JP5380833B2 - Imaging apparatus, subject detection method and program - Google Patents
Imaging apparatus, subject detection method and programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5380833B2 JP5380833B2JP2007321969AJP2007321969AJP5380833B2JP 5380833 B2JP5380833 B2JP 5380833B2JP 2007321969 AJP2007321969 AJP 2007321969AJP 2007321969 AJP2007321969 AJP 2007321969AJP 5380833 B2JP5380833 B2JP 5380833B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- subject
- detection
- search range
- age
- image data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Focusing (AREA)
- Automatic Focus Adjustment (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、撮像装置、被写体検出方法及びプログラムに関する。The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus, asubject detection method, and a program.
従来、被写体を撮影してデジタルの画像データを得るデジタルカメラが知られている。また、画像における顔領域を検出するための探索窓のサイズを設定し、設定した探索窓のサイズに応じた探索範囲で探索窓を走査して顔領域を検出するカメラが考えられている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。そして、この従来のカメラでは、探索窓のサイズがしきい値以下の場合には、画像全域を探索せずに探索範囲を制限するため、顔領域の検出処理の高速化が図られる。
ここで、撮影時においては、大人と比べて子供がカメラの前で静止せずに動き回ることが多々あるため、被写体が子供である場合の顔領域検出の探索範囲を、被写体が大人である場合の探索範囲よりも大きくすることが望ましい。 Here, when shooting, a child often moves around without standing still in front of the camera compared to an adult, so the search range of face area detection when the subject is a child is It is desirable to make it larger than the search range.
しかしながら、上記従来のカメラでは、大人と子供とに探索範囲の大きさを異に設定できなかった。このため、被写体が大人である場合の探索範囲を、被写体が子供である場合の探索範囲と同じにすると、顔領域検出の効率が悪くなるという問題があった。 However, with the conventional camera, the size of the search range cannot be set differently for adults and children. For this reason, if the search range when the subject is an adult is the same as the search range when the subject is a child, there is a problem in that the efficiency of face area detection deteriorates.
本発明の課題は、被写体の動きやすさに応じて、被写体検出処理の効率を最適にすることである。 An object of the present invention is to optimize the efficiency of subject detection processing in accordance with the ease of movement of the subject.
上記課題を解決するために、請求項1に記載の発明の撮像装置は、撮像手段と、前記撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出手段と、前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の動きの大きさを推定する推定手段と、前記推定手段により推定された被写体の動きの大きさに基づき、前記被写体検出手段が被写体を検出する探索範囲を設定する探索範囲設定手段と、前記撮像手段により所定のフレーム間隔ごとに得られる第1の画像データにおける全範囲の被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御するとともに、前記第1の画像データ以外の第2の画像データにおいて、前記探索範囲設定手段により設定された探索範囲内で前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段と、を備える。
請求項2に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の撮像装置において、前記推定手段は、前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の年齢を推定することにより、前記被写体の動きの大きさを推定することを特徴とする。In order to solve the above problem, an imaging apparatus of the first aspect of the present invention, an imaging unit, and the object detecting means for detecting an object in the image datathat issuccessively captured by the imaging means, detected by said subject detection means Estimating means for estimatingthe magnitude ofmovement of the subject, search range setting meansfor setting a search range for detecting the subject by the subject detecting meansbased on the magnitude ofmovement of the subject estimated by the estimating means; Inthe second image data other than the first image data, the subject detection means is controlled to detect the entire range of subjects in the first image data obtained at predetermined frame intervals by the imaging means. subject detection for controlling said object detecting means to detect said objectwithin the search range which ismore set in the search range setting means Includes a control means, the.
According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the imaging apparatus according to the first aspect, the estimation unit estimates the size of the subject by estimating the age of the subject detected by the subject detection unit. It is characterized by doing.
請求項3に記載の発明の撮像装置は、撮像手段と、前記撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出手段と、前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の年齢を推定する推定手段と、被写体の角度に対応付けて被写体検出用データを記憶する記憶手段と、前記推定手段により推定された被写体の年齢に基づき、前記被写体検出手段による前記被写体の検出に用いる前記被写体検出用データの角度範囲を設定する角度範囲設定手段と、前記撮像手段により撮像された画像データにおいて、前記角度範囲設定手段に設定された角度範囲に対応する前記記憶された被写体検出用データを用いて、前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段と、を備える。
請求項4に記載の発明は、請求項3に記載の撮像装置において、前記推定手段により推定された年齢に基づいて、前記被写体検出手段が被写体を検出する探索範囲を設定する探索範囲設定手段を更に備え、前記被写体検出制御手段は、前記探索範囲設定手段により設定された探索範囲内で前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する。An imaging apparatus according to athird aspect of the inventionestimates an age of a subject detected by the imaging means, a subject detection means for detecting a subject in image data sequentially captured by the imaging means, and the subject detection means. An estimation unit; a storage unit that stores subject detection data in association with the angle of the subject; and the subject detection unit used for detection of the subject by the subject detection unit based on the age of the subject estimated by the estimation unit. and angular range setting means for setting the angular range of thedata, the image data imaged bythe imaging means, using the stored object detection datacorresponding to the set angle range to the angular range setting means,and a subject detection control means for controlling said object detecting means to detectthe object.
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, in the imaging device according to the third aspect, the search range setting means for setting a search range in which the subject detection means detects a subject based on the age estimated by the estimation means. Further, the subject detection control means controls the subject detection means so as to detect the subject within the search range set by the search range setting means.
請求項5に記載の発明は、請求項3又は4に記載の撮像装置において、前記角度範囲設定手段は、前記推定手段により推定された被写体の年齢が第1の年齢の場合に、前記第2の年齢の場合に設定される前記角度範囲よりも大きい前記角度範囲を設定する。
請求項6に記載の発明は、請求項2、4、5の何れか一項に記載の撮像装置において、前記探索範囲設定手段は、前記推定手段により推定された被写体の年齢が第1の年齢である場合は第1の探索範囲を、前記推定された被写体の年齢が第1の年齢より低い第2の年齢である場合は前記第1の探索範囲よりも大きい第2の探索範囲を前記被写体検出手段が被写体を検出する探索範囲として設定する。According to afifth aspect of the present invention, in the imaging apparatus according to the thirdor fourth aspect , the angle range setting unit includes the second range when the age of the subject estimated by the estimation unit is the first age. The angle range that is larger than the angle range set in the case of the age of is set.
According to a sixth aspect of the present invention, in the imaging device according to any one of the second, fourth, and fifth aspects, the search range setting unit is configured such that the age of the subject estimated by the estimation unit is a first age. Is the first search range, and when the estimated age of the subject is a second age lower than the first age, the second search range is larger than the first search range. The detection means sets the search range for detecting the subject.
請求項7に記載の発明の被写体検出方法は、撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出ステップと、前記被写体検出ステップにより検出された被写体の動きの大きさを推定する推定ステップと、前記推定ステップにより推定された被写体の動きの大きさに基づき、前記被写体検出ステップで被写体を検出する探索範囲を設定する探索範囲設定ステップと、前記撮像手段により所定のフレーム間隔ごとに得られる第1の画像データにおける全範囲の被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御するとともに、前記第1の画像データ以外の第2の画像データにおいて、前記探索範囲設定ステップにて設定された探索範囲内で前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出を制御する被写体検出制御ステップと、を含む。
請求項8に記載の発明の被写体検出方法は、撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出ステップと、前記被写体検出ステップにより検出された被写体の年齢を推定する推定ステップと、前記推定ステップにより推定された被写体の年齢に基づき、前記被写体検出ステップによる前記被写体の検出に用いる前記被写体検出用データの角度範囲を設定する角度範囲設定ステップと、前記撮像手段により撮像された画像データにおいて、前記角度範囲設定ステップに設定された角度範囲に対応する被写体検出用データを用いて、前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段ステップと、を含むObject detection method of the invention described in claim7 includes the subject detection step of detecting an object in the image datathat issuccessively captured by the imaging means, estimated for estimating themagnitude of the motion of the subject detected by the subject detection step A search range setting stepfor setting a search range for detecting a subject in the subject detection stepbased on the magnitude of themotion of the subject estimated in the estimation step;and obtaining at a predetermined frame interval by the imaging means. controls said object detecting means to detect a subject in the entire range of the first image data to besearchedfor, in the second image data other than the first image data, set by said search range setting step and the subject detection control step of controlling the object detection to detect said objectwithin Including the.
A subject detection method according to an eighth aspect of the present invention is a subject detection step of detecting a subject in image data sequentially captured by an imaging means, an estimation step of estimating the age of the subject detected by the subject detection step, An angle range setting step for setting an angle range of the subject detection data used for the detection of the subject by the subject detection step based on the age of the subject estimated by the estimation step, and image data captured by the imaging means And asubject detection control means step for controlling thesubject detection means to detect thesubject using subject detection data corresponding to the angle range set in the angle range setting step.
請求項9に記載の発明のプログラムは、コンピュータを、撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出手段、前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の動きの大きさを推定する推定手段、前記推定手段により推定された被写体の動きの大きさに基づき、前記被写体検出手段が被写体を検出する探索範囲を設定する探索範囲設定手段、前記撮像手段により所定のフレーム間隔ごとに得られる第1の画像データにおける全範囲の被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御するとともに、前記第1の画像データ以外の第2の画像データにおいて、前記探索範囲設定手段により設定された探索範囲内で前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段、として機能させる。
請求項10に記載の発明のプログラムは、コンピュータを、撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出手段と、前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の年齢を推定する推定手段、前記推定手段により推定された被写体の年齢に基づき、前記被写体検出手段による前記被写体の検出に用いる前記被写体検出用データの角度範囲を設定する角度範囲設定手段と、前記撮像手段により撮像された画像データにおいて、前記角度範囲設定手段に設定された角度範囲に対応する被写体検出用データを用いて、前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段、として機能させる。Program of the invention described in claim9, a computer, a subject detecting means for detecting an object in the image datathat issuccessively captured by the imaging means, estimated for estimating themagnitude of the motion of the subject detected by the subject detecting means A search range setting unitthat sets a search range in which the subject detection unit detects a subjectbased on the magnitude ofmovement of the subject estimated by the estimation unit, and a first rangeobtained by the imaging unit at predetermined frame intervals. controls said object detecting means to detect a subject in the entire range of the first image data, the second image data other than the first image data,within a search range set by the search range setting means It functions as subject detection control means for controlling the subject detection means to detect the subject.
According to a tenth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a program for detecting a subject in image data sequentially captured by an imaging unit, an estimation unit for estimating an age of the subject detected by the subject detection unit, Based on the age of the subject estimated by the estimation means, an angle range setting means for setting an angle range of the subject detection data used for detection of the subject by the subject detection means, and image data captured by the imaging means And using the subject detection data corresponding to the angle range set by the angle range setting means as a subject detection control means for controlling the subject detection means to detect the subject.
本発明によれば、被写体検出処理の効率を最適にできる。According to the present invention,the efficiency ofsubject detection processing can be optimized.
以下、添付図面を参照して本発明に係る好適な実施の形態を詳細に説明する。なお、本発明は、図示例に限定されるものではない。 DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. The present invention is not limited to the illustrated example.
先ず、図1〜図3を参照して、本実施の形態の装置構成を説明する。図1を参照して、本実施の形態の撮像装置としてのデジタルカメラ1の外観を説明する。図1(a)に、本実施の形態のデジタルカメラ1の主に前面の構成を示す。図1(b)に、デジタルカメラ1の主に背面の構成を示す。 First, the device configuration of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. With reference to FIG. 1, an appearance of a
図1(a)に示すように、デジタルカメラ1は、略矩形の薄板状ボディの前面に、撮影レンズ2、を配設し、上面には電源キー3及びシャッタキー4を配する。 As shown in FIG. 1A, the
撮影レンズ2は、合焦動作は行うためのフォーカスレンズとズーム動作を行うためのズームレンズとで構成される。電源キー3は、1回押圧操作する毎に電源をオン/オフするキーである。シャッタキー4は、撮影モード時にレリーズ(画像の記録)等を指示する一方で、メニュー選択等では設定/実行を指示するキーとしても機能するものとする。シャッタキー4は、撮影モード時に、半押しされることで、顔検出を指示し、全押しされることによりレリーズを指示する。 The photographing
また、図1(b)に示すように、デジタルカメラ1の背面には、モードスイッチ(SW)5、メニューキー6、十字キー7及び表示部8を配する。 As shown in FIG. 1B, a mode switch (SW) 5, a
モードスイッチ5は、例えばスライドスイッチにより構成され、撮影モード「R」と再生モード「P」とを切換える。メニューキー6は、各種メニュー選択時に操作する。十字キー7は、各種選択時等に操作する。表示部8は、バックライト付きのカラー液晶パネルで構成されるもので、撮影モード時には電子ファインダとしてモニタ表示(スルー画像表示)を行なう一方で、再生モード時には選択した画像を再生表示する。なお、デジタルカメラ1のボディ下面には蓋付きのメモリカードスロット(図示略)が設けられ、このデジタルカメラ1の記録媒体であるメモリカード28が着脱自在に装着されるものとする。 The
次いで、図2を参照して、デジタルカメラ1の内部構成を説明する。図2に、デジタルカメラ1の内部構成を示す。 Next, the internal configuration of the
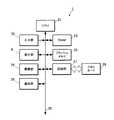
図2に示すように、デジタルカメラ1は、被写体検出手段、推定手段、探索範囲設定手段、被写体検出制御手段、年齢推定手段、角度範囲設定手段、としてのCPU(Central Processing Unit)21と、入力部22と、RAM(Random Access Memory)23と、表示部8と、撮像手段としての撮像部24と、記憶手段としてのフラッシュメモリ25と、通信部26と、記録部27と、を備えて構成され、各部がバス30を介して接続される。 As shown in FIG. 2, the
CPU21は、デジタルカメラ1の各部を中央制御する。また、CPU21は、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶されたシステムプログラム及びアプリケーションプログラムの中から指定されたプログラムを読み出してRAM23に展開し、展開されたプログラムとの協働で各種処理を実行する。 The
CPU21は、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶された被写体検出撮影プログラムとの協働で、シャッタキー4の半押しで、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶された顔検出用情報50を用いて、撮像部24で撮像されたフレームデータの画像(フレーム画像)の探索範囲から被写体の顔を検出するとともに、検出した被写体の年齢を推定し(大人か子供かを判別し)、被写体が子供である場合に、被写体が大人である場合よりも、次フレームの探索範囲を大きくし、シャッタキー4の全押しでその被写体を撮影する。本実施の形態では、被写体の動きやすさを示す情報として、被写体の年齢(大人か子供か)を用いる。年齢が低い(子供)の方が動きやすさが大きく、年齢が高い(大人)の方が動きやすさが小さい。 The
入力部22は、ユーザからの操作入力を受け付けて操作信号をCPU21に出力する。入力部22は、電源キー3、シャッタキー4、モードスイッチ5、メニューキー6、十字キー7等を含み、各種キー、スイッチ等の操作入力を受け付ける。 The input unit 22 receives an operation input from the user and outputs an operation signal to the
RAM23は、情報を一時的に格納する揮発性のメモリであり、各種プログラム及び各種データが展開されるワークエリアを有する。また、RAM23は、撮像部24で撮像された画像データが一時的に格納され、後述する履歴情報60が格納される。 The
表示部8は、液晶ディスプレイであり、CPU21から入力される表示信号に基づいて各種情報を表示する。また、表示部8は、スルー画像、撮影画像等の情報を表示する。また、表示部8は、液晶ディスプレイに限定されるものではなく、ELD(ElectroLuminescent Display)等としてもよい。 The
撮像部24は、被写体を撮像してデジタルの画像データを出力する。撮像部24は、撮影レンズ2などが含まれる。また、撮像部24の内部構成を後述する。 The
フラッシュメモリ25は、情報を読み込み及び書き込み可能な不揮発性の内部メモリである。フラッシュメモリ25は、後述する被写体検出撮影プログラム、顔検出用情報50を記憶する。 The
通信部26は、PC(Personal Computer)等の外部機器とデータの送受信を行う。通信部26は、通信ケーブルを介して外部機器と有線通信を行うものとするが、これに限定されるものではなく、赤外線や無線等で通信を行う構成としてもよい。 The
記録部27は、メモリカード28が着脱自在に接続(セット)され、CPU21から入力される制御信号に従い、接続されたメモリカード28に画像データ等のデータを書き込み、あるいは接続されたメモリカード28から画像データ等のデータを読み込んでCPU21に出力する。メモリカード28は、SD(Secure Digital)カード、メモリースティック等の記録媒体(記録メディア)である。 In the
ここで、図3を参照して、撮像部24の詳細な内部構成を説明する。図3に、撮像部24の詳細な構成を示す。 Here, a detailed internal configuration of the
撮像部24は、レンズ光学系31、絞り機構32、撮像素子33、光学系駆動部34、センサ部35、駆動回路36、アナログ処理回路37、A/D(Analog to Digital)変換回路38、バッファレジスタ39、信号処理回路40、圧縮伸長回路41等を備えて構成される。 The
撮像部24は、CPU21の制御に従い動作する。具体的には、撮像部24は、撮影の際に、フォーカスレンズとズームレンズとで構成される撮影レンズ2を含むレンズ光学系31の光束の開口量が絞り機構32によって調整され、被写体像がレンズ光学系31によってCCD(Charge Coupled Devices)等の撮像素子33上に結像される。また、AF(Auto Focus)時に、合焦のためにフォーカスレンズが光学系駆動部34によって光軸に沿って移動され、AE(Automatic Exposure)時に、適切な露出となるように絞り機構32の開口量が光学系駆動部34によって制御される。また、ズーム時に、ズームレンズが光学系駆動部34によって光軸に沿って移動され、撮影範囲である画角が変更される。 The
また、測距センサや光量センサを含むセンサ部35によって検出された検出値がバス30を介してCPU21に送られ、CPU21によって検出値に基づいて演算された移動量や開口量を示す信号が光学系駆動部34に送られることによって、光学系駆動部34によりレンズ光学系31の移動や絞り機構32の開口量を調整する。 A detection value detected by the
撮像素子33に被写体像が結像されることにより、撮像素子33には入射光量に応じた電荷が蓄積され、蓄積された電荷は駆動回路36から与えられる駆動パルス信号によって順次読み出されその信号がアナログ処理回路37に送られる。アナログ処理回路37では、入力された信号に対して色分離やゲイン調整、ホワイトバランスなどの各種処理が行われ、処理された信号がA/D変換回路38を介してデジタルのフレームデータ(静止画データ)としてバッファレジスタ39に記憶される。 When the subject image is formed on the
バッファレジスタ39に記憶されたフレームデータは、信号処理回路40において輝度信号及び色差信号に変換されバス30を介してRAM23に順次記録される。また、このとき順次記録されているフレームデータの画像(フレーム画像)が表示部8にも表示され、撮影したスルー画像を確認できるようになっている。なお、静止画の撮影の場合には、バッファレジスタ39に記憶されたフレームデータが圧縮伸長回路41によってJPEG(Joint Photographic Coding Experts Group)形式に圧縮され、バス30を介してRAM23に静止画データとして記録される。 The frame data stored in the
次に、図4、図5及び図6を参照して、デジタルカメラ1で扱うデータを説明する。図4に、顔検出用情報50の構成を示す。図5に、テンプレートテーブル51の一例を示す。図6に、履歴情報60の構成を示す。 Next, data handled by the
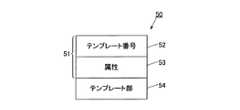
図4に示す顔検出用情報50は、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶され、フレーム画像の顔の検出時に用いられる顔検出用のテンプレートに関する情報である。顔検出用情報50は、テンプレートテーブル51と、テンプレート部54と、を含んで構成される。テンプレートテーブル51は、テンプレート番号52と、属性53とが対応付けられて含められている。 The
テンプレート番号52は、テンプレート部54内の複数のテンプレートの識別情報である。属性53は、テンプレート部54内の各テンプレートの(被写体の)属性情報である。本実施の形態では、属性53が、各テンプレートの登録人物(被写体)を識別する識別情報と、各テンプレートの登録人物が大人であるか子供であるかを示す情報と、各テンプレートの顔の撮影角度を示す角度情報(水平方向及び垂直方向の角度)と、を含むものとする。大人であるか子供であるかを示す情報は、例えば、所定年齢(18歳等)より小さい人物を子供とし、その所定年齢以上の人物を大人とする。 The
テンプレート部54は、属性53毎にテンプレートを有し、テンプレート番号に対応付けられたテンプレートを有する。各テンプレートは、登録人物の顔を撮影した顔画像データであり、顔検出に用いられる。各テンプレートは、例えば、20×20ピクセルの画像データとする。テンプレート部54には、同一の登録人物について、顔の撮影角度に応じたテンプレートが複数格納される。また、テンプレート部54には複数の登録人物のテンプレートが格納されるものとする。 The
図5に示すテンプレートテーブル51は、登録人物aについてのテーブルである。登録人物aは、属性53としての登録人物名である。登録人物aについて、属性53としての顔の角度情報が、水平方向の-90°〜+90°と、垂直方向の-30°〜+30°とであり、それぞれ15°間隔で、テンプレート番号52が1A〜5A,…,1M〜5Mのテンプレートがある。顔の向きが真正面である場合の角度情報を水平角度0°,垂直角度0°とする。 A template table 51 shown in FIG. 5 is a table for the registered person a. The registered person a is a registered person name as the
また、被写体検出撮影処理において図6に示す履歴情報60が生成されてRAM23に格納される。履歴情報60は、顔を検出した検出結果の情報である。履歴情報60は、フレーム番号61、解像度62、探索範囲63、テンプレート番号64等を含んで構成される。 Further, the
フレーム番号61は、撮像部24で撮像されたフレームデータの識別情報である。解像度62は、フレーム番号61のテンプレートと照合を行った際のフレームデータの解像度である。探索範囲63は、顔が検出されたフレーム番号61のフレーム画像中の探索範囲を示す情報であり、探索範囲の中心の位置情報及び探索範囲の大きさ情報を含む。テンプレート番号64は、フレーム番号61のフレームデータと照合を行ったテンプレートのテンプレート番号である。 The
履歴情報60の解像度62に関し、ここで、図7を参照して、解像度ピラミッドを説明する。図7に、解像度ピラミッドの概念構成を示す。 Regarding the
解像度ピラミッドは、様々な大きさの入力画像(フレーム画像)に対してテンプレート照合を行うことで、入力画像の様々な大きさの顔検出を行うためのものである。図7に示すように、フレーム画像内に3人の顔の大きさが異なる被写体A,B,Cが写っている場合を考える。顔の大きさは、顔A>顔B>顔Cである。 The resolution pyramid is used to detect faces of various sizes in the input image by performing template matching on input images (frame images) of various sizes. As shown in FIG. 7, consider a case where subjects A, B, and C having different face sizes are shown in a frame image. The size of the face is face A> face B> face C.
フレーム画像内の被写体A,B,Cの顔検出を行う場合に、テンプレートと照合を行う。その際にテンプレートと、当該テンプレートと同じ大きさ(解像度)の(テンプレート画像の)切り出し画像と、が照合される。このため、先ず、元となるテンプレート画像から解像度の異なるフレーム画像(解像度ピラミッド)が生成される。そして、テンプレートが被写体A,B,Cの顔と同じ大きさとなるフレーム画像の切り出し画像と、テンプレートとが照合される。そして、フレーム画像から被写体の顔が検出されたときの解像度が履歴情報60の解像度62に設定される。解像度62は、例えば、元のフレーム画像に対する解像度の割合で示され、80%,60%等で表される。 When face detection of subjects A, B, and C in a frame image is performed, matching with a template is performed. At that time, the template and the cut-out image (of the template image) having the same size (resolution) as the template are collated. For this reason, first, a frame image (resolution pyramid) having a different resolution is generated from the original template image. Then, the cut-out image of the frame image whose template is the same size as the faces of the subjects A, B, and C is collated with the template. Then, the resolution when the face of the subject is detected from the frame image is set to the
次に、図8及び図9を参照して、デジタルカメラ1の動作を説明する。図8に、被写体検出撮影処理の流れを示す。図9に、探索範囲を示す。 Next, the operation of the
被写体検出撮影処理は、被写体の年齢(大人であるか子供であるか)に応じて顔の探索範囲を変更し、その探索範囲内で顔検出して撮影する処理である。デジタルカメラ1において、例えば、入力部22を介して被写体検出撮影処理の実行指示が操作入力されたことをトリガとして、フラッシュメモリ25から読み出されて適宜RAM23に展開された被写体検出撮影プログラムと、CPU21との協働で被写体検出撮影処理が実行される。 The subject detection photographing process is a process of changing the face search range according to the age of the subject (whether it is an adult or a child), and detecting and photographing the face within the search range. In the
図8に示すように、先ず、撮像部24で撮像されたフレームデータが順次RAM23に格納されて表示部8に表示され、スルー画像表示が開始される(ステップS11)。フレームデータの撮像は、例えば、30[fps]で行われる。そして、シャッタキー4の半押し入力が検知され、半押し入力されたか否かが判別される(ステップS12)。シャッタキー4が半押し入力されていない場合(ステップS12;NO)、ステップS12に移行される。 As shown in FIG. 8, first, frame data imaged by the
シャッタキー4が半押し入力された場合(ステップS12;YES)、フレーム番号Mに1が代入される(ステップS13)。Mは、フレーム番号の変数である。フレーム番号は、ステップS12の半押し検知後のフレームデータを初期値1として、フレームデータ生成ごとに1づつインクリメントされるものとする。 When the shutter key 4 is half-pressed (step S12; YES), 1 is assigned to the frame number M (step S13). M is a variable of the frame number. The frame number is incremented by 1 every time frame data is generated, with the frame data after half-pressing detection in step S12 being the
そして、フレーム番号Mが、予め設定された定数Nの倍数であるか否かが判別される(ステップS15)。フレーム番号Mが定数Nの倍数である場合(ステップS15;YES)、顔検出用情報50がフラッシュメモリ25から読み出され、履歴情報60がRAM23から読み出され、履歴情報60のM番目のフレーム画像に対応する顔検出用情報50のテンプレートを用いてフレーム番号Mのフレーム画像の全範囲で被写体の顔が検出される(ステップS16)。 Then, it is determined whether or not the frame number M is a multiple of a preset constant N (step S15). When the frame number M is a multiple of the constant N (step S15; YES), the
ここで、ステップS16を詳細に説明する。ステップS16においては、M>1の場合に、履歴情報60において、フレーム番号61=Mに対応して後述するステップS21で選択された解像度62が、フレーム番号Mの解像度として取得される。そして、ステップS14で取得されたフレーム番号Mのフレーム画像を基にして、フレーム番号Mの解像度62のフレームデータが生成される。そして、履歴情報60において、フレーム番号61=Mに対応して後述するステップS20で選択されたテンプレート番号64が取得され、このテンプレート番号に対応するテンプレートが顔検出用情報50のテンプレート部54から取得される。 Here, step S16 will be described in detail. In step S16, when M> 1, in the
そして、上記取得された解像度に対応するフレーム番号Mのフレーム画像の全範囲から順に切り出し画像が切り出され、上記取得されたテンプレートと、各切り出し画像とが照合され、一致する場合にそのテンプレートの被写体の顔が検出される。また、被写体の顔検出時に、フレーム画像内における被写体が検出された顔領域の中心位置を示す位置情報が取得され、顔検出されたテンプレートのテンプレート番号及び顔の角度情報が、顔検出用情報50のテンプレート番号52及び属性53から取得される。 Then, a cutout image is cut out sequentially from the entire range of the frame image of frame number M corresponding to the acquired resolution, and the acquired template and each cutout image are collated, and when the template matches, the subject of the template Is detected. Further, when detecting the face of the subject, position information indicating the center position of the face area where the subject is detected in the frame image is acquired, and the template number and face angle information of the face detected template are the
フレーム番号Mのフレーム画像において、テンプレートと同じ大きさ(例えば20×20ピクセル)の画像が順次切り出されて切り出し画像とされる。切り出し画像は、例えば、フレーム番号Mのフレーム画像の探索範囲(ステップS16では全範囲)において、左上→右上→1ピクセル下げた右端→同左端→1ピクセル下げた左端→…→右下又は左下に、順次1ピクセルづつずらして切り出されて、それぞれ照合に使われる。 In the frame image of frame number M, images having the same size as the template (for example, 20 × 20 pixels) are sequentially cut out to be cut out images. The clipped image is, for example, in the search range of the frame image of frame number M (the entire range in step S16) at the upper left → upper right → the right end lowered by 1 pixel → the left end → the left end lowered by 1 pixel → ... → lower right or lower left. Then, the pixels are cut out by shifting one pixel at a time and used for matching.
但し、フレーム番号M=1の場合に、ステップS16においては、対応する履歴情報60がない。このため、先ず、フレーム番号Mのフレーム画像の解像度の異なる全解像度のフレームデータ(解像度ピラミッド)が生成される。その全解像度のフレーム番号Mのフレーム画像に対して、そのフレーム画像の全範囲から切り出し画像が順に切り出され、顔検出用情報50のテンプレート部54の全てのテンプレートと、各切り出し画像とが照合され、一致する場合にそのテンプレートの被写体の顔が検出される。 However, when the frame number M = 1, there is no
図8に戻り、ステップS16の実行後、顔検出用情報50が参照され、ステップS16で検出された被写体の顔の検出に用いたテンプレートのテンプレート番号52に対応する属性53から、被写体の年齢(大人であるか子供であるか)が判別(推定)される(ステップS17)。そして、ステップS16で検出された被写体の位置情報と、ステップS17で判別された被写体の年齢情報とに基づいて、フレーム番号(M+1)のフレーム画像の探索範囲が決定され、履歴情報60のフレーム番号61=(M+1)の探索範囲63に設定され、又はそのフレーム番号61=(M+1)の探索範囲63を有する履歴情報60がRAM23に格納される(ステップS18)。 Returning to FIG. 8, after the execution of step S <b> 16, the
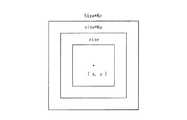
ステップS18においては、被写体が大人であるか子供であるかに応じて、探索範囲の大きさが変えられる。具体的には、図9に示すように、検出された顔領域の中心位置の座標を(x,y)とし、テンプレートの大きさをsizeとした時、以下の範囲に収まる探索範囲が選択されて決定される。KaとKcとは、探索範囲係数であり、値が大きいほど探索範囲が広くなる。Kaが大人用で、Kcが子供用である。Ka<Kcになるように設定されている。ステップS18においては、ステップS16の位置情報から座標(x,y)が決定され、ステップS17の年齢情報から大きさsize*Ka又はsize*Kcが決定され、その決定した中心位置及び大きさを有する探索範囲が決定される。 In step S18, the size of the search range is changed depending on whether the subject is an adult or a child. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 9, when the coordinate of the center position of the detected face area is (x, y) and the size of the template is size, a search range that falls within the following range is selected. Determined. Ka and Kc are search range coefficients. The larger the value, the wider the search range. Ka is for adults and Kc is for children. Ka <Kc is set. In step S18, the coordinates (x, y) are determined from the position information in step S16, and the size size * Ka or size * Kc is determined from the age information in step S17, and has the determined center position and size. A search range is determined.
フレーム番号Mが定数Nの倍数でない場合(ステップS15;NO)、顔検出用情報50がフラッシュメモリ25から読み出され、履歴情報60がRAM23から読み出され、履歴情報60のM番目のフレーム画像に対応する顔検出用情報50のテンプレートを用いてフレーム番号Mのフレーム画像の、フレーム番号が直近のNの倍数の探索範囲63で被写体の顔が検出される(ステップS19)。 When the frame number M is not a multiple of the constant N (step S15; NO), the
ここで、ステップS19を詳細に説明する。ステップS19においては、履歴情報60において、フレーム番号61=Mに対応してステップS21で選択された解像度62が、フレーム番号Mの解像度として取得される。そして、ステップS14で取得されたフレーム番号Mのフレーム画像を基にして、フレーム番号Mの解像度62のフレームデータが生成される。そして、履歴情報60において、フレーム番号61=Mに対応してステップS20で選択されたテンプレート番号64と、フレーム番号61=直近のNの倍数に対応してステップS18で決定された探索範囲63とが取得され、このテンプレート番号に対応するテンプレートが顔検出用情報50のテンプレート部54から取得される。 Here, step S19 will be described in detail. In step S19, in the
そして、上記取得された解像度に対応するテンプレート番号(直近のNの倍数)のフレーム画像の探索範囲63から順に切り出し画像が切り出され、上記取得されたテンプレートと、各切り出し画像とが照合され、一致する場合にそのテンプレートの被写体の顔が検出される。また、被写体の顔検出時に、フレーム画像内における被写体が検出された切り出し画像の中心位置を示す位置情報が取得され、顔検出されたテンプレートのテンプレート番号及び顔の角度情報が、顔検出用情報50のテンプレート番号52及び属性53から取得される。ステップS19では、ステップS16〜S18のようなフレーム画像の全範囲の顔検出を行うことなく、フレーム番号Mの探索範囲62の顔検出を行うため、処理負担が軽減される。また、ステップS19では、ステップS18と同様にして、被写体の年齢情報が判別(推定)される。 Then, the clipped images are cut out in order from the
ステップS18又はS19の実行後、ステップS16又はS19で顔検出されたテンプレートのテンプレート番号と、ステップS16で又はS19で取得された被写体の年齢情報及び角度情報とに基づいて、フレーム番号(M+1)のテンプレート番号が選択され、そのテンプレート番号が、履歴情報60のフレーム番号61=(M+1)のテンプレート番号64に設定され、又はそのフレーム番号61,テンプレート番号64を有する履歴情報60がRAM23に格納される(ステップS20)。 After execution of step S18 or S19, the frame number (M + 1) is determined based on the template number of the template detected in step S16 or S19 and the age information and angle information of the subject acquired in step S16 or S19. A template number is selected, and the template number is set to the
ステップS20のテンプレートの決定ではスナップショットを撮影する際、大人に比べると子供はカメラの前で静止せず、動きが大きいという性質を利用する。子供は大人よりも動きが大きいので、顔の角度が変化する幅が大きくなる。そのため、大人よりも広い範囲の角度で検出処理を行なう必要がある。そこで、子供の場合は、大人よりも、識別可能な顔の角度の範囲を広げてテンプレートを選択する個数を増やす。 In the determination of the template in step S20, when taking a snapshot, the child takes advantage of the fact that the child does not stand still in front of the camera and moves much more than an adult. Because children move more than adults, the range of change in face angle is greater. Therefore, it is necessary to perform detection processing at a wider range of angles than adults. Therefore, in the case of a child, the number of templates that can be selected is increased by expanding the range of face angles that can be identified, compared to adults.
例えば、図3のテンプレートテーブル51において、ステップS16で検出された顔がテンプレート(水平角度0°、垂直角度0°:テンプレート番号3G)で照合された場合、大人の顔ならば、中心のテンプレート(水平角度0°、垂直角度0°:テンプレート番号3G)と、中心のテンプレートに隣接する8つのテンプレート(水平角度-15°,+15°、垂直角度-15°,+15°:テンプレート番号2G〜2H,3F,3H,4G〜4H)との合計9つのテンプレートのテンプレート番号が、フレーム番号(M+1)のテンプレート番号として選択される。 For example, in the template table 51 of FIG. 3, when the face detected in step S16 is collated with a template (horizontal angle 0 °, vertical angle 0 °:
ステップS16で検出された顔がテンプレート(水平角度0°、垂直角度0°:テンプレート番号3G)で照合された場合、子供ならば、中心のテンプレート(水平角度0°、垂直角度0°:テンプレート番号3G)に隣接する8つのテンプレート(水平角度-15°,+15°、垂直角度-15°,+15°:テンプレート番号2G〜2H,3F,3H,4G〜4H)と、さらにその8つに隣接する16のテンプレート(テンプレート番号1E〜1I,2E〜4E,2I〜4I,5E〜5I)との合計25のテンプレートのテンプレート番号が、フレーム番号(M+1)のテンプレート番号として選択される。 If the face detected in step S16 is collated with a template (horizontal angle 0 °, vertical angle 0 °:
ステップS20の実行後、ステップS16又はS19で顔検出されたテンプレートの解像度に基づいて、フレーム番号(M+1)の解像度が選択され、そのテンプレート番号が、履歴情報60のフレーム番号61=(M+1)の解像度62に設定され、又はそのフレーム番号61,解像度62を有する履歴情報60がRAM23に格納される(ステップS21)。 After the execution of step S20, the resolution of the frame number (M + 1) is selected based on the resolution of the template detected in step S16 or S19, and the template number is the
ステップS21においては、具体的には、ステップS16又はS19で顔検出されたテンプレートの解像度と同じ解像度と、一段大きい解像度と、一段小さい解像度とが、選択される。また、ステップS20、S21では、時間的に連続するフレーム間(フレーム番号M,(M+1))において画像内容の変化は小さい、という性質を用いて、前回検出された顔と近いテンプレート及び解像度を選択するという手法を用いている。 Specifically, in step S21, the same resolution as the template detected in step S16 or S19, a larger resolution, and a smaller resolution are selected. Also, in steps S20 and S21, a template and resolution close to the previously detected face are selected using the property that the change in image content is small between temporally consecutive frames (frame numbers M and (M + 1)). Is used.
ステップS21の実行後、シャッタキー4の全押し入力が検知され、全押し入力されたか否かが判別される(ステップS22)。そして、シャッタキー4が全押しされていない場合(ステップS22;NO)、フレーム番号Mが1インクリメントされ(ステップS23)、ステップS14に移行される。 After execution of step S21, full-press input of the shutter key 4 is detected, and it is determined whether or not full-press input has been made (step S22). If the shutter key 4 is not fully pressed (step S22; NO), the frame number M is incremented by 1 (step S23), and the process proceeds to step S14.
そして、シャッタキー4が全押しされた場合(ステップS22;NO)、直前のステップS16又はS19で顔検出された被写体に対して、光学系駆動部34、駆動回路36を介してレンズ光学系31、絞り機構32、撮像素子33が駆動されて、その顔検出された被写体(の顔)に対してAE及びAFが実行されてロックされる(ステップS24)。 Then, when the shutter key 4 is fully pressed (step S22; NO), the lens
そして、ステップS24の状態で、撮像部24により被写体が撮影されてその画像データが取得され、その取得された画像データが記録部27を介してメモリカード28に記録され(ステップS25)、被写体検出撮影処理が終了する。 Then, in the state of step S24, the subject is photographed by the
図10(a)に、所定フレームの両親71,72及び子供73のスルー画像及び顔領域81,82,83を示す。図10(b)に、図10(a)の次フレームの両親71,72及び子供73のスルー画像及び探索範囲91,92,93を示す。 FIG. 10A shows through images and
両親(大人)71,72及び子供73を撮影するケースを考える。図10(a)に示すように、両親71,72及び子供73が静止している際の所定フレームのスルー画像が撮像されたものとする。このとき、スルー画像の全範囲が顔検出されて、両親71,72及び子供73の顔領域81,82,83が検出されたものとする。 Consider a case where parents (adults) 71 and 72 and a
そして、図10(a)の次フレームで、図10(b)に示すように、両親71,72は大人であるため静止しているものの、子供73が大きく動いたものとする。図10(a)の顔検出時に、次フレームの探索範囲91,92,93が、それぞれ顔領域81,82,83を中心にして設定されている。特に、子供73の探索範囲93は、両親71,72の探索範囲91,92よりも大きく設定され、子供73が大きく動いてもその顔が探索範囲93に収まっている。 Then, in the next frame of FIG. 10 (a), as shown in FIG. 10 (b), it is assumed that the
以上、本実施の形態によれば、シャッタキー4の半押しで、フラッシュメモリ25に記憶された顔検出用情報50を用いて、撮像部24で撮像されたフレームデータの画像の探索範囲から被写体の顔を検出するとともに、検出した被写体の年齢を推定し(大人か子供かを判別し)、被写体が子供である場合に、被写体が大人である場合よりも、次フレームの探索範囲を大きくする。このため、動きの少ない大人の探索範囲よりも、動きの激しい子供の探索範囲を広げることで、被写体の年齢(大人か子供か)に応じて、顔領域検出処理の効率を最適にできる。 As described above, according to the present embodiment, when the shutter key 4 is half-pressed, the subject is detected from the search range of the frame data image captured by the
また、シャッタキー4の全押しで、探索範囲で検出された被写体の顔に対してAE及びAFを実行して撮像部24で撮影する。このため、顔検出された被写体を最適に撮影することができる。 Further, when the shutter key 4 is fully pressed, AE and AF are performed on the face of the subject detected in the search range, and the
また、フレーム番号Mが定数Nの倍数になるごとに、探索範囲のフレーム画像の全範囲で顔検出を行う。このため、顔領域検出処理の精度を高めることができる。 Each time the frame number M is a multiple of the constant N, face detection is performed over the entire range of the frame image in the search range. For this reason, the accuracy of the face area detection process can be increased.
また、フレーム番号Mが定数Nの倍数になるごとに、フレーム画像の探索範囲を決定する。このため、全フレームで探索範囲を決定する構成に比べて、顔領域検出処理の処理負担を低減できる。 Each time the frame number M is a multiple of the constant N, the frame image search range is determined. For this reason, the processing load of the face area detection process can be reduced as compared with the configuration in which the search range is determined in all frames.
また、被写体が子供である場合に、被写体が大人である場合よりも、次フレームで用いるテンプレートの顔の角度範囲を大きくする。このため、顔の動きが少ない大人の角度範囲よりも、顔の動きが激しい子供の角度範囲を広げることで、被写体の年齢(大人か子供か)に応じて、顔領域検出処理の効率をさらに最適にできる。 Further, when the subject is a child, the angle range of the face of the template used in the next frame is made larger than when the subject is an adult. For this reason, by expanding the angle range of children with more face movement than the angle range of adults with less face movement, the efficiency of face area detection processing can be further increased according to the age of the subject (adult or child). Can be optimized.
なお、上記実施の形態における記述は、本発明に係る撮像装置、撮像方法及びプログラムの一例であり、これに限定されるものではない。 The description in the above embodiment is an example of an imaging apparatus, an imaging method, and a program according to the present invention, and the present invention is not limited to this.
上記実施の形態では、被写体の年齢の推定(大人であるか子供であるかの推定)を、予め登録された登録人物のテンプレートとを照合して同一人物とされた被写体の属性53を参照して行っていたが、これに限定されるものではない。また、撮影時、顔検出用情報50に登録されていない顔が出現した場合に、その顔の顔画像データを新しくテンプレートとして登録することにより顔検出用情報50を更新していく手法としてもよい。 In the above-described embodiment, the age of the subject (estimation of whether it is an adult or a child) is compared with a template of a registered person registered in advance, and the
また、上記実施の形態では、フレームデータ中の切り出し画像とテンプレートとを照合するテンプレートマッチングの方式を用いる構成としたが、これに限定されるものではない。例えば、切り出し画像とテンプレートとの特徴を抽出し、その特徴同士を比較して類似度を算出し、その類似度により登録人物と被写体との照合を行う構成としてもよい。 In the above embodiment, the template matching method for matching the cut-out image in the frame data with the template is used. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, a feature may be adopted in which features of a cut-out image and a template are extracted, the features are compared with each other, a similarity is calculated, and a registered person and a subject are verified based on the similarity.
また、テンプレートに代えて、識別器を用いる構成としてもよい。識別器とは、ある一定の大きさの画像(例えば20×20ピクセル、本実施の形態では切り出し画像)の特徴ベクトルを入力すると、その画像内容が顔であるか否かを識別し、その結果を出力するものである。より具体的には、顔の切り出し画像の特徴(ベクトル)を入力すると特定の登録人物と同一人物であるか否かの結果を出力する識別器を用いて登録人物と被写体との照合を行う構成としてもよい。顔識別器に用いられているアルゴリズムの代表的なものとしては、主成分分析(PCA)、線形判別分析(LDA)、ニューラル・ネットワーク(NN)、サポートベクターマシーン(SVM)、ブースティング法等を応用したものがある。 Moreover, it is good also as a structure which replaces with a template and uses a discriminator. When a feature vector of an image of a certain size (for example, 20 × 20 pixels, cut-out image in this embodiment) is input, the classifier identifies whether the image content is a face, and the result Is output. More specifically, when a feature (vector) of a face cut-out image is input, a classifier that outputs a result indicating whether or not the person is the same as a specific registered person is used to collate the registered person and the subject. It is good. Typical algorithms used in the face classifier include principal component analysis (PCA), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), neural network (NN), support vector machine (SVM), boosting method, etc. There is something applied.
また、子供識別器及び大人識別器を用いて、被写体の年齢を推定する構成としてもよい。子供識別器は、顔であると識別された切り出し画像の特徴を入力すると、その顔が子供なのか非子供なのか結果を返す識別器である。大人識別器も同様にして、大人/非大人を識別する。この2つの識別器のアルゴリズムには、どんな手法を用いても良いが、顔を識別する識別器と同様のアルゴリズムを用いても良い。 Moreover, it is good also as a structure which estimates the age of a to-be-photographed object using a child discriminator and an adult discriminator. The child discriminator is a discriminator that returns a result indicating whether the face is a child or a non-child when a feature of a cut-out image identified as a face is input. In the same way, the adult discriminator discriminates between adults / non-adults. Any method may be used for the algorithm of these two classifiers, but an algorithm similar to the classifier for identifying a face may be used.
また、上記実施の形態では、対象として動画(スルー画像)から抽出したフレーム画像に関して顔検出する構成であったが、これに限定されるものではない。例えば、顔検出する画像の内容は銀鉛写真をスキャナで取り込んだものでも良いし、CG(Computer Graphics)でも良い。 Moreover, in the said embodiment, although it was the structure which detects a face regarding the frame image extracted from the moving image (through image) as object, it is not limited to this. For example, the content of the image for face detection may be a silver lead photograph captured by a scanner or CG (Computer Graphics).
また、上記実施の形態では、検出の対象が顔である場合を述べてきたが、これに限定されるものではなく、検出の対象が、顔ではなく、任意の物体としても良い。その場合は、顔認識の変わりに、任意の物体の認識を行う必要がある。 In the above embodiment, the case where the detection target is a face has been described. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the detection target may be an arbitrary object instead of a face. In that case, it is necessary to recognize an arbitrary object instead of the face recognition.
また、上記実施の形態では、年齢(大人or子供)によって探索範囲を変化させていたが、その他の分類によって探索範囲を変化させても良い。例えば、あらかじめ動きの早い人物の顔を登録しておいて、その人物(の顔)が検出された時に探索範囲を変化させても良い。あるいは、人の顔だけではなく、動物検出を行なう事を考えた場合に、動きやすさとして動きの早い動物と動きの遅い動物で探索範囲を変化させても良い。 In the above embodiment, the search range is changed according to age (adult or child), but the search range may be changed according to other classifications. For example, the face of a fast-moving person may be registered in advance, and the search range may be changed when that person (face) is detected. Alternatively, when considering not only the human face but also animal detection, the search range may be changed between an animal that moves fast and an animal that moves slowly as the ease of movement.
また、上記実施の形態では、シャッタキー4を半押しすることで、フレーム画像の顔検出を行い、シャッタキー4を全押しすることで、顔検出した被写体にAE,AFを行って撮影を行う構成であるが、この構成に限定されるものではない。例えば、シャッタキー4を半押しすることで、フレーム画像の顔検出を行い、顔検出した被写体にAE,AFを行ってロックし、シャッタキー4を全押しすることで撮影を行う構成としてもよい。 In the above-described embodiment, the face of the frame image is detected by half-pressing the shutter key 4, and the subject whose face is detected is shot by performing AE and AF by fully pressing the shutter key 4. Although it is a structure, it is not limited to this structure. For example, a configuration may be adopted in which the face of the frame image is detected by half-pressing the shutter key 4, the subject whose face is detected is locked by performing AE and AF, and the shutter key 4 is fully pressed to perform shooting. .
また、上記実施の形態におけるデジタルカメラ1の各構成要素の細部構成及び細部動作に関しては、本発明の趣旨を逸脱することのない範囲で適宜変更可能であることは勿論である。 Of course, the detailed configuration and detailed operation of each component of the
1 デジタルカメラ
2 撮影レンズ
3 電源キー
4 シャッタキー
5 モードスイッチ
6 メニューキー
7 十字キー
8 表示部
21 CPU
22 入力部
23 RAM
24 撮像部
25 フラッシュメモリ
26 通信部
27 記録部
28 メモリカード
30 バス1
22
24
Claims (10)
Translated fromJapanese前記撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出手段と、
前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の動きの大きさを推定する推定手段と、
前記推定手段により推定された被写体の動きの大きさに基づき、前記被写体検出手段が被写体を検出する探索範囲を設定する探索範囲設定手段と、
前記撮像手段により所定のフレーム間隔ごとに得られる第1の画像データにおける全範囲の被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御するとともに、前記第1の画像データ以外の第2の画像データにおいて、前記探索範囲設定手段により設定された探索範囲内で前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする撮像装置。Imaging means;
A subject detecting means for detecting an object insequential capturedRu image data by the image pickup means,
Estimating means for estimatingthe magnitude ofmovement of the subject detected by the subject detecting means;
Search range setting meansfor setting a search range inwhich the subject detection means detects a subjectbased on the magnitude ofmovement of the subject estimated by the estimation means;
In the second image data other than the first image data, the subject detection means is controlled to detect the entire range of subjects in the first image data obtained at predetermined frame intervals by the imaging means. and the object detection control means for controlling said object detecting means to detect said objectwithina more setsearch range in the search range setting means,
An imaging apparatus comprising:
前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の年齢を推定することにより、前記被写体の動きの大きさを推定することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の撮像装置。The imaging apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the magnitude of movement of the subject is estimated by estimating an age of the subject detected by the subject detection unit.
前記撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出手段と、
前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の年齢を推定する推定手段と、
被写体の角度に対応付けて被写体検出用データを記憶する記憶手段と、
前記推定手段により推定された被写体の年齢に基づき、前記被写体検出手段による前記被写体の検出に用いる前記被写体検出用データの角度範囲を設定する角度範囲設定手段と、
前記撮像手段により撮像された画像データにおいて、前記角度範囲設定手段に設定された角度範囲に対応する前記記憶された被写体検出用データを用いて、前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする撮像装置。Imaging means;
Subject detection means for detecting a subject in image data sequentially captured by the imaging means;
Estimating means for estimating the age of the subject detected by the subject detecting means;
Storage means for storing subject detection data in association with the angle of the subject;
An angle range setting means for setting an angle range of the subject detection data used for detection of the subject by the subject detection means based on the age of the subject estimated by the estimation means;
In the image data captured by the imaging unit, the subject detection unit is controlled to detect thesubject using the stored subject detection datacorresponding to the angle range set in the angle range setting unit.Subject detection control means;
Imaging device, characterized in thatit comprises a.
前記被写体検出制御手段は、前記探索範囲設定手段により設定された探索範囲内で前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御することを特徴とする請求項3に記載の撮像装置。The imaging apparatus according to claim 3, wherein the subject detection control unit controls the subject detection unit to detect the subject within a search range set by the search range setting unit.
前記被写体検出ステップにより検出された被写体の動きの大きさを推定する推定ステップと、
前記推定ステップにより推定された被写体の動きの大きさに基づき、前記被写体検出ステップで被写体を検出する探索範囲を設定する探索範囲設定ステップと、
前記撮像手段により所定のフレーム間隔ごとに得られる第1の画像データにおける全範囲の被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御するとともに、前記第1の画像データ以外の第2の画像データにおいて、前記探索範囲設定ステップにて設定された探索範囲内で前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出を制御する被写体検出制御ステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする被写体検出方法。A subject detection step of detecting an object in the image datathat issuccessively captured by the imaging means,
An estimation step for estimatingthe magnitude ofmovement of the subject detected by the subject detection step;
A search range setting stepfor setting a search range for detecting a subject in the subject detection stepbased on the magnitude ofmovement of the subject estimated in the estimation step;
In the second image data other than the first image data, the subject detection means is controlled to detect the entire range of subjects in the first image data obtained at predetermined frame intervals by the imaging means . A subject detection control step for controlling the subject detection so as to detect the subjectwithin thesearch range set in the search range setting step;
A method for detecting a subject, comprising:
前記被写体検出ステップにより検出された被写体の年齢を推定する推定ステップと、
前記推定ステップにより推定された被写体の年齢に基づき、前記被写体検出ステップによる前記被写体の検出に用いる前記被写体検出用データの角度範囲を設定する角度範囲設定ステップと、
前記撮像手段により撮像された画像データにおいて、前記角度範囲設定ステップに設定された角度範囲に対応する被写体検出用データを用いて、前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段ステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする被写体検出方法。A subject detection step of detecting a subject in the image data sequentially captured by the imaging means;
An estimation step for estimating the age of the subject detected by the subject detection step;
An angle range setting step for setting an angle range of the subject detection data used for the detection of the subject by the subject detection step based on the age of the subject estimated by the estimation step;
Subject detection control means for controlling thesubject detection means to detect thesubject using the subject detection data corresponding to the angle range set in the angle range setting step in the image data captured by the imagingmeans. Steps,
A method for detecting a subject, comprising:
撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出手段、
前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の動きの大きさを推定する推定手段、
前記推定手段により推定された被写体の動きの大きさに基づき、前記被写体検出手段が被写体を検出する探索範囲を設定する探索範囲設定手段、
前記撮像手段により所定のフレーム間隔ごとに得られる第1の画像データにおける全範囲の被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御するとともに、前記第1の画像データ以外の第2の画像データにおいて、前記探索範囲設定手段により設定された探索範囲内で前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段、
として機能させることを特徴とするプログラム。Computer
Object detecting means for detecting an object in the image data by the imaging meansRu aresuccessively imaged,
Estimating means for estimatingthe magnitude ofmovement of the subject detected by the subject detecting means;
Search range setting meansfor setting a search range inwhich the subject detection means detects a subjectbased on the magnitude ofmovement of the subject estimated by the estimation means;
In the second image data other than the first image data, the subject detection means is controlled to detect the entire range of subjects in the first image data obtained at predetermined frame intervals by the imaging means. Subject detection control means for controlling the subject detection means to detect the subjectwithin thesearch range set by the search range setting means;
A program characterized by functioning as
撮像手段により順次撮像される画像データにおける被写体を検出する被写体検出手段と、Subject detection means for detecting a subject in image data sequentially captured by the imaging means;
前記被写体検出手段により検出された被写体の年齢を推定する推定手段、Estimating means for estimating the age of the subject detected by the subject detecting means;
前記推定手段により推定された被写体の年齢に基づき、前記被写体検出手段による前記被写体の検出に用いる前記被写体検出用データの角度範囲を設定する角度範囲設定手段と、An angle range setting means for setting an angle range of the subject detection data used for detection of the subject by the subject detection means based on the age of the subject estimated by the estimation means;
前記撮像手段により撮像された画像データにおいて、前記角度範囲設定手段に設定された角度範囲に対応する被写体検出用データを用いて、前記被写体を検出するよう前記被写体検出手段を制御する被写体検出制御手段、Subject detection control means for controlling the subject detection means to detect the subject by using subject detection data corresponding to the angle range set in the angle range setting means in the image data taken by the imaging means. ,
として機能させることを特徴とするプログラム。A program characterized by functioning as
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007321969AJP5380833B2 (en) | 2007-12-13 | 2007-12-13 | Imaging apparatus, subject detection method and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007321969AJP5380833B2 (en) | 2007-12-13 | 2007-12-13 | Imaging apparatus, subject detection method and program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009147605A JP2009147605A (en) | 2009-07-02 |
| JP2009147605A5 JP2009147605A5 (en) | 2011-01-27 |
| JP5380833B2true JP5380833B2 (en) | 2014-01-08 |
Family
ID=40917724
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007321969AExpired - Fee RelatedJP5380833B2 (en) | 2007-12-13 | 2007-12-13 | Imaging apparatus, subject detection method and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5380833B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011101202A (en)* | 2009-11-06 | 2011-05-19 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Electronic camera |
| JP2012060529A (en)* | 2010-09-10 | 2012-03-22 | Toshiba Corp | Image processing system and image processing method |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3704045B2 (en)* | 2001-01-15 | 2005-10-05 | 株式会社ニコン | Target object tracking device |
| JP2003015019A (en)* | 2001-06-27 | 2003-01-15 | Minolta Co Ltd | Device for detecting object and camera |
| JP4149301B2 (en)* | 2003-04-14 | 2008-09-10 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Method for extracting feature parts of continuous image, program thereof, and digital camera |
| JP2004318632A (en)* | 2003-04-18 | 2004-11-11 | Yokogawa Electric Corp | Age estimation device |
| JP2005277845A (en)* | 2004-03-25 | 2005-10-06 | Sony Corp | Photographing controller |
| JP2006211139A (en)* | 2005-01-26 | 2006-08-10 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Imaging apparatus |
| JP2007074141A (en)* | 2005-09-05 | 2007-03-22 | Canon Inc | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof |
| JP4968929B2 (en)* | 2007-07-20 | 2012-07-04 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image processing apparatus and image processing method |
- 2007
- 2007-12-13JPJP2007321969Apatent/JP5380833B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009147605A (en) | 2009-07-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6106921B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and imaging program | |
| JP5218508B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| CN100431337C (en) | Photographic device and automatic focus control method | |
| JP4640456B2 (en) | Image recording apparatus, image recording method, image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP5251215B2 (en) | Digital camera | |
| JP4639869B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and timer photographing method | |
| US8411997B2 (en) | Image capture device and program storage medium | |
| JP4577252B2 (en) | Camera, best shot shooting method, program | |
| US20080181460A1 (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging method | |
| US20090080716A1 (en) | Image recognition device for performing image recognition including object identification on each of input images | |
| US8411159B2 (en) | Method of detecting specific object region and digital camera | |
| US20060028576A1 (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| KR20140007529A (en) | Apparatus and method for taking a picture in camera device and wireless terminal having a camera device | |
| CN102625036A (en) | Image processing device, imaging device, and recording medium | |
| CN102469244B (en) | Image capturing apparatus capable of continuously capturing object | |
| JP5434038B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| US8237802B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for determining shaken image by using auto focusing | |
| JP4853707B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| JP4894708B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP4807582B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, imaging apparatus, and program thereof | |
| JP2019186791A (en) | Imaging apparatus, control method of the imaging apparatus, and control program | |
| JP2007265149A (en) | Image processor, image processing method and imaging device | |
| JP5380833B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, subject detection method and program | |
| JP2008028890A (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and imaging program | |
| KR101477535B1 (en) | Image searching method and apparatus, digital photographing apparatus using the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20101207 | |
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20101207 | |
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date:20101207 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20120215 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20120221 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20120417 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20121016 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20121217 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20130903 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20130916 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:5380833 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |