JP4405351B2 - Billing management program and image forming apparatus - Google Patents
Billing management program and image forming apparatusDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4405351B2 JP4405351B2JP2004270240AJP2004270240AJP4405351B2JP 4405351 B2JP4405351 B2JP 4405351B2JP 2004270240 AJP2004270240 AJP 2004270240AJP 2004270240 AJP2004270240 AJP 2004270240AJP 4405351 B2JP4405351 B2JP 4405351B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- service
- billing
- slip
- class
- charge
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Control Or Security For Electrophotography (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、利用者の要求に応じ有料サービスを提供するサービス提供装置またはサービス提供装置と通信可能な課金管理装置に搭載され、利用者によりサービス提供装置に要求されたサービスのサービス料金を算出する課金管理プログラムおよび画像形成装置に関するものである。 The present invention is mounted on a service providing apparatus that provides a paid service in response to a user's request or a charging management apparatus that can communicate with the service providing apparatus, and calculates a service fee for a service requested by the user to the service providing apparatus. The present invention relates to a charge management program and an image forming apparatus.
従来、プリンタ、コピーおよびスキャナなどの複数の機能を一つの筐体内に収納した複合機が知られている。かかる複合機では、UNIX(R)などの汎用OS上に、プリンタアプリ、コピーアプリおよびスキャナアプリと呼ばれる複数のアプリケーションを搭載し、これらのアプリケーションの実行処理を切替えながら複数の機能を実現していた。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, there has been known a multi-function machine in which a plurality of functions such as a printer, a copy, and a scanner are stored in a single casing. In such a multifunction device, a plurality of applications called a printer application, a copy application, and a scanner application are mounted on a general-purpose OS such as UNIX (R), and a plurality of functions are realized while switching execution processes of these applications. .
ところが、上記プリンタアプリ、コピーアプリおよびスキャナアプリは、それぞれエンジン制御、メモリ制御およびシステム制御などを別個におこなっているので、重複処理という無駄が生じていた。 However, since the printer application, the copy application, and the scanner application perform engine control, memory control, system control, and the like separately, wasteful duplication processing has occurred.
このため、特許文献1では、複合機に搭載される複数のアプリケーションがそれぞれ担っていたエンジン制御、メモリ制御およびシステム制御などの処理を共通処理部分(プラットホーム)として各アプリケーションから括り出すことにより、アプリケーションの開発効率の向上を図っている。 For this reason, in
また、特許文献2では、ファックス機能を使用した際に発生する通信回線使用料金をテーブルデータとして記憶し、ファックス機能の提供にともなって発生するプリンタ機能の提供料金と、かかる通信回線使用料金とを加算することで、ファックス機能を提供する際の課金をおこなうこととしている。 In
しかしながら、この特許文献1で開示されている発明は、ハードウェアを制御する処理部分を共通化するものであり、各アプリケーションの内部処理全般を共通化するものではない。このため、複合機上のアプリケーションには、開発効率の向上を図るうえで改善の余地が残されている。 However, the invention disclosed in
たとえば、オペレーションパネル制御ソフトウェアやネットワーク制御ソフトウェアを介して、コピーサービスなどの機能提供要求を受け付け、提供する機能に応じた課金をおこなう課金処理は、複写機上の各アプリケーションに共通して存在する処理であるが、ハードウェアを直接制御する処理ではないため各アプリケーションで別個に実現されており、共通化することが可能である。 For example, a billing process that accepts a function provision request such as a copy service via the operation panel control software or network control software and charges according to the provided function is a process that is common to each application on the copier However, since it is not a process for directly controlling the hardware, it is realized separately for each application and can be shared.
また、特許文献2で開示されている発明は、複合機上の複数の機能を組み合わせたサービスについての課金処理に関するものであり、複数の課金処理を並行しておこなうことを考慮したものではない。したがって、複合機が複数のサービス要求を受け付け、各サービス要求に対する課金処理をおこなう場合には、各課金処理を正確に管理することが困難となり、課金処理が正しくおこなわれず、二重課金や未課金といった課金ミスが発生する可能性が高くなるおそれがある。 The invention disclosed in
これらのことから、複合機に搭載されるアプリケーションの課金処理をいかにして効率よく実現するかが大きな課題となっている。なお、かかる課題は複合機についてのみ生じるものではなく、たとえば、有料サービスに対する課金をおこなう課金管理装置を形成するような場合にも同様に生ずる課題である。 For these reasons, it has become a big issue how to efficiently implement the accounting process of the application installed in the multifunction peripheral. Note that such a problem does not occur only for the multi-function peripheral, but also occurs when, for example, a charging management apparatus that charges a fee-based service is formed.
本発明は、上述した従来技術による問題点を解消するためになされたものであり、課金処理を効率よく実現することができる課金管理プログラムおよび画像形成装置を提供することを目的とする。 SUMMARY An advantage of some aspects of the invention is that it provides a charge management program and an image forming apparatus capable of efficiently realizing charge processing.
上述した課題を解決し、目的を達成するために、請求項1の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、利用者の要求に応じ有料サービスを提供するサービス提供装置または前記サービス提供装置と通信可能な課金管理装置に搭載され、利用者により前記サービス提供装置に要求されたサービスのサービス料金を算出する課金管理プログラムであって、前記サービス提供装置の制御プログラムからサービス要求内容を含むサービス要求通知を受信したならば、前記サービス要求内容および伝票状態を含む注文伝票データを生成して保持し、前記サービス提供装置の制御プログラムからサービス完了通知を受信したならば、前記伝票状態をサービス提供完了状態に更新するとともに課金の実行を担当する課金装置に課金を指示し、前記課金装置から課金完了通知を受信したならば、前記伝票状態を課金完了状態に更新する手段としてコンピュータを機能させることを特徴とする。 In order to solve the above-described problems and achieve the object, a billing management program according to a first aspect of the present invention provides a service providing apparatus that provides a paid service in response to a user's request or a charge that can communicate with the service providing apparatus. A billing management program that is installed in a management device and calculates a service charge for a service requested by the user to the service providing device, and receives a service request notification including a service request content from the control program of the service providing device If so, the order slip data including the service request contents and the slip state is generated and held, and when the service completion notification is received from the control program of the service providing apparatus, the slip state is updated to the service provision completed state. In addition, the charging device in charge of charging is instructed to be charged and charged from the charging device. Upon receiving the completion notification, and characterized by causing a computer to function as means for updating the slip state to the charging completion state.
また、請求項2の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、請求項1の発明において、前記サービス要求通知を受信する注文係手段と、前記注文伝票データと1対1に対応して生成され、前記サービス完了通知を受信する伝票手段と、前記サービス料金を算出して前記課金装置に課金を指示し、前記課金完了通知を受信する会計手段とを備え、前記注文係手段は、前記サービス要求通知を受信した際に、前記伝票手段を生成して木構造の子として管理し、前記伝票手段は、前記注文伝票データを保持し、前記伝票状態が前記サービス提供完了状態となった際に、前記会計手段に課金処理を依頼し、前記会計手段は、前記伝票手段から課金処理を依頼された際に、前記サービス料金を算出して該サービス料金の課金を課金装置に指示し、前記課金完了通知を受信した際に、前記伝票手段に前記伝票状態を前記課金完了状態に遷移させるよう指示することを特徴とする。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided a billing management program according to the first aspect of the invention, wherein the ordering means for receiving the service request notification and the order slip data are generated in one-to-one correspondence with the service Slip means for receiving a completion notice; accounting means for calculating the service charge and instructing the billing device to charge and receiving the charge completion notice; and the order clerk means receives the service request notice The slip means is generated and managed as a child of a tree structure, and the slip means holds the order slip data, and the accounting means when the slip state becomes the service provision completed state. The accounting means calculates the service fee and instructs the charging device to charge the service fee when the billing device requests the billing process. Upon receiving the notification, characterized in that it instructs to shift the slip state to the slip means to the charging completion state.
また、請求項3の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、請求項2の発明において、前記課金装置と一対一に対応して生成される課金対象手段をさらに備え、前記課金対象手段は、該課金装置の残金を照会する残金照会操作と、該課金装置に課金実行を指示する課金操作とを含むことを特徴とする。 According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided a billing management program according to the second aspect of the present invention, further comprising billing target means generated in one-to-one correspondence with the billing device, wherein the billing target means is the billing device. A remaining amount inquiry operation for inquiring about the remaining amount of the remaining amount, and a charging operation for instructing the charging apparatus to execute charging.
また、請求項4の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、請求項2または3の発明において、提供するサービスの単価一覧を保持し、前記会計手段の求めに応じ該当するサービスの単価を検索し該単価を応答する料金表手段をさらに備えたことを特徴とする。 According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, the charge management program according to the second or third aspect of the invention holds a unit price list of services to be provided, searches for the unit price of the corresponding service according to the request of the accounting means, and Is further provided with charge table means for responding to
また、請求項5の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、請求項2、3または4の発明において、前記会計手段の求めに応じ前記課金対象手段を一つ以上選択し選択結果を応答する課金対象決定手段をさらに備えたことを特徴とする。 According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a billing management program according to the second, third, or fourth aspect, wherein a billing object determination is made to select one or more billing target means and respond to a selection result in response to a request from the accounting means. The apparatus further includes means.
また、請求項6の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、請求項2〜5の発明において、前記注文係手段は、前記伝票手段を生成する際に、該伝票手段に前記サービス提供内容を通知し、サービス提供の中止依頼を受信した際に、該伝票手段にサービス提供中止を通知することを特徴とする。 The billing management program according to the invention of
また、請求項7の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、請求項2〜6の発明において、前記伝票手段の集計処理をおこなう集計手段をさらに備え、前記集計手段は、前記伝票手段が保持するデータを記録し、集計依頼を受け付けた際に、記録したデータを所定の形式で集計することを特徴とする。 According to a seventh aspect of the present invention, there is provided a billing management program according to the second to sixth aspects of the present invention, further comprising a totaling unit that performs a totaling process of the slip unit, wherein the totaling unit stores data held by the slip unit. When the recording request is received, the recorded data is totaled in a predetermined format.
また、請求項8の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、請求項1の発明において、前記注文伝票データを生成した際に、前記サービス料金を算出して前記課金装置に残金照会をおこない、残金が該サービス料金よりも小さい場合には、前記サービス提供装置にサービス提供を拒否するよう指示することを特徴とする。 Further, in the invention according to
また、請求項9の発明にかかる課金管理プログラムは、請求項2〜7の発明において、前記会計手段は、前記伝票手段から前記残金照会を依頼された際に、前記サービス料金を算出するとともに前記課金装置に前記残金照会をおこない、残金が該サービス料金よりも小さい場合には、前記サービス提供装置にサービス提供を拒否するよう指示することを特徴とする。 According to a ninth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a billing management program according to any one of the second to seventh aspects, wherein the accounting unit calculates the service fee when requested to make the balance inquiry from the slip unit. The remaining amount is inquired to the billing device, and if the remaining amount is smaller than the service fee, the service providing device is instructed to refuse service provision.
また、請求項10の発明にかかる画像形成装置は、利用者により要求されたサービスのサービス料金を算出し、該サービス料金の課金実行を課金装置に指示する画像形成装置であって、制御プログラムからサービス要求内容を含むサービス要求通知を受信したならば、前記サービス要求内容および伝票状態を含む注文伝票データを生成して保持し、前記制御プログラムからサービス完了通知を受信したならば、前記伝票状態をサービス提供完了状態に更新するとともに前記課金装置に課金を指示し、前記課金装置から課金完了通知を受信したならば、前記伝票状態を課金完了状態に更新する手段を備えたことを特徴とする。 An image forming apparatus according to a tenth aspect of the present invention is an image forming apparatus that calculates a service fee of a service requested by a user and instructs the charging device to perform charging of the service fee. If a service request notification including a service request content is received, order slip data including the service request content and a slip state is generated and held. If a service completion notification is received from the control program, the slip state is updated. The service provision completion state is updated, the billing device is instructed to be billed, and when a billing completion notification is received from the billing device, the voucher state is updated to a billing completion state.
請求項1にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、サービス提供装置の制御プログラムからサービス要求内容を含むサービス要求通知を受信したならば、サービス要求内容および伝票状態を含む注文伝票データを生成して保持し、サービス提供装置の制御プログラムからサービス完了通知を受信したならば、伝票状態をサービス提供完了状態に更新するとともに課金の実行を担当する課金装置に課金を指示し、課金装置から課金完了通知を受信したならば、伝票状態を課金完了状態に更新する手段としてコンピュータを機能させるよう構成したので、複数のサービス要求を並行処理する場合であっても課金状態を正確に管理できるので、課金処理を効率よく実現することができるという効果を奏する。 According to the billing management program of
また、請求項2にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、サービス要求通知を受信する注文係手段と、注文伝票データと1対1に対応して生成され、サービス完了通知を受信する伝票手段と、サービス料金を算出して課金装置に課金を指示し、課金完了通知を受信する会計手段とを備え、注文係手段は、サービス要求通知を受信した際に、伝票手段を生成して木構造の子として管理し、伝票手段は、注文伝票データを保持し、伝票状態がサービス提供完了状態となった際に、会計手段に課金処理を依頼し、会計手段は、伝票手段から課金処理を依頼された際に、サービス料金を算出してサービス料金の課金を課金装置に指示し、課金完了通知を受信した際に、伝票手段に伝票状態を課金完了状態に遷移させる指示をおこなうよう構成したので、各手段の協調関係により、課金処理を効率よく実現することができるという効果を奏する。 According to the billing management program of
また、請求項3にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、課金装置と一対一に対応して生成される課金対象手段をさらに備え、課金対象手段は、課金装置の残金を照会する残金照会操作と、課金装置に課金実行を指示する課金操作とを含むよう構成したので、課金装置の追加や取り外しにも容易に対応することができるという効果を奏する。 The billing management program according to
また、請求項4にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、提供するサービスの単価一覧を保持し、会計手段の求めに応じ該当するサービスの単価を検索し単価を応答する料金表手段をさらに備えるよう構成したので、サービスを提供する機能が異なる場合であっても、共通した課金処理を実現することができるという効果を奏する。 In addition, the billing management program according to
また、請求項5にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、会計手段の求めに応じ課金対象手段を一つ以上選択し選択結果を応答する課金対象決定手段をさらに備えるよう構成したので、複数の課金装置に対して課金実行を指示することができるという効果を奏する。 According to the billing management program of
また、請求項6にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、注文係手段は、伝票手段を生成する際に、伝票手段にサービス提供内容を通知し、サービス提供の中止依頼を受信した際に、伝票手段にサービス提供中止を通知するよう構成したので、課金管理処理の開始および中止を伝票手段の動作に対応づけることにより、課金処理を効率よく実現することができるという効果を奏する。 According to the billing management program of
また、請求項7にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、伝票手段の集計処理をおこなう集計手段をさらに備え、集計手段は、伝票手段が保持するデータを記録し、集計依頼を受け付けた際に、記録したデータを所定の形式で集計するよう構成したので、伝票手段が保持するデータの集計を効率良く実現することができるという効果を奏する。 The accounting management program according to
また、請求項8にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、注文伝票データを生成した際に、サービス料金を算出して課金装置に残金照会をおこない、残金がサービス料金よりも小さい場合には、サービス提供装置にサービス提供を拒否する指示をおこなうよう構成したので、サービス提供に先立って、あらかじめ課金実行の可否を確認することができるという効果を奏する。 According to the billing management program of
また、請求項9にかかる課金管理プログラムによれば、会計手段は、伝票手段から残金照会を依頼された際に、サービス料金を算出するとともに課金装置に残金照会をおこない、残金がサービス料金よりも小さい場合には、サービス提供装置にサービス提供を拒否する指示をおこなうよう構成したので、各手段の協調関係により、サービス提供に先立って、あらかじめ課金実行の可否を確認することができるという効果を奏する。 According to the billing management program of
また、請求項10にかかる画像形成装置は、制御プログラムからサービス要求内容を含むサービス要求通知を受信したならば、サービス要求内容および伝票状態を含む注文伝票データを生成して保持し、制御プログラムからサービス完了通知を受信したならば、伝票状態をサービス提供完了状態に更新するとともに課金装置に課金を指示し、課金装置から課金完了通知を受信したならば、伝票状態を課金完了状態に更新する手段を備えるよう構成したので、複数のサービス要求を並行処理する場合であっても課金状態を正確に管理できるので、課金処理を効率よく実現することができるという効果を奏する。 The image forming apparatus according to
以下に添付図面を参照して、この発明にかかる課金管理プログラム、およびこのプログラムを実行させるためのコンピュータを含んだ画像形成装置の最良な実施の形態を詳細に説明する。なお、本実施の形態では、この発明を画像形成装置に適用した場合について説明するが、本発明はこれに限らず、課金管理をおこなう各種装置に適用することができる。 Exemplary embodiments of an accounting management program according to the present invention and an image forming apparatus including a computer for executing the program will be described below in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. In this embodiment, the case where the present invention is applied to an image forming apparatus will be described. However, the present invention is not limited to this and can be applied to various apparatuses that perform billing management.
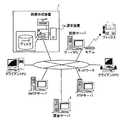
まず、本実施の形態に係る画像形成装置(以下「複合機」と言う)1の概要について図1、図2、図3、図14および図15を用いて説明する。図1は、本実施の形態に係る複合機1を取り巻くネットワーク環境を説明するためのネットワーク図であり、図2は、図1に示した複合機1のハードウェア構成を示すブロック図であり、図3は、図1に示した複合機1のソフトウェアとハードウェアの関係を説明するための説明図であり、図14は、複合機1に搭載されるソフトウェア構成の変遷を説明するための説明図であり、図15は、従来の複合機のソフトウェアとハードウェアの関係を説明するための説明図である。 First, an outline of an image forming apparatus (hereinafter referred to as “multifunction machine”) 1 according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 1, 2, 3, 14, and 15. FIG. 1 is a network diagram for explaining a network environment surrounding the
図1に示すように、近年のネットワーク化の進展により、オフィスなどに設けられたパーソナルコンピュータ(PC)などの機器は、LAN(Local Area Network)などのネットワークに接続され、相互に通信することが通常となった。たとえば、同図に示したように、かかるネットワークには、クライアントPC、SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)サーバ、FTP(File Transfer Protocol)サーバ、課金サーバ2、サーバPCなどが接続され、電子メールの送受信やファイル転送をすることができ、モデム接続された配信サーバは、オフィス外のファックス装置と通信することができる。 As shown in FIG. 1, with the recent progress of networking, devices such as personal computers (PCs) provided in offices are connected to a network such as a LAN (Local Area Network) and can communicate with each other. It became normal. For example, as shown in the figure, a client PC, an SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) server, an FTP (File Transfer Protocol) server, an
このようなネットワーク化の進展に伴い、複合機1もかかるネットワークに接続され、PC等の機器と相互に通信することが可能となり、ハードディスク等の記憶装置を内蔵することで、いわゆるネットワーク複合機へと進化し、ユーザの様々なニーズに応えることができるようになった。 With the progress of such networking, the
たとえば、複合機1は、通常のコピー機能に加えて、クライアントPCからの印刷要求により文書データ等を印刷するプリンタ機能、クライアントPCからのファックス要求により文書データ等をサーバPCに接続されたモデムを経由して他のオフィスのファックス機器に送信するファックス機能、受信したファックス文書やコピー文書を内蔵したハードディスクに蓄積する蓄積機能などを有するようになった。 For example, in addition to the normal copy function, the
また、複合機1は、課金装置1aなどの複合機1本体に直接接続される装置を用いて課金処理をおこなうことに加えて、ネットワークを介して接続される課金サーバ2を用いて課金処理をおこなうことができるようになった。ここで、課金装置1aは、料金徴収用のコインラック装置や、事後的な料金徴収のためにコピー等の使用量を記録するプリセットキーカード装置や、クレジットカード装置といった装置であり、課金サーバ2は、事後的な料金徴収をおこなうために、課金データを管理する装置である。 Further, the
こうして複合化とネットワーク化の進展により必要となった多くの機能を実現するため、複合機1に搭載されるソフトウェアは、規模が大きく、複雑なものとなっている。そして、それにともなって、それらのソフトウェアの開発と維持管理のための工数も大幅に増大している。 In this way, in order to realize many functions required by the progress of compounding and networking, the software installed in the
図2は、かかる複合機1のハードウェア構成を示すブロック図である。同図に示すように、この複合機1は、コントローラ10とエンジン部(Engine)60とをPCI(Peripheral Component Interconnect)バスで接続した構成となる。コントローラ10は、複合機1全体の制御と描画、通信、図示しない操作部からの入力を制御するコントローラである。エンジン部60は、PCIバスに接続可能なプリンタエンジンなどであり、たとえば白黒プロッタ、1ドラムカラープロッタ、4ドラムカラープロッタ、スキャナまたはファックスユニットなどである。なお、このエンジン部60には、プロッタなどのいわゆるエンジン部分に加えて、誤差拡散やガンマ変換などの画像処理部分が含まれる。 FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a hardware configuration of the
コントローラ10は、CPU11と、ノースブリッジ(NB)13と、システムメモリ(MEM−P)12と、サウスブリッジ(SB)14と、ローカルメモリ(MEM−C)17と、ASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit)16と、ハードディスクドライブ(HDD)18とを有し、ノースブリッジ(NB)13とASIC16との間をAGP(Accelerated Graphics Port)バス15で接続した構成となる。また、MEM−P12は、ROM(Read Only Memory)12aと、RAM(Random Access Memory)12bとをさらに有する。 The
CPU11は、複合機1の全体制御をおこなうものであり、NB13、MEM−P12およびSB14からなるチップセットを有し、このチップセットを介して他の機器と接続される。 The
NB13は、CPU11とMEM−P12、SB14、AGP15とを接続するためのブリッジであり、MEM−P12に対する読み書きなどを制御するメモリコントローラと、PCIマスタおよびAGPターゲットとを有する。 The
MEM−P12は、プログラムやデータの格納用メモリ、プログラムやデータの展開用メモリ、プリンタの描画用メモリなどとして用いるシステムメモリであり、ROM12aとRAM12bとからなる。ROM12aは、プログラムやデータの格納用メモリとして用いる読み出し専用のメモリであり、RAM12bは、プログラムやデータの展開用メモリ、プリンタの描画用メモリなどとして用いる書き込みおよび読み出し可能なメモリである。 The MEM-
SB14は、NB13とPCIデバイス、周辺デバイスとを接続するためのブリッジである。このSB14は、PCIバスを介してNB13と接続されており、このPCIバスには、ネットワークインターフェース(I/F)部なども接続される。 The
ASIC16は、画像処理用のハードウェア要素を有する画像処理用途向けのIC(Integrated Circuit)であり、AGP15、PCIバス、HDD18およびMEM−C17をそれぞれ接続するブリッジの役割を有する。このASIC16は、PCIターゲットおよびAGPマスタと、ASIC16の中核をなすアービタ(ARB)と、MEM−C17を制御するメモリコントローラと、ハードウェアロジックなどにより画像データの回転などをおこなう複数のDMAC(Direct Memory Access Controller)と、エンジン部60との間でPCIバスを介したデータ転送をおこなうPCIユニットとからなる。このASIC16には、PCIバスを介してFCU(Fax Control Unit)30、USB(Universal Serial Bus)40、IEEE1394(the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers 1394)インターフェース50が接続される。 The
MEM−C17は、コピー用画像バッファ、符号バッファとして用いるローカルメモリであり、HDD(Hard Disk Drive)18は、画像データの蓄積、プログラムの蓄積、フォントデータの蓄積、フォームの蓄積を行うためのストレージである。 The MEM-
AGP15は、グラフィック処理を高速化するために提案されたグラフィックスアクセラレーターカード用のバスインターフェースであり、MEM−P12に高スループットで直接アクセスすることにより、グラフィックスアクセラレーターカードを高速にするものである。 The
図3は、かかる複合機1のハードウェアおよびソフトウェアの構成を示した概念図であり、具体的には、後述する本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aを含む統合アプリケーション110と、ソフトウェア100およびハードウェア200の階層関係を示している。同図に示すように、ハードウェア200は、ハードウェアリソース201を有し、このハードウェアリソース201は、スキャナ201a、プロッタ201b、HDD(Hard Disk Drive)201c、ネットワーク201dおよびその他のリソース201eを有する。なお、その他のリソース201eは、201a〜201d以外のハードウェアリソース201のことであり、たとえば、操作パネルなどの入出力デバイスを示す。 FIG. 3 is a conceptual diagram showing the hardware and software configurations of the
また、かかるハードウェア200に搭載されるソフトウェア100は階層化されており、オペレーティングシステム103の上層にはサービス層102が構築され、このサービス層102の上層にはアプリケーション層103が構築されている。そして、サービス層102は、各ハードウェアリソース(201a〜201e)を制御するドライバーに相当する、スキャナ制御102部a、プロッタ制御部102b、蓄積制御部102c、配信/メール送受信制御部102d、FAX送受信制御部102e、ネットワーク通信制御部102fおよびその他の制御部102gを有する。 The
ここで、図3に示したソフトウェア100が、かかる階層構造をとるに至った経緯について、図14および図15を用いて説明する。図14は、複合機1に搭載されるソフトウェア構成の変遷を示す説明図である。図14のサービス層分離前アプリケーション501に示すように、多機能化した複合機1に搭載されるソフトウェアは、コピーアプリケーション、FAXアプリケーション、スキャナアプリケーションなどの機能別に独立したアプリケーションとして作成され、図3に示したオペレーティングシステム103上で動作していた。 Here, how the
しかしながら、これらのアプリケーションは、ハードウェアリソースを制御するドライバー(サービス層102)を含んでいたため、各アプリケーションには重複した処理が存在していた。その結果、各アプリケーションの規模は大きなものとなっていた。 However, since these applications include a driver (service layer 102) that controls hardware resources, duplicate processing exists in each application. As a result, the scale of each application has become large.
そこで、図14のサービス層分離後アプリケーション502に示すように、サービス層分離前アプリケーション501のサービス層102相当部分を括りだしサービス層102とするとともに、各アプリケーションは、このサービス層102の上層であるアプリケーション層101に構築する構成とした。かかる階層化構成をとることにより、各アプリケーションはスリム化され開発労力も軽減された。 Therefore, as shown in an
しかしながら、複合機1のネットワーク化、多機能化がさらに進展するに従って、各アプリケーションに共通処理部分が存在することが問題となってきた。具体的には、アプリケーション層101の各アプリケーション、たとえば、コピーアプリケーションやスキャナアプリケーションなどは、それぞれ、スキャナ制御部102aや蓄積制御部102cといったドライバーと通信をおこなう処理や、各種機能が提供するサービスの課金管理などの同様な処理を内部に有していた。このように、同様な処理を各アプリケーションが有していると、各アプリケーションの開発規模が大きくなるとともに、サービス層の仕様変更に対する各アプリケーションの改修規模が大きくなることが問題となってきた。 However, as the networking and multi-functionalization of the
この問題を解決するため、図14の共通ルーチン分離アプリケーション503に示すように、かかる同様な処理(共通処理部分)を共通ルーチンとして括りだすことも考えられた。しかしながら、かかる共通ルーチンは、各アプリケーションにおいて微妙に異なる処理を共通化しようとするものであるため、共通ルーチン内部の処理は複雑なものとなってしまう。また、たとえば、プリンタアプリケーションなどの新規アプリケーションを追加する場合においては、かかる新規アプリケーションに適応するために、共通ルーチンの改修が必要となる。 In order to solve this problem, as shown in the common
しかし、共通ルーチンの内部処理は複雑であるため、改修要員が処理を把握することが困難となり、改修規模の増大や、改修ミスによる他のアプリケーションへの影響が懸念された。 However, since the internal processing of the common routine is complicated, it became difficult for repair personnel to grasp the processing, and there were concerns about the increase in the scale of repair and the impact on other applications due to repair mistakes.
そこで、図14のオブジェクト指向アプリケーション504に示すように、オブジェクト指向による設計手法(オブジェクトモデリング)により、かかる複数のアプリケーションを、統合アプリケーション110に統合することとした。具体的には、各アプリケーションの共通処理部分をオブジェクトモデルとして抽出し、このオブジェクトモデルの集合体から、統合アプリケーション110を構成する。そして、従来のコピー機能やスキャナ機能といった機能は、かかるオブジェクトモデルの協調関係によって実現する。 Therefore, as shown in the object-oriented
このような構成をとることにより、たとえばプリンタ機能のような新規機能の追加は、かかるオブジェクトモデルに属するクラスのサブクラス化などにより対処できる。このため、改修部分が明確となり、改修による他の機能への影響を小さくすることができる。また、オブジェクトモデリングによるプログラムは、従来の手続き型プログラムに比べて、処理の把握が容易であるため、改修要員が処理を把握することも容易となり、改修規模の削減や、改修ミスによる他のアプリケーションへの影響を小さくすることができる。 By adopting such a configuration, for example, addition of a new function such as a printer function can be dealt with by subclassing a class belonging to the object model. For this reason, a repair part becomes clear and the influence on other functions by repair can be made small. In addition, the object modeling program is easier to grasp the process than the conventional procedural program, so it is easier for the repair staff to grasp the process, reducing the scale of the repair, and other applications due to mistakes in the repair. The influence on can be reduced.
図15は、図14に示したサービス層分離後アプリケーション502の段階における従来のアプリケーションの構成と、かかるアプリケーションとサービス層102の各ドライバーの関係を示した説明図である。同図に示すように、アプリケーション層101は、コピーアプリケーション120、スキャナアプリケーション130、ファックスアプリケーション140およびプリンタアプリケーション150を有する。 FIG. 15 is an explanatory diagram showing the configuration of a conventional application at the stage of the service layer separated
たとえば、コピーアプリケーション120は、コピー機能を実現するために、スキャナ制御部102a、プロッタ制御部102b、蓄積制御部102cおよびその他の制御部102gとデータの送受信をおこなう。また、ファックスアプリケーション140は、ファックス機能を実現するために、プロッタ制御部102b、蓄積制御部102c、FAX送受信制御部102e、ネットワーク通信制御部102fおよびその他の制御部102gとデータの送受信をおこなう。このように、アプリケーション層101の各アプリケーションとサービス層102の各ドライバー間の通信は、複雑なものとなっていた。 For example, the
図3の説明に戻ると、上述したオブジェクトモデリングにより、アプリケーション層101に存在した複数のアプリケーションは、統合アプリケーション110に統合されている。そして、各アプリケーションが重複しておこなっていた各ドライバーとの通信処理は、統合アプリケーション110を構成する所定のオブジェクトモデルにおこなわせるように構成したことにより、アプリケーション層101のアプリケーションと、サービス層102の各ドライバー間の通信は、図15と比較して単純になっている。 Returning to the description of FIG. 3, a plurality of applications existing in the
次に、統合アプリケーション110の内部構成について説明する。図4は、統合アプリケーション110の内部構成を示すブロック図である。同図に示すように、統合アプリケーション110は、操作系サブシステム111と、管理系サブシステム112と、実行系サブシステム113とを有する。 Next, the internal configuration of the
操作系サブシステム111は、マンマシンインタフェースを担当するソフトウェア群である。具体的には、この操作系サブシステム111は、ユーザの要求を受け付ける処理と、この要求の実行を指示する処理と、この要求の実行状況と実行結果についての情報をユーザに提供する処理をおこなう。 The
管理系サブシステム112は、画像形成装置1の資源を管理するソフトウェア群である。具体的には、この管理系サブシステム112は、ハードウェアリソース201およびこのハードウェアリソース201が保持するデータ状態を管理するサービスをおこなう。 The
実行系サブシステム113は、ユーザからの要求の実行を担当するソフトウェア群である。具体的には、この実行系サブシステム113は、コピー要求がなされた場合には、原稿の読み取りから成果物の出力までの処理をおこなう。 The
操作系サブシステム111、管理系サブシステム112および実行系サブシステム113は、必要に応じて相互に処理を依頼してその結果を送り合う。このようにそれぞれのサブシステムが協調し合って、統合アプリケーション110全体として複合機1に必要とされるサービスの提供をおこなう。 The
そして、管理系サブシステム112は、本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aを有する。この課金部112aは、課金処理の受付け、課金額の算出、課金処理実行の指示などの課金管理処理をおこなう。 The
図5は、図4に示した各サブシステムを、UML(Unified Modeling Language)のクラス図(UMLクラス図)に置き換えた図である。ここで、UMLとは、OMG(Object Management Group)が仕様を策定しているシステムモデリング言語であり、モデリングの成果を記述する記法を定義したものである。このUMLは、オブジェクト指向によるソフトウェアの設計において広く用いられている。 FIG. 5 is a diagram in which each subsystem shown in FIG. 4 is replaced with a UML (Unified Modeling Language) class diagram (UML class diagram). Here, UML is a system modeling language for which specifications are formulated by OMG (Object Management Group), and defines a notation for describing the results of modeling. This UML is widely used in the design of object-oriented software.
図5に示すように、統合アプリケーション110は複数のパッケージを有し、また、この統合アプリケーション110自体もひとつのパッケージとなっている。ここで、パッケージとはUMLモデルの各構成要素(シンボル)をグループ化したものであり、左上にタブのついたフォルダの形をしたシンボルで表現される。また、各パッケージを相互に結ぶ直線は、各パッケージ間に処理依頼などの関連があることを示している。 As shown in FIG. 5, the
図5に示したように、統合アプリケーション110は、操作系サブシステム111、管理系サブシステム112および実行系サブシステム113の3つのパッケージを内部に有するパッケージである。さらに、管理系サブシステム112は、課金部112aを内部に有するパッケージである。そして、操作系サブシステム111、管理系サブシステム112および実行系サブシステム113を相互に結ぶ直線は、各パッケージ間に処理依頼(たとえば、メッセージ送受信)などの関連があることを示している。なお、操作系サブシステム111、管理系サブシステム112および実行系サブシステム113のタブの右端に記された記号は、かかるパッケージがサブシステムであることを示すUMLのシンボルである。 As shown in FIG. 5, the
次に、本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aについて詳細に説明する。なお、課金部112aは、オブジェクト指向に基づいて設計するにあたって、既存の処理を単純にオブジェクト化せず、機能追加や改修をより一層容易におこなうことができるようにオブジェクトモデルを構成した。かかるオブジェクトモデルの構成について図6〜図8を用いて説明しておく。 Next,
図6は、複合機1の操作パネル400の一例を示した図である。同図に示すように、かかる操作パネル400は、初期設定キー401、コピーキー402、コピーサーバーキー403、プリンタキー404、送信キー405、テンキー406、クリア/ストップキー407、スタートキー408、予熱キー409、リセットキー410および液晶タッチパネル420を有する。 FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example of the
初期設定キー401をタッチすると、液晶タッチパネル420に初期設定用のメニューが表示され、かかるメニューにおいては、収納される用紙サイズなどを設定することができる。また、コピーをしたい場合にはコピーキー402を、コピー結果を複合機1に蓄積したい場合にはコピーサーバーキー403を、プリンタに係る操作をおこないたい場合には、プリンタキー404を、ファックスや蓄積画像などの送信をしたい場合には送信キー405を、それぞれタッチすると、液晶タッチパネル420に対応したメニューが表示される。 When the
図7は液晶タッチパネル420に表示されるメニューの一例である。このメニューは、図6に示したコピーキー402をタッチすることにより表示される。図7に示すように、この液晶タッチパネル420には、自動濃度ボタン421、自動用紙選択ボタン422、等倍ボタン423などが表示される。利用者は、これらのボタンを選択することによりコピー機能の詳細な内容を指示し、この指示を受け取った複合機1は、指示された内容に従ってコピー処理を実行することになる。 FIG. 7 shows an example of a menu displayed on the liquid
そして、かかるコピー処理に対する課金は、コピーの種別(たとえば、モノクロコピーやカラーコピー)、記録紙の種別(たとえば、A4やA3)、コピーの枚数などに基づいておこなわれる。たとえば、A4のモノクロコピーの料金が一枚あたり10円である場合において、利用者が課金装置1aに100円硬貨を一枚投入し、かかるコピーを8枚指示した場合には、課金される料金は80円となり80円が徴収され、20円が返却される。 Billing for such copy processing is performed based on the type of copy (for example, monochrome copy or color copy), the type of recording paper (for example, A4 or A3), the number of copies, and the like. For example, when the charge for A4 monochrome copying is 10 yen per sheet, if the user inserts a 100-yen coin into the charging apparatus 1a and designates 8 such copies, the fee charged Becomes 80 yen, 80 yen is collected, and 20 yen is returned.
また、ネットワークを利用した複数の利用者が、複合機1に対して電子データの印刷を指示したり、電子データのファックスを指示したりする場合には、課金サーバ2には、これらの処理に応じた課金履歴が蓄積されることになる。そして、蓄積された課金履歴に基づいて課金がおこなわれる。 In addition, when a plurality of users using the network instructs the
このように、複合化とネットワーク化の進展により搭載される機能が高度化した複合機1においては、複数の利用者により、複数の機能が同時に使用されることが通常であるので、かかる機能の利用に対する課金は、二重課金や未課金などの課金ミスがないように確実におこなう必要がある。 In this way, in the
そこで、本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aは、レストランなどにおける「伝票」を用いた課金処理の隠喩(メタファ)によりオブジェクトモデリングをおこなうこととした。かかるオブジェクトモデリングにより、複数の利用者に対する課金を確実におこなうことができ、機能追加にも柔軟に対処できる課金処理の仕組みの提供が可能となることが予想される。 Therefore, the
図8は、本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aのオブジェクトモデリングの概要を説明するための説明図である。同図に示すように、レストランに入店した「客」は、「注文係」に料理や飲み物を注文する。注文を受けた「注文係」は、「伝票」に料理名や個数などを記載する。そして、注文された料理や飲み物の用意が完了すると、「ウェイター」は、これらの料理を客のテーブルに届けるとともに、上述した伝票の各料理のチェック欄に「レ点」などのチェックを入れる。食事を済ませた客は、この伝票を「会計」に持っていく。 FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram for explaining an outline of object modeling of the
客から伝票を受け取ったレジ係は、「レ点」の入った提供済みの料理について「料金表」を参照し、「請求方法」(たとえば、現金やクレジットカードなど)を客に確認したうえで、客がクレジットカードによる支払いを指定した場合には、指定された「課金対象」(この場合はクレジットカード)に対して課金処理(精算)をおこなう。また、会計が完了した伝票は保管され、営業日ごとの売上集計や会計監査などの「集計」処理に利用される。 The cashier who received the voucher from the customer refers to the “price list” for the food that has been marked with “R” and confirms the “billing method” (for example, cash or credit card) with the customer, When the customer designates payment by credit card, billing processing (settlement) is performed for the designated “billing object” (in this case, credit card). In addition, vouchers for which accounting has been completed are stored and used for “aggregation” processing such as sales aggregation for each business day and accounting audits.
上述したレストランにおける課金処理を複合機1の課金処理に置き換えると以下のようになる。料理を注文する客は、複合機1の利用者である。この利用者には、複合機1を直接操作する利用者に加えて、ネットワーク経由で利用する利用者も含まれる。利用者が複合機1の操作パネル400を操作した場合について説明すると、かかる操作内容は、統合アプリケーション110の操作系サブシステム111を経由して本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aに通知される。また、ウェイターは、実行系サブシステム113に相当し、コピー処理などが完了すると、かかる処理の完了が課金部112aに通知される。すなわち、図8の実線の矩形で囲まれた部分、言い換えると、図8から「客」と「ウェイター」を除いた部分が、本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aに相当する。 Replacing the billing process in the restaurant described above with the billing process of the
このように、本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aは、図8に示したレストランにおける伝票を用いた課金処理のメタファにより各クラスを設計した。図9は、課金部112aのクラス構成を示すUMLクラス図である。同図に示す課金部112aは、上述した「注文係」に相当する注文係クラス310、「伝票」に相当する伝票クラス320、「会計」に相当する会計クラス330、「料金表」に相当する料金表クラス340、「請求方法」に相当する請求方法クラス350、「課金対象」に相当する課金対象クラス360および「集計」に相当する集計クラス370を有する。なお、集計クラス370は、伝票の履歴を作成するクラスであるので、課金部112aは、この集計クラス370を有しない構成とすることもできる。 As described above, the
また、注文係クラス310、伝票クラス320、会計クラス330、料金表クラス340、請求方法クラス350、課金対象クラス360および集計クラス370は、特許請求の範囲における注文係オブジェクト、伝票オブジェクト、会計オブジェクト、料金表オブジェクト、課金対象決定オブジェクト、課金対象オブジェクトおよび集計オブジェクトにそれぞれ対応する。 Further, the
ここで、「伝票」の単位について説明しておく。伝票の単位は、一つの「伝票」あたり1つの「ジョブ」とすることを基本とするが、かかる伝票の単位をこれと異なるものとすることもできる。なお、「ジョブ」とは、成果物(たとえば、コピーした記録紙)の作成が完了するまでの処理の実行単位をいい、複合機全体として入力の始まりから出力の終了までを示すこととする。 Here, the unit of “slip” will be described. The unit of the slip is basically one “job” per “slip”, but the unit of the slip may be different from this. Note that “job” refers to an execution unit of processing until creation of a product (for example, a copied recording sheet) is completed, and indicates from the start of input to the end of output as the entire multifunction peripheral.
たとえば、利用者がモノクロコピー10枚を依頼した場合、「モノクロコピー10枚」を一つの「ジョブ」とすれば、一つの伝票は「モノクロコピー10枚」の依頼を含むことになる。しかし、「モノクロコピー1枚」を一つの「ジョブ」とすれば、「モノクロコピー1枚」を一つの伝票とすることもできる。また、「カラーコピー5枚」と「モノクロコピー5枚」とを依頼した場合、これらの依頼のそれぞれを一つの伝票とすることが基本となるが、これらの依頼をまとめて一つの伝票とすることもできる。 For example, when the user requests 10 monochrome copies, if “10 monochrome copies” is defined as one “job”, one slip includes a request for “10 monochrome copies”. However, if “one monochrome copy” is defined as one “job”, “one monochrome copy” can be defined as one slip. In addition, when “5 color copies” and “5 monochrome copies” are requested, each of these requests is basically one voucher. However, these requests are combined into one voucher. You can also.
次に、クラスとUMLクラス図におけるクラスの記述方法について説明しておく。クラスとは、オブジェクト指向システムを構成するオブジェクトの設計図に相当する概念であり、オブジェクト内部に有する属性と処理や、他のオブジェクトとの関係を定義するものである。 Next, a class description method in the class and UML class diagram will be described. A class is a concept corresponding to a design drawing of an object constituting an object-oriented system, and defines attributes and processes in an object and a relationship with other objects.
UMLクラス図におけるクラスは、3段の区画を有する矩形として記述される。それぞれの区画は、上から、クラス名を示す名前区画、クラスが有するデータ(属性)を示す属性区画およびクラスが有する処理(操作)を示す操作区画と呼ばれる。たとえば、料金表クラス340を示す矩形の名前区画は、かかるクラスのクラス名が「料金表」であることを示し、属性区画は、かかるクラスが有する属性が、「単価一覧」であることを示し、操作区画は、かかるクラスが有する操作が、「検索する()」であることを示している。 The class in the UML class diagram is described as a rectangle having three sections. From the top, each section is called a name section indicating a class name, an attribute section indicating data (attribute) included in the class, and an operation section indicating processing (operation) included in the class. For example, a rectangular name section indicating the price list class 340 indicates that the class name of the class is “charge list”, and an attribute section indicates that the attribute of the class is “unit price list”. The operation section indicates that the operation of the class is “search ()”.
このように、各クラスは、データ(属性)を所持するための属性区画と、かかる属性の書き込みおよび読み出しをおこなう処理(操作)を所持するための操作区画とを有している。これらのクラスは、プログラム(統合アプリケーション110)の一部として含まれるので、あらかじめROM12aに格納されたこのプログラムが実行されると、各クラスはRAM12bの所定領域に実体化され、属性区画に含まれる各データ(属性)がRAM12b上に展開される。したがって、クラスを実体化したオブジェクトは、RAM12b上の各データ(属性)の書き込みおよび読み出しをすることが可能となる。 Thus, each class has an attribute section for possessing data (attribute) and an operation section for possessing processing (operation) for writing and reading such an attribute. Since these classes are included as a part of the program (integrated application 110), when this program stored in the
なお、属性や操作といったクラスの要素の左側に「−」記号を付した場合は、かかる要素は外部のクラスには非公開であることを示し、「+」記号を付した場合は、かかる要素は外部のクラスに公開されていることを示す。また、操作については「選択する()」のように「()」記号を付することが通例であり、「(引数1,引数2)」のように、かかる操作に引き渡す引数を記述する場合もある。 In addition, if a "-" symbol is attached to the left side of a class element such as attribute or operation, this indicates that the element is private to external classes, and if a "+" symbol is attached, this element Indicates that it is open to external classes. Also, for operations, it is customary to add a “()” symbol such as “Select ()”, and when describing an argument to be passed to the operation, such as “(
次に、本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aのクラスの概要について説明する。上述したように、課金部112aは、注文係クラス310、伝票クラス320、会計クラス330、料金表クラス340、請求方法クラス350、課金対象クラス360および集計クラス370を有する。なお、集計クラス370は、伝票の履歴を作成するクラスであるので、課金部112aは、この集計クラス370を有しない構成とすることもできる。以下では、まず、これらのクラスの概要について説明する。 Next, an outline of the class of charging
注文係クラス310は、課金対象となる機能(たとえば、コピー機能やファックス機能)の詳細な内容(たとえば、用紙サイズやカラーモード)を受け付けるクラスであり、伝票クラス320は、受け付けた詳細な内容を保持するクラスである。また、会計クラス330は、課金装置1aなどの残高と提供したサービス(たとえば、コピーサービス)の料金に基づいてサービスの提供可否を判定し課金をおこなうクラスであり、料金表クラス340は、各サービスの該当料金を保持し検索するクラスである。 The
また、請求方法クラス350は、複数の課金対象(コインラック装置やプリセットキーカード装置)から課金先を決定するクラスであり、課金対象クラス360は、請求方法クラス350が決定した課金先の装置に課金実行を指示するクラスである。さらに、集計クラス370は、処理済状態となった伝票クラス320のオブジェクトの集計をおこなうクラスである。 The billing method class 350 is a class for determining a billing destination from a plurality of billing targets (coin rack device or preset key card device), and the
次に、各クラスの内容についてさらに詳細に説明する。注文係クラス310は、課金対象となる機能(たとえば、コピー機能やファックス機能)の詳細な内容(たとえば、用紙サイズやカラーモード)を受け付けるクラスである。具体的には、この注文係クラス310は、操作として、注文を受ける()310aおよび注文を取り消す()310bを有する。 Next, the contents of each class will be described in more detail. The
注文を受ける()310aは、操作系サブシステム111を経由して利用者の注文を受け付け、新しい注文であれば伝票クラス320のオブジェクトを生成し、その注文内容をこのオブジェクトに引き渡す。また、注文の変更を受け付けた場合には、該当する伝票クラス320のオブジェクトが保持する注文内容を書き換える。 The order received () 310 a accepts the user's order via the
ここで、「注文」とは、コピー機能やファックス機能を利用者が利用する際の利用単位のことをあらわす。たとえば、利用者が「A4モノクロコピー」を10枚指示した場合には、「A4モノクロコピー10枚」を一つの「注文」とする。この場合、「A4モノクロコピー1枚」を一つの「注文」とし、かかる「注文」が10個あることとしてもよい。また、利用者が、「A4モノクロコピー10枚」と「A4カラーコピー10枚」を同時に指示した場合には、「A4モノクロコピー10枚」を一つの「注文」とし、「A4カラーコピー10枚」を一つの「注文」とするが、「A4モノクロコピー10枚」および「A4カラーコピー10枚」を一つの「注文」とすることもできる。なお、「注文内容」とは、用紙サイズやカラーモードといった上記「詳細な内容」のことをあらわす。 Here, the “order” represents a unit of use when the user uses the copy function or the fax function. For example, when the user designates 10 copies of “A4 monochrome copy”, “10 copies of A4 monochrome copy” is set as one “order”. In this case, “one A4 monochrome copy” may be one “order”, and there may be ten such “orders”. If the user instructs “10 A4 monochrome copies” and “10 A4 color copies” at the same time, “10 A4 monochrome copies” is set as one “order” and “10 A4 color copies”. ”Is one“ order ”, but“ 10 A4 monochrome copies ”and“ 10 A4 color copies ”can also be one“ order ”. The “order content” represents the “detailed content” such as the paper size and the color mode.
また、注文を取り消す()310bは、受け付けた注文の取り消し処理をおこなう。具体的には、この注文を取り消す()310bは、注文取り消しの対象となる伝票クラス320のオブジェクトの提供終了チェック()320fを呼び出す。 Further, canceling the order () 310 b performs processing for canceling the received order. Specifically, canceling the order () 310 b calls the provision end check () 320 f of the object of the
伝票クラス320は、受け付けた「注文」の「注文内容」を保持するクラスである。具体的には、この伝票クラス320は、属性として、状態320a、商品名320bおよび数量320cを有し、操作として、記入する()320d、提供チェック()320e、提供終了チェック()320fおよび提供可否を確認する()320gを有する。なお、かかる伝票クラス320を実体化したオブジェクトが生成されると、状態320a、商品名320bおよび数量320cはRAM12b上に展開されるので、これらのデータ(属性)の書き込みおよび読み出しをおこなうことが可能となる。 The
状態320aは、現在の伝票の処理状態をあらわし、この状態には、記入中、提供可、保留中、処理中および処理済の5つがある。ここで、図10を用いてこれらの状態と各状態間の状態遷移について説明しておく。図10は、伝票クラス320の状態遷移(状態320aが保持する状態の状態遷移)を示すUMLステートチャート図である。 The
同図に示すように、現在の状態が「記入中」であれば、「提供可」、「保留中」および「処理済」への状態遷移が可能である。具体的には、「記入中」の状態において記入する()320dが呼び出されると(ステップS1001)、状態は「記入中」のままである。また、提供可否を確認する()320gが呼び出され、その戻り値が「OK」であれば(ステップS1002)、「提供可」状態に状態遷移し、かかる戻り値が「NG」であれば(ステップS1003)、「保留中」状態に状態遷移する。また、提供終了チェック320fが呼び出されると(ステップS1004)、「処理済」状態に状態遷移する。 As shown in the figure, if the current state is “filling in”, state transition to “provision available”, “pending” and “processed” is possible. Specifically, when () 320d for filling in is called in the “filling” state (step S1001), the state remains “filling”. Further, if (320) 320 g for confirming availability is called and the return value is “OK” (step S 1002), the state transitions to the “provision available” state, and if the return value is “NG” ( In step S1003), the state transitions to the “pending” state. When the
また、同図に示したように、現在の状態が「提供可」であれば、「保留中」、「記入中」および「処理中」への状態遷移が可能である。具体的には、「提供可」状態において提供可否を確認する()320gが呼び出され、その戻り値が「NG」であれば(ステップS1005)、「保留中」状態に状態遷移し、記入する()320dが呼び出されると(ステップS1006)、「記入中」状態に状態遷移し、提供チェック()320eが呼び出されると(ステップS1007)、「処理中」状態に状態遷移する。 Also, as shown in the figure, if the current state is “provision available”, the state transition to “pending”, “filling in” and “processing” is possible. More specifically, in the “provision available” state, whether or not provision is possible () 320 g is called, and if the return value is “NG” (step S 1005), the state transitions to the “pending” state and is filled in. When () 320d is called (step S1006), the state transitions to the “filling” state, and when the provision check () 320e is called (step S1007), the state transitions to the “processing” state.
また、同図に示したように、現在の状態が「処理中」であれば、「提供可」、「保留中」および「処理済」状態への状態遷移が可能である。具体的には、「処理中」状態において提供可否を確認する()320gが呼び出され、その戻り値が「OK」であれば(ステップS1008)、「提供可」状態に状態遷移し、かかる戻り値が「NG」であれば(ステップS1009)、「保留中」状態に状態遷移し、提供終了チェック()320fが呼び出されると(ステップS1012)、「処理済」状態に状態遷移する。 Further, as shown in the figure, if the current state is “processing”, it is possible to change the state to “provided”, “pending”, and “processed” states. Specifically, in the “processing” state, whether or not provision is possible () 320 g is called, and if the return value is “OK” (step S 1008), the state transitions to the “provision available” state and the return is made. If the value is “NG” (step S1009), the state transitions to the “pending” state, and when the provision end check () 320f is called (step S1012), the state transitions to the “processed” state.
このように、状態320aの各状態に応じて実行可能な操作が限定されており、実行された操作による遷移先の状態も限定されている。このような「状態」および「状態遷移」の概念を用いることにより、伝票クラス320は、「伝票」の処理状態を的確に把握することができる。 As described above, the operations that can be executed are limited according to the respective states of the
図9に戻って、商品名320bについて説明する。商品名320bは、コピーやファックスといった各機能の機能名とその詳細な内容を保持する。たとえば、「A4モノクロコピー」や「A3カラー両面コピー」といった商品名が保持される。また、数量320cは、商品の数量を保持する。たとえば、コピー10枚の印刷が指示された場合には、この属性には数量「10」が保持される。 Returning to FIG. 9, the product name 320b will be described. The product name 320b holds the function name of each function such as copy and fax and the detailed contents thereof. For example, product names such as “A4 monochrome copy” and “A3 color duplex copy” are held. The
記入する()320dは、注文係クラス310から通知された「注文内容」を、商品名320bに保持させる処理をおこない、提供チェック()320eは、サービス提供完了(たとえば、コピー10枚の依頼に対する出力の完了)の際に、実行系サブシステム113から呼び出され、商品名320bに保持された「商品名」を読み出し、読み出した「商品名」に対応するサービスの料金請求を会計クラス330に依頼する。また、提供終了チェック()320fは、利用者による取り消し操作あるいは会計完了の際に、注文係クラス310あるいは会計クラス330から呼び出され、伝票クラス320の状態320eを「処理済」状態に遷移させ、「伝票」としての使用を終了させる処理をおこなう。 The entry () 320 d performs a process of holding the “order contents” notified from the
また、提供可否を確認する()320gは、サービス提供(たとえば、コピー10枚の依頼に対する出力の開始)に先立って、商品名320bに保持された「商品名」を読み出し、読み出した「商品名」に対応するサービスの料金回収可否の判定を会計クラス330に依頼するとともに、依頼結果に基づいてサービス提供の可否をあらかじめ判定する。このように、サービス提供に先立ってサービス提供の可否を判定することとしたので、料金回収の見込みのないサービス依頼を効率的に取り消すことができる。 Also, whether or not to provide () 320 g reads “product name” held in the product name 320 b prior to service provision (for example, start of output for a request for 10 copies), and reads the “product name” The
会計クラス330は、課金装置1aなどの残高と提供したサービスの料金に基づいてサービスの提供可否を判定するとともに、課金実行の指示をおこなうクラスである。具体的には、この会計クラス330は、操作として、回収可否を判定する()330aおよび請求する()330bを有する。 The
回収可否を判定する()330aは、料金表クラス340の検索する()340bを呼び出してサービス料金の単価を取得し、この単価と数量320cから読み出した数量とを乗ずることによりサービス料金を算出するとともに、課金対象クラス360の残高照会()360dを呼び出してコインラック装置などの残高を取得し、算出したサービス料金と、取得した残高とを比較することにより、サービス料金の回収可否を判定する。たとえば、提供したサービス料金が80円であり、コインラック装置の残高が100円である場合には、サービス料金の回収は可能であると判定する。 Whether to collect () 330 a determines the service charge by calling () 340 b to search the charge table class 340, obtains the unit price of the service charge, and multiplies this unit price by the quantity read from the
請求する()330bは、料金表クラス340の検索する()340bを呼び出してサービス料金の単価を取得し、この単価と数量320cから読み出した数量とを乗ずることによりサービス料金を算出するとともに、算出したサービス料金を課金対象クラス360の課金する()360cに引き渡すことにより、サービス料金の請求を依頼する。なお、回収可否を判定する()330aおよび請求する()330bは、それぞれ料金表クラス340の検索する()340bを呼び出す旨の説明をしたが、回収可否を判定する()330aで算出した料金を会計クラス330の属性として保持することとしてもよい。このように、保持された料金を利用することで、請求する()330bは、料金表の検索をおこなうことなく、該当する料金を取得することができる。 The billing () 330 b calls the () 340 b to be searched for the charge schedule class 340, acquires the unit price of the service charge, and calculates the service charge by multiplying the unit price and the quantity read from the
料金表クラス340は、各サービスの該当料金を保持し検索するクラスである。具体的には、この料金表クラス340は、属性として、単価一覧340aを有し、操作として、検索する()340bを有する。なお、かかる料金表クラス340を実体化したオブジェクトが生成されると、単価一覧340aはRAM12b上に展開されるので、このデータ(属性)の書き込みおよび読み出しをおこなうことが可能となる。 The price list class 340 is a class that holds and searches for the corresponding charges for each service. Specifically, the price list class 340 has a
単価一覧340aは、コピー機能やファックス機能といった機能ごとの単価を、上述した「商品名」ごとに保持する。また、検索する()340bは、会計クラス330の各操作から「商品名」を指定して呼び出され、指定された「商品名」の単価を単価一覧340aの検索により取得し、取得した単価を呼び出し元に通知する。 The
請求方法クラス350は、複数の課金対象(コインラック装置やプリセットキーカード装置)から課金先を決定するクラスであり、操作として、決定する()350aを有する。決定する()350aは、複数の課金対象から料金の引落しをおこなう装置を決定する処理をおこなう。 The billing method class 350 is a class for determining a billing destination from a plurality of billing objects (coin rack device or preset key card device), and has a () 350 a to be determined as an operation. The determining () 350a performs a process of determining a device that withdraws charges from a plurality of charging targets.
課金対象クラス360は、課金先の装置に対応するクラスである。具体的には、この課金対象クラス360は、属性として名称360aおよび残高360bを有し、操作として、課金する()360cおよび残高照会()360dを有する。なお、かかる課金対象クラス360を実体化したオブジェクトが生成されると、名称360aおよび残高360bはRAM12b上に展開されるので、これらのデータ(属性)の書き込みおよび読み出しをすることが可能となる。 The charging
名称360aは、コインラック装置やプリセットキーカード装置といった課金対象の名称(略号などを含む)を保持し、残高360bは、投入された貨幣の残金や、カウント値といった残高を保持する。また、課金する()360cは、該当する課金装置にサービス料金等を通知することにより課金処理を実行させ、残高照会()360dは、該当する課金装置から残高を取得し呼び出し元にこの残金を通知する処理をおこなう。 The
集計クラス370は、処理済状態となった伝票クラス320のオブジェクトの集計をおこなうクラスである。具体的には、この集計クラス370は、操作として、記録する()370aおよび集計する()370bを有する。 The
記録する()370aは、「処理済」状態となった伝票クラス320のオブジェクトの情報履歴(ログ)をHDD18などに記録する。このログには、正常に課金処理がおこなわれた「処理済伝票」に加えて、ハードウェア障害などにより未処理となった「未処理伝票」の情報が含まれる。なお、ログに記録される情報には、伝票クラス320のオブジェクトの各属性(320a〜320c)の他に、課金処理がおこなわれた時刻などが含まれる。 The recording () 370 a records the information history (log) of the object of the
集計する()370bは、システム管理者などが操作パネル400などを操作した際に、操作系サブシステム111から呼び出され、記録する()370aにより記録されたログの集計処理をおこなう。たとえば、「処理済伝票」あるいは「未処理伝票」ごとの集計、提供したサービス(たとえば、コピーサービス)ごとの集計などを、日次、月次などの所定の期間ごとにおこなう。これらの集計を利用することにより、会計監査などを円滑におこなうことができる。 The totaling () 370 b is called from the
次に、図9に示した各クラス間の関係について説明する。同図に示したように、UMLクラス図においては、クラス間に何らかの関係がある場合には、それらのクラスを表す矩形の間が直線で結ばれる。この直線の両端付近の文字はクラスのロールを表し、数字はクラスの多重度を表す。ここで、ロールとは、直線で結ばれた他方のクラスに対する当該クラスの役割のことであり、多重度とは、直線で結ばれた他方のクラスのオブジェクトと関連付けられて生成されるオブジェクトの数のことである。 Next, the relationship between the classes shown in FIG. 9 will be described. As shown in the figure, in the UML class diagram, when there is some relationship between classes, rectangles representing those classes are connected by a straight line. The characters near both ends of this line represent the class role, and the numbers represent the multiplicity of the class. Here, the role is the role of the class with respect to the other class connected by a straight line, and the multiplicity is the number of objects generated in association with the object of the other class connected by a straight line. That is.
たとえば、注文係クラス310からみた伝票クラス320の役割は「注文票」であり、伝票クラス320からみた注文係クラス310の役割は「記入者」である。また、注文係クラス310の多重度は「1」であり、伝票クラス320の多重度は「0..n」である。ここで、「0..n」は、かかる伝票クラス320の多重度が、0からnの範囲であることを示している。また、たとえば、「1..3」の記載をした場合には、かかるクラスの多重度が、1〜3の範囲であることを示す。 For example, the role of the
まず、注文係クラス310と伝票クラス320とのクラス関係について説明する。注文係クラス310のオブジェクトは、課金部112a内に1個のみ存在し、伝票クラス320のオブジェクトは、利用者の「注文」ごとに、注文係クラス310のオブジェクトにより生成され、注文係クラス310のオブジェクトに対して0個以上n個以下の範囲で存在する。ここで、オブジェクト数が0個とは、「注文」がなく伝票クラス320のオブジェクトが存在しない場合を示しており、かかるオブジェクト数の上限数はn個としているものの、当然に、ハードウェア仕様などによる制限を受けるものとする。 First, the class relationship between the
また、注文係クラス310は、伝票クラス320から見ると「記入者」としての役割を有しており、一方、伝票クラス320は、注文係クラス310から見ると「注文票」としての役割を有している。 In addition, the
次に、伝票クラス320と会計クラス330との関係について説明する。伝票クラス320のオブジェクトは、一つの「伝票」ごとに生成され、かかる「伝票」ごとに「会計」がおこなわれる。したがって、伝票クラス320のオブジェクトと会計クラス330のオブジェクトとは、「勘定書」と「請求係」という関係をなしている。また、一つの伝票クラス320のオブジェクトに対して、一つの会計クラス330のオブジェクトが存在するので、それぞれのオブジェクトは1対1の関係をなす。 Next, the relationship between the
次に、会計クラス330と料金表クラス340との関係について説明する。料金表クラス340のオブジェクトは、課金部112a内に1個のみ存在し、会計クラス330のオブジェクトは、伝票クラス340のオブジェクトと同数存在するので、会計クラス330のオブジェクトは、料金表クラス340のオブジェクトに対して0個以上n個以下の範囲で存在する。また、会計クラス330は、料金表を参照して会計処理をおこなうので、会計クラス330と料金表クラス340とは、「参照者」と「料金表」という関係をなしている。 Next, the relationship between the
次に、会計クラス330と請求方法クラス350との関係について説明する。請求方法クラスのオブジェクトは、課金部112a内に1個のみ存在し、会計クラス330のオブジェクトは、伝票クラス320のオブジェクトと同数存在するので、会計クラス330のオブジェクトは、請求方法クラス350のオブジェクトに対して0個以上n個以下の範囲で存在する。また、会計クラス330は、請求方法の決定を請求して会計処理をおこなうので、会計クラス330と請求方法クラス350とは、「請求係」と「請求方法」という関係をなしている。 Next, the relationship between the
次に、請求方法クラス350と課金対象クラス360との関係について説明する。請求方法クラス350のオブジェクトは、課金部112a内に1個のみ存在し、課金対象クラス360のオブジェクトは、コインラック装置やプリセットキーカード装置といった課金対象となる装置数に対応して存在する。したがって、課金対象クラス360のオブジェクトは、請求方法クラス350のオブジェクトに対して1個以上n個以下の範囲で存在する。また、請求方法クラス350は、1個以上の課金先を保有するので、請求方法クラス350と課金対象クラス360とは、「保有元」と「保有する課金先」という関係をなしている。 Next, the relationship between the billing method class 350 and the
次に、会計クラス330と課金対象クラス360との関係について説明する。会計クラス330のオブジェクトは、課金先である課金対象クラス360のオブジェクトに対し課金処理を依頼するが、一回の依頼で、複数の課金先に同時に課金処理を依頼する場合があるので、課金対象クラス360のオブジェクトは、会計クラス330のオブジェクトに対して1個以上n個以下の範囲で存在する。ここで、「n」は、課金先の数のことをあらわし、課金先がコインラック装置とプリセットキーカード装置の2個であれば、かかる「n」は2となる。 Next, the relationship between the
最後に、伝票クラス320と集計クラス370との関係について説明する。伝票クラス320のオブジェクトは、利用者の「注文」ごとに、注文係クラス310のオブジェクトにより生成され、0個以上n個以下の範囲で存在する。また、集計クラス370のオブジェクトは、課金部112a内に1個のみ存在する。「処理済」状態となった伝票クラス320のオブジェクトは、集計クラス370のオブジェクトの集計対象となるので、伝票クラス320と集計クラス370とは、「集計対象」と「集計者」との関係をなしている。 Finally, the relationship between the
このように、注文係クラス310、伝票クラス320、会計クラス330、料金表クラス340、請求方法クラス350、課金対象クラス360および集計クラス370の各オブジェクトは、相互に関連し合い、協調して、課金部112aに必要な機能を実現している。 In this way, the
次に、図9に示した各クラスの操作の実行手順について例をあげて説明する。図11は、注文受け付けがあった際の操作の実行手順を示すUMLシーケンス図である。 Next, an example of the execution procedure of each class operation shown in FIG. 9 will be described. FIG. 11 is a UML sequence diagram illustrating an operation execution procedure when an order is received.
ここで、UMLシーケンス図について説明しておく。図11の上部に並んだ矩形は、それぞれがクラスのオブジェクトを示している。各オブジェクトから下方に伸びた線は、各オブジェクトが生存していることを示す線(ライフライン)であり、上方から下方に向かって時間が流れているものとみなされる。この線上に存在する細長い矩形は、当該のオブジェクトが実際に活動している期間(活性期間)を示す。 Here, the UML sequence diagram will be described. Each rectangle arranged in the upper part of FIG. 11 indicates a class object. A line extending downward from each object is a line (lifeline) indicating that each object is alive, and time is considered to flow from the top to the bottom. An elongated rectangle present on this line indicates a period during which the object is actually active (active period).
各ライフラインの間を結ぶ横向きの矢印は、オブジェクトに含まれるの操作の実行を示す。具体的には、この矢印は、矢印の元のオブジェクトが、矢印の先のオブジェクトに含まれる操作を呼び出すことを示す。また、矢印が自分自身のオブジェクトを指している場合は、オブジェクトが自分に含まれる操作を自身で呼び出すことを意味する。 A horizontal arrow connecting the lifelines indicates execution of an operation included in the object. Specifically, this arrow indicates that the original object of the arrow calls an operation included in the object at the end of the arrow. Further, when the arrow points to its own object, it means that the object calls the operation included in the object by itself.
図11に示すように、利用者が、複合機1の操作パネル400を操作すると、操作系サブシステム111は、注文係オブジェクト311の注文を受ける()310aを呼び出す(ステップS1101)。そして、この注文係オブジェクト311は、伝票オブジェクト321を生成するとともに、生成した伝票オブジェクト321の記入する()を呼び出す(ステップS1102)。このようにして、利用者の「注文内容」を反映した伝票オブジェクト321が生成される。 As shown in FIG. 11, when the user operates the
図12は、提供可否確認があった際の操作の実行手順を示すUMLシーケンス図である。本実施の形態の特徴部分である課金部112aでは、利用者が所望するサービス(たとえば、コピーサービス)の提供に先立って、提供するサービスの代価の課金が可能であるか否かを確認し、課金可能と判定した場合に限りかかるサービスを提供する構成とした。 FIG. 12 is a UML sequence diagram showing an execution procedure of an operation when confirmation of availability is provided. The
図12に示すように、上述したステップS1101およびステップS1102がおこなわれた後、複合機1がサービス(たとえば、コピーサービス)を提供する際に、実行系サブシステム113は、伝票オブジェクト321の提供可否を確認する()320gを呼び出し(ステップS1201)、この伝票オブジェクト321は、会計オブジェクト331の回収可否を判定する()330aを呼び出す(ステップS1202)。 As shown in FIG. 12, after the above-described steps S1101 and S1102 are performed, when the
かかる会計オブジェクト331は、料金表オブジェクト341の検索する()340bを呼び出し(ステップS1203)、その戻り値として「料金」を取得する(ステップS1204)。つづいて、会計オブジェクト331は、請求方法オブジェクト351の決定する()350aを呼び出し(ステップS1205)、その戻り値として「決定した請求方法」を取得する(ステップS1206)。さらに、会計オブジェクト331は、課金対象オブジェクト361の残高照会360dを呼び出し(ステップS1207)、その戻り値として「残高」を取得する(ステップS1208)。 The
このようにして取得した、「料金」および「残高」に基づいて、かかる会計オブジェクト331は、回収可否の判定をおこなう(ステップS1209)。具体的には、「料金」が「残高」以下の場合には回収可能と判定し、それ以外の場合には回収不可能と判定する。なお、複数の課金先が存在する場合には、各課金先の残高の合計額を、上記「残高」として回収可否の判定をおこなう。 Based on the “fee” and “balance” acquired in this manner, the
会計オブジェクト331が回収可否の判定をおこなったならば、会計オブジェクト331は、かかる判定結果を回収可否を判定する()330aの戻り値に設定し、伝票オブジェクト321に通知する(ステップS1210)。かかる戻り値を取得した伝票オブジェクト321は、提供可否を判定し(ステップS1211)、かかる判定結果を提供可否を確認する()320gの戻り値に設定し、実行系サブシステム113に通知する(ステップS1212)。 If the
図13は、提供があった際の操作の実行手順を示すUMLシーケンス図である。同図に示すように、コピーサービスなどのサービスが完了すると、実行系サブシステム113は、伝票オブジェクト321の提供チェック()320eを呼び出す(ステップS1301)。呼び出された伝票オブジェクト321は、提供チェック()320eの引数に設定された情報から「商品名」を読み出し(ステップS1302)、会計オブジェクト331の請求する()330bの引数に、かかる「商品名」を設定したうえで、この請求する()330bを呼び出す(ステップS1303)。 FIG. 13 is a UML sequence diagram showing an operation execution procedure when provided. As shown in the figure, when the service such as the copy service is completed, the
呼び出された会計オブジェクト331は、かかる引数から「商品名」を読み出し(ステップS1304)、料金表オブジェクト341の検索する()340bの引数に、かかる「商品名」を設定したうえで、この検索する()340bを呼び出す(ステップS1305)。料金表オブジェクト341は、受け取った「商品名」に該当する「料金」を検索し、かかる「料金」を検索する()340bの戻り値に設定し、会計オブジェクト331に通知する(ステップS1306)。かかる戻り値を取得した会計オブジェクト331は、課金対象オブジェクト361の課金する()360cを呼び出し(ステップS1307)、かかる「料金」の課金処理を依頼する。 The called
上述してきたように、本実施の形態では、オブジェクト指向設計により課金部の仕組みを構築し、さらに、レストランなどにおける「伝票」を用いた課金処理の隠喩(メタファ)によりオブジェクトモデリングをおこない、注文係クラス、伝票クラス、会計クラス、料金表クラス、請求方法クラス、課金対象クラスおよび集計クラスを用いることにより、かかる課金部を実現したので、ソフトウェア開発者やソフトウェア保守要員が、課金部の構成と役割を容易に把握することができる。また、コピーサービスなどのサービス提供時に、伝票のチェック(「レ点」チェック)をおこなうこととしたので、このチェックを会計および集計において参照することで、二重課金や未課金といった課金ミスを効率的に防止することができるとともに、処理済伝票および未処理伝票の集計を効率的におこなうことができる。 As described above, in the present embodiment, the billing mechanism is constructed by object-oriented design, and object modeling is performed by a metaphor of billing processing using a “slip” in a restaurant or the like. By using the class, slip class, accounting class, fee schedule class, billing method class, chargeable class, and aggregation class, this billing department has been realized, so software developers and software maintenance personnel can configure the billing department and its roles. Can be easily grasped. In addition, when a service such as a copy service is provided, the slip is checked ("check"). By referring to this check in accounting and aggregation, billing mistakes such as double billing and non-billing can be efficiently performed. In addition, it is possible to efficiently collect processed and unprocessed slips.
なお、本実施の形態では、課金部には集計クラスが含まれる構成としたが、この集計クラスを含まない構成とすることもでき、料金表クラス、請求方法クラスおよび課金対象クラスを会計クラスに含めた構成とすることもできる。 In the present embodiment, the accounting unit includes the aggregate class. However, the accounting unit may be configured not to include the aggregate class, and the charge table class, the billing method class, and the chargeable class are accounting classes. It can also be set as the structure included.
また、本実施の形態では、課金部を画像形成装置上に構成したが、かかる課金部を画像形成装置と通信可能なコンピュータに搭載することにより、画像形成装置などの有料サービスを提供する装置の課金を管理する課金管理装置として構成することもできる。さらに、課金の実行を担当する課金装置と、かかる課金管理装置を同一の筐体内に構成することもできる。 In this embodiment, the charging unit is configured on the image forming apparatus. However, by installing the charging unit on a computer that can communicate with the image forming apparatus, the charging unit such as the image forming apparatus is provided. It can also be configured as a billing management device that manages billing. Furthermore, the charging device in charge of charging and the charging management device can be configured in the same casing.
また、本実施の形態の画像形成装置で実行される課金管理プログラムは、インストール可能な形式または実行可能な形式のファイルでCD−ROM(Compact Disc Read Only Memory)、フレキシブルディスク(FD)、CD−R(CD Recordable)、DVD(Digital Versatile Disk)などのコンピュータで読み取り可能な記録媒体に記録して提供するよう構成してもよい。この場合、CPU11が上記記憶媒体から、課金管理プログラムを読み出してMEM−P12上にロードすることで、画像形成装置に、上述した各ステップ、各手段または各部を実現させる。 The charge management program executed in the image forming apparatus according to the present embodiment is a file in an installable format or an executable format, and is a CD-ROM (Compact Disc Read Only Memory), a flexible disc (FD), a CD- You may comprise so that it may record and provide on computer-readable recording media, such as R (CD Recordable) and DVD (Digital Versatile Disk). In this case, the
また、課金管理プログラムを、インターネットなどのネットワークに接続されたコンピュータ上に格納し、ネットワーク経由でダウンロードさせることにより提供するよう構成してもよい。さらに、かかる課金管理プログラムをインターネットなどのネットワーク経由で提供または配布するようにしてもよい。 Further, the billing management program may be provided by being stored on a computer connected to a network such as the Internet and downloaded via the network. Further, such a charge management program may be provided or distributed via a network such as the Internet.
以上のように、本発明にかかる課金管理プログラムおよび画像形成装置は、提供するサービスの対価として課金をおこなう各種装置の課金に有用であり、特に、画像形成装置の課金に適している。 As described above, the charging management program and the image forming apparatus according to the present invention are useful for charging various apparatuses that charge for the services provided, and are particularly suitable for charging the image forming apparatus.
1 画像形成装置(複合機)
1a 課金装置
2 課金サーバ
10 コントローラ
11 CPU
12 MEM−P
12a ROM
12b RAM
13 NB
14 SB
15 AGP
16 ASIC
17 MEM−C
18 HDD
20 キーボード(オペレーションパネル)
30 FCU
40 USB
50 IEEE1394
60 エンジン部(Engine)
100 ソフトウェア
101 アプリケーション層
102 サービス層
102a スキャナ制御部
102b プロッタ制御部
102c 蓄積制御部
102d 配信/メール送受信制御部
102e FAX送受信制御部
102f ネットワーク通信制御部
102g その他の制御部
103 オペレーティングシステム
110 統合アプリケーション
111 操作系サブシステム
112 管理系サブシステム
112a 課金部
113 実行系サブシステム
120 コピーアプリケーション
130 スキャナアプリケーション
140 ファックスアプリケーション
150 プリンタアプリケーション
200 ハードウェア
201 ハードウェアリソース
201a スキャナ
201b プロッタ
201c HDD
201d ネットワーク
201e その他のリソース
310 注文係クラス(注文係手段の一例)
310a 注文を受ける()
310b 注文を取り消す()
311 注文係オブジェクト(注文係手段の一例)
320 伝票クラス(伝票手段の一例)
320a 状態
320b 商品名
320c 数量
320d 記入する()
320e 提供チェック()
320f 提供終了チェック()
320g 提供可否を確認する()
321 伝票オブジェクト(伝票手段の一例)
330 会計クラス(会計手段の一例)
330a 回収可否を判定する()
330b 請求する()
331 会計オブジェクト(会計手段の一例)
340 料金表クラス(料金表手段の一例)
340a 単価一覧
340b 検索する()
341 料金表オブジェクト(料金表手段の一例)
350 請求方法クラス(課金対象決定手段の一例)
350a 決定する()
351 請求方法オブジェクト(課金対象決定手段の一例)
360 課金対象クラス(課金対象手段の一例)
360a 名称
360b 残高
360c 課金する()
360d 残高照会()
361 課金対象オブジェクト(課金対象手段の一例)
370 集計クラス(集計手段の一例)
370a 記録する()
370b 集計する()
400 操作パネル
401 初期設定キー
402 コピーキー
403 コピーサーバーキー
404 プリンタキー
405 送信キー
406 テンキー
407 クリア/ストップキー
408 スタートキー
409 予熱キー
410 リセットキー
420 液晶タッチパネル
421 自動濃度ボタン
422 自動用紙選択ボタン
423 等倍ボタン
501 サービス層分離前アプリケーション
502 サービス層分離後アプリケーション
503 共通ルーチン分離アプリケーション
504 オブジェクト指向アプリケーション1 Image forming device (multifunction machine)
12 MEM-P
12a ROM
12b RAM
13 NB
14 SB
15 AGP
16 ASIC
17 MEM-C
18 HDD
20 Keyboard (Operation panel)
30 FCU
40 USB
50 IEEE1394
60 Engine
DESCRIPTION OF
310a Order received ()
310b Cancel order ()
311 Ordering person object (an example of ordering means)
320 slip class (an example of slip means)
320a state
320e offer check ()
320f Offer end check ()
320g Check availability ()
321 slip object (an example of slip means)
330 Accounting class (an example of accounting method)
330a Judge whether collection is possible or not
330b Request ()
331 Accounting object (an example of accounting means)
340 Price List Class (Example of price list means)
341 Charge table object (an example of charge table means)
350 billing method class (an example of charging object determination means)
350a decide ()
351 Billing method object (an example of charging object determination means)
360 Chargeable class (an example of chargeable means)
360d Balance inquiry ()
361 Charge object (an example of charge object means)
370 Aggregation class (an example of aggregation means)
370a record ()
370b aggregate ()
400
Claims (10)
Translated fromJapanese前記サービス提供装置の制御プログラムからサービス要求内容を含むサービス要求通知を受信したならば、前記サービス要求内容および伝票状態を含む注文伝票データを生成して保持し、前記サービス提供装置の制御プログラムからサービス完了通知を受信したならば、前記伝票状態をサービス提供完了状態に更新するとともに課金の実行を担当する課金装置に課金を指示し、前記課金装置から課金完了通知を受信したならば、前記伝票状態を課金完了状態に更新する手段
としてコンピュータを機能させることを特徴とする課金管理プログラム。Charge management that is installed in a service providing apparatus that provides a paid service according to a user's request or a charge management apparatus that can communicate with the service providing apparatus, and calculates a service charge for the service requested by the user to the service providing apparatus. A program,
If a service request notification including service request contents is received from the control program of the service providing apparatus, order slip data including the service request contents and slip state is generated and held, and service is received from the control program of the service providing apparatus. If a completion notification is received, the voucher status is updated to a service provision completion status, charging is instructed to a charging device in charge of charging, and if a charging completion notification is received from the charging device, the voucher status A charge management program for causing a computer to function as a means for updating a charge to a charge completion state.
前記注文係手段は、前記サービス要求通知を受信した際に、前記伝票手段を生成して木構造の子として管理し、
前記伝票手段は、前記注文伝票データを保持し、前記伝票状態が前記サービス提供完了状態となった際に、前記会計手段に課金処理を依頼し、
前記会計手段は、前記伝票手段から課金処理を依頼された際に、前記サービス料金を算出して該サービス料金の課金を課金装置に指示し、前記課金完了通知を受信した際に、前記伝票手段に前記伝票状態を前記課金完了状態に遷移させるよう指示する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の課金管理プログラム。Ordering means for receiving the service request notification, slip means generated in one-to-one correspondence with the order slip data, and receiving the service completion notification, and calculating the service fee and charging the billing device And accounting means for receiving the billing completion notice,
The ordering means, upon receiving the service request notification, generates the slip means and manages it as a child of a tree structure,
The slip means holds the order slip data, and when the slip state becomes the service provision completion state, requests billing processing to the accounting means,
The accounting means calculates the service charge when requested by the slip means to instruct the charging device to charge the service charge, and receives the charge completion notification when receiving the charge completion notification. The billing management program according to claim 1, wherein the billing state is instructed to transition to the billing completion state.
前記課金対象手段は、該課金装置の残金を照会する残金照会操作と、該課金装置に課金実行を指示する課金操作とを含むことを特徴とする請求項2に記載の課金管理プログラム。A charging object means generated in one-to-one correspondence with the charging device;
The billing management program according to claim 2, wherein the billing target means includes a balance inquiry operation for querying a balance of the billing device and a billing operation for instructing the billing device to execute billing.
前記集計手段は、前記伝票手段が保持するデータを記録し、集計依頼を受け付けた際に、記録したデータを所定の形式で集計することを特徴とする請求項2〜6のいずれか一つに記載の課金管理プログラム。A tally unit for tallying the slip unit;
The said totaling means records the data which the said slip means hold | maintains, and when the totaling request is received, the recorded data is totaled in a predetermined format. The billing management program described.
制御プログラムからサービス要求内容を含むサービス要求通知を受信したならば、前記サービス要求内容および伝票状態を含む注文伝票データを生成して保持し、前記制御プログラムからサービス完了通知を受信したならば、前記伝票状態をサービス提供完了状態に更新するとともに前記課金装置に課金を指示し、前記課金装置から課金完了通知を受信したならば、前記伝票状態を課金完了状態に更新する手段
を備えたことを特徴とする画像形成装置。An image forming apparatus that calculates a service charge for a service requested by a user and instructs the charging apparatus to perform charging of the service charge,
If a service request notification including service request content is received from the control program, order slip data including the service request content and slip status is generated and held, and if a service completion notification is received from the control program, Updating a slip state to a service providing completion state, instructing charging to the billing device, and receiving a billing completion notification from the billing device; and updating the slip state to a billing completion state. An image forming apparatus.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004270240AJP4405351B2 (en) | 2004-09-16 | 2004-09-16 | Billing management program and image forming apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004270240AJP4405351B2 (en) | 2004-09-16 | 2004-09-16 | Billing management program and image forming apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006085476A JP2006085476A (en) | 2006-03-30 |
| JP4405351B2true JP4405351B2 (en) | 2010-01-27 |
Family
ID=36163932
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004270240AExpired - Fee RelatedJP4405351B2 (en) | 2004-09-16 | 2004-09-16 | Billing management program and image forming apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4405351B2 (en) |
- 2004
- 2004-09-16JPJP2004270240Apatent/JP4405351B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006085476A (en) | 2006-03-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3807249B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus and information processing method, charging processing apparatus and charging processing method | |
| JP5509754B2 (en) | Software management apparatus, software distribution system, installation method and program | |
| US7154616B2 (en) | Application charging system, information processing apparatus, and control method therefor and memory medium storing program therefor | |
| RU2509353C2 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method and image forming device | |
| JP6528432B2 (en) | Charge management system, first management device, second management device, and program | |
| JP4081955B2 (en) | Information recording system and information recording method | |
| JP4042321B2 (en) | Information output system and information output control method | |
| JP4042326B2 (en) | Job processing apparatus and job processing method | |
| JP2002133316A (en) | Application program charging system, apparatus, totalizing server, charging management server, application program charging method, charging program, and recording medium recording charging program | |
| JP4405351B2 (en) | Billing management program and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4490841B2 (en) | Document processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, document processing method, and document processing program | |
| JP5824885B2 (en) | Image processing system and job execution method | |
| JP4454787B2 (en) | Printing system | |
| JP2006085477A (en) | Billing management program and image forming apparatus | |
| JP3921933B2 (en) | Image forming server, image forming apparatus, and image forming method | |
| JP2007080209A (en) | Billing management apparatus, billing management method, and billing management program | |
| JP2022032145A (en) | Information processing system, processing execution system, processing execution method, and program | |
| JP4450699B2 (en) | Request management apparatus, image forming apparatus, job processing instruction method, and job processing instruction program | |
| JP2001306315A5 (en) | ||
| JP2002149549A (en) | System and device for distributing data, and device and method for managing data distribution | |
| JP7729096B2 (en) | Information processing device, service providing system, method, and program | |
| JP2002117157A (en) | Application program charging system, charging amount calculating device, totaling server, charging managing server, application program charging method, charging program and recording medium | |
| JP2005267553A (en) | Service cooperation processing device, service cooperation processing method, and service cooperation processing control program | |
| JP2002108480A (en) | Application and program billing system | |
| JP2002116835A (en) | Application program accounting system and its device and its method and totaling server and accounting management server and accounting program and recording medium with accounting program recorded |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20070614 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20091022 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20091027 | |
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20091104 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121113 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131113 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |