JP3695104B2 - Image processing device - Google Patents
Image processing deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3695104B2 JP3695104B2JP35040597AJP35040597AJP3695104B2JP 3695104 B2JP3695104 B2JP 3695104B2JP 35040597 AJP35040597 AJP 35040597AJP 35040597 AJP35040597 AJP 35040597AJP 3695104 B2JP3695104 B2JP 3695104B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- job
- processing
- unit
- reception
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription207
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription42
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsdescription41
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000description22
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description13
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description7
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description6
- 238000013500data storageMethods0.000description5
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description4
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description4
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000description3
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 238000012423maintenanceMethods0.000description2
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000description2
- 208000033748Device issuesDiseases0.000description1
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000description1
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description1
- 239000004973liquid crystal related substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description1
- 239000004065semiconductorSubstances0.000description1
- 238000004904shorteningMethods0.000description1
- 238000012546transferMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Accessory Devices And Overall Control Thereof (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、上位装置からのジョブに対応して印刷処理を行う画像処理装置に係わり、特に印刷すべき画像データを一旦記憶蓄積するスプール機能を有した画像処理装置に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、画像処理装置としては、コンピュータネットワークの普及に伴い、例えばネットワークプリンタのように、複数のホスト装置(パーソナルコンピュータやワークステーション等)と接続して用いられるものが広く知られている。
このような画像処理装置では、一般に、TCP/IP(Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)やSPX/IPX(Sequenced Packet Exchange/Internet Packet Exchange)等の既存の通信プロトコルに従って、それぞれのホスト装置との間の通信を行うようになっており、各ホスト装置から印刷処理要求および印刷すべき画像データをジョブとして受信すると、そのジョブに対応して印刷処理を行うようになっている。また、このとき、各ホスト装置からは通信負荷削減のために例えばページ記述言語で記述された画像データが送信されてくるので、画像処理装置では、受信した画像データを印刷可能なイメージデータに展開した後に印刷処理を行うようになっている。
【0003】
ただし、画像処理装置は、ネットワーク上で用いられる場合に、イメージデータへの展開処理を行いながら画像データを受信していると、その画像データを全て受信して展開するまでホスト装置の送信処理を開放させることができない。また、ネットワーク上に複数のホスト装置が存在している場合には、各ホスト装置からのジョブを受け付ける必要がある。
そこで、通常、ネットワーク上で用いられる画像処理装置は、受信した画像データを一旦記憶蓄積するスプール機能を有することにより、ホスト装置での画像データの送信時間の短縮化を図るとともに、あるジョブにおける画像データの印刷処理が終了していなくても他のジョブの受け付けを可能にしている。
【0004】
このようなスプール機能を有する画像処理装置では、一旦記憶蓄積した画像データを、順次読み出してイメージデータに展開した後に印刷する。そのため、印刷処理中に紙詰まり等の障害が発生した場合でも、その障害の解除後、正常に印刷されなかった部分から展開および印刷を再開するリカバリー処理を行うことが可能である。例えば、特開平5−11939号公報には、画像データとその画像データに関するページ情報とを関連付けて記憶蓄積することにより、印刷処理を行っている最中に障害が発生した場合であっても、その障害が発生したページから印刷処理を再開することを可能にする発明が開示されている。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで、従来のスプール機能を有した画像処理装置では、上述のリカバリー処理を可能にするために、画像データを一旦記憶蓄積するためのメモリを、大容量かつ不揮発性のハードディスク装置等によって形成している。これは、ネットワーク上の各ホスト装置からの画像データを記憶蓄積するために、ある程度の記憶容量が必要となるからであり、しかも、揮発性のものでは電源の切断があると蓄積した画像データを失ってしまい、リカバリー処理を行うことができなくなってしまうおそれがあるからである。そのため、従来のスプール機能を有した画像処理装置では、ハードディスク装置等がRAM(Random Access Memory)等の半導体メモリに比べて多くの読み出しまたは書き込み時間を要し、その大きさも大きく、またコストも高いため、結果として装置全体の高速処理化、小型化、低コスト化を実現するのが困難である。
【0006】
これに対して、スプール機能をRAM等の揮発性メモリで実現し、電源の切断等があった場合にはホスト装置から再度ジョブの発行を行わせることも考えられるが、この場合には、以下の点で問題がある。
例えば、電源の切断等があると、それ以前に画像処理装置が複数のジョブを受け付けていても、ホスト装置からは、これら全てのジョブについて再度印刷処理も要求を最初から繰り返して行う必要がある。つまり、既に受付済のジョブの中で印刷処理が完了しているものと完了していないものとがあっても、電源の切断等によってスプール内容を失われるため、どのジョブが未処理であるかを容易に特定することができず、結果として全てのジョブをホスト装置から発行しなければならない。したがって、各ホスト装置のユーザにとっては、操作上の大きな負担を受けることとなるので、非常に煩わしく、不便なものとなってしまう。また、ネットワークシステム全体としての処理効率向上の妨げにもなる。
【0007】
そこで、本発明は、画像処理装置全体の高速処理化、小型化および低コスト化を実現しつつ、ジョブの処理状態の特定を容易にすることにより、電源の切断等があっても未処理のジョブのみの再発行を可能にする画像処理装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0008】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、上記目的を達成するために案出された画像処理装置で、上位装置から印刷処理要求および印刷すべき画像データをジョブとして受信する受信手段と、前記受信手段がジョブを受信する度にそのジョブの受信完了を検出する受信完了検出手段と、前記受信手段が受信したジョブを蓄積する蓄積手段と、前記蓄積手段が蓄積しているジョブに対応して印刷処理を実行する処理手段と、前記処理手段が印刷処理を実行する度にその印刷処理の実行完了を検出する処理完了検出手段と、前記受信手段が受信したジョブ毎に、前記受信完了検出手段および前記処理完了検出手段による検出結果を、そのジョブについての処理実行状態を表す印刷処理情報として記憶する不揮発性の記憶手段と、所定の条件の下で前記記憶手段が記憶している印刷処理情報を出力する出力手段とを備えることを特徴とするものである。
【0009】
上記構成の画像処理装置によれば、受信手段が上位装置からのジョブを受信すると、受信完了検出手段がその受信完了を検出する。その後、蓄積手段に蓄積されているジョブに対応して処理手段が印刷処理を実行すると、処理完了検出手段がその実行完了を検出する。そして、これらの検出結果を、不揮発性の記憶手段がジョブ毎に印刷処理情報として記憶する。この印刷処理情報は、所定の条件の下で出力手段によって出力される。
したがって、この画像処理装置では、例えば蓄積手段が揮発性のもので、電源の切断等によって蓄積内容を失ってしまった場合であっても、不揮発性の記憶手段が記憶している印刷処理情報は失われることなく、一定の条件の下で出力手段によって出力されるので、その出力結果により蓄積手段内のジョブの印刷処理が完了しているか否か、すなわち各ジョブについての処理実行状態が容易にわかるようになる。
【0010】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、図面に基づき本発明に係わる画像処理装置について説明する。ただし、ここでは、ネットワーク上で用いられるネットワークプリンタに本発明を適用した場合を例に挙げて説明する。
【0011】
図1に示すように、本実施の形態の画像処理装置1は、LAN(ローカルエリアネットワーク)等のネットワーク20上において用いられるもので、そのネットワーク20を介して、図示しないホスト装置と接続されているものである。
【0012】
ホスト装置は、例えばパーソナルコンピュータやワークステーション等からなるもので、画像処理装置の上位装置として機能するものである。このホスト装置では、画像処理装置1に対応したプリンタドライバを有しており、ユーザからの指示に従って、画像処理装置1に印刷処理を行わせるためのジョブを送信するようになっている。
【0013】
ただし、ホスト装置は、ジョブの送信を所定のプロトコル、例えばRFC1179に規定されているLpd(Line Printer Daemon)プロトコルに準拠して行い、しかもそのジョブを、所定フォーマット(例えばページ記述言語による記述)の画像データとこの画像データの印刷処理を指示するコマンドデータとの組み合わせによって構成するようになっている。なお、コマンドデータには、アスキー(ASCII)等の文字列で記載された画像データのファイル名、ホスト装置で印刷指示をしたユーザのログイン名、ホスト装置のホスト名等が含まれているものとする。
【0014】
一方、このようなホスト装置に接続される画像処理装置1は、ネットワークインタフェース部2と、受信データ処理部3と、蓄積装置4と、印刷処理管理部5と、画像データ展開処理部6と、メモリ管理部7と、記録出力部8と、記録出力制御部9と、NVRAM(Nonvolatile Random Access Memory)10と、操作表示処理部11と、システム制御部12と、これらを互いに接続する内部バス13と、を備えているものである。
【0015】
ネットワークインタフェース部2は、ネットワーク20に接続され、そのネットワーク20を介してホスト装置からのジョブ、すなわち画像データおよびコマンドデータを受信するものである。
【0016】
受信データ処理部3は、ネットワークインタフェース部2がジョブを受信すると、これを受け取って、そのジョブに係る画像データを蓄積装置4に蓄積させたり、その蓄積装置4から蓄積されている画像データを読み出したりするものである。そのために、受信データ処理部3は、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aと、受信データ処理制御部3bと、受信データ蓄積部3cと、印刷処理要求部3dと、を備えている。
【0017】
ホストコマンド判定処理部3aは、ネットワークインタフェース部2から受け取ったジョブに対して、画像データとコマンドデータとの判別を行うものである。
【0018】
受信データ処理制御部3bは、画像データの受信管理を行うものであり、その管理の一つとして画像データの受信完了の検出を行うものである。この検出は、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aによる判定結果を基に、ホスト装置からの送信完了を表すコマンドやデータの終わりを表すEOF信号等を認識することによって、ジョブ毎に行う。
また、受信データ処理制御部3bでは、画像データの受信完了を検出した場合、その旨を表すフラグ情報である受信完了情報と、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aで判別されたコマンドデータとを、互いに関連付けてNVRAM10に書き込む処理も行うようになっている。
【0019】
受信データ蓄積部3cは、受信した画像データを蓄積装置4に蓄積させるものである。
【0020】
印刷処理要求部3dは、蓄積装置4に蓄積された画像データについての印刷処理要求を印刷処理管理部5に対して行うとともに、その印刷処理要求が認められた画像データを蓄積装置4から読み出すものである。
【0021】
蓄積装置4は、画像処理装置1におけるスプール機能を実現するためのメモリであり、受信データ蓄積部3cおよび印刷処理要求部3dによる出し入れに従って、画像データを記憶蓄積するものである。ただし、蓄積装置4は、不揮発性メモリであるRAMディスクによって形成されているものとする。RAMディスクとしたのは、画像データを記憶蓄積するための容量を確保しつつ、読み出しまたは書き込み時間の高速化、その大きさの小型化、低コスト化を実現するためである。
【0022】
印刷処理管理部5は、ネットワークインタフェース部2が受信したジョブについての印刷処理を管理するものである。例えば、印刷処理管理部5では、印刷処理要求部3dからの印刷処理要求があった画像データに対して、その要求順に印刷処理を行うように管理を行う。
また、印刷処理管理部5は、詳細を後述するように、所定の条件の下、例えば画像処理装置1への電源投入時に、NVRAM10が保持記憶している情報のうちの一部を、記録出力部8に出力させるようになっている。
【0023】
画像データ展開処理部6は、印刷処理管理部5による管理に従い、印刷処理要求部3dが蓄積装置4から読み出した画像データを受け取って、これをイメージデータ(ビットマップデータ等)に展開するものである。
メモリ管理部7は、画像データ展開処理部6での展開の際に使用されるメモリの管理を行うものである。このメモリ管理部7が管理するメモリとしては、ページメモリ7aやリングバッファ7bがある。
【0024】
記録出力部8は、画像データ展開処理部6が展開したイメージデータを、周知の電子写真方式を用いて、記録用紙等の上に可視画像として出力するものである。つまり、記録出力部8は、ホスト装置から送信されたジョブに対応して、印刷処理を実行するものである。
【0025】
記録出力制御部9は、記録出力部8の制御、例えば記録出力部8の一時停止および再開や、記録出力部8での出力ページ順の管理などを行うものである。
また、記録出力制御部9では、記録出力部8が印刷処理を実行する度に、その印刷処理の実行完了を検出するようになっている。この検出は、記録出力部8からの印刷完了信号を認識することによって、ジョブ毎に行う。
さらに、記録出力制御部9では、印刷処理の実行完了を検出した場合、その旨を表すフラグ情報である実行完了情報を、NVRAM10に書き込む処理も行うようになっている。
【0026】
NVRAM10は、読み出しおよび書き込みを行うことのできる不揮発性メモリからなるものであり、画像処理装置1の初期化パラメータや印刷処理情報等を保持記憶するものである。不揮発性メモリとしたのは、電源の切断があっても、その記憶内容を失うことがないようにするためである。
ここで、印刷処理情報とは、受信データ処理制御部3bによって書き込まれる受信完了情報およびコマンドデータと、これに対応して記録出力制御部9によって書き込まれる実行完了情報とからなる情報のことである。つまり、印刷処理情報は、受信データ処理部3が受信したジョブ毎に、そのジョブについての処理実行状態を、受信データ処理制御部3bでの受信完了の検出結果および記録出力制御部9での印刷完了の検出結果によって表した情報である。
【0027】
操作表示処理部11は、画像処理装置1のユーザが操作するためのもので、液晶パネルやキースイッチ等からなる操作パネルを備え、ユーザからの指示内容を印刷処理管理部5やシステム制御部12に通知するものである。
システム制御部12は、画像処理装置1全体の制御を行う制御部で、ハード的なエラーを検出したり、電源起動時の初期化処理を行ったりするものである。
【0028】
次に、以上のように構成された画像処理装置1における処理動作例について説明する。
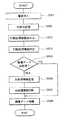
先ず、ここでは、画像処理装置1がホスト装置からのジョブを受信した場合における処理動作例を、図2のフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。
【0029】
ホスト装置からジョブとして画像データおよびコマンドデータが送信されてくると、ネットワークインタフェース部2は、これらのデータの受信を開始して(ステップ101、以下ステップをSと略す)、受信したデータを受信データ処理部3に受け渡す。そして、受信データ処理部3では、受信データ処理制御部3bがこれらの受信を認識するとともに(S102)、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aがその受信内容についてコマンドデータであるか画像データであるかを判別する(S103)。
【0030】
ここで、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aがコマンドデータであると判別すると、続いて、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aは、そのコマンドデータの内容の判定を行う(S104)。
一方、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aが画像データであると判別すると、受信データ蓄積部3cは、その画像データを蓄積装置4に蓄積させる(S105)。
【0031】
その後、受信データ処理制御部3bは、ホスト装置からジョブとして送信された全ての画像データおよびコマンドデータの受信が完了したか否かを判断し(S106)、その受信が完了するまで上述のステップを繰り返す(S102〜S106)。全ての画像データおよびコマンドデータの受信が完了すると、受信データ処理制御部3bは、そのことを検出し、受信完了情報として、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aで判別されたコマンドデータと関連付けて、NVRAM10に保持記憶させる(S107)。このとき、NVRAM10内に新たなデータのための記憶容量がなければ、古いデータ(不要なデータ)を削除するかその上に上書きすればよい。
【0032】
なお、ホスト装置から複数のジョブが送信された場合、あるいは、ネットワーク20上の複数のホスト装置からジョブが送信された場合に、画像処理装置1では、各ジョブ毎に上述した処理を行い、各ジョブに係る画像データを、順次蓄積装置4に蓄積させる。
【0033】
次に、ホスト装置からのジョブの受信完了後、そのジョブに対応した印刷処理を行う場合における処理動作例を、図3のフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。
受信データ処理制御部3bが受信完了を検出すると(S201)、受信した画像データが蓄積装置4内に蓄積されるので、印刷処理要求部3dは、蓄積装置4内における画像データの蓄積状態を確認して(S202)、蓄積装置4内に印刷処理すべき画像データがあるか否かを判断する(S203)。
【0034】
この判断の結果、蓄積装置4内に印刷処理すべき画像データがなければ、印刷処理を行うことができないので、印刷処理要求部3dは、エラー情報を登録して処理を終了する(S204)。
一方、印刷処理すべき画像データがあれば、印刷処理要求部3dは、印刷処理管理部5に印刷要求を発行する(S205)。なお、この印刷要求の発行は、ジョブ毎に行うものとする。
【0035】
印刷処理要求部3dからの印刷要求があると、印刷処理管理部5は、記録出力部8における印刷処理状態を確認して(S206)、新たな印刷処理の開始が可能であるか否かを判断する(S207)。ここで、開始不可能であれば、印刷処理管理部5は、記録出力部8での印刷処理が開始可能になるまで、印刷処理要求部3dからの印刷要求を印刷処理の待ち行列に登録する。
【0036】
また、印刷処理が開始可能であれば、印刷処理要求部3dは、蓄積装置4から印刷処理すべき画像データを読み出しながら(S208)、その画像データを画像データ展開処理部6に送出する。画像データ展開処理部6は、その画像データを印刷可能なイメージデータに展開して(S209)、展開後のイメージデータを記録出力部8に送出する。そして、記録出力部8は、送出されたイメージデータを記録用紙等の上に出力する(S210)。
【0037】
ここで、印刷処理要求部3dは、印刷処理すべき画像データの全て、すなわち一つのジョブあたりの全ての画像データについて、蓄積装置4からの読み出しが終了したか否かを判断し(S211)、その読み出しが終了するまで上述のステップを繰り返す(S208〜S211)。
【0038】
そして、一つのジョブあたりの全ての画像データについての印刷処理が完了すると、記録出力制御部9は、そのことを検出し、印刷完了情報として、ホストコマンド判定処理部3aで判別されたコマンドデータと関連付けて、NVRAM10に保持記憶させる(S212)。
また、記録出力制御部9は、印刷処理の完了を検出すると、その旨を印刷処理管理部5に通知し、次のジョブについての印刷処理の開始を可能にする。
このようにして、画像処理装置1では、複数のジョブに対応した印刷処理を、順次実行する。
【0039】
次に、このような画像処理装置1に電源が投入された起動時における処理動作例を、図4のフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。
この画像処理装置1では、ユーザまたはネットワークのシステム管理者等による電源が投入されると(S301)、システム制御部12が、画像処理装置1全体の初期化処理を行う(S302)。
【0040】
初期化処理が終了すると、続いて、印刷処理管理部5は、NVRAM10から印刷処理情報を読み出して(S303)、その印刷処理情報から、電源投入前、すなわち電源が切断される以前における画像処理装置1での印刷処理実行状態を判定する(S304)。詳しくは、印刷処理管理部5では、印刷処理情報のうちの受信完了情報と実行完了情報とから、画像データの受信が完了しているが印刷が未完了のもの、画像データの受信を開始したが完了していないもの等、未処理のジョブが存在しているか否かを判定する(S305)。
【0041】
この判定の結果、未処理のジョブが存在していなければ、画像処理装置1は、通常通り、ホスト装置からのジョブ送信待ちの待機処理に入る(S308)。
一方、未処理のジョブが存在している場合には、印刷処理管理部5は、受信データ処理部3に蓄積装置4の蓄積内容を問い合わせ、蓄積装置4内にそのジョブに係る画像データがないことを確認した後、印刷が未完了であることを通知するための未処理情報を生成し(S306)、この未処理情報、すなわち印刷処理情報の一部を、記録出力部8に出力させる(S307)。そして、記録出力部8から未処理情報が出力された後に、画像処理装置1は、ホスト装置からのジョブ送信待ちの待機処理に入る(S308)。
【0042】
このようにして、記録出力部8から出力される未処理情報としては、例えば図5に示すようなものがある。すなわち、印刷処理情報のうちのコマンドデータに基づく「ホスト名」、「ユーザ(ログイン)名」および「ファイル名」と、受信完了情報に基づく「受信完了時刻」および「受信状態」と、実行完了情報に基づく「印刷状態」とからなるものがある。なお、「受信完了時刻」は、画像処理装置1内のクロック等を利用して認識すればよい。
【0043】
このうち、受信が完了しているのに印刷処理が終了しているジョブについては、「受信状態」が完了で、「印刷状態」が未了と出力される。また、受信データ処理制御部3bが受信開始を認識したのに受信が完了していないジョブについては、「受信状態」と「印刷状態」との両方共に未了と出力される。
【0044】
ただし、受信と印刷処理とが共に完了しているジョブは、未処理情報としては出力されない。つまり、記録出力部8からは、未処理情報のみ、すなわち印刷処理情報の一部のみが出力される。これは、印刷が完了しているジョブについては、その出力の必要性が低いためであり、また未処理情報の出力時間を短縮するためである。
【0045】
以上のように、本実施の形態の画像処理装置1によれば、受信データ処理制御部3bジョブの受信完了を検出するとともに、記録出力制御部9が印刷処理の実行完了を検出する。そして、これらの検出結果を、NVRAM10がジョブ毎に印刷処理情報として記憶する。
そのため、この画像処理装置1では、蓄積装置4が揮発性のRAMディスクからなるもので、電源の切断等によって蓄積内容を失ってしまった場合であっても、NVRAM10がが記憶している印刷処理情報は失われることない。しかも、その後の電源投入時に、その印刷処理情報を記録出力部8が記録用紙等の上に出力するので、その出力結果を参照すれば、各ジョブについての処理実行状態、具体的には未処理のジョブが容易にわかるようになる。
【0046】
この未処理のジョブには、紙詰まり等の印刷障害によって正しく印刷処理が行われなかったジョブ、ネットワーク上の障害等によって正しく受信されなかったジョブ、電源切断等の装置障害によって受信や印刷処理が行われなかったジョブ等が含まれる。
【0047】
したがって、この画像処理装置1では、電源の切断等によってスプールした内容を失ってしまっても、印刷処理情報に基づいて未処理のジョブのみ再発行すればよいので、スプール機能を実現するための蓄積装置4を揮発性のRAMディスクで形成しても、電源切断時等における各ホスト装置のユーザへの負担を従来よりも軽減することができる。すなわち、蓄積装置4を揮発性のRAMディスクで形成することが可能となり、結果として装置全体の高速処理化、小型化、低コスト化を実現することができる。また、各ホスト装置のユーザへの負担軽減に伴い、煩わしさや不便さをも解消することができる。さらには、未処理のジョブのみ再発行すればよいので、ジョブ再発行時における処理効率を従来よりも向上させることができる。
【0048】
なお、本実施の形態では、印刷処理情報を記録用紙等の上に出力する場合を例に挙げて説明したが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、印刷処理情報を出力することによってその内容をユーザに通知するものであればよい。例えば、印刷処理情報を、ネットワーク20を介して所定のプロトコルでホスト装置へ送信し、そのホスト装置のCRT(Cathode Ray Tube)等で出力させるようにしても、上述の場合と同様の効果が得られ、しかも各ホスト装置のユーザにとっては記録用紙等を必要としなくなるのでより一層便利なものとなる。さらには、印刷処理情報を操作表示処理部11で出力するようにしてもよい。
【0049】
また、本実施の形態では、印刷処理情報を出力する条件として、画像処理装置1に電源が投入された場合を例に挙げて説明したが、例えば、これ以外にも、ホスト装置から印刷処理情報の出力要求があった場合やNVRAM10の記憶容量に余裕が無くなった時点等に出力するようにしてもよい。つまり、印刷処理情報は、所定の条件の下で出力するようにすればよい。
【0050】
また、本実施の形態では、印刷処理情報として、ホスト装置のホスト名、ユーザのログイン名および画像データのファイル名を出力する場合を例に挙げて説明したが、ジョブを特定することが可能であれば、これら以外のもの、例えばネットワークシステム内で一意に定められるジョブID等を出力するようにしてもよい。
さらには、印刷処理情報として、印刷処理あるいは受信処理が完了しなかった場合にシステム制御部12が認識するエラーコード等を、付加することも考えられる。この場合には、エラーコード等によって、これらの処理が完了しなかった理由が分かるようになるので、ネットワーク20に接続された画像処理装置1のメンテナンスを、ユーザや保守員がより一層容易に行うことが可能になる。
【0051】
また、本実施の形態では、蓄積装置4としてRAMディスクを用いた場合について説明したが、その他の揮発性メモリを用いても、印刷処理情報をNVRAM10のような不揮発性メモリに記憶させれば、本発明の効果は得られる。
【0052】
また、本実施の形態では、本発明をネットワークプリンタに適用した場合を例に挙げて説明したが、上位装置からのジョブに対応して印刷処理を行い、かつ、スプール機能を有するものであれば、他のものであっても適用することができる。例えば、複写機能、プリンタ機能、FAX機能を兼ね備えた複合機などについての適用が考えられる。
【0053】
【発明の効果】
以上に説明したように、本発明の画像処理装置は、蓄積手段を揮発性のもので構成しても、印刷処理情報によりジョブの処理実行状態が分かるようになっているので、例えば電源の切断等があってもその印刷処理情報に基づいて未処理のジョブのみ再発行することが可能になる。したがって、蓄積手段を揮発性のもので構成することで、装置全体の高速処理化、小型化、低コスト化を実現することができる。また、蓄積手段を揮発性のもので構成しても、電源切断時等における上位装置での負担を従来よりも軽減することができ、ユーザにとっての煩わしさや不便さが解消できる。さらには、電源の切断等があっても未処理のジョブのみ再発行すればよいので、ジョブ再発行時における処理効率を従来よりも向上させることができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明に係わる画像処理装置の実施の形態の一例の概略構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】 図1の画像処理装置でホスト装置からのジョブを受信した場合における処理動作例を示すフローチャートである。
【図3】 図1の画像処理装置でジョブに対応した印刷処理を行う場合における処理動作例を示すフローチャートである。
【図4】 図1の画像処理装置で電源が投入された起動時における処理動作例を示すフローチャートである。
【図5】 記録用紙上に出力された未処理情報(印刷処理情報)の具体例を示す説明図である。
【符号の説明】
1…画像処理装置、2…ネットワークインタフェース部、3…受信データ処理部、3a…ホストコマンド判定処理部、3b…受信データ処理制御部、3c…受信データ蓄積部、3d…印刷処理要求部、4…蓄積装置、5…印刷処理管理部、8…記録出力部、9…記録出力制御部、10…NVRAM[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an image processing apparatus that performs print processing in response to a job from a host apparatus, and more particularly to an image processing apparatus having a spool function that temporarily stores and accumulates image data to be printed.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, with the spread of computer networks, image processing apparatuses that are used in connection with a plurality of host devices (personal computers, workstations, etc.), such as network printers, are widely known.
In such an image processing apparatus, in general, according to an existing communication protocol such as TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) or SPX / IPX (Sequenced Packet Exchange / Internet Packet Exchange), communication with each host apparatus is performed. Communication is performed, and when a print processing request and image data to be printed are received as a job from each host device, the print processing is performed corresponding to the job. At this time, image data described in, for example, a page description language is transmitted from each host device to reduce the communication load. Therefore, the image processing device develops the received image data into printable image data. After that, print processing is performed.
[0003]
However, when the image processing apparatus is used on a network and receives image data while performing image data expansion processing, the image processing apparatus performs transmission processing of the host device until all the image data is received and expanded. It cannot be opened. Further, when a plurality of host devices exist on the network, it is necessary to accept a job from each host device.
Therefore, an image processing apparatus normally used on a network has a spool function that temporarily stores and accumulates received image data, thereby shortening the transmission time of the image data in the host apparatus and image data in a certain job. Even if the data printing process is not completed, other jobs can be accepted.
[0004]
In an image processing apparatus having such a spool function, image data once stored and accumulated are sequentially read out and developed into image data, and then printed. Therefore, even when a failure such as a paper jam occurs during the printing process, it is possible to perform a recovery process for resuming development and printing from a portion that has not been printed normally after the failure is cleared. For example, in JP-A-5-11939, even when a failure occurs during printing processing by associating and storing image data and page information related to the image data, An invention is disclosed that makes it possible to resume the printing process from the page where the failure has occurred.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
By the way, in a conventional image processing apparatus having a spool function, a memory for temporarily storing and storing image data is formed by a large-capacity non-volatile hard disk device or the like in order to enable the above-described recovery processing. Yes. This is because a certain amount of storage capacity is required to store and store the image data from each host device on the network, and in the case of a volatile one, if the power is cut off, the stored image data is stored. This is because it may be lost and the recovery process cannot be performed. Therefore, in a conventional image processing apparatus having a spool function, a hard disk device or the like requires more reading or writing time than a semiconductor memory such as a RAM (Random Access Memory), its size is large, and its cost is high. As a result, it is difficult to realize high-speed processing, downsizing, and low cost of the entire apparatus.
[0006]
On the other hand, it is conceivable that the spool function is realized by a volatile memory such as a RAM, and when the power supply is cut off, the host device issues a job again. In this case, There is a problem in terms of.
For example, when the power is turned off, even if the image processing apparatus accepts a plurality of jobs before that, it is necessary to repeat the print processing from the beginning for all these jobs from the host device. . In other words, even if there is a job that has already been received and a job that has not been completed, the spool contents are lost due to power-off etc., so which job is unprocessed As a result, all jobs must be issued from the host device. Therefore, it is very cumbersome and inconvenient for the user of each host device because it is subjected to a large operational burden. It also hinders improvement in processing efficiency of the entire network system.
[0007]
Therefore, the present invention realizes high-speed processing, downsizing, and low cost of the entire image processing apparatus, and makes it easy to specify the job processing state, so that unprocessed data can be processed even if the power is cut off. An object of the present invention is to provide an image processing apparatus that can reissue only a job.
[0008]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention is an image processing apparatus devised to achieve the above object, receiving means for receiving a print processing request and image data to be printed from a host apparatus as a job, and each time the receiving means receives a job. Receiving completion detecting means for detecting completion of reception of the job, storage means for storing the job received by the receiving means, processing means for executing print processing corresponding to the job stored in the storing means, A processing completion detecting unit for detecting completion of execution of the printing process every time the processing unit executes the printing process, and detection by the reception completion detecting unit and the processing completion detecting unit for each job received by the receiving unit. Non-volatile storage means for storing the result as print processing information indicating the processing execution state for the job, and a mark stored in the storage means under a predetermined condition It is characterized in that an output means for outputting processed information.
[0009]
According to the image processing apparatus configured as described above, when the receiving unit receives a job from the host device, the reception completion detecting unit detects the reception completion. Thereafter, when the processing unit executes the printing process corresponding to the job stored in the storage unit, the processing completion detection unit detects the execution completion. These detection results are stored as print processing information for each job by the non-volatile storage means. This print processing information is output by the output means under a predetermined condition.
Accordingly, in this image processing apparatus, for example, even when the storage means is volatile and the stored content is lost due to power-off or the like, the print processing information stored in the nonvolatile storage means is Since it is output by the output means under a certain condition without being lost, whether or not the print processing of the job in the storage means has been completed based on the output result, that is, the processing execution state for each job is easy I will understand.
[0010]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The image processing apparatus according to the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. However, here, a case where the present invention is applied to a network printer used on a network will be described as an example.
[0011]
As shown in FIG. 1, an
[0012]
The host device is composed of, for example, a personal computer or a workstation, and functions as a host device of the image processing device. This host apparatus has a printer driver corresponding to the
[0013]
However, the host device performs job transmission in accordance with a predetermined protocol, for example, the Lpd (Line Printer Daemon) protocol defined in RFC1179, and the job is transmitted in a predetermined format (for example, description in a page description language). The image data and the command data for instructing the printing process of the image data are combined. The command data includes the file name of the image data written in a character string such as ASCII (ASCII), the login name of the user who has instructed printing on the host device, the host name of the host device, etc. To do.
[0014]
On the other hand, the
[0015]
The
[0016]
When the
[0017]
The host command determination processing unit 3a determines image data and command data for a job received from the
[0018]
The reception data processing control unit 3b performs reception management of image data, and detects completion of reception of image data as one of the managements. This detection is performed for each job by recognizing a command indicating transmission completion from the host device, an EOF signal indicating the end of data, and the like based on the determination result by the host command determination processing unit 3a.
When the reception data processing control unit 3b detects the completion of reception of image data, the reception data processing control unit 3b associates the reception completion information, which is flag information indicating that fact, with the command data determined by the host command determination processing unit 3a. Thus, the process of writing into the
[0019]
The reception
[0020]
The print
[0021]
The storage device 4 is a memory for realizing the spool function in the
[0022]
The print processing management unit 5 manages print processing for jobs received by the
Further, as will be described in detail later, the print processing management unit 5 records a part of the information held and stored in the
[0023]
The image data development processing unit 6 receives image data read from the storage device 4 by the print
The memory management unit 7 manages the memory used when the image data expansion processing unit 6 performs expansion. The memory managed by the memory management unit 7 includes a page memory 7a and a
[0024]
The recording output unit 8 outputs the image data developed by the image data development processing unit 6 as a visible image on a recording sheet or the like using a known electrophotographic method. That is, the recording output unit 8 executes print processing corresponding to the job transmitted from the host device.
[0025]
The recording output control unit 9 controls the recording output unit 8, for example, temporarily stops and resumes the recording output unit 8, and manages the output page order in the recording output unit 8.
The recording output control unit 9 detects the completion of the printing process every time the recording output unit 8 executes the printing process. This detection is performed for each job by recognizing a print completion signal from the recording output unit 8.
Further, when the recording output control unit 9 detects the completion of execution of the printing process, the recording output control unit 9 also performs a process of writing execution completion information, which is flag information indicating the fact, to the
[0026]
The
Here, the print processing information is information including reception completion information and command data written by the reception data processing control unit 3b, and execution completion information written by the recording output control unit 9 corresponding thereto. . That is, the print processing information includes, for each job received by the reception
[0027]
The operation
The
[0028]
Next, a processing operation example in the
First, an example of processing operation when the
[0029]
When image data and command data are transmitted as a job from the host device, the
[0030]
Here, if the host command determination processing unit 3a determines that it is command data, then the host command determination processing unit 3a determines the contents of the command data (S104).
On the other hand, if the host command determination processing unit 3a determines that the data is image data, the received
[0031]
Thereafter, the reception data processing control unit 3b determines whether or not reception of all image data and command data transmitted as a job from the host device has been completed (S106), and performs the above steps until the reception is completed. Repeat (S102 to S106). When the reception of all the image data and command data is completed, the reception data processing control unit 3b detects this and associates it with the command data determined by the host command determination processing unit 3a as reception completion information in the
[0032]
When a plurality of jobs are transmitted from the host device, or when jobs are transmitted from a plurality of host devices on the
[0033]
Next, an example of a processing operation in the case where a print process corresponding to a job is performed after completion of reception of the job from the host device will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
When the reception data processing control unit 3b detects the completion of reception (S201), the received image data is stored in the storage device 4. Therefore, the print
[0034]
As a result of this determination, if there is no image data to be printed in the storage device 4, the printing process cannot be performed, so the printing
On the other hand, if there is image data to be printed, the print
[0035]
When there is a print request from the print
[0036]
If the print processing can be started, the print
[0037]
Here, the print
[0038]
When the print processing for all the image data per job is completed, the recording output control unit 9 detects that and the command data determined by the host command determination processing unit 3a as print completion information. In association therewith, the
Further, when the recording output control unit 9 detects the completion of the printing process, the recording output control unit 9 notifies the printing process management unit 5 to that effect and enables the printing process for the next job to be started.
In this way, the
[0039]
Next, an example of processing operation at the time of startup when the
In the
[0040]
When the initialization process is completed, the print process management unit 5 reads the print process information from the NVRAM 10 (S303), and from the print process information, the image processing apparatus before the power is turned on, that is, before the power is turned off. 1 is determined (S304). Specifically, the print processing management unit 5 starts receiving image data from the reception completion information and execution completion information of the print processing information that have been received but have not yet been printed. It is determined whether or not there is an unprocessed job such as a job that has not been completed (S305).
[0041]
If there is no unprocessed job as a result of this determination, the
On the other hand, if there is an unprocessed job, the print processing management unit 5 inquires the received
[0042]
In this way, the unprocessed information output from the recording output unit 8 is, for example, as shown in FIG. That is, “host name”, “user (login) name” and “file name” based on command data in print processing information, “reception completion time” and “reception status” based on reception completion information, and execution completion Some of them consist of “printing status” based on information. The “reception completion time” may be recognized using a clock in the
[0043]
Among these, for a job for which printing has been completed although reception has been completed, the “reception state” is completed and the “printing state” is output as incomplete. For a job whose reception data processing control unit 3b has recognized the start of reception but has not completed reception, both “reception state” and “printing state” are output as incomplete.
[0044]
However, a job for which both reception and print processing have been completed is not output as unprocessed information. That is, only the unprocessed information, that is, only a part of the print processing information is output from the recording output unit 8. This is because the necessity of outputting a job for which printing has been completed is low, and the output time of unprocessed information is shortened.
[0045]
As described above, according to the
Therefore, in this
[0046]
This unprocessed job includes a job that was not correctly printed due to a print failure such as a paper jam, a job that was not correctly received due to a network failure, or a device failure such as a power failure. Jobs that were not performed are included.
[0047]
Therefore, in this
[0048]
In this embodiment, the case where print processing information is output on a recording sheet or the like has been described as an example. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and by outputting print processing information. What is necessary is just to notify the user of the content. For example, even if the print processing information is transmitted to the host device via the
[0049]
In the present exemplary embodiment, the case where the
[0050]
In this embodiment, the case where the host name of the host device, the login name of the user, and the file name of the image data are output as print processing information has been described as an example. However, a job can be specified. If there is, other than these, for example, a job ID uniquely determined in the network system may be output.
Furthermore, it is also conceivable to add an error code or the like recognized by the
[0051]
Further, in the present embodiment, the case where a RAM disk is used as the storage device 4 has been described. However, even if another volatile memory is used, if the print processing information is stored in a nonvolatile memory such as the
[0052]
In the present embodiment, the case where the present invention is applied to a network printer has been described as an example. However, any printing process corresponding to a job from a higher-level apparatus and having a spool function may be used. It can be applied to other things. For example, it is conceivable to apply to a multifunction device having a copying function, a printer function, and a FAX function.
[0053]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, the image processing apparatus according to the present invention can know the job processing execution state based on the print processing information even if the storage unit is configured to be volatile. Etc., only unprocessed jobs can be reissued based on the print processing information. Therefore, by configuring the storage means with a volatile one, it is possible to realize high-speed processing, downsizing, and cost reduction of the entire apparatus. Even if the storage means is composed of a volatile one, the burden on the host device when the power is turned off can be reduced as compared with the conventional case, and the troublesomeness and inconvenience for the user can be solved. Furthermore, since it is sufficient to reissue only an unprocessed job even if the power is cut off, the processing efficiency at the time of reissuing the job can be improved as compared with the prior art.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of an example of an embodiment of an image processing apparatus according to the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a processing operation when a job from a host apparatus is received by the image processing apparatus of FIG.
3 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a processing operation when a printing process corresponding to a job is performed in the image processing apparatus of FIG.
4 is a flowchart showing an example of a processing operation at the time of start-up when power is turned on in the image processing apparatus of FIG.
FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a specific example of unprocessed information (print processing information) output on a recording sheet.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (3)
Translated fromJapanese前記受信手段がジョブを受信する度に該ジョブの受信完了を検出する受信完了検出手段と、
前記受信手段が受信したジョブを蓄積する蓄積手段と、
前記蓄積手段が蓄積しているジョブに対応して印刷処理を実行する処理手段と、
前記処理手段が印刷処理を実行する度に該印刷処理の実行完了を検出する処理完了検出手段と、
前記受信手段が受信したジョブ毎に、前記受信完了検出手段および前記処理完了検出手段による検出結果を、該ジョブについての処理実行状態を表す印刷処理情報として記憶する不揮発性の記憶手段と、
所定の条件の下で前記記憶手段が記憶している印刷処理情報を出力する出力手段と
を備えることを特徴とする画像処理装置。Receiving means for receiving a print processing request and image data to be printed from the host device as a job;
A reception completion detection means for detecting completion of reception of the job each time the reception means receives a job;
Storing means for storing the job received by the receiving means;
Processing means for executing print processing corresponding to the job stored in the storage means;
A process completion detection unit that detects completion of execution of the print process each time the processing unit executes the print process;
Non-volatile storage means for storing detection results by the reception completion detection means and the processing completion detection means for each job received by the reception means as print processing information indicating a processing execution state for the job;
An image processing apparatus comprising: output means for outputting print processing information stored in the storage means under a predetermined condition.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP35040597AJP3695104B2 (en) | 1997-12-19 | 1997-12-19 | Image processing device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP35040597AJP3695104B2 (en) | 1997-12-19 | 1997-12-19 | Image processing device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH11180004A JPH11180004A (en) | 1999-07-06 |
| JP3695104B2true JP3695104B2 (en) | 2005-09-14 |
Family
ID=18410280
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP35040597AExpired - Fee RelatedJP3695104B2 (en) | 1997-12-19 | 1997-12-19 | Image processing device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3695104B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6265589B2 (en)* | 2012-07-09 | 2018-01-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | Job processing apparatus, job management method, job management system, and program |
- 1997
- 1997-12-19JPJP35040597Apatent/JP3695104B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH11180004A (en) | 1999-07-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4817474B2 (en) | Data processing apparatus, data processing method, and storage medium storing computer-readable program | |
| US8477356B2 (en) | User selected setting update between image processing apparatuses on a network | |
| JPH10143340A (en) | Printer | |
| US7538902B2 (en) | Print control program and information processing apparatus | |
| JPH0325523A (en) | computer peripherals | |
| JP4934073B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing method | |
| JP2006041764A (en) | Log recording apparatus, log recording program, and recording medium | |
| JP2004341728A (en) | Printing apparatus, printing system and canceling method | |
| JP3695104B2 (en) | Image processing device | |
| JPH11314438A (en) | Printing apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP2010208075A (en) | Image forming apparatus, method for controlling image formation, program for controlling image formation and recording medium | |
| JP3080000B2 (en) | Information processing device and storage medium | |
| JPH1097395A (en) | Print control apparatus, print control method for print apparatus, and storage medium storing computer-readable program | |
| JP5062750B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2003241948A (en) | Method or apparatus for recovering a failed print job | |
| JP2001047706A (en) | Image formation system in network environment | |
| JP3174771B2 (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP2008027217A (en) | Printing system including information processing apparatus and printing apparatus | |
| JP2004341733A (en) | Printing apparatus, printing method, and program | |
| US7589859B2 (en) | Print apparatus, print control method, storage medium storing computer-readable program, and program | |
| JPH11175268A (en) | Information processing apparatus and retransmission data management method thereof | |
| JPH10320139A (en) | PRINT CONTROL DEVICE, PRINT CONTROL METHOD, AND COMPUTER-READABLE RECORDING MEDIUM CONTAINING PRINT CONTROL PROGRAM | |
| JP2007136824A (en) | Printing apparatus, printing method, computer program, and storage medium | |
| JP2000343772A (en) | Printing system | |
| JP2006256041A (en) | Image forming apparatus and image forming method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20040426 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20040511 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20050607 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20050620 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20080708 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090708 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100708 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110708 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110708 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120708 Year of fee payment:7 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130708 Year of fee payment:8 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |