JP2025044256A - system - Google Patents
systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2025044256A JP2025044256AJP2024161839AJP2024161839AJP2025044256AJP 2025044256 AJP2025044256 AJP 2025044256AJP 2024161839 AJP2024161839 AJP 2024161839AJP 2024161839 AJP2024161839 AJP 2024161839AJP 2025044256 AJP2025044256 AJP 2025044256A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- user
- voice
- destination
- information
- data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本開示の技術は、システムに関する。The technology disclosed herein relates to a system.
特許文献1には、少なくとも一つのプロセッサにより遂行される、ペルソナチャットボット制御方法であって、ユーザ発話を受信するステップと、前記ユーザ発話を、チャットボットのキャラクターに関する説明と関連した指示文を含むプロンプトに追加するステップと前記プロンプトをエンコードするステップと、前記エンコードしたプロンプトを言語モデルに入力して、前記ユーザ発話に応答するチャットボット発話を生成するステップ、を含む、方法が開示されている。Patent document 1 discloses a persona chatbot control method performed by at least one processor, the method including the steps of receiving a user utterance, adding the user utterance to a prompt including a description of the chatbot character and an associated instruction sentence, encoding the prompt, and inputting the encoded prompt into a language model to generate a chatbot utterance in response to the user utterance.
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望に応じた目的地のサーチや設定が困難である。また、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う機能が欠けている。With conventional navigation systems, it is difficult to search for and set destinations that meet the user's specific requests. In addition, they lack the functionality to make reservations based on the user's requests.
本発明は、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段を含むシステムを提供する。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に応じた目的地のサーチや設定、さらには予約までを一元的に行うことが可能となる。The present invention provides a system that includes a means for learning information from various information sources, a means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, a means for setting a destination based on the search results, and a means for providing navigation to the set destination. This makes it possible to centrally search for and set a destination according to the user's specific requests, and even make reservations.
以下、添付図面に従って本開示の技術に係るシステムの実施形態の一例について説明する。Below, an example of an embodiment of a system related to the technology disclosed herein is described with reference to the attached drawings.
先ず、以下の説明で使用される文言について説明する。First, let us explain the terminology used in the following explanation.
以下の実施形態において、符号付きのプロセッサ(以下、単に「プロセッサ」と称する)は、1つの演算装置であってもよいし、複数の演算装置の組み合わせであってもよい。また、プロセッサは、1種類の演算装置であってもよいし、複数種類の演算装置の組み合わせであってもよい。演算装置の一例としては、CPU(Central Processing Unit)、GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)、GPGPU(General-Purpose computing on Graphics Processing Units)、APU(Accelerated Processing Unit)、又はTPU(TENSOR PROCESSING UNIT(登録商標))等が挙げられる。In the following embodiments, the coded processor (hereinafter simply referred to as the "processor") may be a single arithmetic device or a combination of multiple arithmetic devices. The processor may be a single type of arithmetic device or a combination of multiple types of arithmetic devices. Examples of arithmetic devices include a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), a GPGPU (General-Purpose computing on Graphics Processing Units), an APU (Accelerated Processing Unit), or a TPU (TENSOR PROCESSING UNIT (registered trademark)).
以下の実施形態において、符号付きのRAM(Random Access Memory)は、一時的に情報が格納されるメモリであり、プロセッサによってワークメモリとして用いられる。In the following embodiments, a signed random access memory (RAM) is a memory in which information is temporarily stored and is used as a working memory by the processor.
以下の実施形態において、符号付きのストレージは、各種プログラム及び各種パラメータ等を記憶する1つ又は複数の不揮発性の記憶装置である。不揮発性の記憶装置の一例としては、フラッシュメモリ(SSD(Solid State Drive))、磁気ディスク(例えば、ハードディスク)、又は磁気テープ等が挙げられる。In the following embodiments, the coded storage is one or more non-volatile storage devices that store various programs, various parameters, etc. Examples of non-volatile storage devices include flash memory (SSD (Solid State Drive)), magnetic disks (e.g., hard disks), and magnetic tapes.
以下の実施形態において、符号付きの通信I/F(Interface)は、通信プロセッサ及びアンテナ等を含むインタフェースである。通信I/Fは、複数のコンピュータ間での通信を司る。通信I/Fに対して適用される通信規格の一例としては、5G(5th Generation Mobile Communication System)、Wi-Fi(登録商標)、又はBluetooth(登録商標)等を含む無線通信規格が挙げられる。In the following embodiments, a communication I/F (Interface) with a code is an interface including a communication processor and an antenna, etc. The communication I/F controls communication between multiple computers. Examples of communication standards applied to the communication I/F include wireless communication standards including 5G (5th Generation Mobile Communication System), Wi-Fi (registered trademark), and Bluetooth (registered trademark).
以下の実施形態において、「A及び/又はB」は、「A及びBのうちの少なくとも1つ」と同義である。つまり、「A及び/又はB」は、Aだけであってもよいし、Bだけであってもよいし、A及びBの組み合わせであってもよい、という意味である。また、本明細書において、3つ以上の事柄を「及び/又は」で結び付けて表現する場合も、「A及び/又はB」と同様の考え方が適用される。In the following embodiments, "A and/or B" is synonymous with "at least one of A and B." In other words, "A and/or B" means that it may be only A, only B, or a combination of A and B. In addition, in this specification, the same concept as "A and/or B" is also applied when three or more things are expressed by connecting them with "and/or."
[第1実施形態][First embodiment]
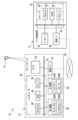
図1には、第1実施形態に係るデータ処理システム10の構成の一例が示されている。Figure 1 shows an example of the configuration of a
図1に示すように、データ処理システム10は、データ処理装置12及びスマートデバイス14を備えている。データ処理装置12の一例としては、サーバが挙げられる。As shown in FIG. 1, the
データ処理装置12は、コンピュータ22、データベース24、及び通信I/F26を備えている。コンピュータ22は、本開示の技術に係る「コンピュータ」の一例である。コンピュータ22は、プロセッサ28、RAM30、及びストレージ32を備えている。プロセッサ28、RAM30、及びストレージ32は、バス34に接続されている。また、データベース24及び通信I/F26も、バス34に接続されている。通信I/F26は、ネットワーク54に接続されている。ネットワーク54の一例としては、WAN(Wide Area Network)及び/又はLAN(Local Area Network)等が挙げられる。The
スマートデバイス14は、コンピュータ36、受付装置38、出力装置40、カメラ42、及び通信I/F44を備えている。コンピュータ36は、プロセッサ46、RAM48、及びストレージ50を備えている。プロセッサ46、RAM48、及びストレージ50は、バス52に接続されている。また、受付装置38、出力装置40、及びカメラ42も、バス52に接続されている。The
受付装置38は、タッチパネル38A及びマイクロフォン38B等を備えており、ユーザ入力を受け付ける。タッチパネル38Aは、指示体(例えば、ペン又は指等)の接触を検出することにより、指示体の接触によるユーザ入力を受け付ける。マイクロフォン38Bは、ユーザの音声を検出することにより、音声によるユーザ入力を受け付ける。制御部46Aは、タッチパネル38A及びマイクロフォン38Bによって受け付けたユーザ入力を示すデータをデータ処理装置12に送信する。データ処理装置12では、特定処理部290が、ユーザ入力を示すデータを取得する。The
出力装置40は、ディスプレイ40A及びスピーカ40B等を備えており、データをユーザ20が知覚可能な表現形(例えば、音声及び/又はテキスト)で出力することでデータをユーザ20に対して提示する。ディスプレイ40Aは、プロセッサ46からの指示に従ってテキスト及び画像等の可視情報を表示する。スピーカ40Bは、プロセッサ46からの指示に従って音声を出力する。カメラ42は、レンズ、絞り、及びシャッタ等の光学系と、CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)イメージセンサ又はCCD(Charge Coupled Device)イメージセンサ等の撮像素子とが搭載された小型デジタルカメラである。The
通信I/F44は、ネットワーク54に接続されている。通信I/F44及び26は、ネットワーク54を介してプロセッサ46とプロセッサ28との間の各種情報の授受を司る。The communication I/
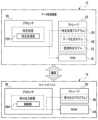
図2には、データ処理装置12及びスマートデバイス14の要部機能の一例が示されている。Figure 2 shows an example of the main functions of the
図2に示すように、データ処理装置12では、プロセッサ28によって特定処理が行われる。ストレージ32には、特定処理プログラム56が格納されている。特定処理プログラム56は、本開示の技術に係る「プログラム」の一例である。プロセッサ28は、ストレージ32から特定処理プログラム56を読み出し、読み出した特定処理プログラム56をRAM30上で実行する。特定処理は、プロセッサ28がRAM30上で実行する特定処理プログラム56に従って特定処理部290として動作することによって実現される。As shown in FIG. 2, in the
ストレージ32には、データ生成モデル58及び感情特定モデル59が格納されている。データ生成モデル58及び感情特定モデル59は、特定処理部290によって用いられる。
スマートデバイス14では、プロセッサ46によって受付出力処理が行われる。ストレージ50には、受付出力プログラム60が格納されている。受付出力プログラム60は、データ処理システム10によって特定処理プログラム56と併用される。プロセッサ46は、ストレージ50から受付出力プログラム60を読み出し、読み出した受付出力プログラム60をRAM48上で実行する。受付出力処理は、プロセッサ46がRAM48上で実行する受付出力プログラム60に従って、制御部46Aとして動作することによって実現される。In the
次に、データ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理について説明する。Next, we will explain the specific processing performed by the
「形態例1」"Example 1"
本発明の一実施形態として、車載用のナビゲーションシステムが考えられる。このシステムは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段として、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いる。具体的には、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得し、これを学習する。また、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段として、自然言語処理技術を用いる。ユーザーからの質問を解析し、それに基づいて適切な目的地をサーチする。さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段として、GPS技術を用いる。ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定する。最後に、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段として、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いる。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。One embodiment of the present invention is an in-vehicle navigation system. This system uses a machine learning algorithm as a means of learning information from various information sources. Specifically, information is acquired from a database that includes information such as restaurant reviews and the availability of parking spaces, and this information is learned. Natural language processing technology is also used as a means of searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests. Questions from the user are analyzed, and an appropriate destination is searched for based on the results. GPS technology is also used as a means of setting the destination based on the search results. The optimal route is calculated based on the user's current location and the search results, and the destination is set. Finally, a voice guidance system is used as a means of providing navigation to the set destination. This allows the user to be safely guided to their destination even while driving.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
本発明の別の実施形態として、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションが考えられる。このアプリケーションは、前述の車載用ナビゲーションシステムと同様の機能を持つが、さらにユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う機能を含む。具体的には、ユーザーが「電話で予約して」という要望を出した場合、システムは自動的に該当するレストランに電話をかけ、予約を行う。この機能は、音声認識技術と自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて実現される。Another embodiment of the present invention is a smartphone application. This application has the same functions as the in-car navigation system described above, but also includes a function for making reservations based on the user's request. Specifically, when a user requests to "make a reservation by phone," the system automatically calls the corresponding restaurant and makes the reservation. This function is realized using voice recognition technology and an automatic dialing system.
以下に、各形態例の処理の流れについて説明する。The process flow for each example is explained below.
「形態例1」"Example 1"
ステップ1:システムは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得し、これを機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて学習する。Step 1: The system learns information from various sources. Specifically, it obtains information from a database that includes information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available, and learns from this information using machine learning algorithms.
ステップ2:ユーザーからの細かい要望が入力されると、システムは自然言語処理技術を用いてこれを解析する。Step 2: Once the user has entered their detailed request, the system analyzes it using natural language processing technology.
ステップ3:解析結果に基づいて、システムは適切な目的地をサーチする。Step 3: Based on the analysis results, the system searches for suitable destinations.
ステップ4:サーチ結果とユーザーの現在位置を基に、システムはGPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定する。Step 4: Based on the search results and the user's current location, the system uses GPS technology to calculate the optimal route and set the destination.
ステップ5:設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供するため、システムは音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーを誘導する。Step 5: The system guides the user using the voice guidance system to provide navigation to the set destination.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
ステップ1:スマートフォン用のアプリケーションは、前述の車載用ナビゲーションシステムと同様の機能を持つ。Step 1: The smartphone application has the same functions as the in-car navigation system mentioned above.
ステップ2:ユーザーが「電話で予約して」という要望を出した場合、システムは自動的に該当するレストランに電話をかける。Step 2: If the user requests to "make a reservation by phone," the system will automatically call the relevant restaurant.
ステップ3:システムは音声認識技術と自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う。Step 3: The system uses voice recognition technology and an automated dialing system to make the reservation.
(実施例1)(Example 1)
次に、形態例1の実施例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマートデバイス14を「端末」と称する。Next, a first embodiment of the first embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチすることが困難であり、また、ユーザーの質問に対する適切な回答を生成することができなかった。さらに、目的地の設定やナビゲーションの提供においても、ユーザーの現在位置やサーチ結果を効果的に利用することができなかった。これにより、ユーザーの利便性が低下し、運転中の安全性も確保されにくかった。With conventional navigation systems, it was difficult to search for a destination based on the user's specific requests, and they were unable to generate appropriate answers to the user's questions. Furthermore, they were unable to effectively use the user's current location or search results when setting a destination or providing navigation. This reduced user convenience and made it difficult to ensure safety while driving.
実施例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、音声入力をテキストに変換する手段と、自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析する手段と、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを学習する手段と、位置情報を取得する手段と、音声ガイダンスを生成する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいた目的地のサーチと設定が可能となり、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導されることが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for converting voice input to text, means for analyzing the user's questions using natural language processing techniques, means for learning data using machine learning algorithms, means for acquiring location information, and means for generating voice guidance. This makes it possible to search for and set a destination based on the user's detailed requests, and allows the user to be safely guided to the destination even while driving.
「情報源」とは、データを提供するあらゆる媒体やシステムを指す。"Source" refers to any medium or system that provides data.
「学習する手段」とは、データを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出するためのアルゴリズムや技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to the algorithms and techniques used to analyze data and extract patterns and knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて求める詳細な要求を指す。"Specific user requests" refers to the detailed requirements that users have based on their specific conditions and preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to the technology or algorithms used to search for an appropriate destination based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補や情報を指す。"Search results" refers to destination candidates and information obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果に基づいて最適な目的地を決定するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to the technology or algorithm used to determine the optimal destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、ユーザーが目的地に到達するための経路案内を行う技術やシステムを指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to technologies and systems that provide route guidance to help users reach their destination.
「音声入力をテキストに変換する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声を解析し、文字情報に変換する技術やシステムを指す。"Means of converting voice input into text" refers to technology or systems that analyze the user's voice and convert it into text information.
「自然言語処理技術」とは、人間の言語を解析し、理解するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Natural language processing technology" refers to the techniques and algorithms for analyzing and understanding human language.
「機械学習アルゴリズム」とは、データからパターンや知識を学習し、予測や分類を行うためのアルゴリズムを指す。"Machine learning algorithms" refer to algorithms that learn patterns and knowledge from data and make predictions and classifications.
「位置情報を取得する手段」とは、ユーザーの現在位置を特定するための技術やシステムを指す。"Means of acquiring location information" refers to technologies and systems for identifying the user's current location.
「音声ガイダンスを生成する手段」とは、ユーザーに音声で指示を出すための技術やシステムを指す。"Means for generating audio guidance" refers to technology or systems for providing audio instructions to the user.
発明を実施するための形態Form for implementing the invention
この発明は、車載用ナビゲーションシステムに関するものであり、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチし、最適なルートを提供するためのシステムである。このシステムは、サーバ、端末、ユーザーの三者が連携して動作する。This invention relates to an in-vehicle navigation system that searches for destinations based on the user's specific requests and provides the optimal route. This system works in cooperation with a server, a terminal, and a user.
1. プログラムの生成1. Program generation
サーバは、車載用ナビゲーションシステムのプログラムを生成する。このプログラムは、機械学習アルゴリズムと自然言語処理技術を組み合わせて構築される。具体的には、PythonのPandas、Scikit-learn、NLTK、SpaCy、Google(登録商標) Maps API、Amazon PollyなどのライブラリやAPIを使用する。The server generates the program for the in-car navigation system. This program is built by combining machine learning algorithms and natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses libraries and APIs such as Python's Pandas, Scikit-learn, NLTK, SpaCy, Google (registered trademark) Maps API, and Amazon Polly.
2. プログラムの処理2. Program processing
サーバは、以下の手順でデータを処理する。The server processes the data in the following steps:
1. データ取得と学習:1. Data acquisition and learning:
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースからデータを取得する。具体的には、PythonのPandasライブラリを使用してデータを読み込む。次に、サーバはScikit-learnを用いて機械学習アルゴリズムでデータを学習する。例えば、レストランの評価情報を基に、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを作成する。The server retrieves data from a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. Specifically, it reads the data using Python's Pandas library. The server then uses Scikit-learn to train the data with machine learning algorithms. For example, it creates a model that predicts highly rated restaurants based on restaurant rating information.
2. ユーザーの質問解析:2. User question analysis:
端末は、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。例えば、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」という質問を受け取る。端末は、この質問を自然言語処理技術を用いて解析する。具体的には、PythonのNLTKやSpaCyを使用して、質問の意図を理解する。The device receives questions from users. For example, it may receive a question such as, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby." The device then analyzes the question using natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses Python's NLTK and SpaCy to understand the intent of the question.
3. 目的地の設定:3. Set your destination:
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。具体的には、Google Maps APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を取得し、最適なルートを計算する。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results. Specifically, it uses the Google Maps API to obtain the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants, and calculates the optimal route.
4. ナビゲーションの提供:4. Providing navigation:
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する。具体的には、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに音声で指示を出す。例えば、Amazon Pollyを使用して、「右に曲がってください」などの音声ガイダンスを生成する。The device provides navigation to the set destination. Specifically, it uses a voice guidance system to give voice instructions to the user. For example, it uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance such as "Turn right."
3. 具体例3. Specific examples
具体例として、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と質問した場合を考える。As a concrete example, consider the case where a user asks, "Can you tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby?"
1. データ取得と学習:1. Data acquisition and learning:
サーバは、データベースに接続し、レストランの評価情報を取得する。The server connects to the database and retrieves restaurant rating information.
サーバは、Pandasを用いてデータをDataFrameに変換する。The server converts the data into a DataFrame using Pandas.
サーバは、Scikit-learnのRandomForestClassifierを用いて、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを学習する。The server uses Scikit-learn's RandomForestClassifier to train a model to predict highly rated restaurants.
2. ユーザーの質問解析:2. User question analysis:
ユーザーは、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と端末に話しかける。The user speaks to the device saying, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby."
端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換する。The device converts voice input into text.
端末は、NLTKを用いてテキストをトークン化し、SpaCyを用いて質問の意図を解析する。The device uses NLTK to tokenize the text and SpaCy to analyze the intent of the question.
3. 目的地の設定:3. Set your destination:
端末は、GPSセンサーを用いてユーザーの現在位置を取得する。The device uses the GPS sensor to obtain the user's current location.
サーバは、Google Maps APIを用いて、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を基にルートを計算する。The server uses the Google Maps API to calculate a route based on the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants.
サーバは、計算結果を端末に送信する。The server sends the calculation results to the terminal.
4. ナビゲーションの提供:4. Providing navigation:
端末は、サーバから受け取ったルート情報を基に、ナビゲーションを開始する。The device begins navigation based on the route information received from the server.
端末は、Amazon Pollyを用いて音声ガイダンスを生成し、ユーザーに指示を出す。The device uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance and give instructions to the user.
ユーザーは、音声ガイダンスに従って運転する。The user drives by following the voice guidance.
プロンプト文の例:Example prompt:
「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて。」"Can you tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby?"
このようにして、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。In this way, users are safely guided to their destination while driving.
実施例1における特定処理の流れについて図11を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 1 is explained using Figure 11.
ステップ1:データ取得と学習Step 1: Data acquisition and learning
サーバは、データベースからレストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を取得する。入力として、データベース接続情報とSQLクエリを使用する。サーバは、PythonのPandasライブラリを用いてデータをDataFrameに変換する。次に、サーバはScikit-learnを用いて機械学習アルゴリズムでデータを学習する。具体的には、RandomForestClassifierを使用して、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを作成する。出力として、学習済みのモデルが得られる。The server retrieves information from the database, such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. As input, it uses the database connection information and a SQL query. The server converts the data into a DataFrame using Python's Pandas library. The server then uses Scikit-learn to train the data with a machine learning algorithm. Specifically, it uses RandomForestClassifier to create a model that predicts highly rated restaurants. As output, it obtains the trained model.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
サーバは、データベースに接続し、SQLクエリを実行してデータを取得する。The server connects to the database and executes SQL queries to retrieve data.
サーバは、取得したデータをPandasのDataFrameに変換する。The server converts the retrieved data into a Pandas DataFrame.
サーバは、Scikit-learnのRandomForestClassifierを用いて、レストランの評価を予測するモデルを学習する。The server uses Scikit-learn's RandomForestClassifier to train a model to predict restaurant ratings.
ステップ2:ユーザーの質問解析Step 2: Analyze user questions
端末は、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。入力として、ユーザーの音声質問が使用される。端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換するために音声認識技術を使用する。次に、端末は、自然言語処理技術を用いて質問を解析する。具体的には、PythonのNLTKやSpaCyを使用して、質問の意図を理解する。出力として、解析されたテキストデータが得られる。The terminal receives a question from the user. As input, the user's voice question is used. The terminal uses speech recognition technology to convert the voice input into text. The terminal then analyzes the question using natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses Python's NLTK and SpaCy to understand the intent of the question. As output, the analyzed text data is obtained.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
ユーザーは、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と端末に話しかける。The user speaks to the device saying, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby."
端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換する。The device converts voice input into text.
端末は、NLTKを用いてテキストをトークン化し、SpaCyを用いて質問の意図を解析する。The device uses NLTK to tokenize the text and SpaCy to analyze the intent of the question.
ステップ3:目的地の設定Step 3: Set your destination
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。入力として、ユーザーの現在位置と解析されたテキストデータが使用される。サーバは、Google Maps APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を取得し、最適なルートを計算する。出力として、計算されたルート情報が得られる。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results. The user's current location and parsed text data are used as input. The server uses the Google Maps API to obtain the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants, and calculates the optimal route. The calculated route information is obtained as output.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
端末は、GPSセンサーを用いてユーザーの現在位置を取得する。The device uses the GPS sensor to obtain the user's current location.
サーバは、Google Maps APIを用いて、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を基にルートを計算する。The server uses the Google Maps API to calculate a route based on the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants.
サーバは、計算結果を端末に送信する。The server sends the calculation results to the terminal.
ステップ4:ナビゲーションの提供Step 4: Provide navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する。入力として、計算されたルート情報が使用される。端末は、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに音声で指示を出す。具体的には、Amazon Pollyを使用して、「右に曲がってください」などの音声ガイダンスを生成する。出力として、音声ガイダンスが得られる。The device provides navigation to the set destination. The calculated route information is used as input. The device uses a voice guidance system to give voice instructions to the user. Specifically, it uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance such as "Turn right". The voice guidance is obtained as output.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
端末は、サーバから受け取ったルート情報を基に、ナビゲーションを開始する。The device begins navigation based on the route information received from the server.
端末は、Amazon Pollyを用いて音声ガイダンスを生成し、ユーザーに指示を出す。The device uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance and give instructions to the user.
ユーザーは、音声ガイダンスに従って運転する。The user drives by following the voice guidance.
(応用例1)(Application example 1)
次に、形態例1の応用例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマートデバイス14を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 1 of embodiment example 1 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする機能が限定的であり、ユーザーの質問に対する適切な回答を生成する能力が不足している。また、現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスを提供する機能も十分ではない。これにより、ユーザーは目的地への移動中に不便を感じることが多い。Traditional navigation systems have limited functionality for searching for destinations based on the user's specific requests and lack the ability to generate appropriate answers to user questions. They also lack the ability to calculate the optimal route between the current location and the destination and provide voice guidance. This often causes inconvenience to users while traveling to their destination.
応用例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する自然言語処理手段と、現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する手段と、音声ガイダンスを提供する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチし、最適なルートを計算して音声ガイダンスを提供することが可能となる。The identification process by the
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するための出典やリソースである。A "source" is a source or resource that provides data or knowledge.
「情報を学習する手段」とは、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて、様々な情報源から取得したデータを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出する方法である。"Means of learning information" refers to the use of machine learning algorithms to analyze data obtained from various sources and extract patterns and knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて求める詳細な要求や希望である。"User specific requests" are the detailed demands and wishes that a user has based on their specific conditions and preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための方法や技術である。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods or technologies for searching for an appropriate destination based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、目的地をサーチする手段によって得られた検索結果である。"Search results" means the results of a search obtained by a means of searching for a destination.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果に基づいてユーザーの目的地を決定する方法や技術である。"Means for setting a destination" refers to a method or technology for determining a user's destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、ユーザーが目的地に到達するための経路案内や指示を提供する方法や技術である。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods or technologies that provide route guidance or directions to help a user reach a destination.
「自然言語処理手段」とは、ユーザーの質問や要求を解析し、適切な回答を生成するための技術である。"Natural language processing means" is technology for analyzing users' questions and requests and generating appropriate answers.
「ルートを計算する手段」とは、現在位置と目的地の間の最適な経路を計算するための方法や技術である。"Means for calculating a route" refers to a method or technique for calculating the optimal route between a current location and a destination.
「音声ガイダンスを提供する手段」とは、計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供する方法や技術である。"Means for providing audio guidance" refers to methods or technologies that convert calculated route information into audio and provide it to the user.
この発明を実施するための形態として、以下のようなシステムが考えられる。The following system is considered as a form for implementing this invention.
まず、サーバは様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段を持つ。この手段は、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出するものである。具体的には、データベースから情報を取得し、これを学習する。First, the server has a means of learning information from various sources. This means uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data such as restaurant reviews and the availability of parking spaces, and extract patterns and knowledge. Specifically, it retrieves information from a database and learns from it.
次に、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段がある。この手段は、自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な目的地をサーチするものである。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」と質問すると、システムはその質問を解析し、適切なレストランを検索する。Next, there is a means to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests. This means uses natural language processing technology to analyze the user's question and search for an appropriate destination. For example, if a user asks, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" the system will analyze the question and search for an appropriate restaurant.
さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段がある。この手段は、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定するものである。具体的には、Geopyライブラリを使用して、現在位置と目的地の間の距離を計算する。In addition, there is a method for setting a destination based on search results. This method calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and search results, and sets the destination. Specifically, it uses the Geopy library to calculate the distance between the current location and the destination.
最後に、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段がある。この手段は、Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)ライブラリを使用して、計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供するものである。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。Finally, there is a method to provide navigation to the set destination. This method uses the Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) library to convert the calculated route information into voice and provide it to the user. This allows the user to be safely guided to their destination while driving.
具体例として、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」と質問すると、システムは以下のように動作する。As a concrete example, when a user asks, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" the system works as follows:
1. 自然言語処理手段がユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する。1. Natural language processing tools analyze the user's question and generate an appropriate answer.
2. 情報を学習する手段がデータベースからレストランの評価情報を取得し、解析する。2. The means for learning information retrieves restaurant rating information from the database and analyzes it.
3. ルートを計算する手段が現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する。3. A route calculation means calculates the optimal route between the current location and the destination.
4. 音声ガイダンスを提供する手段が計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供する。4. A means for providing audio guidance converts the calculated route information into audio and provides it to the user.
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが考えられる。Some examples of prompt statements include:
ユーザーの質問: 「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」User Question: "What are some highly rated restaurants near me?"
コンテキスト: 「レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無など」Context: "Restaurant ratings, availability of parking, etc."
このプロンプト文を使用して、生成AIモデルに質問を解析させ、適切な回答を得ることができる。This prompt can then be used by a generative AI model to parse the question and provide an appropriate answer.
応用例1における特定処理の流れについて図12を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 1 is explained using Figure 12.
ステップ1:Step 1:
サーバは、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。入力はユーザーの質問であり、例えば「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」というテキストデータである。出力は解析のための準備が整ったテキストデータである。The server receives a question from a user. The input is the user's question, which is text data, for example, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" The output is text data ready for analysis.
ステップ2:Step 2:
サーバは、自然言語処理手段を用いて、ユーザーの質問を解析する。入力はステップ1で受け取ったユーザーの質問であり、出力は解析結果としての適切な検索クエリである。具体的には、生成AIモデルを使用して質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する。The server uses natural language processing means to analyze the user's question. The input is the user's question received in step 1, and the output is an appropriate search query as a result of the analysis. Specifically, it uses a generative AI model to analyze the question and generate an appropriate answer.
ステップ3:Step 3:
サーバは、情報を学習する手段を用いて、データベースからレストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを取得する。入力はステップ2で生成された検索クエリであり、出力は取得された評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータである。具体的には、データベースに対してクエリを実行し、必要な情報を取得する。The server uses a means for learning information to obtain data such as restaurant rating information and whether or not parking is available from the database. The input is the search query generated in step 2, and the output is the obtained rating information, parking availability, and other data. Specifically, the server executes a query against the database to obtain the required information.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバは、取得した情報を基に、ユーザーの現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する。入力はユーザーの現在位置とステップ3で取得された目的地情報であり、出力は計算された最適なルート情報である。具体的には、Geopyライブラリを使用して距離を計算し、最適なルートを決定する。The server calculates the optimal route between the user's current location and the destination based on the acquired information. The input is the user's current location and the destination information acquired in step 3, and the output is the calculated optimal route information. Specifically, the Geopy library is used to calculate the distance and determine the optimal route.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバは、計算されたルート情報を音声ガイダンスに変換する。入力はステップ4で計算されたルート情報であり、出力は音声ファイルである。具体的には、Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)ライブラリを使用して、テキスト情報を音声に変換する。The server converts the calculated route information into voice guidance. The input is the route information calculated in step 4, and the output is an audio file. Specifically, it uses the Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) library to convert the text information into voice.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末は、生成された音声ガイダンスをユーザーに提供する。入力はステップ5で生成された音声ファイルであり、出力はユーザーに対する音声案内である。具体的には、音声ファイルを再生し、ユーザーに対してナビゲーション情報を提供する。The terminal provides the generated voice guidance to the user. The input is the audio file generated in step 5, and the output is audio guidance for the user. Specifically, the audio file is played and navigation information is provided to the user.
(実施例2)(Example 2)
次に、形態例2の実施例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマートデバイス14を「端末」と称する。Next, a second embodiment of the second embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、目的地の設定やナビゲーション機能を提供するだけであり、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいた予約機能を持たないため、ユーザーが手動で予約を行う必要があった。また、音声指示を解析して自動的に予約を行うシステムも存在しなかったため、ユーザーの利便性が低かった。これにより、ユーザーは目的地の設定と予約の両方を別々に行う手間がかかり、効率的な利用が難しかった。Conventional navigation systems only provided destination setting and navigation functions, and did not have a reservation function based on the user's specific requests, so users had to make reservations manually. There was also no system that analyzed voice instructions and made reservations automatically, which resulted in low user convenience. This meant that users had to take the time to set a destination and make reservations separately, making it difficult to use the system efficiently.
実施例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声指示を解析する手段と、解析された音声指示に基づいて予約内容を抽出する手段と、抽出された予約内容に基づいて予約しようとする店に自動的に電話をかける手段と、予約しようとする店の従業員に対して電話を通じて予約内容を音声で伝える手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーは音声指示を出すだけで目的地の設定と予約が自動的に行われ、利便性が大幅に向上することが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for analyzing the user's voice instructions, means for extracting reservation details based on the analyzed voice instructions, means for automatically calling the establishment for which a reservation is to be made based on the extracted reservation details, and means for audibly conveying the reservation details over the phone to an employee of the establishment for which a reservation is to be made. As a result, the user only needs to give voice instructions for the destination to be set and the reservation to be made to be made automatically, greatly improving convenience.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「ユーザー」とは、システムを利用する個人または団体を指す。"User" refers to an individual or organization that uses the system.
「目的地」とは、ユーザーが到達したい場所を指す。"Destination" refers to the place the user wants to reach.
「サーチ」とは、特定の情報を探し出す行為を指す。"Search" refers to the act of finding specific information.
「ナビゲーション」とは、目的地までの経路を案内する機能を指す。"Navigation" refers to the function of providing route guidance to a destination.
「音声指示」とは、ユーザーが音声を用いてシステムに対して行う指示を指す。"Voice instructions" refers to instructions given by the user to the system using voice.
「解析」とは、データや情報を詳細に調べて意味や構造を理解する行為を指す。"Analysis" refers to the act of examining data or information in detail to understand its meaning and structure.
「予約内容」とは、予約に必要な情報(日時、人数、場所など)を指す。"Reservation details" refers to the information required for making a reservation (date and time, number of people, location, etc.).
「自動的」とは、人の手を介さずに機械やシステムが独自に動作することを指す。"Automatic" refers to a machine or system that operates independently without human intervention.
「電話をかける」とは、通信装置を用いて他の通信装置に接続を試みる行為を指す。"Making a phone call" refers to the act of using a communication device to attempt to connect to another communication device.
「音声で伝える」とは、音声を用いて情報を他者に伝達する行為を指す。"Communicating by voice" refers to the act of conveying information to others using voice.
発明を実施するための形態Form for implementing the invention
この発明は、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションとして実施される。このアプリケーションは、ユーザーの音声指示に基づいて目的地の設定と予約を自動的に行うシステムである。以下に、このシステムの具体的な実施形態を説明する。This invention is implemented as an application for smartphones. This application is a system that automatically sets a destination and makes reservations based on the user's voice instructions. A specific embodiment of this system is described below.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
このシステムは、以下のハードウェアおよびソフトウェアを使用する。This system uses the following hardware and software:
スマートフォン(端末)Smartphone (device)
音声認識技術(Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API)Voice recognition technology (Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API)
データベース管理システム(Firebase Firestore)Database management system (Firebase Firestore)
自動ダイヤルシステム(Twilio API)Automatic dialing system (Twilio API)
音声合成技術(Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API)Speech synthesis technology (Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API)
データ加工およびデータ演算Data processing and data calculations
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、音声で「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示する。端末はGoogle Cloud Speech-to-Text APIを使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。この変換処理はリアルタイムで行われる。The user launches the application on their smartphone and says, "Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm." The device uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API to convert the user's voice instructions into text. This conversion process occurs in real time.
次に、端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、予約内容(日時、人数)を抽出する。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」というテキストから「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という情報を取り出す。Then, the device analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details (date, time, number of people). For example, from the text "Make a reservation for four people at 7 p.m. tomorrow," the information "tomorrow at 7 p.m." and "four people" is extracted.
端末はFirebase Firestoreに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。このリクエストには、ユーザの位置情報や好みのレストランの条件が含まれる。サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をFirebase Firestoreから取得し、端末に返す。返される情報には、レストランの名前、電話番号、住所などが含まれる。The device sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in Firebase Firestore. This request includes the user's location and preferred restaurant conditions. The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from Firebase Firestore, and returns it to the device. The returned information includes the restaurant's name, phone number, address, etc.
端末はTwilio APIを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。この処理はユーザの手を煩わせることなく行われる。電話が接続されると、端末はGoogle Cloud Text-to-Speech APIを使用して、事前に抽出した予約内容を音声でレストランの従業員に伝える。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声が再生される。The device uses the Twilio API to automatically call the restaurant's phone number, without any user intervention. Once the call is connected, the device uses the Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API to verbally communicate the reservation details it extracted in advance to the restaurant employee. For example, it might say, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7 p.m."
具体例Specific examples
具体例として、ユーザが「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示した場合の動作を以下に示す。As a concrete example, the behavior when a user instructs "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow night" is shown below.
1. ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と音声で指示する。1. The user launches the smartphone application and gives a voice command such as, "Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
2. 端末はGoogle Cloud Speech-to-Text APIを使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。2. The device uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API to convert the user's voice commands into text.
3. 端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という予約内容を抽出する。3. The device analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details: "tomorrow night at 7pm" and "4 people."
4. 端末はFirebase Firestoreに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。4. The device sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in Firebase Firestore.
5. サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をFirebase Firestoreから取得し、端末に返す。5. The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from Firebase Firestore, and returns it to the device.
6. 端末はTwilio APIを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。6. The device uses the Twilio API to automatically call the restaurant's phone number.
7. 電話が接続されると、端末はGoogle Cloud Text-to-Speech APIを使用して、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声をレストランに伝える。7. Once the call is connected, the device uses the Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API to communicate to the restaurant, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが考えられる。Some examples of prompt statements include:
「ユーザが「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示した場合、アプリケーションはどのように処理を行うか説明してください。」"If a user says, 'Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm,' how should the application handle that?"
このプロンプト文を生成AIモデルに入力することで、上記の具体例に基づいた処理の説明を得ることができる。By inputting this prompt into the generative AI model, we can obtain an explanation of the process based on the specific example above.
実施例2における特定処理の流れについて図13を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 2 is explained using Figure 13.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザが音声指示を出す。The user gives voice instructions.
ユーザはスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と音声で指示する。この音声指示が入力となる。The user launches the smartphone application and gives a voice command such as, "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow night." This voice command becomes the input.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末が音声をテキストに変換する。Your device will convert the voice to text.
端末は音声認識技術を使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。この処理には音声認識APIが使用される。入力はユーザの音声指示であり、出力はテキスト形式の指示である。The device uses voice recognition technology to convert the user's voice instructions into text. This process uses a voice recognition API. The input is the user's voice instructions, and the output is the instructions in text format.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末がテキストを解析し、予約内容を抽出する。The device analyzes the text and extracts the reservation details.
端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、予約内容(日時、人数)を抽出する。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」というテキストから「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という情報を取り出す。入力はテキスト形式の指示であり、出力は予約内容のデータである。The terminal analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details (date, time, number of people). For example, from the text "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow," the information "tomorrow at 7pm" and "four people" is extracted. The input is instructions in text format, and the output is the reservation details data.
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末がサーバにレストラン情報をリクエストする。The device requests restaurant information from the server.
端末はデータベース管理システムに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。このリクエストには、ユーザの位置情報や好みのレストランの条件が含まれる。入力は予約内容とユーザの位置情報であり、出力はレストラン情報のリクエストである。The terminal sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in the database management system. This request includes the user's location information and preferred restaurant conditions. The input is the reservation details and the user's location information, and the output is a request for restaurant information.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバがレストラン情報を返す。The server returns the restaurant information.
サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をデータベースから取得し、端末に返す。返される情報には、レストランの名前、電話番号、住所などが含まれる。入力はレストラン情報のリクエストであり、出力はレストラン情報である。The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from the database, and returns it to the terminal. The returned information includes the restaurant's name, phone number, address, etc. The input is a request for restaurant information, and the output is the restaurant information.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末が自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて電話をかける。The device makes the call using an automatic dialing system.
端末は自動ダイヤルシステムを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。この処理はユーザの手を煩わせることなく行われる。入力はレストランの電話番号であり、出力は電話接続の確立である。The terminal uses an automatic dialing system to automatically call the restaurant's phone number, without any user intervention. The input is the restaurant's phone number, and the output is the establishment of a telephone connection.
ステップ7:Step 7:
端末が予約内容を音声で伝える。The device will announce the reservation details aloud.
電話が接続されると、端末は音声合成技術を使用して、事前に抽出した予約内容を音声でレストランに伝える。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声が再生される。入力は予約内容のデータであり、出力は音声メッセージである。When the phone is connected, the device uses voice synthesis technology to verbally communicate the reservation details extracted in advance to the restaurant. For example, a voice may be played saying, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7 p.m." The input is the reservation details data, and the output is a voice message.
(応用例2)(Application example 2)
次に、形態例2の応用例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマートデバイス14を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 2 of embodiment example 2 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムや予約システムは、ユーザーが手動で操作する必要があり、利便性に欠ける点があった。また、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を活用して最適な提案を行う機能が不足していたため、ユーザーの要望に迅速かつ的確に応えることが難しかった。さらに、音声認識技術や自動ダイヤルシステムを効果的に組み合わせることで、ユーザー体験を向上させることが求められていた。Conventional navigation and reservation systems required users to operate them manually, which made them less convenient. They also lacked the functionality to utilize the user's past behavioral history to make optimal suggestions, making it difficult to respond to user requests quickly and accurately. Furthermore, there was a need to effectively combine voice recognition technology and an automatic dialing system to improve the user experience.
応用例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段と、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段と、音声フィードバックを提供する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーは音声指示のみで目的地の検索や予約を行うことができ、過去の行動履歴に基づいた最適な提案を受けることが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for understanding the user's requests using voice recognition technology, means for making reservations using an automatic dialing system, means for learning the user's past behavioral history and making optimal suggestions, and means for providing voice feedback. This allows the user to search for and make reservations at destinations using only voice instructions, and to receive optimal suggestions based on the user's past behavioral history.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報を収集し、解析し、理解するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to the methods and techniques used to collect, analyze, and understand information.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods and technologies for searching for an appropriate location based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた情報やデータを指す。"Search results" refers to the information or data obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、検索結果に基づいて最終的な目的地を決定するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to the method or technology for determining a final destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道案内を行うための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods and technologies for providing directions to a set destination.
「音声認識技術」とは、音声を解析し、テキストやコマンドに変換する技術を指す。"Voice recognition technology" refers to the technology that analyzes voice and converts it into text or commands.
「自動ダイヤルシステム」とは、指定された電話番号に自動的に電話をかけるシステムを指す。"Automatic dialing system" refers to a system that automatically dials a specified telephone number.
「予約を行う手段」とは、指定された場所やサービスの予約を自動的に行うための方法や技術を指す。"Means of making a reservation" refers to methods or technologies for automatically making a reservation for a specified location or service.
「過去の行動履歴」とは、ユーザーが以前に行った行動や選択の記録を指す。"Past behavioral history" refers to records of actions and choices a user has previously made.
「最適な提案を行う手段」とは、過去の行動履歴や現在の要望に基づいて、ユーザーに最も適した選択肢を提示するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of making optimal suggestions" refers to methods and technologies for presenting the most suitable options to users based on their past behavioral history and current needs.
「音声フィードバックを提供する手段」とは、システムが音声を用いてユーザーに情報や結果を伝えるための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing audio feedback" refers to methods or technologies that allow a system to communicate information or results to a user using audio.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、以下のような構成を持つ。サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段、音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段、自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段、音声フィードバックを提供する手段を含む。A system for implementing this invention has the following configuration: The server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for understanding the user's requests using voice recognition technology, means for making reservations using an automatic dialing system, means for learning the user's past behavioral history and making optimal suggestions, and means for providing voice feedback.
プログラムの処理の説明Explanation of program processing
ハードウェアとソフトウェアHardware and software
このシステムは、スマートフォンのマイクとスピーカーをハードウェアとして使用する。また、音声認識にはspeech_recognitionライブラリ、音声フィードバックにはpyttsx3ライブラリ、データ通信にはrequestsライブラリを使用する。The system uses the smartphone's microphone and speaker as hardware. It also uses the speech_recognition library for voice recognition, the pyttsx3 library for voice feedback, and the requests library for data communication.
データ加工とデータ演算Data processing and data calculations
1. 音声認識: ユーザーがスマートフォンのマイクに向かって要望を話すと、speech_recognitionライブラリがその音声をテキストに変換する。1. Speech recognition: When the user speaks their request into the smartphone's microphone, the speech_recognition library converts the speech into text.
2. 要望の解析: 変換されたテキストを解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。例えば、「ピザを注文して」という要望を解析する。2. Request Analysis: Analyze the converted text to understand the user's request. For example, analyze the request "order a pizza."
3. 予約の実行: 要望に基づいて、requestsライブラリを使用してフードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信する。注文が成功した場合、pyttsx3ライブラリを使用して音声フィードバックを提供する。3. Execute reservation: Based on the request, send the order to the food delivery API using the requests library. If the order is successful, provide audio feedback using the pyttsx3 library.
4. 行動履歴の学習: ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、次回以降の最適な提案を行う。4. Learning behavioral history: Learns the user's past behavioral history and provides optimal suggestions for future visits.
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「ピザを注文して」と言った場合、システムは以下のように動作する。For example, if a user says "order a pizza," the system would do the following:
1. ユーザーの音声をマイクで取得する。1. Capture the user's voice using the microphone.
2. 音声をテキストに変換し、「ピザを注文して」というテキストを得る。2. Convert speech to text and get the text "Order pizza."
3. テキストを解析し、「ピザ」の注文を特定する。3. Analyze the text to identify "pizza" orders.
4. フードデリバリーAPIに「ピザ」の注文を送信する。4. Send an order for "Pizza" to the food delivery API.
5. 注文が成功した場合、「ピザの注文が完了しました」と音声でフィードバックする。5. If the order is successful, audio feedback will be provided saying "Your pizza order has been completed."
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
「ユーザーが「ピザを注文して」と言った場合、音声認識技術を用いて音声をテキストに変換し、フードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信するプログラムを作成してください。注文が成功した場合、音声で「ピザの注文が完了しました」とフィードバックしてください。」"When a user says, 'Order a pizza,' please create a program that uses voice recognition technology to convert the speech to text and send the order to the food delivery API. If the order is successful, please provide voice feedback saying, 'The pizza order has been completed.'"
このようにして、ユーザーは音声指示のみで目的地の検索や予約を行うことができ、過去の行動履歴に基づいた最適な提案を受けることが可能となる。In this way, users can search for and book destinations using only voice commands, and receive optimal suggestions based on their past travel history.
応用例2における特定処理の流れについて図14を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 2 is explained using Figure 14.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのマイクに向かって要望を話す。The user speaks their request into the smartphone's microphone.
入力: ユーザの音声。Input: User's voice.
出力: マイクで取得された音声データ。Output: Audio data captured by the microphone.
具体的な動作: ユーザが「ピザを注文して」と話すと、スマートフォンのマイクがその音声をキャプチャする。What happens: When a user says "order a pizza," the smartphone's microphone captures the audio.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末がspeech_recognitionライブラリを使用して音声データをテキストに変換する。The device uses the speech_recognition library to convert the voice data into text.
入力: マイクで取得された音声データ。Input: Audio data captured by the microphone.
出力: テキストデータ(例:「ピザを注文して」)。Output: Text data (e.g. "order pizza").
具体的な動作: 音声認識エンジンが音声データを解析し、対応するテキストに変換する。Specific operation: The speech recognition engine analyzes the voice data and converts it into corresponding text.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末がテキストデータを解析し、ユーザの要望を理解する。The device analyzes the text data and understands the user's needs.
入力: テキストデータ(例:「ピザを注文して」)。Input: Text data (e.g. "order pizza").
出力: 要望の解析結果(例:「ピザの注文」)。Output: Analysis of the request (e.g. "order pizza").
具体的な動作: テキスト解析エンジンが「ピザを注文して」というテキストを解析し、「ピザの注文」という要望を特定する。Specific behavior: The text analysis engine analyzes the text "order a pizza" and identifies the request "order a pizza."
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末がrequestsライブラリを使用してフードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信する。The device uses the requests library to send the order to the food delivery API.
入力: 要望の解析結果(例:「ピザの注文」)。Input: Analysis of the request (e.g. "order pizza").
出力: APIへの注文リクエストとそのレスポンス。Output: The order request to the API and its response.
具体的な動作: フードデリバリーAPIに対して「ピザの注文」を含むリクエストを送信し、注文が成功したかどうかのレスポンスを受け取る。Specific behavior: Send a request to the food delivery API including "order pizza" and receive a response indicating whether the order was successful.
ステップ5:Step 5:
端末がpyttsx3ライブラリを使用して音声フィードバックを提供する。The device provides audio feedback using the pyttsx3 library.
入力: APIからのレスポンス(例:注文成功)Input: Response from the API (e.g. order successful)
出力: 音声フィードバック(例:「ピザの注文が完了しました。」)Output: Audio feedback (e.g. "Your pizza order is complete.")
具体的な動作: 音声合成エンジンが「ピザの注文が完了しました」というメッセージを生成し、スマートフォンのスピーカーを通じてユーザに伝える。Specific action: The speech synthesis engine generates the message "Your pizza order has been completed" and conveys it to the user through the smartphone speaker.
ステップ6:Step 6:
サーバがユーザの過去の行動履歴を学習し、次回以降の最適な提案を行う。The server learns the user's past behavioral history and makes optimal suggestions for future visits.
入力: ユーザの行動履歴データ。Input: User behavioral history data.
出力: 学習結果に基づく提案データ。Output: Proposed data based on learning results.
具体的な動作: サーバがユーザの過去の注文履歴を解析し、次回の注文時に最適なレストランやメニューを提案するためのデータを生成する。Specific operation: The server analyzes the user's past ordering history and generates data to suggest the best restaurant and menu for the next time they order.
更に、ユーザの感情を推定する感情エンジンを組み合わせてもよい。すなわち、特定処理部290は、感情特定モデル59を用いてユーザの感情を推定し、ユーザの感情を用いた特定処理を行うようにしてもよい。Furthermore, an emotion engine that estimates the user's emotion may be combined. That is, the
「形態例1」"Example 1"
本発明の一実施形態として、感情エンジンを組み込んだナビゲーションシステムがある。このシステムは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を認識し、それを考慮に入れて目的地をサーチする。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」という要望を出した場合、その声のトーンが明るければ、システムは活気のあるレストランを、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば、静かなレストランを推薦する。One embodiment of the present invention is a navigation system incorporating an emotion engine. This system recognizes emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc., and searches for a destination taking these into consideration. For example, if a user requests, "Find a nice restaurant nearby," the system will recommend a lively restaurant if the user's tone of voice is cheerful, and a quiet restaurant if the user's tone of voice is sad.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
また、感情エンジンを組み込んだスマートフォン用のアプリケーションも本発明の一実施形態である。このアプリケーションは、ユーザーのテキスト入力や音声入力から感情を認識し、それを考慮に入れてサービスを提供する。例えば、ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力した場合、その感情を認識して、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランや、ユーザーが好きな料理を提供するレストランを推薦する。Another embodiment of the present invention is a smartphone application incorporating an emotion engine. This application recognizes emotions from the user's text and voice input, and provides services taking these into consideration. For example, if the user inputs, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," the application recognizes the emotion and recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere and restaurants that serve the user's favorite dishes.
以下に、各形態例の処理の流れについて説明する。The process flow for each example is explained below.
「形態例1」"Example 1"
ステップ1:ユーザーがナビゲーションシステムに対して音声で要望を出す。Step 1: The user issues a verbal request to the navigation system.
ステップ2:感情エンジンがユーザーの声のトーン、表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を認識する。Step 2: The emotion engine recognizes the user's emotions from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc.
ステップ3:システムが認識した感情を考慮に入れて、目的地をサーチする。Step 3: Search for destinations, taking into account the emotions the system recognizes.
ステップ4:システムがサーチ結果をユーザーに提示する。Step 4: The system presents the search results to the user.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
ステップ1:ユーザーがスマートフォン用のアプリケーションに対してテキスト入力や音声入力で要望を出す。Step 1: The user submits a request to a smartphone application via text or voice input.
ステップ2:感情エンジンがユーザーのテキスト入力や音声入力から感情を認識する。Step 2: The emotion engine recognizes emotions from the user's text or voice input.
ステップ3:アプリケーションが認識した感情を考慮に入れて、サービスを提供する。Step 3: The application takes into account the emotions it recognizes and provides a service.
ステップ4:アプリケーションが提供するサービスの結果をユーザーに提示する。Step 4: Present the user with the results of the services provided by the application.
(実施例1)(Example 1)
次に、形態例1の実施例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマートデバイス14を「端末」と称する。Next, a first embodiment of the first embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮した目的地の推薦が難しく、また、最適なルート計算や音声入力の解析が十分に行われないことが多かった。その結果、ユーザーの満足度が低下し、運転中の安全性も確保されにくいという課題があった。With conventional navigation systems, it was difficult to recommend destinations that took into account the user's detailed requests and feelings, and they often did not adequately calculate optimal routes or analyze voice input. As a result, there were issues with low user satisfaction and difficulty in ensuring safety while driving.
実施例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する手段と、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に最適なルートを計算する手段と、音声入力を解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮した目的地の推薦が可能となり、最適なルート計算や音声入力の解析も行われるため、ユーザーの満足度が向上し、運転中の安全性も確保される。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's emotions and recommending a destination based thereon, means for calculating an optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results, and means for analyzing voice input and understanding the user's requests. This makes it possible to recommend a destination taking into account the user's detailed requests and emotions, and also calculates an optimal route and analyzes voice input, thereby improving user satisfaction and ensuring safety while driving.
「情報源」とは、データを提供するための基となる場所やシステムであり、例えば、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースを指す。An "information source" is a source or system that provides data, such as a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available.
「学習する手段」とは、取得した情報を基に機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを解析し、パターンや特徴を抽出するプロセスを指す。"Means of learning" refers to the process of using machine learning algorithms to analyze data based on acquired information and extract patterns and features.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて出す具体的なリクエストを指す。"User specific requests" refers to specific requests made by users based on their specific conditions or preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースから検索するプロセスを指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to the process of searching a database for an appropriate destination based on the user's request.
「サーチ結果」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて検索された目的地の情報を指す。"Search results" refers to destination information searched for based on a user's request.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果を基にユーザーの目的地を決定し、その情報をシステムに登録するプロセスを指す。"Means of setting a destination" refers to the process of determining the user's destination based on search results and registering that information in the system.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地への道順をユーザーに案内するためのシステムや方法を指す。"Means for providing navigation" refers to a system or method for guiding a user to a set destination.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を解析し、それを理解するプロセスを指す。"Means of recognizing emotions" refers to the process of analyzing and understanding the emotions of the user from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc.
「最適なルートを計算する手段」とは、ユーザーの現在位置と目的地を基に、最も効率的な道順を計算するプロセスを指す。"Means of calculating optimal route" refers to the process of calculating the most efficient route based on the user's current location and destination.
「音声入力を解析する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換し、その内容を理解するための技術や方法を指す。"Means of analyzing voice input" refers to the technology or method for converting a user's voice into text and understanding its content.
本発明は、車載用のナビゲーションシステムに関するものであり、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮して最適な目的地を推薦し、ナビゲーションを提供するシステムである。このシステムは、サーバ、端末、ユーザーの三者が連携して動作する。The present invention relates to an in-vehicle navigation system that provides navigation by recommending optimal destinations while taking into account the user's detailed requests and feelings. This system operates in cooperation with a server, a terminal, and a user.
情報の取得と学習Acquiring and learning information
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得する。このデータベースは、例えば、一般的な地図サービスAPIや評価情報提供サービスAPIを通じてアクセスする。サーバは、取得した情報を機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TENSORFLOW(登録商標)やPyTorch)を用いて学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価や駐車場の有無などの特徴量を抽出し、これをモデルに入力して学習を行う。The server obtains information from a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether or not parking is available. This database is accessed, for example, through a general map service API or a rating information provision service API. The server learns from the obtained information using a machine learning algorithm (for example, TENSORFLOW (registered trademark) or PyTorch). Specifically, it extracts features such as the restaurant's rating and whether or not parking is available, and inputs these into a model for learning.
ユーザーの要望解析Analysis of user needs
端末は、ユーザーからの質問や要望を音声入力として受け取る。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と話しかける。端末は、音声認識技術(例えば、一般的な音声認識API)を用いて音声をテキストに変換する。変換されたテキストは、自然言語処理技術(例えば、一般的な自然言語処理モデル)を用いて解析される。解析結果として、ユーザーの要望が「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図であることを理解する。The device receives questions and requests from the user as voice input. For example, the user says, "Find a nice restaurant nearby." The device converts the voice into text using voice recognition technology (e.g., a general voice recognition API). The converted text is analyzed using natural language processing technology (e.g., a general natural language processing model). As a result of the analysis, it is understood that the user's request is intended to "find a nice restaurant."
目的地のサーチSearch for destinations
サーバは、解析結果に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースからサーチする。例えば、「美味しいレストラン」をキーワードにデータベースを検索する。サーバは、感情エンジンを用いて、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方から感情を認識する。例えば、ユーザーの声のトーンが明るければ、活気のあるレストランを推薦し、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば、静かなレストランを推薦する。The server then searches the database for an appropriate destination based on the analysis results. For example, it searches the database using the keyword "delicious restaurant." The server uses an emotion engine to recognize emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, and choice of words. For example, if the user's tone of voice is cheerful, it will recommend a lively restaurant, and if the tone of voice is sad, it will recommend a quiet restaurant.
ルートの計算と設定Calculate and set route
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。例えば、一般的な地図サービスAPIを用いてルート計算を行う。計算されたルート情報は端末に送信され、目的地が設定される。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location (GPS information) and the search results. For example, the route is calculated using a general map service API. The calculated route information is sent to the device, and the destination is set.
ナビゲーションの提供Provide navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを音声ガイダンスシステム(例えば、一般的なナビゲーションアプリ)を用いて提供する。具体的には、音声で「次の交差点を右折してください」などの指示を出す。ユーザーは、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。The device provides navigation to the set destination using a voice guidance system (e.g., a general navigation app). Specifically, instructions such as "Turn right at the next intersection" are given by voice. The user is safely guided to the destination even while driving.
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と音声入力を行った場合、以下のような具体的な動作が行われる。For example, if a user voice-inputs, "Find a good restaurant nearby," the following specific actions will occur:
1. 端末は、ユーザーの音声を受け取り、音声認識APIを用いてテキストに変換する。1. The device receives the user's voice and converts it into text using a speech recognition API.
2. 端末は、変換されたテキストを自然言語処理モデルに入力し、「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図を解析する。2. The device inputs the converted text into a natural language processing model and analyzes the intent of "find a good restaurant."
3. サーバは、解析結果を受け取り、データベースから「美味しいレストラン」を検索する。3. The server receives the analysis results and searches the database for "good restaurants."
4. サーバは、ユーザーの声のトーンを解析し、明るいトーンであれば活気のあるレストランを、落ち込んだトーンであれば静かなレストランを推薦する。4. The server analyzes the tone of the user's voice and recommends lively restaurants if the tone is cheerful, and quiet restaurants if the tone is depressed.
5. サーバは、地図サービスAPIを用いてユーザーの現在位置から目的地までの最適なルートを計算する。5. The server uses the map service API to calculate the optimal route from the user's current location to the destination.
6. 端末は、計算されたルート情報を受け取り、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーにナビゲーションを提供する。6. The device receives the calculated route information and provides navigation to the user using a voice guidance system.
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
「ユーザーが近くの美味しいレストランを探してと音声入力を行った場合、声のトーンが明るければ活気のあるレストランを、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば静かなレストランを推薦するシステムを設計してください。」"If a user requests a nearby restaurant by voice input, design a system that recommends lively restaurants if the user's voice tone is cheerful, and quiet restaurants if the user's voice tone is depressed."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情や要望に応じた最適なナビゲーションが提供される。In this way, optimal navigation is provided based on the user's emotions and needs.
実施例1における特定処理の流れについて図15を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 1 is explained using Figure 15.
ステップ1:Step 1:
情報の取得と学習Acquiring and learning information
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得する。The server retrieves information from a database that includes information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available.
入力:データベースからの情報(例:レストランの評価、駐車場の有無)Input: Information from a database (e.g. restaurant ratings, availability of parking)
データ加工:取得した情報を機械学習アルゴリズム(例:TensorFlow、PyTorch)を用いて学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価や駐車場の有無などの特徴量を抽出し、これをモデルに入力して学習を行う。Data processing: The acquired information is trained using a machine learning algorithm (e.g. TensorFlow, PyTorch). Specifically, features such as restaurant ratings and whether or not there is parking are extracted, and these are input into the model for training.
出力:学習済みモデルOutput: Trained model
ステップ2:Step 2:
ユーザーの要望解析Analysis of user needs
端末は、ユーザーからの質問や要望を音声入力として受け取る。The device receives questions and requests from the user as voice input.
入力:ユーザーの音声入力(例:「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」)Input: User's voice input (e.g. "Find good restaurants nearby")
データ加工:音声認識技術(例:音声認識API)を用いて音声をテキストに変換する。変換されたテキストを自然言語処理技術(例:自然言語処理モデル)を用いて解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。Data processing: Convert speech to text using speech recognition technology (e.g. speech recognition API). Analyze the converted text using natural language processing technology (e.g. natural language processing model) to understand the user's needs.
出力:解析結果(例:「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図)Output: Analysis results (e.g., the intent "find a good restaurant")
ステップ3:Step 3:
目的地のサーチSearch for a destination
サーバは、解析結果に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースからサーチする。The server searches the database for appropriate destinations based on the analysis results.
入力:解析結果(例:「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図)Input: Analysis results (e.g., the intent to "find a good restaurant")
データ加工:データベースから「美味しいレストラン」を検索する。感情エンジンを用いて、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方から感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する。Data processing: Search for "good restaurants" from a database. Using an emotion engine, recognize emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, and choice of words, and recommend destinations based on that.
出力:サーチ結果(例:活気のあるレストラン、静かなレストラン)Output: Search results (e.g. lively restaurants, quiet restaurants)
ステップ4:Step 4:
ルートの計算と設定Route calculation and setting
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location (GPS information) and the search results.
入力:ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)、サーチ結果Input: User's current location (GPS information), search results
データ加工:地図サービスAPIを用いて最適なルートを計算する。Data processing: Calculate the optimal route using a map service API.
出力:計算されたルート情報Output: Calculated route information
ステップ5:Step 5:
ナビゲーションの提供Providing navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて提供する。The device uses a voice guidance system to provide navigation to the set destination.
入力:計算されたルート情報Input: Calculated route information
データ加工:音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに対して「次の交差点を右折してください」などの指示を出す。Data processing: Using a voice guidance system, give instructions to the user such as "Turn right at the next intersection."
出力:音声ガイダンスOutput: Audio guidance
具体的な動作:ユーザーは、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。Specific operation: Users are safely guided to their destination while driving.
(応用例1)(Application example 1)
次に、形態例1の応用例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマートデバイス14を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 1 of embodiment example 1 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの感情状態を考慮せずに目的地を提案するため、ユーザーの現在の気分や状況に適した目的地を提供することができなかった。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいた最適なルートを提供することができず、ユーザーの満足度を向上させることが困難であった。Conventional navigation systems suggest destinations without taking the user's emotional state into account, making it impossible to provide a destination that suits the user's current mood or situation. In addition, they were unable to provide an optimal route based on the user's emotions, making it difficult to improve user satisfaction.
応用例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes a means for learning information from various information sources, a means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, a means for setting a destination based on the search results, a means for providing navigation to the set destination, a means for recognizing the user's emotions, and a means for suggesting a destination based on the emotion recognition results. This makes it possible to suggest and navigate to the optimal destination according to the user's emotional state.
「情報源」とは、データや情報を提供する元となる媒体やシステムのことである。An "information source" is a medium or system that provides data or information.
「学習する手段」とは、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて情報を解析し、パターンや知識を獲得するための方法である。A "means of learning" is a method for analyzing information and acquiring patterns and knowledge using machine learning algorithms.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望のことである。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user desires.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための方法である。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to a method for searching for an appropriate destination based on the user's requirements.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補のことである。"Search results" refers to destination candidates obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果から最適な目的地を選び、設定するための方法である。"Method of setting a destination" refers to the method for selecting and setting the optimal destination from the search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地への道順を案内するための方法である。"Means of providing navigation" refers to a method for providing directions to a set destination.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情などから感情を解析し、認識するための方法である。"Means of recognizing emotions" refers to a method for analyzing and recognizing emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, etc.
「感情認識結果」とは、感情を認識する手段によって得られたユーザーの感情状態のことである。"Emotion recognition result" refers to the user's emotional state obtained by the emotion recognition means.
「目的地を提案する手段」とは、感情認識結果に基づいてユーザーに適した目的地を推薦するための方法である。"Means for suggesting destinations" refers to a method for recommending suitable destinations to users based on emotion recognition results.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、以下のような構成を持つ。まず、サーバは様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段を備えている。具体的には、機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlowやPyTorch)を用いて、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを解析し、パターンや知識を獲得する。A system for implementing this invention has the following configuration. First, the server has a means for learning information from various information sources. Specifically, a machine learning algorithm (e.g., TensorFlow or PyTorch) is used to analyze data such as restaurant rating information and the availability of parking spaces, and to acquire patterns and knowledge.
次に、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段を備えている。この手段は、自然言語処理技術(例えば、BERTやGPT-3(登録商標))を用いてユーザーの音声コマンドを解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と言った場合、その要望を解析し、適切な目的地を検索する。Next, it is equipped with a means for searching for destinations based on the user's detailed requests. This means uses natural language processing technology (e.g., BERT or GPT-3 (registered trademark)) to analyze the user's voice commands and understand the user's requests. For example, if the user says, "Find a good restaurant nearby," the request is analyzed and an appropriate destination is searched for.
さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段を備えている。サーバは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補から最適な目的地を選び、設定する。この際、ユーザーの現在位置を考慮し、GPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算する。Furthermore, it is equipped with a means for setting a destination based on the search results. The server selects and sets the most suitable destination from the candidate destinations obtained by the search. At this time, it takes into account the user's current location and calculates the optimal route using GPS technology.
また、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段を備えている。サーバは、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へ到達することができる。The system also includes a means for providing navigation to the set destination. The server uses a voice guidance system to guide the user to the destination. This allows the user to reach the destination safely even while driving.
さらに、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段を備えている。サーバは、マイクロフォンとカメラを使用してユーザーの声のトーンや表情をリアルタイムで収集し、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて感情を解析する。例えば、TensorFlowを使用して音声データを解析し、ユーザーの感情状態を分類する。Furthermore, it has a means of recognizing the user's emotions. The server uses a microphone and camera to collect the user's tone of voice and facial expressions in real time, and then uses machine learning algorithms to analyze emotions. For example, it uses TensorFlow to analyze voice data and classify the user's emotional state.
感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段も備えている。サーバは、感情認識結果を基に、ユーザーの現在の感情状態に最も適した目的地を推薦する。例えば、ユーザーが明るいトーンで話している場合、活気のあるレストランを推薦し、落ち着いたトーンで話している場合は静かなカフェを推薦する。The system also has a means of suggesting destinations based on emotion recognition results. The server uses the emotion recognition results to recommend a destination that best suits the user's current emotional state. For example, if the user speaks in a bright tone, the server can recommend a lively restaurant, and if the user speaks in a calm tone, the server can recommend a quiet cafe.
具体例として、ユーザーが「今日はリラックスしたいから、静かなカフェを探して」と言った場合、システムはユーザーの声のトーンが落ち着いていることを認識し、静かなカフェを推薦する。その後、GPSを使用して最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスでユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。For example, if a user says, "I want to relax today, so find me a quiet cafe," the system will recognize that the user's tone of voice is calm and recommend a quiet cafe. It will then use GPS to calculate the optimal route and guide the user to their destination with voice guidance.
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが挙げられる。Examples of prompts include:
「ユーザーの声のトーンと表情を解析し、感情を認識して最適な目的地を提案するナビゲーションシステムを開発してください。ユーザーが「今日はリラックスしたいから、静かなカフェを探して」と言った場合、システムはユーザーの声のトーンが落ち着いていることを認識し、静かなカフェを推薦します。その後、GPSを使用して最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスでユーザーを目的地へ誘導します。」"Develop a navigation system that analyzes the user's tone of voice and facial expressions, recognizes emotions, and suggests the best destination. If the user says, 'I want to relax today, so I'm looking for a quiet cafe,' the system will recognize that the user's tone of voice is calm and recommend a quiet cafe. It will then use GPS to calculate the best route and guide the user to their destination with voice guidance."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが可能となる。In this way, it becomes possible to suggest and navigate to the most suitable destination based on the user's emotional state.
応用例1における特定処理の流れについて図16を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 1 is explained using Figure 16.
ステップ1:Step 1:
サーバは、マイクロフォンとカメラを使用してユーザーの声のトーンと表情をリアルタイムで収集する。入力はユーザーの音声と映像データであり、出力は前処理された音声データと映像データである。具体的には、ノイズ除去や顔認識を行い、解析に適した形式にデータを変換する。The server uses a microphone and camera to collect the user's tone of voice and facial expressions in real time. The input is the user's audio and video data, and the output is preprocessed audio and video data. Specifically, it performs noise removal and facial recognition, and converts the data into a format suitable for analysis.
ステップ2:Step 2:
サーバは、前処理された音声データと映像データを機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlow)に入力し、ユーザーの感情を認識する。入力は前処理された音声データと映像データであり、出力はユーザーの感情状態(例えば、喜び、悲しみ、怒りなど)である。具体的には、音声のトーンや表情の特徴を解析し、感情を分類する。The server inputs the preprocessed audio and video data into a machine learning algorithm (e.g., TensorFlow) to recognize the user's emotions. The input is the preprocessed audio and video data, and the output is the user's emotional state (e.g., joy, sadness, anger, etc.). Specifically, the tone of the voice and facial features are analyzed to classify the emotion.
ステップ3:Step 3:
サーバは、ユーザーの音声コマンドを自然言語処理技術(例えば、BERTやGPT-3)を用いて解析する。入力はユーザーの音声コマンドであり、出力はユーザーの要望を理解したテキストデータである。具体的には、「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」といったコマンドを解析し、ユーザーの要望を抽出する。The server analyzes the user's voice command using natural language processing technology (e.g., BERT or GPT-3). The input is the user's voice command, and the output is text data that represents an understanding of the user's request. Specifically, it analyzes commands such as "Find a good restaurant nearby" and extracts the user's request.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバは、感情認識結果とユーザーの要望を基に、データベースから適切な目的地をサーチする。入力は感情認識結果とユーザーの要望テキストであり、出力は目的地の候補リストである。具体的には、ユーザーが明るいトーンで話している場合、活気のあるレストランをデータベースから検索する。The server searches the database for an appropriate destination based on the emotion recognition results and the user's request. The input is the emotion recognition results and the user's request text, and the output is a list of candidate destinations. Specifically, if the user is speaking in a bright tone, the database is searched for lively restaurants.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバは、サーチ結果から最適な目的地を選び、設定する。入力は目的地の候補リストであり、出力は設定された目的地である。具体的には、ユーザーの現在位置を考慮し、最も適した目的地を選択する。The server selects and sets the optimal destination from the search results. The input is a list of candidate destinations, and the output is the set destination. Specifically, it takes into account the user's current location and selects the most suitable destination.
ステップ6:Step 6:
サーバは、GPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算する。入力はユーザーの現在位置と設定された目的地であり、出力は最適なルート情報である。具体的には、地図データを使用して、最短経路や交通状況を考慮したルートを計算する。The server uses GPS technology to calculate the optimal route. The input is the user's current location and the set destination, and the output is optimal route information. Specifically, it uses map data to calculate the shortest route and a route that takes traffic conditions into account.
ステップ7:Step 7:
サーバは、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。入力は最適なルート情報であり、出力は音声ガイダンスである。具体的には、ユーザーに対して「次の交差点を右折してください」といった指示を音声で提供する。The server uses a voice guidance system to guide the user to the destination. The input is optimal route information, and the output is voice guidance. Specifically, it provides the user with voice instructions such as "Turn right at the next intersection."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが実現される。In this way, optimal destination suggestions and navigation can be achieved based on the user's emotional state.
(実施例2)(Example 2)
次に、形態例2の実施例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマートデバイス14を「端末」と称する。Next, a second embodiment of the second embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が困難であった。また、ユーザーが音声で予約を依頼した場合、自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了する機能が不足していた。これにより、ユーザーは手動で予約を行う必要があり、利便性が低かった。さらに、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行われておらず、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができなかった。Conventional navigation systems had difficulty providing services that took into account the detailed requests and emotions of users. In addition, when a user made a reservation by voice, the system lacked the functionality to automatically make a phone call to complete the reservation. This meant that users had to make the reservation manually, which was inconvenient. Furthermore, the system did not recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, which made it difficult to increase user satisfaction.
実施例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声を認識する手段と、音声認識結果を基にレストランを検索する手段と、自動で電話をかける手段と、予約を完了する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、感情に基づいてレストランを推薦する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が可能となり、音声による予約依頼に対して自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了することができる。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行うことができ、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's voice, means for searching for restaurants based on the voice recognition results, means for automatically making a phone call, means for completing a reservation, means for recognizing the user's emotions, and means for recommending restaurants based on the emotions. This makes it possible to provide a service that takes into account the user's specific requests and emotions, and a reservation can be completed by automatically making a phone call in response to a reservation request made via voice. It is also possible to recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報源から得られたデータを解析し、知識を蓄積するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to methods and techniques for analyzing data obtained from sources and accumulating knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods and technologies for searching for an appropriate location based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた情報やデータを指す。"Search results" refers to the information or data obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果を基にユーザーが訪れるべき場所を決定するための方法や技術を指す。"Destination setting means" refers to the methods and technologies that allow users to determine where they should visit based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道順や案内を提供するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods and technologies for providing directions and guidance to a set destination.
「音声を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声を解析してテキストデータに変換するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of voice recognition" refers to methods and technologies for analyzing a user's voice and converting it into text data.
「レストランを検索する手段」とは、音声認識結果を基に適切な飲食店を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for searching for restaurants" refers to methods and technologies for searching for appropriate restaurants based on voice recognition results.
「自動で電話をかける手段」とは、システムが自動的に電話を発信するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for making automatic phone calls" refers to methods or technologies that allow the system to automatically make phone calls.
「予約を完了する手段」とは、電話を通じて予約手続きを完了するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of completing a reservation" refers to the methods and technologies used to complete the reservation process over the telephone.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの入力や音声から感情を解析するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of emotion recognition" refers to methods and technologies for analyzing emotions from user input or voice.
「レストランを推薦する手段」とは、認識された感情に基づいて適切な飲食店を提案するための方法や技術を指す。"Restaurant recommendation means" refers to methods or technologies for suggesting appropriate dining options based on recognized sentiment.
本発明は、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供を実現するためのシステムである。このシステムは、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションとして実装され、ユーザーの音声やテキスト入力を基に、目的地の検索、予約、ナビゲーション、感情に基づくレストランの推薦を行う。The present invention is a system for providing services that take into account the detailed requests and emotions of users. This system is implemented as a smartphone application, and performs destination search, reservations, navigation, and emotion-based restaurant recommendations based on the user's voice and text input.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
ハードウェア:スマートフォン(iPhone(登録商標)、ANDROID(登録商標)端末など)Hardware: Smartphones (iPhone (registered trademark), Android (registered trademark) devices, etc.)
ソフトウェア:Software:
音声認識技術:音声をテキストに変換するために、音声認識APIを使用する。Speech recognition technology: Uses speech recognition APIs to convert speech to text.
レストラン検索:地図APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。Restaurant search: Use the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
自動ダイヤルシステム:自動的に電話をかけるために、通信APIを使用する。Automatic dialing system: Uses communications APIs to automatically place calls.
感情認識技術:ユーザーの入力から感情を解析するために、感情分析APIを使用する。Emotion recognition technology: Uses sentiment analysis APIs to analyze emotions from user input.
レストラン推薦:レビューサイトAPIを使用して、感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。Restaurant Recommendations: Use review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on sentiment.
システムの具体的な処理Specific processing of the system
ユーザーの要望に基づく予約機能Reservation function based on user requests
1. ユーザーがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「電話で予約して」と音声で指示を出す。1. The user launches the smartphone application and issues a voice command saying, "Make a reservation by phone."
2. 端末は音声認識APIを使用して、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換する。2. The device uses a speech recognition API to convert the user's speech into text.
3. 端末は地図APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。3. The device uses the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
4. 端末は通信APIを使用して、検索結果から選ばれたレストランに自動で電話をかける。4. The device uses a communications API to automatically call the restaurant selected from the search results.
5. 端末は電話を通じてレストランに予約内容を伝え、予約を完了する。5. The terminal then transmits the reservation details to the restaurant via telephone, completing the reservation.
具体例:Example:
ユーザーが「電話で予約して」と言う。The user says, "Make a reservation by phone."
端末は音声認識APIを使用して音声をテキストに変換する。The device uses a speech recognition API to convert speech to text.
端末:「音声を認識中です。」Device: "Recognizing voice."
端末は地図APIを使用して近くのレストランを検索する。The device uses the map API to search for nearby restaurants.
端末:「近くのレストランを検索中です。」Device: "Searching for nearby restaurants."
端末は通信APIを使用して自動的にレストランに電話をかける。The device will automatically call the restaurant using a communications API.
端末:「レストランに電話をかけています。」Device: "Calling restaurant."
端末は予約が完了したことをユーザーに通知する。The device will notify the user that the reservation is complete.
端末:「予約が完了しました。」Device: "Reservation completed."
感情エンジンを用いたサービス提供Providing services using emotion engines
1. ユーザーがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」とテキストまたは音声で入力する。1. The user launches the smartphone application and inputs via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
2. 端末は感情分析APIを使用して、ユーザーの入力から感情を認識する。2. The device uses the sentiment analysis API to recognize emotions from user input.
3. 端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用して、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。3. The device uses review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on the user's sentiment.
具体例:Example:
ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力する。The user types, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
端末は感情分析APIを使用して感情を認識する。The device uses an emotion analysis API to recognize emotions.
端末:「感情を分析中です。」Device: "Analyzing emotions."
端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用してリラックスできるレストランを推薦する。The device uses review site APIs to recommend relaxing restaurants.
端末:「リラックスできるレストランを探しています。」Device: "I'm looking for a relaxing restaurant."
端末:「こちらのレストランはいかがですか?(レストラン名)」Device: "How about this restaurant? (restaurant name)"
以上が、本発明のスマートフォン用アプリケーションの具体的な実施形態である。このシステムにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が可能となり、音声による予約依頼に対して自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了することができる。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行うことができ、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができる。The above is a specific embodiment of the smartphone application of the present invention. This system makes it possible to provide services that take into account the detailed requests and emotions of the user, and can complete reservations by automatically making a phone call in response to a voice reservation request. It can also recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
実施例2における特定処理の流れについて図17を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 2 is explained using Figure 17.
ユーザーの要望に基づく予約機能Reservation function based on user requests
処理ステップProcessing steps
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「電話で予約して」と音声で指示を出す。The user launches the smartphone application and gives the voice command, "Make a reservation by phone."
入力:ユーザの音声指示Input: User's voice command
出力:音声データOutput: Audio data
具体的な動作:ユーザがアプリケーションを起動し、音声で「電話で予約して」と指示を出す。Specific operation: The user launches the application and issues the command "Make a reservation by phone" via voice.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末は音声認識APIを使用して、ユーザの音声をテキストに変換する。The device uses a speech recognition API to convert the user's speech into text.
入力:音声データInput: Audio data
出力:テキストデータOutput: Text data
具体的な動作:端末は音声データを音声認識APIに送信し、テキストデータを受け取る。Specific operation: The device sends voice data to the voice recognition API and receives text data.
端末:「音声を認識中です。」Device: "Recognizing voice."
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末は地図APIを使用して、ユーザの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。The device uses the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
入力:テキストデータ、ユーザの現在地情報Input: text data, user's current location information
出力:レストランのリストOutput: List of restaurants
具体的な動作:端末はユーザの現在地情報を取得し、地図APIにクエリを送信してレストランのリストを受け取る。Specific operation: The device obtains the user's current location information and sends a query to the map API to receive a list of restaurants.
端末:「近くのレストランを検索中です。」Device: "Searching for nearby restaurants."
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末は通信APIを使用して、検索結果から選ばれたレストランに自動で電話をかける。The device uses a communications API to automatically call the restaurant selected from the search results.
入力:レストランのリストEnter: List of restaurants
出力:通話開始Output: Start call
具体的な動作:端末は通信APIに電話番号と通話内容を送信し、通話を開始する。Specific operation: The device sends the phone number and call details to the communication API and starts the call.
端末:「レストランに電話をかけています。」Device: "Calling restaurant."
ステップ5:Step 5:
端末は電話を通じてレストランに予約内容を伝え、予約を完了する。The terminal then communicates the reservation details to the restaurant via telephone, completing the reservation.
入力:通話開始Enter: Start call
出力:予約完了通知Output: Reservation completion notification
具体的な動作:端末は通信APIを通じて通話を管理し、予約が完了したことをユーザに通知する。Specific operation: The device manages the call through the communication API and notifies the user that the reservation has been completed.
端末:「予約が完了しました。」Device: "Reservation completed."
感情エンジンを用いたサービス提供Providing services using emotion engines
処理ステップProcessing steps
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい。」とテキストまたは音声で入力する。The user launches a smartphone application and inputs, either by text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
入力:ユーザのテキストまたは音声入力Input: User text or voice input
出力:テキストデータOutput: Text data
具体的な動作:ユーザがアプリケーションを起動し、テキストまたは音声で「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい。」と入力する。Specific actions: The user launches the application and enters, via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末は感情分析APIを使用して、ユーザの入力から感情を認識する。The device uses a sentiment analysis API to recognize emotions from user input.
入力:テキストデータInput: Text data
出力:感情分析結果Output: Sentiment analysis results
具体的な動作:端末はテキストデータを感情分析APIに送信し、感情分析結果を受け取る。Specific operation: The device sends text data to the sentiment analysis API and receives the sentiment analysis results.
端末:「感情を分析中です。」Device: "Analyzing emotions."
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用して、ユーザの感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。The device uses review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on the user's sentiment.
入力:感情分析結果Input: Sentiment analysis results
出力:レストランの推薦リストOutput: A list of restaurant recommendations
具体的な動作:端末は感情分析結果を基にレビューサイトAPIにクエリを送信し、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランやユーザが好きな料理を提供するレストランのリストを受け取る。Specific operation: Based on the sentiment analysis results, the device sends a query to the review site API and receives a list of restaurants that have a relaxing atmosphere or serve the user's favorite cuisine.
端末:「リラックスできるレストランを探しています。」Device: "I'm looking for a relaxing restaurant."
端末:「こちらのレストランはいかがですか?(レストラン名)」Device: "How about this restaurant? (restaurant name)"
以上が、本発明のスマートフォン用アプリケーションの具体的な処理ステップである。The above are the specific processing steps of the smartphone application of the present invention.
(応用例2)(Application example 2)
次に、形態例2の応用例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマートデバイス14を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 2 of embodiment example 2 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムや予約システムは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮することができず、ユーザー体験が限定されていた。また、ユーザーが音声で要望を入力し、それに基づいて最適なサービスを推薦し、自動的に注文を行う機能が欠如していた。これにより、ユーザーが求めるサービスを迅速かつ的確に提供することが困難であった。Conventional navigation and reservation systems were unable to take into account the detailed requests and feelings of users, limiting the user experience. They also lacked the functionality to have users input their requests by voice, have the system recommend optimal services based on those requests, and automatically place orders. This made it difficult to quickly and accurately provide the services users wanted.
応用例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声入力を認識する手段と、認識された音声入力から感情を分析する手段と、感情分析の結果に基づいて最適なサービスを推薦する手段と、推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの要望や感情を考慮したサービスの提供が可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's voice input, means for analyzing emotions from the recognized voice input, means for recommending optimal services based on the results of the emotion analysis, and means for automatically placing an order for the recommended services. This makes it possible to provide services that take into account the user's requests and emotions.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報源から得られたデータを解析し、知識を蓄積するための方法や装置を指す。"Means of learning" refers to methods and devices for analyzing data obtained from sources and accumulating knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for searching for a destination" refers to a method or device for searching for an appropriate location based on a user's request.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索手段によって得られた情報の集合を指す。"Search Results" refers to the collection of information obtained through a search tool.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果から選ばれた場所を最終的な目的地として決定するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to a method or device for determining a location selected from the search results as the final destination.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道順や案内を提供するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for providing navigation" refers to a method or device for providing directions or guidance to a set destination.
「音声入力を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声をテキストデータに変換するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for recognizing voice input" refers to a method or device for converting a user's voice into text data.
「感情を分析する手段」とは、音声入力やテキストデータからユーザーの感情を解析するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for analyzing emotions" refers to a method or device for analyzing a user's emotions from voice input or text data.
「最適なサービスを推薦する手段」とは、感情分析の結果に基づいてユーザーに最も適したサービスを提案するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for recommending optimal services" refers to a method or device for suggesting the most suitable service to a user based on the results of sentiment analysis.
「自動的に注文を行う手段」とは、推薦されたサービスに対してユーザーの介入なしに注文を完了するための方法や装置を指す。"Automatic ordering means" refers to a method or device for completing an order for recommended services without user intervention.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、ユーザーの音声入力を認識し、感情を分析し、最適なサービスを推薦し、自動的に注文を行う一連の処理を行うものである。以下に、このシステムの具体的な実施形態を説明する。The system for implementing this invention performs a series of processes that recognize the user's voice input, analyze emotions, recommend optimal services, and automatically place an order. A specific embodiment of this system is described below.
システム構成System configuration
システムは、以下の主要なコンポーネントから構成される:The system consists of the following main components:
1. 音声認識モジュール:ユーザーの音声入力をテキストデータに変換する。具体的には、speech_recognitionライブラリを使用する。1. Speech recognition module: Converts the user's voice input into text data. Specifically, it uses the speech_recognition library.
2. 感情分析モジュール:音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを解析し、ユーザーの感情を分析する。具体的には、TextBlobライブラリを使用する。2. Sentiment analysis module: Analyzes the text data obtained from the voice recognition module and analyzes the user's emotions. Specifically, it uses the TextBlob library.
3. サービス推薦モジュール:感情分析の結果に基づいて、ユーザーに最適なサービスを推薦する。3. Service recommendation module: Recommend the most suitable services to users based on the results of sentiment analysis.
4. 自動注文モジュール:推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う。具体的には、requestsライブラリを使用してAPIエンドポイントに注文データを送信する。4. Auto-order module: Automatically places orders for recommended services. Specifically, it uses the requests library to send order data to an API endpoint.
処理の流れProcessing flow
1. 音声入力の認識:ユーザーがスマートフォンに向かって音声で要望を入力する。音声認識モジュールがこの音声をテキストデータに変換する。1. Voice input recognition: The user speaks their request into the smartphone. The voice recognition module converts this voice into text data.
2. 感情の分析:音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを感情分析モジュールに渡し、ユーザーの感情を解析する。2. Sentiment analysis: The text data obtained from the voice recognition module is passed to the sentiment analysis module to analyze the user's emotions.
3. サービスの推薦:感情分析の結果に基づいて、サービス推薦モジュールがユーザーに最適なサービスを選定し、推薦する。3. Service recommendation: Based on the results of sentiment analysis, the service recommendation module selects and recommends the most suitable services to the user.
4. 自動注文の実行:サービス推薦モジュールが選定したサービスに対して、自動注文モジュールが注文を行う。4. Executing automatic orders: The automatic ordering module places an order for the service selected by the service recommendation module.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
ハードウェア:スマートフォン、サーバHardware: smartphones, servers
ソフトウェア:speech_recognitionライブラリ、TextBlobライブラリ、requestsライブラリSoftware: speech_recognition library, TextBlob library, requests library
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と音声入力した場合、システムは以下のように動作する:For example, if a user says, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," the system will act as follows:
1. 音声認識モジュールが音声をテキストに変換し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」というテキストデータを生成する。1. The voice recognition module converts the voice into text and generates text data such as "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
2. 感情分析モジュールがこのテキストデータを解析し、ユーザーが疲れていることを認識する。2. The sentiment analysis module analyzes this text data and recognizes that the user is tired.
3. サービス推薦モジュールがリラックスできる雰囲気のレストランを推薦する。3. The service recommendation module recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere.
4. 自動注文モジュールが推薦されたレストランに対して自動的に注文を行う。4. The auto-order module automatically places orders from the recommended restaurants.
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
生成AIモデルへ入力するプロンプト文の例:Example of a prompt to input to a generative AI model:
ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい。」と音声入力した場合、感情分析を行い、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランを推薦し、自動的に注文を行うPythonプログラムを作成してください。If a user says, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," create a Python program that performs sentiment analysis, recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere, and automatically places the order.
応用例2における特定処理の流れについて図18を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 2 is explained using Figure 18.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンに向かって音声で要望を入力する。音声入力は、スマートフォンのマイクを通じて取得される。入力データは、ユーザの音声データである。The user speaks their request into the smartphone. The voice input is acquired through the smartphone's microphone. The input data is the user's voice data.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末の音声認識モジュールが、ユーザの音声データをテキストデータに変換する。具体的には、speech_recognitionライブラリを使用して音声データを解析し、テキストデータを生成する。出力データは、ユーザの音声をテキストに変換したものである。The device's voice recognition module converts the user's voice data into text data. Specifically, it uses the speech_recognition library to analyze the voice data and generate text data. The output data is the user's voice converted into text.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末の感情分析モジュールが、音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを受け取り、ユーザの感情を解析する。具体的には、TextBlobライブラリを使用してテキストデータの感情を分析する。入力データは、テキストデータであり、出力データは、感情分析の結果である。The terminal's sentiment analysis module receives the text data obtained from the voice recognition module and analyzes the user's sentiment. Specifically, it uses the TextBlob library to analyze the sentiment of the text data. The input data is the text data, and the output data is the result of the sentiment analysis.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバのサービス推薦モジュールが、感情分析の結果に基づいて、ユーザに最適なサービスを選定し、推薦する。入力データは、感情分析の結果であり、出力データは、推薦されたサービスの情報である。具体的には、感情がネガティブであればリラックスできるサービスを、ポジティブであれば人気のサービスを推薦する。The server's service recommendation module selects and recommends the most suitable service to the user based on the results of the sentiment analysis. The input data is the results of the sentiment analysis, and the output data is information about the recommended service. Specifically, if the sentiment is negative, a relaxing service is recommended, and if it is positive, a popular service is recommended.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバの自動注文モジュールが、サービス推薦モジュールから得られた推薦サービス情報を受け取り、自動的に注文を行う。具体的には、requestsライブラリを使用して、推薦されたサービスに対して注文データをAPIエンドポイントに送信する。入力データは、推薦されたサービスの情報であり、出力データは、注文の完了通知である。The server's automatic ordering module receives the recommended service information obtained from the service recommendation module and automatically places the order. Specifically, it uses the requests library to send order data for the recommended service to an API endpoint. The input data is information about the recommended service, and the output data is a notification of order completion.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末が、注文の完了通知をユーザに表示する。入力データは、注文の完了通知であり、出力データは、ユーザに表示される注文完了メッセージである。具体的には、スマートフォンの画面に注文が完了した旨のメッセージを表示する。The terminal displays a notification that the order is complete to the user. The input data is the notification that the order is complete, and the output data is an order completion message that is displayed to the user. Specifically, a message indicating that the order is complete is displayed on the smartphone screen.
特定処理部290は、特定処理の結果をスマートデバイス14に送信する。スマートデバイス14では、制御部46Aが、出力装置40に対して特定処理の結果を出力させる。マイクロフォン38Bは、特定処理の結果に対するユーザ入力を示す音声を取得する。制御部46Aは、マイクロフォン38Bによって取得されたユーザ入力を示す音声データをデータ処理装置12に送信する。データ処理装置12では、特定処理部290が音声データを取得する。The
データ生成モデル58は、いわゆる生成AI(Artificial Intelligence)である。データ生成モデル58の一例としては、ChatGPT(登録商標)(インターネット検索<URL: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt>)等の生成AIが挙げられる。データ生成モデル58は、ニューラルネットワークに対して深層学習を行わせることによって得られる。データ生成モデル58には、指示を含むプロンプトが入力され、かつ、音声を示す音声データ、テキストを示すテキストデータ、及び画像を示す画像データ等の推論用データが入力される。データ生成モデル58は、入力された推論用データをプロンプトにより示される指示に従って推論し、推論結果を音声データ及びテキストデータ等のデータ形式で出力する。ここで、推論とは、例えば、分析、分類、予測、及び/又は要約等を指す。The
生成AIの他の例としては、Gemini(登録商標)(インターネット検索<URL: https://gemini.google.com/?hl=ja>)が挙げられる。Another example of generative AI is Gemini (registered trademark) (Internet search <URL: https://gemini.google.com/?hl=ja>).
上記実施形態では、データ処理装置12によって特定処理が行われる形態例を挙げたが、本開示の技術はこれに限定されず、スマートデバイス14によって特定処理が行われるようにしてもよい。In the above embodiment, an example was given in which the specific processing is performed by the
[第2実施形態][Second embodiment]
図3には、第2実施形態に係るデータ処理システム210の構成の一例が示されている。Figure 3 shows an example of the configuration of a
図3に示すように、データ処理システム210は、データ処理装置12及びスマート眼鏡214を備えている。データ処理装置12の一例としては、サーバが挙げられる。As shown in FIG. 3, the
データ処理装置12は、コンピュータ22、データベース24、及び通信I/F26を備えている。コンピュータ22は、本開示の技術に係る「コンピュータ」の一例である。コンピュータ22は、プロセッサ28、RAM30、及びストレージ32を備えている。プロセッサ28、RAM30、及びストレージ32は、バス34に接続されている。また、データベース24及び通信I/F26も、バス34に接続されている。通信I/F26は、ネットワーク54に接続されている。ネットワーク54の一例としては、WAN(Wide Area Network)及び/又はLAN(Local Area Network)等が挙げられる。The
スマート眼鏡214は、コンピュータ36、マイクロフォン238、スピーカ240、カメラ42、及び通信I/F44を備えている。コンピュータ36は、プロセッサ46、RAM48、及びストレージ50を備えている。プロセッサ46、RAM48、及びストレージ50は、バス52に接続されている。また、マイクロフォン238、スピーカ240、及びカメラ42も、バス52に接続されている。The
マイクロフォン238は、ユーザ20が発する音声を受け付けることで、ユーザ20から指示等を受け付ける。マイクロフォン238は、ユーザ20が発する音声を捕捉し、捕捉した音声を音声データに変換してプロセッサ46に出力する。スピーカ240は、プロセッサ46からの指示に従って音声を出力する。The
カメラ42は、レンズ、絞り、及びシャッタ等の光学系と、CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)イメージセンサ又はCCD(Charge Coupled Device)イメージセンサ等の撮像素子とが搭載された小型デジタルカメラであり、ユーザ20の周囲(例えば、一般的な健常者の視界の広さに相当する画角で規定された撮像範囲)を撮像する。
通信I/F44は、ネットワーク54に接続されている。通信I/F44及び26は、ネットワーク54を介してプロセッサ46とプロセッサ28との間の各種情報の授受を司る。通信I/F44及び26を用いたプロセッサ46とプロセッサ28との間の各種情報の授受はセキュアな状態で行われる。The communication I/
図4には、データ処理装置12及びスマート眼鏡214の要部機能の一例が示されている。図4に示すように、データ処理装置12では、プロセッサ28によって特定処理が行われる。ストレージ32には、特定処理プログラム56が格納されている。Figure 4 shows an example of the main functions of the
特定処理プログラム56は、本開示の技術に係る「プログラム」の一例である。プロセッサ28は、ストレージ32から特定処理プログラム56を読み出し、読み出した特定処理プログラム56をRAM30上で実行する。特定処理は、プロセッサ28がRAM30上で実行する特定処理プログラム56に従って、特定処理部290として動作することによって実現される。The
ストレージ32には、データ生成モデル58及び感情特定モデル59が格納されている。データ生成モデル58及び感情特定モデル59は、特定処理部290によって用いられる。
スマート眼鏡214では、プロセッサ46によって受付出力処理が行われる。ストレージ50には、受付出力プログラム60が格納されている。プロセッサ46は、ストレージ50から受付出力プログラム60を読み出し、読み出した受付出力プログラム60をRAM48上で実行する。受付出力処理は、プロセッサ46がRAM48上で実行する受付出力プログラム60に従って、制御部46Aとして動作することによって実現される。In the
次に、データ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理について説明する。Next, we will explain the specific processing performed by the
「形態例1」"Example 1"
本発明の一実施形態として、車載用のナビゲーションシステムが考えられる。このシステムは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段として、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いる。具体的には、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得し、これを学習する。また、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段として、自然言語処理技術を用いる。ユーザーからの質問を解析し、それに基づいて適切な目的地をサーチする。さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段として、GPS技術を用いる。ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定する。最後に、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段として、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いる。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。One embodiment of the present invention is an in-vehicle navigation system. This system uses a machine learning algorithm as a means of learning information from various information sources. Specifically, information is acquired from a database that includes information such as restaurant reviews and the availability of parking spaces, and this information is learned. Natural language processing technology is also used as a means of searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests. Questions from the user are analyzed, and an appropriate destination is searched for based on the results. GPS technology is also used as a means of setting the destination based on the search results. The optimal route is calculated based on the user's current location and the search results, and the destination is set. Finally, a voice guidance system is used as a means of providing navigation to the set destination. This allows the user to be safely guided to their destination even while driving.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
本発明の別の実施形態として、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションが考えられる。このアプリケーションは、前述の車載用ナビゲーションシステムと同様の機能を持つが、さらにユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う機能を含む。具体的には、ユーザーが「電話で予約して」という要望を出した場合、システムは自動的に該当するレストランに電話をかけ、予約を行う。この機能は、音声認識技術と自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて実現される。Another embodiment of the present invention is a smartphone application. This application has the same functions as the in-car navigation system described above, but also includes a function for making reservations based on the user's request. Specifically, when a user requests to "make a reservation by phone," the system automatically calls the corresponding restaurant and makes the reservation. This function is realized using voice recognition technology and an automatic dialing system.
以下に、各形態例の処理の流れについて説明する。The process flow for each example is explained below.
「形態例1」"Example 1"
ステップ1:システムは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得し、これを機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて学習する。Step 1: The system learns information from various sources. Specifically, it obtains information from a database that includes information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available, and learns from this information using machine learning algorithms.
ステップ2:ユーザーからの細かい要望が入力されると、システムは自然言語処理技術を用いてこれを解析する。Step 2: Once the user has entered their detailed request, the system analyzes it using natural language processing technology.
ステップ3:解析結果に基づいて、システムは適切な目的地をサーチする。Step 3: Based on the analysis results, the system searches for suitable destinations.
ステップ4:サーチ結果とユーザーの現在位置を基に、システムはGPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定する。Step 4: Based on the search results and the user's current location, the system uses GPS technology to calculate the optimal route and set the destination.
ステップ5:設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供するため、システムは音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーを誘導する。Step 5: The system guides the user using the voice guidance system to provide navigation to the set destination.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
ステップ1:スマートフォン用のアプリケーションは、前述の車載用ナビゲーションシステムと同様の機能を持つ。Step 1: The smartphone application has the same functions as the in-car navigation system mentioned above.
ステップ2:ユーザーが「電話で予約して」という要望を出した場合、システムは自動的に該当するレストランに電話をかける。Step 2: If the user requests to "make a reservation by phone," the system will automatically call the relevant restaurant.
ステップ3:システムは音声認識技術と自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う。Step 3: The system uses voice recognition technology and an automated dialing system to make the reservation.
(実施例1)(Example 1)
次に、形態例1の実施例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマート眼鏡214を「端末」と称する。Next, a first embodiment of the first embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチすることが困難であり、また、ユーザーの質問に対する適切な回答を生成することができなかった。さらに、目的地の設定やナビゲーションの提供においても、ユーザーの現在位置やサーチ結果を効果的に利用することができなかった。これにより、ユーザーの利便性が低下し、運転中の安全性も確保されにくかった。With conventional navigation systems, it was difficult to search for a destination based on the user's specific requests, and they were unable to generate appropriate answers to the user's questions. Furthermore, they were unable to effectively use the user's current location or search results when setting a destination or providing navigation. This reduced user convenience and made it difficult to ensure safety while driving.
実施例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、音声入力をテキストに変換する手段と、自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析する手段と、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを学習する手段と、位置情報を取得する手段と、音声ガイダンスを生成する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいた目的地のサーチと設定が可能となり、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導されることが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for converting voice input to text, means for analyzing the user's questions using natural language processing techniques, means for learning data using machine learning algorithms, means for acquiring location information, and means for generating voice guidance. This makes it possible to search for and set a destination based on the user's detailed requests, and allows the user to be safely guided to the destination even while driving.
「情報源」とは、データを提供するあらゆる媒体やシステムを指す。"Source" refers to any medium or system that provides data.
「学習する手段」とは、データを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出するためのアルゴリズムや技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to the algorithms and techniques used to analyze data and extract patterns and knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて求める詳細な要求を指す。"Specific user requests" refers to the detailed requirements that users have based on their specific conditions and preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to the technology or algorithms used to search for an appropriate destination based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補や情報を指す。"Search results" refers to destination candidates and information obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果に基づいて最適な目的地を決定するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to the technology or algorithm used to determine the optimal destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、ユーザーが目的地に到達するための経路案内を行う技術やシステムを指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to technologies and systems that provide route guidance to help users reach their destination.
「音声入力をテキストに変換する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声を解析し、文字情報に変換する技術やシステムを指す。"Means of converting voice input into text" refers to technology or systems that analyze the user's voice and convert it into text information.
「自然言語処理技術」とは、人間の言語を解析し、理解するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Natural language processing technology" refers to the techniques and algorithms for analyzing and understanding human language.
「機械学習アルゴリズム」とは、データからパターンや知識を学習し、予測や分類を行うためのアルゴリズムを指す。"Machine learning algorithms" refer to algorithms that learn patterns and knowledge from data and make predictions and classifications.
「位置情報を取得する手段」とは、ユーザーの現在位置を特定するための技術やシステムを指す。"Means of acquiring location information" refers to technologies and systems for identifying the user's current location.
「音声ガイダンスを生成する手段」とは、ユーザーに音声で指示を出すための技術やシステムを指す。"Means for generating audio guidance" refers to technology or systems for providing audio instructions to the user.
発明を実施するための形態Form for implementing the invention
この発明は、車載用ナビゲーションシステムに関するものであり、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチし、最適なルートを提供するためのシステムである。このシステムは、サーバ、端末、ユーザーの三者が連携して動作する。This invention relates to an in-vehicle navigation system that searches for destinations based on the user's specific requests and provides the optimal route. This system works in cooperation with a server, a terminal, and a user.
1. プログラムの生成1. Program generation
サーバは、車載用ナビゲーションシステムのプログラムを生成する。このプログラムは、機械学習アルゴリズムと自然言語処理技術を組み合わせて構築される。具体的には、PythonのPandas、Scikit-learn、NLTK、SpaCy、Google Maps API、Amazon PollyなどのライブラリやAPIを使用する。The server generates the program for the in-car navigation system. This program is built by combining machine learning algorithms and natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses libraries and APIs such as Python's Pandas, Scikit-learn, NLTK, SpaCy, Google Maps API, and Amazon Polly.
2. プログラムの処理2. Program processing
サーバは、以下の手順でデータを処理する。The server processes the data in the following steps:
1. データ取得と学習:1. Data acquisition and learning:
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースからデータを取得する。具体的には、PythonのPandasライブラリを使用してデータを読み込む。次に、サーバはScikit-learnを用いて機械学習アルゴリズムでデータを学習する。例えば、レストランの評価情報を基に、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを作成する。The server retrieves data from a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. Specifically, it reads the data using Python's Pandas library. The server then uses Scikit-learn to train the data with machine learning algorithms. For example, it creates a model that predicts highly rated restaurants based on restaurant rating information.
2. ユーザーの質問解析:2. User question analysis:
端末は、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。例えば、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」という質問を受け取る。端末は、この質問を自然言語処理技術を用いて解析する。具体的には、PythonのNLTKやSpaCyを使用して、質問の意図を理解する。The device receives questions from users. For example, it may receive a question such as, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby." The device then analyzes the question using natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses Python's NLTK and SpaCy to understand the intent of the question.
3. 目的地の設定:3. Set your destination:
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。具体的には、Google Maps APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を取得し、最適なルートを計算する。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results. Specifically, it uses the Google Maps API to obtain the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants, and calculates the optimal route.
4. ナビゲーションの提供:4. Providing navigation:
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する。具体的には、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに音声で指示を出す。例えば、Amazon Pollyを使用して、「右に曲がってください」などの音声ガイダンスを生成する。The device provides navigation to the set destination. Specifically, it uses a voice guidance system to give voice instructions to the user. For example, it uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance such as "Turn right."
3. 具体例3. Specific examples
具体例として、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と質問した場合を考える。As a concrete example, consider the case where a user asks, "Can you tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby?"
1. データ取得と学習:1. Data acquisition and learning:
サーバは、データベースに接続し、レストランの評価情報を取得する。The server connects to the database and retrieves restaurant rating information.
サーバは、Pandasを用いてデータをDataFrameに変換する。The server converts the data into a DataFrame using Pandas.
サーバは、Scikit-learnのRandomForestClassifierを用いて、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを学習する。The server uses Scikit-learn's RandomForestClassifier to train a model to predict highly rated restaurants.
2. ユーザーの質問解析:2. User question analysis:
ユーザーは、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と端末に話しかける。The user speaks to the device saying, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby."
端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換する。The device converts voice input into text.
端末は、NLTKを用いてテキストをトークン化し、SpaCyを用いて質問の意図を解析する。The device uses NLTK to tokenize the text and SpaCy to analyze the intent of the question.
3. 目的地の設定:3. Set your destination:
端末は、GPSセンサーを用いてユーザーの現在位置を取得する。The device uses the GPS sensor to obtain the user's current location.
サーバは、Google Maps APIを用いて、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を基にルートを計算する。The server uses the Google Maps API to calculate a route based on the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants.
サーバは、計算結果を端末に送信する。The server sends the calculation results to the terminal.
4. ナビゲーションの提供:4. Providing navigation:
端末は、サーバから受け取ったルート情報を基に、ナビゲーションを開始する。The device begins navigation based on the route information received from the server.
端末は、Amazon Pollyを用いて音声ガイダンスを生成し、ユーザーに指示を出す。The device uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance and give instructions to the user.
ユーザーは、音声ガイダンスに従って運転する。The user drives by following the voice guidance.
プロンプト文の例:Example prompt:
「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」"Can you tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby?"
このようにして、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。In this way, users are safely guided to their destination while driving.
実施例1における特定処理の流れについて図11を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 1 is explained using Figure 11.
ステップ1:データ取得と学習Step 1: Data acquisition and learning
サーバは、データベースからレストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を取得する。入力として、データベース接続情報とSQLクエリを使用する。サーバは、PythonのPandasライブラリを用いてデータをDataFrameに変換する。次に、サーバはScikit-learnを用いて機械学習アルゴリズムでデータを学習する。具体的には、RandomForestClassifierを使用して、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを作成する。出力として、学習済みのモデルが得られる。The server retrieves information from the database, such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. As input, it uses the database connection information and a SQL query. The server converts the data into a DataFrame using Python's Pandas library. The server then uses Scikit-learn to train the data with a machine learning algorithm. Specifically, it uses RandomForestClassifier to create a model that predicts highly rated restaurants. As output, it obtains the trained model.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
サーバは、データベースに接続し、SQLクエリを実行してデータを取得する。The server connects to the database and executes SQL queries to retrieve data.
サーバは、取得したデータをPandasのDataFrameに変換する。The server converts the retrieved data into a Pandas DataFrame.
サーバは、Scikit-learnのRandomForestClassifierを用いて、レストランの評価を予測するモデルを学習する。The server uses Scikit-learn's RandomForestClassifier to train a model to predict restaurant ratings.
ステップ2:ユーザーの質問解析Step 2: Analyze user questions
端末は、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。入力として、ユーザーの音声質問が使用される。端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換するために音声認識技術を使用する。次に、端末は、自然言語処理技術を用いて質問を解析する。具体的には、PythonのNLTKやSpaCyを使用して、質問の意図を理解する。出力として、解析されたテキストデータが得られる。The terminal receives a question from the user. As input, the user's voice question is used. The terminal uses speech recognition technology to convert the voice input into text. The terminal then analyzes the question using natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses Python's NLTK and SpaCy to understand the intent of the question. As output, the analyzed text data is obtained.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
ユーザーは、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と端末に話しかける。The user speaks to the device saying, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby."
端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換する。The device converts voice input into text.
端末は、NLTKを用いてテキストをトークン化し、SpaCyを用いて質問の意図を解析する。The device uses NLTK to tokenize the text and SpaCy to analyze the intent of the question.
ステップ3:目的地の設定Step 3: Set your destination
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。入力として、ユーザーの現在位置と解析されたテキストデータが使用される。サーバは、Google Maps APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を取得し、最適なルートを計算する。出力として、計算されたルート情報が得られる。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results. The user's current location and parsed text data are used as input. The server uses the Google Maps API to obtain the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants, and calculates the optimal route. The calculated route information is obtained as output.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
端末は、GPSセンサーを用いてユーザーの現在位置を取得する。The device uses the GPS sensor to obtain the user's current location.
サーバは、Google Maps APIを用いて、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を基にルートを計算する。The server uses the Google Maps API to calculate a route based on the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants.
サーバは、計算結果を端末に送信する。The server sends the calculation results to the terminal.
ステップ4:ナビゲーションの提供Step 4: Provide navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する。入力として、計算されたルート情報が使用される。端末は、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに音声で指示を出す。具体的には、Amazon Pollyを使用して、「右に曲がってください」などの音声ガイダンスを生成する。出力として、音声ガイダンスが得られる。The device provides navigation to the set destination. The calculated route information is used as input. The device uses a voice guidance system to give voice instructions to the user. Specifically, it uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance such as "Turn right". The voice guidance is obtained as output.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
端末は、サーバから受け取ったルート情報を基に、ナビゲーションを開始する。The device begins navigation based on the route information received from the server.
端末は、Amazon Pollyを用いて音声ガイダンスを生成し、ユーザーに指示を出す。The device uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance and give instructions to the user.
ユーザーは、音声ガイダンスに従って運転する。The user drives by following the voice guidance.
(応用例1)(Application example 1)
次に、形態例1の応用例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマート眼鏡214を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 1 of embodiment example 1 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする機能が限定的であり、ユーザーの質問に対する適切な回答を生成する能力が不足している。また、現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスを提供する機能も十分ではない。これにより、ユーザーは目的地への移動中に不便を感じることが多い。Traditional navigation systems have limited functionality for searching for destinations based on the user's specific requests and lack the ability to generate appropriate answers to user questions. They also lack the ability to calculate the optimal route between the current location and the destination and provide voice guidance. This often causes inconvenience to users while traveling to their destination.
応用例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する自然言語処理手段と、現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する手段と、音声ガイダンスを提供する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチし、最適なルートを計算して音声ガイダンスを提供することが可能となる。The identification process by the
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するための出典やリソースである。A "source" is a source or resource that provides data or knowledge.
「情報を学習する手段」とは、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて、様々な情報源から取得したデータを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出する方法である。"Means of learning information" refers to the use of machine learning algorithms to analyze data obtained from various sources and extract patterns and knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて求める詳細な要求や希望である。"User specific requests" are the detailed demands and wishes that a user has based on their specific conditions and preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための方法や技術である。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods or technologies for searching for an appropriate destination based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、目的地をサーチする手段によって得られた検索結果である。"Search results" means the results of a search obtained by a means of searching for a destination.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果に基づいてユーザーの目的地を決定する方法や技術である。"Means for setting a destination" refers to a method or technology for determining a user's destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、ユーザーが目的地に到達するための経路案内や指示を提供する方法や技術である。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods or technologies that provide route guidance or directions to help a user reach a destination.
「自然言語処理手段」とは、ユーザーの質問や要求を解析し、適切な回答を生成するための技術である。"Natural language processing means" is technology for analyzing users' questions and requests and generating appropriate answers.
「ルートを計算する手段」とは、現在位置と目的地の間の最適な経路を計算するための方法や技術である。"Means for calculating a route" refers to a method or technique for calculating the optimal route between a current location and a destination.
「音声ガイダンスを提供する手段」とは、計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供する方法や技術である。"Means for providing audio guidance" refers to methods or technologies that convert calculated route information into audio and provide it to the user.
この発明を実施するための形態として、以下のようなシステムが考えられる。The following system is considered as a form for implementing this invention.
まず、サーバは様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段を持つ。この手段は、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出するものである。具体的には、データベースから情報を取得し、これを学習する。First, the server has a means of learning information from various sources. This means uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data such as restaurant reviews and the availability of parking spaces, and extract patterns and knowledge. Specifically, it retrieves information from a database and learns from it.
次に、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段がある。この手段は、自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な目的地をサーチするものである。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」と質問すると、システムはその質問を解析し、適切なレストランを検索する。Next, there is a means to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests. This means uses natural language processing technology to analyze the user's question and search for an appropriate destination. For example, if a user asks, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" the system will analyze the question and search for an appropriate restaurant.
さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段がある。この手段は、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定するものである。具体的には、Geopyライブラリを使用して、現在位置と目的地の間の距離を計算する。In addition, there is a method for setting a destination based on search results. This method calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and search results, and sets the destination. Specifically, it uses the Geopy library to calculate the distance between the current location and the destination.
最後に、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段がある。この手段は、Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)ライブラリを使用して、計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供するものである。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。Finally, there is a method to provide navigation to the set destination. This method uses the Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) library to convert the calculated route information into voice and provide it to the user. This allows the user to be safely guided to their destination while driving.
具体例として、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」と質問すると、システムは以下のように動作する。As a concrete example, when a user asks, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" the system works as follows:
1. 自然言語処理手段がユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する。1. Natural language processing tools analyze the user's question and generate an appropriate answer.
2. 情報を学習する手段がデータベースからレストランの評価情報を取得し、解析する。2. The means for learning information retrieves restaurant rating information from the database and analyzes it.
3. ルートを計算する手段が現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する。3. A route calculation means calculates the optimal route between the current location and the destination.
4. 音声ガイダンスを提供する手段が計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供する。4. A means for providing audio guidance converts the calculated route information into audio and provides it to the user.
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが考えられる。Some examples of prompt statements include:
ユーザーの質問: 「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」User Question: "What are some highly rated restaurants near me?"
コンテキスト:「レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無など」Context: "Restaurant ratings, availability of parking, etc."
このプロンプト文を使用して、生成AIモデルに質問を解析させ、適切な回答を得ることができる。This prompt can then be used by a generative AI model to parse the question and provide an appropriate answer.
応用例1における特定処理の流れについて図12を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 1 is explained using Figure 12.
ステップ1:Step 1:
サーバは、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。入力はユーザーの質問であり、例えば「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」というテキストデータである。出力は解析のための準備が整ったテキストデータである。The server receives a question from a user. The input is the user's question, which is text data, for example, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" The output is text data ready for analysis.
ステップ2:Step 2:
サーバは、自然言語処理手段を用いて、ユーザーの質問を解析する。入力はステップ1で受け取ったユーザーの質問であり、出力は解析結果としての適切な検索クエリである。具体的には、生成AIモデルを使用して質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する。The server uses natural language processing means to analyze the user's question. The input is the user's question received in step 1, and the output is an appropriate search query as a result of the analysis. Specifically, it uses a generative AI model to analyze the question and generate an appropriate answer.
ステップ3:Step 3:
サーバは、情報を学習する手段を用いて、データベースからレストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを取得する。入力はステップ2で生成された検索クエリであり、出力は取得された評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータである。具体的には、データベースに対してクエリを実行し、必要な情報を取得する。The server uses a means for learning information to obtain data such as restaurant rating information and whether or not parking is available from the database. The input is the search query generated in step 2, and the output is the obtained rating information, parking availability, and other data. Specifically, the server executes a query against the database to obtain the required information.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバは、取得した情報を基に、ユーザーの現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する。入力はユーザーの現在位置とステップ3で取得された目的地情報であり、出力は計算された最適なルート情報である。具体的には、Geopyライブラリを使用して距離を計算し、最適なルートを決定する。The server calculates the optimal route between the user's current location and the destination based on the acquired information. The input is the user's current location and the destination information acquired in step 3, and the output is the calculated optimal route information. Specifically, the Geopy library is used to calculate the distance and determine the optimal route.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバは、計算されたルート情報を音声ガイダンスに変換する。入力はステップ4で計算されたルート情報であり、出力は音声ファイルである。具体的には、Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)ライブラリを使用して、テキスト情報を音声に変換する。The server converts the calculated route information into voice guidance. The input is the route information calculated in step 4, and the output is an audio file. Specifically, it uses the Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) library to convert the text information into voice.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末は、生成された音声ガイダンスをユーザーに提供する。入力はステップ5で生成された音声ファイルであり、出力はユーザーに対する音声案内である。具体的には、音声ファイルを再生し、ユーザーに対してナビゲーション情報を提供する。The terminal provides the generated voice guidance to the user. The input is the audio file generated in step 5, and the output is audio guidance for the user. Specifically, the terminal plays the audio file and provides navigation information to the user.
(実施例2)(Example 2)
次に、形態例2の実施例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマート眼鏡214を「端末」と称する。Next, a second embodiment of the second embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、目的地の設定やナビゲーション機能を提供するだけであり、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいた予約機能を持たないため、ユーザーが手動で予約を行う必要があった。また、音声指示を解析して自動的に予約を行うシステムも存在しなかったため、ユーザーの利便性が低かった。これにより、ユーザーは目的地の設定と予約の両方を別々に行う手間がかかり、効率的な利用が難しかった。Conventional navigation systems only offered destination setting and navigation functions, and did not have a reservation function based on the user's specific requests, so users had to make reservations manually. There was also no system that analyzed voice instructions and made reservations automatically, which resulted in low user convenience. This meant that users had to take the time to both set a destination and make reservations separately, making it difficult to use the system efficiently.
実施例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声指示を解析する手段と、解析された音声指示に基づいて予約内容を抽出する手段と、抽出された予約内容に基づいて自動的に電話をかける手段と、電話を通じて予約内容を音声で伝える手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーは音声指示を出すだけで目的地の設定と予約が自動的に行われ、利便性が大幅に向上することが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for analyzing the user's voice instructions, means for extracting reservation details based on the analyzed voice instructions, means for automatically making a phone call based on the extracted reservation details, and means for audibly communicating the reservation details over the phone. This allows the user to automatically set a destination and make a reservation simply by issuing voice instructions, greatly improving convenience.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「ユーザー」とは、システムを利用する個人または団体を指す。"User" refers to an individual or organization that uses the system.
「目的地」とは、ユーザーが到達したい場所を指す。"Destination" refers to the place the user wants to reach.
「サーチ」とは、特定の情報を探し出す行為を指す。"Search" refers to the act of finding specific information.
「ナビゲーション」とは、目的地までの経路を案内する機能を指す。"Navigation" refers to the function of providing route guidance to a destination.
「音声指示」とは、ユーザーが音声を用いてシステムに対して行う指示を指す。"Voice instructions" refers to instructions given by the user to the system using voice.
「解析」とは、データや情報を詳細に調べて意味や構造を理解する行為を指す。"Analysis" refers to the act of examining data or information in detail to understand its meaning and structure.
「予約内容」とは、予約に必要な情報(日時、人数、場所など)を指す。"Reservation details" refers to the information required for making a reservation (date and time, number of people, location, etc.).
「自動的」とは、人の手を介さずに機械やシステムが独自に動作することを指す。"Automatic" refers to a machine or system that operates independently without human intervention.
「電話をかける」とは、通信装置を用いて他の通信装置に接続を試みる行為を指す。"Making a phone call" refers to the act of using a communication device to attempt to connect to another communication device.
「音声で伝える」とは、音声を用いて情報を他者に伝達する行為を指す。"Communicating by voice" refers to the act of conveying information to others using voice.
発明を実施するための形態Form for implementing the invention
この発明は、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションとして実施される。このアプリケーションは、ユーザーの音声指示に基づいて目的地の設定と予約を自動的に行うシステムである。以下に、このシステムの具体的な実施形態を説明する。This invention is implemented as an application for smartphones. This application is a system that automatically sets a destination and makes reservations based on the user's voice instructions. A specific embodiment of this system is described below.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
このシステムは、以下のハードウェアおよびソフトウェアを使用する。This system uses the following hardware and software:
スマートフォン(端末)Smartphone (device)
音声認識技術(Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API)Voice recognition technology (Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API)
データベース管理システム(Firebase Firestore)Database management system (Firebase Firestore)
自動ダイヤルシステム(Twilio API)Automatic dialing system (Twilio API)
音声合成技術(Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API)Speech synthesis technology (Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API)
データ加工およびデータ演算Data processing and data calculations
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、音声で「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示する。端末はGoogle Cloud Speech-to-Text APIを使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。この変換処理はリアルタイムで行われる。The user launches the application on their smartphone and says, "Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm." The device uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API to convert the user's voice instructions into text. This conversion process occurs in real time.
次に、端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、予約内容(日時、人数)を抽出する。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」というテキストから「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という情報を取り出す。Then, the device analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details (date, time, number of people). For example, from the text "Make a reservation for four people at 7 p.m. tomorrow," the information "tomorrow at 7 p.m." and "four people" is extracted.
端末はFirebase Firestoreに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。このリクエストには、ユーザの位置情報や好みのレストランの条件が含まれる。サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をFirebase Firestoreから取得し、端末に返す。返される情報には、レストランの名前、電話番号、住所などが含まれる。The device sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in Firebase Firestore. This request includes the user's location and preferred restaurant conditions. The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from Firebase Firestore, and returns it to the device. The returned information includes the restaurant's name, phone number, address, etc.
端末はTwilio APIを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。この処理はユーザの手を煩わせることなく行われる。電話が接続されると、端末はGoogle Cloud Text-to-Speech APIを使用して、事前に抽出した予約内容を音声でレストランに伝える。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声が再生される。The device uses the Twilio API to automatically call the restaurant's phone number, without any user intervention. Once the call is connected, the device uses the Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API to communicate the reservation details it extracted in advance to the restaurant via voice. For example, it might say, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
具体例Specific examples
具体例として、ユーザが「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示した場合の動作を以下に示す。As a concrete example, the behavior when a user instructs "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow night" is shown below.
1. ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と音声で指示する。1. The user launches the smartphone application and gives a voice command such as, "Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
2. 端末はGoogle Cloud Speech-to-Text APIを使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。2. The device uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API to convert the user's voice commands into text.
3. 端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という予約内容を抽出する。3. The device analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details: "tomorrow night at 7pm" and "4 people."
4. 端末はFirebase Firestoreに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。4. The device sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in Firebase Firestore.
5. サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をFirebase Firestoreから取得し、端末に返す。5. The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from Firebase Firestore, and returns it to the device.
6. 端末はTwilio APIを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。6. The device uses the Twilio API to automatically call the restaurant's phone number.
7. 電話が接続されると、端末はGoogle Cloud Text-to-Speech APIを使用して、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声をレストランに伝える。7. Once the call is connected, the device uses the Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API to communicate to the restaurant, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが考えられる。Some examples of prompt statements include:
「ユーザが「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示した場合、アプリケーションはどのように処理を行うか説明してください。」"If a user says, 'Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm,' how should the application handle that?"
このプロンプト文を生成AIモデルに入力することで、上記の具体例に基づいた処理の説明を得ることができる。By inputting this prompt into the generative AI model, we can obtain an explanation of the process based on the specific example above.
実施例2における特定処理の流れについて図13を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 2 is explained using Figure 13.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザが音声指示を出す。The user gives voice instructions.
ユーザはスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と音声で指示する。この音声指示が入力となる。The user launches the smartphone application and gives a voice command such as, "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow night." This voice command becomes the input.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末が音声をテキストに変換する。Your device will convert the voice to text.
端末は音声認識技術を使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。この処理には音声認識APIが使用される。入力はユーザの音声指示であり、出力はテキスト形式の指示である。The device uses voice recognition technology to convert the user's voice instructions into text. This process uses a voice recognition API. The input is the user's voice instructions, and the output is the instructions in text format.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末がテキストを解析し、予約内容を抽出する。The device analyzes the text and extracts the reservation details.
端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、予約内容(日時、人数)を抽出する。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」というテキストから「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という情報を取り出す。入力はテキスト形式の指示であり、出力は予約内容のデータである。The terminal analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details (date, time, number of people). For example, from the text "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow," the information "tomorrow at 7pm" and "four people" is extracted. The input is instructions in text format, and the output is the reservation details data.
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末がサーバにレストラン情報をリクエストする。The device requests restaurant information from the server.
端末はデータベース管理システムに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。このリクエストには、ユーザの位置情報や好みのレストランの条件が含まれる。入力は予約内容とユーザの位置情報であり、出力はレストラン情報のリクエストである。The terminal sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in the database management system. This request includes the user's location information and preferred restaurant conditions. The input is the reservation details and the user's location information, and the output is a request for restaurant information.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバがレストラン情報を返す。The server returns the restaurant information.
サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をデータベースから取得し、端末に返す。返される情報には、レストランの名前、電話番号、住所などが含まれる。入力はレストラン情報のリクエストであり、出力はレストラン情報である。The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from the database, and returns it to the terminal. The returned information includes the restaurant's name, phone number, address, etc. The input is a request for restaurant information, and the output is the restaurant information.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末が自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて電話をかける。The device makes the call using an automatic dialing system.
端末は自動ダイヤルシステムを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。この処理はユーザの手を煩わせることなく行われる。入力はレストランの電話番号であり、出力は電話接続の確立である。The terminal uses an automatic dialing system to automatically call the restaurant's phone number, without any user intervention. The input is the restaurant's phone number, and the output is the establishment of a telephone connection.
ステップ7:Step 7:
端末が予約内容を音声で伝える。The device will announce the reservation details aloud.
電話が接続されると、端末は音声合成技術を使用して、事前に抽出した予約内容を音声でレストランに伝える。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声が再生される。入力は予約内容のデータであり、出力は音声メッセージである。When the phone is connected, the device uses voice synthesis technology to verbally communicate the reservation details extracted in advance to the restaurant. For example, a voice may be played saying, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7 p.m." The input is the reservation details data, and the output is a voice message.
(応用例2)(Application example 2)
次に、形態例2の応用例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマート眼鏡214を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 2 of embodiment example 2 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムや予約システムは、ユーザーが手動で操作する必要があり、利便性に欠ける点があった。また、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を活用して最適な提案を行う機能が不足していたため、ユーザーの要望に迅速かつ的確に応えることが難しかった。さらに、音声認識技術や自動ダイヤルシステムを効果的に組み合わせることで、ユーザー体験を向上させることが求められていた。Conventional navigation and reservation systems required users to operate them manually, which made them less convenient. They also lacked the functionality to utilize the user's past behavioral history to make optimal suggestions, making it difficult to respond to user requests quickly and accurately. Furthermore, there was a need to effectively combine voice recognition technology and an automatic dialing system to improve the user experience.
応用例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段と、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段と、音声フィードバックを提供する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーは音声指示のみで目的地の検索や予約を行うことができ、過去の行動履歴に基づいた最適な提案を受けることが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for understanding the user's requests using voice recognition technology, means for making reservations using an automatic dialing system, means for learning the user's past behavioral history and making optimal suggestions, and means for providing voice feedback. This allows the user to search for and make reservations at destinations using only voice instructions, and to receive optimal suggestions based on the user's past behavioral history.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報を収集し、解析し、理解するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to the methods and techniques used to collect, analyze, and understand information.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods and technologies for searching for an appropriate location based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた情報やデータを指す。"Search results" refers to the information or data obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、検索結果に基づいて最終的な目的地を決定するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to the method or technology for determining a final destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道案内を行うための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods and technologies for providing directions to a set destination.
「音声認識技術」とは、音声を解析し、テキストやコマンドに変換する技術を指す。"Voice recognition technology" refers to the technology that analyzes voice and converts it into text or commands.
「自動ダイヤルシステム」とは、指定された電話番号に自動的に電話をかけるシステムを指す。"Automatic dialing system" refers to a system that automatically dials a specified telephone number.
「予約を行う手段」とは、指定された場所やサービスの予約を自動的に行うための方法や技術を指す。"Means of making a reservation" refers to methods or technologies for automatically making a reservation for a specified location or service.
「過去の行動履歴」とは、ユーザーが以前に行った行動や選択の記録を指す。"Past behavioral history" refers to records of actions and choices a user has previously made.
「最適な提案を行う手段」とは、過去の行動履歴や現在の要望に基づいて、ユーザーに最も適した選択肢を提示するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of making optimal suggestions" refers to methods and technologies for presenting the most suitable options to users based on their past behavioral history and current needs.
「音声フィードバックを提供する手段」とは、システムが音声を用いてユーザーに情報や結果を伝えるための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing audio feedback" refers to methods or technologies that allow a system to communicate information or results to a user using audio.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、以下のような構成を持つ。サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段、音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段、自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段、音声フィードバックを提供する手段を含む。A system for implementing this invention has the following configuration: The server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for understanding the user's requests using voice recognition technology, means for making reservations using an automatic dialing system, means for learning the user's past behavioral history and making optimal suggestions, and means for providing voice feedback.
プログラムの処理の説明Explanation of program processing
ハードウェアとソフトウェアHardware and software
このシステムは、スマートフォンのマイクとスピーカーをハードウェアとして使用する。また、音声認識にはspeech_recognitionライブラリ、音声フィードバックにはpyttsx3ライブラリ、データ通信にはrequestsライブラリを使用する。The system uses the smartphone's microphone and speaker as hardware. It also uses the speech_recognition library for voice recognition, the pyttsx3 library for voice feedback, and the requests library for data communication.
データ加工とデータ演算Data processing and data calculations
1. 音声認識: ユーザーがスマートフォンのマイクに向かって要望を話すと、speech_recognitionライブラリがその音声をテキストに変換する。1. Speech recognition: When the user speaks their request into the smartphone's microphone, the speech_recognition library converts the speech into text.
2. 要望の解析: 変換されたテキストを解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。例えば、「ピザを注文して」という要望を解析する。2. Request Analysis: Analyze the converted text to understand the user's request. For example, analyze the request "order a pizza."
3. 予約の実行: 要望に基づいて、requestsライブラリを使用してフードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信する。注文が成功した場合、pyttsx3ライブラリを使用して音声フィードバックを提供する。3. Execute reservation: Based on the request, send the order to the food delivery API using the requests library. If the order is successful, provide audio feedback using the pyttsx3 library.
4. 行動履歴の学習: ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、次回以降の最適な提案を行う。4. Learning behavioral history: Learns the user's past behavioral history and provides optimal suggestions for future visits.
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「ピザを注文して」と言った場合、システムは以下のように動作する。For example, if a user says "order a pizza," the system would do the following:
1. ユーザーの音声をマイクで取得する。1. Capture the user's voice using the microphone.
2. 音声をテキストに変換し、「ピザを注文して」というテキストを得る。2. Convert speech to text and get the text "Order pizza."
3. テキストを解析し、「ピザ」の注文を特定する。3. Analyze the text to identify "pizza" orders.
4. フードデリバリーAPIに「ピザ」の注文を送信する。4. Send an order for "Pizza" to the food delivery API.
5. 注文が成功した場合、「ピザの注文が完了しました」と音声でフィードバックする。5. If the order is successful, audio feedback will be provided saying "Your pizza order has been completed."
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
ユーザーが「ピザを注文して」と言った場合、音声認識技術を用いて音声をテキストに変換し、フードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信するプログラムを作成してください。注文が成功した場合、音声で「ピザの注文が完了しました」とフィードバックしてください。When a user says "Order a pizza," create a program that uses speech recognition technology to convert the speech to text and send the order to a food delivery API. If the order is successful, provide voice feedback saying "Pizza order completed."
このようにして、ユーザーは音声指示のみで目的地の検索や予約を行うことができ、過去の行動履歴に基づいた最適な提案を受けることが可能となる。In this way, users can search for and book destinations using only voice commands, and receive optimal suggestions based on their past travel history.
応用例2における特定処理の流れについて図14を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 2 is explained using Figure 14.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのマイクに向かって要望を話す。The user speaks their request into the smartphone's microphone.
入力: ユーザの音声。Input: User's voice.
出力: マイクで取得された音声データ。Output: Audio data captured by the microphone.
具体的な動作: ユーザが「ピザを注文して」と話すと、スマートフォンのマイクがその音声をキャプチャする。What happens: When a user says "order a pizza," the smartphone's microphone captures the audio.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末がspeech_recognitionライブラリを使用して音声データをテキストに変換する。The device uses the speech_recognition library to convert the voice data into text.
入力: マイクで取得された音声データ。Input: Audio data captured by the microphone.
出力: テキストデータ(例:「ピザを注文して」)。Output: Text data (e.g. "order pizza").
具体的な動作: 音声認識エンジンが音声データを解析し、対応するテキストに変換する。Specific operation: The speech recognition engine analyzes the voice data and converts it into corresponding text.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末がテキストデータを解析し、ユーザの要望を理解する。The device analyzes the text data and understands the user's needs.
入力: テキストデータ(例:「ピザを注文して」)。Input: Text data (e.g. "order pizza").
出力: 要望の解析結果(例:「ピザの注文」)。Output: Analysis of the request (e.g. "order pizza").
具体的な動作: テキスト解析エンジンが「ピザを注文して」というテキストを解析し、「ピザの注文」という要望を特定する。Specific behavior: The text analysis engine analyzes the text "order a pizza" and identifies the request "order a pizza."
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末がrequestsライブラリを使用してフードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信する。The device uses the requests library to send the order to the food delivery API.
入力: 要望の解析結果(例:「ピザの注文」)。Input: Analysis of the request (e.g. "order pizza").
出力: APIへの注文リクエストとそのレスポンス。Output: The order request to the API and its response.
具体的な動作: フードデリバリーAPIに対して「ピザの注文」を含むリクエストを送信し、注文が成功したかどうかのレスポンスを受け取る。Specific behavior: Send a request to the food delivery API including "order pizza" and receive a response indicating whether the order was successful.
ステップ5:Step 5:
端末がpyttsx3ライブラリを使用して音声フィードバックを提供する。The device provides audio feedback using the pyttsx3 library.
入力: APIからのレスポンス(例:注文成功)。Input: Response from the API (e.g. order successful).
出力: 音声フィードバック(例:「ピザの注文が完了しました」)。Output: Audio feedback (e.g. "Your pizza order is complete").
具体的な動作: 音声合成エンジンが「ピザの注文が完了しました」というメッセージを生成し、スマートフォンのスピーカーを通じてユーザに伝える。Specific action: The speech synthesis engine generates the message "Your pizza order has been completed" and conveys it to the user through the smartphone speaker.
ステップ6:Step 6:
サーバがユーザの過去の行動履歴を学習し、次回以降の最適な提案を行う。The server learns the user's past behavioral history and makes optimal suggestions for future visits.
入力: ユーザの行動履歴データ。Input: User behavioral history data.
出力: 学習結果に基づく提案データ。Output: Proposed data based on learning results.
具体的な動作: サーバがユーザの過去の注文履歴を解析し、次回の注文時に最適なレストランやメニューを提案するためのデータを生成する。Specific operation: The server analyzes the user's past ordering history and generates data to suggest the best restaurant and menu for the next time they order.
なお、更に、ユーザの感情を推定する感情エンジンを組み合わせてもよい。すなわち、特定処理部290は、感情特定モデル59を用いてユーザの感情を推定し、ユーザの感情を用いた特定処理を行うようにしてもよい。Furthermore, an emotion engine that estimates the user's emotion may be combined. That is, the
「形態例1」"Example 1"
本発明の一実施形態として、感情エンジンを組み込んだナビゲーションシステムがある。このシステムは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を認識し、それを考慮に入れて目的地をサーチする。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」という要望を出した場合、その声のトーンが明るければ、システムは活気のあるレストランを、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば、静かなレストランを推薦する。One embodiment of the present invention is a navigation system incorporating an emotion engine. This system recognizes emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc., and searches for a destination taking these into consideration. For example, if a user requests, "Find a nice restaurant nearby," the system will recommend a lively restaurant if the user's tone of voice is cheerful, and a quiet restaurant if the user's tone of voice is sad.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
また、感情エンジンを組み込んだスマートフォン用のアプリケーションも本発明の一実施形態である。このアプリケーションは、ユーザーのテキスト入力や音声入力から感情を認識し、それを考慮に入れてサービスを提供する。例えば、ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力した場合、その感情を認識して、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランや、ユーザーが好きな料理を提供するレストランを推薦する。Another embodiment of the present invention is a smartphone application incorporating an emotion engine. This application recognizes emotions from the user's text and voice input, and provides services taking these into consideration. For example, if the user inputs, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," the application recognizes the emotion and recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere and restaurants that serve the user's favorite dishes.
以下に、各形態例の処理の流れについて説明する。The process flow for each example is explained below.
「形態例1」"Example 1"
ステップ1:ユーザーがナビゲーションシステムに対して音声で要望を出す。Step 1: The user issues a verbal request to the navigation system.
ステップ2:感情エンジンがユーザーの声のトーン、表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を認識する。Step 2: The emotion engine recognizes the user's emotions from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc.
ステップ3:システムが認識した感情を考慮に入れて、目的地をサーチする。Step 3: Search for destinations, taking into account the emotions the system recognizes.
ステップ4:システムがサーチ結果をユーザーに提示する。Step 4: The system presents the search results to the user.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
ステップ1:ユーザーがスマートフォン用のアプリケーションに対してテキスト入力や音声入力で要望を出す。Step 1: The user submits a request to a smartphone application via text or voice input.
ステップ2:感情エンジンがユーザーのテキスト入力や音声入力から感情を認識する。Step 2: The emotion engine recognizes emotions from the user's text or voice input.
ステップ3:アプリケーションが認識した感情を考慮に入れて、サービスを提供する。Step 3: The application takes into account the emotions it recognizes and provides a service.
ステップ4:アプリケーションが提供するサービスの結果をユーザーに提示する。Step 4: Present the user with the results of the services provided by the application.
(実施例1)(Example 1)
次に、形態例1の実施例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマート眼鏡214を「端末」と称する。Next, a first embodiment of the first embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮した目的地の推薦が難しく、また、最適なルート計算や音声入力の解析が十分に行われないことが多かった。その結果、ユーザーの満足度が低下し、運転中の安全性も確保されにくいという課題があった。With conventional navigation systems, it was difficult to recommend destinations that took into account the user's detailed requests and feelings, and they often did not adequately calculate optimal routes or analyze voice input. As a result, there were issues with low user satisfaction and difficulty in ensuring safety while driving.
実施例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する手段と、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に最適なルートを計算する手段と、音声入力を解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮した目的地の推薦が可能となり、最適なルート計算や音声入力の解析も行われるため、ユーザーの満足度が向上し、運転中の安全性も確保される。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's emotions and recommending a destination based thereon, means for calculating an optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results, and means for analyzing voice input and understanding the user's requests. This makes it possible to recommend a destination taking into account the user's detailed requests and emotions, and also calculates an optimal route and analyzes voice input, thereby improving user satisfaction and ensuring safety while driving.
「情報源」とは、データを提供するための基となる場所やシステムであり、例えば、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースを指す。An "information source" is a source or system that provides data, such as a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available.
「学習する手段」とは、取得した情報を基に機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを解析し、パターンや特徴を抽出するプロセスを指す。"Means of learning" refers to the process of using machine learning algorithms to analyze data based on acquired information and extract patterns and features.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて出す具体的なリクエストを指す。"User specific requests" refers to specific requests made by users based on their specific conditions or preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースから検索するプロセスを指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to the process of searching a database for an appropriate destination based on the user's request.
「サーチ結果」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて検索された目的地の情報を指す。"Search results" refers to destination information searched for based on a user's request.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果を基にユーザーの目的地を決定し、その情報をシステムに登録するプロセスを指す。"Means of setting a destination" refers to the process of determining the user's destination based on search results and registering that information in the system.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地への道順をユーザーに案内するためのシステムや方法を指す。"Means for providing navigation" refers to a system or method for guiding a user to a set destination.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を解析し、それを理解するプロセスを指す。"Means of recognizing emotions" refers to the process of analyzing and understanding the emotions of the user from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc.
「最適なルートを計算する手段」とは、ユーザーの現在位置と目的地を基に、最も効率的な道順を計算するプロセスを指す。"Means of calculating optimal route" refers to the process of calculating the most efficient route based on the user's current location and destination.
「音声入力を解析する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換し、その内容を理解するための技術や方法を指す。"Means of analyzing voice input" refers to the technology or method for converting a user's voice into text and understanding its content.
本発明は、車載用のナビゲーションシステムに関するものであり、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮して最適な目的地を推薦し、ナビゲーションを提供するシステムである。このシステムは、サーバ、端末、ユーザーの三者が連携して動作する。The present invention relates to an in-vehicle navigation system that provides navigation by recommending optimal destinations while taking into account the user's detailed requests and feelings. This system operates in cooperation with a server, a terminal, and a user.
情報の取得と学習Acquiring and learning information
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得する。このデータベースは、例えば、一般的な地図サービスAPIや評価情報提供サービスAPIを通じてアクセスする。サーバは、取得した情報を機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlowやPyTorch)を用いて学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価や駐車場の有無などの特徴量を抽出し、これをモデルに入力して学習を行う。The server retrieves information from a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. This database is accessed, for example, through a general map service API or a rating information service API. The server learns from the retrieved information using a machine learning algorithm (for example, TensorFlow or PyTorch). Specifically, it extracts features such as the restaurant's rating and whether or not the restaurant has parking, and inputs these into a model for learning.
ユーザーの要望解析Analysis of user needs
端末は、ユーザーからの質問や要望を音声入力として受け取る。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と話しかける。端末は、音声認識技術(例えば、一般的な音声認識API)を用いて音声をテキストに変換する。変換されたテキストは、自然言語処理技術(例えば、一般的な自然言語処理モデル)を用いて解析される。解析結果として、ユーザーの要望が「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図であることを理解する。The device receives questions and requests from the user as voice input. For example, the user says, "Find a nice restaurant nearby." The device converts the voice into text using voice recognition technology (e.g., a general voice recognition API). The converted text is analyzed using natural language processing technology (e.g., a general natural language processing model). As a result of the analysis, it is understood that the user's request is intended to "find a nice restaurant."
目的地のサーチSearch for destinations
サーバは、解析結果に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースからサーチする。例えば、「美味しいレストラン」をキーワードにデータベースを検索する。サーバは、感情エンジンを用いて、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方から感情を認識する。例えば、ユーザーの声のトーンが明るければ、活気のあるレストランを推薦し、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば、静かなレストランを推薦する。The server then searches the database for an appropriate destination based on the analysis results. For example, it searches the database using the keyword "delicious restaurant." The server uses an emotion engine to recognize emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, and choice of words. For example, if the user's tone of voice is cheerful, it will recommend a lively restaurant, and if the tone of voice is sad, it will recommend a quiet restaurant.
ルートの計算と設定Calculate and set route
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。例えば、一般的な地図サービスAPIを用いてルート計算を行う。計算されたルート情報は端末に送信され、目的地が設定される。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location (GPS information) and the search results. For example, the route is calculated using a general map service API. The calculated route information is sent to the device, and the destination is set.
ナビゲーションの提供Provide navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを音声ガイダンスシステム(例えば、一般的なナビゲーションアプリ)を用いて提供する。具体的には、音声で「次の交差点を右折してください」などの指示を出す。ユーザーは、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。The device provides navigation to the set destination using a voice guidance system (e.g., a general navigation app). Specifically, instructions such as "Turn right at the next intersection" are given by voice. The user is safely guided to the destination even while driving.
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と音声入力を行った場合、以下のような具体的な動作が行われる。For example, if a user voice-inputs, "Find a good restaurant nearby," the following specific actions will occur:
1. 端末は、ユーザーの音声を受け取り、音声認識APIを用いてテキストに変換する。1. The device receives the user's voice and converts it into text using a speech recognition API.
2. 端末は、変換されたテキストを自然言語処理モデルに入力し、「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図を解析する。2. The device inputs the converted text into a natural language processing model and analyzes the intent of "find a good restaurant."
3. サーバは、解析結果を受け取り、データベースから「美味しいレストラン」を検索する。3. The server receives the analysis results and searches the database for "good restaurants."
4. サーバは、ユーザーの声のトーンを解析し、明るいトーンであれば活気のあるレストランを、落ち込んだトーンであれば静かなレストランを推薦する。4. The server analyzes the tone of the user's voice and recommends lively restaurants if the tone is cheerful, and quiet restaurants if the tone is depressed.
5. サーバは、地図サービスAPIを用いてユーザーの現在位置から目的地までの最適なルートを計算する。5. The server uses the map service API to calculate the optimal route from the user's current location to the destination.
6. 端末は、計算されたルート情報を受け取り、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーにナビゲーションを提供する。6. The device receives the calculated route information and provides navigation to the user using a voice guidance system.
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
「ユーザーが近くの美味しいレストランを探してと音声入力を行った場合、声のトーンが明るければ活気のあるレストランを、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば静かなレストランを推薦するシステムを設計してください。」"If a user requests a nearby restaurant by voice input, design a system that recommends lively restaurants if the user's voice tone is cheerful, and quiet restaurants if the user's voice tone is depressed."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情や要望に応じた最適なナビゲーションが提供される。In this way, optimal navigation is provided based on the user's emotions and needs.
実施例1における特定処理の流れについて図15を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 1 is explained using Figure 15.
ステップ1:Step 1:
情報の取得と学習Acquiring information and learning
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得する。The server retrieves information from a database that includes information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available.
入力:データベースからの情報(例:レストランの評価、駐車場の有無)Input: Information from a database (e.g. restaurant ratings, availability of parking)
データ加工:取得した情報を機械学習アルゴリズム(例:TensorFlow、PyTorch)を用いて学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価や駐車場の有無などの特徴量を抽出し、これをモデルに入力して学習を行う。Data processing: The acquired information is trained using a machine learning algorithm (e.g. TensorFlow, PyTorch). Specifically, features such as restaurant ratings and whether or not there is parking are extracted, and these are input into the model for training.
出力:学習済みモデルOutput: Trained model
ステップ2:Step 2:
ユーザーの要望解析Analysis of user needs
端末は、ユーザーからの質問や要望を音声入力として受け取る。The device receives questions and requests from the user as voice input.
入力:ユーザーの音声入力(例:「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」)Input: User's voice input (e.g. "Find good restaurants nearby")
データ加工:音声認識技術(例:音声認識API)を用いて音声をテキストに変換する。変換されたテキストを自然言語処理技術(例:自然言語処理モデル)を用いて解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。Data processing: Convert speech to text using speech recognition technology (e.g. speech recognition API). Analyze the converted text using natural language processing technology (e.g. natural language processing model) to understand the user's needs.
出力:解析結果(例:「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図)Output: Analysis results (e.g., the intent "find a good restaurant")
ステップ3:Step 3:
目的地のサーチSearch for a destination
サーバは、解析結果に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースからサーチする。The server searches the database for appropriate destinations based on the analysis results.
入力:解析結果(例:「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図)Input: Analysis results (e.g., the intent to "find a good restaurant")
データ加工:データベースから「美味しいレストラン」を検索する。感情エンジンを用いて、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方から感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する。Data processing: Search for "good restaurants" from a database. Using an emotion engine, recognize emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, and choice of words, and recommend destinations based on that.
出力:サーチ結果(例:活気のあるレストラン、静かなレストラン)Output: Search results (e.g. lively restaurants, quiet restaurants)
ステップ4:Step 4:
ルートの計算と設定Route calculation and setting
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location (GPS information) and the search results.
入力:ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)、サーチ結果Input: User's current location (GPS information), search results
データ加工:地図サービスAPIを用いて最適なルートを計算する。Data processing: Calculate the optimal route using a map service API.
出力:計算されたルート情報Output: Calculated route information
ステップ5:Step 5:
ナビゲーションの提供Providing navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて提供する。The device uses a voice guidance system to provide navigation to the set destination.
入力:計算されたルート情報Input: Calculated route information
データ加工:音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに対して「次の交差点を右折してください」などの指示を出す。Data processing: Using a voice guidance system, give instructions to the user such as "Turn right at the next intersection."
出力:音声ガイダンスOutput: Audio guidance
具体的な動作:ユーザーは、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。Specific operation: Users are safely guided to their destination while driving.
(応用例1)(Application example 1)
次に、形態例1の応用例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマート眼鏡214を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 1 of embodiment example 1 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの感情状態を考慮せずに目的地を提案するため、ユーザーの現在の気分や状況に適した目的地を提供することができなかった。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいた最適なルートを提供することができず、ユーザーの満足度を向上させることが困難であった。Conventional navigation systems suggest destinations without taking the user's emotional state into account, making it impossible to provide a destination that suits the user's current mood or situation. In addition, they were unable to provide an optimal route based on the user's emotions, making it difficult to improve user satisfaction.
応用例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes a means for learning information from various information sources, a means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, a means for setting a destination based on the search results, a means for providing navigation to the set destination, a means for recognizing the user's emotions, and a means for suggesting a destination based on the emotion recognition results. This makes it possible to suggest and navigate to the optimal destination according to the user's emotional state.
「情報源」とは、データや情報を提供する元となる媒体やシステムのことである。An "information source" is a medium or system that provides data or information.
「学習する手段」とは、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて情報を解析し、パターンや知識を獲得するための方法である。A "means of learning" is a method for analyzing information and acquiring patterns and knowledge using machine learning algorithms.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望のことである。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user desires.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための方法である。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to a method for searching for an appropriate destination based on the user's requirements.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補のことである。"Search results" refers to destination candidates obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果から最適な目的地を選び、設定するための方法である。"Method of setting a destination" refers to the method for selecting and setting the optimal destination from the search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地への道順を案内するための方法である。"Means of providing navigation" refers to a method for providing directions to a set destination.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情などから感情を解析し、認識するための方法である。"Means of recognizing emotions" refers to a method for analyzing and recognizing emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, etc.
「感情認識結果」とは、感情を認識する手段によって得られたユーザーの感情状態のことである。"Emotion recognition result" refers to the user's emotional state obtained by the emotion recognition means.
「目的地を提案する手段」とは、感情認識結果に基づいてユーザーに適した目的地を推薦するための方法である。"Means for suggesting destinations" refers to a method for recommending suitable destinations to users based on emotion recognition results.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、以下のような構成を持つ。まず、サーバは様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段を備えている。具体的には、機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlowやPyTorch)を用いて、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを解析し、パターンや知識を獲得する。A system for implementing this invention has the following configuration. First, the server has a means for learning information from various information sources. Specifically, a machine learning algorithm (e.g., TensorFlow or PyTorch) is used to analyze data such as restaurant rating information and the availability of parking spaces, and to acquire patterns and knowledge.
次に、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段を備えている。この手段は、自然言語処理技術(例えば、BERTやGPT-3)を用いてユーザーの音声コマンドを解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と言った場合、その要望を解析し、適切な目的地を検索する。Next, it is equipped with a means to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests. This means uses natural language processing technology (e.g., BERT and GPT-3) to analyze the user's voice commands and understand what the user wants. For example, if the user says, "Find a good restaurant nearby," the request is analyzed and an appropriate destination is searched for.
さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段を備えている。サーバは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補から最適な目的地を選び、設定する。この際、ユーザーの現在位置を考慮し、GPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算する。Furthermore, it is equipped with a means for setting a destination based on the search results. The server selects and sets the most suitable destination from the candidate destinations obtained by the search. At this time, it takes into account the user's current location and calculates the optimal route using GPS technology.
また、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段を備えている。サーバは、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へ到達することができる。The system also includes a means for providing navigation to the set destination. The server uses a voice guidance system to guide the user to the destination. This allows the user to reach the destination safely even while driving.
さらに、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段を備えている。サーバは、マイクロフォンとカメラを使用してユーザーの声のトーンや表情をリアルタイムで収集し、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて感情を解析する。例えば、TensorFlowを使用して音声データを解析し、ユーザーの感情状態を分類する。Furthermore, it has a means of recognizing the user's emotions. The server uses a microphone and camera to collect the user's tone of voice and facial expressions in real time, and then uses machine learning algorithms to analyze emotions. For example, it uses TensorFlow to analyze voice data and classify the user's emotional state.
感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段も備えている。サーバは、感情認識結果を基に、ユーザーの現在の感情状態に最も適した目的地を推薦する。例えば、ユーザーが明るいトーンで話している場合、活気のあるレストランを推薦し、落ち着いたトーンで話している場合は静かなカフェを推薦する。The system also has a means of suggesting destinations based on emotion recognition results. The server uses the emotion recognition results to recommend a destination that best suits the user's current emotional state. For example, if the user speaks in a bright tone, the server can recommend a lively restaurant, and if the user speaks in a calm tone, the server can recommend a quiet cafe.
具体例として、ユーザーが「今日はリラックスしたいから、静かなカフェを探して」と言った場合、システムはユーザーの声のトーンが落ち着いていることを認識し、静かなカフェを推薦する。その後、GPSを使用して最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスでユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。For example, if a user says, "I want to relax today, so find me a quiet cafe," the system will recognize that the user's tone of voice is calm and recommend a quiet cafe. It will then use GPS to calculate the optimal route and guide the user to their destination with voice guidance.
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが挙げられる。Examples of prompts include:
「ユーザーの声のトーンと表情を解析し、感情を認識して最適な目的地を提案するナビゲーションシステムを開発してください。ユーザーが「今日はリラックスしたいから、静かなカフェを探して」と言った場合、システムはユーザーの声のトーンが落ち着いていることを認識し、静かなカフェを推薦します。その後、GPSを使用して最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスでユーザーを目的地へ誘導します。」"Develop a navigation system that analyzes the user's tone of voice and facial expressions, recognizes emotions, and suggests the best destination. If the user says, 'I want to relax today, so I'm looking for a quiet cafe,' the system will recognize that the user's tone of voice is calm and recommend a quiet cafe. It will then use GPS to calculate the best route and guide the user to their destination with voice guidance."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが可能となる。In this way, it becomes possible to suggest and navigate to the most suitable destination based on the user's emotional state.
応用例1における特定処理の流れについて図16を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 1 is explained using Figure 16.
ステップ1:Step 1:
サーバは、マイクロフォンとカメラを使用してユーザーの声のトーンと表情をリアルタイムで収集する。入力はユーザーの音声と映像データであり、出力は前処理された音声データと映像データである。具体的には、ノイズ除去や顔認識を行い、解析に適した形式にデータを変換する。The server uses a microphone and camera to collect the user's tone of voice and facial expressions in real time. The input is the user's audio and video data, and the output is preprocessed audio and video data. Specifically, it performs noise removal and facial recognition, and converts the data into a format suitable for analysis.
ステップ2:Step 2:
サーバは、前処理された音声データと映像データを機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlow)に入力し、ユーザーの感情を認識する。入力は前処理された音声データと映像データであり、出力はユーザーの感情状態(例えば、喜び、悲しみ、怒りなど)である。具体的には、音声のトーンや表情の特徴を解析し、感情を分類する。The server inputs the preprocessed audio and video data into a machine learning algorithm (e.g., TensorFlow) to recognize the user's emotions. The input is the preprocessed audio and video data, and the output is the user's emotional state (e.g., joy, sadness, anger, etc.). Specifically, the tone of the voice and facial features are analyzed to classify the emotion.
ステップ3:Step 3:
サーバは、ユーザーの音声コマンドを自然言語処理技術(例えば、BERTやGPT-3)を用いて解析する。入力はユーザーの音声コマンドであり、出力はユーザーの要望を理解したテキストデータである。具体的には、「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」といったコマンドを解析し、ユーザーの要望を抽出する。The server analyzes the user's voice command using natural language processing technology (e.g., BERT or GPT-3). The input is the user's voice command, and the output is text data that represents an understanding of the user's request. Specifically, it analyzes commands such as "Find a good restaurant nearby" and extracts the user's request.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバは、感情認識結果とユーザーの要望を基に、データベースから適切な目的地をサーチする。入力は感情認識結果とユーザーの要望テキストであり、出力は目的地の候補リストである。具体的には、ユーザーが明るいトーンで話している場合、活気のあるレストランをデータベースから検索する。The server searches the database for an appropriate destination based on the emotion recognition results and the user's request. The input is the emotion recognition results and the user's request text, and the output is a list of candidate destinations. Specifically, if the user is speaking in a bright tone, the database is searched for lively restaurants.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバは、サーチ結果から最適な目的地を選び、設定する。入力は目的地の候補リストであり、出力は設定された目的地である。具体的には、ユーザーの現在位置を考慮し、最も適した目的地を選択する。The server selects and sets the optimal destination from the search results. The input is a list of candidate destinations, and the output is the set destination. Specifically, it takes into account the user's current location and selects the most suitable destination.
ステップ6:Step 6:
サーバは、GPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算する。入力はユーザーの現在位置と設定された目的地であり、出力は最適なルート情報である。具体的には、地図データを使用して、最短経路や交通状況を考慮したルートを計算する。The server uses GPS technology to calculate the optimal route. The input is the user's current location and the set destination, and the output is optimal route information. Specifically, it uses map data to calculate the shortest route and a route that takes traffic conditions into account.
ステップ7:Step 7:
サーバは、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。入力は最適なルート情報であり、出力は音声ガイダンスである。具体的には、ユーザーに対して「次の交差点を右折してください」といった指示を音声で提供する。The server uses a voice guidance system to guide the user to the destination. The input is optimal route information, and the output is voice guidance. Specifically, it provides the user with voice instructions such as "Turn right at the next intersection."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが実現される。In this way, optimal destination suggestions and navigation can be achieved based on the user's emotional state.
(実施例2)(Example 2)
次に、形態例2の実施例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマート眼鏡214を「端末」と称する。Next, a second embodiment of the second embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が困難であった。また、ユーザーが音声で予約を依頼した場合、自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了する機能が不足していた。これにより、ユーザーは手動で予約を行う必要があり、利便性が低かった。さらに、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行われておらず、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができなかった。Conventional navigation systems had difficulty providing services that took into account the detailed requests and emotions of users. In addition, when a user made a reservation by voice, the system lacked the functionality to automatically make a phone call to complete the reservation. This meant that users had to make the reservation manually, which was inconvenient. Furthermore, the system did not recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, which made it difficult to increase user satisfaction.
実施例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声を認識する手段と、音声認識結果を基にレストランを検索する手段と、自動で電話をかける手段と、予約を完了する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、感情に基づいてレストランを推薦する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が可能となり、音声による予約依頼に対して自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了することができる。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行うことができ、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's voice, means for searching for restaurants based on the voice recognition results, means for automatically making a phone call, means for completing a reservation, means for recognizing the user's emotions, and means for recommending a restaurant based on the emotions. This makes it possible to provide a service that takes into account the user's specific requests and emotions, and a reservation can be completed by automatically making a phone call in response to a reservation request made via voice. It is also possible to recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報源から得られたデータを解析し、知識を蓄積するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to methods and techniques for analyzing data obtained from sources and accumulating knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods and technologies for searching for an appropriate location based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた情報やデータを指す。"Search results" refers to the information or data obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果を基にユーザーが訪れるべき場所を決定するための方法や技術を指す。"Destination setting means" refers to the methods and technologies that allow users to determine where they should visit based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道順や案内を提供するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods and technologies for providing directions and guidance to a set destination.
「音声を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声を解析してテキストデータに変換するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of voice recognition" refers to methods and technologies for analyzing a user's voice and converting it into text data.
「レストランを検索する手段」とは、音声認識結果を基に適切な飲食店を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for searching for restaurants" refers to methods and technologies for searching for appropriate restaurants based on voice recognition results.
「自動で電話をかける手段」とは、システムが自動的に電話を発信するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for making automatic phone calls" refers to methods or technologies that allow the system to automatically make phone calls.
「予約を完了する手段」とは、電話を通じて予約手続きを完了するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of completing a reservation" refers to the methods and technologies used to complete the reservation process over the telephone.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの入力や音声から感情を解析するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of emotion recognition" refers to methods and technologies for analyzing emotions from user input or voice.
「レストランを推薦する手段」とは、認識された感情に基づいて適切な飲食店を提案するための方法や技術を指す。"Restaurant recommendation means" refers to methods or technologies for suggesting appropriate dining options based on recognized sentiment.
本発明は、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供を実現するためのシステムである。このシステムは、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションとして実装され、ユーザーの音声やテキスト入力を基に、目的地の検索、予約、ナビゲーション、感情に基づくレストランの推薦を行う。The present invention is a system for providing services that take into account the detailed requests and emotions of users. This system is implemented as a smartphone application, and performs destination search, reservations, navigation, and emotion-based restaurant recommendations based on the user's voice and text input.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
ハードウェア:スマートフォン(iPhone、Android端末など)Hardware: Smartphone (iPhone, Android device, etc.)
ソフトウェア:Software:
音声認識技術:音声をテキストに変換するために、音声認識APIを使用する。Speech recognition technology: Uses speech recognition APIs to convert speech to text.
レストラン検索:地図APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。Restaurant search: Use the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
自動ダイヤルシステム:自動的に電話をかけるために、通信APIを使用する。Automatic dialing system: Uses communications APIs to automatically place calls.
感情認識技術:ユーザーの入力から感情を解析するために、感情分析APIを使用する。Emotion recognition technology: Uses sentiment analysis APIs to analyze emotions from user input.
レストラン推薦:レビューサイトAPIを使用して、感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。Restaurant Recommendations: Use review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on sentiment.
システムの具体的な処理Specific processing of the system
ユーザーの要望に基づく予約機能Reservation function based on user requests
1. ユーザーがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「電話で予約して」と音声で指示を出す。1. The user launches the smartphone application and issues a voice command saying, "Make a reservation by phone."
2. 端末は音声認識APIを使用して、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換する。2. The device uses a speech recognition API to convert the user's speech into text.
3. 端末は地図APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。3. The device uses the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
4. 端末は通信APIを使用して、検索結果から選ばれたレストランに自動で電話をかける。4. The device uses a communications API to automatically call the restaurant selected from the search results.
5. 端末は電話を通じてレストランに予約内容を伝え、予約を完了する。5. The terminal then transmits the reservation details to the restaurant via telephone, completing the reservation.
具体例:Example:
ユーザーが「電話で予約して」と言う。The user says, "Make a reservation by phone."
端末は音声認識APIを使用して音声をテキストに変換する。The device uses a speech recognition API to convert speech to text.
端末:「音声を認識中です。」Device: "Recognizing voice."
端末は地図APIを使用して近くのレストランを検索する。The device uses the map API to search for nearby restaurants.
端末:「近くのレストランを検索中です。」Device: "Searching for nearby restaurants."
端末は通信APIを使用して自動的にレストランに電話をかける。The device will automatically call the restaurant using a communications API.
端末:「レストランに電話をかけています。」Device: "Calling restaurant."
端末は予約が完了したことをユーザーに通知する。The device will notify the user that the reservation is complete.
端末:「予約が完了しました。」Device: "Reservation completed."
感情エンジンを用いたサービス提供Providing services using emotion engines
1. ユーザーがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」とテキストまたは音声で入力する。1. The user launches the smartphone application and inputs via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
2. 端末は感情分析APIを使用して、ユーザーの入力から感情を認識する。2. The device uses the sentiment analysis API to recognize emotions from user input.
3. 端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用して、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。3. The device uses review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on the user's sentiment.
具体例:Example:
ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力する。The user types, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
端末は感情分析APIを使用して感情を認識する。The device uses an emotion analysis API to recognize emotions.
端末:「感情を分析中です。」Device: "Analyzing emotions."
端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用してリラックスできるレストランを推薦する。The device uses review site APIs to recommend relaxing restaurants.
端末:「リラックスできるレストランを探しています。」Device: "I'm looking for a relaxing restaurant."
端末:「こちらのレストランはいかがですか?(レストラン名)」Device: "How about this restaurant? (restaurant name)"
以上が、本発明のスマートフォン用アプリケーションの具体的な実施形態である。このシステムにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が可能となり、音声による予約依頼に対して自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了することができる。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行うことができ、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができる。The above is a specific embodiment of the smartphone application of the present invention. This system makes it possible to provide services that take into account the detailed requests and emotions of the user, and can complete reservations by automatically making a phone call in response to a voice reservation request. It can also recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
実施例2における特定処理の流れについて図17を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 2 is explained using Figure 17.
ユーザーの要望に基づく予約機能Reservation function based on user requests
処理ステップProcessing steps
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「電話で予約して」と音声で指示を出す。The user launches the smartphone application and gives the voice command, "Make a reservation by phone."
入力:ユーザの音声指示Input: User's voice command
出力:音声データOutput: Audio data
具体的な動作:ユーザがアプリケーションを起動し、音声で「電話で予約して」と指示を出す。Specific operation: The user launches the application and issues the command "Make a reservation by phone" via voice.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末は音声認識APIを使用して、ユーザの音声をテキストに変換する。The device uses a speech recognition API to convert the user's speech into text.
入力:音声データInput: Audio data
出力:テキストデータOutput: Text data
具体的な動作:端末は音声データを音声認識APIに送信し、テキストデータを受け取る。Specific operation: The device sends voice data to the voice recognition API and receives text data.
端末:「音声を認識中です。」Device: "Recognizing voice."
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末は地図APIを使用して、ユーザの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。The device uses the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
入力:テキストデータ、ユーザの現在地情報Input: text data, user's current location information
出力:レストランのリストOutput: List of restaurants
具体的な動作:端末はユーザの現在地情報を取得し、地図APIにクエリを送信してレストランのリストを受け取る。Specific operation: The device obtains the user's current location information and sends a query to the map API to receive a list of restaurants.
端末:「近くのレストランを検索中です。」Device: "Searching for nearby restaurants."
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末は通信APIを使用して、検索結果から選ばれたレストランに自動で電話をかける。The device uses a communications API to automatically call the restaurant selected from the search results.
入力:レストランのリストEnter: List of restaurants
出力:通話開始Output: Start call
具体的な動作:端末は通信APIに電話番号と通話内容を送信し、通話を開始する。Specific operation: The device sends the phone number and call details to the communication API and starts the call.
端末:「レストランに電話をかけています。」Device: "Calling restaurant."
ステップ5:Step 5:
端末は電話を通じてレストランに予約内容を伝え、予約を完了する。The terminal then communicates the reservation details to the restaurant via telephone, completing the reservation.
入力:通話開始Enter: Start call
出力:予約完了通知Output: Reservation completion notification
具体的な動作:端末は通信APIを通じて通話を管理し、予約が完了したことをユーザーに通知する。Specific operation: The device manages the call through the communication API and notifies the user that the reservation has been completed.
端末:「予約が完了しました。」Device: "Reservation completed."
感情エンジンを用いたサービス提供Providing services using emotion engines
処理ステップProcessing steps
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」とテキストまたは音声で入力する。The user launches a smartphone application and inputs, via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
入力:ユーザのテキストまたは音声入力Input: User text or voice input
出力:テキストデータOutput: Text data
具体的な動作:ユーザがアプリケーションを起動し、テキストまたは音声で「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力する。Specific actions: The user launches the application and enters, via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末は感情分析APIを使用して、ユーザの入力から感情を認識する。The device uses a sentiment analysis API to recognize emotions from user input.
入力:テキストデータInput: Text data
出力:感情分析結果Output: Sentiment analysis results
具体的な動作:端末はテキストデータを感情分析APIに送信し、感情分析結果を受け取る。Specific operation: The device sends text data to the sentiment analysis API and receives the sentiment analysis results.
端末:「感情を分析中です。」Device: "Analyzing emotions."
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用して、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。The device uses review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on user sentiment.
入力:感情分析結果Input: Sentiment analysis results
出力:レストランの推薦リストOutput: A list of restaurant recommendations
具体的な動作:端末は感情分析結果を基にレビューサイトAPIにクエリを送信し、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランやユーザーが好きな料理を提供するレストランのリストを受け取る。Specific operation: Based on the sentiment analysis results, the device sends a query to the review site API and receives a list of restaurants that have a relaxing atmosphere or serve the user's favorite cuisine.
端末:「リラックスできるレストランを探しています。」Device: "I'm looking for a relaxing restaurant."
端末:「こちらのレストランはいかがですか?(レストラン名)」Device: "How about this restaurant? (restaurant name)"
以上が、本発明のスマートフォン用アプリケーションの具体的な処理ステップである。The above are the specific processing steps of the smartphone application of the present invention.
(応用例2)(Application example 2)
次に、形態例2の応用例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、スマート眼鏡214を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 2 of embodiment example 2 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムや予約システムは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮することができず、ユーザー体験が限定されていた。また、ユーザーが音声で要望を入力し、それに基づいて最適なサービスを推薦し、自動的に注文を行う機能が欠如していた。これにより、ユーザーが求めるサービスを迅速かつ的確に提供することが困難であった。Conventional navigation and reservation systems were unable to take into account the detailed requests and feelings of users, limiting the user experience. They also lacked the functionality to have users input their requests by voice, have the system recommend optimal services based on those requests, and automatically place orders. This made it difficult to quickly and accurately provide the services users wanted.
応用例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声入力を認識する手段と、認識された音声入力から感情を分析する手段と、感情分析の結果に基づいて最適なサービスを推薦する手段と、推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの要望や感情を考慮したサービスの提供が可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's voice input, means for analyzing emotions from the recognized voice input, means for recommending optimal services based on the results of the emotion analysis, and means for automatically placing an order for the recommended services. This makes it possible to provide services that take into account the user's requests and emotions.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報源から得られたデータを解析し、知識を蓄積するための方法や装置を指す。"Means of learning" refers to methods and devices for analyzing data obtained from sources and accumulating knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for searching for a destination" refers to a method or device for searching for an appropriate location based on a user's request.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索手段によって得られた情報の集合を指す。"Search Results" refers to the collection of information obtained through a search tool.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果から選ばれた場所を最終的な目的地として決定するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to a method or device for determining a location selected from the search results as the final destination.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道順や案内を提供するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for providing navigation" refers to a method or device for providing directions or guidance to a set destination.
「音声入力を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声をテキストデータに変換するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for recognizing voice input" refers to a method or device for converting a user's voice into text data.
「感情を分析する手段」とは、音声入力やテキストデータからユーザーの感情を解析するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for analyzing emotions" refers to a method or device for analyzing a user's emotions from voice input or text data.
「最適なサービスを推薦する手段」とは、感情分析の結果に基づいてユーザーに最も適したサービスを提案するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for recommending optimal services" refers to a method or device for suggesting the most suitable service to a user based on the results of sentiment analysis.
「自動的に注文を行う手段」とは、推薦されたサービスに対してユーザーの介入なしに注文を完了するための方法や装置を指す。"Automatic ordering means" refers to a method or device for completing an order for recommended services without user intervention.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、ユーザーの音声入力を認識し、感情を分析し、最適なサービスを推薦し、自動的に注文を行う一連の処理を行うものである。以下に、このシステムの具体的な実施形態を説明する。The system for implementing this invention performs a series of processes that recognize the user's voice input, analyze emotions, recommend optimal services, and automatically place an order. A specific embodiment of this system is described below.
システム構成System configuration
システムは、以下の主要なコンポーネントから構成される:The system consists of the following main components:
1. 音声認識モジュール:ユーザーの音声入力をテキストデータに変換する。具体的には、speech_recognitionライブラリを使用する。1. Speech recognition module: Converts the user's voice input into text data. Specifically, it uses the speech_recognition library.
2. 感情分析モジュール:音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを解析し、ユーザーの感情を分析する。具体的には、TextBlobライブラリを使用する。2. Sentiment analysis module: Analyzes the text data obtained from the voice recognition module and analyzes the user's emotions. Specifically, it uses the TextBlob library.
3. サービス推薦モジュール:感情分析の結果に基づいて、ユーザーに最適なサービスを推薦する。3. Service recommendation module: Recommend the most suitable services to users based on the results of sentiment analysis.
4. 自動注文モジュール:推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う。具体的には、requestsライブラリを使用してAPIエンドポイントに注文データを送信する。4. Auto-order module: Automatically places orders for recommended services. Specifically, it uses the requests library to send order data to an API endpoint.
処理の流れProcessing flow
1. 音声入力の認識:ユーザーがスマートフォンに向かって音声で要望を入力する。音声認識モジュールがこの音声をテキストデータに変換する。1. Voice input recognition: The user speaks their request into the smartphone. The voice recognition module converts this voice into text data.
2. 感情の分析:音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを感情分析モジュールに渡し、ユーザーの感情を解析する。2. Sentiment analysis: The text data obtained from the voice recognition module is passed to the sentiment analysis module to analyze the user's emotions.
3. サービスの推薦:感情分析の結果に基づいて、サービス推薦モジュールがユーザーに最適なサービスを選定し、推薦する。3. Service recommendation: Based on the results of sentiment analysis, the service recommendation module selects and recommends the most suitable services to the user.
4. 自動注文の実行:サービス推薦モジュールが選定したサービスに対して、自動注文モジュールが注文を行う。4. Executing automatic orders: The automatic ordering module places an order for the service selected by the service recommendation module.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
ハードウェア:スマートフォン、サーバHardware: smartphones, servers
ソフトウェア:speech_recognitionライブラリ、TextBlobライブラリ、requestsライブラリSoftware: speech_recognition library, TextBlob library, requests library
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と音声入力した場合、システムは以下のように動作する:For example, if a user says, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," the system will act as follows:
1. 音声認識モジュールが音声をテキストに変換し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」というテキストデータを生成する。1. The voice recognition module converts the voice into text and generates text data such as "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
2. 感情分析モジュールがこのテキストデータを解析し、ユーザーが疲れていることを認識する。2. The sentiment analysis module analyzes this text data and recognizes that the user is tired.
3. サービス推薦モジュールがリラックスできる雰囲気のレストランを推薦する。3. The service recommendation module recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere.
4. 自動注文モジュールが推薦されたレストランに対して自動的に注文を行う。4. The auto-order module automatically places orders from the recommended restaurants.
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
生成AIモデルへ入力するプロンプト文の例:Example of a prompt to input to a generative AI model:
ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と音声入力した場合、感情分析を行い、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランを推薦し、自動的に注文を行うPythonプログラムを作成してください。If a user says, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," create a Python program that performs sentiment analysis, recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere, and automatically places the order.
応用例2における特定処理の流れについて図18を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 2 is explained using Figure 18.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザーがスマートフォンに向かって音声で要望を入力する。音声入力は、スマートフォンのマイクを通じて取得される。入力データは、ユーザの音声データである。The user speaks their request into the smartphone. The voice input is picked up through the smartphone's microphone. The input data is the user's voice data.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末の音声認識モジュールが、ユーザーの音声データをテキストデータに変換する。具体的には、speech_recognitionライブラリを使用して音声データを解析し、テキストデータを生成する。出力データは、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換したものである。The device's voice recognition module converts the user's voice data into text data. Specifically, it uses the speech_recognition library to analyze the voice data and generate text data. The output data is the user's voice converted into text.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末の感情分析モジュールが、音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを受け取り、ユーザーの感情を解析する。具体的には、TextBlobライブラリを使用してテキストデータの感情を分析する。入力データは、テキストデータであり、出力データは、感情分析の結果である。The terminal's sentiment analysis module receives the text data obtained from the voice recognition module and analyzes the user's sentiment. Specifically, it uses the TextBlob library to analyze the sentiment of the text data. The input data is the text data, and the output data is the result of the sentiment analysis.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバのサービス推薦モジュールが、感情分析の結果に基づいて、ユーザに最適なサービスを選定し、推薦する。入力データは、感情分析の結果であり、出力データは、推薦されたサービスの情報である。具体的には、感情がネガティブであればリラックスできるサービスを、ポジティブであれば人気のサービスを推薦する。The server's service recommendation module selects and recommends the most suitable service to the user based on the results of the sentiment analysis. The input data is the results of the sentiment analysis, and the output data is information about the recommended service. Specifically, if the sentiment is negative, a relaxing service is recommended, and if it is positive, a popular service is recommended.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバの自動注文モジュールが、サービス推薦モジュールから得られた推薦サービス情報を受け取り、自動的に注文を行う。具体的には、requestsライブラリを使用して、推薦されたサービスに対して注文データをAPIエンドポイントに送信する。入力データは、推薦されたサービスの情報であり、出力データは、注文の完了通知である。The server's automatic ordering module receives the recommended service information obtained from the service recommendation module and automatically places the order. Specifically, it uses the requests library to send order data for the recommended service to an API endpoint. The input data is information about the recommended service, and the output data is a notification of order completion.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末が、注文の完了通知をユーザに表示する。入力データは、注文の完了通知であり、出力データは、ユーザに表示される注文完了メッセージである。具体的には、スマートフォンの画面に注文が完了した旨のメッセージを表示する。The terminal displays a notification that the order is complete to the user. The input data is the notification that the order is complete, and the output data is an order completion message that is displayed to the user. Specifically, a message indicating that the order is complete is displayed on the smartphone screen.
特定処理部290は、特定処理の結果をスマート眼鏡214に送信する。スマート眼鏡214では、制御部46Aが、スピーカ240に対して特定処理の結果を出力させる。マイクロフォン238は、特定処理の結果に対するユーザ入力を示す音声を取得する。制御部46Aは、マイクロフォン238によって取得されたユーザ入力を示す音声データをデータ処理装置12に送信する。データ処理装置12では、特定処理部290が音声データを取得する。The
データ生成モデル58は、いわゆる生成AI(Artificial Intelligence)である。データ生成モデル58の一例としては、ChatGPT(インターネット検索<URL: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt>)等の生成AIが挙げられる。データ生成モデル58は、ニューラルネットワークに対して深層学習を行わせることによって得られる。データ生成モデル58には、指示を含むプロンプトが入力され、かつ、音声を示す音声データ、テキストを示すテキストデータ、及び画像を示す画像データ等の推論用データが入力される。データ生成モデル58は、入力された推論用データをプロンプトにより示される指示に従って推論し、推論結果を音声データ及びテキストデータ等のデータ形式で出力する。ここで、推論とは、例えば、分析、分類、予測、及び/又は要約等を指す。The
生成AIの他の例としては、Gemini(インターネット検索<URL: https://gemini.google.com/?hl=ja>)が挙げられる。Another example of generative AI is Gemini (Internet search <URL: https://gemini.google.com/?hl=ja>).
上記実施形態では、データ処理装置12によって特定処理が行われる形態例を挙げたが、本開示の技術はこれに限定されず、スマート眼鏡214によって特定処理が行われるようにしてもよい。In the above embodiment, an example was given in which the specific processing is performed by the
[第3実施形態][Third embodiment]
図5には、第3実施形態に係るデータ処理システム310の構成の一例が示されている。Figure 5 shows an example of the configuration of a
図5に示すように、データ処理システム310は、データ処理装置12及びヘッドセット型端末314を備えている。データ処理装置12の一例としては、サーバが挙げられる。As shown in FIG. 5, the
データ処理装置12は、コンピュータ22、データベース24、及び通信I/F26を備えている。コンピュータ22は、本開示の技術に係る「コンピュータ」の一例である。コンピュータ22は、プロセッサ28、RAM30、及びストレージ32を備えている。プロセッサ28、RAM30、及びストレージ32は、バス34に接続されている。また、データベース24及び通信I/F26も、バス34に接続されている。通信I/F26は、ネットワーク54に接続されている。ネットワーク54の一例としては、WAN(Wide Area Network)及び/又はLAN(Local Area Network)等が挙げられる。The
ヘッドセット型端末314は、コンピュータ36、マイクロフォン238、スピーカ240、カメラ42、通信I/F44、及びディスプレイ343を備えている。コンピュータ36は、プロセッサ46、RAM48、及びストレージ50を備えている。プロセッサ46、RAM48、及びストレージ50は、バス52に接続されている。また、マイクロフォン238、スピーカ240、カメラ42、及びディスプレイ343も、バス52に接続されている。The
マイクロフォン238は、ユーザ20が発する音声を受け付けることで、ユーザ20から指示等を受け付ける。マイクロフォン238は、ユーザ20が発する音声を捕捉し、捕捉した音声を音声データに変換してプロセッサ46に出力する。スピーカ240は、プロセッサ46からの指示に従って音声を出力する。The
カメラ42は、レンズ、絞り、及びシャッタ等の光学系と、CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)イメージセンサ又はCCD(Charge Coupled Device)イメージセンサ等の撮像素子とが搭載された小型デジタルカメラであり、ユーザ20の周囲(例えば、一般的な健常者の視界の広さに相当する画角で規定された撮像範囲)を撮像する。
通信I/F44は、ネットワーク54に接続されている。通信I/F44及び26は、ネットワーク54を介してプロセッサ46とプロセッサ28との間の各種情報の授受を司る。通信I/F44及び26を用いたプロセッサ46とプロセッサ28との間の各種情報の授受はセキュアな状態で行われる。The communication I/
図6には、データ処理装置12及びヘッドセット型端末314の要部機能の一例が示されている。図6に示すように、データ処理装置12では、プロセッサ28によって特定処理が行われる。ストレージ32には、特定処理プログラム56が格納されている。Figure 6 shows an example of the main functions of the
特定処理プログラム56は、本開示の技術に係る「プログラム」の一例である。プロセッサ28は、ストレージ32から特定処理プログラム56を読み出し、読み出した特定処理プログラム56をRAM30上で実行する。特定処理は、プロセッサ28がRAM30上で実行する特定処理プログラム56に従って、特定処理部290として動作することによって実現される。The
ストレージ32には、データ生成モデル58及び感情特定モデル59が格納されている。データ生成モデル58及び感情特定モデル59は、特定処理部290によって用いられる。
ヘッドセット型端末314では、プロセッサ46によって受付出力処理が行われる。ストレージ50には、受付出力プログラム60が格納されている。プロセッサ46は、ストレージ50から受付出力プログラム60を読み出し、読み出した受付出力プログラム60をRAM48上で実行する。受付出力処理は、プロセッサ46がRAM48上で実行する受付出力プログラム60に従って、制御部46Aとして動作することによって実現される。In the
次に、データ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理について説明する。Next, we will explain the specific processing performed by the
「形態例1」"Example 1"
本発明の一実施形態として、車載用のナビゲーションシステムが考えられる。このシステムは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段として、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いる。具体的には、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得し、これを学習する。また、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段として、自然言語処理技術を用いる。ユーザーからの質問を解析し、それに基づいて適切な目的地をサーチする。さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段として、GPS技術を用いる。ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定する。最後に、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段として、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いる。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。One embodiment of the present invention is an in-vehicle navigation system. This system uses a machine learning algorithm as a means of learning information from various information sources. Specifically, information is acquired from a database that includes information such as restaurant reviews and the availability of parking spaces, and this information is learned. Natural language processing technology is also used as a means of searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests. Questions from the user are analyzed, and an appropriate destination is searched for based on the results. GPS technology is also used as a means of setting the destination based on the search results. The optimal route is calculated based on the user's current location and the search results, and the destination is set. Finally, a voice guidance system is used as a means of providing navigation to the set destination. This allows the user to be safely guided to their destination even while driving.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
本発明の別の実施形態として、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションが考えられる。このアプリケーションは、前述の車載用ナビゲーションシステムと同様の機能を持つが、さらにユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う機能を含む。具体的には、ユーザーが「電話で予約して」という要望を出した場合、システムは自動的に該当するレストランに電話をかけ、予約を行う。この機能は、音声認識技術と自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて実現される。Another embodiment of the present invention is a smartphone application. This application has the same functions as the in-car navigation system described above, but also includes a function for making reservations based on the user's request. Specifically, when a user requests to "make a reservation by phone," the system automatically calls the corresponding restaurant and makes the reservation. This function is realized using voice recognition technology and an automatic dialing system.
以下に、各形態例の処理の流れについて説明する。The process flow for each example is explained below.
「形態例1」"Example 1"
ステップ1:システムは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得し、これを機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて学習する。Step 1: The system learns information from various sources. Specifically, it obtains information from a database that includes information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available, and learns from this information using machine learning algorithms.
ステップ2:ユーザーからの細かい要望が入力されると、システムは自然言語処理技術を用いてこれを解析する。Step 2: Once the user has entered their detailed request, the system analyzes it using natural language processing technology.
ステップ3:解析結果に基づいて、システムは適切な目的地をサーチする。Step 3: Based on the analysis results, the system searches for suitable destinations.
ステップ4:サーチ結果とユーザーの現在位置を基に、システムはGPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定する。Step 4: Based on the search results and the user's current location, the system uses GPS technology to calculate the optimal route and set the destination.
ステップ5:設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供するため、システムは音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーを誘導する。Step 5: The system guides the user using the voice guidance system to provide navigation to the set destination.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
ステップ1:スマートフォン用のアプリケーションは、前述の車載用ナビゲーションシステムと同様の機能を持つ。Step 1: The smartphone application has the same functions as the in-car navigation system mentioned above.
ステップ2:ユーザーが「電話で予約して」という要望を出した場合、システムは自動的に該当するレストランに電話をかける。Step 2: If the user requests to "make a reservation by phone," the system will automatically call the relevant restaurant.
ステップ3:システムは音声認識技術と自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う。Step 3: The system uses voice recognition technology and an automated dialing system to make the reservation.
(実施例1)(Example 1)
次に、形態例1の実施例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ヘッドセット型端末314を「端末」と称する。Next, a first embodiment of the first embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチすることが困難であり、また、ユーザーの質問に対する適切な回答を生成することができなかった。さらに、目的地の設定やナビゲーションの提供においても、ユーザーの現在位置やサーチ結果を効果的に利用することができなかった。これにより、ユーザーの利便性が低下し、運転中の安全性も確保されにくかった。With conventional navigation systems, it was difficult to search for a destination based on the user's specific requests, and they were unable to generate appropriate answers to the user's questions. Furthermore, they were unable to effectively use the user's current location or search results when setting a destination or providing navigation. This reduced user convenience and made it difficult to ensure safety while driving.
実施例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、音声入力をテキストに変換する手段と、自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析する手段と、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを学習する手段と、位置情報を取得する手段と、音声ガイダンスを生成する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいた目的地のサーチと設定が可能となり、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導されることが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for converting voice input to text, means for analyzing the user's questions using natural language processing techniques, means for learning data using machine learning algorithms, means for acquiring location information, and means for generating voice guidance. This makes it possible to search for and set a destination based on the user's detailed requests, and allows the user to be safely guided to the destination even while driving.
「情報源」とは、データを提供するあらゆる媒体やシステムを指す。"Source" refers to any medium or system that provides data.
「学習する手段」とは、データを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出するためのアルゴリズムや技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to the algorithms and techniques used to analyze data and extract patterns and knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて求める詳細な要求を指す。"Specific user requests" refers to the detailed requirements that users have based on their specific conditions and preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to the technology or algorithms used to search for an appropriate destination based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補や情報を指す。"Search results" refers to destination candidates and information obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果に基づいて最適な目的地を決定するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to the technology or algorithm used to determine the optimal destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、ユーザーが目的地に到達するための経路案内を行う技術やシステムを指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to technologies and systems that provide route guidance to help users reach their destination.
「音声入力をテキストに変換する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声を解析し、文字情報に変換する技術やシステムを指す。"Means of converting voice input into text" refers to technology or systems that analyze the user's voice and convert it into text information.
「自然言語処理技術」とは、人間の言語を解析し、理解するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Natural language processing technology" refers to the techniques and algorithms for analyzing and understanding human language.
「機械学習アルゴリズム」とは、データからパターンや知識を学習し、予測や分類を行うためのアルゴリズムを指す。"Machine learning algorithms" refer to algorithms that learn patterns and knowledge from data and make predictions and classifications.
「位置情報を取得する手段」とは、ユーザーの現在位置を特定するための技術やシステムを指す。"Means of acquiring location information" refers to technologies and systems for identifying the user's current location.
「音声ガイダンスを生成する手段」とは、ユーザーに音声で指示を出すための技術やシステムを指す。"Means for generating audio guidance" refers to technology or systems for providing audio instructions to the user.
発明を実施するための形態Form for implementing the invention
この発明は、車載用ナビゲーションシステムに関するものであり、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチし、最適なルートを提供するためのシステムである。このシステムは、サーバ、端末、ユーザーの三者が連携して動作する。This invention relates to an in-vehicle navigation system that searches for destinations based on the user's specific requests and provides the optimal route. This system works in cooperation with a server, a terminal, and a user.
1. プログラムの生成1. Program generation
サーバは、車載用ナビゲーションシステムのプログラムを生成する。このプログラムは、機械学習アルゴリズムと自然言語処理技術を組み合わせて構築される。具体的には、PythonのPandas、Scikit-learn、NLTK、SpaCy、Google Maps API、Amazon PollyなどのライブラリやAPIを使用する。The server generates the program for the in-car navigation system. This program is built by combining machine learning algorithms and natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses libraries and APIs such as Python's Pandas, Scikit-learn, NLTK, SpaCy, Google Maps API, and Amazon Polly.
2. プログラムの処理2. Program processing
サーバは、以下の手順でデータを処理する。The server processes the data in the following steps:
1. データ取得と学習:1. Data acquisition and learning:
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースからデータを取得する。具体的には、PythonのPandasライブラリを使用してデータを読み込む。次に、サーバはScikit-learnを用いて機械学習アルゴリズムでデータを学習する。例えば、レストランの評価情報を基に、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを作成する。The server retrieves data from a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. Specifically, it reads the data using Python's Pandas library. The server then uses Scikit-learn to train the data with machine learning algorithms. For example, it creates a model that predicts highly rated restaurants based on restaurant rating information.
2. ユーザーの質問解析:2. User question analysis:
端末は、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。例えば、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」という質問を受け取る。端末は、この質問を自然言語処理技術を用いて解析する。具体的には、PythonのNLTKやSpaCyを使用して、質問の意図を理解する。The device receives questions from users. For example, it may receive a question such as, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby." The device then analyzes the question using natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses Python's NLTK and SpaCy to understand the intent of the question.
3. 目的地の設定:3. Set your destination:
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。具体的には、Google Maps APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を取得し、最適なルートを計算する。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results. Specifically, it uses the Google Maps API to obtain the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants, and calculates the optimal route.
4. ナビゲーションの提供:4. Providing navigation:
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する。具体的には、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに音声で指示を出す。例えば、Amazon Pollyを使用して、「右に曲がってください」などの音声ガイダンスを生成する。The device provides navigation to the set destination. Specifically, it uses a voice guidance system to give voice instructions to the user. For example, it uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance such as "Turn right."
3. 具体例3. Specific examples
具体例として、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と質問した場合を考える。As a concrete example, consider the case where a user asks, "Can you tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby?"
1. データ取得と学習:1. Data acquisition and learning:
サーバは、データベースに接続し、レストランの評価情報を取得する。The server connects to the database and retrieves restaurant rating information.
サーバは、Pandasを用いてデータをDataFrameに変換する。The server converts the data into a DataFrame using Pandas.
サーバは、Scikit-learnのRandomForestClassifierを用いて、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを学習する。The server uses Scikit-learn's RandomForestClassifier to train a model to predict highly rated restaurants.
2. ユーザーの質問解析:2. User question analysis:
ユーザーは、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と端末に話しかける。The user speaks to the device saying, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby."
端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換する。The device converts voice input into text.
端末は、NLTKを用いてテキストをトークン化し、SpaCyを用いて質問の意図を解析する。The device uses NLTK to tokenize the text and SpaCy to analyze the intent of the question.
3. 目的地の設定:3. Set your destination:
端末は、GPSセンサーを用いてユーザーの現在位置を取得する。The device uses the GPS sensor to obtain the user's current location.
サーバは、Google Maps APIを用いて、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を基にルートを計算する。The server uses the Google Maps API to calculate a route based on the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants.
サーバは、計算結果を端末に送信する。The server sends the calculation results to the terminal.
4. ナビゲーションの提供:4. Providing navigation:
端末は、サーバから受け取ったルート情報を基に、ナビゲーションを開始する。The device begins navigation based on the route information received from the server.
端末は、Amazon Pollyを用いて音声ガイダンスを生成し、ユーザーに指示を出す。The device uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance and give instructions to the user.
ユーザーは、音声ガイダンスに従って運転する。The user drives by following the voice guidance.
プロンプト文の例:Example prompt:
「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」"Can you tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby?"
このようにして、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。In this way, users are safely guided to their destination while driving.
実施例1における特定処理の流れについて図11を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 1 is explained using Figure 11.
ステップ1:データ取得と学習Step 1: Data acquisition and learning
サーバは、データベースからレストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を取得する。入力として、データベース接続情報とSQLクエリを使用する。サーバは、PythonのPandasライブラリを用いてデータをDataFrameに変換する。次に、サーバはScikit-learnを用いて機械学習アルゴリズムでデータを学習する。具体的には、RandomForestClassifierを使用して、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを作成する。出力として、学習済みのモデルが得られる。The server retrieves information from the database, such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. As input, it uses the database connection information and a SQL query. The server converts the data into a DataFrame using Python's Pandas library. The server then uses Scikit-learn to train the data with a machine learning algorithm. Specifically, it uses RandomForestClassifier to create a model that predicts highly rated restaurants. As output, it obtains the trained model.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
サーバは、データベースに接続し、SQLクエリを実行してデータを取得する。The server connects to the database and executes SQL queries to retrieve data.
サーバは、取得したデータをPandasのDataFrameに変換する。The server converts the retrieved data into a Pandas DataFrame.
サーバは、Scikit-learnのRandomForestClassifierを用いて、レストランの評価を予測するモデルを学習する。The server uses Scikit-learn's RandomForestClassifier to train a model to predict restaurant ratings.
ステップ2:ユーザーの質問解析Step 2: Analyze user questions
端末は、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。入力として、ユーザーの音声質問が使用される。端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換するために音声認識技術を使用する。次に、端末は、自然言語処理技術を用いて質問を解析する。具体的には、PythonのNLTKやSpaCyを使用して、質問の意図を理解する。出力として、解析されたテキストデータが得られる。The terminal receives a question from the user. As input, the user's voice question is used. The terminal uses speech recognition technology to convert the voice input into text. The terminal then analyzes the question using natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses Python's NLTK and SpaCy to understand the intent of the question. As output, the analyzed text data is obtained.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
ユーザーは、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と端末に話しかける。The user speaks to the device saying, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby."
端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換する。The device converts voice input into text.
端末は、NLTKを用いてテキストをトークン化し、SpaCyを用いて質問の意図を解析する。The device uses NLTK to tokenize the text and SpaCy to analyze the intent of the question.
ステップ3:目的地の設定Step 3: Set your destination
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。入力として、ユーザーの現在位置と解析されたテキストデータが使用される。サーバは、Google Maps APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を取得し、最適なルートを計算する。出力として、計算されたルート情報が得られる。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results. The user's current location and parsed text data are used as input. The server uses the Google Maps API to obtain the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants, and calculates the optimal route. The calculated route information is obtained as output.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
端末は、GPSセンサーを用いてユーザーの現在位置を取得する。The device uses the GPS sensor to obtain the user's current location.
サーバは、Google Maps APIを用いて、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を基にルートを計算する。The server uses the Google Maps API to calculate a route based on the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants.
サーバは、計算結果を端末に送信する。The server sends the calculation results to the terminal.
ステップ4:ナビゲーションの提供Step 4: Provide navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する。入力として、計算されたルート情報が使用される。端末は、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに音声で指示を出す。具体的には、Amazon Pollyを使用して、「右に曲がってください」などの音声ガイダンスを生成する。出力として、音声ガイダンスが得られる。The device provides navigation to the set destination. The calculated route information is used as input. The device uses a voice guidance system to give voice instructions to the user. Specifically, it uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance such as "Turn right". The voice guidance is obtained as output.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
端末は、サーバから受け取ったルート情報を基に、ナビゲーションを開始する。The device begins navigation based on the route information received from the server.
端末は、Amazon Pollyを用いて音声ガイダンスを生成し、ユーザーに指示を出す。The device uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance and give instructions to the user.
ユーザーは、音声ガイダンスに従って運転する。The user drives by following the voice guidance.
(応用例1)(Application example 1)
次に、形態例1の応用例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ヘッドセット型端末314を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 1 of embodiment example 1 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする機能が限定的であり、ユーザーの質問に対する適切な回答を生成する能力が不足している。また、現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスを提供する機能も十分ではない。これにより、ユーザーは目的地への移動中に不便を感じることが多い。Traditional navigation systems have limited functionality for searching for destinations based on the user's specific requests and lack the ability to generate appropriate answers to user questions. They also lack the ability to calculate the optimal route between the current location and the destination and provide voice guidance. This often causes inconvenience to users while traveling to their destination.
応用例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する自然言語処理手段と、現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する手段と、音声ガイダンスを提供する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチし、最適なルートを計算して音声ガイダンスを提供することが可能となる。The identification process by the
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するための出典やリソースである。A "source" is a source or resource that provides data or knowledge.
「情報を学習する手段」とは、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて、様々な情報源から取得したデータを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出する方法である。"Means of learning information" refers to the use of machine learning algorithms to analyze data obtained from various sources and extract patterns and knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて求める詳細な要求や希望である。"User specific requests" are the detailed demands and wishes that a user has based on their specific conditions and preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための方法や技術である。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods or technologies for searching for an appropriate destination based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、目的地をサーチする手段によって得られた検索結果である。"Search results" means the results of a search obtained by a means of searching for a destination.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果に基づいてユーザーの目的地を決定する方法や技術である。"Means for setting a destination" refers to a method or technology for determining a user's destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、ユーザーが目的地に到達するための経路案内や指示を提供する方法や技術である。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods or technologies that provide route guidance or directions to help a user reach a destination.
「自然言語処理手段」とは、ユーザーの質問や要求を解析し、適切な回答を生成するための技術である。"Natural language processing means" is technology for analyzing users' questions and requests and generating appropriate answers.
「ルートを計算する手段」とは、現在位置と目的地の間の最適な経路を計算するための方法や技術である。"Means for calculating a route" refers to a method or technique for calculating the optimal route between a current location and a destination.
「音声ガイダンスを提供する手段」とは、計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供する方法や技術である。"Means for providing audio guidance" refers to methods or technologies that convert calculated route information into audio and provide it to the user.
この発明を実施するための形態として、以下のようなシステムが考えられる。The following system is considered as a form for implementing this invention.
まず、サーバは様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段を持つ。この手段は、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出するものである。具体的には、データベースから情報を取得し、これを学習する。First, the server has a means of learning information from various sources. This means uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data such as restaurant reviews and the availability of parking spaces, and extract patterns and knowledge. Specifically, it retrieves information from a database and learns from it.
次に、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段がある。この手段は、自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な目的地をサーチするものである。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」と質問すると、システムはその質問を解析し、適切なレストランを検索する。Next, there is a means to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests. This means uses natural language processing technology to analyze the user's question and search for an appropriate destination. For example, if a user asks, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" the system will analyze the question and search for an appropriate restaurant.
さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段がある。この手段は、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定するものである。具体的には、Geopyライブラリを使用して、現在位置と目的地の間の距離を計算する。In addition, there is a method for setting a destination based on search results. This method calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and search results, and sets the destination. Specifically, it uses the Geopy library to calculate the distance between the current location and the destination.
最後に、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段がある。この手段は、Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)ライブラリを使用して、計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供するものである。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。Finally, there is a mechanism for providing navigation to a set destination. This mechanism uses the Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) library to convert the calculated route information into audio and provide it to the user. This allows the user to be safely guided to their destination while driving.
具体例として、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」と質問すると、システムは以下のように動作する。As a concrete example, when a user asks, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" the system works as follows:
1. 自然言語処理手段がユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する。1. Natural language processing tools analyze the user's question and generate an appropriate answer.
2. 情報を学習する手段がデータベースからレストランの評価情報を取得し、解析する。2. The means for learning information retrieves restaurant rating information from the database and analyzes it.
3. ルートを計算する手段が現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する。3. A route calculation means calculates the optimal route between the current location and the destination.
4. 音声ガイダンスを提供する手段が計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供する。4. A means for providing audio guidance converts the calculated route information into audio and provides it to the user.
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが考えられる。Some examples of prompt statements include:
ユーザーの質問: 「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」User Question: "What are some highly rated restaurants near me?"
コンテキスト: 「レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無など」Context: "Restaurant ratings, availability of parking, etc."
このプロンプト文を使用して、生成AIモデルに質問を解析させ、適切な回答を得ることができる。This prompt can then be used by a generative AI model to parse the question and provide an appropriate answer.
応用例1における特定処理の流れについて図12を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 1 is explained using Figure 12.
ステップ1:Step 1:
サーバは、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。入力はユーザーの質問であり、例えば「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」というテキストデータである。出力は解析のための準備が整ったテキストデータである。The server receives a question from a user. The input is the user's question, which is text data, for example, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" The output is text data ready for analysis.
ステップ2:Step 2:
サーバは、自然言語処理手段を用いて、ユーザーの質問を解析する。入力はステップ1で受け取ったユーザーの質問であり、出力は解析結果としての適切な検索クエリである。具体的には、生成AIモデルを使用して質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する。The server uses natural language processing means to analyze the user's question. The input is the user's question received in step 1, and the output is an appropriate search query as a result of the analysis. Specifically, a generative AI model is used to analyze the question and generate an appropriate answer.
ステップ3:Step 3:
サーバは、情報を学習する手段を用いて、データベースからレストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを取得する。入力はステップ2で生成された検索クエリであり、出力は取得された評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータである。具体的には、データベースに対してクエリを実行し、必要な情報を取得する。The server uses a means for learning information to obtain data such as restaurant rating information and whether or not parking is available from the database. The input is the search query generated in step 2, and the output is the obtained rating information, parking availability, and other data. Specifically, the server executes a query against the database to obtain the required information.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバは、取得した情報を基に、ユーザーの現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する。入力はユーザーの現在位置とステップ3で取得された目的地情報であり、出力は計算された最適なルート情報である。具体的には、Geopyライブラリを使用して距離を計算し、最適なルートを決定する。The server calculates the optimal route between the user's current location and the destination based on the acquired information. The input is the user's current location and the destination information acquired in step 3, and the output is the calculated optimal route information. Specifically, the Geopy library is used to calculate the distance and determine the optimal route.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバは、計算されたルート情報を音声ガイダンスに変換する。入力はステップ4で計算されたルート情報であり、出力は音声ファイルである。具体的には、Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)ライブラリを使用して、テキスト情報を音声に変換する。The server converts the calculated route information into voice guidance. The input is the route information calculated in step 4, and the output is an audio file. Specifically, it uses the Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) library to convert the text information into voice.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末は、生成された音声ガイダンスをユーザーに提供する。入力はステップ5で生成された音声ファイルであり、出力はユーザーに対する音声案内である。具体的には、音声ファイルを再生し、ユーザーに対してナビゲーション情報を提供する。The terminal provides the generated voice guidance to the user. The input is the audio file generated in step 5, and the output is audio guidance for the user. Specifically, the terminal plays the audio file and provides navigation information to the user.
(実施例2)(Example 2)
次に、形態例2の実施例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ヘッドセット型端末314を「端末」と称する。Next, a second embodiment of the second embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、目的地の設定やナビゲーション機能を提供するだけであり、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいた予約機能を持たないため、ユーザーが手動で予約を行う必要があった。また、音声指示を解析して自動的に予約を行うシステムも存在しなかったため、ユーザーの利便性が低かった。これにより、ユーザーは目的地の設定と予約の両方を別々に行う手間がかかり、効率的な利用が難しかった。Conventional navigation systems only provided destination setting and navigation functions, and did not have a reservation function based on the user's specific requests, so users had to make reservations manually. There was also no system that analyzed voice instructions and made reservations automatically, which resulted in low user convenience. This meant that users had to take the time to set a destination and make reservations separately, making it difficult to use the system efficiently.
実施例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声指示を解析する手段と、解析された音声指示に基づいて予約内容を抽出する手段と、抽出された予約内容に基づいて自動的に電話をかける手段と、電話を通じて予約内容を音声で伝える手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーは音声指示を出すだけで目的地の設定と予約が自動的に行われ、利便性が大幅に向上することが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for analyzing the user's voice instructions, means for extracting reservation details based on the analyzed voice instructions, means for automatically making a phone call based on the extracted reservation details, and means for audibly communicating the reservation details over the phone. This allows the user to automatically set a destination and make a reservation simply by issuing voice instructions, greatly improving convenience.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「ユーザー」とは、システムを利用する個人または団体を指す。"User" refers to an individual or organization that uses the system.
「目的地」とは、ユーザーが到達したい場所を指す。"Destination" refers to the place the user wants to reach.
「サーチ」とは、特定の情報を探し出す行為を指す。"Search" refers to the act of finding specific information.
「ナビゲーション」とは、目的地までの経路を案内する機能を指す。"Navigation" refers to the function of providing route guidance to a destination.
「音声指示」とは、ユーザーが音声を用いてシステムに対して行う指示を指す。"Voice instructions" refers to instructions given by the user to the system using voice.
「解析」とは、データや情報を詳細に調べて意味や構造を理解する行為を指す。"Analysis" refers to the act of examining data or information in detail to understand its meaning and structure.
「予約内容」とは、予約に必要な情報(日時、人数、場所など)を指す。"Reservation details" refers to the information required for making a reservation (date and time, number of people, location, etc.).
「自動的」とは、人の手を介さずに機械やシステムが独自に動作することを指す。"Automatic" refers to a machine or system that operates independently without human intervention.
「電話をかける」とは、通信装置を用いて他の通信装置に接続を試みる行為を指す。"Making a phone call" refers to the act of using a communication device to attempt to connect to another communication device.
「音声で伝える」とは、音声を用いて情報を他者に伝達する行為を指す。"Communicating by voice" refers to the act of conveying information to others using voice.
発明を実施するための形態Form for implementing the invention
この発明は、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションとして実施される。このアプリケーションは、ユーザーの音声指示に基づいて目的地の設定と予約を自動的に行うシステムである。以下に、このシステムの具体的な実施形態を説明する。This invention is implemented as an application for smartphones. This application is a system that automatically sets a destination and makes reservations based on the user's voice instructions. A specific embodiment of this system is described below.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
このシステムは、以下のハードウェアおよびソフトウェアを使用する。This system uses the following hardware and software:
スマートフォン(端末)Smartphone (device)
音声認識技術(Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API)Voice recognition technology (Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API)
データベース管理システム(Firebase Firestore)Database management system (Firebase Firestore)
自動ダイヤルシステム(Twilio API)Automatic dialing system (Twilio API)
音声合成技術(Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API)Speech synthesis technology (Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API)
データ加工およびデータ演算Data processing and data calculations
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、音声で「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示する。端末はGoogle Cloud Speech-to-Text APIを使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。この変換処理はリアルタイムで行われる。The user launches the application on their smartphone and says, "Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm." The device uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API to convert the user's voice instructions into text. This conversion process occurs in real time.
次に、端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、予約内容(日時、人数)を抽出する。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」というテキストから「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という情報を取り出す。Then, the device analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details (date, time, number of people). For example, from the text "Make a reservation for four people at 7 p.m. tomorrow," the information "tomorrow at 7 p.m." and "four people" is extracted.
端末はFirebase Firestoreに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。このリクエストには、ユーザの位置情報や好みのレストランの条件が含まれる。サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をFirebase Firestoreから取得し、端末に返す。返される情報には、レストランの名前、電話番号、住所などが含まれる。The device sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in Firebase Firestore. This request includes the user's location and preferred restaurant conditions. The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from Firebase Firestore, and returns it to the device. The returned information includes the restaurant's name, phone number, address, etc.
端末はTwilio APIを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。この処理はユーザの手を煩わせることなく行われる。電話が接続されると、端末はGoogle Cloud Text-to-Speech APIを使用して、事前に抽出した予約内容を音声でレストランに伝える。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声が再生される。The device uses the Twilio API to automatically call the restaurant's phone number, without any user intervention. Once the call is connected, the device uses the Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API to communicate the reservation details it extracted in advance to the restaurant via voice. For example, it might say, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
具体例Specific examples
具体例として、ユーザが「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示した場合の動作を以下に示す。As a concrete example, the behavior when a user instructs "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow night" is shown below.
1. ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と音声で指示する。1. The user launches the smartphone application and gives a voice command such as, "Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
2. 端末はGoogle Cloud Speech-to-Text APIを使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。2. The device uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API to convert the user's voice commands into text.
3. 端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という予約内容を抽出する。3. The device analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details: "tomorrow night at 7pm" and "4 people."
4. 端末はFirebase Firestoreに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。4. The device sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in Firebase Firestore.
5. サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をFirebase Firestoreから取得し、端末に返す。5. The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from Firebase Firestore, and returns it to the device.
6. 端末はTwilio APIを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。6. The device uses the Twilio API to automatically call the restaurant's phone number.
7. 電話が接続されると、端末はGoogle Cloud Text-to-Speech APIを使用して、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声をレストランに伝える。7. Once the call is connected, the device uses the Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API to communicate to the restaurant, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが考えられる。Some examples of prompt statements include:
「ユーザが「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示した場合、アプリケーションはどのように処理を行うか説明してください。」"If a user says, 'Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm,' how should the application handle that?"
このプロンプト文を生成AIモデルに入力することで、上記の具体例に基づいた処理の説明を得ることができる。By inputting this prompt into the generative AI model, we can obtain an explanation of the process based on the specific example above.
実施例2における特定処理の流れについて図13を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 2 is explained using Figure 13.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザが音声指示を出す。The user gives voice instructions.
ユーザはスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と音声で指示する。この音声指示が入力となる。The user launches the smartphone application and gives a voice command such as, "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow night." This voice command becomes the input.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末が音声をテキストに変換する。Your device will convert the voice to text.
端末は音声認識技術を使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。この処理には音声認識APIが使用される。入力はユーザの音声指示であり、出力はテキスト形式の指示である。The device uses voice recognition technology to convert the user's voice instructions into text. This process uses a voice recognition API. The input is the user's voice instructions, and the output is the instructions in text format.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末がテキストを解析し、予約内容を抽出する。The device analyzes the text and extracts the reservation details.
端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、予約内容(日時、人数)を抽出する。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」というテキストから「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という情報を取り出す。入力はテキスト形式の指示であり、出力は予約内容のデータである。The terminal analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details (date, time, number of people). For example, from the text "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow," the information "tomorrow at 7pm" and "four people" is extracted. The input is instructions in text format, and the output is the reservation details data.
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末がサーバにレストラン情報をリクエストする。The device requests restaurant information from the server.
端末はデータベース管理システムに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。このリクエストには、ユーザの位置情報や好みのレストランの条件が含まれる。入力は予約内容とユーザの位置情報であり、出力はレストラン情報のリクエストである。The terminal sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in the database management system. This request includes the user's location information and preferred restaurant conditions. The input is the reservation details and the user's location information, and the output is a request for restaurant information.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバがレストラン情報を返す。The server returns the restaurant information.
サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をデータベースから取得し、端末に返す。返される情報には、レストランの名前、電話番号、住所などが含まれる。入力はレストラン情報のリクエストであり、出力はレストラン情報である。The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from the database, and returns it to the terminal. The returned information includes the restaurant's name, phone number, address, etc. The input is a request for restaurant information, and the output is the restaurant information.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末が自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて電話をかける。The device makes the call using an automatic dialing system.
端末は自動ダイヤルシステムを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。この処理はユーザの手を煩わせることなく行われる。入力はレストランの電話番号であり、出力は電話接続の確立である。The terminal uses an automatic dialing system to automatically call the restaurant's phone number, without any user intervention. The input is the restaurant's phone number, and the output is the establishment of a telephone connection.
ステップ7:Step 7:
端末が予約内容を音声で伝える。The device will announce the reservation details aloud.
電話が接続されると、端末は音声合成技術を使用して、事前に抽出した予約内容を音声でレストランに伝える。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声が再生される。入力は予約内容のデータであり、出力は音声メッセージである。When the phone is connected, the device uses voice synthesis technology to verbally communicate the reservation details extracted in advance to the restaurant. For example, a voice may be played saying, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7 p.m." The input is the reservation details data, and the output is a voice message.
(応用例2)(Application example 2)
次に、形態例2の応用例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ヘッドセット型端末314を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 2 of embodiment example 2 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムや予約システムは、ユーザーが手動で操作する必要があり、利便性に欠ける点があった。また、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を活用して最適な提案を行う機能が不足していたため、ユーザーの要望に迅速かつ的確に応えることが難しかった。さらに、音声認識技術や自動ダイヤルシステムを効果的に組み合わせることで、ユーザー体験を向上させることが求められていた。Conventional navigation and reservation systems required users to operate them manually, which made them less convenient. They also lacked the functionality to utilize the user's past behavioral history to make optimal suggestions, making it difficult to respond to user requests quickly and accurately. Furthermore, there was a need to effectively combine voice recognition technology and an automatic dialing system to improve the user experience.
応用例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段と、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段と、音声フィードバックを提供する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーは音声指示のみで目的地の検索や予約を行うことができ、過去の行動履歴に基づいた最適な提案を受けることが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for understanding the user's requests using voice recognition technology, means for making reservations using an automatic dialing system, means for learning the user's past behavioral history and making optimal suggestions, and means for providing voice feedback. This allows the user to search for and make reservations at destinations using only voice instructions, and to receive optimal suggestions based on the user's past behavioral history.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報を収集し、解析し、理解するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to the methods and techniques used to collect, analyze, and understand information.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods and technologies for searching for an appropriate location based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた情報やデータを指す。"Search results" refers to the information or data obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、検索結果に基づいて最終的な目的地を決定するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to the method or technology for determining a final destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道案内を行うための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods and technologies for providing directions to a set destination.
「音声認識技術」とは、音声を解析し、テキストやコマンドに変換する技術を指す。"Voice recognition technology" refers to the technology that analyzes voice and converts it into text or commands.
「自動ダイヤルシステム」とは、指定された電話番号に自動的に電話をかけるシステムを指す。"Automatic dialing system" refers to a system that automatically dials a specified telephone number.
「予約を行う手段」とは、指定された場所やサービスの予約を自動的に行うための方法や技術を指す。"Means of making a reservation" refers to methods or technologies for automatically making a reservation for a specified location or service.
「過去の行動履歴」とは、ユーザーが以前に行った行動や選択の記録を指す。"Past behavioral history" refers to records of actions and choices a user has previously made.
「最適な提案を行う手段」とは、過去の行動履歴や現在の要望に基づいて、ユーザーに最も適した選択肢を提示するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of making optimal suggestions" refers to methods and technologies for presenting the most suitable options to users based on their past behavioral history and current needs.
「音声フィードバックを提供する手段」とは、システムが音声を用いてユーザーに情報や結果を伝えるための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing audio feedback" refers to methods or technologies that allow a system to communicate information or results to a user using audio.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、以下のような構成を持つ。サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段、音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段、自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段、音声フィードバックを提供する手段を含む。A system for implementing this invention has the following configuration: The server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for understanding the user's requests using voice recognition technology, means for making reservations using an automatic dialing system, means for learning the user's past behavioral history and making optimal suggestions, and means for providing voice feedback.
プログラムの処理の説明Explanation of program processing
ハードウェアとソフトウェアHardware and software
このシステムは、スマートフォンのマイクとスピーカーをハードウェアとして使用する。また、音声認識にはspeech_recognitionライブラリ、音声フィードバックにはpyttsx3ライブラリ、データ通信にはrequestsライブラリを使用する。The system uses the smartphone's microphone and speaker as hardware. It also uses the speech_recognition library for voice recognition, the pyttsx3 library for voice feedback, and the requests library for data communication.
データ加工とデータ演算Data processing and data calculations
1. 音声認識: ユーザーがスマートフォンのマイクに向かって要望を話すと、speech_recognitionライブラリがその音声をテキストに変換する。1. Speech recognition: When the user speaks their request into the smartphone's microphone, the speech_recognition library converts the speech into text.
2. 要望の解析: 変換されたテキストを解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。例えば、「ピザを注文して」という要望を解析する。2. Request Analysis: Analyze the converted text to understand the user's request. For example, analyze the request "order a pizza."
3. 予約の実行: 要望に基づいて、requestsライブラリを使用してフードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信する。注文が成功した場合、pyttsx3ライブラリを使用して音声フィードバックを提供する。3. Execute reservation: Based on the request, send the order to the food delivery API using the requests library. If the order is successful, provide audio feedback using the pyttsx3 library.
4. 行動履歴の学習: ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、次回以降の最適な提案を行う。4. Learning behavioral history: Learns the user's past behavioral history and provides optimal suggestions for future visits.
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「ピザを注文して」と言った場合、システムは以下のように動作する。For example, if a user says "order a pizza," the system would do the following:
1. ユーザーの音声をマイクで取得する。1. Capture the user's voice using the microphone.
2. 音声をテキストに変換し、「ピザを注文して」というテキストを得る。2. Convert speech to text and get the text "Order pizza."
3. テキストを解析し、「ピザ」の注文を特定する。3. Analyze the text to identify "pizza" orders.
4. フードデリバリーAPIに「ピザ」の注文を送信する。4. Send an order for "Pizza" to the food delivery API.
5. 注文が成功した場合、「ピザの注文が完了しました」と音声でフィードバックする。5. If the order is successful, audio feedback will be provided saying "Your pizza order has been completed."
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
「ユーザーが「ピザを注文して」と言った場合、音声認識技術を用いて音声をテキストに変換し、フードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信するプログラムを作成してください。注文が成功した場合、音声で「ピザの注文が完了しました」とフィードバックしてください。」"When a user says, 'Order pizza,' please create a program that uses voice recognition technology to convert the speech to text and send the order to the food delivery API. If the order is successful, please provide voice feedback saying, 'The pizza order has been completed.'"
このようにして、ユーザーは音声指示のみで目的地の検索や予約を行うことができ、過去の行動履歴に基づいた最適な提案を受けることが可能となる。In this way, users can search for and book destinations using only voice commands, and receive optimal suggestions based on their past travel history.
応用例2における特定処理の流れについて図14を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 2 is explained using Figure 14.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのマイクに向かって要望を話す。The user speaks their request into the smartphone's microphone.
入力: ユーザの音声。Input: User's voice.
出力: マイクで取得された音声データ。Output: Audio data captured by the microphone.
具体的な動作: ユーザが「ピザを注文して」と話すと、スマートフォンのマイクがその音声をキャプチャする。What happens: When a user says "order a pizza," the smartphone's microphone captures the audio.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末がspeech_recognitionライブラリを使用して音声データをテキストに変換する。The device uses the speech_recognition library to convert the voice data into text.
入力: マイクで取得された音声データ。Input: Audio data captured by the microphone.
出力: テキストデータ(例:「ピザを注文して」)。Output: Text data (e.g. "order pizza").
具体的な動作: 音声認識エンジンが音声データを解析し、対応するテキストに変換する。Specific operation: The speech recognition engine analyzes the voice data and converts it into corresponding text.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末がテキストデータを解析し、ユーザの要望を理解する。The device analyzes the text data and understands the user's needs.
入力: テキストデータ(例:「ピザを注文して」)。Input: Text data (e.g. "order pizza").
出力: 要望の解析結果(例:「ピザの注文」)。Output: Analysis of the request (e.g. "order pizza").
具体的な動作: テキスト解析エンジンが「ピザを注文して」というテキストを解析し、「ピザの注文」という要望を特定する。Specific behavior: The text analysis engine analyzes the text "order a pizza" and identifies the request "order a pizza."
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末がrequestsライブラリを使用してフードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信する。The device uses the requests library to send the order to the food delivery API.
入力: 要望の解析結果(例:「ピザの注文」)。Input: Analysis of the request (e.g. "order pizza").
出力: APIへの注文リクエストとそのレスポンス。Output: The order request to the API and its response.
具体的な動作: フードデリバリーAPIに対して「ピザの注文」を含むリクエストを送信し、注文が成功したかどうかのレスポンスを受け取る。Specific behavior: Send a request to the food delivery API including "order pizza" and receive a response indicating whether the order was successful.
ステップ5:Step 5:
端末がpyttsx3ライブラリを使用して音声フィードバックを提供する。The device provides audio feedback using the pyttsx3 library.
入力: APIからのレスポンス(例:注文成功)。Input: Response from the API (e.g. order successful).
出力: 音声フィードバック(例:「ピザの注文が完了しました」)。Output: Audio feedback (e.g. "Your pizza order is complete").
具体的な動作: 音声合成エンジンが「ピザの注文が完了しました」というメッセージを生成し、スマートフォンのスピーカーを通じてユーザに伝える。Specific action: The speech synthesis engine generates the message "Your pizza order has been completed" and conveys it to the user through the smartphone speaker.
ステップ6:Step 6:
サーバがユーザの過去の行動履歴を学習し、次回以降の最適な提案を行う。The server learns the user's past behavioral history and makes optimal suggestions for future visits.
入力: ユーザの行動履歴データ。Input: User behavioral history data.
出力: 学習結果に基づく提案データ。Output: Proposed data based on learning results.
具体的な動作: サーバがユーザの過去の注文履歴を解析し、次回の注文時に最適なレストランやメニューを提案するためのデータを生成する。Specific operation: The server analyzes the user's past ordering history and generates data to suggest the best restaurant and menu for the next time they order.
なお、更に、ユーザの感情を推定する感情エンジンを組み合わせてもよい。すなわち、特定処理部290は、感情特定モデル59を用いてユーザの感情を推定し、ユーザの感情を用いた特定処理を行うようにしてもよい。Furthermore, an emotion engine that estimates the user's emotion may be combined. That is, the
「形態例1」"Example 1"
本発明の一実施形態として、感情エンジンを組み込んだナビゲーションシステムがある。このシステムは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を認識し、それを考慮に入れて目的地をサーチする。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」という要望を出した場合、その声のトーンが明るければ、システムは活気のあるレストランを、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば、静かなレストランを推薦する。One embodiment of the present invention is a navigation system incorporating an emotion engine. This system recognizes emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc., and searches for a destination taking these into consideration. For example, if a user requests, "Find a nice restaurant nearby," the system will recommend a lively restaurant if the user's tone of voice is cheerful, and a quiet restaurant if the user's tone of voice is sad.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
また、感情エンジンを組み込んだスマートフォン用のアプリケーションも本発明の一実施形態である。このアプリケーションは、ユーザーのテキスト入力や音声入力から感情を認識し、それを考慮に入れてサービスを提供する。例えば、ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力した場合、その感情を認識して、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランや、ユーザーが好きな料理を提供するレストランを推薦する。Another embodiment of the present invention is a smartphone application incorporating an emotion engine. This application recognizes emotions from the user's text and voice input, and provides services taking these into consideration. For example, if the user inputs, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," the application recognizes the emotion and recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere and restaurants that serve the user's favorite dishes.
以下に、各形態例の処理の流れについて説明する。The process flow for each example is explained below.
「形態例1」"Example 1"
ステップ1:ユーザーがナビゲーションシステムに対して音声で要望を出す。Step 1: The user issues a verbal request to the navigation system.
ステップ2:感情エンジンがユーザーの声のトーン、表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を認識する。Step 2: The emotion engine recognizes the user's emotions from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc.
ステップ3:システムが認識した感情を考慮に入れて、目的地をサーチする。Step 3: Search for destinations, taking into account the emotions the system recognizes.
ステップ4:システムがサーチ結果をユーザーに提示する。Step 4: The system presents the search results to the user.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
ステップ1:ユーザーがスマートフォン用のアプリケーションに対してテキスト入力や音声入力で要望を出す。Step 1: The user submits a request to a smartphone application via text or voice input.
ステップ2:感情エンジンがユーザーのテキスト入力や音声入力から感情を認識する。Step 2: The emotion engine recognizes emotions from the user's text or voice input.
ステップ3:アプリケーションが認識した感情を考慮に入れて、サービスを提供する。Step 3: The application takes into account the emotions it recognizes and provides a service.
ステップ4:アプリケーションが提供するサービスの結果をユーザーに提示する。Step 4: Present the user with the results of the services provided by the application.
(実施例1)(Example 1)
次に、形態例1の実施例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ヘッドセット型端末314を「端末」と称する。Next, a first embodiment of the first embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮した目的地の推薦が難しく、また、最適なルート計算や音声入力の解析が十分に行われないことが多かった。その結果、ユーザーの満足度が低下し、運転中の安全性も確保されにくいという課題があった。With conventional navigation systems, it was difficult to recommend destinations that took into account the user's detailed requests and feelings, and they often did not adequately calculate optimal routes or analyze voice input. As a result, there were issues with low user satisfaction and difficulty in ensuring safety while driving.
実施例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する手段と、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に最適なルートを計算する手段と、音声入力を解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮した目的地の推薦が可能となり、最適なルート計算や音声入力の解析も行われるため、ユーザーの満足度が向上し、運転中の安全性も確保される。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's emotions and recommending a destination based thereon, means for calculating an optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results, and means for analyzing voice input and understanding the user's requests. This makes it possible to recommend a destination taking into account the user's detailed requests and emotions, and also calculates an optimal route and analyzes voice input, thereby improving user satisfaction and ensuring safety while driving.
「情報源」とは、データを提供するための基となる場所やシステムであり、例えば、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースを指す。An "information source" is a source or system that provides data, such as a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available.
「学習する手段」とは、取得した情報を基に機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを解析し、パターンや特徴を抽出するプロセスを指す。"Means of learning" refers to the process of using machine learning algorithms to analyze data based on acquired information and extract patterns and features.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて出す具体的なリクエストを指す。"User specific requests" refers to specific requests made by users based on their specific conditions or preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースから検索するプロセスを指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to the process of searching a database for an appropriate destination based on the user's request.
「サーチ結果」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて検索された目的地の情報を指す。"Search results" refers to destination information searched for based on a user's request.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果を基にユーザーの目的地を決定し、その情報をシステムに登録するプロセスを指す。"Means of setting a destination" refers to the process of determining the user's destination based on search results and registering that information in the system.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地への道順をユーザーに案内するためのシステムや方法を指す。"Means for providing navigation" refers to a system or method for guiding a user to a set destination.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を解析し、それを理解するプロセスを指す。"Means of recognizing emotions" refers to the process of analyzing and understanding the emotions of the user from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc.
「最適なルートを計算する手段」とは、ユーザーの現在位置と目的地を基に、最も効率的な道順を計算するプロセスを指す。"Means of calculating optimal route" refers to the process of calculating the most efficient route based on the user's current location and destination.
「音声入力を解析する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換し、その内容を理解するための技術や方法を指す。"Means of analyzing voice input" refers to the technology or method for converting a user's voice into text and understanding its content.
本発明は、車載用のナビゲーションシステムに関するものであり、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮して最適な目的地を推薦し、ナビゲーションを提供するシステムである。このシステムは、サーバ、端末、ユーザーの三者が連携して動作する。The present invention relates to an in-vehicle navigation system that provides navigation by recommending optimal destinations while taking into account the user's detailed requests and feelings. This system operates in cooperation with a server, a terminal, and a user.
情報の取得と学習Acquiring and learning information
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得する。このデータベースは、例えば、一般的な地図サービスAPIや評価情報提供サービスAPIを通じてアクセスする。サーバは、取得した情報を機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlowやPyTorch)を用いて学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価や駐車場の有無などの特徴量を抽出し、これをモデルに入力して学習を行う。The server retrieves information from a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. This database is accessed, for example, through a general map service API or a rating information service API. The server learns from the retrieved information using a machine learning algorithm (for example, TensorFlow or PyTorch). Specifically, it extracts features such as the restaurant's rating and whether or not the restaurant has parking, and inputs these into a model for learning.
ユーザーの要望解析Analysis of user needs
端末は、ユーザーからの質問や要望を音声入力として受け取る。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と話しかける。端末は、音声認識技術(例えば、一般的な音声認識API)を用いて音声をテキストに変換する。変換されたテキストは、自然言語処理技術(例えば、一般的な自然言語処理モデル)を用いて解析される。解析結果として、ユーザーの要望が「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図であることを理解する。The device receives questions and requests from the user as voice input. For example, the user says, "Find a nice restaurant nearby." The device converts the voice into text using voice recognition technology (e.g., a general voice recognition API). The converted text is analyzed using natural language processing technology (e.g., a general natural language processing model). As a result of the analysis, it is understood that the user's request is intended to "find a nice restaurant."
目的地のサーチSearch for destinations
サーバは、解析結果に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースからサーチする。例えば、「美味しいレストラン」をキーワードにデータベースを検索する。サーバは、感情エンジンを用いて、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方から感情を認識する。例えば、ユーザーの声のトーンが明るければ、活気のあるレストランを推薦し、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば、静かなレストランを推薦する。The server then searches the database for an appropriate destination based on the analysis results. For example, it searches the database using the keyword "delicious restaurant." The server uses an emotion engine to recognize emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, and choice of words. For example, if the user's tone of voice is cheerful, it will recommend a lively restaurant, and if the tone of voice is sad, it will recommend a quiet restaurant.
ルートの計算と設定Calculate and set route
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。例えば、一般的な地図サービスAPIを用いてルート計算を行う。計算されたルート情報は端末に送信され、目的地が設定される。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location (GPS information) and the search results. For example, the route is calculated using a general map service API. The calculated route information is sent to the device, and the destination is set.
ナビゲーションの提供Provide navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを音声ガイダンスシステム(例えば、一般的なナビゲーションアプリ)を用いて提供する。具体的には、音声で「次の交差点を右折してください」などの指示を出す。ユーザーは、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。The device provides navigation to the set destination using a voice guidance system (e.g., a general navigation app). Specifically, instructions such as "Turn right at the next intersection" are given by voice. The user is safely guided to the destination even while driving.
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と音声入力を行った場合、以下のような具体的な動作が行われる。For example, if a user voice-inputs, "Find a good restaurant nearby," the following specific actions will occur:
1. 端末は、ユーザーの音声を受け取り、音声認識APIを用いてテキストに変換する。1. The device receives the user's voice and converts it into text using a speech recognition API.
2. 端末は、変換されたテキストを自然言語処理モデルに入力し、「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図を解析する。2. The device inputs the converted text into a natural language processing model and analyzes the intent of "find a good restaurant."
3. サーバは、解析結果を受け取り、データベースから「美味しいレストラン」を検索する。3. The server receives the analysis results and searches the database for "good restaurants."
4. サーバは、ユーザーの声のトーンを解析し、明るいトーンであれば活気のあるレストランを、落ち込んだトーンであれば静かなレストランを推薦する。4. The server analyzes the tone of the user's voice and recommends lively restaurants if the tone is cheerful, and quiet restaurants if the tone is depressed.
5. サーバは、地図サービスAPIを用いてユーザーの現在位置から目的地までの最適なルートを計算する。5. The server uses the map service API to calculate the optimal route from the user's current location to the destination.
6. 端末は、計算されたルート情報を受け取り、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーにナビゲーションを提供する。6. The device receives the calculated route information and provides navigation to the user using a voice guidance system.
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
「ユーザーが近くの美味しいレストランを探してと音声入力を行った場合、声のトーンが明るければ活気のあるレストランを、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば静かなレストランを推薦するシステムを設計してください。」"If a user requests a nearby restaurant by voice input, design a system that recommends lively restaurants if the user's voice tone is cheerful, and quiet restaurants if the user's voice tone is depressed."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情や要望に応じた最適なナビゲーションが提供される。In this way, optimal navigation is provided based on the user's emotions and needs.
実施例1における特定処理の流れについて図15を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 1 is explained using Figure 15.
ステップ1:Step 1:
情報の取得と学習Acquiring information and learning
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得する。The server retrieves information from a database that includes information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available.
入力:データベースからの情報(例:レストランの評価、駐車場の有無)Input: Information from a database (e.g. restaurant ratings, availability of parking)
データ加工:取得した情報を機械学習アルゴリズム(例:TensorFlow、PyTorch)を用いて学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価や駐車場の有無などの特徴量を抽出し、これをモデルに入力して学習を行う。Data processing: The acquired information is trained using a machine learning algorithm (e.g. TensorFlow, PyTorch). Specifically, features such as restaurant ratings and the availability of parking are extracted, and these are input into the model for training.
出力:学習済みモデルOutput: Trained model
ステップ2:Step 2:
ユーザーの要望解析Analysis of user needs
端末は、ユーザーからの質問や要望を音声入力として受け取る。The device receives questions and requests from the user as voice input.
入力:ユーザーの音声入力(例:「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」)Input: User's voice input (e.g. "Find good restaurants nearby")
データ加工:音声認識技術(例:音声認識API)を用いて音声をテキストに変換する。変換されたテキストを自然言語処理技術(例:自然言語処理モデル)を用いて解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。Data processing: Convert speech to text using speech recognition technology (e.g. speech recognition API). Analyze the converted text using natural language processing technology (e.g. natural language processing model) to understand the user's needs.
出力:解析結果(例:「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図)Output: Analysis results (e.g., the intent "find a good restaurant")
ステップ3:Step 3:
目的地のサーチSearch for a destination
サーバは、解析結果に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースからサーチする。The server searches the database for appropriate destinations based on the analysis results.
入力:解析結果(例:「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図)Input: Analysis results (e.g., the intent to "find a good restaurant")
データ加工:データベースから「美味しいレストラン」を検索する。感情エンジンを用いて、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方から感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する。Data processing: Search for "good restaurants" from a database. Using an emotion engine, recognize emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, and choice of words, and recommend destinations based on that.
出力:サーチ結果(例:活気のあるレストラン、静かなレストラン)Output: Search results (e.g. lively restaurants, quiet restaurants)
ステップ4:Step 4:
ルートの計算と設定Route calculation and setting
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location (GPS information) and the search results.
入力:ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)、サーチ結果Input: User's current location (GPS information), search results
データ加工:地図サービスAPIを用いて最適なルートを計算する。Data processing: Calculate the optimal route using a map service API.
出力:計算されたルート情報Output: Calculated route information
ステップ5:Step 5:
ナビゲーションの提供Providing navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて提供する。The device uses a voice guidance system to provide navigation to the set destination.
入力:計算されたルート情報Input: Calculated route information
データ加工:音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに対して「次の交差点を右折してください」などの指示を出す。Data processing: Using a voice guidance system, give instructions to the user such as "Turn right at the next intersection."
出力:音声ガイダンスOutput: Audio guidance
具体的な動作:ユーザーは、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。Specific operation: Users are safely guided to their destination while driving.
(応用例1)(Application example 1)
次に、形態例1の応用例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ヘッドセット型端末314を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 1 of embodiment example 1 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの感情状態を考慮せずに目的地を提案するため、ユーザーの現在の気分や状況に適した目的地を提供することができなかった。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいた最適なルートを提供することができず、ユーザーの満足度を向上させることが困難であった。Conventional navigation systems suggest destinations without taking the user's emotional state into account, making it impossible to provide a destination that suits the user's current mood or situation. In addition, they were unable to provide an optimal route based on the user's emotions, making it difficult to improve user satisfaction.
応用例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes a means for learning information from various information sources, a means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, a means for setting a destination based on the search results, a means for providing navigation to the set destination, a means for recognizing the user's emotions, and a means for suggesting a destination based on the emotion recognition results. This makes it possible to suggest and navigate to the optimal destination according to the user's emotional state.
「情報源」とは、データや情報を提供する元となる媒体やシステムのことである。An "information source" is a medium or system that provides data or information.
「学習する手段」とは、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて情報を解析し、パターンや知識を獲得するための方法である。A "means of learning" is a method for analyzing information and acquiring patterns and knowledge using machine learning algorithms.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望のことである。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user desires.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための方法である。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to a method for searching for an appropriate destination based on the user's requirements.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補のことである。"Search results" refers to destination candidates obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果から最適な目的地を選び、設定するための方法である。"Method of setting a destination" refers to the method for selecting and setting the optimal destination from the search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地への道順を案内するための方法である。"Means of providing navigation" refers to a method for providing directions to a set destination.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情などから感情を解析し、認識するための方法である。"Means of recognizing emotions" refers to a method for analyzing and recognizing emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, etc.
「感情認識結果」とは、感情を認識する手段によって得られたユーザーの感情状態のことである。"Emotion recognition result" refers to the user's emotional state obtained by the emotion recognition means.
「目的地を提案する手段」とは、感情認識結果に基づいてユーザーに適した目的地を推薦するための方法である。"Means for suggesting destinations" refers to a method for recommending suitable destinations to users based on emotion recognition results.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、以下のような構成を持つ。まず、サーバは様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段を備えている。具体的には、機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlowやPyTorch)を用いて、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを解析し、パターンや知識を獲得する。A system for implementing this invention has the following configuration. First, the server has a means for learning information from various information sources. Specifically, a machine learning algorithm (e.g., TensorFlow or PyTorch) is used to analyze data such as restaurant rating information and the availability of parking spaces, and to acquire patterns and knowledge.
次に、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段を備えている。この手段は、自然言語処理技術(例えば、BERTやGPT-3)を用いてユーザーの音声コマンドを解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と言った場合、その要望を解析し、適切な目的地を検索する。Next, it is equipped with a means to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests. This means uses natural language processing technology (e.g., BERT and GPT-3) to analyze the user's voice commands and understand what the user wants. For example, if the user says, "Find a good restaurant nearby," the request is analyzed and an appropriate destination is searched for.
さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段を備えている。サーバは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補から最適な目的地を選び、設定する。この際、ユーザーの現在位置を考慮し、GPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算する。Furthermore, it is equipped with a means for setting a destination based on the search results. The server selects and sets the most suitable destination from the candidate destinations obtained by the search. At this time, it takes into account the user's current location and calculates the optimal route using GPS technology.
また、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段を備えている。サーバは、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へ到達することができる。The system also includes a means for providing navigation to the set destination. The server uses a voice guidance system to guide the user to the destination. This allows the user to reach the destination safely even while driving.
さらに、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段を備えている。サーバは、マイクロフォンとカメラを使用してユーザーの声のトーンや表情をリアルタイムで収集し、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて感情を解析する。例えば、TensorFlowを使用して音声データを解析し、ユーザーの感情状態を分類する。Furthermore, it has a means of recognizing the user's emotions. The server uses a microphone and camera to collect the user's tone of voice and facial expressions in real time, and then uses machine learning algorithms to analyze emotions. For example, it uses TensorFlow to analyze voice data and classify the user's emotional state.
感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段も備えている。サーバは、感情認識結果を基に、ユーザーの現在の感情状態に最も適した目的地を推薦する。例えば、ユーザーが明るいトーンで話している場合、活気のあるレストランを推薦し、落ち着いたトーンで話している場合は静かなカフェを推薦する。The system also has a means of suggesting destinations based on emotion recognition results. The server uses the emotion recognition results to recommend a destination that best suits the user's current emotional state. For example, if the user speaks in a bright tone, the server can recommend a lively restaurant, and if the user speaks in a calm tone, the server can recommend a quiet cafe.
具体例として、ユーザーが「今日はリラックスしたいから、静かなカフェを探して」と言った場合、システムはユーザーの声のトーンが落ち着いていることを認識し、静かなカフェを推薦する。その後、GPSを使用して最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスでユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。For example, if a user says, "I want to relax today, so find me a quiet cafe," the system will recognize that the user's tone of voice is calm and recommend a quiet cafe. It will then use GPS to calculate the optimal route and guide the user to their destination with voice guidance.
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが挙げられる。Examples of prompts include:
「ユーザーの声のトーンと表情を解析し、感情を認識して最適な目的地を提案するナビゲーションシステムを開発してください。ユーザーが「今日はリラックスしたいから、静かなカフェを探して」と言った場合、システムはユーザーの声のトーンが落ち着いていることを認識し、静かなカフェを推薦します。その後、GPSを使用して最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスでユーザーを目的地へ誘導します。」"Develop a navigation system that analyzes the user's tone of voice and facial expressions, recognizes emotions, and suggests the best destination. If the user says, 'I want to relax today, so I'm looking for a quiet cafe,' the system will recognize that the user's tone of voice is calm and recommend a quiet cafe. It will then use GPS to calculate the best route and guide the user to their destination with voice guidance."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが可能となる。In this way, it becomes possible to suggest and navigate to the most suitable destination based on the user's emotional state.
応用例1における特定処理の流れについて図16を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 1 is explained using Figure 16.
ステップ1:Step 1:
サーバは、マイクロフォンとカメラを使用してユーザーの声のトーンと表情をリアルタイムで収集する。入力はユーザーの音声と映像データであり、出力は前処理された音声データと映像データである。具体的には、ノイズ除去や顔認識を行い、解析に適した形式にデータを変換する。The server uses a microphone and camera to collect the user's tone of voice and facial expressions in real time. The input is the user's audio and video data, and the output is preprocessed audio and video data. Specifically, it performs noise removal and facial recognition, and converts the data into a format suitable for analysis.
ステップ2:Step 2:
サーバは、前処理された音声データと映像データを機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlow)に入力し、ユーザーの感情を認識する。入力は前処理された音声データと映像データであり、出力はユーザーの感情状態(例えば、喜び、悲しみ、怒りなど)である。具体的には、音声のトーンや表情の特徴を解析し、感情を分類する。The server inputs the preprocessed audio and video data into a machine learning algorithm (e.g., TensorFlow) to recognize the user's emotions. The input is the preprocessed audio and video data, and the output is the user's emotional state (e.g., joy, sadness, anger, etc.). Specifically, the tone of the voice and facial features are analyzed to classify the emotion.
ステップ3:Step 3:
サーバは、ユーザーの音声コマンドを自然言語処理技術(例えば、BERTやGPT-3)を用いて解析する。入力はユーザーの音声コマンドであり、出力はユーザーの要望を理解したテキストデータである。具体的には、「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」といったコマンドを解析し、ユーザーの要望を抽出する。The server analyzes the user's voice command using natural language processing technology (e.g., BERT or GPT-3). The input is the user's voice command, and the output is text data that represents an understanding of the user's request. Specifically, it analyzes commands such as "Find a good restaurant nearby" and extracts the user's request.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバは、感情認識結果とユーザーの要望を基に、データベースから適切な目的地をサーチする。入力は感情認識結果とユーザーの要望テキストであり、出力は目的地の候補リストである。具体的には、ユーザーが明るいトーンで話している場合、活気のあるレストランをデータベースから検索する。The server searches the database for an appropriate destination based on the emotion recognition results and the user's request. The input is the emotion recognition results and the user's request text, and the output is a list of candidate destinations. Specifically, if the user is speaking in a bright tone, the database is searched for lively restaurants.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバは、サーチ結果から最適な目的地を選び、設定する。入力は目的地の候補リストであり、出力は設定された目的地である。具体的には、ユーザーの現在位置を考慮し、最も適した目的地を選択する。The server selects and sets the optimal destination from the search results. The input is a list of candidate destinations, and the output is the set destination. Specifically, it takes into account the user's current location and selects the most suitable destination.
ステップ6:Step 6:
サーバは、GPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算する。入力はユーザーの現在位置と設定された目的地であり、出力は最適なルート情報である。具体的には、地図データを使用して、最短経路や交通状況を考慮したルートを計算する。The server uses GPS technology to calculate the optimal route. The input is the user's current location and the set destination, and the output is optimal route information. Specifically, it uses map data to calculate the shortest route and a route that takes traffic conditions into account.
ステップ7:Step 7:
サーバは、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。入力は最適なルート情報であり、出力は音声ガイダンスである。具体的には、ユーザーに対して「次の交差点を右折してください」といった指示を音声で提供する。The server uses a voice guidance system to guide the user to the destination. The input is optimal route information, and the output is voice guidance. Specifically, it provides the user with voice instructions such as "Turn right at the next intersection."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが実現される。In this way, optimal destination suggestions and navigation can be achieved based on the user's emotional state.
(実施例2)(Example 2)
次に、形態例2の実施例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ヘッドセット型端末314を「端末」と称する。Next, a second embodiment of the second embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が困難であった。また、ユーザーが音声で予約を依頼した場合、自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了する機能が不足していた。これにより、ユーザーは手動で予約を行う必要があり、利便性が低かった。さらに、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行われておらず、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができなかった。Conventional navigation systems had difficulty providing services that took into account the detailed requests and emotions of users. In addition, when a user made a reservation by voice, the system lacked the functionality to automatically make a phone call to complete the reservation. This meant that users had to make the reservation manually, which was inconvenient. Furthermore, the system did not recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, which made it difficult to increase user satisfaction.
実施例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声を認識する手段と、音声認識結果を基にレストランを検索する手段と、自動で電話をかける手段と、予約を完了する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、感情に基づいてレストランを推薦する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が可能となり、音声による予約依頼に対して自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了することができる。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行うことができ、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's voice, means for searching for restaurants based on the voice recognition results, means for automatically making a phone call, means for completing a reservation, means for recognizing the user's emotions, and means for recommending a restaurant based on the emotions. This makes it possible to provide a service that takes into account the user's specific requests and emotions, and a reservation can be completed by automatically making a phone call in response to a reservation request made via voice. It is also possible to recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報源から得られたデータを解析し、知識を蓄積するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to methods and techniques for analyzing data obtained from sources and accumulating knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods and technologies for searching for an appropriate location based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた情報やデータを指す。"Search results" refers to the information or data obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果を基にユーザーが訪れるべき場所を決定するための方法や技術を指す。"Destination setting means" refers to the methods and technologies that allow users to determine where they should visit based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道順や案内を提供するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods and technologies for providing directions and guidance to a set destination.
「音声を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声を解析してテキストデータに変換するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of voice recognition" refers to methods and technologies for analyzing a user's voice and converting it into text data.
「レストランを検索する手段」とは、音声認識結果を基に適切な飲食店を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for searching for restaurants" refers to methods and technologies for searching for appropriate restaurants based on voice recognition results.
「自動で電話をかける手段」とは、システムが自動的に電話を発信するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for making automatic phone calls" refers to methods or technologies that allow the system to automatically make phone calls.
「予約を完了する手段」とは、電話を通じて予約手続きを完了するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of completing a reservation" refers to the methods and technologies used to complete the reservation process over the telephone.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの入力や音声から感情を解析するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of emotion recognition" refers to methods and technologies for analyzing emotions from user input or voice.
「レストランを推薦する手段」とは、認識された感情に基づいて適切な飲食店を提案するための方法や技術を指す。"Restaurant recommendation means" refers to methods or technologies for suggesting appropriate dining options based on recognized sentiment.
本発明は、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供を実現するためのシステムである。このシステムは、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションとして実装され、ユーザーの音声やテキスト入力を基に、目的地の検索、予約、ナビゲーション、感情に基づくレストランの推薦を行う。The present invention is a system for providing services that take into account the detailed requests and emotions of users. This system is implemented as a smartphone application, and performs destination search, reservations, navigation, and emotion-based restaurant recommendations based on the user's voice and text input.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
ハードウェア:スマートフォン(iPhone、Android端末など)Hardware: Smartphone (iPhone, Android device, etc.)
ソフトウェア:Software:
音声認識技術:音声をテキストに変換するために、音声認識APIを使用する。Speech recognition technology: Uses speech recognition APIs to convert speech to text.
レストラン検索:地図APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。Restaurant search: Use the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
自動ダイヤルシステム:自動的に電話をかけるために、通信APIを使用する。Automatic dialing system: Uses communications APIs to automatically place calls.
感情認識技術:ユーザーの入力から感情を解析するために、感情分析APIを使用する。Emotion recognition technology: Uses sentiment analysis APIs to analyze emotions from user input.
レストラン推薦:レビューサイトAPIを使用して、感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。Restaurant Recommendations: Use review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on sentiment.
システムの具体的な処理Specific processing of the system
ユーザーの要望に基づく予約機能Reservation function based on user requests
1. ユーザーがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「電話で予約して」と音声で指示を出す。1. The user launches the smartphone application and issues a voice command saying, "Make a reservation by phone."
2. 端末は音声認識APIを使用して、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換する。2. The device uses a speech recognition API to convert the user's speech into text.
3. 端末は地図APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。3. The device uses the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
4. 端末は通信APIを使用して、検索結果から選ばれたレストランに自動で電話をかける。4. The device uses a communications API to automatically call the restaurant selected from the search results.
5. 端末は電話を通じてレストランに予約内容を伝え、予約を完了する。5. The terminal then transmits the reservation details to the restaurant via telephone, completing the reservation.
具体例:Example:
ユーザーが「電話で予約して。」と言う。The user says, "Make a reservation by phone."
端末は音声認識APIを使用して音声をテキストに変換する。The device uses a speech recognition API to convert speech to text.
端末:「音声を認識中です。」Device: "Recognizing voice."
端末は地図APIを使用して近くのレストランを検索する。The device uses the map API to search for nearby restaurants.
端末:「近くのレストランを検索中です。」Device: "Searching for nearby restaurants."
端末は通信APIを使用して自動的にレストランに電話をかける。The device will automatically call the restaurant using a communications API.
端末:「レストランに電話をかけています。」Device: "Calling restaurant."
端末は予約が完了したことをユーザーに通知する。The device will notify the user that the reservation is complete.
端末:「予約が完了しました。」Device: "Reservation completed."
感情エンジンを用いたサービス提供Providing services using emotion engines
1. ユーザーがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」とテキストまたは音声で入力する。1. The user launches the smartphone application and inputs via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
2. 端末は感情分析APIを使用して、ユーザーの入力から感情を認識する。2. The device uses the sentiment analysis API to recognize emotions from user input.
3. 端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用して、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。3. The device uses review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on the user's sentiment.
具体例:Example:
ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力する。The user types, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
端末は感情分析APIを使用して感情を認識する。The device uses an emotion analysis API to recognize emotions.
端末:「感情を分析中です。」Device: "Analyzing emotions."
端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用してリラックスできるレストランを推薦する。The device uses review site APIs to recommend relaxing restaurants.
端末:「リラックスできるレストランを探しています。」Device: "I'm looking for a relaxing restaurant."
端末:「こちらのレストランはいかがですか?(レストラン名)」Device: "How about this restaurant? (restaurant name)"
以上が、本発明のスマートフォン用アプリケーションの具体的な実施形態である。このシステムにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が可能となり、音声による予約依頼に対して自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了することができる。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行うことができ、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができる。The above is a specific embodiment of the smartphone application of the present invention. This system makes it possible to provide services that take into account the detailed requests and emotions of the user, and can complete reservations by automatically making a phone call in response to a voice reservation request. It can also recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
実施例2における特定処理の流れについて図17を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 2 is explained using Figure 17.
ユーザーの要望に基づく予約機能Reservation function based on user requests
処理ステップProcessing steps
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「電話で予約して」と音声で指示を出す。The user launches the smartphone application and gives the voice command, "Make a reservation by phone."
入力:ユーザの音声指示Input: User's voice command
出力:音声データOutput: Audio data
具体的な動作:ユーザがアプリケーションを起動し、音声で「電話で予約して」と指示を出す。Specific operation: The user launches the application and issues the command "Make a reservation by phone" via voice.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末は音声認識APIを使用して、ユーザの音声をテキストに変換する。The device uses a speech recognition API to convert the user's speech into text.
入力:音声データInput: Audio data
出力:テキストデータOutput: Text data
具体的な動作:端末は音声データを音声認識APIに送信し、テキストデータを受け取る。Specific operation: The device sends voice data to the voice recognition API and receives text data.
端末:「音声を認識中です。」Device: "Recognizing voice."
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末は地図APIを使用して、ユーザの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。The device uses the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
入力:テキストデータ、ユーザの現在地情報Input: text data, user's current location information
出力:レストランのリストOutput: List of restaurants
具体的な動作:端末はユーザの現在地情報を取得し、地図APIにクエリを送信してレストランのリストを受け取る。Specific operation: The device obtains the user's current location information and sends a query to the map API to receive a list of restaurants.
端末:「近くのレストランを検索中です。」Device: "Searching for nearby restaurants."
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末は通信APIを使用して、検索結果から選ばれたレストランに自動で電話をかける。The device uses a communications API to automatically call the restaurant selected from the search results.
入力:レストランのリストEnter: List of restaurants
出力:通話開始Output: Start call
具体的な動作:端末は通信APIに電話番号と通話内容を送信し、通話を開始する。Specific operation: The device sends the phone number and call details to the communication API and starts the call.
端末:「レストランに電話をかけています。」Device: "Calling restaurant."
ステップ5:Step 5:
端末は電話を通じてレストランに予約内容を伝え、予約を完了する。The terminal then communicates the reservation details to the restaurant via telephone, completing the reservation.
入力:通話開始Enter: Start call
出力:予約完了通知Output: Reservation completion notification
具体的な動作:端末は通信APIを通じて通話を管理し、予約が完了したことをユーザに通知する。Specific operation: The device manages the call through the communication API and notifies the user that the reservation has been completed.
端末:「予約が完了しました。」Device: "Reservation completed."
感情エンジンを用いたサービス提供Providing services using emotion engines
処理ステップProcessing steps
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」とテキストまたは音声で入力する。The user launches a smartphone application and inputs, via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
入力:ユーザのテキストまたは音声入力Input: User text or voice input
出力:テキストデータOutput: Text data
具体的な動作:ユーザがアプリケーションを起動し、テキストまたは音声で「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力する。Specific actions: The user launches the application and enters, via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末は感情分析APIを使用して、ユーザの入力から感情を認識する。The device uses a sentiment analysis API to recognize emotions from user input.
入力:テキストデータInput: Text data
出力:感情分析結果Output: Sentiment analysis results
具体的な動作:端末はテキストデータを感情分析APIに送信し、感情分析結果を受け取る。Specific operation: The device sends text data to the sentiment analysis API and receives the sentiment analysis results.
端末:「感情を分析中です。」Device: "Analyzing emotions."
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用して、ユーザの感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。The device uses review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on the user's sentiment.
入力:感情分析結果Input: Sentiment analysis results
出力:レストランの推薦リストOutput: A list of restaurant recommendations
具体的な動作:端末は感情分析結果を基にレビューサイトAPIにクエリを送信し、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランやユーザが好きな料理を提供するレストランのリストを受け取る。Specific operation: Based on the sentiment analysis results, the device sends a query to the review site API and receives a list of restaurants that have a relaxing atmosphere or serve the user's favorite cuisine.
端末:「リラックスできるレストランを探しています。」Device: "I'm looking for a relaxing restaurant."
端末:「こちらのレストランはいかがですか?(レストラン名)」Device: "How about this restaurant? (restaurant name)"
以上が、本発明のスマートフォン用アプリケーションの具体的な処理ステップである。The above are the specific processing steps of the smartphone application of the present invention.
(応用例2)(Application example 2)
次に、形態例2の応用例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ヘッドセット型端末314を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 2 of embodiment example 2 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムや予約システムは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮することができず、ユーザー体験が限定されていた。また、ユーザーが音声で要望を入力し、それに基づいて最適なサービスを推薦し、自動的に注文を行う機能が欠如していた。これにより、ユーザーが求めるサービスを迅速かつ的確に提供することが困難であった。Conventional navigation and reservation systems were unable to take into account the detailed requests and feelings of users, limiting the user experience. They also lacked the functionality to have users input their requests by voice, have the system recommend optimal services based on those requests, and automatically place orders. This made it difficult to quickly and accurately provide the services users wanted.
応用例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声入力を認識する手段と、認識された音声入力から感情を分析する手段と、感情分析の結果に基づいて最適なサービスを推薦する手段と、推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの要望や感情を考慮したサービスの提供が可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's voice input, means for analyzing emotions from the recognized voice input, means for recommending optimal services based on the results of the emotion analysis, and means for automatically placing an order for the recommended services. This makes it possible to provide services that take into account the user's requests and emotions.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報源から得られたデータを解析し、知識を蓄積するための方法や装置を指す。"Means of learning" refers to methods and devices for analyzing data obtained from sources and accumulating knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for searching for a destination" refers to a method or device for searching for an appropriate location based on a user's request.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索手段によって得られた情報の集合を指す。"Search Results" refers to the collection of information obtained through a search tool.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果から選ばれた場所を最終的な目的地として決定するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to a method or device for determining a location selected from the search results as the final destination.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道順や案内を提供するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for providing navigation" refers to a method or device for providing directions or guidance to a set destination.
「音声入力を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声をテキストデータに変換するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for recognizing voice input" refers to a method or device for converting a user's voice into text data.
「感情を分析する手段」とは、音声入力やテキストデータからユーザーの感情を解析するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for analyzing emotions" refers to a method or device for analyzing a user's emotions from voice input or text data.
「最適なサービスを推薦する手段」とは、感情分析の結果に基づいてユーザーに最も適したサービスを提案するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for recommending optimal services" refers to a method or device for suggesting the most suitable service to a user based on the results of sentiment analysis.
「自動的に注文を行う手段」とは、推薦されたサービスに対してユーザーの介入なしに注文を完了するための方法や装置を指す。"Automatic ordering means" refers to a method or device for completing an order for recommended services without user intervention.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、ユーザーの音声入力を認識し、感情を分析し、最適なサービスを推薦し、自動的に注文を行う一連の処理を行うものである。以下に、このシステムの具体的な実施形態を説明する。The system for implementing this invention performs a series of processes that recognize the user's voice input, analyze emotions, recommend optimal services, and automatically place an order. A specific embodiment of this system is described below.
システム構成System configuration
システムは、以下の主要なコンポーネントから構成される:The system consists of the following main components:
1. 音声認識モジュール:ユーザーの音声入力をテキストデータに変換する。具体的には、speech_recognitionライブラリを使用する。1. Speech recognition module: Converts the user's voice input into text data. Specifically, it uses the speech_recognition library.
2. 感情分析モジュール:音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを解析し、ユーザーの感情を分析する。具体的には、TextBlobライブラリを使用する。2. Sentiment analysis module: Analyzes the text data obtained from the voice recognition module and analyzes the user's emotions. Specifically, it uses the TextBlob library.
3. サービス推薦モジュール:感情分析の結果に基づいて、ユーザーに最適なサービスを推薦する。3. Service recommendation module: Recommend the most suitable services to users based on the results of sentiment analysis.
4. 自動注文モジュール:推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う。具体的には、requestsライブラリを使用してAPIエンドポイントに注文データを送信する。4. Auto-order module: Automatically places orders for recommended services. Specifically, it uses the requests library to send order data to an API endpoint.
処理の流れProcessing flow
1. 音声入力の認識:ユーザーがスマートフォンに向かって音声で要望を入力する。音声認識モジュールがこの音声をテキストデータに変換する。1. Voice input recognition: The user speaks their request into the smartphone. The voice recognition module converts this voice into text data.
2. 感情の分析:音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを感情分析モジュールに渡し、ユーザーの感情を解析する。2. Sentiment analysis: The text data obtained from the voice recognition module is passed to the sentiment analysis module to analyze the user's emotions.
3. サービスの推薦:感情分析の結果に基づいて、サービス推薦モジュールがユーザーに最適なサービスを選定し、推薦する。3. Service recommendation: Based on the results of sentiment analysis, the service recommendation module selects and recommends the most suitable services to the user.
4. 自動注文の実行:サービス推薦モジュールが選定したサービスに対して、自動注文モジュールが注文を行う。4. Executing automatic orders: The automatic ordering module places an order for the service selected by the service recommendation module.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
ハードウェア:スマートフォン、サーバHardware: smartphones, servers
ソフトウェア:speech_recognitionライブラリ、TextBlobライブラリ、requestsライブラリSoftware: speech_recognition library, TextBlob library, requests library
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と音声入力した場合、システムは以下のように動作する:For example, if a user says, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," the system will act as follows:
1. 音声認識モジュールが音声をテキストに変換し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」というテキストデータを生成する。1. The voice recognition module converts the voice into text and generates text data such as "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
2. 感情分析モジュールがこのテキストデータを解析し、ユーザーが疲れていることを認識する。2. The sentiment analysis module analyzes this text data and recognizes that the user is tired.
3. サービス推薦モジュールがリラックスできる雰囲気のレストランを推薦する。3. The service recommendation module recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere.
4. 自動注文モジュールが推薦されたレストランに対して自動的に注文を行う。4. The auto-order module automatically places orders from the recommended restaurants.
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
生成AIモデルへ入力するプロンプト文の例:Example of a prompt to input to a generative AI model:
「ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と音声入力した場合、感情分析を行い、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランを推薦し、自動的に注文を行うPythonプログラムを作成してください。」"If a user says, 'I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious,' please create a Python program that performs sentiment analysis, recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere, and automatically places the order."
応用例2における特定処理の流れについて図18を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 2 is explained using Figure 18.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンに向かって音声で要望を入力する。音声入力は、スマートフォンのマイクを通じて取得される。入力データは、ユーザの音声データである。The user speaks their request into the smartphone. The voice input is acquired through the smartphone's microphone. The input data is the user's voice data.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末の音声認識モジュールが、ユーザの音声データをテキストデータに変換する。具体的には、speech_recognitionライブラリを使用して音声データを解析し、テキストデータを生成する。出力データは、ユーザの音声をテキストに変換したものである。The device's voice recognition module converts the user's voice data into text data. Specifically, it uses the speech_recognition library to analyze the voice data and generate text data. The output data is the user's voice converted into text.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末の感情分析モジュールが、音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを受け取り、ユーザの感情を解析する。具体的には、TextBlobライブラリを使用してテキストデータの感情を分析する。入力データは、テキストデータであり、出力データは、感情分析の結果である。The terminal's sentiment analysis module receives the text data obtained from the voice recognition module and analyzes the user's sentiment. Specifically, it uses the TextBlob library to analyze the sentiment of the text data. The input data is the text data, and the output data is the result of the sentiment analysis.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバのサービス推薦モジュールが、感情分析の結果に基づいて、ユーザに最適なサービスを選定し、推薦する。入力データは、感情分析の結果であり、出力データは、推薦されたサービスの情報である。具体的には、感情がネガティブであればリラックスできるサービスを、ポジティブであれば人気のサービスを推薦する。The server's service recommendation module selects and recommends the most suitable service to the user based on the results of the sentiment analysis. The input data is the results of the sentiment analysis, and the output data is information about the recommended service. Specifically, if the sentiment is negative, a relaxing service is recommended, and if it is positive, a popular service is recommended.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバの自動注文モジュールが、サービス推薦モジュールから得られた推薦サービス情報を受け取り、自動的に注文を行う。具体的には、requestsライブラリを使用して、推薦されたサービスに対して注文データをAPIエンドポイントに送信する。入力データは、推薦されたサービスの情報であり、出力データは、注文の完了通知である。The server's automatic ordering module receives the recommended service information obtained from the service recommendation module and automatically places the order. Specifically, it uses the requests library to send order data for the recommended service to an API endpoint. The input data is information about the recommended service, and the output data is a notification of order completion.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末が、注文の完了通知をユーザに表示する。入力データは、注文の完了通知であり、出力データは、ユーザに表示される注文完了メッセージである。具体的には、スマートフォンの画面に注文が完了した旨のメッセージを表示する。The terminal displays a notification that the order is complete to the user. The input data is the notification that the order is complete, and the output data is an order completion message that is displayed to the user. Specifically, a message indicating that the order is complete is displayed on the smartphone screen.
特定処理部290は、特定処理の結果をヘッドセット型端末314に送信する。ヘッドセット型端末314では、制御部46Aが、スピーカ240及びディスプレイ343に対して特定処理の結果を出力させる。マイクロフォン238は、特定処理の結果に対するユーザ入力を示す音声を取得する。制御部46Aは、マイクロフォン238によって取得されたユーザ入力を示す音声データをデータ処理装置12に送信する。データ処理装置12では、特定処理部290が音声データを取得する。The
データ生成モデル58は、いわゆる生成AI(Artificial Intelligence)である。データ生成モデル58の一例としては、ChatGPT(インターネット検索<URL: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt>)等の生成AIが挙げられる。データ生成モデル58は、ニューラルネットワークに対して深層学習を行わせることによって得られる。データ生成モデル58には、指示を含むプロンプトが入力され、かつ、音声を示す音声データ、テキストを示すテキストデータ、及び画像を示す画像データ等の推論用データが入力される。データ生成モデル58は、入力された推論用データをプロンプトにより示される指示に従って推論し、推論結果を音声データ及びテキストデータ等のデータ形式で出力する。ここで、推論とは、例えば、分析、分類、予測、及び/又は要約等を指す。The
生成AIの他の例としては、Gemini(インターネット検索<URL: https://gemini.google.com/?hl=ja>)が挙げられる。Another example of generative AI is Gemini (Internet search <URL: https://gemini.google.com/?hl=ja>).
上記実施形態では、データ処理装置12によって特定処理が行われる形態例を挙げたが、本開示の技術はこれに限定されず、ヘッドセット型端末314によって特定処理が行われるようにしてもよい。In the above embodiment, an example was given in which the specific processing is performed by the
[第4実施形態][Fourth embodiment]
図7には、第4実施形態に係るデータ処理システム410の構成の一例が示されている。Figure 7 shows an example of the configuration of a
図7に示すように、データ処理システム410は、データ処理装置12及びロボット414を備えている。データ処理装置12の一例としては、サーバが挙げられる。As shown in FIG. 7, the
データ処理装置12は、コンピュータ22、データベース24、及び通信I/F26を備えている。コンピュータ22は、本開示の技術に係る「コンピュータ」の一例である。The
コンピュータ22は、プロセッサ28、RAM30、及びストレージ32を備えている。プロセッサ28、RAM30、及びストレージ32は、バス34に接続されている。また、データベース24及び通信I/F26も、バス34に接続されている。通信I/F26は、ネットワーク54に接続されている。ネットワーク54の一例としては、WAN(Wide Area Network)及び/又はLAN(Local Area Network)等が挙げられる。The
ロボット414は、コンピュータ36、マイクロフォン238、スピーカ240、カメラ42、通信I/F44、及び制御対象443を備えている。コンピュータ36は、プロセッサ46、RAM48、及びストレージ50を備えている。プロセッサ46、RAM48、及びストレージ50は、バス52に接続されている。また、マイクロフォン238、スピーカ240、カメラ42、及び制御対象443も、バス52に接続されている。The
マイクロフォン238は、ユーザ20が発する音声を受け付けることで、ユーザ20から指示等を受け付ける。マイクロフォン238は、ユーザ20が発する音声を捕捉し、捕捉した音声を音声データに変換してプロセッサ46に出力する。スピーカ240は、プロセッサ46からの指示に従って音声を出力する。The
カメラ42は、レンズ、絞り、及びシャッタ等の光学系と、CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)イメージセンサ又はCCD(Charge Coupled Device)イメージセンサ等の撮像素子とが搭載された小型デジタルカメラであり、ユーザ20の周囲(例えば、一般的な健常者の視界の広さに相当する画角で規定された撮像範囲)を撮像する。
通信I/F44は、ネットワーク54に接続されている。通信I/F44及び26は、ネットワーク54を介してプロセッサ46とプロセッサ28との間の各種情報の授受を司る。通信I/F44及び26を用いたプロセッサ46とプロセッサ28との間の各種情報の授受はセキュアな状態で行われる。The communication I/
制御対象443は、表示装置、目部のLED、並びに、腕、手及び足等を駆動するモータ等を含む。ロボット414の姿勢や仕草は、腕、手及び足等のモータを制御することにより制御される。ロボット414の感情の一部は、これらのモータを制御することにより表現できる。また、ロボット414の目部のLEDの発光状態を制御することによっても、ロボット414の表情を表現できる。The controlled
図8には、データ処理装置12及びロボット414の要部機能の一例が示されている。図8に示すように、データ処理装置12では、プロセッサ28によって特定処理が行われる。ストレージ32には、特定処理プログラム56が格納されている。Figure 8 shows an example of the main functions of the
特定処理プログラム56は、本開示の技術に係る「プログラム」の一例である。プロセッサ28は、ストレージ32から特定処理プログラム56を読み出し、読み出した特定処理プログラム56をRAM30上で実行する。特定処理は、プロセッサ28がRAM30上で実行する特定処理プログラム56に従って、特定処理部290として動作することによって実現される。The
ストレージ32には、データ生成モデル58及び感情特定モデル59が格納されている。データ生成モデル58及び感情特定モデル59は、特定処理部290によって用いられる。
ロボット414では、プロセッサ46によって受付出力処理が行われる。ストレージ50には、受付出力プログラム60が格納されている。プロセッサ46は、ストレージ50から受付出力プログラム60を読み出し、読み出した受付出力プログラム60をRAM48上で実行する。受付出力処理は、プロセッサ46がRAM48上で実行する受付出力プログラム60に従って、制御部46Aとして動作することによって実現される。In the
次に、データ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理について説明する。Next, we will explain the specific processing performed by the
「形態例1」"Example 1"
本発明の一実施形態として、車載用のナビゲーションシステムが考えられる。このシステムは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段として、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いる。具体的には、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得し、これを学習する。また、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段として、自然言語処理技術を用いる。ユーザーからの質問を解析し、それに基づいて適切な目的地をサーチする。さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段として、GPS技術を用いる。ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定する。最後に、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段として、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いる。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。One embodiment of the present invention is an in-vehicle navigation system. This system uses a machine learning algorithm as a means of learning information from various information sources. Specifically, information is acquired from a database that includes information such as restaurant reviews and the availability of parking spaces, and this information is learned. Natural language processing technology is also used as a means of searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests. Questions from the user are analyzed, and an appropriate destination is searched for based on the results. GPS technology is also used as a means of setting the destination based on the search results. The optimal route is calculated based on the user's current location and the search results, and the destination is set. Finally, a voice guidance system is used as a means of providing navigation to the set destination. This allows the user to be safely guided to their destination even while driving.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
本発明の別の実施形態として、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションが考えられる。このアプリケーションは、前述の車載用ナビゲーションシステムと同様の機能を持つが、さらにユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う機能を含む。具体的には、ユーザーが「電話で予約して」という要望を出した場合、システムは自動的に該当するレストランに電話をかけ、予約を行う。この機能は、音声認識技術と自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて実現される。Another embodiment of the present invention is a smartphone application. This application has the same functions as the in-car navigation system described above, but also includes a function for making reservations based on the user's request. Specifically, when a user requests to "make a reservation by phone," the system automatically calls the corresponding restaurant and makes the reservation. This function is realized using voice recognition technology and an automatic dialing system.
以下に、各形態例の処理の流れについて説明する。The process flow for each example is explained below.
「形態例1」"Example 1"
ステップ1:システムは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得し、これを機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて学習する。Step 1: The system learns information from various sources. Specifically, it obtains information from a database that includes information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available, and learns from this information using machine learning algorithms.
ステップ2:ユーザーからの細かい要望が入力されると、システムは自然言語処理技術を用いてこれを解析する。Step 2: Once the user has entered their detailed request, the system analyzes it using natural language processing technology.
ステップ3:解析結果に基づいて、システムは適切な目的地をサーチする。Step 3: Based on the analysis results, the system searches for suitable destinations.
ステップ4:サーチ結果とユーザーの現在位置を基に、システムはGPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定する。Step 4: Based on the search results and the user's current location, the system uses GPS technology to calculate the optimal route and set the destination.
ステップ5:設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供するため、システムは音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーを誘導する。Step 5: The system guides the user using the voice guidance system to provide navigation to the set destination.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
ステップ1:スマートフォン用のアプリケーションは、前述の車載用ナビゲーションシステムと同様の機能を持つ。Step 1: The smartphone application has the same functions as the in-car navigation system mentioned above.
ステップ2:ユーザーが「電話で予約して」という要望を出した場合、システムは自動的に該当するレストランに電話をかける。Step 2: If the user requests to "make a reservation by phone," the system will automatically call the relevant restaurant.
ステップ3:システムは音声認識技術と自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う。Step 3: The system uses voice recognition technology and an automated dialing system to make the reservation.
(実施例1)(Example 1)
次に、形態例1の実施例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ロボット414を「端末」と称する。Next, a first embodiment of the first embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチすることが困難であり、また、ユーザーの質問に対する適切な回答を生成することができなかった。さらに、目的地の設定やナビゲーションの提供においても、ユーザーの現在位置やサーチ結果を効果的に利用することができなかった。これにより、ユーザーの利便性が低下し、運転中の安全性も確保されにくかった。With conventional navigation systems, it was difficult to search for a destination based on the user's specific requests, and they were unable to generate appropriate answers to the user's questions. Furthermore, they were unable to effectively use the user's current location or search results when setting a destination or providing navigation. This reduced user convenience and made it difficult to ensure safety while driving.
実施例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、音声入力をテキストに変換する手段と、自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析する手段と、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを学習する手段と、位置情報を取得する手段と、音声ガイダンスを生成する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいた目的地のサーチと設定が可能となり、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導されることが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for converting voice input to text, means for analyzing the user's questions using natural language processing techniques, means for learning data using machine learning algorithms, means for acquiring location information, and means for generating voice guidance. This makes it possible to search for and set a destination based on the user's detailed requests, and allows the user to be safely guided to the destination even while driving.
「情報源」とは、データを提供するあらゆる媒体やシステムを指す。"Source" refers to any medium or system that provides data.
「学習する手段」とは、データを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出するためのアルゴリズムや技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to the algorithms and techniques used to analyze data and extract patterns and knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて求める詳細な要求を指す。"Specific user requests" refers to the detailed requirements that users have based on their specific conditions and preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to the technology or algorithms used to search for an appropriate destination based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補や情報を指す。"Search results" refers to destination candidates and information obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果に基づいて最適な目的地を決定するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to the technology or algorithm used to determine the optimal destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、ユーザーが目的地に到達するための経路案内を行う技術やシステムを指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to technologies and systems that provide route guidance to help users reach their destination.
「音声入力をテキストに変換する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声を解析し、文字情報に変換する技術やシステムを指す。"Means of converting voice input into text" refers to technology or systems that analyze the user's voice and convert it into text information.
「自然言語処理技術」とは、人間の言語を解析し、理解するための技術やアルゴリズムを指す。"Natural language processing technology" refers to the techniques and algorithms for analyzing and understanding human language.
「機械学習アルゴリズム」とは、データからパターンや知識を学習し、予測や分類を行うためのアルゴリズムを指す。"Machine learning algorithms" refer to algorithms that learn patterns and knowledge from data and make predictions and classifications.
「位置情報を取得する手段」とは、ユーザーの現在位置を特定するための技術やシステムを指す。"Means of acquiring location information" refers to technologies and systems for identifying the user's current location.
「音声ガイダンスを生成する手段」とは、ユーザーに音声で指示を出すための技術やシステムを指す。"Means for generating audio guidance" refers to technology or systems for providing audio instructions to the user.
発明を実施するための形態Form for implementing the invention
この発明は、車載用ナビゲーションシステムに関するものであり、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチし、最適なルートを提供するためのシステムである。このシステムは、サーバ、端末、ユーザーの三者が連携して動作する。This invention relates to an in-vehicle navigation system that searches for destinations based on the user's specific requests and provides the optimal route. This system works in cooperation with a server, a terminal, and a user.
1. プログラムの生成1. Program generation
サーバは、車載用ナビゲーションシステムのプログラムを生成する。このプログラムは、機械学習アルゴリズムと自然言語処理技術を組み合わせて構築される。具体的には、PythonのPandas、Scikit-learn、NLTK、SpaCy、Google Maps API、Amazon PollyなどのライブラリやAPIを使用する。The server generates the program for the in-car navigation system. This program is built by combining machine learning algorithms and natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses libraries and APIs such as Python's Pandas, Scikit-learn, NLTK, SpaCy, Google Maps API, and Amazon Polly.
2. プログラムの処理2. Program processing
サーバは、以下の手順でデータを処理する。The server processes the data in the following steps:
1. データ取得と学習:1. Data acquisition and learning:
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースからデータを取得する。具体的には、PythonのPandasライブラリを使用してデータを読み込む。次に、サーバはScikit-learnを用いて機械学習アルゴリズムでデータを学習する。例えば、レストランの評価情報を基に、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを作成する。The server retrieves data from a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. Specifically, it reads the data using Python's Pandas library. The server then uses Scikit-learn to train the data with machine learning algorithms. For example, it creates a model that predicts highly rated restaurants based on restaurant rating information.
2. ユーザーの質問解析:2. User question analysis:
端末は、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。例えば、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」という質問を受け取る。端末は、この質問を自然言語処理技術を用いて解析する。具体的には、PythonのNLTKやSpaCyを使用して、質問の意図を理解する。The device receives questions from users. For example, it may receive a question such as, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby." The device then analyzes the question using natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses Python's NLTK and SpaCy to understand the intent of the question.
3. 目的地の設定:3. Set your destination:
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。具体的には、Google Maps APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を取得し、最適なルートを計算する。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results. Specifically, it uses the Google Maps API to obtain the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants, and calculates the optimal route.
4. ナビゲーションの提供:4. Providing navigation:
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する。具体的には、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに音声で指示を出す。例えば、Amazon Pollyを使用して、「右に曲がってください」などの音声ガイダンスを生成する。The device provides navigation to the set destination. Specifically, it uses a voice guidance system to give voice instructions to the user. For example, it uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance such as "Turn right."
3. 具体例3. Specific examples
具体例として、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と質問した場合を考える。As a concrete example, consider the case where a user asks, "Can you tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby?"
1. データ取得と学習:1. Data acquisition and learning:
サーバは、データベースに接続し、レストランの評価情報を取得する。The server connects to the database and retrieves restaurant rating information.
サーバは、Pandasを用いてデータをDataFrameに変換する。The server converts the data into a DataFrame using Pandas.
サーバは、Scikit-learnのRandomForestClassifierを用いて、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを学習する。The server uses Scikit-learn's RandomForestClassifier to train a model to predict highly rated restaurants.
2. ユーザーの質問解析:2. User question analysis:
ユーザーは、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて」と端末に話しかける。The user speaks to the device saying, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby."
端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換する。The device converts voice input into text.
端末は、NLTKを用いてテキストをトークン化し、SpaCyを用いて質問の意図を解析する。The device uses NLTK to tokenize the text and SpaCy to analyze the intent of the question.
3. 目的地の設定:3. Set your destination:
端末は、GPSセンサーを用いてユーザーの現在位置を取得する。The device uses the GPS sensor to obtain the user's current location.
サーバは、Google Maps APIを用いて、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を基にルートを計算する。The server uses the Google Maps API to calculate a route based on the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants.
サーバは、計算結果を端末に送信する。The server sends the calculation results to the terminal.
4. ナビゲーションの提供:4. Providing navigation:
端末は、サーバから受け取ったルート情報を基に、ナビゲーションを開始する。The device begins navigation based on the route information received from the server.
端末は、Amazon Pollyを用いて音声ガイダンスを生成し、ユーザーに指示を出す。The device uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance and give instructions to the user.
ユーザーは、音声ガイダンスに従って運転する。The user drives by following the voice guidance.
プロンプト文の例:Example prompt:
「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて。」"Can you tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby?"
このようにして、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。In this way, users are safely guided to their destination while driving.
実施例1における特定処理の流れについて図11を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 1 is explained using Figure 11.
ステップ1:データ取得と学習Step 1: Data acquisition and learning
サーバは、データベースからレストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を取得する。入力として、データベース接続情報とSQLクエリを使用する。サーバは、PythonのPandasライブラリを用いてデータをDataFrameに変換する。次に、サーバはScikit-learnを用いて機械学習アルゴリズムでデータを学習する。具体的には、RandomForestClassifierを使用して、評価が高いレストランを予測するモデルを作成する。出力として、学習済みのモデルが得られる。The server retrieves information from the database, such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. As input, it uses the database connection information and a SQL query. The server converts the data into a DataFrame using Python's Pandas library. The server then uses Scikit-learn to train the data with a machine learning algorithm. Specifically, it uses RandomForestClassifier to create a model that predicts highly rated restaurants. As output, it obtains the trained model.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
サーバは、データベースに接続し、SQLクエリを実行してデータを取得する。The server connects to the database and executes SQL queries to retrieve data.
サーバは、取得したデータをPandasのDataFrameに変換する。The server converts the retrieved data into a Pandas DataFrame.
サーバは、Scikit-learnのRandomForestClassifierを用いて、レストランの評価を予測するモデルを学習する。The server uses Scikit-learn's RandomForestClassifier to train a model to predict restaurant ratings.
ステップ2:ユーザーの質問解析Step 2: Analyze user questions
端末は、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。入力として、ユーザーの音声質問が使用される。端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換するために音声認識技術を使用する。次に、端末は、自然言語処理技術を用いて質問を解析する。具体的には、PythonのNLTKやSpaCyを使用して、質問の意図を理解する。出力として、解析されたテキストデータが得られる。The terminal receives a question from the user. As input, the user's voice question is used. The terminal uses speech recognition technology to convert the voice input into text. The terminal then analyzes the question using natural language processing technology. Specifically, it uses Python's NLTK and SpaCy to understand the intent of the question. As output, the analyzed text data is obtained.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
ユーザーは、「近くの評価が高いレストランを教えて。」と端末に話しかける。The user speaks to the device saying, "Tell me about some highly rated restaurants nearby."
端末は、音声入力をテキストに変換する。The device converts voice input into text.
端末は、NLTKを用いてテキストをトークン化し、SpaCyを用いて質問の意図を解析する。The device uses NLTK to tokenize the text and SpaCy to analyze the intent of the question.
ステップ3:目的地の設定Step 3: Set your destination
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。入力として、ユーザーの現在位置と解析されたテキストデータが使用される。サーバは、Google Maps APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を取得し、最適なルートを計算する。出力として、計算されたルート情報が得られる。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results. The user's current location and parsed text data are used as input. The server uses the Google Maps API to obtain the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants, and calculates the optimal route. The calculated route information is obtained as output.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
端末は、GPSセンサーを用いてユーザーの現在位置を取得する。The device uses the GPS sensor to obtain the user's current location.
サーバは、Google Maps APIを用いて、ユーザーの現在位置と評価が高いレストランの位置を基にルートを計算する。The server uses the Google Maps API to calculate a route based on the user's current location and the locations of highly rated restaurants.
サーバは、計算結果を端末に送信する。The server sends the calculation results to the terminal.
ステップ4:ナビゲーションの提供Step 4: Provide navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する。入力として、計算されたルート情報が使用される。端末は、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに音声で指示を出す。具体的には、Amazon Pollyを使用して、「右に曲がってください」などの音声ガイダンスを生成する。出力として、音声ガイダンスが得られる。The device provides navigation to the set destination. The calculated route information is used as input. The device uses a voice guidance system to give voice instructions to the user. Specifically, it uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance such as "Turn right". The voice guidance is obtained as output.
具体的な動作:Specific actions:
端末は、サーバから受け取ったルート情報を基に、ナビゲーションを開始する。The device begins navigation based on the route information received from the server.
端末は、Amazon Pollyを用いて音声ガイダンスを生成し、ユーザーに指示を出す。The device uses Amazon Polly to generate voice guidance and give instructions to the user.
ユーザーは、音声ガイダンスに従って運転する。The user drives by following the voice guidance.
(応用例1)(Application example 1)
次に、形態例1の応用例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ロボット414を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 1 of embodiment example 1 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする機能が限定的であり、ユーザーの質問に対する適切な回答を生成する能力が不足している。また、現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスを提供する機能も十分ではない。これにより、ユーザーは目的地への移動中に不便を感じることが多い。Traditional navigation systems have limited functionality for searching for destinations based on the user's specific requests and lack the ability to generate appropriate answers to user questions. They also lack the ability to calculate the optimal route between the current location and the destination and provide voice guidance. This often causes inconvenience to users while traveling to their destination.
応用例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する自然言語処理手段と、現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する手段と、音声ガイダンスを提供する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチし、最適なルートを計算して音声ガイダンスを提供することが可能となる。The identification process by the
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するための出典やリソースである。A "source" is a source or resource that provides data or knowledge.
「情報を学習する手段」とは、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて、様々な情報源から取得したデータを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出する方法である。"Means of learning information" refers to the use of machine learning algorithms to analyze data obtained from various sources and extract patterns and knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて求める詳細な要求や希望である。"User specific requests" are the detailed demands and wishes that a user has based on their specific conditions and preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための方法や技術である。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods or technologies for searching for an appropriate destination based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、目的地をサーチする手段によって得られた検索結果である。"Search results" means the results of a search obtained by a means of searching for a destination.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果に基づいてユーザーの目的地を決定する方法や技術である。"Means for setting a destination" refers to a method or technology for determining a user's destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、ユーザーが目的地に到達するための経路案内や指示を提供する方法や技術である。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods or technologies that provide route guidance or directions to help a user reach a destination.
「自然言語処理手段」とは、ユーザーの質問や要求を解析し、適切な回答を生成するための技術である。"Natural language processing means" is technology for analyzing users' questions and requests and generating appropriate answers.
「ルートを計算する手段」とは、現在位置と目的地の間の最適な経路を計算するための方法や技術である。"Means for calculating a route" refers to a method or technique for calculating the optimal route between a current location and a destination.
「音声ガイダンスを提供する手段」とは、計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供する方法や技術である。"Means for providing audio guidance" refers to methods or technologies that convert calculated route information into audio and provide it to the user.
この発明を実施するための形態として、以下のようなシステムが考えられる。The following system is considered as a form for implementing this invention.
まず、サーバは様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段を持つ。この手段は、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを解析し、パターンや知識を抽出するものである。具体的には、データベースから情報を取得し、これを学習する。First, the server has a means of learning information from various sources. This means uses machine learning algorithms to analyze data such as restaurant reviews and the availability of parking spaces, and extract patterns and knowledge. Specifically, it retrieves information from a database and learns from it.
次に、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段がある。この手段は、自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な目的地をサーチするものである。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」と質問すると、システムはその質問を解析し、適切なレストランを検索する。Next, there is a means to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests. This means uses natural language processing technology to analyze the user's question and search for an appropriate destination. For example, if a user asks, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" the system will analyze the question and search for an appropriate restaurant.
さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段がある。この手段は、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算し、目的地を設定するものである。具体的には、Geopyライブラリを使用して、現在位置と目的地の間の距離を計算する。In addition, there is a method for setting a destination based on search results. This method calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location and search results, and sets the destination. Specifically, it uses the Geopy library to calculate the distance between the current location and the destination.
最後に、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段がある。この手段は、Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)ライブラリを使用して、計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供するものである。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。Finally, there is a method to provide navigation to the set destination. This method uses the Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) library to convert the calculated route information into voice and provide it to the user. This allows the user to be safely guided to their destination while driving.
具体例として、ユーザーが「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」と質問すると、システムは以下のように動作する。As a concrete example, when a user asks, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" the system works as follows:
1. 自然言語処理手段がユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する。1. Natural language processing tools analyze the user's question and generate an appropriate answer.
2. 情報を学習する手段がデータベースからレストランの評価情報を取得し、解析する。2. The means for learning information retrieves restaurant rating information from the database and analyzes it.
3. ルートを計算する手段が現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する。3. A route calculation means calculates the optimal route between the current location and the destination.
4. 音声ガイダンスを提供する手段が計算されたルート情報を音声に変換し、ユーザーに提供する。4. A means for providing audio guidance converts the calculated route information into audio and provides it to the user.
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが考えられる。Some examples of prompt statements include:
ユーザーの質問: 「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」User Question: "What are some highly rated restaurants near me?"
コンテキスト:「レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無など」Context: "Restaurant ratings, availability of parking, etc."
このプロンプト文を使用して、生成AIモデルに質問を解析させ、適切な回答を得ることができる。This prompt can then be used by a generative AI model to parse the question and provide an appropriate answer.
応用例1における特定処理の流れについて図12を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 1 is explained using Figure 12.
ステップ1:Step 1:
サーバは、ユーザーからの質問を受け取る。入力はユーザーの質問であり、例えば「近くの評価が高いレストランはどこですか?」というテキストデータである。出力は解析のための準備が整ったテキストデータである。The server receives a question from a user. The input is the user's question, which is text data, for example, "What are some highly rated restaurants nearby?" The output is text data ready for analysis.
ステップ2:Step 2:
サーバは、自然言語処理手段を用いて、ユーザーの質問を解析する。入力はステップ1で受け取ったユーザーの質問であり、出力は解析結果としての適切な検索クエリである。具体的には、生成AIモデルを使用して質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する。The server uses natural language processing means to analyze the user's question. The input is the user's question received in step 1, and the output is an appropriate search query as a result of the analysis. Specifically, a generative AI model is used to analyze the question and generate an appropriate answer.
ステップ3:Step 3:
サーバは、情報を学習する手段を用いて、データベースからレストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを取得する。入力はステップ2で生成された検索クエリであり、出力は取得された評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータである。具体的には、データベースに対してクエリを実行し、必要な情報を取得する。The server uses a means for learning information to obtain data such as restaurant rating information and whether or not parking is available from the database. The input is the search query generated in step 2, and the output is the obtained rating information, parking availability, and other data. Specifically, the server executes a query against the database to obtain the required information.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバは、取得した情報を基に、ユーザーの現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する。入力はユーザーの現在位置とステップ3で取得された目的地情報であり、出力は計算された最適なルート情報である。具体的には、Geopyライブラリを使用して距離を計算し、最適なルートを決定する。The server calculates the optimal route between the user's current location and the destination based on the acquired information. The input is the user's current location and the destination information acquired in step 3, and the output is the calculated optimal route information. Specifically, the Geopy library is used to calculate the distance and determine the optimal route.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバは、計算されたルート情報を音声ガイダンスに変換する。入力はステップ4で計算されたルート情報であり、出力は音声ファイルである。具体的には、Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)ライブラリを使用して、テキスト情報を音声に変換する。The server converts the calculated route information into voice guidance. The input is the route information calculated in step 4, and the output is an audio file. Specifically, it uses the Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) library to convert the text information into voice.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末は、生成された音声ガイダンスをユーザーに提供する。入力はステップ5で生成された音声ファイルであり、出力はユーザーに対する音声案内である。具体的には、音声ファイルを再生し、ユーザーに対してナビゲーション情報を提供する。The terminal provides the generated voice guidance to the user. The input is the audio file generated in step 5, and the output is audio guidance for the user. Specifically, the terminal plays the audio file and provides navigation information to the user.
(実施例2)(Example 2)
次に、形態例2の実施例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ロボット414を「端末」と称する。Next, a second embodiment of the second embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、目的地の設定やナビゲーション機能を提供するだけであり、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいた予約機能を持たないため、ユーザーが手動で予約を行う必要があった。また、音声指示を解析して自動的に予約を行うシステムも存在しなかったため、ユーザーの利便性が低かった。これにより、ユーザーは目的地の設定と予約の両方を別々に行う手間がかかり、効率的な利用が難しかった。Conventional navigation systems only provided destination setting and navigation functions, and did not have a reservation function based on the user's specific requests, so users had to make reservations manually. There was also no system that analyzed voice instructions and made reservations automatically, which resulted in low user convenience. This meant that users had to take the time to set a destination and make reservations separately, making it difficult to use the system efficiently.
実施例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声指示を解析する手段と、解析された音声指示に基づいて予約内容を抽出する手段と、抽出された予約内容に基づいて自動的に電話をかける手段と、電話を通じて予約内容を音声で伝える手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーは音声指示を出すだけで目的地の設定と予約が自動的に行われ、利便性が大幅に向上することが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for analyzing the user's voice instructions, means for extracting reservation details based on the analyzed voice instructions, means for automatically making a phone call based on the extracted reservation details, and means for audibly communicating the reservation details over the phone. This allows the user to automatically set a destination and make a reservation simply by issuing voice instructions, greatly improving convenience.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「ユーザー」とは、システムを利用する個人または団体を指す。"User" refers to an individual or organization that uses the system.
「目的地」とは、ユーザーが到達したい場所を指す。"Destination" refers to the place the user wants to reach.
「サーチ」とは、特定の情報を探し出す行為を指す。"Search" refers to the act of finding specific information.
「ナビゲーション」とは、目的地までの経路を案内する機能を指す。"Navigation" refers to the function of providing route guidance to a destination.
「音声指示」とは、ユーザーが音声を用いてシステムに対して行う指示を指す。"Voice instructions" refers to instructions given by the user to the system using voice.
「解析」とは、データや情報を詳細に調べて意味や構造を理解する行為を指す。"Analysis" refers to the act of examining data or information in detail to understand its meaning and structure.
「予約内容」とは、予約に必要な情報(日時、人数、場所など)を指す。"Reservation details" refers to the information required for making a reservation (date and time, number of people, location, etc.).
「自動的」とは、人の手を介さずに機械やシステムが独自に動作することを指す。"Automatic" refers to a machine or system that operates independently without human intervention.
「電話をかける」とは、通信装置を用いて他の通信装置に接続を試みる行為を指す。"Making a phone call" refers to the act of using a communication device to attempt to connect to another communication device.
「音声で伝える」とは、音声を用いて情報を他者に伝達する行為を指す。"Communicating by voice" refers to the act of conveying information to others using voice.
発明を実施するための形態Form for implementing the invention
この発明は、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションとして実施される。このアプリケーションは、ユーザーの音声指示に基づいて目的地の設定と予約を自動的に行うシステムである。以下に、このシステムの具体的な実施形態を説明する。This invention is implemented as an application for smartphones. This application is a system that automatically sets a destination and makes reservations based on the user's voice instructions. A specific embodiment of this system is described below.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
このシステムは、以下のハードウェアおよびソフトウェアを使用する。This system uses the following hardware and software:
スマートフォン(端末)Smartphone (device)
音声認識技術(Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API)Voice recognition technology (Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API)
データベース管理システム(Firebase Firestore)Database management system (Firebase Firestore)
自動ダイヤルシステム(Twilio API)Automatic dialing system (Twilio API)
音声合成技術(Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API)Speech synthesis technology (Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API)
データ加工およびデータ演算Data processing and data calculations
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、音声で「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示する。端末はGoogle Cloud Speech-to-Text APIを使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。この変換処理はリアルタイムで行われる。The user launches the application on their smartphone and says, "Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm." The device uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API to convert the user's voice instructions into text. This conversion process occurs in real time.
次に、端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、予約内容(日時、人数)を抽出する。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」というテキストから「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という情報を取り出す。Then, the device analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details (date, time, number of people). For example, from the text "Make a reservation for four people at 7 p.m. tomorrow," the information "tomorrow at 7 p.m." and "four people" is extracted.
端末はFirebase Firestoreに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。このリクエストには、ユーザの位置情報や好みのレストランの条件が含まれる。サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をFirebase Firestoreから取得し、端末に返す。返される情報には、レストランの名前、電話番号、住所などが含まれる。The device sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in Firebase Firestore. This request includes the user's location and preferred restaurant conditions. The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from Firebase Firestore, and returns it to the device. The returned information includes the restaurant's name, phone number, address, etc.
端末はTwilio APIを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。この処理はユーザの手を煩わせることなく行われる。電話が接続されると、端末はGoogle Cloud Text-to-Speech APIを使用して、事前に抽出した予約内容を音声でレストランに伝える。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声が再生される。The device uses the Twilio API to automatically call the restaurant's phone number, without any user intervention. Once the call is connected, the device uses the Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API to communicate the reservation details it extracted in advance to the restaurant via voice. For example, it might say, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
具体例Specific examples
具体例として、ユーザが「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示した場合の動作を以下に示す。As a concrete example, the behavior when a user instructs "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow night" is shown below.
1. ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と音声で指示する。1. The user launches the smartphone application and gives a voice command such as, "Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
2. 端末はGoogle Cloud Speech-to-Text APIを使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。2. The device uses the Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API to convert the user's voice commands into text.
3. 端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という予約内容を抽出する。3. The device analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details: "tomorrow night at 7pm" and "4 people."
4. 端末はFirebase Firestoreに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。4. The device sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in Firebase Firestore.
5. サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をFirebase Firestoreから取得し、端末に返す。5. The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from Firebase Firestore, and returns it to the device.
6. 端末はTwilio APIを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。6. The device uses the Twilio API to automatically call the restaurant's phone number.
7. 電話が接続されると、端末はGoogle Cloud Text-to-Speech APIを使用して、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声をレストランに伝える。7. Once the call is connected, the device uses the Google Cloud Text-to-Speech API to communicate to the restaurant, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm."
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが考えられる。Some examples of prompt statements include:
「ユーザが「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と指示した場合、アプリケーションはどのように処理を行うか説明してください。」"If a user says, 'Make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7pm,' how should the application handle that?"
このプロンプト文を生成AIモデルに入力することで、上記の具体例に基づいた処理の説明を得ることができる。By inputting this prompt into the generative AI model, we can obtain an explanation of the process based on the specific example above.
実施例2における特定処理の流れについて図13を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 2 is explained using Figure 13.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザが音声指示を出す。The user gives voice instructions.
ユーザはスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」と音声で指示する。この音声指示が入力となる。The user launches the smartphone application and gives a voice command such as, "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow night." This voice command becomes the input.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末が音声をテキストに変換する。Your device will convert the voice to text.
端末は音声認識技術を使用して、ユーザの音声指示をテキストに変換する。この処理には音声認識APIが使用される。入力はユーザの音声指示であり、出力はテキスト形式の指示である。The device uses voice recognition technology to convert the user's voice instructions into text. This process uses a voice recognition API. The input is the user's voice instructions, and the output is the instructions in text format.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末がテキストを解析し、予約内容を抽出する。The device analyzes the text and extracts the reservation details.
端末は変換されたテキストを解析し、予約内容(日時、人数)を抽出する。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約して」というテキストから「明日の夜7時」と「4人」という情報を取り出す。入力はテキスト形式の指示であり、出力は予約内容のデータである。The terminal analyzes the converted text and extracts the reservation details (date, time, number of people). For example, from the text "Make a reservation for four people at 7pm tomorrow," the information "tomorrow at 7pm" and "four people" is extracted. The input is instructions in text format, and the output is the reservation details data.
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末がサーバにレストラン情報をリクエストする。The device requests restaurant information from the server.
端末はデータベース管理システムに保存されているレストラン情報を取得するために、サーバにリクエストを送信する。このリクエストには、ユーザの位置情報や好みのレストランの条件が含まれる。入力は予約内容とユーザの位置情報であり、出力はレストラン情報のリクエストである。The terminal sends a request to the server to retrieve restaurant information stored in the database management system. This request includes the user's location information and preferred restaurant conditions. The input is the reservation details and the user's location information, and the output is a request for restaurant information.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバがレストラン情報を返す。The server returns the restaurant information.
サーバはリクエストを受け取り、該当するレストランの情報をデータベースから取得し、端末に返す。返される情報には、レストランの名前、電話番号、住所などが含まれる。入力はレストラン情報のリクエストであり、出力はレストラン情報である。The server receives the request, retrieves the relevant restaurant information from the database, and returns it to the terminal. The returned information includes the restaurant's name, phone number, address, etc. The input is a request for restaurant information, and the output is the restaurant information.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末が自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて電話をかける。The device makes the call using an automatic dialing system.
端末は自動ダイヤルシステムを使用して、取得したレストランの電話番号に自動で電話をかける。この処理はユーザの手を煩わせることなく行われる。入力はレストランの電話番号であり、出力は電話接続の確立である。The terminal uses an automatic dialing system to automatically call the restaurant's phone number, without any user intervention. The input is the restaurant's phone number, and the output is the establishment of a telephone connection.
ステップ7:Step 7:
端末が予約内容を音声で伝える。The device will announce the reservation details aloud.
電話が接続されると、端末は音声合成技術を使用して、事前に抽出した予約内容を音声でレストランに伝える。例えば、「明日の夜7時に4人で予約をお願いします」という音声が再生される。入力は予約内容のデータであり、出力は音声メッセージである。When the phone is connected, the device uses voice synthesis technology to verbally communicate the reservation details extracted in advance to the restaurant. For example, a voice may be played saying, "Please make a reservation for four people tomorrow night at 7 p.m." The input is the reservation details data, and the output is a voice message.
(応用例2)(Application example 2)
次に、形態例2の応用例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ロボット414を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 2 of embodiment example 2 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムや予約システムは、ユーザーが手動で操作する必要があり、利便性に欠ける点があった。また、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を活用して最適な提案を行う機能が不足していたため、ユーザーの要望に迅速かつ的確に応えることが難しかった。さらに、音声認識技術や自動ダイヤルシステムを効果的に組み合わせることで、ユーザー体験を向上させることが求められていたConventional navigation and reservation systems required users to operate them manually, which made them less convenient. They also lacked the functionality to utilize the user's past behavioral history to make optimal suggestions, making it difficult to respond quickly and accurately to user requests. Furthermore, there was a need to effectively combine voice recognition technology and an automatic dialing system to improve the user experience.
応用例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段と、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段と、音声フィードバックを提供する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーは音声指示のみで目的地の検索や予約を行うことができ、過去の行動履歴に基づいた最適な提案を受けることが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for understanding the user's requests using voice recognition technology, means for making reservations using an automatic dialing system, means for learning the user's past behavioral history and making optimal suggestions, and means for providing voice feedback. This allows the user to search for and make reservations at destinations using only voice instructions, and to receive optimal suggestions based on the user's past behavioral history.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報を収集し、解析し、理解するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to the methods and techniques used to collect, analyze, and understand information.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods and technologies for searching for an appropriate location based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた情報やデータを指す。"Search results" refers to the information or data obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、検索結果に基づいて最終的な目的地を決定するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to the method or technology for determining a final destination based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道案内を行うための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods and technologies for providing directions to a set destination.
「音声認識技術」とは、音声を解析し、テキストやコマンドに変換する技術を指す。"Voice recognition technology" refers to the technology that analyzes voice and converts it into text or commands.
「自動ダイヤルシステム」とは、指定された電話番号に自動的に電話をかけるシステムを指す。"Automatic dialing system" refers to a system that automatically dials a specified telephone number.
「予約を行う手段」とは、指定された場所やサービスの予約を自動的に行うための方法や技術を指す。"Means of making a reservation" refers to methods or technologies for automatically making a reservation for a specified location or service.
「過去の行動履歴」とは、ユーザーが以前に行った行動や選択の記録を指す。"Past behavioral history" refers to records of actions and choices a user has previously made.
「最適な提案を行う手段」とは、過去の行動履歴や現在の要望に基づいて、ユーザーに最も適した選択肢を提示するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of making optimal suggestions" refers to methods and technologies for presenting the most suitable options to users based on their past behavioral history and current needs.
「音声フィードバックを提供する手段」とは、システムが音声を用いてユーザーに情報や結果を伝えるための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing audio feedback" refers to methods or technologies that allow a system to communicate information or results to a user using audio.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、以下のような構成を持つ。サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段、音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段、自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段、ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段、音声フィードバックを提供する手段を含む。A system for implementing this invention has the following configuration: The server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for understanding the user's requests using voice recognition technology, means for making reservations using an automatic dialing system, means for learning the user's past behavioral history and making optimal suggestions, and means for providing voice feedback.
プログラムの処理の説明Explanation of program processing
ハードウェアとソフトウェアHardware and software
このシステムは、スマートフォンのマイクとスピーカーをハードウェアとして使用する。また、音声認識にはspeech_recognitionライブラリ、音声フィードバックにはpyttsx3ライブラリ、データ通信にはrequestsライブラリを使用する。The system uses the smartphone's microphone and speaker as hardware. It also uses the speech_recognition library for voice recognition, the pyttsx3 library for voice feedback, and the requests library for data communication.
データ加工とデータ演算Data processing and data calculations
1. 音声認識: ユーザーがスマートフォンのマイクに向かって要望を話すと、speech_recognitionライブラリがその音声をテキストに変換する。1. Speech recognition: When the user speaks their request into the smartphone's microphone, the speech_recognition library converts the speech into text.
2. 要望の解析: 変換されたテキストを解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。例えば、「ピザを注文して」という要望を解析する。2. Request Analysis: Analyze the converted text to understand the user's request. For example, analyze the request "order a pizza."
3. 予約の実行: 要望に基づいて、requestsライブラリを使用してフードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信する。注文が成功した場合、pyttsx3ライブラリを使用して音声フィードバックを提供する。3. Execute reservation: Based on the request, send the order to the food delivery API using the requests library. If the order is successful, provide audio feedback using the pyttsx3 library.
4. 行動履歴の学習: ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、次回以降の最適な提案を行う。4. Learning behavioral history: Learns the user's past behavioral history and provides optimal suggestions for future visits.
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「ピザを注文して」と言った場合、システムは以下のように動作する。For example, if a user says "order a pizza," the system would do the following:
1. ユーザーの音声をマイクで取得する。1. Capture the user's voice using the microphone.
2. 音声をテキストに変換し、「ピザを注文して」というテキストを得る。2. Convert speech to text and get the text "Order pizza."
3. テキストを解析し、「ピザ」の注文を特定する。3. Analyze the text to identify "pizza" orders.
4. フードデリバリーAPIに「ピザ」の注文を送信する。4. Send an order for "Pizza" to the food delivery API.
5. 注文が成功した場合、「ピザの注文が完了しました」と音声でフィードバックする。5. If the order is successful, audio feedback will be provided saying "Your pizza order has been completed."
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
ユーザーが「ピザを注文して」と言った場合、音声認識技術を用いて音声をテキストに変換し、フードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信するプログラムを作成してください。注文が成功した場合、音声で「ピザの注文が完了しました」とフィードバックしてください。When a user says "Order a pizza," create a program that uses speech recognition technology to convert the speech to text and send the order to a food delivery API. If the order is successful, provide voice feedback saying "Pizza order completed."
このようにして、ユーザーは音声指示のみで目的地の検索や予約を行うことができ、過去の行動履歴に基づいた最適な提案を受けることが可能となる。In this way, users can search for and book destinations using only voice commands, and receive optimal suggestions based on their past travel history.
応用例2における特定処理の流れについて図14を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 2 is explained using Figure 14.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのマイクに向かって要望を話す。The user speaks their request into the smartphone's microphone.
入力: ユーザの音声。Input: User's voice.
出力: マイクで取得された音声データ。Output: Audio data captured by the microphone.
具体的な動作: ユーザが「ピザを注文して」と話すと、スマートフォンのマイクがその音声をキャプチャする。What happens: When a user says "order a pizza," the smartphone's microphone captures the audio.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末がspeech_recognitionライブラリを使用して音声データをテキストに変換する。The device uses the speech_recognition library to convert the voice data into text.
入力: マイクで取得された音声データ。Input: Audio data captured by the microphone.
出力: テキストデータ(例:「ピザを注文して」)。Output: Text data (e.g. "order pizza").
具体的な動作: 音声認識エンジンが音声データを解析し、対応するテキストに変換する。Specific operation: The speech recognition engine analyzes the voice data and converts it into corresponding text.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末がテキストデータを解析し、ユーザの要望を理解する。The device analyzes the text data and understands the user's needs.
入力: テキストデータ(例:「ピザを注文して」)。Input: Text data (e.g. "order pizza").
出力: 要望の解析結果(例:「ピザの注文」)。Output: Analysis of the request (e.g. "order pizza").
具体的な動作: テキスト解析エンジンが「ピザを注文して」というテキストを解析し、「ピザの注文」という要望を特定する。Specific behavior: The text analysis engine analyzes the text "order a pizza" and identifies the request "order a pizza."
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末がrequestsライブラリを使用してフードデリバリーAPIに注文を送信する。The device uses the requests library to send the order to the food delivery API.
入力: 要望の解析結果(例:「ピザの注文」)。Input: Analysis of the request (e.g. "order pizza").
出力: APIへの注文リクエストとそのレスポンス。Output: The order request to the API and its response.
具体的な動作: フードデリバリーAPIに対して「ピザの注文」を含むリクエストを送信し、注文が成功したかどうかのレスポンスを受け取る。Specific behavior: Send a request to the food delivery API including "order pizza" and receive a response indicating whether the order was successful.
ステップ5:Step 5:
端末がpyttsx3ライブラリを使用して音声フィードバックを提供する。The device provides audio feedback using the pyttsx3 library.
入力: APIからのレスポンス(例:注文成功)。Input: Response from the API (e.g. order successful).
出力: 音声フィードバック(例:「ピザの注文が完了しました」)。Output: Audio feedback (e.g. "Your pizza order is complete").
具体的な動作: 音声合成エンジンが「ピザの注文が完了しました」というメッセージを生成し、スマートフォンのスピーカーを通じてユーザに伝える。Specific action: The speech synthesis engine generates the message "Your pizza order has been completed" and conveys it to the user through the smartphone speaker.
ステップ6:Step 6:
サーバがユーザの過去の行動履歴を学習し、次回以降の最適な提案を行う。The server learns the user's past behavioral history and makes optimal suggestions for future visits.
入力: ユーザの行動履歴データ。Input: User behavioral history data.
出力: 学習結果に基づく提案データ。Output: Proposed data based on learning results.
具体的な動作: サーバがユーザの過去の注文履歴を解析し、次回の注文時に最適なレストランやメニューを提案するためのデータを生成する。Specific operation: The server analyzes the user's past ordering history and generates data to suggest the best restaurant and menu for the next time they order.
なお、更に、ユーザの感情を推定する感情エンジンを組み合わせてもよい。すなわち、特定処理部290は、感情特定モデル59を用いてユーザの感情を推定し、ユーザの感情を用いた特定処理を行うようにしてもよい。Furthermore, an emotion engine that estimates the user's emotion may be combined. That is, the
「形態例1」"Example 1"
本発明の一実施形態として、感情エンジンを組み込んだナビゲーションシステムがある。One embodiment of the present invention is a navigation system that incorporates an emotion engine.
このシステムは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を認識し、それを考慮に入れて目的地をサーチする。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」という要望を出した場合、その声のトーンが明るければ、システムは活気のあるレストランを、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば、静かなレストランを推薦する。The system recognizes the user's emotions from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc., and takes these into consideration when searching for a destination. For example, if a user requests, "Find a nice restaurant nearby," the system will recommend a lively restaurant if the user's tone of voice is cheerful, but a quiet restaurant if the user's tone of voice is sad.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
また、感情エンジンを組み込んだスマートフォン用のアプリケーションも本発明の一実施形態である。このアプリケーションは、ユーザーのテキスト入力や音声入力から感情を認識し、それを考慮に入れてサービスを提供する。例えば、ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力した場合、その感情を認識して、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランや、ユーザーが好きな料理を提供するレストランを推薦する。Another embodiment of the present invention is a smartphone application incorporating an emotion engine. This application recognizes emotions from the user's text and voice input, and provides services taking these into consideration. For example, if the user inputs, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," the application recognizes the emotion and recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere and restaurants that serve the user's favorite dishes.
以下に、各形態例の処理の流れについて説明する。The process flow for each example is explained below.
「形態例1」"Example 1"
ステップ1:ユーザーがナビゲーションシステムに対して音声で要望を出す。Step 1: The user issues a verbal request to the navigation system.
ステップ2:感情エンジンがユーザーの声のトーン、表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を認識する。Step 2: The emotion engine recognizes the user's emotions from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc.
ステップ3:システムが認識した感情を考慮に入れて、目的地をサーチする。Step 3: Search for destinations, taking into account the emotions the system recognizes.
ステップ4:システムがサーチ結果をユーザーに提示する。Step 4: The system presents the search results to the user.
「形態例2」"Example 2"
ステップ1:ユーザーがスマートフォン用のアプリケーションに対してテキスト入力や音声入力で要望を出す。Step 1: The user submits a request to a smartphone application via text or voice input.
ステップ2:感情エンジンがユーザーのテキスト入力や音声入力から感情を認識する。Step 2: The emotion engine recognizes emotions from the user's text or voice input.
ステップ3:アプリケーションが認識した感情を考慮に入れて、サービスを提供する。Step 3: The application takes into account the emotions it recognizes and provides a service.
ステップ4:アプリケーションが提供するサービスの結果をユーザーに提示する。Step 4: Present the user with the results of the services provided by the application.
(実施例1)(Example 1)
次に、形態例1の実施例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ロボット414を「端末」と称する。Next, a first embodiment of the first embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムでは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮した目的地の推薦が難しく、また、最適なルート計算や音声入力の解析が十分に行われないことが多かった。その結果、ユーザーの満足度が低下し、運転中の安全性も確保されにくいという課題があった。With conventional navigation systems, it was difficult to recommend destinations that took into account the user's detailed requests and feelings, and they often did not adequately calculate optimal routes or analyze voice input. As a result, there were issues with low user satisfaction and difficulty in ensuring safety while driving.
実施例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する手段と、ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に最適なルートを計算する手段と、音声入力を解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮した目的地の推薦が可能となり、最適なルート計算や音声入力の解析も行われるため、ユーザーの満足度が向上し、運転中の安全性も確保される。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's detailed requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's emotions and recommending a destination based thereon, means for calculating an optimal route based on the user's current location and the search results, and means for analyzing voice input and understanding the user's requests. This makes it possible to recommend a destination taking into account the user's detailed requests and emotions, and also calculates an optimal route and analyzes voice input, thereby improving user satisfaction and ensuring safety while driving.
「情報源」とは、データを提供するための基となる場所やシステムであり、例えば、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースを指す。An "information source" is a source or system that provides data, such as a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available.
「学習する手段」とは、取得した情報を基に機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを解析し、パターンや特徴を抽出するプロセスを指す。"Means of learning" refers to the process of using machine learning algorithms to analyze data based on acquired information and extract patterns and features.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが特定の条件や好みに基づいて出す具体的なリクエストを指す。"User specific requests" refers to specific requests made by users based on their specific conditions or preferences.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースから検索するプロセスを指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to the process of searching a database for an appropriate destination based on the user's request.
「サーチ結果」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて検索された目的地の情報を指す。"Search results" refers to destination information searched for based on a user's request.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果を基にユーザーの目的地を決定し、その情報をシステムに登録するプロセスを指す。"Means of setting a destination" refers to the process of determining the user's destination based on search results and registering that information in the system.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地への道順をユーザーに案内するためのシステムや方法を指す。"Means for providing navigation" refers to a system or method for guiding a user to a set destination.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方などから感情を解析し、それを理解するプロセスを指す。"Means of recognizing emotions" refers to the process of analyzing and understanding the emotions of the user from their tone of voice, facial expressions, choice of words, etc.
「最適なルートを計算する手段」とは、ユーザーの現在位置と目的地を基に、最も効率的な道順を計算するプロセスを指す。"Means of calculating optimal route" refers to the process of calculating the most efficient route based on the user's current location and destination.
「音声入力を解析する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換し、その内容を理解するための技術や方法を指す。"Means of analyzing voice input" refers to the technology or method for converting a user's voice into text and understanding its content.
本発明は、車載用のナビゲーションシステムに関するものであり、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮して最適な目的地を推薦し、ナビゲーションを提供するシステムである。このシステムは、サーバ、端末、ユーザーの三者が連携して動作する。The present invention relates to an in-vehicle navigation system that provides navigation by recommending optimal destinations while taking into account the user's detailed requests and feelings. This system operates in cooperation with a server, a terminal, and a user.
情報の取得と学習Acquiring and learning information
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得する。このデータベースは、例えば、一般的な地図サービスAPIや評価情報提供サービスAPIを通じてアクセスする。サーバは、取得した情報を機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlowやPyTorch)を用いて学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価や駐車場の有無などの特徴量を抽出し、これをモデルに入力して学習を行う。The server retrieves information from a database that contains information such as restaurant ratings and whether or not the restaurant has parking. This database is accessed, for example, through a general map service API or a rating information service API. The server learns from the retrieved information using a machine learning algorithm (for example, TensorFlow or PyTorch). Specifically, it extracts features such as the restaurant's rating and whether or not the restaurant has parking, and inputs these into a model for learning.
ユーザーの要望解析Analysis of user needs
端末は、ユーザーからの質問や要望を音声入力として受け取る。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と話しかける。端末は、音声認識技術(例えば、一般的な音声認識API)を用いて音声をテキストに変換する。変換されたテキストは、自然言語処理技術(例えば、一般的な自然言語処理モデル)を用いて解析される。解析結果として、ユーザーの要望が「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図であることを理解する。The device receives questions and requests from the user as voice input. For example, the user says, "Find a nice restaurant nearby." The device converts the voice into text using voice recognition technology (e.g., a general voice recognition API). The converted text is analyzed using natural language processing technology (e.g., a general natural language processing model). As a result of the analysis, it is understood that the user's request is intended to "find a nice restaurant."
目的地のサーチSearch for destinations
サーバは、解析結果に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースからサーチする。例えば、「美味しいレストラン」をキーワードにデータベースを検索する。サーバは、感情エンジンを用いて、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方から感情を認識する。例えば、ユーザーの声のトーンが明るければ、活気のあるレストランを推薦し、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば、静かなレストランを推薦する。The server then searches the database for an appropriate destination based on the analysis results. For example, it searches the database using the keyword "delicious restaurant." The server uses an emotion engine to recognize emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, and choice of words. For example, if the user's tone of voice is cheerful, it will recommend a lively restaurant, and if the tone of voice is sad, it will recommend a quiet restaurant.
ルートの計算と設定Calculate and set route
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。例えば、一般的な地図サービスAPIを用いてルート計算を行う。計算されたルート情報は端末に送信され、目的地が設定される。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location (GPS information) and the search results. For example, the route is calculated using a general map service API. The calculated route information is sent to the device, and the destination is set.
ナビゲーションの提供Provide navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを音声ガイダンスシステム(例えば、一般的なナビゲーションアプリ)を用いて提供する。具体的には、音声で「次の交差点を右折してください」などの指示を出す。ユーザーは、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。The device provides navigation to the set destination using a voice guidance system (e.g., a general navigation app). Specifically, instructions such as "Turn right at the next intersection" are given by voice. The user is safely guided to the destination even while driving.
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と音声入力を行った場合、以下のような具体的な動作が行われる。For example, if a user voice-inputs, "Find a good restaurant nearby," the following specific actions will occur:
1. 端末は、ユーザーの音声を受け取り、音声認識APIを用いてテキストに変換する。1. The device receives the user's voice and converts it into text using a speech recognition API.
2. 端末は、変換されたテキストを自然言語処理モデルに入力し、「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図を解析する。2. The device inputs the converted text into a natural language processing model and analyzes the intent of "find a good restaurant."
3. サーバは、解析結果を受け取り、データベースから「美味しいレストラン」を検索する。3. The server receives the analysis results and searches the database for "good restaurants."
4. サーバは、ユーザーの声のトーンを解析し、明るいトーンであれば活気のあるレストランを、落ち込んだトーンであれば静かなレストランを推薦する。4. The server analyzes the tone of the user's voice and recommends lively restaurants if the tone is cheerful, and quiet restaurants if the tone is depressed.
5. サーバは、地図サービスAPIを用いてユーザーの現在位置から目的地までの最適なルートを計算する。5. The server uses the map service API to calculate the optimal route from the user's current location to the destination.
6. 端末は、計算されたルート情報を受け取り、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーにナビゲーションを提供する。6. The device receives the calculated route information and provides navigation to the user using a voice guidance system.
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
「ユーザーが近くの美味しいレストランを探してと音声入力を行った場合、声のトーンが明るければ活気のあるレストランを、声のトーンが落ち込んでいれば静かなレストランを推薦するシステムを設計してください。」"If a user requests a nearby restaurant by voice input, design a system that recommends lively restaurants if the user's voice tone is cheerful, and quiet restaurants if the user's voice tone is depressed."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情や要望に応じた最適なナビゲーションが提供される。In this way, optimal navigation is provided based on the user's emotions and needs.
実施例1における特定処理の流れについて図15を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 1 is explained using Figure 15.
ステップ1:Step 1:
情報の取得と学習Acquiring information and learning
サーバは、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などの情報を含むデータベースから情報を取得する。The server retrieves information from a database that includes information such as restaurant ratings and whether parking is available.
入力:データベースからの情報(例:レストランの評価、駐車場の有無)Input: Information from a database (e.g. restaurant ratings, availability of parking)
データ加工:取得した情報を機械学習アルゴリズム(例:TensorFlow、PyTorch)を用いて学習する。具体的には、レストランの評価や駐車場の有無などの特徴量を抽出し、これをモデルに入力して学習を行う。Data processing: The acquired information is trained using a machine learning algorithm (e.g. TensorFlow, PyTorch). Specifically, features such as restaurant ratings and whether or not there is parking are extracted, and these are input into the model for training.
出力:学習済みモデルOutput: Trained model
ステップ2:Step 2:
ユーザーの要望解析Analysis of user needs
端末は、ユーザーからの質問や要望を音声入力として受け取る。The device receives questions and requests from the user as voice input.
入力:ユーザーの音声入力(例:「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」)Input: User's voice input (e.g. "Find good restaurants nearby")
データ加工:音声認識技術(例:音声認識API)を用いて音声をテキストに変換する。変換されたテキストを自然言語処理技術(例:自然言語処理モデル)を用いて解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。Data processing: Convert speech to text using speech recognition technology (e.g. speech recognition API). Analyze the converted text using natural language processing technology (e.g. natural language processing model) to understand the user's needs.
出力:解析結果(例:「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図)Output: Analysis results (e.g., the intent "find a good restaurant")
ステップ3:Step 3:
目的地のサーチSearch for a destination
サーバは、解析結果に基づいて適切な目的地をデータベースからサーチする。The server searches the database for appropriate destinations based on the analysis results.
入力:解析結果(例:「美味しいレストランを探す」という意図)Input: Analysis results (e.g., the intent to "find a good restaurant")
データ加工:データベースから「美味しいレストラン」を検索する。感情エンジンを用いて、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情、言葉の選び方から感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する。Data processing: Search for "good restaurants" from a database. Using an emotion engine, recognize emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, and choice of words, and recommend destinations based on that.
出力:サーチ結果(例:活気のあるレストラン、静かなレストラン)Output: Search results (e.g. lively restaurants, quiet restaurants)
ステップ4:Step 4:
ルートの計算と設定Route calculation and setting
サーバは、ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)とサーチ結果を基に、最適なルートを計算する。The server calculates the optimal route based on the user's current location (GPS information) and the search results.
入力:ユーザーの現在位置(GPS情報)、サーチ結果Input: User's current location (GPS information), search results
データ加工:地図サービスAPIを用いて最適なルートを計算する。Data processing: Calculate the optimal route using a map service API.
出力:計算されたルート情報Output: Calculated route information
ステップ5:Step 5:
ナビゲーションの提供Providing navigation
端末は、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて提供する。The device uses a voice guidance system to provide navigation to the set destination.
入力:計算されたルート情報Input: Calculated route information
データ加工:音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーに対して「次の交差点を右折してください」などの指示を出す。Data processing: Using a voice guidance system, give instructions to the user such as "Turn right at the next intersection."
出力:音声ガイダンスOutput: Audio guidance
具体的な動作:ユーザーは、運転中でも安全に目的地へと誘導される。Specific operation: Users are safely guided to their destination while driving.
(応用例1)(Application example 1)
次に、形態例1の応用例1について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ロボット414を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 1 of embodiment example 1 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの感情状態を考慮せずに目的地を提案するため、ユーザーの現在の気分や状況に適した目的地を提供することができなかった。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいた最適なルートを提供することができず、ユーザーの満足度を向上させることが困難であった。Conventional navigation systems suggest destinations without taking the user's emotional state into account, making it impossible to provide a destination that suits the user's current mood or situation. In addition, they were unable to provide an optimal route based on the user's emotions, making it difficult to improve user satisfaction.
応用例1におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段と、を含む。これにより、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが可能となる。In this invention, the server includes a means for learning information from various information sources, a means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, a means for setting a destination based on the search results, a means for providing navigation to the set destination, a means for recognizing the user's emotions, and a means for suggesting a destination based on the emotion recognition results. This makes it possible to suggest and navigate to the optimal destination according to the user's emotional state.
「情報源」とは、データや情報を提供する元となる媒体やシステムのことである。An "information source" is a medium or system that provides data or information.
「学習する手段」とは、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて情報を解析し、パターンや知識を獲得するための方法である。A "means of learning" is a method for analyzing information and acquiring patterns and knowledge using machine learning algorithms.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望のことである。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user desires.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な目的地を検索するための方法である。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to a method for searching for an appropriate destination based on the user's requirements.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補のことである。"Search results" refers to destination candidates obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果から最適な目的地を選び、設定するための方法である。"Method of setting a destination" refers to the method for selecting and setting the optimal destination from the search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地への道順を案内するための方法である。"Means of providing navigation" refers to a method for providing directions to a set destination.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの声のトーンや表情などから感情を解析し、認識するための方法である。"Means of recognizing emotions" refers to a method for analyzing and recognizing emotions from the user's tone of voice, facial expressions, etc.
「感情認識結果」とは、感情を認識する手段によって得られたユーザーの感情状態のことである。"Emotion recognition result" refers to the user's emotional state obtained by the emotion recognition means.
「目的地を提案する手段」とは、感情認識結果に基づいてユーザーに適した目的地を推薦するための方法である。"Means for suggesting destinations" refers to a method for recommending suitable destinations to users based on emotion recognition results.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、以下のような構成を持つ。まず、サーバは様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段を備えている。具体的には、機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlowやPyTorch)を用いて、レストランの評価情報や駐車場の有無などのデータを解析し、パターンや知識を獲得する。A system for implementing this invention has the following configuration. First, the server has a means for learning information from various information sources. Specifically, a machine learning algorithm (e.g., TensorFlow or PyTorch) is used to analyze data such as restaurant rating information and the availability of parking spaces, and to acquire patterns and knowledge.
次に、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段を備えている。この手段は、自然言語処理技術(例えば、BERTやGPT-3)を用いてユーザーの音声コマンドを解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する。例えば、ユーザーが「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」と言った場合、その要望を解析し、適切な目的地を検索する。Next, it is equipped with a means to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests. This means uses natural language processing technology (e.g., BERT and GPT-3) to analyze the user's voice commands and understand what the user wants. For example, if the user says, "Find a good restaurant nearby," the request is analyzed and an appropriate destination is searched for.
さらに、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段を備えている。サーバは、検索によって得られた目的地の候補から最適な目的地を選び、設定する。この際、ユーザーの現在位置を考慮し、GPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算する。Furthermore, it is equipped with a means for setting a destination based on the search results. The server selects and sets the most suitable destination from the candidate destinations obtained by the search. At this time, it takes into account the user's current location and calculates the optimal route using GPS technology.
また、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段を備えている。サーバは、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いて、ユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。これにより、ユーザーは運転中でも安全に目的地へ到達することができる。The system also includes a means for providing navigation to the set destination. The server uses a voice guidance system to guide the user to the destination. This allows the user to reach the destination safely even while driving.
さらに、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段を備えている。サーバは、マイクロフォンとカメラを使用してユーザーの声のトーンや表情をリアルタイムで収集し、機械学習アルゴリズムを用いて感情を解析する。例えば、TensorFlowを使用して音声データを解析し、ユーザーの感情状態を分類する。Furthermore, it has a means of recognizing the user's emotions. The server uses a microphone and camera to collect the user's tone of voice and facial expressions in real time, and then uses machine learning algorithms to analyze emotions. For example, it uses TensorFlow to analyze voice data and classify the user's emotional state.
感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段も備えている。サーバは、感情認識結果を基に、ユーザーの現在の感情状態に最も適した目的地を推薦する。例えば、ユーザーが明るいトーンで話している場合、活気のあるレストランを推薦し、落ち着いたトーンで話している場合は静かなカフェを推薦する。The system also has a means of suggesting destinations based on emotion recognition results. The server uses the emotion recognition results to recommend a destination that best suits the user's current emotional state. For example, if the user speaks in a bright tone, the server can recommend a lively restaurant, and if the user speaks in a calm tone, the server can recommend a quiet cafe.
具体例として、ユーザーが「今日はリラックスしたいから、静かなカフェを探して」と言った場合、システムはユーザーの声のトーンが落ち着いていることを認識し、静かなカフェを推薦する。その後、GPSを使用して最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスでユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。For example, if a user says, "I want to relax today, so find me a quiet cafe," the system will recognize that the user's tone of voice is calm and recommend a quiet cafe. It will then use GPS to calculate the optimal route and guide the user to their destination with voice guidance.
プロンプト文の例としては、以下のようなものが挙げられる。Examples of prompts include:
「ユーザーの声のトーンと表情を解析し、感情を認識して最適な目的地を提案するナビゲーションシステムを開発してください。ユーザーが「今日はリラックスしたいから、静かなカフェを探して」と言った場合、システムはユーザーの声のトーンが落ち着いていることを認識し、静かなカフェを推薦します。その後、GPSを使用して最適なルートを計算し、音声ガイダンスでユーザーを目的地へ誘導します。」"Develop a navigation system that analyzes the user's tone of voice and facial expressions, recognizes emotions, and suggests the best destination. If the user says, 'I want to relax today, so I'm looking for a quiet cafe,' the system will recognize that the user's tone of voice is calm and recommend a quiet cafe. It will then use GPS to calculate the best route and guide the user to their destination with voice guidance."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが可能となる。In this way, it becomes possible to suggest and navigate to the most suitable destination based on the user's emotional state.
応用例1における特定処理の流れについて図16を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 1 is explained using Figure 16.
ステップ1:Step 1:
サーバは、マイクロフォンとカメラを使用してユーザーの声のトーンと表情をリアルタイムで収集する。入力はユーザーの音声と映像データであり、出力は前処理された音声データと映像データである。具体的には、ノイズ除去や顔認識を行い、解析に適した形式にデータを変換する。The server uses a microphone and camera to collect the user's tone of voice and facial expressions in real time. The input is the user's audio and video data, and the output is preprocessed audio and video data. Specifically, it performs noise removal and facial recognition, and converts the data into a format suitable for analysis.
ステップ2:Step 2:
サーバは、前処理された音声データと映像データを機械学習アルゴリズム(例えば、TensorFlow)に入力し、ユーザーの感情を認識する。入力は前処理された音声データと映像データであり、出力はユーザーの感情状態(例えば、喜び、悲しみ、怒りなど)である。具体的には、音声のトーンや表情の特徴を解析し、感情を分類する。The server inputs the preprocessed audio and video data into a machine learning algorithm (e.g., TensorFlow) to recognize the user's emotions. The input is the preprocessed audio and video data, and the output is the user's emotional state (e.g., joy, sadness, anger, etc.). Specifically, the tone of the voice and facial features are analyzed to classify the emotion.
ステップ3:Step 3:
サーバは、ユーザーの音声コマンドを自然言語処理技術(例えば、BERTやGPT-3)を用いて解析する。入力はユーザーの音声コマンドであり、出力はユーザーの要望を理解したテキストデータである。具体的には、「近くの美味しいレストランを探して」といったコマンドを解析し、ユーザーの要望を抽出する。The server analyzes the user's voice command using natural language processing technology (e.g., BERT or GPT-3). The input is the user's voice command, and the output is text data that represents an understanding of the user's request. Specifically, it analyzes commands such as "Find a good restaurant nearby" and extracts the user's request.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバは、感情認識結果とユーザーの要望を基に、データベースから適切な目的地をサーチする。入力は感情認識結果とユーザーの要望テキストであり、出力は目的地の候補リストである。具体的には、ユーザーが明るいトーンで話している場合、活気のあるレストランをデータベースから検索する。The server searches the database for an appropriate destination based on the emotion recognition results and the user's request. The input is the emotion recognition results and the user's request text, and the output is a list of candidate destinations. Specifically, if the user is speaking in a bright tone, the database is searched for lively restaurants.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバは、サーチ結果から最適な目的地を選び、設定する。入力は目的地の候補リストであり、出力は設定された目的地である。具体的には、ユーザーの現在位置を考慮し、最も適した目的地を選択する。The server selects and sets the optimal destination from the search results. The input is a list of candidate destinations, and the output is the set destination. Specifically, it takes into account the user's current location and selects the most suitable destination.
ステップ6:Step 6:
サーバは、GPS技術を用いて最適なルートを計算する。入力はユーザーの現在位置と設定された目的地であり、出力は最適なルート情報である。具体的には、地図データを使用して、最短経路や交通状況を考慮したルートを計算する。The server uses GPS technology to calculate the optimal route. The input is the user's current location and the set destination, and the output is optimal route information. Specifically, it uses map data to calculate the shortest route and a route that takes traffic conditions into account.
ステップ7:Step 7:
サーバは、音声ガイダンスシステムを用いてユーザーを目的地へ誘導する。入力は最適なルート情報であり、出力は音声ガイダンスである。具体的には、ユーザーに対して「次の交差点を右折してください」といった指示を音声で提供する。The server uses a voice guidance system to guide the user to the destination. The input is optimal route information, and the output is voice guidance. Specifically, it provides the user with voice instructions such as "Turn right at the next intersection."
このようにして、ユーザーの感情状態に応じた最適な目的地の提案とナビゲーションが実現される。In this way, optimal destination suggestions and navigation can be achieved according to the user's emotional state.
(実施例2)(Example 2)
次に、形態例2の実施例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ロボット414を「端末」と称する。Next, a second embodiment of the second embodiment will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が困難であった。また、ユーザーが音声で予約を依頼した場合、自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了する機能が不足していた。これにより、ユーザーは手動で予約を行う必要があり、利便性が低かった。さらに、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行われておらず、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができなかったConventional navigation systems had difficulty providing services that took into account the detailed requests and emotions of users. In addition, when a user made a reservation by voice, the system lacked the functionality to automatically make a phone call to complete the reservation. This meant that users had to make the reservation manually, which was inconvenient. Furthermore, the system did not recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, which made it difficult to increase user satisfaction.
実施例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声を認識する手段と、音声認識結果を基にレストランを検索する手段と、自動で電話をかける手段と、予約を完了する手段と、ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、感情に基づいてレストランを推薦する手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が可能となり、音声による予約依頼に対して自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了することができる。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行うことができ、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's voice, means for searching for restaurants based on the voice recognition results, means for automatically making a phone call, means for completing a reservation, means for recognizing the user's emotions, and means for recommending a restaurant based on the emotions. This makes it possible to provide a service that takes into account the user's specific requests and emotions, and a reservation can be completed by automatically making a phone call in response to a reservation request made via voice. It is also possible to recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報源から得られたデータを解析し、知識を蓄積するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of learning" refers to methods and techniques for analyzing data obtained from sources and accumulating knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of searching for a destination" refers to methods and technologies for searching for an appropriate location based on the user's requests.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索によって得られた情報やデータを指す。"Search results" refers to the information or data obtained through a search.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果を基にユーザーが訪れるべき場所を決定するための方法や技術を指す。"Destination setting means" refers to the methods and technologies that allow users to determine where they should visit based on search results.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道順や案内を提供するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of providing navigation" refers to methods and technologies for providing directions and guidance to a set destination.
「音声を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声を解析してテキストデータに変換するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of voice recognition" refers to methods and technologies for analyzing a user's voice and converting it into text data.
「レストランを検索する手段」とは、音声認識結果を基に適切な飲食店を検索するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for searching for restaurants" refers to methods and technologies for searching for appropriate restaurants based on voice recognition results.
「自動で電話をかける手段」とは、システムが自動的に電話を発信するための方法や技術を指す。"Means for making automatic phone calls" refers to methods or technologies that allow the system to automatically make phone calls.
「予約を完了する手段」とは、電話を通じて予約手続きを完了するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of completing a reservation" refers to the methods and technologies used to complete the reservation process over the telephone.
「感情を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの入力や音声から感情を解析するための方法や技術を指す。"Means of emotion recognition" refers to methods and technologies for analyzing emotions from user input or voice.
「レストランを推薦する手段」とは、認識された感情に基づいて適切な飲食店を提案するための方法や技術を指す。"Restaurant recommendation means" refers to methods or technologies for suggesting appropriate dining options based on recognized sentiment.
本発明は、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供を実現するためのシステムである。このシステムは、スマートフォン用のアプリケーションとして実装され、ユーザーの音声やテキスト入力を基に、目的地の検索、予約、ナビゲーション、感情に基づくレストランの推薦を行う。The present invention is a system for providing services that take into account the detailed requests and emotions of users. This system is implemented as a smartphone application, and performs destination search, reservations, navigation, and emotion-based restaurant recommendations based on the user's voice and text input.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
ハードウェア:スマートフォン(iPhone、Android端末など)Hardware: Smartphone (iPhone, Android device, etc.)
ソフトウェア:Software:
音声認識技術:音声をテキストに変換するために、音声認識APIを使用する。Speech recognition technology: Uses speech recognition APIs to convert speech to text.
レストラン検索:地図APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。Restaurant search: Use the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
自動ダイヤルシステム:自動的に電話をかけるために、通信APIを使用する。Automatic dialing system: Uses communications APIs to automatically place calls.
感情認識技術:ユーザーの入力から感情を解析するために、感情分析APIを使用する。Emotion recognition technology: Uses sentiment analysis APIs to analyze emotions from user input.
レストラン推薦:レビューサイトAPIを使用して、感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。Restaurant Recommendations: Use review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on sentiment.
システムの具体的な処理Specific processing of the system
ユーザーの要望に基づく予約機能Reservation function based on user requests
1. ユーザーがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「電話で予約して」と音声で指示を出す。1. The user launches the smartphone application and issues a voice command saying, "Make a reservation by phone."
2. 端末は音声認識APIを使用して、ユーザーの音声をテキストに変換する。2. The device uses a speech recognition API to convert the user's speech into text.
3. 端末は地図APIを使用して、ユーザーの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。3. The device uses the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
4. 端末は通信APIを使用して、検索結果から選ばれたレストランに自動で電話をかける。4. The device uses a communications API to automatically call the restaurant selected from the search results.
5. 端末は電話を通じてレストランに予約内容を伝え、予約を完了する。5. The terminal then transmits the reservation details to the restaurant via telephone, completing the reservation.
具体例:Example:
ユーザーが「電話で予約して」と言う。The user says, "Make a reservation by phone."
端末は音声認識APIを使用して音声をテキストに変換する。The device uses a speech recognition API to convert speech to text.
端末:「音声を認識中です...」Device: "Recognizing voice..."
端末は地図APIを使用して近くのレストランを検索する。The device uses the map API to search for nearby restaurants.
端末:「近くのレストランを検索中です...」Device: "Searching for nearby restaurants..."
端末は通信APIを使用して自動的にレストランに電話をかける。The device will automatically call the restaurant using a communications API.
端末:「レストランに電話をかけています...」Device: "Calling restaurant..."
端末は予約が完了したことをユーザーに通知する。The device will notify the user that the reservation is complete.
端末:「予約が完了しました。」Device: "Reservation completed."
感情エンジンを用いたサービス提供Providing services using emotion engines
1. ユーザーがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」とテキストまたは音声で入力する。1. The user launches the smartphone application and inputs via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
2. 端末は感情分析APIを使用して、ユーザーの入力から感情を認識する。2. The device uses the sentiment analysis API to recognize emotions from user input.
3. 端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用して、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。3. The device uses review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on the user's sentiment.
具体例:Example:
ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力する。The user types, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
端末は感情分析APIを使用して感情を認識する。The device uses an emotion analysis API to recognize emotions.
端末:「感情を分析中です。」Device: "Analyzing emotions."
端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用してリラックスできるレストランを推薦する。The device uses review site APIs to recommend relaxing restaurants.
端末:「リラックスできるレストランを探しています。」Device: "I'm looking for a relaxing restaurant."
端末:「こちらのレストランはいかがですか?(レストラン名)」Device: "How about this restaurant? (restaurant name)"
以上が、本発明のスマートフォン用アプリケーションの具体的な実施形態である。このシステムにより、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮に入れたサービス提供が可能となり、音声による予約依頼に対して自動的に電話をかけて予約を完了することができる。また、ユーザーの感情に基づいたレストランの推薦も行うことができ、ユーザーの満足度を高めることができる。The above is a specific embodiment of the smartphone application of the present invention. This system makes it possible to provide services that take into account the detailed requests and emotions of the user, and can complete reservations by automatically making a phone call in response to a voice reservation request. It can also recommend restaurants based on the user's emotions, thereby increasing user satisfaction.
実施例2における特定処理の流れについて図17を用いて説明する。The flow of the identification process in Example 2 is explained using Figure 17.
ユーザーの要望に基づく予約機能Reservation function based on user requests
処理ステップProcessing steps
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「電話で予約して」と音声で指示を出す。The user launches the smartphone application and gives the voice command, "Make a reservation by phone."
入力:ユーザの音声指示Input: User's voice command
出力:音声データOutput: Audio data
具体的な動作:ユーザがアプリケーションを起動し、音声で「電話で予約して」と指示を出す。Specific operation: The user launches the application and issues the command "Make a reservation by phone" via voice.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末は音声認識APIを使用して、ユーザの音声をテキストに変換する。The device uses a speech recognition API to convert the user's speech into text.
入力:音声データInput: Audio data
出力:テキストデータOutput: Text data
具体的な動作:端末は音声データを音声認識APIに送信し、テキストデータを受け取る。Specific operation: The device sends voice data to the voice recognition API and receives text data.
端末:「音声を認識中です。」Device: "Recognizing voice."
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末は地図APIを使用して、ユーザの現在地周辺のレストランを検索する。The device uses the map API to search for restaurants near the user's current location.
入力:テキストデータ、ユーザの現在地情報Input: text data, user's current location information
出力:レストランのリストOutput: List of restaurants
具体的な動作:端末はユーザの現在地情報を取得し、地図APIにクエリを送信してレストランのリストを受け取る。Specific operation: The device obtains the user's current location information and sends a query to the map API to receive a list of restaurants.
端末:「近くのレストランを検索中です。」Device: "Searching for nearby restaurants."
ステップ4:Step 4:
端末は通信APIを使用して、検索結果から選ばれたレストランに自動で電話をかける。The device uses a communications API to automatically call the restaurant selected from the search results.
入力:レストランのリストEnter: List of restaurants
出力:通話開始Output: Start call
具体的な動作:端末は通信APIに電話番号と通話内容を送信し、通話を開始する。Specific operation: The device sends the phone number and call details to the communication API and starts the call.
端末:「レストランに電話をかけています。」Device: "Calling restaurant."
ステップ5:Step 5:
端末は電話を通じてレストランに予約内容を伝え、予約を完了する。The terminal then communicates the reservation details to the restaurant via telephone, completing the reservation.
入力:通話開始Enter: Start call
出力:予約完了通知Output: Reservation completion notification
具体的な動作:端末は通信APIを通じて通話を管理し、予約が完了したことをユーザに通知する。Specific operation: The device manages the call through the communication API and notifies the user that the reservation has been completed.
端末:「予約が完了しました。」Device: "Reservation completed."
感情エンジンを用いたサービス提供Providing services using emotion engines
処理ステップProcessing steps
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンのアプリケーションを起動し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」とテキストまたは音声で入力する。The user launches a smartphone application and inputs, via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
入力:ユーザのテキストまたは音声入力Input: User text or voice input
出力:テキストデータOutput: Text data
具体的な動作:ユーザがアプリケーションを起動し、テキストまたは音声で「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と入力する。Specific actions: The user launches the application and enters, via text or voice, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末は感情分析APIを使用して、ユーザの入力から感情を認識する。The device uses a sentiment analysis API to recognize emotions from user input.
入力:テキストデータInput: Text data
出力:感情分析結果Output: Sentiment analysis results
具体的な動作:端末はテキストデータを感情分析APIに送信し、感情分析結果を受け取る。Specific operation: The device sends text data to the sentiment analysis API and receives the sentiment analysis results.
端末:「感情を分析中です。」Device: "Analyzing emotions."
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末はレビューサイトAPIを使用して、ユーザの感情に基づいたレストランを推薦する。The device uses review site APIs to recommend restaurants based on the user's sentiment.
入力:感情分析結果Input: Sentiment analysis results
出力:レストランの推薦リストOutput: A list of restaurant recommendations
具体的な動作:端末は感情分析結果を基にレビューサイトAPIにクエリを送信し、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランやユーザが好きな料理を提供するレストランのリストを受け取る。Specific operation: Based on the sentiment analysis results, the device sends a query to the review site API and receives a list of restaurants that have a relaxing atmosphere or serve the user's favorite cuisine.
端末:「リラックスできるレストランを探しています。」Device: "I'm looking for a relaxing restaurant."
端末:「こちらのレストランはいかがですか?(レストラン名)」Device: "How about this restaurant? (restaurant name)"
以上が、本発明のスマートフォン用アプリケーションの具体的な処理ステップである。The above are the specific processing steps of the smartphone application of the present invention.
(応用例2)(Application example 2)
次に、形態例2の応用例2について説明する。以下の説明では、データ処理装置12を「サーバ」と称し、ロボット414を「端末」と称する。Next, application example 2 of embodiment example 2 will be described. In the following description, the
従来のナビゲーションシステムや予約システムは、ユーザーの細かい要望や感情を考慮することができず、ユーザー体験が限定されていた。また、ユーザーが音声で要望を入力し、それに基づいて最適なサービスを推薦し、自動的に注文を行う機能が欠如していた。これにより、ユーザーが求めるサービスを迅速かつ的確に提供することが困難であった。Conventional navigation and reservation systems were unable to take into account the detailed requests and feelings of users, limiting the user experience. They also lacked the functionality to have users input their requests by voice, have the system recommend optimal services based on those requests, and automatically place orders. This made it difficult to quickly and accurately provide the services users wanted.
応用例2におけるデータ処理装置12の特定処理部290による特定処理を、以下の各手段により実現する。The specific processing by the
この発明では、サーバは、様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、ユーザーの音声入力を認識する手段と、認識された音声入力から感情を分析する手段と、感情分析の結果に基づいて最適なサービスを推薦する手段と、推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う手段を含む。これにより、ユーザーの要望や感情を考慮したサービスの提供が可能となる。In this invention, the server includes means for learning information from various information sources, means for searching for a destination based on the user's specific requests, means for setting a destination based on the search results, means for providing navigation to the set destination, means for recognizing the user's voice input, means for analyzing emotions from the recognized voice input, means for recommending optimal services based on the results of the emotion analysis, and means for automatically placing an order for the recommended services. This makes it possible to provide services that take into account the user's requests and emotions.
「情報源」とは、データや知識を提供するあらゆる出所を指す。"Source" refers to any source of data or knowledge.
「学習する手段」とは、情報源から得られたデータを解析し、知識を蓄積するための方法や装置を指す。"Means of learning" refers to methods and devices for analyzing data obtained from sources and accumulating knowledge.
「ユーザーの細かい要望」とは、ユーザーが具体的に求める条件や希望を指す。"The user's detailed requests" refer to the specific conditions and wishes that the user has.
「目的地をサーチする手段」とは、ユーザーの要望に基づいて適切な場所を検索するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for searching for a destination" refers to a method or device for searching for an appropriate location based on a user's request.
「サーチ結果」とは、検索手段によって得られた情報の集合を指す。"Search Results" refers to the collection of information obtained through a search tool.
「目的地を設定する手段」とは、サーチ結果から選ばれた場所を最終的な目的地として決定するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for setting a destination" refers to a method or device for determining a location selected from the search results as the final destination.
「ナビゲーションを提供する手段」とは、設定された目的地までの道順や案内を提供するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for providing navigation" refers to a method or device for providing directions or guidance to a set destination.
「音声入力を認識する手段」とは、ユーザーの音声をテキストデータに変換するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for recognizing voice input" refers to a method or device for converting a user's voice into text data.
「感情を分析する手段」とは、音声入力やテキストデータからユーザーの感情を解析するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for analyzing emotions" refers to a method or device for analyzing a user's emotions from voice input or text data.
「最適なサービスを推薦する手段」とは、感情分析の結果に基づいてユーザーに最も適したサービスを提案するための方法や装置を指す。"Means for recommending optimal services" refers to a method or device for suggesting the most suitable service to a user based on the results of sentiment analysis.
「自動的に注文を行う手段」とは、推薦されたサービスに対してユーザーの介入なしに注文を完了するための方法や装置を指す。"Automatic ordering means" refers to a method or device for completing an order for recommended services without user intervention.
この発明を実施するためのシステムは、ユーザーの音声入力を認識し、感情を分析し、最適なサービスを推薦し、自動的に注文を行う一連の処理を行うものである。以下に、このシステムの具体的な実施形態を説明する。The system for implementing this invention performs a series of processes that recognize the user's voice input, analyze emotions, recommend optimal services, and automatically place an order. A specific embodiment of this system is described below.
システム構成System configuration
システムは、以下の主要なコンポーネントから構成される:The system consists of the following main components:
1. 音声認識モジュール:ユーザーの音声入力をテキストデータに変換する。具体的には、speech_recognitionライブラリを使用する。1. Speech recognition module: Converts the user's voice input into text data. Specifically, it uses the speech_recognition library.
2. 感情分析モジュール:音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを解析し、ユーザーの感情を分析する。具体的には、TextBlobライブラリを使用する。2. Sentiment analysis module: Analyzes the text data obtained from the voice recognition module and analyzes the user's emotions. Specifically, it uses the TextBlob library.
3. サービス推薦モジュール:感情分析の結果に基づいて、ユーザーに最適なサービスを推薦する。3. Service recommendation module: Recommend the most suitable services to users based on the results of sentiment analysis.
4. 自動注文モジュール:推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う。具体的には、requestsライブラリを使用してAPIエンドポイントに注文データを送信する。4. Auto-order module: Automatically places orders for recommended services. Specifically, it uses the requests library to send order data to an API endpoint.
処理の流れProcessing flow
1. 音声入力の認識:ユーザーがスマートフォンに向かって音声で要望を入力する。音声認識モジュールがこの音声をテキストデータに変換する。1. Voice input recognition: The user speaks their request into the smartphone. The voice recognition module converts this voice into text data.
2. 感情の分析:音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを感情分析モジュールに渡し、ユーザーの感情を解析する。2. Sentiment analysis: The text data obtained from the voice recognition module is passed to the sentiment analysis module to analyze the user's emotions.
3. サービスの推薦:感情分析の結果に基づいて、サービス推薦モジュールがユーザーに最適なサービスを選定し、推薦する。3. Service recommendation: Based on the results of sentiment analysis, the service recommendation module selects and recommends the most suitable services to the user.
4. 自動注文の実行:サービス推薦モジュールが選定したサービスに対して、自動注文モジュールが注文を行う。4. Executing automatic orders: The automatic ordering module places an order for the service selected by the service recommendation module.
使用するハードウェアおよびソフトウェアHardware and software used
ハードウェア:スマートフォン、サーバHardware: smartphones, servers
ソフトウェア:speech_recognitionライブラリ、TextBlobライブラリ、requestsライブラリSoftware: speech_recognition library, TextBlob library, requests library
具体例Specific examples
例えば、ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と音声入力した場合、システムは以下のように動作する:For example, if a user says, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," the system will act as follows:
1. 音声認識モジュールが音声をテキストに変換し、「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」というテキストデータを生成する。1. The voice recognition module converts the voice into text and generates text data such as "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious."
2. 感情分析モジュールがこのテキストデータを解析し、ユーザーが疲れていることを認識する。2. The sentiment analysis module analyzes this text data and recognizes that the user is tired.
3. サービス推薦モジュールがリラックスできる雰囲気のレストランを推薦する。3. The service recommendation module recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere.
4. 自動注文モジュールが推薦されたレストランに対して自動的に注文を行う。4. The auto-order module automatically places orders from the recommended restaurants.
プロンプト文の例Example of a prompt
生成AIモデルへ入力するプロンプト文の例:Example of a prompt to input to a generative AI model:
ユーザーが「今日は疲れた。美味しいものを食べたい」と音声入力した場合、感情分析を行い、リラックスできる雰囲気のレストランを推薦し、自動的に注文を行うPythonプログラムを作成してください。If a user says, "I'm tired today. I want to eat something delicious," create a Python program that performs sentiment analysis, recommends restaurants with a relaxing atmosphere, and automatically places the order.
応用例2における特定処理の流れについて図18を用いて説明する。The flow of the specific processing in application example 2 is explained using Figure 18.
ステップ1:Step 1:
ユーザがスマートフォンに向かって音声で要望を入力する。音声入力は、スマートフォンのマイクを通じて取得される。入力データは、ユーザの音声データである。The user speaks their request into the smartphone. The voice input is acquired through the smartphone's microphone. The input data is the user's voice data.
ステップ2:Step 2:
端末の音声認識モジュールが、ユーザの音声データをテキストデータに変換する。具体的には、speech_recognitionライブラリを使用して音声データを解析し、テキストデータを生成する。出力データは、ユーザの音声をテキストに変換したものである。The device's voice recognition module converts the user's voice data into text data. Specifically, it uses the speech_recognition library to analyze the voice data and generate text data. The output data is the user's voice converted into text.
ステップ3:Step 3:
端末の感情分析モジュールが、音声認識モジュールから得られたテキストデータを受け取り、ユーザの感情を解析する。具体的には、TextBlobライブラリを使用してテキストデータの感情を分析する。入力データは、テキストデータであり、出力データは、感情分析の結果である。The terminal's sentiment analysis module receives the text data obtained from the voice recognition module and analyzes the user's sentiment. Specifically, it uses the TextBlob library to analyze the sentiment of the text data. The input data is the text data, and the output data is the result of the sentiment analysis.
ステップ4:Step 4:
サーバのサービス推薦モジュールが、感情分析の結果に基づいて、ユーザに最適なサービスを選定し、推薦する。入力データは、感情分析の結果であり、出力データは、推薦されたサービスの情報である。具体的には、感情がネガティブであればリラックスできるサービスを、ポジティブであれば人気のサービスを推薦する。The server's service recommendation module selects and recommends the most suitable service to the user based on the results of the sentiment analysis. The input data is the results of the sentiment analysis, and the output data is information about the recommended service. Specifically, if the sentiment is negative, a relaxing service is recommended, and if it is positive, a popular service is recommended.
ステップ5:Step 5:
サーバの自動注文モジュールが、サービス推薦モジュールから得られた推薦サービス情報を受け取り、自動的に注文を行う。具体的には、requestsライブラリを使用して、推薦されたサービスに対して注文データをAPIエンドポイントに送信する。入力データは、推薦されたサービスの情報であり、出力データは、注文の完了通知である。The server's automatic ordering module receives the recommended service information obtained from the service recommendation module and automatically places the order. Specifically, it uses the requests library to send order data for the recommended service to an API endpoint. The input data is information about the recommended service, and the output data is a notification of order completion.
ステップ6:Step 6:
端末が、注文の完了通知をユーザに表示する。入力データは、注文の完了通知であり、出力データは、ユーザに表示される注文完了メッセージである。具体的には、スマートフォンの画面に注文が完了した旨のメッセージを表示する。The terminal displays a notification that the order is complete to the user. The input data is the notification that the order is complete, and the output data is an order completion message that is displayed to the user. Specifically, a message indicating that the order is complete is displayed on the smartphone screen.
特定処理部290は、特定処理の結果をロボット414に送信する。ロボット414では、制御部46Aが、スピーカ240及び制御対象443に対して特定処理の結果を出力させる。マイクロフォン238は、特定処理の結果に対するユーザ入力を示す音声を取得する。制御部46Aは、マイクロフォン238によって取得されたユーザ入力を示す音声データをデータ処理装置12に送信する。データ処理装置12では、特定処理部290が音声データを取得する。The
データ生成モデル58は、いわゆる生成AI(Artificial Intelligence)である。データ生成モデル58の一例としては、ChatGPT(インターネット検索<URL: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt>)等の生成AIが挙げられる。データ生成モデル58は、ニューラルネットワークに対して深層学習を行わせることによって得られる。データ生成モデル58には、指示を含むプロンプトが入力され、かつ、音声を示す音声データ、テキストを示すテキストデータ、及び画像を示す画像データ等の推論用データが入力される。データ生成モデル58は、入力された推論用データをプロンプトにより示される指示に従って推論し、推論結果を音声データ及びテキストデータ等のデータ形式で出力する。ここで、推論とは、例えば、分析、分類、予測、及び/又は要約等を指す。The
生成AIの他の例としては、Gemini(インターネット検索<URL: https://gemini.google.com/?hl=ja>)が挙げられる。Another example of generative AI is Gemini (Internet search <URL: https://gemini.google.com/?hl=ja>).
上記実施形態では、データ処理装置12によって特定処理が行われる形態例を挙げたが、本開示の技術はこれに限定されず、ロボット414によって特定処理が行われるようにしてもよい。In the above embodiment, an example was given in which the specific processing is performed by the
なお、感情エンジンとしての感情特定モデル59は、特定のマッピングに従い、ユーザの感情を決定してよい。具体的には、感情特定モデル59は、特定のマッピングである感情マップ(図9参照)に従い、ユーザの感情を決定してよい。また、感情特定モデル59は、同様に、ロボットの感情を決定し、特定処理部290は、ロボットの感情を用いた特定処理を行うようにしてもよい。The emotion identification model 59, which serves as an emotion engine, may determine the emotion of the user according to a specific mapping. Specifically, the emotion identification model 59 may determine the emotion of the user according to an emotion map (see FIG. 9), which is a specific mapping. Similarly, the emotion identification model 59 may determine the emotion of the robot, and the
図9は、複数の感情がマッピングされる感情マップ400を示す図である。感情マップ400において、感情は、中心から放射状に同心円に配置されている。同心円の中心に近いほど、原始的状態の感情が配置されている。同心円のより外側には、心境から生まれる状態や行動を表す感情が配置されている。感情とは、情動や心的状態も含む概念である。同心円の左側には、概して脳内で起きる反応から生成される感情が配置されている。同心円の右側には概して、状況判断で誘導される感情が配置されている。同心円の上方向及び下方向には、概して脳内で起きる反応から生成され、かつ、状況判断で誘導される感情が配置されている。また、同心円の上側には、「快」の感情が配置され、下側には、「不快」の感情が配置されている。このように、感情マップ400では、感情が生まれる構造に基づいて複数の感情がマッピングされており、同時に生じやすい感情が、近くにマッピングされている。9 is a diagram showing an
これらの感情は、感情マップ400の3時の方向に分布しており、普段は安心と不安のあたりを行き来する。感情マップ400の右半分では、内部的な感覚よりも状況認識の方が優位に立つため、落ち着いた印象になる。These emotions are distributed in the three o'clock direction of
感情マップ400の内側は心の中、感情マップ400の外側は行動を表すため、感情マップ400の外側に行くほど、感情が目に見える(行動に表れる)ようになる。The inside of
ここで、人の感情は、姿勢や血糖値のような様々なバランスを基礎としており、それらのバランスが理想から遠ざかると不快、理想に近づくと快という状態を示す。ロボットや自動車やバイク等においても、姿勢やバッテリー残量のような様々なバランスを基礎として、それらのバランスが理想から遠ざかると不快、理想に近づくと快という状態を示すように感情を作ることができる。感情マップは、例えば、光吉博士の感情地図(音声感情認識及び情動の脳生理信号分析システムに関する研究、徳島大学、博士論文:https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/500000375379)に基づいて生成されてよい。感情地図の左半分には、感覚が優位にたつ「反応」と呼ばれる領域に属する感情が並ぶ。また、感情地図の右半分には、状況認識が優位にたつ「状況」と呼ばれる領域に属する感情が並ぶ。Here, human emotions are based on various balances such as posture and blood sugar level, and when these balances are far from the ideal, it indicates an unpleasant state, and when they are close to the ideal, it indicates a pleasant state. Emotions can also be created for robots, cars, motorcycles, etc., based on various balances such as posture and remaining battery power, so that when these balances are far from the ideal, it indicates an unpleasant state, and when they are close to the ideal, it indicates a pleasant state. The emotion map may be generated, for example, based on the emotion map of Dr. Mitsuyoshi (Research on speech emotion recognition and emotion brain physiological signal analysis system, Tokushima University, doctoral dissertation: https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/500000375379). The left half of the emotion map is lined with emotions that belong to an area called "reaction" where sensation is dominant. The right half of the emotion map is lined with emotions that belong to an area called "situation" where situation recognition is dominant.
感情マップでは学習を促す感情が2つ定義される。1つは、状況側にあるネガティブな「懺悔」や「反省」の真ん中周辺の感情である。つまり、「もう2度とこんな想いはしたくない」「もう叱られたくない」というネガティブな感情がロボットに生じたときである。もう1つは、反応側にあるポジティブな「欲」のあたりの感情である。つまり、「もっと欲しい」「もっと知りたい」というポジティブな気持ちのときである。The emotion map defines two emotions that encourage learning. The first is the negative emotion around the middle of "repentance" or "remorse" on the situation side. In other words, this is when the robot experiences negative emotions such as "I never want to feel this way again" or "I don't want to be scolded again." The other is the positive emotion around "desire" on the response side. In other words, this is when the robot has positive feelings such as "I want more" or "I want to know more."
感情特定モデル59は、ユーザ入力を、予め学習されたニューラルネットワークに入力し、感情マップ400に示す各感情を示す感情値を取得し、ユーザの感情を決定する。このニューラルネットワークは、ユーザ入力と、感情マップ400に示す各感情を示す感情値との組み合わせである複数の学習データに基づいて予め学習されたものである。また、このニューラルネットワークは、図10に示す感情マップ900のように、近くに配置されている感情同士は、近い値を持つように学習される。図10では、「安心」、「安穏」、「心強い」という複数の感情が、近い感情値となる例を示している。The emotion identification model 59 inputs user input to a pre-trained neural network, obtains emotion values indicating each emotion shown in the
上記実施形態では、1台のコンピュータ22によって特定処理が行われる形態例を挙げたが、本開示の技術はこれに限定されず、コンピュータ22を含めた複数のコンピュータによる特定処理に対する分散処理が行われるようにしてもよい。In the above embodiment, an example was given in which a specific process is performed by one
上記実施形態では、ストレージ32に特定処理プログラム56が格納されている形態例を挙げて説明したが、本開示の技術はこれに限定されない。例えば、特定処理プログラム56がUSB(Universal Serial Bus)メモリなどの可搬型のコンピュータ読み取り可能な非一時的格納媒体に格納されていてもよい。非一時的格納媒体に格納されている特定処理プログラム56は、データ処理装置12のコンピュータ22にインストールされる。プロセッサ28は、特定処理プログラム56に従って特定処理を実行する。In the above embodiment, an example has been described in which the
また、ネットワーク54を介してデータ処理装置12に接続されるサーバ等の格納装置に特定処理プログラム56を格納させておき、データ処理装置12の要求に応じて特定処理プログラム56がダウンロードされ、コンピュータ22にインストールされるようにしてもよい。The
なお、ネットワーク54を介してデータ処理装置12に接続されるサーバ等の格納装置に特定処理プログラム56の全てを格納させておいたり、ストレージ32に特定処理プログラム56の全てを記憶させたりしておく必要はなく、特定処理プログラム56の一部を格納させておいてもよい。It is not necessary to store all of the
特定処理を実行するハードウェア資源としては、次に示す各種のプロセッサを用いることができる。プロセッサとしては、例えば、ソフトウェア、すなわち、プログラムを実行することで、特定処理を実行するハードウェア資源として機能する汎用的なプロセッサであるCPUが挙げられる。また、プロセッサとしては、例えば、FPGA(Field-Programmable Gate Array)、PLD(Programmable Logic Device)、又はASIC(Application Specific Integrated Circuit)などの特定の処理を実行させるために専用に設計された回路構成を有するプロセッサである専用電気回路が挙げられる。何れのプロセッサにもメモリが内蔵又は接続されており、何れのプロセッサもメモリを使用することで特定処理を実行する。The various processors listed below can be used as hardware resources for executing specific processes. Examples of processors include a CPU, which is a general-purpose processor that functions as a hardware resource for executing specific processes by executing software, i.e., a program. Examples of processors include dedicated electrical circuits, such as FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays), PLDs (Programmable Logic Devices), or ASICs (Application Specific Integrated Circuits), which are processors with a circuit configuration designed specifically to execute specific processes. All of these processors have built-in or connected memory, and all of these processors execute specific processes by using the memory.
特定処理を実行するハードウェア資源は、これらの各種のプロセッサのうちの1つで構成されてもよいし、同種又は異種の2つ以上のプロセッサの組み合わせ(例えば、複数のFPGAの組み合わせ、又はCPUとFPGAとの組み合わせ)で構成されてもよい。また、特定処理を実行するハードウェア資源は1つのプロセッサであってもよい。The hardware resource that executes the specific process may be composed of one of these various processors, or may be composed of a combination of two or more processors of the same or different types (e.g., a combination of multiple FPGAs, or a combination of a CPU and an FPGA). The hardware resource that executes the specific process may also be a single processor.
1つのプロセッサで構成する例としては、第1に、1つ以上のCPUとソフトウェアの組み合わせで1つのプロセッサを構成し、このプロセッサが、特定処理を実行するハードウェア資源として機能する形態がある。第2に、SoC(System-on-a-chip)などに代表されるように、特定処理を実行する複数のハードウェア資源を含むシステム全体の機能を1つのICチップで実現するプロセッサを使用する形態がある。このように、特定処理は、ハードウェア資源として、上記各種のプロセッサの1つ以上を用いて実現される。As an example of a configuration using a single processor, first, there is a configuration in which one processor is configured by combining one or more CPUs with software, and this processor functions as a hardware resource that executes a specific process. Secondly, there is a configuration in which a processor is used that realizes the functions of the entire system, including multiple hardware resources that execute a specific process, on a single IC chip, as typified by SoC (System-on-a-chip). In this way, a specific process is realized using one or more of the various processors mentioned above as hardware resources.
更に、これらの各種のプロセッサのハードウェア的な構造としては、より具体的には、半導体素子などの回路素子を組み合わせた電気回路を用いることができる。また、上記の特定処理はあくまでも一例である。従って、主旨を逸脱しない範囲内において不要なステップを削除したり、新たなステップを追加したり、処理順序を入れ替えたりしてもよいことは言うまでもない。More specifically, the hardware structure of these various processors can be an electric circuit that combines circuit elements such as semiconductor elements. The specific processing described above is merely an example. It goes without saying that unnecessary steps can be deleted, new steps can be added, and the processing order can be changed without departing from the spirit of the invention.
以上に示した記載内容及び図示内容は、本開示の技術に係る部分についての詳細な説明であり、本開示の技術の一例に過ぎない。例えば、上記の構成、機能、作用、及び効果に関する説明は、本開示の技術に係る部分の構成、機能、作用、及び効果の一例に関する説明である。よって、本開示の技術の主旨を逸脱しない範囲内において、以上に示した記載内容及び図示内容に対して、不要な部分を削除したり、新たな要素を追加したり、置き換えたりしてもよいことは言うまでもない。また、錯綜を回避し、本開示の技術に係る部分の理解を容易にするために、以上に示した記載内容及び図示内容では、本開示の技術の実施を可能にする上で特に説明を要しない技術常識等に関する説明は省略されている。The above description and illustrations are a detailed explanation of the parts related to the technology of the present disclosure, and are merely an example of the technology of the present disclosure. For example, the above explanation of the configuration, functions, actions, and effects is an explanation of an example of the configuration, functions, actions, and effects of the parts related to the technology of the present disclosure. Therefore, it goes without saying that unnecessary parts may be deleted, new elements may be added, or replacements may be made to the above description and illustrations, within the scope of the gist of the technology of the present disclosure. Also, in order to avoid confusion and to facilitate understanding of the parts related to the technology of the present disclosure, the above description and illustrations omit explanations of technical common knowledge that do not require particular explanation to enable the implementation of the technology of the present disclosure.
本明細書に記載された全ての文献、特許出願及び技術規格は、個々の文献、特許出願及び技術規格が参照により取り込まれることが具体的かつ個々に記された場合と同程度に、本明細書中に参照により取り込まれる。All publications, patent applications, and technical standards described in this specification are incorporated by reference into this specification to the same extent as if each individual publication, patent application, and technical standard was specifically and individually indicated to be incorporated by reference.
以上の実施形態に関し、更に以下を開示する。The following is further disclosed regarding the above embodiment.
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
The system includes a means for learning information from various information sources, a means for searching for a destination based on a user's specific requests, a means for setting a destination based on the search results, and a means for providing navigation to the set destination.
(請求項2)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
2. The system of claim 1, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer to a question from the user.
(請求項3)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system according to claim 1, wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation based on a user's request.
(請求項4)
前記様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段が、ユーザーの感情を認識する感情エンジンを含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 4)
The system of claim 1 , wherein the means for learning information from various sources includes an emotion engine for recognizing an emotion of a user.
(請求項5)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーの感情を考慮して回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項2記載のシステム。(Claim 5)
3. The system according to claim 2, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer taking into account the user's emotions.
(請求項6)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの感情を考慮して予約を行う手段を含む、請求項3記載のシステム。(Claim 6)
The system according to claim 3 , wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation taking into consideration a user's emotions.
「実施例1」"Example 1"
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、
ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
音声入力をテキストに変換する手段と、
自然言語処理技術を用いてユーザーの質問を解析する手段と、
機械学習アルゴリズムを用いてデータを学習する手段と、
位置情報を取得する手段と、
音声ガイダンスを生成する手段を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
A means of learning information from a variety of sources;
A way to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests,
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
A means for converting voice input into text;
A means for analyzing a user's question using natural language processing technology;
A means for learning the data using a machine learning algorithm;
A means for acquiring location information;
A system including a means for generating audio guidance.
(請求項2)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
2. The system of claim 1, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer to a question from the user.
(請求項3)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system according to claim 1, wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation based on a user's request.
「応用例1」"Application Example 1"
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、
ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
ユーザーの質問を解析し、適切な回答を生成する自然言語処理手段と、
現在位置と目的地の間の最適なルートを計算する手段と、
音声ガイダンスを提供する手段と、
を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
A means of learning information from a variety of sources;
A way to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests,
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
A natural language processing means for analyzing a user's question and generating an appropriate answer;
A means for calculating an optimal route between a current location and a destination;
a means for providing audio guidance;
A system including:
(請求項2)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
2. The system of claim 1, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer to a question from the user.
(請求項3)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system according to claim 1, wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation based on a user's request.
「実施例2」"Example 2"
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、
ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
ユーザーの音声指示を解析する手段と、
解析された音声指示に基づいて予約内容を抽出する手段と、
抽出された予約内容に基づいて自動的に電話をかける手段と、
電話を通じて予約内容を音声で伝える手段を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
A means of learning information from a variety of sources;
A way to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests,
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
A means for analyzing a user's voice instructions;
A means for extracting reservation details based on the analyzed voice instructions;
a means for automatically placing a call based on the extracted reservation details;
A system including a means for audibly transmitting reservation details via telephone.
(請求項2)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
2. The system of claim 1, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer to a question from the user.
(請求項3)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system according to claim 1, wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation based on a user's request.
「応用例2」"Application Example 2"
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、
ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
音声認識技術を用いてユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、
自動ダイヤルシステムを用いて予約を行う手段と、
ユーザーの過去の行動履歴を学習し、最適な提案を行う手段と、
音声フィードバックを提供する手段
を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
A means of learning information from a variety of sources;
A way to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests,
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
A means of understanding user requests using voice recognition technology;
means for making reservations using an automated dialing system;
A means to learn the user's past behavioral history and make optimal suggestions,
The system includes a means for providing audio feedback.
(請求項2)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
2. The system of claim 1, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer to a question from the user.
(請求項3)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system according to claim 1, wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation based on a user's request.
「感情エンジンを組み合わせた場合の実施例1」"Example 1 of combining emotion engines"
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、
ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
ユーザーの感情を認識し、それに基づいて目的地を推薦する手段と、
ユーザーの現在位置とサーチ結果を基に最適なルートを計算する手段と、
音声入力を解析し、ユーザーの要望を理解する手段と、
を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
A means of learning information from a variety of sources;
A way to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests,
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
A means of recognizing user emotions and recommending destinations based on them; and
A means for calculating the optimal route based on the user's current location and search results;
A means of analyzing voice input and understanding what the user wants;
A system including:
(請求項2)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
2. The system of claim 1, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer to a question from the user.
(請求項3)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system according to claim 1, wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation based on a user's request.
「感情エンジンを組み合わせた場合の応用例1」"Application example 1 when combining emotion engines"
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、
ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、
感情認識結果に基づいて目的地を提案する手段と、
を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
A means of learning information from a variety of sources;
A way to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests,
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
A means for recognizing the user's emotions; and
A means for suggesting a destination based on the emotion recognition result;
A system including:
(請求項2)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
2. The system of claim 1, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer to a question from the user.
(請求項3)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system according to claim 1, wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation based on a user's request.
「感情エンジンを組み合わせた場合の実施例2」"Example 2 of combining emotion engines"
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、
ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
ユーザーの音声を認識する手段と、
音声認識結果を基にレストランを検索する手段と、
自動で電話をかける手段と、
予約を完了する手段と、
ユーザーの感情を認識する手段と、
感情に基づいてレストランを推薦する手段
を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
A means of learning information from a variety of sources;
A way to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests,
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
A means for recognizing a user's voice;
A means of searching for restaurants based on the results of voice recognition;
Automated calling and
A means to complete your booking;
A means for recognizing the user's emotions; and
The system includes a means for recommending restaurants based on sentiment.
(請求項2)
ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
The system of claim 1 further comprising means for generating answers to questions posed by a user.
(請求項3)
ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system of claim 1, further comprising means for making reservations based on user requests.
「感情エンジンを組み合わせた場合の応用例2」"Application example 2 when combining emotion engines"
(請求項1)
様々な情報源からの情報を学習する手段と、
ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
ユーザーの音声入力を認識する手段と、
認識された音声入力から感情を分析する手段と、
感情分析の結果に基づいて最適なサービスを推薦する手段と、
推薦されたサービスに対して自動的に注文を行う手段を含むシステム。(Claim 1)
A means of learning information from a variety of sources;
A way to search for destinations based on the user's specific requests,
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
a means for recognizing a user's voice input;
means for analyzing emotion from the recognized speech input;
A means for recommending optimal services based on the results of sentiment analysis;
The system includes means for automatically placing an order for the recommended services.
(請求項2)
前記ユーザーの細かい要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段が、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 2)
2. The system of claim 1, wherein the means for searching for a destination based on the specific needs of the user includes means for generating an answer to a question from the user.
(請求項3)
前記サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段が、ユーザーの要望に基づいて予約を行う手段を含む、請求項1記載のシステム。(Claim 3)
2. The system according to claim 1, wherein the means for setting a destination based on the search results includes means for making a reservation based on a user's request.
10、210、310、410 データ処理システム
12 データ処理装置
14 スマートデバイス
214 スマート眼鏡
314 ヘッドセット型端末
414 ロボット10, 210, 310, 410
Claims (3)
Translated fromJapanese自然言語処理技術を用いてテキスト情報を解析することにより、ユーザーの指示内容を把握する手段と、
ユーザーからの音声入力を感情エンジンで解析することによりユーザーの感情状態を認識する手段と、
認識したユーザーの感情状態と、ユーザーの指示内容とに基づいて、目的地を推薦する手段と、
目的地を推薦されたユーザーからの要望に基づいて目的地をサーチする手段と、
サーチ結果を基に目的地を設定する手段と、
設定された目的地へのナビゲーションを提供する手段と、
を含むシステム。 A means for converting voice input from a user into text information using voice recognition technology;
A means for understanding the content of a user's instructions by analyzing text information using natural language processing technology;
means for recognizing an emotional state of a user by analyzing speech input from the user with an emotion engine;
means for recommending destinations based on the recognized emotional state of the user and the user's instructions;
A means for searching for a destination based on a request from a user who has recommended the destination;
A means for setting a destination based on the search results;
a means for providing navigation to a set destination;
A system including:
生成されたプロンプト文と、生成AIモデルとを用いて、ユーザーからの質問に対する回答を生成する手段と、
生成された回答を音声によってユーザーに出力する手段と、
をさらに含む請求項1記載のシステム。 a means for analyzing a question received from a user by using a natural language processing means and generating a prompt sentence instructing generation of an answer to the analyzed question from the user;
A means for generating an answer to a question from a user using the generated prompt sentence and the generative AI model;
a means for outputting the generated answer to a user by voice;
The system of claim 1 further comprising:
抽出された予約指示に基づいて予約しようとする店に自動的に電話をかける手段と、
予約しようとする店の従業員に対して電話を通じて予約内容を音声で伝えることにより予約を完了させる手段と、
予約が完了すると、予約が完了したことをユーザーに通知する手段と、
をさらに含む請求項1記載のシステム。 A means for extracting a reservation instruction included in the instruction content from a user;
means for automatically calling the establishment to be reserved based on the extracted reservation instructions;
A means for completing a reservation by verbally conveying the reservation details to an employee of the store to which the reservation is made;
Once the reservation is complete, a means of notifying the user that the reservation is complete;
The system of claim 1 further comprising:
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023151283 | 2023-09-19 | ||
| JP2023151283 | 2023-09-19 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2025044256Atrue JP2025044256A (en) | 2025-04-01 |
Family
ID=95204961
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2024161839APendingJP2025044256A (en) | 2023-09-19 | 2024-09-19 | system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2025044256A (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20130005303A1 (en)* | 2011-06-29 | 2013-01-03 | Song Seungkyu | Terminal and control method thereof |
| JP2019508820A (en)* | 2015-12-21 | 2019-03-28 | グーグル エルエルシー | Automatic suggestions for message exchange threads |
| JP2021144290A (en)* | 2020-03-10 | 2021-09-24 | 株式会社デンソー | Agent system |
| JP2022103553A (en)* | 2020-12-28 | 2022-07-08 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Information providing equipment, information providing method, and program |
| US20230036771A1 (en)* | 2021-07-28 | 2023-02-02 | Avaya Management L.P. | Systems and methods for providing digital assistance relating to communication session information |
- 2024
- 2024-09-19JPJP2024161839Apatent/JP2025044256A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20130005303A1 (en)* | 2011-06-29 | 2013-01-03 | Song Seungkyu | Terminal and control method thereof |
| JP2019508820A (en)* | 2015-12-21 | 2019-03-28 | グーグル エルエルシー | Automatic suggestions for message exchange threads |
| JP2021144290A (en)* | 2020-03-10 | 2021-09-24 | 株式会社デンソー | Agent system |
| JP2022103553A (en)* | 2020-12-28 | 2022-07-08 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Information providing equipment, information providing method, and program |
| US20230036771A1 (en)* | 2021-07-28 | 2023-02-02 | Avaya Management L.P. | Systems and methods for providing digital assistance relating to communication session information |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2025044256A (en) | system | |
| JP2025056776A (en) | system | |
| JP2025049088A (en) | system | |
| JP2025051697A (en) | system | |
| JP2025049103A (en) | system | |
| JP2025049107A (en) | system | |
| JP2025055166A (en) | system | |
| JP2025051692A (en) | system | |
| JP2025049051A (en) | system | |
| JP2025054763A (en) | system | |
| JP2025045326A (en) | system | |
| JP2025073100A (en) | system | |
| JP2025044281A (en) | system | |
| JP2025057747A (en) | system | |
| JP2025049651A (en) | system | |
| JP2025047330A (en) | system | |
| JP2025045714A (en) | system | |
| JP2025044997A (en) | system | |
| JP2025057639A (en) | system | |
| JP2025052619A (en) | system | |
| JP2025054755A (en) | system | |
| JP2025046485A (en) | system | |
| JP2025044798A (en) | system | |
| JP2025047003A (en) | system | |
| JP2025054329A (en) | system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20241122 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20250617 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20250703 |