JP4015435B2 - Heating and cooling devices using thermoelectric elements - Google Patents
Heating and cooling devices using thermoelectric elementsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4015435B2 JP4015435B2JP2002037466AJP2002037466AJP4015435B2JP 4015435 B2JP4015435 B2JP 4015435B2JP 2002037466 AJP2002037466 AJP 2002037466AJP 2002037466 AJP2002037466 AJP 2002037466AJP 4015435 B2JP4015435 B2JP 4015435B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- thermoelectric module
- partial
- thermoelectric
- heating
- stage
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Cooling Or The Like Of Electrical Apparatus (AREA)
- Cooling Or The Like Of Semiconductors Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
熱電素子を使って加熱および冷却を行うための技術に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来の、熱電モジュールを使ったヒートポンプで加熱または冷却する装置ではCOPを上げる方法として、熱電モジュールの絶縁プレートに接合されている放熱器および吸熱器の能力を上げる方法が使われていた。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
熱電モジュールを使った加熱および冷却デバイスのCOPは、熱電モジュールに結合された放熱器や吸熱器の能力と熱電モジュール自体のCOPによって決まる。ところが熱電モジュールのCOPはその低温サイドと高温サイドの温度差によって変化する。従来の熱電モジュールを使った加熱および冷却デバイスでは熱電モジュールの低温サイドと高温サイドの温度差は使用環境で決まってしまうのでCOPを上げるために前記温度差を制御することはできなかった。
【0004】
さらに、熱電モジュールはその低温サイドと高温サイド間に温度差があるため熱応力を発生する。この熱応力が熱電素子、接合部、絶縁プレートに繰り返しかかると破損することがよくあった。
【0005】
【課題を解決するための手段】
熱電モジュールをヒートポンプとして使った場合、図4に示すように低温サイドと高温サイドの温度差が低いほどCOPが高い。一方、熱電モジュールを多段にして負荷を分担し、各段の部分熱電モジュール4にそれぞれ電極をつけて電気的に独立させ、さらに各絶縁プレートに温度センサーを取り付けた構造とすれば、部分熱電モジュール4に流す電流を各絶縁プレートの温度をもとにして個別に制御できる。そこで、電流を制御して、各部分熱電モジュール4の低温サイドと高温サイドの温度差を、高いCOPを得られる温度差にすればエネルギー効率の良い加熱または冷却を行うことができる。
【0006】
本発明の多段熱電モジュールはその低温サイドと高温サイド間の温度差を各部分熱電モジュールに分散しているため発生する熱応力も小さくすることができる。そして各部分熱電モジュールと絶縁プレートの接着を半田付けなどの固着方法ではなく、相対的な動きを許すメカニカルな接合とすればさらに熱応力を軽減することができ、熱応力による破損を防止することができる。
【0007】
【発明の実施の形態】
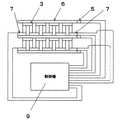
図1、2、3、5は本発明の実施例を説明する図である。本発明の多段熱電モジュール8(図2、図5)は、P型半導体熱電素子1とN型半導体熱電素子2が導電ブリッジ3にて接合されている部分熱電モジュール4が絶縁プレート6を介して多段に結合されている。各段の部分熱電モジュールは電気的に絶縁されており、それぞれ電極7が付けられている。そして絶縁プレート6には温度センサ5が取りつけられている。各段の部分熱電モジュール4の電極7、および絶縁プレート6の温度センサ5は制御機9に接続されている。制御機9は各部分熱電モジュール4に電気を供給する電源と制御部からなる。制御部は部分熱電モジュールの高温サイドと低温サイドの温度差が所定の温度差になるように部分熱電モジュール4に供給する電流を制御する。
【0008】
図5に示す多段熱電モジュール8は熱応力低減を特に考慮した、本発明に使用する多段熱電モジュールの一例で、部分熱電モジュール4の高温サイドと低温サイドに絶縁プレート6を半田付けしたものをさらに結合した多段熱電モジュールである。1段目部分熱電モジュールと2段目部分熱電モジュールはスプリングを介してボルトで結合されている。したがって、それぞれの部分熱電モジュールは互いにスライド可能で、その結果熱応力を低減できる。
【0009】
【発明の効果】
本発明の多段熱電モジュールは電気的に独立した部分熱電モジュールを多段にしているため、各部分熱電モジュールの電流を制御することでCOPの高い温度差で熱電モジュールを使うことができる。
【0010】
また本発明の多段熱電モジュールは一段当りの低温サイドと高温サイド間の温度差を低くすることができ、その結果熱応力を低くすることができる。また各部分熱モジュール間や絶縁プレートと部分熱電モジュール間の接合をメカニカルなものにすることでさらに熱応力を低減することができる。その結果熱応力による破損を防止することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の、熱電素子を用いた加熱および冷却デバイスの一例である。
【図2】本発明に使用する多段熱電モジュールの一例の側面図である。
【図3】本発明の熱電モジュールに使う部分熱電モジュールの一例である。
【図4】通常の熱電モジュールにおけるCOP値と温度差の関係
【図5】本発明に使用する、特に熱応力を考慮した多段熱電モジュールの一例の側面図である。
【符号の説明】
1 P型半導体の熱電素子
2 N型半導体の熱電素子
3 導電ブリッジ
4 部分熱電モジュール
5 温度センサー
6 絶縁プレート
7 電極
8 多段熱電モジュール
9 制御機
10 放熱器
11 吸熱器
12 スプリング
13 ボルト、ナット[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a technique for heating and cooling using a thermoelectric element.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In a conventional apparatus for heating or cooling with a heat pump using a thermoelectric module, as a method of increasing COP, a method of increasing the ability of a radiator and a heat absorber bonded to an insulating plate of the thermoelectric module has been used.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
The COP of the heating and cooling device using the thermoelectric module is determined by the ability of the radiator and heat sink coupled to the thermoelectric module and the COP of the thermoelectric module itself. However, the COP of the thermoelectric module changes depending on the temperature difference between the low temperature side and the high temperature side. In a conventional heating and cooling device using a thermoelectric module, the temperature difference between the low temperature side and the high temperature side of the thermoelectric module is determined by the usage environment, and thus the temperature difference cannot be controlled to increase COP.
[0004]
Further, the thermoelectric module generates thermal stress because of the temperature difference between the low temperature side and the high temperature side. When this thermal stress is repeatedly applied to the thermoelectric element, the joint, and the insulating plate, it is often damaged.
[0005]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
When the thermoelectric module is used as a heat pump, the COP increases as the temperature difference between the low temperature side and the high temperature side decreases, as shown in FIG. On the other hand, if the thermoelectric module is divided into multiple stages, the load is shared, electrodes are attached to the partial
[0006]
Since the multi-stage thermoelectric module of the present invention distributes the temperature difference between the low temperature side and the high temperature side to each partial thermoelectric module, the generated thermal stress can be reduced. And if the bonding of each partial thermoelectric module and the insulating plate is not a fixing method such as soldering but mechanical bonding that allows relative movement, thermal stress can be further reduced and damage due to thermal stress can be prevented. Can do.
[0007]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
1, 2, 3, and 5 are diagrams for explaining an embodiment of the present invention. The multi-stage thermoelectric module 8 (FIGS. 2 and 5) of the present invention includes a partial
[0008]
A multi-stage
[0009]
【The invention's effect】
Since the multi-stage thermoelectric module of the present invention has multi-stages of electrically independent partial thermoelectric modules, the thermoelectric module can be used with a high COP temperature difference by controlling the current of each partial thermoelectric module.
[0010]
In addition, the multistage thermoelectric module of the present invention can reduce the temperature difference between the low temperature side and the high temperature side per step, and as a result, the thermal stress can be reduced. Moreover, thermal stress can be further reduced by mechanically joining each partial heat module or between the insulating plate and the partial thermoelectric module. As a result, damage due to thermal stress can be prevented.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is an example of a heating and cooling device using a thermoelectric element of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a side view of an example of a multi-stage thermoelectric module used in the present invention.
FIG. 3 is an example of a partial thermoelectric module used in the thermoelectric module of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a side view of an example of a multi-stage thermoelectric module used in the present invention, particularly considering thermal stress.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (2)
Translated fromJapanesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002037466AJP4015435B2 (en) | 2002-01-08 | 2002-01-08 | Heating and cooling devices using thermoelectric elements |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002037466AJP4015435B2 (en) | 2002-01-08 | 2002-01-08 | Heating and cooling devices using thermoelectric elements |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003204087A JP2003204087A (en) | 2003-07-18 |
| JP4015435B2true JP4015435B2 (en) | 2007-11-28 |
Family
ID=27655102
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002037466AExpired - Fee RelatedJP4015435B2 (en) | 2002-01-08 | 2002-01-08 | Heating and cooling devices using thermoelectric elements |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4015435B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4528576B2 (en)* | 2003-08-15 | 2010-08-18 | 株式会社東芝 | Heat flow control system |
| US7587901B2 (en) | 2004-12-20 | 2009-09-15 | Amerigon Incorporated | Control system for thermal module in vehicle |
| JP4622585B2 (en)* | 2005-03-02 | 2011-02-02 | 株式会社Ihi | Cascade module for thermoelectric conversion |
| US8222511B2 (en) | 2006-08-03 | 2012-07-17 | Gentherm | Thermoelectric device |
| US20080087316A1 (en) | 2006-10-12 | 2008-04-17 | Masa Inaba | Thermoelectric device with internal sensor |
| US9105809B2 (en) | 2007-07-23 | 2015-08-11 | Gentherm Incorporated | Segmented thermoelectric device |
| WO2009036077A1 (en) | 2007-09-10 | 2009-03-19 | Amerigon, Inc. | Operational control schemes for ventilated seat or bed assemblies |
| US8181290B2 (en) | 2008-07-18 | 2012-05-22 | Amerigon Incorporated | Climate controlled bed assembly |
| CN114715003A (en) | 2008-02-01 | 2022-07-08 | 金瑟姆股份公司 | Condensation and humidity sensor for thermoelectric devices |
| JP5315874B2 (en)* | 2008-09-16 | 2013-10-16 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | Temperature controller and its preheating or precooling method |
| WO2013052823A1 (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2013-04-11 | Gentherm Incorporated | Thermoelectric device controls and methods |
| US9989267B2 (en) | 2012-02-10 | 2018-06-05 | Gentherm Incorporated | Moisture abatement in heating operation of climate controlled systems |
| US20130291555A1 (en)* | 2012-05-07 | 2013-11-07 | Phononic Devices, Inc. | Thermoelectric refrigeration system control scheme for high efficiency performance |
| DE102012214701A1 (en) | 2012-08-17 | 2014-02-20 | Behr Gmbh & Co. Kg | Thermoelectric device |
| DE102012214702A1 (en) | 2012-08-17 | 2014-02-20 | Behr Gmbh & Co. Kg | Thermoelectric device |
| DE102012214704A1 (en) | 2012-08-17 | 2014-03-27 | Behr Gmbh & Co. Kg | Thermoelectric module |
| JP2014052127A (en)* | 2012-09-06 | 2014-03-20 | Toshiba Corp | Peltier cooling device, and its cooling method |
| DE102012224486A1 (en)* | 2012-12-28 | 2014-04-10 | Behr Gmbh & Co. Kg | Heat exchanger |
| US9662962B2 (en) | 2013-11-05 | 2017-05-30 | Gentherm Incorporated | Vehicle headliner assembly for zonal comfort |
| WO2015123585A1 (en) | 2014-02-14 | 2015-08-20 | Gentherm Incorporated | Conductive convective climate controlled seat |
| US10458683B2 (en) | 2014-07-21 | 2019-10-29 | Phononic, Inc. | Systems and methods for mitigating heat rejection limitations of a thermoelectric module |
| WO2016077843A1 (en) | 2014-11-14 | 2016-05-19 | Cauchy Charles J | Heating and cooling technologies |
| US11857004B2 (en) | 2014-11-14 | 2024-01-02 | Gentherm Incorporated | Heating and cooling technologies |
| US11639816B2 (en) | 2014-11-14 | 2023-05-02 | Gentherm Incorporated | Heating and cooling technologies including temperature regulating pad wrap and technologies with liquid system |
| WO2017164104A1 (en)* | 2016-03-23 | 2017-09-28 | 国立研究開発法人産業技術総合研究所 | Thermoelectric module power generation evaluation device |
| KR102147181B1 (en)* | 2018-05-30 | 2020-08-25 | 주식회사 에프에스티 | Temperature controlling device and Processing apparatus of semiconductor including the same |
| US11223004B2 (en) | 2018-07-30 | 2022-01-11 | Gentherm Incorporated | Thermoelectric device having a polymeric coating |
| CN113167510B (en) | 2018-11-30 | 2025-10-03 | 金瑟姆股份公司 | Thermoelectric regulation system and method |
| US11152557B2 (en) | 2019-02-20 | 2021-10-19 | Gentherm Incorporated | Thermoelectric module with integrated printed circuit board |
- 2002
- 2002-01-08JPJP2002037466Apatent/JP4015435B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003204087A (en) | 2003-07-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4015435B2 (en) | Heating and cooling devices using thermoelectric elements | |
| JP6513577B2 (en) | Thermoelectric-based thermal management of electrical devices | |
| JP7091878B2 (en) | Power modules, power converters, and methods for manufacturing power modules | |
| JP2007526650A (en) | Improvement of thermoelectric heat pump or related to it | |
| JP6705393B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and power converter | |
| US6679064B2 (en) | Wafer transfer system with temperature control apparatus | |
| WO1995002794A1 (en) | Integrated thermoelectric system with full/half wave rectifier control | |
| CN100403569C (en) | Thermoelectric conversion device and method for manufacturing thermoelectric conversion device | |
| JP4479408B2 (en) | Thermoelectric generator | |
| US20110036384A1 (en) | Thermoelectric device | |
| CN106165134A (en) | Thermoelectric conversion module | |
| WO2003083537A1 (en) | Temperature controller and array waveguide lattice type optical wavelength multiplexer/demultiplexer | |
| US20120159967A1 (en) | Thermoelectric apparatus | |
| US20160247996A1 (en) | Large footprint, high power density thermoelectric modules for high temperature applications | |
| JP2008177356A (en) | Thermoelectric generator | |
| JPH0529667A (en) | Thermoelectric conversion module | |
| JP7065687B2 (en) | Thermoelectric converter | |
| JP2005251950A (en) | Thermoelectric conversion module and thermoelectric conversion system including a plurality of electrical circuits | |
| JP4336205B2 (en) | Power semiconductor module | |
| US20120111029A1 (en) | Ac powered thermoelectric device | |
| KR20100042197A (en) | Electric mat having a high degree of efficiency | |
| JP7313660B2 (en) | Thermoelectric conversion module | |
| JP2003179274A (en) | Thermoelectric converter | |
| KR20200014021A (en) | Thermo-electric conversion module and thermo-electric conversion module system | |
| WO2018189948A1 (en) | Semiconductor module, method for manufacturing semiconductor module, and power conversion apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20050107 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20070530 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20070614 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20070812 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20070910 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20070913 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100921 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100921 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130921 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |