JP3628505B2 - Image processing device - Google Patents
Image processing deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3628505B2 JP3628505B2JP30337297AJP30337297AJP3628505B2JP 3628505 B2JP3628505 B2JP 3628505B2JP 30337297 AJP30337297 AJP 30337297AJP 30337297 AJP30337297 AJP 30337297AJP 3628505 B2JP3628505 B2JP 3628505B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- application
- key card
- card device
- abnormal state
- image processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Control Or Security For Electrophotography (AREA)
- Facsimiles In General (AREA)
Description
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
この発明は各アプリケーションに対する使用者の制限情報及び部門毎の複写枚数の制限情報等を個別に管理するキーカード装置を備える画像処理装置、特にキーカード装置の異常時における各アプリケーションの動作制限に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
画像処理装置である複写機及びファクシミリ装置等においては、例えば特開平6−22066号公報に掲載された画像形成装置のように、キーカード装置を備え、各種アプリケーションの使用者及び使用量を制限して管理効率等を高めている装置がある。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上記キーカード装置に故障が発生した場合に、本来利用者を制限しなくても良いアプリケーションまでが使用できなくなったり、逆に使用量を制限すべきアプリケーションの使用量の管理が行なわれなくなったりしていた。
【0004】
また、キーカード装置に異常が発生した際のアプリケーションがそのままの状態で残っていると、他の利用者が間違ってそのアプリケーションを続行してしまう場合があった。
【0006】
この発明はかかる短所を解消するためになされたものであり、キーカード装置に故障が発生した場合の動作を適正に制限することで、利用効率を高めることを目的とする。
【0007】
【課題を解決するための手段】
この発明に係る画像処理装置は、各アプリケーションに対する使用者別の制限情報及び使用量の制限情報等を個別に管理するキーカード装置を備え、更に使用が制限されているアプリケーションを記憶する利用制限アプリケーション記憶手段と、キーカード装置からの信号を基にキーカード装置が異常状態に陥っているか否かを検知する異常検知手段と、異常検知手段によってキーカード装置が異常状態に陥ったと検知した場合は、利用制限アプリケーション記憶手段に記憶されているアプリケーションと動作中のアプリケーションとを比較し、比較の結果、動作中のアプリケーションが、使用が制限されているアプリケーションである場合は当該アプリケーションの動作を中断し、比較の結果、動作中のアプリケーションが、使用が制限されていないアプリケーションである場合は、当該アプリケーションの動作を続行するアプリケーション制御手段とを有している。よって、本来利用を制限しなくても良いアプリケーションまでが使用できなくなったり、逆に使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対する制限が行われなくなったりすることを防止する。
【0012】
また、他の画像処理装置は、各アプリケーションに対する使用者の制限情報及び使用量の制限情報等を個別に管理するキーカード装置を備え、キーカード装置が異常状態であっても使用を許可するアプリケーションを予め記憶し、キーカード装置が異常状態に陥ると、使用を許可されているアプリケーションのみを起動できるようにして、本来利用を制限しなくても良いアプリケーションまでが使用できなくなったり、逆に使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対して制限が行なわれなくなったりすることを防止する。
【0013】
さらに、キーカード装置が異常状態にあり、装置の使用者がキーカード装置の異常状態において使用を許可するアプリケーション以外のアプリケーションを選択するとそのアプリケーションの起動は行なわずに警告を出力して、そのアプリケーションが使用できない旨を利用者に通知する。
【0014】
さらに、キーカード装置が異常状態に陥った際に、予め登録したキーカード装置の異常状態において使用を許可するアプリケーション以外のアプリケーションが起動した状態であると自動的にそのアプリケーションを終了し、予め登録したキーカード装置の異常状態において使用を許可するアプリケーションを起動して、キーカード装置に異常が発生している際に使用を許可していないアプリケーションが動作することを防止する。
【0018】
【発明の実施の形態】
この発明の画像処理装置は、各アプリケーションに対する使用者の制限情報及び使用量の制限情報等を個別に管理するキーカード装置を備え、特にキーカード装置に異常が発生した場合の各アプリケーションの動作を制御することによりキーカード装置に異常が発生したことによる装置稼働率及び管理状況への影響を少なくするものである。
【0019】
画像処理装置は、例えばコピーアプリケーション部(以下、「コピーアプリ部」という。)、プリンタアプリケーション部(以下、「プリンタアプリ部」という。)、ファクシミリアプリケーション部(以下、「FAXアプリ部」という。)、システムコントローラ、操作部コントローラ、画像形成コントローラ、画像読取コントローラ、周辺機コントローラ、入出力制御部、操作表示部、画像形成部、画像読取部及びキーカード装置を有する。
【0020】
コピーアプリ部、プリンタアプリ部及びFAXアプリ部は、それぞれコピーアプリケーション、プリンタアプリケーション及びファクシミリアプリケーションの制御を記憶する。
【0021】
システムコントローラは、例えば利用制限アプリケーション記憶部(以下、「利用制限アプリ記憶部」という。)とロギング記憶部とアプリケーション制御部(以下、「アプリ制御部」という。)と異常検知部を備える。利用制限アプリ記憶部は、使用者制限、部門毎の複写枚数制限及び通信料金制限等の使用制限をされているアプリケーションを記憶する。ロギング記憶部は、異常状態に陥った状態で、例えば複写枚数制限及び通信料金制限等の使用量制限がされているアプリケーションを稼働した場合の部門毎の複写枚数及び通信料金等の使用履歴データであるログデータを記憶する。アプリ制御部は、コピーアプリケーション、プリンタアプリケーション及びファクシミリアプリケーションの起動及び中止等を制御する部分であり、例えば使用が制限されているアプリケーションの動作中にキーカード装置が異常状態に陥った場合はそのアプリケーションの動作を中断し、使用が制限されていないアプリケーションの動作中にキーカード装置が異常状態に陥った場合はそのアプリケーションの動作を続行するように制御する。異常検知部はキーカード装置からの信号を基にキーカード装置が異常状態に陥っているか否かを検知する。
【0022】
操作部コントローラ、画像形成コントローラ、画像読取コントローラ及び周辺機コントローラは入出力制御部を介して操作表示部、画像形成部、画像読取部及びキーカード装置を制御する。キーカード装置は、キーカードを備え、キーカードに対して使用者制限、部門毎の利用枚数制限及び通信料金制限等の制限情報並びに部門毎の複写枚数及び通信料金等の使用履歴データであるログデータを読み書きする。
【0023】
上記のように構成した場合において、例えば使用が制限されているアプリケーションの動作中にキーカード装置が異常状態に陥った場合はそのアプリケーションの動作を中断し、使用が制限されていないアプリケーションの動作中にキーカード装置が異常状態に陥った場合はそのアプリケーションの動作を続行することにより、本来利用を制限しなくても良いアプリケーションまでが使用できなくなったり、逆に使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対する制限が行なわれなくなったりすることを防止することができる。
【0024】
また、キーカード装置が異常状態に陥った際の使用者がキーカード装置が異常状態から回復した際の使用者と同一か否かを調べ、キーカードの異常状態の前後の使用者が異なる場合は装置全体をリセットして、他の利用者が間違って異常発生時のアプリケーションを処理することを防止する。
【0025】
さらに、キーカード装置が異常状態である間は一定周期でキーカード装置にリセット信号を出力し、キーカード装置を自動的に復旧すると良い。
【0026】
【実施例】
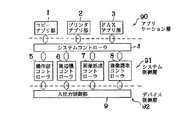
図1はこの発明の一実施例の画像処理装置の構成図である。図に示すように、画像処理装置は、例えばコピーアプリ部1、プリンタアプリ部2、FAXアプリ部3、システムコントローラ4、操作部コントローラ5、画像形成コントローラ6、画像読取コントローラ7、周辺機コントローラ8、入出力制御部9、操作表示部10、画像形成部11、画像読取部12及びキーカード装置13を有する。
【0027】
コピーアプリ部1、プリンタアプリ部2及びFAXアプリ部3は、それぞれ画像処理装置のアプリケーションであるコピーアプリケーション(以下、「コピーアプリ」という。)、プリンタアプリケーション(以下、「プリンタアプリ」という。)及びファクシミリアプリケーション(以下、「FAXアプリ」という。)における制御手順等を記憶する。
【0028】
システムコントローラ4は、例えば利用制限アプリ記憶部41とロギング記憶部42とアプリ制御部43と異常検知部44を備える。利用制限アプリ記憶部41は、使用者制限、部門毎の複写枚数制限及び通信料金制限等の使用制限をされているアプリケーションを記憶する。ロギング記憶部42は、キーカード装置13が異常状態に陥った状態で、例えば複写枚数制限及び通信料金制限等の使用量制限がされているアプリケーションを稼働した場合の部門毎の複写枚数及び通信料金等の使用履歴データであるログデータを記憶する。アプリ制御部43は、コピーアプリ、プリンタアプリ及びFAXアプリの起動及び中止等を制御する部分であり、例えば使用が制限されているアプリケーションの動作中にキーカード装置13が異常状態に陥った場合はそのアプリケーションの動作を中断し、使用が制限されていないアプリケーションの動作中にキーカード装置13が異常状態に陥った場合はそのアプリケーションの動作を続行するように制御する。異常検知部44は、後に説明するようにしてキーカード装置13からの信号を基にキーカード装置13が異常状態に陥っているか否かを検知する。
【0029】
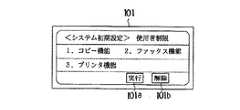
操作部コントローラ5、画像形成コントローラ6、画像読取コントローラ7及び周辺機コントローラ8は入出力制御部9を介してそれぞれ操作表示部10、画像形成部11、画像読取部12及びキーカード装置13を制御する。操作表示部10は操作ガイダンス等を表示し、複写操作等を入力する部分であり、例えば図2に示すようにプログラムモードの登録及び呼出しに用いる「プログラム登録/呼出し」キー102、初期設定を行なうときに用いる「初期設定」キー104、ファクシミリモードのプログラムの割当てに用いるファクシミリ用短縮キー群105、テンキー106、各アプリケーションの切り替えに用いる「アプリケーション切り替え」キー107及びメニューの表示に用いる「メニュー」キー108等を備える。また、操作表示部10はLCD101を備え、図3及び図4に示すように各アプリケーションに対する使用者制限等をするか否か等の入力ガイダンスを表示して、その選択を入力する。例えばコピーアプリにおいて使用者制限をする場合は、図3で示す画面が表示されている状態で操作表示部10のテンキー(不図示)から「1」を入力してコピー機能の使用者制限を指定する。コピー機能の使用者制限をすることにより、操作表示部10のLCD101は、図4に示すような設定画面を表示する。この画面が表示されている状態で、操作表示部10のテンキーから「1」を入力して使用者制限を指定することを選択し、その後、「実行」キー101aを押下することにより使用者制限することを設定する。ここで、「実行」キー101aを押下する代わりに「解除」キー101bを押下すると、操作表示部10のLCD101は、図3に示すシステム初期設定画面に戻る。
【0030】
画像形成部11は画像イメージデータを基に、例えば電子写真、感熱、熱転写又はインクジェット等の手段により普通紙又は感熱紙等に画像を形成する。画像読取部12は光源部(不図示)から原稿を照射し、その反射光をCCD(不図示)で電気信号に変換し、必要な画像処理を行なって原稿からの画像読み取りを行なう。キーカード装置13は、磁気カード等から成るキーカード15を両面から読み取り可能な差し込み式カードリーダを備え、キーカード15に対して使用者制限、部門毎の利用枚数制限及び通信料金制限等の制限情報並びに部門毎の複写枚数及び通信料金等の使用履歴データであるログデータを読み書きする。さらに、キーカード15は上記使用者制限の情報等を記憶する他に、使用者を識別するために各使用者に固有の識別コードを記録する。以後、この識別コードをキーカード識別コードという。
【0031】
上記画像処理装置の各制御部はその機能毎に分けると、例えば図5に示すようにアプリケーション層90、システム制御層91及びデバイス制御層92に分かれる。アプリケーション層90はコピーアプリ部1、プリンタアプリ部2及びFAXアプリ部3から成り、複写機としてのアプリケーション、プリンタ装置としてのアプリレーション及びファクシミリ装置としてのアプリケーションを制御する。システム制御部91はシステムコントローラ4、操作部コントローラ5、画像形成コントローラ6、画像読取コントローラ7及び周辺機コントローラ8から成り、既に説明したような各種の制御を行ない、各構成部を機能単位にリソースとして扱い、一つのリソースを複数のアプリケーションで共有するための管理を行ないマルチタスク型の動作を実現している。デバイス制御層92は、システム制御層91からのコマンド、及び制御信号等の論理的指示を基にクラッチ、センサ、モータ等の機械的入出力装置を駆動を行なう部分であり、システム制御層91による制御を操作表示部10、画像形成部11、画像読取部12及びキーカード装置13に伝達したり、これらからの情報をシステム制御層91に伝達したりする。
【0032】
上記のように構成した画像処理装置において、図6に示すようにコピーアプリ80、プリンタアプリ81及びFAXアプリ82の各アプリケーションは、あたかもシステム制御層91を介してそれぞれ仮想操作表示部70a,70b,70c、仮想画像形成部71a,71b,71c及び仮想画像読取部72a,72b,72cを制御するかのように動作する。例えばコピーアプリ80とプリンタアプリ81が動作する場合は、コピーアプリ80は仮想操作表示部70aと仮想画像形成部71aと仮想画像読取部72aを制御し、プリンタアプリ81は仮想画像形成部71bを制御する。同様に、プリンタアプリ81とFAXアプリ82が動作する場合は、プリンタアプリ81は仮想画像形成部71bを制御し、FAXアプリ82は仮想操作表示部70cと仮想画像読取部72cを制御する。ここで、画像形成部11等のリソースは1つずつしかないので、複数のアプリケーションによるリソース使用要求が競合した場合、実際のリソース使用権を渡すためには排他制御又は時分割割付けによる制御を行なう必要がある。排他制御を行なうか又は時分割割付けによる制御を行なうかは、リソースの種類及び装置の使用者による設定によって異なる。
【0033】
次ぎに、システムコントローラ4と操作部コントローラ5等との通信、システムコントローラ4とコピーアプリ部1等との通信及びシステムコントローラ4とキーカード装置13との通信について説明する。ここでは、シリアル通信を用いてハンドシェイクする場合について説明する。
【0034】
ここでは、シリアル通信のプロトコルとして伝送速度を9600bit/sとし、同期方式を調歩同期式(非同期)とし、データ長を8bitとし、スタートビット及びストップビットを1ビットとし、また、パリティビットとして奇数ビットを規定している。データ等の送受信はフレーム単位で行ない、図7に示す受信局における状態を示す状態遷移図のように通信上の誤りの検出にAcknowledge(以下、「ACK」という。)及びNon−Acknowledge(以下、「NAK」という。)を用いている。送信局は受信局からACKを受信すると(ステップS5)、受信局がフレームを正常に受信し、そのフレームを取り込んだものとする(ステップS7)。一方、送信局は受信局からNAKを受信すると(ステップS4)、回線上のエラー(例えばパリティエラー、フレーミングエラー等)が発生したものとして、送信フレームを再送して回復を図る(ステップS2)。また、一定時間(例えば300ms)を経過してもACKもNAKも受信しなかった場合(タイムアウトエラーが発生した場合)は、送信局は送信フレームを再送して回復を図る(ステップS2)。さらに、フレームの再送を何回か行なっても(例えば4回行なっても)、送信局がACKを受信しない場合は送信局は受信局に異常が発生しているとして、送信を中止する。ここで、データのフレームには、例えばASCII文字列(020H〜0FFH)を用い、ACKには04H,NAKには05Hを用いる。また、バッファが一杯になったことを示すBuffer Full(以下、「BFL」という。)には03Hを用いる。
【0035】
同様に、図8に示すように送信局の場合はフレームを送信した後(ステップS13,S15)、NAK又はBFLを受信すると送信フレームを再送して回復を図る。また、一定時間を経過してもACK,NAK,BFLのいずれもも受信しなかった場合(タイムアウトエラーが発生した場合)は、送信局は、例えば3回まで送信フレームを再送して回復を図る(ステップS14、S16)。さらに、3回再送しても、ACKを受信しない場合は受信局に異常が発生しているとして、システムエラーを通知して(ステップS17)、送信を中止する。
【0036】
システムコントローラ4の異常検知部44は、キーカード装置13が受信局である場合に上記のようにしてキーカード装置13の異常を検知したり、キーカード装置13からの異常検知信号を基に異常を検知して、アプリ制御部43に異常の検知を通知する。
【0037】
上記構成の画像処理装置においてキーカード装置13が異常状態になった場合の動作について、図9のフローチャートを参照して説明する。
【0038】
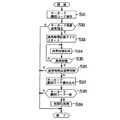
異常検知部44がキーカード装置13の異常を検出し(ステップS21)、いずれかのアプリケーションが動作中であると(ステップS22)、アプリ制御部43は利用制限アプリ記憶部41に記憶したアプリケーションと動作中のアプリケーションとを比較して動作中のアプリケーションが利用制限されているアプリケーションか否かを調べる。動作中のアプリケーションが利用制限されているアプリケーションである場合は(ステップS23)、アプリ制御部43は動作中のアプリケーションを中断する(ステップS24)。これにより、キーカード装置13の異常発生が原因で、本来利用を制限しなくても良いアプリケーションが使用できなくなったり、逆に使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対する制限が行なわれなくなったりすることを防止することができる。
【0039】
その後、ログを記憶する対象となる事項が発生すると(ステップS25)、アプリ制御部43がロギングを行ないロギング記憶部42にログデータを記憶する(ステップS26)。アプリ制御部43はキーカード装置13が異常状態から回復するまでこのロギング処理(ステップS25,S26)を繰り返す(ステップS27)。
【0040】
キーカード装置13が異常状態から回復すると(ステップS27)、アプリ制御部43はロギング記憶部42を調べて、キーカード装置13の異常中にログをとったログデータがあるか否かを調べる。キーカード装置13の異常中に行なったログデータがある場合は(ステップS28)、アプリ制御部43はロギング記憶部42に記憶したログデータをキーカード装置13に送り、キーカード15にそのログデータを登録する(ステップS29)。これにより、キーカード装置13の異常中であってもログデータを喪失することを防止できる。
【0041】
また、他の実施例の画像処理装置はキーカード装置13に異常が発生すると、キーカード装置13が復旧した後に装置を初期状態にして、キーカード装置13に異常が発生した際のアプリケーションがそのままの状態で残って他の利用者が間違ってそのアプリケーションを続行してしまうことを防止する。
【0042】
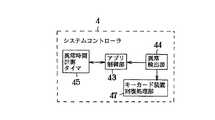
画像処理装置のシステムコントローラ4は、図10に示すようにアプリ制御部43と異常検知部44と異常時間計測タイマ45を備える。異常時間計測タイマ45は、既に説明したようにして異常検知部44がキーカード装置13に異常が発生したことを検知すると、時間間隔の計測を開始し、キーカード装置13の異常が回復すると、時間間隔の計測を終了する。
【0043】
上記構成の画像処理装置の動作について、図11のフローチャートを参照して説明する。
【0044】
キーカード装置13はキーカード15が入れ替えられたり、新たにキーカード15を差し込まれた場合にそのキーカード15からキーカード識別コードを読み取り、読み取ったキーカード識別コードを入出力制御部9を介してシステムコントローラ4に送信する。システムコントローラ4は、キーカード装置13からキーカード識別コードを受信すると、その受信したキーカード識別コードをメモリ(不図示)に保存する(ステップS31)。異常検知部44が既に説明したようにしてキーカード装置13の異常を検知すると(ステップS32)、アプリ制御部43は異常時間計測タイマ45をスタートし、異常状態の継続時間の計測を開始する(ステップS33)。
【0045】
システムコントローラ4は、その後、例えば定期的にキーカード装置13にコマンドを送信して異常状態の回復を図ったり、キーカード装置13に対してリセットコマンドを送ったりしてキーカード装置13の異常状態を回復する(ステップS34)。キーカード装置13の異常状態が回復すると(ステップS35)、システムコントローラ4のアプリ制御部43は異常時間計測タイマ45による計時を停止し、異常時間計測タイマ45が計測した異常状態の継続時間と予め定めた基準時間とを比較し、異常状態の継続時間が基準時間を越えない場合は異常状態の前後における利用者が等しいとみなして処理をそのまま続行する(ステップS36)。これにより、処理のやり直し等を行なう必要がある状態になることを少なくし、キーカード装置13に異常状態が発生した場合の処理時間の短縮を図ることができる。
【0046】
異常状態の継続時間が基準時間を越える場合は、システムコントローラ4はキーカード装置13かキーカード15のキーカード識別コードを読み込み(ステップS37)、読み込んだキーカード識別コードと異常状態発生前に保存したキーカード識別コードが一致しているか否かを調べる(ステップS38)。今回読み込んだキーカード識別コードと異常状態発生前に保存したキーカード識別コードが一致していない場合は、異常状態発生前の利用者と異常状態回復後の利用者とが異なっている場合であるので、システムコントローラ4は装置全体をリセットして装置全体を初期状態に戻す(ステップS39)。これにより、キーカード装置13に異常が発生した際のアプリケーションがそのままの状態で残って他の利用者が間違ってそのアプリケーションを続行してしまうことを防止することができる。
【0047】
また、他の実施例の画像処理装置は、キーカード装置13が異常状態に陥っている際に予め許可されたアプリケーションのみを動作可能にして、キーカード装置13が異常状態に陥った際の稼働率の低下を最小限に留める。
【0048】
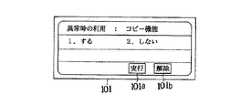
この場合、画像処理装置のシステムコントローラ4は、図12に示すように利用可能アプリケーション記憶部(以下、「利用可能アプリ記憶部」という。)46とアプリ制御部43と異常検知部44を備える。利用可能アプリ記憶部46は、例えば図13及び図14に示すキーカード装置13の異常時の利用可能アプリケーションの設定画面を基に設定したアプリケーションを記憶する。ここで、図13及び図14におけるアプリケーションの設定方法は、図3及び図4における使用者制限アプリケーションの設定方法と同様である。
【0049】
上記構成の画像処理装置の動作について、図15のフローチャートを参照して説明する。
【0050】
キーカード装置13の異常中にアプリケーションの切り替え指示を入力すると(ステップS41,S42)、アプリ制御部43は利用可能アプリ記憶部46に記憶したアプリケーションと起動を指示されたアプリケーションとを比較し、起動を指示されたアプリケーションがキーカード装置13の異常中であっても動作可能なアプリケーションとして予め登録されたアプリケーションか否かを調べる。起動を指示されたアプリケーションがキーカード装置13の異常中であっても動作可能なアプリケーションである場合は(ステップS43)、アプリ制御部43は指示されたアプリケーションを起動し、そのアプリケーションでの処理を始める(ステップS44)。これにより、キーカード装置13の異常中であっても利用を制限しなくても良いアプリケーションまでが使用できなくなったり、逆に使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対して制限が行なわれなくなったりすることを防止することができ、キーカード装置13の異常状態継続中であっても、装置の稼働率の低下を最小限に抑えることができる。
【0051】
一方、起動を指示されたアプリケーションがキーカード装置13の異常中であっても動作可能なアプリケーションでない場合は(ステップS43)、アプリ制御部43は、図16に示すような警告画面を表示してキーカード装置13の異常状態が未回復なため指示されたアプリケーションを起動できない旨を表示する(ステップS45)。このように動作することにより、使用者は利用しようとするアプリケーションが異常状態であっても使用を許可されたものか否かを意識せずにアプリケーションを選択することができ、かつ、異常状態において使用をすることができないものである場合はその旨を容易に知ることができる。
【0052】
さらに、キーカード装置13が異常状態に陥った際に利用を制限していたアプリケーションが動作中の場合もあるので、キーカード装置13が異常状態に陥った際に、異常状態において使用を許可するアプリケーション以外のアプリケーションが動作している状態であると自動的にそのアプリケーションを終了し、予め登録した異常状態において使用を許可するアプリケーションを起動し、異常状態において使用を許可するアプリケーションの登録がない場合はキーカード装置13の異常により動作できるアプリケーションがない旨の警告を表示しても良い。このように、キーカード装置13に異常が発生している際に使用を許可していないアプリケーションが動作することを防止するので、使用を制限すべきアプリケーションが動作することを防止できる。
【0053】
また、画像処理装置はキーカード装置13が異常状態に陥った場合にキーカード装置13を自動的にリセットするようにしても良い。この場合、画像処理装置のシステムコントローラ4は、図17に示すように異常検知部44とキーカード装置回復処理部47とアプリ制御部43と異常時間計測タイマ45を備える。
【0054】
キーカード装置回復処理部47は、異常検知部44がキーカード装置13の異常を検知すると、異常検知部44がキーカード装置13の異常を検知している間は周辺機コントローラ8を介して定期的にキーカード装置13に対してリセット信号を出力し、キーカード装置13をリセットする。アプリ制御部43は、既に説明した動作の他に、アプリケーションの動作中に異常検知部44がキーカード装置13のを検知すると、そのアプリケーションの動作を中断し、予め定めた一定期間内にキーカード装置13が回復した場合は、中断したアプリケーションの動作を自動的に再開する。
【0055】
上記構成の画像処理装置の動作について、コピーアプリを実行している場合を例にして、図18のフローチャートを参照して説明する。
【0056】
コピーアプリ実行の際には、図19に示すような基本画面で倍率、用紙、セット枚数等を表示する。キーカード装置13が接続されている状態で(ステップS51)、異常検知部44がキーカード装置13の異常を検出すると(ステップS52)、アプリ制御部43は実行中のジョブがあるか否かを調べ、実行中のジョブがある場合は(ステップS53)、実行中のジョブを中断し、中断したジョブの状態を記憶した後に(ステップS54)、ジョブ中断フラグ(不図示)をオンにし、異常時間計測タイマ45による時間計測を開始する(ステップS56)。これにより、キーカード装置13の異常発生が原因で、使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対する制限が行なわれなくなったりすることを防止することができる。さらに、アプリ制御部44は操作表示部10のLCD101から、例えば図20に示すような画面を表示し、キーカード装置のエラーが原因で処理が中断していることを使用者に通知している。
【0057】
また、異常検知部44がキーカード装置13の異常を検出すると(ステップS52)、キーカード装置回復処理部47は、周辺機コントローラ8を介してキーカード装置13にリセット信号を送る(ステップS57)。これにより、キーカード装置13を自動的に回復することができ、装置全体の状態を迅速に回復することができ、装置稼働率を高めることができる。さらに、一定時間経過(例えば約100ms)すると、キーカード装置回復処理部47は、再び異常検知部44がキーカード装置13の異常を検出しているか否かを調べ、異常を検出している場合は再びキーカード装置13に対してリセット信号を出力する(ステップS58,S52〜S57)。このように、キーカード装置13が異常状態にある間は、予め定めた一定周期でキーカード装置13にリセット信号を送るので、キーカード装置13がある程度の時間が経過した後にリセット可能な状態になった場合においても、すみやかにキーカード装置13をリセットすることができ、さらに迅速、且つ、確実に、装置を回復し、稼働率を高めることができる。
【0058】
異常検知部44がキーカード装置13の異常を検出していなかった場合は、アプリ制御部43はジョブ中断フラグがオンになっているか否かを調べる(ステップS59)。ジョブ中断フラグがオンになっている場合は、キーカード装置13に異常が発生し、実行中のジョブが中断している状態なので、アプリ制御部43は異常時間計測タイマ45から異常が発生してからの経過時間を読み出し、読み出した経過時間が、予め定めた一定時間を経過していない場合は(ステップS60)、その中断したジョブの状態を読み出して、中断したジョブを再開する(ステップS60)。また、アプリ制御部43はジョブ中断フラグをオフにして、中断中のジョブが無い旨を設定する。(ステップS62)。このように、ジョブ中断フラグがオンになっていて、且つ、異常を検知してからの経過時間が予め定めた時間を経過していない場合にはジョブを再開するので、中断したジョブの動作を自動的に再開することができ、処理の効率化を図ることができる。また、ジョブ中断フラグがオンになっていて、且つ、異常を検知してからの経過時間が予め定めた時間を経過している場合には、ジョブ中断フラグをオフにするだけで、ジョブの動作を再開しないので、異常発生後に他の使用者が装置を使用とした場合に、突然異常発生前のアプリケーションの動作が再開することを防止できる。
【0059】
【発明の効果】
この発明は以上説明したように、キーカード装置が異常状態に陥った場合は、本体装置に記憶されていたアプリケーションと動作中のアプリケーションとを比較し、比較の結果、動作中のアプリケーションが、使用が制限されているアプリケーションである場合は当該アプリケーションの動作を中断し、比較の結果、動作中のアプリケーションが、使用が制限されていないアプリケーションである場合は、当該アプリケーションの動作を続行するので、本来利用を制限しなくても良いアプリケーションまでが使用できなくなったり、逆に使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対する制限が行われなくなったりすることを防止することができる。
【0064】
また、キーカード装置が異常状態であっても使用を許可するアプリケーションを予め登録し、キーカード装置が異常状態に陥った際は使用を許可されているアプリケーションのみを起動できるようにするので、本来利用を制限しなくても良いアプリケーションまでが使用できなくなったり、逆に使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対して制限が行なわれなくなったりすることを防止することができる。
【0065】
さらに、キーカード装置が異常状態に陥った際に、キーカード装置が異常状態であっても使用を許可するアプリケーション以外のアプリケーションを選択するとそのアプリケーションの起動は行なわずに警告を出力して、そのアプリケーションが使用できない旨を利用者に通知するので、使用者は利用しようとするアプリケーションが異常状態であっても使用を許可されたものか否かを意識せずにアプリケーションを選択することができ、異常状態において使用をすることができないものである場合はその旨を容易に知ることができる。
【0066】
さらに、キーカード装置が異常状態に陥った際に、予め登録した異常状態において使用を許可するアプリケーション以外のアプリケーションが起動した状態であると自動的にそのアプリケーションを終了し、予め登録した異常状態において使用を許可するアプリケーションを起動して、キーカード装置に異常が発生している際に使用を許可していないアプリケーションが動作することを防止するので、使用を制限すべきアプリケーションに対する制限が行なわれなくなったりすることを防止することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】この発明の画像処理装置の構成図である。
【図2】操作表示部の構成図である。
【図3】システム初期設定で使用者制限を選択する画面の構成図である。
【図4】コピーアプリにおいて使用者制限を設定する画面の構成図である。
【図5】各層の構成図である。
【図6】各アプリケーションによるアクセスの概念図である。
【図7】受信局の通信手順を示す状態遷移図である。
【図8】送信局の通信手順を示す状態遷移図である。
【図9】異常状態発生の際にアプリケーションを中断するフローチャートである。
【図10】異常継続時間に応じて初期設定をするシステムコントローラの構成図である。
【図11】異常継続時間に応じて初期設定する場合の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図12】アプリケーションに応じて起動するシステムコントローラの構成図である。
【図13】システム初期設定で異常時の利用可能機能を選択する画面の構成図である。
【図14】コピーアプリを異常時に利用可能に設定する画面の構成図である。
【図15】アプリケーションに応じて起動する場合の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図16】操作表示部上の警告画面の構成図である。
【図17】キーカード装置を自動回復するシステムコントローラの構成図である。
【図18】キーカード装置をリセットする動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図19】コピーアプリケーション動作の際の画面の構成図である。
【図20】警告表示の際の画面の構成図である。
【符号の説明】
1 コピーアプリ部
2 プリンタアプリ部
3 FAXアプリ部
4 システムコントローラ
41 利用制限アプリ記憶部
42 ロギング記憶部
43 アプリ制御部
44 異常検知部
45 異常時間計測タイマ
46 利用可能アプリ記憶部
47 キーカード装置回復処理部
10 操作表示部
101 LCD
11 画像形成部
12 画像読取部
13 キーカード装置
15 キーカード[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an image processing apparatus having a key card device that individually manages user restriction information for each application, copy number restriction information for each department, and the like.To the limitIt is related.
[0002]
[Prior art]
A copying machine, a facsimile machine, or the like, which is an image processing apparatus, is provided with a key card device such as an image forming apparatus described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. Hei 6-22066, and limits the user and amount of use of various applications. Some devices have improved management efficiency.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, when a failure occurs in the key card device, it is not possible to use even applications that do not need to restrict users, or conversely, the usage of applications whose usage should be restricted cannot be managed. I was doing.
[0004]
Further, if an application when an abnormality occurs in the key card device remains as it is, another user may continue the application by mistake.
[0006]
The present invention has been made to eliminate such disadvantages, and an object of the present invention is to increase the use efficiency by appropriately limiting the operation when a failure occurs in the key card device.
[0007]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The image processing apparatus according to the present invention includes a key card device that individually manages user-specific restriction information and usage amount restriction information for each application,MoreRestricted use applicationsThe use restriction application storage means for storing the error, the abnormality detection means for detecting whether or not the key card apparatus is in an abnormal state based on a signal from the key card apparatus, and the key card apparatus is in an abnormal state by the abnormality detection means. If it is detected that the application is stored, the application stored in the use restriction application storage means is compared with the application in operation. As a result of the comparison, if the application in operation is an application whose use is restricted, When the application is interrupted as a result of the comparison, and the application being operated is an application whose use is not restricted, application control means for continuing the operation of the application is provided. Therefore, it is possible to prevent an application that does not necessarily need to be restricted from being used, or a restriction on an application that should be restricted from being used.
[0012]
In addition, the other image processing apparatus includes a key card device that individually manages user restriction information, usage amount restriction information, and the like for each application, and permits use even when the key card device is in an abnormal state. If the key card device falls into an abnormal state, only applications that are permitted to be used can be started, and even applications that do not need to be restricted can no longer be used or used in reverse. It is prevented that the restriction is not applied to the application that should be restricted.
[0013]
Further, when the key card device is in an abnormal state and the user of the device selects an application other than the application that is permitted to be used in the abnormal state of the key card device, a warning is output without starting the application, and the application Notify users that cannot be used.
[0014]
Furthermore, when the key card device falls into an abnormal state, if an application other than an application that permits use in the abnormal state of the key card device registered in advance is activated, the application is automatically terminated and registered in advance. An application that is permitted to be used in an abnormal state of the key card device is activated, and an application that is not permitted to be used is prevented from operating when an abnormality has occurred in the key card device.
[0018]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The image processing apparatus of the present invention includes a key card device that individually manages user restriction information, usage amount restriction information, and the like for each application, and in particular, operates each application when an abnormality occurs in the key card device. By controlling, the influence on the device operating rate and the management status due to the occurrence of an abnormality in the key card device is reduced.
[0019]
The image processing apparatus includes, for example, a copy application section (hereinafter referred to as “copy application section”), a printer application section (hereinafter referred to as “printer application section”), and a facsimile application section (hereinafter referred to as “FAX application section”). A system controller, an operation unit controller, an image forming controller, an image reading controller, a peripheral device controller, an input / output control unit, an operation display unit, an image forming unit, an image reading unit, and a key card device.
[0020]
The copy application unit, printer application unit, and FAX application unit store control of a copy application, a printer application, and a facsimile application, respectively.
[0021]
The system controller includes, for example, a use restriction application storage unit (hereinafter referred to as “usage restriction application storage unit”), a logging storage unit, an application control unit (hereinafter referred to as “application control unit”), and an abnormality detection unit. The use restriction application storage unit stores applications that have use restrictions such as user restrictions, copy number restrictions for each department, and communication charge restrictions. The logging storage unit contains usage history data such as the number of copies and communication charges for each department when an application that is in an abnormal state, such as a copy number limit and a communication charge limit, is used. Store some log data. The application control unit is a part that controls the start and stop of the copy application, the printer application, and the facsimile application. For example, when the key card device falls into an abnormal state during the operation of the application whose use is restricted, the application control unit If the key card device falls into an abnormal state during the operation of an application whose use is not restricted, the operation of the application is controlled to continue. The abnormality detection unit detects whether or not the key card device is in an abnormal state based on a signal from the key card device.
[0022]
The operation unit controller, image forming controller, image reading controller, and peripheral device controller control the operation display unit, image forming unit, image reading unit, and key card device via the input / output control unit. The key card device is provided with a key card, and log information including restriction information such as a user restriction, a usage limit for each department and a communication charge restriction, and usage history data such as a copy number and a communication charge for each department. Read and write data.
[0023]
In the case of the above configuration, for example, if the key card device falls into an abnormal state during the operation of an application whose use is restricted, the operation of the application is interrupted and the application whose use is not restricted is operating If the key card device falls into an abnormal state, the operation of the application is continued, so that even applications that do not need to be restricted can no longer be used, or there are restrictions on applications that should be restricted. It can be prevented from being performed.
[0024]
Also, if the user when the key card device is in an abnormal state is the same as the user when the key card device is recovered from the abnormal state, the users before and after the key card abnormal state are different Resets the entire device to prevent other users from accidentally processing the application when an error occurs.
[0025]
Furthermore, while the key card device is in an abnormal state, it is preferable to output a reset signal to the key card device at a constant cycle to automatically restore the key card device.
[0026]
【Example】
FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an image processing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the image processing apparatus includes, for example, a
[0027]
The
[0028]
The
[0029]
The
[0030]
Based on the image image data, the
[0031]
Each control unit of the image processing apparatus is divided into functions, for example, an
[0032]
In the image processing apparatus configured as described above, as shown in FIG. 6, the copy application 80, the
[0033]
Next, communication between the
[0034]
Here, as a serial communication protocol, the transmission speed is 9600 bits / s, the synchronization method is asynchronous (asynchronous), the data length is 8 bits, the start bit and the stop bit are 1 bit, and the parity bit is an odd number of bits. Is stipulated. Transmission / reception of data and the like is performed in units of frames, and acknowledged (hereinafter referred to as “ACK”) and non-acknowledge (hereinafter referred to as “ACK”) are used to detect communication errors as in the state transition diagram showing the state in the receiving station shown in FIG. "NAK"). When the transmitting station receives ACK from the receiving station (step S5), it is assumed that the receiving station has received the frame normally and has taken in the frame (step S7). On the other hand, when the transmitting station receives the NAK from the receiving station (step S4), it assumes that an error on the line (for example, parity error, framing error, etc.) has occurred and resends the transmission frame to recover (step S2). If neither ACK nor NAK is received after a certain time (for example, 300 ms) (timeout error occurs), the transmitting station resends the transmission frame to recover (step S2). Furthermore, even if the frame is retransmitted several times (for example, four times), if the transmitting station does not receive the ACK, the transmitting station cancels transmission because an abnormality has occurred in the receiving station. Here, for example, an ASCII character string (020H to 0FFH) is used for the data frame, 04H is used for ACK, and 05H is used for NAK. Also, 03H is used as a buffer full (hereinafter referred to as “BFL”) indicating that the buffer is full.
[0035]
Similarly, as shown in FIG. 8, in the case of a transmitting station, after transmitting a frame (steps S13 and S15), when a NAK or BFL is received, the transmission frame is retransmitted for recovery. If none of ACK, NAK, and BFL is received after a certain time has elapsed (when a time-out error occurs), the transmitting station resends the transmission frame, for example, up to three times for recovery. (Steps S14 and S16). Further, if the ACK is not received even after three retransmissions, it is determined that an abnormality has occurred in the receiving station, a system error is notified (step S17), and transmission is stopped.
[0036]
The
[0037]
An operation when the
[0038]
When the
[0039]
Thereafter, when an item to be stored is generated (step S25), the
[0040]
When the
[0041]
In the image processing apparatus according to another embodiment, when an abnormality occurs in the
[0042]
As shown in FIG. 10, the
[0043]
The operation of the image processing apparatus having the above configuration will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
[0044]
The
[0045]
Thereafter, the
[0046]
If the duration of the abnormal state exceeds the reference time, the
[0047]
In addition, the image processing apparatus according to another embodiment can operate only an application permitted in advance when the
[0048]
In this case, the
[0049]
The operation of the image processing apparatus having the above configuration will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
[0050]
When an application switching instruction is input while the
[0051]
On the other hand, if the application instructed to start is not an operable application even when the
[0052]
Furthermore, since an application that has been restricted in use when the
[0053]
Further, the image processing apparatus may automatically reset the
[0054]
When the
[0055]
The operation of the image processing apparatus having the above configuration will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. 18 taking a case where a copy application is being executed as an example.
[0056]
When executing the copy application, the magnification, paper, number of sheets set, etc. are displayed on the basic screen as shown in FIG. When the
[0057]
When the
[0058]
If the
[0059]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, the present inventionKi-If the card device falls into an abnormal stateCompare the application stored in the main unit with the active application, and if the result of the comparison is that the active application is an application whose use is restricted,Interrupt the application,As a result of comparison, if the running application is an application whose use is not restricted,Since the operation of the application is continued, it is possible to prevent an application that does not necessarily have to be restricted from being used, or a restriction on an application that should be restricted from being used.
[0064]
In addition, since applications that are allowed to be used are registered in advance even if the key card device is in an abnormal state, and only the applications that are permitted to be used can be activated when the key card device falls into an abnormal state, It can be prevented that even applications that do not need to be restricted can not be used, or conversely, the application that should be restricted from being restricted is not restricted.
[0065]
Furthermore, when the key card device is in an abnormal state, if an application other than the application that is allowed to be used is selected even if the key card device is in an abnormal state, a warning is output without starting the application, Since the user is notified that the application cannot be used, the user can select the application without being aware of whether or not the application is permitted even if the application to be used is in an abnormal state. If it cannot be used in an abnormal state, it can be easily known.
[0066]
Furthermore, when the key card device falls into an abnormal state, if an application other than the application that permits use in the abnormal state registered in advance is activated, the application is automatically terminated, and the abnormal state registered in advance Start applications that allow use and prevent applications that are not allowed to operate when an abnormality has occurred in the key card device, so there is no restriction on applications that should be restricted. Can be prevented.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of an image processing apparatus according to the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a configuration diagram of an operation display unit.
FIG. 3 is a configuration diagram of a screen for selecting a user restriction in the system initial setting.
FIG. 4 is a configuration diagram of a screen for setting user restrictions in a copy application.
FIG. 5 is a configuration diagram of each layer.
FIG. 6 is a conceptual diagram of access by each application.
FIG. 7 is a state transition diagram showing a communication procedure of a receiving station.
FIG. 8 is a state transition diagram showing a communication procedure of a transmitting station.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart for interrupting an application when an abnormal state occurs.
FIG. 10 is a configuration diagram of a system controller that performs initial setting according to an abnormal continuation time.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing an operation in the case of initial setting according to an abnormal continuation time.
FIG. 12 is a configuration diagram of a system controller that is activated in accordance with an application.
FIG. 13 is a configuration diagram of a screen for selecting an available function at the time of abnormality in the system initial setting.
FIG. 14 is a configuration diagram of a screen for setting a copy application to be usable when an abnormality occurs.
FIG. 15 is a flowchart showing an operation in the case of activation according to an application.
FIG. 16 is a configuration diagram of a warning screen on the operation display unit.
FIG. 17 is a configuration diagram of a system controller for automatically recovering a key card device.
FIG. 18 is a flowchart showing an operation of resetting the key card device.
FIG. 19 is a configuration diagram of a screen during a copy application operation.
FIG. 20 is a configuration diagram of a screen when a warning is displayed.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 Copy application section
2 Printer application part
3 FAX application section
4 System controller
41 Restricted application storage
42 Logging storage
43 Application control unit
44 Anomaly detector
45 Abnormal time measurement timer
46 Available application storage
47 Key card device recovery processing section
10 Operation display
101 LCD
11 Image forming unit
12 Image reader
13 Key card device
15 key card
Claims (8)
Translated fromJapanese使用が制限されているアプリケーションを本体装置で記憶し、
キーカード装置が異常状態に陥った場合は、前記本体装置に記憶されていたアプリケーションと動作中のアプリケーションとを比較し、
前記比較の結果、動作中のアプリケーションが、使用が制限されているアプリケーションである場合は当該アプリケーションの動作を中断し、
前記比較の結果、動作中のアプリケーションが、使用が制限されていないアプリケーションである場合は、当該アプリケーションの動作を続行することを特徴とする画像処理装置。In an image processing apparatus including a key card device that individually manages user-specific restriction information and usage amount restriction information for each application,
Store the restricted applications on the main unit,
· The Kado if the device falls into the abnormalstate, compares the running application and the previously stored in the main device applications,
Result of the comparison, the application during operation, if an application has been limited use interruptstheoperation ofthe application,
Result of the comparison, the application during operation, if an application that is not limited use to an image processing apparatus characterized by continuing theoperation ofthe application.
キーカード装置が異常状態であっても使用を許可するアプリケーションを予め記憶し、キーカード装置が異常状態にあると使用を許可されているアプリケーションのみを起動できるようにすることを特徴とする画像処理装置。In an image processing apparatus including a key card device that individually manages user-specific restriction information and usage amount restriction information for each application,
Image processing characterizedin thatan application permitting use even when the key card device is in an abnormal state is stored in advance, and only an application permitted to be used can be activated when the key card device is in an abnormal state. apparatus.
使用が制限されているアプリケーションを記憶する利用制限アプリケーション記憶手段と、
キーカード装置からの信号を基にキーカード装置が異常状態に陥っているか否かを検知する異常検知手段と、
該異常検知手段によってキーカード装置が異常状態に陥ったと検知した場合は、前記利用制限アプリケーション記憶手段に記憶されているアプリケーションと動作中のアプリケーションとを比較し、前記比較の結果、動作中のアプリケーションが、使用が制限されているアプリケーションである場合は当該アプリケーションの動作を中断し、前記比較の結果、動作中のアプリケーションが、使用が制限されていないアプリケーションである場合は、当該アプリケーションの動作を続行するアプリケーション制御手段と
を有することを特徴とする画像処理装置。In an image processing apparatus including a key card device that individually manages user-specific restriction information and usage amount restriction information for each application,
A use restriction application storage means for storing an application whose use is restricted;
An abnormality detection means for detecting whether or not the key card device is in an abnormal state based on a signal from the key card device;
When the abnormality detection unit detects that the key card device has entered an abnormal state, the application stored in the use restriction application storage unit is compared with the active application, and as a result of the comparison, the active application However, if the application is restricted in use, the operation of the application is interrupted. If the result of the comparison indicates that the active application is an application that is not restricted in use, the operation of the application is continued. Application control means to
An image processing apparatus comprising:
キーカード装置が異常状態であっても使用を許可するアプリケーションを予め記憶する利用可能アプリケーション記憶手段と、
キーカード装置からの信号を基にキーカード装置が異常状態に陥っているか否かを検知する異常検知手段と、
該異常検知手段によってキーカード装置が異常状態に陥ったと検知した場合は、前記利用可能アプリケーション記憶手段に記憶されている使用を許可するアプリケーションと起動を指示されたアプリケーションとを比較し、前記比較の結果、起動を指示されたアプリケーションが、使用を許可されているアプリケーションである場合は当該アプリケーションを起動し、前記比較の結果、起動を指示されたアプリケーションが、使用を許可されているアプリケーションでない場合は、当該アプリケーションを起動しないアプリケーション制御手段と
を有することを特徴とする画像処理装置。In an image processing apparatus including a key card device that individually manages user-specific restriction information and usage amount restriction information for each application,
Available application storage means for storingin advance an application that permits use even when the key card device is in an abnormal state;
An abnormality detection means for detecting whether or not the key card device is in an abnormal state based on a signal from the key card device;
When the abnormality detecting unit detects that the key card device has entered an abnormal state, the application permitting use stored in the available application storage unit and the application instructed to start are compared, and the comparison As a result, if the application instructed to start is an application permitted to use, the application is started. If the result of the comparison indicates that the application instructed to start is not an application permitted to use And application control means that does not start the application
An image processing apparatus comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP30337297AJP3628505B2 (en) | 1997-07-18 | 1997-10-20 | Image processing device |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP9-208419 | 1997-07-18 | ||
| JP20841997 | 1997-07-18 | ||
| JP30337297AJP3628505B2 (en) | 1997-07-18 | 1997-10-20 | Image processing device |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004221454ADivisionJP3802036B2 (en) | 1997-07-18 | 2004-07-29 | Image processing device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH1184965A JPH1184965A (en) | 1999-03-30 |
| JP3628505B2true JP3628505B2 (en) | 2005-03-16 |
Family
ID=26516820
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP30337297AExpired - Fee RelatedJP3628505B2 (en) | 1997-07-18 | 1997-10-20 | Image processing device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3628505B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4081720B2 (en) | 2004-02-17 | 2008-04-30 | ブラザー工業株式会社 | Image forming apparatus |
| JP6155865B2 (en)* | 2013-06-07 | 2017-07-05 | 株式会社リコー | Information processing system, information processing method, and program |
- 1997
- 1997-10-20JPJP30337297Apatent/JP3628505B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH1184965A (en) | 1999-03-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102006520B1 (en) | Image forming apparatus and control method | |
| US6032001A (en) | Remote diagnosis system and method for an image forming apparatus | |
| EP1122912B1 (en) | Image forming device management system and method | |
| US7701597B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image forming system | |
| JP3628505B2 (en) | Image processing device | |
| JP3802036B2 (en) | Image processing device | |
| JP3967360B2 (en) | Image processing device | |
| JPH04200168A (en) | facsimile machine | |
| JPH11161111A (en) | Image processing device | |
| JPH11311927A (en) | Digital copier | |
| JP3931868B2 (en) | Image recording device | |
| JP3652153B2 (en) | Image output apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JPH09233213A (en) | Processing status notification method and processing status notification system | |
| US6825954B1 (en) | Information communication apparatus | |
| JP3518833B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| JPS60228180A (en) | recording device | |
| JP2833691B2 (en) | Notification device and notification method | |
| KR100283757B1 (en) | Engine interface device | |
| JP2001260493A (en) | Network printer system | |
| JPH10294813A (en) | Digital copying system | |
| JP2856756B2 (en) | Facsimile machine | |
| JP2003046592A (en) | Image processing system, communication method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP2603815B2 (en) | Facsimile machine | |
| JP2000215008A (en) | Image processing device | |
| JP2022057252A (en) | Image processing equipment and image processing system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20040601 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20040729 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20041207 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20041208 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20071217 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20081217 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20081217 Year of fee payment:4 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091217 Year of fee payment:5 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101217 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101217 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111217 Year of fee payment:7 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111217 Year of fee payment:7 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121217 Year of fee payment:8 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131217 Year of fee payment:9 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |