JP4010058B2 - Document association apparatus, document browsing apparatus, computer-readable recording medium recording a document association program, and computer-readable recording medium recording a document browsing program - Google Patents
Document association apparatus, document browsing apparatus, computer-readable recording medium recording a document association program, and computer-readable recording medium recording a document browsing programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4010058B2 JP4010058B2JP22293498AJP22293498AJP4010058B2JP 4010058 B2JP4010058 B2JP 4010058B2JP 22293498 AJP22293498 AJP 22293498AJP 22293498 AJP22293498 AJP 22293498AJP 4010058 B2JP4010058 B2JP 4010058B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- document
- keyword
- identifier
- target
- elements
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsdescription98
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription56
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000claimsdescription33
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000claimsdescription10
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description34
- 230000000877morphologic effectEffects0.000description8
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description6
- 238000007796conventional methodMethods0.000description4
- 238000009825accumulationMethods0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 239000004065semiconductorSubstances0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は文書関連付け装置、文書閲覧装置、文書関連付けプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体、及び文書閲覧プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体に関し、特に文書中のあるキーワードとそのキーワードに関連する他の文書の内容を関連付ける文書関連付け装置、文書中のあるキーワードとそのキーワードに関連する他の文書の内容とが関連付けられた文書群中の文書を閲覧する文書閲覧装置、前記文書関連付け装置をコンピュータ上で実現するための文書関連付けプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体、及び前記文書閲覧装置をコンピュータ上で実現するための文書閲覧プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
ネットワーク上に散在する電子文書群をリンクによって関連付けることが可能な、いわゆるハイパーテキストシステムが、World Wide Web(WWW) の普及により、一般に広く利用されるようになってきている。ハイパーテキストシステムでは、ある文書中のキーワードに対して、より詳しい情報を持つ他の文書の内容へのハイパーリンクを付与しておく。これによって、利用者がその文書を閲覧していて、ハイパーリンクが付与された記述に関してより詳しく知りたいと思ったときには、そのハイパーリンクを辿ることによって関連情報を知ることができる。
【0003】
ところが、一般的にこのようなハイパーテキスト文書を作成するためには、文書の作成者が手作業でキーワードと他の文書との関連付けを行ってハイパーリンクを作成する必要があり、多大の労力と時間を要する。そこで、この問題を解決するために、文書中のキーワードを自動抽出して、他の文書から同一または同義のキーワードを含むものを検索することによって、文書間の関連付けすなわちハイパーリンクを自動的に作成することが考えられている。
【0004】
このとき単純に同一または同義のキーワードを手がかりとして文書を関連付けるだけでは、ハイパーリンクを辿ることによって、より詳しい説明が得られるという保証がない。なぜならば、関連付けられた文書のいずれにおいても同一または同義のキーワードが一言参照されているだけでそのキーワードの説明に当たる記述がない場合が往々にしてあり得るからである。
【0005】
この問題を解決する1つの方法として、特開平5−20362号公報に開示された「文書テキスト間の連鎖自動作成システム」がある。この公報に開示された方法では、まず、文書テキストから重要キーワードを抽出し、抽出したキーワードの文書における重要度を算出する。その上で、同一のキーワードを共有する文書どうしで、キーワードの重要度の低い方の文書からキーワードの重要度の高い方の文書への、単方向の関連付けを自動生成する。この方法では、同一のキーワードを手がかりとして文書を関連付けているが、同一キーワードの文書における重要度の高い文書のほうが、重要度の低い文書よりも、そのキーワードに関してより詳しく説明されているものと仮定している。これによって、文書中のあるキーワードから、より詳しい説明が記述された他の文書に対するハイパーリンクが自動的に生成される。以下のこの方法を第1の従来技術とする。
【0006】
また、上記問題を解決する別の方法として特開平7−325827号公報に開示された「ハイパーテキスト自動生成装置」がある。この公報には、同一または同義のキーワードを持つ文書どうしを関連付ける際に、一方の文書のキーワードから、他の文書の同一または同義のキーワードを持つ章や節の見出しに対してハイパーリンクを生成する方法が示されている。この方法では、あるキーワードが見出しに含まれる場合、見出し以下の内容において、そのキーワードについて詳しく説明されている可能性が高いと仮定している。これによって、文書中のあるキーワードから、より詳しい説明に対するハイパーリンクが自動的に生成される。以下のこの方法を第2の従来技術とする。
【0007】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかし、いずれの従来技術においても、以下のような問題点があった。
第1の従来技術では、関連付けの対象はある文書中のキーワードと他の文書全体である。そのため、関連付けられる他の文書の記述量が多い場合には、たとえ関連付けられたキーワードに対する詳しい説明が文書中に記述されていたとしても、文書中で関連する記述を見つけ出すことが困難である。
【0008】
第2の従来技術では、ある文書中のキーワードに対して、同一または同義のキーワードが含まれる他の文書が複数存在する場合には、予め与えられた戦略に従って候補をいずれか1つに絞るようになっている。そのため、利用者が実際に知りたい情報が関連付けの対象から洩れてしまうおそれがある。なお、この問題については、例えば関連付けの対象となる候補が複数存在する場合にその候補全てを関連付けてしまうことによって洩れを防ぐことができる。しかし、この場合には、利用者が複数の関連付けられた記述を順次閲覧し、必要な情報を探すという手間がかかる。
【0009】
さらに、上記2つの従来技術のいずれにおいても、関連付けの対象となるキーワードを自動抽出するために、文書全体に対して形態素解析を行う必要がある。形態素解析を高精度に行うには、かなり複雑な処理を行わなければならない。そのため、従来の技術を用いて大量の文書間のハイパーリンクを自動作成するには、処理に非常に時間がかかってしまうという問題点があった。
【0010】
本発明はこのような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、文書中のキーワードを他の文書中の最小限の関連記述に関連付ける処理を高速に行うことができる文書関連付け装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0011】
また、本発明の第2の目的は、文書中のキーワードを他の文書中の最小限の関連記述に関連付けられた文書群内の文書を閲覧するための文書閲覧装置を提供することである。
【0012】
また、本発明の第3の目的は、文書中のキーワードを他の文書中の最小限の関連記述に関連付ける処理をコンピュータに高速に行わせることができる文書関連付けプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体を提供することである。
【0013】
また、本発明の第4の目的は、文書中のキーワードを他の文書中の最小限の関連記述に関連付けられた文書群内の文書をコンピュータを用いて閲覧するための文書閲覧プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体を提供することである。
【0014】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明では上記課題を解決するために、文書間の関連付けを行う文書関連付け装置において、属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段と、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定する識別子設定手段と、前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段と、前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段と、前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段と、を有することを特徴とする文書関連付け装置が提供される。
【0015】
このような文書関連付け装置によれば、階層構造関連付け手段により、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている文書が被関連付け対象文書とされ、被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、その要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子が設定される。また、キーワード抽出手段により、被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードが抽出される。すると、文書内容検索手段により、キーワード抽出手段が抽出したキーワードを含む文書が文書蓄積手段内から検索される。そして、キーワード関連付け手段により、文書内容検索手段により検索された文書中のキーワードの複数登録可能なタグに、キーワードの抽出元となる被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、被関連付け対象文書内のキーワードを含む処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値が複数設定される。
【0016】
また上記課題を解決するために、構造化文書の内容を閲覧する文書閲覧装置において、属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段と、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定する識別子設定手段と、前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段と、前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段と、前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段と、文書閲覧要求に応じて、当該文書閲覧要求で指定された文書を前記文書蓄積手段から抽出し、表示する文書表示手段と、操作入力により、前記文書表示手段にて表示された文書中で、他の文書中の要素を示す1つ以上の属性値が登録されたタグを有する前記キーワードが選択されると、当該キーワードのタグに設定された属性値に基づいて、当該キーワードに関連する前記被関連付け対象文書中の処理対象要素を抽出する要素抽出手段と、前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記処理対象要素の内容を表示する内容表示手段と、を有することを特徴とする文書閲覧装置が提供される。
【0017】
このような文書閲覧装置によれば、階層構造関連付け手段により、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている文書が被関連付け対象文書とされ、被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、その要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子が設定される。また、キーワード抽出手段により、被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードが抽出される。すると、文書内容検索手段により、キーワード抽出手段が抽出したキーワードを含む文書が文書蓄積手段内から検索される。そして、キーワード関連付け手段により、文書内容検索手段により検索された文書中のキーワードの複数登録可能なタグに、キーワードの抽出元となる被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、被関連付け対象文書内のキーワードを含む処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値が複数設定される。さらに、文書閲覧要求が入力されると、文書表示手段により、文書閲覧要求に応じた文書が文書蓄積手段から抽出される。この文書表示手段にて抽出された文書中で、キーワード関連付け手段により関連付けられたキーワードが選択されると、要素抽出手段により、キーワードに対して関連付けられた1又は複数の被関連付け対象文書中の関連要素が抽出される。
【0018】
さらに、内容表示手段により、前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記関連要素の内容が抽出され、表示される。
また上記課題を解決するために、文書間の関連付けを行うための文書関連付けプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体において、属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定する識別子設定手段、前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段、前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段、前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段、としてコンピュータを機能させることを特徴とする文書関連付けプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体が提供される。
【0019】
この記録媒体に記録された文書関連付けプログラムをコンピュータに実行させれば、上記本発明に係る文書関連付け装置の機能がコンピュータ上に構築される。
【0020】
また上記課題を解決するために、構造化文書の内容を閲覧するための文書閲覧プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体において、コンピュータを、属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定する識別子設定手段、前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段、前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段、前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段、文書閲覧要求に応じて、当該文書閲覧要求で指定された文書を前記文書蓄積手段から抽出し、表示する文書表示手段、操作入力により、前記文書表示手段にて表示された文書中で、他の文書中の要素を示す1つ以上の属性値が登録されたタグを有する前記キーワードが選択されると、当該キーワードのタグに設定された属性値に基づいて、当該キーワードに関連する前記被関連付け対象文書中の処理対象要素を抽出する要素抽出手段、前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記処理対象要素の内容を表示する内容表示手段、として機能させることを特徴とする文書閲覧プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体が提供される。
【0021】
この記録媒体に記録された文書閲覧プログラムをコンピュータに実行させれば、上記本発明に係る文書閲覧装置の機能がコンピュータ上に構築される。
【0022】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面を参照して説明する。
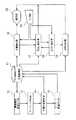
図1は、本発明の原理構成図である。本発明の文書関連付け装置は、以下の要素で構成される。
【0023】
文書蓄積手段1は、階層的な論理構造の文書群を蓄積する。構造化された文書としては、SGMLの規定に従って作成された文書などがある。
階層構造関連付け手段2は、文書蓄積手段1から被関連付け対象文書2aを読み込み、読み込んだ被関連付け対象文書2aを構成する各要素の上位構造と下位構造とを関連付ける。例えば、各要素に識別子を与える。そして、各要素に対して、その要素の下位構造となる要素の識別子の情報を持たせる。要素間の関連付けを行った被関連付け対象文書2aは、文書蓄積手段1に戻す。
【0024】
キーワード抽出手段3は、被関連付け対象文書2a中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出する。例えば、表題としての属性を有する要素と、見出しとしての属性を有する要素とを、処理対象要素とする。すると、キーワード抽出手段3は、抽出元の要素の識別子と、その要素から抽出されたキーワードの集合とを対応づけたキーワード対応表3aを内部で生成する。そして、被関連付け対象文書2aに関するキーワード対応表3aを文書内容検索手段4に渡す。
【0025】
文書内容検索手段4は、キーワード抽出手段3により抽出されたキーワードに基づいて、文書蓄積手段1に蓄積されている他の文書の内容を検索する。見つけ出した文書4aは、キーワード関連付け手段5に渡す。
【0026】
キーワード関連付け手段5は、文書内容検索手段4により検出された文書4aの内容中のキーワードと、キーワードの抽出元となる被関連付け対象文書2aの処理対象要素とを関連付ける。被関連付け対象文書2aの特定の要素への関連付けを行った文書5aは、文書蓄積手段1に格納する。
【0027】
このような文書関連付け装置によれば、階層構造関連付け手段2に読み込まれた被関連付け対象文書2aは、各要素の上位構造と下位構造との関連付けが行われ、文書蓄積手段1に戻される。このとき、キーワード抽出手段3により、各要素の内容の中からキーワードが抽出される。すると、文書内容検索手段4により、抽出されたキーワードに基づいて文書蓄積手段1内の文書が検索される。検出された文書4aはキーワード関連付け手段5に渡され、文書4aの内容中のキーワードと、キーワードの抽出元となる被関連付け対象文書2aの処理対象要素とが関連付けられる。そして、処理対象要素との関連付けが行われた文書5aは、文書蓄積手段1に戻される。
【0028】
このような処理を、文書蓄積手段1に格納されている全ての文書を被関連付け対象文書2aとして実行すれば、ある文書中のキーワードが他の文書中の特定の要素(表題や見出し)に関連付けられ、さらに、その要素から下位構造に関連付けられる。そのため、文書蓄積手段1内の文書を閲覧する場合には、文書中のキーワードから他の文書中の必要最小限の関連付けられた内容を参照することができる。
【0029】
しかも、関連付けに際して文書中の表題もしくは見出しなどの特定の要素だけを対象としてキーワード抽出処理を行うので、形態素解析のようなキーワード抽出に必要な煩雑な処理を文書全体に対して施す必要がなくなる。その結果、関連付けの処理効率が向上する。
【0030】
次に、本発明の文書関連付け装置によって文書間の関連付けを行い、それらの文書を閲覧することができる文書閲覧装置を第1の実施の形態として以下に説明する。
【0031】
図2は、本発明を適用した文書閲覧装置の構成を示す図である。この文書閲覧装置は、文書蓄積部11、階層構造関連付け部12、キーワード抽出部13、文書内容検索部14、キーワード関連付け部15、文書抽出部16、見出し抽出部17、見出し選択部18、内容抽出部19、表示部20、及び入力部21から構成されている。
【0032】
文書蓄積部11は、表題、章の見出し、節の見出し、段落等の論理構造を有する文書群を蓄積する。
階層構造関連付け部12は、文書蓄積部11に蓄積された文書を読み込み、表題、見出しの階層( 章見出し、節見出しなど) 、見出しに対応する内容( 例えばある節の段落の並び) を関連付ける。
【0033】
キーワード抽出部13は、階層構造関連付け部12にて関連付けられた表題および見出しの階層からキーワードを抽出する。
文書内容検索部14は、キーワード抽出部13にて抽出されたキーワードを用いて、文書蓄積部11に蓄積された文書群を対象に、与えられたキーワードを内容に持つ文書を検索する。
【0034】
キーワード関連付け部15は、文書内容検索部14にて検索された文書中のキーワードと、該キーワードを抽出した表題および見出しの階層を関連付ける。
文書抽出部16は、文書蓄積部11に蓄積された文書群から、入力部21で利用者が入力した要求に応じて文書を抽出し、表示部20に表示する。
【0035】
見出し抽出部17は、文書抽出部16により抽出され、表示部20に表示された文書中で、利用者が入力部21によりキーワードを指定した場合に、指定されたキーワードで関連付けられている他の文書の表題もしくは見出しを文書蓄積部11から抽出し、表示部20に表示する。また、抽出された前記表題もしくは見出しのさらに下位の見出しを文書蓄積部11から抽出し、表示部20に表示する。
【0036】
見出し選択部18は、入力部21で利用者が入力した要求に応じて、見出し抽出部17により表題もしくは見出しが複数抽出された場合にはそのうちの1つの表題もしくは見出しを選択し、前記表題もしくは見出しに下位の見出しが複数存在する場合にはそのうちの1つの見出しを選択する。
【0037】
内容抽出部19は、見出し抽出部17により抽出された表題、見出しもしくは順次抽出された下位の見出しが、その見出しに対応する内容と関連付けられている場合に、文書蓄積部11からその内容を抽出し、表示部20に表示する。
【0038】
表示部20は、文書抽出部16により抽出された文書、見出し抽出部17により抽出された他の文書の表題もしくは見出し、および内容抽出部19により抽出された他の文書の内容を、画面上に表示する。
【0039】
入力部21は、文書抽出部16により抽出する文書の指定、文書抽出部16により抽出された文書中でのキーワードの選択、見出し抽出部17により抽出された表題もしくは見出しが複数存在する場合の選択の指示等を行う。
【0040】
次に、このような構成の文書閲覧装置により、文書蓄積部11に格納されている文書群に対して文書間の関連付けを行う手順について説明する。
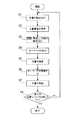
図3は、文書間の関連付けを行う手順を示すフローチャートである。以下の処理をステップ番号に沿って説明する。
[S1]階層構造関連付け部12が、文書蓄積部11から未処理の文書を1つ読み込む。
[S2]階層構造関連付け部12が、読み込んだ文書の構造を解析する。
[S3]階層構造関連付け部12が、表題、見出し、及び内容を関連付ける。
[S4]キーワード抽出部13が、表題及び見出しの内容の中からキーワードを抽出する。
[S5]文書内容検索部14が、キーワード抽出部13が抽出したキーワードを含む文書を、文書蓄積部11の中から検索する。
[S6]キーワード関連付け部15が、文書内容検索部14によって検出された文書内のキーワードに合致した部分に対して、そのキーワードの抽出元となった表題もしくは見出しを関連付ける。
[S7]キーワード関連付け部15が、キーワードの関連付けの終了した文書を文書蓄積部11へ格納する。
[S8]階層構造関連付け部12は、文書蓄積部11に格納されている全ての文書の処理を行ったか否かを判断し、全ての文書に対する処理が終了していれば文書間の関連付け処理を終了し、そうでなければステップS1に進み未処理の文書に対する処理を行う。
【0041】
このような処理を行うことにより、各文書の内容に含まれるキーワードから、そのキーワードを表題もしくは見出しとして含む文書の該当する表題若しくは見出しへリンクを張ることができる。
【0042】
以下に、具体例を用いて処理内容の詳細を説明する。なお、以下の例では、表題、見出し等の論理構造を有する文書の一例として、国際規格であるSGML(Standard Generalized Markup Language; ISO8879) に基づく表現を用いているが、表題、見出し、見出しに対応する内容が表現できる体系であればSGMLでなくともよい。
【0043】
まず、階層構造関連付け部12が、文書蓄積部11に蓄積された文書を1つ読み込む(ステップS1)。ここで、以下のような文書を読み込んだものとする。図4は、関連付けの対象となるキーワードを見出しに含む文書の第1の例を示す図である。この文書31は、以下のような構造定義に従って作成されている。
【0044】
文書中の各要素は、その開始と終了を示すタグによって囲まれている。ある要素Aについて、開始タグは<A>、終了タグは</A>で示される。文書は、文書の開始を示すタグ<doc >と、文書の終了を示すタグ</doc >によって囲まれている。文書要素(doc) は表題を示す要素(title) と章を示す要素(sect1) の並びとを包含している。章要素(sect1) は見出しを示す要素(head)と段落を示す要素(para)の並びとを包含しているか、もしくは、見出し要素(head)と節を示す要素(sect2) の並びを包含している。節要素(sect2) は見出し要素(head)と段落要素(para)の並びを包含している。また、表題要素(title) 、見出し要素(head)、段落要素(para)は、その内容としてテキスト(文字列)を持つ。
【0045】
なお、本実施の形態で例示する文書では、要素の名前としてdoc 、title 、sect1 、sect2 、head、paraを用いているが、文書中で表題、見出し、本文が特定できれば、名前はなんでもよい。また、章や節の構造はさらに深く入れ子になっていてもよい。例えば、節要素(sect2) がさらに下位の節要素(sect3) を含むようになっていてもよい。
【0046】
このような文書31を読み込んだ階層構造関連付け部12は、読み込んだ文書の表題、見出し、段落等の文書構造を解析し、文書中の各要素に一意な識別子を付与する(ステップS2)。
【0047】
図5は、各要素に一意な識別子を付与した文書を示す図である。この図では、各要素に属性名「id」の値として識別子を付与している。この文書32では、文書要素(doc) に「d1」という識別子を付与している。文書要素の識別子が、文書32自身の識別子となる。そのため、文書要素の識別子は、文書蓄積部11に格納されている文書の中で一意に識別できるような記号が用いられる。
【0048】
文書32中の文書要素以外の要素に関しては、文書32内において一意に識別できればよい。ここでは、表題要素(title) に「t1」という識別子を付与し、章要素(sect1) にそれぞれ「s1」、「s2」、「s3」という識別子を付与し、見出し要素(head)にそれぞれ「h1」、「h2」、「h3」という識別子を付与し、段落要素(para)にそれぞれ「p1」、「p2」、「p3」、「p4」という識別子を付与している。
【0049】
次に、階層構造関連付け部12は文書32の表題、見出し、もしあれば下位の見出し、見出しに対応する段落の並びを関連付ける( ステップS3) 。本実施の形態では、文書の表題から見出しへの関連付けを、表題要素(title) の属性として見出しの識別子の並びを設定することによって表現する。また、見出しから下位の見出しへの関連付けもしくは見出しから対応する内容への関連付けは、見出し要素(head)の属性として下位の見出し要素の識別子もしくは内容となる段落要素(para)の識別子の並びを設定することによって表現する。
【0050】
図6は、表題、見出し、内容を関連付けた文書の例を示す図である。この文書33は、図5に示す文書32の表題要素および見出し要素に、関連付ける見出し要素もしくは段落要素の識別子の並びを属性名「ref 」の値として付与したものである。この例では、識別子の並びを空白文字によって区切っている。例えば、表題要素(title) の下位には3つの見出し要素(head)があるため、表題要素(title) の属性名「ref 」の値は、「h1 h2 h3」となる。
【0051】
次に、キーワード抽出部13が階層構造関連付け部12によって関連付けられた表題もしくは見出しからキーワードを抽出する(ステップS4)。キーワードの抽出方法としては、従来の形態素解析などの手法を利用すればよい。本実施の形態では、形態素解析の結果から名詞と判定された単語をキーワードとして利用する。また、ひらがな語など、キーワードになりにくいものは、予めストップワードとして登録しておき、キーワードの抽出対象から外す。キーワード抽出部13は、要素と、その要素に含まれるキーワードとの対応関係を示すキーワード対応表を作成し、一時的に保持する。
【0052】
図7は、キーワード対応表の例を示す図である。これは、図6に示した文書33の表題要素(title) および見出し要素(head)と、そこから抽出したキーワードとの対応関係を示すキーワード対応表41である。キーワード対応表41には、「要素の種類」、「識別子」、および「キーワード」の項目が設けられている。「要素の種類」の項目には、キーワードの抽出を行った要素の種類が設定される。この例は、「表題」か「見出し」のいずれかである。「識別子」の項目には、キーワードの抽出を行った要素の識別子が設定される。「キーワード」の項目には、キーワードの抽出を行った要素に含まれていたキーワードの集合が設定される。
【0053】
このように、文書中の表題要素および見出し要素のみに対して形態素解析処理を行うので、文書全体に対して形態素解析処理を行う必要はない。一般に文書の表題や見出しに含まれるテキストの量は、文書全体のテキスト量に比して非常に少ないので、形態素解析の処理コストを大幅に削減することができる。
【0054】
次に、文書内容検索部14は、キーワード抽出部13により抽出されたキーワードを用いて、文書蓄積部11に蓄積された他の文書の内容を検索する(ステップS5)。例えば、表題要素(title) から抽出された「SGML」というキーワードを用いて、文書蓄積部11内の文書を検索を行った場合、以下のような文書が検出される。
【0055】
図8は、関連付けの対象となるキーワードを本文中に含む文書の例を示す図である。この文書51は、段落要素(para)の内容に含まれるテキスト「...SGML へ変換する。... 」の「SGML」が一致したことにより、検出される。なお、この文書51は、図4に示した文書31と同様の構造定義に従って作成された文書である。
【0056】
図8のような文書51が見つかったら、そのキーワード関連付け部15はキーワードと一致する文書51の内容と、そのキーワードを含む表題もしくは見出しを関連付ける(ステップS6)。具体的には、テキスト「...SGML へ変換する。... 」中の「SGML」を参照元要素としてタグ付けし、図6に示した文書33の表題要素(title) の識別子を、参照元の要素の属性として設定する。
【0057】
図9は、キーワードと表題との関連付けが行われた文書の例を示す図である。この文書52では、キーワード「SGML」は関連付けを示す要素(link)の開始タグと終了タグによって囲まれ、link要素の属性「ref 」の値として文書「d1」の表題「t1」への関連付けが設定されている。ここで属性「ref 」の値として、文書要素の識別子「d1」と表題要素の識別子「t1」を「. 」によって接続しているのは、識別子「t1」が他の文書のある要素においてたまたま使われている場合に、関連付けの対象を一意に決定できなくなることを防ぐためである。
【0058】
なお、本実施の形態では文書要素の識別子と表題要素もしくは見出し要素とを接続するために「. 」を用いているので、要素に識別子を付与する際には識別子自身に「. 」を含めないようにする。
【0059】
また、本実施の形態では、文書要素(doc) の識別子が、文書蓄積部11に蓄積されている文書を一意に識別できるように付与されているため、この文書要素を用いて文書を識別しているが、文書を識別するための識別子を文書全体に対して付与して、それを関連付けの識別子として用いてもよい。このような識別子としては、文書の実体がファイルである場合にはファイル名を用いたり、文書がWWW(World Wide Web)上で公開される場合にはURL(Uniform Resource Locator)を用いたりすることができる。
【0060】
ステップS4にて抽出された全てのキーワードに対して他の文書内容を検索し、ステップS6にてキーワードの関連付けが終了したら、関連付けされた文書は文書蓄積部11に格納される(ステップS7)。このとき、関連付けの対象となった元の文書の内容は上書きされる。
【0061】
そして、文書蓄積部11に蓄積された全ての文書について、上記ステップS1〜ステップS7の処理が行われたかどうかを調べ(ステップS8)、まだ処理されていない文書があればステップS1へ戻って処理を継続し、全ての文書について処理が終了していれば、文書間の関連付けの処理を終了する。
【0062】
以上の処理が行われることにより、図9に示した文書52に対しても、階層構造の関連付けが行われる。
図10は、図9の文書に対して階層構造の関連付けを行った結果を示す図である。この文書53は、文書要素(doc) の識別子として「d2」が付与されている。
【0063】
次に、本発明に基づく文書関連付け装置により、関連付けを利用して、文書中のあるキーワードから、そのキーワードに対する説明記述を参照する手順について説明する。
【0064】
図11は、関連付けの利用手順を示すフローチャートである。このフローチャートをステップ番号に沿って簡単に説明する。
[S11]利用者が入力部21を用いて文書の表示要求を入力すると、文書抽出部16が該当する文書を文書蓄積部11内から抽出する。抽出した文書の内容は、表示部20の画面に表示される。
[S12]利用者が入力部21を用いてキーワードを選択する。
[S13]見出し抽出部17が、ステップS12にて選択されたキーワードの関連付け情報すなわちlink要素の属性「ref 」の識別子を参照し、文書蓄積部11から該当する識別子を持つ文書の表題もしくは見出しを抽出する。あるいは後述するステップS14,S15で見出し選択部18によって選択された表題もしくは見出しの下位の見出しを、文書蓄積部11から抽出する。そして、抽出した表題もしくは見出しを表示部20に表示する。
[S14]見出し選択部18が、見出し抽出部17によって抽出された見出しが複数か否かを判断し、複数であればステップS15へ処理を進め、1つだけであればその表題もしくは見出しを選択してステップS16へ処理を進める。
[S15]見出し選択部18が、入力部21で利用者が入力した要求に応じて、見出し抽出部17により表題もしくは見出しが複数抽出された場合にはそのうちの1つの表題もしくは見出しを選択する。
[S16]見出し選択部18は、選択された表題もしくは見出しに関して、下位の見出しが存在するか否かを判断する。この実施の形態では、ステップS13にて抽出された表題要素(title) もしくは見出し要素(head)の属性「ref 」の値として設定されている識別子を持つ要素を特定し、その要素が見出し要素(title) であるかないかを判定する。下位の見出しが存在していればステップS13に進み、存在していなければステップS17に進む。
[S17]内容抽出部19が、ステップS15にて選択された見出し要素に関連付けられた内容に対応する要素を抽出し、表示部20の画面に表示する。
【0065】
以下に、関連付けの利用に関する処理を具体例を用いて説明する。
まず利用者が図10に示した文書53の表示要求を入力部21により指示したものとする。すると、文書53の内容が表示部20の画面に表示される。
【0066】
図12は、文書の内容を表示した際の表示画面の例を示す図である。この表示画面61では、文書中のタグにより表題、見出し、段落、関連付けられたキーワードなどを識別し、それぞれに対して適切なレイアウトを定めて画面表示を行っている。例えば表題は大きめのフォントでセンタリングして表示し、見出しは大きめのフォントで番号を付与して表示し、他の文書の見出し等に関連付けられたキーワードは下線を付与して強調している。
【0067】
次に、利用者が、表示部20に表示された文書を参照し、関連付けの付与された「SGML」の表示箇所をマウスでクリックするなどの方法で選択したものとする(ステップS12)。すると、見出し抽出部17が、選択されたキーワード「SGML」の関連付け情報すなわちlink要素の属性「ref 」の識別子を参照し、文書蓄積部11から該当する識別子「d1」を持つ文書33内の該当する表題「t1」を抽出し、表示部20に表示する(ステップS13)。
【0068】
図13は、見出しを表示した際の表示画面の例を示す図である。前述の関連付けの処理によりキーワード「SGML」は関連付けを示すlink要素によってタグ付けされており、その属性「ref 」の値として「d1.t1 」が設定されているので、図6に示した文書33の表題要素( 識別子は「t1」) が見出し抽出部17により抽出され、表題要素の内容「SGMLによる電子出版」を含む表示画面62が、表示部20により表示される。
【0069】
このとき、抽出された表題が複数か否かの判定が見出し抽出部17によって行われるが(ステップS14)、この例では抽出された表題もしくは見出しが1つだけである。そこで、見出し抽出部17は、抽出された見出しに関連付けられた下位の見出しが存在するかどうかを判定する(ステップS16)。この例では、識別子「t1」を持つ表題要素の属性「ref 」の値として、「h1 h2 h3」の3つの要素が関連付けられており、いずれも見出し要素である。従って、ステップS13へ戻り見出しの抽出が行われる。
【0070】
図14は、下位の見出しを表示した際の表示画面の例を示す図である。これは、図13に示した表示画面62の例から、「SGMLによる電子出版」を内容に持つ表題要素に関連付けられている下位の見出しを表示部20に表示したときの表示画面63の例を示したものである。すなわち、図6に示した文書33において、識別子「t1」を持つ表題要素の属性「ref 」の値として設定されている3つの見出し要素( 識別子はh1、h2、h3) の内容「はじめに」「電子出版の歴史」「関連ツール」を抽出し、表示部20の画面に表示している。
【0071】
ここで、再び見出し選択部18が、抽出された見出しが複数であるか否かの判断を行う(ステップS14)。ここでは、3つの見出しが抽出されているので、利用者は表示部20に表示されている複数の表題もしくは見出しから入力部21により1つを選択する(ステップS15)。この例では、図14に表示されている3つの見出しの内容のうち「関連ツール」をマウス等で選択したものとする。
【0072】
すると、見出し選択部18が、選択された見出し「関連ツール」に関連付けられた下位の見出しが存在するかどうかを判定する(ステップS16)。図6に示した文書33において、「関連ツール」を内容に持つ見出し要素( 識別子は「h3」) の属性「ref 」の値として設定されている識別子p3、p4、...の要素はいずれも見出しではない。したがって、内容抽出部19が、内容の抽出を行う(ステップS17)。
【0073】
図15は、内容を表示した際の表示画面の例を示す図である。これは、図14に示した表示画面63の例から、「関連ツール」を内容に持つ見出し要素に関連付けられている内容を表示部20に表示したときの表示画面64の例である。すなわち、図6に示した文書33において、識別子「h3」を持つ見出し要素の属性「ref 」の値として設定されている段落要素(識別子p3、p4、...)の内容を抽出し、表示部20に表示する。
【0074】
このように、関連する内容の候補が複数存在する場合にも、見出しを表示して選択することにより必要最小限の関連付けられた内容を参照することができる。また、表示部20に表示される表題もしくは見出しから、利用者が内容を参照する必要がないと判断した場合は、内容の参照を行う前に処理を中断することも可能である。したがって、利用者は内容の詳細を全て読むことなく必要な情報を効率良く見つけることが可能である。
【0075】
次に、第2の実施の形態について説明する。第2の実施の形態は、ある文書内容中のキーワードに対して、他の文書の表題もしくは見出しが複数関連付けられている場合に、関連付けられた内容をさらに効率的に抽出できるようにした文書閲覧装置である。なお、第2の実施の形態の構成要素は、図2に示した第1の実施の形態の構成要素と同じであるため、図2に示した構成を用いて第2の実施の形態を説明する。また、第2の実施の形態における文書間の関連付け処理は、第1の実施の形態と同様であるため説明を省略する。
【0076】
そこで、第2の実施の形態による関連付け参照処理について、以下に説明する。
図16は、第2の実施の形態における関連付け参照の処理の流れを示すフローチャートである。以下の処理をステップ番号に沿って説明する。
[S21]利用者が文書蓄積部11に蓄積された文書群から抽出する文書を入力部21により指示すると、文書抽出部16は、指示された文書を抽出し、表示部20に表示する。
[S22]利用者が表示部20に表示された文書を参照し、入力部21より関連付けの付与されたキーワードの表示箇所をマウスでクリックするなどの方法で選択する。
[S23]見出し抽出部17は、ステップS22にて選択されたキーワードの関連付け情報すなわちlink要素の属性「ref 」の識別子を参照し、文書蓄積部11から該当する識別子を持つ文書の表題もしくは見出しを抽出する。
[S24]見出し抽出部17は、ステップS23にて抽出された表題もしくは見出しが1つであるか複数であるかを判定し、抽出された表題もしくは見出しが複数あれば、ステップS25へ進み、1つしかなければステップS29へ進む。
[S25]見出し抽出部17は、ステップS24にて抽出された表題もしくは見出しが複数あると判定されると、それらの表題もしくは見出しを文書ごとにグループ化する。
[S26]見出し抽出部17は、ステップS25にてまとめられた文書ごとの関連付けのグループを、同一文書内への関連付けの数、および関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しの階層の深さから算出される重要度に応じて並べ替える。
[S27]見出し抽出部17は、ステップS25にて文書ごとにグループ化された関連付けを、関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しの階層の深さから算出される重要度に応じて各グループ内で並び替える。
[S28]利用者は表示部20に表示されている複数の表題もしくは見出しから入力部21により1つを選択する。
[S29]見出し抽出部17は、ステップS23にて抽出された表題もしくは見出しが1つである場合またはステップS28にて見出しが選択された場合に、その表題もしくは見出しに関連付けられた下位の見出しが存在するかどうかを判定する。もし下位の見出しが存在すればステップS23に戻って下位の見出しを抽出する。下位の見出しが存在しなければステップS30へ進む。
[S30]内容抽出部19が、ステップS28にて選択された見出し要素に関連付けられた内容に対応する要素を抽出し、表示部20の画面に表示する。
【0077】
このようにして、ある文書内容中のキーワードに対して、他の文書の表題もしくは見出しが複数関連付けられている場合に、関連付けられた内容を効率的に抽出することができる。以下にこの処理の詳細を、具体例を用いて説明する。
【0078】
本実施の形態では、第1の実施の形態で示した文書以外に、関連付けの対象となるキーワード「SGML」を表題に含む次のような文書が、文書蓄積部11に格納されているものとする。
【0079】
図17は、関連付けの対象となるキーワードを表題に含む文書の第2の例を示す図である。この文書71には、文書要素(doc) に「d3」という識別子が付与されている。また、「id="t1" 」の表題要素(title) 、「id="h2" 」の見出し要素(head)、および「id="h3" 」の見出し要素(head)の内容に「SGML」のキーワードが含まれている。
【0080】
図18は、関連付けの対象となるキーワードを表題に含む文書の第3の例を示す図である。この文書81には、文書要素(doc) に「d4」という識別子が付与されている。また、「id="h21"」の見出し要素(head)と「id="h22"」の見出し要素(head)との内容に「SGML」のキーワードが含まれている。
【0081】
図4に示した文書31に加え、図17,図18に示した文書71,81に対して関連付け処理が行われると、図8に示した文書51は以下のように、他の文書の表題もしくは見出しに関連付けられる。
【0082】
図19は、キーワードと表題もしくは見出しとの関連付けを行った文書の例を示す図である。この図に示すように、文書54は、他の複数の文書の表題もしくは見出しに関連付けられている。すなわち、図19において、キーワード「SGML」に対してそれをタグ付けするlink要素の属性によって、文書「d1」の表題「t1」( 内容は「SGMLによる電子出版」) 、文書「d3」の表題「t1」( 内容は「SGMLへの招待」) 、見出し「h2」( 内容は「SGMLとHTML」) および見出し「h3」( 内容は「SGMLとXML 」) 、文書「d4」の見出し「h21 」( 内容は「SGML文書の検索」) および見出し「h22 」( 内容は「SGMLデータベースシステム」) の合計6個の表題もしくは見出しが関連付けられている。
【0083】
以下、このように関連付けられている文書群を対象として、図16に示したフローチャートに沿って関連付け参照の処理の流れを説明する。
まず利用者が文書蓄積部11に蓄積された文書群から抽出する文書を入力部21により指示すると、文書抽出部16は、指示された文書を抽出し、表示部20に表示する(ステップS21)。ここで表示部20に表示される文書は図19に示した文書54であるものとする。図19に示す文書54を表示部20に表示した場合、link要素の属性値は画面上に表示されないので、第1の実施の形態の場合と同じく図12に示すように表示画面61が表示される。
【0084】
次に、利用者が表示部20に表示された文書54を参照し、入力部21より関連付けの付与されたキーワード「SGML」の表示箇所をマウスでクリックするなどの方法で選択する(ステップS22)。見出し抽出部17は、ステップS22にて選択されたキーワードの関連付け情報すなわちlink要素の属性「ref 」の識別子を参照し、文書蓄積部11から該当する識別子を持つ文書の表題もしくは見出しを抽出する(ステップS23)。
【0085】
次に、見出し抽出部17は、ステップS23にて抽出された表題もしくは見出しが1つであるか複数であるかを判定する(ステップS24)。図19に示した例では、合計6個の表題もしくは見出しが抽出されるので、ステップS25へ進む。
【0086】
次に、見出し抽出部17は、ステップS24にて抽出された表題もしくは見出しが複数あると判定されると、それらの表題もしくは見出しを文書ごとにグループ化する(ステップS25)。図19の文書54では、文書「d1」の表題「t1」を1つのグループに、文書「d2」の表題「t1」、見出し「h2」および見出し「h3」を1つのグループに、文書「d3」の見出し「h21 」および見出し「h22 」を1つのグループにまとめる。
【0087】
このように、抽出された表題もしくは見出しを文書ごとにグループ化することで、同一文書内の関連する記述を連続して参照することができるようになる。
次に、見出し抽出部17は、ステップS25にてまとめられた文書ごとの関連付けのグループを、同一文書内への関連付けの数、および関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しの階層の深さから算出される重要度に応じて並べ替える(ステップS26)。本実施の形態では文書ごとの重要度を次の式によって算出する。
【0088】
【数1】
【0089】
式(1)において、nは、その文書で関連付けられている表題もしくは見出しに対して1から順に割り振られた数字の最大値を表す。diは、数字(i)が割り振られた表題もしくは見出しの階層構造における深さを表す( 表題の深さを0とする) 。すなわち、表題についてはdi=0、第1レベルの見出しについてはdi=1、第2レベルの見出しについてはdi=2などとなる。式(1)に従って各文書の重要度を計算すると、図6に示した文書33は表題「t1」が1つだけ関連付けられているので重要度=2-0=1、図17に示した文書71は表題「t1」、見出し「h2」および見出し「h3」の3つが関連付けられているので重要度=2-0+2-1+2-1=2、図18に示した文書81は見出し「h21 」および見出し「h22 」の2つが関連付けられているので重要度=2-2+2-2=0.5となる。したがって、文書ごとの重要度にしたがって文書「d2」、文書「d1」、文書「d3」の順に関連付けのグループを並べ替える。
【0090】
なお、文書ごとの重要度の算出方法は、式(1)に示したものに限定されるわけではない。関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しが多いほうが重要度がより高くなるように、また、関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しの階層の深さが浅いほうが重要度がより高くなるように重要度を決めればよい。このような重要度の決定方法は、同一文書内で関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しが多いほうが、そのキーワードが文書全体の主題に関係する可能性が高いと考えられ、また、関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しの階層の深さが浅いほうが、そのキーワードについてより包括的に説明されている可能性が高いと考えられるので、有効な方法である。
【0091】
次に、見出し抽出部17は、ステップS25にて文書ごとにグループ化された関連付けを、関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しの階層の深さから算出される重要度に応じて各グループ内で並び替える(ステップS27)。本実施の形態では、階層の深さが浅いほうが重要度が高いものとする。また、階層の深さが同一である場合には、文書中で先に出現するほうが重要度が高いものとする。あるいは、文書中での出現順序を優先した重要度を用いてもよい。
【0092】
以上の処理が行われた後、抽出された表題もしくは見出しが表示部20に表示される。
図20は、複数の見出しを表示する表示画面の例を示す図である。これは、図12に示した表示画面61中でキーワード「SGML」を選択したときに表示される表示画面101の例を示したものである。図20に表示されている表題もしくは見出しは、上記処理により、文書ごとにグループ化され、重要度順に並べ替えられている。
【0093】
次に、利用者は表示部20に表示されている複数の表題もしくは見出しから入力部21により1つを選択する(ステップS28)。すると、見出し抽出部17は、ステップS23にて抽出された表題もしくは見出しが1つである場合またはステップS28にて見出しが選択された場合に、その表題もしくは見出しに関連付けられた下位の見出しが存在するかどうかを判定する(ステップS29)。
【0094】
このように、関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しが同一文書内に複数存在する場合や、関連付けられる表題もしくは見出しを持つ文書が複数存在する場合に、重要なものから優先的に参照できるので、たとえ1つのキーワードに多量の文書の表題や見出しが関連付けられている場合でも、効率的に関連付けられた内容を参照することができる。
【0095】
なお、上記の処理機能は、コンピュータによって実現することができる。その場合、文書関連付け装置及び文書閲覧装置が有すべき機能の処理内容は、コンピュータで読み取り可能な記録媒体に記録されたプログラムに記述しておく。そして、このプログラムをコンピュータで実行することにより、上記処理がコンピュータで実現される。コンピュータで読み取り可能な記録媒体としては、磁気記録装置や半導体メモリ等がある。市場に流通させる場合には、CD−ROM(Compact Disk Read Only Memory) やフロッピーディスク等の可搬型記録媒体にプログラムを格納して流通させたり、ネットワークを介して接続されたコンピュータの記憶装置に格納しておき、ネットワークを通じて他のコンピュータに転送することもできる。コンピュータで実行する際には、コンピュータ内のハードディスク装置等にプログラムを格納しておき、メインメモリにロードして実行する。
【0096】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明の文書関連付け装置では、文書中のキーワードと被関連付け対象文書の処理対象要素とを関連付けるとともに、被関連付け対象文書中の要素の上位構造と下位構造とを関連付けるようにしたため、文書中のキーワードから他の文書中の要素及びその要素の下位構造を順次辿ることができ、必要最小限の関連付けられた内容を参照することができる。しかも、特定の要素からのみキーワードの抽出を行うため、キーワード抽出に伴う複雑な処理を限られた範囲に対して実行することができ、関連付け処理を高速に行うことが可能となる。
【0097】
また、本発明の文書閲覧装置では、文書中のキーワードと被関連付け対象文書の処理対象要素とを関連付けるとともに、被関連付け対象文書中の要素の上位構造と下位構造とを関連付けておき、文書中のキーワードが指定されると、そのキーワードの関連要素の内容とその下位構造の内容を抽出するようにしたため、キーワードを指定したユーザは、そのキーワードに関する必要最小限の関連要素の内容を参照することができる。
【0098】
また、本発明の文書関連付けプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体では、記録された文書関連付けプログラムをコンピュータに実行させることにより、文書中のキーワードと被関連付け対象文書の処理対象要素とを関連付けるとともに、被関連付け対象文書中の要素の上位構造と下位構造とを関連付ける処理を、コンピュータに高速に行わせることが可能となる。すなわち、文書中のキーワードを他の文書の最小限の関連記述に関連付ける処理を、コンピュータに高速に行わせることができる。
【0099】
また、本発明の文書閲覧プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体では、記録された文書閲覧プログラムをコンピュータに実行させることにより、文書中のキーワードと被関連付け対象文書の処理対象要素とを関連付けるとともに、被関連付け対象文書中の要素の上位構造と下位構造とを関連付けておき、文書中のキーワードが指定されると、そのキーワードの関連要素の内容とその下位構造の内容を抽出するような処理をコンピュータに行わせることが可能となる。すなわち、コンピュータに対してキーワードを指定したユーザは、そのキーワードに関する必要最小限の関連要素の内容を参照することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明の原理構成図である。
【図2】 本発明を適用した文書閲覧装置の構成を示す図である。
【図3】 文書間の関連付けを行う手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図4】 関連付けの対象となるキーワードを見出しに含む文書の第1の例を示す図である。
【図5】 各要素に一意な識別子を付与した文書を示す図である。
【図6】 表題、見出し、内容を関連付けた文書の例を示す図である。
【図7】 キーワード対応表の例を示す図である。
【図8】 関連付けの対象となるキーワードを本文中に含む文書の例を示す図である。
【図9】 キーワードと表題との関連付けが行われた文書の例を示す図である。
【図10】 図9の文書に対して階層構造の関連付けを行った結果を示す図である。
【図11】 関連付けの利用手順を示すフローチャートである。
【図12】 文書の内容を表示した際の表示画面の例を示す図である。
【図13】 見出しを表示した際の表示画面の例を示す図である。
【図14】 下位の見出しを表示した際の表示画面の例を示す図である。
【図15】 内容を表示した際の表示画面の例を示す図である。
【図16】 第2の実施の形態における関連付け参照の処理の流れを示すフローチャートである。
【図17】 関連付けの対象となるキーワードを表題に含む文書の第2の例を示す図である。
【図18】 関連付けの対象となるキーワードを表題に含む文書の第3の例を示す図である。
【図19】 キーワードと表題もしくは見出しとの関連付けを行った文書の例を示す図である。
【図20】 複数の見出しを表示する表示画面の例を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1 文書蓄積手段
2 階層構造関連付け手段
2a 被関連付け対象文書
3 キーワード抽出手段
3a キーワード対応表
4 文書内容検索手段
4a 文書
5 キーワード関連付け手段
5a 文書[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a document association apparatus, a document browsing apparatus, a computer-readable recording medium that records a document association program, and a computer-readable recording medium that records a document browsing program, and particularly relates to a certain keyword in the document and the keyword. A document correlating device for associating the contents of another document to be viewed, a document browsing device for browsing a document in a document group in which a certain keyword in the document is associated with the content of another document related to the keyword, and the document correlating device. The present invention relates to a computer-readable recording medium that records a document association program to be realized on a computer, and a computer-readable recording medium that records a document browsing program to realize the document browsing apparatus on a computer.
[0002]
[Prior art]
A so-called hypertext system capable of associating a group of electronic documents scattered on a network by a link has been widely used with the spread of the World Wide Web (WWW). In the hypertext system, a hyperlink to the content of another document having more detailed information is given to a keyword in a document. As a result, when the user browses the document and wants to know more about the description to which the hyperlink is added, the related information can be known by tracing the hyperlink.
[0003]
However, in general, in order to create such a hypertext document, it is necessary for the creator of the document to manually create a hyperlink by associating a keyword with another document. It takes time. Therefore, in order to solve this problem, keywords in documents are automatically extracted, and by searching for documents containing the same or synonymous keywords from other documents, associations between documents, that is, hyperlinks are automatically created. It is considered to be.
[0004]
At this time, simply associating documents with the same or synonymous keywords as clues, there is no guarantee that a more detailed explanation can be obtained by following the hyperlink. This is because it is often the case that the same or synonymous keyword is referred to in one word in any of the associated documents, and there is no description that explains the keyword.
[0005]
As one method for solving this problem, there is a “system for automatically creating a chain between document texts” disclosed in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 5-20362. In the method disclosed in this publication, first, an important keyword is extracted from the document text, and the importance of the extracted keyword in the document is calculated. In addition, a unidirectional association is automatically generated between documents sharing the same keyword from a document having a lower keyword importance to a document having a higher keyword importance. In this method, documents are associated with the same keyword as a clue, but it is assumed that a document with a higher importance in a document with the same keyword is described in more detail with respect to that keyword than a document with a lower importance. is doing. Thereby, a hyperlink to another document in which a more detailed description is described is automatically generated from a certain keyword in the document. This method described below is the first prior art.
[0006]
Another method for solving the above problem is an “hypertext automatic generation device” disclosed in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 7-325827. In this publication, when documents having the same or synonymous keywords are associated with each other, a hyperlink is generated from the keyword of one document to the chapter or section heading of the other document having the same or synonymous keyword. The method is shown. In this method, when a certain keyword is included in the headline, it is assumed that there is a high possibility that the keyword is described in detail in the contents below the headline. As a result, hyperlinks to more detailed explanations are automatically generated from certain keywords in the document. This method described below is the second prior art.
[0007]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, each of the conventional techniques has the following problems.
In the first prior art, the target of association is a keyword in a document and the entire other document. For this reason, when there is a large amount of description in another document associated with the document, it is difficult to find a related description in the document even if a detailed description for the associated keyword is described in the document.
[0008]
In the second prior art, when there are a plurality of other documents containing the same or synonymous keywords with respect to the keywords in a certain document, the candidates are narrowed down to any one according to a predetermined strategy. It has become. Therefore, there is a possibility that information that the user actually wants to know is leaked from the association target. As for this problem, for example, when there are a plurality of candidates to be associated, it is possible to prevent leakage by associating all the candidates. However, in this case, it takes time and effort for the user to sequentially browse a plurality of associated descriptions and search for necessary information.
[0009]
Furthermore, in any of the above two conventional techniques, it is necessary to perform morphological analysis on the entire document in order to automatically extract keywords to be associated. In order to perform morphological analysis with high accuracy, it is necessary to perform fairly complicated processing. For this reason, there is a problem that it takes a very long time to automatically create hyperlinks between a large number of documents using the conventional technique.
[0010]
The present invention has been made in view of these points, and an object of the present invention is to provide a document association apparatus capable of performing a process of associating a keyword in a document with a minimum related description in another document at high speed. And
[0011]
A second object of the present invention is to provide a document browsing apparatus for browsing a document in a document group in which a keyword in a document is associated with a minimum related description in another document.
[0012]
A third object of the present invention is a computer-readable record recording a document association program that can cause a computer to perform a process of associating a keyword in a document with a minimum related description in another document at high speed. To provide a medium.
[0013]
A fourth object of the present invention is to record a document browsing program for browsing a document in a document group in which a keyword in a document is associated with a minimum related description in another document using a computer. It is to provide a computer-readable recording medium.
[0014]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In the present invention, in order to solve the above problem, in a document association apparatus for performing association between documents,A document accumulating unit configured to store a plurality of documents each having an attribute set and a document identifier set; and a plurality of documents stored in the document accumulating unit are sequentially selected as related documents; An identifier setting unit that sets an element identifier for uniquely identifying the element with respect to a tag of the element in the selected document to be associated, and the associated item in which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting unit A keyword extracting unit that extracts a keyword from contents included in a processing target element having a specific attribute in the target document, and a keyword extraction source that includes the keyword for each keyword extracted by the keyword extracting unit. Document content search means for searching for a document other than the related target document from the document storage means; For each document containing a keyword searched by the search means, a tag associated with the keyword in the document and indicating a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword can be registered in the tag. And a keyword association unit that sets a plurality of attribute values including a set of a document identifier of the associated target document as an extraction source and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document. Document association apparatus characterized by the above Is provided.
[0015]
According to such a document associating apparatus, the document stored in the document accumulating unit is set as a related document by the hierarchical structure associating unit,An element identifier for uniquely identifying the element is set for the tag of the element in the associated document. . Further, the keyword extraction means extracts a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document. Thendocuments A document including the keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit is searched from the document storage unit by the content search unit. Then, by the keyword association means, the document content search meansSearch Keywords in the selected documentA plurality of attribute values consisting of a set of a document identifier of an associated target document from which a keyword is extracted and an element identifier of a processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document are set in the plurality of tags that can be registered. .
[0016]
In order to solve the above problems,In a document browsing apparatus for browsing the contents of a structured document, a document storage unit configured to store a plurality of documents each having an attribute set and a document identifier set, and stored in the document storage unit An identifier setting unit that sequentially selects a plurality of documents as associated documents, and sets an element identifier for uniquely identifying the element in a tag of the element in the selected associated document; and the identifier For each keyword extracted by the keyword extracting means, a keyword extracting means for extracting a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document set with the element identifier; , Storing the document including the keyword other than the related target document from which the keyword is extracted. Document content search means for searching from within the stage, and for each document including the keyword searched by the document content search means, elements in other documents associated with the keyword and associated with the keyword From a set of a document identifier of the associated target document that is the source of the keyword and an element identifier of the processing target element that includes the keyword in the associated target document in a tag that can be registered with a plurality of attribute values A keyword association unit that sets a plurality of attribute values, a document display unit that extracts and displays a document specified in the document browsing request from the document storage unit in response to the document browsing request; In the document displayed by the display unit, the keyword having a tag in which one or more attribute values indicating elements in another document are registered is selected. The element extraction means for extracting the processing target element in the related target document related to the keyword based on the attribute value set in the tag of the keyword, and the processing extracted by the element extraction means A document browsing device comprising: content display means for displaying the content of the target element Is provided.
[0017]
According to such a document browsing apparatus, the document stored in the document storage unit is set as a related target document by the hierarchical structure association unit,An element identifier for uniquely identifying the element is set for the tag of the element in the associated document. . Further, the keyword extraction means extracts a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document. Thendocuments A document including the keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit is searched from the document storage unit by the content search unit. Then, by the keyword association means, the document content search meansSearch Keywords in the selected documentA plurality of attribute values consisting of a set of a document identifier of an associated target document from which a keyword is extracted and an element identifier of a processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document are set in the plurality of tags that can be registered. . Furthermore, when a document browsing request is entered, the documentdisplay The means extracts a document corresponding to the document browsing request from the document storage means. This documentdisplay In the document extracted by the means, when the keyword associated by the keyword association means is selected, the element extraction means associates the keyword with the keyword.One or more Related elements in related documentsBut Extracted.
[0018]
In addition, the contentdisplay Of the related elements extracted by the element extracting means.Yong ExtractedDisplayed The
In order to solve the above problems,Document storage means for storing a plurality of documents each having an attribute set and a document identifier in a computer-readable recording medium recording a document association program for performing association between documents, A plurality of documents stored in the document storage means are sequentially selected as related documents, and element identifiers for uniquely identifying the elements are set for the tags of the elements in the selected related documents. An identifier setting unit that extracts a keyword from contents included in a processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document in which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting unit, and the keyword extraction unit. For each extracted keyword, it is the source of the keyword, including the keyword A document content search unit that searches a document other than the related target document from the document storage unit, and a document that includes a keyword searched by the document content search unit is associated with the keyword in the document, To a tag that can register a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword, the document identifier of the associated document to be extracted from the keyword and the keyword in the associated document A computer-readable recording medium having a document association program recorded thereon, wherein the computer functions as a keyword association unit that sets a plurality of attribute values including pairs of element identifiers of the processing target elements. Is provided.
[0019]
If the computer executes the document association program recorded on the recording medium, the function of the document association apparatus according to the present invention is constructed on the computer.
[0020]
In order to solve the above problems,In a computer-readable recording medium recording a document browsing program for browsing the contents of a structured document, the computer is composed of a plurality of elements having attributes set, and stores a plurality of documents having document identifiers set. Document storage means, sequentially selecting a plurality of documents stored in the document storage means as related documents, and uniquely identifying the elements with respect to the tags of the elements in the selected related documents Identifier setting means for setting an element identifier, keyword extraction means for extracting a keyword from contents included in a processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document in which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting means, For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction means, the keyword including the keyword For each document including a keyword searched by the document content search unit, a document content search unit that searches the document storage unit for a document other than the associated target document from which the document is extracted. A tag associated with a keyword and capable of registering a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword, a document identifier of the related target document from which the keyword is extracted, and the related target Keyword associating means for setting a plurality of attribute values consisting of element identifiers of the processing target elements including the keyword in the document, and in response to the document browsing request, the document specified in the document browsing request is stored as the document storage means. The document display means to be extracted and displayed, and the elements in other documents in the document displayed by the document display means are indicated by operation input When the keyword having a tag in which two or more attribute values are registered is selected, the processing target element in the related target document related to the keyword is selected based on the attribute value set in the keyword tag. A computer-readable recording medium having a document browsing program recorded thereon, which functions as element extracting means for extracting, and content display means for displaying the contents of the processing target element extracted by the element extracting means Is provided.
[0021]
If the computer executes the document browsing program recorded on the recording medium, the function of the document browsing apparatus according to the present invention is constructed on the computer.
[0022]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a principle configuration diagram of the present invention. The document association apparatus of the present invention includes the following elements.
[0023]
The
The hierarchical
[0024]
The keyword extraction means 3 extracts a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the
[0025]
The document content search means 4 searches the contents of other documents stored in the document storage means 1 based on the keywords extracted by the keyword extraction means 3. The found
[0026]
The
[0027]
According to such a document associating apparatus, the associating
[0028]
If such a process is executed for all the documents stored in the
[0029]
Moreover, since the keyword extraction processing is performed only for specific elements such as titles or headings in the document at the time of association, it is not necessary to perform complicated processing necessary for keyword extraction such as morphological analysis on the entire document. As a result, the association processing efficiency is improved.
[0030]
Next, a document browsing apparatus capable of associating documents with the document association apparatus of the present invention and browsing these documents will be described as a first embodiment.
[0031]
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a configuration of a document browsing apparatus to which the present invention is applied. This document browsing apparatus includes a
[0032]
The
The hierarchical
[0033]
The
Using the keywords extracted by the
[0034]
The
The
[0035]
In the document extracted by the
[0036]
The
[0037]
The
[0038]
The
[0039]
The
[0040]
Next, a procedure for associating documents with the document group stored in the
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a procedure for associating documents. The following processing will be described along with step numbers.
[S1] The hierarchical
[S2] The hierarchical
[S3] The hierarchical
[S4] The
[S5] The document
[S6] The
[S7] The
[S8] The hierarchical
[0041]
By performing such processing, it is possible to link from the keyword included in the contents of each document to the corresponding title or heading of the document including the keyword as the title or heading.
[0042]
Details of processing contents will be described below using specific examples. In the following example, an expression based on the international standard SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language: ISO8879) is used as an example of a document having a logical structure such as a title and a heading. If it is a system that can express the contents to be processed, it is not necessary to be SGML.
[0043]
First, the hierarchical
[0044]
Each element in the document is surrounded by a tag indicating its start and end. For a certain element A, the start tag is indicated by <A> and the end tag is indicated by </A>. The document is surrounded by a tag <doc> indicating the start of the document and a tag </ doc> indicating the end of the document. The document element (doc) includes an element (title) indicating a title and a sequence of elements (sect1) indicating chapters. The chapter element (sect1) contains either a heading element (head) and a paragraph element (para) sequence, or a heading element (head) and a section element (sect2) sequence. ing. The section element (sect2) contains a sequence of head elements (head) and paragraph elements (para). The title element (title), heading element (head), and paragraph element (para) have text (character string) as their contents.
[0045]
In the document exemplified in the present embodiment, doc, title, sect1, sect2, head, and para are used as element names. However, any name may be used as long as the title, heading, and body can be specified in the document. Also, the structure of chapters and sections may be more deeply nested. For example, the node element (sect2) may include a lower-level node element (sect3).
[0046]
The hierarchical
[0047]
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a document in which a unique identifier is assigned to each element. In this figure, an identifier is assigned to each element as the value of the attribute name “id”. In this
[0048]
Any element other than the document element in the
[0049]
Next, the hierarchical
[0050]
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document in which titles, headings, and contents are associated with each other. This
[0051]
Next, the
[0052]
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example of the keyword correspondence table. This is a keyword correspondence table 41 showing the correspondence between the title element (title) and heading element (head) of the
[0053]
Thus, since the morphological analysis process is performed only on the title element and the heading element in the document, it is not necessary to perform the morphological analysis process on the entire document. In general, the amount of text included in the title and heading of a document is very small compared to the amount of text in the entire document, so that the processing cost of morphological analysis can be greatly reduced.
[0054]
Next, the document
[0055]
FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document including a keyword to be associated in the text. This
[0056]
When the
[0057]
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document in which an association between a keyword and a title is performed. In this
[0058]
In this embodiment, “.” Is used to connect the identifier of the document element to the title element or heading element. Therefore, when the identifier is given to the element, “.” Is not included in the identifier itself. Like that.
[0059]
In the present embodiment, since the document element (doc) identifier is assigned so that the document stored in the
[0060]
When other document contents are searched for all the keywords extracted in step S4 and the keyword association is completed in step S6, the associated document is stored in the document storage unit 11 (step S7). At this time, the contents of the original document to be associated are overwritten.
[0061]
Then, for all the documents stored in the
[0062]
By performing the above processing, the hierarchical structure is also associated with the
FIG. 10 is a diagram showing a result of associating a hierarchical structure with the document of FIG. This
[0063]
Next, a procedure for referring to an explanation description for a keyword from a certain keyword in the document by using the association by the document association apparatus according to the present invention will be described.
[0064]
FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing the association use procedure. This flowchart will be briefly described along with step numbers.
[S11] When the user inputs a document display request using the
[S12] The user selects a keyword using the
[S13] The
[S14] The
[S15] The
[S16] The
[S17] The
[0065]
In the following, processing relating to the use of association will be described using a specific example.
First, it is assumed that the user instructs the
[0066]
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen when the contents of a document are displayed. On the
[0067]
Next, it is assumed that the user refers to the document displayed on the
[0068]
FIG. 13 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen when a headline is displayed. The keyword “SGML” is tagged with the link element indicating the association by the above-described association processing, and “d1.t1” is set as the value of the attribute “ref”. Therefore, the
[0069]
At this time, the
[0070]
FIG. 14 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen when a lower-level headline is displayed. This is an example of the
[0071]
Here, the
[0072]
Then, the
[0073]
FIG. 15 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen when content is displayed. This is an example of the
[0074]
As described above, even when there are a plurality of related content candidates, the minimum necessary associated content can be referred to by displaying and selecting the headline. If it is determined from the title or heading displayed on the
[0075]
Next, a second embodiment will be described. According to the second embodiment, when a plurality of titles or headings of other documents are associated with a keyword in a certain document content, the document browsing can be extracted more efficiently. Device. Note that the components of the second embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 2, and therefore the second embodiment will be described using the configuration shown in FIG. To do. In addition, the association process between documents in the second embodiment is the same as that in the first embodiment, and a description thereof will be omitted.
[0076]
Therefore, the association reference process according to the second embodiment will be described below.
FIG. 16 is a flowchart illustrating a flow of association reference processing according to the second embodiment. The following processing will be described along with step numbers.
[S21] When the user designates a document to be extracted from the document group accumulated in the
[S22] The user refers to the document displayed on the
[S23] The
[S24] The
[S25] If it is determined that there are a plurality of titles or headings extracted in step S24, the
[S26] The
[S27] The
[S28] The user selects one from the plurality of titles or headings displayed on the
[S29] When there is one title or headline extracted in step S23 or when a headline is selected in step S28, the
[S30] The
[0077]
In this way, when a plurality of titles or headings of other documents are associated with a keyword in a certain document content, the associated content can be efficiently extracted. Details of this processing will be described below using a specific example.
[0078]
In the present embodiment, in addition to the document shown in the first embodiment, the following document including the keyword “SGML” to be associated in the title is stored in the
[0079]
FIG. 17 is a diagram illustrating a second example of a document including a keyword to be associated in the title. In this
[0080]
FIG. 18 is a diagram illustrating a third example of a document including a keyword to be associated in the title. In the
[0081]
When the association processing is performed on the
[0082]
FIG. 19 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document in which a keyword is associated with a title or a headline. As shown in this figure, the
[0083]
Hereinafter, the flow of the association reference process will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. 16 for the document group associated in this way.
First, when the user designates a document to be extracted from the document group accumulated in the
[0084]
Next, the user refers to the
[0085]
Next, the
[0086]
Next, when it is determined that there are a plurality of titles or headings extracted in step S24, the
[0087]
Thus, by grouping the extracted titles or headings for each document, related descriptions in the same document can be continuously referred to.
Next, the
[0088]
[Expression 1]
[0089]
In Expression (1), n represents the maximum value of numbers assigned in order from 1 to the title or headline associated with the document. di represents the depth in the hierarchical structure of the title or heading to which the number (i) is assigned (the depth of the title is 0). That is, di = 0 for the title, di = 1 for the first level heading, di = 2 for the second level heading, and so on. When the importance of each document is calculated according to the equation (1), the
[0090]
Note that the method of calculating the importance for each document is not limited to the one shown in Expression (1). The importance may be determined so that the more important the titles or headings are related, the higher the importance is, and the more important the titles or headings that are related, the deeper the depth is. In this method of determining importance, it is considered that the more titles or headings that are associated in the same document, the more likely that the keyword is related to the subject of the entire document, and the hierarchy of associated titles or headings. The shallower the depth of is, the more likely it is that the keyword is explained more comprehensively, so it is an effective method.
[0091]
Next, the
[0092]
After the above processing is performed, the extracted title or heading is displayed on the
FIG. 20 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen that displays a plurality of headings. This is an example of the
[0093]
Next, the user selects one from the plurality of titles or headings displayed on the
[0094]
In this way, when there are a plurality of associated titles or headings in the same document, or when there are a plurality of documents having associated titles or headings, it is possible to preferentially refer to the important ones. Even when a large number of document titles and headings are associated with each other, the associated contents can be referred to efficiently.
[0095]
The above processing functions can be realized by a computer. In this case, the processing contents of the functions that the document association apparatus and the document browsing apparatus should have are described in a program recorded on a computer-readable recording medium. Then, by executing this program on a computer, the above processing is realized by the computer. Examples of the computer-readable recording medium include a magnetic recording device and a semiconductor memory. When distributing to the market, store the program in a portable recording medium such as a CD-ROM (Compact Disk Read Only Memory) or floppy disk, or store it in a computer storage device connected via a network. In addition, it can be transferred to another computer through the network. When executed by a computer, the program is stored in a hard disk device or the like in the computer, loaded into the main memory, and executed.
[0096]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, in the document association apparatus of the present invention, the keyword in the document is associated with the processing target element of the associated document, and the upper structure and the lower structure of the element in the associated document are associated. Therefore, the elements in other documents and the substructures of the elements can be sequentially traced from the keywords in the document, and the minimum associated contents can be referred to. Moreover, since keywords are extracted only from specific elements, complicated processing associated with keyword extraction can be performed on a limited range, and association processing can be performed at high speed.
[0097]
In the document browsing apparatus of the present invention, the keyword in the document is associated with the processing target element of the associated document, and the upper structure and the lower structure of the element in the associated document are associated with each other. When a keyword is specified, the contents of the related elements of the keyword and the contents of the substructure are extracted. Therefore, the user who specified the keyword can refer to the contents of the minimum necessary related elements related to the keyword. it can.
[0098]
In the computer-readable recording medium on which the document association program of the present invention is recorded, the recorded document association program is executed by the computer, thereby associating the keyword in the document with the processing target element of the associated document. Thus, it is possible to cause the computer to perform the process of associating the upper structure and the lower structure of the element in the associated document at high speed. That is, it is possible to cause a computer to perform a process of associating a keyword in a document with a minimum related description of another document at high speed.
[0099]
In the computer-readable recording medium on which the document browsing program of the present invention is recorded, the recorded document browsing program is executed by the computer, thereby associating the keyword in the document with the processing target element of the related target document. , The process of extracting the contents of the related elements of the keyword and the contents of the substructure when the keyword in the document is specified by associating the upper structure and the lower structure of the element in the target document. It is possible to make the computer perform. That is, a user who has specified a keyword for the computer can refer to the contents of the minimum necessary related elements related to the keyword.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a principle configuration diagram of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of a document browsing apparatus to which the present invention is applied.
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a procedure for associating documents.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a first example of a document including a keyword to be associated in a heading.
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a document in which a unique identifier is assigned to each element.
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document in which titles, headings, and contents are associated with each other.
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example of a keyword correspondence table.
FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document including a keyword to be associated in a text.
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document in which a keyword and a title are associated with each other.
10 is a diagram showing a result of associating a hierarchical structure with the document of FIG. 9. FIG.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing an association usage procedure;
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen when the contents of a document are displayed.
FIG. 13 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen when a heading is displayed.
FIG. 14 is a diagram showing an example of a display screen when a lower heading is displayed.
FIG. 15 is a diagram showing an example of a display screen when content is displayed.
FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing a flow of association reference processing in the second embodiment;
FIG. 17 is a diagram illustrating a second example of a document including a keyword to be associated in the title.
FIG. 18 is a diagram illustrating a third example of a document including a keyword to be associated in a title.
FIG. 19 is a diagram illustrating an example of a document in which a keyword is associated with a title or a heading.
FIG. 20 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen that displays a plurality of headings.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 Document storage means
2 Hierarchical structure association means
2a Target document
3 Keyword extraction means
3a Keyword correspondence table
4 Document content search means
4a Document
5 Keyword association means
5a Document
Claims (14)
Translated fromJapanese属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段と、
前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定する識別子設定手段と、
前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段と、
前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段と、
前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段と、
を有することを特徴とする文書関連付け装置。In a document association apparatus that associates documents,
A document accumulating unitconfigured to store aplurality of documents each having an attribute set and a document identifier set ;
The document storage meansa plurality of documents stored in thesequentially selected as the target associated with the target document,the tag of the selected element of the object to be associated in the target document, element identifiers for uniquely identifying the elements Identifier setting means for setting
Keyword extracting means for extracting a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target documentin which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting means ;
Foreach keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, a document content search unit that searches the document storage unitfor a document other than the associated target document that is the source of the keyword, includingthe keyword ,
For each document that contains the search keywords by the document contents searchmeans,associated withthe keywords inthedocument, the attribute value is more registerable tag indicating elements other in the document associated with the keyword,a document identifier of the target associated target document becomesthe keyword to extract theplurality set to that keyword association meansthe attribute value consists of a set of theelement identifier of the processed elementcontaining the keyword ofthe target associated target document When,
A document association apparatus characterized by comprising:
属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段と、 A document accumulating unit configured to store a plurality of documents each having an attribute set and a document identifier set;
前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定する識別子設定手段と、 A plurality of documents stored in the document storage means are sequentially selected as related documents, and element identifiers for uniquely identifying the elements are selected for the tags of the elements in the selected related documents. Identifier setting means to be set;
前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段と、 Keyword extracting means for extracting a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document in which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting means;
前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段と、 For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, a document content search unit that searches the document storage unit for a document other than the associated target document that is the source of the keyword, including the keyword,
前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段と、 For each document including a keyword searched by the document content search means, a tag that is associated with the keyword in the document and that can register a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword, A keyword associating means for setting a plurality of attribute values consisting of a set of a document identifier of the associated target document from which the keyword is extracted and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document; ,
文書閲覧要求に応じて、当該文書閲覧要求で指定された文書を前記文書蓄積手段から抽出し、表示する文書表示手段と、 In response to a document browsing request, a document display unit that extracts and displays the document specified in the document browsing request from the document storage unit;
操作入力により、前記文書表示手段にて表示された文書中で、他の文書中の要素を示す1つ以上の属性値が登録されたタグを有する前記キーワードが選択されると、当該キーワードのタグに設定された属性値に基づいて、当該キーワードに関連する前記被関連付け対象文書中の処理対象要素を抽出する要素抽出手段と、 When the keyword having a tag in which one or more attribute values indicating elements in another document are registered is selected in the document displayed by the document display unit by operation input, the tag of the keyword is selected. Element extraction means for extracting a processing target element in the related target document related to the keyword based on the attribute value set in
前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記処理対象要素の内容を表示する内容表示手段と、 Content display means for displaying the contents of the processing target element extracted by the element extraction means;
を有することを特徴とする文書閲覧装置。 A document browsing apparatus comprising:
属性が設定された複数の要素による階層的な論理構造が形成されており、文書識別子が A hierarchical logical structure is formed by multiple elements with attributes, and the document identifier is設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段と、Document storage means for storing a plurality of set documents;
前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定し、当該被関連付け対象文書の階層構造における上位構造の要素のタグに対して、下位構造の要素の要素識別子を設定する階層構造関連付け手段と、 A plurality of documents stored in the document storage means are sequentially selected as related documents, and element identifiers for uniquely identifying the elements are selected for the tags of the elements in the selected related documents. A hierarchical structure association means for setting and setting an element identifier of an element of a lower structure for a tag of an element of an upper structure in the hierarchical structure of the related target document;
前記階層構造関連付け手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容から、キーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段と、 Keyword extracting means for extracting a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the related target document in which the element identifier is set by the hierarchical structure associating means;
前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段と、 For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, a document content search unit that searches the document storage unit for a document other than the associated target document that is the source of the keyword, including the keyword,
前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段と、 For each document including a keyword searched by the document content search means, a tag that is associated with the keyword in the document and that can register a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword, A keyword associating means for setting a plurality of attribute values consisting of a set of a document identifier of the associated target document from which the keyword is extracted and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document; ,
文書閲覧要求に応じて、当該文書閲覧要求で指定された文書を前記文書蓄積手段から抽出し、表示する文書表示手段と、 In response to a document browsing request, a document display unit that extracts and displays the document specified in the document browsing request from the document storage unit;
操作入力により、前記文書表示手段にて表示された文書中で、他の文書中の要素を示す1つ以上の属性値が登録されたタグを有する前記キーワードが選択されると、当該キーワードのタグに設定された属性値に基づいて、当該キーワードに関連する前記被関連付け対象文書中の処理対象要素を抽出すると共に、抽出した前記処理対象要素のタグに設定された要素識別子に基づいて、当該処理対象要素の下位構造の要素を順次抽出する要素抽出手段と、 When the keyword having a tag in which one or more attribute values indicating elements in another document are registered is selected in the document displayed by the document display unit by operation input, the tag of the keyword is selected. Based on the attribute value set in the process, the process target element in the related target document related to the keyword is extracted, and the process is performed based on the element identifier set in the tag of the extracted process target element. Element extraction means for sequentially extracting elements of the substructure of the target element;
前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記処理対象要素の内容及び前記処理対象要素に関連付けられている下位の要素の内容を表示する内容表示手段と、 Content display means for displaying the content of the processing target element extracted by the element extraction means and the content of a lower element associated with the processing target element;
を有することを特徴とする文書閲覧装置。 A document browsing apparatus comprising:
ことを特徴とする請求項4記載の文書閲覧装置。The element extraction means has aplurality of attribute values set in the tag of the selected keyword, and when a plurality of processing target elements are extracted based on the attribute values, the element display means displays When an operation input for selecting one of a plurality of processing target elements is received, only the selected processing target element is extracted as a substructure element, and when a plurality of substructure elements are extracted, the contents Receiving an operation input for selecting one of a plurality of substructure elements displayed by the display means, and further extracting substructure elements only for the selected substructure elements;
The document browsing apparatus according to claim4, wherein:
前記文書表示手段は、前記要素抽出手段で並べられた順に前記処理対象要素の内容を表示することを特徴とする請求項4記載の文書閲覧装置。When aplurality of attribute values are set for the tag of the selected keyword , the element extraction unitdetermines a document including a processing target element corresponding to the attribute value based on a document identifier included in each attribute value. , Group multiple processing elements included in the same document into the same group, arrange the processing elements so that multiple processing elements belonging to the same group are continuous,
5. The document browsing apparatus according to claim4, wherein the document display means displays the contents of the processing target elements in the order arranged by the element extraction means .
属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段、 A document storage unit configured to store a plurality of documents having document identifiers, each of which includes a plurality of elements having attributes set;
前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定する識別子設定手段、 A plurality of documents stored in the document storage means are sequentially selected as related documents, and element identifiers for uniquely identifying the elements are selected for the tags of the elements in the selected related documents. Identifier setting means to set,
前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段、 Keyword extracting means for extracting a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document in which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting means;
前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段、 For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, a document content search unit that searches the document storage unit for a document other than the related target document that is the keyword extraction source, including the keyword,
前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段、 For each document including a keyword searched by the document content search means, a tag that is associated with the keyword in the document and that can register a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword, Keyword association means for setting a plurality of attribute values consisting of a set of a document identifier of the associated target document from which the keyword is extracted and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document;
としてコンピュータを機能させることを特徴とする文書関連付けプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。 A computer-readable recording medium recording a document association program characterized by causing a computer to function as
コンピュータを、 Computer
属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段、 A document storage unit configured to store a plurality of documents having document identifiers, each of which includes a plurality of elements having attributes set;
前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定する識別子設定手段、 A plurality of documents stored in the document storage means are sequentially selected as related documents, and an element identifier for uniquely identifying the element is selected with respect to the tag of the element in the selected related document. Identifier setting means to set,
前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段、 Keyword extracting means for extracting a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document in which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting means;
前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段、 For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, a document content search unit that searches the document storage unit for a document other than the related target document that is the keyword extraction source, including the keyword,
前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段、 For each document including a keyword searched by the document content search means, a tag that is associated with the keyword in the document and that can register a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword, Keyword association means for setting a plurality of attribute values consisting of a set of a document identifier of the associated target document from which the keyword is extracted and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document;
文書閲覧要求に応じて、当該文書閲覧要求で指定された文書を前記文書蓄積手段から抽出し、表示する文書表示手段、 In response to a document browsing request, a document display unit that extracts and displays the document specified in the document browsing request from the document storage unit,
操作入力により、前記文書表示手段にて表示された文書中で、他の文書中の要素を示す1つ以上の属性値が登録されたタグを有する前記キーワードが選択されると、当該キーワードのタグに設定された属性値に基づいて、当該キーワードに関連する前記被関連付け対象文書中の処理対象要素を抽出する要素抽出手段、 When the keyword having a tag in which one or more attribute values indicating elements in another document are registered is selected in the document displayed by the document display unit by operation input, the tag of the keyword is selected. Element extracting means for extracting a processing target element in the related target document related to the keyword based on the attribute value set in
前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記処理対象要素の内容を表示する内容表示手段、 Content display means for displaying the contents of the processing target element extracted by the element extraction means;
として機能させることを特徴とする文書閲覧プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。 A computer-readable recording medium on which a document browsing program is recorded.
コンピュータを Computer
属性が設定された複数の要素による階層的な論理構造が形成されており、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納する文書蓄積手段、 A document accumulating means for storing a plurality of documents having document identifiers formed in a hierarchical logical structure by a plurality of elements having attributes set;
前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定し、当該被関連付け対象文書の階層構造における上位構造の要素のタグに対して、下位構造の要素の要素識別子を設定する階層構造関連付け手段、 A plurality of documents stored in the document storage means are sequentially selected as related documents, and element identifiers for uniquely identifying the elements are selected for the tags of the elements in the selected related documents. A hierarchical structure associating means for setting and setting an element identifier of an element of a lower structure for a tag of an element of a higher structure in the hierarchical structure of the related target document
前記階層構造関連付け手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容から、キーワードを抽出するキーワード抽出手段、 Keyword extracting means for extracting a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the related target document in which the element identifier is set by the hierarchical structure associating means;
前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索する文書内容検索手段、 For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, a document content search unit that searches the document storage unit for a document other than the related target document that is the keyword extraction source, including the keyword,
前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定するキーワード関連付け手段、 For each document including a keyword searched by the document content search means, a tag that is associated with the keyword in the document and that can register a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword, Keyword association means for setting a plurality of attribute values consisting of a set of a document identifier of the associated target document from which the keyword is extracted and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document;
文書閲覧要求に応じて、当該文書閲覧要求で指定された文書を前記文書蓄積手段から抽出し、表示する文書表示手段、 In response to a document browsing request, a document display unit that extracts and displays the document specified in the document browsing request from the document storage unit,
操作入力により、前記文書表示手段にて表示された文書中で、他の文書中の要素を示す1つ以上の属性値が登録されたタグを有する前記キーワードが選択されると、当該キーワードのタグに設定された属性値に基づいて、当該キーワードに関連する前記被関連付け対象文書中の処理対象要素を抽出すると共に、抽出した前記処理対象要素のタグに設定された要素識別子に基づいて、当該処理対象要素の下位構造の要素を順次抽出する要素抽出手段、 When the keyword having a tag in which one or more attribute values indicating elements in another document are registered is selected in the document displayed by the document display unit by operation input, the tag of the keyword is selected. Based on the attribute value set in the process, the process target element in the related target document related to the keyword is extracted, and the process is performed based on the element identifier set in the tag of the extracted process target element. Element extraction means for sequentially extracting elements of a substructure of the target element;
前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記処理対象要素の内容及び前記処理対象要素に関連付けられている下位の要素の内容を表示する内容表示手段、 Content display means for displaying the content of the processing target element extracted by the element extraction means and the content of a lower element associated with the processing target element;
として機能させることを特徴とする文書閲覧プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。 A computer-readable recording medium on which a document browsing program is recorded.
文書蓄積手段が、属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納し、 The document storage means is composed of a plurality of elements with attributes set, stores a plurality of documents with document identifiers set,
識別子設定手段が、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定し、 The identifier setting unit sequentially selects a plurality of documents stored in the document storage unit as the association target document, and uniquely identifies the element with respect to the tag of the element in the selected association target document. Set the element identifier for
キーワード抽出手段が、前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出し、 A keyword extracting unit extracts a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document in which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting unit;
文書内容検索手段が、前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索し、 For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, the document content search unit searches the document storage unit for a document other than the associated target document that is the keyword extraction source, including the keyword,
キーワード関連付け手段が、前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定する、 For each document including the keyword searched by the document content search means, the keyword association means associates with the keyword in the document and registers a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword A plurality of attribute values including a set of a document identifier of the associated target document from which the keyword is extracted and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document are set in a possible tag To
ことを特徴とする文書関連付け方法。 A document association method characterized by the above.
文書蓄積手段が、属性が設定された複数の要素で構成され、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納し、 The document storage means is composed of a plurality of elements with attributes set, stores a plurality of documents with document identifiers set,
識別子設定手段が、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定し、 The identifier setting unit sequentially selects a plurality of documents stored in the document storage unit as the association target document, and uniquely identifies the element with respect to the tag of the element in the selected association target document. Set the element identifier for
キーワード抽出手段が、前記識別子設定手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容からキーワードを抽出し、 A keyword extracting unit extracts a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the associated target document in which the element identifier is set by the identifier setting unit;
文書内容検索手段が、前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索し、 For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, the document content search unit searches the document storage unit for a document other than the associated target document that is the keyword extraction source, including the keyword,
キーワード関連付け手段が、前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定し、 For each document that includes the keyword searched by the document content search means, the keyword association means associates with the keyword in the document and registers a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword A plurality of attribute values including a set of a document identifier of the associated target document from which the keyword is extracted and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document are set in a possible tag And
文書表示手段が、文書閲覧要求に応じて、当該文書閲覧要求で指定された文書を前記文書蓄積手段から抽出し、表示し、 In response to the document browsing request, the document display means extracts and displays the document designated by the document browsing request from the document storage means,
要素抽出手段が、操作入力により、前記文書表示手段にて表示された文書中で、他の文書中の要素を示す1つ以上の属性値が登録されたタグを有する前記キーワードが選択されると、当該キーワードのタグに設定された属性値に基づいて、当該キーワードに関連する前記被関連付け対象文書中の処理対象要素を抽出し、 When the element extraction unit selects the keyword having a tag in which one or more attribute values indicating an element in another document are registered in the document displayed by the document display unit by an operation input. , Based on the attribute value set in the tag of the keyword, extract the processing target element in the related target document related to the keyword,
内容表示手段が、前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記処理対象要素の内容を表示する、 A content display means displays the content of the processing target element extracted by the element extraction means.
ことを特徴とする文書閲覧方法。 A document browsing method characterized by the above.
文書蓄積手段が、属性が設定された複数の要素による階層的な論理構造が形成されており、文書識別子が設定された文書を複数格納し、 The document storage means has a hierarchical logical structure formed by a plurality of elements having attributes set, stores a plurality of documents having document identifiers set,
階層構造関連付け手段が、前記文書蓄積手段に格納されている複数の文書を被関連付け対象文書として順次選択し、選択した当該被関連付け対象文書中の要素のタグに対して、当該要素を一意に識別するための要素識別子を設定し、当該被関連付け対象文書の階層構造における上位構造の要素のタグに対して、下位構造の要素の要素識別子を設定し、 The hierarchical structure associating means sequentially selects a plurality of documents stored in the document storage means as related documents, and uniquely identifies the elements with respect to the tags of the elements in the selected related documents. Set the element identifier of the substructure element for the tag of the upper structure element in the hierarchical structure of the related target document,
キーワード抽出手段が、前記階層構造関連付け手段によって前記要素識別子が設定された前記被関連付け対象文書中の特定の属性を有する処理対象要素に含まれる内容から、キーワードを抽出し、 A keyword extracting unit extracts a keyword from the content included in the processing target element having a specific attribute in the related target document in which the element identifier is set by the hierarchical structure associating unit;
文書内容検索手段が、前記キーワード抽出手段により抽出されたキーワードごとに、当該キーワードを含む、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書以外の文書を、前記文書蓄積手段内より検索し、 For each keyword extracted by the keyword extraction unit, the document content search unit searches the document storage unit for a document other than the associated target document that is the keyword extraction source, including the keyword,
キーワード関連付け手段が、前記文書内容検索手段により検索されたキーワードを含む文書ごとに、当該文書中の当該キーワードに対応付けられ、当該キーワードに関連する他の文書中の要素を示す属性値が複数登録可能なタグに、当該キーワードの抽出元となる前記被関連付け対象文書の文書識別子と、当該被関連付け対象文書内の当該キーワードを含む前記処理対象要素の要素識別子との組からなる属性値を複数設定し、 For each document that includes the keyword searched by the document content search means, the keyword association means associates with the keyword in the document and registers a plurality of attribute values indicating elements in other documents related to the keyword A plurality of attribute values including a set of a document identifier of the associated target document from which the keyword is extracted and an element identifier of the processing target element including the keyword in the associated target document are set in a possible tag And
文書表示手段が、文書閲覧要求に応じて、当該文書閲覧要求で指定された文書を前記文書蓄積手段から抽出し、表示し、 In response to the document browsing request, the document display means extracts and displays the document designated by the document browsing request from the document storage means,
要素抽出手段が、操作入力により、前記文書表示手段にて表示された文書中で、他の文書中の要素を示す1つ以上の属性値が登録されたタグを有する前記キーワードが選択されると、当該キーワードのタグに設定された属性値に基づいて、当該キーワードに関連する前記被関連付け対象文書中の処理対象要素を抽出すると共に、抽出した前記処理対象要素のタグに設定された要素識別子に基づいて、当該処理対象要素の下位構造の要素を順次抽出し、 When the element extraction unit selects the keyword having a tag in which one or more attribute values indicating an element in another document are registered in the document displayed by the document display unit by an operation input. Based on the attribute value set in the tag of the keyword, the processing target element in the related target document related to the keyword is extracted, and the element identifier set in the extracted tag of the processing target element Based on the subordinate elements of the processing target element,
内容表示手段が、前記要素抽出手段により抽出された前記処理対象要素の内容及び前記 Content display means, the content of the processing target element extracted by the element extraction means, and the処理対象要素に関連付けられている下位の要素の内容を表示する、Display the contents of the lower element associated with the element to be processed,
ことを特徴とする文書閲覧方法。 A document browsing method characterized by the above.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP22293498AJP4010058B2 (en) | 1998-08-06 | 1998-08-06 | Document association apparatus, document browsing apparatus, computer-readable recording medium recording a document association program, and computer-readable recording medium recording a document browsing program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP22293498AJP4010058B2 (en) | 1998-08-06 | 1998-08-06 | Document association apparatus, document browsing apparatus, computer-readable recording medium recording a document association program, and computer-readable recording medium recording a document browsing program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2000057152A JP2000057152A (en) | 2000-02-25 |
| JP2000057152A5 JP2000057152A5 (en) | 2005-01-13 |
| JP4010058B2true JP4010058B2 (en) | 2007-11-21 |
Family
ID=16790167
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP22293498AExpired - Fee RelatedJP4010058B2 (en) | 1998-08-06 | 1998-08-06 | Document association apparatus, document browsing apparatus, computer-readable recording medium recording a document association program, and computer-readable recording medium recording a document browsing program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4010058B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7813915B2 (en) | 2000-09-25 | 2010-10-12 | Fujitsu Limited | Apparatus for reading a plurality of documents and a method thereof |
| US7698626B2 (en) | 2004-06-30 | 2010-04-13 | Google Inc. | Enhanced document browsing with automatically generated links to relevant information |
| JP4963386B2 (en)* | 2006-09-01 | 2012-06-27 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Document data management apparatus and program |
| WO2008038368A1 (en)* | 2006-09-28 | 2008-04-03 | Navitime Japan Co., Ltd. | Window display system |
| WO2009154241A1 (en)* | 2008-06-18 | 2009-12-23 | 日本電気株式会社 | Search expression creating system, search expression creating method, search expression creating program, and recording medium |
| JP5301641B2 (en)* | 2011-12-16 | 2013-09-25 | 株式会社ナビタイムジャパン | Window display system |
| WO2015125209A1 (en)* | 2014-02-18 | 2015-08-27 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Information structuring system and information structuring method |
| WO2016190446A1 (en)* | 2015-05-26 | 2016-12-01 | Hiroyuki Tanaka | Electronic file structure, non-transitory computer-readable storage medium, electronic file generation apparatus, electronic file generation method, and electronic file |
| JP5723472B1 (en)* | 2014-08-07 | 2015-05-27 | 廣幸 田中 | Data link generation device, data link generation method, data link structure, and electronic file |
| CN113204578B (en)* | 2021-04-29 | 2024-12-03 | 北京金山数字娱乐科技有限公司 | Content association method, system, device, electronic device and storage medium |
- 1998
- 1998-08-06JPJP22293498Apatent/JP4010058B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2000057152A (en) | 2000-02-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Lu et al. | Annotating search results from web databases | |
| Lu et al. | Annotating structured data of the deep web | |
| Liu et al. | Vide: A vision-based approach for deep web data extraction | |
| KR101443475B1 (en) | Search suggestion clustering and presentation | |
| RU2335013C2 (en) | Methods and systems for improving search ranging with application of information about article | |
| US7496581B2 (en) | Information search system, information search method, HTML document structure analyzing method, and program product | |
| CN100394427C (en) | network searching system and method | |
| KR100957080B1 (en) | Display of search results based on document structure | |
| US8983965B2 (en) | Document rating calculation system, document rating calculation method and program | |
| US7024405B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for improved internet searching | |
| JP2009151749A (en) | Method and system for filtering subject related web page based on navigation path information | |
| JP2005122295A (en) | Relationship diagram creation program, relationship diagram creation method, and relationship diagram creation device | |
| US6847967B1 (en) | Information set importance determination system and information set importance determination method | |
| JP4010058B2 (en) | Document association apparatus, document browsing apparatus, computer-readable recording medium recording a document association program, and computer-readable recording medium recording a document browsing program | |
| US20100082594A1 (en) | Building a topic based webpage based on algorithmic and community interactions | |
| US8612431B2 (en) | Multi-part record searches | |
| US20110252313A1 (en) | Document information selection method and computer program product | |
| CN111966940B (en) | A kind of target data positioning method and device based on user request sequence | |
| JP2002197115A (en) | Web page retrieval method with usage of evaluation reference data and storage medium | |
| JP2004192368A (en) | Related classification extraction method and apparatus | |
| JP2000339320A (en) | Information retrieval method and apparatus and recording medium recording information retrieval program | |
| JP2002297662A (en) | Method and device for editing structured document, terminal, and program | |
| KR100942902B1 (en) | A computer readable recording medium recording a web page searching method and a program for implementing the method on a computer. | |
| JP2008269106A (en) | Schema extraction method, information processing apparatus, computer program, and recording medium | |
| Amin et al. | An efficient web-based wrapper and annotator for tabular data |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20040218 | |
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20040218 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20070306 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20070410 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20070611 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20070814 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20070827 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100914 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110914 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120914 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120914 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130914 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |