JP3730432B2 - Storage system, storage device, and storage data protection method - Google Patents
Storage system, storage device, and storage data protection methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3730432B2 JP3730432B2JP05472699AJP5472699AJP3730432B2JP 3730432 B2JP3730432 B2JP 3730432B2JP 05472699 AJP05472699 AJP 05472699AJP 5472699 AJP5472699 AJP 5472699AJP 3730432 B2JP3730432 B2JP 3730432B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- recording medium
- access device
- encrypted
- data
- information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription102
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000description6
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description5
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description5
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description5
- 238000013500data storageMethods0.000description4
- 238000005192partitionMethods0.000description2
- 238000012217deletionMethods0.000description1
- 230000037430deletionEffects0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000description1
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Signal Processing For Digital Recording And Reproducing (AREA)
- Storage Device Security (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、記録媒体を用いた記憶システム、記憶装置及び記憶データ保護方法に関し、特に、データを暗号化して記憶する記憶システム、記憶装置及び記憶データ保護方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
コンピュータ等によりアクセス(データの読み書き及び消去)可能な記録媒体として、ハードディスク装置や、MO(Magneto-Optical disk)や、フラッシュメモリが用いられている。これらの記録媒体は、データの保存や複数のコンピュータ間のデータの移転などのために利用されている。
これらの記録媒体に記録されたデータを不正なアクセスから保護するため、従来は、データを暗号化した上で記憶するようにしていた。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかし、データを暗号化して記憶する記録媒体にアクセスするためには、そのデータを復号化する必要がある。
このため、このような記録媒体にアクセスするコンピュータ等は、ユーザが所有するすべての記録媒体に記憶されているデータの復号化を行うことを可能とするために、記録媒体を交換する度にプログラムをインストールし直したり、あるいは、ユーザが所有する各記録媒体に記憶されているデータを復号化するために必要なプログラムを予め記憶しておく必要があった。
【0004】
従って、コンピュータ等の管理やアクセスのための操作が煩雑になり、また、復号化のためのプログラムによりハードディスク装置等の外部記憶装置の記憶領域の効率的な利用が妨げられていた。
【0005】
この発明は上記実状に鑑みてなされたもので、既存の装置に加えるべき変更が少なく、簡単な操作で、データを暗号化して記憶する記録媒体へのアクセスを処理で行うことができる記憶システム、記憶装置及び記憶データ保護方法を提供することを目的とする。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するため、本発明の第1の観点にかかる記憶システムは、
記録媒体と、アクセス装置と、前記記録媒体に接続され、前記アクセス装置に着脱可能に装着される記録媒体コントローラとを備え、
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶する手段を備え、
前記記録媒体コントローラは、
前記記録媒体より前記暗号処理プログラムを取得して前記アクセス装置に供給する手段と、
前記アクセス装置から供給される暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記アクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定手段と、
前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体より前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して前記アクセス装置に供給する手段と、
前記アクセス装置から供給される読み出し指示に従って、前記記録媒体から前記暗号データを取得して前記アクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御手段と、
前記アクセス装置から供給される書き込み指示に従い、前記アクセス装置が生成した当該暗号データを前記アクセス装置から取得して前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御手段と、を備え、
前記読み出し制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記書き込み指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記アクセス装置は、
前記記録媒体コントローラより前記暗号処理プログラムを取得するプログラム取得手段と、
操作者の操作に従ってパスワードを取得する手段と、
前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムが表す処理を実行することにより、前記パスワードを暗号化して前記暗号化パスワードを生成し、当該暗号化パスワードを前記記録媒体コントローラに供給する手段と、
前記記録媒体コントローラが供給した前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号化ブート情報を復号化して前記ブート情報を復元する手段と、
前記読み出し制御手段に、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定してデータの読み出しを行うことを指示する前記読み出し指示を供給し、当該読み出し制御手段が供給した前記暗号データを取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号データを復号化する手段と、
前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を暗号化して前記暗号データを生成し、自己が生成した当該暗号データを前記記録媒体に格納するため、前記書き込み制御手段に、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法によるデータの書き込みを行うことを指示する前記書き込み指示を供給する手段と、を備える、
ことを特徴とする。
【0007】
このような記憶システムによれば、アクセス装置は暗号処理プログラムを読み出して実行することにより、暗号データの復号化や暗号データの生成と記録媒体への格納を行う。従って、アクセス装置の管理や操作は簡単になる。また、既存のコンピュータは、実質的に変更を加えられることなくアクセス装置として機能する。
【0008】
また、記録媒体へのアクセスのための処理がアクセス装置と記録媒体コントローラにより分担され、アクセス装置の処理の負担が軽減される。
【0009】
また、アクセス装置が記録媒体にアクセスするのに先立って、操作者の認証や、記録媒体の認証が行われる。この結果、記録媒体への不正なアクセスが防止される。
【0010】
また、本発明の第2の観点にかかる記憶システムは、
記録媒体と、アクセス装置と、前記記録媒体に接続され、前記アクセス装置に着脱可能に装着される記録媒体コントローラと、を備え、
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶する手段を備え、
前記記録媒体コントローラは、
前記記録媒体より前記暗号処理プログラムを取得するプログラム取得手段と、
操作者の操作に従ってパスワードを取得する手段と、
前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムが表す処理を実行することにより、前記パスワードを暗号化して暗号化パスワードを生成し、当該暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記アクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定手段と、
前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体より前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号化ブート情報を復号化して前記ブート情報を復元する手段と、
前記アクセス装置から供給される、前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定した読み出し指示に従って、前記記録媒体から、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記暗号データを取得し、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより当該暗号データを復号化して前記アクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御手段と、
前記アクセス装置が供給する、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記アクセス装置から取得し、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することによりその情報を暗号化して前記暗号データを生成し、生成した暗号データを、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御手段と、を備え、
前記読み出し制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記アクセス装置から取得することを拒絶し、
前記アクセス装置は、
前記読み出し制御手段に前記読み出し指示を供給し、前記読み出し制御手段が供給する復号化された前記暗号データを取得する手段と、
前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を供給する手段と、を備える、
ことを特徴とする。
【0011】
このような記憶システムによれば、記録媒体コントローラが暗号処理プログラムを読み出して実行することにより、暗号データの復号化や暗号データの生成と記録媒体への格納を行う。従って、アクセス装置の管理や操作は簡単になる。また、既存のコンピュータは、実質的に変更を加えられることなくアクセス装置として機能する。
【0012】
また、アクセス装置が記録媒体にアクセスするのに先立って、操作者の認証や、記録媒体の認証が行われる。この結果、記録媒体への不正なアクセスが防止される。
【0013】
また、本発明の第3の観点にかかる記憶装置は、
記録媒体と、記録媒体コントローラと、を備える記憶装置であって、
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶する手段を備え、
前記記録媒体コントローラは、外部のアクセス装置に着脱可能に装着されるものであって、
前記記録媒体より前記暗号処理プログラムを取得するプログラム取得手段と、
操作者の操作に従ってパスワードを取得する手段と、
前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムが表す処理を実行することにより、前記パスワードを暗号化して暗号化パスワードを生成し、当該暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記外部のアクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定手段と、
前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体より前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号化ブート情報を復号化して前記ブート情報を復元する手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置から供給される、前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定した読み出し指示に従って、前記記録媒体から、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記暗号データを取得し、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより当該暗号データを復号化して前記外部のアクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置が供給する、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記外部のアクセス装置から取得し、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することによりその情報を暗号化して前記暗号データを生成し、生成した暗号データを、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御手段と、を備え、
前記読み出し制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記外部のアクセス装置から取得することを拒絶する、
ことを特徴とする。
【0014】
このような記憶装置によれば、外部のアクセス装置は暗号処理プログラムを読み出して実行することにより、暗号データの復号化や暗号データの生成と記録媒体への格納を行う。従って、外部のアクセス装置の管理や操作は簡単になる。また、既存のコンピュータは、実質的に変更を加えられることなく外部のアクセス装置として機能する。
【0015】
また、アクセス装置が記録媒体にアクセスするのに先立って、操作者の認証や、記録媒体の認証が行われる。この結果、記録媒体への不正なアクセスが防止される。
【0016】
また、本発明の第4の観点にかかる記憶装置は、
記録媒体と、記録媒体コントローラと、を備える記憶装置であって、
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶する手段を備え、
前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記暗号処理プログラムを取得して実行する外部のアクセス装置に着脱可能に装着されるものであって、
前記記録媒体が記憶する前記暗号処理プログラムを前記外部のアクセス装置に取得させるプログラム供給手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置が前記暗号処理プログラムに従ってパスワードを暗号化することにより生成した暗号化パスワードを取得し、取得した前記暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記外部のアクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定手段と、
前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体が記憶する前記暗号化ブート情報を前記外部のアクセス装置に取得させる手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置から、前記暗号化ブート情報より復元されたブート情報が指定する手法により前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定してデータの読み出しを行うことを指示する読み出し指示を供給されたとき、当該読み出し指示に従い、前記記録媒体から前記暗号データを取得して前記外部のアクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置が前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を暗号化して生成した前記暗号データを前記外部のアクセス装置から取得して、当該暗号データを、前記暗号化ブート情報より復元されたブート情報が指定する手法によるデータの書き込みを行うことを指示するものとして前記外部のアクセス装置より供給される書き込み指示に従って、前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御手段と、を備え、
前記読み出し制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記暗号データを前記外部のアクセス装置から取得することを拒絶する、
ことを特徴とする。
【0017】
このような記憶装置によれば、記録媒体コントローラは暗号処理プログラムを読み出して実行することにより、暗号データの復号化や暗号データの生成と記録媒体への格納を行う。従って、外部のアクセス装置の管理や操作は簡単になる。また、既存のコンピュータは、実質的に変更を加えられることなく外部のアクセス装置として機能する。
【0018】
また、アクセス装置が記録媒体にアクセスするのに先立って、操作者の認証や、記録媒体の認証が行われる。この結果、記録媒体への不正なアクセスが防止される。
【0019】
また、本発明の第5の観点にかかる記憶データ保護方法は、
記録媒体と、外部のアクセス装置に着脱可能に装着される記録媒体コントローラと、を備える記憶装置に記憶されるデータを保護するための記憶データ保護方法であって、
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶し、
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記記録媒体より前記暗号処理プログラムを取得するプログラム取得ステップと、
前記記録媒体コントローラが、操作者の操作に従ってパスワードを取得するステップと、
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記プログラム取得ステップで取得した暗号処理プログラムが表す処理を実行することにより、前記パスワードを暗号化して暗号化パスワードを生成し、当該暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記外部のアクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定ステップと、
前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記記録媒体より前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号化ブート情報を復号化して前記ブート情報を復元するステップと、
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記外部のアクセス装置から供給される、前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定した読み出し指示に従って、前記記録媒体から、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記暗号データを取得し、前記プログラム取得ステップで取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより当該暗号データを復号化して前記外部のアクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御ステップと、
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記外部のアクセス装置が供給する、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記外部のアクセス装置から取得し、前記プログラム取得ステップで取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することによりその情報を暗号化して前記暗号データを生成し、生成した暗号データを、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御ステップと、より構成されており、
前記読み出し制御ステップで前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御ステップで前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記外部のアクセス装置から取得することを拒絶する、
ことを特徴とする。
【0020】
このような記憶データ保護方法によれば、記録媒体コントローラが暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、暗号データの復号化や暗号データの生成と、記録媒体への暗号データの格納を行う。従って、暗号データへのアクセスを必要としている外部の装置の管理や操作は簡単になる。また、既存のコンピュータは、実質的に変更を加えられることなく、記録媒体コントローラにより復号化された暗号データを取得したり、記録媒体コントローラに記録媒体への暗号データの格納を行わせたりする。
また、本発明の第6の観点にかかる記憶データ保護方法は、
記録媒体と、外部のアクセス装置に着脱可能に装着される記録媒体コントローラと、を備える記憶装置に記憶されるデータを保護するための記憶データ保護方法であって、
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶し、
前記外部のアクセス装置は、前記暗号処理プログラムを取得して実行するものであって、
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記記録媒体が記憶する前記暗号処理プログラムを前記外部のアクセス装置に取得させるプログラム供給ステップと、
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記外部のアクセス装置が前記暗号処理プログラムに従ってパスワードを暗号化することにより生成した暗号化パスワードを取得し、取得した前記暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記外部のアクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定ステップと、
前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記記録媒体が記憶する前記暗号化ブート情報を前記外部のアクセス装置に取得させるステップと、
前記外部のアクセス装置から、前記暗号化ブート情報より復元されたブート情報が指定する手法により前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定してデータの読み出しを行うことを指示する読み出し指示を供給されたとき、前記記録媒体コントローラが、当該読み出し指示に従い、前記記録媒体から前記暗号データを取得して前記外部のアクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御ステップと、
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記外部のアクセス装置が前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を暗号化して生成した前記暗号データを前記外部のアクセス装置から取得して、当該暗号データを、前記暗号化ブート情報より復元されたブート情報が指定する手法によるデータの書き込みを行うことを指示するものとして前記外部のアクセス装置より供給される書き込み指示に従って、前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御ステップと、より構成されており、
前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し制御ステップで前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記書き込み制御ステップで前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記暗号データを前記外部のアクセス装置から取得することを拒絶する、
ことを特徴とする。
【0021】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、この発明の実施の形態を、フラッシュメモリを備えたメモリカードにアクセスするメモリカードシステムを例とし、図面を参照して説明する。
【0022】
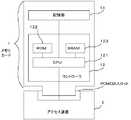
図1は、この発明の実施の形態にかかるメモリカードシステムの物理的構成を示すブロック図である。図示するように、このメモリカードシステムは、メモリカード1と、アクセス装置2とを備える。
メモリカード1は、アクセス装置2が備えるスロットを介して、アクセス装置2に着脱可能に装着される。
【0023】
メモリカード1は、記憶部11及びコントローラ12を備える。記憶部11及びコントローラ12は互いに接続されている。
【0024】
記憶部11は、例えば、EEPROM(Electrically Erasable/Programable Read Only Memory)等を備える。
記憶部11は、コントローラ12が行うアクセスに応答し、アクセス装置2から供給されたデータの記憶と、記憶しているデータのアクセス装置2への供給と、記憶しているデータの消去とを行う。
【0025】
記憶部11が有する記憶領域は、例えば、図2に示すように8192個のページからなり、各々のページは528バイトの記憶容量を有する。ページには連続的に0から8191までのページアドレスが付与され、各ページに含まれるメモリセルには、連続的に0から527までの番地が与えられている。
【0026】
各ページは、先頭から16ページ単位で1つのブロックを構成する。各ブロックは8キロバイトの記憶容量を有し、記憶領域全体は、512個のブロックから構成され、先頭から連続的に0から511までの物理ブロックアドレスを与えられている。
【0027】
また、各ページは、図示するように、先頭から512バイトの領域を占めるデータ領域と、末尾16バイトを占める冗長部とから構成される。
データ領域には、本来のデータ(アクセス装置2から供給され書き込まれるデータや、アクセス装置2に供給される対象となるデータ)が格納され、冗長部には、本来のデータの内容が破壊されていないことを確認するためのエラーチェックコード等が格納される。
【0028】
また、各々のブロックに属する各ページの冗長部には、そのブロックに割り当てられている論理ブロックアドレスの値が格納される。
論理ブロックアドレスは、記憶部11が後述する動作により読み書きされるときに、コントローラ12により、データ読み書きの単位として認識される単位である。論理ブロックアドレスが割り当てられているブロックの総量は、記憶部11が物理的に備えるブロックの総量より小さい所定量、例えば500個である。
【0029】
記憶部11は、メモリカード1のコントローラ12より、特定のブロックのデータを消去するよう指示されると、当該ブロックに含まれるすべてのメモリセルの記憶内容をリセットする(例えば、記憶部11がNAND型のフラッシュメモリからなる場合は、各メモリセルの記憶値を「1」とする)。
【0030】
そして、図2に示すように、記憶部11の記憶領域を構成する各ブロックのうち先頭から所定の個数のブロックはカード固有情報記憶領域を形成し、その他の各ブロックは一般データ記憶領域を形成する。
【0031】
カード固有情報記憶領域の記憶内容は、実質的にみて、外部からのアクセスによっては更新することができない。従って、アクセス装置2及びコントローラ12は、記憶部11に格納されている情報の内容を更新することを実質的に禁止される。
【0032】
カード固有情報記憶領域には、メモリカード1の製造者等により、予め暗号化ブート情報、暗号鍵、認証用ドライバ、暗号化パスワード及び暗号化固定データが格納されている。
【0033】
暗号化ブート情報は、記憶部11の記憶領域の大きさや構造を表すパラメータや、データの読み書きの手法や速度を指定するパラメータを含むデータであるブート情報を、暗号鍵を用いて暗号化したものである。
【0034】
暗号鍵は、アクセス装置2が、一般データ記憶領域に格納されている後述の一般データを復号化する後述の処理を行うために用いるものである。また、この暗号鍵は、アクセス装置2が、一般データ記憶領域に一般データとして格納する対象のデータを暗号化する後述の処理を行うためにも用いられる。
認証用ドライバは、アクセス装置2が、暗号鍵を用いて一般データの復号化及びデータの暗号化を行う上述の処理を表すプログラムデータである。
【0035】
暗号化パスワードは、このメモリカードシステムが実行する後述の初期処理において、このメモリカードシステムのユーザが正規のユーザであるか否かを認証するために用いるパスワードを、暗号鍵を用いて暗号化したものである。
暗号化固定データは、アクセス装置2が記憶する所定の固定データを暗号鍵を用いて暗号化したものである。暗号化固定データは、上述の初期処理において、メモリカード1が正規に製造されたものであるか否かを認証するために用いられる。
【0036】
一般データ記憶領域には、アクセス装置2が実行する処理を表すプログラムデータのうち認証用ドライバ以外のものや、アクセス装置2が実行する処理において参照されるデータを含む一般データが格納される。
ただし、一般データは、カード固有情報記憶領域に格納されている暗号鍵を用いて暗号化された状態で格納されている。そして、暗号化されている一般データは、アクセス装置2により読み出された後、当該暗号鍵を用いてアクセス装置2により復号化される。
【0037】
コントローラ12は、図1に示すように、CPU(Central Processing Unit)121と、ROM(Read Only Memory)122と、SRAM(Static Random Access Memory)123とを備えている。
CPU121は、ROM122、SRAM123及び記憶部11に接続されており、また、アクセス装置2が備えるPCMCIAスロットを介してアクセス装置2に着脱可能に接続されている。
【0038】
CPU121は、コントローラ12の製造者等によって予めROM122に格納されているプログラムの処理に従って、後述する処理を行う。そして、CPU121は、アクセス装置2から供給される命令を取得すると、その命令を実行する。CPU121が実行する命令には、記憶部11にアクセスする命令が含まれる。
ROM122には、予め、コントローラ12の製造者等によって、CPU121が実行する上述の処理を表すプログラムデータが格納されている。
【0039】
SRAM123は、CPU121の作業領域として用いられ、また、CPU121が後述する処理により作成するBSI(Block Search Index)及びBPT(Block Pointer Table)を記憶する。
【0040】
BSIは、記憶部11の各ブロックのいずれが空きブロック(すなわち、リセットされた状態にあるブロック)であるかを表す情報を格納する。
BSIは、コントローラ12の後述する処理に従って作成され、SRAM123に格納される。
【0041】
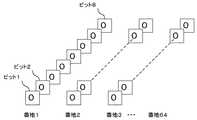
記憶部11のブロックの総数が512個であるときのBSIの構造の一例を図3に示す。図示するように、BSIは、64バイトのデータからなり、先頭のビットから順に、ブロック0からブロック511に1対1に対応し、対応するブロックが空きブロックであるとき”1”、空きブロックでないとき”0”を格納する。
【0042】
BPTは、後述する論理ブロックアドレス及び物理ブロックアドレスの対応関係を示す情報を格納するものであり、BSIが作成される度に後述する処理に従って作成され、SRAM123に格納される。
BPTは、SRAM123の記憶領域中の所定の論理的位置を占め、各々の論理ブロックアドレスに対応付けられた物理ブロックアドレスを記憶するための記憶領域を備える。
【0043】
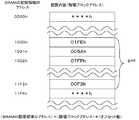
具体的には、BPTは、例えば図4に示すデータ構造を有する。
すなわち、例えば論理ブロックアドレスの総数が500個である場合、BPTは、図示するように、先頭から1ワード毎に付されたアドレスが1000h〜11F3hである、合計500ワードの記憶領域を備える。
【0044】
そして、BPTを形成する記憶領域に付された各々のアドレスは、論理ブロックアドレスと、BPTを形成する記憶領域に付されたアドレスの最小値(オフセット値)との和に等しい。そして、各々のアドレスを付された1ワードの記憶領域に格納されている内容は、当該アドレスが示す論理ブロックアドレスに対応付けられているブロックの物理ブロックアドレスを表す。
【0045】
具体的には、例えば図4に示すように、アドレス1001hを付された記憶領域に値”005Ah”が格納されているとする。この場合、オフセット値が1000hであれば、物理ブロックアドレスが005Ahであるブロックには、論理ブロックアドレスとして0001hが対応付けられている。
【0046】
ただし、各々のアドレスを付された記憶領域に格納されている内容が所定の値を表す場合(例えば、図示するように、値”07FFh”を表す場合)は、その値を格納している記憶領域のアドレスが示す論理ブロックアドレスには、物理ブロックアドレスが対応付けられていないことを表す。
【0047】
アクセス装置2は、上述の通りスロットを備える。このスロットは、例えば、PCMCIAバスを中継するためのPCMCIAスロットからなる。アクセス装置2は、OS及びアクセス用ドライバを表すプログラムデータを記憶し、電源投入後、OSを実行する。そして、スロットにメモリカード1が装着されたことを検知すると、OSの処理に従って、メモリカード1より認証用ドライバを読み込んで起動する。
【0048】
認証用ドライバの処理を行うアクセス装置2は、メモリカード1から暗号鍵及び暗号化ブート情報を読み込み、読み込んだ暗号鍵を用いて暗号化ブート情報を復号化することによりブート情報を復元する。そして、認証用ドライバの処理を行うアクセス装置2は、アクセス用ドライバを呼び出して、復元されたブート情報を、アクセス用ドライバの処理に引き渡す。
【0049】
アクセス用ドライバの処理を行うアクセス装置2は、コントローラ12に上述した命令を供給したり、記憶部11に書き込む対象のデータを供給して、コントローラ12に、記憶部11へのデータの書き込みを行わせる。そして、自らが供給した命令に従ってコントローラ12が記憶部11から読み出して自らに供給したデータを、コントローラ12より取得する。
すなわち、アクセス装置2は、コントローラ12を介して記憶部11へのアクセスを行う。
【0050】
また、アクセス装置2は、ユーザの操作に従って当該ユーザよりパスワードの供給を受けるための入力手段を備え、また、上述の固定データを記憶する。固定データは、上述の目的のために特に作成されたものである必要はなく、このメモリカードシステムを正規に構成するためのアクセス装置2が記憶している任意のデータであればよく、例えば、OSのプログラムの一部であればよい。
【0051】
(動作)
次に、このメモリカードシステムの動作を、図5を参照して説明する。
図5は、初期処理を示すフローチャートである。
【0052】
(初期処理)
アクセス装置2のスロットにメモリカード1が装着された状態でアクセス装置2が起動し、アクセス装置2がOSの実行を開始すると、このメモリカードシステムは、図5に示す初期処理を実行する。
【0053】
初期処理を開始すると、まず、メモリカード1のコントローラ12のCPU121が、記憶部11のカード固有情報記憶領域より認証用ドライバを読み出してアクセス装置2に供給する(ステップS101)。アクセス装置2は、認証用ドライバを供給されると、その認証用ドライバが表す処理を実行する。
【0054】
なお、アクセス装置2は、自己に供給された認証用ドライバを不揮発性の記憶領域に格納する必要はなく、例えば、アクセス装置2が、CPUと、RAM(Random Access Memory)を備える主記憶部と、を備えるものである場合は、当該RAMの記憶領域に格納すれば足りる。
【0055】
アクセス装置2は、認証用ドライバの処理を開始すると、ユーザがアクセス装置2を操作して、自己にパスワードを供給するのを待機する(ステップS102)。そして、パスワードが供給されると、記憶部11のカード固有情報記憶領域より暗号鍵を読み出し、その暗号鍵を用いて、自己に供給されたパスワードを暗号化し、暗号化済みのパスワードをCPU121に供給する(ステップS103)。
【0056】
CPU121は、暗号化済みのパスワードを供給されると、記憶部11のカード固有情報記憶領域より暗号化パスワードを読み出し、読み出された暗号化パスワードが、アクセス装置2から供給された暗号化済みのパスワードと実質的に一致するか否かを判別する(ステップS104)。
【0057】
そして、一致しないと判別すると、アクセス装置2に、認証の失敗を表すメッセージを供給する(ステップS105)。当該メッセージを供給されたアクセス装置2は、正常なメモリカード1が自己のスロットに装着されていないものとして初期処理を終了させる。初期処理を終了後、アクセス装置2が再びメモリカード1が装着されたことを検知すると、このメモリカードシステムは、初期処理をステップS101より実行する。
【0058】
一方、一致すると判別すると、CPU121は、カード固有情報記憶領域より暗号化固定データを読み出して、アクセス装置2へ供給する(ステップS106)。アクセス装置2は、暗号化固定データを供給されると、その暗号化固定データを復号化し(ステップS107)、自己が記憶する固定データと実質的に一致するか否かを判別する(ステップS108)。
【0059】
そして、一致しないと判別すると、アクセス装置2は、正常なメモリカード1が自己のスロットに装着されていないものとして初期処理を終了させる。一致すると判別すると、認証の成功をCPU121に通知する(ステップS109)。
【0060】
CPU121は、認証の成功を通知されると、SRAM123の記憶領域のうち、BPT及びBSIを格納する部分の初期化を行う(ステップS110)。
【0061】
ステップS110においてCPU121は、具体的には、SRAM123の記憶領域のうちBPTを格納する部分について、1ワード毎に付された上述のアドレスにより示される各区画に、物理ブロックアドレスが対応付けられていないことを示す所定の値(例えば、上述の値”07FFh”)を書き込む。また、BSIを格納する部分のビットの論理値を、すべて”0”とする。
【0062】
次に、CPU121は、記憶部11の各ブロックのうち、未だ論理ブロックアドレスを読み出されていないブロックであって最も物理ブロックアドレスが若いものを特定し、特定されたブロックに属するページの冗長部より、論理ブロックアドレスを読み出す(ステップS111)。
【0063】
そして、CPU121は、BPTを格納するためのSRAM123の記憶領域中、記憶部11から読み出した論理ブロックアドレスに相当するアドレスを付された部分に、その論理ブロックアドレスを読み出したブロックの物理ブロックアドレスを書き込む(ステップS112)。これにより、BPTに、物理ブロックアドレスと論理ブロックアドレスとの対応付けを示す新たな情報が追加される。
【0064】
次に、CPU121は、ステップS111で最後に論理ブロックアドレスを読み出したブロックが空きブロックであるか否かを判別する(ステップS113)。具体的には、ステップS111で最後に論理ブロックアドレスを読み出したブロックに属するページの冗長部に、所定の形式の空きブロックコードが格納されているか否かを判別する。
【0065】
そして、空きブロックでないと判別すると、CPU121は、処理をステップS115に移す。一方、空きブロックであると判別すると、CPU121は、その空きブロックを示す物理ブロックアドレスから、BSIを格納するためのSRAM123の記憶領域中、その物理ブロックアドレスを示すビットの位置を算出し、そのビットの論理値を”1”に書き換え(ステップS114)、処理をステップS115に移す。
【0066】
ステップS115で、CPU121は、ステップS111で論理ブロックアドレスを読み出したブロックの次のブロックが存在するか否かを判別し、存在すると判別すると、処理をステップS111に戻す。存在しないと判別すると、初期処理を正常終了する。
以上説明した初期処理により、メモリカード1−アクセス装置2相互の認証と、アクセス装置2による暗号化ブート情報の読込とが行われ、CPU121によりBSI及びBPTが作成される。
【0067】
(一般データ読み出しの処理)
ステップS115において初期処理が正常終了して以降、メモリカード1のCPU121は、アクセス装置2より、記憶部11へのアクセスの指示を受け付ける。
アクセス装置2は、CPU121に記憶部11からの一般データの読み出しを指示するときは、一般データの読み出しを指示する命令と、一般データを読み出す対象となる記憶領域を指定する情報とを、CPU121に供給する。
【0068】
一般データを読み出す対象の記憶領域を指定する情報としては、具体的には、例えば、記憶部11の記憶領域の大きさに相当する大きさの仮想の記憶領域を、シリンダ、ヘッド及びセクタの3段階の階層に従って区分した場合の各区画を表すCHS(Cylinder-Head-Sector)形式の情報が用いられる。なお、アクセス装置2は、例えば、自己が取得したブート情報から、記憶部11の記憶領域の大きさを取得すればよい。
【0069】
ただし、一般データを読み出す対象の記憶領域を指定する情報の形式は任意であり、例えば、記憶部11の記憶領域の大きさに相当する大きさの仮想の記憶領域を512バイト毎の区画に分け、各区画に0から始まる連番を付した場合の当該連番、すなわちLBA(Logic Block Address)形式の情報を用いてもよい。
【0070】
一般データの読み出しを指示する命令と、一般データを読み出す対象の記憶領域を指定する情報とを供給されたCPU121は、記憶領域を特定する情報を変換して、以下に(A)及び(B)として表す情報を作成する。
【0071】
すなわち、CPU121は、
(A)指定された記憶領域が、記憶部11の記憶領域のうち、いずれの論理ブロックアドレスを付されたブロックに相当するか、を表す情報と、
(B)指定された記憶領域が、(A)の情報により表されるブロックの中のどの位置にあるページに相当するか、を表す情報と、
を作成する。なお、(A)の情報が示すブロックの数は1個に限られず、(B)の情報が示すページの数も1個に限られない。
【0072】
次に、CPU121は、(A)の情報が示す論理ブロックアドレスに対応付けられている物理ブロックアドレスを、BPTより索出する。そして、索出された物理ブロックアドレスと、上述の(B)の情報とより、読み出す対象のページを特定し、そのページより一般データを読み出す。
【0073】
読み出された一般データはアクセス装置2に供給される。アクセス装置2は、自己に供給された一般データを認証用ドライバの処理に引き渡し、認証用ドライバに一般データの復号化を指示する。認証用ドライバを実行するアクセス装置2は、初期処理のステップS103で読み出した暗号鍵を用いて、自己に供給された一般データを復号化し、復号化された一般データを、自己に一般データを供給した処理(すなわち、アクセス用ドライバの処理)に引き渡す。
以上説明した処理により、暗号化されている一般データが記憶部11から読み出され、復号化される。
【0074】
(データ書き込みの処理)
また、初期処理の正常終了後において、アクセス装置2は、記憶部11へのデータの書き込みを指示するときは、まず、書き込み対象のデータを認証用ドライバの処理に引き渡し、当該データの暗号化を指示する。認証用ドライバを実行するアクセス装置2は、ステップS103で読み出した暗号鍵を用いて当該データを暗号化し、暗号化された書き込み対象のデータを、自己に一般データを供給した処理に引き渡す。
【0075】
そして、アクセス装置2は、CPU121に、暗号化された書き込み対象のデータと、自己が取得したブート情報が示す手法による記憶部11への一般データの書き込みを指示する命令と、データを書き込む対象となる記憶領域を指定する情報とを供給する。
【0076】
データの書き込みを指示する命令と、暗号化された書き込み対象のデータと、データを書き込む対象となる記憶領域を指定する情報とを供給されたCPU121は、記憶領域を特定する情報を変換して、上述の(A)及び(B)の情報を作成する。
そして、CPU121は、BSIを検索して、(A)の情報が示すブロックの個数と同数の空きブロックの物理ブロックアドレスを索出する。
【0077】
次に、CPU121は、(A)の情報が示す論理ブロックアドレスに対応付けられている物理ブロックアドレスをBPTより索出する。そして、BPTより索出された物理ブロックアドレスを付された各ブロックに属するページを、(B)の情報が示すページ(書き込み該当ページ)と、その他のページ(非該当ページ)とに分類する。
【0078】
ただし、(A)の情報が示す論理ブロックアドレスに対応付けられている物理ブロックアドレスが存在しない場合、CPU121は、BSIより索出された物理ブロックアドレスが示すブロックに、アクセス装置2より供給された書き込み対象のデータを書き込む。
そして、CPU121はBSIの内容を変更し、変更後のBSIの内容が、データが書き込まれたブロックが空きブロックであることを表さないようにする。また、CPU121は、BPTのうち、物理ブロックアドレスが対応付けられていないことを示す情報が書き込まれている記憶領域に、新たにデータを書き込まれたブロックの物理ブロックアドレスを書き込む。そして、BSI及びBPTの内容の変更が完了すると、処理を終了する。
【0079】
一方、(A)の情報が示す論理ブロックアドレスに対応付けられている物理ブロックアドレスが存在する場合、CPU121は、索出された物理ブロックアドレスにより示されるブロックと、(A)の情報が示す各ブロックとを1対1に対応付ける。そして、(A)の情報が示す各々のブロックに属するページに記憶されている内容を、当該ブロックに対応付けられたブロック中、先頭からの順番が当該ページと同一であるページに転記する。
ただし、書き込み該当ページであると分類されたページの内容は転記せず、そのページの内容に代えて、アクセス装置2から供給された書き込み対象のデータのうち、その書き込み該当ページに書き込むべきものとして供給された部分を書き込む。
【0080】
また、CPU121は、BSIより索出された各々の空きブロックへのデータの書き込みが完了する毎に、その空きブロックに対応付けられたブロックをリセットし、リセットしたブロックに属するページの冗長部に、空きブロックコードを書き込む。
【0081】
そして、CPU121はBPTにアクセスし、変更後のBPTのうち、リセットされたブロックの物理ブロックアドレスが格納されている記憶領域に、書き込みが完了したブロックの物理ブロックアドレスを上書きする。これにより、リセットされたブロックに従前対応付けられていた論理ブロックアドレスは、新たに書き込みが完了したブロックに対応付けられる。
また、CPU121はBSIにもアクセスし、変更後のBSIの内容が、書き込みが完了したブロックが空きブロックであることを表さないようにし、リセットされたブロックが空きブロックであることを表すようにする。
【0082】
そして、CPU121は、BSIより索出されたすべての空きブロックへのデータの書き込みと、BSI及びBPTの変更とが終了すると、書き込みの処理を終了する。
以上説明した処理により、アクセス装置2から供給されたデータが、暗号化された状態で記憶部11に格納される。また、BSIの内容が、データの書き込みの結果新たに生じた空きブロック及び消滅した空きブロックを示すよう変更される。一方、BPTの内容も変更され、新たに空きブロックとなったブロックに割り当てられていた論理ブロックアドレスが、そのブロックに従前から記録されていたデータの転記を受けたブロックに新たに割り当てられる。
【0083】
(データ消去の処理)
また、アクセス装置2は、記憶部11に格納されているデータを、同一ブロックに格納されているもの毎に一括して消去するときは、データの消去を指示する命令と、消去の対象となるデータがあるブロックを示す論理ブロックアドレスとを、CPU121に供給する。
【0084】
CPU121は、データの消去を指示する命令と、消去の対象となるデータがあるブロックを示す論理ブロックアドレスとを供給されると、その論理ブロックアドレスに対応付けられている物理ブロックアドレスを、BPTより索出する。そして、CPU121は、索出された物理ブロックアドレスにより示されるブロックをリセットし、リセットしたブロックに属するページの冗長部に、空きブロックコードを書き込む。
【0085】
次に、CPU121は、SRAM123に格納されているBSIの内容を変更し、変更後のBSIの内容が、リセットされたブロックが空きブロックであることを表すようにして、処理を終了する。
【0086】
以上説明した処理により、記憶部11に格納されたデータがブロック単位で消去され、消去の結果新たに生じた空きブロックを示す情報がBSIに加えられる。
なお、必ずしもブロック単位で表されない任意の範囲の記憶領域に格納されたデータを消去する場合は、アクセス装置2から供給されたデータを書き込むべきところを、何らの書き込み操作を行わないようにして、上述のデータ書き込みの処理を行えばよい。
【0087】
なお、メモリカード1の構成は、上述のものに限られない。
例えば、記憶部11は、EEPROMに限らず任意の種類の記憶装置を備えていてもよい。また、記憶部11の記憶容量や、記憶領域のデータ構造も上述のものに限られない。例えば、記憶部11の記憶領域中、カード固有情報記憶領域が占める論理的位置は随時変動してもよい。この場合、例えば、記憶部11やコントローラ12が、カード固有情報記憶領域の論理的位置を示す情報を初期処理のステップS101の処理の前にアクセス装置2に供給し、アクセス装置2が、供給された情報が示す論理的位置へのアクセスを行うようにしてもよい。
【0088】
また、認証用ドライバの処理は、アクセス装置2が行う必要はなく、例えば、コントローラ12のCPU121が行うようにしてもよい。この場合は、アクセス装置2がメモリカードを装着した状態で起動した直後に、例えばアクセス装置2がCPU121に初期処理の開始を指示し、CPU121がこの指示に応答して、認証用ドライバのプログラムを記憶部11から読み出し、認証用ドライバの処理を実行するようにすればよい。
【0089】
認証用ドライバの処理をCPU121が行う場合、CPU121は、ステップS109における認証の成功の通知に代えて、ステップS115の処理において初期処理を正常終了した後、初期処理の終了をアクセス装置2に通知する処理を行うようにしてもよい。この場合、CPU121は、初期処理の終了をアクセス装置2に通知して以降、アクセス装置2から、記憶部11へのアクセスの指示を受け付けるようにすればよい。
【0090】
また、認証用ドライバの処理をCPU121が行う場合、CPU121は、記憶部から読み出した一般データを自ら復号化してアクセス装置2に供給すればよい。また、この場合、アクセス装置2は記憶部11に格納する対象のデータを暗号化することなくCPU121に供給し、CPU121が当該データを暗号化してから記憶部11に格納するようにすればよい。
【0091】
また、認証用ドライバの処理を行うアクセス装置2は、初期処理において認証に失敗したとき、認証に失敗した回数が所定の回数に達したか否かを判別して、達したと判別して以降は、新たにメモリカード1の装着を検出しても初期処理を再開しないようにしてもよい。認証用ドライバの処理をCPU121が行う場合は、初期処理において認証に失敗した回数が所定の回数に達したと判別して以降は、アクセス装置2より初期処理の開始を指示されても、初期処理の再開を拒絶するようにすればよい。
【0092】
また、このメモリカードシステムは、ユーザの操作によりアクセス装置2に供給されたパスワードを、当該パスワードに基づく認証が成功したか否かに係わらず記憶し、更に、当該パスワードに基づく認証が成功したか否かを表す情報や、当該パスワードが供給された時刻を表す情報を記憶するようにしてもよい。
これにより、不正なユーザによりアクセスが試みられた場合などに、そのアクセスの時刻や、その際に入力されたパスワードなどを参照することが可能となる。
【0093】
また、このメモリカードシステムは、記憶部11に格納されている一般データのうち所定の条件に合致するものへのアクセスがアクセス装置2からメモリカード1に指示されたとき、そのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定するため、更にユーザの認証を行ってもよい。
【0094】
具体的には、例えば、記憶部11が、ユーザに固有の再認証用パスワードを暗号化したものと、その再認証用パスワードを用いた認証に成功したときアクセスを許可すべき対象の一般データを示す再認証対象指定データとを記憶する。
そして、CPU121は、アクセス装置2から一般データへのアクセスの指示があったとき、アクセスの対象である一般データが、再認証対象指定データにより示されるものに該当するか否かを判別する。該当すると判別したとき、アクセス装置2又はCPU121は、ユーザがアクセス装置2を操作して再認証用パスワードを入力するのを待機し、入力された再認証用パスワードを、ステップS103で読み込んだ暗号鍵を用いて暗号化する。そして、暗号化された再認証用パスワードが、記憶部11に予め格納されている暗号化済みの再認証用パスワードと一致するか否かを判別し、一致すると判別すると、CPU121は、アクセス装置2がアクセスの対象として指定した当該一般データにアクセスするものとする。
【0095】
以上、この発明の実施の形態を説明したが、この発明の記憶システムは、専用のシステムによらず、通常のコンピュータシステムを用いて実現可能である。例えば、メモリカード1を装着するスロットを備えるパーソナルコンピュータに、上述のアクセス装置2の動作を実行するためのプログラムを格納した媒体(フロッピーディスク、CD−ROM等)から該プログラムをインストールすることにより、上述の処理を実行する記憶システムを構成することができる。
【0096】
また、コンピュータにプログラムを供給するための媒体は、通信媒体(通信回線、通信ネットワーク、通信システムのように、一時的且つ流動的にプログラムを保持する媒体)でも良い。例えば、通信ネットワークの掲示板(BBS)に該プログラムを掲示し、これをネットワークを介して配信してもよい。
そして、このプログラムを起動し、OSの制御下に、他のアプリケーションプログラムと同様に実行することにより、上述の処理を実行することができる。
【0097】
なお、OSが処理の一部を分担する場合、あるいは、OSが本願発明の1つの構成要素の一部を構成するような場合には、記録媒体には、その部分をのぞいたプログラムを格納してもよい。この場合も、この発明では、その記録媒体には、コンピュータが実行する各機能又はステップを実行するためのプログラムが格納されているものとする。
【0098】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、この発明によれば、既存の装置に加えるべき変更が少なく、簡単な操作で、データを暗号化して記憶する記録媒体へのアクセスを行うことができる記憶システム、記憶装置及び記憶データ保護方法が実現される。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の形態にかかるメモリカードシステムの構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】記憶部の記憶領域の論理的構造を模式的に示す図である。
【図3】BSIのデータ構造を模式的に示す図である。
【図4】BPTの構成の一例を示す図である。
【図5】初期処理を示すフローチャートである。
【符号の説明】
1 メモリカード
11 記憶部
12 コントローラ
121 CPU
122 ROM
123 SRAM
2 アクセス装置[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a storage system using a recording medium, a storage device, and a stored data protection method, and more particularly, to a storage system, a storage device, and a stored data protection method for encrypting and storing data.
[0002]
[Prior art]
A hard disk device, an MO (Magneto-Optical disk), or a flash memory is used as a recording medium that can be accessed (data read / write and erase) by a computer or the like. These recording media are used for storing data and transferring data between a plurality of computers.
In order to protect the data recorded on these recording media from unauthorized access, conventionally, the data is encrypted and stored.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in order to access a recording medium that stores encrypted data, it is necessary to decrypt the data.
For this reason, a computer or the like that accesses such a recording medium has a program every time the recording medium is exchanged in order to be able to decrypt data stored in all the recording media owned by the user. It is necessary to store the program necessary for re-installing or decrypting data stored in each recording medium owned by the user in advance.
[0004]
Accordingly, management and access operations for the computer and the like become complicated, and the decryption program hinders efficient use of the storage area of the external storage device such as the hard disk device.
[0005]
The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and there are few changes to be made to existing devices, and a storage system capable of performing processing to access a recording medium for storing data encrypted and stored with a simple operation, It is an object to provide a storage device and a stored data protection method.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, a storage system according to the first aspect of the present invention provides:
Recording medium and access deviceA recording medium controller connected to the recording medium and detachably attached to the access device;With
The recording medium is encrypted data representing encrypted information.And encrypted boot information corresponding to information obtained by encrypting boot information including a parameter specifying a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium,And means for storing a cryptographic processing program representing a process of encrypting data and decrypting the encrypted data,
The recording medium controller
Means for obtaining the cryptographic processing program from the recording medium and supplying the cryptographic processing program to the access device;
Determining means for deciding whether to permit access to the recording medium by the access device based on an encrypted password supplied from the access device;
Means for obtaining the encrypted boot information from the recording medium and supplying the encrypted boot information to the access device when the determining means determines to permit the access;
Read control means for acquiring the encrypted data from the recording medium and supplying the encrypted data to the access device according to a read instruction supplied from the access device;
Write control means for acquiring the encrypted data generated by the access device from the access device and storing it in the recording medium in accordance with a write instruction supplied from the access device;
The read control means refuses to follow the read instruction when the determining means determines that the access is not permitted,
The write control means refuses to follow the write instruction when the decision means decides not to allow the access;
The access device is:
SaidRecording medium controllerProgram acquisition means for acquiring the cryptographic processing program from
Means for obtaining a password according to the operation of the operator;
Means for encrypting the password to generate the encrypted password by executing processing represented by the cryptographic processing program acquired by the program acquisition means, and supplying the encrypted password to the recording medium controller;
Means for obtaining the encrypted boot information supplied by the recording medium controller and executing the encryption processing program obtained by the program obtaining means to decrypt the encrypted boot information and restore the boot information; ,
The read control means is supplied with the read instruction for instructing to read data by designating a predetermined area in the storage area by a method designated by the restored boot information, and the read control means Obtain the supplied encrypted data,By executing the cryptographic processing program acquired by the program acquisition means,ConcernedMeans for decrypting the encrypted data;
By executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition means, the information to be stored in the recording medium is encrypted to generate the encrypted data, and the encrypted data generated by itself is stored in the recording mediumTherefore, the write control unit is supplied with the write instruction for instructing to write data by a method specified by the restored boot information.Means,
It is characterized by that.
[0007]
According to such a storage system, the access device reads and executes the encryption processing program, thereby decrypting the encryption data, generating the encryption data, and storing it in the recording medium. Therefore, management and operation of the access device are simplified. Further, the existing computer functions as an access device without being substantially changed.
[0008]
AlsoThe processing for accessing the recording medium is shared by the access device and the recording medium controller, thereby reducing the processing burden on the access device.
[0009]
AlsoBefore the access device accesses the recording medium, authentication of the operator and authentication of the recording medium are performed. As a result, unauthorized access to the recording medium is prevented.
[0010]
The storage system according to the second aspect of the present invention is
A recording medium, an access device, and a recording medium controller connected to the recording medium and detachably attached to the access device;
The recording medium is encrypted data representing encrypted information.And encrypted boot information corresponding to information obtained by encrypting boot information including a parameter specifying a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium,And means for storing a cryptographic processing program representing a process of encrypting data and decrypting the encrypted data,
The recording medium controller
Program acquisition means for acquiring the cryptographic processing program from the recording medium;
Means for obtaining a password according to the operation of the operator;
The password is encrypted to generate an encrypted password by executing the process represented by the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition unit, and the access device accesses the recording medium based on the encrypted password Determining means for determining whether or not to permit,
When the determining unit determines to permit the access, the encrypted boot information is decrypted by acquiring the encrypted boot information from the recording medium and executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquiring unit. Means for restoring the boot information,
Supplied from the access device, Specified a predetermined area in the storage areaAccording to the read instruction, from the recording mediumBy the method specified by the restored boot informationRead control means for obtaining the encrypted data and decrypting the encrypted data by executing the encryption processing program obtained by the program obtaining means and supplying the encrypted data to the access device;
The information to be stored in the recording medium supplied by the access device is acquired from the access device, and the encrypted data is generated by executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition unit to generate the encrypted data And the generated encrypted dataBy the method specified by the restored boot informationWrite control means for storing in the recording medium,
The read control means refuses to follow the read instruction when the determining means determines that the access is not permitted,
The write control means, when the decision means decides not to allow the access, refuses to obtain from the access device information to be stored in the recording medium;
The access device is:
Means for supplying the read instruction to the read control means, and obtaining the decrypted encrypted data supplied by the read control means;
Means for supplying information to be stored in the recording medium,
It is characterized by that.
[0011]
According to such a storage system, the recording medium controller reads and executes the encryption processing program, thereby decrypting the encrypted data, generating the encrypted data, and storing the encrypted data in the recording medium. Therefore, management and operation of the access device are simplified. Further, the existing computer functions as an access device without being substantially changed.
[0012]
AlsoBefore the access device accesses the recording medium, authentication of the operator and authentication of the recording medium are performed. As a result, unauthorized access to the recording medium is prevented.
[0013]
A storage device according to the third aspect of the present invention is
A storage device comprising a recording medium and a recording medium controller,
The recording medium is encrypted data representing encrypted information.And encrypted boot information corresponding to information obtained by encrypting boot information including a parameter specifying a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium,And means for storing a cryptographic processing program representing a process of encrypting data and decrypting the encrypted data,
The recording medium controller is detachably attached to an external access device,
Program acquisition means for acquiring the cryptographic processing program from the recording medium;
Means for obtaining a password according to the operation of the operator;
By executing the process represented by the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition means, the password is encrypted to generate an encrypted password, and based on the encrypted password, to the recording medium by the external access device A determination means for determining whether or not to allow access to
When the determining unit determines to permit the access, the encrypted boot information is decrypted by acquiring the encrypted boot information from the recording medium and executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquiring unit. Means for restoring the boot information,
Supplied from the external access device, Specified a predetermined area in the storage areaAccording to the read instruction, from the recording mediumBy the method specified by the restored boot informationRead control means for obtaining the encrypted data and decrypting the encrypted data by executing the encryption processing program obtained by the program obtaining means and supplying the encrypted access data to the external access device;
The information to be stored in the recording medium supplied by the external access device is acquired from the external access device, and the information is encrypted by executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition means, and Generate encrypted data, and generate the encrypted dataBy the method specified by the restored boot informationWrite control means for storing in the recording medium,
The read control means refuses to follow the read instruction when the determining means determines that the access is not permitted,
The write control unit rejects acquisition of information to be stored in the recording medium from the external access device when the determination unit determines not to permit the access;
It is characterized by that.
[0014]
According to such a storage device, the external access device reads and executes the encryption processing program, thereby decrypting the encrypted data, generating the encrypted data, and storing it in the recording medium. Therefore, management and operation of the external access device are simplified. Further, the existing computer functions as an external access device without being substantially changed.
[0015]
AlsoBefore the access device accesses the recording medium, authentication of the operator and authentication of the recording medium are performed. As a result, unauthorized access to the recording medium is prevented.
[0016]
A storage device according to the fourth aspect of the present invention is
A storage device comprising a recording medium and a recording medium controller,
The recording medium is encrypted data representing encrypted information.And encrypted boot information corresponding to information obtained by encrypting boot information including a parameter specifying a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium,And means for storing a cryptographic processing program representing a process of encrypting data and decrypting the encrypted data,
The recording medium controller is detachably attached to an external access device that acquires and executes the cryptographic processing program,
Program supply means for causing the external access device to acquire the cryptographic processing program stored in the recording medium;
The external access device acquires an encrypted password generated by encrypting a password according to the encryption processing program, and based on the acquired encrypted password, the external access device accesses the recording medium. A decision means for deciding whether to allow,
Means for causing the external access device to acquire the encrypted boot information stored in the recording medium when the determining means determines to permit the access;
From the external access deviceA read instruction for instructing to read data by designating a predetermined area in the storage area by a method designated by the boot information restored from the encrypted boot information.SuppliedWhenRead control means for acquiring the encrypted data from the recording medium and supplying the encrypted data to the external access device according to a read instruction;
The encrypted data generated by encrypting information to be stored in the recording medium by the external access device is acquired from the external access device.In accordance with the write instruction supplied from the external access device as an instruction to write the data by the method specified by the boot information restored from the encrypted boot information, the encrypted data,Write control means for storing in the recording medium,
The read control means refuses to follow the read instruction when the determining means determines that the access is not permitted,
The write control means rejects obtaining the encrypted data from the external access device when the decision means decides not to permit the access;
It is characterized by that.
[0017]
According to such a storage device, the recording medium controller reads and executes the encryption processing program, thereby decrypting the encrypted data, generating the encrypted data, and storing it in the recording medium. Therefore, management and operation of the external access device are simplified. Further, the existing computer functions as an external access device without being substantially changed.
[0018]
AlsoBefore the access device accesses the recording medium, authentication of the operator and authentication of the recording medium are performed. As a result, unauthorized access to the recording medium is prevented.
[0019]
A stored data protection method according to the fifth aspect of the present invention includes:
A storage data protection method for protecting data stored in a storage device comprising a recording medium and a recording medium controller detachably attached to an external access device,
The recording medium is information obtained by encrypting boot information including encrypted data representing encrypted information and a parameter that specifies a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium. And storing encryption boot information corresponding to, storing an encryption processing program representing a process of performing encryption of data and decryption of the encrypted data,
A program acquisition step in which the recording medium controller acquires the cryptographic processing program from the recording medium;
The recording medium controller obtaining a password in accordance with an operation of an operator;
The recording medium controller performs processing represented by the encryption processing program acquired in the program acquisition step to generate an encrypted password by encrypting the password, and based on the encrypted password, the external access A determining step for determining whether or not to allow access to the recording medium by a device;
When it is determined that the access is permitted in the determining step, the recording medium controller acquires the encrypted boot information from the recording medium, and executes the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition unit, thereby Decrypting the encrypted boot information to restore the boot information;
In accordance with a read instruction that designates a predetermined area in the storage area, which is supplied from the external access device, the recording medium controller uses the method that the boot information restored from the recording medium designates the encrypted data. A read control step of decrypting the encrypted data and supplying it to the external access device by executing the cryptographic processing program acquired in the program acquisition step;
The recording medium controller obtains information to be stored in the recording medium supplied from the external access device from the external access device, and executes the cryptographic processing program obtained in the program obtaining step. A write control step of encrypting information to generate the encrypted data, and storing the generated encrypted data in the recording medium by a method specified by the restored boot information, and
In the read control step, when the recording medium controller determines not to permit the access in the determination step, it refuses to follow the read instruction;
In the write control step, the recording medium controller rejects acquisition of information to be stored in the recording medium from the external access device when it is determined that the access is not permitted in the determination step.
It is characterized by that.
[0020]
According to such stored data protection method,Recording medium controllerBy executing the encryption processing program, decryption of encryption data and generation of encryption data,recoding mediaStore encrypted data in Therefore, management and operation of an external device that requires access to the encrypted data is simplified. In addition, existing computers are substantially unchanged,Recording medium controllerByRecoveryGet encrypted data,Recording medium controllerInrecoding mediaTo store the encrypted data.
A stored data protection method according to the sixth aspect of the present invention includes:
A storage data protection method for protecting data stored in a storage device comprising a recording medium and a recording medium controller detachably attached to an external access device,
The recording medium is information obtained by encrypting boot information including encrypted data representing encrypted information and a parameter that specifies a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium. And storing encryption boot information corresponding to, storing an encryption processing program representing a process of performing encryption of data and decryption of the encrypted data,
The external access device acquires and executes the cryptographic processing program,
A program supply step in which the recording medium controller causes the external access device to acquire the cryptographic processing program stored in the recording medium;
The recording medium controller acquires an encrypted password generated by the external access device encrypting a password according to the encryption processing program, and based on the acquired encrypted password, the external access device performs the A decision step for deciding whether or not to permit access to the recording medium;
When it is determined in the determining step that the access is permitted, the recording medium controller causes the external access device to acquire the encrypted boot information stored in the recording medium;
A read instruction is supplied from the external access device to instruct to read data by designating a predetermined area in the storage area by a method designated by boot information restored from the encrypted boot information. A read control step in which the recording medium controller obtains the encrypted data from the recording medium and supplies the encrypted data to the external access device according to the read instruction;
The recording medium controller obtains the encrypted data generated by encrypting information to be stored in the recording medium by the external access device from the external access device, and the encrypted data is stored in the encrypted boot. A write control step for storing in the recording medium in accordance with a write instruction supplied from the external access device as an instruction to write data by a method specified by the boot information restored from the information. And
When it is determined in the determining step that the access is not permitted, the recording medium controller in the reading control step refuses to follow the reading instruction;
When it is determined in the determining step that the access is not permitted, the recording medium controller rejects the acquisition of the encrypted data from the external access device in the writing control step.
It is characterized by that.
[0021]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings, taking a memory card system for accessing a memory card having a flash memory as an example.
[0022]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a physical configuration of a memory card system according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, this memory card system includes a
The
[0023]
The
[0024]
The
In response to the access performed by the
[0025]
The storage area of the
[0026]
Each page constitutes one block in units of 16 pages from the top. Each block has a storage capacity of 8 kilobytes, and the entire storage area is composed of 512 blocks, and physical block addresses from 0 to 511 are continuously given from the top.
[0027]
Each page is composed of a data area occupying an area of 512 bytes from the head and a redundant part occupying the last 16 bytes, as shown.
Original data (data supplied and written from the
[0028]
Further, the redundant part of each page belonging to each block stores the value of the logical block address assigned to that block.
The logical block address is a unit recognized as a data read / write unit by the
[0029]
When the
[0030]
As shown in FIG. 2, among the blocks constituting the storage area of the
[0031]
The stored contents of the card specific information storage area cannot be substantially updated by external access. Therefore, the
[0032]
In the card unique information storage area, encrypted boot information, an encryption key, an authentication driver, an encrypted password, and encrypted fixed data are stored in advance by the manufacturer of the
[0033]
The encrypted boot information is obtained by encrypting boot information, which is data including parameters indicating the size and structure of the storage area of the
[0034]
The encryption key is used by the
The authentication driver is program data representing the above-described processing in which the
[0035]
The encrypted password is obtained by encrypting a password used for authenticating whether or not the user of the memory card system is a legitimate user in an initial process to be described later executed by the memory card system using an encryption key. Is.
The encrypted fixed data is obtained by encrypting predetermined fixed data stored in the
[0036]
The general data storage area stores program data representing processing executed by the
However, the general data is stored in an encrypted state using the encryption key stored in the card specific information storage area. The encrypted general data is read by the
[0037]
As shown in FIG. 1, the
The
[0038]
The
The
[0039]
The
[0040]
The BSI stores information indicating which of the blocks in the
The BSI is created according to the process described later of the
[0041]
An example of the BSI structure when the total number of blocks in the
[0042]
The BPT stores information indicating a correspondence relationship between a logical block address and a physical block address, which will be described later. The BPT is generated according to a process described later every time a BSI is generated, and stored in the
The BPT occupies a predetermined logical position in the storage area of the
[0043]
Specifically, the BPT has a data structure shown in FIG. 4, for example.
That is, for example, when the total number of logical block addresses is 500, as shown in the figure, the BPT includes a storage area of a total of 500 words in which addresses given from the top of each word are 1000h to 11F3h.
[0044]
Each address assigned to the storage area forming the BPT is equal to the sum of the logical block address and the minimum value (offset value) of the address assigned to the storage area forming the BPT. The contents stored in the one-word storage area assigned with each address represent the physical block address of the block associated with the logical block address indicated by the address.
[0045]
Specifically, for example, as shown in FIG. 4, it is assumed that the value “005Ah” is stored in the storage area assigned the
[0046]
However, when the content stored in the storage area to which each address is assigned represents a predetermined value (for example, when the value represents “07FFh” as shown in the figure), the memory storing the value is stored. This indicates that a physical block address is not associated with the logical block address indicated by the address of the area.
[0047]
The
[0048]
The
[0049]
The
That is, the
[0050]
The
[0051]
(Operation)
Next, the operation of this memory card system will be described with reference to FIG.
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing the initial processing.
[0052]
(Initial processing)
When the
[0053]
When the initial processing is started, first, the
[0054]
The
[0055]
When the
[0056]
When the encrypted password is supplied, the
[0057]
If it does not match, a message indicating authentication failure is supplied to the access device 2 (step S105). The
[0058]
On the other hand, if it is determined that they match, the
[0059]
If it is determined that they do not match, the
[0060]
When notified of the success of the authentication, the
[0061]
In step S110, the
[0062]
Next, the
[0063]
Then, the
[0064]
Next, the
[0065]
If it is determined that the block is not an empty block, the
[0066]
In step S115, the
Through the initial processing described above, mutual authentication of the memory card 1-
[0067]
(General data read processing)
After the initial processing ends normally in step S115, the
When the
[0068]
As information for designating the storage area from which the general data is read, specifically, for example, a virtual storage area having a size corresponding to the size of the storage area of the
[0069]
However, the format of the information for specifying the storage area from which the general data is read is arbitrary. For example, a virtual storage area having a size corresponding to the storage area of the
[0070]
The
[0071]
That is, the
(A) Information indicating which logical block address is assigned to the designated storage area in the storage area of the
(B) information indicating which position in the block represented by the information of (A) the specified storage area corresponds to;
Create The number of blocks indicated by the information (A) is not limited to one, and the number of pages indicated by the information (B) is not limited to one.
[0072]
Next, the
[0073]
The read general data is supplied to the
Through the processing described above, the encrypted general data is read from the
[0074]
(Data writing process)
When the
[0075]
Then, the
[0076]
The
Then, the
[0077]
Next, the
[0078]
However, when there is no physical block address associated with the logical block address indicated by the information (A), the
Then, the
[0079]
On the other hand, when there is a physical block address associated with the logical block address indicated by the information in (A), the
However, the contents of the page classified as the page to be written are not transferred, and instead of the contents of the page, the data to be written supplied from the
[0080]
In addition, every time data writing to each empty block retrieved from the BSI is completed, the
[0081]
Then, the
The
[0082]
Then, when the writing of data to all the empty blocks searched from the BSI and the change of the BSI and BPT are completed, the
Through the processing described above, the data supplied from the
[0083]
(Data deletion process)
Further, when the
[0084]
When the
[0085]
Next, the
[0086]
Through the processing described above, the data stored in the
Note that when erasing data stored in an arbitrary range of storage areas not necessarily expressed in units of blocks, the data supplied from the
[0087]
The configuration of the
For example, the
[0088]
Further, the processing of the authentication driver does not need to be performed by the
[0089]
When the
[0090]
When the
[0091]
Further, the
[0092]
In addition, the memory card system stores the password supplied to the
As a result, when access is attempted by an unauthorized user, it is possible to refer to the access time, the password entered at that time, and the like.
[0093]
The memory card system also permits access when the
[0094]
Specifically, for example, the
When the
[0095]
Although the embodiment of the present invention has been described above, the storage system of the present invention can be realized using a normal computer system, not a dedicated system. For example, by installing the program from a medium (floppy disk, CD-ROM, etc.) storing a program for executing the operation of the
[0096]
The medium for supplying the program to the computer may be a communication medium (a medium that temporarily and fluidly holds the program, such as a communication line, a communication network, or a communication system). For example, the program may be posted on a bulletin board (BBS) of a communication network and distributed via the network.
The above-described processing can be executed by starting this program and executing it under the control of the OS in the same manner as other application programs.
[0097]
When the OS shares a part of processing, or when the OS constitutes a part of one component of the present invention, a program excluding the part is stored in the recording medium. May be. Also in this case, in the present invention, it is assumed that the recording medium stores a program for executing each function or step executed by the computer.
[0098]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, a storage system, a storage device, and a storage system that can access a recording medium for storing data encrypted with a simple operation with few changes to be made to an existing device. A stored data protection method is implemented.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a memory card system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram schematically showing a logical structure of a storage area of a storage unit.
FIG. 3 is a diagram schematically illustrating a data structure of BSI.
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of a configuration of a BPT.
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing an initial process.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 Memory card
11 Storage unit
12 Controller
121 CPU
122 ROM
123 SRAM
2 Access device
Claims (6)
Translated fromJapanese前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶する手段を備え、
前記記録媒体コントローラは、
前記記録媒体より前記暗号処理プログラムを取得して前記アクセス装置に供給する手段と、
前記アクセス装置から供給される暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記アクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定手段と、
前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体より前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して前記アクセス装置に供給する手段と、
前記アクセス装置から供給される読み出し指示に従って、前記記録媒体から前記暗号データを取得して前記アクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御手段と、
前記アクセス装置から供給される書き込み指示に従い、前記アクセス装置が生成した当該暗号データを前記アクセス装置から取得して前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御手段と、を備え、
前記読み出し制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記書き込み指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記アクセス装置は、
前記記録媒体コントローラより前記暗号処理プログラムを取得するプログラム取得手段と、
操作者の操作に従ってパスワードを取得する手段と、
前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムが表す処理を実行することにより、前記パスワードを暗号化して前記暗号化パスワードを生成し、当該暗号化パスワードを前記記録媒体コントローラに供給する手段と、
前記記録媒体コントローラが供給した前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して、前記プログラム 取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号化ブート情報を復号化して前記ブート情報を復元する手段と、
前記読み出し制御手段に、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定してデータの読み出しを行うことを指示する前記読み出し指示を供給し、当該読み出し制御手段が供給した前記暗号データを取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号データを復号化する手段と、
前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を暗号化して前記暗号データを生成し、自己が生成した当該暗号データを前記記録媒体に格納するため、前記書き込み制御手段に、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法によるデータの書き込みを行うことを指示する前記書き込み指示を供給する手段と、を備える、
ことを特徴とする記憶システム。A recording medium, an access device, anda recording medium controller connected to the recording medium and detachably attached to the access device ;
The recording medium isinformation obtained by encrypting boot information including encrypted data representing encrypted information anda parameter that specifies a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium. And a means for storing a cryptographic processing program representing a process of performing encryption of data and decryption of the encrypted data,
The recording medium controller
Means for obtaining the cryptographic processing program from the recording medium and supplying the cryptographic processing program to the access device;
Determining means for deciding whether to permit access to the recording medium by the access device based on an encrypted password supplied from the access device;
Means for obtaining the encrypted boot information from the recording medium and supplying the encrypted boot information to the access device when the determining means determines to permit the access;
Read control means for acquiring the encrypted data from the recording medium and supplying the encrypted data to the access device according to a read instruction supplied from the access device;
Write control means for acquiring the encrypted data generated by the access device from the access device and storing it in the recording medium in accordance with a write instruction supplied from the access device;
The read control means refuses to follow the read instruction when the determining means determines that the access is not permitted,
The write control means refuses to follow the write instruction when the decision means decides not to allow the access;
The access device is:
Program acquisition means for acquiring the cryptographic processing program from therecording medium controller ;
Means for obtaining a password according to the operation of the operator;
Means for encrypting the password to generate the encrypted password by executing processing represented by the cryptographic processing program acquired by the program acquisition means, and supplying the encrypted password to the recording medium controller;
Means for obtaining the encrypted boot information supplied by the recording medium controller and executing the encryption processing program obtained by the program obtaining means to decrypt the encrypted boot information and restore the boot information; ,
The read control means is supplied with the read instruction for instructing to read data by designating a predetermined area in the storage area by a method designated by the restored boot information, and the read control means acquires the supplied the encrypted data by performing encryption processing program the program acquisition unit has acquired, and means for decryptingthe encrypted data,
By executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition means, the information to be stored in the recording medium is encrypted to generate the encrypted data, and the encrypted data generated by itself is stored in the recording mediumTherefore, meansfor supplying the write instruction to instruct the write control means to write data by a method specified by the restored boot information ,
A storage system characterized by that.
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶する手段を備え、
前記記録媒体コントローラは、
前記記録媒体より前記暗号処理プログラムを取得するプログラム取得手段と、
操作者の操作に従ってパスワードを取得する手段と、
前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムが表す処理を実行することにより、前記パスワードを暗号化して暗号化パスワードを生成し、当該暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記アクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定手段と、
前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体より前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号化ブート情報を復号化して前記ブート情報を復元する手段と、
前記アクセス装置から供給される、前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定した読み出し指示に従って、前記記録媒体から、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記暗号データを取得し、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより当該暗号データを復号化して前記アクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御手段と、
前記アクセス装置が供給する、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記アクセス装置から取得し、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することによりその情報を暗号化して前記暗号データを生成し、生成した暗号データを、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御手段と、を備え、
前記読み出し制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記アクセス装置から取得することを拒絶し、
前記アクセス装置は、
前記読み出し制御手段に前記読み出し指示を供給し、前記読み出し制御手段が供給する復号化された前記暗号データを取得する手段と、
前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を供給する手段と、を備える、
ことを特徴とする記憶システム。A recording medium, an access device, and a recording medium controller connected to the recording medium and detachably attached to the access device;
The recording medium isinformation obtained by encryptingboot information including encrypted data representing encrypted information anda parameter that specifies a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium.And a means for storing a cryptographic processing program representing a process of performing encryption of data and decryption of the encrypted data,
The recording medium controller
Program acquisition means for acquiring the cryptographic processing program from the recording medium;
Means for obtaining a password according to the operation of the operator;
The password is encrypted to generate an encrypted password by executing the process represented by the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition unit, and the access device accesses the recording medium based on the encrypted password Determining means for determining whether or not to permit,
When the determining unit determines to permit the access, the encrypted boot information is decrypted by acquiring the encrypted boot information from the recording medium and executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquiring unit. Means for restoring the boot information,
In accordancewith a read instructionspecifying a predetermined area in the storage area supplied from the access device, the encrypted data is acquired fromthe recording mediumby a method specified by the restored boot information , and the program acquisition means A read control means for decrypting the encrypted data by executing the acquired cryptographic processing program and supplying it to the access device;
The information to be stored in the recording medium supplied by the access device is acquired from the access device, and the encrypted data is generated by executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition unit to generate the encrypted data And write control means for storing the generated encrypted data inthe recording mediumby a method specified by the restored boot information ,
The read control means refuses to follow the read instruction when the determining means determines that the access is not permitted,
The write control means, when the decision means decides not to allow the access, refuses to obtain from the access device information to be stored in the recording medium;
The access device is:
Means for supplying the read instruction to the read control means, and obtaining the decrypted encrypted data supplied by the read control means;
Means for supplying information to be stored in the recording medium,
A storage system characterized by that.
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶する手段を備え、
前記記録媒体コントローラは、外部のアクセス装置に着脱可能に装着されるものであって、
前記記録媒体より前記暗号処理プログラムを取得するプログラム取得手段と、
操作者の操作に従ってパスワードを取得する手段と、
前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムが表す処理を実行することにより、前記パスワードを暗号化して暗号化パスワードを生成し、当該暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記外部のアクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定手段と、
前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体より前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号化ブート情報を復号化して前記ブート情報を復元する手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置から供給される、前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定した読み出し指示に従って、前記記録媒体から、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記暗号データを取得し、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより当該暗号データを復号化して前記外部のアクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置が供給する、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記外部のアクセス装置から取得し、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することによりその情報を暗号化して前記暗号データを生成し、生成した暗号データを、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御手段と、を備え、
前記読み出し制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記外部のアクセス装置から取得することを拒絶する、
ことを特徴とする記憶装置。A storage device comprising a recording medium and a recording medium controller,
The recording medium isinformation obtained by encrypting boot information including encrypted data representing encrypted information anda parameter that specifies a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium. And a means for storing a cryptographic processing program representing a process of performing encryption of data and decryption of the encrypted data,
The recording medium controller is detachably attached to an external access device,
Program acquisition means for acquiring the cryptographic processing program from the recording medium;
Means for obtaining a password according to the operation of the operator;
By executing the process represented by the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition means, the password is encrypted to generate an encrypted password, and based on the encrypted password, to the recording medium by the external access device A determination means for determining whether or not to allow access to
When the determining unit determines to permit the access, the encrypted boot information is decrypted by acquiring the encrypted boot information from the recording medium and executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquiring unit. Means for restoring the boot information,
In accordancewith a read instructionthat designates a predetermined area in the storage area supplied from the external access device, the encrypted data is obtained fromthe recording mediumby a method designated by the restored boot information , and the program A read control unit that decrypts the encrypted data by executing the encryption processing program acquired by the acquisition unit and supplies the decrypted encryption data to the external access device;
The information to be stored in the recording medium supplied by the external access device is acquired from the external access device, and the information is encrypted by executing the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition means, and Write control means for generating encrypted data, and storing the generated encrypted data inthe recording mediumby a method specified by the restored boot information ,
The read control means refuses to follow the read instruction when the determining means determines that the access is not permitted,
The write control unit rejects acquisition of information to be stored in the recording medium from the external access device when the determination unit determines not to permit the access;
A storage device.
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶する手段を備え、
前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記暗号処理プログラムを取得して実行する外部のアクセス装置に着脱可能に装着されるものであって、
前記記録媒体が記憶する前記暗号処理プログラムを前記外部のアクセス装置に取得させるプログラム供給手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置が前記暗号処理プログラムに従ってパスワードを暗号化することにより生成した暗号化パスワードを取得し、取得した前記暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記外部のアクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定手段と、
前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体が記憶する前記暗号化ブート情報を前記外部のアクセス装置に取得させる手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置から、前記暗号化ブート情報より復元されたブート情報が指定する手法により前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定してデータの読み出しを行うことを指示する読み出し指示を供給されたとき、当該読み出し指示に従い、前記記録媒体から前記暗号データを取得して前記外部のアクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御手段と、
前記外部のアクセス装置が前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を暗号化して生成した前記暗号データを前記外部のアクセス装置から取得して、当該暗号データを、前記暗号化ブート情報より復元されたブート情報が指定する手法によるデータの書き込みを行うことを指示するものとして前記外部のアクセス装置より供給される書き込み指示に従って、前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御手段と、を備え、
前記読み出し制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、
前記書き込み制御手段は、前記決定手段が前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記暗号データを前記外部のアクセス装置から取得することを拒絶する、
ことを特徴とする記憶装置。A storage device comprising a recording medium and a recording medium controller,
The recording medium isinformation obtained by encrypting boot information including encrypted data representing encrypted information anda parameter that specifies a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium. And a means for storing a cryptographic processing program representing a process of performing encryption of data and decryption of the encrypted data,
The recording medium controller is detachably attached to an external access device that acquires and executes the cryptographic processing program,
Program supply means for causing the external access device to acquire the cryptographic processing program stored in the recording medium;
The external access device acquires an encrypted password generated by encrypting a password according to the encryption processing program, and based on the acquired encrypted password, the external access device accesses the recording medium. A decision means for deciding whether to allow,
Means for causing the external access device to acquire the encrypted boot information stored in the recording medium when the determining means determines to permit the access;
A read instruction is supplied fromthe external access device toinstruct to read data by designating a predetermined area in the storage area by a method designated by boot information restored fromthe encrypted boot information. when, in accordance withthe read instruction, a read control means for supplying to the external access device acquires the encrypted data from said recording medium,
The encrypted data generated by encrypting the information to be stored in the recording medium by the external access device is acquired from the external access device, and the encrypted data is booted from the encrypted boot information. Write control means for storing in the recording mediumaccording to a write instruction supplied from the external access device as an instruction to write data by a method specified by information ,
The read control means refuses to follow the read instruction when the determining means determines that the access is not permitted,
The write control means rejects obtaining the encrypted data from the external access device when the decision means decides not to permit the access;
A storage device.
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶し、The recording medium is information obtained by encrypting boot information including encrypted data representing encrypted information and a parameter that specifies a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium. And storing encryption boot information corresponding to, storing an encryption processing program representing a process of performing encryption of data and decryption of the encrypted data,
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記記録媒体より前記暗号処理プログラムを取得するプログラム取得ステップと、A program acquisition step in which the recording medium controller acquires the cryptographic processing program from the recording medium;
前記記録媒体コントローラが、操作者の操作に従ってパスワードを取得するステップと、The recording medium controller obtaining a password in accordance with an operation of an operator;
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記プログラム取得ステップで取得した暗号処理プログラムが表す処理を実行することにより、前記パスワードを暗号化して暗号化パスワードを生成し、当該暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記外部のアクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定ステップと、The recording medium controller performs processing represented by the encryption processing program acquired in the program acquisition step to generate an encrypted password by encrypting the password, and based on the encrypted password, the external access A determining step for determining whether or not to allow access to the recording medium by a device;
前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記記録媒体より前記暗号化ブート情報を取得して、前記プログラム取得手段が取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより、当該暗号化ブート情報を復号化して前記ブート情報を復元するステップと、When it is determined that the access is permitted in the determining step, the recording medium controller acquires the encrypted boot information from the recording medium, and executes the encryption processing program acquired by the program acquisition unit, thereby Decrypting the encrypted boot information to restore the boot information;
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記外部のアクセス装置から供給される、前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定した読み出し指示に従って、前記記録媒体から、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記暗号データを取得し、前記プログラム取得ステップで取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することにより当該暗号データを復号化して前記外部のアクセス装置に供給する読み出し制御ステップと、In accordance with a read instruction that designates a predetermined area in the storage area, which is supplied from the external access device, the recording medium controller uses the method that the boot information restored from the recording medium designates the encrypted data. A read control step of decrypting the encrypted data and supplying it to the external access device by executing the cryptographic processing program acquired in the program acquisition step;
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記外部のアクセス装置が供給する、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記外部のアクセス装置から取得し、前記プログラム取得ステップで取得した暗号処理プログラムを実行することによりその情報を暗号化して前記暗号データを生成し、生成した暗号データを、復元された前記ブート情報が指定する手法により前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御ステップと、より構成されており、The recording medium controller obtains information to be stored in the recording medium supplied from the external access device from the external access device, and executes the cryptographic processing program obtained in the program obtaining step. A write control step of encrypting information to generate the encrypted data, and storing the generated encrypted data in the recording medium by a method specified by the restored boot information, and
前記読み出し制御ステップで前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、In the read control step, when the recording medium controller determines not to permit the access in the determination step, it refuses to follow the read instruction;
前記書き込み制御ステップで前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を前記外部のアクセス装置から取得することを拒絶する、In the write control step, the recording medium controller rejects acquisition of information to be stored in the recording medium from the external access device when it is determined that the access is not permitted in the determination step.
ことを特徴とする記憶データ保護方法。A method for protecting stored data.
前記記録媒体は、暗号化された情報を表す暗号データと、前記記録媒体の記憶領域の構造及び前記記録媒体へのデータの読み書きの手法を指定するパラメータを含むブート情報を暗号化して得られる情報に相当する暗号化ブート情報と、を記憶し、データの暗号化及び前記暗号データの復号化を行う処理を表す暗号処理プログラムを記憶し、The recording medium is information obtained by encrypting boot information including encrypted data representing encrypted information and a parameter that specifies a structure of a storage area of the recording medium and a method for reading and writing data to the recording medium. And storing encryption boot information corresponding to, storing an encryption processing program representing a process of performing encryption of data and decryption of the encrypted data,
前記外部のアクセス装置は、前記暗号処理プログラムを取得して実行するものであって、The external access device acquires and executes the cryptographic processing program,
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記記録媒体が記憶する前記暗号処理プログラムを前記外部のアクセス装置に取得させるプログラム供給ステップと、A program supply step in which the recording medium controller causes the external access device to acquire the cryptographic processing program stored in the recording medium;
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記外部のアクセス装置が前記暗号処理プログラムに従ってパスワードを暗号化することにより生成した暗号化パスワードを取得し、取得した前記暗号化パスワードに基づいて、前記外部のアクセス装置による前記記録媒体へのアクセスを許可するか否かを決定する決定ステップと、The recording medium controller acquires an encrypted password generated by the external access device encrypting a password according to the encryption processing program, and based on the acquired encrypted password, the external access device performs the A decision step for deciding whether or not to permit access to the recording medium;
前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可すると決定したとき、前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記記録媒体が記憶する前記暗号化ブート情報を前記外部のアクセス装置に取得させるステップと、 When it is determined in the determining step that the access is permitted, the recording medium controller causes the external access device to acquire the encrypted boot information stored in the recording medium;
前記外部のアクセス装置から、前記暗号化ブート情報より復元されたブート情報が指定する手法により前記記憶領域内の所定の領域を指定してデータの読み出しを行うことを指示する読み出し指示を供給されたとき、前記記録媒体コントローラが、当該読み出し指示に従い、前記記録媒体から前記暗号データを取得して前記外部のアクセス装置に供給するA read instruction is supplied from the external access device to instruct to read data by designating a predetermined area in the storage area by a method designated by boot information restored from the encrypted boot information. The recording medium controller acquires the encrypted data from the recording medium and supplies it to the external access device in accordance with the read instruction.読み出し制御ステップと、A read control step;
前記記録媒体コントローラが、前記外部のアクセス装置が前記記録媒体に記憶させる対象の情報を暗号化して生成した前記暗号データを前記外部のアクセス装置から取得して、当該暗号データを、前記暗号化ブート情報より復元されたブート情報が指定する手法によるデータの書き込みを行うことを指示するものとして前記外部のアクセス装置より供給される書き込み指示に従って、前記記録媒体に格納する書き込み制御ステップと、より構成されており、The recording medium controller obtains the encrypted data generated by encrypting information to be stored in the recording medium by the external access device from the external access device, and the encrypted data is stored in the encrypted boot. A write control step for storing in the recording medium in accordance with a write instruction supplied from the external access device as an instruction to write data by a method specified by the boot information restored from the information. And
前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記読み出し制御ステップで前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記読み出し指示に従うことを拒絶し、When it is determined in the determining step that the access is not permitted, the recording medium controller in the reading control step refuses to follow the reading instruction;
前記決定ステップで前記アクセスを許可しないと決定したとき、前記書き込み制御ステップで前記記録媒体コントローラは、前記暗号データを前記外部のアクセス装置から取得することを拒絶する、 When it is determined in the determining step that the access is not permitted, the recording medium controller rejects the acquisition of the encrypted data from the external access device in the writing control step.
ことを特徴とする記憶データ保護方法。A method for protecting stored data.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP05472699AJP3730432B2 (en) | 1999-03-02 | 1999-03-02 | Storage system, storage device, and storage data protection method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP05472699AJP3730432B2 (en) | 1999-03-02 | 1999-03-02 | Storage system, storage device, and storage data protection method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2000250818A JP2000250818A (en) | 2000-09-14 |
| JP3730432B2true JP3730432B2 (en) | 2006-01-05 |
Family
ID=12978819
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP05472699AExpired - Fee RelatedJP3730432B2 (en) | 1999-03-02 | 1999-03-02 | Storage system, storage device, and storage data protection method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3730432B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI20001073A7 (en)* | 2000-05-08 | 2001-11-09 | Nokia Corp | Method for protecting a memory card and memory card |
| US7281273B2 (en)* | 2002-06-28 | 2007-10-09 | Microsoft Corporation | Protecting content on medium from unfettered distribution |
| KR100952951B1 (en) | 2003-05-09 | 2010-04-15 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | How to secure hard disk access of personal computer |
| JP4717396B2 (en)* | 2004-08-30 | 2011-07-06 | キヤノン株式会社 | Data communication apparatus, data communication method, and data communication program |
| JP4717398B2 (en)* | 2004-09-10 | 2011-07-06 | キヤノン株式会社 | Method for controlling data processing apparatus |
| US8190920B2 (en)* | 2007-09-17 | 2012-05-29 | Seagate Technology Llc | Security features in an electronic device |
| JP6531429B2 (en)* | 2015-03-02 | 2019-06-19 | 株式会社バッファロー | INFORMATION PROCESSING SYSTEM, INFORMATION PROCESSING DEVICE, STORAGE DEVICE, AUTHENTICATION METHOD AND PROGRAM IN INFORMATION PROCESSING DEVICE |
| DE102021131424B4 (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2025-06-26 | Swissbit Ag | Methods and systems for session-based and secure access control to a data storage system |
- 1999
- 1999-03-02JPJP05472699Apatent/JP3730432B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2000250818A (en) | 2000-09-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11507284B2 (en) | Storage device and control method | |
| TWI716023B (en) | Memory system | |
| TWI763780B (en) | storage device | |
| US7900063B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for securing data on a portable storage device | |
| US20100058073A1 (en) | Storage system, controller, and data protection method thereof | |
| US6457126B1 (en) | Storage device, an encrypting/decrypting device and method of accessing a non-volatile memory | |
| TWI775284B (en) | Memory system, its control method and information processing system | |
| US20100058066A1 (en) | Method and system for protecting data | |
| JP4463320B1 (en) | ENCRYPTION STORAGE DEVICE, INFORMATION DEVICE, AND ENCRYPTION STORAGE DEVICE SECURITY METHOD | |
| CN108874300A (en) | data storage device and operation method thereof | |
| CN112463805A (en) | Key management device for data encryption and decryption and processor chip | |
| JP3730432B2 (en) | Storage system, storage device, and storage data protection method | |
| US11468159B2 (en) | Memory system | |
| CN112468300A (en) | Key management device with bypass channel and processor chip | |
| JP2008225672A (en) | Semiconductor memory device | |
| JP2000250817A (en) | Storage system, storage device and stored data protecting method | |
| JP2021149417A (en) | Storage device and control method | |
| JP2000030375A (en) | Data processing system, access device, and recording media | |
| US12229432B2 (en) | Memory system and random number generation device | |
| JP4031693B2 (en) | Nonvolatile memory and data storage device having the same | |
| CN120780623A (en) | Memory system, control method of memory system, and information processing system | |
| CN118747384A (en) | A data security storage device and storage method based on security chip | |
| CN113343265A (en) | Key configuration method, device and related equipment | |
| JP4773757B2 (en) | Area management type memory device | |
| JP2003273859A (en) | Method for storing encrypted information into flash memory and drive for flash memory |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20041207 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20041221 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20050221 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20050913 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20051006 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091014 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091014 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091014 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |