JP5539555B2 - Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program - Google Patents
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5539555B2 JP5539555B2JP2013022371AJP2013022371AJP5539555B2JP 5539555 B2JP5539555 B2JP 5539555B2JP 2013022371 AJP2013022371 AJP 2013022371AJP 2013022371 AJP2013022371 AJP 2013022371AJP 5539555 B2JP5539555 B2JP 5539555B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- area
- feature amount
- query
- image feature
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Processing Or Creating Images (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、画像を特徴付ける情報として、画像から局所的な特徴を抽出する画像処理装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to an image processing apparatus that extracts local features from an image as information that characterizes the image.
近年、類似画像を比較・検索するための技術が多く提案されている。例えば、画像を複数のブロックに分け、それぞれの画像特徴量(代表色)を用いてパターンマッチングを行うことで色の位置情報を利用して類似画像を比較・検索する方法がある(特許文献1)。しかし、特許文献1に開示された方法の場合、検索時に画像全体の画素値から特徴量を計算するため、例えば画像内の特定のオブジェクトが切り取られたり、その位置が変わったりした場合には比較・検索が困難になってしまうという問題があった。 In recent years, many techniques for comparing and searching for similar images have been proposed. For example, there is a method of comparing and retrieving similar images using color position information by dividing an image into a plurality of blocks and performing pattern matching using each image feature amount (representative color) (Patent Document 1). ). However, in the case of the method disclosed in Patent Document 1, the feature amount is calculated from the pixel values of the entire image at the time of search. For example, when a specific object in the image is cut out or its position is changed, the comparison is performed.・ There was a problem that the search would be difficult.
そこで、画像全体の画素から算出される特徴量を使うのではなく、画像の局所的な領域から算出される特徴量(以下、局所特徴量と称す)を使って類似画像の比較や検索を行う方法が提案されている。(非特許文献1)これらの方法では、まず画像からエッジやコーナなどの特徴点を抽出する。次に、特徴点とその近傍の画像情報とから、その特徴点に関する局所特徴量を計算する。局所特徴量として扱う値には、輝度の変化情報や、形状パターンなど、様々なものがある。画像の検索は、局所特徴量同士の類似度計算(マッチング)を行うことで実現する。 Therefore, instead of using the feature amount calculated from the pixels of the entire image, a feature amount calculated from a local region of the image (hereinafter referred to as a local feature amount) is used to compare and search for similar images. A method has been proposed. (Non-Patent Document 1) In these methods, first, feature points such as edges and corners are extracted from an image. Next, a local feature amount relating to the feature point is calculated from the feature point and image information in the vicinity thereof. There are various values such as luminance change information and shape patterns to be handled as local feature amounts. Image retrieval is realized by performing similarity calculation (matching) between local feature quantities.
局所特徴量を用いた画像の比較を行う場合には、まず、比較する2つの画像のそれぞれから画素値の変動が大きい点を特徴点として抽出し、その特徴点に関する局所特徴量を抽出する。そして、局所特徴量同士を比較することで、2つの画像間で対応する特徴点の組み合わせを決定し、特徴点の対応度合いを基に類似度の判定を行う。 When comparing images using local feature values, first, a point having a large variation in pixel value is extracted as a feature point from each of the two images to be compared, and a local feature value related to the feature point is extracted. Then, by comparing the local feature amounts with each other, a combination of feature points corresponding to the two images is determined, and similarity is determined based on the degree of correspondence between the feature points.
類似画像を検索する場合に検索条件(クエリ)として画像を用いるが、例えば色々なオブジェクトを含むサンプル画像から精度良く所望の検索結果を得るためには、ユーザがクエリとして用いる領域をサンプル画像の中から指定する必要がある。 An image is used as a search condition (query) when searching for similar images. For example, in order to obtain a desired search result with high accuracy from sample images including various objects, an area used by the user as a query is included in the sample image. It is necessary to specify from.
しかし非特許文献1の方法で、ユーザに選択された領域に対応する部分画像をサンプル画像から切り取ってから特徴点及び特徴量を抽出し、検索をすると、以下のような問題が考えられる。 However, when the method of Non-Patent Document 1 is used to extract a feature point and a feature amount after cutting out a partial image corresponding to a region selected by the user from a sample image, the following problems can be considered.
非特許文献1の方法で算出する局所特徴量は、特徴点の近傍の特定領域の画素値も用いるため、ユーザに選択された画像領域の端の方では、算出される特徴量の信頼性が低下する可能性がある。特徴点を中心とする半径r画素の領域の画素から算出する局所特徴量が定義される場合、矩形の領域がユーザに指定された場合、矩形の角近くの特徴点から抽出される局所特徴量は矩形の中心から抽出されるものと比べて4分の3近くの画素を無視していることになる。一方で矩形の角近くの特徴点は除外するようにしてしまうと、ユーザが選択した領域内で場所によっては同等に計算されないので、ユーザにとって意図しない検索になってしまう。 Since the local feature amount calculated by the method of Non-Patent Document 1 also uses the pixel value of the specific region in the vicinity of the feature point, the reliability of the calculated feature amount is closer to the edge of the image region selected by the user. May be reduced. When a local feature amount calculated from pixels in an area of radius r pixels centering on a feature point is defined, when a rectangular region is designated by the user, a local feature amount extracted from a feature point near the corner of the rectangle Is ignoring pixels that are close to three-quarters compared to those extracted from the center of the rectangle. On the other hand, if feature points near the corners of the rectangle are excluded, they are not calculated equally depending on the location in the region selected by the user, and the search is unintended for the user.
また、サンプル画像から特徴点と局所特徴量を算出してからユーザに領域を選択させる手法が考えられるが、領域を指定することで特徴点及び局所特徴量を算出する処理対象を減らせる点は処理時間の短縮に貢献する。従って本発明は、処理時間を節約しつつ、ユーザの指定した領域に関する情報を用いて精度の良いクエリを作成する装置、方法及びプログラムを提供することを目的とする。 In addition, a method of calculating a feature point and a local feature amount from a sample image and then allowing the user to select a region can be considered, but by specifying a region, it is possible to reduce processing targets for calculating feature points and local feature amounts. Contributes to shortening of processing time. Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus, a method, and a program for creating an accurate query using information related to a region designated by a user while saving processing time.
上記目的を達成するための本発明に係る画像処理装置は、画像特徴量を用いて類似する画像を検索する画像処理装置であって、画像を入力する入力手段と、前記画像において検索に用いる領域を、前記画像を表示する画面の操作により指定領域として指定する指定手段と、前記指定領域内の画像特徴量を抽出するのに必要な領域の大きさに関する情報に基づいて前記指定領域を拡大したものをクエリ領域として決定する決定手段と、前記クエリ領域から画像特徴量を抽出する抽出手段と、前記抽出手段の抽出した画像特徴量に基づいて、該画像特徴量に類似する画像を検索する検索手段とを有することを特徴とする。In order to achieve the above object, an image processing apparatus according to the present invention is an image processing apparatus for searching for a similar image using an image feature amount, and an input means for inputting an image, and an area used for the search in the image The designated area is enlarged based on information relating to the size of the area necessary for extractingthe image feature amountin the designated area and designation means for designating as a designated areaby operating the screen for displayingthe image A determination means for determining an object as a query area; an extraction means for extracting an image feature quantity from the query area; and a search for searching for an image similar to the image feature quantity based on the image feature quantity extracted by the extraction means Means.
ユーザに指定された領域情報を用いて、領域情報内の位置によらず精度の良い特徴量の算出を実現するので、処理時間を節約しつつ精度の良いクエリの生成が可能になる。従って類似画像検索の検索精度が向上し処理時間も短縮される。 Using the region information designated by the user, it is possible to calculate the feature quantity with high accuracy regardless of the position in the region information, so that it is possible to generate an accurate query while saving processing time. Accordingly, the retrieval accuracy of similar image retrieval is improved and the processing time is shortened.
<実施形態1>
図2は、本実施形態における画像処理装置(以降、画像検索装置200)の概略機能を示すブロック図ある。図2に示すように、画像検索装置200は、変換部201、抽出部202、決定部203、算出部204を有する。<Embodiment 1>
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a schematic function of the image processing apparatus (hereinafter, image search apparatus 200) in the present embodiment. As illustrated in FIG. 2, the image search apparatus 200 includes a
画像検索装置200は、入力画像206を画像特徴データベース205に登録する登録処理と、入力画像206から検索条件(クエリ)を作成し画像特徴データベースに登録された画像から検索する検索処理とを行う。 The image search apparatus 200 performs a registration process for registering the
登録用に入力される入力画像206は図1のNCU108を介して通信可能に接続されたネットワークスキャナ、デジタルスチルカメラ、画像データを保持した外部記憶装置等、スキャナ109によって入力される。そして、読み込んだ画像はRAM103や外部記憶装置106などに一時的に保持される。 The
抽出部203が抽出した特徴点、局所特徴量などの情報を関連付けて画像特徴データベース205に記憶する。記憶する際には登録する画像を特定する画像IDを割り当てることで管理する。 Information such as feature points and local feature amounts extracted by the
[画像登録処理]
図3は、画像特徴データベース205に画像を登録する際に行う、画像の特徴点・局所特徴量を抽出する処理の手順の概略を表すフローチャートである。[Image registration process]
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing an outline of a processing procedure for extracting feature points and local feature amounts of an image performed when an image is registered in the
ステップS301では、変換部201が入力画像206を読み込む。次に、ステップS302では、変換部201が画像データから輝度成分を抽出する処理を行い、抽出した輝度成分に基づき輝度成分画像を生成する。 In step S301, the
ステップS303では、ステップS302で作成した輝度成分画像を変換部201が縮小率pに従って入力画像206をn回縮小し、n+1種の解像度の画像を有する多重画像を取得する。図4は、変換部202が入力画像206を縮小率2の(―1/4)乗で8回縮小することで作成した多重画像を示している。 In step S303, the
ステップS304では、抽出部203がステップS305の作成した多重画像の夫々から特徴点を抽出する。ステップS305では、ステップS305の処理で得られた特徴点の各々について、特徴点に関する局所特徴量を算出して特徴量ベクトルを作成する。そして、ステップS306で画像データと算出した特徴量ベクトルとを関連付けて画像特徴データベース205に登録する。 In step S304, the
本実施形態では多重画像を作成することで拡大・縮小画像に対しての検索精度が上げている。 In the present embodiment, the search accuracy with respect to the enlarged / reduced image is increased by creating multiple images.
[特徴点と局所特徴量]
抽出部202が図4で示す各画像に、エッジやコーナなど画素値の変化の度合いが大きいほど大きい値を返すHarris作用素を作用させる。そして、Harris作用素を作用させて得られた出力画像の夫々について、着目する画素と着目する画素を囲む8画素(合計9画素)の画素値を比較する。そして、着目する画素の画素値が9画素の中で最大になり且つしきい値以上である画素を特徴点として抽出する。こうして、得られる特徴点は画素値の変化の度合いが周囲に比べて大きく、画像の特徴をよく表す点として扱うことができる。[Feature points and local features]
The
局所特徴量としては、特徴点近傍の模様を数値化するLocal Jet及びそれらの導関数の組み合わせを用いる。 As the local feature amount, a local jet that digitizes a pattern near a feature point and a combination of derivatives thereof are used.
具体的には、たとえば以下の式1により局所特徴量を算出する。 Specifically, for example, the local feature amount is calculated by the following formula 1.
V(x,y)は画像の中で座標(x,y)にある特徴点に関する局所特徴量である。なお、ここで言う座標とはデジタル画像においては画素位置を示すこととする。デジタル画像における画素位置は離散的であるので(整数で表されるので)、計算結果としての実数座標から画素位置を特定しなければならない場合には、座標の整数化が必要となる。本実施形態では、座標が実数値で表されるときには、実数値を丸めて整数値にすることで画素位置を特定する。実数値を丸める方法には四捨五入、小数点以下切り上げ、小数点以下切捨てなどの方法があるが、本実施形態ではどの方法を選択しても良い。ただし、処理の途中で方法を変更しないこととする。 V (x, y) is a local feature amount relating to a feature point at coordinates (x, y) in the image. The coordinates referred to here indicate pixel positions in a digital image. Since the pixel position in the digital image is discrete (because it is represented by an integer), if the pixel position has to be specified from the real number coordinates as the calculation result, it is necessary to convert the coordinates into integers. In the present embodiment, when the coordinates are represented by real values, the pixel positions are specified by rounding the real values to integer values. There are methods for rounding a real value, such as rounding off, rounding up after the decimal point, and rounding down after the decimal point. Any method may be selected in this embodiment. However, the method is not changed during the process.
式(1)の右辺で用いている記号は、以下に示す式(2)〜(7)で定義される。ここで、式(2)右辺のG(x,y)はガウス関数、I(x,y)は画像の座標(x,y)における画素値であり、“*”は畳み込み演算を表す記号である。また、式(3)は式(2)で定義された変数Lのxに関する偏導関数、式(4)は変数Lのyに関する偏導関数である。式(5)は式(3)で定義された変数Lxのyに関する偏導関数、式(6)は式(3)で定義された変数Lxのxに関する偏導関数、式(7)は式(4)で定義されたLyのyに関する偏導関数である。 Symbols used on the right side of Expression (1) are defined by Expressions (2) to (7) shown below. Here, G (x, y) on the right side of Expression (2) is a Gaussian function, I (x, y) is a pixel value at image coordinates (x, y), and “*” is a symbol representing a convolution operation. is there. Equation (3) is a partial derivative of variable L defined by equation (2) with respect to x, and equation (4) is a partial derivative of variable L with respect to y. Equation (5) is the partial derivative of variable Lx defined in equation (3) with respect to y, equation (6) is the partial derivative of variable Lx defined in equation (3) with respect to x, and equation (7) is the equation. It is a partial derivative with respect to y of Ly defined in (4).
ここで、G(x,y)はガウス関数であるので、通常は標準偏差σを変数として持つが、式(2)では省略している。本実施形態ではσ=arとして予め定められる。ここでaは定数であり、rは着目している特徴点を中心とする円形領域の半径を示し、着目している特徴点に関する局所特徴量を算出する際に参照する領域(以降、算出領域と称す)である。 Here, since G (x, y) is a Gaussian function, it normally has the standard deviation σ as a variable, but is omitted in Equation (2). In this embodiment, it is predetermined as σ = ar. Here, a is a constant, r indicates the radius of a circular area centered on the feature point of interest, and is an area to be referred to when calculating the local feature amount related to the feature point of interest (hereinafter, calculation area) It is called).
なお、特徴点を含む画素と特徴点近傍の画素の特徴を示す局所特徴量を算出可能な方法であれば、上述の方法以外でもよい。上述の局所特徴量は5つの要素から成るが、要素の数は5つでなくてもよい。例えば、SIFT(要素数128)やPCA−SIFT(要素数20〜30程度)においても本発明は適用可能である。 Note that any method other than the above-described method may be used as long as it is a method capable of calculating local feature amounts indicating features of pixels including feature points and pixels near the feature points. The local feature amount described above is composed of five elements, but the number of elements may not be five. For example, the present invention can be applied to SIFT (128 elements) and PCA-SIFT (20 to 30 elements).
図3で示される特徴点・局所特徴量の抽出処理により得られた特徴点を図示したものが図5である。図5で、画像510は入力された画像データであり、点520及び点530が特徴点を例示したものである。この点520及び530の特徴点は、それぞれに関して式(1)によって求めた局所特徴量に関連付けられている。Harris作用素を用いた場合には、輝度画像上で形状に特徴のある部分が特徴点として抽出されることになる。 FIG. 5 shows the feature points obtained by the feature point / local feature amount extraction process shown in FIG. In FIG. 5, an
また、本実施形態ではHarris作用素を用いて説明しているが、画像中の画素値の変動が大きい箇所を検出する処理であれば他の処理であっても適用できるので、本発明はHarris作用素に限定されない。 In the present embodiment, the Harris operator is used. However, the present invention can be applied to other processes as long as it is a process that detects a portion where the variation of the pixel value in the image is large. It is not limited to.
[画像の検索処理]
検索を行う場合、検索条件(クエリ)を作成するために用いる入力画像206が画像検索装置200に与えられる。入力画像206は、図1のNCT108によって通信可能に接続されたネットワークスキャナ、デジタルスチルカメラ、外部記憶装置等や、スキャナ109から入力される。[Image search processing]
When performing a search, an
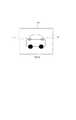
図6は入力画像206からクエリを作成する画面である。欄601には、入力されたクエリ画像が表示される。表示画面のサイズによっては、クエリ画像の縮小画像やサムネイル画像などを表示してもよい。ここでは、2台の自動車が写っている画像がクエリ画像として表示されている。 FIG. 6 is a screen for creating a query from the
ボタン603は検索で使用するクエリ画像の入力を指示するためのボタンで、このボタンを押下すると、クエリ画像の入力先を指定するための画面が表示され、ユーザによって入力先が指定されるとクエリ画像の入力処理が行われ、欄601に表示されることになる。 A
ボタン604を押下するとクエリとして用いる領域を選択するモードに切替わる。欄601にサンプル画像が表示されている中でキーボードやマウスやタッチパネルなどの入力装置104を使用して、クエリとして用いる部分領域の指定を行うことができる。楕円602は入力装置104によってクエリとして用いる領域が選択された一例である。以降、楕円602の様にクエリとして用いるように指定された領域を指定領域と称する。指定領域は楕円602の様に線で囲ったり、色を反転させたりする等、ユーザが識別可能な様に表示されればよい。 When a
ボタン605は、ユーザ指定領域とサンプル画像とから、クエリを生成して画像検索を行うことを指示するためのボタンで、このボタンを押下すると、検索処理が行われ、検索結果の画面が表示される。指定領域が指定されずに検索される場合は画像全体の画素からクエリを生成するようにしてもよい。 A
図7は、前述の処理にて生成したサンプル画像と指定領域とからクエリを生成する処理を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing a process for generating a query from the sample image generated in the above-described process and the designated area.
図8(a)はサンプル画像について指定領域801を図示したものである。図8(b)は指定領域801と算出領域802の大きさとに基づいて指定領域801を拡大したものをクエリ領域804として図示したものである。図8(c)は図8(b)の算出領域802付近を拡大して図示したものである。なお、図8(b)、(c)に示す算出領域802は指定領域801の外縁上の特徴点805を仮定した際の、特徴点805に関する局所特徴量の算出領域である。 FIG. 8A illustrates a designated
図7のステップS701では、図6の処理で得られた指定領域を示す情報と、特徴点及び局所特徴量を算出する際に用いる領域の大きさを示す情報を取得する。算出領域の形や大きさは、局所特徴量の計算方式によって異なるので、予めユーザが決定部203に算出領域の形や大きさを示す情報を設定しておいてもよい。本実施形態では前述した式(1)局所特徴量を算出する際に、特徴点を中心とする半径rの円状の領域に重みをつける、円状の領域の外は重みが0なのでその点における局所特徴量の算出処理の対象からは除外される。従って、局所特徴量の算出領域は特徴点を中心とする半径rの円状の領域となる。図8に示す算出領域802はその一例である。 In step S701 of FIG. 7, information indicating the designated area obtained by the process of FIG. 6 and information indicating the size of the area used when calculating the feature point and the local feature amount are acquired. Since the shape and size of the calculation area vary depending on the local feature amount calculation method, the user may set information indicating the shape and size of the calculation area in the
ステップS702では、ステップS701で得られた情報を元に、検索クエリ生成するのに用いる領域(以降、クエリ領域)を設定する。本実施形態の局所特徴量は特定の領域の画素から算出される為、単純に指定領域内の画像から、特徴点を抽出して、更に局所特徴量を計算しようとすると指定領域の端の方では正確な値を取得することが難しくなる。例えば図8のように、指定領域801内の画素を単純に用いて特徴点805に関する局所特徴量を算出しようとすると、特徴点805を中心とする半径rの円状の領域802の画素値から局所特徴量を算出することになる。しかし、算出領域802において指定領域801からはみ出ている部分について画素を参照することができないため、正確な局所特徴量を算出できない。さらに、特徴点の抽出方法においても、所定の算出領域から特徴点を抽出しようとするので、仮に特徴点を抽出する際の算出領域が算出領域802であるとすると、半分近くの画素値を参照できないため抽出できないことがある。 In step S702, an area (hereinafter referred to as a query area) used to generate a search query is set based on the information obtained in step S701. Since the local feature amount of the present embodiment is calculated from pixels in a specific region, if a feature point is simply extracted from an image in the specified region and further a local feature amount is to be calculated, the end of the specified region Then, it becomes difficult to obtain an accurate value. For example, as shown in FIG. 8, when a local feature amount relating to the
以上のような理由により、本実施形態では指定領域に対して、特徴点・局所特徴量の計算方式に応じて計算に必要な画素分画像サイズ分だけ拡大してクエリ領域として決定する。 For the reasons described above, in the present embodiment, the designated area is determined as a query area by enlarging the designated area by the pixel size required for calculation according to the feature point / local feature amount calculation method.
ステップS703では、サンプル画像からステップS702で決定されたクエリ領域をクエリ画像として切り取る(クエリ領域以外をマスクして処理対象から外してもよい)。 In step S703, the query area determined in step S702 is cut out from the sample image as a query image (other than the query area may be masked and excluded from the processing target).
そしてステップS704において、クエリ画像について図3の処理によって、特徴点及び局所特徴量を算出して、検索に用いるクエリ(画像特徴量を示すベクトル)を生成する。 In step S704, the feature point and the local feature amount are calculated for the query image by the processing of FIG. 3, and a query (vector indicating the image feature amount) used for the search is generated.
図7の処理を図8を用いて説明する。 The process of FIG. 7 will be described with reference to FIG.
生成したクエリに基づいて、画像特徴データベースに登録されている画像の中で類似する局所特徴量を有する画像を検索する。類似性はクエリと画像データベースに登録されている夫々の局所特徴量との特徴量空間におけるマハラノビス距離によって求められる。しかし、ベクトル同士の類似度を算出可能な公知の方法であってもよいので、本発明はこれに限定されない。また、比較する画像間で局所特徴量の類似する対応点についてロバスト推定に用いられるRANSAC(RANdom SAmple Consensus)を用いても良い。RANSACによって変換行列の解を推定し、その変換行列で他の対応点を同様に変換できるかを評価することで類似度を算出する。 Based on the generated query, an image having a similar local feature is searched for among images registered in the image feature database. Similarity is calculated | required by Mahalanobis distance in the feature-value space of a query and each local feature-value registered into the image database. However, since a known method capable of calculating the similarity between vectors may be used, the present invention is not limited to this. Further, RANSAC (RANdom Sample Consensus) used for robust estimation of corresponding points having similar local feature amounts between images to be compared may be used. The degree of similarity is calculated by estimating the solution of the transformation matrix by RANSAC and evaluating whether other corresponding points can be similarly transformed by the transformation matrix.
検索結果は、類似度の高い順に所定数の候補を表示する。類似度が閾値未満のものは省くようにしてもよい。 The search result displays a predetermined number of candidates in descending order of similarity. You may make it abbreviate | omit that whose similarity is less than a threshold value.
図9は、本実施形態における検索結果を表示する画面を示した図である。 FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a screen for displaying the search result in the present embodiment.
欄901は、クエリを生成するのに用いたサンプル画像を表示する部分である。クエリ画像の縮小画像やサムネイル画像などが表示されてもよい。ここでは、2台の自動車が写っている画像が選択されている。楕円905は指定領域の部分で、ユーザがクエリを生成するために指定領域として選択した部分を示す。 A
欄902は、検索結果を表示するための領域であり、図2の検索結果208として得られた画像IDに対応した画像のサムネイルや画像ファイル名等を一覧表示する部分である。サムネイルは、画像登録時に作成され、画像IDに対応付けられたもので図2の画像特徴データベース205や、図1の外部記憶装置等106に登録されている。検索結果の数が多く、一つの画面で表示できない場合には、表示サイズに応じた件数ずつ組にして表示を行う。本例では、6件ずつ検索結果が表示されている。ボタン903は、現在表示している検索結果の前の6件を表示するためのボタンであり、ボタン904は、現在表示している検索結果の次の6件を表示するためのボタンである。また、図9の例では、サムネイルと画像ファイルの名前を表示しているが、検索処理で求めたクエリ画像との類似度や画像に付与されているメタデータ等を表示してもよい。また、欄902の領域に表示されているサムネイルの一つを選択すると、別の画面が表示されて、画像に付与されているメタデータ等を各画像に対する詳細情報として表示するようにしてもよい。 A
以上、本実施形態によってサンプル画像の中からクエリとして用いる指定領域を指定する部分画像検索方式において、指定領域の端の辺りからも精度良く特徴点や局所特徴量を算出可能になる。また、ユーザの指示に沿った精度の良いクエリを作成しつつ、特徴点および局所特徴量を算出する計算対象を削減できる。 As described above, according to the present embodiment, in the partial image search method for designating a designated area to be used as a query from sample images, it is possible to calculate feature points and local feature quantities with high accuracy from the edge of the designated area. In addition, it is possible to reduce the number of calculation targets for calculating feature points and local feature amounts while creating an accurate query in accordance with a user instruction.
<実施形態2>
本実施形態では、ユーザの指定した領域が本来ユーザが囲みたかった画像内のオブジェクトを分断しているかどうかを判定して、その判定結果と算出領域の大きさとを考慮してクエリ領域を決定する。<Embodiment 2>
In the present embodiment, it is determined whether or not the area specified by the user is dividing an object in the image that the user originally wanted to enclose, and the query area is determined in consideration of the determination result and the size of the calculation area. .
なお、実施形態1と同一機能を有する構成や工程には同一符号を付すとともに、構成的、機能的に変わらないものについてはその説明を省略する。 In addition, while attaching | subjecting the same code | symbol to the structure and process which have the same function as Embodiment 1, the description is abbreviate | omitted about the thing which does not change structurally and functionally.
図10は、本実施形態におけるクエリ領域の決定手順を示すフローチャートである。ステップS1001でユーザの指定した指定領域と、算出領域の大きさに関する情報を取得する。ステップS1002では指定領域と算出領域の大きさに基づいて拡大領域を決定する。拡大領域を決定する処理については実施形態1でクエリ領域を求める処理と同じである。なお、拡大領域は指定領域を包含する関係にある。ステップS1003では指定領域内の画像から特徴点を抽出する。特徴点を抽出する処理は図3のステップS302〜S304の処理と同じである。 FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing a procedure for determining a query area in the present embodiment. In step S1001, information related to the designated area designated by the user and the size of the calculation area is acquired. In step S1002, an enlargement area is determined based on the size of the designated area and the calculation area. The process for determining the enlarged area is the same as the process for obtaining the query area in the first embodiment. The enlarged area has a relationship including the designated area. In step S1003, feature points are extracted from the image in the designated area. The process of extracting feature points is the same as the process of steps S302 to S304 in FIG.
ステップS1003では拡大領域からエッジを抽出する。ステップS1004では拡大領域内の画像から特徴点を抽出する。ステップS1005ではステップS1004で抽出した特徴点の中からクエリ生成に用いる特徴点を選択する。まず、図8(a)の指定領域801から抽出された特徴点は確定特徴点として選択する。そして図8(b)の拡大領域803から抽出された特徴点を候補特徴点とする。指定領域801と拡大領域803との境界線上で抽出された特徴点805については、確定特徴点と候補特徴点とのどちらに分類しても良いが、本実施形態では確定特徴点として選択する。 In step S1003, an edge is extracted from the enlarged region. In step S1004, feature points are extracted from the image in the enlarged region. In step S1005, a feature point used for query generation is selected from the feature points extracted in step S1004. First, feature points extracted from the designated
候補特徴点の選別については、以下の処理を行う。まず、拡大領域から抽出したエッジセグメントが、指定領域801の外縁と交わる場合、指定領域内のオブジェクトが指定領域801の外縁によって分断されているかどうかを判定する。そして、分断されていると判定された場合に、候補特徴点の中でこのエッジセグメント上にある特徴点をクエリ生成に用いる特徴点として追加する。ただし、オブジェクトが分断されているか否かが判断できればどのような方法を使ってもよく、本発明はこの方法に限定されるものではない。 For selection of candidate feature points, the following processing is performed. First, when the edge segment extracted from the enlarged region intersects with the outer edge of the designated
そしてステップS1006において、指定領域と拡大領域と選択した特徴点とからクエリ領域を決定する。詳細には、指定領域に拡大領域と拡大領域から抽出された特徴点の算出領域とを加えてクエリ領域とする。簡略的には、ステップS1005で決定した全ての特徴点の算出領域としてもよい。 In step S1006, a query area is determined from the designated area, the enlarged area, and the selected feature point. Specifically, an enlarged area and a feature point calculation area extracted from the enlarged area are added to the designated area to obtain a query area. For simplicity, it may be a calculation region for all feature points determined in step S1005.
クエリ領域を決定した後は、クエリ領域内の特徴点について局所特徴量を算出しクエリを生成する処理をする実施形態1で説明した処理なので省略する。しかし、一度求めた特徴点を用いればよいので、クエリ領域から特徴点を抽出する処理を繰り返す必要はない。 After the query region is determined, the description is omitted because it is the processing described in Embodiment 1 in which the local feature amount is calculated for the feature points in the query region and the query is generated. However, since it is sufficient to use the feature points obtained once, there is no need to repeat the process of extracting the feature points from the query area.
〔エッジ抽出処理〕
エッジ抽出ステップS1003において、本実施例では、拡大領域にLOG(Laplacian of Gaussian)フィルタを施した結果の画像を調べ画像の画素値の符号が変化する点(零交差点)をエッジとして抽出する。[Edge extraction processing]
In the edge extraction step S1003, in this embodiment, an image obtained as a result of applying a LOG (Laplacian of Gaussian) filter to the enlarged region is examined, and a point (zero crossing point) where the sign of the pixel value of the image changes is extracted as an edge.
なお、本実施形態ではエッジ抽出処理にLOGを利用するが、本発明においては、特にLOGだけに限定されるものではない。エッジが抽出できるならば、DOG(Difference of Gaussian)や、その他のエッジ抽出フィルタを使ってもよい。また、エッジの細線化や、所定長以下のエッジを除去する等、一般的なノイズを落とす処理を行っても良い。 In the present embodiment, LOG is used for edge extraction processing. However, the present invention is not limited to LOG. If edges can be extracted, DOG (Difference of Gaussian) or other edge extraction filters may be used. In addition, general noise reduction processing such as thinning an edge or removing an edge having a predetermined length or less may be performed.
以上、本実施形態ではユーザの指定した領域が本来ユーザが囲みたかった画像内のオブジェクトを分断しているかどうかをエッジに基づいて判定して、最適なクエリ領域を決定できる。 As described above, in the present embodiment, it is possible to determine based on the edge whether or not the region designated by the user is dividing the object in the image that the user originally wanted to surround, and the optimum query region can be determined.
<その他の実施形態>
実施形態2の図10のステップS1005の処理において、拡大領域から抽出したエッジセグメントが、指定領域801の外縁と交わらず、拡大領域804の外縁と交わるかどうかを判定してもよい。すなわち、指定領域内のオブジェクトと関係の無いオブジェクトを拡大領域が含んでしまっているかどうかを判定する。そして、候補特徴点の中でこのエッジセグメント上にある特徴点を候補特徴点から除外する。本実施形態でエッジセグメントを除外する方法は、エッジセグメントを含む近傍の画素値を、拡大領域内のエッジセグメント以外の画素の平均値で置き換える処理で実現される。画素値を置き換える代わりに、エッジセグメントを含む近傍の画素を局所特徴量の計算から除外するように画素毎に情報を加えてもよい。<Other embodiments>
In the process of step S1005 in FIG. 10 of the second embodiment, it may be determined whether the edge segment extracted from the enlarged region intersects with the outer edge of the
また、上述の実施形態に限らず本発明は、特徴量として輪郭形状特徴量を利用し、拡大領域内にある輪郭(エッジ)が指定領域と交差する場合に、輪郭を追跡してクエリ領域に追加するようにしてもよい。 Further, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and the present invention uses a contour shape feature amount as a feature amount, and when the contour (edge) in the enlarged region intersects the designated region, the contour is tracked to the query region. You may make it add.
まず、図11のステップS1101で画像データを読み込み、ステップS1102で輝度成分を抽出し、ステップS1103の画像を二値化し、ステップS1104で輪郭形状の抽出を境界線追跡法によって行う。 First, the image data is read in step S1101 in FIG. 11, the luminance component is extracted in step S1102, the image in step S1103 is binarized, and the contour shape is extracted by the boundary tracking method in step S1104.
輪郭形状の抽出は、既存の技術を使用することが可能である。ここでは一例として、を用いる。まず、画像の左上から右下方向に向かってラスタ走査し、黒点を探し、最初に見つかった黒点を開始点とする。次に、近傍8画素において、左に隣接する画素から始めて反時計回りに連結されている画素かどうかの判定を行う。連結されている画素が無いとき、または、追跡先が開始点と一致したとき、一連の画素に対し、同じセグメントIDを与える。さらに、輪郭形状の内部の画素に対しては、非輪郭画素フラグを付す。次に、次の追跡開始点を探索する。直前の追跡処理の開始点から右下方向に向かってラスタ走査し、黒点を探す。その際、輪郭形状の一部としてセグメントIDが与えられている画素、非輪郭画素をスキップする。そうして見つかった黒点を開始点とし、前述の近傍8画素における追跡処理を行う。追跡開始点を探すステップにおいて、画像の右下に達した時点で、本輪郭形状の抽出ステップは終了する。 An existing technique can be used for extracting the contour shape. Here, as an example, is used. First, raster scanning is performed from the upper left to the lower right of the image, a black point is searched, and the first black point found is set as the start point. Next, it is determined whether or not the neighboring 8 pixels are pixels connected in the counterclockwise direction starting from the pixel adjacent to the left. When there is no connected pixel, or when the tracking destination matches the start point, the same segment ID is given to a series of pixels. Furthermore, a non-contour pixel flag is attached to the pixels inside the contour shape. Next, the next tracking start point is searched. Raster scanning is performed from the start point of the immediately preceding tracking process toward the lower right, and a black point is searched. At that time, pixels having a segment ID as a part of the contour shape and non-contour pixels are skipped. The black point thus found is used as a starting point, and the tracking process is performed on the above-described neighboring 8 pixels. In the step of searching for the tracking start point, when the lower right corner of the image is reached, the contour shape extraction step ends.
次にステップS1105で、抽出された輪郭形状ごとに、輪郭形状特徴量の算出を行う。まず輪郭を等間隔にサンプリングして得た複数の座標を、x座標、y座標ごとに個別に一次元信号化する。その信号をローパスフィルタによって段階的に凹部を除去する。各段階において、曲率のゼロクロス点(凹凸の境界)を抽出し、Curvature Scale Space(CSS、曲率尺度空間)を作成し、CSS画像の頂点の座標を特徴量とする。 In step S1105, a contour shape feature value is calculated for each extracted contour shape. First, a plurality of coordinates obtained by sampling the contour at equal intervals are individually converted into one-dimensional signals for each of the x and y coordinates. The recess is removed stepwise from the signal by a low-pass filter. In each stage, a zero cross point (bump of unevenness) of curvature is extracted to create a Curve Scale Space (CSS, curvature scale space), and the coordinates of the vertexes of the CSS image are used as feature amounts.
指定領域を用いて輪郭形状を抽出すると、図12の(A)に示す画像に対し、図12の(B)に示す輪郭形状が抽出されるが、上述の追跡処理を行うことにより、図12の(A)に示す画像に対し、図12の(C)に示す輪郭形状が抽出される。また、単純に拡大領域のみを用いた輪郭形状を抽出する処理では、図12の(A)に示す画像に対し、図12の(D)に示す輪郭形状が抽出されてしまう。 When the contour shape is extracted using the designated region, the contour shape shown in FIG. 12B is extracted from the image shown in FIG. 12A. By performing the tracking process described above, FIG. The contour shape shown in FIG. 12C is extracted from the image shown in FIG. Further, in the process of simply extracting the contour shape using only the enlarged region, the contour shape shown in FIG. 12D is extracted from the image shown in FIG.
また、輪郭形状特徴量の特徴量間の類似度の算出方法を説明する。クエリのCSS画像の頂点の座標がN個あり、それぞれの座標を(x1,y1),・・・,(xN,yN)とし、比較先のCSS画像の頂点の座標がM個あり、それぞれの座標を(u1,v1),・・・,(uM,vM)としたとき、類似度(距離)DCSSは次の式(8)からで算出できる。 Also, a method for calculating the similarity between the feature amounts of the contour shape feature amount will be described. There are N coordinates of the vertex of the CSS image of the query, each coordinate is (x1, y1), ..., (xN, yN), and there are M coordinates of the vertex of the CSS image of the comparison destination. When the coordinates are (u1, v1),..., (UM, vM), the similarity (distance) DCSS can be calculated from the following equation (8).
ユーザが入力装置104としてスタイラスなどを用いてクエリさ作成する領域を指定すると、本来検索して欲しいと思われる自動車の一部が、指定領域からはみ出してしまうことがある。このような場合、指定領域から輪郭形状を抽出すると、はみ出した部分が切り取られた輪郭形状になってしまう。この切り取られた部分の輪郭の特徴が強い場合、この部分に対する処理の違いによって、検索結果が変わることとなる。すなわち、この指定領域よりはみ出したオブジェクトの部分でも輪郭追跡を行って輪郭形状を抽出し、検索時に利用するようにすることで、検索のユーザの操作に対しても安定したクエリを作成し、精度良い検索が可能になる。 When the user designates an area to be queried using a stylus or the like as the
図1は前述した実施形態の画像処理装置の概略構成を示す図である。CPU101は画像処理装置における各種制御を実行する。その制御内容は、後述するROM102やRAM103のプログラムに記述されている。また、CPU自身の機能や、計算機プログラムの機構により、複数の計算機プログラムを並列に動作させることもできる。 FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of the image processing apparatus according to the above-described embodiment. The
ROM102は、CPU101が本発明を実現するための制御をするためのプログラムやデータが格納されている。 The
RAM103は、CPU101が処理するための制御プログラムを格納するとともに、CPU101が各種制御を実行する際の様々なデータの作業領域を提供する。 The
入力装置104は、カーソル移動を指示するカーソル移動キー等のような機能キーを備えたものである。なお、マウスのようなポインティングデバイスを有してもよい。 The
バス105は各構成に接続されているアドレスバス、データバスなどである。 A
外部記憶装置106は、さまざまなデータ等を記憶するための外部記憶装置である。例えば、ハードディスクやフロッピー(登録商標)ディスク、光ディスク、磁気ディスク、光磁気ディスク、磁気テープ、不揮発性のメモリカード等の記録媒体と、記憶媒体を駆動し、情報を記録するドライブなどを有する。保管されたプログラムやデータは入力装置等の指示や、各種計算機プログラムの指示により、必要な時にRAMに展開される。 The
表示器107は、液晶ディスプレイなどの表示手段を有し、各種入力操作の状態をユーザに対して表示する。 The
NCU108は、他のコンピュータ装置等と通信を行うための通信デバイスNCUであり、ネットワーク(LAN)等を介して、図にはないが遠隔地に存在する装置と通信し、本実施形態のプログラムやデータを共有することが可能になる。NCU108としては、USB、IEEE1394、P1284、SCSI、Ethernet(登録商標)等の有線通信や、Bluetooth(登録商標)、赤外線通信、IEEE801.11b等の無線通信等、通信可能に接続するものであればよい。 The
スキャナ109は、画像を読み取るためのイメージスキャナであり、セットされた紙原稿を1枚ずつ光学的に読み取り、イメージ信号をデジタル信号列に変換する。読み取られた画像データは、外部記憶装置やRAM等に格納することができる。 The
ROM102やRAM103などの記憶媒体には、本実施形態の処理をコンピュータに実現させる計算機プログラムやデータなどが格納されており、これらを、CPUが読み出し実行することによって本発明の機能を実現する。また、本発明に係わるプログラムやデータを格納した外部記録装置を本システムあるいは本装置に供給して、RAM103などの書き換え可能な記憶媒体上に前記の外部記憶装置から、そのプログラムがRAM上にコピーしてもよい。例えば、外部記憶装置としては、フロッピー(登録商標)ディスク、CD−ROM、ハードディスク、メモリカード、光磁気ディスクなどが挙げられる。 A storage medium such as the
また、画像データは、NCU108の通信デバイスによって接続されているネットワークスキャナ、コピー装置、デジタルスチルカメラフィルムスキャナ等の入力機器を介して入力されてもよい。また、デジタル画像データを保持する外部記憶装置から通信デバイスを介して入力されてもよい。また、スキャナ109で読み取った画像データは、外部記憶装置やRAM等ではなく、通信デバイスによって接続されたサーバやコピー機等の外部記憶装置等に格納してもよい。 Further, the image data may be input via an input device such as a network scanner, a copying apparatus, or a digital still camera film scanner connected by a communication device of the
尚、本発明は複数の機器(例えば、ホストコンピュータ、インターフェース機器、リーダ、プリンタなど)から構成されるシステムに適用しても、1つの機器からなる装置(例えば、複写機、ファクシミリ装置など)に適用しても良い。 Even if the present invention is applied to a system constituted by a plurality of devices (for example, a host computer, an interface device, a reader, a printer, etc.), it is applied to an apparatus (for example, a copying machine, a facsimile machine, etc.) comprising a single device. It may be applied.
本発明の目的は、前述した実施形態の機能を実現するソフトウェアのプログラムコードを記録した記録媒体(または記憶媒体)を、システムあるいは装置に供給し、そのシステムあるいは装置のコンピュータ(またはCPUやMPU)が記録媒体に格納されたプログラムコードを読み出し実行することによっても、達成されることは言うまでもない。この場合、記録媒体から読み出されたプログラムコード自体が前述した実施形態の機能を実現することになり、そのプログラムコードを記録した記録媒体は本発明を構成することになる。 An object of the present invention is to supply a recording medium (or storage medium) that records software program codes for realizing the functions of the above-described embodiments to a system or apparatus, and the computer of the system or apparatus (or CPU or MPU). Needless to say, this can also be achieved by reading and executing the program code stored in the recording medium. In this case, the program code itself read from the recording medium realizes the functions of the above-described embodiment, and the recording medium on which the program code is recorded constitutes the present invention.
また、コンピュータが読み出したプログラムコードを実行することにより、前述した実施形態の機能が実現されるだけでなく、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、コンピュータ上で稼働しているオペレーティングシステム(OS)などが実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって前述した実施形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。 Further, by executing the program code read by the computer, not only the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized, but also an operating system (OS) running on the computer based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that a case where the function of the above-described embodiment is realized by performing part or all of the actual processing and the processing is included.
さらに、記録媒体から読み出されたプログラムコードが、コンピュータに挿入された機能拡張カードやコンピュータに接続された機能拡張ユニットに備わるメモリに書込まれた後、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、その機能拡張カードや機能拡張ユニットに備わるCPUなどが実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって前述した実施形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。 Furthermore, after the program code read from the recording medium is written into a memory provided in a function expansion card inserted into the computer or a function expansion unit connected to the computer, the function is based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that the CPU or the like provided in the expansion card or the function expansion unit performs part or all of the actual processing and the functions of the above-described embodiments are realized by the processing.
本発明を上記記録媒体に適用する場合、その記録媒体には、先に説明したフローチャートに対応するプログラムコードが格納されることになる。 When the present invention is applied to the recording medium, program code corresponding to the flowchart described above is stored in the recording medium.
101 CPU
102 ROM
103 RAM
104 入力装置(ポインティングデバイス)
105 バス
106 外部記憶装置
107 表示器
108 NCU
109 スキャナ
200 画像検索装置
201 変換部
202 抽出部
203 決定部
204 算出部
205 画像特徴データベース
206 入力画像
207 領域情報
208 検索結果101 CPU
102 ROM
103 RAM
104 Input device (pointing device)
105
109 Scanner 200
Claims (9)
Translated fromJapanese画像を入力する入力手段と、
前記画像において検索に用いる領域を、前記画像を表示する画面の操作により指定領域として指定する指定手段と、
前記指定領域内の画像特徴量を抽出するのに必要な領域の大きさに関する情報に基づいて前記指定領域を拡大したものをクエリ領域として決定する決定手段と、
前記クエリ領域から画像特徴量を抽出する抽出手段と、
前記抽出手段の抽出した画像特徴量に基づいて該画像特徴量に類似する画像を検索する検索手段とを有することを特徴とする画像処理装置。An image processing apparatus that searches for similar images using image feature amounts,
An input means for inputting an image;
The area used for the search in theimage, and designation means for designatingas a designated area by an operation of a screen for displaying the image,
Determining means for determining, as a query area, an enlarged version of the designated areabased on information on the size of the area necessary for extracting the image feature amount in the designated area;
Extracting means for extracting an image feature amount from the query region;
An image processing apparatus comprising: search means for searching for an image similar to the image feature quantity based on the image feature quantity extracted by the extraction means.
該特徴点に関する画像特徴量を抽出する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の画像処理装置。The determining unit determines a feature point and a size of an area necessary for extracting theimage feature amount, and the extracting unit extracts a feature point and animage feature amount related to the feature point from the query region. The image processing apparatus according to claim 1.
画像を入力する入力工程と、
前記画像において検索に用いる領域を、前記画像を表示する画面の操作により指定領域として指定する指定工程と、
前記指定領域内の前記画像特徴量を抽出するのに必要な領域の大きさに関する情報に基づいて前記指定領域を拡大したものをクエリ領域として決定する決定工程と、
前記クエリ領域から画像特徴量を抽出する抽出工程と、
前記抽出工程において抽出した画像特徴量に基づいて該画像特徴量に類似する画像を検索する検索工程と
を有することを特徴とする画像処理方法。An image processing method for searching for similar images using image feature amounts,
An input process for inputting an image;
The area used for the search in theimage, a designation step of designatingas a designated area by an operation of a screen for displaying the image,
A determination step of determining, as a query area, an enlarged version of the designated areabased on information related to a size of an area necessary for extracting the image feature amount in the designated area;
An extraction step of extracting an image feature amount from the query region;
And a search step for searching for an image similar to the image feature amount based on the image feature amount extracted in the extraction step.
画像を入力する入力工程と、
前記画像において検索に用いる領域を、前記画像を表示する画面の操作により指定領域として指定する指定工程と、
前記指定領域内の画像特徴量を抽出するのに必要な領域の大きさに関する情報に基づいて前記指定領域を拡大したものをクエリ領域として決定する決定工程と、
前記クエリ領域から画像特徴量を抽出する抽出工程と、
前記抽出工程において抽出した画像特徴量に基づいて該画像特徴量に類似する画像を検索する検索工程と
を実行させることを特徴とするプログラム。On the computer,
An input process for inputting an image;
The area used for the search in theimage, a designation step of designatingas a designated area by an operation of a screen for displaying the image,
A determination step of determining, as a query area, an enlarged version of the designated areabased on information on the size of the area necessary for extracting the image feature amount in the designated area;
An extraction step of extracting an image feature amount from the query region;
And a search step of searching for an image similar to the image feature amount based on the image feature amount extracted in the extraction step.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013022371AJP5539555B2 (en) | 2013-02-07 | 2013-02-07 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013022371AJP5539555B2 (en) | 2013-02-07 | 2013-02-07 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008304603ADivisionJP5197328B2 (en) | 2008-11-28 | 2008-11-28 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013127809A JP2013127809A (en) | 2013-06-27 |
| JP5539555B2true JP5539555B2 (en) | 2014-07-02 |
Family
ID=48778259
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013022371AActiveJP5539555B2 (en) | 2013-02-07 | 2013-02-07 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5539555B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5933675B1 (en)* | 2014-12-09 | 2016-06-15 | エヌ・ティ・ティ・コムウェア株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program |
| US11055343B2 (en) | 2015-10-05 | 2021-07-06 | Pinterest, Inc. | Dynamic search control invocation and visual search |
| US11609946B2 (en) | 2015-10-05 | 2023-03-21 | Pinterest, Inc. | Dynamic search input selection |
| US11126653B2 (en) | 2017-09-22 | 2021-09-21 | Pinterest, Inc. | Mixed type image based search results |
| US11841735B2 (en) | 2017-09-22 | 2023-12-12 | Pinterest, Inc. | Object based image search |
| US10942966B2 (en) | 2017-09-22 | 2021-03-09 | Pinterest, Inc. | Textual and image based search |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3754786B2 (en)* | 1997-02-19 | 2006-03-15 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image processing apparatus and method |
| JP2008090814A (en)* | 2006-09-08 | 2008-04-17 | Seiko Epson Corp | Printing apparatus, image search method, and image search program |
- 2013
- 2013-02-07JPJP2013022371Apatent/JP5539555B2/enactiveActive
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013127809A (en) | 2013-06-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5139716B2 (en) | Image search apparatus and image search method | |
| JP5539555B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP5183392B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP5694234B2 (en) | Electronic device, handwritten document display method, and display program | |
| JP7186075B2 (en) | A method for guessing character string chunks in electronic documents | |
| JP2004240750A (en) | Image retrieval device | |
| JPS61267177A (en) | Retrieving system for document picture information | |
| JP5197328B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP2014086021A (en) | Electronic apparatus, handwritten document display method, and display program | |
| JP5094682B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| US20230205820A1 (en) | Geometry-based design data search tool | |
| JP5147640B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP5735126B2 (en) | System and handwriting search method | |
| JP2000322417A (en) | Image filing apparatus and method, and storage medium | |
| JP5330576B1 (en) | Information processing apparatus and handwriting search method | |
| JP2004240751A (en) | Image retrieval device | |
| JP2013239203A (en) | Electronic apparatus, method and program | |
| JP2021140831A (en) | Document image processing system, document image processing method, and document image processing program | |
| JP2009020689A (en) | Data search method and data search apparatus | |
| JP5361315B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus and information processing method | |
| JP2010092426A (en) | Image processing device, image processing method, and program | |
| JP5067182B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing program | |
| JPH11187231A (en) | Image retrieval apparatus and image retrieval method | |
| JP4050677B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, program, and recording medium | |
| JPWO2015004730A1 (en) | Method and electronic device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20131218 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20140107 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20140310 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20140401 | |
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration | Ref document number:5539555 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20140430 |