JP3990928B2 - Television broadcast receiving apparatus, reproducing method and program - Google Patents
Television broadcast receiving apparatus, reproducing method and programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3990928B2 JP3990928B2JP2002077188AJP2002077188AJP3990928B2JP 3990928 B2JP3990928 B2JP 3990928B2JP 2002077188 AJP2002077188 AJP 2002077188AJP 2002077188 AJP2002077188 AJP 2002077188AJP 3990928 B2JP3990928 B2JP 3990928B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- content
- application
- data
- control module
- attribute data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Stored Programmes (AREA)
- Two-Way Televisions, Distribution Of Moving Picture Or The Like (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、例えば、文字、画像、音声、及び映像等の各データが多重化されたディジタル放送波を受信し、当該受信データに基づいて、表示、再生、及びアプリケーションプログラムの実行処理を行う機能を有する装置或いはシステムに用いられる、テレビジョン放送受信装置、再生方法及びそれを実施するためのプログラムに関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年では、例えば、映像を含むテレビジョン放送信号をディジタル化し、当該ディジタルテレビジョン放送を放送衛星或いは通信衛星等を介して伝送し、各家庭で当該ディジタルテレビジョン放送を受信するようになされたシステムが運用されている。
【0003】
上述のディジタルテレビジョン放送により、各家庭等において、ディジタルテレビジョン放送を受信して再生するテレビジョン放送受信装置(所謂テレビ若しくはテレビ受像機)は、見るものから使うものへと変わりつつあると言われる。
【0004】
例えば、従来では、放送される番組を見るための手段でしかなかったテレビが、放送のディジタル化に伴い、動画、音声、及び各種データ等が多重化された電波を受信し、ユーザのリモートコントローラ(リモコン)等の操作に応じて、各種データ等を表示する、ということが可能になってきている。
【0005】
また、テレビジョン放送としてのBSディジタル放送では、データ放送サービスが既に開始されている。これは、放送局が、表示データやスクリプトプログラム等を含むデータ群をテレビジョン放送波に重畳して送信し、テレビジョン放送受信装置側が、当該テレビジョン放送波を受信及び蓄積し、ユーザのリモコン操作等に応じて、該当するデータを画面上に表示する、ということが可能となるサービスである。
【0006】
一方、言うまでも無く従来から、パーソナルコンピュータ(パソコン)により、アプリケーションプログラムを主体に利用する環境が実現されており、ユーザがパソコン上でアプリケーションプログラムを利用する場合、ユーザが、アプリケーションプログラムの提供側であるソフトウェア販売会社側に対して一定の料金を支払うようになされている。これによりユーザは、パソコン上でのアプリケーションプログラムの利用が可能となる。
【0007】
具体的には例えば、ユーザは、所望するアプリケーションプログラムのパッケージを、ソフトウェア販売会社側から購入し、当該アプリケーションプログラムをパソコンに対してインストールする。或いは、ユーザは、パソコン操作により、インターネット等を介して所望するアプリケーションプログラムの提供側にアクセスし、クレジットカード番号等のユーザ情報を入力後、当該アプリケーションプログラムのダウンロードを行う。或いは、ユーザは、パソコン操作により、インターネット等を介して所望するアプリケーションプログラムの提供側にアクセスし、当該アプリケーションプログラムのダウンロード後、この料金の入金を行い、当該アプリケーションプログラムの提供側からのキーコードの開示を受けてから、当該アプリケーションプログラムを利用する。
【0008】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上述したような従来のディジタル放送の受信装置では、放送中の番組のデータに含まれる一部のスクリプト又はプログラムの実行のみが可能であり、また、この実行は、当該番組の放送の間のみ可能であった。
すなわち、従来のテレビジョン放送受信装置は、ユーザが、ある目的を達成するためにアプリケーションプログラムを主体的に利用したい、などという要求に答えられるものではなかった。
【0009】
また、上述のようなテレビジョン放送受信装置においてもユーザが好きなときにアプリケーションプログラムを主体的で利用できる環境を求める要求がある一方で、アプリケーションプログラムの利用に関しては、アプリケーションプログラムを手軽に使用し、さらに可能であれば無料で使用したい、ということが強く要望されている。特に、基本的に無料で番組視聴することが常識であるテレビジョン放送の利用環境においては、アプリケーションプログラムに対しても、同様の環境を求める要望が強い。
【0010】
また、例えば、企業におけるアプリケーションソフトウェア開発には、膨大な資金が必要なものの、当該企業が、アプリケーションソフトウェアをユーザに無料で配布するサービスが度々行われている。
【0011】
しかしながら、上記のサービスは、ユーザが、当該企業のアプリケーションソフトウェア(プログラム)を利用するために必須である、一般的には高価なハードウェア或いはオペレーティングソフトウェア等を同企業から購入することを前提にしたものであるため、当該サービスを行える企業(事業者)が限られてしまうという問題があった。
【0012】
また、例えば、特開2001−43282号等に記載された分散データ処理システムでは、WWWブラウザ表示の一部に対して広告を挿入することで、ユーザのオンライン通信料コストを削減し、アプリケーションプログラムを手軽に利用可能としている。
【0013】
しかしながら、上記のシステムでは、ユーザが利用可能となるアプリケーションプログラムが、インターネットコンテンツの閲覧アプリケーション限定されるため、インターネット接続を行わないアプリケーションプログラムに対して適応できなかった。
【0014】
そこで、本発明は、上記の欠点を除去するために成されたもので、テレビジョン放送受信装置をアプリケーションを主体に利用可能とすると共に、従来のパソコン環境とも異なり、テレビジョン放送受信装置ならではの手軽なアプリケーションの利用環境を実現するためのアプリケーション実行制御機能を提供する、テレビジョン放送受信装置、再生方法及びそれを実施するためのプログラムを提供することを目的とする。
【0015】
【課題を解決するための手段】
斯かる目的下において、本発明に係るテレビジョン放送受信装置は、映像及び音声の少なくとも何れかを含むコンテンツ及び将来配信されるコンテンツに関する属性データが多重されたテレビジョン放送波を受信して処理するテレビジョン放送受信装置であって、上記コンテンツの蓄積処理、及び上記将来配信されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理を行うコンテンツ蓄積手段と、上記コンテンツ蓄積手段内のコンテンツを再生する再生手段と、任意のアプリケーションプログラムを実行するアプリケーション実行手段と、上記アプリケーションプログラムを利用するための条件データを蓄積するアプリケーション利用条件蓄積手段とを備え、上記コンテンツ蓄積手段は、上記属性データと、上記アプリケーション利用条件蓄積手段に蓄積された条件データとの比較結果に基づいて、上記属性データにより示されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理及び蓄積処理を実行することを特徴とする。
【0024】
また、本発明に係る再生方法は、映像及び音声の少なくとも何れかを含むコンテンツ及び将来配信されるコンテンツに関する属性データが多重されたテレビジョン放送波を受信して再生処理するための再生方法であって、上記コンテンツの蓄積処理、及び上記将来配信されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理を行うコンテンツ蓄積ステップと、上記コンテンツ蓄積ステップにより蓄積されたコンテンツを再生する再生ステップと、アプリケーションプログラムを起動及び実行するアプリケーション実行ステップと、上記アプリケーションプログラムを利用するための条件データを蓄積するアプリケーション利用条件蓄積ステップとを含み、上記コンテンツ蓄積ステップは、上記属性データと、上記アプリケーション利用条件蓄積ステップにより蓄積された条件データとが一致した場合に、上記属性データにより示されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理及び蓄積処理を実行するステップを含むことを特徴とする。
【0029】
また、本発明に係るプログラムは、コンピュータを所定の手段として機能させるためのプログラムであって、上記所定の手段は、映像及び音声の少なくとも何れかを含むコンテンツ及び将来配信されるコンテンツに関する属性データが多重されたテレビジョン放送波の当該コンテンツの蓄積処理、及び上記将来配信されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理を行うコンテンツ蓄積手段と、上記コンテンツ蓄積手段内のコンテンツを再生する再生手段と、任意のアプリケーションプログラムを実行するアプリケーション実行手段と、上記アプリケーションプログラムを利用するための条件データを蓄積するアプリケーション利用条件蓄積手段とを備え、上記コンテンツ蓄積手段は、上記属性データと、上記アプリケーション利用条件蓄積手段に蓄積された条件データとの比較結果に基づいて、上記属性データにより示されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理及び蓄積処理を実行することを特徴とする。
【0031】
上述のような本発明の構成によれば、例えば、ハードディスク等の蓄積手段に予め蓄積されたコンテンツ或いはコンテンツ群を再生中であるか否か等の再生状態に基づき、アプリケーションプログラムの起動及び実行の制御を行うことができる。すなわち、予め蓄積されたコンテンツが再生されていることを条件に、ユーザに対して、アプリケーションの利用を許可することが可能となる。
【0032】
また、ユーザがアプリケーションプログラムを利用している曜日や時間等に応じて、コンテンツ再生内容の優先度を変化させたり、ユーザが予め登録したユーザに関する情報に応じて、コンテンツ再生内容の優先度を変化させることができる。
【0033】
また、実行するアプリケーションプログラム毎に再生するコンテンツを変化させる制御や、アプリケーションプログラムの状態に応じて再生するコンテンツを変化させる制御が可能となる。
【0034】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態について図面を用いて説明する。
【0035】
[第1の実施の形態]
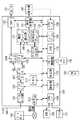
本発明は、例えば、図1に示すような、ディジタルのテレビジョン放送(ディジタル放送)を受信するテレビジョン放送受信装置(ディジタルテレビ受信装置)100に適用される。
【0036】
まず、本実施の形態では、ディジタル放送の放送局(不図示)において、テレビ番組の映像コンテンツ(音声をも含むコンテンツ)、及び当該映像コンテンツに関するデータ(コンテンツ属性データ)が符号化され、当該符号化後の各データが多重化された後に変調され、当該変調後のデータが放送波として、放送局のアンテナ(不図示)から送出される。放送局のアンテナから送出された放送波は、不図示の放送衛星(BS)を介して、ディジタルテレビ受信装置100(ユーザ側端末装置)で受信される。
【0037】
以下、上述のような放送波を受信して処理する、本実施の形態のディジタルテレビ受信装置100について具体的に説明する。
【0038】
<ディジタルテレビ受信装置100の構成及び一連の動作>
上記図1に示すディジタルテレビ受信装置100において、先ず、アンテナ160は、放送局からの放送波(ディジタル放送波)を受信する。
ディジタルチューナ部101は、アンテナ160の受信波(ディジタル放送波)から、ユーザ操作等により選択されたチャンネルの周波数帯域の信号を選択して入力すると共に、当該入力信号に対して、復調及び誤り訂正等の処理を施し、トランスポートストリーム(TS)と呼ばれる形式のディジタルデータを生成し、更に、当該トランスポートストリーム(以下、「TSデータ」と言う)をデスクランブラ102に対して出力する。
【0039】
デスクランブラ102は、ディジタルチューナ部101からのTSデータが、視聴制限のためのスクランブルがかけられているTSデータである場合、当該TSデータに含まれるデスクランブル(スクランブル解除)のための鍵情報、及び後述するICカード制御部117から出力される鍵情報に基づいて、当該TSデータに対してスクランブル解除を施し、当該スクランブル解除後のTSデータをトランスポートデコーダ103に対して出力する。
【0040】
また、デスクランブラ102は、ディジタルチューナ部101からのTSデータが、視聴制限のためのスクランブルがかけられているTSデータでない場合、当該TSデータをトランスポートデコーダ103に対して出力する。
【0041】
ICカード制御部117から情報が読み取られるICカード135には、ユーザの契約情報、及び受信波から得られるTSデータに含まれるデスクランブラのため鍵情報を解くため鍵情報等が記録されている。
【0042】
ICカード制御部117は、ICカード135に対して、デスクランブラ102におけるデスクランブルのための鍵情報を解くため鍵情報が記録されていた場合、当該鍵情報をICカード135から読み出し、これをバス122を介してデスクランブラ102に対して出力する。
【0043】
トランスポートデコーダ103は、デスクランブラ102からのTSデータを処理することで、当該TSデータから不要なデータを取り去った「パーシャルTS」と呼ばれる形式のデータを生成し、当該パーシャルTSデータ(映像コンテンツ及びコンテンツ属性データを含むデータ)をバス122を介してハードディスク119に蓄積する。
【0044】
また、トランスポートデコーダ103は、既にハードディスク119に蓄積されたパーシャルTSデータを読み込み、当該パーシャルTSデータに含まれるパケットデータを抽出すると共に、パケット毎に、映像、音声、及びコンテンツ属性データ(以下、「放送データ」とも言う)に振り分けて出力する。
【0045】
ビデオデコーダ106は、トランスポートデコーダ103で得られた、符号化された状態の映像データを復号化し、当該復号化後の映像データをグラフィックバッファ121内の動画プレーン107に対して出力する。
【0046】
オーディオデコーダ104は、トランスポートデコーダ103で得られた、符号化された状態の音声データを復号化し、当該復号化後の音声データをディジタル/アナログコンバータ(DAC)105に対して出力する。
DAC105は、オーディオデコーダ104からの音声データをアナログ化してスピーカ133から出力する。
【0047】
CPU118は、所定の処理プログラムを読み出して実行する等して、ディジタルテレビ受信装置100全体の動作制御を司るものである。
【0048】
例えば、CPU118は、ハードディスク119或いはメモリ112に格納されたアプリケーションプログラムを読み出して実行することで、各種のデータ処理を実施すると共に、グラフィック生成部110に対してデータ転送を行うことで、グラフィック表示制御を実施する。
【0049】
グラフィック生成部110は、CPU118から供給されたデータに基づいて、文字や図形の画像データを生成し、当該画像データを、グラフィックバッファ121の文字図形プレーン109又は静止画プレーン108を転送する。
【0050】
画面合成部111は、グラフィックバッファ121内の動画(映像)プレーン107、文字図形プレーン109、及び静止画プレーン108に格納されたデータの合成処理或いは切換処理を実行し、当該処理後データを表示器134に対して出力する。
表示器134は、画面合成部111からのデータを画面表示する。
【0051】
バス122には、上述したデスクランブラ102、メモリ112、トランスポートデコーダ103、ビデオデコーダ106、グラフィック生成部110、グラフィックバッファ121、画面合成部111、ハードディスク119、ICカード制御部117、及びCPU118と共に、IEEE1394インターフェース114、モデム113、表示器134と通信可能なシリアルインターフェース120、リモートコントローラ(リモコン)132の受光部116、及びユーザからの各種動作指示を受け付ける操作部115が接続されている。
バス122に接続された各構成部は、バス122を介して互いに通信可能である。
【0052】
IEEE1394インターフェース114は、ディジタルテレビ受信装置100の本体に外部接続されたVTR(ビデオテープレコーダ)130やプリンタ131とプロトコル通信を行うためのインターフェースである。
【0053】
モデム113は、電話回線経由でインターネット等のネットワーク(不図示)に接続するためのインターフェースであり、例えば、当該ネットワーク上の放送事業者側のデータサーバ150と情報通信を行うために用いられる。
【0054】
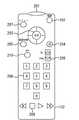
図2は、リモコン132の構成の一例を示したものである。
尚、リモコン132の構成としては、上記図2に示される構成に限られるものではない。上記図2は、本実施の形態の説明の簡単のために、必要な機能を実現するための操作を行うボタンのみを示しており、実際のテレビジョン放送の受信及びその処理に必要なボタンはこの限りでない。
【0055】
上記図2において、201は、リモコン132と、上記図1に示したディジタルテレビ受信装置100の受光部115との赤外線通信を行うための発光部である。
202は、ディジタルテレビ受信装置100の電源をON/OFFするための電源キーである。
203は、スティック状のカーソルキーであり、これを上下(前後)左右に傾けることで4方向のカーソル移動入力となり、スティック自体を押し込むことで「決定」入力となるように構成されている。
【0056】
204は、ディジタル放送波から得られるデータ放送の表示を行うための「d」キー(dボタン)である。
205は、表示器134での表示画面の切り替えを行う画面切替キーである。206は、マトリクス状に配置された数字キーであり、207は、表示器134でメニュー画面を表示するためメニューボタンである。
【0057】
208は、UP及びDownの2つのキーからなるUP/Downキーである。
209は、ハードディスク119に保存されたコンテンツを再生し、さらに再生中での早戻し、停止、再生、及び早送りをするためのボタン群である。
210は、表示器134でアプリケーション選択リストを表示するためのアプリケーションキーである。
【0058】
<ディジタルテレビ受信装置100のソフトウェア構成>
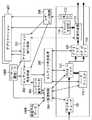
図3は、ディジタルテレビ受信装置100において、CPU118で実行されるソフトウェアによる機能構成を示したものである。
【0059】
CPU118により実施される機能は、上記図5に示すように、アプリケーション実行制御部301、コンテンツ再生制御部302、コンテンツ属性データ303、蓄積制御部304、コンテンツ再生処理部305、ユーザイベント制御部306、アプリケーション(プログラム)307、ユーザ情報308、及びシステムクロック309を含んでいる。
【0060】
上記の構成部301〜309はそれぞれ、まとまった機能を有するソフトウェアモジュールで実施されるものであり、まず、コンテンツ再生処理部(コンテンツ再生処理モジュール)305は、ハードディスク119、トランスポートデコーダ103、ビデオデコーダ106、オーディオデコーダ104、及び画面合成部111等のハードウェアで構成される各構成部を制御しながら、ハードディスク119に蓄積されたパーシャルTSストリームのデコード処理や、映像表示及び音声再生処理を実施する。
【0061】
アプリケーション実行制御部(アプリケーション実行制御モジュール)301は、ハードディスク119に蓄積されたアプリケーションプログラムを読み出してメモリ112へロードし、また、プログラムの初期化等の実行制御を実施する。
【0062】
コンテンツ属性データ(コンテンツ属性データモジュール)302は、ハードディスク119に蓄積された各パーシャルTSデータに含まれる、映像コンテンツのコンテンツ属性データをまとめたデータモジュールである。
ユーザ情報(ユーザ情報モジュール)308は、ユーザが予め設定したユーザ本人に関する情報モジュールである。
【0063】
ユーザイベント制御部(ユーザイベント制御モジュール)306は、リモコン132からのユーザ入力を受信し、当該受信情報に基づいて、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302及びアプリケーション実行制御モジュール301に対してイベントを送信する。
【0064】
ここでのアプリケーション307は、ハードディスク119に蓄積されたものであり、実行状態であるものとする。
【0065】
コンテンツ再生制御部(コンテンツ再生制御モジュール)302は、ハードディスク119に蓄積された映像コンテンツ(パーシャルTSデータ)を構成するデータの中で、何れのデータを再生するかを選択するための処理や、コンテンツ再生処理部(コンテンツ再生処理モジュール)305に対する再生開始及び停止等の制御処理等を実施する。
【0066】
蓄積制御部(蓄積制御モジュール)304は、ディジタルチューナ101からのデータ(テレビ放送コンテンツ)を、トランスポートデコーダ103を介してハードディスク119に蓄積する際の蓄積制御を実施する。
【0067】
<ディジタルテレビ受信装置100の具体的な動作>
ここでは、上記図3に示したソフトウェア構成により実施される、ディジタルテレビ受信装置100の主な動作について説明する。
【0068】
(蓄積制御モジュール304の動作)
本実施の形態では、放送局から予め決められた日時に、映像コンテンツの配信が行われる。
したがって、蓄積制御モジュール304は、決められた日時になると、ディジタルチューナ101を制御することで、予め定められたコンテンツ配信が行われるチャンネルを選局し、その受信を開始する。そして、蓄積制御モジュール304は、トランスポートデコーダ103を制御することで、受信コンテンツのTSデータからパーシャルTSデータへの変換を行い、これをハードディスク119に蓄積する。
【0069】
ここで、放送局から配信されるディジタル放送には、上述したように、映像コンテンツ(以下、単に「コンテンツ」とも言う)と共に、当該映像コンテンツのコンテンツ属性データが含まれている。
コンテンツ属性データは、サービスインフォメーション(SI)情報として、コンテンツの名前(番組名)、再生時間、及び当該コンテンツに関わるその他の属性情報を含んでいる。
【0070】
したがって、蓄積制御モジュール304は、ハードディスク119への上記コンテンツ(パーシャルTSデータ)の蓄積を行う際に、当該コンテンツのコンテンツ属性データをコンテンツ属性データモジュール303に格納する。
【0071】
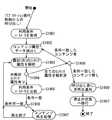
図4は、蓄積制御モジュール304によりコンテンツ属性データモジュール303に格納されたコンテンツ属性データの状態を示したものである。
上記図4では、一例として、4つのコンテンツについてのコンテンツ属性データが、コンテンツ属性データモジュール303に格納されたものとしている。
【0072】
上記図4に示すように、4つのコンテンツにはそれぞれ、識別番号(ID)が付加されている。
また、ここでのコンテンツ属性データは、例えば、XML(extensible Markup Language)に基づいて記述されたテキスト形式を用いたデータでおり、そのデータの内容となる各要素は、開始タグ<xxx>と終了タグ</xxx>に囲まれた領域に記述され、さらに、各要素の内部には、他の要素を含むことができるるようになされている。
【0073】
上記図4に示す(a)は、1つ目のコンテンツ属性データを表すコンテンツ属性要素(id=1)であり、その要素の中には、ファイル、タイムオフセット、コンテンツ名、タイム、有効期限、及び優先再生条件等の要素が含まれている。さらに、優先再生条件要素の中には、再生曜日、再生時間帯、ユーザー層、及びユーザ性別等の要素が含まれている。
以降の2つ目〜4つ目のコンテンツ属性要素についても、1つ目のコンテンツ属性要素と同様の構成で内部要素を含んでいる。
【0074】
上記図4に示したコンテンツ属性要素の内容は、蓄積制御モジュール304が、放送局から放送波と共にサービスインフォメーション(SI)情報として送られてきた情報をXMLに基づいて変換及び記述した内容である。
【0075】
但し、唯一ファイル要素は、蓄積制御モジュール304が、コンテンツの蓄積処理を行う際に新規に追加した情報である。このファイル要素は、蓄積制御モジュール304がハードディスク119に対してコンテンツの蓄積処理を行う際に付加したファイル名であり、後にコンテンツ再生処理モジュール305がハードディスク119から当該コンテンツを読み出して再生処理する際に使用される。
【0076】
タイムオフセット要素は、1本のパーシャルTSデータに複数のコンテンツが含まれている場合に、個々のコンテンツを特定するために使用される要素である。具体的には、タイムオフセット要素とは、あるパーシャルTSデータの開始から、何分再生後に目的とするコンテンツがセットされているかを示すデータである。
タイム要素は、1本のパーシャルTSデータに複数のコンテンツが含まれている場合に、個々のコンテンツを再生するため必要な時間を示したデータである。
【0077】
優先再生条件要素は、再生時間帯要素及びユーザ層要素を含んだ要素である。再生時間帯要素は、再生時間の初めと終わりを24時間単位での数字で表し[−]で結んだ表現がなされているデータである。ユーザ層要素についても同様に、ユーザ年齢層の幅の初めと終わりを[−]で結んだ記述となっている。
【0078】
尚、上記図4では、4つのコンテンツ全てが、1つの「0001」というIDのファイルとして記述されているが、それぞれが異なるIDのファイルとして記述されるものとしてもよい。
【0079】
(アプリ実行制御モジュール301の動作)
アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、予めハードディスク119に蓄積されたアプリケーションプログラムの起動処理、終了処理、及びアプリケーションプログラムが有する4つの状態(Loaded、Paused、Active、Destroyed)の遷移を司る状態変更処理等を実施する。
【0080】
本実施の形態におけるアプリケーションプログラムは、例えば、Java(R)言語で記述されたソースコードを予めコンパイル処理された所謂Java(R)バイトコード(以下、「Java(R)クラスファイル」とも言う)と共に、アプリケーションプログラムが実行中に使用する画像データ、音声データ、及びその他のデータを含む構成としている。
【0081】
図5は、アプリ実行制御モジュール301の動作を示したものである。
尚、上記図5において、「●」(黒い丸)は処理開始を意味し、二重丸は処理終了を意味し、ひし形は判断と分岐を意味している。
【0082】
ユーザが、リモコン132のアプリケーションキー210を押下することで、アプリケーション起動を要求すると、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、先ず、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302に対して、コンテンツの再生要求を発行する(ステップS501)。
【0083】
コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、上記図4に示したようなコンテンツ属性データ303を取得し、コンテンツ属性データ303により、再生コンテンツが存在しているか否かを確認する。
そして、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、上記の確認の結果、再生すべきコンテンツが存在しない場合、その旨をアプリケーション実行制御モジュール301に対して通知する。
【0084】
アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302からの通知を受けると、その通知により、再生すべきコンテンツが存在しない場合、即座にアプリケーションの起動処理を中断及び終了する(ステップS502)。
【0085】
一方、再生すべきコンテンツが存在した場合、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、アプリケーションの初期化処理を開始する(ステップS503)。
すなわち、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、アプリケーションの起動時処理として、バイトコードの読出し及びメモリ112へのロード処理(ステップS503a)、アプリケーションをポーズ状態にするための関数呼出処理(ステップS503b)、及びアプリケーションを実行状態(アクティブ)にするための関数呼出処理(ステップS503c)を実行する。
【0086】
図6は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301によるアプリケーション起動処理後の、表示器134での表示画面610の一例を示したものである。
上記図6に示すように、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301が合成制御部111を制御することで、表示画面610は2つの領域611及び612に分けられ、表示領域612にはアプリケーションが表示され、表示領域611には再生コンテンツが表示される。
【0087】
図7は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301において、アプリケーション実行中の動作を示したものである。
【0088】
アプリケーション実行後のアプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、CPU118が有するタイマ機能により周期的に発生するイベント、或いはユーザのリモコン132の操作により発生するユーザイベントにより動作開始されるイベントドリブンの処理を実行する。
【0089】
先ず、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302に対して、コンテンツ再生中であるか否かを確認する呼び出しを行い(ステップS701)、この結果、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302がコンテンツ再生中である場合(ステップS702)には即に本処理終了する。
【0090】
一方、上記の確認の結果、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302がコンテンツ再生中でない場合、或いはユーザがリモコン132の操作で停止指示したことによりコンテンツ再生が停止された場合(ステップS702)、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、アプリケーションの実行中画面(上記図6参照、画面610の表示領域612)に対して警告表示を行う(ステップS703)。
図8は、ステップS703の処理実行により表示される警告表示620の表示例を示したものである。
【0091】
アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、警告表示620中にユーザがリモコン132のアプリケーション(APP)ボタン210を押下したと認識した場合(ステップS704)、アプリケーションの実行を中断するための終了処理を実行する(ステップS707)。
【0092】
また、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、警告表示620中に、ユーザがリモコン132の操作で再生指示したことにより、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302に対する問い合わせ結果がコンテンツ再生中である場合(ステップS705、ステップS706)、アプリケーションの実行を継続するために何も処理は実行せずに本処理終了する。
【0093】
図9は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301と、他のソフトウェアモジュール或いはハードウェアによる構成部の動作の関係を示したものである。
尚、上記図9では、下方向に出ている線は時間の経過(time)を示しており、下に行くほどに後の方に処理が実行されることを示している。
【0094】
例えば、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301からの問い合わせに対して(ステップS901)、「再生中」と応答する(ステップS902)。
また、ユーザのリモコン132の操作により、コンテンツ再生が停止された場合(ステップS903、捨てプS904)、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301からの問い合わせに対して(ステップS905)、「非再生中」と応答する(ステップS906)。
【0095】
アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302からの応答を受け、警告表示を行う(ステップS907)。
【0096】
さらに、ユーザがリモコン132の操作により、コンテンツ再生が開始された場合(ステップS908、捨てプS909)、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301からの問い合わせに対して(ステップS910)、「再生中」と応答する(ステップS911)。
【0097】
アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302からの応答を受け、警告表示を解除(消去)する(ステップS912)。
【0098】
(コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302の動作)
図10〜図12は、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302の動作を示したものである。
コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、上述したようにアプリケーション実行制御モジュール301からのコンテンツ再生要求を受けて、該当する処理を開始する。
【0099】
図10に示すように、先ず、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、上記図4に示したようなコンテンツ属性データ303を取得し、コンテンツ属性データ303により、再生コンテンツが存在するか否かを確認する(ステップS1001)。
【0100】
ステップS1001の確認の結果、再生コンテンツが存在しない場合、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、コンテンツ再生を停止中状態とすると同時に(ステップS1004)、上述したように、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301に対して再生コンテンツが存在しない旨を通知する(ステップS1005)。
【0101】
ステップS1001の確認の結果、再生コンテンツが存在する場合、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、優先コンテンツの検索処理を実行する(ステップS1002)。
【0102】
具体的には、図11に示すように、 コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、優先コンテンツ検索処理を実行するにあたり、先ず、現在の曜日、時間情報、及び後述するユーザ情報を取得し(ステップS1002a)、さらにコンテンツ属性データ303の内容を読み出して、存在するコンテンツ属性データの全てについて、ステップS1002bからの処理を実行する。
【0103】
すなわち、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、先ず処理対象のコンテンツ属性データの内容を読み出し(ステップS1002b)、当該コンテンツ属性データの内容に含まれる優先再生条件の内容と、現在の曜日、時間情報、及びユーザ情報とを比較し(ステップS1002d)、この比較の結果、全てが一致(該当)した場合(ステップS1002e)、コンテンツの再生処理を実行する(ステップS1010)。
【0104】
ステップS1002dについて具体的に説明すると、例えば、コンテンツ属性データが、上記図4に示したようなデータである場合、その先頭に記述されたコンテンツ属性id=1のコンテンツ属性データでは、優先再生条件が再生曜日として「月火水木金」と記述されている。この場合、現在の曜日が、これに該当することが必要となる。また、再生時間帯として「10−15」と記述されているので、現在の時間帯が10時から15時の間であることが必要である。さらに、ユーザ層として「20−70」と記述されているので、登録されたユーザの年齢層情報が20歳から70歳の間である必要がある。
【0105】
上述のような優先再生条件に含まれる全ての要素が、現在の曜日、時刻、及びテレビジョン放送受信装置100で設定された情報と一致した場合に、コンテンツの再生処理が実行されることになる。
また、例えば、上記図4に示した、コンテンツ属性id=1のコンテンツ属性データの場合、ハードディスク119に対して、ファイルID=0001として蓄積されたデータの先頭から60秒後の部分から120秒間のコンテンツ再生が実行されることになる。
【0106】
上述のように、ステップS1002の優先コンテンツ検索処理では、コンテンツ属性データ303の内容に従って再生コンテンツが決定され、その後直ちに、当該コンテンツの再生が実行される。
そして、全てのコンテンツ属性データについて処理終了後(ステップS1002c)、通常コンテンツ検索処理の実行に移る(ステップS1003)。
【0107】
通常コンテンツ検索処理(ステップS1003)においては、例えば、図12に示すように、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、上記図4に示したようなコンテンツ属性データ303を取得し、再生コンテンツの決定処理を実行するが、ここでは、特に優先再生条件との比較は行わず、単純にコンテンツ属性データ303に登録されているコンテンツを最初から最後まで順番に選択し、再生処理を実行する(ステップS1003a、ステップS1003b、ステップS1010)。
【0108】
そして、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、全てのコンテンツのコンテンツ属性データを読み出し、そしてコンテンツの再生を実行し終えると、再び優先コンテンツ検索処理を実行する(ステップS1002)。
【0109】
上述のように本実施の形態においては、優先コンテンツ検索処理(ステップS1002)と通常コンテンツ検索処理(ステップS1003)を交互に繰り替えて実行するように構成したので、優先再生の対象となるコンテンツは、他の通常コンテンツに対して、2倍の優先度で再生されることになる。また、優先再生の対象となるコンテンツは、ユーザがアプリケーションを利用する曜日や時間と共に変化していくことになる。
【0110】
ここで、本実施の形態における「ユーザ情報」とは、ユーザがテレビジョン放送受信装置100を購入した後等に、予め設定される情報である。
図13は、ユーザ情報の設定画面1300の一例を示したものである。
【0111】
例えば、ユーザは、表示器134で表示された設定画面1300が表示されると、リモコン132を操作することで、設定画面1300上のカーソルキー(不図示)を移動させ、変更すべき表示領域を選択し、リモコン132の数字キー206を操作することで、年齢層の値を設定或いは変更する。また、ユーザは、リモコン132の操作により、男女構成についても設定する。
【0112】
設定画面1300による設定情報は、上記図3に示したユーザ情報モジュール308により保持され、上記図10及び図11に示した優先コンテンツ検索処理において処理パラメータとして使用される。
【0113】
以上詳記してきたような本実施の形態によれば、ハードディスク119に予め蓄積されたコンテンツ群を再生中であるか否かに応じて、アプリケーションプログラムの実行制御を行うことが可能となる。すなわち、予め蓄積されたコンテンツが再生されていることを条件に、ユーザにアプリケーションの利用を許可することが可能となる。
【0114】
また、上記図10〜図12に示したようなコンテンツ再生制御を実施することで、ユーザがアプリケーションプログラムを利用した曜日や時間等に応じて、コンテンツ再生内容の優先度を変化させたり、ユーザが予め登録したユーザに関する情報に応じて、コンテンツ再生内容の優先度を変化させることができるようになる。
【0115】
尚、本実施の形態では、上記図10〜図12に示したコンテンツ再生制御において、優先コンテンツ検索処理(ステップS1002)と通常コンテンツ検索処理(ステップS1003)を交互に、比率1:1等で実施するように構成したが本発明の主旨からすればこれに限ることなく、例えば、優先コンテンツ検索処理と通常コンテンツ検索処理の比率を2:1として実施する、或いは比率3:1として実施するようにしてもよい。
【0116】
また、本実施の形態では、設定可能なユーザ情報を、ユーザの年齢層の範囲及び男女構成の情報としたが、勿論これ以外の情報を含むようにしてもよい。例えば、ユーザが好む音楽ジャンルや、ユーザが所望する製品のジャンル等の情報を、ユーザ情報に含ませるようにしてもよい。
【0117】
また、本実施の形態では、コンテンツ属性データの記述を、XMLに基づく記述としたが、本発明の主旨からすれば勿論これに限ることはなく、例えば、他の方式に基づいてテキスト記述する、或いはバイナリデータブロックとして記述するようにしてもよい。
【0118】
また、本実施の形態では、放送局からコンテンツが予め決められた時刻に配信されるものとしたが、これに限ることなく、例えば、ユーザが手動で、ディジタル放送受信装置100に対するコンテンツの入力動作を行うようにしてもよい。
【0119】
また、本実施の形態では、上記図4に示したように、蓄積コンテンツのファイルIDを全てID=0001としたが、これに限ることなく、ファイルIDを変えて個別のファイルで扱うようにしてもよい。
【0120】
[第2の実施の形態]
本実施の形態では、上記図1に示したテレビジョン放送受信装置100の構成及び動作を、以下に説明するような構成及び動作とする。
尚、ここでは、第1の実施の形態と異なる構成及び動作についてのみ具体的に説明するものとする。
【0121】
まず、本実施の形態では、ディジタル放送の放送局(不図示)において、テレビ番組の映像データ、音声データ、及び「放送データ」が符号化され、当該符号化後の各データが多重化された後に変調され、当該変調後のデータが放送波として、放送局のアンテナ(不図示)から送出される。放送局のアンテナから送出された放送波は、不図示の放送衛星(BS)を介して、ディジタルテレビ受信装置100(ユーザ側端末装置)で受信される。
【0122】
上記の「放送データ」とは、放送チャンネルや放送番組の内容を示した「サービスインフォメーションデータ」(SIデータ)、マークアップ言語で記述されたテキストデータ、画像データ、及び音声データを含む「データ放送コンテンツデータ」、そしてアプリケーションプログラムコード及びその関連データファイルを含む「アプリケーションデータ」等を含んだデータである。
【0123】
<ディジタルテレビ受信装置100のソフトウェア構成>
図14は、本実施の形態のディジタルテレビ受信装置100において、CPU118で実行されるソフトウェアによる機能構成を示したものである。
尚、上記図14に示すソフトウェア構成において、上記図3に示したソフトウェア構成と同様に機能する個所には同じ符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。
【0124】
本実施の形態におけるソフトウェア構成は、録画予約データ1409、アプリケーション属性データ1408、及びアプリケーション1407を含む構成としている。
【0125】
コンテンツ再生処理モジュール305は、ハードディスク119、トランスポートデコーダ103、ビデオデコーダ106、オーディオデコーダ104、及び画面合成部111等のハードウェア構成部を制御することで、ハードディスク119に蓄積されたパーシャルTSストリームのデコード処理や、映像表示及び音声再生処理を実施する。
【0126】
アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、ハードディスク119に蓄積されたアプリケーションプログラムを読み出してメモリ112へロードし、また、プログラムの初期化等の実行制御を実施する。
【0127】
コンテンツ属性データモジュール303は、ハードディスク119に蓄積された各パーシャルTSデータに含まれるコンテンツのコンテンツ属性データをまとめたデータモジュールである。
【0128】
ユーザイベント制御モジュール306は、リモコン132からのユーザ入力を受信し、当該受信情報に基づいて、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302及びアプリケーション実行制御モジュール301に対してイベントを送信する。
【0129】
アプリケーション1407は、放送局から放送波により配信されたアプリケーションであり、デジタルチューナ101で受信された後、トランスポートデコーダ103でデコード処理され、ハードディスク119に蓄積される。
ここでのアプリケーション1407は、ハードディスク119に蓄積された後、メモリ112にロードされ、実行されている状態でるものとする。
【0130】
コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、ハードディスク119に蓄積されたコンテンツ(パーシャルTSデータ)のうち、何れを再生するかを選択するための処理や、コンテンツ再生処理モジュール305に対する再生開始及び停止等の制御処理等を実施する。
【0131】
蓄積制御モジュール304は、ディジタルチューナ101からの入力コンテンツ(TSデータ)を、トランスポートデコーダ103を介してハードディスク119に蓄積する際の蓄積制御を実施する。
【0132】
アプリケーション属性データ1408は、アプリケーションの属性データを格納しているデータモジュールである。
録画予約データ1409は、蓄積制御モジュール304が自動蓄積動作を行う際に、録画すべき番組の時間及びチャンネル等を格納するためのデータモジュールである。
【0133】
<ディジタルテレビ受信装置100の具体的な動作>
ここでは、上記図14に示したソフトウェア構成により実施される、ディジタルテレビ受信装置100の主な動作について説明する。
【0134】
(蓄積制御モジュール304の動作)
本実施の形態においては、第1の実施の形態と同様に、放送局から予め決められた日時にコンテンツの配信が行われる。
したがって、蓄積制御モジュール304は決められた日時になると、ディジタルチューナ101に対して、予め定められたコンテンツ配信が行われるチャンネルを選局させ、その受信を開始させる。そして、蓄積制御モジュール304は、トランスポートデコーダ103を制御することで、TSデータからパーシャルTSデータへの変換を行い、当該パーシャルTSデータをハードディスク119に蓄積する。
【0135】
ここで、放送局から配信されるディジタル放送には、第1の実施の形態と同様に、コンテンツと共に、当該コンテンツのコンテンツ属性データが含まれている。
コンテンツ属性データは、サービスインフォメーション(SI)情報として、コンテンツの名前(番組名)、再生時間、及び当該コンテンツに関わるその他の属性情報を含んでいる。
【0136】
したがって、蓄積制御モジュール304は、ハードディスク119への上記コンテンツ(パーシャルTSデータ)の蓄積を行う際に、当該コンテンツのコンテンツ属性データをコンテンツ属性データモジュール303に格納する。
【0137】
図15は、蓄積制御モジュール304によりコンテンツ属性データモジュール303に格納されたコンテンツ属性データの状態を示したものである。
上記図15では、一例として、6つのコンテンツについてのコンテンツ属性データが、コンテンツ属性データモジュール303に格納されたものとしている。
【0138】
上記図15に示すように、6つのコンテンツにはそれぞれ、識別番号(ID)が付加されている。
また、ここでのコンテンツ属性データは、第1の実施の形態と同様に、XML(eXtensible Markup Language)に基づいて記述されたテキスト形式を用いたデータである。
また、本実施の形態では、対象とするコンテンツを、例えば、製品の広告のコンテンツとしている。
【0139】
上記図15に示す(a)は、1つ目のコンテンツ属性データを表すコンテンツ属性要素(id=1)であり、その要素の中には、ファイル、タイムオフセット、コンテンツ名、提供社名、セクション、カテゴリ、タイム、及び有効期限等の要素が含まれている。
以降の2つ目〜6つ目のコンテンツ属性要素についても、1つ目のコンテンツ属性要素と同様の構成で内部要素を含んでいる。
【0140】
上記図15に示したコンテンツ属性要素の内容は、蓄積制御モジュール304が、放送局から放送波と共にサービスインフォメーション(SI)情報として送られてきた情報をXMLに基づいて変換及び記述した内容である。
【0141】
但し、ファイル要素については、蓄積制御モジュール304が、コンテンツの蓄積処理を行う際に新規に追加した情報である。このファイル要素は、蓄積制御モジュール304がハードディスク119に対してコンテンツの蓄積処理を行う際に付加したファイル名であり、後にコンテンツ再生処理モジュール305がハードディスク119から当該コンテンツを読み出して再生処理する際に使用される。
【0142】
タイムオフセット要素は、1本のパーシャルTSデータに複数のコンテンツが含まれている場合に、個々のコンテンツを特定するために使用される要素である。具体的には、タイムオフセット要素とは、あるパーシャルTSデータの開始から、何分再生後に目的とするコンテンツがセットされているかを示すデータである。
タイム要素は、1本のパーシャルTSデータに複数のコンテンツが含まれている場合に、個々のコンテンツを再生するため必要な時間を示したデータである。
【0143】
提供社名要素及びセクション要素は、当該コンテンツを作成及び提供している側(企業)の名前、及び当該企業の中における担当セクションを表す要素である。
例えば、上記図15のid=1で示すコンテンツ属性要素では、「マイケルソフト」という会社名の「オフィスソフト事業部」というセクションにより、当該コンテンツが作成及び提供されていることになる。
【0144】
尚、上記図15に示したコンテンツ属性要素において、セクション要素及びカテゴリ要素に関しては、オプション扱い可能であり、必ずしもこれらの要素を持つ必要はない。
【0145】
(アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301の動作)
まず、図16は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301で扱うアプリケーション属性データ1408の内容の一例を示したものである。
【0146】
アプリケーション属性データ1408は、ハードディスク119に既に蓄積されている幾つかのアプリケーションについての属性情報がXML形式で記述されたデータである。
【0147】
アプリケーションの属性情報は、アプリケーション名及び利用条件コンテンツの2つの要素と、利用条件コンテンツとの要素の中にコンテンツ要素が含まれ、さらにその要素中に、社名、名前、セクション、及びカテゴリの要素が含まれた構成としている。
【0148】
尚、アプリケーションの属性情報において、コンテンツ要素に含まれる要素としては、社名、名前、セクション、及びカテゴリの要素を全てを用いる必要はなく、例えば、これらの要素の中の1つの要素を用いるようにしてもよい。
【0149】
図17は、アプリ実行制御モジュール301の動作を示したものである。
上記図17において、「●」(黒い丸)は処理開始を意味し、二重丸は処理終了を意味し、ひし形は判断と分岐を意味している。
【0150】
尚、本実施の形態におけるアプリケーションプログラムは、第1の実施の形態と同様に、例えば、Java(R)言語で記述されたソースコードを予めコンパイル処理された所謂Java(R)バイトコード(Java(R)クラスファイル)と共に、アプリケーションプログラムが実行中に使用する画像データ、音声データ、及びその他のデータを含む構成としている。
【0151】
ユーザが、リモコン132のアプリケーションキー210を押下することで、アプリケーション起動を要求すると、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、先ず、アプリケーション属性データ1408を取得する(ステップS1701)。
【0152】
次に、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、ステップS1701で取得したアプリケーション属性データ1408、すなわち今起動しようとしているアプリケーションの属性に含まれる利用条件要素を読み出し、当該利用条件要素をパラメータとして、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302に対してコンテンツ再生の要求を発行する(ステップS1702)。
【0153】
具体的には例えば、アプリケーション属性データ1408が、上記図16に示したようなデータである場合で、起動対象のアプリケーションが、同図中(A)で示す「マイケルソフトワード for TV」である場合、利用条件要素は、
(1)タイプ=企業広告、社名=マイケルソフト、セクション=オフィスソフト事業部
(2)タイプ=企業広告、社名=マイケルソフト、名前=マイケルソフトオフィス2000
(3)タイプ=非営利団体広告、社名=世界平和連盟事務局、名前=地雷撲滅キャンペーン
の3つの要素となる。これらの要素が条件パラメータとして、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302に対してコンテンツ再生の要求が発行される。
【0154】
コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、詳細は後述するが、上述したようなコンテンツ属性データ303を読み出し、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301から指定された条件パラメータと一致する再生コンテンツが存在しているか否かをチェックするための検索処理を実行する。
【0155】
例えば、上記のマイケルソフトの例では、上記図12の(a)及び(c)で示したコンテンツ要素id=1及びid=3で示される2つのコンテンツが、当該条件パラメータと一致することになる。
【0156】
アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302での検索処理の結果により、条件に一致するコンテンツが存在しない場合、グラフィック生成部110を制御することで、例えば、図18に示すような、利用条件となるコンテンツをテレビジョン放送受信装置100が保持していないことをユーザに告げるための表示を行い(ステップS1704)、本処理(アプリケーションの起動処理)を中断及び終了する。
【0157】
一方、条件と一致するコンテンツが存在した場合、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、アプリケーションの起動時処理として、バイトコードの読出処理及びメモリへのロード処理(ステップS1705a)、アプリケーション内部をポーズ状態にするための関数呼出処理(ステップS1705b)、及びアプリケーションを実行(アクティブ)状態にするための関数呼出処理(ステップS1705c)を順次実行する(ステップS1705)。
【0158】
尚、本実施の形態においても第1の実施の形態と同様に、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、画面合成部111を制御することで、上記図6に示したように、画面を2つの領域611,612に分け、領域612をアプリケーション表示画面とし、領域611をコンテンツ再生画面とする。
【0159】
また、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301の、アプリケーションの実行中の動作に関しては、第1の実施の形態と同様に、上記図7に示したような動作を行う。さらに、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、定期的にコンテンツが再生中であるか否かを確認し、ユーザのリモコン132の操作等によりコンテンツ再生が止められた状態を確認すると、上記図8に示したような警告表示を行う。
【0160】
(コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302の動作)
図19は、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302の動作を示したものである。
【0161】
先ず、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301からコンテンツ再生要求を受けると、このときパラメータとして与えられた利用条件パラメータを取得する(ステップS1901)。
【0162】
次に、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、コンテンツ属性データ1408を読み出し(ステップS1902)、そのコンテンツ属性データ1408に含まれるコンテンツ属性要素を順次に解析する(ステップS1903)。
【0163】
すなわち、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、未解析のコンテンツ属性要素について(ステップS1904)、利用条件パラメータとの比較を行い(ステップS1905)、この一致が認められると(ステップS1906)、当該コンテンツの再生を実行する(ステップS1907)。
一方、条件が一致しない場合、又はコンテンツの再生が終了した場合、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、次のコンテンツ属性について利用条件パラメータとの比較処理を実行する。
【0164】
本実施の形態における上記比較処理では、アプリケーション属性データ1408で示される各コンテンツ要素に含まれる条件が全て一致する必要がある。例えば、上記図16のid=2で示される「スモールメールfor TV」のアプリケーションの場合、
(1)タイプ=企業広告、社名=21世紀商社株式会社、セクション=輸入車事業部
(2)タイプ=企業広告、社名=毎日ビール、名前=2000年お歳暮キャンペーン
(3)タイプ=企業広告、社名=毎日ビール、名前=スーパースムースビール
(4)タイプ=企業広告、社名=日本橋百貨店
(5)タイプ=企業広告、社名=渋谷テレビ放送、カテゴリ=番組
という5つの条件を有し、これらの条件のそれぞれと一致するコンテンツが検索されることになる。
【0165】
また、上記図15に示したコンテンツ属性データであれば、上記(1)の条件では同図(b)と示した内容が条件一致となり、上記(3)の条件では同図(d)と示した内容が条件一致となる。
したがって、この場合に再生されるコンテンツは、上記図15(b)及び(d)に示した2つのコンテンツということになる。
【0166】
尚、上記比較処理においては、アプリケーション属性データ1408のコンテンツ要素に対して、指定された条件のみ一致すればよく、コンテンツ属性データ1408側に他のパラメータが存在したとしても、上記比較処理では無視される。
【0167】
そして、コンテンツ属性データ303に含まれる全てのコンテンツ属性を解析し終えると(ステップS1908)、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、条件と一致するコンテンツが一つもなかった場合、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301に対して、非再生状態通知する(ステップ1909)。
また、条件一致するコンテンツが存在した場合、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、再びコンテンツ属性データ303の先頭からの処理を開始し、条件が一致するコンテンツの再生を行う。これにより、上述した「スモールメール for TV」の場合、上記図15(b)及び(d)に示したコンテンツが交互に再生されていくことになる。
【0168】
以上説明したようなアプリケーション実行制御の動作、及びコンテンツ再生制御の動作により、本実施の形態のテレビジョン放送受信装置100では、ユーザが起動するアプリケーションに対して指定された属性情報に応じて、再生コンテンツを変更することが可能となる。
【0169】
また、本実施の形態のアプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、さらにアプリケーション動作中に、アプリケーションからの状態変更通知を受け、当該通知に基づき、コンテンツ再生条件の変更を行う。
【0170】
図20は、上記の動作について、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302と、他のソフトウェアモジュール又はハードウェア構成部との関係を示したものである。
尚、上記図20では、下方向に出ている線は時間の経過(time)を示しており、下に行くほどに後の方に処理が実行されることを示している。
【0171】
先ず、ユーザがリモコン132の操作を行うことで、アプリケーションの状態が変化すると(ステップS2001、ステップS2002)、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301に対して、新たな状態を示すデータが通知される(ステップS2003)。
【0172】
次に、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、状態変更通知を受けると、実行中のアプリケーションのアプリケーション属性データ1408を確認し(ステップS2004)、コンテンツ要素に対して、「状態指定」というタイプが指定されていた場合、アプリケーションからの状態変更通知によって伝えられた状態と一致するコンテンツ要素を検索し、当該コンテンツ要素が含む内容を新たなパラメータとして、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302に対して設定する(ステップS2005)。
【0173】
コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301からの新たなパラメータを受けると、コンテンツ属性データ303の内容を確認し、新たなパラメータと条件が一致するコンテンツを検索する(ステップS2006)。
【0174】
コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302は、上記の検索の結果、該当するコンテンツを検索できた場合、コンテンツ再生処理モジュール305に対して、当該コンテンツの再生を指示する(ステップS2007)。
【0175】
具体的には例えば、上記図16に示したようなアプリケーション属性データ1408である場合、同図(C)に示す「ビック写真管理for TV」というアプリケーションには、利用条件となるコンテンツ要素として「状態指定」という属性が設定されている。この場合、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、当該アプリケーション実行中に、同アプリケーションからの状態変更通知を受けると、当該通知(状態値「1」又は「2」)により、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302に対する条件パラメータを変化させて、コンテンツ再生要求を行う。
【0176】
すなわち、アプリケーションから、状態値「1」が通知された場合、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、
・タイプ="企業広告"、社名=BICカメラ、カテゴリ=パソコン
・タイプ="企業広告"、社名=BICカメラ、カテゴリ=AV機器
・タイプ="企業広告" 社名=BICカメラ、カテゴリ=生活家電
という3つの条件をパラメータとして、コンテンツ再生要求を発行する。一方、条件値「2」がアプリケーションから通知された場合、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、
・タイプ="企業広告"、社名=BICカメラ、カテゴリ=パソコン周辺機器
という条件をパラメータとして、コンテンツ再生要求を発行する。
【0177】
また、ステップS2004の、アプリケーション属性データ1408の確認処理において、実行中のアプリケーションのアプリケーション属性データ1408の中に「状態指定」というタイプを有するコンテンツ要素が存在しなかった場合、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、アプリケーションの実行を維持したままとする。
【0178】
また、コンテンツ再生制御モジュール302における検索処理(ステップS2006)において、条件と一致するコンテンツを検索できなかった場合、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール301は、その旨をコンテンツ再生制御モジュール302から受け(非再生通知、ステップS2007')、上記図6に示したステップS703の処理以降と同様の処理を実行し、上記図8に示したような警告表示を行う(ステップS2008)。
【0179】
上述のような動作を行うことで、本実施の形態のテレビジョン放送受信装置100は、ユーザが利用中のアプリケーションの「状態」に応じて、再生するコンテンツの内容を変化させることができるようになる。
【0180】
(蓄積制御モジュール304の動作)
まず、先の説明では、蓄積制御モジュール302が、予め決められた時間にコンテンツの蓄積を行うものとした。これに対して本実施の形態では、これに加え蓄積制御モジュール302自らが、サービスインフォメーション(SI)データを解析し、蓄積すべきコンテンツを検索し、録画予約処理及び録画処理を実行する。
図21及び図22は、本実施の形態における蓄積制御モジュール304の動作を示したものである。
【0181】
図21に示すように、先ず、蓄積制御モジュール304は、アプリケーション属性データ1408を取得し(ステップS2101)、さらに、トランスポートデコーダ103に対して、TS(トランスポートストリーム)データに多重されたサービスインフォメーション(SI)の取得を要求し、当該SI情報を取得する(ステップS2102)。
【0182】
図23は、本実施の形態におけるSI情報に含まれるテーブル情報の1つであるEIT(Event Information Table)の一例を示したものである。
EITとは、放送されるそれぞれの番組コンテンツ(イベント)に関する情報が記述されているテーブルであり、本実施の形態のEITでは、イベント情報記述領域2に対して番組コンテンツ名(イベント名)が含まれ、イベント記述領域3に対して番組(イベント)の属性データ、提供社名、セクション、及びカテゴリ等の情報が含まれている。
【0183】
蓄積制御モジュール304は、SI情報に含まれる将来放送予定の番組のEITを読み出し、この読出情報と、ステップS2101の処理で取得したアプリケーション属性データ1408との比較を行い(ステップS2103)、一致している番組が存在し、且つ当該番組が未蓄積で未予約のコンテンツである場合、すなわちコンテンツ属性データ303に対して未登録であり、且つ録画予約データ1409に対して未登録であるコンテンツの場合(ステップS2105)、当該コンテンツの放送時間、終了時間、チャンネル、及びイベントIDを、録画予約データ1409に対して登録する。(ステップS2106)。
【0184】
そして、図22に示すように、蓄積制御モジュール304は、録画予約データ1409に登録された放送時間になると、ディジタルチューナ101、トランスポートデコーダ103、及びハードディスク119を制御することで、コンテンツの蓄積実行動作を実施する(ステップS2107、ステップS2108)。
さらに、蓄積制御モジュール304は、蓄積した番組コンテンツの名前、提供社名、セクション、及びカテゴリ等の情報を、コンテンツ属性データ303に対して登録する(ステップS2109)。
【0185】
以上詳記してきたように本実施の形態によれば、予め指定されたコンテンツの再生がなされていることを条件に、アプリケーションの実行及び継続利用を許可する動作が可能となる。また、アプリケーション毎に再生するコンテンツを変化させる動作、さらにアプリケーションの状態に応じて再生するコンテンツを変化させる動作が可能となる。
また、コンテンツを予め指定された時間に蓄積するだけでなく、アプリケーション属性データ1408に登録されているアプリケーション属性で指定された条件に一致するコンテンツを、サービスインフォメーションから検索して、自動的に蓄積動作が行えるようになる。
【0186】
尚、第1及び第2の実施の形態では、ユーザがテレビジョン受信装置100に対して動作指示或いはデータ入力を行うための手段として、リモコン132を例に挙げ、さらにリモコン132の機能として、上記図2に示したような必要最小限のボタンによる機能を挙げたが、本発明の主旨からすればこれに限ることはなく、例えば、リモコン132の他に、キーボードやマウスを設けるようにしてもよい。また、リモコン132に対して、ローマ字や数字等を入力するためのボタンを設けるようにしてもよい。
【0187】
また、第1及び第2の実施の形態では、リモコン132のアプリケーションボタン210の押下で、アプリケーションが起動するように構成したが、例えば、ハードディスク119に複数のアプリケーションが既に蓄積されている場合、アプリケーションボタン210の押下のタイミングで、利用可能なアプリケーションのリスト表示を表示器134で行い、当該リスト上から所望するものをユーザに選択させ、当該選択アプリケーションの起動を行うようにしてもよい。
【0188】
また、第1及び第2の実施の形態では、アプリケーションが予めハードディスク119に蓄積されているものとしたが、本発明の主旨からすればこれに限ることはなく、例えば、データ放送により、テレビ放送波を用いてダウンロードされたアプリケーションであっても適用可能である。或いは、カードメディアやディスクメディア等の記録媒体を介して、テレビジョン放送受信装置100内に取り込まれたものであってもよい。
【0189】
また、第1及び第2の実施の形態では、コンテンツ属性データ303として、XMLに基づき記述されたテキストデータを用いたが、これに限ることなく、他の言語等で記述されたデータをも適用可能である。
【0190】
また、第1及び第2の実施の形態では、コンテンツが有するコンテンツ名、提供社名、セクション、及びカテゴリ名等の情報をそれぞれ、XMLに基づいた要素として記述するものとしたが、これに限ることなく、例えば、コンテンツを識別するURI(Uniform Resource indicator)記述として、
等のように記述するようにしてもよい。
【0191】
また、本発明の目的は、第1及び第2の実施の形態のホスト及び端末の機能を実現するソフトウェアのプログラムコードを記憶した記憶媒体を、システム或いは装置に供給し、そのシステム或いは装置のコンピュータ(又はCPUやMPU)が記憶媒体に格納されたプログラムコードを読みだして実行することによっても、達成されることは言うまでもない。
この場合、記憶媒体から読み出されたプログラムコード自体が第1及び第2の実施の形態の機能を実現することとなり、そのプログラムコードを記憶した記憶媒体及び当該プログラムコードは本発明を構成することとなる。
プログラムコードを供給するための記憶媒体としては、ROM、フレキシブルディスク、ハードディスク、光ディスク、光磁気ディスク、CD−ROM、CD−R、磁気テープ、不揮発性のメモリカード等を用いることができる。
また、コンピュータが読みだしたプログラムコードを実行することにより、第1及び第2の実施の形態の機能が実現されるだけでなく、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、コンピュータ上で稼動しているOS等が実際の処理の一部又は全部を行い、その処理によって第1及び第2の実施の形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。
さらに、記憶媒体から読み出されたプログラムコードが、コンピュータに挿入された拡張機能ボードやコンピュータに接続された機能拡張ユニットに備わるメモリに書き込まれた後、そのプログラムコードの指示に基づき、その機能拡張ボードや機能拡張ユニットに備わるCPUなどが実際の処理の一部又は全部を行い、その処理によって第1及び第2の実施の形態の機能が実現される場合も含まれることは言うまでもない。
【0192】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように本発明によれば、例えば、次のような効果(1)〜(7)が得られる。
【0193】
(1)ユーザは、放送中の番組内容とは関係なく好きな時間に、テレビジョン放送と共にアプリケーションプログラムを利用できる。
【0194】
(2)指定された蓄積済のコンテンツを再生していることを条件に、ユーザに対してアプリケーションプログラムの利用を許可することができる。これにより、再生するコンテンツを、例えば、コマーシャルや商品やサービスの紹介番組等のコンテンツとすることで、アプリケーションプログラムの提供者は、テレビジョン放送及びアプリケーションプログラムを利用しているユーザに対しても、動画や音声を用いた広告宣伝が可能なる。
【0195】
したがって、本発明によれば、例えば、あるアプリケーションソフトウェア会社がアプリケーションを開発及び提供し、自社のパーソナルコンピュータ(パソコン)用のアプリケーションのコマーシャルコンテンツを視聴することを条件に、ユーザに対して、当該アプリケーションの利用を許可するというサービス形態が実施可能となる。
【0196】
また、従来のテレビジョン番組制作と同様に、複数のスポンサーからの出資により、あるアプリケーションソフトウェア会社がアプリケーションを開発及び提供し、ユーザに対して、スポンサーのコマーシャル群を視聴することを条件に、当該アプリケーションの利用を許可するというサービス形態が実施可能となる。
【0197】
これにより、テレビジョン放送受信装置或いはシステムならではの、新たなアプリケーション利用サービスが提供可能となり、新たなアプリケーション提供サービスモデルが実現可能となる。また、ユーザにとっても、当該アプリケーションを使用する際に、無料若しくは極低料金での利用が可能となる。
【0198】
(3)例えば、従来より、表示画面の一部にバナー広告を表示することで、無料でインターネット閲覧アプリケーションの利用を許可する、という技術が提案されていたが、これに対して本発明によれば、テレビジョン放送の画面を用いた動画による広告サービスが可能となり、従来よりもはるかに、高い広告効果が得られるばかりでなく、インターネット閲覧アプリケーションに限らず、テレビジョン放送で利用できる様々なアプリケーションであっても、無料利用サービスが実現可能となる。さらに、従来のように個々のアプリケーションで利用条件の監視等を行うのではなく、利用条件(条件データ)の監視等を行うことで、個々のアプリケーションの開発が容易になる。
【0199】
(4)ユーザがアプリケーションプログラムを利用している曜日や時間等に応じて、コンテンツ再生内容の優先度を変化させたり、ユーザが予め登録したユーザに関する情報に応じて、コンテンツ再生内容の優先度を変化させることができる。
例えば、10時から12時までは主に、主婦をターゲットにした生活用品や洋服等のコマーシャルコンテンツを優先的に再生するようにしたり、また、週末には釣りや園芸用品等のコマーシャルコンテンツを優先的に再生するようにしたり、或いは女性に対してのみ女性下着等のコマーシャルコンテンツを優先的に再生するようにすることが可能となるので、効果的な宣伝が可能となる。
【0200】
(5)ユーザが利用しているアプリケーションプログラムに応じて、コンテンツ再生内容を変化させることが可能となるので、例えば、ユーザがゲームアプリケーションを実行中に新発売のゲームのコマーシャルを再生することや、また、例えば、ユーザがあるアプリケーションを利用中はそのアプリケーションを提供している企業のコマーシャルコンテンツのみを再生することが可能となる。
【0201】
(6)アプリケーションプログラムの状態に応じて、コンテンツ再生内容を変化させることが可能となるので、例えば、大型量販店が提供するアプリケーションのような場合、ユーザがプリント動作をしようとしたときに、新製品のプリンタのコマーシャルやインク等の消耗品の特価情報のコマーシャルを再生するということも可能となり、従来よりも更に効果的な宣伝が可能となる。
【0202】
(7)アプリケーションプログラムから再生すべきコンテンツを直接個別に指定するのではなく、提供会社名、セクション、及びカテゴリ等の、従来の番組コンテンツ指定には無かった方法で指定できるため、一つのアプリケーションプログラムを利用する際に、再生するコンテンツを初めから固定するのではなく、毎週入れ替えを行ったり、随時新しいコンテンツに入れ替えることも可能となる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】第1の実施の形態において、本発明を適用したテレビジョン放送受信装置の構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】上記テレビジョン放送受信装置のリモートコントローラ(リモコン)の構成を説明するための図である。
【図3】上記テレビジョン放送受信装置のソフトウェアの構成を示すブロック図である。
【図4】コンテンツ属性データを説明するための図である。
【図5】アプリケーション実行制御モジュールのアプリケーション起動時の動作を説明するための図である。
【図6】アプリケーション実行中の表示画面の一例を説明するための図である。
【図7】アプリケーション実行制御モジュールのアプリケーション実行中の動作を説明するための図である。
【図8】アプリケーション実行中の表示画面において、警告表示を説明するための図である。
【図9】アプリケーション実行中にユーザ操作によりコンテンツの再生が停止した場合の動作を説明するための図である。
【図10】コンテンツ再生制御モジュールの動作を説明するための図である。
【図11】コンテンツ再生制御モジュールの動作において、優先コンテンツ検索処理を説明するための図である。
【図12】コンテンツ再生制御モジュールの動作において、通常コンテンツ検索処理を説明するための図である。
【図13】ユーザ情報入力画面の一例を説明するための図である。
【図14】第2の実施の形態において、本発明を適用したテレビジョン放送受信装置のソフトウェアの構成を示すブロック図である。
【図15】第2の実施の形態におけるコンテンツ属性データを説明するための図である。
【図16】第2の実施の形態におけるアプリケーション属性データを説明するための図である。
【図17】第2の実施の形態におけるアプリケーション実行制御モジュールのアプリケーション起動時の動作を説明するための図である。
【図18】アプリケーション起動時に利用条件となるコンテンツが再生されなかった際に表示する警告表示の一例を説明するための図である。
【図19】第2の実施の形態におけるコンテンツ再生制御モジュールの動作を説明するための図である。
【図20】アプリケーション実行中にリモコン入力をきっかけとしたアプリケーションの状態変化があった場合のアプリケーション、アプリケーション実行制御モジュール、及びコンテンツ再生制御モジュールの連携動作を説明するための図である。
【図21】第2の実施の形態における蓄積制御モジュールの動作(〜ステップS2106)を説明するための図である。
【図22】第2の実施の形態における蓄積制御モジュールの動作(ステップS2107〜)を説明するための図である。
【図23】第2の実施の形態において、放送局から配信されるEIT(Event Infotmation Table)を説明するための図である。
【符号の説明】
100 テレビジョン放送受信装置
101 ディジタルチューナ部
102 デスクランブラ
103 トランスポートデコーダ
104 オーディオデコーダ
105 ディジタル/アナログ変換器(DAC)
106 ビデオデコーダ
107 動画プレーン
108 静止画プレーン
109 文字図形プレーン
110 グラフィック生成部
111 画像合成部
112 メモリ
113 モデム
114 1394インターフェース
115 操作部
116 受光部
117 ICカード制御部
118 CPU
119 ハードディスク
120 シリアルインターフェース
121 バッファ
122 バス
130 VTR
131 プリンタ
132 リモコン
133 スピーカ
134 表示器
135 ICカード
150 データサーバ
160 アンテナ
301 アプリケーション実行制御モジュール
302 コンテンツ再生制御部
303 コンテンツ属性データ
304 蓄積制御部
305 コンテンツ再生処理部
306 ユーザイベント制御部
307 アプリケーション(プログラム)
308 ユーザ情報
309 システムクロック[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention receives, for example, a digital broadcast wave in which data such as characters, images, sounds, and videos are multiplexed, and performs display, reproduction, and application program execution processing based on the received data. The present invention relates to a television broadcast receiving apparatus, a reproducing method, and a program for implementing the same, which are used in an apparatus or a system including
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, for example, a system in which a television broadcast signal including video is digitized, the digital television broadcast is transmitted via a broadcast satellite or a communication satellite, and the digital television broadcast is received at each home. Is in operation.
[0003]
According to the above-mentioned digital television broadcasting, it is said that television broadcast receivers (so-called televisions or television receivers) that receive and reproduce digital television broadcasts at homes and the like are changing from what they see to what they use. Is called.
[0004]
For example, in the past, a television that was only a means for viewing a broadcast program received radio waves multiplexed with moving images, sound, various data, and the like as the broadcast was digitized, and the user's remote controller It has become possible to display various data according to the operation of (remote controller) or the like.
[0005]
In BS digital broadcasting as television broadcasting, a data broadcasting service has already been started. This is because a broadcast station transmits a data group including display data, a script program, etc. superimposed on a television broadcast wave, and the television broadcast receiver side receives and stores the television broadcast wave, and the user's remote control This is a service that allows the corresponding data to be displayed on the screen in accordance with an operation or the like.
[0006]
On the other hand, it goes without saying that an environment in which an application program is mainly used has been realized by a personal computer (personal computer). When a user uses an application program on a personal computer, the user must provide the application program. A certain fee is paid to the software sales company. As a result, the user can use the application program on the personal computer.
[0007]
Specifically, for example, the user purchases a package of a desired application program from the software sales company side, and installs the application program on a personal computer. Alternatively, the user accesses a desired application program provider via the Internet or the like by operating a personal computer, inputs user information such as a credit card number, and then downloads the application program. Alternatively, the user accesses a desired application program provider via the Internet or the like by operating a personal computer, and after downloading the application program, pays this fee and receives the key code from the provider of the application program. After receiving the disclosure, the application program is used.
[0008]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in the conventional digital broadcast receiving apparatus as described above, it is possible to execute only a part of scripts or programs included in the data of the program being broadcast, and this execution is performed during the broadcast of the program. Was only possible.
That is, the conventional television broadcast receiving apparatus cannot answer the request that the user wants to use the application program in order to achieve a certain purpose.
[0009]
In addition, in the television broadcast receiving apparatus as described above, there is a demand for an environment in which an application program can be proactively used when the user likes it. On the other hand, for using an application program, the application program is easily used. In addition, there is a strong demand to use it for free if possible. In particular, in a television broadcast usage environment where it is common sense to basically watch a program for free, there is a strong demand for a similar environment for application programs.
[0010]
In addition, for example, application software development in a company requires a huge amount of money, but the company often provides a service for distributing application software to users free of charge.
[0011]
However, the above services are based on the premise that the user purchases expensive hardware or operating software from the same company, which is indispensable for the user to use the application software (program) of the company. Therefore, there is a problem that companies (operators) that can perform the service are limited.
[0012]
Further, for example, in the distributed data processing system described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2001-43282 and the like, by inserting an advertisement into a part of the WWW browser display, the online communication fee cost of the user is reduced, and the application program is Easy to use.
[0013]
However, in the above system, application programs that can be used by the user are limited to Internet content browsing applications, and thus cannot be applied to application programs that do not connect to the Internet.
[0014]
Therefore, the present invention was made to eliminate the above-described drawbacks, and the television broadcast receiver can be used mainly for applications, and unlike the conventional personal computer environment, it is unique to the television broadcast receiver. It is an object of the present invention to provide a television broadcast receiver, a playback method, and a program for implementing the same, which provide an application execution control function for realizing a simple application usage environment.
[0015]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
Under such an object, the television broadcast receiver according to the present invention receives and processes a television broadcast wave in which attribute data relating to content including at least one of video and audio and content to be distributed in the future is multiplexed. A television broadcast receiving apparatus, wherein the content storage means performs the content storage processing and the storage reservation processing of the content to be distributed in the future, the playback means for playing back the content in the content storage means, and any application Application execution means for executing a program and application usage condition storage means for storing condition data for using the application program, wherein the content storage means stores the attribute data and the application usage condition storage means. Article Based on the comparison result between the data, and executes the accumulation reservation processing and storage processing of content indicated by the attribute data.
[0024]
The playback method according to the present invention is a playback method for receiving and playing back a television broadcast wave on which attribute data relating to content including at least one of video and audio and content to be distributed in the future is multiplexed. The content storage step for performing the content storage processing and the storage reservation processing for the content to be distributed in the future, the playback step for playing back the content stored in the content storage step, and the application for starting and executing the application program Including an execution step and an application use condition storage step for storing condition data for using the application program, wherein the content storage step stores the attribute data and the application use condition storage step. In the case where the condition data matches, characterized in that it comprises the step of performing the accumulation reservation processing and storage processing of content indicated by the attribute data.
[0029]
The program according to the present invention is a program for causing a computer to function as predetermined means, and the predetermined means includes attribute data relating to content including at least one of video and audio and content to be distributed in the future. Content storage means for performing processing for storing the content of the multiplexed television broadcast wave, and storage reservation processing for the content to be distributed in the future, playback means for playing back the content in the content storage means, and any application program And an application usage condition storage means for storing condition data for using the application program. The content storage means is stored in the attribute data and the application usage condition storage means. Based on the comparison result of the condition data, and executes the accumulation reservation processing and storage processing of content indicated by the attribute data.
[0031]
According to the configuration of the present invention as described above, for example, the activation and execution of the application program is performed based on the reproduction state such as whether or not the content or the content group stored in advance in the storage unit such as a hard disk is being reproduced. Control can be performed. That is, it is possible to permit the user to use the application on the condition that the content stored in advance is being reproduced.
[0032]
Also, the priority of the content playback content is changed according to the day of the week or time when the user uses the application program, or the priority of the content playback content is changed according to the information about the user registered in advance by the user. Can be made.
[0033]
In addition, it is possible to control to change the content to be reproduced for each application program to be executed, or to change the content to be reproduced according to the state of the application program.
[0034]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0035]
[First embodiment]
The present invention is applied to, for example, a television broadcast receiver (digital television receiver) 100 that receives digital television broadcast (digital broadcast) as shown in FIG.
[0036]
First, in this embodiment, in a digital broadcast station (not shown), video content (content including audio) of a television program and data (content attribute data) related to the video content are encoded. Each of the converted data is modulated after being multiplexed, and the modulated data is transmitted as a broadcast wave from an antenna (not shown) of the broadcasting station. The broadcast wave transmitted from the antenna of the broadcast station is received by the digital television receiver 100 (user side terminal device) via a broadcast satellite (BS) (not shown).
[0037]
Hereinafter, the
[0038]
<Configuration and Series of Operations of
In the
The
[0039]
When the TS data from the
[0040]
Further, when the TS data from the
[0041]
The
[0042]
The IC
[0043]
The
[0044]
In addition, the
[0045]
The
[0046]
The
The
[0047]
The
[0048]
For example, the
[0049]
The
[0050]
The
The
[0051]
The
The components connected to the
[0052]
The
[0053]
The
[0054]
FIG. 2 shows an example of the configuration of the
Note that the configuration of the
[0055]
In FIG. 2, 201 is a light emitting unit for performing infrared communication between the
[0056]
[0057]
[0058]
<Software Configuration of
FIG. 3 shows a functional configuration by software executed by the
[0059]
As shown in FIG. 5, the functions performed by the
[0060]
Each of the above-described
[0061]
An application execution control unit (application execution control module) 301 reads an application program stored in the
[0062]
The content attribute data (content attribute data module) 302 is a data module in which the content attribute data of the video content included in each partial TS data stored in the
The user information (user information module) 308 is an information module related to the user himself / herself set in advance by the user.
[0063]
A user event control unit (user event control module) 306 receives a user input from the
[0064]
The
[0065]
The content reproduction control unit (content reproduction control module) 302 selects a process for selecting which data is to be reproduced among the data constituting the video content (partial TS data) stored in the
[0066]
The storage control unit (storage control module) 304 performs storage control when data (television broadcast content) from the
[0067]
<Specific Operation of
Here, the main operation of the
[0068]
(Operation of the accumulation control module 304)
In the present embodiment, video content is distributed at a date and time determined in advance from the broadcasting station.
Therefore, the accumulation control module 304 controls the
[0069]
Here, as described above, the digital broadcast distributed from the broadcasting station includes the content attribute data of the video content along with the video content (hereinafter also simply referred to as “content”).
The content attribute data includes, as service information (SI) information, a content name (program name), a reproduction time, and other attribute information related to the content.
[0070]
Therefore, the accumulation control module 304 stores the content attribute data of the content in the content
[0071]
FIG. 4 shows the state of the content attribute data stored in the content
In FIG. 4, as an example, it is assumed that content attribute data for four contents is stored in the content
[0072]
As shown in FIG. 4, an identification number (ID) is added to each of the four contents.
Further, the content attribute data here is data using a text format described based on XML (extensible Markup Language), for example, and each element that is the content of the data is a start tag. <xxx> and end tag </ xxx> is described in an area surrounded by </ xxx>, and each element can include other elements.
[0073]
(A) shown in FIG. 4 is a content attribute element (id = 1) representing the first content attribute data, which includes a file, a time offset, a content name, a time, an expiration date, And elements such as preferential playback conditions are included. Further, the priority reproduction condition elements include elements such as a reproduction day of the week, a reproduction time zone, a user group, and a user sex.
The subsequent second to fourth content attribute elements also include internal elements with the same configuration as the first content attribute element.
[0074]
The content attribute element shown in FIG. 4 is the content that the storage control module 304 converts and describes information sent as service information (SI) information from the broadcast station together with the broadcast wave based on XML.
[0075]
However, the only file element is information newly added by the storage control module 304 when the content storage processing is performed. This file element is a file name added when the storage control module 304 performs content storage processing on the
[0076]
The time offset element is an element used for specifying individual contents when a plurality of contents are included in one partial TS data. Specifically, the time offset element is data indicating how many minutes after the start of certain partial TS data the target content is set.
The time element is data indicating a time required for reproducing each content when a plurality of contents are included in one partial TS data.
[0077]
The priority playback condition element is an element including a playback time zone element and a user layer element. The reproduction time zone element is data in which the beginning and the end of the reproduction time are expressed in numbers in units of 24 hours and expressed with [−]. Similarly, the user layer element has a description in which the beginning and end of the width of the user age group are connected by [-].
[0078]
In FIG. 4, all four contents are described as one file with an ID of “0001”, but each may be described as a file with a different ID.
[0079]
(Operation of the application execution control module 301)
The application
[0080]
The application program according to the present embodiment is, for example, a so-called Java (R) byte code (hereinafter, also referred to as “Java (R) class file”) obtained by compiling a source code described in the Java (R) language in advance. In addition, image data, audio data, and other data used during execution of the application program are included.
[0081]
FIG. 5 shows the operation of the application
In FIG. 5, “●” (black circle) means start of processing, double circle means end of processing, and diamond means determination and branching.
[0082]
When the user requests application activation by pressing the
[0083]
The content
Then, if there is no content to be reproduced as a result of the above confirmation, the content
[0084]
Upon receiving the notification from the content
[0085]
On the other hand, if there is content to be played, the application
That is, the application
[0086]
FIG. 6 shows an example of the
As shown in FIG. 6, the application
[0087]
FIG. 7 shows an operation during application execution in the application
[0088]
The application
[0089]
First, the application
[0090]
On the other hand, as a result of the confirmation, if the content
FIG. 8 shows a display example of the
[0091]
When the application
[0092]
In addition, the application
[0093]
FIG. 9 shows the relationship between the operation of the component execution unit by the application
In FIG. 9, the line extending downward indicates the passage of time (time), and indicates that the processing is executed later as it goes downward.
[0094]
For example, in response to an inquiry from the application execution control module 301 (step S901), the content
When the content reproduction is stopped by the user's operation of the remote controller 132 (step S903, discarding step S904), the content
[0095]
The application
[0096]
Furthermore, when content reproduction is started by the user operating the remote controller 132 (step S908, discarding step S909), the content
[0097]
In response to the response from the content
[0098]
(Operation of Content Playback Control Module 302)
10 to 12 show the operation of the content
The content
[0099]
As shown in FIG. 10, first, the content
[0100]
As a result of the confirmation in step S1001, if the reproduction content does not exist, the content
[0101]
As a result of the confirmation in step S1001, if there is playback content, the content
[0102]
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 11, in executing the priority content search process, the content
[0103]
That is, the content
[0104]
The step S1002d will be specifically described. For example, when the content attribute data is data as shown in FIG. 4, the content attribute data with the content attribute id = 1 described at the top thereof has a priority reproduction condition. “Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday” is described as the reproduction day. In this case, the current day of the week needs to correspond to this. In addition, since “10-15” is described as the playback time zone, the current time zone needs to be between 10:00 and 15:00. Furthermore, since “20-70” is described as the user group, the age group information of the registered user needs to be between 20 and 70 years old.
[0105]
When all the elements included in the priority playback condition as described above match the current day of the week, time, and information set by the television
Also, for example, in the case of the content attribute data of content attribute id = 1 shown in FIG. 4 above, 120 seconds from the portion 60 seconds after the beginning of the data stored as file ID = 0001 on the
[0106]
As described above, in the priority content search process in step S1002, the playback content is determined according to the content of the
Then, after the processing is completed for all content attribute data (step S1002c), the process proceeds to execution of normal content search processing (step S1003).
[0107]
In the normal content search process (step S1003), for example, as shown in FIG. 12, the content
[0108]
Then, the content
[0109]
As described above, in the present embodiment, since the priority content search process (step S1002) and the normal content search process (step S1003) are executed alternately, the content that is the target of priority playback is The other normal contents are reproduced with twice the priority. In addition, the content that is subject to priority reproduction changes with the day of the week and the time when the user uses the application.
[0110]
Here, the “user information” in the present embodiment is information that is set in advance after the user purchases the television
FIG. 13 shows an example of a user
[0111]
For example, when the
[0112]
The setting information on the
[0113]
According to the present embodiment as described in detail above, it is possible to perform execution control of an application program depending on whether or not a content group stored in advance on the
[0114]
Further, by executing the content reproduction control as shown in FIGS. 10 to 12 above, the priority of the content reproduction content can be changed according to the day of the week or the time when the user uses the application program, or the user can The priority of the content reproduction content can be changed according to the information related to the user registered in advance.
[0115]
In the present embodiment, in the content reproduction control shown in FIGS. 10 to 12, the priority content search process (step S1002) and the normal content search process (step S1003) are alternately performed at a ratio of 1: 1 or the like. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, the ratio between the priority content search process and the normal content search process is set to 2: 1, or the ratio is set to 3: 1. May be.
[0116]
Further, in the present embodiment, user information that can be set is information on the range of the user's age group and gender composition, but other information may of course be included. For example, the user information may include information such as a music genre preferred by the user and a product genre desired by the user.
[0117]
In the present embodiment, the description of the content attribute data is a description based on XML. However, of course, the description is not limited to the gist of the present invention. For example, text description is described based on other methods. Alternatively, it may be described as a binary data block.
[0118]
In the present embodiment, content is distributed from a broadcasting station at a predetermined time. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and for example, the user manually inputs content to the digital
[0119]
Further, in the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 4 above, the file IDs of the stored contents are all set to ID = 0001. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the file IDs are changed and handled as individual files. Also good.
[0120]
[Second Embodiment]
In the present embodiment, the configuration and operation of the television
Here, only the configuration and operation different from those of the first embodiment will be specifically described.
[0121]
First, in the present embodiment, video data, audio data, and “broadcast data” of a television program are encoded in a digital broadcast station (not shown), and each encoded data is multiplexed. The data is modulated later, and the modulated data is transmitted as a broadcast wave from an antenna (not shown) of the broadcasting station. The broadcast wave transmitted from the antenna of the broadcast station is received by the digital television receiver 100 (user side terminal device) via a broadcast satellite (BS) (not shown).
[0122]
The above “broadcast data” means “service information data” (SI data) indicating the contents of broadcast channels and broadcast programs, “data broadcasting” including text data, image data, and audio data described in a markup language. Data including “content data” and “application data” including application program code and related data files.
[0123]
<Software Configuration of
FIG. 14 shows a functional configuration by software executed by
In the software configuration shown in FIG. 14, parts that function in the same way as the software configuration shown in FIG. 3 are given the same reference numerals, and detailed descriptions thereof are omitted.
[0124]
The software configuration in the present embodiment includes
[0125]
The content
[0126]
The application
[0127]
The content
[0128]
The user
[0129]
An
Assume that the
[0130]
The content
[0131]
The accumulation control module 304 performs accumulation control when the input content (TS data) from the
[0132]
The
[0133]
<Specific Operation of
Here, the main operation of the
[0134]
(Operation of the accumulation control module 304)
In the present embodiment, as in the first embodiment, content distribution is performed at a date and time determined in advance from a broadcasting station.
Accordingly, the accumulation control module 304 causes the
[0135]
Here, the digital broadcast distributed from the broadcasting station includes content attribute data of the content as well as the content, as in the first embodiment.
The content attribute data includes, as service information (SI) information, a content name (program name), a reproduction time, and other attribute information related to the content.
[0136]
Therefore, the accumulation control module 304 stores the content attribute data of the content in the content
[0137]
FIG. 15 shows the state of the content attribute data stored in the content
In FIG. 15, as an example, content attribute data for six contents are stored in the content
[0138]
As shown in FIG. 15, an identification number (ID) is added to each of the six contents.
The content attribute data here is data using a text format described based on XML (eXtensible Markup Language), as in the first embodiment.
In the present embodiment, the target content is, for example, product advertisement content.
[0139]
(A) shown in FIG. 15 is a content attribute element (id = 1) representing the first content attribute data, and includes a file, a time offset, a content name, a provider name, a section, Elements such as category, time, and expiration date are included.
The subsequent second to sixth content attribute elements also include internal elements with the same configuration as the first content attribute element.
[0140]
The contents of the content attribute element shown in FIG. 15 are contents obtained by the storage control module 304 converting and describing information transmitted as service information (SI) information together with broadcast waves from a broadcast station based on XML.
[0141]
However, the file element is information newly added by the storage control module 304 when the content storage processing is performed. This file element is a file name added when the storage control module 304 performs content storage processing on the
[0142]
The time offset element is an element used for specifying individual contents when a plurality of contents are included in one partial TS data. Specifically, the time offset element is data indicating how many minutes after the start of certain partial TS data the target content is set.
The time element is data indicating a time required for reproducing each content when a plurality of contents are included in one partial TS data.
[0143]
The provider company name element and the section element are elements that represent the name of the side (company) that creates and provides the content and the section in charge in the company.
For example, in the content attribute element indicated by id = 1 in FIG. 15, the content is created and provided by the section “Office Software Division” of the company name “Michael Soft”.
[0144]
In the content attribute element shown in FIG. 15, the section element and the category element can be treated as options, and it is not always necessary to have these elements.
[0145]
(Operation of application execution control module 301)
First, FIG. 16 shows an example of the contents of
[0146]
The
[0147]
The attribute information of the application includes content elements in two elements of application name and usage condition content and elements of usage condition content. Further, the elements of company name, name, section, and category are included in the elements. It is included.
[0148]
In addition, in the attribute information of the application, it is not necessary to use all elements of the company name, name, section, and category as elements included in the content element. For example, one element among these elements is used. May be.
[0149]
FIG. 17 shows the operation of the application
In FIG. 17, “●” (black circle) means start of processing, double circle means end of processing, and diamond means determination and branching.
[0150]
As in the first embodiment, the application program in the present embodiment is, for example, a so-called Java (R) byte code (Java () that is pre-compiled from a source code written in the Java (R) language. R) class file) and image data, audio data, and other data used by the application program during execution.
[0151]
When the user requests application activation by pressing the
[0152]
Next, the application
[0153]
Specifically, for example, when the
(1) Type = company advertisement, company name = Michael Soft, section = office software division
(2) Type = company advertisement, company name = Michael Soft, name = Michael Soft Office 2000
(3) Type = non-profit organization advertisement, company name = World Peace Federation secretariat, name = landmine eradication campaign
These are the three elements. Using these elements as condition parameters, a content reproduction request is issued to the content
[0154]
Although the details will be described later, the content
[0155]
For example, in the above-mentioned Michael Soft example, the two contents indicated by the content elements id = 1 and id = 3 shown in FIGS. 12A and 12C match the condition parameter. .
[0156]
The application
[0157]
On the other hand, if there is content that matches the conditions, the application
[0158]
In the present embodiment as well, as in the first embodiment, the application
[0159]
As for the operation of the application
[0160]
(Operation of Content Playback Control Module 302)
FIG. 19 shows the operation of the content
[0161]
First, when the content
[0162]
Next, the content
[0163]
In other words, the content
On the other hand, when the conditions do not match or when the content reproduction ends, the content
[0164]
In the comparison processing in the present embodiment, all the conditions included in each content element indicated by the
(1) Type = company advertisement, company name = 21st century trading company, section = import car division
(2) Type = company advertisement, company name = daily beer, name = 2000 year-end gift campaign
(3) Type = company advertisement, company name = daily beer, name = super smooth beer
(4) Type = company advertisement, company name = Nihonbashi Department Store
(5) Type = company advertisement, company name = Shibuya TV broadcast, category = program
Content that matches each of these conditions is retrieved.
[0165]
Further, in the case of the content attribute data shown in FIG. 15, the content shown in FIG. 15B matches the condition in the condition (1), and the condition (3) in FIG. The contents match.
Therefore, the content reproduced in this case is the two contents shown in FIGS. 15B and 15D.
[0166]
In the comparison process, only the specified condition needs to be matched with the content element of the
[0167]
When all content attributes included in the
If there is content that matches the condition, the content
[0168]
With the application execution control operation and the content reproduction control operation as described above, the television
[0169]
Further, the application
[0170]
FIG. 20 shows the relationship between the content
In FIG. 20, the line extending downward indicates the passage of time (time), and indicates that the processing is executed later as it goes downward.
[0171]
First, when the user changes the state of the application by operating the remote controller 132 (steps S2001 and S2002), the application
[0172]
Next, upon receiving the state change notification, the application
[0173]
When the content
[0174]
As a result of the search, the content
[0175]
Specifically, for example, in the case of the
[0176]
That is, when the status value “1” is notified from the application, the application
・ Type = "company advertisement", company name = BIC camera, category = computer
・ Type = "company advertisement", company name = BIC camera, category = AV equipment
・ Type = "Corporate Advertising" Company name = BIC Camera, Category = Home Appliance
A content reproduction request is issued using these three conditions as parameters. On the other hand, when the condition value “2” is notified from the application, the application
・ Type = "company advertisement", company name = BIC camera, category = computer peripherals
A content reproduction request is issued using the condition as a parameter.
[0177]
Also, in the confirmation process of the
[0178]
Also, in the search process (step S2006) in the content
[0179]
By performing the operation as described above, the television
[0180]
(Operation of the accumulation control module 304)
First, in the above description, it is assumed that the
21 and 22 show the operation of the accumulation control module 304 in the present embodiment.
[0181]
As shown in FIG. 21, first, the accumulation control module 304 acquires application attribute data 1408 (step S2101), and further, for the
[0182]
FIG. 23 shows an example of an EIT (Event Information Table) which is one of the table information included in the SI information in the present embodiment.
The EIT is a table in which information about each program content (event) to be broadcast is described. In the EIT according to the present embodiment, the program content name (event name) is included in the event
[0183]
The storage control module 304 reads the EIT of the program scheduled to be broadcasted in the SI information, compares the read information with the
[0184]
Then, as shown in FIG. 22, when the broadcast time registered in the
Furthermore, the storage control module 304 registers information such as the name, provider name, section, and category of the stored program content in the content attribute data 303 (step S2109).
[0185]
As described above in detail, according to the present embodiment, it is possible to perform an operation of permitting execution and continuous use of an application on condition that a content designated in advance is being reproduced. Further, it is possible to perform an operation for changing the content to be reproduced for each application, and an operation for changing the content to be reproduced according to the state of the application.
In addition to accumulating content at a predesignated time, the content that matches the condition specified by the application attribute registered in the
[0186]
In the first and second embodiments, the
[0187]
In the first and second embodiments, the application is started by pressing the
[0188]
In the first and second embodiments, the application is stored in the
[0189]
In the first and second embodiments, text data described based on XML is used as the
[0190]
In the first and second embodiments, the content name, provider name, section, category name, and other information of the content are described as elements based on XML. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, as a URI (Uniform Resource indicator) description for identifying content,
Or the like.
[0191]
Another object of the present invention is to supply a storage medium storing software program codes for realizing the functions of the host and terminal according to the first and second embodiments to the system or apparatus, and the computer of the system or apparatus. Needless to say, this can also be achieved by (or CPU or MPU) reading and executing the program code stored in the storage medium.
In this case, the program code itself read from the storage medium realizes the functions of the first and second embodiments, and the storage medium storing the program code and the program code constitute the present invention. It becomes.
As a storage medium for supplying the program code, ROM, flexible disk, hard disk, optical disk, magneto-optical disk, CD-ROM, CD-R, magnetic tape, nonvolatile memory card, and the like can be used.
Further, by executing the program code read by the computer, not only the functions of the first and second embodiments are realized, but also an OS running on the computer based on the instruction of the program code. Needless to say, the present invention includes a case where the functions of the first and second embodiments are realized by performing part or all of the actual processing.
Further, after the program code read from the storage medium is written to the memory provided in the extension function board inserted in the computer or the function extension unit connected to the computer, the function extension is performed based on the instruction of the program code. It goes without saying that the CPU or the like provided in the board or the function expansion unit performs part or all of the actual processing and the functions of the first and second embodiments are realized by the processing.
[0192]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, for example, the following effects (1) to (7) can be obtained.
[0193]
(1) The user can use the application program together with the television broadcast at any time regardless of the contents of the program being broadcast.
[0194]
(2) The user can be permitted to use the application program on the condition that the specified accumulated content is being reproduced. As a result, the content to be reproduced is, for example, content such as an introduction program for commercials, products and services, etc., so that the provider of the application program can also provide users who use the television broadcast and the application program. Advertising using video and audio becomes possible.
[0195]
Therefore, according to the present invention, for example, a certain application software company develops and provides an application, and views the commercial content of the application for its own personal computer (personal computer) to the user. It is possible to implement a service form that permits the use of.
[0196]
In addition, as in the case of conventional television program production, the application software company develops and provides an application with investment from a plurality of sponsors, and on the condition that the commercial group of the sponsor is viewed to the user. A service form that permits the use of an application can be implemented.
[0197]
Thereby, a new application use service unique to the television broadcast receiving apparatus or system can be provided, and a new application providing service model can be realized. In addition, the user can use the application for free or at an extremely low charge.
[0198]
(3) For example, conventionally, a technique has been proposed in which a banner advertisement is displayed on a part of the display screen to allow free use of the Internet browsing application. For example, it is possible to provide an advertising service using video on a television broadcast screen, which not only provides a much higher advertising effect than before, but also various applications that can be used in television broadcasting, not limited to Internet browsing applications. Even so, a free service can be realized. Furthermore, instead of monitoring usage conditions or the like with individual applications as in the past, development of individual applications is facilitated by monitoring usage conditions (condition data) or the like.
[0199]
(4) The priority of the content reproduction content is changed according to the day of the week or time when the user uses the application program, or the content reproduction content priority is set according to the information about the user registered in advance by the user. Can be changed.
For example, from 10:00 to 12:00, mainly commercial contents such as household goods and clothes targeted at housewives are played preferentially, and commercial contents such as fishing and gardening supplies are given priority on weekends. Therefore, it is possible to reproduce the content or to preferentially reproduce the commercial content such as the female underwear only for the female, so that effective advertising can be performed.
[0200]
(5) Since the content playback content can be changed according to the application program used by the user, for example, the user can play a commercial of a newly released game while executing the game application, Further, for example, when a user uses an application, it is possible to reproduce only commercial content of a company that provides the application.
[0201]
(6) Since the content playback content can be changed according to the state of the application program, for example, in the case of an application provided by a large mass retailer, a new operation is performed when the user tries to perform a print operation. It is also possible to reproduce commercials of product printers and special information on consumables such as ink, and more effective advertising than before is possible.
[0202]
(7) The content to be reproduced from the application program is not directly specified individually, but can be specified by a method such as a provider company name, section, category, etc., which has not been specified in the conventional program content specification. When using, the content to be played is not fixed from the beginning, but can be replaced weekly or replaced with new content at any time.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a television broadcast receiving apparatus to which the present invention is applied in a first embodiment.
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining the configuration of a remote controller (remote controller) of the television broadcast receiver.
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a software configuration of the television broadcast receiving apparatus.
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining content attribute data;
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining an operation of an application execution control module when starting an application.
FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining an example of a display screen during execution of an application.
FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining an operation during application execution of the application execution control module;
FIG. 8 is a diagram for explaining warning display on a display screen during execution of an application.
[Fig. 9] Fig. 9 is a diagram for explaining an operation when content reproduction is stopped by a user operation during application execution.
FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining an operation of a content reproduction control module.
FIG. 11 is a diagram for explaining priority content search processing in the operation of the content reproduction control module;
FIG. 12 is a diagram for explaining normal content search processing in the operation of the content reproduction control module.
FIG. 13 is a diagram for explaining an example of a user information input screen.
FIG. 14 is a block diagram showing a software configuration of a television broadcast receiving apparatus to which the present invention is applied in the second embodiment.
FIG. 15 is a diagram for explaining content attribute data in the second embodiment;
FIG. 16 is a diagram for explaining application attribute data in the second embodiment;
FIG. 17 is a diagram for explaining the operation at the time of application activation of the application execution control module in the second embodiment;
FIG. 18 is a diagram for explaining an example of a warning display that is displayed when content that is a use condition is not reproduced when an application is activated;
FIG. 19 is a diagram for explaining the operation of the content reproduction control module according to the second embodiment.
FIG. 20 is a diagram for explaining a cooperative operation of an application, an application execution control module, and a content reproduction control module when an application state change is triggered by a remote control input during application execution.
FIG. 21 is a diagram for explaining an operation (˜step S2106) of the accumulation control module according to the second embodiment.
FIG. 22 is a diagram for explaining an operation (from step S2107) of the accumulation control module according to the second embodiment;
FIG. 23 is a diagram for explaining an EIT (Event Infotmation Table) distributed from a broadcasting station in the second embodiment.
[Explanation of symbols]
100 Television broadcast receiver
101 Digital tuner section
102 Descrambler
103 Transport decoder
104 Audio decoder
105 Digital / Analog Converter (DAC)
106 Video decoder
107 Movie plane
108 Still image plane
109 character graphic plane
110 Graphic generator
111 Image composition unit
112 memory
113 Modem
114 1394 interface
115 Operation unit
116 light receiving part
117 IC card controller
118 CPU
119 hard disk
120 serial interface
121 buffers
122 Bus
130 VTR
131 Printer
132 remote control
133 Speaker
134 Display
135 IC card
150 Data server
160 Antenna
301 Application execution control module
302 content reproduction control unit
303 Content attribute data
304 Storage control unit
305 Content playback processing unit
306 User event control unit
307 Application (program)
308 User information
309 system clock
Claims (3)
Translated fromJapanese上記コンテンツの蓄積処理、及び上記将来配信されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理を行うコンテンツ蓄積手段と、
上記コンテンツ蓄積手段内のコンテンツを再生する再生手段と、
任意のアプリケーションプログラムを実行するアプリケーション実行手段と、
上記アプリケーションプログラムを利用するための条件データを蓄積するアプリケーション利用条件蓄積手段とを備え、
上記コンテンツ蓄積手段は、上記属性データと、上記アプリケーション利用条件蓄積手段に蓄積された条件データとの比較結果に基づいて、上記属性データにより示されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理及び蓄積処理を実行することを特徴とするテレビジョン放送受信装置。A television broadcast receiving apparatus that receives and processes a television broadcast wave in which attribute data relating to content including at least one of video and audio and content to be distributed in the future is multiplexed,
Content storage means for performing the content storage processing and the storage reservation processing of the content to be distributed in the future;
Playback means for playing back the content in the content storage means;
Application execution means for executing an arbitrary application program;
Application use condition storage means for storing condition data for using the application program,
The content storage means executes a storage reservation process and a storage process of the content indicated by the attribute data based on a comparison result between the attribute data and the condition data stored in the application usage condition storage means. A featured television broadcast receiver.
上記コンテンツの蓄積処理、及び上記将来配信されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理を行うコンテンツ蓄積ステップと、
上記コンテンツ蓄積ステップにより蓄積されたコンテンツを再生する再生ステップと、
アプリケーションプログラムを起動及び実行するアプリケーション実行ステップと、
上記アプリケーションプログラムを利用するための条件データを蓄積するアプリケーション利用条件蓄積ステップとを含み、
上記コンテンツ蓄積ステップは、上記属性データと、上記アプリケーション利用条件蓄積ステップにより蓄積された条件データとが一致した場合に、上記属性データにより示されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理及び蓄積処理を実行するステップを含むことを特徴とする再生方法。A reproduction method for receiving and reproducing a television broadcast wave in which attribute data relating to content including at least one of video and audio and content to be distributed in the future is multiplexed,
A content storage step for performing the content storage processing and the storage reservation processing of the content to be distributed in the future;
A reproduction step of reproducing the content accumulated in the content accumulation step;
An application execution step for starting and executing an application program;
An application use condition storage step for storing condition data for using the application program,
The content accumulation step includes a step of executing an accumulation reservation process and an accumulation process for the content indicated by the attribute data when the attribute data matches the condition data accumulated in the application usage condition accumulation step. A reproduction method characterized by the above.
上記所定の手段は、
映像及び音声の少なくとも何れかを含むコンテンツ及び将来配信されるコンテンツに関する属性データが多重されたテレビジョン放送波の当該コンテンツの蓄積処理、及び上記将来配信されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理を行うコンテンツ蓄積手段と、
上記コンテンツ蓄積手段内のコンテンツを再生する再生手段と、
任意のアプリケーションプログラムを実行するアプリケーション実行手段と、
上記アプリケーションプログラムを利用するための条件データを蓄積するアプリケーション利用条件蓄積手段とを備え、
上記コンテンツ蓄積手段は、上記属性データと、上記アプリケーション利用条件蓄積手段に蓄積された条件データとの比較結果に基づいて、上記属性データにより示されるコンテンツの蓄積予約処理及び蓄積処理を実行することを特徴とするプログラム。A program for causing a computer to function as a predetermined means,
The predetermined means is:
Content storage means for storing the content of the television broadcast wave in which attribute data relating to content including at least one of video and audio and content to be distributed in the future are multiplexed, and storing reservation processing for the content to be distributed in the future When,
Playback means for playing back the content in the content storage means;
Application execution means for executing an arbitrary application program;
Application use condition storage means for storing condition data for using the application program,
The content storage means executes the content storage reservation process and the storage process indicated by the attribute data based on a comparison result between the attribute data and the condition data stored in the application usage condition storage means. A featured program.
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002077188AJP3990928B2 (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2002-03-19 | Television broadcast receiving apparatus, reproducing method and program |
| US10/385,615US7886332B2 (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2003-03-12 | Television broadcast receiving apparatus |
| EP03251603AEP1349376B1 (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2003-03-17 | Receiving apparatus for television broadcast |
| DE60321417TDE60321417D1 (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2003-03-17 | Receiver for television broadcasting |
| CNB031206433ACN1242606C (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2003-03-18 | TV broadcast receiving device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002077188AJP3990928B2 (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2002-03-19 | Television broadcast receiving apparatus, reproducing method and program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003274306A JP2003274306A (en) | 2003-09-26 |
| JP2003274306A5 JP2003274306A5 (en) | 2005-09-02 |
| JP3990928B2true JP3990928B2 (en) | 2007-10-17 |
Family
ID=29205643
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002077188AExpired - Fee RelatedJP3990928B2 (en) | 2002-03-19 | 2002-03-19 | Television broadcast receiving apparatus, reproducing method and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3990928B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW200518070A (en) | 2003-10-10 | 2005-06-01 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co Ltd | Recording medium, reproduction device, program, and reproduction method |
| KR100844706B1 (en) | 2003-10-10 | 2008-07-07 | 샤프 가부시키가이샤 | Reproducing apparatus, video data reproducing method, content recording medium, and computer-readable recording medium |
| JP5133313B2 (en)* | 2003-10-10 | 2013-01-30 | シャープ株式会社 | REPRODUCTION DEVICE, VIDEO DATA REPRODUCTION METHOD, CONTROL PROGRAM, AND CONTENT RECORDING MEDIUM |
| EP2270795A3 (en) | 2003-11-10 | 2015-03-18 | Panasonic Corporation | Recording medium, playback apparatus, program, playback method, system integrated circuit |
| JP4557149B2 (en)* | 2004-11-12 | 2010-10-06 | キヤノンマーケティングジャパン株式会社 | Printing control method and program, information processing apparatus, and printing system |
| JP5151110B2 (en) | 2006-10-06 | 2013-02-27 | ソニー株式会社 | Data broadcast processing apparatus and method, and program |
- 2002
- 2002-03-19JPJP2002077188Apatent/JP3990928B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003274306A (en) | 2003-09-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8495679B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for delivery of television programs and targeted de-coupled advertising | |
| US8554752B2 (en) | Information providing system, information receiving apparatus, information providing apparatus, information providing method and program | |
| JP5243070B2 (en) | Information providing apparatus, receiving terminal, information providing system, information providing method, and program | |
| CN100373945C (en) | Interactive TV Program Guide System with List Groups | |
| CN102098537B (en) | Systems and methods for episode tracking in an interactive media environment | |
| CN101127884B (en) | Program switching method | |
| JP4680106B2 (en) | CONTENT REPRODUCTION DEVICE, CONTENT REPRODUCTION DEVICE CONTROL METHOD, CONTROL PROGRAM, AND RECORDING MEDIUM | |
| US8881196B2 (en) | Video playback apparatus, information providing apparatus, information providing system, information providing method and program | |
| JP2004519893A (en) | Broadcasting and processing of meta information related to content materials | |
| JP2004128795A (en) | Data processing apparatus, data processing method and program, and data processing system | |
| US20080288981A1 (en) | Receiving device, information providing device, information providing system, information providing method, and programs | |
| JP2004030327A (en) | Device and method for providing contents-related information, electronic bulletin board system and computer program | |
| JP2002077784A (en) | Apparatus, system and method for providing program related information | |
| JP3990928B2 (en) | Television broadcast receiving apparatus, reproducing method and program | |
| JP4181785B2 (en) | Television broadcast receiving apparatus and television broadcast receiving method | |
| US20090138914A1 (en) | Information providing system, receiving device, information providing device, information providing method and program | |
| US8887219B2 (en) | Information providing apparatus, information receiving terminal, information providing system, information providing method and program | |
| US8510776B2 (en) | Information providing system, information receiving terminal, information providing apparatus, information providing method and program | |
| JP4500024B2 (en) | Advertising management system and computer program and method for realizing the same | |
| JP2021193845A (en) | Recording/playback device | |
| JP2004102679A (en) | Content distribution system, content distributing method, and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20050303 | |
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20050303 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20070119 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20070424 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20070615 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20070717 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20070723 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100727 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:3990928 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100727 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110727 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120727 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120727 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130727 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |