JP4947948B2 - Cell preservation solution - Google Patents
Cell preservation solutionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4947948B2 JP4947948B2JP2005296593AJP2005296593AJP4947948B2JP 4947948 B2JP4947948 B2JP 4947948B2JP 2005296593 AJP2005296593 AJP 2005296593AJP 2005296593 AJP2005296593 AJP 2005296593AJP 4947948 B2JP4947948 B2JP 4947948B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- ion
- preservation solution
- cell
- solution
- sodium
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000003761preservation solutionSubstances0.000titleclaimsdescription135
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000claimsdescription187
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-NGlucoseNatural productsOC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OWQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N0.000claimsdescription48
- 239000008103glucoseSubstances0.000claimsdescription48
- 230000003204osmotic effectEffects0.000claimsdescription39
- 229910001415sodium ionInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription38
- 229910001414potassium ionInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription36
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000claimsdescription35
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-MBicarbonateChemical compoundOC([O-])=OBVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsdescription33
- FKNQFGJONOIPTF-UHFFFAOYSA-NSodium cationChemical compound[Na+]FKNQFGJONOIPTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription33
- NPYPAHLBTDXSSS-UHFFFAOYSA-NPotassium ionChemical compound[K+]NPYPAHLBTDXSSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription31
- 238000003860storageMethods0.000claimsdescription31
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-LCarbonateChemical compound[O-]C([O-])=OBVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription29
- 210000004698lymphocyteAnatomy0.000claimsdescription23
- BHPQYMZQTOCNFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NCalcium cationChemical compound[Ca+2]BHPQYMZQTOCNFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription22
- 229910001424calcium ionInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription22
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-MChloride anionChemical compound[Cl-]VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsdescription21
- JLVVSXFLKOJNIY-UHFFFAOYSA-NMagnesium ionChemical compound[Mg+2]JLVVSXFLKOJNIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription21
- 150000001720carbohydratesChemical class0.000claimsdescription21
- 229910001425magnesium ionInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription21
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-KphosphateChemical compound[O-]P([O-])([O-])=ONBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription21
- 229940085991phosphate ionDrugs0.000claimsdescription20
- 238000004321preservationMethods0.000claimsdescription18
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-LSulfateChemical compound[O-]S([O-])(=O)=OQAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription17
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription15
- -1lactate ionChemical class0.000claimsdescription13
- OWEGMIWEEQEYGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N100676-05-9Natural productsOC1C(O)C(O)C(CO)OC1OCC1C(O)C(O)C(O)C(OC2C(OC(O)C(O)C2O)CO)O1OWEGMIWEEQEYGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-PICCSMPSSA-NMaltoseNatural productsO[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1OGUBGYTABKSRVRQ-PICCSMPSSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000007864aqueous solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription7
- 150000002500ionsChemical class0.000claimsdescription7
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-NGlycerineChemical compoundOCC(O)COPEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000005057refrigerationMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000012258culturingMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000011550stock solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000000725suspensionSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000012136culture methodMethods0.000claims1
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium bicarbonateChemical compound[Na+].OC([O-])=OUIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description52
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description50
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium chlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-]FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description36
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description34
- WCUXLLCKKVVCTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-MPotassium chlorideChemical compound[Cl-].[K+]WCUXLLCKKVVCTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description26
- 235000017557sodium bicarbonateNutrition0.000description26
- 229910000030sodium bicarbonateInorganic materials0.000description26
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-LMagnesium sulfateChemical compound[Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-]CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description20
- 239000007924injectionSubstances0.000description19
- 238000002347injectionMethods0.000description19
- 239000011780sodium chlorideSubstances0.000description18
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description15
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-NHydrochloric acidChemical compoundClVEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description14
- 239000001103potassium chlorideSubstances0.000description13
- 235000011164potassium chlorideNutrition0.000description13
- 230000004083survival effectEffects0.000description13
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium hydroxideChemical compound[OH-].[Na+]HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description12
- UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-UHFFFAOYSA-LCalcium chlorideChemical compound[Cl-].[Cl-].[Ca+2]UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description10
- 239000001110calcium chlorideSubstances0.000description10
- 229910001628calcium chlorideInorganic materials0.000description10
- 230000003833cell viabilityEffects0.000description10
- LVXHNCUCBXIIPE-UHFFFAOYSA-Ldisodium;hydrogen phosphate;hydrateChemical compoundO.[Na+].[Na+].OP([O-])([O-])=OLVXHNCUCBXIIPE-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description10
- 229910052943magnesium sulfateInorganic materials0.000description10
- 235000019341magnesium sulphateNutrition0.000description10
- 230000018044dehydrationEffects0.000description8
- 238000006297dehydration reactionMethods0.000description8
- 229940001447lactateDrugs0.000description8
- HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-UHFFFAOYSA-Nα-D-glucopyranosyl-α-D-glucopyranosideNatural productsOC1C(O)C(O)C(CO)OC1OC1C(O)C(O)C(O)C(CO)O1HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description7
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NDimethylsulphoxideChemical compoundCS(C)=OIAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description7
- HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-WSWWMNSNSA-NTrehaloseNatural productsO[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-WSWWMNSNSA-N0.000description7
- 238000005138cryopreservationMethods0.000description7
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description7
- CYDQOEWLBCCFJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N4-(4-fluorophenyl)oxane-4-carboxylic acidChemical compoundC=1C=C(F)C=CC=1C1(C(=O)O)CCOCC1CYDQOEWLBCCFJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-ND-MannitolChemical compoundOC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)COFBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N0.000description6
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-REOHCLBHSA-NL-lactic acidChemical compoundC[C@H](O)C(O)=OJVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-REOHCLBHSA-N0.000description6
- TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-LMagnesium chlorideChemical compound[Mg+2].[Cl-].[Cl-]TWRXJAOTZQYOKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description6
- 229930195725MannitolNatural products0.000description6
- 229930006000SucroseNatural products0.000description6
- HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-LIZSDCNHSA-Nalpha,alpha-trehaloseChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1HDTRYLNUVZCQOY-LIZSDCNHSA-N0.000description6
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-Nbeta-D-glucoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OWQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N0.000description6
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description6
- 239000000594mannitolSubstances0.000description6
- 235000010355mannitolNutrition0.000description6
- 239000002609mediumSubstances0.000description6
- 229910000403monosodium phosphateInorganic materials0.000description6
- 235000019799monosodium phosphateNutrition0.000description6
- AJPJDKMHJJGVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-Msodium dihydrogen phosphateChemical compound[Na+].OP(O)([O-])=OAJPJDKMHJJGVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description6
- 239000001540sodium lactateSubstances0.000description6
- 235000011088sodium lactateNutrition0.000description6
- 229940005581sodium lactateDrugs0.000description6
- 239000005720sucroseSubstances0.000description6
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-NSucroseChemical compoundO[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N0.000description5
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QUYVBRFLSA-Nbeta-maltoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)O[C@@H]2CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OGUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QUYVBRFLSA-N0.000description5
- 238000004113cell cultureMethods0.000description5
- 238000001802infusionMethods0.000description5
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description5
- 238000002156mixingMethods0.000description5
- 239000006285cell suspensionSubstances0.000description4
- 239000004615ingredientSubstances0.000description4
- 230000036962time dependentEffects0.000description4
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylene glycolChemical compoundOCCOLYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 210000001744T-lymphocyteAnatomy0.000description3
- GLNADSQYFUSGOU-GPTZEZBUSA-JTrypan blueChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].C1=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C=C2C=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C(/N=N/C3=CC=C(C=C3C)C=3C=C(C(=CC=3)\N=N\C=3C(=CC4=CC(=CC(N)=C4C=3O)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)C)=C(O)C2=C1NGLNADSQYFUSGOU-GPTZEZBUSA-J0.000description3
- 239000004480active ingredientSubstances0.000description3
- 239000003795chemical substances by applicationSubstances0.000description3
- ZPWVASYFFYYZEW-UHFFFAOYSA-Ldipotassium hydrogen phosphateChemical compound[K+].[K+].OP([O-])([O-])=OZPWVASYFFYYZEW-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description3
- 229910000396dipotassium phosphateInorganic materials0.000description3
- 235000019797dipotassium phosphateNutrition0.000description3
- BNIILDVGGAEEIG-UHFFFAOYSA-Ldisodium hydrogen phosphateChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].OP([O-])([O-])=OBNIILDVGGAEEIG-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description3
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000description3
- 229910001629magnesium chlorideInorganic materials0.000description3
- 238000010899nucleationMethods0.000description3
- LWIHDJKSTIGBAC-UHFFFAOYSA-Kpotassium phosphateSubstances[K+].[K+].[K+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OLWIHDJKSTIGBAC-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000description3
- BUKHSQBUKZIMLB-UHFFFAOYSA-Lpotassium;sodium;dichlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-].[Cl-].[K+]BUKHSQBUKZIMLB-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description3
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description3
- 239000001488sodium phosphateSubstances0.000description3
- 238000010186stainingMethods0.000description3
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description3
- 230000035899viabilityEffects0.000description3
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000description3
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-LCalcium carbonateChemical compound[Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=OVTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description2
- 241000124008MammaliaSpecies0.000description2
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-LSodium CarbonateChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=OCDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description2
- 108700042768University of Wisconsin-lactobionate solutionProteins0.000description2
- 239000003242anti bacterial agentSubstances0.000description2
- 239000003963antioxidant agentSubstances0.000description2
- 235000006708antioxidantsNutrition0.000description2
- 230000004071biological effectEffects0.000description2
- 210000000170cell membraneAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000002738chelating agentSubstances0.000description2
- 230000002338cryopreservative effectEffects0.000description2
- XMOCLSLCDHWDHP-IUODEOHRSA-Nepi-GallocatechinChemical compoundC1([C@H]2OC3=CC(O)=CC(O)=C3C[C@H]2O)=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1XMOCLSLCDHWDHP-IUODEOHRSA-N0.000description2
- 238000007710freezingMethods0.000description2
- 230000008014freezingEffects0.000description2
- 150000004676glycansChemical class0.000description2
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000description2
- 150000002772monosaccharidesChemical class0.000description2
- 150000007524organic acidsChemical class0.000description2
- 239000008055phosphate buffer solutionSubstances0.000description2
- 230000035790physiological processes and functionsEffects0.000description2
- 239000002504physiological saline solutionSubstances0.000description2
- 229920001282polysaccharidePolymers0.000description2
- 239000005017polysaccharideSubstances0.000description2
- XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-Mpotassium benzoateChemical compound[K+].[O-]C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- 159000000000sodium saltsChemical class0.000description2
- 235000000346sugarNutrition0.000description2
- WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-o-gallateChemical compoundO([C@@H]1CC2=C(O)C=C(C=C2O[C@@H]1C=1C=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C=1)O)C(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N0.000description1
- VAWYEUIPHLMNNF-OESPXIITSA-N1-kestoseChemical compoundO[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)OC[C@]1(O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1VAWYEUIPHLMNNF-OESPXIITSA-N0.000description1
- GIUOHBJZYJAZNP-DVZCMHTBSA-N1-kestoseNatural productsOC[C@@H]1O[C@](CO)(OC[C@]2(O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]3O)O[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OGIUOHBJZYJAZNP-DVZCMHTBSA-N0.000description1
- 241000251468ActinopterygiiSpecies0.000description1
- 102000009027AlbuminsHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010088751AlbuminsProteins0.000description1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-QTVWNMPRSA-ND-mannopyranoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OWQZGKKKJIJFFOK-QTVWNMPRSA-N0.000description1
- HMFHBZSHGGEWLO-SOOFDHNKSA-ND-ribofuranoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1OHMFHBZSHGGEWLO-SOOFDHNKSA-N0.000description1
- 102000002322Egg ProteinsHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010000912Egg ProteinsProteins0.000description1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229930091371FructoseNatural products0.000description1
- 239000005715FructoseSubstances0.000description1
- RFSUNEUAIZKAJO-ARQDHWQXSA-NFructoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@](O)(CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1ORFSUNEUAIZKAJO-ARQDHWQXSA-N0.000description1
- 108060003393GranulinProteins0.000description1
- 241000238631HexapodaSpecies0.000description1
- 241000282412HomoSpecies0.000description1
- 102000008100Human Serum AlbuminHuman genes0.000description1
- 108091006905Human Serum AlbuminProteins0.000description1
- 229920001612Hydroxyethyl starchPolymers0.000description1
- XMOCLSLCDHWDHP-UHFFFAOYSA-NL-EpigallocatechinNatural productsOC1CC2=C(O)C=C(O)C=C2OC1C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1XMOCLSLCDHWDHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910002651NO3Inorganic materials0.000description1
- PYMYPHUHKUWMLA-LMVFSUKVSA-NRiboseNatural productsOC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=OPYMYPHUHKUWMLA-LMVFSUKVSA-N0.000description1
- 244000269722Thea sinensisSpecies0.000description1
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000description1
- 239000000654additiveSubstances0.000description1
- 230000000996additive effectEffects0.000description1
- HMFHBZSHGGEWLO-UHFFFAOYSA-Nalpha-D-Furanose-RiboseNatural productsOCC1OC(O)C(O)C1OHMFHBZSHGGEWLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-PHYPRBDBSA-Nalpha-D-galactoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1OWQZGKKKJIJFFOK-PHYPRBDBSA-N0.000description1
- 150000001413amino acidsChemical class0.000description1
- 230000003698anagen phaseEffects0.000description1
- 229940088710antibiotic agentDrugs0.000description1
- 230000003078antioxidant effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000002449bone cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000002798bone marrow cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000872bufferSubstances0.000description1
- NKWPZUCBCARRDP-UHFFFAOYSA-Lcalcium bicarbonateChemical compound[Ca+2].OC([O-])=O.OC([O-])=ONKWPZUCBCARRDP-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 229910000020calcium bicarbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 229910000019calcium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 150000004649carbonic acid derivativesChemical class0.000description1
- 230000036978cell physiologyEffects0.000description1
- 238000002659cell therapyMethods0.000description1
- 238000005119centrifugationMethods0.000description1
- 210000001612chondrocyteAnatomy0.000description1
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 150000002016disaccharidesChemical class0.000description1
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description1
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 235000013601eggsNutrition0.000description1
- 210000002889endothelial cellAnatomy0.000description1
- DZYNKLUGCOSVKS-UHFFFAOYSA-NepigallocatechinNatural productsOC1Cc2cc(O)cc(O)c2OC1c3cc(O)c(O)c(O)c3DZYNKLUGCOSVKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 210000002919epithelial cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000003722extracellular fluidAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000945fillerSubstances0.000description1
- FTSSQIKWUOOEGC-RULYVFMPSA-NfructooligosaccharideChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@@](CO)(OC[C@@]2(OC[C@@]3(OC[C@@]4(OC[C@@]5(OC[C@@]6(OC[C@@]7(OC[C@@]8(OC[C@@]9(OC[C@@]%10(OC[C@@]%11(O[C@H]%12O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]%12O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]%11O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]%10O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]9O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]8O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]7O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]6O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]5O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]4O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OFTSSQIKWUOOEGC-RULYVFMPSA-N0.000description1
- 229940107187fructooligosaccharideDrugs0.000description1
- 229930182830galactoseNatural products0.000description1
- 229940053838glucose 1000 mgDrugs0.000description1
- 125000002791glucosyl groupChemical groupC1([C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O1)CO)*0.000description1
- 235000009569green teaNutrition0.000description1
- 239000001963growth mediumSubstances0.000description1
- 210000003958hematopoietic stem cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000003494hepatocyteAnatomy0.000description1
- 229940050526hydroxyethylstarchDrugs0.000description1
- 210000002865immune cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000004153islets of langerhanAnatomy0.000description1
- VAWYEUIPHLMNNF-UHFFFAOYSA-NkestotrioseNatural productsOC1C(O)C(CO)OC1(CO)OCC1(OC2C(C(O)C(O)C(CO)O2)O)C(O)C(O)C(CO)O1VAWYEUIPHLMNNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- AIHDCSAXVMAMJH-GFBKWZILSA-NlevanChemical compoundO[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)OC[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@](CO)(CO[C@@H]2[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@](O)(CO)O2)O)O1AIHDCSAXVMAMJH-GFBKWZILSA-N0.000description1
- ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-Lmagnesium carbonateChemical compound[Mg+2].[O-]C([O-])=OZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 239000001095magnesium carbonateSubstances0.000description1
- 229910000021magnesium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000012423maintenanceMethods0.000description1
- 125000003071maltose groupChemical group0.000description1
- 229910021645metal ionInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000011259mixed solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 210000000663muscle cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000002569neuronAnatomy0.000description1
- 231100000252nontoxicToxicity0.000description1
- 230000003000nontoxic effectEffects0.000description1
- 229920001542oligosaccharidePolymers0.000description1
- 239000000162organ preservation solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004681ovumAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000007793ph indicatorSubstances0.000description1
- 150000008442polyphenolic compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 235000013824polyphenolsNutrition0.000description1
- 239000001267polyvinylpyrrolidoneSubstances0.000description1
- 229920000036polyvinylpyrrolidonePolymers0.000description1
- 235000013855polyvinylpyrrolidoneNutrition0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description1
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description1
- 210000002966serumAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000004927skin cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 229910000029sodium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- POECFFCNUXZPJT-UHFFFAOYSA-Msodium;carbonic acid;hydrogen carbonateChemical compound[Na+].OC(O)=O.OC([O-])=OPOECFFCNUXZPJT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description1
- 230000007480spreadingEffects0.000description1
- 238000003892spreadingMethods0.000description1
- 210000000130stem cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 125000000185sucrose groupChemical group0.000description1
- 150000005846sugar alcoholsChemical class0.000description1
- 150000008163sugarsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000010257thawingMethods0.000description1
- 230000001225therapeutic effectEffects0.000description1
- 231100000331toxicToxicity0.000description1
- 230000002588toxic effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000003440toxic substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 238000002054transplantationMethods0.000description1
- 125000000647trehalose groupChemical group0.000description1
- 150000004043trisaccharidesChemical class0.000description1
- 239000011782vitaminSubstances0.000description1
- 229940088594vitaminDrugs0.000description1
- 229930003231vitaminNatural products0.000description1
- 235000013343vitaminNutrition0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、少なくとも糖類、ナトリウムイオン及びカリウムイオンを含有し、カリウムイオンのモル濃度に対するナトリウムイオンのモル濃度の比が1以上であることを特徴とする細胞保存液、及びそれを用いた細胞保存方法に関する。 The present invention includes at least a saccharide, sodium ion, and potassium ion, wherein the ratio of the molar concentration of sodium ion to the molar concentration of potassium ion is 1 or more, and cell storage using the same Regarding the method.
生細胞は、生理機能や生物学的活性を有しており、多方面で利用価値がある。しかしながら、温度の高い条件下に放置すると代謝や変性するため、細胞の生理機能や生物学的活性が低下若しくは消失してしまう。そこで、細胞を凍結して保存することが必要となる。細胞の凍結保存には従来から細胞膜透過型凍結保存剤としてDMSO(ジメチルスルフォキシド)、エチレングリコール、グリセロールなどが用いられ、細胞膜非透過型凍結保存剤としてはポリビニルピロリドン等が用いられてきた。また、精製アルブミンとDMSOとを含有する細胞保存液を用いれば、-80℃で、短期間であれば-4℃程度でも細胞を保存できることが開示されている(特許文献1)。 Living cells have physiological functions and biological activities, and are useful in many fields. However, if the cells are left under high temperature conditions, they are metabolized and denatured, so that the physiological functions and biological activities of the cells are reduced or lost. Therefore, it is necessary to freeze and store the cells. In the cryopreservation of cells, DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), ethylene glycol, glycerol and the like have been conventionally used as cell membrane permeation type cryopreservation agents, and polyvinylpyrrolidone and the like have been used as a cell membrane non-permeation type cryopreservation agent. Further, it is disclosed that cells can be preserved even at about -4 ° C. at -80 ° C. and for a short period when a cell preservation solution containing purified albumin and DMSO is used (Patent Document 1).
しかしながら、一般にこれらの凍結保存剤は高濃度にすると細胞に対して毒性を示すという問題がある。また凍結保存された細胞を培養などに用いる場合には、予め細胞から凍結保存剤を除去しておくことが必要となり、その作業は煩雑である。また、凍結保存は、例えば-80℃といった非常に低い温度条件で行われるが、これは専門の高価な冷凍装置を必要とするという問題を有する。また、凍結・融解という工程は、細胞に著しい損傷を与える可能性があるため、生存率を低下させてしまう。さらに、細胞種によっては、凍結保存できないものもある。 However, generally, these cryopreservatives have a problem that they are toxic to cells at high concentrations. In addition, when using cryopreserved cells for culture or the like, it is necessary to remove the cryopreservative from the cells in advance, which is complicated. In addition, the cryopreservation is performed under a very low temperature condition, for example, -80 ° C., but this has a problem of requiring a specialized and expensive freezing apparatus. In addition, the process of freezing / thawing may cause significant damage to the cells, thus reducing the survival rate. Furthermore, some cell types cannot be cryopreserved.
凍結保存用の、DMSO等の毒性を示す可能性のある物質を含まないような細胞・組織等の保存液として、多糖類のレバン又はレバンオリゴ糖を含有する保存液(特許文献2)、フラクオリゴ糖の一種である1-ケストースを有効成分として含有する保存液(特許文献3)等が開示されている。 As a preservation solution for cryopreservation, such as DMSO or other non-toxic substances such as cells and tissues, a preservation solution containing polysaccharide levan or levan oligosaccharide (Patent Document 2), fructooligosaccharide A preservation solution containing 1-kestose as an active ingredient (Patent Document 3) is disclosed.
一方、トレハロースとマトリクス蛋白質充填剤と単糖とを緩衝液に含有させた組成物(特許文献4)や、抗酸化作用をもつポリフェノールを含有させた保存液(特許文献5)、また、水に混和可能なアルコールにキレート剤等を加えた溶液などが開示されている(特許文献6)。 On the other hand, a composition containing trehalose, a matrix protein filler, and a monosaccharide in a buffer (Patent Document 4), a preservation solution containing an antioxidant polyphenol (Patent Document 5), and water A solution in which a chelating agent or the like is added to a miscible alcohol is disclosed (Patent Document 6).
上述の溶液以外に、従来から用いられている細胞・組織保存液としては、ユーロ−コリンズ液(Euro-Collins液)(非特許文献1)、UW液(University of Wisconsin液)(非特許文献2)、ET-Kyoto液(特許文献7)及びユーロ−コリンズ液やUW液に有効成分として緑茶カテキンのエピガロカテキンガレードを添加した溶液(特許文献8)などが開示されている。
本発明の目的は、製造コスト及び製造容易性に優れ、容易な細胞の冷蔵保存を可能にした細胞保存液を提供することである。好ましくは、保存液を除去するための洗浄を必要とせず、保存液が存在していても細胞の培養等を可能とする細胞保存液を提供することである。 An object of the present invention is to provide a cell preservation solution that is excellent in production cost and ease of production and enables easy refrigeration storage of cells. Preferably, it is to provide a cell preservation solution that does not require washing for removing the preservation solution and enables cell culture or the like even in the presence of the preservation solution.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明者らは鋭意研究を進めた結果、少なくとも糖類、ナトリウムイオン及びカリウムイオンを含有し、カリウムイオンのモル濃度に対するナトリウムイオンのモル濃度の比を1以上とすることにより、従来の細胞保存液、例えばユーロ−コリンズ液に比べて細胞保存性能が向上することを見出し、本発明の細胞保存液を完成した。 In order to solve the above-mentioned problems, the present inventors have conducted intensive research. As a result, the present invention contains at least a saccharide, sodium ion, and potassium ion, and the ratio of the molar concentration of sodium ion to the molar concentration of potassium ion is 1 or more. As a result, it was found that the cell preservation performance was improved as compared with a conventional cell preservation solution such as Euro-Collins solution, and the cell preservation solution of the present invention was completed.
すなわち本発明は以下よりなる。
1.少なくとも糖類、ナトリウムイオン及びカリウムイオンを含有し、カリウムイオンのモル濃度に対するナトリウムイオンのモル濃度の比が1以上であることを特徴とする細胞保存液。
2.カリウムイオンとナトリウムイオンのモル比が、1:1 〜 1:85である前項1に記載の細胞保存液。
3.糖類の含有量が、0.5 〜 150 mMである前項1又は2に記載の細胞保存液。
4.糖類が、グルコース、マルトース、マンニトール、スクロース及びトレハロースからなる群より選ばれるいずれか1種又は複数種である前項1〜3のいずれか1に記載の細胞保存液。
5.糖類が、グルコース及び/又はマルトースである前項1〜3のいずれか1に記載の細胞保存液。
6.さらに炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオンを含有する前項1〜5のいずれか1に記載の細胞保存液。
7.炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオンの含有量が、1 〜 75 mMである前項6に記載の細胞保存液。
8.さらに、カルシウムイオン、マグネシウムイオン、塩化物イオン、リン酸イオン、硫酸イオン及び乳酸イオンからなる群より選ばれるいずれか1種又は複数種のイオンを含む前項1〜7のいずれか1に記載の細胞保存液。
9.1,000 mLの水溶液中、以下の組成を含む前項8に記載の細胞保存液:
糖類 0.5 〜 150 mM
ナトリウムイオン 20 〜 260 mM
カリウムイオン 3 〜 125 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 1 〜 75 mM
カルシウムイオン 1 〜 4 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0 〜 1 mM
塩化物イオン 75 〜 245 mM
リン酸イオン 0.5 〜 65 mM
硫酸イオン 0 〜 1 mM
乳酸イオン 0 〜 20 mM
10.日本薬局方リンゲル液、日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム注射液及び市販の脱水補給液からなりを、該日本薬局方リンゲル液、日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム注射液及び市販の脱水補給液の体積比が、80:3:20〜50であることを特徴とする前項1〜9のいずれか1に記載の細胞保存液の調製方法。
11.市販の脱水補給液が、以下の1)又は2)の注射液より選択される前項10に記載の細胞保存液の調製方法:
1)1,000 mLの水溶液中に以下の成分を含有する注射液
塩化ナトリウム 1.92 g
塩化カリウム 1.00 g
乳酸ナトリウム 2.80 g
塩化マグネシウム 0.10 g
リン酸一ナトリウム 0.14 g
リン酸ニカリウム 1.00 g
ブドウ糖 23.5 g
2)以下の組成からなる注射液
塩化ナトリウム 0.270 w/v%
塩化カリウム 0.149 w/v%
乳酸ナトリウム 0.224 w/v%
リン酸ニ水素ナトリウム 0.031 w/v%
リン酸一水素ナトリウム 0.287 w/v%
ブドウ糖 3.2 w/v%
L-乳酸 8 mEq/L
12.前項1〜9のいずれか1に記載の細胞保存液を用いて細胞を冷蔵条件で保存することを特徴とする細胞保存方法。
13.細胞が、リンパ球である前項12に記載の細胞保存方法。
14.前項1〜9のいずれか1に記載の細胞保存液に細胞を懸濁し、該懸濁液を培地にそのまま播種して、該細胞を培養することを特徴とする細胞培養方法。That is, this invention consists of the following.
1. A cell preservation solution comprising at least a saccharide, sodium ion and potassium ion, wherein a ratio of molar concentration of sodium ion to molar concentration of potassium ion is 1 or more.
2. 2. The cell preservation solution according to item 1 above, wherein the molar ratio of potassium ion to sodium ion is 1: 1 to 1:85.
3. 3. The cell preservation solution according to
4). 4. The cell preservation solution according to any one of items 1 to 3, wherein the saccharide is any one kind or plural kinds selected from the group consisting of glucose, maltose, mannitol, sucrose and trehalose.
5. 4. The cell preservation solution according to any one of items 1 to 3, wherein the saccharide is glucose and / or maltose.
6). The cell preservation solution according to any one of 1 to 5 above, further containing hydrogen carbonate ions and / or carbonate ions.
7). 7. The cell preservation solution according to
8). Furthermore, the cell of any one of the preceding clauses 1-7 containing any 1 type or multiple types of ion chosen from the group which consists of calcium ion, magnesium ion, chloride ion, phosphate ion, sulfate ion, and lactate ion. Stock solution.
9. The cell preservation solution according to
Saccharide 0.5 to 150 mM
Sodium ion 20-260 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 1-75 mM
Calcium ion 1-4 mM
Chloride ion 75-245 mM
Phosphate ion 0.5 to 65 mM
Lactate ion 0-20 mM
10. The volume ratio of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution, the Japanese Pharmacopoeia sodium hydrogen carbonate injection solution and the commercially available dehydration replenisher is 80, 3: The method for preparing a cell preservation solution according to any one of items 1 to 9, which is 20 to 50.
11. The method for preparing a cell preservation solution according to
1) Injection solution containing the following ingredients in 1,000 mL of aqueous solution: 1.92 g of sodium chloride
Potassium chloride 1.00 g
Sodium lactate 2.80 g
Magnesium chloride 0.10 g
Monosodium phosphate 0.14 g
Dipotassium phosphate 1.00 g
Glucose 23.5 g
2) Injection solution consisting of the following composition Sodium chloride 0.270 w / v%
Potassium chloride 0.149 w / v%
Sodium lactate 0.224 w / v%
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate 0.031 w / v%
Sodium monohydrogen phosphate 0.287 w / v%
Glucose 3.2 w / v%
L-
12 10. A method for preserving cells, comprising storing cells under refrigerated conditions using the cell preservation solution according to any one of 1 to 9 above.
13. 13. The method for preserving cells according to the above item 12, wherein the cells are lymphocytes.
14 10. A cell culture method comprising suspending cells in the cell preservation solution according to any one of items 1 to 9, seeding the suspension as it is in a medium, and culturing the cells.
本発明の少なくとも糖類、ナトリウムイオン及びカリウムイオンを含有し、カリウムイオンのモル濃度に対するナトリウムイオンのモル濃度の比が1以上である細胞保存液は、細胞の生存率の上昇、細胞の生理機能の維持をもたらし、細胞保存性能を高い状態で維持することができる。また、本発明の細胞保存液は、凍結保存のみならず冷蔵条件下での細胞保存も可能とする。さらに本発明の細胞保存液は、洗浄等の工程を経ずに、細胞を該保存液に懸濁したまま培地に播種して細胞を培養することを可能とする。 The cell preservation solution containing at least saccharide, sodium ion, and potassium ion of the present invention and having a molar concentration ratio of sodium ion to molar concentration of 1 or more is increased in cell viability and cell physiology. Maintenance, and cell preservation performance can be maintained at a high level. Moreover, the cell preservation solution of the present invention enables not only cryopreservation but also cell preservation under refrigerated conditions. Furthermore, the cell preservation solution of the present invention makes it possible to culture cells by seeding them in a medium while suspending the cells in the preservation solution without passing through a step such as washing.
本発明の細胞保存液は、少なくとも糖類、ナトリウムイオン及びカリウムイオンを含有し、カリウムイオンのモル濃度に対するナトリウムイオンのモル濃度の比が1以上であることを特徴とするものである。 The cell preservation solution of the present invention contains at least saccharides, sodium ions and potassium ions, and is characterized in that the ratio of the molar concentration of sodium ions to the molar concentration of potassium ions is 1 or more.
ここで使用される糖類とは、例えば、グルコース、ガラクトース、フルクトース、リボース、マンノース、トレハロース、スクロース、マルトース、マンニトール等をはじめとした各種の単糖類、二糖類、三糖類、多糖類、糖アルコールを含む。これらの糖は1種又は複数種を組み合わせて用いてもよい。なかでもグルコース、マルトース、マンニトール、スクロース、トレハロースが経済性・扱い易さの点で好ましく、さらに好ましくはグルコース、マルトースである。これらの糖類は、市販のものを用いることができる。 細胞保存液における糖類の含有量は、0.5 〜 150 mM、好ましくは0.5 〜 100 mM、さらに好ましくは0.5 〜 50 mMである。糖類の含有量が150 mMを超えると、細胞の保存時に細胞が凝集し、塊を形成することがあり、該塊をほぐすのに煩雑な作業を要する。 Examples of the saccharide used here include various monosaccharides such as glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose, mannose, trehalose, sucrose, maltose, mannitol, disaccharides, trisaccharides, polysaccharides, and sugar alcohols. Including. These sugars may be used alone or in combination. Of these, glucose, maltose, mannitol, sucrose, and trehalose are preferable from the viewpoint of economy and ease of handling, and glucose and maltose are more preferable. Commercially available saccharides can be used. The saccharide content in the cell preservation solution is 0.5 to 150 mM, preferably 0.5 to 100 mM, and more preferably 0.5 to 50 mM. If the saccharide content exceeds 150 mM, the cells may aggregate and form a lump during cell storage, and a complicated operation is required to loosen the lump.
ここで使用されるナトリウムイオン及びカリウムイオンは、有機酸のナトリウム塩若しくはカリウム塩、塩化ナトリウム等の添加により含有させることができる。該含有するナトリウムイオンのモル濃度がカリウムイオンのモル濃度に比べて高いとは、細胞外液に近い組成であることをいう。カリウムイオンとナトリウムイオンのモル比としては、1:1 〜 1:85、好ましくは1:2 〜 1:60の範囲であり、より好適には1:5 〜 1:30の範囲である。ナトリウムイオン含有量は20 〜 260 mM、好ましくは50 〜 200 mM、さらに好ましくは100 〜 150 mMである。また、カリウムイオンとナトリウムイオンのモル比が上記条件に適合する範囲内であれば、カリウムイオンの含有量は特に限定されるものではなく、例えば、3 〜 125 mM、好ましくは3 〜 100 mM、さらに好ましくは3 〜 75 mMから選択することができる。 The sodium ion and potassium ion used here can be contained by adding a sodium salt or potassium salt of organic acid, sodium chloride or the like. That the molar concentration of sodium ions contained is higher than the molar concentration of potassium ions means that the composition is close to the extracellular fluid. The molar ratio of potassium ion to sodium ion is in the range of 1: 1 to 1:85, preferably 1: 2 to 1:60, and more preferably in the range of 1: 5 to 1:30. The sodium ion content is 20 to 260 mM, preferably 50 to 200 mM, more preferably 100 to 150 mM. In addition, the content of potassium ions is not particularly limited as long as the molar ratio of potassium ions to sodium ions is within the range suitable for the above conditions, for example, 3 to 125 mM, preferably 3 to 100 mM, More preferably, it can be selected from 3 to 75 mM.
本発明の細胞保存液は、さらに炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオンを含ませることが好ましい。ここで炭酸水素イオンとはHCO3-を示し、炭酸イオンとはCO32-を示す。これらのイオンは、溶液中では平衡状態にあり、pH等の条件により変化しうる。炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオンは、種々の炭酸塩、炭酸水素塩を細胞保存液に添加することによって、当該保存液に含ませることができる。このような化合物の例としては、炭酸水素ナトリウム(「重曹」ともいう。)、炭酸ナトリウム、炭酸カルシウム、重炭酸カルシウム、炭酸マグネシウム等が挙げられる。特に炭酸水素ナトリウム(重曹)が経済性・扱い易さの点で好適であるが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではない。炭酸水素ナトリウムは市販のものを用いることができる(下記の実施例では和光純薬工業株式会社製を使用)。細胞保存液における炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオンの含有量は、1〜75 mM、好ましくは10〜50 mM、さらに好ましくは20〜30 mMから選択することができるが、特に限定されるものではない。The cell preservation solution of the present invention preferably further contains hydrogen carbonate ions and / or carbonate ions. Here, the bicarbonate ion indicates HCO3− , and the carbonate ion indicates CO32− . These ions are in an equilibrium state in the solution and can change depending on conditions such as pH. Hydrogen carbonate ions and / or carbonate ions can be included in the preservation solution by adding various carbonates and bicarbonates to the cell preservation solution. Examples of such compounds include sodium hydrogen carbonate (also referred to as “bicarbonate”), sodium carbonate, calcium carbonate, calcium bicarbonate, magnesium carbonate, and the like. In particular, sodium hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) is preferable in terms of economy and ease of handling, but the present invention is not limited to this. Commercially available sodium bicarbonate can be used (in the following examples, Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) is used. The hydrogen carbonate ion and / or carbonate ion content in the cell preservation solution can be selected from 1 to 75 mM, preferably 10 to 50 mM, more preferably 20 to 30 mM, but is not particularly limited. Absent.
本発明の細胞保存液では、細胞及び組織が保存中に膨張又は収縮するのを防ぐこと等によって、細胞の生存率を向上させることが好ましい。このため該細胞保存液の浸透圧は、200〜500 mOsm/kgに調整され、好ましくは200〜400 mOsm/kg、より好ましくは250〜350 mOsm/kgに調整される。保存液の浸透圧は、該保存液に含有されるイオンを含む全物質の濃度により定まる。保存液の浸透圧は、糖類、炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン、その他の保存液に含まれるイオンの含有量を変化させることにより、適宜調整することができ、あるいはヒドロキシエチル澱粉等の無害な浸透圧調整剤を添加してもよい。
また本発明の細胞保存液は、pHが5.0〜8.5、好ましくは6.0〜8.5、より好ましくは7.0〜8.0に調整される。pHは、上述した有機酸のナトリウム塩若しくはカリウム塩等の電解質を添加することにより調整することができるが、これに限定されるものではない。In the cell preservation solution of the present invention, it is preferable to improve cell viability by preventing cells and tissues from expanding or contracting during storage. For this reason, the osmotic pressure of the cell preservation solution is adjusted to 200 to 500 mOsm / kg, preferably 200 to 400 mOsm / kg, more preferably 250 to 350 mOsm / kg. The osmotic pressure of the preservation solution is determined by the concentration of all substances including ions contained in the preservation solution. The osmotic pressure of the preservation solution can be appropriately adjusted by changing the content of saccharides, hydrogen carbonate ions and / or carbonate ions, and other ions contained in the preservation solution, or harmless such as hydroxyethyl starch. An osmotic pressure adjusting agent may be added.
Further, the cell preservation solution of the present invention is adjusted to a pH of 5.0 to 8.5, preferably 6.0 to 8.5, more preferably 7.0 to 8.0. Although pH can be adjusted by adding electrolytes, such as a sodium salt or potassium salt of the organic acid mentioned above, it is not limited to this.
本発明の細胞保存液は、さらにカルシウムイオン、マグネシウムイオン等の金属イオン、塩化物イオン、リン酸イオン、硝酸イオン、硫酸イオン、及び乳酸イオン等を含んでいてもよい。これらのイオンは1種又は複数種を組み合わせて用いてもよく、特に限定されるものではない。これらのイオンの濃度は、保存液の浸透圧、pH、及び保存液における他の物質の含有量等に依存するため、当業者が適宜設定できるものであり、特に限定されるものではないが、例えばマグネシウムイオンが0.0 〜 1 mM、好ましくは0.2 〜 0.8 mM、カルシウムイオンが1 〜 4 mM、好ましくは1.5 〜 3.5、塩化物イオンが75 〜 245 mM、好ましくは100 〜 150 mM、リン酸イオンが0.5 〜 65 mM、好ましくは0.5 〜 2 mM、硫酸イオンが0 〜 1 mM、好ましくは0.5 〜 1 mM、乳酸イオンが0 〜 20 mM、好ましくは0 〜 15 mMから選択することができる。 The cell preservation solution of the present invention may further contain metal ions such as calcium ions and magnesium ions, chloride ions, phosphate ions, nitrate ions, sulfate ions, and lactate ions. These ions may be used alone or in combination, and are not particularly limited. The concentration of these ions depends on the osmotic pressure, pH, and content of other substances in the preservation solution, and can be appropriately set by those skilled in the art, and is not particularly limited. For example, magnesium ion is 0.0 to 1 mM, preferably 0.2 to 0.8 mM, calcium ion is 1 to 4 mM, preferably 1.5 to 3.5, chloride ion is 75 to 245 mM, preferably 100 to 150 mM, phosphate ion is It can be selected from 0.5 to 65 mM, preferably 0.5 to 2 mM,
本発明の細胞保存液には、従来の保存液における他の成分、例えば抗生物質、抗菌剤、抗酸化剤、血清、ビタミン、タンパク質、アミノ酸、pH指示薬、キレート剤等を適宜含有させることもできる。 The cell preservation solution of the present invention may appropriately contain other components in the conventional preservation solution, such as antibiotics, antibacterial agents, antioxidants, serum, vitamins, proteins, amino acids, pH indicators, chelating agents, and the like. .
また、本発明の細胞保存液は、日本薬局方リンゲル液及び日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム溶液に、市販の輸液製剤である脱水補給液を必要な成分が必要濃度含まれるように無菌条件下で混合する方法により調製することができる。その他の方法として、例えば必要な成分を各々必要量秤量し、純水に混合し、混合した溶液を除菌ろ過することにより調製してもよい。
市販の輸液製剤である脱水補給液として、例えば総合電解質輸液、輸液用電解質液として販売されている薬剤を使用することができる。より具体的には、以下の1)又は2)の組成を有する注射液が挙げられる。In addition, the cell preservation solution of the present invention is mixed under aseptic conditions with a Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution and a Japanese Pharmacopoeia sodium bicarbonate solution so that a dehydration replenisher that is a commercially available infusion preparation contains the necessary components at the required concentration. It can be prepared by a method. As another method, for example, a necessary amount of each necessary component may be weighed, mixed with pure water, and the mixed solution may be sterilized and filtered.
As a dehydration replenisher which is a commercially available infusion preparation, for example, a drug sold as a general electrolyte infusion or an electrolyte for infusion can be used. More specifically, an injection solution having the following composition 1) or 2) can be mentioned.
1)1,000 mLの水溶液中に以下の成分を含有する注射液
塩化ナトリウム 1.92 g
塩化カリウム 1.00 g
乳酸ナトリウム 2.80 g
塩化マグネシウム 0.10 g
リン酸一ナトリウム 0.14 g
リン酸ニカリウム 1.00 g
ブドウ糖 23.5 g1) Injection solution containing the following ingredients in 1,000 mL of aqueous solution: 1.92 g of sodium chloride
Potassium chloride 1.00 g
Sodium lactate 2.80 g
Magnesium chloride 0.10 g
Monosodium phosphate 0.14 g
Dipotassium phosphate 1.00 g
Glucose 23.5 g
2)以下の組成からなる注射液
塩化ナトリウム 0.270 w/v%
塩化カリウム 0.149 w/v%
乳酸ナトリウム 0.224 w/v%
リン酸ニ水素ナトリウム 0.031 w/v%
リン酸一水素ナトリウム 0.287 w/v%
ブドウ糖 3.2 w/v%
L-乳酸 8 mEq/L2) Injection solution consisting of the following composition Sodium chloride 0.270 w / v%
Potassium chloride 0.149 w / v%
Sodium lactate 0.224 w / v%
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate 0.031 w / v%
Sodium monohydrogen phosphate 0.287 w / v%
Glucose 3.2 w / v%
L-
上記日本薬局方リンゲル液、日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム溶液及び市販の輸液製剤は、体積比80:3:20〜50の割合で混合することにより、本発明の細胞保存液を調製することができる。具体的には、例えば日本薬局方リンゲル液800 mL、日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム溶液30 mLに上記1)の注射液を250 〜 300 mL混合して調製することができる。さらに別の方法として例えば日本薬局方リンゲル液800 mL、日本薬局方炭酸水素30 mLに上記2)の注射液を400 〜 450 mL混合して調製することができる。 The cell preservation solution of the present invention can be prepared by mixing the Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution, the Japanese Pharmacopoeia sodium bicarbonate solution and the commercially available infusion preparation at a volume ratio of 80: 3: 20-50. Specifically, for example, it can be prepared by mixing 250 to 300 mL of the injection solution of 1) above with 800 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution and 30 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia sodium bicarbonate solution. As another method, for example, 800 to 450 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution and 30 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia bicarbonate can be prepared by mixing 400 to 450 mL of the injection solution of 2) above.
本発明の細胞保存液を用いて保存することのできる細胞としては、例えば、ヒトを含む哺乳動物から単離した種々の細胞、例えばリンパ球、幹細胞、皮膚細胞、粘膜細胞、肝細胞、膵島細胞、神経細胞、軟骨細胞、内皮細胞、上皮細胞、骨細胞、筋細胞等、骨髄細胞、造血幹細胞あるいは、哺乳動物以外では魚類の精子・卵子・受精卵、昆虫細胞等を挙げることができる。本発明の細胞保存液は、特にヒトの活性化リンパ球を保存するのに適しているが、これに限定されるものではない。 Examples of cells that can be stored using the cell preservation solution of the present invention include various cells isolated from mammals including humans, such as lymphocytes, stem cells, skin cells, mucosal cells, hepatocytes, islet cells. Examples thereof include nerve cells, chondrocytes, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, bone cells, muscle cells, bone marrow cells, hematopoietic stem cells, and fish sperm / ovum / fertilized eggs and insect cells other than mammals. The cell preservation solution of the present invention is particularly suitable for preserving human activated lymphocytes, but is not limited thereto.
本発明は、上記細胞保存液を用いた細胞保存方法にも及ぶ。保存の方法としては、細胞保存液に細胞を懸濁した後、従来通り凍結させて保存することもできるが、凍結させず冷蔵条件で保存することもできる。冷蔵条件とは、溶液が凍結しない条件であって、低温であれば特に限定されるものではないが、好ましくは、0〜25℃、より好ましくは0〜10℃、特に好ましくは4〜6℃の範囲である。 The present invention also extends to a cell preservation method using the above cell preservation solution. As a preservation method, after suspending cells in a cell preservation solution, the cells can be frozen and stored as usual, but can also be preserved under refrigerated conditions without being frozen. The refrigerated condition is a condition in which the solution does not freeze and is not particularly limited as long as the temperature is low, but is preferably 0 to 25 ° C, more preferably 0 to 10 ° C, particularly preferably 4 to 6 ° C. Range.
また、本発明の細胞保存液による細胞の保存期間は、細胞種、保存温度等の条件に依存するため一律には規定しがたいが、目安としては8〜12日程度まで、好ましくは4〜6日程度まで可能である。具体的な使用態様としては、例えば、活性リンパ球を受託培養施設から患者の元に輸送する際の保存に用いることができる。このような短期間の保存の場合、冷蔵条件下で保存できるという点で、本発明の保存液及び保存方法には利点がある。 In addition, the cell storage period of the cell storage solution of the present invention depends on conditions such as the cell type and storage temperature, and thus cannot be uniformly defined, but as a guideline, it is about 8 to 12 days, preferably 4 to 4 days. Up to about 6 days is possible. As a specific use mode, for example, the active lymphocytes can be used for preservation when transported from a contract culture facility to a patient. In the case of such short-term storage, the storage solution and storage method of the present invention are advantageous in that they can be stored under refrigerated conditions.
保存の際に、細胞保存液に懸濁させる細胞の濃度は、細胞種、細胞の大きさ、保存期間等の条件に依存するため、当業者により適宜決定されるものであり、特に限定されるものではないが、例えば、1.0×104〜1.0×108 cells/mL程度、好ましくは1.0×105〜1.0×108 cells/mL程度である。また保存容器は、細胞種、保存温度、保存期間、保存後の細胞の用途等を考慮して、公知の容器から適宜選択して用いることができる。During storage, the concentration of cells suspended in the cell storage solution depends on conditions such as cell type, cell size, storage period, and the like, and is appropriately determined by those skilled in the art and is particularly limited. For example, it is about 1.0 × 104 to 1.0 × 108 cells / mL, preferably about 1.0 × 105 to 1.0 × 108 cells / mL. The storage container can be appropriately selected from known containers in consideration of the cell type, storage temperature, storage period, use of the cell after storage, and the like.
さらに本発明は、上記のように保存した細胞を用いた細胞培養方法にも及ぶ。保存後の細胞は、遠心分離などによって細胞保存液と分離した後、通常の培地に播種して培養してもよいが、細胞保存液で保存した、細胞懸濁液を通常の培地にそのまま播種して培養することができる。 Furthermore, the present invention extends to a cell culture method using the cells preserved as described above. The cells after storage may be separated from the cell preservation solution by centrifugation or the like, and then seeded and cultured in a normal medium, but the cell suspension stored in the cell preservation solution is seeded in a normal medium as it is. And can be cultured.
(実施例1)グルコース及び重曹を含有した細胞保存液
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。浸透圧は約283.5 mOsm/kgであった。浸透圧はOSMOMETER OM 802-D (VOGEL社製)を用いて測定した。
グルコース(和光純薬工業株式会社製)1,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 6,976.8 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2,000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N塩酸 2.8 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 1) Cell preservation solution containing glucose and sodium bicarbonate A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The osmotic pressure was about 283.5 mOsm / kg. The osmotic pressure was measured using OSMOMETER OM 802-D (manufactured by VOGEL).
Glucose (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) 1,000 mg
Sodium chloride 6,976.8 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2,000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N hydrochloric acid 2.8 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.5 mM
ナトリウムイオン 143.8 mM
カリウムイオン 5.4 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.7 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 130.8 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.5 mM
Sodium ion 143.8 mM
Potassium ion 5.4 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.7 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 130.8 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例2)マルトース及び重曹を含有した細胞保存液
実施例1におけるグルコースを、マルトース(和光純薬工業株式会社製)に置き換えた以外は実施例1と同様の細胞保存液を調製した。ちなみに、マルトースの含量は、実施例1のグルコースの含量と同じである。(Example 2) Cell preservation solution containing maltose and sodium bicarbonate A cell preservation solution similar to Example 1 was prepared except that glucose in Example 1 was replaced with maltose (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.). Incidentally, the maltose content is the same as the glucose content of Example 1.
(実施例3)マンニトール及び重曹を含有した細胞保存液
実施例1におけるグルコースを、マンニトール(和光純薬工業株式会社製)に置き換えた以外は実施例1と同様の細胞保存液を調製した。ちなみに、マンニトールの含量は、実施例1のグルコースの含量と同じである。(Example 3) Cell preservation solution containing mannitol and sodium bicarbonate A cell preservation solution similar to Example 1 was prepared, except that glucose in Example 1 was replaced with mannitol (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.). Incidentally, the content of mannitol is the same as the content of glucose in Example 1.
(実施例4)スクロース及び重曹を含有した細胞保存液
実施例1におけるグルコースを、スクロース(シグマ社製)に置き換えた以外は実施例1と同様の細胞保存液を調製した。ちなみに、スクロースの含量は、実施例1のグルコースの含量と同じである。(Example 4) Cell preservation solution containing sucrose and sodium bicarbonate A cell preservation solution similar to Example 1 was prepared, except that glucose in Example 1 was replaced with sucrose (manufactured by Sigma). Incidentally, the sucrose content is the same as the glucose content of Example 1.
(実施例5)トレハロース及び重曹を含有した細胞保存液
実施例1におけるグルコースを、トレハロース(和光純薬工業株式会社製)に置き換えた以外は実施例1と同様の細胞保存液を調製した。ちなみに、トレハロースの含量は、実施例1のグルコースの含量と同じである。(Example 5) Cell preservation solution containing trehalose and sodium bicarbonate A cell preservation solution similar to Example 1 was prepared except that glucose in Example 1 was replaced with trehalose (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.). Incidentally, the trehalose content is the same as the glucose content of Example 1.
(実施例6)炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオンを含有しない細胞保存液
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン(重曹)を含まないこと以外は実施例1と同様の細胞保存液を調製した。つまり、実施例1の組成から、炭酸水素ナトリウムを除いた以下の組成である。この時の浸透圧は、約283.5 mOsm/kgであった
グルコース 1,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 8,228 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 0 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N水酸化ナトリウム水溶液 0.72 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 6) Cell preservation solution containing no hydrogen carbonate ions and / or carbonate ions A cell preservation solution similar to Example 1 was prepared except that it did not contain hydrogen carbonate ions and / or carbonate ions (bicarbonate). That is, it is the following composition except sodium hydrogencarbonate from the composition of Example 1. The osmotic pressure at this time was about 283.5 mOsm / kg.Glucose 1,000 mg
Sodium chloride 8,228 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution 0.72 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.5 mM
ナトリウムイオン 142.4 mM
カリウムイオン 5.4 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 0 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 132.4 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.5 mM
Sodium ion 142.4 mM
Potassium ion 5.4 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 132.4 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例7)浸透圧200 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。細胞保存液の浸透圧は約200 mOsm/kgであった。
グルコース 1,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 4,000 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2,000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N塩酸 2.4 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 7) Cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of 200 mOsm / kg A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The osmotic pressure of the cell preservation solution was about 200 mOsm / kg.
Glucose 1,000 mg
Sodium chloride 4,000 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2,000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N hydrochloric acid 2.4 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.5 mM
ナトリウムイオン 93.0 mM
カリウムイオン 5.4 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.8 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 79.6 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.5 mM
Sodium ion 93.0 mM
Potassium ion 5.4 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.8 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 79.6 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例8)浸透圧240 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液
浸透圧約240 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液を調製した。浸透圧は実施例7の組成に、さらに塩化ナトリウムを1240mg添加することで調整した。(Example 8) Cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of 240 mOsm / kg A cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of about 240 mOsm / kg was prepared. The osmotic pressure was adjusted by adding 1240 mg of sodium chloride to the composition of Example 7.
(実施例9)浸透圧300 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液
浸透圧約300 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液を調製した。浸透圧は実施例7の組成に、さらに塩化ナトリウムを3100mgを添加することで調整した。(Example 9) Cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of 300 mOsm / kg A cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of about 300 mOsm / kg was prepared. The osmotic pressure was adjusted by adding 3100 mg of sodium chloride to the composition of Example 7.
(実施例10)浸透圧400 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液
浸透圧約400 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液を調製した。浸透圧は実施例7の組成に、さらに塩化ナトリウムを6200mgを添加することで調整した。(Example 10) Cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of 400 mOsm / kg A cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of about 400 mOsm / kg was prepared. The osmotic pressure was adjusted by adding 6200 mg of sodium chloride to the composition of Example 7.
(実施例11)浸透圧500 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液
浸透圧約500 mOsm/kgの細胞保存液を調製した。浸透圧は実施例7の組成に、さらに塩化ナトリウムを96100mgを添加することで調整した。(Example 11) Cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of 500 mOsm / kg A cell preservation solution having an osmotic pressure of about 500 mOsm / kg was prepared. The osmotic pressure was adjusted by adding 96100 mg of sodium chloride to the composition of Example 7.
(実施例12)pH 5.0の細胞保存液
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。細胞保存液の浸透圧は約299 mOsm/kg、pHは約5.0であった。
グルコース 1,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 4,000 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2,000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N水酸化ナトリウム水溶液 1.08 mL
1N塩酸 23.2 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 12) Cell preservation solution of pH 5.0 A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The cell preservation solution had an osmotic pressure of about 299 mOsm / kg and a pH of about 5.0.
Glucose 1,000 mg
Sodium chloride 4,000 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2,000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution 1.08 mL
1N hydrochloric acid 23.2 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.4 mM
ナトリウムイオン 138.8 mM
カリウムイオン 5.2 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.2 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 145.0 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.4 mM
Sodium ion 138.8 mM
Potassium ion 5.2 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.2 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 145.0 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例13)pH 6.0の細胞保存液
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。細胞保存液の浸透圧は約293 mOsm/kg、pHは約6.0であった。
グルコース 1,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 4,000 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2,000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N塩酸 1.4 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 13) Cell preservation solution of pH 6.0 A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The cell preservation solution had an osmotic pressure of about 293 mOsm / kg and a pH of about 6.0.
Glucose 1,000 mg
Sodium chloride 4,000 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2,000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N hydrochloric acid 1.4 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.5 mM
ナトリウムイオン 139.2 mM
カリウムイオン 5.3 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.5 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 137.4 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.5 mM
Sodium ion 139.2 mM
Potassium ion 5.3 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.5 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 137.4 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例14)pH 7.0の細胞保存液
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。細胞保存液の浸透圧は約283 mOsm/kg、pHは約7.0であった。
グルコース 1,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 4,000 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2,000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N塩酸 2.8 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 14) Cell preservation solution of pH 7.0 A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The cell preservation solution had an osmotic pressure of about 283 mOsm / kg and a pH of about 7.0.
Glucose 1,000 mg
Sodium chloride 4,000 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2,000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N hydrochloric acid 2.8 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.5 mM
ナトリウムイオン 140.8 mM
カリウムイオン 5.4 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.7 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 127.8 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.5 mM
Sodium ion 140.8 mM
Potassium ion 5.4 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.7 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 127.8 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例15)pH 8.0の細胞保存液
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。細胞保存液の浸透圧は約281 mOsm/kg、pHは約8.0であった。
グルコース 1,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 4,000 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2,000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N水酸化ナトリウム水溶液 0.6 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 15) Cell preservation solution at pH 8.0 A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The cell preservation solution had an osmotic pressure of about 281 mOsm / kg and a pH of about 8.0.
Glucose 1,000 mg
Sodium chloride 4,000 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2,000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution 0.6 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.5 mM
ナトリウムイオン 141.7 mM
カリウムイオン 5.4 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.8 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 125.2 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.5 mM
Sodium ion 141.7 mM
Potassium ion 5.4 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.8 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 125.2 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例16)
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。この時の浸透圧は約288 mOsm/kgであった。
グルコース 10,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 6,960 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2,000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N塩酸 2.6 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 16)
A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The osmotic pressure at this time was about 288 mOsm / kg.
Glucose 10,000 mg
Sodium chloride 6,960 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2,000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N hydrochloric acid 2.6 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 47.8 mM
ナトリウムイオン 121.4 mM
カリウムイオン 4.6 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 20.5 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.6 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.7 mM
塩化物イオン 110.0 mM
リン酸イオン 0.9 mM
硫酸イオン 0.7 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 47.8 mM
Sodium ion 121.4 mM
Potassium ion 4.6 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 20.5 mM
Calcium ion 1.6 mM
Magnesium ion 0.7 mM
Chloride ion 110.0 mM
Phosphate ion 0.9 mM
Sulfate ion 0.7 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例17)
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。この時の浸透圧は約283 mOsm/kgであった。
グルコース 1,000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 4,000 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2,000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N塩酸 2.8 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Example 17)
A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The osmotic pressure at this time was about 283 mOsm / kg.
Glucose 1,000 mg
Sodium chloride 4,000 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2,000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N hydrochloric acid 2.8 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.5 mM
ナトリウムイオン 140.8 mM
カリウムイオン 5.4 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.7 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 127.8 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.5 mM
Sodium ion 140.8 mM
Potassium ion 5.4 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.7 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 127.8 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実施例18)
日本薬局方リンゲル液800 mLに、以下の1)の組成からなる注射液(市販の脱水補給液)250 mL及び日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム注射液30 mLを混合し、細胞保存液を調製した。
1)1,000 mLの水溶液中に以下の成分を含有する注射液
塩化ナトリウム 1.92g
塩化カリウム 1.00g
乳酸ナトリウム 2.80g
塩化マグネシウム 0.10g
リン酸一ナトリウム 0.14g
リン酸ニカリウム 1.00g
ブドウ糖 23.5 g(Example 18)
To 800 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution, 250 mL of an injection solution (commercial dehydration replenisher) having the following composition 1) and 30 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia sodium bicarbonate injection solution were mixed to prepare a cell preservation solution.
1) Injection solution containing the following ingredients in 1,000 mL of aqueous solution: 1.92 g of sodium chloride
Potassium chloride 1.00g
Sodium lactate 2.80g
Magnesium chloride 0.10g
Monosodium phosphate 0.14g
Dipotassium phosphate 1.00g
Glucose 23.5 g
この時の、最終組成は以下の2)のとおりであり、浸透圧約317.7 mOsm/kg、pH 7.749(24.4℃)であった。
2)最終組成
グルコース 30.2 mM
ナトリウムイオン 145.7 mM
カリウムイオン 8.7 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.1 mM
カルシウムイオン 3.3 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.2 mM
塩化物イオン 126.4 mM
リン酸イオン 1.6 mM
乳酸イオン 5.8 mM
合計液量 1,080 mLAt this time, the final composition was as shown in 2) below, and the osmotic pressure was about 317.7 mOsm / kg, pH 7.749 (24.4 ° C.).
2) Final composition Glucose 30.2 mM
Sodium ion 145.7 mM
Potassium ion 8.7 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.1 mM
Calcium ion 3.3 mM
Magnesium ion 0.2 mM
Chloride ion 126.4 mM
Phosphate ion 1.6 mM
Lactate ion 5.8 mM
Total liquid volume 1,080 mL
(実施例19)
日本薬局方リンゲル液800 mLに、実施例18の1)の組成からなる注射液(市販の脱水補給液)300 mL及び日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム注射液30 mLを混合し、細胞保存液を調製した。
この時の、最終組成は以下のとおりであり、浸透圧約316.7 mOsm/kg、pH 7.351(25.2℃)であった。
最終組成
グルコース 34.6 mM
ナトリウムイオン 141.9 mM
カリウムイオン 9.4 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 22.1 mM
カルシウムイオン 3.2 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.3 mM
塩化物イオン 122.9 mM
リン酸イオン 1.8 mM
乳酸イオン 6.6 mM
合計液量 1,130 mL(Example 19)
800 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution was mixed with 300 mL of an injection solution (commercial dehydration replenisher) of Example 18 1) and 30 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia sodium bicarbonate injection solution to prepare a cell preservation solution. .
The final composition at this time was as follows, and the osmotic pressure was about 316.7 mOsm / kg, pH 7.351 (25.2 ° C.).
Final composition Glucose 34.6 mM
Sodium ion 141.9 mM
Potassium ion 9.4 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 22.1 mM
Calcium ion 3.2 mM
Magnesium ion 0.3 mM
Chloride ion 122.9 mM
Phosphate ion 1.8 mM
Lactate ion 6.6 mM
Total liquid volume 1,130 mL
(実施例20)
日本薬局方リンゲル液800 mLに、以下の1)の組成からなる注射液(市販の脱水補給液)400 mL及び日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム注射液30 mLを混合し、細胞保存液を調製した。
1)1,000 mLの水溶液中に以下の成分を含有する注射液
塩化ナトリウム 0.270 w/v%
塩化カリウム 0.149 w/v%
乳酸ナトリウム 0.224 w/v%
リン酸ニ水素ナトリウム 0.031 w/v%
リン酸一水素ナトリウム 0.287 w/v%
ブドウ糖 3.2 w/v%
添加物としてのL-乳酸 8 mEq/L(Example 20)
A cell preservation solution was prepared by mixing 800 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution with 400 mL of an injection solution (commercial dehydration replenisher) having the following composition 1) and 30 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia sodium bicarbonate injection solution.
1) Injection solution containing the following ingredients in 1,000 mL of aqueous solution Sodium chloride 0.270 w / v%
Potassium chloride 0.149 w / v%
Sodium lactate 0.224 w / v%
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate 0.031 w / v%
Sodium monohydrogen phosphate 0.287 w / v%
Glucose 3.2 w / v%
L-lactic acid as additive 8 mEq / L
この時の、最終組成は以下の2)のとおりであり、浸透圧約339.7 mOsm/kg、pH 7.442(24.2℃)であった。
2)最終組成
グルコース 57.8 mM
ナトリウムイオン 143.3 mM
カリウムイオン 9.1 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 20.3 mM
カルシウムイオン 2.9 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.0 mM
塩化物イオン 122.7 mM
リン酸イオン 3.3 mM
乳酸イオン 9.1 mM
純水
合計 1,230 mLThe final composition at this time was as shown in 2) below, and the osmotic pressure was about 339.7 mOsm / kg and pH 7.442 (24.2 ° C.).
2) Final composition Glucose 57.8 mM
Sodium ion 143.3 mM
Potassium ion 9.1 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 20.3 mM
Calcium ion 2.9 mM
Magnesium ion 0.0 mM
Chloride ion 122.7 mM
Phosphate ion 3.3 mM
Lactate ion 9.1 mM
Pure water Total 1,230 mL
(実施例21)
日本薬局方リンゲル液800 mLに、実施例20の1)の組成からなる注射液(市販の脱水補給液)450 mL及び日本薬局方炭酸水素ナトリウム注射液30 mLを混合し、細胞保存液を調製した。
この時の、最終組成は以下のとおりであり、浸透圧約316.7 mOsm/kg、pH 7.351(25.2℃)であった。
最終組成
グルコース 62.4 mM
ナトリウムイオン 141.0 mM
カリウムイオン 9.5 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 19.5 mM
カルシウムイオン 2.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.0 mM
塩化物イオン 120.5 mM
リン酸イオン 3.5 mM
乳酸イオン 9.8 mM
純水
合計 1,1280 mL(Example 21)
A cell preservation solution was prepared by mixing 800 mL of the Japanese Pharmacopoeia Ringer's solution with 450 mL of an injection solution (commercial dehydration replenisher) of Example 20 1) and 30 mL of Japanese Pharmacopoeia sodium bicarbonate injection solution. .
The final composition at this time was as follows, and the osmotic pressure was about 316.7 mOsm / kg, pH 7.351 (25.2 ° C.).
Final composition Glucose 62.4 mM
Sodium ion 141.0 mM
Potassium ion 9.5 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 19.5 mM
Calcium ion 2.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.0 mM
Chloride ion 120.5 mM
Phosphate ion 3.5 mM
Lactate ion 9.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,1280 mL
(比較例1)糖類を含有しない細胞保存液
グルコースを含まないこと以外は実施例1と同様の細胞保存液を調製した。したがって、以下の組成からなる。
グルコース 0 mM
ナトリウムイオン 145.3 mM
カリウムイオン 5.4 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.7 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 132.4 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Comparative example 1) Cell preservation | save liquid which does not contain saccharides The cell preservation | save liquid similar to Example 1 was prepared except not containing glucose. Therefore, it consists of the following compositions.
Sodium ion 145.3 mM
Potassium ion 5.4 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.7 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 132.4 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(比較例2)リン酸緩衝液
一般に細胞保存液として使用されるリン酸緩衝液を細胞保存液とした。Comparative Example 2 Phosphate Buffer Solution A phosphate buffer solution generally used as a cell preservation solution was used as a cell preservation solution.
(比較例3)生理食塩水
一般に細胞保存液として使用される生理食塩水(2.5v/v%のヒトアルブミン含有)を細胞保存液とした。(Comparative Example 3) Physiological saline Physiological saline (containing 2.5 v / v% human albumin) generally used as a cell preservation solution was used as a cell preservation solution.
(比較例4)ユーロ−コリンズ液
一般に臓器保存液として市販されているユーロ−コリンズ液を細胞保存液とした。本比較例におけるユーロコリンズの組成中、糖含有量としてグルコース194.3mMであり、ナトリウムイオン濃度10.0mM、カリウムイオン濃度115.0mMであった。(Comparative example 4) Euro-Collins solution Euro-Collins solution generally marketed as an organ preservation solution was used as a cell preservation solution. In the composition of Eurocollins in this comparative example, the sugar content was 194.3 mM glucose, the sodium ion concentration was 10.0 mM, and the potassium ion concentration was 115.0 mM.
(比較例5)pH 9.0の細胞保存液
以下の成分を純水に溶解することにより細胞保存液を調製した。細胞保存液の浸透圧は約285 mOsm/kg、pHは約9.0であった。
グルコース 1000 mg
塩化ナトリウム 4188 mg
塩化カリウム 400 mg
塩化カルシウム 200 mg
炭酸水素ナトリウム 2000 mg
リン酸水素ナトリウム・水和物 140 mg
硫酸マグネシウム 98 mg
1N水酸化ナトリウム水溶液 3.2 mL
純水
合計 1,000 mL(Comparative Example 5) Cell preservation solution at pH 9.0 A cell preservation solution was prepared by dissolving the following components in pure water. The cell preservation solution had an osmotic pressure of about 285 mOsm / kg and a pH of about 9.0.
Glucose 1000 mg
Sodium chloride 4188 mg
Potassium chloride 400 mg
Calcium chloride 200 mg
Sodium bicarbonate 2000 mg
Sodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 140 mg
Magnesium sulfate 98 mg
1N sodium hydroxide aqueous solution 3.2 mL
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
したがって、イオン組成は以下のとおりである。
グルコース 5.5 mM
ナトリウムイオン 147.1 mM
カリウムイオン 5.3 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン 23.7 mM
カルシウムイオン 1.8 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0.8 mM
塩化物イオン 128.1 mM
リン酸イオン 1.0 mM
硫酸イオン 0.8 mM
純水
合計 1,000 mLTherefore, the ionic composition is as follows.
Glucose 5.5 mM
Sodium ion 147.1 mM
Potassium ion 5.3 mM
Bicarbonate ion and / or carbonate ion 23.7 mM
Calcium ion 1.8 mM
Magnesium ion 0.8 mM
Chloride ion 128.1 mM
Phosphate ion 1.0 mM
Sulfate ion 0.8 mM
Pure water Total 1,000 mL
(実験例1)本発明の細胞保存液における細胞の生存率
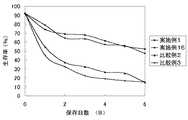
保存液の浸透圧を一定にした場合における、各種糖類含有の細胞保存性能の比較及び従来の細胞保存液との比較を行った。具体的には、実施例1〜6、比較例1〜4の細胞保存液を用いてリンパ球(Tリンパ球)を細胞懸濁液の濃度を約2.0×106 cells/mLとし、各保存液中で冷蔵条件(4℃)で保存した。保存後4日目のリンパ球の生存率を、トリパンブルー染色による生死判定で算出した。その結果を表1に示す。
表1の結果から明らかなように糖類及び炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオンを有効成分とする細胞保存液(実施例1〜6)は比較例に比べて高い生存率を示し、実施例1、2は特に高い生存率を示した。 As is clear from the results in Table 1, the cell preservation solutions (Examples 1 to 6) containing saccharides and hydrogen carbonate ions and / or carbonate ions as active ingredients showed higher survival rates than the comparative examples. 2 showed a particularly high survival rate.
(実験例2)細胞保存液の浸透圧の影響
保存液の浸透圧依存性を検討した。具体的には、実施例7〜11の細胞保存液を用いてリンパ球(Tリンパ球)を細胞懸濁液の濃度を約1.5×106 cells/mLとし、各保存液中で冷蔵条件(4℃)で保存した。保存後4日目のリンパ球の生存率を、トリパンブルー染色による生死判定で算出した。その結果を表2に示す。比較は市販の細胞保存液(比較例2、3)で行った。
表2の結果から糖類、カルシウムイオン及びナトリウムイオンを有効成分とし、浸透圧が200〜500 mOsm/kgの範囲のいずれ(実施例7〜11)においても市販の細胞保存液(比較例2、3)よりも細胞生存率が高く、本発明の有効性を示した。特に200〜300 mOsm/kgの範囲(実施例7〜9)でより高い生存率を示した。 From the results shown in Table 2, a commercially available cell preservation solution (Comparative Examples 2, 3) was used in any of the osmotic pressures ranging from 200 to 500 mOsm / kg (Examples 7 to 11). The cell viability was higher than that of), indicating the effectiveness of the present invention. In particular, a higher survival rate was shown in the range of 200 to 300 mOsm / kg (Examples 7 to 9).
(実験例3)細胞保存液のpHの影響
細胞保存液中にグルコース、カルシウムイオン及びナトリウムイオンが存在し、かつ浸透圧を略一定にした場合におけるpH依存性を検討した。具体的には、実施例12〜15、比較例5の細胞保存液を用いてリンパ球(Tリンパ球)を細胞懸濁液の濃度を約1.0×106 cells/mLとし、各保存液中で冷蔵条件(4℃)で保存した。保存後4日目のリンパ球の生存率を、トリパンブルー染色による生死判定で算出した。その結果を表3に示す。
表3の結果から明らかなようにpH 5.0〜8.0の範囲(実施例12〜15)で比較的高い生存率を示し、pH 6.0〜8.0(実施例13〜15)で特に高い生存率を示した。 As is clear from the results in Table 3, a relatively high survival rate was exhibited in the range of pH 5.0 to 8.0 (Examples 12 to 15), and a particularly high survival rate was exhibited in the pH 6.0 to 8.0 (Examples 13 to 15). .
(実験例4)細胞生存率の経時変化
図1は、実施例1、16の細胞保存液と従来の細胞保存液(比較例2、3)の細胞生存率の経時変化を測定した結果である。本発明の細胞保存液は保存開始から6日経過しても比較的高い生存率を示した。(Experimental Example 4) Time-dependent change in cell viability FIG. 1 shows the results of measuring the time-dependent changes in cell viability of the cell preservation solutions of Examples 1 and 16 and conventional cell preservation solutions (Comparative Examples 2 and 3). . The cell preservation solution of the present invention showed a relatively high survival rate even after 6 days from the start of the preservation.
(実験例5)保存後の細胞培養
活性化培養開始後5日目の対数増殖期にあるリンパ球を、実施例17の細胞保存液を用いて、20×106 cells/mLの濃度で4日間冷蔵保存した。保存後の細胞を回収し洗浄操作を行わず、その一部をFBSを10%含有したリンパ球用培地(ALyS505N培地、細胞科学研究所社製)にそのまま添加し、播種時濃度2.7×105 cells/mLで37℃、5% CO2雰囲気下で、4日間培養した。その結果、4日後にはリンパ球濃度が1.7×106 cells/mLとなった。よって実施例17の細胞保存液は、細胞の培養を阻害するものではないことが確認された。(Experimental example 5) Cell culture after storage The lymphocytes in the logarithmic growth phase on the fifth day after the start of activation culture were treated with the cell preservation solution of Example 17 at a concentration of 20 × 106 cells / mL. Refrigerated for days. The cells after storage are collected and washed, but a part of the cells is added as it is to a lymphocyte culture medium containing 10% FBS (ALyS505N medium, manufactured by Cell Science Laboratories) and the seeding concentration is 2.7 × 105 The cells were cultured at 37 ° C. in a 5
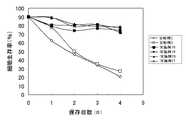
(実験例6)細胞生存率の経時変化
図2は、実施例18〜21の各細胞保存液と従来の細胞保存液(比較例2、3)の細胞生存率の経時変化を測定した結果である。本発明の細胞保存液は保存開始から4日経過しても比較的高い生存率を示した。(Experimental example 6) Change with time of cell viability FIG. 2 shows the results of measuring the change with time of cell viability of each cell preservation solution of Examples 18 to 21 and conventional cell preservation solutions (Comparative Examples 2 and 3). is there. The cell storage solution of the present invention showed a relatively high survival rate even after 4 days from the start of storage.
以上説明した通り、本発明の細胞保存液を使用することにより、冷蔵条件下でも細胞保存性能を向上させて、細胞生存率の増加が可能になる。また、本発明によれば冷蔵条件での細胞保存方法を提供するため、これまで保存が困難であった細胞種を保存することも可能となる。また、凍結保存に必要であったプログラミングフリーザー等の高価な装置・設備が準備できないような場合でも、細胞を保存することが可能となる。さらに本発明の細胞保存液を用いれば、洗浄等の工程を経ずに、細胞を該保存液に懸濁したまま培地に播種して細胞を培養することが可能となるため、簡便に細胞培養を行うことできる。例えば、本発明の細胞保存液は、近年広まりつつある免疫細胞療法の分野において、活性化培養したリンパ球を受託培養施設から患者の元へ輸送する際に使用することができる。これにより、細胞生存率の低下を抑制して細胞の品質を保持し、最終的には治療への活用にも役立つものと考えられる。 As described above, by using the cell preservation solution of the present invention, the cell preservation performance can be improved even under refrigerated conditions, and the cell viability can be increased. In addition, according to the present invention, since a cell storage method under refrigerated conditions is provided, cell types that have been difficult to store can be stored. In addition, even when an expensive device or facility such as a programming freezer required for cryopreservation cannot be prepared, cells can be preserved. Furthermore, if the cell preservation solution of the present invention is used, it is possible to inoculate cells in a medium while suspending the cells in the preservation solution without passing through washing or the like. Can be done. For example, the cell preservation solution of the present invention can be used for transporting activated cultured lymphocytes from a consignment culture facility to a patient in the field of immune cell therapy, which is spreading in recent years. Thereby, it is considered that the decrease in cell viability is suppressed and the quality of the cells is maintained, and finally, it is useful for therapeutic use.
Claims (8)
Translated fromJapanese糖類 0.5 〜 150 mM
ナトリウムイオン 20 〜 260 mM
カリウムイオン 3 〜 125 mM
炭酸水素イオン及び/又は炭酸イオン20 〜 75 mM
カルシウムイオン 1 〜 4 mM
マグネシウムイオン 0 〜 1 mM
塩化物イオン 75 〜 245 mM
リン酸イオン 0.5 〜 65 mM
硫酸イオン 0 〜 1 mM
乳酸イオン 0 〜 20 mMThe cell preservation solutionfor refrigerated storage according to claim4 , comprising the following composition in a 1,000 mL aqueous solution:
Saccharide 0.5 to 150 mM
Sodium ion 20-260 mM
Potassium ion 3 to 125 mM
Bicarbonate ions and / or carbonate ions20 ~ 75 mM
Calcium ion 1-4 mM
Magnesium ion 0 to 1 mM
Chloride ion 75-245 mM
Phosphate ion 0.5 to 65 mM
Sulfate ion 0 to 1 mM
Lactate ion 0-20 mM
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005296593AJP4947948B2 (en) | 2004-10-12 | 2005-10-11 | Cell preservation solution |
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004297532 | 2004-10-12 | ||
| JP2004297532 | 2004-10-12 | ||
| JP2005022170 | 2005-01-28 | ||
| JP2005022170 | 2005-01-28 | ||
| JP2005296593AJP4947948B2 (en) | 2004-10-12 | 2005-10-11 | Cell preservation solution |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006230396A JP2006230396A (en) | 2006-09-07 |
| JP4947948B2true JP4947948B2 (en) | 2012-06-06 |
Family
ID=37038710
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005296593AExpired - Fee RelatedJP4947948B2 (en) | 2004-10-12 | 2005-10-11 | Cell preservation solution |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4947948B2 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021166022A1 (en) | 2020-02-17 | 2021-08-26 | 日本ベクトン・ディッキンソン株式会社 | Sample preservation composition |
| WO2023038037A1 (en) | 2021-09-08 | 2023-03-16 | 株式会社ガイアバイオメディシン | Method for treating cells |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5394932B2 (en)* | 2007-11-02 | 2014-01-22 | 日本ケミカルリサーチ株式会社 | Pharmaceutical composition containing human mesenchymal stem cells |
| US20120149108A1 (en) | 2009-08-19 | 2012-06-14 | Masashige Tanabe | Cell preservation method |
| JP6778113B2 (en) | 2014-11-11 | 2020-10-28 | 田畑 泰彦 | Preservatives for biological components and methods for recovering biological components |
| AU2016287037B2 (en)* | 2015-06-30 | 2017-09-07 | Sysmex Corporation | Cell preservative solution, use of same, and method for producing cell preservative solution |
| JP6314201B1 (en)* | 2016-11-21 | 2018-04-18 | テラファーマ株式会社 | Dendritic cell washing solution, dendritic cell washing method using the same, and method for preparing dendritic cell-containing composition |
| JP6385607B2 (en)* | 2018-02-13 | 2018-09-05 | テラファーマ株式会社 | Dendritic cell vaccine |
| WO2019172112A1 (en)* | 2018-03-06 | 2019-09-12 | ゼノアックリソース株式会社 | Cell cryopreservation solution and use thereof |
| JP6594578B1 (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2019-10-23 | セルトラスト・アニマル・セラピューティクス株式会社 | Cell preservation method and cell suspension |
| KR102749801B1 (en)* | 2019-04-26 | 2025-01-03 | 가부시기가이샤오오쓰까세이야꾸고오죠오 | Mammalian cell preservation solution containing trehalose |
| EP4056680A4 (en)* | 2019-11-08 | 2024-01-03 | Bmg Incorporated | COLD STORAGE SOLUTION FOR STEM CELLS |
| WO2021145364A1 (en)* | 2020-01-17 | 2021-07-22 | 株式会社大塚製薬工場 | Hematopoietic-cell storage solution containing trehalose |
| JP2021136883A (en) | 2020-03-02 | 2021-09-16 | 株式会社ガイアバイオメディシン | Treatment method of highly active NK cells |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB0001172D0 (en)* | 2000-01-20 | 2000-03-08 | Res Del International Limited | Physiological medium for perfusing, preserving and storing isolated cell tissue and organ samples |
- 2005
- 2005-10-11JPJP2005296593Apatent/JP4947948B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021166022A1 (en) | 2020-02-17 | 2021-08-26 | 日本ベクトン・ディッキンソン株式会社 | Sample preservation composition |
| WO2023038037A1 (en) | 2021-09-08 | 2023-03-16 | 株式会社ガイアバイオメディシン | Method for treating cells |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006230396A (en) | 2006-09-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20060078872A1 (en) | Cell-preservation liquid | |
| JP4947948B2 (en) | Cell preservation solution | |
| US7270946B2 (en) | Method for treatment of cellular materials with sugars prior to preservation | |
| JP3723494B2 (en) | Cell preservation solution | |
| US6060233A (en) | Methods for the lyophilization of platelets, platelet membranes or erythrocytes | |
| AU2005327576B2 (en) | Compositions and methods for the storage of red blood cells | |
| JPH0768082B2 (en) | Solution for organ preservation | |
| JP6333513B2 (en) | Cell vitrification preservation solution | |
| US20020042131A1 (en) | Cryopreservation method using cryoprotective composition of propanediol and a vehicle solution | |
| JP7607703B2 (en) | Freezing medium | |
| JP7524077B2 (en) | Cell Cryopreservation Solution | |
| CN113490414B (en) | Stem Cell Preservation | |
| JP2001247401A (en) | Tissue cold storage solution | |
| EP1476014B1 (en) | Process for preserving cells, tissues and organs | |
| EP1018866B1 (en) | Compositions and methods for the preservation of living tissues | |
| JP2008104407A (en) | Cell preservation method | |
| JP2006306821A (en) | Anti-freezing solution for cells and tissues and cryopreservation method | |
| JP2020527601A (en) | Preservation solution | |
| US20230056314A1 (en) | Cytoprotective compositions for short-term cells storage and transportation without cryopreservation and deep freezing | |
| JPH03188001A (en) | Organ preservation solution | |
| US6040132A (en) | Methods for the lyophilization of living biological materials | |
| WO2002009516A2 (en) | Carrier solution for vitrifiable concentrations of cryoprotectants, and cryoprotectant mixtures | |
| CN107949277B (en) | Agent for preserving organ or tissue and method for preserving organ or tissue | |
| JP7755927B2 (en) | Platelet activators | |
| KR20010002227A (en) | Composition for the Preservation of Organs and Blood Cells |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20051028 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20051215 | |
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20081006 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20110714 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20110909 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20120215 | |
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20120306 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150316 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number:4947948 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313117 | |
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |