 (candidates 1-5), the sum of the connection costs of the top candidate (candidate 1) is the smallest, so the top candidate (candidate 1) is selected as the result (intermediate result) of the morphological analysis.
以上説明したように、本実施形態における形態素解析装置110では、単語辞書140に複合語が登録される。そのため、複合語は内部の接続コストが”0”になり、複合語は形態素解析の結果に含まれやすくなる。複合語自体は1つの単語として他の語との結合コストが定義されるので、形態素解析の結果として選択される可能性が過度に高まらない。 As described above, in the
従って、本実施形態における形態素解析装置110は、単語辞書に登録された情報を効率的に修正して、高精度な形態素解析を実現することができる。 Therefore, the
尚、本実施形態では、形態素解析手段が単語間の接続コストに基づき形態素解析を実行する場合について説明したが、形態素解析方法は、単語辞書を用いる形態素解析方法であればよく、具体的内容は特に限定されない。
(第2の実施形態)
本実施形態の説明においては、第1の実施形態と本実施形態とで共通する説明は省略し、第1の実施形態に対する本実施形態の相違点のみについて説明する。In the present embodiment, the case where the morpheme analysis unit executes the morpheme analysis based on the connection cost between words has been described. However, the morpheme analysis method may be any morpheme analysis method using a word dictionary. There is no particular limitation.
(Second Embodiment)
In the description of the present embodiment, descriptions common to the first embodiment and the present embodiment are omitted, and only the differences of the present embodiment from the first embodiment will be described.
本実施形態における形態素解析装置115の構成は、図1に示した第1の実施形態における形態素解析装置110の構成と同じである。但し、形態素解析装置115の形態素解析手段125の動作は、図4に示した第1の実施形態における形態素解析装置110の形態素解析手段120の動作と異なる。更に、形態素解析装置115の形態素細分割手段135の動作は、図4に示した第1の実施形態における形態素解析装置110の形態素細分割手段130の動作と異なる。すなわち、本実施形態における形態素解析手段125は、単語間で定義された接続コストの代わりに、品詞間で定義された接続コストに基づき形態素解析を実行する。また、本実施形態における形態素細分割手段135は、複合語中の区切り記号で特定された分割位置の代わりに、複合語の先頭からの文字数で特定された分割位置に基づきさらなる分割を実行する。 The configuration of the
図6は、本実施形態における形態素解析装置の処理手順の具体例を説明するための図である。 FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining a specific example of the processing procedure of the morphological analyzer according to the present embodiment.
単語辞書145には、予め7個の単語(番号1−7):「そう」(副詞)、「する」(動詞)、「つもり」(名詞)、「つもりだ」(助動詞)、「で」(助詞)、「でいる」(助動詞)、「いる」(動詞)及び1個の複合語(番号10):「つもりでいる」(助動詞)が登録される。但し、単語として「見出し語」が登録されており、単語辞書145には、「見出し語」の活用形「そう」、「する」、「つもり」、「つもり」、「で」、「でいる」、「いる」及び「つもりでいる」も登録される。尚、活用形は「各見出し語」に1つ示されているが、複数個の活用形を含んでもよい。あるいは、「見出し語」の「活用型」の情報が登録されてもよい。更に、単語辞書145には、「各見出し語」の品詞種別が登録される。 The
単語辞書145では、「語切り情報」は、複合語内で区切られた単語の開始位置を示す数字(例えば、“3”)として保持される。単語辞書145では、「語切り情報」として、更に複合語(番号10):「つもりでいる(助動詞)」に含まれる2つの単語「つもりだ(助動詞)」(番号4)と「でいる(助動詞)」(番号6)の情報が含まれる。 In the
形態素解析手段125は、単語辞書145に基づいて、与えられた原文126「そうするつもりでいる」の形態素解析を実行する(ステップS11)。 Based on the
形態素解析手段125は、単語辞書145に基づいて、可能な5つの形態素所解析の候補127(候補1−5)から、例えば、形態素所解析の結果として、中間結果128「/そう(1)/する(2)/つもりでいる(10)」を選択する。 Based on the
形態素細分割手段135は、単語辞書135に含まれる「語切り情報」に基づいて、形態素解析手段125による中間結果128「/そう(1)/する(2)/つもりでいる(10)」に含まれる複合語「つもりでいる(10)」を、3文字目において、単語「つもり(4)」と「でいる(6)」とに分割する(ステップS12)。 The
図7は、本実施形態における形態素解析装置のコスト計算の具体例を説明するための表である。 FIG. 7 is a table for explaining a specific example of cost calculation of the morphological analyzer according to the present embodiment.
形態素解析手段125が、定義された単語間の接続コストに基づき形態素解析を実行する場合の詳細について説明する。 Details when the
図7の上側の表は、形態素解析手段125が保持する単語間の接続コストが定義された接続コストテーブルの一例である。接続コストテーブルには、8つの接続コスト(番号1−8)が定義さている。例えば、先頭のルール(番号1)は、「副詞」に「動詞」が続く場合の接続コストが”10”であることを示す。 The upper table in FIG. 7 is an example of a connection cost table in which connection costs between words held by the
図7の下側の表は、図6に示された可能な5つの形態素所解析の候補127(候補1−5)毎の接続コストの総和の一例である。例えば、先頭の候補(候補1)は、「そう(1)」と「する(2)」の接続に対して先頭のルール(番号1)が適用された結果コスト”10”が、「する(2)」と「つもりでいる(10)」の接続に対して3番目のルール(番号3)が適用された結果コスト”10”が加算され、接続コストの総和が”20”であることを示す。可能な5つの形態素所解析の候補127(候補1−5)毎の接続コストの総和が計算された結果、先頭の候補(候補1)の接続コストの総和が最も小さいので、先頭の候補(候補1)が形態素解析の結果(中間結果)として選択される。 The table on the lower side of FIG. 7 is an example of the sum of connection costs for each of the five possible morphological analysis candidates 127 (candidates 1-5) shown in FIG. For example, the top candidate (candidate 1) has the cost “10” as a result of applying the top rule (number 1) to the connection of “Yes (1)” and “Yes (2)”. 2) "and" I'm going to (10) "connection, the result of applying the third rule (number 3), the cost" 10 "is added, and the total of connection costs is" 20 " Show. As a result of calculating the sum of the connection costs for each of the five possible morphological analysis candidates 127 (candidates 1-5), the sum of the connection costs of the top candidate (candidate 1) is the smallest, so the top candidate (candidate 1) is selected as the result (intermediate result) of the morphological analysis.
以上説明したように、本実施形態における形態素解析装置115では、単語辞書145に単語が見出し語、見出し語が属する品詞、見出し語の活用形の情報が登録される。そのため、単語が単語の活用形毎に単語辞書145に登録される必要が無い。 As described above, in the
従って、本実施形態における形態素解析装置115は、第1の実施形態における形態素解析装置110の効果に加え、単語辞書の登録及び接続コストの設定をより簡素化できるという効果を有する。 Therefore, the
尚、本実施形態では、形態素解析手段が単語間の接続コストに基づき形態素解析を実行する場合について説明したが、形態素解析方法は、単語辞書を用いる形態素解析方法であればよく、具体的内容は特に限定されない。 In the present embodiment, the case where the morpheme analysis unit executes the morpheme analysis based on the connection cost between words has been described. However, the morpheme analysis method may be any morpheme analysis method using a word dictionary. There is no particular limitation.
尚、図3の形態素解析装置の各処理は、ソフトウェアによって実行されてもよい。すなわち、各処理を行うためのコンピュータプログラムが、形態素解析装置が備えるCPU(図2:903)によって読み込まれ、実行されてもよい。プログラムを用いて各処理を行っても、上述の実施形態の処理と同内容の処理を行うことができる。そして、上記のプログラムは、ROM(Read Only Memory)、RAM(Random Access Memory)、フラッシュメモリ等の半導体記憶装置、光ディスク、磁気ディスク、光磁気ディスク等、非一時的な媒体に格納されてもよい。 Each process of the morphological analyzer of FIG. 3 may be executed by software. That is, a computer program for performing each process may be read and executed by a CPU (FIG. 2: 903) provided in the morphological analyzer. Even if each process is performed using a program, the same process as the process of the above-described embodiment can be performed. The above program may be stored in a non-transitory medium such as a ROM (Read Only Memory), a RAM (Random Access Memory), a semiconductor memory device such as a flash memory, an optical disk, a magnetic disk, or a magneto-optical disk. .
あるいは、各処理は、個別の回路等の構成要素によって実行されてもよい。 Alternatively, each process may be executed by a component such as an individual circuit.
尚、本願発明は、上述の実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本願発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲で種々変更、変形して実施することができる。 In addition, this invention is not limited to the above-mentioned embodiment, It can implement in various changes and deformation | transformation in the range which does not deviate from the summary of this invention.
本発明の形態素解析装置は、例えば、機械翻訳システムやテキストマイニングシステム等の一部としても利用することができる。 The morpheme analyzer of the present invention can be used as a part of, for example, a machine translation system or a text mining system.
又、本発明の形態素解析は、実施形態で説明した形態素解析装置だけでなく、例えば、かな漢字システムや音声認識システム等の一部にも適用することができる。 The morpheme analysis of the present invention can be applied not only to the morpheme analyzer described in the embodiment but also to a part of, for example, a Kana-Kanji system or a speech recognition system.
Claims (10)
Translated fromJapanese能な位置に関する語切り情報が登録された単語辞書に基づいて、前記複合語を1つの単語
として文章の形態素解析を実行する形態素解析手段と、
前記形態素解析手段が前記形態素解析を実行した後、前記単語辞書に基づいて、前記形態素解析の結果に含まれる前記複合語を前記所定の単語に分割する形態素細分割手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする形態素解析装置。A morpheme of a sentence using the compound word as one word based on a word, a compound word that is a sequence of predetermined words, and a word dictionary in which word cutting information relating to positions where the compound word can be divided into the predetermined words is registered Morphological analysis means for performing analysis;
After the morpheme analysis unit performs the morpheme analysis , based on the word dictionary, a morpheme subdivision unit that divides the compound word included in the result of the morpheme analysis into the predetermined words;
A morphological analysis device comprising:
記所定の単語の識別子の並びである
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の形態素解析装置。2. The morpheme analyzer according to claim 1, wherein the word cut information is a predetermined symbol inserted at the position, an array of the predetermined words, or an array of identifiers of the predetermined words.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の形態素解析装置。The morphological analysis apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the word cut information is the number of characters from the beginning or end of the compound word that represents the position.
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至3のいずれか1項に記載の形態素解析装置。The morpheme analyzer according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the word that is an inflected form is registered in the word dictionary.
見出し語の活用形に関する情報が登録される
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至3のいずれか1項に記載の形態素解析装置。4. The information as to claim 1, wherein the word dictionary includes information about the word that is a headword and a utilization form of the headword associated with the headword. 5. The morphological analyzer described.
前記文章中における前記第1の接続コストの総和が最小になる前記単語の並びを形態素解
析の結果として選択する
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至5のいずれか1項に記載の形態素解析装置。The morphological analysis means holds information of a first connection cost when the word is connected,
The morpheme analyzer according to any one of claims 1 to 5, wherein an arrangement of the words that minimizes the total sum of the first connection costs in the sentence is selected as a result of morpheme analysis.
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至6のいずれか1項に記載の形態素解析装置。The morpheme analyzer according to claim 1, wherein information on a part of speech to which the word belongs is registered in the word dictionary.
の情報を保持し、前記文章中における前記第2の接続コストの総和が最小になる前記単語
の並びを形態素解析の結果として選択する
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至5のいずれか1項又は請求項7に記載の形態素解析装置。The morpheme analyzing means retains information on a second connection cost when the words having different parts of speech are connected, and the morpheme is an arrangement of the words that minimizes the sum of the second connection costs in the sentence. The morpheme analyzer according to claim 1, wherein the morpheme analyzer is selected as a result of analysis.
可能な位置に関する語切り情報が登録された単語辞書に基づいて、前記複合語を1つの単
語として文章の形態素解析を実行し、
前記形態素解析を実行した後、前記単語辞書に基づいて、前記形態素解析の結果に含まれる前記複合語を前記所定の単語に分割することを特徴とする形態素解析方法。Based on a word dictionary in which words, compound words that are a sequence of predetermined words, and word dictionary information regarding positions that can be divided into the predetermined words in the compound words are registered, the compound words as one word Perform morphological analysis,
After executing the morpheme analysis, the morpheme analysis method divides the compound word included in the result of the morpheme analysis into the predetermined words based on the word dictionary.
可能な位置に関する語切り情報が登録された単語辞書を備える形態素解析装置の備えるコ
ンピュータを、
前記単語辞書に基づいて、前記複合語を1つの単語として文章の形態素解析を実行する
形態素解析手段と、
前記形態素解析手段が前記形態素解析を実行した後、前記単語辞書に基づいて、前記形態素解析の結果に含まれる前記複合語を前記所定の単語に分割する形態素細分割手段と、
して機能させるための形態素解析プログラム。A computer provided with a morpheme analyzer including a word, a compound word that is a sequence of predetermined words, and a word dictionary in which word cutting information relating to positions that can be divided into the predetermined words in the compound word is registered;
Based on the word dictionary, morpheme analysis means for executing a morpheme analysis of a sentence with the compound word as one word;
After the morpheme analysis unit performs the morpheme analysis , based on the word dictionary, a morpheme subdivision unit that divides the compound word included in the result of the morpheme analysis into the predetermined words;
A morphological analysis program to make it function.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013133481AJP6232774B2 (en) | 2013-06-26 | 2013-06-26 | Morphological analyzer, morphological analysis method, and morphological analysis program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013133481AJP6232774B2 (en) | 2013-06-26 | 2013-06-26 | Morphological analyzer, morphological analysis method, and morphological analysis program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015007943A JP2015007943A (en) | 2015-01-15 |
| JP6232774B2true JP6232774B2 (en) | 2017-11-22 |
Family
ID=52338160
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013133481AExpired - Fee RelatedJP6232774B2 (en) | 2013-06-26 | 2013-06-26 | Morphological analyzer, morphological analysis method, and morphological analysis program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6232774B2 (en) |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07175810A (en)* | 1993-12-18 | 1995-07-14 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Morphological analyzer |
| JPH0844739A (en)* | 1994-07-29 | 1996-02-16 | Atr Onsei Honyaku Tsushin Kenkyusho:Kk | Morpheme analysis device |
| JP3880087B2 (en)* | 1995-11-28 | 2007-02-14 | 富士通株式会社 | Morphological analyzer |
| JPH11120186A (en)* | 1997-10-09 | 1999-04-30 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Database creation method and apparatus, medium recording program thereof, database search method, apparatus and medium recording program thereof |
| JP2002251402A (en)* | 2001-02-26 | 2002-09-06 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Document search method and document search device |
| JP4001283B2 (en)* | 2003-02-12 | 2007-10-31 | インターナショナル・ビジネス・マシーンズ・コーポレーション | Morphological analyzer and natural language processor |
| JP4979637B2 (en)* | 2008-06-06 | 2012-07-18 | ヤフー株式会社 | Compound word break estimation device, method, and program for estimating compound word break position |
| JP5853595B2 (en)* | 2011-10-31 | 2016-02-09 | 富士通株式会社 | Morphological analyzer, method, program, speech synthesizer, method, program |
- 2013
- 2013-06-26JPJP2013133481Apatent/JP6232774B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2015007943A (en) | 2015-01-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI636452B (en) | Method and system of voice recognition | |
| JP5462001B2 (en) | Contextual input method | |
| JP5362095B2 (en) | Input method editor | |
| JP2019526142A (en) | Search term error correction method and apparatus | |
| US20140039879A1 (en) | Generic system for linguistic analysis and transformation | |
| JP2000513843A (en) | Natural language parser with part-of-speech probability based on dictionary | |
| KR101709693B1 (en) | Method for Web toon Language Automatic Translating Using Crowd Sourcing | |
| Shaalan et al. | A hybrid approach for building Arabic diacritizer | |
| Ganfure et al. | Design and implementation of morphology based spell checker | |
| JPH10326275A (en) | Method and device for morpheme analysis and method and device for japanese morpheme analysis | |
| JP2002117027A (en) | Feeling information extracting method and recording medium for feeling information extracting program | |
| JP2017004127A (en) | Text division program, text division device, and text division method | |
| CN112530406A (en) | Voice synthesis method, voice synthesis device and intelligent equipment | |
| Elshafei | Machine generation of Arabic diacritical marks | |
| Hall et al. | Russian stress prediction using maximum entropy ranking | |
| JP6232774B2 (en) | Morphological analyzer, morphological analysis method, and morphological analysis program | |
| Ivanova et al. | A free/open-source morphological analyser and generator for Sakha | |
| de Mendonça Almeida et al. | Evaluating phonetic spellers for user-generated content in Brazilian Portuguese | |
| Lehal | Conversion between scripts of Punjabi: Beyond simple transliteration | |
| Okhovvat et al. | A hidden Markov model for Persian part-of-speech tagging | |
| Lu et al. | Language model for Mongolian polyphone proofreading | |
| JP5795302B2 (en) | Morphological analyzer, method, and program | |
| JP2632806B2 (en) | Language analyzer | |
| Aggarwal et al. | A survey on parts of speech tagging for Indian languages | |
| JP7243818B2 (en) | Reading disambiguation device, reading disambiguation method, and reading disambiguation program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20160516 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20170414 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20170425 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20170621 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20170926 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20171009 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:6232774 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |