JP3887597B2 - Security system and security method - Google Patents
Security system and security methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3887597B2 JP3887597B2JP2002325881AJP2002325881AJP3887597B2JP 3887597 B2JP3887597 B2JP 3887597B2JP 2002325881 AJP2002325881 AJP 2002325881AJP 2002325881 AJP2002325881 AJP 2002325881AJP 3887597 B2JP3887597 B2JP 3887597B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- security
- information
- related information
- monitoring target
- monitoring
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Telephonic Communication Services (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、監視対象の異常を検知して、所望のセキュリティ関連処理を行うセキュリティシステム及びセキュリティ方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来のセキュリティシステムは、ある建物で防犯センサや火災探知器などにより異常を検知すると、その建物で警報を発したり、警備会社に連絡するといった処理を行っていた。
【0003】
また、同様のセキュリティシステムとして、異常を検知した建物から通信回線を通じて周辺の建物に異常を送信し、周辺の建物においても警報を発するという処理を行って広範囲に異常を伝え、侵入者への威嚇の効果や周辺住人に対する注意の呼びかけの効果を高め、また、犯人逮捕のための目撃情報を増やすことにより、防犯効果を高めるセキュリティシステムが考案されている(特許文献1参照)。
【0004】
また、インターネットを通じて、特定の地域や業種に特化した情報を効率よく検索する方法として、インターネットを通じて、特定の地域や業種に特化した情報を効率よく検索する情報検索方法及び情報検索システムが提案されている(特許文献2参照)。
【0005】
【特許文献1】
特開2002-109661号公報
【特許文献2】
特開2002-163281号公報
【0006】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
従来のセキュリティシステムは、防犯センサや火災報知器にて異常が検知されると、犯人逮捕や避難・火災延焼防止のための事後処理を行っている。また、上述した特許文献1に開示されたセキュリティシステムも、周辺建物へのネットワークを利用して、広範囲へ異常の発生を知らせているが、あくまでも事後処理である。
【0007】
一方、空き巣や放火などの犯罪は、同一の犯人により比較的狭い地域で同様な方法で連続して行われることが多い。
【0008】
しかしながら、従来のセキュリティシステムでは、事件・災害が起こった直後に警報を鳴らすだけで、このような犯罪傾向・火災傾向を踏まえた処理は、公共機関やメディアを通じた公報や、地域消防団などの見回りと言った、人を介在とした処理しか行われていないのが現状である。これらの方法では、人を介在としているため、リアルタイム性、人件費及びプライバシー等の問題がある。
【0009】
本発明は、このような点に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、監視対象だけでなく、その周辺の情報を取得してセキュリティ性能の向上を図ったセキュリティシステム及びセキュリティ方法を提供することにある。
【0010】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明の一態様によれば、監視対象のセキュリティ上必要となるセキュリティ関連情報が蓄積されたセキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段と、前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段にセキュリティ関連情報を蓄積する制御を行う蓄積制御手段と、前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積された情報の中から監視対象の監視に必要な情報を収集する情報照会手段と、監視対象を観測して、監視対象の顔認証を行う監視観測手段と、前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積されている過去から現在までのセキュリティ関連情報の履歴情報を前記情報照会手段を介して取得し、取得した履歴情報と前記監視観測手段による現在の監視結果とに応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うセキュリティ関連処理実行手段と、前記情報照会手段で収集された情報に基づいて、前記セキュリティ関連処理実行手段を制御する制御手段と、を備え、前記セキュリティ関連情報は、前記監視対象の周辺で発生した事件に関する情報と前記事件の発生時刻に関する情報とを含み、前記セキュリティ関連処理実行手段は、前記監視観測手段が顔画像を取得した時刻と、前記監視対象の周辺で発生した時刻の発生時刻との時間差が所定時間以内の場合、対応する顔画像の取得回数を更新し、前記取得回数に応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うことを特徴とするセキュリティシステムが提供される。
【0011】
また、本発明の一態様によれば、監視対象のセキュリティ上必要となるセキュリティ関連情報をセキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積するステップと、前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段にセキュリティ関連情報を蓄積する制御を行うステップと、前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積された情報の中から監視対象の監視に必要な情報を情報照会手段により収集するステップと、監視対象を観測して、監視対象の顔認証を行うステップと、前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積されている過去から現在までのセキュリティ関連情報の履歴情報を前記情報照会手段を介して取得し、取得した履歴情報と前記監視観測手段による現在の監視結果とに応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うステップと、を備え、前記セキュリティ関連情報は、前記監視対象の周辺で発生した事件に関する情報と前記事件の発生時刻に関する情報とを含み、前記セキュリティ関連処理では、顔認証を行った時刻と、前記監視対象の周辺で発生した事件の発生時刻との時間差が所定時間以内の場合、顔認証を行った人間の観測回数を更新し、前記観測回数に応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うことを特徴とするセキュリティ方法が提供される。
【0012】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明に係るセキュリティシステム及びセキュリティ方法について、図面を参照しながら具体的に説明する。
【0013】
(第1の実施形態)
図1は本発明に係るセキュリティシステムの第1の実施形態の概略構成を示すブロック図である。図1のセキュリティシステムは、監視対象1のセキュリティ上必要となるセキュリティ関連情報が蓄積された情報データベース2と、情報データベース2に蓄積された情報の中から監視対象1の監視に必要な情報を収集する情報照会部3と、監視対象1の監視を行う監視観測部4と、情報データベース2に蓄積されている過去から現在までのセキュリティ関連情報の履歴情報を情報照会部3を介して取得し、取得した履歴情報と監視観測部4による現在の監視結果とに応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行う対応処理部5と、情報照会部3で収集された情報に基づいて、対応処理部5を制御する制御部6と、を備えている。
【0014】
図1に示した各部の処理は、実際には、警備会社等が所持するホストコンピュータが行う。この種のホストコンピュータは、ある地域内の複数の住宅のセキュリティ関連情報を統括するものである。
【0015】
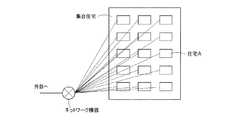
図2はこの種のホストコンピュータ7の概略的な動作を説明する図である。図2では、近所Cの近くの近所A,Bからのセキュリティ関連情報と警察・警備会社8からのセキュリティ関連情報とに基づいて、近所Cに対して所望のセキュリティ関連処理を行う例を示している。
【0016】
例えば、近所Aの敷地内で放火などによる出火が起きたり、近所Bの近くで不審者が徘徊していた場合には、近所A,Bの住人はそれぞれ火災報知器やドアロックなどのセキュリティ機能の警戒レベルを上げることになる。
【0017】
このような各住宅での警戒レベルの変更は、ホストコンピュータ7にも伝達される。ホストコンピュータ7は、各住宅から送られてくる情報に基づいて、放火や空き巣などの危険地区を自動的に判定し、危険地区内の各住宅に警戒情報を送信する。また、ホストコンピュータ7は、警察・警備会社等からのセキュリティ関連情報をネットワークを介して取得する。例えば、警察・警備会社等からピッキング犯罪情報を取得した場合は、犯罪発生場所が近隣地区でなくても、同種類の鍵を使用している各住宅に対して警戒を促すことができる。
【0018】
ホストコンピュータ7からの警戒情報を受けた各住宅は、家族や同居人に警戒情報を伝達して警戒を呼びかけたり、ドアロックなどのセキュリティ機器や火災報知器などの感度を上げる等の警戒処理を行う。
【0019】
なお、ホストコンピュータ7は、1台のコンピュータで構成してもよいし、ネットワークを介して相互にデータ通信を行う複数のコンピュータで構成してもよい。
【0020】
図3は自宅からの距離に応じて警戒レベルを変更する例を示す図である。家はそれぞれ、警戒度の高さと誤作動の兼ね合いから任意に警戒範囲を設定することができる。図3では、家B,C,Dのそれぞれが住居からの距離に応じて警戒範囲▲1▼と警戒範囲▲2▼を設定する例を示している。
【0021】
放火の場合は火災報知器の感度を上げ、空き巣の場合はドアロックの感度を上げるというように、犯罪の種類により警戒方法が異なり、近隣での連続犯行性も異なることから、警戒対象に応じて警戒レベルを設定するのが望ましい。
【0022】
例えば、家Aが放火や空き巣の被害にあった場合、家Bは家Aの近くであるため、警戒範囲▲1▼に設定している犯罪に対しても、警戒範囲▲2▼に設定している犯罪に対しても、家Bの警戒度を高める。
【0023】
一方、家C,Dの警戒範囲内には家Aは入っていないため、家Aで犯罪等が起こっても家C,Dは警戒度を高める措置を採らない。
【0024】
なお、図3では、警戒範囲を円形に設定したが、道路や鉄道等を考慮に入れて警戒範囲を設定してもよい。すなわち、鉄道や主要幹線道路など、距離が遠くても短時間で行くことができる範囲は警戒度を高めてもよい。
【0025】
図4は集合住宅に対する警戒範囲を説明する図である。集合住宅や建売戸建住宅などのように、同種類の住宅が複数近接して配置されている場合は、ある住居で犯罪等が起こった場合に、近隣の住宅すべてが同様の警戒を行うのが望ましい。
【0026】
そこで、集合住宅や建売戸建住宅などでは、警戒対象からの距離が異なっても、同一の警戒レベルに設定してもよい。
【0027】
このように、第1の実施形態では、近隣情報と警察・警備会社からのセキュリティ関連情報とに基づいて、警戒対象に応じた警戒レベルを設定するため、犯罪等の可能性を事前に察知してその予防を図ることができ、セキュリティ性能を向上できる。
【0028】
上述した第1の実施形態において、機密性を保持するために、暗号化したセキュリティ関連情報を情報データベース2に蓄積しておき、情報照会部3は、セキュリティ上必要最小限のセキュリティ関連情報のみを情報照会部3で収集するようにしてもよい。これにより、情報の漏洩を確実に防止できる。
【0029】
(第2の実施形態)
第2の実施形態は、各住居にセキュリティロボットを配置するものである。
【0030】
図5は本発明に係るセキュリティシステムの第2の実施形態の概略構成を示すブロック図である。
【0031】
図5のセキュリティシステムは、近隣情報データベース11と、ネットワーク12を介して近隣情報データベース11に接続される照会部13と、一般データベース14と、一般データベース検索部15と、家庭内セキュリティシステム16と、対応処理部17とを備えている。
【0032】
近隣情報データベース11は、各住居を訪問して各種サービス等を提供する訪問者に関する情報を登録する。家庭内セキュリティシステム16は、セキュリティロボットを有する。セキュリティロボットは、近隣情報データベース11に登録されている訪問者の情報を取得し、訪問者を認識・チェックする。これにより、家人が不在でも、セキュリティロボットが家人の代わりに各種サービス等の提供を受けることができる。
【0033】
具体的には、その地区の配達を担当する郵便局の職員や宅配業者の担当者、電気やガス、水道等の検針を行う担当者等の情報(氏名、顔写真、所属、・・・)が、各サービス提供会社等より近隣情報データベース11に登録されており、セキュリティロボットは常に最新の登録情報をそこから取得することができる。家人が不在時に来訪者があった場合、セキュリティロボットは来訪者の顔や氏名、用件等を画像および音声で確認し、近隣情報データベース11から取得した情報と比較・チェックすることで、来訪者が誰かを判断し、例えば宅配業者の担当者であれば家人に代わって荷物を受け取ることができる。
【0034】
近隣情報データベース11の内容としては、犯罪情報、防災情報、交通情報などの公共機関が公表する公共情報と、本セキュリティシステムがセンサ入力情報として登録するローカル情報がある。後者のローカル情報については、本セキュリティシステム間でのやりとりとなるため、自動的に行うことができる。前者の公共情報については、公共機関の協力が得られれば問題ないが、得られない場合、自動的な処理が困難となる。
【0035】
そこで、一つの構築方法として、既存のネットワーク12情報を有効活用できるよう、一般データベース14(インターネット上の公共機関18の情報)から、必要となるデータを取得してもよい。(取得方法としては、既存の交通・天気情報など、公共機関18の情報は定型フォーマットになっているものが多いため、比較的容易に検索可能となる。)
このように、第2の実施形態によれば、来訪者があやしい者でないかどうかを確実に認証してから、応対することになるため、家人が不在時でも安心してセキュリティロボットに来訪者の応対をさせることができる。また、万一何か問題が発生した時でも、来訪者が誰であったかがきちんと確認できるので、後からの事実確認や問題解決が容易になる。
【0036】
また、近隣情報データベース11にローカル情報だけでなく、公共情報も蓄積することにより、犯罪や災害に対する確実な予防を図ることができる。
【0037】
(第3の実施形態)
本発明に係るセキュリティシステムの第3の実施形態は、図5と同様のブロック構成を有する。照会部13は、外来者がインターホンを押すと、自動的に応答して画像と会話を記録する。そしてその外来者の顔認証を行い、近隣情報データベース11で照合する。外来者がインターホンを押した時間帯と当該地域の侵入窃盗事件の発生時間が近ければ、登録部はそのときの外来者を近隣情報データベース11に登録する。制御部6は、登録された回数が多いほど「あやしさ」の点数を増やす。
【0038】
そして、制御部6は、あやしさ点が高い外来者が来ると、インターホンの室内受け側にあやしいということを表示し、留守時には画像などをメールや電話で事前に指定した住人などに知らせる。
【0039】
また、留守であることを分かりにくいように、幼稚園児風の声と言葉遣いで対応し、対応している間にユーザの携帯電話などに電話をかけて、インターホン接続を試み、接続できればユーザが対応し、接続できなければ、機械音声で「いまおるすばんでだれもいれちゃいけないっていわれているの」等のように答えてもよい。
【0040】
あるいは、外来者が近隣情報データベース11に登録されている不審者(指名手配犯など)である場合には、家人がいれば家人に注意を促し、留守中であれば、警察・セキュリティ会社への通報をする。またその情報を近隣情報データベース11に登録する。
【0041】
このように、第3の実施形態では、外来者の画像と会話を近隣情報データベース11に登録するため、外来者が不審者かどうかを迅速かつ正確に判断でき、犯罪を未然に防止できる。
【0042】
(第4の実施形態)
図6は本発明に係るセキュリティシステムの第4の実施形態の概略構成を示すブロック図である。図6のセキュリティシステムは、電話回線などの公衆網21を介して相互に接続される犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22と、移動端末23と、LANなどの拠点網24を介して相互に接続される拠点リスク分析サーバ25と、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26と、公衆網21及び拠点網24を橋渡しする公衆網アクセスサーバ27と、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26により制御される警備装置28とを備えている。
【0043】
犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22は、例えば日本全国のような広域の過去所定期間に渡って通報された犯罪と災害について、少なくとも発生日時・発生地域・発生態様を記録した広域犯罪災害情報を外部から読み取り可能に提供するデータベースサーバである。
【0044】
図6では、犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22を1台のサーバ装置として描いているが、例えば、各地域の警察署や消防署の運営するサーバ、政府官庁や地方自治体の運営するサーバ、報道機関や警備保障会社など民間の提供するサーバなどの複数のサーバを通信回線を介して接続してもよい。この場合、これら複数のサーバ全体が犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22に相当する。
【0045】
広域犯罪災害情報は、例えば日本全国のような広域の過去所定期間に渡って通報された犯罪と災害について、犯罪や災害の発生日時、発生地域及び発生態様を少なくとも記述したデータレコードである。発生日時は当該犯罪あるいは災害が発生したとされる日時を表す数値データであり、発生地域は当該犯罪あるいは災害の発生した都道府県市町村の丁目までを表すエリア記号列である。
【0046】
発生態様は、当該犯罪や災害の種別(強盗、空き巣、放火、殺人、火災、床下浸水、床上浸水、地震による倒壊など)を示す記号列と、犯罪であるならその手口(押し込み、偽装、窓から侵入、ピッキングなど)を示す記号列と、その状況(犯人逃走中、解決、継続中、沈静化など)を示す記号列などを含むデータである。広域犯罪災害情報は、発生地域を特定する情報として詳細な地番や被害者名などを含まないようにすることで、プライバシーの保護に配慮している。
【0047】
公衆網21は、犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22や移動端末23が接続される例えば電話回線網などの公衆通信回線である。また、拠点網24は、本実施形態の利用者やその家族の居住する住居内に敷設されたLANである。そして、公衆網アクセスサーバ27は、本実施例装置の利用者の住居内に設置された、公衆網21と拠点網24とを結ぶ通信中継装置である。なお、本実施形態では、拠点網24の範囲を利用者の住居内に限定して説明するが、複数の住居を含む集合住宅や地域など、ある程度の広がりのある範囲を拠点網24としてもよい。
【0048】
移動端末23は、公衆網21を介して犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22や公衆網アクセスサーバ27と通信可能な端末装置であり、本実施例装置の利用者やその家族がそれぞれ携行する携帯電話などで実現される。なお、移動端末23は、図示していない衛星からの電波を受信することにより自己の位置を同定可能なGPS機能を備えている。
【0049】
移動端末23の現在位置情報は、公衆網21と公衆網アクセスサーバ27を経由してリスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26に定期的に送信される。この結果、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は、利用者やその家族の現在位置を把握することができる。また、移動端末23がリスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26と交信する度毎に、当該端末装置から該端末が正規の端末であることを示す認証鍵情報がリスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26に送信され、この認証鍵情報を検証することにより、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は正規の端末以外からの不正アクセスを拒絶することができるようになっている。この結果、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は移動端末23から安全に遠隔操作可能となっている。
【0050】
リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は、移動端末23から定期的に送られてくる現在位置情報に基づいて、当該位置を含む地域(都道府県市町村の丁目)において現在特に警戒すべき犯罪及び災害の態様を調査するよう拠点リスク分析サーバ25に定期的に依頼する。また、これに併せて、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は、自己の設置される住居の位置する地域(都道府県市町村の丁目)において現在特に警戒すべき犯罪及び災害の態様を調査するよう拠点リスク分析サーバ25に定期的に依頼する。
【0051】
なお、現在位置や住居位置から特定される地域を拠点地域情報、各拠点地域において現在特に警戒すべき犯罪及び災害の態様を拠点リスク分析サーバ25に調査させるための依頼を拠点リスク分析依頼と呼ぶ。
【0052】
拠点リスク分析サーバ25は、拠点リスク分析依頼を受けると、そこに記される拠点地域に関係した広域犯罪災害情報を犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22から検索する。検索の基準は、(1)過去所定期間(例えば1週間)内に広域(例えば日本全国)で所定件数以上発生している犯罪、(2)現在解決や沈静化に至っていない犯罪や災害で、発生地域が拠点地域に近い犯罪や災害である。検索された犯罪や災害は、それぞれの拠点地域において現在特に警戒すべき犯罪や災害の態様を表している。拠点リスク分析サーバ25は、この検索された犯罪や災害の態様情報とその検索の元となった拠点地域情報とを拠点犯罪災害リスクという情報に編集してリスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26に返信する。
【0053】
リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は、拠点犯罪災害リスクの返信を受けると、移動端末23の現在位置においてリスクが予測される犯罪災害態様については、その態様を拠点犯罪災害予報として移動端末23に送信する。この結果、移動中の利用者やその家族は、現在位置において例えば通学路で痴漢被害の恐れがあるとか、旅行先で水害の恐れがあるなどの警告を本実施例装置から受けることができるようになる。
【0054】
また、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は、住居においてリスクが予測される犯罪災害態様については、その態様に対応して住居を警備するための重点警備設定を決定して警備装置28に適用する。
【0055】
警備装置28は、重点警備設定に従って、現在特に警戒すべき犯罪や災害の態様に応じた住宅の警備を実施することができるようになっている。例えば、近隣で空き巣被害が続発しているような場合、警備装置28は、通常は反応しないようなわずかな物音にも反応して犯罪災害通報を移動端末23に発信するようになる。この犯罪災害通報を受けた利用者はリスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26を介して警備装置28を遠隔操作して状況確認を行い、もし、空き巣などの侵入を確認したら、携行する移動端末23を用いて状況確認後通報を警察や警備保障会社などに送ることができる。この状況確認後通報は一度人間の判断をくぐった通報なので誤報の危険はほとんどない。状況確認後通報を受けた警察や警備保障会社は事態を収拾するために出動を行う。なお、状況確認後通報により知らされる新たな犯罪や災害の情報はプライバシー保護に配慮した所定の加工を施されて自動的に犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22に追加登録され、他の利用者のために供される。
【0056】
なお、警備装置28の擁する各種センサの反応データや犯罪災害通報は後刻状況を詳細に分析する際に重要な証拠となる。そこで、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は、警備装置28の擁する各種センサの反応データや犯罪災害通報を自身で記録保存するとともに、その写しを拠点リスク分析サーバ25に送って記録の分散化を図り、一方のサーバが破壊されても、他方に記録が残るようにする。
【0057】
なお、上記のごとく記録の多重化を行う必要が小さいときは、拠点リスク分析サーバ25とリスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26を一体化することも可能である。
【0058】
このように、第4の実施形態では、拠点リスク分析サーバ25で分析された犯罪情報や災害情報を、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26を介して移動端末23に送るため、ユーザは移動中であっても、犯罪情報や災害情報を迅速に入手できる。また、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26には警備装置28が接続されているため、現在特に警戒すべき犯罪や災害の態様に応じた的確な警備を迅速に行うことができ、犯罪を未然に防止できるとともに、災害による被害を軽減できる。
【0059】
(第5の実施形態)
第4の実施形態では、ユーザの住居内に設置された拠点リスク分析サーバ25により各拠点の犯罪災害リスクを求めていたが、リスク分析機能を公衆網21上に置くことも可能である。この場合の概略構成は図7のようなブロック図になる。
【0060】
図7の公衆網21、犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22、移動端末23、拠点網24、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26、公衆網アクセスサーバ27及び警備装置28の各々はそれぞれ、図7の公衆網21、犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22、移動端末23、拠点網24、リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26、公衆網アクセスサーバ27及び警備装置28とほぼ同様であるが、拠点リスク分析サーバ25を設ける代わりに、公衆網21に接続された広域リスク分析サーバ29にてリスク分析を行う点に特徴がある。
【0061】
広域リスク分析サーバ29は、犯罪災害情報DBサーバ22の広域犯罪災害情報を定期的に分析して犯罪災害リスク情報のデータベースを構築している。犯罪災害リスク情報は、各地域毎に警戒を要する犯罪や災害の態様を含むデータレコードである。
【0062】
リスク適応型セキュリティサーバ26は、拠点地域に関する犯罪災害リスク情報を返送するよう拠点リスク分析依頼を広域リスク分析サーバ29に送信する。広域リスク分析サーバ29は、これを受け取ると該当地域の犯罪災害リスク情報を検索して拠点犯罪災害リスクとして返信する。
【0063】
このように、第5の実施形態では、公衆網21に接続された公衆網アクセスサーバ27にてリスク分析を行うため、各住宅がリスク分析機能をもたなくて済み、設備コストを安くできる。
【0064】
上述した実施形態で説明したセキュリティシステムは、ハードウェアで構成してもよいし、ソフトウェアで構成してもよい。ソフトウェアで構成する場合には、セキュリティシステムの機能を実現するプログラムをフロッピーディスクやCD−ROM等の記録媒体に収納し、コンピュータに読み込ませて実行させてもよい。記録媒体は、磁気ディスクや光ディスク等の携帯可能なものに限定されず、ハードディスク装置やメモリなどの固定型の記録媒体でもよい。
【0065】
また、セキュリティシステムの機能を実現するプログラムを、インターネット等の通信回線(無線通信も含む)を介して頒布してもよい。さらに、同プログラムを暗号化したり、変調をかけたり、圧縮した状態で、インターネット等の有線回線や無線回線を介して、あるいは記録媒体に収納して頒布してもよい。
【0066】
【発明の効果】
以上詳細に説明したように、本発明によれば、セキュリティ関連情報の履歴情報と監視対象の現在の監視結果とに応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うため、犯罪や災害の可能性をいち早く察知して、適切な対応を取ることができ、セキュリティ性能を向上できる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明に係るセキュリティシステムの第1の実施形態の概略構成を示すブロック図。
【図2】この種のホストコンピュータ7の概略的な動作を説明する図。
【図3】自宅からの距離に応じて警戒レベルを変更する例を示す図。
【図4】集合住宅に対する警戒範囲を説明する図。
【図5】本発明に係るセキュリティシステムの第2の実施形態の概略構成を示すブロック図。
【図6】本発明に係るセキュリティシステムの第4の実施形態の概略構成を示すブロック図。
【図7】リスク分析機能を公衆網上に設けたセキュリティシステムの第5の実施形態の概略構成を示すブロック図。
【符号の説明】
1 監視対象
2 セキュリティ関連情報蓄積部
3 情報照会部
4 監視観測部
5 セキュリティ関連処理実行部
6 制御部
7 ホストコンピュータ
11 近隣情報データベース
12 ネットワーク
13 照会部
14 一般データベース
15 一般データベース検索部
16 家庭内セキュリティシステム
17 対応処理部[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a security system and a security method for detecting a monitoring target abnormality and performing desired security-related processing.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventional security systems perform processing such as issuing an alarm or contacting a security company when an abnormality is detected by a security sensor or a fire detector in a building.
[0003]
In addition, as a similar security system, an abnormality is transmitted from the building where the abnormality is detected to the surrounding buildings through the communication line, and an alarm is also issued in the surrounding buildings to convey the abnormality to a wide area and threaten the intruder. A security system has been devised that enhances the crime prevention effect by increasing the effect of calling attention to neighboring residents and increasing witness information for arresting the criminal (see Patent Document 1).
[0004]
In addition, as a method for efficiently searching for information specific to a specific region or industry via the Internet, an information search method and information search system for efficiently searching for information specific to a specific region or industry via the Internet is proposed. (See Patent Document 2).
[0005]
[Patent Document 1]
Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2002-109661
[Patent Document 2]
JP 2002-163281 A
[0006]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In the conventional security system, when an abnormality is detected by a security sensor or a fire alarm, post-processing is performed for arresting a criminal or preventing evacuation and fire spread. Also, the security system disclosed in Patent Document 1 described above uses a network to surrounding buildings to notify the occurrence of an abnormality over a wide area, but it is a post process.
[0007]
On the other hand, crimes such as burial and arson are often carried out continuously in a similar manner in a relatively small area by the same criminal.
[0008]
However, with the conventional security system, the alarm is sounded immediately after the incident / disaster occurs, and the processing based on such criminal and fire trends can be handled by a bulletin through public institutions and the media, local fire brigades, etc. The current situation is that only human intervention, such as patrol, is performed. Since these methods involve humans, there are problems such as real-time performance, labor costs, and privacy.
[0009]
The present invention has been made in view of the above points, and an object of the present invention is to provide a security system and a security method for improving security performance by acquiring not only the monitoring target but also the surrounding information. There is.
[0010]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
According to one aspect of the present invention, security-related information storage means in which security-related information necessary for monitoring target security is stored, and storage control means for performing control to store security-related information in the security-related information storage means And information inquiry means for collecting information necessary for monitoring the monitoring target from information stored in the security-related information storage means, monitoring observation means for observing the monitoring target and performing face authentication of the monitoring target; The history information of the security related information from the past to the present stored in the security related information storage means is acquired through the information inquiry means, and the acquired history information and the current monitoring result by the monitoring observation means are obtained. Security-related processing execution means for performing security-related processing in accordance with the information collected by the information inquiry means. Control means for controlling the security-related processing execution means, and the security-related information includes information related to an incident that occurred in the vicinity of the monitoring target and information related to the occurrence time of the incident. The process execution means updates the number of times of acquisition of the corresponding face image when the time difference between the time when the monitoring and observation means acquires the face image and the occurrence time of the time generated around the monitoring target is within a predetermined time. A security system is provided that performs security-related processing according to the number of acquisitions.
[0011]
Further, according to one aspect of the present invention, a step of accumulating security related information necessary for security to be monitored in the security related information accumulating unit and a control for accumulating the security related information in the security related information accumulating unit are performed. A step of collecting information necessary for monitoring the monitoring target from information stored in the security-related information storage unit by an information inquiry unit, and a step of observing the monitoring target and performing face authentication of the monitoring target And history information of security related information from the past to the present stored in the security related information storage means is acquired via the information inquiry means, the acquired history information and the current monitoring result by the monitoring observation means, Performing security-related processing according to the security-related information, Information related to the incident that occurred around the monitored object and information related to the time when the incident occurred, and in the security-related processing, the time when the face authentication was performed, the time when the incident occurred around the monitored object, When the time difference between the two is within a predetermined time, a security method is provided, in which the number of observations of a person who has performed face authentication is updated and security-related processing is performed according to the number of observations.
[0012]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, a security system and a security method according to the present invention will be specifically described with reference to the drawings.
[0013]
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a first embodiment of a security system according to the present invention. The security system of FIG. 1 collects information necessary for monitoring the monitoring target 1 from the
[0014]
The processing of each unit shown in FIG. 1 is actually performed by a host computer possessed by a security company or the like. This type of host computer supervises security related information of a plurality of houses in a certain area.
[0015]
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining the schematic operation of this type of
[0016]
For example, if a fire occurs due to arson in the site of neighborhood A, or if a suspicious person is hesitant near neighborhood B, the residents in neighborhood A and B will have security functions such as fire alarms and door locks. Will increase the alert level.
[0017]
Such a change of the alert level in each house is also transmitted to the
[0018]
Each house that has received warning information from the
[0019]
The
[0020]
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating an example in which the alert level is changed according to the distance from the home. Each house can arbitrarily set a warning range based on the balance between high warning level and malfunction. FIG. 3 shows an example in which each of the houses B, C, and D sets a warning range (1) and a warning range (2) according to the distance from the residence.
[0021]
Depending on the type of crime, the warning method varies depending on the type of crime, such as increasing the sensitivity of the fire alarm in the case of arson and increasing the sensitivity of the door lock in the case of an empty nest, so depending on the target of the alert It is desirable to set a vigilance level.
[0022]
For example, if House A is arson or damaged by a vacant nest, House B is close to House A, so even for crimes that are set in the warning range (1), set the warning range (2). Raise the alertness of House B for crimes that are being held.
[0023]
On the other hand, since house A does not fall within the alert range of houses C and D, even if a crime or the like occurs in house A, houses C and D do not take measures to increase the alertness.
[0024]
In FIG. 3, the warning range is set to be circular, but the warning range may be set in consideration of roads, railways, and the like. That is, the warning level may be increased in a range that can be reached in a short time even if the distance is long, such as a railway or a main trunk road.
[0025]
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining a warning range for an apartment house. If multiple houses of the same type are placed close together, such as in a multifamily house or a detached house, if a crime occurs in a house, all neighboring houses will be warned in the same way. Is desirable.
[0026]
Therefore, in a housing complex or a detached house, the same alert level may be set even if the distance from the alert target is different.
[0027]
As described above, in the first embodiment, since a warning level is set according to a security target based on neighboring information and security-related information from the police / security company, the possibility of a crime or the like is detected in advance. Can be prevented and security performance can be improved.
[0028]
In the first embodiment described above, in order to maintain confidentiality, the encrypted security-related information is stored in the
[0029]
(Second Embodiment)
In the second embodiment, a security robot is arranged in each residence.
[0030]
FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of the second embodiment of the security system according to the present invention.
[0031]
The security system of FIG. 5 includes a
[0032]
The
[0033]
Specifically, information (name, face photo, affiliation, etc.) such as post office staff responsible for delivery in the area, courier staff, and staff responsible for meter reading of electricity, gas, water, etc. However, it is registered in the
[0034]
The contents of the
[0035]
Therefore, as one construction method, necessary data may be acquired from the general database 14 (information of the
As described above, according to the second embodiment, since it is necessary to authenticate whether or not the visitor is a suspicious person and then respond, the visitor can respond to the security robot with peace of mind even when the housekeeper is absent. Can be made. In addition, even if a problem occurs, it is possible to confirm exactly who the visitor was, so it becomes easier to confirm the fact and solve the problem later.
[0036]
Further, by storing not only local information but also public information in the
[0037]
(Third embodiment)
The third embodiment of the security system according to the present invention has the same block configuration as FIG. When the visitor presses the intercom, the
[0038]
Then, when an outpatient with a high suspicion point comes, the
[0039]
Also, in order to make it difficult to understand that you are away, you can use a kindergarten-like voice and language, and while you are working, call the user's mobile phone and try to connect to the interphone. If you can't connect and connect, you can answer with a machine voice such as "I'm told that nobody is allowed to do it now".
[0040]
Or, if the outpatient is a suspicious person registered in the neighborhood information database 11 (such as a wanted person), the resident is alerted if there is a resident, and if the alien is away, the police / security company is contacted. Make a report. The information is registered in the
[0041]
As described above, in the third embodiment, since the image and conversation of the visitor are registered in the
[0042]
(Fourth embodiment)
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of the fourth embodiment of the security system according to the present invention. The security system of FIG. 6 includes a crime disaster
[0043]
The crime disaster
[0044]
In FIG. 6, the crime disaster
[0045]
The wide-area crime disaster information is a data record that describes at least the date and time of occurrence of a crime or disaster, the occurrence area, and the manner of occurrence of crimes and disasters reported over a predetermined period of time in a wide area such as the whole of Japan. The date and time of occurrence is numerical data representing the date and time when the crime or disaster occurred, and the occurrence area is an area symbol string representing the streets of the prefectural municipalities where the crime or disaster occurred.
[0046]
The mode of occurrence is a symbol string indicating the type of crime or disaster (robbery, empty nest, arson, murder, fire, underfloor inundation, underfloor inundation, collapse due to an earthquake, etc.) The data includes a symbol string indicating the status (intrusion, picking, etc.) and a symbol string indicating the status (criminal runaway, resolution, ongoing, calming, etc.). Wide-area criminal disaster information takes into consideration the protection of privacy by not including detailed lot numbers and victim names as information for identifying the occurrence area.
[0047]
The
[0048]
The
[0049]
The current location information of the
[0050]
Based on the current location information periodically sent from the
[0051]
The area specified from the current position and the residence position is referred to as base area information, and a request for causing the base
[0052]
When the site
[0053]
When the risk-
[0054]
Moreover, the risk
[0055]
The
[0056]
It should be noted that reaction data of various sensors possessed by the
[0057]
When it is not necessary to multiplex records as described above, the site
[0058]
Thus, in the fourth embodiment, since the crime information and disaster information analyzed by the site
[0059]
(Fifth embodiment)
In the fourth embodiment, the crime risk at each site is obtained by the site
[0060]
Each of the
[0061]
The wide area
[0062]
The risk
[0063]
Thus, in the fifth embodiment, since risk analysis is performed by the public
[0064]
The security system described in the above-described embodiment may be configured by hardware or software. When configured by software, a program for realizing the function of the security system may be stored in a recording medium such as a floppy disk or a CD-ROM and read and executed by a computer. The recording medium is not limited to a portable medium such as a magnetic disk or an optical disk, but may be a fixed recording medium such as a hard disk device or a memory.
[0065]
Further, a program for realizing the function of the security system may be distributed via a communication line (including wireless communication) such as the Internet. Further, the program may be distributed in a state where the program is encrypted, modulated or compressed, and stored in a recording medium via a wired line such as the Internet or a wireless line.
[0066]
【The invention's effect】
As described above in detail, according to the present invention, since security-related processing is performed according to the history information of security-related information and the current monitoring result of the monitoring target, the possibility of a crime or a disaster is quickly detected. Appropriate response can be taken and security performance can be improved.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a first embodiment of a security system according to the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining the schematic operation of this type of
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of changing the alert level according to the distance from the home.
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining a warning range for an apartment house.
FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a second embodiment of a security system according to the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a fourth embodiment of a security system according to the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a fifth embodiment of a security system in which a risk analysis function is provided on a public network.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 Monitoring target
2 Security-related information storage
3 Information inquiry department
4 Monitoring and Observation Department
5 Security-related processing execution part
6 Control unit
7 Host computer
11 Neighborhood information database
12 network
13 Inquiry Department
14 General database
15 General database search section
16 Domestic security system
17 Corresponding processing section
Claims (7)
Translated fromJapanese前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段にセキュリティ関連情報を蓄積する制御を行う蓄積制御手段と、
前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積された情報の中から監視対象の監視に必要な情報を収集する情報照会手段と、
監視対象を観測して、監視対象の顔認証を行う監視観測手段と、
前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積されている過去から現在までのセキュリティ関連情報の履歴情報を前記情報照会手段を介して取得し、取得した履歴情報と前記監視観測手段による現在の監視結果とに応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うセキュリティ関連処理実行手段と、
前記情報照会手段で収集された情報に基づいて、前記セキュリティ関連処理実行手段を制御する制御手段と、を備え、
前記セキュリティ関連情報は、前記監視対象の周辺で発生した事件に関する情報と前記事件の発生時刻に関する情報とを含み、
前記セキュリティ関連処理実行手段は、前記監視観測手段が顔認証を行った時刻と、前記監視対象の周辺で発生した事件の発生時刻との時間差が所定時間以内の場合、顔認証を行った人間の観測回数を更新し、前記観測回数に応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うことを特徴とするセキュリティシステム。Security-related information storage means in which security-related information necessary for monitoring target security is stored;
Storage control means for performing control to store security related information in the security related information storage means;
Information inquiry means for collecting information necessary for monitoring the monitoring target from the information stored in the security related information storage means;
A monitoring observation means for observing themonitoring target and performing face recognition of the monitoring target ;
The history information of the security related information from the past to the present stored in the security related information storage means is acquired via the information inquiry means, and according to the acquired history information and the current monitoring result by the monitoring observation means Security-related processing execution means for performing security related processing;
Control means for controlling the security-related process execution means based on the information collected by the information inquiry means,
The security related information includes information related to an incident that occurred in the vicinity of the monitoring target and information related to the occurrence time of the incident,
The security-related processing execution unit is configured to determine whether or not the time difference between the time at which the monitoring and observation unit performs face authentication and the occurrence time of an incident that occurred in the vicinity of the monitoring target is within a predetermined time. A security systemthat updates the number of observations and performs security-related processing according to the number of observations .
前記制御手段は、セキュリティ上必要最小限のセキュリティ関連情報のみを前記情報照会手段に収集させることを特徴とする請求項1に記載のセキュリティシステム。The security related information storage means stores information obtained by encrypting security related information,
The security system according to claim1, wherein the control unit causes the information inquiry unit to collect only the minimum security-related information necessary for security.
前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段にセキュリティ関連情報を蓄積する制御を行うステップと、
前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積された情報の中から監視対象の監視に必要な情報を情報照会手段により収集するステップと、
監視対象を観測して、監視対象の顔認証を行うステップと、
前記セキュリティ関連情報蓄積手段に蓄積されている過去から現在までのセキュリティ関連情報の履歴情報を前記情報照会手段を介して取得し、取得した履歴情報と前記監視観測手段による現在の監視結果とに応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うステップと、を備え、
前記セキュリティ関連情報は、前記監視対象の周辺で発生した事件に関する情報と前記事件の発生時刻に関する情報とを含み、
前記セキュリティ関連処理では、顔認証を行った時刻と、前記監視対象の周辺で発生した事件の発生時刻との時間差が所定時間以内の場合、顔認証を行った人間の観測回数を更新し、前記観測回数に応じたセキュリティ関連処理を行うことを特徴とするセキュリティ方法。Storing security related information necessary for security of the monitoring target in the securityrelated information storing means ;
Performing control to store security related information in the security related information storage means;
Collecting information necessary for monitoring a monitoring target from information stored in the security-related information storage means by an information inquiry means;
Observing the monitoring target and performing face recognition of the monitoring target ;
The history information of the security related information from the past to the presentstored in the security related information storage means isacquired via the information inquiry means, and according to the acquired history information and the current monitoring resultby the monitoring observation means Performing security related processing,
The security related information includes information related to an incident that occurred in the vicinity of the monitoring target and information related to the occurrence time of the incident,
In the security-related processing, when the time difference between the time when the face authentication is performed and the time when the incident occurred around the monitoring target is within a predetermined time, the number of observations of the person who performed the face authentication is updated, A security method characterizedby performing security-related processing according to the number of observations .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002325881AJP3887597B2 (en) | 2002-11-08 | 2002-11-08 | Security system and security method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002325881AJP3887597B2 (en) | 2002-11-08 | 2002-11-08 | Security system and security method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004164022A JP2004164022A (en) | 2004-06-10 |
| JP3887597B2true JP3887597B2 (en) | 2007-02-28 |
Family
ID=32804970
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002325881AExpired - Fee RelatedJP3887597B2 (en) | 2002-11-08 | 2002-11-08 | Security system and security method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3887597B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006320024A (en)* | 2006-08-16 | 2006-11-24 | Intelligent Wave Inc | Unauthorized connection detection system |
| JP5059373B2 (en)* | 2006-10-20 | 2012-10-24 | 株式会社竹中工務店 | Crime risk assessment apparatus and crime risk assessment program |
| JP5253977B2 (en)* | 2008-11-18 | 2013-07-31 | ホーチキ株式会社 | Patrol information totaling apparatus and patrol information totaling method |
| JP5356050B2 (en)* | 2009-01-21 | 2013-12-04 | トヨタホーム株式会社 | Security system for subdivisions |
| JP2010286950A (en)* | 2009-06-10 | 2010-12-24 | Toyota Home Kk | Security system for housing complex |
| JP2012248100A (en)* | 2011-05-30 | 2012-12-13 | Toshiba Corp | Intruder detection level variable television receiver |
| JP2014178884A (en)* | 2013-03-14 | 2014-09-25 | Osaka Gas Co Ltd | Security system |
| CN106205022B (en)* | 2016-09-18 | 2018-07-24 | 瞿洪桂 | A kind of security system and method for home security |
| JP2021097397A (en)* | 2019-12-16 | 2021-06-24 | Assest株式会社 | Degree of risk determination program and system |
| JP6739119B6 (en)* | 2019-12-16 | 2020-09-09 | Assest株式会社 | Risk determination program and system |
| KR102131437B1 (en)* | 2020-03-09 | 2020-07-08 | (주)지인테크 | Adaptive video surveillance system and method |
| WO2024080126A1 (en)* | 2022-10-12 | 2024-04-18 | ソフトバンクグループ株式会社 | Information processing system, information processing device, control device, and program |
- 2002
- 2002-11-08JPJP2002325881Apatent/JP3887597B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004164022A (en) | 2004-06-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11527149B2 (en) | Emergency alert system | |
| US10257469B2 (en) | Neighborhood camera linking system | |
| US10854058B2 (en) | Emergency alert system | |
| US6542075B2 (en) | System and method for providing configurable security monitoring utilizing an integrated information portal | |
| CN102622861B (en) | Security monitoring alarm system based on geographical position and method therefor | |
| US20060244589A1 (en) | Method and system for an insurance auditor to audit a premise alarm system | |
| KR101841882B1 (en) | Unmanned Crime Prevention System and Method | |
| US20120297049A9 (en) | System and method for providing configurable security monitoring utilizing an integrated information system | |
| US20020143934A1 (en) | System and method for providing configurable security monitoring utilizing an integrated information system | |
| US20030117280A1 (en) | Security communication and remote monitoring/response system | |
| JP2017511544A (en) | Person authentication and tracking system | |
| JP3887597B2 (en) | Security system and security method | |
| US20220198913A1 (en) | Security systems and methods of operation | |
| JP4265744B2 (en) | Regional mutual crime prevention system | |
| KR100343045B1 (en) | A burglar alarm and method thereof by internet | |
| JP2005284861A (en) | Security system and security method | |
| JP2002024975A (en) | Security system | |
| JP4112481B2 (en) | Specific area crime prevention system | |
| CA3039210A1 (en) | Distributed home security system and method of responding to an alert condition therefrom | |
| JP2010527091A (en) | Security service provision method using the Internet | |
| US20070085671A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for providing a programmable chime for security system proximity alerts | |
| KR100863181B1 (en) | How to provide security service using the Internet | |
| KR20210004920A (en) | Safety check service method using smart device | |
| EP3959700A1 (en) | Monitoring system | |
| US12444294B2 (en) | Community security system using intelligent information sharing |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20040607 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20060630 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20060707 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20060905 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20061114 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20061127 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |