JP2023169727A - Construction method for road surface sign and masking sheet - Google Patents
Construction method for road surface sign and masking sheetDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2023169727A JP2023169727AJP2022081020AJP2022081020AJP2023169727AJP 2023169727 AJP2023169727 AJP 2023169727AJP 2022081020 AJP2022081020 AJP 2022081020AJP 2022081020 AJP2022081020 AJP 2022081020AJP 2023169727 AJP2023169727 AJP 2023169727A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- masking
- masking sheet
- road surface
- road
- marking
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A30/00—Adapting or protecting infrastructure or their operation
- Y02A30/60—Planning or developing urban green infrastructure
Landscapes
- Road Repair (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、減速路面標示などの路面標示を施工する方法およびこの方法に用いるマスキングシートに関する。 The present invention relates to a method for constructing road markings such as deceleration road markings, and a masking sheet used in this method.
自動車が通行する舗装された道路の路面には、交通の安全と円滑を促進するために、白色や黄色、青色などの色彩を有する路面標示が描かれている。路面標示のうち、減速を促す路面標示(減速路面標示)は、減速マークまたは減速レーンマークとも称されるが、破線型とマーク型とに大別でき、マーク型の減速路面標示は、下り勾配やカーブ進入時における減速効果を狙って、坂やカーブの路面に施工されることが多いのに対して、破線型の減速路面標示は、幅員(道幅)を狭く見せることにより減速効果を期待され、坂やカーブに加えて、交差点などの追突事故の多い区間で施工されることが多い。 BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Road markings in colors such as white, yellow, and blue are painted on the surfaces of paved roads used by automobiles to promote safe and smooth traffic. Among road markings, road markings that encourage deceleration (deceleration road markings) are also called deceleration marks or deceleration lane marks, and can be roughly divided into broken line type and mark type. On the other hand, broken-line deceleration road markings are often installed on slopes and curved roads to reduce speed when entering a curve or curve, while dashed deceleration road markings are expected to have a deceleration effect by making the width of the road appear narrower. , In addition to slopes and curves, they are often constructed in areas where rear-end collisions occur frequently, such as intersections.
減速路面標示において、破線型の減速マークは、ドットライン(矢羽根型路面標示)とも称されるが、ドットラインの施工例について、図1を用いて説明する。 In deceleration road markings, broken line-type deceleration marks are also called dot lines (arrow-feather road markings), and an example of the construction of dot lines will be described with reference to FIG. 1.
図1は、ドットラインが施工された2車線の道路の一例である。図1において、一方の車線11と他方の車線12とからなる2車線の道路の路面には、道路の中央で車の流れ方向(車進行方向)に破線状に延びる中央線(センターライン)17と、道路の両側部で車の流れ方向に延び、かつ路側帯と車線とを区画するための一対の白線18,19とが施工されている。さらに、図1の道路では、一方の車線11の路面には、車線11の両側部で車の流れ方向に延びる一対のドットライン13,14が施工され、他方の車線12の路面には、車線12の両側部で車の流れ方向に延びる一対のドットライン15,16が施工されている。 FIG. 1 is an example of a two-lane road on which dot lines have been constructed. In FIG. 1, on the road surface of a two-lane road consisting of one
詳しくは、一方の車線11では、ドットライン13は、白線18側の側部において、白線18と間隔をおいて、白線18に沿って破線状に形成されており、このドットライン13と対をなすドットライン14は、中央線17側の側部において、中央線17と間隔をおいて、中央線17に沿って破線状に形成されている。ドットライン13,14の破線を構成する各ドット13a,14aの形状はいずれも平行四辺形であり、各ドット13a,14aはそれぞれ等間隔で破線状に配列されている。特に、減速路面標示では、ドット13aとドット14aとは、それぞれの平行四辺形の鋭角が車進行方向側において対向する向きで、前記進行方向の車線軸に対して対称に配列されている。ドット13aおよびドット14aが、このような向きで対称に配列されることにより、一対のドットライン13,14は、車線11を車で走行するドライバーに対して、車の進行方向に向かって車線を狭く見せる印象を与えることができる。 Specifically, in one
また、他方の車線12の両側部においても、白線19および中央線17に沿って、それぞれ、ドット15aが配列したドットライン15と、このドットライン15と対をなすドット16aが配列したドットライン16とが形成されており、ドットライン15およびドットライン16は、それぞれドットライン13および14に対応しており、同形状に形成されている。すなわち、他方の車線12でも、車の進行方向に向かって車線を狭く見せるドットライン15,16が形成されている。 Also, on both sides of the
前記ドットライン13は、路面にドットラインの塗装領域を特定するためのケガキ線(けがき線)を引く第1のケガキ工程、路面上の汚れを除去する汚れ除去工程、ドットラインの塗装領域にプライマーを塗布するプライマー処理工程、合板を用いて残りのケガキ線を引く第2のケガキ工程、マスキング材を用いてドットラインの非塗装領域をマスキングするマスキング工程、マスキングした路面にドットラインを形成するための塗料を塗布する塗布工程、塗料が固化する前に塗料が塗布された前記マスキング材を除去するマスキング材除去工程、塗料を固化してドットラインを完成させる固化工程を経て得られる。このような従来のドットラインの施工方法について、図2を用いて説明する。 The
第1のケガキ工程では、ドットライン13の塗装領域を特定するためのケガキ(下書き)を路面上に行う。詳しくは、図2(a)に示すように、ドット部13aの車の流れ方向の輪郭のうち、中央線側の輪郭に相当するケガキ線21(白線18に平行なケガキ線)を路面上に引くとともに、ドット部13aを施工する間隔に合わせて、白線18と直交する方向にケガキ線22を引く。 In the first marking process, marks (drafts) are made on the road surface to specify the painting area of the
汚れ除去工程では、路面に大きな汚れがある場合は、ブロアーで埃などを除去する。 In the dirt removal process, if there is large dirt on the road surface, a blower is used to remove dust.
プライマー処理工程では、必要に応じて、ドットライン13の塗装領域にプライマーを塗布する。 In the primer treatment step, a primer is applied to the painting area of the
第2のケガキ工程では、各ドット部13aの車の流れ方向の輪郭は、白線18に対して45°の角度で交差する角度で形成されているため、図2(b)に示すように、平面形状が直角二等辺三角形である合板23を用いて、路面上にケガキを行う。詳しくは、合板23の平面形状は、直角二等辺三角形であるため、合板23の頂角を形成する一辺をケガキ線21またはケガキ線22に合わせることにより、ドット13aの車の流れ方向の輪郭(流れ方向と交差する輪郭)に相当するケガキ線24を引くことができる。なお、図2では示されていないが、ケガキ線24を引いた後には、合板23は取り除かれる。 In the second marking step, the outline of each
マスキング工程では、図2(c)に示すように、平行四辺形の平面形状を有するドット部13aを形成するために、ドットラインを形成するための塗料が塗装されない領域(非塗装部)に対して、塗装におけるマスキング材としてクラフトテープ25を貼付する。詳しくは、まず、ケガキ線24に沿って、クラフトテープ25(約400mm長×75mm幅程度)を貼付した後、塗料が非塗装部に浸入する隙間が生じないように端部同士を重ね合わせて、さらにクラフトテープを順次貼付し、上下各合計6枚のクラフトテープ25を貼付する。隙間が生じないように端部同士を重ねて貼付された6枚のクラフトテープ25は、ドットラインの塗装におけるマスキング材として機能する。この作業は、中腰で行われ、クラフトテープの隙間から塗料が路面に浸み込むことを防止するために、端部同士を厳密に合わせて何度も貼付する必要があり、作業者にとって煩雑な作業であるとともに、重労働である。 In the masking process, as shown in FIG. 2(c), in order to form
塗布工程では、図2(d)に示すように、路面に貼付されたクラフトテープ25の上から、ドット部13aに相当する領域に、塗装機を用いて溶融型塗料を加熱して塗布し、ドット前駆体13bを路面上に形成する。溶融型塗料の温度は、土木工事共通仕様書(非特許文献1)において、常に180~220℃の温度で塗料を塗布できるように溶解層を管理する必要があると記載されている。 In the coating process, as shown in FIG. 2(d), a coating machine is used to heat and coat melt-type paint onto the area corresponding to the
マスキング材除去工程で、塗料が固化する前に、塗料が塗布された状態のクラフトテープ25を回収した後、固化工程で、路面上に残存した塗料を固化させると、図2(e)に示すように、路面にドット部13aが形成される。 In the masking material removal process, before the paint solidifies, the
路面標示の施工は、野外で行われるため、天候に左右される上に、路面標示を形成するための塗料は高温で塗布する必要があるため、過酷な作業環境である。しかも、このような路面標示の施工は、全ての作業が人力で行われるため、作業者への負担を軽減することが要求される。しかし、従来の路面標示の施工方法では、工程数が多く、作業に長時間や多大な労力を要するため、作業者への負担が大きいという課題があった。また、ドットラインを施工するためには道路を封鎖する必要があるため、通行止めの期間を短縮する観点からも施工性を改善する必要があった。さらに、従来の施工方法では、マスキング材がクラフトテープのみで形成されているため、耐熱性および防水性が低く、高温の塗料や水分の影響を受け易く、道路状況や天候に左右されるため、マスキング材の取り扱い性も困難であり、施工性が低かった。 Construction of road markings is carried out outdoors, which is subject to weather conditions, and the paint used to form road markings must be applied at high temperatures, creating a harsh working environment. Moreover, since all the work in constructing such road markings is done manually, it is required to reduce the burden on the workers. However, the conventional road marking construction method involves a large number of steps, requires a long time and a great deal of effort, and has the problem of placing a heavy burden on workers. Furthermore, since it is necessary to close the road in order to construct the dot line, it was necessary to improve construction efficiency from the perspective of shortening the period of road closure. Furthermore, in conventional construction methods, the masking material is made only of craft tape, which has low heat resistance and waterproof properties, is easily affected by high-temperature paint and moisture, and is affected by road conditions and weather. The masking material was also difficult to handle, resulting in poor workability.
従って、本発明の目的は、減速路面標示などの路面標示を簡便に施工できる路面標示の施工方法およびこの方法に用いるマスキングシートを提供することにある。 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a method for easily constructing road surface markings such as deceleration road markings, and a masking sheet for use in this method.
本発明の他の目的は、高温に晒されたり、水分の存在下であっても、取り扱い性に優れ、路面標示の施工性を向上できるマスキングシートを提供することにある。 Another object of the present invention is to provide a masking sheet that has excellent handling properties even when exposed to high temperatures or in the presence of moisture, and can improve the workability of road markings.
本発明者らは、前記課題を達成するため鋭意検討した結果、マスキングシートを用いて路面標示の非塗装領域をマスキングした後、マスキングした路面に路面標示を形成するための塗料を塗布することにより、減速路面標示などの路面標示を簡便に施工できることを見出し、本発明を完成した。 As a result of intensive studies to achieve the above-mentioned object, the inventors of the present invention discovered that, after masking the non-painted area of the road marking using a masking sheet, the paint for forming the road marking was applied to the masked road surface. , discovered that road markings such as deceleration road markings can be easily constructed, and completed the present invention.
本開示の態様[1]としての路面標示の施工方法は、マスキングシートを用いて路面標示の非塗装領域をマスキングするマスキング工程、前記マスキング工程でマスキングした路面に路面標示を形成するための塗料を塗布する塗布工程を含む。 The road marking construction method as aspect [1] of the present disclosure includes a masking step of masking the non-painted area of the road marking using a masking sheet, and a coating for forming the road marking on the road surface masked in the masking step. It includes a coating process.
本開示の態様[2]は、前記態様[1]において、前記マスキングシートが、アスファルトを含む態様である。 Aspect [2] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which the masking sheet contains asphalt in the aspect [1].
本開示の態様[3]は、前記態様[1]または[2]において、前記塗料の温度が100℃以上である態様である。 Aspect [3] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which the temperature of the paint is 100° C. or higher in the aspect [1] or [2].
本開示の態様[4]は、前記態様[1]~[3]のいずれかの態様において、前記塗料が溶融型塗料である態様である。 Aspect [4] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which the paint is a melt-type paint in any of the aspects [1] to [3].
本開示の態様[5]は、前記態様[1]~[4]のいずれかの態様において、前記マスキングシートが、アスファルトを含む繊維構造体である態様である。 Aspect [5] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which the masking sheet is a fibrous structure containing asphalt in any of the aspects [1] to [4].
本開示の態様[6]は、前記態様[1]~[5]のいずれかの態様において、前記路面表示が、湾曲部および/または非直角部を有する路面標示である態様である。 Aspect [6] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which, in any of the aspects [1] to [5], the road surface marking is a road surface marking having a curved portion and/or a non-right angle portion.
本開示の態様[7]は、前記態様[1]~[6]のいずれかの態様において、前記路面標示が車の流れ方向に対して斜め方向に交差する方向に延びる斜辺を有している態様である。 Aspect [7] of the present disclosure is the aspect [1] to [6], in which the road marking has an oblique side extending in a direction diagonally intersecting the direction of flow of vehicles. It is a mode.
本開示の態様[8]は、前記態様[1]~[7]のいずれかの態様において、前記路面標示が減速路面標示である態様である。 Aspect [8] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which the road marking is a deceleration road marking in any one of the aspects [1] to [7].
本開示の態様[9]は、前記態様[8]において、前記減速路面標示が、複数のドット部が車の流れ方向に沿って所定の間隔に並列した破線状(または点線状)であり、前記ドット部における車の流れ方向の上流端および下流端は、車の流れ方向に対して斜め方向に交差する方向に延びる斜辺である態様である。 Aspect [9] of the present disclosure is that in the aspect [8], the deceleration road surface marking has a broken line shape (or dotted line shape) in which a plurality of dot portions are arranged in parallel at predetermined intervals along the direction of vehicle flow; The upstream end and the downstream end of the dot portion in the direction of traffic flow are oblique sides extending in a direction obliquely intersecting the direction of traffic flow.
本開示の態様[10]は、前記態様[1]~[9]のいずれかの態様のマスキング工程において、前記マスキングシートを粘着テープで路面に固定する態様である。 Aspect [10] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which the masking sheet is fixed to the road surface with an adhesive tape in the masking step of any of the aspects [1] to [9].
本開示の態様[11]は、前記態様[10]のマスキング工程において、路面標示の塗装領域に対して隙間を設けて前記マスキングシートを載置し、前記粘着テープで前記隙間をマスキングするとともに、前記マスキングシートを路面に固定する態様である。 Aspect [11] of the present disclosure is that in the masking step of the aspect [10], the masking sheet is placed with a gap provided to the painted area of the road marking, and the gap is masked with the adhesive tape. This is a mode in which the masking sheet is fixed to the road surface.
本開示の態様[12]は、前記態様[1]~[11]のいずれかの態様の塗布工程において、スリット式開口部を有するフローコーター式施工機で前記塗料を塗布する態様である。 Aspect [12] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which the paint is applied with a flow coater-type construction machine having a slit-type opening in the coating process of any of the aspects [1] to [11].
本開示の態様[13]は、前記態様[7]~[12]のいずれかの態様において、車の流れ方向に対して斜め方向に交差する方向に延びる斜辺に対応するケガキ線を引くためのケガキ工程を含まない態様である。 Aspect [13] of the present disclosure is, in any of the aspects [7] to [12], a method for drawing a marking line corresponding to a hypotenuse extending in a direction diagonally intersecting the direction of vehicle flow. This is an embodiment that does not include a marking process.
本開示には、態様[14]として、マスキングシートを用いて路面標示の非塗装領域をマスキングするマスキング工程、前記マスキング工程でマスキングした路面に路面標示を形成するための塗料を塗布する塗布工程を含む路面標示の施工方法に用いられるマスキングシートも含まれる。 The present disclosure includes, as aspect [14], a masking step of masking a non-painted area of a road marking using a masking sheet, and a coating step of applying a paint for forming a road marking to the road surface masked in the masking step. Also included are masking sheets used in construction methods for road markings.
本開示の態様[15]は、前記態様[14]において、前記マスキングシートが、アスファルトを含む態様である。 Aspect [15] of the present disclosure is an aspect in which the masking sheet contains asphalt in the aspect [14].
本開示の態様[16]は、前記態様[14]または[15]において、前記マスキングシートの平面形状が、直角二等辺三角形状の本体部と、前記本体部の斜辺から突出し、前記斜辺と路面標示の輪郭との間に隙間を形成するための凸部とを有する形状である態様である。 Aspect [16] of the present disclosure is that in the aspect [14] or [15], the planar shape of the masking sheet includes a main body portion in the shape of a right-angled isosceles triangle and a hypotenuse of the main body portion, and a surface of This is an aspect in which the shape has a convex portion for forming a gap with the outline of the sign.
本開示の態様[17]は、前記態様[16]において、前記凸部が、斜辺の一方の端部から突出する直角三角形状の第1の凸部と、斜辺の他方の端部から突出する平行四辺形状の第2の凸部とで構成されている態様である。 Aspect [17] of the present disclosure is the aspect [16], wherein the convex portion is a right triangular first convex portion protruding from one end of the hypotenuse, and a first convex portion protruding from the other end of the hypotenuse. In this embodiment, the second convex portion has a parallelogram shape.
本開示の態様[18]は、前記態様[16]において、前記マスキングシートが、ケガキ線を引いた路面に対して位置決めするための切欠部が形成されている態様である。 Aspect [18] of the present disclosure is the aspect [16], in which the masking sheet is formed with a notch for positioning it with respect to the road surface on which the marking line is drawn.
本開示では、マスキングシートを用いて路面標示の非塗装領域をマスキングし、路面標示を形成するための塗料を路面に塗布すると、減速路面標示などの路面標示を簡便に施工できる。しかも、マスキングシートがアスファルトを含むと、耐熱性および防水性に優れるため、取り扱い性も向上できる。 In the present disclosure, by masking the non-painted area of the road marking using a masking sheet and applying paint for forming the road marking to the road surface, road markings such as deceleration road markings can be easily constructed. In addition, when the masking sheet contains asphalt, it has excellent heat resistance and waterproof properties, so that handling properties can also be improved.
[路面標示の施工方法]
本開示の路面標示の施工方法は、マスキングシートを用いて路面標示の非塗装領域をマスキングし、路面標示を形成するための塗料を路面に塗布する塗布工程を含むことを特徴とする。前記マスキングシートを用いて路面標示を施工すると、従来の施工方法に比べて、ケガキ線を引く作業やクラフトテープなどのマスキング材を固定する作業が大きく簡略化され、作業者の負担が軽減される。[Road marking construction method]
The road marking construction method of the present disclosure is characterized by including a coating step of masking the non-painted area of the road marking using a masking sheet and applying a paint for forming the road marking to the road surface. When constructing road markings using the masking sheet, the work of drawing marking lines and fixing masking materials such as craft tape is greatly simplified compared to conventional construction methods, reducing the burden on workers. .
以下、このマスキングシートを用いた本開示の施工方法について、図面を参照して説明する。 Hereinafter, the construction method of the present disclosure using this masking sheet will be explained with reference to the drawings.
本開示の路面標示の施工方法は、例えば、路面に路面標示の塗装領域(路面標示を形成する領域)を特定するためのケガキ線を引くケガキ工程、路面上の汚れを除去する汚れ除去工程、路面標示の塗装領域にプライマーを塗布するプライマー処理工程、マスキングシートを用いて路面標示の非塗装領域(非塗装領域全体の一部の領域)をマスキングするマスキング工程、マスキングした路面に路面標示を形成するための塗料を塗布する塗布工程、塗料が固化する前に塗料が塗布された前記マスキングシートを除去するマスキングシート除去工程、塗料を固化して路面標示を完成させる固化工程を含む施工方法であってもよい。 The road marking construction method of the present disclosure includes, for example, a marking process of drawing marking lines on the road surface to specify the painted area of the road marking (area where the road marking will be formed), a dirt removal process of removing dirt on the road surface, A primer treatment process in which a primer is applied to the painted area of the road marking, a masking process in which the non-painted area of the road marking (a part of the entire non-painted area) is masked using a masking sheet, and a road marking is formed on the masked road surface. The construction method includes a coating step of applying a paint to make the road marking, a masking sheet removal step of removing the masking sheet on which the paint has been applied before the paint hardens, and a hardening step of hardening the paint to complete the road marking. You can.
ケガキ工程、汚れ除去工程、プライマー処理工程および固化工程は、従来の施工方法における第1のケガキ工程、汚れ除去工程、プライマー処理工程および固化工程を利用できる。そのため、従来の施工方法と同様に、汚れ除去工程およびプライマー処理工程は、必要に応じて施工される任意の工程であり、路面の状況に応じて省略してもよい。 As the scribing step, stain removal step, primer treatment step, and solidification step, the first scribe step, stain removal step, primer treatment step, and solidification step in the conventional construction method can be used. Therefore, similarly to the conventional construction method, the stain removal step and the primer treatment step are optional steps that are performed as necessary, and may be omitted depending on the road surface condition.
本開示の施工方法では、従来の施工方法と異なり、合板を用いた第2のケガキ工程が必須の工程ではなく、マスキングシートの形状を第2のケガキ線に対応した形状に形成することにより、第2のケガキ工程を省略できる。従来の施工方法では、例えば、路面標示がドットライン(波線型の減速路面標示)である場合、白線および中央線(車の流れ方向)に対して平行するケガキ線と車の流れ方向に直交するケガキ線とを引く第1のケガキ工程に加えて、第2のケガキ線を引くための補助具または定規として、平面形状が直角二等辺三角形である合板を用いて、白線および中央線に対して斜めに交差する方向に延びる第2のケガキ線を引く第2のケガキ工程が必須の工程であった。これに対して、本開示の施工方法において、第2のケガキ線に対応した形状を有するマスキングシートをマスキング材として用いることにより、第2のケガキ工程を経ずに、マスキング工程に進むこともできる。 In the construction method of the present disclosure, unlike conventional construction methods, the second marking step using plywood is not an essential step, but by forming the masking sheet into a shape corresponding to the second marking line, The second marking step can be omitted. In conventional construction methods, for example, if the road marking is a dot line (a wavy deceleration road marking), a marked line parallel to the white line and center line (direction of traffic flow) and a marking line perpendicular to the direction of traffic flow are used. In addition to the first marking process of drawing the marking lines, a plywood whose planar shape is a right isosceles triangle is used as an auxiliary tool or ruler for drawing the second marking line, and the white line and center line are drawn. A second scribing step in which second scribing lines extending in diagonal directions were drawn was an essential step. In contrast, in the construction method of the present disclosure, by using a masking sheet having a shape corresponding to the second marking line as a masking material, it is possible to proceed to the masking step without going through the second marking step. .
(マスキング工程)
マスキング工程では、マスキングシートによって路面標示の非塗装領域をマスキングする(路面標示の輪郭の外側にマスキングシートを載置する)ことにより、次工程の塗布工程で前記マスキングシートの上から塗料を塗布することにより容易に路面上に路面標示の形状を形成できる。(Masking process)
In the masking process, the non-painted area of the road marking is masked with a masking sheet (the masking sheet is placed outside the contour of the road marking), and paint is applied from above the masking sheet in the next coating process. This allows the shape of road markings to be easily formed on the road surface.
路面標示が破線型の減速マーク(平行四辺形状のドット部を有するドットライン)である場合、前記減速マークの施工方法におけるマスキング工程で用いるマスキングシートの一例を図3に示す。 When the road marking is a broken deceleration mark (a dot line having parallelogram-shaped dots), an example of a masking sheet used in the masking step in the deceleration mark construction method is shown in FIG.
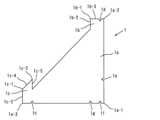
図3に示すように、マスキングシート1は、略直角三角形状の本体部1aと、この本体部1aの斜辺の両端部から、それぞれ突出する第1の凸部1bおよび第2の凸部1cとで構成されている。 As shown in FIG. 3, the masking
詳しくは、前記本体部1aは、直角三角形の直角部の頂点に相当する頂点1a-1から頂点1a-2まで延びる第1の辺(例えば、長さ400~440mm)と、前記頂点1a-1から、この第1の辺と直角に交差する方向に頂点1a-3まで延びる第2の辺(例えば、長さ400~440mm)とを有する略直角三角形状である。 Specifically, the
前記第1の凸部1bは、本体部1aの斜辺の第1の辺側の端部から、斜辺を共有して直角三角形状に突出しており、前記第1の凸部1bの頂点1b-1は、直角三角形の直角部の頂点に相当する。前記第1の凸部1bは、第1の頂点1b-1から本体部1aの第1の辺に沿って延び、本体部1aの斜辺に至る内側壁1b-2(例えば、長さ30~70mm)と、第1の頂点1b-1から第2の辺に沿って延び、本体部1aの頂点1a-2に至る外側壁1b-3(例えば、長さ50~90mm)とを備えている。 The first
前記第2の凸部1cは、本体部1aの斜辺の第2の辺側の端部から、斜辺を共有して平行四辺形状に突出している。前記第2の凸部1cは、前記本体部1aの頂点1a-3から本体部1aの第1の辺に沿って延び、鈍角部の頂点1c-1に至る外側壁1c-3(例えば、長さ50~90mm)と、前記頂点1c-1から前記本体部1aの斜辺に沿って延び、鋭角部の頂点1c-2に至る上部壁1c-4と、前記頂点1c-2から前記本体部1aの第1の辺に沿って延び、前記本体部1aの斜辺に至る内側壁1c-5とを備えている。 The second
このような形状を有するマスキングシート1には、路面に載置するマスキングシート1の位置決めを容易化して施工性を向上させるために、切欠部を形成してもよく、この例では5箇所に切欠部1d,1e,1f,1g,1hが形成されている。 The
すなわち、第1の凸部1bの外側壁には、前記頂点1a-2の近傍に第1の切欠部1dが形成されている。詳しくは、前記第1の切欠部1dは、前記本体部1aの頂点1a-2から10~30mm程度の位置において、5~20mm程度の深さでV字状またはU字状に形成されている。 That is, a
前記本体部1aの第1辺には、前記第2の凸部1cの頂点1c-2と対向する部位に第2の切欠部1eが形成されている。すなわち、第2の切欠部1eは、前記本体部1aの頂点1a-1から100~140mm程度の位置において、5~20mm程度の深さでV字状またはU字状に形成されている。 A
前記本体部1aの第2辺には、前記切欠部1dと対向する位置に第3の切欠部1fが形成され、前記第1の凸部1bの頂点1b-1と対向する位置に第4の切欠部1gが形成され、前記第2の凸部1cの頂点1c-2と対向する位置に第5の切欠部1hが形成されている。すなわち、第3の切欠部1fおよび第4の切欠部1gは、それぞれ前記頂点1a-1から10~30mm程度および50~90mm程度の位置において、5~20mm程度の深さでV字状またはU字状に形成され、第5の切欠部1hは、前記頂点1a-3から30~70mm程度の位置において、5~20mm程度の深さでV字状またはU字状に形成されている。 A
さらに、このマスキングシート1において、略直角三角形状本体部1aの斜辺と第1の辺または第2の辺との角度は45°であり、頂点1a-3と切欠部1dと切欠部1fとを結ぶ線が直角二等辺三角形となる。すなわち、マスキングシート1の本体部1aは、厳密には、前記直角二等辺三角形において、切欠部1dと切欠部1fとを結ぶ辺から10~30mm程度幅の帯状部(長方形)が第1の辺側に延出した台形状である。 Furthermore, in this
マスキングシート1は、アスファルトを含んでいてもよく、この例ではアスファルト含浸紙である。マスキングシート1はアスファルトを含むため、耐熱性および防水性に優れており、取り扱い性を向上できる。 The
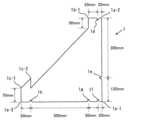
マスキング工程では、このマスキングシート1を用いてドットラインの非塗装領域がマスキングされる。このマスキング工程では、ケガキ工程でケガキした路面において、ドットラインを構成するドット部の非塗装領域をマスキングシート1および粘着テープ2でマスキングした状態を図4に示す。 In the masking step, the masking
図4では、両側に白線3aと白線3bとがそれぞれ施工された道路において、複数のドット部が破線状に配列したドットラインを両白線の内側にそれぞれ施工するために、車の流れ方向に平行に引かれたケガキ線および車の流れ方向に垂直に引かれたケガキ線に基づいて、前記マスキングシート1が載置され、粘着テープ2で前記マスキングシート1が固定されている。 In Fig. 4, on a road where a
詳しくは、前記路面では、平行四辺形状であり、車の流れ方向の長さ(長辺の長さ)が1000mmであり、かつ幅(車の流れ方向に垂直な方向の高さ)が300mmの平行四辺形形状を有するドット部を施工するために、図4に示すように、白線3a,3bの内側(対向する車線側)輪郭から350mmの間隔をおいて、それぞれ車の流れ方向(白線3a,3b)に沿ったケガキ線4a,4bが引かれ、車の流れ方向に対して垂直な方向には、1000mmの間隔をおいて、ケガキ線5a,5bが引かれている。このようなケガキ線が引かれた路面に複数のマスキングシート1が載置されており、白線3aとケガキ線4aとケガキ線5aとケガキ線5bとで囲まれた第1の領域、白線3bとケガキ線4bとケガキ線5aとケガキ線5bとで囲まれた第2の領域のそれぞれの領域に対応した前記ドット部が施工される。 Specifically, the road surface has a parallelogram shape, a length in the direction of traffic flow (length of the long side) of 1000 mm, and a width (height in the direction perpendicular to the direction of traffic flow) of 300 mm. In order to construct the dot portions having a parallelogram shape, as shown in Fig. 4, dots are placed at intervals of 350 mm from the inside (on the opposite lane side) contours of the
第1の領域において、車の流れ方向の上流側では、ケガキ線5bを跨いだ状態でマスキングシート1が載置されている。詳しくは、図4に示されるように、前記マスキングシート1は、第1の凸部1bが下流側となる向きで切欠部1gおよび切欠部1eを、それぞれケガキ線4aおよびケガキ線5bに合わせることにより、第2の凸部1cの外側壁1c-3が白線3aの内側輪郭に一致した状態で載置されている。マスキングシート1をこのような配置で路面に載置することにより、第2の凸部1cの上部壁1c-4と、第1の凸部1bの頂点1b-1とを結ぶ直線が、車の流れ方向の上流側におけるドット部の輪郭(境界)と一致する。そのため、図4に示すように、この直線に沿って、粘着テープ2をマスキングシート1側に貼付することにより、前記直線(輪郭)とマスキングシート1との間の隙間(第1の凸部1bと第2の凸部1cとの間の領域)を、粘着テープ2によってマスキングできる。また、マスキングシート1の第1の凸部1b-1および第2の凸部1cを粘着テープ2で路面に固定することによって、マスキングシート1を路面に固定できる。さらに、マスキングシート1を路面に固定した状態で、粘着テープ2が路面と密着するため、次工程である塗布工程において、ドット部を形成するための塗料がマスキングシート1と路面との間に浸入するのを抑制できる。特に、粘着テープ2の幅を第1の凸部1b-1および第2の凸部1cの高さ(頂点1b-1、頂点1c-1または頂点1c-2から斜辺までの最短距離)よりも大きくすることにより、粘着テープ2とマスキングシート1とが重なり合って密着するため、粘着テープ2とマスキングシート1との隙間から前記塗料が侵入するのも有効に抑制できる。 In the first region, on the upstream side in the direction of traffic flow, the masking
第1の領域において、車の流れ方向の下流側では、ケガキ線5aの下流側にマスキングシート1が載置されている。詳しくは、図4に示されるように、前記マスキングシート1は、ケガキ線5aの下流側において、第1の凸部1bが上流側となる向きで切欠部1dを白線3aの内側輪郭ケガキ線5aとの交点に合わせ、かつ切欠部1fを白線3aの内側輪郭に合わせることにより、第2の凸部1cの内側壁1c-5がケガキ線4aに一致し、かつ切欠部1hがケガキ線4aに一致した状態で載置されている。マスキングシート1をこのような配置で載置することにより、第1の凸部1bの頂点1b-1と、第2の凸部1cの上部壁1c-4とを結ぶ直線が、車の流れ方向の下流側におけるドット部の輪郭(境界)と一致する。そのため、図4に示すように、前記上流側と同様に、この直線に沿って、粘着テープ2をマスキングシート1側に貼付することにより、前記直線(輪郭)とマスキングシート1との間の隙間を、粘着テープ2によってマスキングできる。 In the first region, the masking
第2の領域では、図4に示されるように、車の流れ方向の上流側において、マスキングシート1は、第1の領域における上流側のマスキングシート1に対応する態様で載置されており、車線の中心軸に対して対向する両マスキングシート1は、前記中心軸に対して線対称に配置されている。一方、図4に示されるように、車の流れ方向の下流側においても、マスキングシート1は、第1の領域における下流側のマスキングシート1に対応する態様で載置されており、車線の中心軸に対して対向する両マスキングシート1は、前記中心軸に対して線対称に配置されている。 In the second region, as shown in FIG. 4, on the upstream side in the direction of vehicle flow, the masking
この施工方法では、粘着テープ2が、車の流れ方向に対して斜めに交差する方向に延びるドット部の輪郭と一致するため、前記輪郭を特定するためのケガキ線を引くための第2のケガキ工程が不要となり、作業性を大きく向上できる。 In this construction method, since the
本開示の施工方法において、マスキング工程は、マスキングシートを用いて路面をマスキングする工程であればよく、路面標示の種類に応じて適宜選択でき、図4に示すように、路面に載置したマスキングシートを粘着テープで固定する工程に限定されない。 In the construction method of the present disclosure, the masking step may be any step of masking the road surface using a masking sheet, and can be selected as appropriate depending on the type of road marking. The process is not limited to fixing sheets with adhesive tape.
マスキングシートを用いて路面をマスキングする方法は、マスキングシートを路面に固定することなく、路面に載置するだけの方法であってもよいが、風雨などの天候に左右されず、作業性に優れる上に、マスキングシートと路面との間への塗料の浸入を抑制できる点から、マスキングシートを路面に固定する方法が好ましい。 The method of masking the road surface using a masking sheet may be a method of simply placing the masking sheet on the road surface without fixing it to the road surface, but it is not affected by weather such as wind and rain and has excellent workability. In addition, a method in which the masking sheet is fixed to the road surface is preferable because it can prevent paint from entering between the masking sheet and the road surface.
マスキングシートを路面に固定する方法は、例えば、マスキングシート自体が粘着機能を有する場合などのように、粘着テープを用いることなく、マスキングシートを路面に固定する方法であってもよいが、簡便性などの点から、粘着テープでマスキングシートを路面に固定する方法が好ましい。 The method of fixing the masking sheet to the road surface may be a method of fixing the masking sheet to the road surface without using adhesive tape, for example, when the masking sheet itself has an adhesive function. From these points of view, it is preferable to use adhesive tape to fix the masking sheet to the road surface.
(塗布工程)
塗布工程では、前記マスキング工程で、前述のようにマスキングシート1と粘着テープ2とを組み合わせて、ドット部の非塗装領域をマスキングした路面に、塗装機を用いて加熱した塗料を塗布する。塗装機は、加熱して溶融した塗料を貯留するための溶解槽と、溶解槽から送られる溶融塗料を路面に流下させて塗布するためのスリット状開口部とを備えており、フローコーター式施工機(スリッター式施工機)とも称される。塗料は、塗装機の溶解槽内で加熱溶融されており、180~220℃の温度で路面に塗布されるが、マスキングシート1はアスファルト含浸紙で形成されているため、耐熱性および不燃性に優れ、塗料の熱によって変形したり、燃焼するのを抑制できる。(Coating process)
In the coating step, the masking
図5は、図4の第1の領域に対して、塗装機として、スリット開口部を有する手押し式のフローコーター式施工機(路面標示施工機)を用いてドットラインを形成するための塗料を路面に塗布している状態を示す概略斜視図である。図5に示すように、作業者6は、白線3a(車の流れ方向)に沿って、車の流れ方向とは逆行する方向に塗装機7を進行させて、スリット状開口部から前記塗料を塗布する。塗膜の幅は、ケガキ線4aから白線3a側に300mmの幅であり、厚みは1.5mm程度である。塗布は、マスキングシート1上において、ドット部を形成する領域(上流側の粘着テープ2の下流端とケガキ線4aとの交点)の手前から開始し、車の流れ方向に沿って塗装機を進行させて前記塗料を塗布し、ドット部を形成する領域が終了する箇所(下流側の粘着テープ2との境界)を通過した粘着テープ2またはマスキングシート1上で塗布を終了させる。下流側の粘着テープ2の上流端とケガキ線4aとの交点よりも車の流れ方向の下流側では、ケガキ線4aよりも内側(白線3b側)にマスキングシート1が70mm幅で延出(はみ出し)しているため、マスキングシート1上に塗布された塗料がマスキングシート1の積層されていない路面に流出するのを抑制できる。なお、図5では、塗装機の進行方向は、車の流れ方向に逆行する方向であるが、車の流れ方向であってもよい。第2の領域においても、第1の領域と同様の方法で塗料を塗布することができる。 FIG. 5 shows how paint is applied to the first region of FIG. 4 to form dot lines using a hand-pushed flow coater type construction machine (road marking construction machine) having a slit opening as a coating machine. It is a schematic perspective view showing the state where it is applied to the road surface. As shown in FIG. 5, the
本開示の施工方法において、塗布工程は、塗料を路面に塗布して路面標示を形成する工程であればよく、路面標示の種類に応じて適宜選択でき、図5に示すように、手押し式のスリット状開口部を有するフローコーター式施工機を用いて、加熱溶融した塗料を塗布する工程に限定されない。 In the construction method of the present disclosure, the application step may be any step of applying paint to the road surface to form a road marking, and can be selected as appropriate depending on the type of road marking. The present invention is not limited to the process of applying heated and molten paint using a flow coater type construction machine having a slit-like opening.
塗料を路面に塗布する方法は、塗装機を用いることなく、刷毛などを用いて塗布する方法や、貼付式路面標示材を用いる方法でもよいが、生産性の点から、塗装機を用いる方法が好ましい。 The method of applying paint to the road surface may be by using a brush or the like without using a coating machine, or by using adhesive road marking materials, but from the viewpoint of productivity, it is preferable to use a coating machine. preferable.
塗装機を用いて塗料を路面に塗布する方法としては、路面標示で慣用的に利用されている塗装機を用いることができ、車載式塗装機(車載式路面標示施工機)や噴射式施工機(スプレー式施工機)などであってもよいが、簡便性などの点から、スリット状開口部を有するフローコーター式施工機が好ましい。スリット状開口部を有するフローコーター式施工機は、手押し式塗装機であってもよい。 As a method of applying paint to the road surface using a coating machine, it is possible to use a coating machine that is conventionally used for road markings, such as an on-vehicle coating machine (vehicle-mounted road marking application machine) or a spraying machine. (spray-type construction machine), etc., but a flow coater-type construction machine having a slit-like opening is preferred from the viewpoint of simplicity. The flow coater type construction machine having a slit-like opening may be a hand-push type coating machine.
塗料の温度(塗布温度)は、特に限定されず、塗料の種類に応じて適宜選択でき、常温であってもよいが、マスキングシートが耐熱性を有しており、加熱作業に適している点から、50℃以上であってもよく、100℃以上が好ましく、例えば120~250℃、好ましくは150~230℃、さらに好ましくは180~220℃である。 The temperature of the paint (application temperature) is not particularly limited and can be selected appropriately depending on the type of paint, and may be at room temperature, but the masking sheet has heat resistance and is suitable for heating work. The temperature may be 50°C or higher, preferably 100°C or higher, for example 120 to 250°C, preferably 150 to 230°C, and more preferably 180 to 220°C.
塗料の種類は、特に限定されず、路面標示で利用されている慣用のトラフィックペイントを利用できる。トラフィックペイントとしては、例えば、常温型トラフィックペイント(ペイント式水性型、ペイント式溶剤型)、加熱型トラフィックペイント(ペイント式水性型、ペイント式溶剤型)、溶融型トラフィックペイントなどが挙げられる。トラフィックペイントは、JIS K5665で規定されている路面標示用塗料であってもよい。これらのうち、加熱型トラフィックペイント、溶融型トラフィックペイントが好ましく、路面標示を厚肉にでき、かつ作業性に優れる点から、溶融型トラフィックペイント(溶融型塗料)が特に好ましい。 The type of paint is not particularly limited, and conventional traffic paint used for road markings can be used. Examples of the traffic paint include room temperature traffic paint (paint type water-based type, paint type solvent type), heating type traffic paint (paint type water-based type, paint type solvent type), melting type traffic paint, and the like. The traffic paint may be a road marking paint specified by JIS K5665. Among these, heating type traffic paint and melting type traffic paint are preferred, and melting type traffic paint (melting type paint) is particularly preferred since it allows thick road markings and is excellent in workability.
トラフィックペイントは、ホットメルト接着性樹脂を含んでいてもよく、ホットメルト接着性樹脂に加えて、ガラスビーズなどの無機フィラーを含んでいてもよい。 The traffic paint may contain a hot melt adhesive resin, and may contain an inorganic filler such as glass beads in addition to the hot melt adhesive resin.
無機フィラーとしては、例えば、ガラスビーズ、炭酸カルシウム、酸化チタンなどが挙げられる。これらのうち、ガラスビーズが好ましい。無機フィラーの平均粒径は、例えば0.05~5mm、好ましくは0.08~3mm、さらに好ましくは0.1~1mm程度である。 Examples of the inorganic filler include glass beads, calcium carbonate, and titanium oxide. Among these, glass beads are preferred. The average particle size of the inorganic filler is, for example, about 0.05 to 5 mm, preferably about 0.08 to 3 mm, and more preferably about 0.1 to 1 mm.
ホットメルト接着性樹脂としては、例えば、エチレン-メタクリル酸共重合樹脂、ロジン変性樹脂、石油樹脂、エステル変性石油樹脂などが挙げられる。 Examples of hot-melt adhesive resins include ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer resins, rosin-modified resins, petroleum resins, and ester-modified petroleum resins.
無機フィラーの割合は、ホットメルト接着性樹脂100質量部に対して、例えば1~100質量部、好ましくは3~50質量部、さらに好ましくは5~30質量部程度である。 The proportion of the inorganic filler is, for example, about 1 to 100 parts by weight, preferably 3 to 50 parts by weight, and more preferably about 5 to 30 parts by weight, based on 100 parts by weight of the hot melt adhesive resin.
特に好ましい塗布方法は、スリット状開口部を有するフローコーター式施工機を用いて溶融型塗料を路面に塗布する方法である。本開示のマスキングシートはアスファルトを含むため、塗料の温度に対する影響が少ない上に、前記マスキングシートを用いて複雑な形状の路面標示を容易に施工できる。 A particularly preferred application method is a method of applying the molten paint to the road surface using a flow coater type application machine having a slit-like opening. Since the masking sheet of the present disclosure contains asphalt, it has less influence on the temperature of the paint, and the masking sheet can be used to easily construct road markings with complicated shapes.
(マスキングシート除去工程)
マスキングシート除去工程では、前記塗布工程において、粘着テープ2で固定したマスキングシート1を、塗料が塗布された状態で路面から、粘着テープ2とともに路面から剥離することにより、路面上に残存した塗料によってドット部の形態を形成できる。特に、加熱した状態で塗布された塗料が冷却されて固化する前に、マスキングシート1および粘着テープ2を路面から剥離することにより、作業の円滑性も向上する上に、図5に示すドット部8のように、マスクされた形態に忠実な形態を形成できる。(Masking sheet removal process)
In the masking sheet removal step, the masking
(他の工程)
他の工程は、従来の施工方法と同様である。汚れ除去工程では、例えば、ブロアーなどの送風機を用いて埃を除去する方法などを利用できる。プライマー処理工程では、例えば、シリコーン系接着剤、オレフィン系接着剤、アクリル系接着剤、ポリエステル系接着剤、ウレタン系接着剤、エポキシ系接着剤、アスファルト系接着剤、ゴム系接着剤などの慣用の接着剤を、慣用の方法、例えば、ローラー塗装、機械塗装、スポンジ塗装する方法などを利用できる。マスキングシートの形状に応じて、必要であれば、第2のケガキ工程を設けて、車の流れ方向に対して斜めに交差する方向に延びるケガキ線などを引いてもよい。固化工程では、例えば、塗料が溶融型塗料である場合、塗料に散水することによって冷却してもよい。(Other processes)
Other steps are similar to conventional construction methods. In the dirt removal step, for example, a method of removing dust using an air blower such as a blower can be used. In the priming process, conventional adhesives such as silicone adhesives, olefin adhesives, acrylic adhesives, polyester adhesives, urethane adhesives, epoxy adhesives, asphalt adhesives, and rubber adhesives are used. The adhesive can be applied by conventional methods such as roller coating, machine coating, sponge coating, and the like. Depending on the shape of the masking sheet, if necessary, a second marking step may be provided to draw marking lines extending in a direction diagonally intersecting the direction of traffic flow. In the solidification step, for example, if the paint is a melt-type paint, the paint may be cooled by sprinkling water on the paint.
(路面標示)
本開示の施工方法において、路面標示の形状は、特に限定されないが、マスキングによる施工が効果的である点から、湾曲部および/または非直角部(直角でない屈曲部)を有する形状が好ましく、鋭角部や鈍角部などの非直角部を有する形状が特に好ましい。なかでも、作業性に優れるフローコーター式施工機や噴射式施工機などの塗装機を用いて施工する場合は、複雑な形状の路面標示を形成するのが困難であるため効果的である。さらに、スリット状開口部を有するフローコーター式施工機では、正方形状または長方形状の路面標示は、マスキング材を用いることなく、容易に施工できるため、車の流れ方向に対して斜めに交差する方向に延びる輪郭を有する形状、曲線状または湾曲状の輪郭を有する形状が好ましく、施工数が多く、作業が煩雑である点から、車の流れ方向に対して斜めに交差する方向に延びる輪郭を有する形状が特に好ましい。車の流れ方向に対して斜めに交差する方向に延びる輪郭を有する形状としては、例えば、平行四辺形状、菱形状、矢羽根形状、三角形状などが挙げられる。これらのうち、平行四辺形状、菱形状が好ましく、連続した作業によって作業効率を向上できる点から、平行四辺形状または菱形状が所定の間隔(特に、等間隔)で配列された破線型(または点線型)が特に好ましい。(Road markings)
In the construction method of the present disclosure, the shape of the road marking is not particularly limited, but from the viewpoint that construction by masking is effective, a shape having a curved part and/or a non-right angle part (a bent part that is not a right angle) is preferable, and a shape with an acute angle is preferable. Particularly preferred is a shape having a non-right angle part such as a corner or an obtuse angle part. In particular, it is effective to use a coating machine such as a flow coater type construction machine or a spray type construction machine, which has excellent workability, since it is difficult to form road markings with complicated shapes. Furthermore, with a flow coater type construction machine that has a slit-shaped opening, square or rectangular road markings can be easily constructed without using masking material. It is preferable to have a shape that has an outline that extends in the direction of the vehicle, a shape that has a curved shape, or a shape that has a curved outline.Since the number of constructions is large and the work is complicated, the shape has an outline that extends in a direction diagonally intersecting the direction of traffic flow. The shape is particularly preferred. Examples of the shape having an outline extending in a direction obliquely intersecting the direction of traffic flow include a parallelogram shape, a rhombus shape, an arrow feather shape, and a triangular shape. Among these, parallelogram shapes and rhombus shapes are preferable, and from the viewpoint of improving work efficiency through continuous work, a dashed line shape (or dotted line shape) in which parallelogram shapes or rhombus shapes are arranged at predetermined intervals (especially at equal intervals) is preferable. type) is particularly preferred.
路面標示のうち、施工数が多く、作業性を向上できる点から、減速路面標示(減速マークまたは減速レーンマーク)が好ましい。減速路面標示は、マーク型路面標示であってもよいが、作業性を向上できる点から、破線型路面標示が好ましい。 Among road markings, deceleration road markings (deceleration marks or deceleration lane marks) are preferable because they require a large number of constructions and can improve workability. Although the deceleration road marking may be a mark type road marking, a broken line type road marking is preferable from the viewpoint of improving workability.
[マスキングシート]
本開示のマスキングシートの形状は、路面標示の形状に応じて選択でき、図3に示す形状に限定されない。そのため、路面標示が湾曲した輪郭を有する場合は、湾曲した輪郭を有するマスキングシートであってもよい。[Masking sheet]
The shape of the masking sheet of the present disclosure can be selected depending on the shape of the road marking, and is not limited to the shape shown in FIG. 3. Therefore, when the road marking has a curved outline, a masking sheet having a curved outline may be used.
本開示のマスキングシートは、路面標示が破線型減速路面標示である場合、ケガキ線や白線または中央線を基準にマスキングシートを載置することにより、前記路面標示の車の流れ方向に対して斜めに交差する方向に延びる輪郭と一致する線を特定できる形状であれば特に限定されない。例えば、図3に示すように、路面標示を形成する領域(境界)に対して隙間を形成できるマスキングシートに限定されず、隙間を形成せずにマスキングシート単独で路面標示を形成する領域をマスキングできるマスキングシートであってもよい。このようなマスキングシートは、裏面に路面に固定するための粘着層を有していてもよい。 In the case where the road marking is a dashed deceleration road marking, the masking sheet of the present disclosure can be applied diagonally to the direction of traffic on the road marking by placing the masking sheet with reference to the marking line, white line, or center line. The shape is not particularly limited as long as it can identify a line that matches the contour extending in the direction intersecting the . For example, as shown in Fig. 3, the masking sheet is not limited to a masking sheet that can form a gap in the area (boundary) where a road marking is formed, but the masking sheet alone can mask the area where a road marking is to be formed without forming a gap. It may also be a masking sheet that can be used. Such a masking sheet may have an adhesive layer on the back surface for fixing it to a road surface.
マスキングシートが、路面標示を形成する領域(境界)に対して隙間を形成し、粘着テープで路面に固定するマスキングシートである場合であっても、マスキングシートの平面形状は、図3に示す形状に限定されず、略台形状などであってもよい。また、マスキングシートの平面形状が直角三角形状である場合であっても、直角二等辺三角形状に限定されず、路面標示の形状に応じた鋭角を有する直角非二等辺三角形状などであってもよい。さらに、マスキングシートは、図3および図4に示すような一枚のマスキングシートを用いる態様に限定されず、複数枚の形状の異なるマスキングシートを用いる態様であってもよく、特に、マスキングシートの形状が直角二等辺三角形でない場合は、形状の異なる複数枚のマスキングシートを組み合わせて用いるのが好ましい。 Even if the masking sheet is a masking sheet that forms a gap with the area (boundary) forming the road marking and is fixed to the road surface with adhesive tape, the planar shape of the masking sheet is the shape shown in Figure 3. The shape is not limited to this, and may be approximately trapezoidal or the like. Furthermore, even if the planar shape of the masking sheet is a right-angled triangle, it is not limited to a right-angled isosceles triangular shape, and may be a right-angled non-isosceles triangular shape having an acute angle depending on the shape of the road marking. good. Furthermore, the masking sheet is not limited to an embodiment using a single masking sheet as shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, but may also be an embodiment using a plurality of masking sheets with different shapes. When the shape is not a right isosceles triangle, it is preferable to use a combination of multiple masking sheets with different shapes.
これらのうち、平行四辺形状または菱形状のドット部を有するドットラインの施工においては、1枚のマスキングシートによって施工できる点から、平面形状が直角三角形状であるマスキングシートが好ましく、作業性に優れる点から、平面形状が、直角二等辺三角形状の本体部と、前記本体部の斜辺から突出する凸部とを有する形状であるマスキングシート(凸部を有する直角三角形状マスキングシート)が特に好ましい。この凸部を有する直角三角形状マスキングシートでは、前記凸部によって、前記斜辺と路面標示の輪郭との間に隙間を形成でき、前記凸部と前記隙間とを利用して粘着テープで路面に固定することにより、高い作業性でマスキングできる。 Among these, in constructing dot lines having parallelogram-shaped or rhomboid-shaped dots, a masking sheet with a planar shape of a right triangular shape is preferred because it can be constructed with a single masking sheet, and has excellent workability. From this point of view, a masking sheet (right triangular masking sheet having a convex portion) having a planar shape having a main body portion in the shape of a right isosceles triangle and a convex portion protruding from the oblique side of the main body portion is particularly preferred. In this right triangular masking sheet having a convex portion, the convex portion allows a gap to be formed between the oblique side and the outline of the road marking, and the convex portion and the gap are used to fix the masking sheet to the road surface with an adhesive tape. By doing so, masking can be performed with high workability.
前記凸部を有する直角三角形状マスキングシートは、路面標示の輪郭に対応する線を特定できる凸部が形成されていればよく、図3に示す形状に限定されない。 The right triangular masking sheet having the protrusions is not limited to the shape shown in FIG. 3 as long as the protrusions are formed so that a line corresponding to the contour of the road marking can be specified.
凸部の数は、斜辺において、1以上であればよいが、路面上で位置決めし易く、マスキング材と路面との間に塗料が浸入するのを抑制し易い点から、2以上が好ましく、2が特に好ましい。凸部の位置は、斜辺の中央部などであってもよいが、マスキング材と路面との間に塗料が浸入するのを抑制し易い点から、斜辺の端部が好ましく、斜辺の両端部が特に好ましい。 The number of protrusions may be 1 or more on the oblique side, but 2 or more is preferable from the viewpoint of easy positioning on the road surface and easy prevention of paint from entering between the masking material and the road surface. is particularly preferred. The position of the convex part may be the center of the oblique side, but it is preferable to place it at the end of the oblique side in order to easily prevent the paint from entering between the masking material and the road surface. Particularly preferred.
凸部の形状は、路面標示の輪郭に対応する線を特定できる凸部が形成されていればよく、図3に示す形状に限定されない。凸部の組み合わせは、例えば、三角形状凸部同士の組み合わせや、平行四辺形状凸部同士の組み合わせであってもよく、正方形状凸部や長方形状凸部なども含めた2種以上の凸部の組み合わせであってもよい。減速路面標示のドット部が45°の鋭角を有する平行四辺形状または菱形状である場合、形状の異なる複数枚のマスキングシートを用いることなく、1枚のマスキングシートを用いて簡便に、路面標示を形成する領域をマスキングできる点から、図3に示すような直角三角形状の凸部と平行四辺形状の凸部との組み合わせが好ましい。 The shape of the convex portion is not limited to the shape shown in FIG. 3, as long as the convex portion can identify a line corresponding to the contour of the road marking. The combination of protrusions may be, for example, a combination of triangular protrusions, a combination of parallelogram protrusions, or two or more types of protrusions including square protrusions, rectangular protrusions, etc. It may be a combination of If the dots of the deceleration road marking are in the shape of a parallelogram or rhombus with an acute angle of 45°, the road marking can be easily marked using one masking sheet without using multiple masking sheets with different shapes. A combination of a right triangular convex portion and a parallelogram-shaped convex portion as shown in FIG. 3 is preferable from the viewpoint of masking the area to be formed.
凸部の大きさは、斜辺からの凸部の高さが粘着テープの幅よりも小さくなるように調整するのが好ましい。凸部の高さを粘着テープの幅よりも小さく調整することにより、凸部の頂部に沿って粘着テープでマスキングシートを固定した場合、粘着テープとマスキングシートとが重なり合うため、塗料の浸入を抑制できる。 The size of the convex portion is preferably adjusted so that the height of the convex portion from the oblique side is smaller than the width of the adhesive tape. By adjusting the height of the convex part to be smaller than the width of the adhesive tape, when the masking sheet is fixed with adhesive tape along the top of the convex part, the adhesive tape and masking sheet overlap, which prevents paint from penetrating. can.
本開示のマスキングシートは、ケガキ線を引いた路面に位置決めするための目印を設けるのが好ましく、図3に示すような端部の切欠部に限定されず、線や点などの目印であってもよい。 It is preferable that the masking sheet of the present disclosure is provided with a mark for positioning on the road surface with a marked line, and is not limited to a notch at the end as shown in FIG. 3, but may be a mark such as a line or a dot. Good too.
マスキングシートの平均厚みは0.01~5mm程度の範囲から選択でき、作業性の点から3mm以下が好ましく、例えば0.1~3mm、好ましくは0.3~2mm、さらに好ましくは0.4~1mm、より好ましくは0.4~0.8mmである。マスキングシートの厚みが薄すぎると、耐熱性および防水性が低下する虞があり、逆に厚すぎると、作業性が低下する虞がある。 The average thickness of the masking sheet can be selected from a range of about 0.01 to 5 mm, and from the viewpoint of workability, it is preferably 3 mm or less, for example, 0.1 to 3 mm, preferably 0.3 to 2 mm, more preferably 0.4 to 2 mm. 1 mm, more preferably 0.4 to 0.8 mm. If the thickness of the masking sheet is too thin, there is a risk that heat resistance and waterproofness will be reduced, and if it is too thick, there is a risk that workability will be reduced.
マスキングシートは、一方の面に粘着層が積層されていてもよく、粘着層を有するマスキングシートを用いる場合は、粘着テープを用いることなく、マスキングシートを路面に固定できる。これらのうち、マスキングシート自体の生産性が高い上に、粘着テープで路面に固定することにより、高い作業性で路面にマスキングシートを位置決めできる点から、粘着層を有していないマスキングシートが好ましい。 The masking sheet may have an adhesive layer laminated on one side, and when a masking sheet having an adhesive layer is used, the masking sheet can be fixed to the road surface without using an adhesive tape. Among these, masking sheets without an adhesive layer are preferable because the masking sheet itself has high productivity and the masking sheet can be positioned on the road surface with high workability by fixing it to the road surface with adhesive tape. .
本開示のマスキングシートの材質は、特に限定されず、有機材料、無機材料のいずれであってもよい。有機材料で形成されたマスキングシートとしては、例えば、プラスチックシート、紙類や不織布などの繊維構造体などが挙げられる。無機材料で形成されたマスキングシートとしては、例えば、鉄板、ステンレス板などの金属板、セラミックスシートなどが挙げられる。マスキングシートは、燃え易い材質で形成されたシートあってもよいが、高い溶融温度で加熱される前記塗料による影響を受け難い点から、燃え難い材料で形成されたシートが好ましく、着火時間が15秒以上である材料で形成されたシートが特に好ましい。さらに、燃え難い材料で形成されたシートの中でも、着火時間が15秒以上であるマスキングシートが特に好ましい。 The material of the masking sheet of the present disclosure is not particularly limited, and may be either an organic material or an inorganic material. Examples of the masking sheet made of an organic material include a plastic sheet, a fibrous structure such as paper, and nonwoven fabric. Examples of the masking sheet made of an inorganic material include metal plates such as iron plates and stainless steel plates, and ceramic sheets. The masking sheet may be a sheet made of a material that is easily flammable, but it is preferably a sheet that is made of a material that is difficult to burn, since it is not easily affected by the paint that is heated at a high melting temperature, and the ignition time is 15. Particularly preferred are sheets made of materials that are more than sec. Further, among sheets made of materials that are difficult to burn, masking sheets whose ignition time is 15 seconds or more are particularly preferred.
本開示において、マスキングシートの着火時間は、バーナーの炎が着火する時間で測定でき、詳細には、後述する実施例に記載の方法で測定できる。 In the present disclosure, the ignition time of the masking sheet can be measured by the time it takes for the flame of the burner to ignite, and in detail, it can be measured by the method described in the Examples below.
着火時間が15秒以上であるマスキングシートとしては、鉄板などの金属板であってもよいが、取り扱い性などの点から、難燃剤を含むマスキングシートが好ましく、アスファルトを含むマスキングシートが特に好ましい。なかでも、耐熱性および防水性が高く、かつ柔軟であるため、道路状況や天候に左右されることなく利用でき、かつ施工性にも優れる点から、マスキングシートは、アスファルトを含む繊維構造体であるのが最も好ましい。 The masking sheet with an ignition time of 15 seconds or more may be a metal plate such as an iron plate, but from the viewpoint of ease of handling, a masking sheet containing a flame retardant is preferable, and a masking sheet containing asphalt is particularly preferable. Among these, masking sheets are made of fiber structures containing asphalt because they are highly heat resistant, waterproof, and flexible, so they can be used regardless of road conditions or weather, and they are also easy to install. It is most preferable to have one.
アスファルトとしては、例えば、天然アスファルト(レイクアスファルト、ロックアスファルト、オイルサンド、アスファルトタイトなど)、石油アスファルト(ストレートアスファルト、ブローンアスファルトなど)などが挙げられる。これらのアスファルトは単独でまたは二種以上組み合わせて使用できる。これらのうち、ストレートアスファルトなどの石油アスファルトなどが汎用される。 Examples of asphalt include natural asphalt (lake asphalt, rock asphalt, oil sand, asphaltite, etc.), petroleum asphalt (straight asphalt, blown asphalt, etc.), and the like. These asphalts can be used alone or in combination. Among these, petroleum asphalt such as straight asphalt is commonly used.
アスファルトの針入度(1/10mm)は、特に限定されないが、JIS K2207-1996に準拠した方法において、0~300程度の範囲から選択でき、例えば10~280、好ましくは20~250、さらに好ましくは50~200である。 The penetration degree (1/10 mm) of asphalt is not particularly limited, but can be selected from the range of about 0 to 300, for example, 10 to 280, preferably 20 to 250, more preferably is between 50 and 200.
アスファルトの割合は、繊維構造体100質量部に対して、例えば10~300質量部、好ましくは30~200質量部、さらに好ましくは50~150質量部である。 The proportion of asphalt is, for example, 10 to 300 parts by weight, preferably 30 to 200 parts by weight, and more preferably 50 to 150 parts by weight, based on 100 parts by weight of the fibrous structure.
前記アスファルトは、改質剤と組み合わせることにより、改質アスファルト(アスファルト系粘着剤)として使用してもよい。改質剤には、有機系改質剤、無機系改質剤が含まれる。 The asphalt may be used as a modified asphalt (asphalt adhesive) by combining it with a modifier. Modifiers include organic modifiers and inorganic modifiers.
有機系改質剤としては、例えば、ポリオレフィン、ビニル系重合体(例えば、ポリ塩化ビニル、アクリル樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル、エチレン-酢酸ビニル共重合体、エチレン-ビニルアルコール共重合体、エチレン-アクリル酸共重合体、エチレン-アクリル酸メチル共重合体、エチレン-アクリル酸エチル共重合体など)、ポリアミド、ポリエステル、合成ゴムまたはエラストマー(例えば、ポリブタジエン、ポリイソプレン、スチレン-ブタジエン共重合体など)、天然ゴム、粘着付与剤(例えば、テルペン樹脂、天然ロジンや変性ロジンなどのロジン樹脂、石油樹脂、変性オレフィン重合体など)、油脂類(例えば、ナフテン系原料油など)などが挙げられる。これらの有機系改質剤は、単独でまたは二種以上組み合わせて使用できる。これらの有機系改質剤のうち、熱可塑性エラストマー、粘着付与剤、油脂類が好ましく、スチレン-ブタジエン-スチレンブロック共重合体などのスチレン-ジエン系共重合体が特に好ましい。 Examples of organic modifiers include polyolefins, vinyl polymers (e.g., polyvinyl chloride, acrylic resins, polyvinyl acetate, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymers, ethylene-acrylic acid). copolymers, ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymers, ethylene-ethyl acrylate copolymers, etc.), polyamides, polyesters, synthetic rubbers or elastomers (e.g. polybutadiene, polyisoprene, styrene-butadiene copolymers, etc.), natural Rubbers, tackifiers (for example, terpene resins, rosin resins such as natural rosin and modified rosin, petroleum resins, modified olefin polymers, etc.), oils and fats (for example, naphthenic raw material oils, etc.), and the like. These organic modifiers can be used alone or in combination of two or more. Among these organic modifiers, thermoplastic elastomers, tackifiers, and oils and fats are preferred, and styrene-diene copolymers such as styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymers are particularly preferred.
無機系改質剤としては、例えば、鉄、銅、錫、亜鉛、ニッケル、ステンレス鋼などの金属粒子(粉末);酸化鉄、三二酸化鉄、四三酸化鉄、フェライト、酸化錫、酸化亜鉛、亜鉛華、酸化銅、酸化アルミニウムなどの金属酸化物粒子;硫酸バリウム、硫酸カルシウム、硫酸アルミニウム、亜硫酸カルシウム、炭酸カルシウム、重炭酸カルシウム、炭酸バリウム、水酸化マグネシウムなどの金属塩粒子;製鋼スラグ、スレートチップ、マイカ、クレー、タルク、ウォラストナイト、けい藻土、けい砂、軽石粉、シリカバルーン、ガラスバルーン、シラスバルーンなどの鉱物粒子;ガラス繊維や炭素繊維などの無機繊維などが挙げられる。これらの無機系改質剤は、単独でまたは二種以上組み合わせて使用できる。これらの無機系改質剤のうち、鉄粒子、各種酸化鉄粒子、製鋼スラグ粒子、タルク、(重)炭酸カルシウム粒子などの粒子状改質剤が好ましい。粒子状改質剤の平均粒径は0.01~0.5mm(特に0.05~0.2mm)である。 Examples of inorganic modifiers include metal particles (powder) of iron, copper, tin, zinc, nickel, stainless steel, etc.; iron oxide, iron sesquioxide, triiron tetroxide, ferrite, tin oxide, zinc oxide, Metal oxide particles such as zinc white, copper oxide, and aluminum oxide; Metal salt particles such as barium sulfate, calcium sulfate, aluminum sulfate, calcium sulfite, calcium carbonate, calcium bicarbonate, barium carbonate, and magnesium hydroxide; steelmaking slag, slate Examples include mineral particles such as chips, mica, clay, talc, wollastonite, diatomaceous earth, silica sand, pumice powder, silica balloons, glass balloons, and shirasu balloons; inorganic fibers such as glass fibers and carbon fibers. These inorganic modifiers can be used alone or in combination of two or more. Among these inorganic modifiers, particulate modifiers such as iron particles, various iron oxide particles, steelmaking slag particles, talc, and (bi)calcium carbonate particles are preferred. The average particle size of the particulate modifier is 0.01 to 0.5 mm (particularly 0.05 to 0.2 mm).
なお、本明細書および特許請求の範囲において、平均粒径は、レーザー回折式粒度分布計を用いて体積基準で測定された中心粒径(D50)を意味する。 Note that in this specification and claims, the average particle size means the center particle size (D50) measured on a volume basis using a laser diffraction particle size distribution analyzer.
有機系改質剤と無機系改質剤とは、耐熱性および防水性を向上させるために、両者を組み合わせて用いてもよい。 The organic modifier and the inorganic modifier may be used in combination to improve heat resistance and waterproofness.
アスファルトと改質剤との質量割合は、例えば、アスファルト/改質剤=100/0~30/70程度の範囲から選択でき、例えば99/1~40/60、好ましくは98/2~50/50、さらに好ましくは95/5~60/40程度の範囲から選択できる。改質剤が有機系改質剤である場合は、両者の質量割合は、例えば、アスファルト/有機系改質剤=100/0~70/30、好ましくは99/1~80/20、さらに好ましくは95/5~85/15程度である。改質剤の割合が少なすぎると、改質効果が発現せず、多すぎると、粘性が上がり加工が困難となる上に、経済性も低下する虞がある。 The mass ratio of asphalt and modifier can be selected from the range of, for example, asphalt/modifier = 100/0 to 30/70, for example, 99/1 to 40/60, preferably 98/2 to 50/70. 50, more preferably from a range of about 95/5 to 60/40. When the modifier is an organic modifier, the mass ratio of both is, for example, asphalt/organic modifier = 100/0 to 70/30, preferably 99/1 to 80/20, more preferably is about 95/5 to 85/15. If the proportion of the modifier is too small, the modification effect will not be exhibited, and if it is too large, the viscosity will increase, making processing difficult, and there is a possibility that the economical efficiency will also decrease.
有機系改質剤と無機系改質剤とを組み合わせる場合、両者の質量割合は、例えば、有機系改質剤/無機系改質剤=99/1~1/99程度の範囲から選択でき、例えば90/10~10/90、好ましくは80/20~20/80、さらに好ましくは70/30~30/70である。 When combining an organic modifier and an inorganic modifier, the mass ratio of both can be selected from the range of, for example, organic modifier/inorganic modifier = 99/1 to 1/99, For example, the ratio is 90/10 to 10/90, preferably 80/20 to 20/80, and more preferably 70/30 to 30/70.
改質剤で改質された改質アスファルトの針入度(1/10mm)は、0~100程度の範囲から選択でき、例えば5~80、好ましくは10~50、さらに好ましくは20~30である。 The penetration degree (1/10 mm) of the modified asphalt modified with a modifier can be selected from the range of about 0 to 100, for example 5 to 80, preferably 10 to 50, more preferably 20 to 30. be.
繊維構造体を構成する繊維としては、例えば、天然繊維(綿、麻などのセルロース繊維など)、再生繊維(レーヨンなど)、半合成繊維(セルロースエステル繊維など)、合成繊維[ポリオレフィン系繊維(ポリエチレン系繊維、ポリプロピレン系繊維など)、スチレン系繊維、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン系繊維、アクリル系繊維、ビニルアルコール系繊維(エチレンビニルアルコール系繊維など)、ポリエステル系繊維(ポリエチレンテレフタレート、ポリエチレンナフタレートなどのポリC2-4アルキレン-アリレート系繊維、液晶ポリエステル繊維などの全芳香族ポリエステル系繊維など)、ポリアミド系繊維(ポリアミド6、ポリアミド66などの脂肪族ポリアミド系繊維、アラミド繊維などの全芳香族ポリアミド系繊維など)、ポリウレタン系繊維など]、無機繊維(炭素繊維やガラス繊維など)などが例示できる。前記合成繊維は、異種の樹脂成分を組み合わせた複合繊維であってもよい。これらの繊維は、単独でまたは二種以上組み合わせて使用できる。これらの繊維のうち、ポリオレフィン系繊維やポリエステル系繊維などの合成繊維や無機繊維などが汎用されるが、紫外線に対する耐光性などの点から、ポリエチレンテレフタレート繊維などのポリC2-4アルキレン-アリレート系繊維が好ましい。The fibers that make up the fiber structure include, for example, natural fibers (cellulose fibers such as cotton and hemp), regenerated fibers (rayon, etc.), semi-synthetic fibers (cellulose ester fibers, etc.), synthetic fibers [polyolefin fibers (polyethylene polypropylene fibers, polypropylene fibers, etc.), styrene fibers, polytetrafluoroethylene fibers, acrylic fibers, vinyl alcohol fibers (ethylene vinyl alcohol fibers, etc.), polyester fibers (polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene naphthalate, etc.) C2-4 alkylene-arylate fibers, fully aromatic polyester fibers such as liquid crystal polyester fibers, etc.), polyamide fibers (fully aromatic polyamide fibers such as aliphatic polyamide fibers such as
繊維構造体には、織布、編布、不織布、ネット、紙などが含まれる。これらのうち、アスファルト含浸性などに優れる点から、紙、不織布が好ましく、紙が特に好ましい。 Fibrous structures include woven fabrics, knitted fabrics, nonwoven fabrics, nets, paper, and the like. Among these, paper and nonwoven fabric are preferred, and paper is particularly preferred, in view of their excellent asphalt impregnation properties.
紙(または原紙)は、少なくともパルプを含んでいる。パルプとしては、材質の点から、木材パルプ(針葉樹パルプ、広葉樹パルプなど)、非木材パルプ(ラグパルプ、リンターパルプ、リネンパルプ、楮・三椏・雁皮パルプ、ワラパルプ、バガスパルプ、ケナフパルプ、竹パルプなど)、合成繊維パルプ、古紙パルプ(再生紙など)などが例示できる。また、パルプは、パルプ化手段の点から、機械パルプであってもよく、強度の点から、化学パルプ(クラフトパルプ、サルファイトパルプなど)であってもよい。さらに、パルプは、未漂白パルプであってもよく、漂白パルプであってもよい。 Paper (or base paper) contains at least pulp. In terms of material, pulps include wood pulp (softwood pulp, hardwood pulp, etc.), non-wood pulp (rag pulp, linter pulp, linen pulp, kozo, mitsumata, gampi pulp, straw pulp, bagasse pulp, kenaf pulp, bamboo pulp, etc.), Examples include synthetic fiber pulp and waste paper pulp (recycled paper, etc.). Further, the pulp may be mechanical pulp from the viewpoint of pulping means, or may be chemical pulp (kraft pulp, sulfite pulp, etc.) from the viewpoint of strength. Furthermore, the pulp may be unbleached pulp or bleached pulp.
紙は、パルプに加えて、パルプ以外の繊維を含んでいてもよい。また、紙は、慣用の添加剤、例えば、充填剤(クレー、タルク、炭酸カルシウム、二酸化チタンなど)、サイズ剤(ロジンなどの酸性サイズ剤;アルキルテケンダイマーなどの中性サイズ剤など)、紙力増強剤(デンプン、ポリアクリルアミドなど)、顔料(または染料)、消泡剤などを含んでいてもよい。 In addition to pulp, paper may also contain fibers other than pulp. Paper also contains conventional additives, such as fillers (clay, talc, calcium carbonate, titanium dioxide, etc.), sizing agents (acid sizing agents such as rosin; neutral sizing agents such as alkylteken dimer, etc.), paper It may also contain strength enhancers (starch, polyacrylamide, etc.), pigments (or dyes), antifoaming agents, etc.
紙は、慣用の方法、例えば、必要により叩解したパルプと水とを含む組成物(スラリー)を湿式抄造することにより調製できる。湿式抄造は、慣用の抄紙機、例えば、長網抄紙機、円網抄紙機などを用いて行ってもよい。 Paper can be prepared by a conventional method, for example, by wet-forming a composition (slurry) containing optionally beaten pulp and water. Wet papermaking may be performed using a conventional paper machine, such as a Fourdrinier paper machine or a cylinder paper machine.
[粘着テープ]
粘着テープは、繊維シートの一方の面に粘着層が積層されていれば、特に限定されず、紙の一方の面に粘着層が積層された粘着テープ、布帛の一方の面に粘着層が積層された粘着テープなどであってもよい。これらのうち、容易に切断でき、作業性などに優れる点から、紙の一方の面に粘着層が積層された粘着テープが好ましく、クラフトテープが特に好ましい。[Adhesive tape]
Adhesive tapes are not particularly limited as long as they have an adhesive layer laminated on one side of a fiber sheet, and include adhesive tapes with an adhesive layer laminated on one side of paper, and adhesive tapes with an adhesive layer laminated on one side of fabric. It may also be adhesive tape or the like. Among these, adhesive tapes in which an adhesive layer is laminated on one side of paper are preferred, and kraft tapes are particularly preferred, since they can be easily cut and have excellent workability.
粘着テープの幅は、路面標示を形成する領域に対して隙間を設けマスキングシートを載置し、粘着テープで前記隙間をマスキングするとともに、前記マスキングシートを路面に固定する場合、前記隙間をマスキングできる幅でよいが、粘着テープとマスキングシートとの隙間から塗料が侵入するのを抑制できる点から、粘着テープの幅を前記隙間の幅よりも大きくするのが好ましい。粘着テープの幅を前記隙間の幅よりも大きくすることにより、粘着テープによる固定箇所において、マスキングシートと粘着テープとが重なり合うことにより、塗料の浸入を抑制できる。 The width of the adhesive tape is such that when a masking sheet is placed on an area where a road marking is to be formed, and the adhesive tape is used to mask the gap, and the masking sheet is fixed to the road surface, the gap can be masked. Although any width may be used, it is preferable to make the width of the adhesive tape larger than the width of the gap in order to prevent paint from entering through the gap between the adhesive tape and the masking sheet. By making the width of the adhesive tape larger than the width of the gap, the masking sheet and the adhesive tape overlap at the location where the adhesive tape is fixed, thereby suppressing infiltration of paint.
粘着テープの幅は、前記隙間の幅に対して1.05倍以上であってもよく、例えば1.05~5倍、好ましくは1.1~3倍、さらに好ましくは1.2~2倍、より好ましくは1.3~1.7倍である。 The width of the adhesive tape may be 1.05 times or more the width of the gap, for example 1.05 to 5 times, preferably 1.1 to 3 times, more preferably 1.2 to 2 times. , more preferably 1.3 to 1.7 times.
以下、実施例により、本発明をさらに具体的に説明するが、本発明はこれらの実施例に何ら限定されるものではない。 EXAMPLES Hereinafter, the present invention will be explained in more detail with reference to Examples, but the present invention is not limited to these Examples at all.
実施例1
ドットラインを以下の工程に準じて施工した。まず、マスキングシートを載置するために、図4に示すケガキ線を車線の路面に引いた。Example 1
The dot line was constructed according to the following process. First, in order to place the masking sheet, marking lines shown in Figure 4 were drawn on the road surface of the lane.
次に、ブロアーを用いて、路面の埃を除去した後、ドットラインの施工領域に、プライマー散布機を用いて、プライマーを塗布した。 Next, after removing dust from the road surface using a blower, a primer was applied to the dot line construction area using a primer sprayer.
図4に示すように、図6に示す平面形状を有するマスキングシート(厚み0.6mm、ラグ原紙に、針入度60~80のアスファルトを113質量%の割合で含浸させたアスファルト含浸紙)を路面に載置し、幅75mm、長さ400mmのクラフトテープで固定した。 As shown in FIG. 4, a masking sheet (thickness 0.6 mm, asphalt-impregnated paper made by impregnating rag paper with asphalt with a penetration rate of 60 to 80 at a ratio of 113% by mass) having the planar shape shown in FIG. It was placed on the road surface and fixed with craft tape 75 mm wide and 400 mm long.
図5に示すように、スリット状開口部を有する手押し式のフローコーター式施工機を用いて、車の流れ方向に平行なケガキ線に沿って、マスキングシートの上から、幅300mmおよび厚み1.5mmで溶融塗料を塗工した。 As shown in FIG. 5, using a hand-operated flow coater type construction machine with a slit-shaped opening, a width of 300 mm and a thickness of 1. A molten paint was applied with a thickness of 5 mm.
塗工後、塗料が固化する前に、塗料が塗布されたマスキングシートおよびクラフトテープを回収した。 After coating, the masking sheet and craft tape coated with the paint were collected before the paint solidified.
図7に示すように、マスキングシート31を燃焼試験箱の底面32に対して45°の角度で設置し、バーナー33は炎の高さを65mmに調整し、炎の先端がマスキングシートに触れる状態で焙り、着火時間を確認した結果、約54秒であった。 As shown in FIG. 7, the masking
実施例2
ドットラインを以下の工程に準じて施工した。まず、マスキングシートを載置するために、図4に示すケガキ線を車線の路面に引いた。Example 2
The dot line was constructed according to the following process. First, in order to place the masking sheet, marking lines shown in Figure 4 were drawn on the road surface of the lane.
次に、ブロアーを用いて、路面の埃を除去した後、ドットラインの施工領域に、プライマー散布機を用いて、プライマーを塗布した。 Next, after removing dust from the road surface using a blower, a primer was applied to the dot line construction area using a primer sprayer.
図4で示されているケガキ線に加えて、平面形状が直角二等辺三角形状の合板を用いて、マスキングシートをクラフトテープで固定する箇所を示す斜めのケガキ線を引いた。 In addition to the marking lines shown in FIG. 4, diagonal marking lines were drawn using plywood with a right isosceles triangular planar shape to indicate the locations where the masking sheet was to be fixed with craft tape.
図8に示す平面形状を有するマスキングシート(厚み0.6mm、ラグ原紙に、針入度60~80のアスファルトを113質量%の割合で含浸させたアスファルト含浸紙)を、直角三角形の斜辺と前記斜めのケガキ線との間隔が50mmとなるように調整して路面に載置した(マスキングシートの配置は図4と同様)。幅75mm、長さ400mmのクラフトテープを前記ケガキ線に沿ってマスキングシート側に貼付し、前記マスキングシートを路面に固定した。 A masking sheet (0.6 mm thick, asphalt-impregnated paper made by impregnating rug base paper with 113% by mass of asphalt with a penetration of 60 to 80) having the planar shape shown in FIG. It was placed on the road surface with the distance from the diagonal marking line adjusted to 50 mm (the arrangement of the masking sheet was the same as in Figure 4). A craft tape with a width of 75 mm and a length of 400 mm was attached to the masking sheet side along the marking lines to fix the masking sheet to the road surface.
実施例1と同様の方法で塗工した後、塗料が固化する前に、塗料が塗布されたマスキングシートおよびクラフトテープを回収した。 After coating in the same manner as in Example 1, the masking sheet and craft tape coated with the paint were collected before the paint solidified.
比較例1
ドットラインを以下の工程に準じて施工した。まず、路面をマスキングするために、図4に示すケガキ線を車線の路面に引いた。Comparative example 1
The dot line was constructed according to the following process. First, in order to mask the road surface, marking lines shown in Figure 4 were drawn on the road surface of the lane.
次に、ブロアーを用いて、路面の埃を除去した後、ドットラインの施工領域に、プライマー散布機を用いて、プライマーを塗布した。 Next, after removing dust from the road surface using a blower, a primer was applied to the dot line construction area using a primer sprayer.
図4で示されているケガキ線に加えて、平面形状が直角二等辺三角形状の合板を用いて、図2に示すように、クラフトテープでマスキングする箇所を示すケガキ線を引いた。 In addition to the marking lines shown in FIG. 4, marking lines were drawn to indicate the areas to be masked with craft tape, as shown in FIG. 2, using plywood with a right isosceles triangular planar shape.
前記ケガキ線に沿って、実施例1および実施例2と同様の箇所に、幅75mm、長さ400mmのクラフトテープを貼付した後、図2に示すように、実施例1および実施例2ではマスキングシートが載置される領域に対して、比較例1ではクラフトテープを順次貼付し、合計6本のクラフトテープで塗料の非塗装領域をマスキングした。 After affixing craft tape with a width of 75 mm and a length of 400 mm to the same locations as in Examples 1 and 2 along the marking lines, as shown in FIG. In Comparative Example 1, craft tapes were sequentially applied to the area where the sheet was placed, and the unpainted area was masked with a total of six craft tapes.
図5に示すように、手押し式のスリッター式施工機を用いて、車の流れ方向のケガキ線に沿って、マスキングシートの上から、幅300mmおよび厚み1.5mmで溶融塗料を塗工した。 As shown in FIG. 5, a hand-operated slitter-type construction machine was used to apply molten paint to a width of 300 mm and a thickness of 1.5 mm from above the masking sheet along the marking line in the direction of traffic.
実施例1と同様の方法で塗工した後、塗料が固化する前に、塗料が塗布されたクラフトテープを回収した。 After coating in the same manner as in Example 1, the coated craft tape was collected before the coating solidified.
実施例および比較例のそれぞれの施工において、作業員2名で作業し、20カ所以上にドット部を施工し、1カ所のドット部の領域を特定するための作業時間(プライマー処理後から塗料を塗布できる状態にするまでの時間)の平均値を比較した。実施例1では19.6秒であったのに対して、実施例2および比較例1では23.1秒であった。比較例1では、実施例に比べて溶融塗料や天候の影響を受け易い上に、実施例1よりも作業性も低かった。また、比較例1では、クラフトテープを中腰で貼付する作業を複数回繰り返す必要があり、実施例1および実施例2に比べて、作業者の肉体的な負担も大きかった。 In the construction of each of the examples and comparative examples, two workers worked, the dots were constructed in more than 20 locations, and the working time required to specify the area of one dot (paint was applied after primer treatment) The average values of the time taken to reach a state ready for application) were compared. In Example 1, the time was 19.6 seconds, whereas in Example 2 and Comparative Example 1, it was 23.1 seconds. In Comparative Example 1, it was more susceptible to the effects of melted paint and weather than in Examples, and the workability was also lower than in Example 1. Further, in Comparative Example 1, it was necessary to repeat the work of applying the craft tape half-heartedly multiple times, and the physical burden on the worker was greater than in Examples 1 and 2.
マスキングシートの代わりに、クラフトテープの着火時間について、実施例と同様の方法で測定した結果、約6秒であり、実施例1の約54秒と比較すると、大幅に短かった。実施例1で使用したマスキングシートでは、比較例1のクラフトテープに比べ、着火しにくく、安全に作業ができることが確認できた。 The ignition time of the craft tape instead of the masking sheet was measured in the same manner as in Example, and was approximately 6 seconds, which was significantly shorter than the approximately 54 seconds of Example 1. It was confirmed that the masking sheet used in Example 1 was less likely to catch fire than the craft tape of Comparative Example 1, and that the work could be performed safely.
本開示のマスキングシートは、減速路面標示などの路面標示を形成するための塗料を路面に塗布する塗布工程において、路面標示の非塗装領域をマスキングするために用いられ、破線型の減速マークまたは減速レーンマークの施工に特に有用である。 The masking sheet of the present disclosure is used to mask unpainted areas of road markings in the coating process of applying paint to the road surface to form road markings such as deceleration road markings, and is used to mask unpainted areas of road markings such as dashed deceleration marks or deceleration marks. It is particularly useful for constructing lane markings.
1…マスキングシート
1a…本体部
1b…第1の凸部
1c…第2の凸部
1d~1h…切欠部
2…粘着テープ
3a,3b…白線
4a,4b,5a,5b…ケガキ線
6…作業者
7…塗装機
8…ドット部1... Masking
Claims (18)
Translated fromJapanesePriority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022081020AJP7165282B1 (en) | 2022-05-17 | 2022-05-17 | Road marking construction method and masking sheet |
| JP2022155140AJP7382472B1 (en) | 2022-05-17 | 2022-09-28 | Road marking construction method and masking sheet |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022081020AJP7165282B1 (en) | 2022-05-17 | 2022-05-17 | Road marking construction method and masking sheet |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022155140ADivisionJP7382472B1 (en) | 2022-05-17 | 2022-09-28 | Road marking construction method and masking sheet |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP7165282B1 JP7165282B1 (en) | 2022-11-02 |
| JP2023169727Atrue JP2023169727A (en) | 2023-11-30 |
Family
ID=83887085
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022081020AActiveJP7165282B1 (en) | 2022-05-17 | 2022-05-17 | Road marking construction method and masking sheet |
| JP2022155140AActiveJP7382472B1 (en) | 2022-05-17 | 2022-09-28 | Road marking construction method and masking sheet |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022155140AActiveJP7382472B1 (en) | 2022-05-17 | 2022-09-28 | Road marking construction method and masking sheet |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP7165282B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117552307B (en)* | 2024-01-11 | 2024-04-02 | 山西路桥建设集团有限公司 | Road bridge construction marking device |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS52159033U (en)* | 1976-05-28 | 1977-12-02 | ||
| JPS56163474U (en)* | 1980-05-10 | 1981-12-04 | ||
| JPS5772484U (en)* | 1980-10-17 | 1982-05-04 | ||
| JPS6059184A (en)* | 1983-09-12 | 1985-04-05 | Tajima Le-Fuingu Kk | Asphalt-based laminated roofing sheet |
| JPH0554617U (en)* | 1991-12-25 | 1993-07-23 | 日昌株式会社 | Line masking tape |
| JP2007024918A (en)* | 2005-07-12 | 2007-02-01 | Sekisui Jushi Co Ltd | Road marking, road marking forming method, and road marking sheet |
| JP2018076680A (en)* | 2016-11-08 | 2018-05-17 | 王子ホールディングス株式会社 | Masking tape for use when constructing asphalt pavement and manufacturing method for the same |
| JP2021105332A (en)* | 2019-12-26 | 2021-07-26 | 七王工業株式会社 | Waterproof sheet and method of using the same |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0957895A (en)* | 1995-08-21 | 1997-03-04 | Nisshin Shoji Kk | Water-barrier sheet |
| JPH10325107A (en)* | 1997-03-24 | 1998-12-08 | Nichireki Co Ltd | Pavement repair structure and method for use in small-scale pavement restoration work |
| JP2000345514A (en) | 1999-06-03 | 2000-12-12 | Voc Direct:Kk | Road marking construction method and template used for it |
| JP2010065461A (en)* | 2008-09-11 | 2010-03-25 | Sanei Kikaku:Kk | Laying sheet, method of laying using the same, method of fixing of road surface marking material, and laying material |
| JP6145426B2 (en)* | 2014-05-28 | 2017-06-14 | 株式会社パーカーコーポレーション | Bitumen tape applicator |
| JP7299093B2 (en) | 2019-07-25 | 2023-06-27 | 株式会社高速道路総合技術研究所 | Laminated waterproof reinforcement sheet and waterproof reinforcement construction method of concrete girder using it |
- 2022
- 2022-05-17JPJP2022081020Apatent/JP7165282B1/enactiveActive
- 2022-09-28JPJP2022155140Apatent/JP7382472B1/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS52159033U (en)* | 1976-05-28 | 1977-12-02 | ||
| JPS56163474U (en)* | 1980-05-10 | 1981-12-04 | ||
| JPS5772484U (en)* | 1980-10-17 | 1982-05-04 | ||
| JPS6059184A (en)* | 1983-09-12 | 1985-04-05 | Tajima Le-Fuingu Kk | Asphalt-based laminated roofing sheet |
| JPH0554617U (en)* | 1991-12-25 | 1993-07-23 | 日昌株式会社 | Line masking tape |
| JP2007024918A (en)* | 2005-07-12 | 2007-02-01 | Sekisui Jushi Co Ltd | Road marking, road marking forming method, and road marking sheet |
| JP2018076680A (en)* | 2016-11-08 | 2018-05-17 | 王子ホールディングス株式会社 | Masking tape for use when constructing asphalt pavement and manufacturing method for the same |
| JP2021105332A (en)* | 2019-12-26 | 2021-07-26 | 七王工業株式会社 | Waterproof sheet and method of using the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP7165282B1 (en) | 2022-11-02 |
| JP2023169850A (en) | 2023-11-30 |
| JP7382472B1 (en) | 2023-11-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US3915771A (en) | Pavement-marking tape | |
| JP7382472B1 (en) | Road marking construction method and masking sheet | |
| US12091859B2 (en) | Roofing materials including a parting agent layer | |
| CA2383862A1 (en) | Curtain coater and method for curtain coating | |
| EP2896669B1 (en) | Edge coatings for adhesive tapes | |
| JPS59272B2 (en) | Spray painting method | |
| JP3057423B2 (en) | Torch waterproofing method | |
| JP3278139B2 (en) | Method for producing decorative material having natural stone pattern | |
| JP6979508B2 (en) | Tarpaulin and how to use it | |
| JP3940545B2 (en) | Building board and painting method | |
| JP3454251B2 (en) | Building materials with mark | |
| JPH05156614A (en) | Method and device of constructing road surface marking material for melting and road surface marking line drawn by using the same | |
| GB2265404A (en) | Stencilled paving | |
| US1214659A (en) | Apparatus for producing ornamental roofing. | |
| JP2021090415A (en) | Weed-proof sheet and method of application for the same | |
| JP2023082518A (en) | Method for forming temporary road marking and method for removing the same | |
| KR100530634B1 (en) | Auxiliary tape for painting and cover sheet having thereof | |
| DE4444846C1 (en) | Stencil for rough surfaces | |
| JPH08135104A (en) | Roof with repeated pattern and method for producing the same | |
| JP2008038484A (en) | Interior finishing material | |
| AU651752B2 (en) | Stencilled paving | |
| US1931554A (en) | Building strip | |
| JP2006212564A (en) | Covering sheet for use upon coating of vehicles and method for covering vehicle parts not to be coated | |
| US1673991A (en) | Roofing and method of laying the same | |
| KR100416644B1 (en) | One Artificial Marble Panel with the Two Patterns and the Method of Manufacturing therof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20220803 | |
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date:20220803 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20220830 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20220928 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20221018 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20221021 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:7165282 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |