JP2025073061A - Atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing device, atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing method, atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing program, and recording medium - Google Patents
Atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing device, atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing method, atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing program, and recording mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2025073061A JP2025073061AJP2024109770AJP2024109770AJP2025073061AJP 2025073061 AJP2025073061 AJP 2025073061AJP 2024109770 AJP2024109770 AJP 2024109770AJP 2024109770 AJP2024109770 AJP 2024109770AJP 2025073061 AJP2025073061 AJP 2025073061A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- atrial fibrillation
- duration
- information
- patient
- trained model
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本開示は、心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置、心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造方法、心房細動の持続期間推定支援プログラム、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラム及び記録媒体に関する。The present disclosure relates to an atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device, an atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model production device, an atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method, an atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model production method, an atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program, an atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model production program, and a recording medium.
近年、超高齢化社会の進行とともに心房細動の患者が増加している。心房細動の治療手法としては、カテーテルアブレーション手術であることが知られている。例えば、特許文献1には、心房細動等の治療に利用可能な、カテーテルアブレーションシステムが記載されている。In recent years, the number of patients with atrial fibrillation has been increasing with the progress of the super-aging society. Catheter ablation surgery is known as a method of treating atrial fibrillation. For example, Patent Document 1 describes a catheter ablation system that can be used to treat atrial fibrillation and the like.
心房細動の治療においては、患者が心房細動を発症してからの期間(持続期間)が、カテーテルアブレーション手術後の心房細動の再発率に関係することが知られている。しかしながら、臨床現場において、患者の心房細動の持続期間については、患者自身からの問診に頼っており、患者本人の記憶があいまいである場合もあり、心房細動患者には、自覚症状がない無症状患者もいることから、心房細動患者において、正確な持続期間を知ることが難しいという課題がある。In the treatment of atrial fibrillation, it is known that the period from when a patient develops atrial fibrillation (duration) is related to the recurrence rate of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation surgery. However, in clinical practice, the duration of atrial fibrillation relies on interviews with the patient themselves, and patients may not remember clearly. In addition, some atrial fibrillation patients are asymptomatic and do not experience any symptoms, making it difficult to know the exact duration of atrial fibrillation.
そこで本開示は、心房細動患者の持続期間を推定可能な心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置を提供することを目的とする。Therefore, the present disclosure aims to provide an atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device that can estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation in patients.
前記目的を達成するために、本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置は、
心電図情報取得部、持続期間推定部、及び出力部を含み、
前記心電図情報取得部は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定部は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力部は、前記持続期間を出力する。 In order to achieve the above object, the present disclosure provides an atrial fibrillation duration estimation assistance device,
The device includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition unit, a duration estimation unit, and an output unit,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition unit acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient having atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation unit estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output unit outputs the duration.
本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置は、
学習用情報取得部、及び学習済みモデル生成部を含み、
前記学習用情報取得部は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成部は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する。 The trained model generating device for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation according to the present disclosure comprises:
A learning information acquisition unit and a trained model generation unit are included,
The learning information acquisition unit acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
The trained model generation unit generates a duration estimation model as a trained model, which outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, through machine learning using the duration as a correct label for the electrocardiogram information.
本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法は、
心電図情報取得工程、持続期間推定工程、及び出力工程を含み、
前記心電図情報取得工程は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定工程は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力工程は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各工程が、コンピュータにより実行される方法である。 The method for assisting in estimating duration of atrial fibrillation according to the present disclosure includes:
The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquiring step, a duration estimating step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquiring step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient having atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration,
Each of the steps is a computer-implemented method.
本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造方法は、
学習用情報取得工程、及び学習済みモデル生成工程を含み、
前記学習用情報取得工程は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成工程は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する。 The method for generating a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation disclosed herein includes the steps of:
The method includes a learning information acquisition step and a trained model generation step,
The learning information acquiring step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
The trained model generation process uses machine learning with the duration as a correct label for the electrocardiogram information to generate a duration estimation model as a trained model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of the subject when the subject's electrocardiogram information is input.
本開示の持続期間推定支援プログラムは、
心電図情報取得手順、持続期間推定手順、及び出力手順を含み、
前記心電図情報取得手順は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力手順は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定支援プログラムである。 The duration estimation support program of the present disclosure is
The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition step, a duration estimation step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient with atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step includes estimating a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration;
The atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program causes a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムは、
学習用情報取得手順、及び学習済みモデル生成手順を含み、
前記学習用情報取得手順は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムである。 The present disclosure relates to a program for creating a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation,
The method includes a learning information acquisition procedure and a trained model generation procedure,
The learning information acquisition step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
the trained model generation step generates, as a trained model, a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for the electrocardiogram information;
This is a program for creating a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, which causes a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
本開示の記録媒体は、
心電図情報取得手順、持続期間推定手順、及び出力手順を含み、
前記心電図情報取得手順は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力手順は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定支援プログラムを記録しているコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体である。 The recording medium of the present disclosure includes:
The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition step, a duration estimation step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient with atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step includes estimating a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration;
The present invention is a computer-readable recording medium having recorded thereon an atrial fibrillation duration estimation assistance program for causing a computer to execute each of the above-mentioned procedures.
本開示の記録媒体は、
学習用情報取得手順、及び学習済みモデル生成手順を含み、
前記学習用情報取得手順は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムを記録しているコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体である。 The recording medium of the present disclosure includes:
The method includes a learning information acquisition procedure and a trained model generation procedure,
The learning information acquisition step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
the trained model generation step generates, as a trained model, a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for the electrocardiogram information;
This is a computer-readable recording medium that records a program for creating a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, causing a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
本開示によれば、心房細動患者の持続期間を推定できる。This disclosure makes it possible to estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation in patients.
次に、本開示の実施形態について図を用いて説明する。本開示は、以下の実施形態には限定されない。以下の各図において、同一部分には、同一符号を付している。また、各実施形態の説明は、特に言及がない限り、互いの説明を援用でき、各実施形態の構成は、特に言及がない限り、組合せ可能である。Next, an embodiment of the present disclosure will be described with reference to the drawings. The present disclosure is not limited to the following embodiment. In each of the drawings, the same parts are given the same reference numerals. Furthermore, the explanations of each embodiment can be mutually incorporated unless otherwise specified, and the configurations of each embodiment can be combined unless otherwise specified.
[実施形態1]
本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置について、図1を用いて説明する。図1は、本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置10の一例の構成を示すブロック図である。図1に示すように、心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置10(以下、「本装置10」ともいう)は、心電図情報取得部11、持続期間推定部12、及び出力部13を含む。また、本装置10は、図示していないが、例えば、入力部、出力部、表示部及び/又は記憶部を含んでもよい。[Embodiment 1]
The atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device of this embodiment will be described with reference to Fig. 1. Fig. 1 is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of an atrial fibrillation duration
本装置10は、例えば、前記各部を含む1つの装置でもよいし、前記各部が、通信回線網を介して接続可能な装置でもよい。また、本装置10は、通信回線網を介して、後述する外部装置と接続可能である。通信回線網は、特に制限されず、公知のネットワークを使用でき、例えば、有線でも無線でもよい。通信回線網は、例えば、インターネット回線、WWW(World Wide Web)、電話回線、LAN(Local Area Network)、SAN(Storage Area Network)、DTN(Delay Tolerant Networking)、LPWA(Low Power Wide Area)、L5G(ローカル5G)、等があげられる。無線通信としては、例えば、Wi-Fi(登録商標)、Bluetooth(登録商標)、ローカル5G、LPWA等が挙げられる。前記無線通信としては、各装置が直接通信する形態(Ad Hoc通信)、インフラストラクチャ(infrastructure通信)、アクセスポイントを介した間接通信等であってもよい。本装置10は、例えば、システムとしてサーバに組み込まれていてもよい。また、本装置10は、例えば、本開示のプログラムがインストールされたパーソナルコンピュータ(PC、例えば、デスクトップ型、ノート型)、スマートフォン、タブレット端末等であってもよい。さらに、本装置10は、例えば、前記各部のうち少なくとも一つがサーバ上にあり、その他の前記各部が端末上にあるような、クラウドコンピューティングやエッジコンピューティング等の形態であってもよい。The
図2に、本装置10のハードウェア構成のブロック図を例示する。本装置10は、例えば、中央処理装置101、メモリ102、バス103、記憶装置104、入力装置105、出力装置106、通信デバイス(通信部)107等を含む。本装置10の各部は、それぞれのインタフェース(I/F)により、バス103を介して相互に接続されている。Figure 2 shows an example block diagram of the hardware configuration of the
中央処理装置101は、コントローラ(システムコントローラ、I/Oコントローラ等)等により、他の構成と連携動作し、本装置10の全体の制御を担う。本装置10において、中央処理装置101により、例えば、本開示のプログラムやその他のプログラムが実行され、また、各種情報の読み込みや書き込みが行われる。具体的には、例えば、中央処理装置101が、心電図情報取得部11、持続期間推定部12、及び出力部13として機能する。本装置10は、演算装置として、CPU、GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)、APU(Accelerated Processing Unit)等の他の演算装置を備えてもよいし、これらの組合せを備えてもよい。The
バス103は、例えば、外部装置とも接続できる。前記外部装置は、例えば、外部記憶装置(外部データベース等)、心電計、プリンタ、外部入力装置、外部表示装置、スピーカ等の音声出力装置、カメラ等の外部撮像装置、および加速度センサ、地磁気センサ、方向センサ等の各種センサ等があげられる。本装置10は、例えば、バス103に接続された通信デバイス107により、外部ネットワーク(前記通信回線網)に接続でき、外部ネットワークを介して、他の装置と接続することもできる。The
メモリ102は、例えば、メインメモリ(主記憶装置)が挙げられる。中央処理装置101が処理を行う際には、例えば、後述する記憶装置104に記憶されている本開示のプログラム等の種々の動作プログラムを、メモリ102が読み込み、中央処理装置101は、メモリ102からデータを受け取って、プログラムを実行する。前記メインメモリは、例えば、RAM(ランダムアクセスメモリ)である。また、メモリ102は、例えば、ROM(読み出し専用メモリ)であってもよい。The
記憶装置104は、例えば、前記メインメモリ(主記憶装置)に対して、いわゆる補助記憶装置ともいう。前述のように、記憶装置104には、本開示のプログラムを含む動作プログラムが格納されている。記憶装置104は、例えば、記録媒体と、記録媒体に読み書きするドライブとの組合せであってもよい。前記記録媒体は、特に制限されず、例えば、内蔵型でも外付け型でもよく、HD(ハードディスク)、CD-ROM、CD-R、CD-RW、MO、DVD、フラッシュメモリー、メモリーカード等が挙げられる。記憶装置104は、例えば、記録媒体とドライブとが一体化されたハードディスクドライブ(HDD)、及びソリッドステートドライブ(SSD)であってもよい。本装置10が、例えば、前記記憶部を含む場合、記憶装置104が前記記憶部として機能する。記憶装置104は、例えば、後述する持続期間推定モデルを記憶していてもよい。The
本装置10において、メモリ102及び記憶装置104は、ログ情報、外部データベース(図示せず)や外部の装置から取得した情報、本装置10によって生成した情報、本装置10が処理を実行する際に用いる情報等の種々の情報を記憶することも可能である。なお、少なくとも一部の情報は、例えば、メモリ102及び記憶装置104以外の外部サーバに記憶されていてもよいし、複数の端末にブロックチェーン技術等を用いて分散して記憶されていてもよい。In the
本装置10は、例えば、さらに、入力装置105、出力装置106を備える。入力装置105は、例えば、タッチパネル、トラックパッド、マウス等のポインティングデバイス;キーボード;カメラ、スキャナ等の撮像手段;ICカードリーダ、磁気カードリーダ等のカードリーダ;マイク等の音声入力手段;等があげられる。出力装置106は、例えば、LEDディスプレイ、液晶ディスプレイ等の表示装置;スピーカ等の音声出力装置;プリンタ;等があげられる。本実施形態1において、入力装置105と出力装置106とは、別個に構成されているが、入力装置105と出力装置106とは、タッチパネルディスプレイのように、一体として構成されてもよい。The
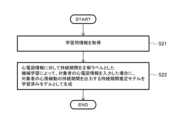
つぎに、本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法の一例を、図3のフローチャートに基づき説明する。本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法は、例えば、図1および図2に示す心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置10を用いて、次のように実施できる。なお、本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法は、図1および図2の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置10の使用には限定されない。Next, an example of the atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method of this embodiment will be described based on the flowchart in FIG. 3. The atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method of this embodiment can be implemented as follows, for example, using the atrial fibrillation duration
まず、心電図情報取得部11は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得する(S1、心電図情報取得工程)。前記心電図情報は、例えば、前記心房細動患者の心電図を記録したグラフ画像の情報である。前記心電図の記録方法は、特に制限されず、例えば、12誘導心電図検査により記録されたものでもよいし、食道内心電図検査により記録されたものでもよいし、心内心電図検査により記録されたものでもよいし、心電図モニタにより記録されたものでもよい。また、前記心房細動患者の心電図検査方法は、特に制限されず、例えば、安静時心電図でもよいし、負荷心電図でもよいし、ホルター心電図でもよいし、胎児心電図でもよい。心電図情報取得部11は、例えば、心電図測定用の各種機器(心電計)から前記心電図情報を取得してもよいし、前記心電図情報を記録した記録媒体から前記心電図情報を取得してもよい。First, the electrocardiogram
心電図情報取得部11は、例えば、前記心電図情報と紐づけてその他の情報を取得してもよい。前記その他の情報は、例えば、前記心房細動患者の識別情報;心房細動患者の患者情報;等があげられる。前記識別情報は、前記心房細動患者を識別可能な情報であれば特に制限されず、例えば、氏名、住所、電話番号、メールアドレス、識別番号(例えば、病院の診察券番号、健康保険証の番号、マイナンバー(個人番号)等)等があげられる。前記患者情報は、例えば、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含む。前記属性情報は、特に制限されず、例えば、心筋梗塞履歴、心不全、および透析等の既往歴;性別;年齢;血液検査結果、血圧等のバイタルデータ;喫煙、飲酒等の生活習慣;身長、体重等の身体的特徴の情報;等があげられる。前記問診情報は、例えば、前記心房細動の自覚症状に関する問診の問いと回答の組の情報である。前記問診の具体例として、例えば、「いつから動悸がありますか?」「初めて心房細動と指摘されたのはいつですか?」等の、心房細動の発症時期に関連する質問とその回答があげられるが、これには限定されない。また、前記心エコー情報は、例えば、心エコー検査(心臓超音波検査)の結果の情報である。The electrocardiogram
つぎに、持続期間推定部12は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する(S2、持続期間推定工程)。持続期間推定部12は、例えば、持続期間推定モデルに前記心電図情報を入力して、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定することができる。前記持続期間推定モデルは、前記心電図情報に対して心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者である心房細動患者の心電図情報が入力された場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力するように学習されたモデルである。前記持続期間推定モデルは、例えば、予めメモリ102及び記憶装置104に記憶されていてもよいし、通信回線網を介して外部の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置(例えば、後述の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20)から取得してもよい。持続期間推定部12は、例えば、前記持続期間として、心房細動患者の心房細動発症からの日数を推定してもよいし、心房細動発症からの経過期間を推定してもよい。後者の場合、持続期間推定部12は、例えば、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間に基づく分類を推定してもよい。前記分類は、例えば、持続期間が発症から7日以内の発作性心房細動;持続期間が発症から7日を超え、且つ1年以内の持続性心房細動;持続期間が発症から1年を超える長期持続性心房細動;等があげられる。持続期間推定部12は、例えば、推定した持続期間を本装置10の前記記憶部に記憶してもよい。Next, the
前記持続期間推定モデルは、例えば、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間との組を教師データとして用いた機械学習によって生成できる。前記機械学習は、例えば、公知の機械学習方法が採用できる。具体例として、前記機械学習に採用される統計モデルとしては、例えば、単純線形回帰モデル、Ridge回帰、Lasso回帰、Elastic Net回帰、LightGBM(Light Gradient Boosting Machine)、Logistic regression、一般加法モデル、ランダムフォレスト回帰、ルールフィット回帰、勾配ブースティング決定木、エクストラツリー、サポートベクトル回帰、ガウス過程回帰、k近傍法による回帰、カーネルリッジ回帰、ニューラルネットワーク等があげられる。なお、前記持続期間推定モデルは、例えば、予め生成された学習済みモデルでもよい。また、前記学習済みモデルは、前記教師データと、既に生成された学習済みモデルとを用いて、再学習させた学習済みモデル(派生モデル)でもよい。さらに、前記学習済みモデルは、前記教師データを用いて生成した学習済みモデルを用いて転移学習することにより得られた学習済みモデルでもよいし、前記教師データを用いて生成した学習済みモデルをモデル圧縮することにより生成した学習済みモデルでもよい。The duration estimation model can be generated by machine learning using, for example, a pair of electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and the duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient as training data. For example, a known machine learning method can be used for the machine learning. As a specific example, a statistical model used for the machine learning includes, for example, a simple linear regression model, Ridge regression, Lasso regression, Elastic Net regression, LightGBM (Light Gradient Boosting Machine), Logistic regression, General Additive Model, Random Forest Regression, Rule Fit Regression, Gradient Boosting Decision Tree, Extra Tree, Support Vector Regression, Gaussian Process Regression, Regression by k-Nearest Neighbor Method, Kernel Ridge Regression, and Neural Network. The duration estimation model may be, for example, a trained model generated in advance. The trained model may also be a trained model (derived model) that is retrained using the training data and a trained model that has already been generated. Furthermore, the trained model may be a trained model obtained by transfer learning using a trained model generated using the training data, or may be a trained model generated by model compression of a trained model generated using the training data.
前記持続期間推定モデルは、例えば、心電図情報を入力する入力層と、前記持続期間を出力する出力層と、入力層と出力層との間に設けられる少なくとも1層の中間層とを含んだネットワークであってもよい。この場合、前記持続期間推定モデルは、人工知能ソフトウェアの一部であるプログラムモジュールであってもよい。多層化ネットワークとしては、例えば、ニューラルネットワーク等が挙げられる。前記ニューラルネットワークとしては、例えば、畳み込みニューラルネットワーク(Convolution Neural Network:CNN)等が挙げられるが、CNNに限定されず、CNN以外のニューラルネットワーク、SVM(Support Vector Machine)、ベイジアンネットワーク、回帰木等の他の学習アルゴリズムで構築された学習済みモデルであってもよい。The duration estimation model may be a network including, for example, an input layer for inputting electrocardiogram information, an output layer for outputting the duration, and at least one intermediate layer provided between the input layer and the output layer. In this case, the duration estimation model may be a program module that is a part of artificial intelligence software. An example of a multi-layered network is a neural network. An example of the neural network is a convolution neural network (CNN), but it is not limited to CNN and may be a trained model constructed with other learning algorithms such as a neural network other than CNN, a support vector machine (SVM), a Bayesian network, or a regression tree.
S1において前記患者情報が取得されている場合、持続期間推定部12は、例えば、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定してもよい。この場合、持続期間推定部12は、例えば、持続期間推定モデルに前記心電図情報および前記患者情報を入力して、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定することができる。この場合の持続期間推定モデルは、例えば、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報の組み合わせに対して心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者である心房細動患者の心電図情報および患者情報が入力された場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力するように学習されたモデルであること以外は、前述と同様である。When the patient information is acquired in S1, the
そして、出力部13は、前記持続期間を出力する(S3、出力工程)。前記出力は、例えば、本装置10の出力装置106(例えば、ディスプレイ)への出力でもよいし、本装置10外の外部装置への出力でもよい。出力部13は、例えば、前記持続期間を前記心房細動患者の識別情報と紐づけて出力してもよい。Then, the
心房細動の患者において、患者の問診に基づいて医師が心房細動の持続期間を推定した場合、その予測能(AUC:Area Under Curve)が0.65であった。また、前記問診に加え、心エコー検査の結果に基づいて医師が持続期間を推定した場合、その予測能(AUC)が0.72であった。これに対し、本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置によれば、予測能(AUC)が0.79と高精度に心房細動の持続期間を推定することができた。このため、本開示によれば、患者の心電図情報に基づいて、客観的かつ精度のよい心房細動患者の持続期間推定が可能になる。これにより、例えば、持続期間が短くカテーテルアブレーション手術の効果が高く期待できる患者にはカテーテルアブレーション手術を提案し、逆に持続期間が長くカテーテルアブレーション手術の効果があまり期待できない(再発可能性が高い)患者に対してはカテーテルアブレーション手術以外の処置を提案するなど、治療の最適化が可能になる。このため、本開示によれば、治療の最適化による医療費の抑制効果も期待できる。In patients with atrial fibrillation, when a doctor estimated the duration of atrial fibrillation based on the patient's interview, the predictive ability (AUC: Area Under Curve) was 0.65. In addition, when a doctor estimated the duration based on the results of an echocardiogram in addition to the interview, the predictive ability (AUC) was 0.72. In contrast, the atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device disclosed herein was able to estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation with a high degree of accuracy, with a predictive ability (AUC) of 0.79. Therefore, according to the present disclosure, it is possible to objectively and accurately estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation in patients based on the patient's electrocardiogram information. This makes it possible to optimize treatment, for example, by proposing catheter ablation surgery to patients whose duration is short and for whom catheter ablation surgery is expected to be highly effective, and by proposing treatment other than catheter ablation surgery to patients whose duration is long and for whom catheter ablation surgery is not expected to be very effective (high recurrence rate). Therefore, according to the present disclosure, it is expected that the optimization of treatment will have an effect of reducing medical expenses.
[実施形態2]
実施形態2は、本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置の他の例である。[Embodiment 2]
The second embodiment is another example of an atrial fibrillation duration estimation assistance device according to the present disclosure.
図4は、持続期間推定支援装置10Aの一例の構成を示すブロック図である。図4に示すように、持続期間推定支援装置10Aは、実施形態1の持続期間推定支援装置10の構成に加えて、再発予測部14を含む。持続期間推定支援装置10Aのハードウェア構成は、図2の持続期間推定支援装置10のハードウェア構成において、中央処理装置101が、図1の持続期間推定支援装置10の構成に代えて、図4の持続期間推定支援装置10Aの構成を備える以外は同様である。以下、再発予測部14の処理を説明する。再発予測部14の処理は、例えば、前記実施形態1で説明した図3のフローチャートにおける任意の位置に適宜挿入してもよいし、図5に示すように、別途独立した処理としてもよい。Figure 4 is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the duration
再発予測部14は、例えば、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方に基づいて、前記心房細動患者の再発率を予測する(S11、再発予測工程)。前記再発率は、例えば、カテーテルアブレーション手術等の、心房細動に対する根治術による治療後の心房細動の再発症の可能性である。再発予測部14は、例えば、前記再発率を定性的に予測してもよいし、定量的に予測してもよい。前記定性的な予測は、例えば、再発の可能性があるか、ないかの予測であり、前記定量的な予測は、例えば、再発の確率がn%(nは正の数)等の再発可能性を数値で表す予測である。再発予測部14は、例えば、前記心電図情報に基づいて再発率を予測してもよいし、前記持続期間に基づいて再発率を予測してもよいし、前記心電図情報と前記持続期間とに基づいて再発率を予測してもよい。再発予測部14は、例えば、機械学習済みモデルを利用して前記再発率を予測できる。前記機械学習済みモデルは、例えば、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方に対し、前記心房細動患者の再発率を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方が入力された場合に、心房細動患者の再発率を出力するように学習されたモデルである。前記学習済みモデルは、例えば、予めメモリ102及び記憶装置104に記憶されていてもよいし、通信回線網を介して外部の装置から取得してもよい。The
出力部13は、例えば、前記再発率を出力する(S12、出力工程(再発率出力工程))。前記出力は、例えば、本装置10の出力装置106(例えば、ディスプレイ)への出力でもよいし、本装置10外の外部装置への出力でもよい。出力部13は、例えば、前記再発率を前記心房細動患者の識別情報と紐づけて出力してもよい。The
本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置10Aによれば、例えば、再発予測部14により、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方に基づいて、前記心房細動患者の再発率を予測できる。これにより、例えば、再発率が低く、カテーテルアブレーション手術の効果が高く期待できる患者にはカテーテルアブレーション手術を提案し、逆に再発率が高くカテーテルアブレーション手術の効果があまり期待できない患者に対してはカテーテルアブレーション手術以外の処置を提案するなど、治療の最適化が可能になる。このため、本開示によれば、治療の最適化による医療費の抑制効果も期待できる。According to the atrial fibrillation duration
[実施形態3]
実施形態3は、本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置の例である。[Embodiment 3]
Embodiment 3 is an example of a trained model creation device for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation of the present disclosure.
本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置について、図6を用いて説明する。図6は、本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20の一例の構成を示すブロック図である。図6に示すように、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20(以下、「本装置20」ともいう)は、学習用情報取得部21、及び学習済みモデル生成部22を含む。また、本装置20は、図示していないが、例えば、入力部、出力部、表示部及び/又は記憶部を含んでもよい。The trained model producing device for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation of this embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 6. FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing an example of the configuration of the trained
心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20は、例えば、前記各部を含む1つの装置でもよいし、前記各部が、通信回線網を介して接続可能な装置でもよい。また、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20は、通信回線網を介して、後述する外部装置と接続可能である。通信回線網は、特に制限されず、公知のネットワークを使用でき、例えば、有線でも無線でもよい。通信回線網は、例えば、インターネット回線、WWW(World Wide Web)、電話回線、LAN(Local Area Network)、SAN(Storage Area Network)、DTN(Delay Tolerant Networking)、LPWA(Low Power Wide Area)、L5G(ローカル5G)、等があげられる。無線通信としては、例えば、Wi-Fi(登録商標)、Bluetooth(登録商標)、ローカル5G、LPWA等が挙げられる。前記無線通信としては、各装置が直接通信する形態(Ad Hoc通信)、インフラストラクチャ(infrastructure通信)、アクセスポイントを介した間接通信等であってもよい。心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20は、例えば、システムとしてサーバに組み込まれていてもよい。また、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20は、例えば、本開示のプログラムがインストールされたパーソナルコンピュータ(PC、例えば、デスクトップ型、ノート型)、スマートフォン、タブレット端末等であってもよい。さらに、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20は、例えば、前記各部のうち少なくとも一つがサーバ上にあり、その他の前記各部が端末上にあるような、クラウドコンピューティングやエッジコンピューティング等の形態であってもよい。The trained
図7に、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20のハードウェア構成のブロック図を例示する。図7に示すように、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20は、例えば、中央処理装置201、メモリ202、バス203、記憶装置204、入力装置205、出力装置206、通信デバイス207等を備える。心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20の各構成の説明は、心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置10の各構成の説明を援用できる。心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20の各部は、それぞれのインタフェース(I/F)により、バス203を介して接続されている。心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20において、中央処理装置201が学習用情報取得部21、及び学習済みモデル生成部22として機能する。Figure 7 illustrates a block diagram of the hardware configuration of the trained
つぎに、本実施形態の学習済みモデルの製造方法の一例を、図8のフローチャートに基づき説明する。本実施形態の学習済みモデルの製造方法は、例えば、図6及び7の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20を用いて、次のように実施する。なお、本実施形態の学習済みモデルの製造方法は、図6及び図7の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置20の使用には限定されない。Next, an example of a method for manufacturing a trained model of this embodiment will be described based on the flowchart of FIG. 8. The method for manufacturing a trained model of this embodiment is implemented, for example, as follows, using the trained
まず、学習用情報取得部21により、学習用情報を取得する(S21、学習用情報取得工程)。前記学習用情報は、例えば、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含む。また、前記学習用情報は、例えば、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含んでもよい。前記学習用情報が含む各情報については、前記実施形態1および2と同様であり、その説明を援用できる。学習用情報取得部21は、例えば、予めメモリ202及び記憶装置204に記憶されている情報を取得してもよいし、通信回線網を介して外部のデータベースに記憶されている情報を取得してもよい。First, the learning
つぎに、学習済みモデル生成部22は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する(S22、学習工程)。学習済みモデル生成部22は、例えば、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間との組を教師データとして用いた機械学習によって前記持続期間推定モデルを生成できる。前記機械学習は、例えば、公知の機械学習方法が採用できる。具体例として、前記機械学習に採用される統計モデルとしては、例えば、単純線形回帰モデル、Ridge回帰、Lasso回帰、Elastic Net回帰、LightGBM(Light Gradient Boosting Machine)、Logistic regression、一般加法モデル、ランダムフォレスト回帰、ルールフィット回帰、勾配ブースティング決定木、エクストラツリー、サポートベクトル回帰、ガウス過程回帰、k最近傍法による回帰、カーネルリッジ回帰、ニューラルネットワーク等があげられる。なお、前記持続期間推定モデルは、例えば、予め生成された学習済みモデルでもよい。また、前記学習済みモデルは、前記教師データと、既に生成された学習済みモデルとを用いて、再学習させた学習済みモデル(派生モデル)でもよい。さらに、前記学習済みモデルは、前記教師データを用いて生成した学習済みモデルを用いて転移学習することにより得られた学習済みモデルでもよいし、前記教師データを用いて生成した学習済みモデルをモデル圧縮することにより生成した学習済みモデルでもよい。Next, the trained
学習済みモデル生成部22は、例えば、前記持続期間推定モデルとして、心電図情報を入力する入力層と、前記持続期間を出力する出力層と、入力層と出力層との間に設けられる少なくとも1層の中間層とを含んだネットワークを生成してもよい。この場合、前記持続期間推定モデルは、人工知能ソフトウェアの一部であるプログラムモジュールであってもよい。多層化ネットワークとしては、例えば、ニューラルネットワーク等が挙げられる。前記ニューラルネットワークとしては、例えば、畳み込みニューラルネットワーク(Convolution Neural Network:CNN)等が挙げられるが、CNNに限定されず、CNN以外のニューラルネットワーク、SVM(Support Vector Machine)、ベイジアンネットワーク、回帰木等の他の学習アルゴリズムで構築された学習済みモデルであってもよい。The trained
前記学習用情報が前記患者情報を含む場合、学習済みモデル生成部22は、例えば、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報の組み合わせに対して心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者である心房細動患者の心電図情報および患者情報が入力された場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力するように学習された持続期間推定モデルを生成してもよい。この場合の持続期間推定モデルは、例えば、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報の組み合わせに対して心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者である心房細動患者の心電図情報および患者情報が入力された場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力するように学習されたモデルであること以外は、前述と同様である。When the learning information includes the patient information, the trained
本実施形態によって生成される学習済みモデルは、例えば、前記実施形態1および2に記載の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置に使用される。これにより、心房細動患者の心電図情報に基づいて心房細動の持続期間が推定可能になる。The trained model generated by this embodiment is used, for example, in the atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device described in the first and second embodiments. This makes it possible to estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation based on electrocardiogram information from a patient with atrial fibrillation.
[実施形態4]
本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定支援プログラムは、前述の心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法の各工程を、コンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムである。具体的に、本実施形態の持続期間推定支援プログラムは、コンピュータに、心電図情報取得手順、持続期間推定手順、及び出力手順を実行させるためのプログラムである。[Embodiment 4]
The atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program of this embodiment is a program for causing a computer to execute each step of the above-mentioned atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method. Specifically, the atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program of this embodiment is a program for causing a computer to execute an electrocardiogram information acquisition procedure, a duration estimation procedure, and an output procedure.
心電図情報取得手順、持続期間推定手順、及び出力手順を含み、
前記心電図情報取得手順は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力手順は、前記持続期間を出力する。The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition step, a duration estimation step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient with atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step includes estimating a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration.
また、本実施形態の持続期間推定支援プログラムは、コンピュータを、心電図情報取得手順、持続期間推定手順、及び出力手順として機能させるプログラムということもできる。The duration estimation assistance program of this embodiment can also be described as a program that causes a computer to function as an electrocardiogram information acquisition procedure, a duration estimation procedure, and an output procedure.
本実施形態の持続期間推定支援プログラムは、前記本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置および心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法における記載を援用できる。前記各手順は、例えば、「手順」を「処理」と読み替え可能である。また、本実施形態のプログラムは、例えば、コンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体に記録されてもよい。前記記録媒体は、特に制限されず、例えば、ランダムアクセスメモリ(RAM)、読み出し専用メモリ(ROM)、ハードディスク(HD)、フラッシュメモリー(例えば、SSD(Solid State Drive)、USBフラッシュメモリー、SD/SDHCカード等)、光ディスク(例えば、CD‐R/CD‐RW、DVD‐R/DVD‐RW、BD‐R/BD‐RE等)、光磁気ディスク(MO)、フロッピー(登録商標)ディスク(FD)等があげられる。また、本実施形態の持続期間推定支援プログラム(例えば、プログラミング製品、又は持続期間推定支援プログラム製品ともいう)は、例えば、外部のコンピュータから配信される形態であってもよい。前記「配信」は、例えば、通信回線網を介した配信でもよいし、有線で接続された装置を介した配信であってもよい。本実施形態の持続期間推定支援プログラムは、配信された装置にインストールされて実行されてもよいし、インストールされずに実行されてもよい。The duration estimation support program of this embodiment can refer to the description in the atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device and atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method of the present disclosure. For example, the "procedure" in each of the steps can be read as "processing". The program of this embodiment may be recorded in a computer-readable recording medium. The recording medium is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), hard disk (HD), flash memory (e.g., SSD (Solid State Drive), USB flash memory, SD/SDHC card, etc.), optical disk (e.g., CD-R/CD-RW, DVD-R/DVD-RW, BD-R/BD-RE, etc.), magneto-optical disk (MO), floppy (registered trademark) disk (FD), etc. Furthermore, the duration estimation assistance program of this embodiment (also referred to as, for example, a programming product or a duration estimation assistance program product) may be in a form distributed from an external computer, for example. The "distribution" may be, for example, distribution via a communication network, or distribution via a device connected by wire. The duration estimation assistance program of this embodiment may be installed and executed on the device to which it is distributed, or may be executed without being installed.
[実施形態5]
本実施形態の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムは、前述の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造方法の各工程を、コンピュータに実行させるためのプログラムである。具体的に、本実施形態の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムは、コンピュータに、学習用情報取得部、及び学習済みモデル生成部を実行させるためのプログラムである。[Embodiment 5]
The trained model creation program for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation of this embodiment is a program for causing a computer to execute each step of the trained model creation method for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation described above. Specifically, the trained model creation program for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation of this embodiment is a program for causing a computer to execute a training information acquisition unit and a trained model generation unit.
前記学習用情報取得手順は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する。The learning information acquisition step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
The trained model generation procedure uses machine learning with the duration as a correct label for the electrocardiogram information to generate a duration estimation model as a trained model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of the subject when the subject's electrocardiogram information is input.
また、本実施形態の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムは、コンピュータを、学習用情報取得手順、及び学習済みモデル生成手順として機能させるプログラムということもできる。The program for creating a trained model for duration estimation in this embodiment can also be described as a program that causes a computer to function as a training information acquisition procedure and a trained model generation procedure.
本実施形態の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムは、前記本開示の心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置および心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造方法における記載を援用できる。前記各手順は、例えば、「手順」を「処理」と読み替え可能である。また、本実施形態のプログラムは、例えば、コンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体に記録されてもよい。前記記録媒体は、特に制限されず、例えば、ランダムアクセスメモリ(RAM)、読み出し専用メモリ(ROM)、ハードディスク(HD)、フラッシュメモリー(例えば、SSD(Solid State Drive)、USBフラッシュメモリー、SD/SDHCカード等)、光ディスク(例えば、CD‐R/CD‐RW、DVD‐R/DVD‐RW、BD‐R/BD‐RE等)、光磁気ディスク(MO)、フロッピー(登録商標)ディスク(FD)等があげられる。また、本実施形態の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラム(例えば、プログラミング製品、又は持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラム製品ともいう)は、例えば、外部のコンピュータから配信される形態であってもよい。前記「配信」は、例えば、通信回線網を介した配信でもよいし、有線で接続された装置を介した配信であってもよい。本実施形態の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムは、配信された装置にインストールされて実行されてもよいし、インストールされずに実行されてもよい。The program for producing a trained model for estimating duration of atrial fibrillation of the present disclosure may be implemented using the description of the trained model producing device for estimating duration of atrial fibrillation of the present disclosure and the trained model producing method for estimating duration of atrial fibrillation of the present disclosure. In each of the steps, for example, "step" can be read as "processing". The program of the present embodiment may be recorded, for example, in a computer-readable recording medium. The recording medium is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), hard disk (HD), flash memory (for example, SSD (Solid State Drive), USB flash memory, SD/SDHC card, etc.), optical disk (for example, CD-R/CD-RW, DVD-R/DVD-RW, BD-R/BD-RE, etc.), magneto-optical disk (MO), floppy (registered trademark) disk (FD), etc. In addition, the trained model manufacturing program for duration estimation of this embodiment (e.g., also referred to as a programming product or a trained model manufacturing program product for duration estimation) may be in a form distributed from an external computer, for example. The "distribution" may be, for example, distribution via a communication network or distribution via a device connected by wire. The trained model manufacturing program for duration estimation of this embodiment may be installed and executed on the device to which it is distributed, or may be executed without being installed.
次に、本開示の実施例について説明する。ただし、本開示は、下記実施例により制限されない。市販の試薬および機器は、特に示さない限り、それらのプロトコルに基づいて使用した。Next, examples of the present disclosure will be described. However, the present disclosure is not limited to the following examples. Commercially available reagents and equipment were used according to their protocols unless otherwise indicated.
[実施例1]
本開示の持続期間推定支援装置により、心房細動患者の持続期間が推定できることを確認した。[Example 1]
It was confirmed that the duration estimation support device disclosed herein can estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation in patients.
(1)心房細動患者
まず、日本赤十字社京都第二病院において、2015年1月1日~2023年12月31日の間に初回カテーテルアブレーション(CA)として入院し、その後3か月以内に心電図、患者背景、心エコー、検査データが得られた20~90歳の患者272人を対象とした。そして、心電図にペースメーカーリズムが記録されていた14人、QRS波の除外が困難または抽出したF波が短すぎて特徴解析が困難であった30人、心房細動持続期間の判定が困難であった39人を除外し、計189人を試験対象患者とした。(1) Patients with atrial fibrillation First, 272 patients aged 20 to 90 years old who were admitted to the Japanese Red Cross Kyoto Second Hospital for their first catheter ablation (CA) between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2023, and whose electrocardiogram, patient background, echocardiogram, and test data were available within the following three months, were included in the study. After excluding 14 patients with pacemaker rhythm recorded on the electrocardiogram, 30 patients in whom it was difficult to exclude QRS waves or the extracted F waves were too short for characteristic analysis, and 39 patients in whom it was difficult to determine the duration of atrial fibrillation, a total of 189 patients were included in the study.
つぎに、各患者について、以下の基準に従って、PeAF(心房細動持続期間1年未満)またはLsPeAF(Long standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation、心房細動持続期間1年以上)に分類した。下記の基準のいずれにも当てはまらない患者については、期間不明症例として除外した。
・PeAF(心房細動持続期間1年未満)
除細動後の心電図を除き、1年以内に心電図で洞調律が記録され、その後に心房細動が連続して記録された患者、または、明らかに心房細動に関連する臨床症状または不整脈の発現が1年以内に確認され、その後に心房細動が連続して記録された患者。
・LsPeAF(心房細動持続期間1年以上)
心房細動の心電図記録が1年以上連続して確認された患者、または、明らかに心房細動に関連する臨床症状または不整脈が1年以上前に発症し、その後1年以内に心房細動の心電図記録が連続して確認された患者。 Next, each patient was classified as having PeAF (atrial fibrillation duration <1 year) or LsPeAF (long standing persistent atrial fibrillation, atrial fibrillation duration ≥1 year) according to the following criteria: Patients who did not meet any of the following criteria were excluded as cases of unknown duration.
・PeAF (atrial fibrillation lasting less than one year)
Patients who had a continuous record of atrial fibrillation after a sinus rhythm recorded on an electrocardiogram within one year, excluding electrocardiograms after defibrillation, or who had a continuous record of atrial fibrillation after clinical symptoms or arrhythmias clearly related to atrial fibrillation within one year.
・LsPeAF (atrial fibrillation lasting for more than one year)
Patients with electrocardiogram records of atrial fibrillation confirmed for more than one year consecutively, or patients who have had clinical symptoms or arrhythmias clearly related to atrial fibrillation for more than one year prior and have had electrocardiogram records of atrial fibrillation confirmed for more than one year thereafter.
下記表1~3に、試験対象患者の情報を示す。下記表1は、試験対象患者(全患者、PeAF患者、LsPeAF患者)の年齢(age)、性別(Sex)、身長(Height)、体重(Weight)、ボディマス指数(Body Mass Index :BMI)、体表面積(Body Surface Area:BSA)を示す表である。下記表2は、試験対象患者(全患者、PeAF患者、LsPeAF患者)の既往歴を示し、心不全(Heart Failure)、脳卒中(Stroke)、高血圧(Hypertension)、糖尿病(Diabetes)、脂質異常症(Dyslipidemia)、慢性腎臓病(Chronic Kidney Disease:CKD)、慢性肺疾患(Chronic Pulmonary Disease :CPD)の数(n)および全体に対する割合(%)を示す表である。下記表3は、試験対象患者の心エコーデータを示す表であり、左房径(LAD:Left Atrial Diameter)、駆出分画(Ejection Fraction)、僧帽弁逆流(MR: Mitral Regurgitation)を示す。Tables 1 to 3 below show information on the study patients. Table 1 below shows the age, sex, height, weight, body mass index (BMI), and body surface area (BSA) of the study patients (all patients, PeAF patients, and LsPeAF patients). Table 2 below shows the medical history of the study patients (all patients, PeAF patients, and LsPeAF patients), and shows the number (n) and percentage (%) of patients with heart failure, stroke, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease (CKD), and chronic pulmonary disease (CPD). Table 3 below shows the echocardiographic data of the test patients, including left atrial diameter (LAD), ejection fraction, and mitral regurgitation (MR).
(2)心電図データ分析
試験対象患者189名について、12誘導心電図記録装置(FCP-8800またはFCP-8700、いずれもフクダ電子株式会社製)を用いて、10秒間の心電図データを解析し、各患者の心拍数(HR)、QRS幅、S1振幅、RV5振幅、R+S(=S1振幅+RV5振幅)を得た。下記表4に、試験対象患者(全患者、PeAF患者、LsPeAF患者)の心電図データを示す。表4は、試験対象患者の心電図データを示す表であり、心拍数(Heart Rate)、QRS幅(QRS width)、SV1振幅(SV1 amplitude)、RV5振幅(RV5 amplitude)、および、SV1振幅およびRV5振幅(R+S: SV1 amplitude+RV5 amplitude)を示す。(2) Electrocardiogram Data Analysis For 189 test patients, 10 seconds of electrocardiogram data was analyzed using a 12-lead electrocardiogram recording device (FCP-8800 or FCP-8700, both manufactured by Fukuda Denshi Co., Ltd.), and the heart rate (HR), QRS width, S1 amplitude, RV5 amplitude, and R+S (=S1 amplitude+RV5 amplitude) of each patient were obtained. Table 4 below shows the electrocardiogram data of the test patients (all patients, PeAF patients, and LsPeAF patients). Table 4 is a table showing the electrocardiogram data of the test patients, and shows the heart rate, QRS width, SV1 amplitude, RV5 amplitude, and SV1 amplitude and RV5 amplitude (R+S: SV1 amplitude+RV5 amplitude).
つぎに、10秒間の心電図データから、F波を抽出した。F波は、4~9Hzの帯域にあるため、カットオフ周波数を0.8~40Hzに設定した。QRSTキャンセルのためにQRST間隔を検出し、R波時間はPan- Tompkinsアルゴリズムを適用してピーク検出した。Q波時間は、R波時間から典型的な心室活性化時間である37msを減算して求めた。T波時間は、R波時間に200msを加算して求めた。各QRST間隔について、主成分分析を用いてf波を抽出した。f波は4-9Hzの帯域にあるため、カットオフ周波数を3-20Hzに設定した。抽出したF波の一例を図9に示す。Next, F waves were extracted from 10 seconds of ECG data. Since F waves are in the 4-9 Hz band, the cutoff frequency was set to 0.8-40 Hz. To cancel QRST, QRST intervals were detected, and the R wave time was peak-detected using the Pan-Tompkins algorithm. The Q wave time was calculated by subtracting 37 ms, a typical ventricular activation time, from the R wave time. The T wave time was calculated by adding 200 ms to the R wave time. For each QRST interval, f waves were extracted using principal component analysis. Since f waves are in the 4-9 Hz band, the cutoff frequency was set to 3-20 Hz. An example of an extracted F wave is shown in Figure 9.
つぎに、抽出したF波の特徴を分析した。振幅の二乗平均平方根(RMS)は、時間領域における信号振幅の二乗の算術平均である平均二乗の平方根として定義された。サンプルエントロピー(SampEn)は、f波の不規則性の評価に使用された。SampEnは、エントロピーの指標であり、近似エントロピーの偏りを減らし、よりロバストな統計量を得るために設計された手法である。サンプルエントロピーの定義を下記式1に示す。閾値は3.5、サンプルサイズは3とした。高速フーリエ変換後、ドミナント波形(DF:Dominant Frequency)と組織指数(OI:Organization Index)を求めた。DFは、F波の周波数分析に最も広く使われている指標の一つで、周波数分布の中で最もパワー値が高い周波数をDFと定義した。OIは、F波の組織化の指標として用いられた。OIは、3-15Hz帯域のスペクトルの残りの部分に対する、最高ピークとその高調波(第5高調波のピークを含まない)の下の面積の比率として定義した。Next, the characteristics of the extracted F-waves were analyzed. The root mean square (RMS) of the amplitude was defined as the square root of the mean square, which is the arithmetic mean of the squares of the signal amplitudes in the time domain. Sample entropy (SampEn) was used to evaluate the irregularity of the f-waves. SampEn is an index of entropy and is a method designed to reduce the bias of approximate entropy and obtain more robust statistics. The definition of sample entropy is shown in Equation 1 below. The threshold was 3.5 and the sample size was 3. After fast Fourier transformation, the dominant frequency (DF) and organization index (OI) were obtained. DF is one of the most widely used indices for frequency analysis of F-waves, and the frequency with the highest power value in the frequency distribution was defined as DF. OI was used as an index of organization of F-waves. OI was defined as the ratio of the area under the highest peak and its harmonics (not including the 5th harmonic peak) to the rest of the spectrum in the 3-15 Hz band.
表5~8に、試験対象患者(全患者、PeAF患者、LsPeAF患者)のF波の特徴を示す。Tables 5 to 8 show the F wave characteristics of the study patients (all patients, PeAF patients, and LsPeAF patients).
(3)学習済みモデル(持続期間推定モデル)の構築
試験対象患者189名のうち、145名分の心電図情報をトレーニングデータ群とし、残りの44名分の心電図情報をテストデータ群として、PeAFまたはLsPeAFを予測するモデルを構築した。具体的に、LsPeAF=1の患者とPeAF=0の患者を目的変数として2値分類を行い、勾配ブースティング決定木(Gradient Boosting Decision Tree:GBDT)を使用してモデル訓練をした。GBDTは、XGBoost (eXtreme Gradient Boost)を実装した。XGBoostのハイパーパラメータは以下の通りとした。
Learning rate: 0.3703
Max depth: 2
min child weight: 2
subsample: 0.9100
colsample_bytree: 0.1043
reg lambda: 0.0056
reg alpha: 0.0041
gamma: 0.4426(3) Construction of trained model (duration estimation model) Of the 189 test patients, electrocardiogram information from 145 patients was used as the training data group, and electrocardiogram information from the remaining 44 patients was used as the test data group to construct a model to predict PeAF or LsPeAF. Specifically, a binary classification was performed using patients with LsPeAF=1 and patients with PeAF=0 as the objective variable, and the model was trained using a Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT). GBDT implemented XGBoost (eXtreme Gradient Boost). The hyperparameters of XGBoost were as follows:
Learning rate: 0.3703
Max depth: 2
Min child weight: 2
subsample: 0.9100
colsample_bytree: 0.1043
reg lambda: 0.0056
reg alpha: 0.0041
gamma: 0.4426
モデルの評価には、層別5分割クロスバリデーションを用い、各分割においてクラスのバランスが保たれるようにした。具体的には、データセットを5つの部分に分割し、それぞれの部分を検証データとして使用し、残りの部分を訓練データとして使用することを5回繰り返した。訓練に用いた心電図情報としては、表1~8に示す試験対象患者の各種情報から、単変量解析でp値が0.05未満の変数を抽出し、さらに、ステップワイズ法で選択した情報を使用した。また、多重共線性を排除するため、相関係数の高い特徴は除外した。AUCの算出にはROC曲線を用い、連続変数のカットオフ値は最大ユーデン指数に基づいて算出した。統計解析にはPythonバージョン3.10.12(Python Software Foundation, Wilmington, DE, US)を使用した。To evaluate the model, we used stratified 5-fold cross-validation to ensure that the classes were balanced in each division. Specifically, the dataset was divided into 5 parts, and each part was used as validation data, and the remaining part was used as training data, and this was repeated 5 times. For the ECG information used for training, variables with p values less than 0.05 in univariate analysis were extracted from the various information of the test patients shown in Tables 1 to 8, and the information selected using the stepwise method was used. In addition, features with high correlation coefficients were excluded to eliminate multicollinearity. AUC was calculated using an ROC curve, and the cutoff value for continuous variables was calculated based on the maximum Youden index. Statistical analysis was performed using Python version 3.10.12 (Python Software Foundation, Wilmington, DE, US).
(4)学習済みモデル(持続期間推定モデル)の予測精度評価
評価方法としては、テストデータ群を用いてモデルの精度を評価した。5つの異なるランダムシードを設定し、それぞれの設定でのモデルの平均ROC曲線-AUCを算出し、Youden indexを用いて最適なカットオフ点を選択した。ROC曲線-AUCの平均値は、0.82であった。また、モデルの解釈にはSHARP値を使用し、各特徴量の重要度を評価した。本開示の持続期間推定モデルは、心拍数(HR)を最も重要な特徴量として扱った。その他の特徴量の重要度は、RMS、SampEn、振幅、左室駆出率、性別、起立耐性失調、肥満度、QRS波振幅、QRS幅、左房径(LAD)、年齢の順であった。(4) Evaluation of prediction accuracy of trained model (duration estimation model) As an evaluation method, the accuracy of the model was evaluated using a test data group. Five different random seeds were set, the average ROC curve-AUC of the model for each setting was calculated, and the optimal cutoff point was selected using the Youden index. The average value of the ROC curve-AUC was 0.82. In addition, the SHARP value was used to interpret the model, and the importance of each feature was evaluated. In the duration estimation model disclosed herein, heart rate (HR) was treated as the most important feature. The importance of other features was RMS, SampEn, amplitude, left ventricular ejection fraction, sex, orthostatic intolerance, obesity level, QRS wave amplitude, QRS width, left atrial diameter (LAD), and age, in that order.
表9に、持続期間推定モデルによるテストデータの予測結果を示す。表9に示すように、本開示の持続期間推定モデルは、テストデータの予測精度(Accuracy)が0.82、感度(Sensitivity)が0.72、特異度(Specificity)が0.89あり、高精度で心房細動患者の持続期間を推定することができた。Table 9 shows the prediction results of the test data using the duration estimation model. As shown in Table 9, the duration estimation model disclosed herein had a prediction accuracy of 0.82, sensitivity of 0.72, and specificity of 0.89 for the test data, and was able to estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation patients with high accuracy.
(5)学習済みモデル(持続期間推定モデル)の予測精度と医師の予測精度との比較
10人の循環器専門医(グループA)により、テストデータとした44人の試験対象患者の心電図データを診断させ、患者の情報をもとに、各患者が少なくとも1年以上持続している心房細動であるかどうかを回答させた(Phase 1)。その後、各医師に本開示の持続期間推定モデルによる持続期間の予測結果と、モデルの予測結果に対する各変数(特徴量)の寄与度を算出したSHAP値を提示した後、再度回答させた(Phase 2)。さらに、他の10名の維持(グループB)には、グループAの医師の診断結果を示し、医師の心房細動持続期間の診断能力を事前に認識した上で、グループAと同様に、Phase1およびPhase2の回答を行わせる2相試験を行った。結果を図10に示す。図10は、グループAおよびグループBの医師による診断精度を示すグラフである。グループAおよびグループBのグラフにおいて、実線で接続された黒丸は、同一の医師によるPhase1および2における結果を示す。また、図10のグラフにおいて、本開示の持続期間推定モデル(MLモデル)による予測精度を示す。図10に示すように、本開示の持続期間推定モデルは、医師による診断精度よりも高い精度で心房細動患者の持続期間を推定できることがわかった。(5) Comparison of the prediction accuracy of the trained model (duration estimation model) with that of doctors
Ten cardiologists (Group A) diagnosed the electrocardiogram data of 44 test patients as test data, and based on the patient information, answered whether each patient had atrial fibrillation that had lasted for at least one year (Phase 1). After that, each doctor was presented with the predicted results of the duration estimation model of the present disclosure and the SHAP value calculated by the contribution of each variable (feature amount) to the predicted results of the model, and then asked to answer again (Phase 2). Furthermore, a two-phase test was conducted in which the other 10 patients (Group B) were shown the diagnosis results of the doctors in Group A, and were made to answer Phase 1 and Phase 2 in the same way as Group A, after being aware of the doctors' diagnostic ability of the doctors for atrial fibrillation duration in advance. The results are shown in FIG. 10. FIG. 10 is a graph showing the diagnostic accuracy by doctors in Group A and Group B. In the graphs for Group A and Group B, the black circles connected by solid lines indicate the results in Phase 1 and Phase 2 by the same doctor. Moreover, the prediction accuracy by the duration estimation model (ML model) of the present disclosure is shown in the graph of Fig. 10. As shown in Fig. 10, it was found that the duration estimation model of the present disclosure can estimate the duration of an atrial fibrillation patient with higher accuracy than the accuracy of diagnosis by a doctor.
なお、グループAの正解率は、Phase1で63.9±9.6%であったが、Phase2では71.6±9.3%に改善した(p=0.01)。グループBの正解率は、Phase1では59.8±5.3%であったが、Phase2では68.2±5.9%に改善した(p<0.01)。Phase2では、グループAとBとに正解率に差はなかった(p=0.48)。Phase2で本開示の持続期間推定モデルの予測と異なった回答(本開示の持続期間推定モデルの予測が正しく、医師が不正解であった回答)を行った医師の割合の平均は、グループAで17.3±10.3%であり、グループBで20.9±5.0%であった。このため、グループAおよびBの間で正解率の上昇に有意差はなかった(p=0.85)。すなわち、本開示の持続期間推定モデルによれば、循環器専門医による診断精度を有意に向上できることがわかった。The accuracy rate of Group A was 63.9 ± 9.6% in Phase 1, but improved to 71.6 ± 9.3% in Phase 2 (p = 0.01). The accuracy rate of Group B was 59.8 ± 5.3% in Phase 1, but improved to 68.2 ± 5.9% in Phase 2 (p < 0.01). There was no difference in the accuracy rate between Groups A and B in Phase 2 (p = 0.48). The average percentage of doctors who gave answers different from the predictions of the duration estimation model of this disclosure in Phase 2 (answers in which the predictions of the duration estimation model of this disclosure were correct and the doctors gave incorrect answers) was 17.3 ± 10.3% in Group A and 20.9 ± 5.0% in Group B. Therefore, there was no significant difference in the increase in the accuracy rate between Groups A and B (p = 0.85). In other words, it was found that the duration estimation model of this disclosure can significantly improve the diagnostic accuracy of cardiologists.
以上、実施形態を参照して本開示を説明したが、本開示は、上記実施形態に限定されるものではない。本開示の構成や詳細には、本開示のスコープ内で当業者が理解しうる様々な変更をできる。Although the present disclosure has been described above with reference to the embodiments, the present disclosure is not limited to the above-mentioned embodiments. Various modifications that can be understood by a person skilled in the art can be made to the configuration and details of the present disclosure within the scope of the present disclosure.
この出願は、2023年10月25日に出願された日本出願特願2023-183282を基礎とする優先権を主張し、その開示のすべてをここに取り込む。This application claims priority based on Japanese Patent Application No. 2023-183282, filed on October 25, 2023, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein in its entirety.
<付記>
上記の実施形態の一部または全部は、以下の付記のように記載されうるが、以下には限られない。
(付記1)
心電図情報取得部、持続期間推定部、及び出力部を含み、
前記心電図情報取得部は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定部は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力部は、前記持続期間を出力する、心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置。
(付記2)
前記持続期間推定部は、持続期間推定モデルに前記心電図情報を入力して、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、付記1記載の持続期間推定支援装置。
(付記3)
前記心電図情報取得部は、前記心電図情報と紐づけて前記心房細動患者の患者情報を取得し、
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記持続期間推定部は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、付記1または2記載の持続期間推定支援装置。
(付記4)
再発予測部を含み、
前記再発予測部は、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方に基づいて、前記心房細動患者の再発率を予測し、
前記出力部は、前記再発率を出力する、付記1から3のいずれかに記載の持続期間推定支援装置。
(付記5)
学習用情報取得部、及び学習済みモデル生成部を含み、
前記学習用情報取得部は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成部は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置。
(付記6)
前記学習用情報は、前記心房細動患者の患者情報を含み、
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成部は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報の組み合わせに対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報および患者情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、付記5記載の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置。
(付記7)
心電図情報取得工程、持続期間推定工程、及び出力工程を含み、
前記心電図情報取得工程は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定工程は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力工程は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各工程が、コンピュータにより実行される、心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法。
(付記8)
前記持続期間推定工程は、持続期間推定モデルに前記心電図情報を入力して、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、付記7記載の持続期間推定支援方法。
(付記9)
前記心電図情報取得工程は、前記心電図情報と紐づけて前記心房細動患者の患者情報を取得し、
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記持続期間推定工程は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、付記7または8記載の持続期間推定支援方法。
(付記10)
再発予測工程を含み、
前記再発予測工程は、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方に基づいて、前記心房細動患者の再発率を予測し、
前記出力工程は、前記再発率を出力する、付記7から9のいずれかに記載の持続期間推定支援方法。
(付記11)
学習用情報取得工程、及び学習済みモデル生成工程を含み、
前記学習用情報取得工程は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成工程は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造方法。
(付記12)
前記学習用情報は、前記心房細動患者の患者情報を含み、
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成工程は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報の組み合わせに対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報および患者情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、付記11記載の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造方法。
(付記13)
心電図情報取得手順、持続期間推定手順、及び出力手順を含み、
前記心電図情報取得手順は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力手順は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定支援プログラム。
(付記14)
前記持続期間推定手順は、持続期間推定モデルに前記心電図情報を入力して、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、付記13記載の持続期間推定支援プログラム。
(付記15)
前記心電図情報取得手順は、前記心電図情報と紐づけて前記心房細動患者の患者情報を取得し、
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、付記13または14記載の持続期間推定支援プログラム。
(付記16)
再発予測手順を含み、
前記再発予測手順は、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方に基づいて、前記心房細動患者の再発率を予測し、
前記出力手順は、前記再発率を出力する、付記13から15のいずれかに記載の持続期間推定支援プログラム。
(付記17)
学習用情報取得手順、及び学習済みモデル生成手順を含み、
前記学習用情報取得手順は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラム。
(付記18)
前記学習用情報は、前記心房細動患者の患者情報を含み、
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報の組み合わせに対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報および患者情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、付記17記載の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラム。
(付記19)
心電図情報取得手順、持続期間推定手順、及び出力手順を含み、
前記心電図情報取得手順は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力手順は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定支援プログラムを記録しているコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。
(付記20)
前記持続期間推定手順は、持続期間推定モデルに前記心電図情報を入力して、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、付記19記載の記録媒体。
(付記21)
前記心電図情報取得手順は、前記心電図情報と紐づけて前記心房細動患者の患者情報を取得し、
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、付記19または20記載の記録媒体。
(付記22)
再発予測手順を含み、
前記再発予測手順は、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方に基づいて、前記心房細動患者の再発率を予測し、
前記出力手順は、前記再発率を出力する、付記19から21のいずれかに記載の記録媒体。
(付記23)
学習用情報取得手順、及び学習済みモデル生成手順を含み、
前記学習用情報取得手順は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムを記録しているコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。
(付記24)
前記学習用情報は、前記心房細動患者の患者情報を含み、
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報の組み合わせに対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報および患者情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、付記23記載の記録媒体。<Additional Notes>
Some or all of the above embodiments may be described as follows, but are not limited to the following:
(Appendix 1)
The device includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition unit, a duration estimation unit, and an output unit,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition unit acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient having atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation unit estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output unit outputs the duration.
(Appendix 2)
2. The duration estimation support device according to claim 1, wherein the duration estimation unit inputs the electrocardiogram information to a duration estimation model to estimate a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient.
(Appendix 3)
the electrocardiogram information acquisition unit acquires patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient in association with the electrocardiogram information;
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information,
3. The duration estimation assistance device according to claim 1, wherein the duration estimation unit estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information and the patient information.
(Appendix 4)
A recurrence prediction unit is included,
The recurrence prediction unit predicts a recurrence rate of the atrial fibrillation patient based on at least one of the electrocardiogram information and the duration,
The duration estimation assistance device according to any one of appendix 1 to 3, wherein the output unit outputs the recurrence rate.
(Appendix 5)
A learning information acquisition unit and a trained model generation unit are included,
The learning information acquisition unit acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
The trained model generation unit is a trained model manufacturing device for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, which generates a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, as a trained model through machine learning using the duration as a correct label for the electrocardiogram information.
(Appendix 6)
the learning information includes patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient,
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information,
The trained model generation unit of the device for producing a trained model for duration estimation described in Appendix 5 generates, as a trained model, a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when the subject's electrocardiogram information and patient information are input, by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for a combination of the electrocardiogram information and the patient information.
(Appendix 7)
The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquiring step, a duration estimating step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquiring step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient having atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration,
A method for assisting in estimation of duration of atrial fibrillation, wherein each of the steps is executed by a computer.
(Appendix 8)
8. The duration estimation support method according to claim 7, wherein the duration estimation step inputs the electrocardiogram information to a duration estimation model to estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient.
(Appendix 9)
the electrocardiogram information acquiring step acquires patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient in association with the electrocardiogram information;
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information,
9. The duration estimation support method according to claim 7, wherein the duration estimation step estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information and the patient information.
(Appendix 10)
A recurrence prediction step is included,
the recurrence prediction step predicts a recurrence rate of the atrial fibrillation patient based on at least one of the electrocardiogram information and the duration;
The duration estimation support method according to any one of appendices 7 to 9, wherein the output step outputs the recurrence rate.
(Appendix 11)
The method includes a learning information acquisition step and a trained model generation step,
The learning information acquiring step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
The trained model generation process is a method for producing a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, which generates a duration estimation model as a trained model by machine learning using the duration as a correct label for the electrocardiogram information, when the electrocardiogram information of a subject is input.
(Appendix 12)
the learning information includes patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient,
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information;
The trained model generation process of the method for producing a trained model for duration estimation described in
(Appendix 13)
The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition step, a duration estimation step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient with atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step includes estimating a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration;
An atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program for causing a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
(Appendix 14)
14. The duration estimation support program according to
(Appendix 15)
the electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient in association with the electrocardiogram information;
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information;
15. The duration estimation support program according to
(Appendix 16)
Includes a recurrence prediction procedure;
the recurrence prediction step predicts a recurrence rate of the atrial fibrillation patient based on at least one of the electrocardiogram information and the duration;
16. The program for estimating disease duration according to any one of
(Appendix 17)
The method includes a learning information acquisition procedure and a trained model generation procedure,
The learning information acquisition step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
the trained model generation step generates, as a trained model, a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for the electrocardiogram information;
A program for creating a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, for causing a computer to execute each of the above steps.
(Appendix 18)
the learning information includes patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient,
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information;
The trained model generation procedure is a program for creating a trained model for duration estimation described in Appendix 17, which generates a duration estimation model as a trained model by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for a combination of the electrocardiogram information and the patient information, when the electrocardiogram information and patient information of a subject are input.
(Appendix 19)
The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition step, a duration estimation step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient with atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step includes estimating a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration;
A computer-readable recording medium having recorded thereon an atrial fibrillation duration estimation assistance program for causing a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
(Appendix 20)
20. The recording medium of claim 19, wherein the duration estimation step inputs the electrocardiogram information into a duration estimation model to estimate a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient.
(Appendix 21)
the electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient in association with the electrocardiogram information;
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information;
21. The recording medium according to claim 19, wherein the duration estimation step estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information and the patient information.
(Appendix 22)
Includes a recurrence prediction procedure;
the recurrence prediction step predicts a recurrence rate of the atrial fibrillation patient based on at least one of the electrocardiogram information and the duration;
22. The recording medium according to any one of appendices 19 to 21, wherein the output step outputs the recurrence rate.
(Appendix 23)
The method includes a learning information acquisition procedure and a trained model generation procedure,
The learning information acquisition step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
the trained model generation step generates, as a trained model, a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for the electrocardiogram information;
A computer-readable recording medium recording a program for creating a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, for causing a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
(Appendix 24)
the learning information includes patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient,
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information;
The recording medium described in Appendix 23, wherein the trained model generation procedure generates, as a trained model, a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when the subject's electrocardiogram information and patient information are input through machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for a combination of the electrocardiogram information and the patient information.
本開示によれば、心電図情報に基づいて心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定できる。このため、本開示は、例えば、医療分野において有用である。According to the present disclosure, it is possible to estimate the duration of atrial fibrillation in a patient with atrial fibrillation based on electrocardiogram information. Therefore, the present disclosure is useful, for example, in the medical field.
10、10A 心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置
11 心電図情報取得部
12 持続期間推定部
13 出力部
14 再発予測部
101 中央処理装置
102 メモリ
103 バス
104 記憶装置
105 入力装置
106 出力装置
107 通信デバイス
20 心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置
21 学習用情報取得部
22 学習済みモデル生成部
201 中央処理装置
202 メモリ
203 バス
204 記憶装置
205 入力装置
206 出力装置
207 通信デバイス
10, 10A Atrial fibrillation duration
Claims (12)
Translated fromJapanese前記心電図情報取得部は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定部は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力部は、前記持続期間を出力する、心房細動の持続期間推定支援装置。The device includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition unit, a duration estimation unit, and an output unit,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition unit acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient having atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation unit estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output unit outputs the duration.
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記持続期間推定部は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定する、請求項1または2記載の持続期間推定支援装置。the electrocardiogram information acquisition unit acquires patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient in association with the electrocardiogram information;
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information;
3. The duration estimation assistance device according to claim 1, wherein the duration estimation unit estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information and the patient information.
前記再発予測部は、前記心電図情報および前記持続期間の少なくとも一方に基づいて、前記心房細動患者の再発率を予測し、
前記出力部は、前記再発率を出力する、請求項1または2記載の持続期間推定支援装置。A recurrence prediction unit is included,
The recurrence prediction unit predicts a recurrence rate of the atrial fibrillation patient based on at least one of the electrocardiogram information and the duration,
The duration estimation assistance device according to claim 1 , wherein the output unit outputs the recurrence rate.
前記学習用情報取得部は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成部は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置。A learning information acquisition unit and a trained model generation unit are included,
The learning information acquisition unit acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
The trained model generation unit is a trained model manufacturing device for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, which generates a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, as a trained model through machine learning using the duration as a correct label for the electrocardiogram information.
前記患者情報は、前記心房細動患者の属性情報、問診情報、および心エコー情報からなる群から選択された少なくとも一つを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成部は、前記心電図情報および前記患者情報の組み合わせに対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報および患者情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、請求項5記載の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造装置。the learning information includes patient information of the atrial fibrillation patient,
The patient information includes at least one selected from the group consisting of attribute information of the atrial fibrillation patient, interview information, and echocardiographic information;
The trained model generation unit of the device for producing a trained model for duration estimation as described in claim 5 generates a duration estimation model as a trained model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when the subject's electrocardiogram information and patient information are input, by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for a combination of the electrocardiogram information and the patient information.
前記心電図情報取得工程は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定工程は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力工程は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各工程が、コンピュータにより実行される、心房細動の持続期間推定支援方法。The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquiring step, a duration estimating step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquiring step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient having atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step estimates a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration,
A method for assisting in estimation of duration of atrial fibrillation, wherein each of the steps is executed by a computer.
前記学習用情報取得工程は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成工程は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成する、心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造方法。The method includes a learning information acquisition step and a trained model generation step,
The learning information acquiring step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
The trained model generation process is a method for producing a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, which generates a duration estimation model as a trained model by machine learning using the duration as a correct label for the electrocardiogram information, when the electrocardiogram information of a subject is input.
前記心電図情報取得手順は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力手順は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定支援プログラム。The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition step, a duration estimation step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient with atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step includes estimating a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration;
An atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program for causing a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
前記学習用情報取得手順は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラム。The method includes a learning information acquisition procedure and a trained model generation procedure,
The learning information acquisition step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
the trained model generation step generates, as a trained model, a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for the electrocardiogram information;
A program for creating a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, for causing a computer to execute each of the above steps.
前記心電図情報取得手順は、心房細動患者の心電図情報を取得し、
前記持続期間推定手順は、前記心電図情報に基づいて前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間を推定し、
前記出力手順は、前記持続期間を出力し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定支援プログラムを記録しているコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。The method includes an electrocardiogram information acquisition step, a duration estimation step, and an output step,
The electrocardiogram information acquisition step acquires electrocardiogram information of a patient with atrial fibrillation,
the duration estimation step includes estimating a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient based on the electrocardiogram information;
The output step outputs the duration;
A computer-readable recording medium having recorded thereon an atrial fibrillation duration estimation assistance program for causing a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
前記学習用情報取得手順は、学習用情報を取得し、
前記学習用情報は、心房細動患者の心電図情報と、前記心房細動患者の心房細動の持続期間とを含み、
前記学習済みモデル生成手順は、前記心電図情報に対して前記持続期間を正解ラベルとした機械学習によって、対象者の心電図情報を入力した場合に、前記対象者の心房細動の持続期間を出力する持続期間推定モデルを学習済みモデルとして生成し、
前記各手順を、コンピュータに実行させるための心房細動の持続期間推定用学習済みモデル製造プログラムを記録しているコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。
The method includes a learning information acquisition procedure and a trained model generation procedure,
The learning information acquisition step acquires learning information,
the learning information includes electrocardiogram information of an atrial fibrillation patient and a duration of atrial fibrillation of the atrial fibrillation patient;
the trained model generation step generates, as a trained model, a duration estimation model that outputs the duration of atrial fibrillation of a subject when electrocardiogram information of the subject is input, by machine learning using the duration as a correct answer label for the electrocardiogram information;
A computer-readable recording medium recording a program for creating a trained model for estimating the duration of atrial fibrillation, for causing a computer to execute each of the above procedures.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023183282 | 2023-10-25 | ||
| JP2023183282 | 2023-10-25 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2025073061Atrue JP2025073061A (en) | 2025-05-12 |
Family
ID=95693848
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2024109770APendingJP2025073061A (en) | 2023-10-25 | 2024-07-08 | Atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing device, atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing method, atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing program, and recording medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2025073061A (en) |
- 2024
- 2024-07-08JPJP2024109770Apatent/JP2025073061A/enactivePending
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Elias et al. | Deep learning electrocardiographic analysis for detection of left-sided valvular heart disease | |
| US11540879B2 (en) | Personalized heart rhythm therapy | |
| JP7262452B2 (en) | ECG-based Cardiac Ejection Fraction Screening | |
| JP7402879B2 (en) | Methods and systems for identifying physiological or biological conditions or diseases in a subject | |
| CN114173645B (en) | Methods and systems for assessing disease using dynamic analysis of biophysical signals | |
| US20230335289A1 (en) | Systems and methods for generating health risk assessments | |
| Altan et al. | A new approach to early diagnosis of congestive heart failure disease by using Hilbert–Huang transform | |
| RU2657384C2 (en) | Method and system for noninvasive screening physiological parameters and pathology | |
| US20230420132A1 (en) | Noninvasive heart failure detection | |
| Mannhart et al. | Clinical validation of an artificial intelligence algorithm offering cross-platform detection of atrial fibrillation using smart device electrocardiograms | |
| Sathi et al. | An interpretable electrocardiogram-based model for predicting arrhythmia and ischemia in cardiovascular disease | |
| Agrawal et al. | A machine learning approach for classifying healthy and infarcted patients using heart rate variabilities derived vector magnitude | |
| Lampert et al. | A novel ECG-based deep learning algorithm to predict cardiomyopathy in patients with premature ventricular complexes | |
| Ramesh et al. | Performance analysis of machine learning algorithms to predict cardiovascular disease | |
| Sowmya et al. | Detecting anomalies in fetal electrocardiogram records using deep learning models | |
| WO2022221014A1 (en) | Detection and prediction of hypertension induced organ damage using ecg and blood pressure data | |
| US10588577B2 (en) | Patient signal analysis based on affine template matching | |
| JP2025073061A (en) | Atrial fibrillation duration estimation support device, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing device, atrial fibrillation duration estimation support method, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing method, atrial fibrillation duration estimation support program, atrial fibrillation duration estimation trained model manufacturing program, and recording medium | |
| Yousefi et al. | Using the Electrocardiogram Signal to Identify and Detection Heart Diseases by Combining Time and Frequency Characteristics | |
| Mamun | An Innovative Multimodal Bio-Signal Fusion with Hybrid Deep Learning Techniques for the Development of a Non-Invasive Cuffless Blood Pressure Monitoring System and a Heart Disease Detection Algorithm | |
| Radha et al. | Hrudyalysis: A Novel Cloud-Based ECG Analytics Method | |
| Gilani | Machine learning classifiers for critical cardiac conditions | |
| Bryk et al. | Multi-parameter hemodynamic monitoring via machine learning: a data-driven framework for cardiovascular physiology | |
| Irshad et al. | Meta-Learning and Deep Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network with Foraging Phero Trap Optimization for Heart Disease Prediction | |
| Valenzuela et al. | Electrocardiogram and Phonocardiogram Signal Data Fusion Using Deep Learning System |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20240919 |