JP4627962B2 - Database publishing method and apparatus - Google Patents
Database publishing method and apparatusDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4627962B2 JP4627962B2JP2002299080AJP2002299080AJP4627962B2JP 4627962 B2JP4627962 B2JP 4627962B2JP 2002299080 AJP2002299080 AJP 2002299080AJP 2002299080 AJP2002299080 AJP 2002299080AJP 4627962 B2JP4627962 B2JP 4627962B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- template
- page
- property
- small
- database
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Document Processing Apparatus (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、データベースに記録された物件データを紙に印刷したり画面に表示するための組版用電子文書を生成するためのデータベースパブリッシング方法及びその装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、HTML(HyperText Markup Language)電子文書に置き換わる電子文書としてXML(eXtensible Markup Language)電子文書が注目されている。XML電子文書は、テキスト形式で表現され、内容を成す文字列をタグ形式の予約語で挟み込む。また、XML電子文書は、電子文書の構造をDTD(Document Type Definition;文書型定義)という文書型定義文書にすることで、表現方法の指定や文章中の文字列に意味を付加するような独自のタグを拡張できる。更に、XML電子文書は、オブジェクト指向の階層構造、認証機能によるドキュメントのチェック機能、強力なハイパーリンク機能などを特徴とする。
【0003】
また近年、XML(eXtensible Markup Language)電子文書から組版用電子文書としてのXSL−FO(eXtensible Stylesheet Language-Formatting Object)電子文書を生成する方法として次に説明する方法が登場している。すなわち、この方法は、XML電子文書からXSL−FO電子文書を生成するための所定の規則を記述したXSLT(eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformation)スタイルシートと呼ばれるXSLT電子文書の記述内容に従って、XSLTプロセッサがXML電子文書を基に組版用電子文書としてのXSL−FO電子文書を生成するものである。XSL−FOプロセッサは、生成されたXSL−FO電子文書を基に印刷や画面表示を行う。
【0004】
なお、この出願の発明に関連する先行技術文献情報としては次のものがある。
【0005】
【特許文献1】
特開2001−84388
【特許文献2】
特開2001−14792
【特許文献3】
特開2002−99524
【非特許文献1】
「印刷界2002.7月号」、発行国:日本国、発行所:日本印刷新聞社、発行年月日:2002年7月10日
【非特許文献2】
カタログ「DBPublisher1.0、DBPress4.0」、発行国:日本国、販売元:有限会社ディー・ティー・アイ、開発元:リンクス
【0006】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで、中古車情報誌、住宅情報誌、求人情報誌、旅行情報誌、チケット情報誌等の物件情報掲載誌においては、掲載する物件の数は数百乃至数千程度と膨大であるが、各物件を掲載するための小組の様式の種類は少ない。即ち、各物件情報掲載誌では、所定の数個から十数個程度の僅かな種類の小組様式しか用いられず、限られた種類の小組を組み合わせた組版に多数の物件の情報を割り当てている。
【0007】
また、物件情報掲載誌に掲載する物件の数は膨大であり、また、物件の追加、削除の頻度が高いので、このような物件のデータは、通常は、データベースに記録されている。
【0008】
また、物件情報掲載誌の各ページには、小組が並べられ、各小組に各物件のデータが入れられるが、各ページにおける小組の配置は、単に小組を行列状に並べるだけのものが多く、定型的であり、自由度が少なかった。
【0009】
更に、種々の物件情報掲載誌を出版する出版社においては、1つのデータベースパブリッシングソフトウェアで多種類の物件情報掲載誌を扱うこととなるが、物件情報掲載誌の種類に応じて小組の種類及びページレイアウトが異なるのが一般的である。従って、1つのデータベースパブリッシングソフトウェアで多種類の小組テンプレート及び多種類のページテンプレートを扱うことになるが、各物件情報掲載誌で用いる小組テンプレート及びページテンプレートの種類は相対的に少ない。従って、各物件情報掲載誌のページにページテンプレート及び小組テンプレートを割り当てるときに多種類のページテンプレート及び多種類の小組テンプレートが選択肢として用意されていると、割り当てを決める手順及び手間が増大し、作業効率が悪化する。
【0010】
本発明は、物件情報掲載誌を印刷又は表示するための組版用電子文書を物件情報掲載誌の特徴を考慮してデータベースを基に生成するデータベースパブリッシング方法及びその装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0011】
また、本発明は、各ページに小組をある程度の自由度をもって配置することを可能とするデータベースパブリッシング方法及びその装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0012】
更に、本発明は、1つのデータベースパブリッシングソフトウェアで多種類の物件情報掲載誌を扱う場合であっても、ページへのページテンプレート及び小組テンプレートの割当てを効率的に行うことができることを可能とするデータベースパブリッシング方法及びその装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0013】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明によれば、物件データベースであって、これに記録された物件データを紙に印刷したり画面に表示するための組版用電子文書に組み込まれる小組テンプレートを含む物件データベースを生成するための物件データベース生成方法において、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、小組についてのDTP(Desk Top Publishing)データを基に小組についてのXSL−FO文書形式の小組スタイル情報であって、前記DTPデータの属性が反映された小組スタイル情報を生成し、生成された小組スタイル情報を記録媒体に書き込むステップと、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記小組スタイル情報を前記記録媒体から読み出し、小組についての前記小組スタイル情報に含まれる実データをパラメータ化することにより、小組の様式が記述され、更に、該小組にデータが挿入されるべき物件を特定できる情報と特定された物件の該小組に挿入されるべきデータとが前記物件データベースを表すXML文書のXPATHとして記述され、更に、該小組の位置が仮引数として記述されたXSLT文書形式の小組テンプレートを生成し、前記記録媒体に書き込むステップと、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記小組テンプレートを複数の前記物件が登録された物件データベースに登録するステップと、を有することを特徴とする物件データベース生成方法が提供される。
【0014】
また、本発明によれば、物件データベースに記録された物件データを紙に印刷したり画面に表示するための組版用電子文書を生成するためのデータベースパブリッシング方法において、上記の物件データベース生成方法の各ステップと、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てるステップと、を有することを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング方法が提供される。
【0015】
上記のデータベースパブリッシング方法において、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記ページテンプレートにおいて使用可能な小組テンプレートを選択して、選択した小組テンプレートを前記ページテンプレートに割り当てるステップと、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた前記ページテンプレートを前記物件データベースに登録するステップと、を有し、前記物件データベースに登録された小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てるステップは、前記物件データベースに登録されている前記ページテンプレートを用いて行われるようにしてもよい。
【0016】
上記の物件データベース生成方法は、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、1又は2以上の前記小組テンプレートを含む小組テンプレート群のファイルを生成し、生成されたファイルを記録媒体に書き込むステップを有していてもよい。
【0017】
また、本発明によれば、物件データベースに記録された物件データを紙に印刷したり画面に表示するための組版用電子文書を生成するためのデータベースパブリッシング方法において、上記の物件データベース生成方法の各ステップと、コンピュータが、前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているもの又は前記小組テンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てるステップと、を有することを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング方法が提供される。
【0018】
上記のデータベースパブリッシング方法において、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記ページテンプレートにおいて使用可能な小組テンプレートを選択して、選択した小組テンプレートを前記ページテンプレートに割り当てるステップと、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた前記ページテンプレートを前記物件データベースに登録するステップと、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた1又は2以上の前記ページテンプレートを含むページテンプレート群のファイルを生成し、生成されたファイルを記録媒体に書き込むステップと、を有し、前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているもの又は前記小組テンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てるステップは、前記物件データベースに登録されている前記ページテンプレート又は前記ページテンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記ページテンプレートを用いて行われるようにしてもよい。
また、本発明によれば、物件データベースに記録された物件データを紙に印刷したり画面に表示するための組版用電子文書に組み込まれる小組テンプレートを生成するための小組テンプレート生成方法において、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、小組についてのDTP(Desk Top Publishing)データを基に小組についてのXSL−FO文書形式の小組スタイル情報であって、前記DTPデータの属性が反映された小組スタイル情報を生成し、生成された小組スタイル情報を記録媒体に書き込むステップと、コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記小組スタイル情報を前記記録媒体から読み出し、小組についての前記小組スタイル情報に含まれる実データをパラメータ化することにより、小組の様式が記述され、更に、該小組にデータが挿入されるべき物件を特定できる情報と特定された物件の該小組に挿入されるべきデータとが前記物件データベースを表すXML文書のXPATHとして記述され、更に、該小組の位置が仮引数として記述されたXSLT文書形式の小組テンプレートを生成するステップと、を有することを特徴とする小組テンプレート生成方法が提供される。
【0019】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施形態について詳細に説明する。
【0020】
[実施形態1]
本実施形態では、中古車情報誌の出版に係るデータベースパブリッシング方法及びその装置を例に取り説明するが、他の物件情報掲載誌にも本実施形態を適用することができる。
【0021】
図1〜3に本発明の実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の構成を示す。
【0022】
図1を参照すると、本発明の実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置は、データベース作成手段101、DTP(Desk Top Publishing)手段102、小組スタイル情報生成手段103、小組テンプレート生成手段104及びマスターレイアウト生成手段105を備える。図2を参照すると、本発明の実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置は、更に、小組配置・物件割当手段106、XSLT文書生成手段107を備える。図3を参照すると、本発明の実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置は、更に、XSLTプロセッサ108、XSL−FOプロセッサ109、110を備える。
【0023】
なお、これらの手段及びプロセッサは、コンピュータがコンピュータプログラムを読み込んで実行することにより、コンピュータのハードウェア資源を用いて実現することができる。
【0024】
図1を参照すると、データベース作成手段101は、物件データベースを定義し、物件データを物件データベースに入れて、定義された構造で物件データが体系化された物件データベース121を出力する。DTP手段102は、各小組のレイアウトをオペレータの操作により作成し、小組のレイアウトのデータをDTPデータ122として出力する。小組スタイル情報生成手段103は、DTPデータの形式の小組のレイアウトのデータを基に、小組スタイル情報123を生成し、これを出力する。小組テンプレート生成手段104は、小組スタイル情報123を基に、小組テンプレートを生成して、小組テンプレート群125のファイルを出力する。マスターレイアウト生成手段105は、小組テンプレートを基に、マスターレイアウトを生成し、マスターレイアウト群125のファイルを出力する。
【0025】
図2を参照すると、小組配置・物件割当手段106は、物件データベース121、小組テンプレート群124、マスターレイアウト群125及びフィルタ141を基に、XML文書126及び小組配置・物件割当データ127を生成し、これらを出力する。XSLT文書生成手段107は、小組テンプレート群124及び小組配置・物件割当データ127を基に、XSLT文書128を生成し、これを出力する。
【0026】
図3を参照すると、XSLTプロセッサ108は、XML文書126及びXSLT文書128を基に、XSL−FO文書129を生成し、これを出力する。XSL−FOプロセッサ109は、XSL−FO文書129を基に、表示画面130を生成し、これを出力する。XSL−FOプロセッサ110は、XSL−FO文書129を基に、印刷物131を生成し、これを出力する。
【0027】
次に、本発明の実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の各部の動作及び各データについて説明する。
【0028】
まず、物件データを記録したデータベース121は、図4に示すような構造を有するリレーショナルデータベースである。図4を参照すると、このリレーショナルデータベースは、物件テーブル、複数の参照テーブル、繰り返し項目テーブルを有する。物件テーブルは、物件ID、物件名、価格、メーカID、車両ID等をフィールドとして有する。参照テーブルとしては、メーカ車両テーブル、メーカテーブル、エリアテーブル、販売店テーブル、オプションテーブルがある。メーカ車両テーブルは、メーカID、車両ID、車両名をフィールドとして有する。メーカテーブルはメーカID、メーカ名をフィールドとして有する。エリアテーブルはエリアID、エリア名をフィールドとして有する。販売店テーブルは販売店ID、販売店名等をフィールドとして有する。オプションテーブルは、オプションID、オプション名等をフィールドとして有する。繰り返し項目テーブルとしては、物件オプションテーブルがある。物件オプションテーブルは、物件ID、順番号、オプションIDをフィールドとして有する。物件テーブルと物件オプションテーブルは、物件IDによりリレーションが付けられ、物件テーブルとメーカ車両テーブルは、メーカIDと車両IDによりリレーションが付けられ、物件テーブルとエリアテーブルはエリアIDによりリレーションが付けられ、物件テーブルと販売店テーブルは販売店IDによりリレーションが付けられ、物件オプションテーブルとオプションテーブルはオプションIDによりリレーションが付けられ、メーカ車両テーブルとメーカテーブルはメーカIDによりリレーションが付けられる。
【0029】
また、物件データベース121から物件データを抽出するためのフィルタ141としては、次に述べるものを作成する。すなわち、特定の販売店の物件データを抽出するフィルタ、特定の地域の特定の販売店の物件データを抽出するフィルタ、特定のメーカの特定の車種の物件データを抽出するフィルタ等である。このようなフィルタは、図5に示すようなツリーで管理できるようにしておく。図5に示すように、特定の販売店の物件データを抽出するフィルタは一階層で表現され、特定の地域の特定の販売店の物件データを抽出するフィルタ及び特定のメーカの特定の車種の物件データを抽出するフィルタは二階層で表現される。
【0030】
次に、DTP手段102、小組スタイル情報生成手段103及び小組テンプレート生成手段104により小組テンプレート群124の各小組テンプレートを生成する動作を説明する。
【0031】
小組テンプレート群124の各小組テンプレートは、DTP手段102で作成された小組のレイアウトのDTPデータ122を基に、小組スタイル情報123を経て作成される。また、小組テンプレート群124の各小組テンプレートは、XSL−FO文書形式により記述され、XSL−FOプロセッサ109、110に入力するXSL−FO文書129に組み込まれる。
【0032】
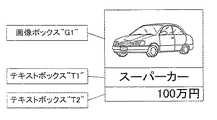
小組のレイアウトは、例えば、デザイン会社等でデザイナがDTP手段102を用いて作成する。作成された小組のレイアウトのサンプルを図6に示す。図6を参照すると、この小組のサンプルは、画像ボックス”G1”、テキストボックス”T1”及びテキストボックス”T2”を有する。画像ボックス”G1”には、中古車の画像のサンプルが貼付され、テキストボックス”T1”には、中古車の名称のサンプル「スーパーカー」が記述され、テキストボックス”T2”には、中古車の価格のサンプル「100万円」が記述される。DTP手段102は、この小組のレイアウトのDTPデータ122を生成し、出力する。
【0033】
次に、小組スタイル情報生成手段103(実際には、DTPソフトウェアの本発明による小組スタイル情報生成用のアドオンソフトウェア)により、小組のDTPデータ122を基に小組スタイル情報123を生成する。小組スタイル情報123は、XSL−FO文書形式で作成される。図6に示す小組から生成される小組スタイル情報123を図7に示し、図7に示す小組スタイル情報123のツリー構造を図8に示す。
【0034】
図7を参照すると、枠211内の記述から明らかなように、小組の左上座標として仮の座標(0cm、0cm)が記述され、小組の高さ(height)として10cmが記述され、小組の幅(width)として10cmが記述され、その他背景色等(background-color, background-tint, border-style, border-color, border-width, border-tint)の値が記述されている。小組の高さ、幅その他背景色等の値は、DTPデータ122から読み取ったものである。
【0035】
また、枠212内の記述は、テキストボックス”T1”についてのものであるが、この記述から明らかなように、テキストボックス”T1”の高さとしては2.5cmが記述され、その幅としては10cmが記述され、その小組内での左上座標としては(0cm、5cm)が記述されている。これらの値もDTPデータ122から読み取ったものである。また、テキストボックス”T1”に記述されていた「スーパーカー」も記述されているが、これは小組テンプレート群124の各小組テンプレートに変換された後にはパラメータとなるデータである。
【0036】
同様に、枠213内の記述は、テキストボックス”T2”についてのものであるが、この記述から明らかなように、テキストボックス”T2”の高さとしては2.5cmが記述され、その幅としては10cmが記述され、その小組内での左上座標としては(0cm、7.5cm)が記述されている。これらの値もDTPデータ122から読み取ったものである。また、テキストボックス”T2”に記述されていた「100万円」も記述されているが、これは小組テンプレートに変換された後にはパラメータとなるデータである。
【0037】
枠214内の記述は、画像ボックス”G1”についてのものであるが、この記述から明らかなように、画像ボックス”G1”の高さとしては5cmが記述され、その幅としては10cmが記述され、その小組内での左上座標としては(0cm、0cm)が記述されている。これらの値もDTPデータ122から読み取ったものである。スケーリング(scaling)としてはnon-uniformが記述されている。また、画像ボックス”G1”に貼付されていた画像名「SuperCar.jpg」も記述されているが、これは小組テンプレートに変換された後にはパラメータとなるデータである。
【0038】
次に、小組スタイル情報生成手段103が、小組のDTPデータ122から小組スタイル情報123を生成する方法を図9〜11を参照して説明する。
【0039】
図9に示すように、まず、「kogumi_style_info」等の枠215(図7)の部分を出力する(ステップS251)。ここで、出力するとは、小組スタイル情報123のファイルに直接又はバッファを介して書き込むことである。
【0040】
次に、小組全体についての「fo:block-container開始タグ」(枠211の部分)を出力する(ステップS252)。
【0041】
次に、小組内の全てのボックスについてステップS254〜S257を繰り返す(ステップS253)。図7の例では、3つのボックスがあるので、これらのステップS254〜S257を3回繰り返すことになる。繰り返しの中では、まず、ボックスがテキストボックスであるか否かを判断する(ステップS254)。ボックスがテキストボックスであれば、テキストボックスの処理を行う(ステップS255)。この処理の詳細は後述する。また、ボックスがテキストボックスでなければ、テキストボックスが画像ボックスであるか否かを判断する(ステップS256)。ボックスが画像ボックスであれば、画像ボックスの処理を行う(ステップS257)。この処理の詳細は後述する。
【0042】
次に、小組の終了タグである「fo:block-container」の終了タグを出力する(ステップS258)。このステップで出力される部分は、符号216(図7)で示す部分である。
【0043】
最後に、「kogumi_style_info」の終了タグを出力する(ステップS259)。このステップで出力される部分は、符号217(図7)で示す部分である。
【0044】
次に、テキストボックスの処理(ステップS255)の詳細を図10を参照して説明する。この処理では、枠212又は枠213で示す部分を出力する。
【0045】
まず、テキストボックスについての「fo:block-container」開始タグを出力する(ステップS261)。次に、DTPデータ122からテキストボックスの属性を取得する(ステップS262)。この属性とは、テキストボックスの高さ、幅、左上座標等である。次に、ステップS262で取得したテキストボックスの属性を出力する(ステップS263)。次に、テキストボックスについての「fo:block」開始タグを出力する(ステップS264)。次に、テキストデータの処理を行う(ステップS265)。この処理の詳細は後述する。次に、テキストボックスについての「fo:block」終了タグを出力する(ステップS266)。最後に、テキストボックスについての「fo:block-container」終了タグを出力する(ステップS267)。
【0046】
テキストデータの処理(ステップS265)では、まず、「fo:inline」開始タグを出力する(ステップS271)。次に、DTPデータ122からテキストデータと文字属性を取得する(ステップS272)。次に、取得した文字属性が反映された「fo:inline」の属性(font-family, font-style, font-size等)を出力する(ステップS273)。次に、取得したテキストデータ(図7の例では、「スーパーカー」又は「100万円」)を出力する(ステップS274)。最後に、「fo:inline」終了タグを出力する(ステップS275)。
【0047】
次に、画像ボックスの処理(ステップS257)の詳細を図11を参照して説明する。この処理では、枠214で示す部分を出力する。
【0048】
まず、画像ボックスについての「fo:block-container」開始タグを出力する(ステップS281)。次に、DTPデータ122から画像ボックスの属性を取得する(ステップS282)。この属性とは、画像ボックスの高さ、幅、左上座標等である。次に、ステップS282で取得した画像ボックスの属性を出力する(ステップS283)。次に、画像ボックスについての「fo:block」開始タグを出力する(ステップS284)。次に、画像データの処理を行う(ステップS285)。この処理の詳細は後述する。次に、画像ボックスについての「fo:block」終了タグを出力する(ステップS286)。最後に、画像ボックスについての「fo:block-container」終了タグを出力する(ステップS287)。
【0049】
画像データの処理(ステップS285)では、まず、「fo:external-graphic」開始タグを出力する(ステップS291)。次に、DTPデータ122から画像データの画像名及び属性を取得する(ステップS292)。この属性とは、画像ボックスへDTPデータ122を貼付する方法であり、例えば、スケーリング方法等である。次に、「fo:external-graphic」の属性を出力する(ステップS293)。ここでいう属性には、画像データの画像名(図7の例では、「SuperCar.jpg」)も含まれる。最後に、「fo:external-graphic」終了タグを出力する(ステップS294)。
【0050】
以上の方法で、小組のDTPデータ122から小組スタイル情報123が生成され、小組スタイル情報123のファイルが記録媒体に記録される。
【0051】
次に、上記の方法で生成された小組スタイル情報123から小組テンプレート群124の各小組テンプレートを小組テンプレート生成手段104により生成する。小組テンプレート群124の各小組テンプレートも、XSL−FO文書形式で作成される。図7に示す小組スタイル情報123から生成される小組テンプレートを図12に示す。
【0052】
図7と図12を比較すると明らかなように、小組テンプレートの大部分は小組スタイル情報と同一であるが、一部が次の点において異なる。
【0053】
(1)枠215の記述が、枠301の記述に置き換わる
(2)枠302、303で示すテンプレートの記述がある。
【0054】
(3)枠304で示す小組全体についての「fo:block-container」の記述において、小組の「ID」が付加され、パラメータ「content-id」が付加され、左上座標がパラメータ化され、小組の「name」が付加され、「absolute-position="absoulte"」が付加されている。
【0055】
(4)枠305で示す「inline」の記述において、文字列「スーパーカー」が変数「物件名」に変更されている。
【0056】
(5)枠306で示す「inline」の記述において、文字列「100万円」が変数「価格」に変更されている。
【0057】
(6)枠307で示す画像ボックスについての「fo:block」において、画像名「SuperCar.jpg」が変数「画像名」に変更されている。
【0058】
図12に示す小組テンプレートに対応したXML文書のツリー構造を図13に示す。図13においては、1つの物件についてのツリーしか表示していないが、他の物件についても同様なツリーが構築されている。
【0059】
このように小組テンプレートにおいては、物件データのID、物件データの各項目がパラメータ化されているので、XSL−FO文書にこの小組テンプレートを挿入した場合に、XSL−FO文書の他の部分からこれらのパラメータを指定してこの小組テンプレートを呼び出すことが可能となる。パラメータとして指定される値は、XML文書から読み出されたものである。
【0060】
次に、本発明による小組テンプレート生成手段104が、小組スタイル情報123から小組テンプレート群124の各小組テンプレートを生成する方法を図14〜19を参照して説明する。
【0061】
図14を参照すると、まず、小組スタイル情報123をファイルから読み込む(ステップS351)。次に、読み込んだ小組スタイル情報123の図8に示すツリー構造をメモリ上に構築する(ステップS352)。次に、各テキストボックス又は各画像ボックスに代入するべきXML文書の項目をパラメータとして設定するための繰り返し動作に入る(ステップS353)。
【0062】
各繰り返しの最初においては、図16に示すように、小組スタイル情報123に従って、小組のレイアウトを表示する。表示されたレイアウト上でオペレータがテキストボックスの項目を選択したならば(ステップS354においてYES)、テキストボックス項目の設定を行う(ステップS355)。テキストボックス項目の設定の動作は後述する。表示されたレイアウト上でオペレータが画像ボックスの項目を選択したならば(ステップS356でYES)、画像ボックス項目の設定を行う(ステップS357)。画像ボックス項目の設定の動作は後述する。
【0063】
テキスト項目の設定においては、まず、図17に示す画面を表示する。オペレータが項目追加ボタン401を押したならば、図18に示す画面を表示する。図18の画面には小組テンプレート生成手段104を起動したときに表示されるログインのダイアログで選択された物件データベースのうちの物件テーブルの項目及び物件テーブルと関連付けられているテーブル(メーカ車両テーブル、メーカテーブル等)の項目が表示される。ただし、図18の例では、説明の簡単のために、物件テーブルの物件名、価格、画像名のみを表示している。物件テーブルと関連付けられているテーブルの項目の表示様式については、後述する。オペレータがある項目を選択し(図18の例ではハッチングの入った「物件名」)、「OK」ボタンを押すと、選択された項目名が図17の画面の流し込み項目の欄402に表示される。図17の画面で流し込み項目についての種々の設定をして(説明は省略する。)、オペレータが図17の画面の「OK」ボタンを押すと、図16の画面で選択されたテキストボックスに流し込む項目として図18の画面で選択された項目が設定される(ステップS361)。次に、メモリに構築されている図8に示すツリー構造において、項目を流し込むべきテキストボックスの先頭ノードfo:block-containerを検索する(ステップS362)。例えば、物件名を流し込むべきテキストボックスとして符号403(図16)で示すテキストボックスが選択されているとすれば、符号404(図8)で示すノードを検索する。次に、ステップS362で選択されたノードに下にある「fo:inline」のノード(例えば符号405(図8)で示すノードである。)の下に記述されているサンプルデータを、物件データベース121のうちの選択されたテーブルの選択された項目の、物件データベース121から生成されたXML文書におけるノード「bukken」(各物件のノードである。符号406(図13))からみた相対パス(XML文書におけるXPATH)をパラメータとして指定する記述に置き換える(ステップS363)。なお、物件データベースからXML文書を生成する方法については後述する。
【0064】
画像項目の設定においては、まず、図19に示す画面を表示する。オペレータが項目追加ボタン407を押したならば、テキスト項目の設定の場合と同様に、図18に示す画面を表示する。オペレータがある項目を選択し(この例では、図18にかかわらず「画像名」)、「OK」ボタンを押すと、選択された項目名が図19の画面の流し込み項目の欄408に表示される。図19の画面で流し込み項目についての種々の設定をして(説明は省略する。)、オペレータが図19の画面の「OK」ボタンを押すと、図16の画面で選択された画像ボックスに、流し込むべき画像の画像名が記述された項目として図18の画面で選択された項目が設定される(ステップS371)。次に、メモリに構築されている図8に示すツリー構造において、画像を流し込むべき画像ボックスの先頭ノードfo:block-containerを検索する(ステップS372)。例えば、画像を流し込むべき画像ボックスとして符号409(図16)で示す画像ボックスが選択されているとすれば、符号410(図8)で示すノードを検索する。次に、ステップS372で選択されたノードに下にある「fo:external-graphic」のノード(例えば符号411(図8)で示すノードである。)の下に記述されているサンプルデータを、物件データベース121のうちの選択されたテーブルの選択された項目の、物件データベース121から生成されたXML文書におけるノードbukken(各物件のノードである。符号406(図13))からみた相対パス(XML文書におけるXPATH)をパラメータとして指定する記述に置き換える(ステップS366)。
【0065】
テキストボックス項目及び画像ボックス項目の設定が完了したならば、すなわち、メモリ上に構築されたツリー構造における上記の置き換えが完了したならば、メモリ上で更新されたツリー構造を基に小組テンプレートを作成する。
【0066】
小組テンプレート生成手段104が行う以上の方法により、小組スタイル情報123から小組テンプレートが生成される。
【0067】
小組テンプレート生成手段104は、生成した各小組テンプレートを、一旦、データベースパブリッシング装置が管理するプロジェクトファイル133に登録する(ステップS358)。
【0068】
次に、小組テンプレート生成手段104は、以下に説明する動作により、プロジェクトファイル133に登録された1又は2以上の小組テンプレートをまとめて小組テンプレート群124のファイルにエクスポートする。
【0069】
図20に示すメニュー[ファイル→エクスポート→小組テンプレートエクスポート]がオペレータにより選択されると、小組テンプレート生成手段104は、図21に示すダイアログボックスを表示する。このダイアログボックスの左側の小組テンプレートのリストボックスにはプロジェクトファイル133に登録されている全ての小組テンプレートが表示される。オペレータは、左側の小組テンプレートのリストボックスに表示されている小組テンプレートのうちから小組テンプレート群124のファイルにエクスポートしたい小組を右側のエクスポートする小組テンプレートのリストボックスに移動し、OKボタンを押す。すると、小組テンプレート生成手段104は、図22に示すダイアログボックスを表示する。オペレータがこのダイアログで小組テンプレート群124のファイル名とその格納場所を指定して、保存ボタンを押すと、小組テンプレート生成手段104は、図21のダイアログの右側のリストボックスにある小組テンプレートをまとめた小組テンプレート群124のファイルをエクスポートする。
次に、マスターレイアウト生成手段105によるマスターレイアウト群125を生成する方法について説明する。
【0070】
まず、ページの分割数の指定を入力する。図23の例では、縦方向の分割数は7であり、横方向の分割数は10である。次に、各升目に配置する小組の種類を指定する。図23の例では、第3〜7行各列に配置する小組の種類は、小組1である。
【0071】
マスターレイアウト生成手段105は、小組テンプレート生成手段104と同様に、生成した各マスターレイアウトを一旦プロジェクトファイル133に登録し、その後、図21、22に示すダイアログボックスと同様のダイアログボックスを用いて、オペレータにより選択された1又は2以上のマスターレイアウトを含むマスターレイアウト群125のファイルをエクスポートする。
【0072】
次に、小組配置・物件割当手段106による各ページについてのXML文書126及び小組配置・物件割当データ127の生成方法について説明する。
【0073】
まず、オペレータの操作により表示した図24に示す「物件データ一括割り付け」の画面の「フィルタ」の文字の右隣の「参照」ボタンがオペレータの操作により押されたならば、対象ページに割り付けるデータを抽出するためのフィルタを選択するための画面(図25)を表示する。図25の画面は、図5に示すツリー構造を基に生成される。図25の画面では、オペレータは既に作成してある何れかのフィルタを選択する。オペレータは、選択の際には、図25の画面内の上のコンボボックスでフィルタのカテゴリを選択した後で、図25の画面内の下のリストで目的のフィルタを選択する。こうすることにより、フィルタ141によりデータベース121から抽出された物件データが対象ページに割り当てられる。
【0074】
次に、図24の画面の「並べ替え」の文字の右隣の「参照」ボタンがオペレータの操作により押されたならば、フィルタにより抽出された物件データを並べ替える順序を指定するための画面(図26)を表示する。図26の画面では、オペレータは、並べ替えに使用する項目又は作成済みの複数項目の組み合わせ(例えば、ボディ形状とグレードの組み合わせ)を1又は2以上選択する。例えば、図26の画面の右枠に上から順にメーカー名及び車両名が入力されたならば、並べ替え順序は、「メーカー名・車両名」となる。
【0075】
次に、図24の画面のページ指定の区分のテキストボックスにオペレータにより入力された開始ページを受け付けることにより対象ページを決定する。なお、終了ページの入力がない場合には、フィルタ141により抽出された物件データが終了するまでページを作成する。一方、終了ページの入力がある場合には、フィルタ141により抽出された物件データが余っていても、入力された終了ページでページの作成を終了する。
【0076】
次に、図24の画面のレイアウト指定の区分のマスターレイアウトのコンボボックスを利用して、既に作成してあるマスターレイアウトからの対象ページに適用するマスターレイアウトの選択をオペレータから受け付ける。マスターレイアウトのコンボボックスに含まれるマスターレイアウトは、小組配置・物件割当手段106が事前にインポートしたマスターレイアウト群125に含まれているものである。
【0077】
次に、図24の画面の小組配置方向の区分にある何れかの図付きのボタン(単ページについての4種類のボタン又は見開きページについての6種類のボタンのうちの何れかのボタン)をオペレータが押すことで小組配置方向を選択することを受け付けることにより、抽出された物件データをどのような順序で小組に割り当てるかを決定する。
【0078】
次に、図24の画面の改ページ・改段の区分で、改ページ又は改段を行うか否かを決定するためのチェックボックスへのオペレータによる入力(チェック付け又はチェック外し)を受け付ける。改段とは、同一の高さ(行)にある小組のグループを1つの段とみなし、指定の階層の項目内容が変化した時に、段を改めることである。改ページ又は改段を行う場合には、改ページ又は改段を行うタイミングの指定のオペレータによる入力を受け付ける。このタイミングは、階層1、階層2、…階層Nといった階層の番号により指定できる。例えば、フィルタとして地域・販売店によるフィルタを指定した場合には、階層1を指定すると、地域が変化したときに改ページ又は改段を行い、階層2を指定すると、販売店が変化したときに改ページ又は改段を行う。また、改ページ又は改段を行う場合には、改ページを行うのか又は改段を行うのかの指定をラジオボタンを通してオペレータから入力し、改ページが指定された場合には、1つのカテゴリに割り当てるページ数の指定を入力し、改段が指定された場合には、1つのカテゴリに割り当てる段数の指定を入力する。ここで、カテゴリとは、指定されたフィルタの指定された階層の項目のことである。例えば、フィルタとして地域・販売店によるフィルタが指定され、タイミングとして階層2が指定され、1つのカテゴリに割り当てるページ数として2ページが指定された場合には、1つの販売店に2ページが割り当てられる。
【0079】
図24の画面で上記の設定が行われた後、図24の「OK」ボタンがオペレータにより押されることにより、対象ページにおいて、選択されたマスターレイアウトに従って配置される小組に、選択されたフィルタ141に従って物件データベース121から抽出された物件データが、選択された順序に従って割り当てられる。なおここで、選択された順序とは、並べ替え順序及び小組配置方向により決定される順序である。但し、選択された順序は並べ替え順序又は小組配置方向のうちの一方だけであっても良い。
【0080】
次に、小組配置・物件割当手段106は、必要に応じて、図27に示すレイアウトビューを通して、マスターレイアウトに従った小組の配置の変更を入力しても良い。図27の例では、図23のマスターレイアウトを、第3行第1〜5列をブランクとし、第4〜5行第1〜3列に小組2を配置し、第6〜7行第1〜3列にも小組2を配置するように変更している。ここで、配置可能な小組は、小組配置・物件割当手段106が事前にインポートした小組テンプレート群124に含まれている小組テンプレートに対応したものである。
【0081】
また、小組配置・物件割当手段106は、必要に応じて、図28に示すページプレビューで、各小組に割り当てる各物件の変更を入力しても良い。
【0082】
また、小組配置・物件割当手段106は、図27に示すレイアウトビューの代わりに、図29に示すデータシートビューで、マスターレイアウトに従った小組の配置の変更を受け付けても良く、図28に示すページプレビューの代わりに、図29に示すデータシートビューで、各小組に割り当てる各物件の変更を受け付けても良い。図29に示すデータビューシートで小組の配置又は各小組に割り当てる各物件を変更する際には、該当する欄のデータを変更する。また、データビューシートで小組を削除する際には、データシートビューで表示されるテーブルのレコードを削除し、データシートビューで小組を追加する際には、データシートビューで表示されるテーブルのレコードを追加する。
【0083】
以上のようにして、各ページに掲載する物件が決定され、各物件を割り当てる小組の種類と位置も決定される。これらのデータはXML文書126及び小組配置・物件割当データ127に記録される。すなわち、XML文書126には、物件データベース121にある物件データのうちの選択されたフィルタ141により抽出された物件データが記述され、小組配置・物件割当データ127には、各ページの各升目に配置する小組の種類及び位置並びに各小組に割り当てる物件が記述される。なお、ページの分割数により図29の「割り付け位置」の項目で示される小組の割り付け位置(例えば、「1−4」(第1列第4行を示す。)、「4−4」(第4列第4行を示す。)等)に対応したページ上での座標が異なるが、割り付け位置とページ上での座標との対応関係は、分割数により決定されるので、分割数を各ページについて小組配置・物件割当データ127に記録しておく。又は、各ページの各割り付け位置と該割り付け位置のページ上での座標との関係を算出して、その対応関係を小組配置・物件割当データ127に記録しても良い。
【0084】
XSLT電子文書生成手段107は、小組配置・物件割当データ127を基にXSLT文書128を生成する。
【0085】
実際に生成するXSLT電子文書128について説明する前に、本実施形態で生成するXSLT電子文書の様式を、図30、31に示す。
【0086】
図30、31を参照すると、ブロック(A)で示す記述は、ページの余白の大きさを指定するための記述である。ブロック(B)で示す記述は、各ページ毎の記述であり、図30では、1ページ分だけ記載しているが、実際には中古車情報誌の中古車情報を掲載する全てのページの数だけ繰り返す。ブロック(C)で示す記述は、各物件を各ページの各小組に割り当てるための記述であり、図30では、1物件分だけ掲載しているが、実際には各ページに掲載する物件の数だけ繰り返す。ブロック(E)で示す記述は、各種類毎の小組の様式の記述する小組テンプレートであり、図30では、1種類の小組分だけ掲載しているが、中古車情報誌で使用する小組の種類の数だけ繰り返す。
【0087】
ブロック(C)を見ると、文(1)は、各ページに割り付ける物件を所定の順序で指定するための文であり、この文により実引数として指定された各物件にテンプレート2(ブロック(F)で示す)を適用する。文(2)は、文(1)で指定された物件のデータを割り当てるべき小組の名前(小組の名前は小組の種類を表す。)をテンプレート2に実引数として引き渡すための文であり、文(3)は、テンプレート2に小組の左側の辺のX座標を実引数として引き渡すための文であり、文(4)は、テンプレート2に小組の上側の辺のY座標を実引数として引き渡すための文である。
【0088】
テンプレート2を見ると、文(5)は、小組の名前である実引数を受け取るための仮引数が記述された文であり、文(6)は、小組の左側の辺のX座標である実引数を受け取るための仮引数が記述された文であり、文(7)は、小組の上側の辺のY座標である実引数を受け取るための仮引数が記述された文である。文(21)は、選択肢のある条件付き処理を行うことの宣言文であり、文(22)は、小組の名前(kogumi-type)が所定の文字(図31の例では'K1')であるときに、文(24)の前までの処理を行うための判定文である。文(23)は、各種類の小組の様式並びに仮引数として記述された該小組にデータが挿入されるべき物件を特定できる情報、特定された物件の該小組に挿入されるべきデータ及び該小組の位置を記述した文である。図31に示すXSLT文書の例では、文(23)の内容を省略して記載しているが、図32〜37に示すXSLT文書の例では文(23)の内容、つまり、各種類の小組の様式並びに仮引数として記述された該小組にデータが挿入されるべき物件を特定できる情報、特定された物件の該小組に挿入されるべきデータ及び該小組の位置を具体的に記載している。
【0089】
原データから各ページに掲載する全ての物件の識別子、それらの物件を割り当てる小組の種類及び座標を読み込んで、これらの読み込まれたデータを文(1)、(2)、(3)、(4)に当てはめて、ブロック(B)、(C)、(E)を必要な数だけ繰り返すことにより、XSLT電子文書を生成することができる。
【0090】
XML電子文書の生成方法については後述するが、本実施形態で生成するXML電子文書の簡単な例を図38に示す。図38を参照すると、このXML文書は、bukken_dataの下にbukkenがあり、bukkenの下に物件についての複数のitemがある階層構造を有する。このXML文書は、全ページ(この例では2ページ)に掲載する物件についてのbukken_dataの集合である。従って、フィルタ141を用いて物件データベース121から物件データを抽出して、抽出された物件データと所定のタグを組み合わせることにより、全ページについてのXML文書を生成することができる。
【0091】
図38に示すXML電子文書と同時に生成する具体的なXSLT電子文書の内容を図32〜37に示す。
【0092】
また、XSLT電子文書128及びXML電子文書126の構造及びそれらの関係を示す概念図を図39に示す。
【0093】
XSLTプロセッサ108は、上記の方法で生成したXML電子文書126及びXSLT電子文書128を入力して、XML電子文書126に記述されたデータより、XSLT電子文書128に記述された書式に従って、XSL−FO電子文書129を生成する。図38に示すXML電子文書と図32〜37に示すXSLT電子文書を基に、XSLTプロセッサ108が生成したXSL−FO電子文書128を図40〜44に示す。
【0094】
図38は説明を簡単にするための単純なXML文書であるが、小組配置・物件割当手段106により物件データベース121から生成される実際のXML文書の構造について説明する。なお、物件データベース121から所定のフィルタ141により抽出されたデータのみがXML文書126に記述されるが、ここでは、抽出については考慮せず、XML文書の構造のみに着目して説明する。なお、物件の並び替えは、XSLT文書での物件と小組との対応付け及び小組の配置位置により行うので、XML文書で物件の並び替えをしておく必要はない。
【0095】
図4に示す物件データベース121からそのまま単純にXML文書を作成すると、図45に示すように、各テーブルについてのサブツリーがルートの直下に並列に配置されるツリーが構成される。しかし、このような構成を用いた場合、例えば、ある物件レコードで参照されている車両名を知りたい場合、まず、物件テーブルのうちのその物件レコードに記述されているメーカID及び車両IDを読み込んでから、メーカ車両テーブルのうちのそのメーカID及び車両IDを有するレコードを検索し、そのレコードの車両名を検索しなければならないため、処理が複雑となり、時間も多く費やされることとなる。
【0096】
そこで、本発明では、物件データベース121から生成されるXML文書126を上記のような検索を不要とし、物件テーブルで参照されるデータを簡単なXPATHで表現することができる構造を有するものとする。本実施形態で生成するXML文書の構造を図46〜50に示す。なお、図面の都合上、1つのXML文書の構造を図46〜50に分割して記載している。
【0097】
図4、46〜50を参照すると、物件テーブルの各レコードに直接記述されているデータである物件名、価格等はXML文書においては、通常通り物件bukken501(図46)の下の項目item(2つの例として、項目(項目名:name_asc="BKN_NAME"、表示用項目名:name_jp="物件名")502(図46)及び項目(項目名:name_asc="KAKAKU"、表示用項目名:name_jp="価格")503(図46))の下に記述されている。
【0098】
物件テーブルの各レコードから1つの項目より成る単純インデックスで参照されているエリアテーブルのエリア名は、物件bukken501(図46)の下の項目item(項目名:name_asc="AREA_ID"、表示項目名:name_jp="エリアID")504(図48)の下の参照テーブル(エリアテーブル)ref_table(項目名:name_asc="AREA")505(図48)の下の項目item(項目名:name_asc="AREA_NAME"、表示用項目名:name_jp="エリア名")506(図50)の下に記述されている。
【0099】
物件テーブルの各レコードから2つの項目より成る複合インデックスで参照されているメーカ車両テーブルの車両名は、冗長となるが2つ重複して記述されている。2つ重複して記述されている理由は、複合インデックスが2つの項目より成ることである。1つの記述は、物件bukken501(図46)の下の項目ref_item(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_ID"、表示項目名:name_jp="メーカID")507(図46)の下の参照テーブルref_table(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_SHARYOU")508(図46)の下の項目item(項目名:name_asc="SHARYOU_NAME"、表示用項目名:name_jp="車両名")509(図47)の下の記述であり、他の記述は、物件bukken501(図46)の下の項目ref_item(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_ID"、表示項目名:name_jp="メーカID")510(図48)の下の参照テーブルref_table(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_SHARYOU")511(図48)の下の項目item(項目名:name_asc="SHARYOU_NAME"、表示用項目名:name_jp="車両名")512(図49)の下の記述である。
【0100】
物件テーブルのレコードから2つの項目より成る複合インデックスで参照されているメーカ車両テーブルより1つの項目メーカIDより成る単純インデックスで参照されているメーカテーブルのメーカ名も、冗長となるが2つ重複して記述されている。2つ重複して記述されている理由は、複合インデックスが2つの項目より成ることである。1つの記述は、物件bukken501(図46)の下の項目ref_item(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_ID"、表示項目名:name_jp="メーカID")507(図46)の下の参照テーブルref_table(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_SHARYOU")508(図46)の下の項目ref_item(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_ID"、表示用項目名:name_jp="メーカID")513(図47)の下の参照テーブルref_table(項目名:name_asc="MAKER)514(図47)の下の項目item(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_NAME"、表示項目名:name_jp="メーカ名")515(図47)の下の記述であり、他の記述は、物件bukken501(図46)の下の項目ref_item(項目名:name_asc="SHARYOU_ID"、表示項目名:name_jp="車両ID")510(図48)の下の参照テーブルref_table(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_SHARYOU")511(図48)の下の項目ref_item(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_ID"、表示用項目名:name_jp="メーカID")516(図49)の下の参照テーブルref_table(項目名:name_asc="MAKER)517(図49)の下の項目item(項目名:name_asc="MAKER_NAME"、表示項目名:name_jp="メーカ名")518(図49)の下の記述である。
【0101】
上述の通り、XML文書の各物件のブロック内では、車両ID、車両名、メーカID、メーカ名がそれぞれ2つ重複して記述されているので、車両ID、車両名、メーカID及びメーカ名のXPATHは2通りある。小組テンプレートにおいては、車両ID、車両名、メーカID及びメーカ名のうちでは印刷項目である車両名及びメーカ名を仮引数として記述することとなるが、2通りのXPATHのうちのどちらのXPATHを用いて記述してもよい。どちらのXPATHを用いて記述されるかは、オペレータが流し込むべき項目を選択する図51の画面で選択した項目により決定される。なお、図51の画面が実際に用いられる画面であり、説明のために単純化した図18の画面は実際には図51の画面に置き換わる。メーカ名については、図51の符号521で示すメーカ名を選択したときには、項目515(図47)の下のメーカ名が選択され、このときのXPATHは、
ref_item[@name_asc='MAKER_ID']/ref_table[@name_asc='MAKER_SHARYOU']/ref_item[@name_asc='MAKER_ID']/ref_table[@name_asc='MAKER']/item[@name_asc='MAKER_NAME']
となるが、図51の符号522で示すメーカ名を選択したときには、項目518(図49)の下のメーカ名が選択され、このときにXPATHは、
ref_item[@name_asc='SHARYOU_ID']/ref_table[@name_asc='MAKER_SHARYOU']/ref_item[@name_asc='MAKER_ID']/ref_table[@name_asc='MAKER']/item[@name_asc='MAKER_NAME']
となる。このようなXPATHで指定された項目が小組テンプレートで仮引数として記述される。そしてこのような小組テンプレートがXSLTプロセッサ108にかけるXSLT文書127に組み込まれる。
【0102】
複合インデックスで参照される項目を図51の画面で1通りの方法のみで表示する場合には、XML文書では、その項目をその表示方法に対応した1つの方法で記述するのみでよいが、例えば2つの項目より成る複合インデックスで参照される項目を図51の画面で2通りの方法で表示する場合には、XML文書では、その項目をそれらの表示方法に対応した上述の2つの方法で記述する。図51の画面に表示される項目のツリー構造は、物件データベース121の物件テーブル等のテーブル及びこれらの間の関係の定義データから直接作成される。
【0103】
図4に示す物件データベース121を基に生成された図45〜50に示す構造を有するXML文書126の1つの物件についての部分を図52〜58に示す。
【0104】
[実施形態2]
実施形態1では、最終的に得られるページのレイアウトは、図28の画面のレイアウトビューに示すようなものである。このレイアウトでは、ページ全体が1組の行列に分割され、行列内の各列各行、複数列各行、各列複数行又は複数列複数行に1つの小組が配置される。
【0105】
これに対し、実施形態2では、最終的に得られるページのレイアウトは、図59の画面のレイアウトビューに示すようなものである。このレイアウトでは、ページ全体に複数の行列が配置され、各行列内の各列各行、複数列各行、各列複数行又は複数列複数行に1つの小組が配置される。ページ全体に配置する各行列の位置及び大きさを自由に設定することができるので、ページに配置される小組の配置をある程度自由にすることができる。
【0106】
図60及び図61に本実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の一部を示す。なお、図3、図60及び図61に示す各部分を合わせたものが本実施形態による全体のデータベースパブリッシング装置を構成する。図60及び図61においては、図1及び図2に示す実施形態1と同一の部分については同一の符号を付してある。
【0107】
図60及び図61を図1及び図2と比較すると明らかなように、本実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置が実施形態1のものと異なる点は、マスターレイアウト生成手段105が削除され、ページスタイル情報生成手段201、ページテンプレート生成手段202、ページテンプレート割当手段203が追加され、DTP手段102がDTP手段102Bに変更され、小組配置・物件割当手段106が小組配置・物件割当手段106Bに変更された点である。
【0108】
本実施形態の小組スタイル情報生成手段103、小組テンプレート生成手段104、XSLT文書生成手段107、XSLTプロセッサ108及びXSL−FOプロセッサ109、110の構成と動作は、実施形態1のものと同様であるので、これらの説明を省略する。
【0109】
次に、本実施形態に特有のDTP手段102B、ページスタイル情報生成手段201、ページテンプレート生成手段202、ページテンプレート割当手段203及び小組配置・物件割当手段106Bについて詳細に説明する。なお、これらの手段は、実施形態1と同様にコンピュータがコンピュータプログラムを読み込んで実行することにより、コンピュータのハードウェア資源を用いて実現することができる。
【0110】
DTP手段102Bは、実施形態1のDTP手段102の機能を有すると共に、各ページテンプレートに1又は2以上のエリアを設定する機能を有する。
【0111】
DTP手段102Bは、図62に示すようなページテンプレートの画面を表示し、オペレータのキーボード又はマウスの操作により、図62に示すようなページテンプレート上のエリアを設定する。図62の例ではページテンプレートに4つのエリア(左側の2つの横長のエリア及び右側の2つの縦長のエリア)が設定されている。DTP手段102Bは、エリアの設定されたページテンプレートのデータをDTPデータ122Bの一部として出力する。なお、DTPデータ122Bの他の部分は、実施形態1の小組レイアウトのデータである。
【0112】
ページスタイル情報生成手段201は、DTPデータ122Bのうちエリアの設定されたページテンプレートのデータを読み込み、各エリアのパラメータを設定し、パラメータの設定されたエリアを含むページテンプレートのデータをページスタイル情報221として出力する。
【0113】
オペレータが図62の画面に表示されているエリアを選択し、所定の操作をすると、ページスタイル情報生成手段201は、図63に示す画面を表示する。
【0114】
ページスタイル情報生成手段201は、エリア原点座標の欄の「左上を原点に設定」のラジオボタンが選択されているときには、選択されたエリアの左上座標をDTPデータ122Bから読込み、この欄内に表示する。一方、エリア原点座標の欄の「右上を原点に設定」のラジオボタンが選択されているときには、選択されたエリアの右上座標をDTPデータ122Bから読込み、この欄内に表示する。ただし、オペレータがこの欄で原点座標を修正することも可能である。
【0115】
また、ページスタイル情報生成手段201は、エリアサイズをDTPデータ122Bから読込み、エリアサイズの欄内に表示する。「小組間隔を自動計算」のラジオボタンが選択されているときには、オペレータがこの欄でエリアサイズを修正することも可能である。
【0116】
オペレータは「エリアサイズを自動計算」のラジオボタンを選択したときには、コラムサイズの欄の設定項目(小組の幅及び高さ並びに小組の左右間隔及び上下間隔)及びコラム数の欄の設定項目(縦横の列数)に希望値を設定し、「自動計算」のボタンを押す。すると、エリアサイズが自動計算され、それがエリアサイズの欄に表示される。
【0117】
他方、オペレータは、「小組間隔を自動計算」のラジオボタンを選択したときには、コラムサイズの欄の設定項目(小組の幅及び高さ)及びコラム数の欄の設定項目(縦横の列数)に希望値を設定し、「自動計算」のボタンを押す。すると、小組間隔が自動計算され、それがコラムサイズの欄に表示される。
【0118】
上記の設定や自動計算が行われ、エリア原点、エリアサイズ、コラムサイズ、コラム数の欄の諸項目が決定したならば、オペレータは「OK」ボタンを押して、当該エリアについてのパラメータの設定を終了する。
【0119】
ページテンプレート内の全てのエリアについてパラメータの設定が終了して、オペレータが所定の操作をすると、ページスタイル情報生成手段201は、図64に示すようなページスタイル情報221をファイルとして出力する。
【0120】
なお、図64のページスタイル情報においては、見開きページのうちの右側のページのデータを最初に記述し、左側のページのデータを後に記述してある。ただし、この時点では、左開きか右開きかは定まっておらず、ページスタイル情報を両方の開き方に適用することができる。
【0121】
ページテンプレート生成手段202は、ページスタイル情報221を読込み、所定の設定を行った後、ページテンプレート群222をファイルとして出力する。
【0122】
ページテンプレート生成手段202を起動すると、これは図65に示す画面を表示する。左側の欄には、ページスタイル情報生成手段201が生成した全てのページスタイルが表示される。右側の欄には、左側で選択されているページスタイルのレイアウトが表示される。
【0123】
オペレータが右側の欄に表示されているレイアウト上で希望のエリアを選択し、所定のメニュー操作をすると、ページテンプレート生成手段202は、図66に示す画面を表示する。
【0124】
エリア情報には、ページスタイル情報221から読み込まれた情報(基本小組サイズ、コラム数、小組間隔)が表示される。
【0125】
オペレータは、ページ内流し込み順番のコンボボックスで当該エリアの順番を選択する。ページ内流し込み順番とは、ページ内でデータを流し込むエリアの順番である。
【0126】
また、オペレータは、小組流し込み方向の4つのトグルボタンのうちの1つのものを選択する。小組流し込み方向とは、エリア内でデータを流し込む順番である。
【0127】
ページテンプレート生成手段202は、小組スタイル情報123を読込み、登録されている全ての小組スタイルを「使用可能な小組スタイルの設定」の欄の左側の「小組スタイル」のリストボックスに表示する。オペレータは、このリストボックスに表示されている小組スタイルのうちから希望するものを右隣の「使用可能な小組スタイル」のリストボックスに移動する。
【0128】
ページテンプレート生成手段202は、「使用可能な小組スタイル」のリストボックスに移動してきた小組スタイルを「基本小組スタイル」のコンボボックスに登録する。オペレータは、このコンボボックスで、基本小組スタイルを選択する。基本小組スタイルとは、ディフォルトで各セル(基本小組サイズの領域)に設定する小組スタイルのことである。
【0129】
上記の設定が行われ、ページ内流し込み順番、小組流し込み方向、使用可能な小組スタイル及び基本小組スタイルが決定したならば、オペレータは「OK」ボタンを押して、当該エリアについてのこれらの項目の設定を終了する。
【0130】
ページテンプレート内の全てのエリアについて上記項目の設定が終了して、オペレータが所定の操作をすると、ページテンプレート生成手段202は、図67に示すようなページテンプレート222を生成する。
【0131】
ページテンプレート生成手段202は、生成した各ページテンプレートを、一旦、データベースパブリッシング装置が管理するプロジェクトファイル133に登録する。
【0132】
次に、ページテンプレート生成手段202は、以下に説明する動作により、プロジェクトファイル133に登録された1又は2以上のページテンプレートをまとめてページテンプレート群222のファイルにエクスポートする。
【0133】
図20に示すメニュー[ファイル→エクスポート→ページテンプレートエクスポート]がオペレータにより選択されると、ページテンプレート生成手段202は、図68に示すダイアログボックスを表示する。このダイアログボックスの左側のページテンプレートのリストボックスにはプロジェクトファイル133に登録されている全てのページテンプレートが表示される。オペレータは、左側のページテンプレートのリストボックスに表示されているページテンプレートのうちからページテンプレート群222のファイルにエクスポートしたいページテンプレートを右側のエクスポートするページテンプレートのリストボックスに移動し、OKボタンを押す。すると、ページテンプレート生成手段202は、図69に示すダイアログボックスを表示する。オペレータがこのダイアログでページテンプレート群222のファイル名とその格納場所を指定して、保存ボタンを押すと、ページテンプレート生成手段202は、図68のダイアログの右側のリストボックスにあるページテンプレートをまとめたページテンプレート群222のファイルをエクスポートする。
【0134】
なお、図67のページテンプレートにおいても、見開きページのうちの右側のページのデータを最初に記述し、左側のページのデータを後に記述してある。ただし、この時点では、左開きか右開きかは定まっておらず、ページテンプレートを両方の開き方に適用することができる。ページ内流し込み順番によりページテンプレートが右開きに適用するものであるのか又は左開きに適用するものであるのかが実質的に略決まってしまうこともあるが、例えば、ページ内流し込み順番がランダムであれば、ページテンプレートを両方の開き方に適用することができる。
【0135】
ページテンプレート割当手段203は、図59又は77の画面の所定のメニューを辿ることにより起動される。ページテンプレート割当手段203は、起動されると、図70に示す画面を表示する。オペレータが現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌で用いたいページテンプレートを含んでいるページテンプレート群222のファイルの名称を図70のファイル名の欄に入力し、「開く」ボタンを押すと、ページテンプレート割当手段203はそのページテンプレート群222のファイルをインポートし、それに含まれている全てのページテンプレートを物件データベース121に物件情報掲載誌の識別子と対応付けて記録する。こうすることにより、作業が中断した場合や複数のオペレータがデータベースパブリッシング装置を用いている場合であっても、インポートを1度のみ行えば済むようになる。
【0136】
インポートしたファイルに記述されているページテンプレート群は、図71に示す画面で確認することができる。
【0137】
ページテンプレート割当手段203は、ページテンプレート群222のファイルをインポートした後に、図72に示す画面を表示する。この画面のページテンプレートのコンボボックスには、インポートしたファイルに記述されている全てのページテンプレートが表示される。オペレータがこの画面に開始ページ、終了ページ及びこれらの間のページに割り当てることを希望するページテンプレートを入力して「OK」ボタンを押すと、ページテンプレート割当手段203は、この入力に従って、ページにページテンプレートを割り当てる。
【0138】
小組配置・物件割当手段106Bも、図59又は77に示す画面で別の所定のメニューを辿ることにより起動される。小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、起動されると、図73に示す画面を表示する。オペレータが現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌で用いたいページテンプレートに含まれている小組テンプレートを含んでいる小組テンプレート群124のファイルの名称を図73のファイル名の欄に入力し、「開く」ボタンを押すと、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bはその小組テンプレート群124のファイルをインポートし、それに含まれている全ての小組テンプレートを物件データベース121に物件情報掲載誌の識別子と対応付けて記録する。こうすることにより、作業が中断した場合や複数のオペレータがデータベースパブリッシング装置を用いている場合であっても、インポートを1度行えば済むようになる。
【0139】
図71に示す画面に表示されているディフォルトの小組テンプレートを図66の画面の「使用可能な小組スタイル」のリストボックスに移動した小組テンプレートであって、上記の手順でインポートした小組テンプレートに置き換えることが可能である。この置き換えをするときの画面を図74に示す。
【0140】
なお、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、物件データベース121に登録されている物件データ及び小組テンプレートのみならず、ページテンプレート割当手段203が物件データベース121に物件情報掲載誌と関連付けて登録したページテンプレート群222のファイルに含まれているページテンプレートも読み出すことができる。
【0141】
小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、小組テンプレート群222のファイルをインポートした後に、図75に示す画面を表示する。 オペレータが割り付けるカテゴリ指定の欄の参照ボタンを押すと、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、図25の画面を表示する。実施形態1と同様に、図25の画面は、図5に示すツリー構造を基に生成される。図25の画面では、オペレータは既に作成してある何れかのフィルタを選択する。オペレータは、選択の際には、図25の画面内の上の「カテゴリ」のコンボボックスでフィルタのカテゴリを選択した後で、図25の画面内の下の「割り付け範囲選択」のリストで目的のフィルタを選択する。こうすることにより、フィルタ141によりデータベース121から抽出された物件データが対象ページに割り当てられる。なお、図25の画面では、「割り付け範囲選択」のリストボックスで複数の項目を連続的に選択することが可能であり、フィルタはその複数の項目を選択するためのものとなる。図75の例では、割り付けるカテゴリ指定の開始が「販売店で分類/MAX川口」であり、その終了が「販売店で分類/中山川口店」であるが、これは、図25の画面の「割り付け範囲選択」のリストボックスで「MAX川口」、「ケーツー商会」及び「中山川口店」が連続的に選択されたことを示す。従って、図72の画面で設定されたページ範囲の有効ページには、「MAX川口」、「ケーツー商会」及び「ナカヤマ浦和店」のデータが割り当てられる。
【0142】
オペレータがページ指定の欄の「範囲指定する」のチェックボックスをチェックすると、開始のエリア及びエリア内位置並びに終了のページ、エリア及びエリア内位置を指定することが可能となる。一方、このチェックボックスをチェックしないと、開始のエリア及びエリア内位置のみを指定することが可能となる。なお、エリアの指定は、上記ページ内流し込み順番に従い、エリア内位置は、上記小組流し込み方向に従う。
【0143】
開始ページには、図72の画面で指定されたページ範囲のうち図77と同様の画面(但し、物件ID及び物件名が空白の状態であるもの)で現在選択されている位置(右向き黒塗り矢印601で示す位置)が割り付け開始位置となるため、第115ページは、物件データの割当対象とはならない。図75の画面では、開始ページを変更することはできないが、エリア及びエリア内位置を変更することが可能である。
【0144】
ページ指定の欄の参照ボタンは、「範囲指定する」のチェックボックスがチェックされているときにのみ有効であり、このボタンが有効であるときにオペレータがこのボタンを押すと、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、図76に示す画面を表示する。オペレータが、この画面で終了ページを選択して「OK」ボタンを押すと、終了ページが設定される。
【0145】
改ページ、改段は実施形態1と同様のものである。また、これらに関連したタイミングも実施形態1と同様のものである。改エリアは実施形態2に特有のものであるが、これは、タイミングとして指定された階層の内容が変化したときに、新たなエリアから物件の割当を開始することである。
【0146】
オペレータが「空白セルを挿入する」のチェックボックスをチェックすると、タイミングとして指定された階層の内容が変化したときに、各エリアの小組流し込み方向に従った順で最初のセルが空白となる。
【0147】
なお、タイミングとして指定された階層の内容が変化したときに改ページ、改エリア又は改段するようにしたときには、1カテゴリに割り当てるページ数、エリア数又は段数を指定することもしないこともできる。
【0148】
オペレータが図75に示す画面で割り付けるカテゴリ、ページ範囲、改ページ等を設定し、「OK」ボタンを押すと、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、設定内容に従って、各ページの各エリアの各小組に物件データを割り当てる。
【0149】
小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、図77に示す画面も表示する。
【0150】
図77の画面は、図75の画面で設定した内容を反映したものであるが、この画面でオペレータは各セルの区分の変更、各セルに割り当てる小組テンプレートの種類の変更、各セルに割り当てる小組区分の変更、各小組に割り当てる物件データの変更等を行うことができる。
【0151】
セルの区分の変更の際には、セル区分としては、「見出しセル」、「割り付けセル」又は「空きセル」を選択することができる。「見出しセル」とは、販売店等の見出しを割り当てるためのセルであり、「割り付けセル」とは、物件データを割り当てるためのセルであり、「空きセル」とは、何も割り当てられないセルであり、「空きセル」の領域では背景が表示される。「見出しセル」又は「空きセル」が挿入されると、物件データは繰り下げて割り当てられる。
【0152】
セルに割り当てる小組テンプレートの種類の変更は、区分が「見出しセル」又は「割り付けセル」であるセルに対してのみ可能である。セルに割り当てる小組テンプレートの種類の変更に際しては、ページテンプレート生成手段202が画面63で設定した使用可能な小組スタイルであって小組配置・物件割当手段106Bがインポートした小組テンプレート群124のファイルに含まれているものに対応した小組テンプレートを選択することができる。
【0153】
セルに割り当てる小組区分の変更は、区分が「割り付けセル」であるセルに対して可能である。セルに割り当てる小組区分の変更に際しては、「見出し」又は「物件」を選択することができる。
【0154】
特殊な組み合わせの例として、「セル区分」が「割り付け」であり、「小組テンプレート」の種類が「小組1」であり、「小組区分」が「見出し」であるセルに対しては、「浮動見出し」が設定される。「浮動見出し」とは、物件の挿入及び削除により移動する見出しのことである。これに対し、「セル区分」が「見出し」であるセルに対しては、「固定見出し」が設定される。「固定見出し」とは、物件の挿入又は削除により移動しない見出しのことである。
【0155】
セル区分、小組テンプレート及び小組区分の組み合わせとセルに表示されるデータとの関係を下表に示す。
【0156】
【表1】
上表より明らかなように、「セル区分」が「見出し」であるセルには「固定見出し」が設定される。「セル区分」が「割り付け」であり「小組区分」が「見出し」であるセルには「小組テンプレート」にどのような小組が設定されていても「浮動見出し」が設定され、「セル区分」が「割り付け」であり「小組区分」が「物件」であるセルには「小組テンプレート」にどのような小組が設定されていても「物件」が設定される。これは、例えば、「midashi1」の小組テンプレートが見出し用のテンプレートであることや、「小組1」の小組テンプレートが物件用のテンプレートであることをコンピュータに認識させていないためである。従って、実際には、上表の(3)の組み合わせ及び(6)の組み合わせはオペレータの判断で避けることとなる。
【0157】
小組名が「midashi1」であるセルには、小組の設計次第で販売店等のデータを流し込むことも可能であり、固定データのみを表示させることも可能である。
【0158】
図77の画面での設定に従ったレイアウトビューを図59に示す。
【0159】
小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、図75の画面で設定され、必要に応じて図77の画面で修正が加えられた小組配置及び物件割当に従ったXML文書126及び小組配置・物件割当データ127を出力する。
【0160】
[実施形態3]
実施形態2では、小組テンプレート生成手段104が、自ら作成した各小組テンプレートを一旦プロジェクトファイル133に記録した後に、プロジェクトファイル133に登録された1又は2以上の小組テンプレートを含む小組テンプレート群124のファイルをエクスポートする。そして、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bが、オペレータにより選択された小組テンプレート群124のファイルをインポートし、インポートしたファイルに含まれている小組テンプレートを物件データベース121に物件情報掲載誌と関連付けて登録する。
【0161】
また、実施形態2では、ページテンプレート生成手段202が、自ら作成した各ページテンプレートを一旦プロジェクトファイル133に記録した後に、プロジェクトファイル133に登録された1又は2以上のページテンプレートを含むページテンプレート群222のファイルをエクスポートする。そして、ページテンプレート割当手段203が、オペレータにより選択されたページテンプレート群222のファイルをインポートし、インポートしたファイルに含まれているページテンプレートを物件データベース121に物件情報掲載誌と関連付けて登録する。
【0162】
しかしながら、上記の実施形態2の構成及び動作では、オペレータは、エクスポート及びインポートを行わなければならず、作業効率が悪化する。また、同一のデータベースパブリッシング装置で複数種類の物件情報掲載誌を扱う場合に多種類の小組テンプレート及び多種類のページテンプレートをインポートし、その中から現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌に必要な小組テンプレート及びテンプレートを物件データベースに登録することになるので、作業効率が悪化する。更に、1つの小組テンプレート群124のファイルに1つの物件情報掲載誌に必要な小組テンプレートが含まれているとは限らず、そうでない場合にはオペレータは複数の小組テンプレート群124のファイルをインポートしなければならなくなり、作業効率が悪化する。同様に、1つのページテンプレート群222のファイルに1つの物件情報掲載誌に必要なページテンプレートが含まれているとは限らず、そうでない場合にはオペレータは複数のページテンプレート群222のファイルをインポートしなければならなくなり、作業効率が悪化する。
【0163】
実施形態3は、このような問題点を解決するものである。
【0164】
図78及び図79に本実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の一部を示す。なお、図3、図78及び図79に示す各部分を合わせたものが本実施形態による全体のデータベースパブリッシング装置を構成する。図78及び図79においては、図60及び図61に示す実施形態2と同一の部分については同一の符号を付してある。
【0165】
図78及び図79を図60及び図61と比較すると明らかなように、本実施形態によるデータベースパブリッシング装置が実施形態1のものと構成上異なる点は、小組テンプレート群124及びページテンプレート群222が削除されている点及び小組テンプレート生成手段104、ページテンプレート生成手段202C、ページテンプレート割当手段203C及び小組配置・物件割当手段106Cがそれぞれ小組テンプレート生成手段104、ページテンプレート生成手段202C、ページテンプレート割当手段203C及び小組配置・物件割当手段106Cに変更されている点である。
【0166】
また、図78の信号の流れを示す矢印から明らかなように、小組テンプレート生成手段104Cは、小組テンプレートを何れかの物件情報掲載誌に関連付けて物件データベース121に登録し、ページテンプレート生成手段202Cはページテンプレートを何れかの物件情報掲載誌に関連付けて物件データベース121に登録する。
【0167】
更に、図79の信号の流れを示す矢印から明らかなように、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bは、現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌に関連付けられて物件データベース121に登録されている小組テンプレートを物件データベース121から読み出し、ページテンプレート割当手段203Cは、現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌に関連付けられて物件データベース121に登録されているページテンプレートを物件データベース121から読出す。
【0168】
小組テンプレート生成手段104Cは、小組テンプレートの出力先を除けば、小組テンプレート生成手段104と同一である。ページテンプレート生成手段202Cは、ページテンプレートの出力先を除けば、ページテンプレート生成手段202と同一である。小組配置・物件割当手段106Cは、小組テンプレート群124のファイルから小組テンプレートを入力しない点及び物件データベース121に小組テンプレートを出力しない点を除けば、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bと同一である。ページテンプレート割当手段203は、ページテンプレート群222の入力先を除けば、ページテンプレート割当手段203と同一である。
【0169】
次に、小組テンプレート生成手段104C、ページテンプレート生成手段202C、ページテンプレート割当手段203C及び小組配置・物件割当手段106Cの本発明に特有の動作について詳細に説明する。なお、これらの手段は、実施形態2と同様にコンピュータがコンピュータプログラムを読み込んで実行することにより、コンピュータのハードウェア資源を用いて実現することができる。
【0170】
図80に示すメニュー[ファイル→データベースへ登録→小組テンプレートの登録]がオペレータにより選択されると、小組テンプレート生成手段104Cは、図81に示すダイアログボックスを表示する。このダイアログボックスの左側の小組テンプレートのリストボックスにはプロジェクトファイル133に登録されている全ての小組テンプレートが表示される。オペレータは、左側の小組テンプレートのリストボックスに表示されている小組テンプレートのうちから物件データベース121にエクスポートしたい小組テンプレートを右側の登録する小組テンプレートのリストボックスに移動し、移動した小組テンプレートを関連付けたい物件情報掲載誌を登録先カタログのコンボボックスで選択し、OKボタンを押す。すると、小組テンプレート生成手段104Cは、図81のダイアログの右側のリストボックスにある小組テンプレートを登録先カタログのコンボボックスで選択された物件情報掲載誌に関連付けて物件データベース121に登録する。
【0171】
同様に、図80に示すメニュー[ファイル→データベースへ登録→ページテンプレートの登録]がオペレータにより選択されると、ページテンプレート生成手段202Cは、図82に示すダイアログボックスを表示する。このダイアログボックスの左側のページテンプレートのリストボックスにはプロジェクトファイル133に登録されている全てのページテンプレートが表示される。オペレータは、左側のページテンプレートのリストボックスに表示されているページテンプレートのうちから物件データベース121にエクスポートしたいページテンプレートを右側の登録する小組テンプレートのリストボックスに移動し、移動したページテンプレートを関連付けたい物件情報掲載誌を登録先カタログのコンボボックスで選択し、OKボタンを押す。すると、ページテンプレート生成手段202Cは、図82のダイアログの右側のリストボックスにあるページテンプレートを登録先カタログのコンボボックスで選択された物件情報掲載誌に関連付けて物件データベース121に登録する。
【0172】
ページテンプレート割当手段203Cは、図59又は77の画面の所定のメニューを辿ることにより起動される。ページテンプレート割当手段203Cは、起動されると、図70に示す画面を表示することはせずに、図72に示す画面を表示する。この画面のページテンプレートのコンボボックスには、現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌に関連付けられて物件データベース121に登録されているページテンプレートが表示される。オペレータがこの画面に開始ページ、終了ページ及びこれらの間のページに割り当てることを希望するページテンプレートを入力して「OK」ボタンを押すと、ページテンプレート割当手段203Cは、この入力に従って、ページにページテンプレートを割り当てる。
【0173】
なお、現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌に関連付けられて登録されているページテンプレートは、図83に示す画面で確認することができる。図83に示す画面は、画面下にあるページテンプレートのタブを選択したときのものである。
【0174】
小組配置・物件割当手段106Cも、図59又は77に示す画面で別の所定のメニューを辿ることにより起動される。小組配置・物件割当手段106Cは、起動されると、図73に示す画面を表示することはせずに、図75に示す画面を表示する。この表示後の小組配置・物件割当手段106Cの動作は、小組配置・物件割当手段106Bのものと同一であるので、説明を省略する。
【0175】
なお、現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌に関連付けられて登録されている小組テンプレートは、図84に示す画面で確認することができる。図84に示す画面は、画面下にある小組テンプレートのタブを選択したときのものである。
【0176】
なお、実施形態2及び実施形態3を複合させて、オペレータが、小組テンプレートの出力先を小組テンプレート群のファイルにするか、又は、物件データベースにするかを選択することができ、また、ページテンプレートの出力先をページテンプレート群のファイルにするか、又は、物件データベースにするかを選択することができるようにしてもよい。また、このように複合させた場合には、実施形態3を基本として小組テンプレート生成手段及びページレイアウト生成手段が予め物件データベースに小組テンプレート及びページテンプレートを登録しておきながらも、実施形態2によりエクスポート及びインポートを経て小組配置・物件割当手段及びページテンプレート割当手段が小組テンプレート及びページテンプレートを物件データベースに追登録することも可能となる。
【0177】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように本発明によれば以下の効果が奏される。
【0178】
小組配置・物件割当手段が起動されたときに、既に、小組テンプレート生成手段により小組テンプレートが、現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌に関連付けられて物件データベースに登録されているので、小組配置・物件割当手段は、小組テンプレート群から必要な小組テンプレートを選択する必要が無くなる。従って、小組テンプレート群が多数の小組テンプレートを含んでいる場合にその選択により作業効率が低下することを防止することができる。
【0179】
同様に、ページテンプレート割当手段が起動されたときに、既に、ページテンプレート生成手段によりページテンプレートが、現在扱っている物件情報掲載誌に関連付けられて物件データベースに登録されているので、ページテンプレート割当手段は、ページテンプレート群から必要なページテンプレートを選択する必要が無くなる。従って、ページテンプレート群が多数のページテンプレートを含んでいる場合にその選択により作業効率が低下することを防止することができる。
【0180】
また、1つのデータベースパブリッシングソフトウェアで多種類の物件情報掲載誌を扱う場合でも、ページへのページテンプレート及び小組テンプレートの割当てを効率的に行うことが可能となる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施形態1によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の構成を示すブロック図(1/3)である。
【図2】本発明の実施形態1によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の構成を示すブロック図(2/3)である。
【図3】本発明の実施形態1及び2によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の構成を示すブロック図(3/3)である。
【図4】本発明の実施形態1による物件データベースの構造を示す図である。
【図5】本発明の実施形態1による物件を抽出するためのフィルタを管理するツリーの構造を示す図である。
【図6】本発明の実施形態1によるDTP手段が作成した小組レイアウトの例を示す図である。
【図7】本発明の実施形態1による小組スタイル情報生成手段が図6の小組レイアウトの例を基に生成した小組スタイル情報を示す図である。
【図8】図7に示す小組スタイル情報の階層構造を示す図である。
【図9】本発明の実施形態1による小組スタイル情報生成手段の動作を示すフローチャート(1/3)である。
【図10】本発明の実施形態1による小組スタイル情報生成手段の動作を示すフローチャート(2/3)である。
【図11】本発明の実施形態1による小組スタイル情報生成手段の動作を示すフローチャート(3/3)である。
【図12】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が図7に示す小組スタイル情報を基に生成する小組テンプレートを示す図である。
【図13】本発明の実施形態1による図12に示す小組テンプレートに対応したXML文書の構造を示す図である。
【図14】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段の動作を示すフローチャート(1/2)である。
【図15】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段の動作を示すフローチャート(2/2)である。
【図16】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が表示する画面を示す図(1/4)である。
【図17】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が表示する画面を示す図(2/4)である。
【図18】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が表示する画面を示す図(3/4)である。
【図19】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が表示する画面を示す図(4/4)である。
【図20】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート又はページテンプレートをエクスポートするためのメニューを表示した画面の図である。
【図21】本発明の実施形態1によるエクスポートする小組テンプレートを選択するための画面の図である。
【図22】本発明の実施形態1によるエクスポートする小組テンプレート群を格納するファイルを指定するための画面の図である。
【図23】本発明の実施形態1によるマスターレイアウトを作成するための画面を示す図である。
【図24】本発明の実施形態1による原データを作成するための画面を示す図である。
【図25】本発明の実施形態1による対象ページに割り当てる物件データを抽出するためのフィルタを選択するための画面を示す図である。
【図26】本発明の実施形態1による対象ページに割り当てる物件データを並べ替える順序を決定するための画面を示す図である。
【図27】本発明の実施形態1によるマスターレイアウトに従った小組の配置を変更するための画面を示す図である。
【図28】本発明の実施形態1による各小組に割り当てる各物件を変更するための画面を示す図である。
【図29】本発明の実施形態1による各ページにおいて各割り付け位置に割り付ける小組の種類と物件を表示し、変更するための画面を示す図である。
【図30】本発明の実施形態1で生成するXSLT電子文書の第1の例を示す図(1/2)である。
【図31】本発明の実施形態1で生成するXSLT電子文書の第1の例を示す図(2/2)である。
【図32】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と同時に生成するXSLT電子文書の第2の例を示す図(1/6)である。
【図33】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と同時に生成するXSLT電子文書の第2の例を示す図(2/6)である。
【図34】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と同時に生成するXSLT電子文書の第2の例を示す図(3/6)である。
【図35】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と同時に生成するXSLT電子文書の第2の例を示す図(4/6)である。
【図36】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と同時に生成するXSLT電子文書の第2の例を示す図(5/6)である。
【図37】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と同時に生成するXSLT電子文書の第2の例を示す図(6/6)である。
【図38】本発明の本実施形態1で生成するXML電子文書の例を示す図である。
【図39】本発明の実施形態1により生成されるXSLT電子文書とXML電子文書の構造及びそれらの関係を示す概念図である。
【図40】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と図32〜37に示すXSLT電子文書から生成するXSLT電子文書を示す図(1/5)である。
【図41】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と図32〜37に示すXSLT電子文書から生成するXSLT電子文書を示す図(2/5)である。
【図42】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と図32〜37に示すXSLT電子文書から生成するXSLT電子文書を示す図(3/5)である。
【図43】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と図32〜37に示すXSLT電子文書から生成するXSLT電子文書を示す図(4/5)である。
【図44】本発明の実施形態1で図38に示すXML電子文書と図32〜37に示すXSLT電子文書から生成するXSLT電子文書を示す図(5/5)である。
【図45】物件データベースから単純に生成されたXML文書の構造を示す図である。
【図46】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が生成する小組テンプレートに対応したXML文書の構造を示す図(1/5)である。
【図47】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が生成する小組テンプレートに対応したXML文書の構造を示す図(2/5)である。
【図48】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が生成する小組テンプレートに対応したXML文書の構造を示す図(3/5)である。
【図49】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が生成する小組テンプレートに対応したXML文書の構造を示す図(4/5)である。
【図50】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が生成する小組テンプレートに対応したXML文書の構造を示す図(5/5)である。
【図51】本発明の実施形態1による小組テンプレート生成手段が表示する画面を示す図であって、図18に示す図に置き換わるものである。
【図52】本発明の実施形態1による図46〜50に示す構造を有するXML文書の1つの物件についての部分(1/7)を示す図である。
【図53】本発明の実施形態1による図46〜50に示す構造を有するXML文書の1つの物件についての部分(2/7)を示す図である。
【図54】本発明の実施形態1による図46〜50に示す構造を有するXML文書の1つの物件についての部分(3/7)を示す図である。
【図55】本発明の実施形態1による図46〜50に示す構造を有するXML文書の1つの物件についての部分(4/7)を示す図である。
【図56】本発明の実施形態1による図46〜50に示す構造を有するXML文書の1つの物件についての部分(5/7)を示す図である。
【図57】本発明の実施形態1による図46〜50に示す構造を有するXML文書の1つの物件についての部分(6/7)を示す図である。
【図58】本発明の実施形態1による図46〜50に示す構造を有するXML文書の1つの物件についての部分(7/7)を示す図である。
【図59】本発明の実施形態2による小組配置・物件割当手段が生成したページを表示する画面の図である。
【図60】本発明の実施形態2によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の構成を示すブロック図(1/3)である。
【図61】本発明の実施形態2によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の構成を示すブロック図(2/3)である。
【図62】本発明の実施形態2によるDTP手段がページテンプレートにエリアを設定するために表示する画面の図である。
【図63】本発明の実施形態2によるページスタイル情報生成手段がエリアのパラメータを設定するために表示する画面の図である。
【図64】本発明の実施形態2によるページスタイル情報生成手段が生成したページスタイル情報の例を示す図である。
【図65】本発明の実施形態2によるページスタイル情報生成手段が生成したページスタイル情報を表示する画面の図である。
【図66】本発明の実施形態2によるページテンプレート生成手段がページテンプレート中の各エリアのパラメータを設定するために表示する画面の図である。
【図67】本発明の実施形態2によるページテンプレート生成手段が生成したページテンプレートの例を示す図である。
【図68】本発明の実施形態2によるエクスポートするページテンプレートを選択するための画面の図である。
【図69】本発明の実施形態2によるエクスポートするページテンプレート群を格納するファイルを指定するための画面の図である。
【図70】本発明の実施形態2によるインポートするページテンプレート群を格納するファイルを指定するための画面の図である。
【図71】本発明の実施形態2によるページテンプレート生成手段が生成したページテンプレートを表示する画面の図である。
【図72】本発明の実施形態2によるページテンプレート割当手段が表示する画面の図である。
【図73】本発明の実施形態2によるインポートする小組テンプレート群を格納するファイルを指定するための画面の図である。
【図74】本発明の実施形態2による小組テンプレートを変更するための画面の図である。
【図75】本発明の実施形態2による小組配置・物件割当手段が物件割当等のために表示する画面の図である。
【図76】図75の画面から終了ページを設定するために呼び出される画面の図である。
【図77】本発明の実施形態2による小組配置・物件割当手段が小組配置及び物件割当の修正等のために表示する画面の図である。
【図78】本発明の実施形態3によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の構成を示すブロック図(1/3)である。
【図79】本発明の実施形態3によるデータベースパブリッシング装置の構成を示すブロック図(2/3)である。
【図80】本発明の実施形態3による小組テンプレート又はページテンプレートを物件データベースに登録するためのメニューを表示した画面の図である。
【図81】本発明の実施形態3による物件データベースに登録する小組テンプレートを選択するための画面の図である。
【図82】本発明の実施形態3による物件データベースに登録するページテンプレートを選択するための画面の図である。
【図83】本発明の実施形態3による物件データベースに登録されているページテンプレートを確認するための画面の図である。
【図84】本発明の実施形態3による物件データベースに登録されている小組テンプレートを確認するための画面の図である。
【符号の説明】
101 データベース作成手段
102 DTP手段
103 小組スタイル情報生成手段
104、104C 小組テンプレート生成手段
105 マスターレイアウト生成手段
106、106B、106C 小組配置・物件割当手段
107 XSLT文書生成手段
108 XSLTプロセッサ
109、110 XSL−FOプロセッサ
133 プロジェクトファイル
201 ページスタイル情報生成手段
202、202C ページテンプレート生成手段
203、203C ページテンプレート割当手段[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a database publishing method and apparatus for generating a typesetting electronic document for printing property data recorded in a database on paper or displaying it on a screen.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, XML (eXtensible Markup Language) electronic documents have attracted attention as electronic documents that replace HTML (HyperText Markup Language) electronic documents. The XML electronic document is expressed in a text format, and a character string constituting the content is sandwiched between reserved words in a tag format. In addition, an XML electronic document is a unique document type definition document called DTD (Document Type Definition) that specifies the expression method and adds meaning to a character string in a sentence. You can extend the tag. Further, the XML electronic document is characterized by an object-oriented hierarchical structure, a document check function using an authentication function, a powerful hyperlink function, and the like.
[0003]
In recent years, the following method has appeared as a method for generating an XSL-FO (eXtensible Stylesheet Language-Formatting Object) electronic document as an electronic document for typesetting from an XML (eXtensible Markup Language) electronic document. That is, according to the description contents of an XSLT electronic document called an XSLT (eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformation) style sheet in which a predetermined rule for generating an XSL-FO electronic document from an XML electronic document is described, the XSLT processor performs the XML electronic processing. An XSL-FO electronic document as a typesetting electronic document is generated based on the document. The XSL-FO processor performs printing and screen display based on the generated XSL-FO electronic document.
[0004]
Note that prior art document information relating to the invention of this application includes the following.
[0005]
[Patent Document 1]
JP 2001-84388 A
[Patent Document 2]
JP 2001-14792 A
[Patent Document 3]
JP 2002-99524 A
[Non-Patent Document 1]
"Printing world 2002. July issue", publishing country: Japan, publishing place: Nihon Printing Shimbun, publication date: July 10, 2002
[Non-Patent Document 2]
Catalog “DBPublisher 1.0, DBPress 4.0”, publisher: Japan, distributor: DTE, limited company, developer: Lynx
[0006]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
By the way, in the property information publication magazines such as used car information magazines, housing information magazines, job information magazines, travel information magazines, ticket information magazines, etc., the number of properties to be posted is enormous, about hundreds to thousands, There are few types of small groups for listing properties. In other words, in each property information publication magazine, only a few types of small group styles of about a few to a dozen or so are used, and information on a large number of properties is assigned to a typesetting that combines limited types of small groups. .
[0007]
In addition, since the number of properties to be published in the property information publication magazine is enormous and the frequency of addition and deletion of properties is high, data on such properties is usually recorded in a database.
[0008]
In addition, each page of the property information magazine has a small group arranged, and each small group is filled with the data of each property, but the layout of the small group on each page is often simply arranged in a matrix, It was typical and had little freedom.
[0009]
Furthermore, publishers that publish various property information publication magazines handle many types of property information publication magazines with a single database publishing software. Depending on the type of property information publication magazine, Generally, the layout is different. Therefore, one database publishing software handles many types of small templates and multiple types of page templates, but the types of small templates and page templates used in each property information magazine are relatively small. Therefore, if multiple types of page templates and multiple types of small set templates are prepared as options when assigning page templates and small set templates to pages of each property information publication magazine, the procedure and labor for determining the allocation increase, and work Efficiency deteriorates.
[0010]
It is an object of the present invention to provide a database publishing method and apparatus for generating a typesetting electronic document for printing or displaying a property information publication magazine based on a database in consideration of characteristics of the property information publication magazine. .
[0011]
Another object of the present invention is to provide a database publishing method and apparatus capable of arranging small sets on each page with a certain degree of freedom.
[0012]
Furthermore, the present invention provides a database capable of efficiently assigning page templates and small set templates to pages even when dealing with various types of property information publication magazines with a single database publishing software. It is an object to provide a publishing method and an apparatus therefor.
[0013]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
According to the present invention, a property database for generating a property database including a small template that is incorporated into an electronic document for composition for printing the property data recorded on the paper or displaying it on a screen In the database generation method,A computer uses a CPU,Based on DTP (Desk Top Publishing) data about the small set, the small group style information that reflects the attributes of the DTP data is generated in the XSL-FO document format for the small set.And write the generated small group style information to the recording medium.Steps,The computer reads the small group style information from the recording medium using a CPU,By parameterizing the actual data contained in the set style information for the set, the style of the set is described, and,Information that can identify the property into which data should be insertedWhenData to be inserted into the sub-set of the identified propertyAre described as XPATH of an XML document representing the property database, andGenerates a XSLT document format subset template in which the location of the subset is described as a dummy argumentAnd write to the recording mediumSteps,A computer uses a CPU,Registering the small set template in a property database in which a plurality of properties are registered.
[0014]
Further, according to the present invention, in the database publishing method for generating the electronic document for composition for printing the property data recorded in the property database on a paper or displaying it on the screen, each of the property database generation methods described above Steps,A computer uses a CPU,A database publishing method comprising the steps of: assigning a page template assigned to a page that is usable in the small template registered in the property database to the page.
[0015]
In the above database publishing method,A computer uses a CPU,Selecting a subset template available in the page template and assigning the selected subset template to the page template;A computer uses a CPU,And registering the page template to which the usable sub-set template is assigned to the property database, the sub-set template being registered in the property database and usable in the page template assigned to the page. The step of assigning what is to the page may be performed using the page template registered in the property database.
[0016]
The property database generation method above isA computer uses a CPU,Generates a template template group file including one or more of the template templates.And write the generated file to the recording medium.You may have steps.
[0017]
Further, according to the present invention, in the database publishing method for generating the electronic document for composition for printing the property data recorded in the property database on a paper or displaying it on the screen, each of the property database generation methods described above Steps,ComputerThe small group template registered in the property database and usable in the page template allocated to the page, or the small group template included in the small group template file and the page allocated to the page Assigning what is enabled in the template to a page. A database publishing method is provided.
[0018]
In the above database publishing method,A computer uses a CPU,Selecting a subset template available in the page template and assigning the selected subset template to the page template;A computer uses a CPU,Registering the page template to which the usable sub-template is assigned to the property database;A computer uses a CPU,Generate a page template group file containing one or more of the page templates to which usable sub-templates are assignedAnd write the generated file to the recording medium.A sub-template that is registered in the property database and that can be used in a page template assigned to a page or the sub-template included in the sub-group template file. The step of assigning a page template that can be used in a page template assigned to a page to the page includes the page template registered in the property database or the page template included in the file of the page template group. May be used.
According to the present invention, in the small template generation method for generating the small template incorporated in the electronic document for typesetting for printing the property data recorded in the property database on a paper or displaying it on the screen, ,Using the CPUBased on DTP (Desk Top Publishing) data about the small set, the small group style information that reflects the attributes of the DTP data is generated in the XSL-FO document format for the small set.And write the generated small group style information to the recording medium.Step and computer,Using the CPU, read the small group style information from the recording medium,By parameterizing the actual data contained in the set style information for the set, the style of the set is described, and,Information that can identify the property into which data should be insertedWhenData to be inserted into the sub-set of the identified propertyAre described as XPATH of an XML document representing the property database, andGenerating a small template in the form of an XSLT document in which the position of the small group is described as a dummy argument.
[0019]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[0020]
[Embodiment 1]
In the present embodiment, a database publishing method and apparatus for publishing a used car information magazine will be described as an example, but the present embodiment can also be applied to other property information publication magazines.
[0021]
1 to 3 show a configuration of a database publishing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
[0022]
Referring to FIG. 1, a database publishing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a
[0023]
Note that these means and processor can be realized by using computer hardware resources by causing a computer to read and execute a computer program.
[0024]
Referring to FIG. 1, the database creation means 101 defines a property database and puts property data into the property database., ConstantWith a defined structureProperty dataThe systemized
[0025]
Referring to FIG. 2, the small group arrangement / property allocation means 106 generates an
[0026]
Referring to FIG. 3, the
[0027]
Next, operations and data of each unit of the database publishing apparatus according to the embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0028]
First, the
[0029]
Further, as the
[0030]
Next, an operation of generating each small template of the
[0031]
Each small template of the
[0032]
The small layout is created by a designer using a DTP means 102 at a design company or the like, for example. A sample layout of the created small set is shown in FIG. Referring to FIG. 6, the small sample includes an image box “G1”, a text box “T1”, and a text box “T2”. A sample of a used car image is pasted in the image box “G1”, a sample “supercar” of a used car name is described in the text box “T1”, and a used car is written in the text box “T2”. A sample of “1 million yen” is described. The DTP unit 102 generates and outputs the
[0033]
Next, the small
[0034]
Referring to FIG. 7, as is clear from the description in the
[0035]
The description in the
[0036]
Similarly, the description in the
[0037]
The description in the
[0038]
Next, a method in which the small group style
[0039]
As shown in FIG. 9, first, a portion of a frame 215 (FIG. 7) such as “kogumi_style_info” is output (step S251). Here, outputting means writing to the file of the small
[0040]
Next, the “fo: block-container start tag” (portion 211) for the entire small group is output (step S252).
[0041]
Next, steps S254 to S257 are repeated for all boxes in the small set (step S253). Since there are three boxes in the example of FIG. 7, these steps S254 to S257 are repeated three times. In the repetition, first, it is determined whether or not the box is a text box (step S254). If the box is a text box, the text box is processed (step S255). Details of this processing will be described later. If the box is not a text box, it is determined whether the text box is an image box (step S256). If the box is an image box, the image box is processed (step S257). Details of this processing will be described later.
[0042]
Next, an end tag of “fo: block-container”, which is a small set end tag, is output (step S258). The portion output in this step is a portion indicated by reference numeral 216 (FIG. 7).
[0043]
Finally, an end tag of “kogumi_style_info” is output (step S259). The portion output in this step is a portion indicated by reference numeral 217 (FIG. 7).
[0044]
Next, details of the text box processing (step S255) will be described with reference to FIG. In this process, the portion indicated by the
[0045]
First, the “fo: block-container” start tag for the text box is output (step S261). Next, the attribute of the text box is acquired from the DTP data 122 (step S262). This attribute is the height, width, upper left coordinate, etc. of the text box. Next, the text box attribute acquired in step S262 is output (step S263). Next, the “fo: block” start tag for the text box is output (step S264). Next, text data is processed (step S265). Details of this processing will be described later. Next, the “fo: block” end tag for the text box is output (step S266). Finally, the “fo: block-container” end tag for the text box is output (step S267).
[0046]
In the text data processing (step S265), first, a “fo: inline” start tag is output (step S271). Next, text data and character attributes are acquired from the DTP data 122 (step S272). Next, “fo: inline” attributes (font-family, font-style, font-size, etc.) reflecting the acquired character attributes are output (step S273). Next, the acquired text data ("supercar" or "1 million yen" in the example of FIG. 7) is output (step S274). Finally, an “fo: inline” end tag is output (step S275).
[0047]
Next, details of the image box processing (step S257) will be described with reference to FIG. In this process, the portion indicated by the
[0048]
First, the “fo: block-container” start tag for the image box is output (step S281). Next, the attribute of the image box is acquired from the DTP data 122 (step S282). This attribute is the height, width, upper left coordinate, etc. of the image box. Next, the attribute of the image box acquired in step S282 is output (step S283). Next, the “fo: block” start tag for the image box is output (step S284). Next, image data processing is performed (step S285). Details of this processing will be described later. Next, the “fo: block” end tag for the image box is output (step S286). Finally, the “fo: block-container” end tag for the image box is output (step S287).
[0049]
In the processing of image data (step S285), first, a “fo: external-graphic” start tag is output (step S291). Next, the image name and attribute of the image data are acquired from the DTP data 122 (step S292). This attribute is a method of attaching the
[0050]
With the above method, the small
[0051]
Next, each small template of the
[0052]
As is clear from a comparison between FIG. 7 and FIG. 12, most of the small template is the same as the small style information, but a part is different in the following points.
[0053]
(1) Description of
(2) There is a description of the template indicated by
[0054]
(3) In the description of “fo: block-container” for the entire small group indicated by the
[0055]
(4) In the description of “inline” indicated by a
[0056]
(5) In the description of “inline” indicated by a
[0057]
(6) In “fo: block” for the image box indicated by the
[0058]
FIG. 13 shows a tree structure of an XML document corresponding to the small template shown in FIG. In FIG. 13, only a tree for one property is displayed, but similar trees are constructed for other properties.
[0059]
In this way, in the small template, property dataIDSince each item of property data is parameterized, when this small template is inserted into an XSL-FO document, this small template is called by specifying these parameters from other parts of the XSL-FO document. Is possible. The value specified as the parameter is read from the XML document.
[0060]
Next, a method in which the small
[0061]
Referring to FIG. 14, first, the small
[0062]
At the beginning of each iteration, a small layout is displayed according to the small
[0063]
In setting the text item, first, the screen shown in FIG. 17 is displayed. If the operator presses the
[0064]
In setting the image item, first, the screen shown in FIG. 19 is displayed. If the operator presses the
[0065]
When the setting of the text box item and the image box item is completed, that is, when the above replacement in the tree structure constructed on the memory is completed, a small template is created based on the tree structure updated on the memory. To do.
[0066]
A small template is generated from the small
[0067]
The small
[0068]
Next, the small
[0069]
When the menu [File-> Export-> Export small template] shown in FIG. 20 is selected by the operator, the small template generation means 104 displays a dialog box shown in FIG. All the small templates registered in the
Next, a method for generating the
[0070]
First, the designation of the number of page divisions is input. In the example of FIG. 23, the number of divisions in the vertical direction is 7, and the number of divisions in the horizontal direction is 10. Next, the type of small group to be arranged in each cell is designated. In the example of FIG. 23, the type of the small group arranged in each column of the third to seventh rows is the
[0071]
The master
[0072]
Next, a method for generating the
[0073]
First, if the “reference” button to the right of the “filter” character on the “Property Data Batch Assignment” screen shown in FIG. 24 displayed by the operator's operation is pressed by the operator's operation, the data to be assigned to the target page A screen (FIG. 25) for selecting a filter for extracting. The screen in FIG. 25 is generated based on the tree structure shown in FIG. In the screen of FIG. 25, the operator selects any filter that has already been created. When selecting, the operator selects a filter category in the upper combo box in the screen of FIG. 25, and then selects a target filter in the lower list in the screen of FIG. By doing so, the property data extracted from the
[0074]
Next, if the “reference” button to the right of the “reorder” character on the screen of FIG. 24 is pressed by an operator's operation, a screen for designating the order of reordering the property data extracted by the filter (FIG. 26) is displayed. In the screen of FIG. 26, the operator selects one or more items to be used for rearrangement or combinations of a plurality of created items (for example, combinations of body shape and grade). For example, if a manufacturer name and a vehicle name are input in order from the top in the right frame of the screen of FIG. 26, the rearrangement order is “manufacturer name / vehicle name”.
[0075]
Next, the target page is determined by receiving the start page input by the operator in the text box of the page designation section on the screen of FIG. If there is no end page input, pages are created until the property data extracted by the
[0076]
Next, using the master layout combo box in the layout designation category of the screen in FIG. 24, selection of the master layout to be applied to the target page from the already created master layout is received from the operator. The master layout included in the master layout combo box is included in the
[0077]
Next, any button with a figure (any one of the four types of buttons for a single page or the six types of buttons for a spread page) in the section arrangement direction of the screen in FIG. By accepting the selection of the small group arrangement direction by pressing, it is determined in what order the extracted property data is allocated to the small group.
[0078]
Next, an input (checked or unchecked) by an operator to a check box for determining whether or not to perform a page break or page break is accepted in the page break / page break classification of the screen of FIG. “Stamp” means that a group of small groups at the same height (row) is regarded as one step, and the item is changed when the item content of a specified hierarchy changes. When performing a page break or page break, an input by an operator for designating the timing for page break or page break is accepted. This timing can be specified by a hierarchy number such as
[0079]
After the above settings are made on the screen of FIG. 24, the “OK” button of FIG. 24 is pressed by the operator, so that the selected
[0080]
Next, the small group arrangement / property allocating unit 106 may input a change in the arrangement of the small group according to the master layout through the layout view shown in FIG. 27 as necessary. In the example of FIG. 27, the master layout of FIG. 23 is set such that the third row, first to fifth columns are blank, the
[0081]
Further, the small group arrangement / property allocating means 106 may input a change of each property allocated to each small group in the page preview shown in FIG. 28 as necessary.
[0082]
Also, the small group arrangement / property allocating means 106 may accept a change in the arrangement of the small group according to the master layout in the data sheet view shown in FIG. 29 instead of the layout view shown in FIG. 27, as shown in FIG. Instead of the page preview, a change of each property to be assigned to each small group may be received in the data sheet view shown in FIG. When changing the arrangement of a small group or each property assigned to each small group in the data view sheet shown in FIG. 29, the data in the corresponding column is changed. Also, when deleting a set in the data view sheet, delete the table record displayed in the data sheet view. When adding a set in the data sheet view, delete the table record displayed in the data sheet view. Add
[0083]
As described above, the property to be posted on each page is determined, and the type and position of the small group to which each property is allocated are also determined. These data are recorded in the
[0084]
The XSLT electronic
[0085]
Before describing the XSLT
[0086]
Referring to FIGS. 30 and 31, the description indicated by the block (A) is a description for designating the size of the page margin. The description shown in the block (B) is a description for each page. In FIG. 30, only one page is described, but in actuality, the number of used pages in the used car information magazine is the number of all used pages. Just repeat. The description shown in the block (C) is a description for assigning each property to each sub-group on each page. In FIG. 30, only one property is listed, but in reality, the number of properties listed on each page Just repeat. The description shown in the block (E) is a small group template describing the type of small group for each type. In FIG. 30, only one type of small group is shown, but the type of small group used in the used car information magazine. Repeat as many times as
[0087]
Looking at the block (C), the sentence (1) is a sentence for designating the property to be assigned to each page in a predetermined order, and the template 2 (block (F (F ) Is applied. Sentence (2) is a sentence for passing the name of the small group (the name of the small group represents the type of the small group) to which the property data specified in sentence (1) is assigned as an actual argument to
[0088]
Looking at
[0089]
Read the identifiers of all the properties to be posted on each page from the original data, the type and coordinates of the subgroups to which those properties are assigned, and read these data into sentences (1), (2), (3), (4 ) And repeating the blocks (B), (C), and (E) as many times as necessary, an XSLT electronic document can be generated.
[0090]
A method for generating an XML electronic document will be described later. FIG. 38 shows a simple example of an XML electronic document generated in this embodiment. Referring to FIG. 38, this XML document has a hierarchical structure in which bukken is under bukken_data and a plurality of items about the property are under bukken. This XML document is a set of bukken_data for properties to be posted on all pages (2 pages in this example). Therefore, by extracting property data from the
[0091]
The content of the concrete XSLT electronic document produced | generated simultaneously with the XML electronic document shown in FIG. 38 is shown in FIGS.
[0092]
FIG. 39 is a conceptual diagram showing the structures of the XSLT
[0093]
The
[0094]
FIG. 38 is a simple XML document for ease of explanation, but the structure of an actual XML document generated from the
[0095]
If an XML document is simply created from the
[0096]
Therefore, in the present invention, the
[0097]
Referring to FIGS. 4 and 46 to 50, the property name, price, etc., which are data directly described in each record of the property table, are displayed as usual in the item item (2) under the property bukken 501 (FIG. 46) in the XML document. As an example, item (item name: name_asc = "BKN_NAME", display item name: name_jp = "property name") 502 (Fig. 46) and item (item name: name_asc = "KAKAKU", display item name: name_jp = "Price") 503 (FIG. 46)).
[0098]
The area name of the area table referenced by a simple index consisting of one item from each record of the property table is the item item (item name: name_asc = "AREA_ID", the display item name under the property bukken 501 (FIG. 46): name_jp = "area ID") Reference item (area table) under 504 (Fig. 48) ref_table (item name: name_asc = "AREA") Item item (item name: name_asc = "AREA_NAME" under 505 (Fig. 48) “, Display item name: name_jp =“ area name ”) 506 (FIG. 50).
[0099]
The vehicle names in the manufacturer vehicle table referenced by the composite index composed of two items from each record in the property table are redundant but are described twice. The reason why two are described in duplicate is that the composite index consists of two items. One description is a reference table ref_table (item) under the item ref_item (item name: name_asc = "MAKER_ID", display item name: name_jp = "maker ID") 507 (Fig. 46) under the property bukken 501 (Fig. 46). Name: name_asc = "MAKER_SHARYOU") 508 (Fig. 46) under item item (item name: name_asc = "SHARYOU_NAME", display item name: name_jp = "vehicle name") 509 (Fig. 47) Yes, the other description is the reference table ref_table under the item ref_item (item name: name_asc = "MAKER_ID", display item name: name_jp = "maker ID") 510 (Fig. 48) under the property bukken 501 (Fig. 46). (Item name: name_asc = "MAKER_SHARYOU") 511 (Fig. 48) under item item (item name: name_asc = "SHARYOU_NAME", display item name: name_jp = "vehicle name") 512 (Fig. 49) It is a description.
[0100]
The manufacturer name of the manufacturer table referenced by the simple index consisting of one item manufacturer ID from the manufacturer vehicle table referenced by the composite index consisting of two items from the record of the property table is also redundant but duplicated Is described. The reason why two are described in duplicate is that the composite index consists of two items. One description is a reference table ref_table (item) under the item ref_item (item name: name_asc = "MAKER_ID", display item name: name_jp = "maker ID") 507 (Fig. 46) under the property bukken 501 (Fig. 46). Name: name_asc = "MAKER_SHARYOU") Reference table under item ref_item (item name: name_asc = "MAKER_ID", display item name: name_jp = "maker ID") 513 (Fig. 47) under 508 (Fig. 46) Description under the item item (item name: name_asc = "MAKER_NAME", display item name: name_jp = "maker name") 515 (Fig. 47) under the ref_table (item name: name_asc = "MAKER) 514 (Fig. 47) Other description is the reference table under the item ref_item (item name: name_asc = "SHARYOU_ID", display item name: name_jp = "vehicle ID") 510 under the item bukken 501 (Fig. 46) (Fig. 48). Item ref_item (item name: name_asc = "MAKER_ID", item for display under ref_table (item name: name_asc = "MAKER_SHARYOU") 511 (Fig. 48) Name: name_jp = "maker ID") Reference item ref_table (item name: name_asc = "MAKER) 516 (Fig. 49) under item item (item name: name_asc =" MAKER_NAME ") under 517 (Fig. 49), Display item name: name_jp = "maker name") 518 (FIG. 49).
[0101]
As described above, since two vehicle IDs, vehicle names, manufacturer IDs, and manufacturer names are described in duplicate in each property block of the XML document, the vehicle ID, vehicle name, manufacturer ID, and manufacturer name are duplicated. There are two types of XPATH. In the small template, among the vehicle ID, the vehicle name, the manufacturer ID, and the manufacturer name, the vehicle name and manufacturer name, which are print items, are described as formal arguments. May be used to describe. Which XPATH is used for the description is determined by the item selected on the screen of FIG. 51 in which the operator selects the item to be poured. Note that the screen of FIG. 51 is a screen that is actually used, and the screen of FIG. 18 simplified for explanation is actually replaced with the screen of FIG. As for the manufacturer name, when the manufacturer name indicated by the
ref_item [@ name_asc = 'MAKER_ID'] / ref_table [@ name_asc = 'MAKER_SHARYOU'] / ref_item [@ name_asc = 'MAKER_ID'] / ref_table [@ name_asc = 'MAKER'] / item [@ name_asc = 'MAKER_NAME']
However, when the manufacturer name indicated by the reference numeral 522 in FIG. 51 is selected, the manufacturer name under the item 518 (FIG. 49) is selected.
ref_item [@ name_asc = 'SHARYOU_ID'] / ref_table [@ name_asc = 'MAKER_SHARYOU'] / ref_item [@ name_asc = 'MAKER_ID'] / ref_table [@ name_asc = 'MAKER'] / item [@ name_asc = 'MAKER_NAME']
It becomes. The item specified by such XPATH is described as a dummy argument in the small template. Then, such a small template is incorporated into the
[0102]
When the item referred to by the composite index is displayed by only one method on the screen of FIG. 51, the XML document only needs to be described by one method corresponding to the display method. When an item referenced by a composite index composed of two items is displayed in two ways on the screen of FIG. 51, the XML document describes the item by the above-described two methods corresponding to those display methods. To do. The tree structure of items displayed on the screen of FIG. 51 is created directly from a table such as a property table of the
[0103]
FIG. 4 generated based on the
[0104]
[Embodiment 2]
In the first embodiment, the finally obtained page layout is as shown in the screen layout view of FIG. In this layout, the entire page is divided into a set of matrices, and one small set is arranged in each row, each row, each row, each row, or each row in the matrix.
[0105]
On the other hand, in the second embodiment, the finally obtained page layout is as shown in the layout view of the screen in FIG. In this layout, a plurality of matrices are arranged over the entire page, and one small set is arranged in each column, each row, each column, each row, or each column. Since the position and size of each matrix arranged on the entire page can be freely set, the arrangement of small sets arranged on the page can be made somewhat free.
[0106]
60 and 61 show a part of the database publishing apparatus according to the present embodiment. 3, 60, and 61 constitute the entire database publishing apparatus according to the present embodiment. 60 and 61, the same reference numerals are given to the same portions as those in the first embodiment shown in FIGS.
[0107]
As apparent from a comparison of FIGS. 60 and 61 with FIGS. 1 and 2, the database publishing apparatus according to the present embodiment is different from that of the first embodiment in that the master layout generation means 105 is deleted and page style information generation is performed.
[0108]
The configuration and operation of the small group style
[0109]
Next, the DTP unit 102B, the page style
[0110]
The DTP unit 102B has a function of setting one or two or more areas in each page template as well as the function of the DTP unit 102 of the first embodiment.
[0111]
The DTP unit 102B displays a page template screen as shown in FIG. 62, and sets an area on the page template as shown in FIG. 62 by the operator's keyboard or mouse operation. In the example of FIG. 62, four areas (two horizontally long areas on the left side and two vertically long areas on the right side) are set in the page template. The DTP unit 102B outputs the page template data in which the area is set as a part of the DTP data 122B. The other part of the DTP data 122B is the small layout data of the first embodiment.
[0112]
The page style
[0113]
When the operator selects an area displayed on the screen of FIG. 62 and performs a predetermined operation, the page style
[0114]
The page style
[0115]
Further, the page style
[0116]
When the operator selects the "Automatic area size calculation" radio button, the column size field setting items (width and height of the small set and the horizontal and vertical intervals of the small group) and column number field setting items (vertical and horizontal) Set the desired value in (Number of columns) and press the “Automatic calculation” button. Then, the area size is automatically calculated and displayed in the area size column.
[0117]
On the other hand, when the radio button of “automatically calculate subgroup interval” is selected, the operator sets the setting items in the column size column (width and height of the subgroup) and the setting items in the column number column (number of columns in the vertical and horizontal directions). Set the desired value and press the “Automatic calculation” button. Then, the small group interval is automatically calculated and displayed in the column size column.
[0118]
Once the above settings and automatic calculations have been performed and the items in the area origin, area size, column size, and number of columns have been determined, the operator presses the “OK” button to finish parameter settings for that area. To do.
[0119]
When the parameter setting is completed for all areas in the page template and the operator performs a predetermined operation, the page style
[0120]
In the page style information of FIG. 64, the data on the right page of the spread pages is described first, and the data on the left page is described later. However, at this point in time, it is not determined whether the opening is left or right, and the page style information can be applied to both opening methods.
[0121]
The page
[0122]
When the page
[0123]
When the operator selects a desired area on the layout displayed in the right column and performs a predetermined menu operation, the page template generation means 202 displays the screen shown in FIG.
[0124]
In the area information, information (basic small group size, number of columns, small group interval) read from the
[0125]
The operator selects the order of the areas in the combo box of the in-page order. The in-page flow order is the order of areas into which data is flowed in a page.
[0126]
In addition, the operator selects one of the four toggle buttons in the small set pouring direction. The small group flow direction is the order in which data is flowed within an area.
[0127]
The page
[0128]
The page
[0129]
Once the above settings have been made and the in-page flow order, sub-set flow direction, available sub-set styles and basic sub-set styles have been determined, the operator presses the “OK” button to set these items for the area. finish.
[0130]
When the setting of the above items is completed for all the areas in the page template and the operator performs a predetermined operation, the page
[0131]
The page
[0132]
Next, the page template generation means 202 collectively exports one or more page templates registered in the
[0133]
When the menu [File → Export → Page Template Export] shown in FIG. 20 is selected by the operator, the page template generation means 202 displays a dialog box shown in FIG. All page templates registered in the
[0134]
In the page template of FIG. 67, the data on the right page of the spread pages is described first, and the data on the left page is described later. However, at this point in time, it is not determined whether the opening is left or right, and the page template can be applied to both opening methods. Depending on the flow order within the page, it may be substantially determined whether the page template is applied to the right opening or the left opening. For example, if the flow order within the page is random. For example, a page template can be applied to both opening methods.
[0135]
The page template assigning means 203 is activated by following a predetermined menu on the screen shown in FIG. When the page template assigning means 203 is activated, it displays the screen shown in FIG. When the name of the file of the
[0136]
The page template group described in the imported file can be confirmed on the screen shown in FIG.
[0137]
The page template assigning means 203 displays the screen shown in FIG. 72 after importing the
[0138]
The small group arrangement / property allocation means 106B is also activated by following another predetermined menu on the screen shown in FIG. When activated, the small group arrangement / property assignment means 106B displays the screen shown in FIG. The name of the file of the
[0139]
The data displayed on the screen shown in FIG.IIt is possible to replace the default small template template with the small template template that has been moved to the “usable small group style” list box on the screen of FIG. 66 and has been imported in the above procedure. A screen for this replacement is shown in FIG.
[0140]
Note that the small group placement / property allocation means 106B is not limited to the property data and small template registered in the
[0141]
The small group arrangement / property allocating means 106B displays the screen shown in FIG. 75 after importing the
[0142]
When the operator checks the “Specify range” check box in the page designation column, it is possible to designate the start area and the position in the area and the end page, area and the position in the area. On the other hand, if this check box is not checked, only the start area and the position in the area can be designated. The designation of the area follows the in-page flow order, and the position in the area follows the small flow direction.
[0143]
In the start page, the position currently selected on the same screen as in FIG. 77 in the page range specified on the screen in FIG. Since the position indicated by the
[0144]
The reference button in the page specification column is valid only when the “Specify range” check box is checked, and when this button is enabled, if the operator presses this button, sub-group placement and property assignment The means 106B displays the screen shown in FIG. When the operator selects an end page on this screen and presses an “OK” button, the end page is set.
[0145]
Page breaks and page breaks are the same as those in the first embodiment. In addition, timings related to these are the same as those in the first embodiment. The reform area is unique to the second embodiment, and this is to start property allocation from a new area when the contents of the hierarchy designated as the timing change.
[0146]
When the operator checks the “Insert blank cell” check box, when the contents of the hierarchy specified as the timing change, the first cell is blanked in the order according to the small group pouring direction of each area.
[0147]
It should be noted that when page breaks, page break areas or page breaks are made when the contents of the hierarchy designated as the timing change, the number of pages, the number of areas or the number of steps allocated to one category may not be designated.
[0148]
When the operator sets the category, page range, page break, etc. assigned on the screen shown in FIG. 75 and presses the “OK” button, the small group placement / property allocating means 106 B Assign property data to.
[0149]
The small group arrangement / property allocation means 106B also displays the screen shown in FIG.
[0150]
The screen of FIG. 77 reflects the contents set on the screen of FIG. 75. On this screen, the operator changes the classification of each cell, changes the type of the small template assigned to each cell, and the small sets assigned to each cell. It is possible to change the classification, change the property data assigned to each subgroup, and so on.
[0151]
When changing the cell classification, "Heading cell", "Allocated cell" or "Free cell" can be selected as the cell classification. “Heading cell” is a cell for assigning a headline such as a store, “allocation cell” is a cell for assigning property data, and “empty cell” is a cell to which nothing is assigned. The background is displayed in the “empty cell” area. When the “heading cell” or “empty cell” is inserted, the property data is moved down and assigned.
[0152]
The type of the small template assigned to the cell can be changed only for a cell whose classification is “Heading cell” or “Allocated cell”. When changing the type of a small template assigned to a cell, it is included in the file of the
[0153]
The change of the subgroup assigned to a cell is possible for a cell whose classification is “assigned cell”. When changing the sub-group division assigned to the cell, “Heading” or “Property” can be selected.
[0154]
As an example of a special combination, “floating” is assigned to a cell whose “cell classification” is “assignment”, the type of “small group template” is “
[0155]
The table below shows the relationship between the combination of the cell category, small template, and small category and the data displayed in the cell.
[0156]
[Table 1]
As is clear from the above table, a “fixed heading” is set for a cell whose “cell classification” is “heading”. A cell whose “cell classification” is “assignment” and whose “sub-group classification” is “heading” is set to “floating heading” regardless of what sub-group is set in the “sub-group template”. “Property” is set to a cell whose “assignment” is “assignment” and “sub-compartment classification” is “property”, no matter what sub-assembly is set in the “sub-assembly template”. This is because, for example, the computer does not recognize that the small template “midashi1” is a headline template, and that the small template “
[0157]
Depending on the design of the small group, it is possible to fill the cell with the small group name “midashi1” with the data of a store or the like, or it is possible to display only fixed data.
[0158]
A layout view according to the setting on the screen of FIG. 77 is shown in FIG.
[0159]
The small group arrangement / property allocation means 106B is set on the screen of FIG. 75, and the
[0160]
[Embodiment 3]
In the second embodiment, the small
[0161]
In the second embodiment, the page
[0162]
However, in the configuration and operation of the second embodiment described above, the operator must perform export and import, and work efficiency deteriorates. In addition, when handling multiple types of property information publication journals with the same database publishing device, import many types of small template templates and multiple types of page templates, and among them, the small template template required for the current property information publication magazine Since the template is registered in the property database, the work efficiency is deteriorated. Further, the files of one
[0163]
[0164]
78 and 79 show a part of the database publishing apparatus according to the present embodiment. 3, 78, and 79 together constitute the entire database publishing apparatus according to the present embodiment. 78 and 79, the same parts as those of the second embodiment shown in FIGS. 60 and 61 are denoted by the same reference numerals.
[0165]
As apparent from a comparison of FIGS. 78 and 79 with FIGS. 60 and 61, the database publishing apparatus according to the present embodiment is different from that of the first embodiment in that the
[0166]
As is clear from the arrows indicating the signal flow in FIG. 78, the small
[0167]
Further, as is apparent from the arrow indicating the signal flow in FIG. 79, the small group placement / property allocation means 106B uses the small template registered in the
[0168]
The small
[0169]
Next, operations unique to the present invention of the small
[0170]
When the menu [File → Register to database → Register small template] shown in FIG. 80 is selected by the operator, the small template generation means 104C displays a dialog box shown in FIG. All the small templates registered in the
[0171]
Similarly, when the menu [File → Register to database → Register page template] shown in FIG. 80 is selected by the operator, the page template generation means 202C displays a dialog box shown in FIG. All page templates registered in the
[0172]
The page template assigning means 203C is activated by following a predetermined menu on the screen of FIG. When the page template assigning unit 203C is activated, it does not display the screen shown in FIG. 70 but displays the screen shown in FIG. In the page template combo box on this screen, the page template registered in the
[0173]
Note that the page template registered in association with the property information publication magazine currently being handled can be confirmed on the screen shown in FIG. The screen shown in FIG. 83 is obtained when the page template tab at the bottom of the screen is selected.
[0174]
The small group arrangement / property allocation means 106C is also activated by following another predetermined menu on the screen shown in FIG. When activated, the small group arrangement / property allocation means 106C displays the screen shown in FIG. 75 without displaying the screen shown in FIG. Since the operation of the small group arrangement / property allocating unit 106C after this display is the same as that of the small group arrangement / property allocating unit 106B, description thereof is omitted.
[0175]
In addition, the small set template registered in association with the property information publication magazine currently handled can be confirmed on the screen shown in FIG. The screen shown in FIG. 84 is when the small template tab at the bottom of the screen is selected.
[0176]
In addition, by combining the second and third embodiments, the operator can select whether the output destination of the small template is a file of the small template group or the property database, and the page template It may be possible to select whether the output destination is a page template group file or a property database. Further, when combined in this way, the small template generation unit and the page layout generation unit preliminarily register the small template and the page template in the property database on the basis of the third embodiment. And, through the import, the small group arrangement / property allocating unit and the page template allocating unit can additionally register the small group template and the page template in the property database.
[0177]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, the following effects can be obtained.
[0178]
When the small group placement / property allocation means is activated, the small group template has already been registered in the property database in association with the current property information publication by the small template generation means. The means eliminates the need to select a required small template from the small template group. Therefore, when the small set template group includes a large number of small set templates, it is possible to prevent the work efficiency from being lowered due to the selection.
[0179]
Similarly, when the page template assigning means is activated, the page template generating means has already registered the page template in the property database in association with the property information magazine currently being handled. Eliminates the need to select a required page template from the page template group. Therefore, when the page template group includes a large number of page templates, it is possible to prevent the work efficiency from being reduced due to the selection.
[0180]
Further, even when a variety of property information publication magazines are handled with one database publishing software, it is possible to efficiently assign page templates and small set templates to pages.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram (1/3) showing a configuration of a database publishing apparatus according to
FIG. 2 is a block diagram (2/3) showing the configuration of the database publishing apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a block diagram (3/3) showing the configuration of the database publishing apparatus according to the first and second embodiments of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the structure of a property database according to
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a tree structure for managing a filter for extracting a property according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing an example of a small layout created by the DTP unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
7 is a diagram showing small group style information generated by the small group style information generation unit according to the first exemplary embodiment of the present invention based on the small group layout example of FIG. 6; FIG.
FIG. 8 is a diagram showing a hierarchical structure of the small group style information shown in FIG. 7;
FIG. 9 is a flowchart (1/3) showing the operation of the small group style information generating unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 10 is a flowchart (2/3) showing the operation of the small group style information generating unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart (3/3) showing the operation of the small group style information generating unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
12 is a diagram showing a small template generated by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention based on the small group style information shown in FIG. 7; FIG.
FIG. 13 is a diagram showing the structure of an XML document corresponding to the small template shown in FIG. 12 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 14 is a flowchart (1/2) illustrating the operation of the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 15 is a flowchart (2/2) illustrating the operation of the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 16 is a diagram (1/4) illustrating a screen displayed by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 17 is a diagram (2/4) illustrating a screen displayed by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 18 is a diagram (3/4) illustrating a screen displayed by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 19 is a diagram (4/4) showing a screen displayed by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 20 is a diagram showing a screen displaying a menu for exporting a small template or page template according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 21 is a screen for selecting a small template to be exported according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 22 is a diagram of a screen for designating a file storing a small template group to be exported according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 23 is a diagram showing a screen for creating a master layout according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 24 is a diagram showing a screen for creating original data according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 25 is a diagram showing a screen for selecting a filter for extracting property data to be allocated to a target page according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 26 is a diagram showing a screen for determining the order in which the property data to be allocated to the target page according to the first embodiment of the present invention is rearranged.
FIG. 27 is a diagram showing a screen for changing the arrangement of small sets according to the master layout according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 28 is a diagram showing a screen for changing each property assigned to each small group according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 29 is a diagram showing a screen for displaying and changing the type and property of a small group to be allocated to each allocation position on each page according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 30 is a diagram (1/2) illustrating a first example of the XSLT electronic document generated in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 31 is a diagram (2/2) illustrating a first example of the XSLT electronic document generated in the first embodiment of the present invention.
32 is a diagram (1/6) showing a second example of the XSLT electronic document generated simultaneously with the XML electronic document shown in FIG. 38 in the first embodiment of the present invention. FIG.
FIG. 33 is a diagram (2/6) illustrating a second example of the XSLT electronic document generated simultaneously with the XML electronic document illustrated in FIG. 38 in the first embodiment of the present invention.
34 is a diagram (3/6) illustrating a second example of the XSLT electronic document generated simultaneously with the XML electronic document illustrated in FIG. 38 in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 35 is a diagram (4/6) illustrating a second example of the XSLT electronic document generated simultaneously with the XML electronic document shown in FIG. 38 in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 36 is a diagram (5/6) illustrating a second example of the XSLT electronic document generated simultaneously with the XML electronic document shown in FIG. 38 in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 37 is a diagram (6/6) illustrating a second example of the XSLT electronic document generated simultaneously with the XML electronic document shown in FIG. 38 in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 38 is a diagram showing an example of an XML electronic document generated in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 39 is a conceptual diagram showing structures of XSLT electronic documents and XML electronic documents generated according to the first embodiment of the present invention and their relationships;
40 is a diagram (1/5) illustrating the XSLT electronic document generated from the XML electronic document illustrated in FIG. 38 and the XSLT electronic document illustrated in FIGS. 32-37 according to the first embodiment of the present invention. FIG.
FIG. 41 is a diagram (2/5) illustrating the XSLT electronic document generated from the XML electronic document illustrated in FIG. 38 and the XSLT electronic document illustrated in FIGS.
42 is a diagram (3/5) illustrating the XSLT electronic document generated from the XML electronic document illustrated in FIG. 38 and the XSLT electronic document illustrated in FIGS. 32-37 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
43 is a diagram (4/5) illustrating the XSLT electronic document generated from the XML electronic document illustrated in FIG. 38 and the XSLT electronic document illustrated in FIGS. 32 to 37 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
44 is a diagram (5/5) illustrating the XSLT electronic document generated from the XML electronic document illustrated in FIG. 38 and the XSLT electronic document illustrated in FIGS. 32-37 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 45 is a diagram showing the structure of an XML document simply generated from a property database.
FIG. 46 is a diagram (1/5) showing the structure of an XML document corresponding to a small template generated by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 47 is a diagram (2/5) illustrating the structure of an XML document corresponding to a small template generated by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 48 is a diagram (3/5) showing the structure of an XML document corresponding to a small template generated by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 49 is a diagram (4/5) illustrating the structure of an XML document corresponding to a small template generated by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 50 is a diagram (5/5) showing the structure of an XML document corresponding to a small template generated by the small template generation unit according to
51 is a diagram showing a screen displayed by the small template generation unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention, which replaces the diagram shown in FIG.
FIG. 52 is a diagram showing a portion (1/7) of one property of the XML document having the structure shown in FIGS. 46 to 50 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 53 is a diagram showing a part (2/7) of one property of the XML document having the structure shown in FIGS. 46 to 50 according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 54 is a view showing a part (3/7) of one property of the XML document having the structure shown in FIGS. 46 to 50 according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 55 is a diagram showing a part (4/7) of one property of the XML document having the structure shown in FIGS. 46 to 50 according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 56 is a view showing a part (5/7) of one property of the XML document having the structure shown in FIGS. 46 to 50 according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 57 is a view showing a part (6/7) of one property of the XML document having the structure shown in FIGS. 46 to 50 according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 58 is a diagram showing a part (7/7) of one property of the XML document having the structure shown in FIGS. 46 to 50 according to the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 59 is a view showing a screen displaying a page generated by the small group arrangement / property allocating unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 60 is a block diagram (1/3) showing a configuration of a database publishing apparatus according to
FIG. 61 is a block diagram (2/3) showing the configuration of the database publishing apparatus according to
FIG. 62 is a view of a screen displayed by the DTP unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention to set an area in the page template.
FIG. 63 is a view of a screen displayed by the page style information generating unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention for setting area parameters.
FIG. 64 is a diagram showing an example of page style information generated by the page style information generating unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 65 is a diagram of a screen that displays page style information generated by the page style information generating unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 66 is a diagram of a screen displayed by the page template generation unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention to set parameters for each area in the page template.
FIG. 67 is a diagram showing an example of a page template generated by a page template generation unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 68 is a diagram of a screen for selecting a page template to be exported according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 69 is a diagram of a screen for designating a file storing a page template group to be exported according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 70 is a view of a screen for designating a file storing a page template group to be imported according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 71 is a diagram of a screen that displays a page template generated by a page template generation unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 72 is a diagram of a screen displayed by the page template assigning unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 73 is a diagram showing a screen for designating a file for storing a small template group to be imported according to the second embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 74 is a view showing a screen for changing a small template according to the second embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 75 is a diagram of a screen displayed by the small group arrangement / property allocating unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention for property allocation or the like.
76 is a diagram of a screen that is called to set an end page from the screen of FIG. 75. FIG.
77 is a view of a screen displayed by the small group arrangement / property allocating unit according to the second embodiment of the present invention for correcting the small group arrangement and the property allocation. FIG.
FIG. 78 is a block diagram (1/3) showing a configuration of a database publishing apparatus according to
FIG. 79 is a block diagram (2/3) showing the configuration of the database publishing apparatus according to
FIG. 80 is a diagram of a screen displaying a menu for registering a small template or page template in the property database according to
FIG. 81 is a diagram of a screen for selecting a small template to be registered in the property database according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 82 is a diagram of a screen for selecting a page template to be registered in the property database according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 83 is a diagram of a screen for confirming a page template registered in the property database according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 84 is a diagram of a screen for confirming a small template registered in the property database according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
[Explanation of symbols]
101 Database creation means
102 DTP means
103 Small group style information generation means
104, 104C Small template generation means
105 Master layout generation means
106, 106B, 106C Small group placement / property allocation means
107 XSLT document generation means
108 XSLT processor
109, 110 XSL-FO processor
133 Project file
201 Page style information generation means
202, 202C Page template generation means
203, 203C Page template assigning means
Claims (15)
Translated fromJapaneseコンピュータが、CPUを用いて、小組についてのDTP(Desk Top Publishing)データを基に小組についてのXSL−FO文書形式の小組スタイル情報であって、前記DTPデータの属性が反映された小組スタイル情報を生成し、生成された小組スタイル情報を記録媒体に書き込むステップと、
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記小組スタイル情報を前記記録媒体から読み出し、小組についての前記小組スタイル情報に含まれる実データをパラメータ化することにより、小組の様式が記述され、更に、該小組にデータが挿入されるべき物件を特定できる情報と特定された物件の該小組に挿入されるべきデータとが前記物件データベースを表すXML文書のXPATHとして記述され、更に、該小組の位置が仮引数として記述されたXSLT文書形式の小組テンプレートを生成し、前記記録媒体に書き込むステップと、
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記小組テンプレートを複数の前記物件が登録された物件データベースに登録するステップと、
を有することを特徴とする物件データベース生成方法。In a property database generation method for generating a property database including a small template that is embedded in an electronic document for typesetting for printing on paper or displaying the property data recorded on the property database,
Using theCPU, the computeruses the DTP (Desk Top Publishing) data forthe small groupto generate the XSL-FO document format small group style information that reflects the attributes of the DTP data. Generatingand writing the generated sub-style information to a recording medium ;
Computer,using the CPU, reading out the subassembly style information from the recording medium, by parameters of the actual data contained in the subassembly style information for small sets, small sets manner is described,further, to the small group Informationthat can specify the property into which the data is to be inserted and data to be inserted into the small set of the specified property aredescribed as XPATH of an XML document representing the property database, and the position ofthe small set is used as a formal argument. Generatinga written XSLT document format sub-template andwriting to the recording medium ;
A step of registering the small template in a property database in which a plurality of the properties are registeredusing a CPU ;
A property database generation method characterized by comprising:
請求項1に記載の物件データベース生成方法の各ステップと、
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てるステップと、
を有することを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング方法。In a database publishing method for generating an electronic document for composition for printing on paper or displaying the property data recorded in the property database,
Each step of the property database generation method according to claim 1;
A computerusing a CPU to assign a page template that is registered in the property database and is usable in a page template assigned to a page;
A database publishing method comprising:
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記ページテンプレートにおいて使用可能な小組テンプレートを選択して、選択した小組テンプレートを前記ページテンプレートに割り当てるステップと、
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた前記ページテンプレートを前記物件データベースに登録するステップと、
を有し、
前記物件データベースに登録された小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てるステップは、前記物件データベースに登録されている前記ページテンプレートを用いて行われることを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング方法。The database publishing method according to claim 2.
A computerusing a CPU to select a subset template usable in the page template and assigning the selected subset template to the page template;
A step of registering the page template to which a usable sub-template is assigned to the property databaseusing a CPU ;
Have
The step of assigning to a page a page template assigned to a page that is a small template registered in the property database is performed using the page template registered in the property database. A database publishing method characterized by the above.
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、1又は2以上の前記小組テンプレートを含む小組テンプレート群のファイルを生成し、生成されたファイルを記録媒体に書き込むステップを有することを特徴とする物件データベース生成方法。In the property database generation method according to claim 1,
A property database generation method, comprising: a computerusing a CPU to generate a file of a small template group including one or more of the small template templates,and writing the generated file to a recording medium .
請求項4に記載の物件データベース生成方法の各ステップと、
コンピュータが、前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているもの又は前記小組テンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てるステップと、
を有することを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング方法。In a database publishing method for generating an electronic document for composition for printing on paper or displaying the property data recorded in the property database,
Each step of the property database generation method according to claim 4,
The computer is the small set template registered in the property database, which is usable in the page template assigned to the page, or the small set template included in the file of the small set template group. Assigning to a page what is available in the assigned page template;
A database publishing method comprising:
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記ページテンプレートにおいて使用可能な小組テンプレートを選択して、選択した小組テンプレートを前記ページテンプレートに割り当てるステップと、
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた前記ページテンプレートを前記物件データベースに登録するステップと、
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた1又は2以上の前記ページテンプレートを含むページテンプレート群のファイルを生成し、生成されたファイルを記録媒体に書き込むステップと、
を有し、
前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているもの又は前記小組テンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てるステップは、前記物件データベースに登録されている前記ページテンプレート又は前記ページテンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記ページテンプレートを用いて行われることを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング方法。The database publishing method according to claim 5.
A computerusing a CPU to select a subset template usable in the page template and assigning the selected subset template to the page template;
A step of registering the page template to which a usable sub-template is assigned to the property databaseusing a CPU ;
A computerusing a CPU to generate a file of a page template group including one or more of the page templates towhich a usable short template is assigned,and writing the generated file to a recording medium ;
Have
The small group template registered in the property database and usable in the page template allocated to the page, or the small group template included in the small group template file and the page allocated to the page The step of assigning a usable page in a template to a page is performed using the page template included in the page template or the file of the page template group registered in the property database. Database publishing method.
小組についてのDTP(Desk Top Publishing)データを基に小組についてのXSL−FO文書形式の小組スタイル情報であって、前記DTPデータの属性が反映された小組スタイル情報を生成する手段と、
小組についての前記小組スタイル情報に含まれる実データをパラメータ化することにより、小組の様式が記述され、更に、該小組にデータが挿入されるべき物件を特定できる情報と特定された物件の該小組に挿入されるべきデータとが前記物件データベースを表すXML文書のXPATHとして記述され、更に、該小組の位置が仮引数として記述されたXSLT文書形式の小組テンプレートを生成する手段と、
前記小組テンプレートを複数の前記物件が登録された物件データベースに登録する手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする物件データベース生成装置。In the property database generation device for generating a property database including a small template that is embedded in an electronic document for typesetting for printing the property data recorded on the paper or displaying it on a screen.
Means for generating small group style information in the XSL-FO document format for the small group based on DTP (Desk Top Publishing) data for the small group, and reflecting the attribute of the DTP data;
By parameterizing the actual data included in the small group style information for the small group, the format of the small group is described, and further, informationthat can specify the property into which data is to be inserted into the small group and the small group of the identified property Means for generating a XSLT document format sub-set template in which the data to be inserted into isdescribed as XPATH of an XML document representing the property database, and the position of the sub-set is described as a dummy argument;
Means for registering the small template in a property database in which a plurality of the properties are registered;
A property database generation device comprising:
請求項7に記載の物件データベース生成装置の各手段と、
前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てる手段と、
を備えることを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング装置。In a database publishing device for generating electronic documents for typesetting for printing property data recorded in the property database on paper or displaying it on the screen,
Each means of the property database generation device according to claim 7;
Means for allocating to the page the set template registered in the property database and usable in the page template assigned to the page;
A database publishing apparatus comprising:
前記ページテンプレートにおいて使用可能な小組テンプレートを選択して、選択した小組テンプレートを前記ページテンプレートに割り当てる手段と、
使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた前記ページテンプレートを前記物件データベースに登録する手段と、
を備え、
前記物件データベースに登録された小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てる手段は、当該割当てを前記物件データベースに登録されている前記ページテンプレートを用いて行うことを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング装置。The database publishing apparatus according to claim 8.
Means for selecting a subset template usable in the page template and assigning the selected subset template to the page template;
Means for registering in the property database the page template to which a usable sub-template is assigned;
With
The means for allocating a small template registered in the property database, which is usable in the page template allocated to the page, to the page uses the page template registered in the property database. A database publishing apparatus characterized in that:
1又は2以上の前記小組テンプレートを含む小組テンプレート群のファイルを生成する手段を備えることを特徴とする物件データベース生成装置。In the property database generation device according to claim 7,
A property database generation device comprising means for generating a file of a small template group including one or two or more small templates.
請求項10に記載の物件データベース生成装置の各手段と、
前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているもの又は前記小組テンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てる手段と、
を備えることを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング装置。In a database publishing device for generating electronic documents for typesetting for printing property data recorded in the property database on paper or displaying it on the screen,
Each means of the property database generation device according to claim 10,
The small group template registered in the property database and usable in the page template allocated to the page, or the small group template included in the file of the small group template and the page allocated to the page A means of assigning what is enabled in the template to the page;
A database publishing apparatus comprising:
前記ページテンプレートにおいて使用可能な小組テンプレートを選択して、選択した小組テンプレートを前記ページテンプレートに割り当てる手段と、
使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた前記ページテンプレートを前記物件データベースに登録する手段と、
使用可能な小組テンプレートが割り当てられた1又は2以上の前記ページテンプレートを含むページテンプレート群のファイルを生成する手段と、
を有し、
前記物件データベースに登録された前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているもの又は前記小組テンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記小組テンプレートであってページに割り当てたページテンプレートにおいて使用可能とされているものをページに割り当てる手段は、当該割当てを前記物件データベースに登録されている前記ページテンプレート又は前記ページテンプレート群のファイルに含まれている前記ページテンプレートを用いて行うことを特徴とするデータベースパブリッシング装置。The database publishing apparatus according to claim 11.
Means for selecting a subset template usable in the page template and assigning the selected subset template to the page template;
Means for registering in the property database the page template to which a usable sub-template is assigned;
Means for generating a file of page template groups including one or more of the page templates assigned with usable sub-templates;
Have
The small group template registered in the property database and usable in the page template allocated to the page, or the small group template included in the small group template file and the page allocated to the page The means for allocating what can be used in a template to a page is performed using the page template included in the page template or the file of the page template group registered in the property database. A database publishing apparatus.
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、小組についてのDTP(Desk Top Publishing)データを基に小組についてのXSL−FO文書形式の小組スタイル情報であって、前記DTPデータの属性が反映された小組スタイル情報を生成し、生成された小組スタイル情報を記録媒体に書き込むステップと、
コンピュータが、CPUを用いて、前記小組スタイル情報を前記記録媒体から読み出し、小組についての前記小組スタイル情報に含まれる実データをパラメータ化することにより、小組の様式が記述され、更に、該小組にデータが挿入されるべき物件を特定できる情報と特定された物件の該小組に挿入されるべきデータとが前記物件データベースを表すXML文書のXPATHとして記述され、更に、該小組の位置が仮引数として記述されたXSLT文書形式の小組テンプレートを生成するステップと、
を有することを特徴とする小組テンプレート生成方法。In a small template generation method for generating a small template to be embedded in an electronic document for typesetting for printing the property data recorded in the property database on paper or displaying it on the screen,
Using theCPU, the computeruses the DTP (Desk Top Publishing) data forthe small groupto generate the XSL-FO document format small group style information that reflects the attributes of the DTP data. Generatingand writing the generated sub-style information to a recording medium ;
The computerreads out the small group style information from the recording medium using theCPU, and parameterizes the actual data included in the small group style information forthe small group. Informationthat can specify the property into which the data is to be inserted and data to be inserted into the small set of the specified property aredescribed as XPATH of an XML document representing the property database, and the position ofthe small set is used as a formal argument. Generating a described XSLT document format sub-set template;
A small template generation method characterized by comprising:
コンピュータが、小組についてのDTP(Desk Top Publishing)データを基に小組についてのXSL−FO文書形式の小組スタイル情報であって、前記DTPデータの属性が反映された小組スタイル情報を生成する手段と、
コンピュータが、小組についての前記小組スタイル情報に含まれる実データをパラメータ化することにより、小組の様式が記述され、更に、該小組にデータが挿入されるべき物件を特定できる情報と特定された物件の該小組に挿入されるべきデータとが前記物件データベースを表すXML文書のXPATHとして記述され、更に、該小組の位置が仮引数として記述されたXSLT文書形式の小組テンプレートを生成する手段と、
を有することを特徴とする小組テンプレート生成装置。In a small set template generation device for generating a small set template to be embedded in an electronic document for typesetting for printing on paper or displaying the property data recorded in the property database,
Means for generating, in accordance with DTP (Desk Top Publishing) data for a small group, small group style information in the XSL-FO document format for the small group, which reflects the attribute of the DTP data;
The computer specifies the actual data included in the small group style information for the small group, so that the format of the small group is described, and further, the property identified as informationthat can identify the property into which the data is to be inserted. Means for generating a XSLT document format subset template in which the data to be inserted intothe subset is described as an XPATH of an XML document representing the property database, and the positionof the subset is described as a dummy argument;
A small template generating apparatus characterized by comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002299080AJP4627962B2 (en) | 2002-10-11 | 2002-10-11 | Database publishing method and apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002299080AJP4627962B2 (en) | 2002-10-11 | 2002-10-11 | Database publishing method and apparatus |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008016434ADivisionJP2008112472A (en) | 2008-01-28 | 2008-01-28 | Database publishing method and apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004133784A JP2004133784A (en) | 2004-04-30 |
| JP4627962B2true JP4627962B2 (en) | 2011-02-09 |
Family
ID=32288318
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002299080AExpired - Fee RelatedJP4627962B2 (en) | 2002-10-11 | 2002-10-11 | Database publishing method and apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4627962B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9229231B2 (en) | 2011-12-07 | 2016-01-05 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Updating printed content with personalized virtual data |
| US9183807B2 (en)* | 2011-12-07 | 2015-11-10 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Displaying virtual data as printed content |
| US9182815B2 (en) | 2011-12-07 | 2015-11-10 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Making static printed content dynamic with virtual data |
| US9165381B2 (en) | 2012-05-31 | 2015-10-20 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Augmented books in a mixed reality environment |
- 2002
- 2002-10-11JPJP2002299080Apatent/JP4627962B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004133784A (en) | 2004-04-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9430455B2 (en) | Methods and systems for intelligent form-filling and electronic document generation | |
| JP4633137B2 (en) | Automatic layout and formatting of content for media design | |
| US7124398B2 (en) | Rapid GUI refacing of a legacy application | |
| US20020152189A1 (en) | Process and system for providing a table view of a form layout for a database | |
| US20040189716A1 (en) | System and method for designing electronic forms and hierarchical schemas | |
| US20030079177A1 (en) | Automatic layout of content in a design for a medium | |
| JPH04503881A (en) | Document management and creation system | |
| JP2009217831A (en) | Additional data generating method, additional data generating device, additional data generating program, and recording medium recording the program | |
| US20050193334A1 (en) | Layout system, layout apparatus, layout program, template selection program, storage medium having stored therein layout program, and storage medium having stored therein template selection program, as well as layout method | |
| CN109948133B (en) | Data form realization method based on Layu | |
| JP4627962B2 (en) | Database publishing method and apparatus | |
| JP3910048B2 (en) | Database publishing method and apparatus | |
| JP5289851B2 (en) | Data management apparatus, data management method, program, and computer-readable recording medium | |
| CN117688921A (en) | Method for unifying format and personalized data setting of automatically generated ppt | |
| KR100658029B1 (en) | Computer-readable recording media for recording document writing programs, document writing systems and document writing methods | |
| JP2008112472A (en) | Database publishing method and apparatus | |
| CN115859933A (en) | Digital certificate service development system and method | |
| JP2008112473A (en) | Database publishing method and apparatus | |
| JP6817523B2 (en) | Information processing device, control method of information processing device, and program | |
| JP2006244283A (en) | Database management apparatus and database management method | |
| JP4828318B2 (en) | Multiple form integrated printing method, system and program | |
| WO2016133153A2 (en) | Information management device, and file management method | |
| JP2003345782A (en) | Method and device for publishing database | |
| JP2004213636A (en) | Media production information system | |
| JP3677852B2 (en) | Document processing method and apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20051005 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20070706 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20070710 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20070904 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20071128 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20080128 | |
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date:20080207 | |
| A912 | Removal of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date:20080321 | |
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date:20100323 | |
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20101109 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131119 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |