JP2025065751A - Information management device, information management method, vehicle system, and program - Google Patents
Information management device, information management method, vehicle system, and programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2025065751A JP2025065751AJP2023175172AJP2023175172AJP2025065751AJP 2025065751 AJP2025065751 AJP 2025065751AJP 2023175172 AJP2023175172 AJP 2023175172AJP 2023175172 AJP2023175172 AJP 2023175172AJP 2025065751 AJP2025065751 AJP 2025065751A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- driving
- vehicles
- information
- speed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、情報管理装置、情報管理方法、車両システム、およびプログラムに関する。The present invention relates to an information management device, an information management method, a vehicle system, and a program.
近年、交通参加者の中でも脆弱な立場にある人々にも配慮した持続可能な輸送システムへのアクセスを提供する取り組みが活発化している。この実現に向けて運転支援技術に関する研究開発を通して交通の安全性や利便性をより一層改善する研究開発に注力している。これに関連して、近年では、車速と制限速度に応じて運転者の安全運転を評価する技術が知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。In recent years, efforts to provide access to sustainable transportation systems that take into consideration vulnerable transport participants have been gaining momentum. To achieve this, efforts are being made to further improve road safety and convenience through research and development of driving assistance technologies. In this regard, technology that evaluates the safe driving of drivers according to vehicle speed and speed limits has become known in recent years (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
ところで、運転支援技術においては、周辺車両の走行状況に応じた運転に対する適切な評価ができていない場合があるというのが課題である。However, one issue with driving assistance technology is that it is sometimes not possible to properly evaluate driving in accordance with the driving conditions of surrounding vehicles.
本願は上記課題の解決のため、運転に対する評価を、周辺車両の走行状況に応じて、より適切に行うことができる情報管理装置、情報管理方法、車両システム、およびプログラムを提供することを目的の一つとしたものである。そして、延いては持続可能な輸送システムの発展に寄与するものである。"In order to solve the above problems, one of the objectives of this application is to provide an information management device, an information management method, a vehicle system, and a program that can more appropriately evaluate driving in accordance with the driving conditions of surrounding vehicles. This will ultimately contribute to the development of a sustainable transportation system. "
この発明に係る情報管理装置、情報管理方法、車両システム、およびプログラムは、以下の構成を採用した。
(1):この発明の一態様に係る情報管理装置は、複数の車両と通信する通信部と、前記通信部により前記複数の車両の走行情報を取得する取得部と、前記複数の車両に含まれる車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行う評価判定部と、を備え、前記評価判定部は、前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて前記不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、前記車両の速度と、取得した前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、情報管理装置である。 An information management device, an information management method, a vehicle system, and a program according to the present invention employ the following configuration.
(1): An information management device according to one embodiment of the present invention includes a communication unit that communicates with a plurality of vehicles, an acquisition unit that acquires driving information of the plurality of vehicles via the communication unit, and an evaluation and judgment unit that performs an evaluation and judgment of whether or not a driver of the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving based on the vehicle driving information included in the plurality of vehicles, wherein when the evaluation and judgment unit determines that the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, it acquires other vehicles that were present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time the unsafe driving occurred based on the driving information of the other vehicles, and evaluates the unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speed or positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling.
(2):上記(1)の態様において、前記評価判定部は、前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、取得した他車両のうち少なくとも一つが前記車両の後方に存在する場合に、前記車両の速度と、前記車両の後方に存在する他車両の速度と、前記制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行うものである。(2): In the above aspect (1), the evaluation and determination unit acquires other vehicles that are present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time when the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving related to speed, and if at least one of the acquired other vehicles is present behind the vehicle, evaluates the unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the speed of the other vehicles present behind the vehicle, and the speed limit.
(3):上記(1)の態様において、前記評価判定部は、前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、取得した他車両のうち少なくとも一つが、前記車両の後方に存在し、且つ前記車両の車線変更が困難な状況である場合に、前記車両の速度と、前記車両の後方に存在する他車両の速度と、前記制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行うものである。(3): In the above aspect (1), the evaluation and determination unit acquires other vehicles that are present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time when the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, and when at least one of the acquired other vehicles is present behind the vehicle and in a situation in which it is difficult for the vehicle to change lanes, evaluates the unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the speed of the other vehicles present behind the vehicle, and the speed limit.
(4):上記(3)の態様において、前記車両の車線変更が困難な状況は、車線変更先の隣接車線に前記車両から所定距離以内に他車両が存在する状況を含むものである。(4): In the above aspect (3), the situation in which it is difficult for the vehicle to change lanes includes a situation in which another vehicle is present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle in an adjacent lane to which the vehicle is to change lanes.
(5):上記(1)の態様において、前記通信部は、前記運転者の端末装置と通信し、前記運転者による前記車両の運転終了後の所定のタイミングで、前記車両の不安全運転に関する情報を前記車両または前記運転者の端末装置に提供する提供部を更に備えるものである。(5): In the above aspect (1), the communication unit further includes a provision unit that communicates with the driver's terminal device and provides information regarding unsafe driving of the vehicle to the vehicle or the driver's terminal device at a predetermined timing after the driver has finished driving the vehicle.
(6):上記(3)の態様において、前記通信部は、前記運転者に対応付けられた第三者の端末装置と通信し、前記運転者による前記車両の運転終了後の所定のタイミングで、前記車両の不安全運転に関する情報を前記第三者の端末装置に提供する提供部を更に備えるものである。(6): In the above aspect (3), the communication unit further includes a provision unit that communicates with a third party's terminal device associated with the driver and provides information regarding unsafe driving of the vehicle to the third party's terminal device at a predetermined timing after the driver has finished driving the vehicle.
(7):上記(1)の態様において、前記評価判定部は、前記車両の速度超過を判定し、速度超過をした理由が前記車両の周辺車両に影響を受けたことによるものであると判定された場合に、他の理由で速度超過した場合と異なる評価を行うものである。(7): In the aspect of (1) above, the evaluation and determination unit determines whether the vehicle is speeding, and if it determines that the speeding was caused by the influence of surrounding vehicles, performs an evaluation that is different from the evaluation in cases where the speeding was caused by other reasons.
(8):この発明の一態様に係る情報管理方法は、コンピュータが、複数の車両と通信し、前記複数の車両の走行情報を取得し、前記複数の車両に含まれる車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行い、前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて前記不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、前記車両の速度と、取得した前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、情報管理方法である。(8): An information management method according to one aspect of the present invention is an information management method in which a computer communicates with a plurality of vehicles, acquires driving information of the plurality of vehicles, evaluates whether or not the driver of the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving based on the driving information of the vehicles included in the plurality of vehicles, and when it is determined that the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving related to speed, acquires other vehicles that were present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time the unsafe driving occurred based on the driving information of the other vehicles, and evaluates the unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speed or positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling.
(9):この発明の一態様に係る車両システムは、車両の周辺状況を認識する認識部と、前記車両の走行情報および前記周辺状況に基づく他車両の走行情報を取得する取得部と、前記車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定をする評価判定部と、を備え、前記評価判定部は、前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、前記車両の速度と、取得した前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、車両システムである。(9): A vehicle system according to one aspect of the present invention includes a recognition unit that recognizes the surrounding conditions of the vehicle, an acquisition unit that acquires driving information of the vehicle and driving information of other vehicles based on the surrounding conditions, and an evaluation and judgment unit that evaluates and judges whether the driver of the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving based on the driving information of the vehicle. When the evaluation and judgment unit determines that the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, it acquires other vehicles that are present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle, and evaluates the unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speed or positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling.
(10):この発明の一態様に係るプログラムは、コンピュータに、複数の車両と通信させ、前記複数の車両の走行情報を取得させ、前記複数の車両に含まれる車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行わせ、前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて前記不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得させ、前記車両の速度と、取得された前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行わせる、プログラムである。(10): A program according to one aspect of the present invention is a program that causes a computer to communicate with a plurality of vehicles, acquire driving information of the plurality of vehicles, and evaluate and determine whether or not the driver of the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving based on the driving information of the vehicles included in the plurality of vehicles. If it is determined that the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving related to speed, acquire other vehicles that were present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time the unsafe driving was engaged based on the driving information of the other vehicles, and evaluate the unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speed or positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling.
上記(1)~(10)の態様によれば、運転に対する評価を、周辺車両の走行状況に応じて、より適切に行うことができる。According to the above aspects (1) to (10), driving can be more appropriately evaluated depending on the driving conditions of surrounding vehicles.
以下、図面を参照し、本発明の情報管理装置、情報管理方法、車両システム、およびプログラムの実施形態について説明する。Below, with reference to the drawings, an embodiment of the information management device, information management method, vehicle system, and program of the present invention will be described.
図1は、実施形態の情報管理装置を含む情報管理システム1の構成の一例を示す図である。情報管理システム1は、例えば、複数の車両M1~Mnと、車両M1~Mnを運転する運転者D1~Dnが利用する端末装置200-1~200-nと、情報管理システム1の利用者Uが利用する端末装置300と、情報管理装置400とを備える。以下、車両M1~Mnのそれぞれを識別して説明する場合を除き、単に車両Mと称して説明する。運転者D、端末装置200についても同様とする。車両Mと、端末装置200,300と、情報管理装置400とは、例えば、ネットワークNWを介して通信する。ネットワークNWは、例えば、セルラー網や、Wi-Fi網、Bluetooth(登録商標)、インターネット、WAN(Wide Area Network)、LAN(Local Area Network)、公衆回線、プロバイダ装置、専用回線、無線基地局等を含む。また、車両Mは、端末装置200,300と、Wi-Fi網、Bluetooth等の近距離通信網を介して直接通信してもよい。FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of an
車両Mは、例えば、二輪や三輪、四輪等の車両であり、その駆動源は、ディーゼルエンジンやガソリンエンジン等の内燃機関、電動機、或いはこれらの組み合わせである。電動機は、内燃機関に連結された発電機による発電電力、或いは二次電池や燃料電池の放電電力を使用して動作する。また、車両Mは、運転者Dの手動運転により走行するが、運転支援機能が作動可能な車両であってもよい。運転支援機能には、例えば、RDM(Road Departure Mitigation)、FCW(Forward Collision Warning)、CMBS(Collision Mitigation Braking System)、ACC(Adaptive Cruise Control)、ALCA(Auto Lane Change Assist)等が含まれるが、これらの機能に限定されるものではない。運転支援機能が作動している場合、運転者Dの運転操作によらずに、車両Mの操舵または速度のうち一方または双方が車両システムによって自動に制御される。The vehicle M is, for example, a two-wheeled, three-wheeled, four-wheeled, or other vehicle, and its drive source is an internal combustion engine such as a diesel engine or a gasoline engine, an electric motor, or a combination of these. The electric motor operates using power generated by a generator connected to the internal combustion engine, or discharged power from a secondary battery or a fuel cell. The vehicle M is driven manually by the driver D, but may also be a vehicle capable of operating a driving assistance function. Examples of the driving assistance function include, but are not limited to, RDM (Road Departure Mitigation), FCW (Forward Collision Warning), CMBS (Collision Mitigation Braking System), ACC (Adaptive Cruise Control), and ALCA (Auto Lane Change Assist). When the driving assistance function is operating, one or both of the steering and speed of the vehicle M are automatically controlled by the vehicle system, regardless of the driving operation of the driver D.
車両Mは、車両Mの走行に関する情報(走行情報)を取得し、取得した走行情報を情報管理装置400に送信する。走行情報には、FCD(Floating Car Data)が含まれる。具体的に走行情報には、例えば、運転者Dによる車両Mの運転操作に関する情報が含まれる。運転操作に関する情報には、例えば、車両Mの速度、加速度、ヨーレート、操舵角、位置情報等の挙動情報だけでなく、運転操作子に対する操作量、ヘッドライトの点灯、ワイパーの作動等の車載機器の操作内容が含まれてよい。また、走行情報には、車両Mの認識部による認識結果が含まれてよく、運転支援機能の作動(実行)状況に関する情報(例えば、作動した時間や位置、運転支援機能の種別)が含まれてもよい。The vehicle M acquires information (travel information) related to the travel of the vehicle M, and transmits the acquired travel information to the
端末装置200、300は、例えば、スマートフォンやタブレット端末である。端末装置200は、車両Mに連結して車載装置として機能してもよい。端末装置200は、情報管理装置400から車両Mが実行した運転支援機能に関する情報を取得したり、特定の運転支援機能(例えば、RDM)の作動を抑制するか否かを問合せるための情報を取得し、取得した情報を画像表示や音声出力して運転者Dに提供する。また、端末装置200は、運転者Dにより入力された情報示を情報管理装置400に送信する。端末装置300は、運転者Dに対応付けられた人物(例えば、運転者Dの家族や仕事等の管理者)等の利用者Uに利用され、情報管理装置400からの情報を取得し、取得した情報を画像表示や音声出力して利用者Uに提供する。利用者Uは、「第三者」の一例である。The
情報管理装置400は、例えば、サーバ装置やPC(Personal Computer)でもよく、一以上の情報処理装置からなるクラウドコンピューティングにより構成されたクラウドサーバ等でもよい。情報管理装置400は、複数の車両Mから走行情報を取得して車両Mごとに運転者Dの運転状況を管理する。また、情報管理装置400は、車速に関する運転者Dの不安全運転の評価判定を行い、判定結果に関する情報を車両Mや、端末装置200、300等に提供する。以下、車両M、端末装置200,300、および情報管理装置400のそれぞれの機能について具体的に説明する。なお、端末装置200と300とは、同じ機能を適用することが可能であるため、以下では端末装置200に関して説明し、端末装置300の説明は省略する。The
[車両]
図2は、車両Mに搭載される車両システムの機能構成の一例を示す図である。車両Mに搭載される車両システムは、例えば、カメラ10と、レーダ装置12と、LIDAR(Light Detection and Ranging)14と、物体認識装置16と、通信装置20と、HMI(Human Machine Interface)30と、車両センサ40と、ナビゲーション装置50と、MPU(Map Positioning Unit)60と、運転操作子80と、走行駆動力出力装置92と、ブレーキ装置94と、ステアリング装置96と、運転支援装置120と、を備える。これらの装置や機器は、CAN(Controller Area Network)通信線等の多重通信線やシリアル通信線、無線通信網等によって互いに接続される。図2に示す構成はあくまで一例であり、構成の一部が省略されてもよいし、更に別の構成が追加されてもよい。 [vehicle]
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an example of a functional configuration of a vehicle system mounted on a vehicle M. The vehicle system mounted on the vehicle M includes, for example, a
カメラ10は、例えば、CCD(Charge Coupled Device)やCMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)等の固体撮像素子を利用したデジタルカメラである。カメラ10は、車両Mの任意の箇所に取り付けられる。前方を撮像する場合、カメラ10は、フロントウインドシールド上部やルームミラー裏面等に取り付けられる。カメラ10は、例えば、周期的に繰り返し車両Mの周辺を撮像する。カメラ10は、ステレオカメラであってもよい。The
レーダ装置12は、車両Mの周辺にミリ波等の電波を放射すると共に、物体によって反射された電波(反射波)を検出して少なくとも物体の位置(距離および方位)を検出する。レーダ装置12は、車両Mの任意の箇所に取り付けられる。レーダ装置12は、FM-CW(Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave)方式によって物体の位置および速度を検出してもよい。The
LIDAR14は、車両Mの周辺に光(或いは光に近い波長の電磁波)を照射し、散乱光を測定する。LIDAR14は、発光から受光までの時間に基づいて、対象までの距離を検出する。照射される光は、例えば、パルス状のレーザー光である。LIDAR14は、車両Mの任意の箇所に取り付けられる。The
物体認識装置16は、カメラ10、レーダ装置12、およびLIDAR14のうち一部または全部による検出結果に対してセンサフュージョン処理を行って、物体の位置、種類、速度等を認識する。物体認識装置16は、認識結果を運転支援装置120に出力する。物体認識装置16は、カメラ10、レーダ装置12、およびLIDAR14の検出結果をそのまま運転支援装置120に出力してよい。車両Mから物体認識装置16が省略されてもよい。The
通信装置20は、例えば、TCU(Telematics Control Unit)を備える。通信装置20は、例えば、セルラー網やWi-Fi網、Bluetooth、DSRC(Dedicated Short Range Communication)等のネットワークNWを利用して、情報管理装置400、車両Mの周辺に存在する他車両と通信し、或いは他の各種サーバ装置と通信する。また、通信装置20は、Wi-Fi網、Bluetooth等の近距離通信網により、車両Mに搭乗する運転者Dの端末装置200と無線通信を行ってもよく、通信ケーブル等に接続されることで端末装置200と有線通信を行ってもよい。The
HMI30は、車両Mに搭乗した運転者Dに対して各種情報を提示すると共に、運転者Dによる入力操作を受け付ける。HMI30は、例えば、表示装置と、スピーカと、振動装置とを備える。表示装置は、例えば、LCD(Liquid Crystal Display)や有機EL(Electro Luminescence)ディスプレイ等である。表示装置は、例えば、車両Mのインストルメントパネルの中央部や運転席の前方に設けられ、車両Mの走行速度を表す速度計(スピードメータ)または車両Mが備える内燃機関の回転数(回転速度)を表す回転速度計(タコメータ)等、運転支援機能の作動状況等、車両Mにおける種々の情報を表示させるディスプレイ装置、いわゆるマルチインフォメーションディスプレイである。スピーカは、警報やメッセージ音、音声等を出力する。振動装置は、例えば、運転席やステアリングホイール等の運転操作子80に対して所定の強さの振動を与えて運転者Dに状況や指示等を行う。また、HMI30は、例えば、ブザー、タッチパネル、マイク、キー等を含んでいてもよい。また、HMI30には、車両Mの車線変更先や右左折を外部に伝えるウインカーの点灯や点灯解除の指示操作を受け付けるウインカースイッチや、ワイパーの作動または停止の指示を受け付けるワイパースイッチ等を含んでいてもよい。The
車両センサ40は、車両Mの速度を検出する車速センサ、加速度を検出する加速度センサ、鉛直軸回りの角速度を検出するヨーレートセンサ、操舵角を検出する操舵角センサ等を含む。また、車両センサ40には、車両Mの位置を取得する位置センサが含まれてよい。位置センサは、例えば、GPS(Global Positioning System)装置から位置情報(経度・緯度情報)を取得するセンサである。また、位置センサは、ナビゲーション装置50のGNSS(Global Navigation Satellite System)受信機51を用いて位置情報を取得するセンサであってもよい。車両センサ40により検出された情報は、運転支援装置120に出力される。The
ナビゲーション装置50は、例えば、GNSS受信機51と、ナビHMI52と、経路決定部53とを備える。ナビゲーション装置50は、HDD(Hard Disk Drive)やフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置に第1地図情報54を保持している。GNSS受信機51は、GNSS衛星から受信した信号に基づいて、車両Mの位置を特定する。車両Mの位置は、車両センサ40の出力を利用したINS(Inertial Navigation System)によって特定または補完されてもよい。ナビHMI52は、表示装置、スピーカ、タッチパネル、キー等を含む。ナビHMI52は、前述したHMI30と一部または全部が共通化されてもよい。経路決定部53は、例えば、GNSS受信機51により特定された車両Mの位置(或いは入力された任意の位置)から、ナビHMI52を用いて運転者Dにより入力された目的地までの経路(以下、地図上経路)を、第1地図情報54を参照して決定する。第1地図情報54は、例えば、道路を示すリンクと、リンクによって接続されたノードとによって道路形状が表現された情報である。第1地図情報54は、道路の曲率や勾配、POI(Point Of Interest)情報等を含んでもよい。地図上経路は、MPU60に出力される。ナビゲーション装置50は、地図上経路に基づいて、ナビHMI52を用いた経路案内を行ってもよい。ナビゲーション装置50は、例えば、運転者Dの端末装置200の機能によって実現されてもよい。ナビゲーション装置50は、通信装置20を介してナビゲーションサーバに現在位置と目的地を送信し、ナビゲーションサーバから地図上経路と同等の経路を取得してもよい。The
MPU60は、例えば、推奨車線決定部61を含み、HDDやフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置に第2地図情報62を保持している。推奨車線決定部61は、ナビゲーション装置50から提供された地図上経路を複数のブロックに分割し(例えば、車両進行方向に関して100[m]毎に分割し)、第2地図情報62を参照してブロックごとに推奨車線を決定する。推奨車線決定部61は、左から何番目の車線を走行するといった決定を行う。推奨車線決定部61は、地図上経路に分岐箇所が存在する場合、車両Mが、分岐先に進行するための合理的な経路を走行できるように、推奨車線を決定する。第2地図情報62は、第1地図情報54よりも高精度な地図情報である。第2地図情報62は、例えば、車線の中央の情報、或いは車線の境界(道路区画線)の情報等を含んでいる。第2地図情報62には、道路の車線数や道路幅(幅員)等の道路情報、交通規制情報(例えば、道路の制限速度、一時停止位置、駐車禁止位置)、住所情報(住所・郵便番号)、施設情報、電話番号情報等が含まれてよい。第2地図情報62は、通信装置20が他装置と通信することにより、随時、アップデートされてよい。The
運転操作子80は、例えば、ステアリングホイール、アクセルペダル、ブレーキペダル、シフトレバー、方向指示器の操作スイッチ、その他の操作子を含む。運転操作子80には、操作量、或いは操作の有無を検出するセンサが取り付けられており、その検出結果は、運転支援装置120、もしくは、走行駆動力出力装置92、ブレーキ装置94、およびステアリング装置96のうち一部または全部に出力される。The driving
走行駆動力出力装置92は、車両が走行するための走行駆動力(トルク)を駆動輪に出力する。走行駆動力出力装置92は、例えば、内燃機関、電動機、および変速機等の組み合わせと、これらを制御するECU(Electronic Control Unit)とを備える。ECUは、運転支援装置120から入力される情報、或いは運転操作子80から入力される情報に従って、上記の構成を制御する。The driving
ブレーキ装置94は、例えば、ブレーキキャリパーと、ブレーキキャリパーに油圧を伝達するシリンダと、シリンダに油圧を発生させる電動モータと、ブレーキECUとを備える。ブレーキECUは、運転支援装置120から入力される情報、或いは運転操作子80から入力される情報に従って電動モータを制御し、制動操作に応じたブレーキトルクが各車輪に出力されるようにする。ブレーキ装置94は、運転操作子80に含まれるブレーキペダルの操作によって発生させた油圧を、マスターシリンダを介してシリンダに伝達する機構をバックアップとして備えてよい。なお、ブレーキ装置94は、上記説明した構成に限らず、運転支援装置120から入力される情報に従ってアクチュエータを制御して、マスターシリンダの油圧をシリンダに伝達する電子制御式油圧ブレーキ装置であってもよい。The
ステアリング装置96は、例えば、ステアリングECUと、電動モータとを備える。電動モータは、例えば、ラックアンドピニオン機構に力を作用させて転舵輪の向きを変更する。ステアリングECUは、運転支援装置120から入力される情報、或いは運転操作子80から入力される情報に従って、電動モータを駆動し、転舵輪の向きを変更させる。また、ステアリング装置96には、運転支援装置120の制御により、運転者Dが操作したステアリングホイールの操舵方向に対して反対方向にステアリングホイールを回転させるように(操舵方向に回転しにくくなるように)所定の反力を与えて、運転者Dの操舵操作を抑制する操舵反力機構が設けられていてもよい。The
運転支援装置120は、例えば、認識部122と、走行制御部124と、走行情報取得部126と、HMI制御部130と、記憶部140とを備える。認識部122と、走行制御部124と、走行情報取得部126と、HMI制御部130とのうち一部または全部は、例えば、CPU(Central Processing Unit)等のハードウェアプロセッサがプログラム(ソフトウェア)を実行することにより実現される。これらの構成要素のうち一部または全部は、LSI(Large Scale Integration)やASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit)、FPGA(Field-Programmable Gate Array)、GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)等のハードウェア(回路部;circuitryを含む)によって実現されてもよいし、ソフトウェアとハードウェアの協働によって実現されてもよい。プログラムは、予め運転支援装置120のHDDやフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置(非一過性の記憶媒体を備える記憶装置)に格納されていてもよいし、DVDやCD-ROM等の着脱可能な記憶媒体に格納されており、記憶媒体(非一過性の記憶媒体)がドライブ装置に装着されることで運転支援装置120のHDDやフラッシュメモリにインストールされてもよい。The driving
記憶部140は、例えば、HDD、フラッシュメモリ、EEPROM(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)、ROM(Read Only Memory)、またはRAM(Random Access Memory)等により実現される。記憶部140には、例えば、走行履歴データ142、プログラム、その他各種情報が格納される。また、走行履歴データ142は、走行情報取得部126により取得される車両Mの走行情報の履歴情報である。The
認識部122は、カメラ10、レーダ装置12、およびLIDAR14から物体認識装置16を介して入力された情報に基づいて、車両Mの周辺状況を認識する。例えば、認識部122は、入力された情報に基づいて、車両Mの周辺(所定距離以内)にある物体(例えば、他車両、歩行者、道路構造物)の位置(車両Mとの相対位置)、および速度(車両Mとの相対速度)、加速度等の状態を認識する。物体の位置は、例えば、車両Mの代表点(重心や駆動軸中心等)を原点とした絶対座標上の位置として認識され、制御に使用される。物体の位置は、その物体の重心やコーナー等の代表点で表されてもよいし、領域で表されてもよい。物体の「状態」とは、物体の加速度やジャーク、或いは「行動状態」(例えば車線変更をしている、またはしようとしているか否か)を含んでもよい。The
認識部122は、例えば、車両Mが走行している車線(走行車線)を認識する。例えば、認識部122は、第2地図情報62から得られる道路区画線のパターン(例えば実線と破線の配列)と、カメラ画像から認識される車両Mの周辺の道路区画線のパターンとを比較することで、走行車線を認識する。認識部122は、道路区画線に限らず、路肩、縁石、中央分離帯、ガードレール等を含む走路境界(道路境界)を認識することで、走行車線を認識してもよい。この認識において、ナビゲーション装置50から取得される車両Mの位置やINSによる処理結果が加味されてもよい。認識部122は、一時停止線、障害物、赤信号、料金所、その他の道路事象を認識する。また、認識部122は、カメラ画像によって撮像された画像の解析結果および地図情報に基づいて、周辺の車線数や道路標識を認識してもよい。The
また、認識部122は、走行車線を認識する際に、走行車線に対する車両Mの位置や姿勢を認識する。認識部122は、例えば、車両Mの基準点(例えば、重心や中心)の車線中央からの乖離度合、および車両Mの進行方向の車線中央を連ねた線に対してなす角度を、走行車線に対する車両Mの相対位置および姿勢として認識してもよい。これに代えて、認識部122は、走行車線のいずれかの側端部(道路区画線または道路境界)に対する車両Mの基準点の位置等を、走行車線に対する車両Mの相対位置として認識してもよい。When recognizing the travel lane, the
走行制御部124は、運転者Dによる運転操作子80を用いた手動運転時において、認識部122により認識された周辺状況に基づいて、車両Mが作動(実行)可能な運転支援機能(例えば、RDM、FCW、CMBS、ACC、ALCA)のうち、予め決められた所定の作動条件を満たした運転支援機能を作動させる。例えば、走行制御部124は、周辺状況に対応させた運転支援機能を作動させた場合に、画像表示や音声出力させたり、振動や操舵反力等による所定の警報を行い運転者Dに注意喚起を行う。走行制御部124は、運転支援機能の作動による画像表示や音声出力を行う場合には、HMI制御部130に所定の画像や音声をHMI30から出力させる。また、走行制御部124は、ステアリングホイールや運転席を振動させる場合には、振動装置36に所定の振動を出力するよう制御する。また、走行制御部124は、操舵反力を行う場合には、ステアリング装置96の操舵反力機構に所定方向への操舵反力を与えるように制御する。During manual driving by the driver D using the
また、走行制御部124は、運転支援機能の作動時に、周辺の物体に接触することなくMPU60により決定された推奨車線に沿って車両Mが走行するように目標軌道を生成し、生成した目標軌道によって車両Mが走行するように、走行駆動力出力装置92、ブレーキ装置94、およびステアリング装置96のうち少なくとも一つを制御してもよい。これにより、車両Mの操舵または速度のうち、一方または双方が制御され、目的に応じた車両Mの自動運転が実行される。The driving
走行情報取得部126は、車両Mの走行情報を取得する。例えば、走行情報取得部126は、HMI30により入力された情報、車両センサ40の検出結果(少なくとも車両Mの速度を含む)、運転操作子80に設けられたセンサの検出結果(操作量)、認識部122による認識結果、走行制御部124による制御内容(運転支援機能の作動結果)等に基づいて走行情報を取得する。これらは入力、検出、または制御された時間情報と共に、走行履歴データ142として記憶部140に格納される。また、走行情報取得部126は、取得した情報(走行履歴データ142)を所定のタイミング(例えば、運転終了時または所定周期)で情報管理装置400に送信する。また、走行情報取得部126は、なお、送信する情報には、車両Mを識別する識別情報(例えば、車両ID)や運転者Dを識別する識別情報(例えば、運転者ID)が付与されてよい。The driving
HMI制御部130は、HMI30により、車両Mの運転者Dに所定の情報を通知したり、HMI30を介して受け付けられた運転者Dの操作内容を取得する。所定の情報には、例えば、車両Mの状態に関する情報や作動中の運転支援機能に関する情報等の車両Mの走行に関連のある情報が含まれる。車両Mの状態に関する情報には、例えば、車両Mの速度、エンジン回転数、シフト位置等の情報が含まれる。また、運転制御に関する情報には、例えば、どの運転支援機能が作動中であるかを示す情報が含まれてよい。また、所定の情報には、運転者Dによる車両Mの不安全運転に関する情報(例えば、後述する評価判定結果)等が含まれる。また、所定の情報には、テレビ番組、DVD等の記憶媒体に記憶されたコンテンツ(例えば、映画)等の車両Mの走行制御に関連しない情報が含まれてもよい。The
例えば、HMI制御部130は、上述した所定の情報を含む画像(静止画でも動画でもよい)を生成し、生成した画像をHMI30の表示装置に表示させてもよく、所定の情報を示す音声を生成し、生成した音声をHMI30のスピーカに出力させてもよい。For example, the
[端末装置]
図3は、端末装置200の機能構成の一例を示す図である。端末装置200は、例えば、端末側通信部210と、入力部220と、出力部230と、制御部240と、アプリ実行部250と、端末側記憶部260とを備える。制御部240と、アプリ実行部250とのうち一部または全部は、例えば、CPU等のハードウェアプロセッサがプログラム(ソフトウェア)を実行することにより実現される。また、これらの構成要素のうち一部または全部は、LSIやASIC、FPGA、GPU等のハードウェア(回路部;circuitryを含む)によって実現されてもよいし、ソフトウェアとハードウェアの協働によって実現されてもよい。プログラムは、予めHDDやフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置(非一過性の記憶媒体を備える記憶装置)に格納されていてもよいし、DVDやCD-ROM等の着脱可能な記憶媒体(非一過性の記憶媒体)に格納されており、記憶媒体がドライブ装置や端末装置200のカードスロット等に装着されることで記憶装置にインストールされてもよい。 [Terminal Device]
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of the functional configuration of the
端末側記憶部260は、上記の各種記憶装置、或いはEEPROM、ROM、RAM等により実現されてもよい。端末側記憶部260には、例えば、運転評価アプリ262、プログラム、その他の各種情報が格納される。The terminal-
端末側通信部210は、例えば、ネットワークNWを介して、情報管理装置400、その他の外部装置と通信を行う。また、端末側通信部210は、近距離通信網またはネットワークNWを介して車両Mと通信を行ってもよい。The terminal-
入力部220は、例えば、各種キーやボタン等の操作による運転者Dの入力を受け付ける。また、入力部220は、運転者Dの音声の入力を受け付けるマイクを備えていてもよい。入力部220は、例えば、情報管理装置400が提供するサービスの利用要求や、運転者情報、運転支援機能を抑制するか否かの問合わせに関する回答情報の入力を受け付ける。The
出力部230は、例えば、表示部232と、スピーカ234とを備える。出力部230は、表示部232やスピーカ234に所定の情報を出力する。表示部232は、例えば、LCDや有機ELディスプレイ等である。入力部220は、タッチパネルとして表示部232と一体に構成されていてもよい。表示部232は、実施形態における各種情報を表示する。スピーカ234は、所定の音声を出力する。例えば、出力部230は、情報管理装置400により提供された情報に対応する画像や音声を出力したり、入力部220により入力された情報を出力させる。The
制御部240は、端末装置200の機能全体を制御する。例えば、制御部240は、端末側通信部210による通信制御、入力部220および出力部230による入出力制御、アプリ実行部250による運転評価アプリ262の実行制御等を行う。The
アプリ実行部250は、端末側記憶部260に記憶された運転評価アプリ262が実行されることで実現される。運転評価アプリ262は、例えば、ネットワークNWを介して外部装置からダウンロードしたものが端末装置200にインストールされている。運転評価アプリ262は、情報管理装置400から車両Mの運転者Dの不安全運転に関する情報を取得し、取得した情報を出力部230に出力するアプリケーションソフトウェアである。不安全運転に関する情報には、不安全運転に対する評価結果が含まれてよい。また、運転評価アプリ262は、入力部220により入力された情報を情報管理装置400に送信したりする。なお、送信する情報には、端末装置200を識別する識別情報(例えば、端末ID)や運転者Dを識別する運転者IDが付与されてよい。The
端末装置300の機能構成の場合、上述した端末装置200の機能構成の説明において、「端末装置200」を「端末装置300」と読み替えると共に、「運転者D」に提供される情報は「利用者U」に提供される。In the case of the functional configuration of the
[情報管理装置]
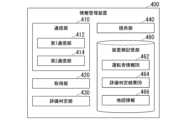
図4は、情報管理装置400の機能構成の一例を示す図である。情報管理装置400は、例えば、通信部410と、取得部420と、評価判定部430と、提供部440と、装置側記憶部460とを備える。取得部420と、評価判定部430と、提供部440とのうち一部または全部は、例えば、CPU等のハードウェアプロセッサがプログラム(ソフトウェア)を実行することにより実現される。また、これらの構成要素のうち一部または全部は、LSIやASIC、FPGA、GPU等のハードウェア(回路部;circuitryを含む)によって実現されてもよいし、ソフトウェアとハードウェアの協働によって実現されてもよい。プログラムは、予めHDDやフラッシュメモリ等の記憶装置(非一過性記憶媒体)に格納されていてもよいし、DVDやCD-ROM等の着脱可能な記憶媒体(非一過性記憶媒体)に格納されており、記憶媒体が情報管理装置400のドライブ装置に装着されることでインストールされてもよい。情報管理装置400は、クラウドサーバに運転支援機能提供サービスの運営者がプログラムをインストールすることで実現されてもよく、その場合、情報管理装置400のハードウェアの保有者とサービスの運営者とは異なっていてもよい。 [Information Management Device]
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example of the functional configuration of the
装置側記憶部460は、上記の各種記憶装置、或いはEEPROM、ROM、RAM等により実現されてもよい。装置側記憶部460には、例えば、運転者情報DB(Database)462、評価判定結果DB464、地図情報466、プログラム、その他各種情報が格納される。地図情報466は、上述した地図情報(第1地図情報54および第2地図情報62)と同じ地図情報でもよく、更に高精細および広範囲の地図情報でもよい。装置側記憶部460に含まれる情報の少なくとも一部は、情報管理装置400と通信可能な外部装置(例えば、DBサーバ)に格納されてよい。The device-
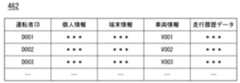
図5は、運転者情報DB462の内容の一例を示す図である。運転者情報DB462は、例えば、運転者IDに、個人情報、端末情報、車両情報、および走行履歴データが対応付けられた情報である。個人情報には、例えば、氏名、年齢、性別、住所、連絡先等の情報が含まれる。端末情報は、運転者Dが利用する端末装置200を識別する識別情報(例えば、端末ID)である。また、端末情報には、情報管理装置400が端末装置200と通信するためのアドレス情報等が含まれてよい。また、端末情報には、上述した情報に加えて運転者Dに対応付けられた利用者U(例えば、運転者Dの家族や仕事の管理者)等の端末装置300と通信するためのアドレス情報が含まれてもよい。車両情報は、例えば、運転者Dが運転する車両の識別情報(車両ID)である。また、車両情報には、情報管理装置400が車両Mと通信するためのアドレス情報等が含まれてよい。走行履歴データは、例えば車両Mの走行情報の履歴データである。また、運転者情報DB462には、情報管理装置400が運転者Dを認証するための認証情報(例えば、パスワード等)が格納されてもよい。これらの情報は、端末装置200からの登録処理により登録されてもよく、車両Mから所定のタイミングで送信されるデータから取得してもよい。FIG. 5 is a diagram showing an example of the contents of the
図6は、評価判定結果DB464の内容の一例を示す図である。評価判定結果DB464は、例えば、時間情報と、位置情報と、不安全運転種別と、評価判定結果とが対応付けられた情報である。時間情報には、評価判定部430により運転者Dが不安全運転を行ったと判定された日時情報が格納される。位置情報には、不安全運転を行った位置情報が格納される。不安全運転種別に関する情報が格納される。評価判定結果には、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転に対する評価結果が格納される。これらの情報は、例えば、運転者IDごとに格納される。評価判定結果DB464は、評価判定部430により生成される。Figure 6 is a diagram showing an example of the contents of the evaluation judgment result DB464. The evaluation judgment result DB464 is information in which, for example, time information, position information, unsafe driving type, and evaluation judgment result are associated with each other. The time information stores date and time information at which the
図4に戻り、通信部410は、ネットワークNW等を介して各種装置と通信する。通信部410は、例えば、第1通信部412と、第2通信部414とを備える。第1通信部412は、ネットワークNWまたは通信ケーブルにより接続された運転者Dの端末装置200および利用者Uの端末装置300と通信する。第2通信部414は、ネットワークNWを介して車両Mと通信する。例えば、第2通信部414は、例えば、運転支援機能を備え、且つ走行情報を取得可能な複数の車両Mと通信する。第1通信部412と第2通信部414は、異なるハードウェアにより実装されてもよく、異なるソフトウェアにより実装されてもよい。また、通信部410は、ネットワークNWを介して、他の外部装置と通信してもよい。Returning to FIG. 4, the communication unit 410 communicates with various devices via a network NW or the like. The communication unit 410 includes, for example, a
取得部420は、通信部410により受信した情報に基づいて、端末装置200や車両M、ネットワークNWを介して接続した外部装置等から各種情報を取得する。例えば、取得部420は、車両Mから、車両Mの走行履歴データ(走行情報)や運転者Dに関する情報を取得する。取得部420は、取得した情報を車両ID等に対応付けて、運転者情報DB462に格納する。また、取得部420は、端末装置300から情報を取得してもよい。Based on the information received by the communication unit 410, the
評価判定部430は、例えば、第2通信部414が複数の車両Mから取得した情報(走行情報等)により、それぞれの車両M(運転者D)ごとに運転者Dが車両Mの運転時に不安全運転を行ったか否かを判定する。不安全運転は、例えば、道路交通法等の規則に違反する運転であってもよく、規則以外に事前に設定した安全運転ではないと推定される運転であってもよい。不安全運転には、例えば、速度超過(制限速度違反、スピード違反)、一時停止義務違反、駐停車禁止違反、車線逸脱(はみ出し)運転、急停止、急発進等が含まれる。The evaluation and
例えば、評価判定部430は、運転者情報DB462から所定期間における運転者ごとの走行履歴データを取得し、走行履歴データに含まれる所定時間ごとの車両Mの速度と位置情報とを取得する。次に、評価判定部430は、位置情報に基づいて地図情報466を参照し、車両Mが走行する道路の交通規制情報(制限速度、一時停止位置、駐車禁止位置等)を取得する。そして、評価判定部430は、例えば、車両Mの速度が制限速度よりも所定速度以上超過している場合に、速度超過の不安全運転であると判定する。また、評価判定部430は、一時停止位置付近の車両Mの速度がゼロ(0)になっていない(停止していない場合)に、一時停止違反の不安全運転であると判定する。また、評価判定部430は、車両Mの速度がゼロである状態(停止状態)が所定時間以上であり、その位置が駐車禁止位置である場合に、駐車禁止違反の不安全運転であると判定する。また、評価判定部430は、車両Mに搭載された運転支援機能のうち、RDMが作動した場合に車線逸脱の不安全運転であると判定してもよい。また、評価判定部430は、所定時間における速度変化量が所定量以上である場合に、速度増加または速度減少に応じて、急発進または急減速の不安全運転であると判定してもよい。なお、不安全運転の種類についてはこれに限定されるものではない。For example, the evaluation and
また、評価判定部430は、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転に対して、周辺車両の走行状況に基づく評価を行う。車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転である判定された場合の評価処理については、後述する。評価判定部430は、運転者Dの運転が不安全運転であると判定された場合に、その時間情報と、位置情報と、判定された不安全運転の種別とを対応付けて評価判定結果DB464に格納する。また、評価判定部430は、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転に対して、後述する評価結果を評価判定結果として評価判定結果DB464に格納する。The evaluation and
提供部440は、評価判定部430により判定された運転者Dの不安全運転に関する情報(例えば、評価判定結果DB464に格納された情報)を所定のタイミングで車両Mまたは運転者Dの端末装置200に提供する。所定のタイミングとは、例えば、運転者Dが車両Mの運転を終了してから所定のタイミングであり、更に具体的には、運転者Dが車両Mを運転した日の終わりに、若しくは、車両Mの運転が終了してから所定時間経過後である。また、提供部440は、車両Mまたは端末装置200から問い合わせがあったタイミングで不安全運転に関する情報を提供してもよい。車両Mまたは端末装置200は、提供された情報を出力することで、運転者Dに自分の運転履歴を振り返らせることができ、次回以降の運転において不安全運転を抑制させ易くすることができる。また、提供部440は、予め設定した所定周期で情報を提供することで、継続した情報提供を行うことができ、安全運転を習慣化させることができる。The providing
また、提供部440は、不安全運転に関する情報を運転者Dに対応付けられた利用者Uの端末装置300に提供してもよい。これにより、例えば、運転者Dの運転状況(不安全運転)を第三者(運転者Dの家族や仕事上の管理者等)が見守ることができる。このような見守りサービスを提供することにより、第三者から運転者Dに運転のアドバイスや注意喚起を促すことができ、運転者Dに、より安全な運転を意識させることができる。The providing
[車両の速度に関する不安全運転である場合の評価処理]
次に、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転である判定された場合の評価処理の具体例について説明する。例えば、評価判定部430は、車両Mが速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて不安全運転を行った時刻に車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、車両の速度と、取得した他車両の速度または他車両の位置関係と、車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、車両の不安全運転の評価を行う。以下に、幾つかの場面(ケース)における評価内容について説明する。また、以下の例では、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転が速度超過であるものとして説明する。 [Evaluation process for unsafe driving regarding vehicle speed]
Next, a specific example of the evaluation process when it is determined that the vehicle M has driven unsafely in terms of speed will be described. For example, when it is determined that the vehicle M has driven unsafely in terms of speed, the
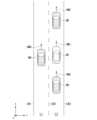
<第1の場面>
図7は、車両の速度に関する不安全運転の第1の場面について説明するための図である。図7の例では、同一方向(図中X軸方向)に進行可能な二つの車線L1とL2を示している。車線L1は、道路区画線LN1およびLN2によって区画され、車線L2は、道路区画線LN2およびLN3によって区画されている。図7の例において、道路区画線LN2は、車線L1、K2の間で車線変更が可能であることを示す区画線である。車両M1(以下、自車両M1と称する)は、車線L2を速度VM1で車線L2の延伸方向に沿って走行している。車両M2~M4は、自車両M1から所定距離以内に存在する周辺車両(自車両M1からみた他車両)である(以下、他車両M2~M4と称する)。図7の例において、他車両M2は、自車両M1の前方で同一車線上を速度VM2で走行している。他車両M3は、自車両M1の後方で同一車線上を速度VM3で走行している。他車両M4は、自車両M1の走行車線に隣接する隣接車線上(車線L1)上であって、自車両M1と同一の進行方向を速度VM4で走行している。 <
FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining a first scene of unsafe driving related to the speed of a vehicle. In the example of FIG. 7, two lanes L1 and L2 that can travel in the same direction (X-axis direction in the figure) are shown. The lane L1 is divided by road dividing lines LN1 and LN2, and the lane L2 is divided by road dividing lines LN2 and LN3. In the example of FIG. 7, the road dividing line LN2 is a dividing line that indicates that a lane change is possible between the lanes L1 and K2. The vehicle M1 (hereinafter referred to as the host vehicle M1) is traveling on the lane L2 at a speed VM1 along the extension direction of the lane L2. The vehicles M2 to M4 are surrounding vehicles (other vehicles as viewed from the host vehicle M1) that exist within a predetermined distance from the host vehicle M1 (hereinafter referred to as the other vehicles M2 to M4). In the example of FIG. 7, the other vehicle M2 is traveling on the same lane ahead of the host vehicle M1 at a speed VM2. Another vehicle M3 is traveling behind the host vehicle M1 in the same lane at a speed VM3. Another vehicle M4 is traveling in an adjacent lane (lane L1) adjacent to the lane in which the host vehicle M1 is traveling, in the same traveling direction as the host vehicle M1 at a speed VM4.
例えば、評価判定部430は、自車両M1が速度に関する不安全運転を行った時刻に自車両M1から所定距離以内に存在する他車両M2~M4を取得し、取得した他車両M2~M4のうち服なくとも一つが自車両M1の後方に存在し、且つ自車両M1の車線変更が困難な状況である場合に、自車両M1の速度と、自車両M1の後方に存在する他車両M3の速度VM3と、車線L2の制限速度とに基づいて、自車両M1の不安全運転の評価を行う。自車両M1の車線変更が困難な状況とは、例えば、車線変更先の隣接車線において自車両Mから所定距離以内に他車両が存在する状況が含まれる。また、自車両M1の車線変更が困難な状況には、隣接車線が工事中である状況や車線変更の禁止区間である状況等が含まれる。For example, the evaluation and
例えば、第1の場面では、自車両M1から前後の所定距離以内に他車両M2、M3が存在し、自車両M1の走行する車線L2の隣接車線(車線L1)において、自車両M1から所定距離以内に他車両M4が存在している。このような場面では、自車両M1は、車線L2からL1に車線変更を行うことが困難であり、車群から抜け出すことができない。したがって、他車両M2~M4の速度VM2~VM4が車線L1、L2に対する制限速度を超過して走行している場合には、自車両M1の速度VM1も超過してしまう可能性が高い。したがって、第1の場面で、自車両M1(運転者D)が速度超過の不安全運転であると判定した場合、評価判定部430は、この判定結果は、自車両M1の運転者Dが周辺車両(他車両M2~M4)の影響を受けたことによるもの(言い換えると、周辺車両の走行状況に応じて仕方なく速度超過した、または、周りの車両の走行状況に合わせた運転であり酌量の余地あり)と評価する。For example, in a first scenario, other vehicles M2 and M3 are present within a predetermined distance in front of and behind the host vehicle M1, and another vehicle M4 is present within a predetermined distance from the host vehicle M1 in an adjacent lane (lane L1) to the lane L2 in which the host vehicle M1 is traveling. In such a scenario, the host vehicle M1 has difficulty changing lanes from lane L2 to lane L1, and is unable to leave the group of vehicles. Therefore, if the speeds VM2-VM4 of the other vehicles M2-M4 are traveling at speeds exceeding the speed limits for lanes L1 and L2, there is a high possibility that the host vehicle M1 will also exceed the speed VM1. Therefore, in the first situation, if it is determined that the driver of the vehicle M1 (driver D) is driving unsafely by exceeding the speed limit, the evaluation and
<第2の場面>
図8は、車両の速度に関する不安全運転の第2の場面について説明するための図である。図8の例では、図7の例と比較して、他車両M2~M4のうち、自車両M1の前方を走行する他車両M2が存在しない点で相違する。この場合にも、他車両M3、M4が制限速度を超過して走行している場合には、自車両M1は、車線変更が困難な状況であり、他車両M3、M4に合わせた速度で走行してしまう。したがって、図8に示すような場合にも、評価判定部350は、自車両M1(運転者D)が速度超過の不安全運転であると判定し、この判定は、自車両M1の運転者Dが周辺車両(他車両M3~M4)の影響を受けたことによるものと評価する。 <Second Scene>
FIG. 8 is a diagram for explaining a second scene of unsafe driving related to the speed of the vehicle. The example of FIG. 8 is different from the example of FIG. 7 in that there is no other vehicle M2 traveling ahead of the host vehicle M1 among the other vehicles M2 to M4. In this case, too, when the other vehicles M3 and M4 are traveling at a speed exceeding the speed limit, the host vehicle M1 is in a situation where it is difficult to change lanes, and travels at a speed that matches the other vehicles M3 and M4. Therefore, even in the case shown in FIG. 8, the evaluation and determination unit 350 determines that the host vehicle M1 (driver D) is driving unsafely by exceeding the speed limit, and evaluates that this determination is due to the driver D of the host vehicle M1 being influenced by surrounding vehicles (other vehicles M3 to M4).
<第3の場面>
図9は、車両の速度に関する不安全運転の第3の場面について説明するための図である。図9の例では、図8の例と比較して、他車両M3~M4のうち、自車両M1の走行車線に隣接する車線L1を走行する他車両M4が存在しない点で相違する。第3の場面でも、評価判定部430は、他車両M3が自車両M1の後方に存在する場合に、自車両M1の速度VM1と、自車両M1の後方に存在する他車両M3の速度VM3と、車線L2の制限速度とに基づいて、自車両M1の不安全運転の評価を行う。 <Scene 3>
9 is a diagram for explaining a third scene of unsafe driving related to the speed of the vehicle. The example of FIG. 9 is different from the example of FIG. 8 in that, among the other vehicles M3 to M4, there is no other vehicle M4 traveling in the lane L1 adjacent to the driving lane of the host vehicle M1. Even in the third scene, when the other vehicle M3 is present behind the host vehicle M1, the
例えば、第3の場面のように、隣接車線に他車両が存在しないが、他車両M3が制限速度を超過して走行している場合には、自車両M1は、他車両M3から不必要に車間距離を短くして接近されたり、後方から煽られている状況となる。そのため、自車両M1は、他車両M3の速度VM3に応じて加速してしまう可能性が高い。したがって、図9に示すような第3の場面の場合にも、評価判定部430は、自車両M1(運転者D)が速度超過の不安全運転であると判定した場合に、この判定は、自車両M1の運転者Dが周辺車両(特に後続する他車両M3)の影響を受けているものとして評価する。For example, in the third scenario, when there is no other vehicle in the adjacent lane, but the other vehicle M3 is traveling at a speed exceeding the speed limit, the host vehicle M1 is approached by the other vehicle M3 with an unnecessarily short distance between the vehicles, or is tailgated from behind. Therefore, the host vehicle M1 is likely to accelerate according to the speed VM3 of the other vehicle M3. Therefore, even in the third scenario shown in FIG. 9, when the evaluation and
<第4の場面>
図10は、車両の速度に関する不安全運転の第4の場面について説明するための図である。図9の例では、図7の例と比較して、他車両M2~M4のうち、自車両M1の後方を走行する他車両M3および自車両M1の走行車線に隣接する車線L1を走行する他車両M4が存在しない点で相違する。第4の場面では、後方の車両や隣接車線に車両が存在しないため、自車両M1の速度VM1は、他車両M2の速度VM2に関係なく、運転者Dが自ら速度を調整することができる。したがって、第4の場面の場合、評価判定部350は、自車両M1(運転者D)が速度超過の不安全運転であると判定し、この判定は、自車両M1の運転者Dが周辺車両(他車両M2)の影響を受けていない(言い換えると、運転者Dの意図で(または単独で)速度超過している)として評価する。 <Scene 4>
FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining a fourth scene of unsafe driving related to the speed of the vehicle. The example of FIG. 9 is different from the example of FIG. 7 in that, among the other vehicles M2 to M4, the other vehicle M3 traveling behind the vehicle M1 and the other vehicle M4 traveling in the lane L1 adjacent to the lane of the vehicle M1 do not exist. In the fourth scene, since there are no vehicles behind or in the adjacent lanes, the speed VM1 of the vehicle M1 can be adjusted by the driver D himself, regardless of the speed VM2 of the other vehicle M2. Therefore, in the case of the fourth scene, the evaluation determination unit 350 determines that the vehicle M1 (driver D) is driving unsafely by speeding, and this determination is evaluated as the driver D of the vehicle M1 not being influenced by the surrounding vehicle (other vehicle M2) (in other words, the driver D is speeding at the will of the driver D (or alone)).
このように、評価判定部430は、自車両M1の速度超過を判定し、速度超過をした理由が自車両M1の周辺車両に影響を受けたことによるものであると判定された場合に、他の理由で速度超過した場合と異なる評価を行う。これにほり、周辺車両の速度と自車両M1との位置関係に基づいて、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転に対して、より適切な評価判定を行うことができる。In this way, the
なお、上述の例において、評価判定部430は、他車両の速度情報や位置情報等を、他車両から取得した走行情報(走行履歴データ)から取得したが、これに限定されるものではなく、例えば自車両M1の走行履歴データから自車両M1の認識部122により認識された周辺状況の認識結果を取得し、その認識結果に含まれる周辺の他車両の相対位置や相対速度の情報に基づいて、上述した各場面における評価を行ってもよい。In the above example, the evaluation and
[提供部]
次に、提供部440により提供される情報について具体的に説明する。例えば、提供部440は、評価判定部430により不安全運転であると判定された評価判定結果に基づいて、評価判定結果DB464に格納された情報に基づく不安全運転に関する情報を生成し、生成した情報を所定のタイミングで車両M、運転者Dの端末装置200、および、利用者Uの端末装置300のうち少なくとも一つに提供する。 [Provision Department]
Next, a specific description will be given of the information provided by the providing
図11は、提供部440により提供される画像IM10の一例を示す図である。なお、画像IM10のレイアウトや表示内容等の表示態様については、図11の例に限定されるものではない。画像IM10は、運転状況の評価結果画面として、例えば、不安全運転内容表示領域AR11と、評価コメント表示領域AR12と、スイッチ表示領域AR13とを有する。不安全運転内容表示領域AR11には、情報を提供する運転者Dの所定期間(例えば、1日または1週間等)の車両Mの運転において、不安全運転であると判定された日時、地点、不安全運転の種類に関する情報が表示される。なお、速度超過の場合には、何キロ超過しているか等の情報が表示されてもよい。Figure 11 is a diagram showing an example of an image IM10 provided by the providing
評価コメント表示領域AR12には、不安全運転の判定に対する評価内容が表示される。例えば、評価コメント表示領域AR12には、不安全運転を行った理由が周辺車両の走行状況によるものとして評価されている場合に、その評価結果に応じたコメントを表示させる。図11の例において、評価コメント表示領域AR12には、「速度超過が多いようです。ただし、C地点での速度超過は周辺車両の影響を受けていたようですね。」といった文字情報が表示されている。なお、評価コメントについては、これに限定されるものではなく、例えば「周りの車両の走行状況に合わせた運転を行っており、酌量の余地あり」等であってもよい。これにより、単に車速に関する不安全運転を厳しく指摘するのではなく、周辺状況に応じて、ある程度許容した評価内容を通知することで、運転者に不快感を与えにくくすると共に納得度を向上させて、より前向きに安全運転を心掛けさせることができる。The evaluation comment display area AR12 displays the evaluation content of the unsafe driving judgment. For example, when the reason for unsafe driving is evaluated as being due to the driving conditions of surrounding vehicles, the evaluation comment display area AR12 displays a comment according to the evaluation result. In the example of FIG. 11, the evaluation comment display area AR12 displays text information such as "It seems that there are many cases of speeding. However, the speeding at point C seems to have been influenced by surrounding vehicles." Note that the evaluation comment is not limited to this, and may be, for example, "The driver is driving in accordance with the driving conditions of the surrounding vehicles, so there is room for leniency." In this way, by notifying the driver of the evaluation content that is somewhat tolerant depending on the surrounding conditions rather than simply pointing out unsafe driving related to the vehicle speed, it is possible to reduce discomfort for the driver and increase the driver's level of satisfaction, thereby encouraging the driver to be more proactive in driving safely.
なお、提供部440は、画像IM10の内容を利用者Uの端末装置300に提供する場合には、評価コメント表示領域AR12に表示される内容を含めなくてもよい。When the providing
スイッチ表示領域AR13には、例えば、端末装置200または300に表示された画像IM10を閉じる(表示を終了する)ことを受け付けるアイコンIC11が含まれる。アイコンIC11は、例えば、GUI(Graphical User Interface)スイッチである。例えば、運転者Dが端末装置200に表示されたアイコンIC11を選択したことを受け付けた場合、端末装置200は画像IM10の表示を終了する。また、利用者Uが端末装置300に表示されたアイコンIC11を選択したことを受け付けた場合、端末装置300は、画像IM10の表示を終了する。The switch display area AR13 includes, for example, an icon IC11 that accepts closing (ending the display) of the image IM10 displayed on the
[処理フロー]
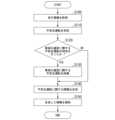
図12は、実施形態における情報管理装置400によって実行される処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。図12の例では、情報管理装置400によって実行される各種処理のうち、主に不安全運転の評価判定処理を中心として説明する。 [Processing flow]
Fig. 12 is a flowchart showing an example of a process executed by the
図12の例において、取得部420は、複数の車両Mから走行情報を取得する(ステップS100)。次に、評価判定部430は、走行情報に基づいて運転者Dが車両Mに対する不安全運転を判定する(ステップS110)。次に、評価判定部430は、不安全運転であると判定されたもののうち、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転の判定を行ったか否かを判定する(ステップS120)。不安全運転の判定を行ったと判定した場合、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転を評価する(ステップS130)。ステップS130の処理後、または、ステップS120の処理において、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転の判定を行っていないと判定された場合、提供部440は、不安全運転に関する情報を生成し(ステップS140)、生成した情報を車両M、運転者Dの端末装置200、および運転者Dに対応付けられた利用者Uのうち、少なくとも一つに提供する(ステップS150)。これにより、本フローチャートの処理は、終了する。12, the
[変形例]
実施形態では、情報管理装置400が備える機能のうち、少なくとも一部を車両Mが備えていてもよい。例えば、評価判定部430は、車両Mの運転支援装置側に設けられていてもよい。図13は、実施形態の変形例における運転支援装置120Aの機能の一例を示す図である。図13に示す運転支援装置120Aは、図2に示す車両システムの運転支援装置120に置き換わるものである。運転支援装置120Aは、認識部122と、走行制御部124と、走行情報取得部126と、評価判定部128と、HMI制御部130と、記憶部140とを備える。図13の例において、走行情報取得部126は、「取得部」の一例である。運転支援装置120Aは、運転支援装置120と比較すると、評価判定部128を有している点で相違する。したがって、以下では、主に評価判定部128を中心として説明する。 [Modification]
In the embodiment, at least a part of the functions of the
評価判定部128は、上述した評価判定部430と同様に、車両Mの走行情報(走行履歴データ142)に基づいて、車両Mの運転者Dの不安全運転の判定を行う。また、不安全運転の判定結果のうち、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転の判定を行っている場合に、不安全運転の評価を行う。この場合、走行情報取得部126は、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転を行った位置と時間に関する情報を情報管理装置400に問い合わせ、同時刻に不安全運転を行った位置付近に存在した他車両の走行情報を取得する。そして、評価判定部128は、上述した評価判定部430と同様に、速度超過が周辺車両の走行状況の影響によるものかの評価を行う。また、評価判定部128は、車両Mの認識部122により認識された周辺状況に基づいて、車両Mの速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定された場合に、その周辺に存在する他車両の速度や位置関係を取得し、更に位置情報から地図情報(例えば、第2地図情報62)を参照して走行車線の制限速度を取得し、速度超過が周辺車両の走行状況の影響によるものか否かの評価を行ってもよい。The evaluation and
また、HMI制御部130は、評価判定部128による評価判定結果に基づいて不安全運転に関する情報(例えば、画像IM10)を生成し、生成した情報をHMI30や端末装置200、300に提供する。なお、変形例における車両システム側の処理の流れは、図12に示す処理フローと同様である。ただし変形例では、図12の説明における「取得部420」、「評価判定部430」、「提供部440」は、それぞれ「走行情報取得部126」、「評価判定部128」、「HMI制御部130」と読み替えるものとする。The
このように、変形例によれば、車両システム側で不安全運転に関する評価判定処理や不安全運転に関する情報を提供することができる。In this way, according to the modified example, the vehicle system can provide evaluation and judgment processing regarding unsafe driving and information regarding unsafe driving.
また、実施形態の車両システムでは、運転支援機能が設けられていなくてもよい。また、上述の実施形態において、「不安全運転」は、「違反運転」と言い換えてもよい。この場合、提供部440は、違反運転に関する情報を、交通の取り締まり等を行う機関の端末装置に提供してもよい。この場合にも、評価コメント等を含む情報が提供される。The vehicle system of the embodiment may not be provided with a driving assistance function. In the above-described embodiment, "unsafe driving" may be rephrased as "violating driving." In this case, the providing
以上説明したように、実施形態によれば、情報管理装置400において、複数の車両と通信する通信部410と、通信部410により複数の車両の走行情報を取得する取得部420と、複数の車両に含まれる車両の走行情報に基づいて車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行う評価判定部430と、を備え、評価判定部430は、車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて不安全運転を行った時刻に車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、車両の速度と、取得した他車両の速度または他車両の位置関係と、車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、車両の不安全運転の評価を行うことにより、運転に対する評価を、周辺車両の走行状況に応じて、より適切に行うことができる。As described above, according to the embodiment, the
また、実施形態によれば、車両システムにおいて、車両の周辺状況を認識する認識部122と、車両の走行情報および周辺状況に基づく他車両の走行情報を取得する取得部(走行情報取得部126)と、車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定をする評価判定部128と、を備え、評価判定部128は、車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、車両の速度と、取得した他車両の速度または他車両の位置関係と、車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、車両の不安全運転の評価を行うことにより、運転に対する評価を、周辺車両の走行状況に応じて、より適切に行うことができる。In addition, according to the embodiment, the vehicle system includes a
また、実施形態によれば、例えば、周りの交通の流れに合わせたことによる速度超過と、交通の流れが無い中での単独での速度超過とで異なる評価を行うことができるため、速度超過の状況や背景を詳しく把握することができ、判定や評価結果の納得度を向上させることができる。また、実施形態によれば、評価判定結果に基づいて、改善行動の区分けに活用することが可能となる。Furthermore, according to the embodiment, for example, different evaluations can be made for speeding caused by adapting to the surrounding traffic flow and speeding caused independently when there is no traffic flow, so that the situation and background of the speeding can be grasped in detail, and the degree of acceptability of the judgment and evaluation results can be improved.Furthermore, according to the embodiment, it is possible to use the evaluation judgment results to classify improvement actions.
例えば、実施形態では、車速に関する不安全運転を行った場合には、その時に付近を走行していた車両を抽出し、そのときの車両の速度、周辺車両の車速、制限速度から総合的に判断して、不安全運転を評価判定する。この場合、制限速度に対して超過していれば、判定としては「不安全」となるが、評価コメントとして「周りの車両の走行状況に合わせた運転を行っており、酌量の余地あり」等の評価コメントを付与することで、運転者や運転者に対応付けられた利用者の違和感を低減することができる。For example, in an embodiment, if unsafe driving is performed in relation to vehicle speed, vehicles traveling nearby at the time are extracted, and unsafe driving is evaluated and determined based on a comprehensive assessment of the vehicle's speed at the time, the speed of surrounding vehicles, and the speed limit. In this case, if the speed limit is exceeded, the determination is "unsafe," but by adding an evaluation comment such as "The driver is driving in accordance with the driving conditions of the surrounding vehicles, so there is room for leniency," it is possible to reduce discomfort felt by the driver or the user associated with the driver.
また、実施形態によれば、例えば、車両を運転した日の終わりに、若しくは、車両の運転が終了し所定時間が経過した後等の所定のタイミングで、その日の不安全運転についての通知を受け取るようにことにより、自分の運転履歴を振り返ることができ、次回以降の運転において不安全運転を抑制させ易くすることができる。また、通知するタイミングを予め設定した所定周期で提供することで、継続した情報提供を行うことができ、安全運転を習慣化させることができる。In addition, according to the embodiment, for example, by receiving a notification about unsafe driving on that day at a specified timing, such as at the end of the day when the vehicle was driven or after a specified time has elapsed since the vehicle driving ended, the driver can look back on his/her driving history and can easily suppress unsafe driving in subsequent driving. In addition, by providing notifications at a preset periodicity, continuous information can be provided and safe driving can be made a habit.
上記説明した実施形態は、以下のように表現することができる。
コンピュータによって読み込み可能な命令(computer-readable instructions)を格納する記憶媒体(storage medium)と、
前記記憶媒体に接続されたプロセッサと、を備え、
前記プロセッサは、前記コンピュータによって読み込み可能な命令を実行することにより(the processor executing the computer-readable instructions to:)、
複数の車両と通信し、
前記複数の車両の走行情報を取得し、
前記複数の車両に含まれる車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行い、
前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて前記不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、
前記車両の速度と、取得した前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、
情報管理装置。 The above-described embodiment can be expressed as follows.
a storage medium for storing computer-readable instructions;
a processor coupled to the storage medium;
The processor executes the computer-readable instructions to:
Communicate with multiple vehicles,
Acquire driving information of the plurality of vehicles;
Evaluating and determining whether or not a driver of a vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving based on driving information of the vehicle included in the plurality of vehicles;
When it is determined that the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, other vehicles that were present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time when the unsafe driving occurred are acquired based on travel information of the other vehicles;
evaluating unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speeds of the other vehicles or the positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling;
Information management device.
また、上記説明した実施形態は、以下のように表現することもできる。
コンピュータによって読み込み可能な命令(computer-readable instructions)を格納する記憶媒体(storage medium)と、
前記記憶媒体に接続されたプロセッサと、を備え、
前記プロセッサは、前記コンピュータによって読み込み可能な命令を実行することにより(the processor executing the computer-readable instructions to:)、
車両の周辺状況を認識し、
前記車両の走行情報および前記周辺状況に基づく他車両の走行情報を取得し、
前記車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行い、
前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、
前記車両の速度と、取得した前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、
車両システム。 The above-described embodiment can also be expressed as follows.
a storage medium for storing computer-readable instructions;
a processor coupled to the storage medium;
The processor executes the computer-readable instructions to:
Recognize the vehicle's surroundings,
Acquire driving information of the vehicle and driving information of other vehicles based on the surrounding conditions;
Evaluating and determining whether or not the driver of the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving based on the driving information of the vehicle;
When it is determined that the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, other vehicles present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle are acquired;
evaluating unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speeds of the other vehicles or the positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling;
Vehicle systems.
以上、本発明を実施するための形態について実施形態を用いて説明したが、本発明はこうした実施形態に何等限定されるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲内において種々の変形および置換を加えることができる。The above describes the form for carrying out the present invention using an embodiment, but the present invention is not limited to such an embodiment, and various modifications and substitutions can be made without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
1…情報管理システム、10…カメラ、12…レーダ装置、14…LIDAR、16…物体認識装置、20…通信装置、30…HMI、40…車両センサ、50…ナビゲーション装置、60…MPU、80…運転操作子、120、120A…運転支援装置、122…認識部、124…走行制御部、126…走行情報取得部、128、430…評価判定部、130…HMI制御部、140…記憶部、200…端末装置、210…端末側通信部、220…入力部、230…出力部、240…制御部、250…アプリ実行部、260…端末側記憶部、400…情報管理装置、410…通信部、420…取得部、430…評価判定部、440…提供部、460…装置側記憶部1... Information management system, 10... Camera, 12... Radar device, 14... LIDAR, 16... Object recognition device, 20... Communication device, 30... HMI, 40... Vehicle sensor, 50... Navigation device, 60... MPU, 80... Driving operator, 120, 120A... Driving support device, 122... Recognition unit, 124... Driving control unit, 126... Driving information acquisition unit, 128, 430... Evaluation and judgment unit, 130... HMI control unit, 140... Storage unit, 200... Terminal device, 210... Terminal side communication unit, 220... Input unit, 230... Output unit, 240... Control unit, 250... Application execution unit, 260... Terminal side storage unit, 400... Information management device, 410... Communication unit, 420... Acquisition unit, 430... Evaluation and judgment unit, 440... Provision unit, 460... Device side storage unit
Claims (10)
Translated fromJapanese前記通信部により前記複数の車両の走行情報を取得する取得部と、
前記複数の車両に含まれる車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行う評価判定部と、を備え、
前記評価判定部は、
前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて前記不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、
前記車両の速度と、取得した前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、
情報管理装置。 A communication unit that communicates with a plurality of vehicles;
an acquisition unit that acquires driving information of the plurality of vehicles by the communication unit;
An evaluation and determination unit that performs an evaluation and determination as to whether or not a driver of the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving based on vehicle driving information included in the plurality of vehicles,
The evaluation and determination unit is
When it is determined that the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, other vehicles that were present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time when the unsafe driving occurred are acquired based on travel information of the other vehicles;
evaluating unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speeds of the other vehicles or the positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling;
Information management device.
請求項1に記載の情報管理装置。 the evaluation and determination unit acquires other vehicles present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time when the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving related to speed, and when at least one of the acquired other vehicles is present behind the vehicle, evaluates the unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the speed of the other vehicles present behind the vehicle, and the speed limit.
The information management device according to claim 1 .
取得した他車両のうち少なくとも一つが、前記車両の後方に存在し、且つ前記車両の車線変更が困難な状況である場合に、前記車両の速度と、前記車両の後方に存在する他車両の速度と、前記制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、
請求項1に記載の情報管理装置。 The evaluation and determination unit acquires other vehicles that are present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at a time when the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed,
When at least one of the acquired other vehicles is present behind the vehicle and it is difficult for the vehicle to change lanes, an evaluation of unsafe driving of the vehicle is performed based on the speed of the vehicle, the speed of the other vehicles present behind the vehicle, and the speed limit.
The information management device according to claim 1 .
請求項3に記載の情報管理装置。 The situation in which it is difficult for the vehicle to change lanes includes a situation in which another vehicle is present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle in an adjacent lane to which the vehicle is to change lanes.
The information management device according to claim 3.
前記運転者による前記車両の運転が終了した後の所定のタイミングで、前記車両の不安全運転に関する情報を前記車両または前記運転者の端末装置に提供する提供部を更に備える、
請求項1に記載の情報管理装置。 The communication unit communicates with a terminal device of the driver,
A providing unit that provides information regarding unsafe driving of the vehicle to the vehicle or a terminal device of the driver at a predetermined timing after the driver has finished driving the vehicle.
The information management device according to claim 1 .
前記運転者による前記車両の運転が終了した後の所定のタイミングで、前記車両の不安全運転に関する情報を前記第三者の端末装置に提供する提供部を更に備える、
請求項1に記載の情報管理装置。 The communication unit communicates with a terminal device of a third party associated with the driver,
A providing unit that provides information regarding unsafe driving of the vehicle to the third party's terminal device at a predetermined timing after the driver has finished driving the vehicle.
The information management device according to claim 1 .
請求項1に記載の情報管理装置。 The evaluation and determination unit determines whether the vehicle is speeding, and when it is determined that the reason for the speeding is due to the influence of surrounding vehicles of the vehicle, performs an evaluation different from that when the vehicle is speeding for other reasons.
The information management device according to claim 1 .
複数の車両と通信し、
前記複数の車両の走行情報を取得し、
前記複数の車両に含まれる車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行い、
前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて前記不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、
前記車両の速度と、取得した前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、
情報管理方法。 The computer
Communicate with multiple vehicles,
Acquire driving information of the plurality of vehicles;
Evaluating and determining whether or not a driver of a vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving based on driving information of the vehicle included in the plurality of vehicles;
When it is determined that the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, other vehicles that were present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time when the unsafe driving occurred are acquired based on travel information of the other vehicles;
evaluating unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speeds of the other vehicles or the positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling;
How information is managed.
前記車両の走行情報および前記周辺状況に基づく他車両の走行情報を取得する取得部と、
前記車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定をする評価判定部と、を備え、
前記評価判定部は、
前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得し、
前記車両の速度と、取得した前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行う、
車両システム。 A recognition unit that recognizes a surrounding situation of the vehicle;
an acquisition unit that acquires driving information of the vehicle and driving information of other vehicles based on the surrounding conditions;
An evaluation and determination unit that evaluates and determines whether or not a driver of the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving based on driving information of the vehicle,
The evaluation and determination unit is
When it is determined that the vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, other vehicles present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle are acquired;
evaluating unsafe driving of the vehicle based on the speed of the vehicle, the acquired speeds of the other vehicles or the positional relationship of the other vehicles, and the speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling;
Vehicle systems.
複数の車両と通信させ、
前記複数の車両の走行情報を取得させ、
前記複数の車両に含まれる車両の走行情報に基づいて前記車両の運転者が不安全運転を行ったか否かの評価判定を行わせ、
前記車両が速度に関する不安全運転を行ったと判定した場合に、他車両の走行情報に基づいて前記不安全運転を行った時刻に前記車両から所定距離以内に存在する他車両を取得させ、
前記車両の速度と、取得された前記他車両の速度または前記他車両の位置関係と、前記車両の走行車線の制限速度とに基づいて、前記車両の不安全運転の評価を行わせる、
プログラム。 On the computer,
Communicate with multiple vehicles,
Acquiring driving information of the plurality of vehicles;
evaluating and determining whether or not a driver of a vehicle has engaged in unsafe driving based on driving information of the vehicle included in the plurality of vehicles;
when it is determined that the vehicle engaged in unsafe driving in terms of speed, acquiring other vehicles that were present within a predetermined distance from the vehicle at the time when the unsafe driving was engaged based on travel information of the other vehicles;
evaluating unsafe driving of the vehicle based on a speed of the vehicle, the acquired speed or positional relationship of the other vehicle, and a speed limit of the lane in which the vehicle is traveling;
program.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023175172AJP2025065751A (en) | 2023-10-10 | 2023-10-10 | Information management device, information management method, vehicle system, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023175172AJP2025065751A (en) | 2023-10-10 | 2023-10-10 | Information management device, information management method, vehicle system, and program |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2025065751Atrue JP2025065751A (en) | 2025-04-22 |
Family
ID=95449439
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023175172APendingJP2025065751A (en) | 2023-10-10 | 2023-10-10 | Information management device, information management method, vehicle system, and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2025065751A (en) |
- 2023
- 2023-10-10JPJP2023175172Apatent/JP2025065751A/enactivePending
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6662828B2 (en) | Driving support system, driving support device, and driving support method | |
| CN109515434B (en) | Vehicle control device, vehicle control method, and storage medium | |
| CN110099834B (en) | Vehicle control system, vehicle control method, and storage medium | |
| CN110001649B (en) | Vehicle control system, vehicle control method, and storage medium | |
| US20180090009A1 (en) | Dynamic traffic guide based on v2v sensor sharing method | |
| US12258017B2 (en) | Vehicle controller, vehicle, and vehicle control method | |
| CN109983305A (en) | Vehicle display control unit, vehicle display control method and vehicle display control program | |
| CN109720343B (en) | vehicle control equipment | |
| CN113401071B (en) | Display control device, display control method, and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN114802292B (en) | Vehicle Controls | |
| JP2018124855A (en) | Vehicle control system, vehicle control method, and vehicle control program | |
| CN111161551A (en) | Apparatus, system and method for detecting, alerting and responding to emergency vehicles | |
| JP2025059425A (en) | Vehicle control device, vehicle control method, and program | |
| CN115230732B (en) | Remote function selection device | |
| JP2022088809A (en) | Vehicle control devices, vehicle control methods, and programs | |
| CN116940971A (en) | Processing device, processing method, processing program, processing system | |
| JP7720890B2 (en) | Vehicle control device, vehicle control method, and program | |
| JP2025059408A (en) | Vehicle control device, vehicle control method, and program | |
| WO2017141375A1 (en) | Hazard prediction device, mobile terminal, and hazard prediction method | |
| JP2025065751A (en) | Information management device, information management method, vehicle system, and program | |
| CN114475639A (en) | Vehicle notification device and vehicle notification system | |
| JP2025065898A (en) | Information management device, information management method, vehicle system, and program | |
| JP7573672B2 (en) | Vehicle control device, vehicle control method, and program | |
| JP7051767B2 (en) | Controls, control methods, and programs | |
| JP7588520B2 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |