JP4125938B2 - Mobile phone terminal - Google Patents
Mobile phone terminalDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4125938B2 JP4125938B2JP2002296639AJP2002296639AJP4125938B2JP 4125938 B2JP4125938 B2JP 4125938B2JP 2002296639 AJP2002296639 AJP 2002296639AJP 2002296639 AJP2002296639 AJP 2002296639AJP 4125938 B2JP4125938 B2JP 4125938B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- owner
- information
- personal authentication
- mobile phone
- phone terminal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Telephone Function (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、個人情報の保護が必要とされる携帯電話端末装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、インターネットの普及、デジタル放送の開始、モバイル革命に見られるように、デジタル技術の進展により、情報通信ネットワークが急速に高度化しつつある。なかでもモバイルの分野における携帯電話端末装置は、多機能化・高機能化され、それに伴い個人的な情報を多く含むようになっている。現在では、携帯電話端末装置を用いて有線・無線の通信ネットワークを介して電子情報や画像情報の送受信が行えるようになり、さらに銀行決裁、電子商取引、株取引等をも行えるようになっている。
【0003】
したがって、携帯電話端末装置は、多機能化・高機能化に伴い、時と場所を問わずに使用する機会が増えている。その一方で、時と場所を問わずに使用する機会が増えると、移動途中で盗難に遭遇したり、不注意によって紛失したりすることによって他人の手に渡る機会も増えることになる。
【0004】
このように多機能化・高機能化された携帯電話端末装置を利用する場合には、ユーザは、アプリケーションを起動する度にIDやパスワードを入力することで個人の認証を行う。また、銀行決裁、電子商取引を行う場合には、ユーザは、利用銀行等の口座番号や暗証番号を入力することで個人の認証を行うようになっている。しかし、上記のように他人の手に渡ると、端末内の個人情報が参照、悪用される危険性がある。
【0005】
そこで、従来では、このような端末の紛失や盗難時に秘密性の高い情報を保護するための方策として、各種の提案がなされている(例えば、特許文献1(携帯端末および携帯端末情報保護方法)、特許文献2(バイオメトリスク情報による個人認証機能を有する携帯電子装置)等)。以下、図5、図6を参照して、その概要を説明する。
【0006】
図5は、特許文献1で提案されている情報保護システムにおいて実施される保護手順を示すシーケンス図である。特許文献1では、紛失した携帯端末内に残された個人情報の保護と回収を実施する方法が開示されている。
【0007】
図5において、携帯端末503の所有者は、無線ネットワークに接続されたセキュリティコントローラ501に、予め当該携帯端末503のセキュリティ管理データを登録しておく。
【0008】
携帯端末503の紛失に気付いた所有者が、電話機500を操作して保護要求504をセキュリティコントローラ501に送ると(動作U1)、セキュリティコントローラ501から認証確認505が返送されるので(動作S1)、所有者は、電話機500を操作して認証データ506をセキュリティコントローラ501に送る(動作U2)。これに対してセキュリティコントローラ501は、要求確認507を返送する(動作S2)。
【0009】
所有者が、電話機500を操作して保護要求508をセキュリティコントローラ501に送ると(動作U3)、セキュリティコントローラ501は、PHSシステムDB502に対して携帯端末検索要求510を送信する(動作S3)。PHSシステムDB502が、位置登録の有無を検索し、その検索結果を携帯端末検索レスポンス511としてセキュリティコントローラ501に送る(動作N1)。
【0010】
セキュリティコントローラ501は、目的の携帯端末503が位置登録されている場合、その携帯端末503に対し情報保護命令512を送信する(動作S4)。情報保護命令512を受信した携帯端末503は、保護プログラムを実行し、保護データを伴う保護完了報告/データをセキュリティコントローラ501に送る(動作P1)。このように紛失した携帯端末503内重要情報のセキュリティコントローラ501への回収と無効化が行われると、セキュリティコントローラ501は、電話機500に対し、終了通知509を送り、所有者に知らせる(動作S5)。
【0011】
また、図6は、特許文献2で提案されているバイオメトリスク情報による個人認証機能を有する携帯電子装置の構成を示すブロック図である。特許文献2では、盗難や模倣が不可能なバイオメトリクス情報による個人認証を用いて秘密情報を保護する方法が開示されている。
【0012】
図6において、バイオメトリクス情報入力部614は、認証対象者のバイオメトリクス情報を計測して入力する。バイオメトリクス特徴情報抽出部615は、バイオメトリクス情報入力部614にて計測されたバイオメトリクス情報から照合用バイオメトリクス特徴情報を抽出する。参照用バイオメトリクス特徴情報保存部616は、当該装置の所有者についての参照用バイオメトリクス特徴情報を予め保存している。
【0013】
バイオメトリクス特徴情報照合部617は、バイオメトリクス特徴情報抽出部615にて抽出された照合用バイオメトリクス特徴情報と参照用バイオメトリクス特徴情報保存部616に保存されている参照用バイオメトリクス特徴情報とを比較照合する。
【0014】
照合用バイオメトリクス特徴情報と参照用バイオメトリクス特徴情報とを照合した結果、照合用バイオメトリクス特徴情報が所有者本人のものであると認識されると、表示制御部620が秘密情報を暗証コード保存部619から読み出し、その秘密情報を情報表示部618に表示させるように制御する。
【0015】
【特許文献1】
特開平9−215057号公報
【特許文献2】
特開2001−236324号公報
【0016】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、従来の携帯電話端末装置においては、端末紛失時に端末内の残された個人情報の保護のために無線ネットワークを利用しているので、端末が電波の届かない圏外領域にある場合には、個人情報の保護、回収が不可能となるという問題がある。
【0017】
また、一度個人認証がなされると、重要な個人情報を見ることができるので、個人認証が行われた後に携帯電話端末装置の紛失や盗難にあった場合には、個人情報の保護ができなくなるという問題もある。
【0018】
本発明では、かかる点に鑑みてなされたものであり、ネットワークを用いずに携帯電話端末装置内の構成のみによって個人情報を保護し、かつ一度個人認証がなされた後に紛失や盗難にあっても個人情報を保護することのできる携帯電話端末装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0019】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明の携帯電話端末装置は、使用者の生体情報を入力する入力手段と、所有者の生体情報を参照用生体情報として保存する所有者判定用メモリと、使用時に前記入力手段から入力される前記使用者の生体情報と前記所有者判定用メモリに保存される前記参照用生体情報とを比較・照合する個人認証手段と、使用時に前記個人認証手段を起動する個人認証起動手段と、前記個人認証手段の判定結果を受けて、不一致と判定された場合には、当該携帯電話端末装置の主電源をOFF状態に制御し、一致と判定された場合には、前記主電源をON状態に制御する主電源制御手段と、少なくとも前記入力手段と前記所有者判定用メモリと前記個人認証手段と前記主電源制御手段とに電源を供給する補助電源と、前記主電源から電源供給を受けて当該携帯電話端末装置を通常機能使用可能状態に制御する第1保護手段と、前記通常機能使用可能状態にあるときに、一定期間不使用が継続したときは個人情報を退避させ、使用があったとき前記個人認証手段を起動して比較・照合の判定結果を取得し、一致と判定された場合に前記退避させた個人情報を元の状態に復元する第2保護手段と、を具備した構成を採る。
【0022】
この構成によれば、無線ネットワークを使用せずに端末の紛失又は盗難時に個人情報の保護が可能となるので、端末が電波の届かない圏外領域にある場合でも個人情報の保護を行うことができる。また、個人情報の閲覧時に紛失した場合や盗難に遭遇した場合にも一定時間使用していないと、再度個人認証が行われるので、個人情報の保護が可能となる。さらに、補助電源を使用することで主電源が個人認証動作によって消費されることがなくなるので、携帯電話端末装置の長時間使用が可能となる。
【0023】
本発明の携帯電話端末装置は、上記の発明において、当該携帯電話端末装置の現在位置を取得する位置情報取得手段と、前記使用者と前記所有者との生体情報が不一致の場合に、前記位置情報取得手段にて取得された現在位置を警察又はサービス会社に通報する通報手段と、を具備する構成を採る。
【0024】
この構成によれば、端末の紛失又は盗難時には位置情報を警察又はサービス会社に送信することができるので、端末回収が可能となる。
【0025】
本発明の携帯電話端末装置は、上記の発明において、前記使用者と前記所有者との生体情報が不一致の場合に非所有者である前記使用者の生体情報を保存する非所有者保存メモリを具備し、前記通報手段は、前記現在位置に前記非所有者保存メモリに保存した非所有者の生体情報を付加して警察又はサービス会社に通報する構成を採る。
【0026】
この構成によれば、端末の紛失又は盗難時には端末や個人情報の悪用を試みた非所有者の生体情報を警察又はサービス会社に送信できるので、端末回収が可能になるとともに、悪用を未然に防ぐことが可能となる。
【0027】
【発明の実施の形態】
本発明の骨子は、当該携帯電話端末装置の使用時に生体情報(例えば指紋、掌紋、指型、音声、網膜、虹彩)を用いて個人認証を行い、個人認証ができた場合でも不使用期間の後に使用が行われた場合には再度個人認証を行うようにし、認証のための特別な無線ネットワークを必要とせずに個人情報の保護が行えるようにすることである。
【0028】
以下、本発明の実施の形態について、図面を用いて詳細に説明する。
【0029】
(実施の形態1)
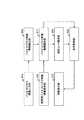
図1は、本発明の実施の形態1に係る携帯電話端末装置の構成を示すブロック図である。
【0030】
図1に示す本実施の形態1に係る携帯電話端末装置100は、中央演算処理装置(CPU)101と、個人認証部102と、入力装置103と、所有者判定用メモリ104、退避/復元部105と、主電源装置106とを備えている。
【0031】
CPU101は、各種情報処理やデータ通信を行う機能を実現する他、個人認証部102と入力装置103と所有者判定用メモリ104と退避/復元部105と主電源装置106とを制御して、個人情報の保護機能を実現する。
【0032】
入力装置103は、認識対象者である使用者の生体情報を取得し、取得した生体情報を個人認証部102に渡す。ここで、生体情報は、例えば、指紋、掌紋、指型、音声、網膜、虹彩などである。
【0033】
所有者判定用メモリ104には、所有者の生体情報が参照用生体情報として予め保存されている。
【0034】
個人認証部102は、入力装置103にて取得された認識対象者である使用者の生体情報と、予め所有者判定用メモリ104に保存されている所有者の生体情報との一致比較を行い、所有者/非所有者の判定結果をCPU101に渡す。
【0035】
主電源装置106は、CPU101と、個人認証部102と、入力装置103と、所有者判定用メモリ104と、退避/復元部105とに電源を供給する。
【0036】
CPU101は、使用時に個人認証部102を起動して所有者/非所有者の判定結果を取得し、その判定結果に応じて、当該携帯電話端末装置を通常機能使用可能状態に移行させるか、主電源装置106をOFFするかの制御を行う。
【0037】
CPU101は、当該携帯電話端末装置を通常機能使用可能状態に移行させた後は、使用状態を監視し、当該携帯電話端末装置が一定時間不使用の状態が続いた場合に、退避/復元部105を制御して、直前までのプログラムカウンタや動作していたメモリ領域を退避させ、使用に備えて個人認証部102を起動し、生体情報の入力を待機する。
【0038】
そして、CPU101は、上記の不使用処理の後において行われた個人認証によって所有者と認められた場合に、退避/復元部105を制御して、上記退避させたプログラムカウンタや動作していたメモリ領域を元の状態に復元させる。
【0039】
次に、以上のように構成された携帯電話端末装置の動作について説明する。使用者が主電源装置106をONすると、CPU101は、まず個人認証部102を起動させる。使用者が入力装置103によって生体情報を当該携帯電話端末装置内に入力すると、個人認証部102は、入力された使用者の生体情報と所有者判定用メモリ104内の所有者の生体情報との一致不一致を比較・照合し、所有者/非所有者判定結果をCPU101に渡す。
【0040】
CPU101は、個人認証の判定結果が所有者である場合には当該携帯電話端末装置を通常機能使用可能状態に移行させる制御を行い、個人認証モードを解除する一方、個人認証の判定結果が非所有者である場合には主電源装置106をOFFする。
【0041】
また、CPU101は、通常機能使用可能状態において使用状態を監視し、一定時間使用していない状態が続いた場合には、退避/復元部105を制御し、プログラムカウンタ、実行中のアプリケーションや動作メモリ領域を退避させる。併せて、CPU101は、個人認証部102を起動し、待機状態に入る。
【0042】
このように不使用処理が行われた後も個人認証モードは維持されるので、使用者が再度携帯電話端末装置を使用する場合には、上記と同様な個人認証が行われ、同時にCPU101がアクティブ状態へと変更される。
【0043】
CPU101は、個人認証の判定結果が所有者である場合には、退避/復元部105を制御し、プログラムカウンタ、実行中であったアプリケーションや動作メモリ領域を復元させ、通常機能使用可能状態へと状態を変更する。これによって個人認証モードは解除される。但し、CPU101は、個人認証の判定結果が非所有者である場合には個人認証モードは解除しない。
【0044】
このとき、個人認証部102が起動している場合であっても、当該携帯電話端末装置の所有者は、電話やメールの着信、ニュースや天気予報などの各種情報サービスが受けられるように予め設定することが可能である。
【0045】
以上のように、本実施の形態1によれば、無線ネットワークを使用せずに端末の紛失又は盗難時に個人情報の保護が可能となるので、端末が電波の届かない圏外領域にある場合でも個人情報の保護を行うことができる。
【0046】
また、個人認証が行えたときでも一定期間使用していないと、再度個人認証が行われるので、個人情報の閲覧時に紛失した場合や盗難に遭遇した場合にも個人情報の保護が可能となる。
【0047】
(実施の形態2)
図2は、本発明の実施の形態2に係る携帯電話端末装置の構成を示すブロック図である。なお、図2では、図1に示した構成と同一ないしは同等である構成要素には同一の符号が付されている。ここでは、実施の形態2に関わる部分を中心に説明する。
【0048】
図2に示す本実施の形態2に係る携帯電話端末装置200では、図1に示した構成において、個人認証部102を起動する個人認証起動部201と、個人認証部102から所有者/非所有者の判定結果を受ける制御部202と制御部202の出力を一方の入力とするAND回路203とが設けられている。
【0049】
個人認証起動部201は、使用者とのインタフェースであり、使用者の動作に反応して個人認証部102を起動するようになっている。使用者の動作としては、例えば、入力装置103がカメラである場合にそのカメラレンズの蓋を外す行為、当該携帯電話端末装置のキーを操作する行為、当該携帯電話端末装置が折り畳み式である場合にフリップを開く行為、などを挙げることができる。
【0050】
制御部202は、個人認証部102での判定結果が、所有者である場合には出力を高レベルにし、非所有者である場合には出力を低レベルにする。
【0051】
また、主電源装置106に代えて主電源装置204が設けられ、補助電源装置205が追加されている。主電源装置204は、例えばバッテリパックであり、装着状態を示すnLVA信号をAND回路203の他方の入力に与えるようになっている。nLVA信号は、装着時には高レベルとなり、非装着時には低レベルとなる信号である。
【0052】
補助電源装置205は、個人認証部102と入力装置103と所有者判定用メモリ104と個人認証起動部201と制御部202とに電源を供給するようになっている。
【0053】
主電源装置204は、AND回路203の出力がリセット解除を示す高レベルのとき、ON動作を行い、CPU101,退避/復元部105など補助電源装置205を電源としていない各部に電源供給を行う。また、主電源装置204は、CPU101の制御を受けて、OFF動作を行う点は、主電源装置106と同様である。
【0054】
次に、以上のように構成された携帯電話端末装置の動作について説明する。使用者が個人認証起動部201を動作させたときに、個人認証部102は起動する。ここで、入力装置103が例えばカメラである場合には、個人認証起動部201は、カメラレンズのふたを外すという行為に応答して個人認証部102を起動することになる。
【0055】
使用者が入力装置103によって生体情報を当該携帯電話端末装置内に入力すると、個人認証部102は、入力された使用者の生体情報と所有者判定用メモリ104内の所有者の生体情報との一致不一致を比較し、所有者/非所有者判定結果を制御部202に渡す。
【0056】
制御部202は、個人認証部102からの判定結果が、使用者が所有者でないこと示す場合には、出力を低レベルにするので、AND回路203の出力は、主電源装置204からのnLVA信号のレベルとは無関係に、低レベルとなる。その結果、主電源装置204は、AND回路203からリセット解除信号が入力されないので、ON動作をしない。
【0057】
一方、制御部202は、個人認証部102からの判定結果が、使用者が所有者であることを示す場合には、出力を高レベルにする。そして、主電源装置204が装着されている場合には、nLVA信号は高レベルになっている。その結果、AND回路203の出力は、高レベルとなり、主電源装置204は、AND回路203からリセット解除信号が入力され、ON動作をする。
【0058】
CPU101は、電源が供給されると、携帯電話端末装置を通常機能使用可能状態に移行させる制御を行う。そして、CPU101は、通常機能使用可能状態において使用状態を監視する。
【0059】
CPU101は、一定時間使用していない状態が続いた場合には、退避/復元部105を制御し、プログラムカウンタ、実行中のアプリケーションや動作メモリ領域を退避させる。併せて、CPU101は、個人認証部102を起動し、待機状態に入る。
【0060】
このように不使用処理が行われた後も個人認証モードは維持されるので、使用者が再度携帯電話端末装置を使用する場合には、CPU101は、個人認証部102から入力される所有者/非所有者の判定結果が、所有者である場合には、退避/復元部105を制御し、プログラムカウンタ、実行中であったアプリケーションや動作メモリ領域を復元させ、通常機能使用可能状態へと状態を変更する。これによって個人認証モードは解除される。但し、CPU101は、個人認証の判定結果が非所有者である場合には個人認証モードは解除しない。
【0061】
このとき、個人認証部102が起動している場合であっても、当該携帯電話端末装置の所有者は、電話やメールの着信、ニュースや天気予報などの各種情報サービスが受けられるように予め設定することが可能である。
【0062】
以上のように、本実施の形態2によれば、無線ネットワークを使用せずに端末の紛失又は盗難時に個人情報の保護が可能となるので、端末が電波の届かない圏外領域にある場合でも個人情報の保護を行うことができる。
【0063】
また、個人認証が行えたときでも一定期間使用していないと、再度個人認証が行われるので、個人情報の閲覧時に紛失した場合や盗難に遭遇した場合にも個人情報の保護が可能となる。
【0064】
加えて、個人認証部への電源供給を補助電源によって行い、主電源が個人認証部の認証動作によって消費されないようにしたので、携帯電話端末装置の長時間使用が可能となる。
【0065】
(実施の形態3)
図3は、本発明の実施の形態3に係る携帯電話端末装置の構成を示すブロック図である。なお、図3では、図1に示した構成と同一ないしは同等である構成要素には同一の符号が付されている。ここでは、実施の形態2に関わる部分を中心に説明する。
【0066】
図3に示す本実施の形態3に係る携帯電話端末装置300では、図1に示した構成において、位置情報取得部301と通報部302とが追加されている。
【0067】
位置情報取得部301は、GPSを用いて携帯電話端末装置の位置情報を取得し、CPU101に与える。
【0068】
通報部302は、CPU101から指令を受けて、警察又は携帯電話サービス会社と通信を行い、位置情報取得部301が取得した位置情報その他のデータを送信する。
【0069】
次に、以上のように構成された携帯電話端末装置の動作について説明する。CPU101は、個人認証部102の判定結果が非所有者である場合に、位置情報取得部301から取得した位置情報を通報部302から警察又は携帯電話サービス会社に送信させる。この処理は、通常機能使用可能状態時に一定時間使用しない状態が続いた場合の個人認証においても同様に行われる。
【0070】
このとき、個人認証部102が起動している場合であっても、当該携帯電話端末装置の所有者は、電話やメールの着信、ニュースや天気予報などの各種情報サービスが受けられるように予め設定することが可能である。
【0071】
以上のように、本実施の形態3によれば、実施の形態1,2と同様の効果が得られるのに加えて、端末の紛失又は盗難時には位置情報を警察又はサービス会社に送信することができるので、端末回収が可能となる。
【0072】
なお、実施の形態3では実施の形態1への適用例を示すが、実施の形態2にも同様に適用できることは言うまでもない。
【0073】
(実施の形態4)
図4は、本発明の実施の形態4に係る携帯電話端末装置の構成を示すブロック図である。なお、図4では、図3に示した構成と同一ないしは同等である構成要素には同一の符号が付されている。ここでは、実施の形態4に関わる部分を中心に説明する。
【0074】
図4に示す本実施の形態4に係る携帯電話端末装置400では、図3に示した構成において、所有者以外の生体情報を保存する非所有者保存メモリ401が個人認証部102に接続されている。
【0075】
次に、以上のように構成された携帯電話端末装置の動作について説明する。個人認証部102は、使用者の生体情報と所有者の生体情報とを比較し、判定結果をCPU101に渡すとともに、非所有者であると判定したときその非所有者の生体情報を非所有者保存メモリ401の格納する。
【0076】
CPU101は、判定結果が非所有者である場合に、位置情報取得部301から取得した位置情報及び非所有者保存メモリ401から読み出した非所有者の生体情報を通報部302から警察又は携帯電話サービス会社に送信させる。この処理は、通常機能使用可能状態時に一定時間使用しない状態が続いた場合の個人認証においても同様に行われる。
【0077】
このとき、個人認証部102が起動している場合であっても、当該携帯電話端末装置の所有者は、電話やメールの着信、ニュースや天気予報などの各種情報サービスが受けられるように予め設定することが可能である。
【0078】
以上のように、本実施の形態4によれば、実施の形態1,2と同様の効果が得られるのに加えて、端末の紛失又は盗難時には位置情報および非所有者の生体情報を警察又はサービス会社に送信することができるので、端末回収が可能になるのに加えて、悪用を未然に防ぐことが可能となる。
【0079】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明によれば、無線ネットワークを使用せずに個人情報を保護することができるので、端末が電波の届かない圏外領域にある場合でも個人情報の保護を行うことができる。そして、認証が取れたとしても一定期間使用していない場合には再度認証を行うので、個人情報の閲覧時に紛失した場合や盗難に遭遇した場合にも個人情報の保護が可能となり、端末や個人情報の悪用が未然に防げる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の形態1に係る携帯電話端末装置の構成を示すブロック図
【図2】本発明の実施の形態2に係る携帯電話端末装置の構成を示すブロック図
【図3】本発明の実施の形態3に係る携帯電話端末装置の構成を示すブロック図
【図4】本発明の実施の形態4に係る携帯電話端末装置の構成を示すブロック図
【図5】従来の情報保護システムにおいて実施される保護手順を示すシーケンス図
【図6】従来のバイオメトリスク情報による個人認証機能を有する携帯電子装置の構成を示すブロック図
【符号の説明】
100、200、300、400 携帯電話端末装置
101 中央演算処理装置(CPU)
102 個人認証部
103 入力装置
104 所有者判定用メモリ
105 退避/復元部
106、204 主電源装置
201 個人認証起動部
202 制御部
203 AND回路
205 補助電源装置
301 位置情報取得部
302 通報部
401 非所有者保存メモリ[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a mobile phone terminal device that requires protection of personal information.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, as seen in the spread of the Internet, the start of digital broadcasting, and the mobile revolution, the advancement of digital technology has led to rapid advancement of information and communication networks. In particular, mobile phone terminal devices in the mobile field have become multifunctional and highly functional, and accordingly, a lot of personal information is included. At present, electronic information and image information can be transmitted and received via a wired / wireless communication network using a mobile phone terminal device, and bank approval, electronic commerce, stock trading, etc. can also be performed. .
[0003]
Accordingly, with the increase in functionality and functionality of mobile phone terminals, opportunities to use them regardless of time and place are increasing. On the other hand, if the opportunity to use it at any time and place increases, there will be more opportunities to reach the other person's hand by encountering theft in the middle of moving or being lost carelessly.
[0004]
When using a multi-function / high-function mobile phone terminal device in this way, the user authenticates the individual by entering an ID or password each time the application is started. In addition, when performing bank approval and electronic commerce, the user authenticates the individual by inputting an account number or a personal identification number of the bank used. However, if it is in the hands of others as described above, there is a risk that personal information in the terminal will be referenced and misused.
[0005]
Therefore, conventionally, various proposals have been made as measures for protecting highly confidential information when such a terminal is lost or stolen (for example, Patent Document 1 (mobile terminal and mobile terminal information protection method)). Patent Document 2 (a portable electronic device having a personal authentication function based on biometric risk information)). Hereinafter, the outline will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0006]
FIG. 5 is a sequence diagram showing a protection procedure performed in the information protection system proposed in Patent Document 1. Patent Document 1 discloses a method for protecting and collecting personal information left in a lost mobile terminal.
[0007]
In FIG. 5, the owner of the portable terminal 503 registers the security management data of the portable terminal 503 in advance in the security controller 501 connected to the wireless network.
[0008]
When the owner who notices the loss of the portable terminal 503 operates the telephone 500 and sends a protection request 504 to the security controller 501 (operation U1), an authentication confirmation 505 is returned from the security controller 501 (operation S1). The owner operates telephone 500 to send authentication data 506 to security controller 501 (operation U2). In response to this, the security controller 501 returns a request confirmation 507 (operation S2).
[0009]
When the owner operates the telephone 500 to send a protection request 508 to the security controller 501 (operation U3), the security controller 501 transmits a mobile terminal search request 510 to the PHS system DB 502 (operation S3). The PHS system DB 502 searches for the presence / absence of location registration, and sends the search result to the security controller 501 as a mobile terminal search response 511 (operation N1).
[0010]
When the target portable terminal 503 is registered in the location, the security controller 501 transmits an information protection instruction 512 to the portable terminal 503 (operation S4). Receiving the information protection instruction 512, the portable terminal 503 executes the protection program and sends a protection completion report / data with protection data to the security controller 501 (operation P1). When the lost important information in the portable terminal 503 is collected and invalidated in the security controller 501, the security controller 501 sends an end notification 509 to the telephone 500 to notify the owner (operation S5). .
[0011]
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a portable electronic device having a personal authentication function based on biometric risk information proposed in Patent Document 2. Patent Document 2 discloses a method for protecting secret information using personal authentication based on biometric information that cannot be stolen or imitated.
[0012]
In FIG. 6, a biometric
[0013]
The biometrics feature
[0014]
When the collation biometric feature information and the reference biometric feature information are collated, if it is recognized that the collation biometric feature information belongs to the owner, the
[0015]
[Patent Document 1]
Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 9-215057 [Patent Document 2]
JP 2001-236324 A [0016]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in the conventional mobile phone terminal device, since the wireless network is used to protect the personal information remaining in the terminal when the terminal is lost, when the terminal is in an out-of-service area where radio waves do not reach, There is a problem that it becomes impossible to protect and collect personal information.
[0017]
In addition, once personal authentication is performed, important personal information can be viewed. Therefore, if the mobile phone terminal is lost or stolen after personal authentication, personal information cannot be protected. There is also a problem.
[0018]
The present invention has been made in view of such points, and protects personal information only by the configuration in the mobile phone terminal device without using a network, and even if the personal information is once lost or stolen. An object of the present invention is to provide a mobile phone terminal device capable of protecting personal information.
[0019]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The cellular phone terminal device of the present inventionis input from the input means for inputting the user's biometric information, the owner determination memory for storing the biometric information of the owner as reference biometric information, and the input means at the time of use. Personal authentication means for comparing / collating the biometric information of the user with the reference biometric information stored in the owner determination memory, personal authentication starting means for starting the personal authentication means when used, and the individual If the determination result of the authentication means is received and it is determined that they do not match, the main power supply of the mobile phone terminal device is controlled to be in the OFF state, and if it is determined that they match, the main power supply is controlled to be in the ON state. Main power control means, auxiliary power for supplying power to at least the input means, the owner determination memory, the personal authentication means, and the main power control means, and the power supply from the main power supply A first protection means for controlling the mobile phone terminal device to a normal function usable state; and when the normal function usable state is in use, the personal information is evacuated and used when it is not used for a certain period of time. The personal authentication unit is activated to obtain a comparison / collation determination result, and when it is determined to match, the second protection unit restores the saved personal information to the original state. .
[0022]
According to this configuration, since personal information can be protected when the terminal is lost or stolen without using a wireless network, personal information can be protected even when the terminal is in an out-of-service area where radio waves do not reach. . In addition, even when the personal information is lost during browsing or when it is stolen, if the personal information is not used for a certain period of time, personal authentication is performed again, so that the personal information can be protected. Further, since the main power source is not consumed by the personal authentication operation by using the auxiliary power source, the mobile phone terminal device can be used for a long time.
[0023]
The mobile phone terminal device of the present invention is the mobile phone terminal device according to the above invention, wherein the location information acquisition means for acquiring the current location of the mobile phone terminal device and the biometric information of the user and the owner do not match. And a reporting means for reporting the current position acquired by the information acquisition means to the police or a service company.
[0024]
According to this configuration, when the terminal is lost or stolen, the position information can be transmitted to the police or the service company, so that the terminal can be collected.
[0025]
The mobile phone terminal device according to the present invention provides a non-owner storage memory for storing the biometric information of the user who is a non-owner when the biometric information of the user and the owner does not match in the above invention. And the reporting means adds the non-owner's biometric information stored in the non-owner storage memory to the current position and reports to the police or service company.
[0026]
According to this configuration, when the terminal is lost or stolen, the biometric information of the non-owner who attempted to misuse the terminal or personal information can be transmitted to the police or service company, so that the terminal can be collected and misuse can be prevented in advance. It becomes possible.
[0027]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The essence of the present invention is that personal authentication is performed using biometric information (for example, fingerprint, palm print, finger type, voice, retina, iris) when the mobile phone terminal device is used, and even when personal authentication is possible, When it is used later, personal authentication is performed again, and personal information can be protected without requiring a special wireless network for authentication.
[0028]
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[0029]
(Embodiment 1)
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile phone terminal apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
[0030]
A cellular
[0031]
The
[0032]
The
[0033]
In the
[0034]
The
[0035]
The main
[0036]
The
[0037]
The
[0038]
The
[0039]
Next, the operation of the mobile phone terminal device configured as described above will be described. When the user turns on the main
[0040]
If the determination result of personal authentication is the owner, the
[0041]
Further, the
[0042]
Since the personal authentication mode is maintained even after the non-use processing is performed in this way, when the user uses the mobile phone terminal again, the personal authentication similar to the above is performed and the
[0043]
If the determination result of the personal authentication is the owner, the
[0044]
At this time, even if the
[0045]
As described above, according to the first embodiment, personal information can be protected when a terminal is lost or stolen without using a wireless network. Therefore, even if the terminal is in an out-of-service area where radio waves do not reach, Information can be protected.
[0046]
Further, even if personal authentication can be performed, personal authentication is performed again if it has not been used for a certain period of time. Therefore, personal information can be protected even when it is lost or stolen when browsing personal information.
[0047]
(Embodiment 2)
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the mobile phone terminal apparatus according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In FIG. 2, the same reference numerals are given to components that are the same as or equivalent to the configuration shown in FIG. 1. Here, the description will focus on the parts related to the second embodiment.
[0048]
In the mobile
[0049]
The personal
[0050]
The
[0051]
Further, a main
[0052]
The auxiliary
[0053]
When the output of the AND
[0054]
Next, the operation of the mobile phone terminal device configured as described above will be described. When the user operates the personal
[0055]
When the user inputs biometric information into the mobile phone terminal device using the
[0056]
When the determination result from the
[0057]
On the other hand, if the determination result from the
[0058]
When power is supplied, the
[0059]
When the
[0060]
Since the personal authentication mode is maintained even after the non-use processing is performed in this way, when the user uses the mobile phone terminal again, the
[0061]
At this time, even if the
[0062]
As described above, according to the second embodiment, personal information can be protected when a terminal is lost or stolen without using a wireless network. Therefore, even if the terminal is in an out-of-service area where radio waves do not reach, Information can be protected.
[0063]
Further, even if personal authentication can be performed, personal authentication is performed again if it has not been used for a certain period of time. Therefore, personal information can be protected even when it is lost or stolen when browsing personal information.
[0064]
In addition, since the power supply to the personal authentication unit is performed by the auxiliary power source and the main power source is not consumed by the authentication operation of the personal authentication unit, the mobile phone terminal device can be used for a long time.
[0065]
(Embodiment 3)
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the mobile phone terminal apparatus according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. In FIG. 3, the same reference numerals are given to components that are the same as or equivalent to the configuration shown in FIG. 1. Here, the description will focus on the parts related to the second embodiment.
[0066]
In the mobile
[0067]
The position
[0068]
The
[0069]
Next, the operation of the mobile phone terminal device configured as described above will be described. When the determination result of the
[0070]
At this time, even if the
[0071]
As described above, according to the third embodiment, in addition to the same effects as those of the first and second embodiments, the location information can be transmitted to the police or service company when the terminal is lost or stolen. Since it can, terminal collection becomes possible.
[0072]
In addition, although the application example to Embodiment 1 is shown in Embodiment 3, it cannot be overemphasized that it is applicable to Embodiment 2 similarly.
[0073]
(Embodiment 4)
FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile phone terminal apparatus according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention. In FIG. 4, constituent elements that are the same as or equivalent to those shown in FIG. 3 are given the same reference numerals. Here, the description will be focused on the portion related to the fourth embodiment.
[0074]
In the mobile
[0075]
Next, the operation of the mobile phone terminal device configured as described above will be described. The
[0076]
When the determination result is a non-owner, the
[0077]
At this time, even if the
[0078]
As described above, according to the fourth embodiment, in addition to the same effects as those of the first and second embodiments, the location information and the non-owner's biometric information can be obtained from the police or the terminal when the terminal is lost or stolen. Since it can be transmitted to the service company, it becomes possible to collect the terminal and to prevent misuse in advance.
[0079]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, personal information can be protected without using a wireless network, so that personal information can be protected even when the terminal is in an out-of-service area where radio waves do not reach. . And even if it can be authenticated, if it has not been used for a certain period of time, it will be authenticated again, so it will be possible to protect personal information even if it is lost when browsing personal information or if it is stolen. Information misuse can be prevented.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile phone terminal apparatus according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile phone terminal apparatus according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile phone terminal apparatus according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile phone terminal apparatus according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention. FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a portable electronic device having a personal authentication function based on biometric risk information.
100, 200, 300, 400
102
Claims (3)
Translated fromJapanesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002296639AJP4125938B2 (en) | 2002-10-09 | 2002-10-09 | Mobile phone terminal |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002296639AJP4125938B2 (en) | 2002-10-09 | 2002-10-09 | Mobile phone terminal |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004134989A JP2004134989A (en) | 2004-04-30 |
| JP4125938B2true JP4125938B2 (en) | 2008-07-30 |
Family
ID=32286561
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002296639AExpired - Fee RelatedJP4125938B2 (en) | 2002-10-09 | 2002-10-09 | Mobile phone terminal |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4125938B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006146441A (en)* | 2004-11-17 | 2006-06-08 | Miyoshi:Kk | Identification information registered portable telephone, identification system using portable telephone, and identification device |
| JP2006195669A (en)* | 2005-01-12 | 2006-07-27 | Tokyo Medical & Dental Univ | Medical support system |
| US20070242887A1 (en)* | 2005-03-15 | 2007-10-18 | Sharp Kabushiki Kaisha | Portable Terminal, Image Information Matching Method for Portable Terminal, Image Information Matching Program, and Recording Medium |
| JP4736505B2 (en)* | 2005-03-30 | 2011-07-27 | 日本電気株式会社 | Mobile communication terminal, control method thereof, and terminal unauthorized use prevention system |
| JP4685515B2 (en)* | 2005-06-09 | 2011-05-18 | 株式会社日立製作所 | User authentication system and user authentication method thereof |
| JP2008227557A (en)* | 2005-06-24 | 2008-09-25 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Function use restriction method for wireless communication terminal, function use restriction program, and wireless communication terminal |
| JP4618103B2 (en)* | 2005-11-11 | 2011-01-26 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Information display device |
| JP2009015423A (en)* | 2007-07-02 | 2009-01-22 | Chugoku Electric Power Co Inc:The | Meter-reading handy terminal and charge collection management system |
| JP2014014194A (en)* | 2013-10-23 | 2014-01-23 | Kyocera Corp | Portable terminal device |
| JP6457471B2 (en)* | 2016-12-12 | 2019-01-23 | ファナック株式会社 | Operator identification system |
- 2002
- 2002-10-09JPJP2002296639Apatent/JP4125938B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004134989A (en) | 2004-04-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3969094B2 (en) | Information processing device | |
| US8224128B2 (en) | Portable information terminal device | |
| CN101960493B (en) | Biometric smart card for mobile devices | |
| US7275695B2 (en) | Portable terminal and function limiting method | |
| JP3258632B2 (en) | Fingerprint authentication device | |
| EP1569480B1 (en) | Mobile phone with restriction on use thereof and method for restricting use of mobile phone | |
| JP4125938B2 (en) | Mobile phone terminal | |
| US20090150993A1 (en) | Mobile Device with Frequently Operated Biometric Sensors | |
| CN107292150A (en) | Save user identification confirmation method and apparatus in information processing from damage | |
| US20090165119A1 (en) | Method, apparatus and computer program product for providing power control security features | |
| JP2003242428A (en) | Cellular phone with card function and cellular phone with settlement function | |
| JP2008276345A (en) | Electronic device, authentication method and program | |
| JP6383795B2 (en) | Information processing method, terminal, server, communication method, and system | |
| JP5119801B2 (en) | Portable information terminal, portable information terminal authentication method, and portable information terminal authentication program | |
| CN108347730B (en) | Wireless communication processing method and device | |
| JPH1051441A (en) | Radio communication terminal equipment | |
| JP2001245354A (en) | Automatic dial lock system for mobile phones | |
| JPH11262059A (en) | Portable terminal for mobile communication and personal identification method | |
| KR100705164B1 (en) | User registration system and method using mobile terminal | |
| JP4601042B2 (en) | Mobile terminal and power supply control method | |
| JP2003274006A (en) | Mobile phone having fingerprint authentication function and personal authentication method thereof | |
| JP2009290481A (en) | Portable electronic apparatus and network system of portable electronic apparatus | |
| JP2003203215A (en) | Memory card reader, portable terminal device and portable terminal system | |
| KR20050095710A (en) | The security solution of mobile handset by using fingerprint indentity module | |
| JP2004355057A (en) | Network login system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20051007 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20070423 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20070619 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20070809 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20080115 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20080214 | |
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date:20080325 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20080415 | |
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20080509 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110516 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110516 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120516 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120516 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130516 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130516 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |