JP2022113593A - Information management system, information management method, server, and program - Google Patents
Information management system, information management method, server, and programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2022113593A JP2022113593AJP2021009925AJP2021009925AJP2022113593AJP 2022113593 AJP2022113593 AJP 2022113593AJP 2021009925 AJP2021009925 AJP 2021009925AJP 2021009925 AJP2021009925 AJP 2021009925AJP 2022113593 AJP2022113593 AJP 2022113593A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- user
- information
- health
- analysis result
- analysis
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription174
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription320
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription272
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000claimsdescription11
- 230000001737promoting effectEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description80
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description68
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description50
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description23
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description17
- 230000010365information processingEffects0.000description12
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description7
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description7
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description6
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description6
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description5
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description5
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description5
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description5
- 230000008520organizationEffects0.000description5
- 230000008450motivationEffects0.000description4
- 230000036772blood pressureEffects0.000description3
- 230000037213dietEffects0.000description3
- 235000005911dietNutrition0.000description3
- 230000001747exhibiting effectEffects0.000description3
- 240000006829Ficus sundaicaSpecies0.000description2
- 206010019345Heat strokeDiseases0.000description2
- 230000001133accelerationEffects0.000description2
- 210000004204blood vesselAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000036760body temperatureEffects0.000description2
- 238000002591computed tomographyMethods0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 230000012447hatchingEffects0.000description2
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description2
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000description2
- 230000002159abnormal effectEffects0.000description1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000007621cluster analysisMethods0.000description1
- 239000003086colorantSubstances0.000description1
- 238000013135deep learningMethods0.000description1
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000description1
- 235000015872dietary supplementNutrition0.000description1
- 238000010801machine learningMethods0.000description1
- 238000012067mathematical methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000000474nursing effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description1
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description1
- 239000004065semiconductorSubstances0.000description1
- 238000007619statistical methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000013589supplementSubstances0.000description1
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、情報管理システム、情報管理方法、サーバ、及びプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to an information management system, an information management method, a server, and a program.
従来、ユーザに関する様々な情報を取得し、これらの情報を活用する技術が知られている。
例えば、特許文献1には、ユーザの健康情報を分析することにより、ユーザが熱中症となるリスクを求めるという技術が開示されている。この特許文献1に開示の技術によれば、リスクの高さに応じて警告をする等の手段で、ユーザに対する注意喚起をすることができる。2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, techniques for acquiring various information about a user and utilizing this information are known.
For example,
ところで、特許文献1に開示されているような一般的な技術では、ユーザに関する情報(例えば、ユーザから取得した健康情報)に基づいて、或る特定の分析(例えば、熱中症となるリスク指標を求める)を行うと共に、この分析結果を或る特定のユーザ(例えば、健康情報の取得元のユーザ)に対して提示することのみを目的としていた。
しかしながら、このようなユーザに関する情報について、より活用する余地があると考えられる。By the way, in the general technology disclosed in
However, it is considered that there is room for further utilization of such user-related information.
本発明は、このような状況に鑑みてなされたものである。そして、本発明の課題は、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用することである。 The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances. An object of the present invention is to make further use of user information.
上記課題を解決するため、本発明の一態様の情報管理システムは、
端末と、前記端末と通信可能に接続されたサーバと、を備える情報管理システムであって、
前記端末は、
ユーザの健康に関する情報である健康情報を、前記ユーザから取得する情報取得手段、
を備え、
前記サーバは、
前記情報取得手段が取得した前記健康情報に基づいて、前記ユーザの健康に関する分析を行う分析手段と、
前記分析手段による第1の分析結果を前記ユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、前記分析手段による前記第1の分析結果とは少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果である第2の分析結果を前記ユーザ以外の閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う提示制御手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする。In order to solve the above problems, an information management system according to one aspect of the present invention includes:
An information management system comprising a terminal and a server communicably connected to the terminal,
The terminal is
Information acquiring means for acquiring health information, which is information about the user's health, from the user;
with
The server is
analysis means for analyzing the user's health based on the health information acquired by the information acquisition means;
controlling presentation of a first analysis result by the analysis means to the user, and presenting a second analysis result, which is an analysis result at least partially different from the first analysis result by the analysis means, to the Presentation control means for controlling presentation to viewers other than the user;
characterized by comprising
本発明によれば、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用することが可能となる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, it becomes possible to utilize the information regarding a user further.
以下、本発明の実施形態について図面を参照して説明する。 BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[システム構成]
図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る情報管理システムSのシステム構成を示す図である。図1に示すように、情報管理システムSは、複数のユーザ端末10と、情報管理サーバ20と、複数の閲覧装置30と、を含んで構成される。
これら情報管理システムSの構成要素のそれぞれは、ネットワークNを介して相互に通信可能に構成されている。このネットワークNは、例えば、インターネットや、LAN(Local Area Network)によって実現される。[System configuration]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the system configuration of an information management system S according to one embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1, the information management system S includes a plurality of
Each component of the information management system S is configured to communicate with each other via a network N. FIG. This network N is realized by, for example, the Internet or a LAN (Local Area Network).
ここで、ユーザ端末10及び閲覧装置30の符号の末尾に記載した、「n」及び「m」は、それぞれ1以上の任意の整数値である。すなわち、これは、ユーザ端末10及び閲覧装置30の台数は、それぞれ特に限定されないことを示している。また、情報管理サーバ20についても1台のみ図示しているが、その台数は特に限定されない。
ただし、以下の説明において、複数存在する同一の装置について、それぞれを区別することなく説明する場合には、符号の末尾を省略して称する。例えば、ユーザ端末10-1、・・・、ユーザ端末10―nそれぞれを区別することなく説明する場合には、符号の末尾を省略して、単にユーザ端末10と称する。Here, “n” and “m” described at the end of the reference numerals of the
However, in the following description, when a plurality of identical devices are described without distinguishing between them, the suffixes of the reference numerals are omitted. For example, when the user terminals 10-1, .
また、以下では説明のための一例として、情報管理システムSは、ユーザ端末10を利用するユーザの健康に関する情報である「健康情報」を対象として管理することを想定する。
ここで、健康情報には、ユーザの身長や体重や血圧等の一般的な健康診断における検査で得られる情報のみならず、その他、日々の生活における食事や睡眠や運動強度等の情報や、周期的に測定された各種の生体情報や、医学的な診断や治療に関する情報等の、ユーザの身体や医療に関する多様な情報を含むことを想定する。In the following description, as an example, it is assumed that the information management system S manages "health information", which is information related to the health of the user who uses the
Here, the health information includes not only information obtained from examinations in general medical examinations, such as the user's height, weight, and blood pressure, but also other information such as diet, sleep, exercise intensity, etc. in daily life, period It is assumed that various information related to the user's body and medical care, such as various biological information that is physically measured and information related to medical diagnosis and treatment, is included.
このような健康情報は、様々な分析を行う対象とすることができる。また、その様々な分析の分析結果は、ユーザの健康状態の把握等の目的で、様々な提示先に提示することができる。そして、情報管理システムSにて実現される機能は、これらの様々な分析や様々な提示を行う用途に好適である。そのため、以下の説明では、健康情報を対象として管理することを想定する。
ただし、これは説明のための一例に過ぎず、本実施形態の適用範囲を限定する趣旨ではない。Such health information may be the subject of various analyses. In addition, the analysis results of the various analyzes can be presented to various presentation destinations for the purpose of grasping the health condition of the user. The functions realized by the information management system S are suitable for these various analyses, and various presentations. Therefore, in the following description, it is assumed that health information is managed.
However, this is merely an example for explanation, and is not intended to limit the scope of application of the present embodiment.
ユーザ端末10は、ユーザの健康状態の把握等を目的としたアプリケーションソフトウェア(以下、「健康アプリ」と称する。)を実行する。また、ユーザ端末10は、健康アプリを動作させると共に、生体センサによる測定やユーザの入力操作等により、ユーザ端末10を利用するユーザの健康情報を取得する。さらに、ユーザ端末10は、取得した健康情報を、情報管理サーバ20に対して送信する。さらに、ユーザ端末10は、後述の情報管理サーバ20から受信した分析結果を、ユーザに対して提示する。ユーザは、ユーザ端末10において提示された分析結果を閲覧することにより、自身の健康状態を把握することができる。
このようなユーザ端末10は、ユーザが装着して利用可能なウェアラブル端末や、スマートフォンや、所定の施設(例えば、スポーツクラブ、介護施設、自治体健康施設、病院、及び、その他専門施設)に設置された測定装置等の、情報処理装置によって実現される。The
Such a
情報管理サーバ20は、情報管理システムS全体で送受される情報を管理する。この管理において、各ユーザ端末10から受信した各ユーザの健康情報を分析する。また、情報管理サーバ20は、その分析結果を各ユーザ端末10や各閲覧装置30において提示させるために、その分析結果を各ユーザ端末10や各閲覧装置30に対して送信する。
このような情報管理サーバ20は、情報管理システムSを運用する事業者が管理するサーバコンピュータ等の、情報処理装置によって実現される。The
The
閲覧装置30は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した分析結果を、閲覧者に対して提示する。この閲覧者とは、ユーザ端末10のユーザに関連するものであり、例えば、ユーザの所属する企業や団体や自治体や、ユーザを診察等する医療従事者である。これら閲覧者は、閲覧装置30において提示された分析結果を閲覧することにより、各ユーザへの健康状態の把握や、各ユーザに対する健康に関する指導を行うことができる。
このような閲覧装置30は、パーソナルコンピュータ等の、情報処理装置によって実現される。The
Such a
以上図1を参照して説明した構成において、情報管理システムSに含まれる各装置は、「情報管理処理」を行う。ここで、情報管理処理とは、ユーザに関する情報(ここでは、健康情報)を適切に管理することにより、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用する一連の処理である。 In the configuration described above with reference to FIG. 1, each device included in the information management system S performs "information management processing". Here, the information management process is a series of processes for making better use of the user-related information (here, health information) by appropriately managing the user-related information.
このような情報管理処理が行われる場合、ユーザ端末10は、ユーザ端末10のユーザの健康に関する情報である健康情報を、ユーザ端末10のユーザから取得する。
また、情報管理サーバ20は、ユーザ端末10が取得した健康情報に基づいて、ユーザ端末10のユーザの健康に関する分析を行う。
そして、情報管理サーバ20は、情報管理サーバ20による第1の分析結果をユーザ端末10のユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、情報管理サーバ20による第1の分析結果とは少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果である第2の分析結果をユーザ端末10のユーザ以外の、閲覧装置30を利用する閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う。When such information management processing is performed, the
The
The
このように、情報管理システムSによれば、複数の提示先において、それぞれ異なる分析結果が提示される。そのため、ユーザや閲覧者は、ユーザや閲覧者によってそれぞれ異なる、各ユーザや閲覧者にとって好適な分析結果を閲覧することができる。
これにより、ユーザや閲覧者は、ユーザの健康状態を適切に把握し、例えば、ユーザが病状の発生する前の段階(すなわち、未病の段階)にあることを早期に発見することができる。また、ユーザの日々の健康状態の変化を継続的に観察することができる。
したがって、本発明の実施形態に係る情報管理システムSによれば、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用することができる。Thus, according to the information management system S, different analysis results are presented to a plurality of presentation destinations. Therefore, users and viewers can view analysis results suitable for each user and viewer, which are different for each user and viewer.
As a result, the user and viewers can appropriately grasp the user's health condition, and can, for example, quickly discover that the user is in a pre-disease stage (i.e., pre-disease stage). In addition, it is possible to continuously observe changes in the user's daily health condition.
Therefore, according to the information management system S according to the embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to further utilize the information regarding the user.
また、それに加えて、情報管理システムSを運用する事業者は、情報管理システムSを運用することにより、様々なビジネスモデルを構築することができる。
例えば、分析結果を提示する対価として、ユーザや後述の閲覧者から所定の使用料を徴収するというビジネスモデルを構築することができる。この場合に、この事業者は、ユーザの支払う所定の使用料を、直接ユーザから徴収することもできるし、閲覧者を介して徴収することもできる。In addition, by operating the information management system S, the business operator that operates the information management system S can construct various business models.
For example, it is possible to construct a business model in which a predetermined usage fee is collected from a user or a later-described viewer in exchange for presenting the analysis results. In this case, the operator can collect the predetermined usage fee paid by the user directly from the user or through the viewer.
また、他にも、例えば、ユーザ端末10の販売経路を管理したりするというビジネスモデルを構築することができる。この場合に、この事業者は、ユーザに対して直接ユーザ端末10を販売することもできるし、閲覧者を介して販売することもできる。
また、これらの場合に、例えば、所定の使用料にユーザ端末10のリース料を含ませるというビジネスモデルを構築することもできる。
すなわち、この事業者は、情報管理システムSを運用することにより、ビジネス対象のユーザや閲覧者のニーズ等を考慮した上で、幅広くビジネスを展開することが可能となる。In addition, for example, it is possible to construct a business model such as managing the sales channel of the
Also, in these cases, for example, a business model can be constructed in which the lease fee for the
In other words, by operating the information management system S, the business operator can develop a wide range of businesses in consideration of the needs of business users and viewers.
[ハードウェア構成]
次に、情報管理システムSに含まれる各装置のハードウェア構成を説明する。
情報管理システムSに含まれる各装置は、上述したようにサーバコンピュータ、パーソナルコンピュータ、ウェアラブル装置、スマートフォン、あるいは施設に設置された測定装置等の情報処理装置によって構成され、その基本的構成は各装置でそれぞれ同様である。[Hardware configuration]
Next, the hardware configuration of each device included in the information management system S will be described.
Each device included in the information management system S is configured by an information processing device such as a server computer, a personal computer, a wearable device, a smartphone, or a measuring device installed in a facility as described above, and the basic configuration is each device , respectively.
図2は、情報管理システムSに含まれる各装置を構成する情報処理装置800のハードウェア構成を示す図である。
図2に示すように、各装置を構成する情報処理装置800は、CPU(Central Processing Unit)811と、ROM(Read Only Memory)812と、RAM(Random Access Memory)813と、バス814と、入力部815と、出力部816と、記憶部817と、通信部818と、ドライブ819と、センサ部820と、を備えている。FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the hardware configuration of an
As shown in FIG. 2, an
CPU811は、ROM812に記録されているプログラム、又は、記憶部817からRAM813にロードされたプログラムにしたがって各種の処理を実行する。
RAM813には、CPU811が各種の処理を実行する上において必要なデータ等も適宜記憶される。The
The
CPU811、ROM812及びRAM813は、バス814を介して相互に接続されている。バス814には、入力部815、出力部816、記憶部817、通信部818、ドライブ819及びセンサ部820が接続されている。 The
入力部815は、各種ボタン等で構成され、指示操作に応じて各種情報を入力する。また、入力部815は、マイクをさらに含んでおり、音声を集音する。
出力部816は、ディスプレイやスピーカ等で構成され、画像や音声を出力する。The
The
記憶部817は、ハードディスクあるいはDRAM(Dynamic Random Access Memory)等で構成され、各サーバで管理される各種データを記憶する。
通信部818は、ネットワークNを介して他の装置との間で行う通信を制御する。The
A
ドライブ819には、磁気ディスク、光ディスク、光磁気ディスク、あるいは半導体メモリ等よりなる、リムーバブルメディア831が適宜装着される。ドライブ819によってリムーバブルメディア831から読み出されたプログラムは、必要に応じて記憶部817にインストールされる。 A
センサ部820は、各種のセンサ等によって構成され、センサに対応した種々の情報を計測する。例えば、センサ部820は、ユーザの心拍や血圧や体温や血中酸素濃度や血管の状態等の生体情報を計測する生体センサ、位置情報を計測するGPS(Global Positioning System)等に準拠した測位センサ、ユーザの運動状態を計測する加速度センサやジャイロセンサ等により構成される。 The
なお、情報処理装置800が情報管理サーバ20や閲覧装置30として構成される場合には、センサ部820を省略した構成とすることも可能である。また、情報処理装置800が施設に設置されるユーザ端末10として構成される場合には、センサ部820を医学的に専門性が高い医療用ハードウェア(例えば、X線CT(Computed Tomography)装置)等により構成することも可能である。さらに、情報処理装置800がスマートフォン等により構成される場合には、入力部815をタッチセンサによって構成し、出力部816のディスプレイに重ねて配置することにより、タッチパネルを備える構成とすることも可能である。 Note that when the
[機能的構成]
次に、情報管理システムSにおける各装置の機能的構成について説明する。[Functional configuration]
Next, the functional configuration of each device in the information management system S will be described.
[ユーザ端末10の機能的構成]
図3は、ユーザ端末10の機能的構成を示すブロック図である。
図3に示すように、ユーザ端末10のCPU811においては、健康アプリ実行部151と、健康情報取得部152と、情報提示部153と、が機能する。
また、図3に示すように、ユーザ端末10の記憶部817においては、健康情報記憶部171と、第1の分析結果記憶部172と、が形成される。
これらの各機能ブロック間では、以下で明示しない場合も含めて、それぞれの機能ブロックの機能を発揮するために必要な情報が、適宜送受される。[Functional Configuration of User Terminal 10]
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing the functional configuration of the
As shown in FIG. 3, in the
In addition, as shown in FIG. 3, in the
Information necessary for exhibiting the function of each functional block is appropriately transmitted and received between these functional blocks, even if it is not explicitly stated below.
健康アプリ実行部151は、健康アプリを実行する。この健康アプリの実行とは、例えば、健康アプリを提供する事業者(情報管理システムSを運営する事業者と同一であっても異なっていてもよい。)が管理する外部サーバ(図示を省略する。)等から健康アプリを取得して、この健康アプリを閲覧装置30にインストールする処理や、健康アプリに対応する機能を実現する処理や、健康アプリの動作に関する各種情報を管理する処理や、これら各種情報を提示するためのユーザインタフェースを含んだ表示画面等を生成する処理や、他の機能ブロックと連携する処理等を含む。 Health
健康アプリ実行部151が実行する健康アプリは、上述したように、ユーザの健康状態の把握等を目的としたものであればよく、特に限定されない。例えば、健康アプリは、取得した健康情報をそのまま提示する処理を行うものであってもよいし、この取得した健康情報を管理する処理をしたり、健康情報に対して統計的な処理をしたりといった、所定の処理をさらに行うものであってもよい。 The health application executed by health
健康アプリ実行部151が管理する各種情報は、例えば、健康情報と第1の分析結果を含む。
健康情報は、健康アプリの種別によって異なるが、例えば、ユーザの心拍や血圧や体温等の健康状態を示す各種生体情報や、ユーザの運動、睡眠、及び食事等の生活状態を示す情報といった、健康アプリの機能に関連して取得される情報である。なお、これら健康情報には、ユーザを識別する識別子や、ユーザの氏名、パスワード、及びメールアドレスといったユーザの属性を示す情報や、ユーザと関連する閲覧者を識別する識別子等の情報がさらに含まれる。これらのユーザに関する情報は、情報管理システムSにおいて、健康アプリでのユーザ登録や、健康情報とユーザを対応付けるための識別情報として利用される。
第1の分析結果は、情報提示部153により受信され、第1の分析結果記憶部172に記憶される。第1の分析結果の詳細については、情報提示部153の説明と共に後述する。Various types of information managed by health
The health information varies depending on the type of health application. For example, various types of biological information indicating the user's health condition such as heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, etc., and information indicating the user's living condition such as exercise, sleep, diet, etc. Information obtained in connection with the functionality of the app. The health information further includes information such as an identifier that identifies the user, information that indicates attributes of the user such as the user's name, password, and email address, and identifiers that identify viewers related to the user. . In the information management system S, these user-related information are used as identification information for user registration in health applications and for associating health information with users.
The first analysis result is received by the
健康情報取得部152は、健康アプリ実行部151による健康アプリの実行に伴う制御に基づいて、健康情報を取得する。そして、健康情報取得部152は、取得した健康情報を健康アプリ実行部151に対して出力する。例えば、健康情報が、ユーザの各種生体情報である場合には、健康情報取得部152は、センサ部820による測定を制御することによりこれらの健康情報を取得する。また、健康情報取得部152は、入力部815を介して受け付けたユーザによる健康情報の内容の入力操作等によっても、健康情報を取得する。さらに、例えば、健康情報が、ユーザの運動、睡眠、及び食事等の生活状態を示す情報である場合は、健康情報取得部152は、各種生体情報等を統計的に処理して、これらの健康情報を取得する。 Health
そして、健康情報取得部152は、取得した健康情報を健康情報記憶部171に記憶させる。すなわち、健康情報記憶部171は、健康情報を記憶する記憶部として機能する。また、健康情報取得部152は、取得した健康情報を、情報管理サーバ20に対して送信する。 Then, the health
情報提示部153は、情報管理サーバ20からユーザの健康情報に対応する第1の分析結果を受信する。
ここで、上述したように、情報管理サーバ20は、ユーザ端末10と閲覧装置30とに対して、それぞれ少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果を送信する。すなわち、ユーザ端末10に対して「第1の分析結果」を送信する。一方で、閲覧装置30に対して「第2の分析結果」を送信する。
これにより、複数の提示先において、それぞれ異なる分析結果が提示される。すなわち、様々な分析結果を、それを求めるユーザや閲覧者に対して提示することができる。そのため、ユーザや閲覧者は、ユーザや閲覧者によってそれぞれ異なる、各ユーザや閲覧者にとって好適な分析結果を閲覧することができる。The
Here, as described above, the
As a result, different analysis results are presented to a plurality of presentation destinations. That is, various analysis results can be presented to users and viewers who request them. Therefore, users and viewers can view analysis results suitable for each user and viewer, which are different for each user and viewer.
具体的に、例えば、第1の分析結果と第2の分析結果とで、分析対象とするユーザを異ならせるようにする。
この場合、第1の分析結果としては、そのユーザ端末10を利用するユーザ自身から取得した健康情報の分析結果を提示する。これにより、ユーザは自身の健康状態を把握することが可能となる。
一方で、第2の分析結果としては、閲覧者に関連する複数のユーザから取得した健康情報の分析結果を提示する。これにより、閲覧者は、自身に関連する複数のユーザ全員の健康状態を把握できる。Specifically, for example, the users to be analyzed are made different between the first analysis result and the second analysis result.
In this case, as the first analysis result, the analysis result of the health information acquired from the user who uses the
On the other hand, as the second analysis result, the analysis result of health information acquired from a plurality of users related to the viewer is presented. This allows the viewer to grasp the health conditions of all of the users associated with him/herself.
他にも、例えば、第1の分析結果と第2の分析結果とで、分析対象とする項目や分析の詳細さを異ならせる。
例えば、第1の分析結果には、多数の項目についての詳細な分析結果を含ませる。これにより、ユーザは、多数の項目の分析結果を閲覧でき、より詳細に自身の健康状態を把握できる。
一方で、例えば、第2の分析結果には、主要な項目についてある程度大まかな分析結果のみを含ませる。これにより、閲覧者は、主要な項目の分析結果のみを一覧で閲覧でき、より簡易に複数のユーザ全員の健康状態を把握できる。In addition, for example, the items to be analyzed and the details of the analysis are made different between the first analysis result and the second analysis result.
For example, the first analysis result includes detailed analysis results for many items. As a result, the user can browse the analysis results of many items and grasp his/her own health condition in more detail.
On the other hand, for example, the second analysis result includes only a somewhat rough analysis result for main items. As a result, the viewer can view only the analysis results of the main items in a list, and can more easily grasp the health conditions of all the users.
他にも、例えば、ユーザによって第1の分析結果を異ならせてもよい。また、例えば、閲覧者によって第2の分析結果を異ならせてもよい。
例えば、ユーザや閲覧者が、一般的なユーザや一般的な企業等である場合には、第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果に、医学的な専門性がそれほど高くない項目についての分析結果のみ含ませる。
一方で、ユーザや閲覧者が、医療従事者等である場合には、第2の分析結果に医学的に専門性が高い項目についての分析結果を含ませる。
これにより、ユーザや閲覧者は、自身が容易に理解可能な範囲で、分析結果を閲覧でき、より適切に健康状態を把握できる。Alternatively, for example, the first analysis result may differ depending on the user. Also, for example, the second analysis result may differ depending on the viewer.
For example, if the user or the viewer is a general user or a general company, the first analysis result and the second analysis result may include an analysis of an item that does not have a high level of medical expertise. Include only results.
On the other hand, if the user or viewer is a medical professional or the like, the second analysis result includes the analysis result of items with high medical expertise.
As a result, users and viewers can view the analysis results within a range that they can easily understand, and can more appropriately grasp their health conditions.
他にも、ユーザや閲覧者が自身の要望に応じて設定を行うようにし、この設定に基づいて、第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果を異ならせるようにしてもよい。 Alternatively, the user or viewer may make settings according to his or her own wishes, and the first analysis result and the second analysis result may differ based on this setting.
また、何れの場合であっても、分析結果は、その内容や重要性に応じて、把握が用意となるように様々な形式で提示するようにする。
例えば、分析結果として、分析で算出された値そのものを提示したり、分析で判定された良否の度合い等の指標を提示したり、分析で所定の閾値と比較した結果を提示したりする。また、場合によっては、分析結果の一部として健康情報そのものを提示したりする。
これらの場合に、これらの値等をそのままテキスト形式で提示してもよいし、値等の時系列の変化を示すグラフの形式で提示してもよいし、レーダーチャート等の形式で提示してもよいし、警告音等を発報する等の形式で提示してもよい。In any case, the results of the analysis should be presented in various formats, depending on their content and importance, so that they can be easily grasped.
For example, as the analysis result, the value itself calculated in the analysis is presented, an index such as the degree of pass/fail determined in the analysis is presented, or the result of comparison with a predetermined threshold value in the analysis is presented. In some cases, the health information itself is presented as part of the analysis results.
In these cases, these values, etc. may be presented as they are in text format, may be presented in the form of graphs showing time-series changes in values, etc., or may be presented in the form of radar charts, etc. Alternatively, it may be presented in a form such as issuing a warning sound or the like.
以上例示したようにして、本実施形態では、ユーザや閲覧者のそれぞれが求める様々な第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果を、ユーザや閲覧者が容易に把握できるような様々な形式で提示することができる。 As exemplified above, in the present embodiment, various first analysis results and second analysis results desired by users and viewers are provided in various formats so that users and viewers can easily grasp them. can be presented.
情報提示部153は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した第1の分析結果を、ユーザに対して提示する。この提示は、例えば、出力部816に含まれるディスプレイへの表示や、スピーカからの音声出力により実現される。また、提示を行うタイミングについては、例えば、第1の分析結果を取得した時点でリアルタイムに行うようにしてもよいし、健康アプリ実行部151が実行する健康アプリの動作と連携して行うようにしてもよい。 The
このように、健康アプリ実行部151が実行する健康アプリの動作と連携して提示を行うために、情報提示部153は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した第1の分析結果を、第1の分析結果記憶部172に記憶させる。すなわち、第1の分析結果記憶部172は、第1の分析結果を記憶する記憶部として機能する。 In this way, in order to perform presentation in cooperation with the operation of the health application executed by health
[情報管理サーバ20の機能的構成]
図4は、情報管理サーバ20の機能的構成を示すブロック図である。
図4に示すように、情報管理サーバ20のCPU811においては、管理処理実行部251と、分析部252と、提示制御部253と、情報提示部254と、課題管理部255と、が機能する。
また、図4に示すように、情報管理サーバ20の記憶部817においては、健康情報記憶部271と、各分析結果記憶部272と、ポイント情報記憶部273と、が形成される。
これらの各機能ブロック間では、以下で明示しない場合も含めて、それぞれの機能ブロックの機能を発揮するために必要な情報が、適宜送受される。[Functional Configuration of Information Management Server 20]
FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing the functional configuration of the
As shown in FIG. 4, in the
Further, as shown in FIG. 4, in the
Information necessary for exhibiting the function of each functional block is appropriately transmitted and received between these functional blocks, even if it is not explicitly stated below.
管理処理実行部251は、情報管理システムSで送受される情報を管理するための処理を実行する。情報を管理するための処理とは、例えば、健康情報や第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果等の各種情報を管理する処理や、これら各種情報を提示するためのユーザインタフェースを含んだ表示画面等を生成する処理や、他の機能ブロックと連携する処理等を含む。 The management
管理処理実行部251が管理する各種情報は、例えば、健康情報と第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果といった各分析結果とポイント情報を含む。
健康情報は、各ユーザ端末10から受信した健康情報である。ここで、健康情報には上述したように、ユーザを識別する識別子やユーザの属性を示す情報が含まれる。そこで、管理処理実行部251は、これらの情報に基づいて、各ユーザ端末10から受信した各健康情報が何れのユーザに対応する健康情報であるかを特定する。Various types of information managed by the management
Health information is health information received from each
そして、管理処理実行部251は、特定した各健康情報と各ユーザとの対応付けが整合するようにした上で、各健康情報を健康情報記憶部271に記憶させる。すなわち、健康情報記憶部271は、健康情報を記憶する記憶部として機能する。また、管理処理実行部251は、閲覧者に関連するユーザの健康情報を、閲覧装置30に対して送信する。 Then, the management
このような管理処理実行部251による管理で、健康情報記憶部271は、各ユーザの全ての健康情報というビッグデータを記憶するデータベースとして機能する。そして、情報管理サーバ20を利用する、情報管理システムSの事業者は、分析結果のみならず、このビッグデータを各ユーザの了承を得た上で、販売等するといったビジネスモデルを構築することもできる。 With such management by the management
各分析結果は、各分析結果記憶部272が生成し、第1の分析結果記憶部172に記憶される。
ポイント情報は、課題管理部255により各ユーザに付与されるポイントの情報であり、第2の分析結果記憶部372に記憶される。ポイント情報の詳細については、課題管理部255の説明と共に後述する。Each analysis result is generated by each analysis
The point information is information on points given to each user by the
分析部252は、健康情報記憶部271に記憶されている各ユーザの健康情報に基づいて、各ユーザの健康に関する分析を行う。分析は、様々な手法に基づいて行われてよい。例えば、生体情報の測定値の積算値や差分値等を算出するといった数学的手法や、過去の健康情報等に基づいた統計的手法や、所定の基準値との比較といった所定のルールに基づいたルールベースの手法や、クラスタ分析やディープラーニングといった機械学習を用いた手法や、これらを組み合わせた手法を用いることができる。各分析結果記憶部272は、このような手法に基づいた分析を行うことにより、上述した第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果を生成する。 The
そして、各分析結果記憶部272は、生成した第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果といった各分析結果を各分析結果記憶部272に記憶させる。すなわち、各分析結果記憶部272は、各分析結果を記憶する記憶部として機能する。 Then, each analysis
提示制御部253は、各分析結果記憶部272に記憶されている第1の分析結果をユーザ端末10のユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、各分析結果記憶部272に記憶されている第1の分析結果とは少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果である第2の分析結果をユーザ端末10のユーザ以外の、閲覧装置30を利用する閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う。 The
この提示する制御とは、例えば、第1の分析結果に対応するユーザのユーザ端末10を特定し、この特定したユーザ端末10に対して、提示のために第1の分析結果を送信することである。また、例えば、第2の分析結果に対応する閲覧者の閲覧装置30を特定し、この特定した閲覧装置30に対して、提示のために第2の分析結果を送信することである。この場合に、提示制御部253は、単に各分析結果を送信するのみでなく、各分析結果を提示するタイミング等の指示を含ませるようにしてもよい。このような、提示制御部253の提示する制御により、上述したユーザ端末10の情報提示部153による第1の分析結果の提示や、後述する閲覧装置30の情報提示部352による第2の分析結果の提示が実現される。 This presentation control is, for example, specifying the
情報提示部254は、各分析結果記憶部272が記憶する各分析結果を、情報管理サーバ20を利用する事業者(例えば、情報管理システムSを運用する事業者)に対して提示する。この提示は、例えば、出力部816に含まれるディスプレイへの表示や、スピーカからの音声出力により実現される。また、提示を行うタイミングについては、例えば、各分析結果が取得された時点でリアルタイムに行うようにしてもよいし、管理処理実行部251が実行する処理と連携して行うようにしてもよい。 The
課題管理部255は、ユーザが解決すべき、健康を増進するための課題が解決されたか否かに応じて、ユーザに対して所定の対価を付与する。ユーザが解決すべき、健康を増進するための課題とは、例えば、ユーザが、徒歩での移動や、ダンスや、ストレッチといった所定の運動等を行うという課題である。 The
例えば、課題が、ユーザが徒歩での移動を行うというものである場合、提示制御部253は、この課題の内容を、第1の分析結果の提示と同様にして、ユーザ端末10のユーザに対して提示する制御を行う。これにより、ユーザ端末10の情報提示部153により、ユーザに対して課題の内容が提示される。この場合の課題の内容の提示の方法や、提示のタイミングについても、第1の分析結果を提示する場合と同様とすることができる。 For example, when the task is that the user moves on foot, the
そして、この課題を得たユーザが、実際に課題を解決するために徒歩での移動を行った場合、ユーザ端末10にて、この徒歩での移動が行われていることを示す健康情報(例えば、加速度センサの測定値や、測位センサの測定値)が取得される。一方で、ユーザが徒歩での移動を行っていない場合には、このような徒歩での移動が行われていることを示す健康情報は取得されない。そのため、健康情報を受信した分析部252は、健康情報に基づいて、ユーザにより課題が解決されたか否かを分析することができる。 Then, when the user who has obtained this task actually moves on foot in order to solve the problem, the
そして、課題管理部255は、ユーザにより課題が解決されたと分析部252が分析した場合に、このユーザに対して所定の対価を付与する。この所定の対価は、課題が全て解決した場合に付与してもよいし、課題の解決度合い(例えば、課題全体の何割程度が解決されたか)に応じて適宜付与してもよい。また、この所定の対価をどのようなものとするのかは適宜定めることができるが、ここでは、一例としてポイントを所定の対価としてユーザに付与する。この場合、課題管理部255は、健康情報に含まれるユーザを識別する識別子やユーザの属性を示す情報に基づいて、課題を解決したユーザを特定し、このユーザと付与するポイントとを対応付けてポイント情報記憶部273に記憶させる。すなわち、ポイント情報記憶部273は、健康情報を記憶する記憶部として機能する。 Then, when the
そして、ポイントの付与後は、管理処理実行部251とユーザ端末10の健康アプリ実行部151が連携して、ポイント管理を行う。この管理では、ユーザからの要求に応じてポイントを消費することと引き換えに、ユーザに対して所定の利益を与えるようにする。この所定の利益とは、例えば、ユーザが、ポイントを所望の物品(例えば、何らかの商品)と交換することや、ポイントを情報管理システムSの使用をするための使用料とすることや、ポイントを情報管理システムS以外の他のシステムで利用できるポイント(例えば、電子マネー)に還元することである。 After giving the points, the management
本実施形態では、このようにユーザに対して単に課題を提示するのみでなく、この課題が解決されたか否かを、健康情報に基づいて、客観的に分析することができる。また、課題を解決することができたユーザに対して、所定の対価(ここでは、ポイント)という報酬を付与することで、ユーザによる課題を解決することについてのモチベーションを高めることができる。 In this embodiment, in addition to simply presenting the problem to the user in this way, it is possible to objectively analyze whether or not the problem has been solved based on the health information. In addition, by giving a predetermined compensation (here, points) to a user who has successfully solved a problem, it is possible to increase the user's motivation to solve the problem.
[閲覧装置30の機能的構成]
図5は、閲覧装置30の機能的構成を示すブロック図である。
図5に示すように、閲覧装置30のCPU811においては、閲覧処理実行部351と、情報提示部352と、が機能する。
また、図5に示すように、閲覧装置30の記憶部817においては、健康情報記憶部371と、第2の分析結果記憶部372と、が形成される。
これらの各機能ブロック間では、以下で明示しない場合も含めて、それぞれの機能ブロックの機能を発揮するために必要な情報が、適宜送受される。[Functional Configuration of Viewing Device 30]
FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing the functional configuration of the
As shown in FIG. 5, in the
In addition, as shown in FIG. 5, in the
Information necessary for exhibiting the function of each functional block is appropriately transmitted and received between these functional blocks, even if it is not explicitly stated below.
閲覧処理実行部351は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した健康情報や第2の分析結果を、閲覧者に対して提示するための処理を実行する。提示するための処理とは、例えば、健康情報や第2の分析結果等の各種情報を管理する処理や、これら各種情報を提示するためのユーザインタフェースを含んだ表示画面等を生成する処理や、他の機能ブロックと連携する処理等を含む。 The browsing
閲覧処理実行部351が管理する各種情報は、例えば、健康情報と第2の分析結果を含む。
健康情報は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した健康情報である。閲覧処理実行部351は、閲覧装置30を利用する閲覧者に関連する各ユーザの健康情報を情報管理サーバ20から受信する。そして、閲覧処理実行部351は、受信した健康情報を健康情報記憶部371に記憶させる。すなわち、健康情報記憶部371は、健康情報を記憶する記憶部として機能する。
第2の分析結果は、情報提示部352により受信され、第2の分析結果記憶部372に記憶される。Various types of information managed by the viewing
Health information is health information received from the
The second analysis result is received by the
情報提示部352は、情報管理サーバ20から閲覧者に関連する各ユーザの第2の分析結果を受信する。
そして、情報提示部352は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した健康情報や第2の分析結果を、ユーザに対して提示する。この提示は、例えば、出力部816に含まれるディスプレイへの表示や、スピーカからの音声出力により実現される。また、提示を行うタイミングについては、例えば、第2の分析結果を取得した時点でリアルタイムに行うようにしてもよいし、情報提示部352が実行する処理の動作と連携して行うようにしてもよい。The
Then, the
このように、情報提示部352が実行する処理の動作と連携して提示を行うために、情報提示部352は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した第2の分析結果を、第2の分析結果記憶部372に記憶させる。すなわち、第2の分析結果記憶部372は、第2の分析結果を記憶する記憶部として機能する。 In this way, in order to perform presentation in cooperation with the operation of the process executed by the
[動作]
次に、情報管理システムSに含まれる各装置それぞれにおける、情報管理処理時の動作を説明する。なお、上述したように、情報管理処理とは、ユーザに関する情報(ここでは、健康情報)を適切に管理することにより、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用する一連の処理である。[motion]
Next, the operation of each device included in the information management system S during information management processing will be described. Note that, as described above, the information management process is a series of processes for more effectively utilizing user-related information (here, health information) by appropriately managing user-related information.
[ユーザ端末10の動作]
図6は、ユーザ端末10が実行する、情報管理処理時の動作の流れを示すフローチャートである。
ユーザ端末10における動作は、ユーザ端末10の起動に伴い健康アプリ実行部151が機能すると共に開始される。[Operation of user terminal 10]
FIG. 6 is a flow chart showing the flow of operations during information management processing executed by the
The operation of the
ステップS11において、健康情報取得部152は、健康情報の取得を開始するか否かを判定する。例えば、健康情報取得部152は、健康アプリ実行部151から健康情報の取得を開始するための制御をされた場合に、健康情報の取得を開始する。健康情報の取得を開始する場合は、ステップS11においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS12に進む。一方で、健康情報の取得を開始しない場合は、ステップS11においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS15に進む。
ステップS12において、健康情報取得部152は、健康情報を取得する。In step S11, the health
In step S12, the health
ステップS13において、健康情報取得部152は、健康情報の取得を終了するか否かを判定する。例えば、健康情報取得部152は、健康アプリ実行部151から健康情報の取得を終了するための制御をされた場合に、健康情報の取得を終了する。健康情報の取得を終了する場合は、ステップS13においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS14に進む。一方で、健康情報の取得を終了しない場合は、ステップS13においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS12に戻り、繰り返される。
ステップS14において、健康情報取得部152は、取得した健康情報を、情報管理サーバ20に対して送信する。In step S13, the health
In step S<b>14 , the health
ステップS15において、情報提示部153は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した第1の分析結果を、ユーザに対して提示するか否かを判定する。例えば、情報提示部153は、提示を行うタイミングが到来した場合に、第1の分析結果を提示する。第1の分析結果を提示する場合は、ステップS15においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS16に進む。一方で、第1の分析結果を提示しない場合は、ステップS15においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS17に進む。
ステップS16において、情報提示部153は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した第1の分析結果を、ユーザに対して提示する。In step S15, the
In step S<b>16 , the
ステップS17において、情報提示部153は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した、ユーザが解決すべき、健康を増進するための課題を、ユーザに対して提示するか否かを判定する。例えば、情報提示部153は、提示を行うタイミングが到来した場合に、課題を提示する。課題を提示する場合は、ステップS17においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS18に進む。一方で、課題を提示しない場合は、ステップS17においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS19に進む。
ステップS18において、情報管理サーバ20から受信した課題を、ユーザに対して提示する。In step S<b>17 , the
In step S18, the assignment received from the
ステップS19において、健康アプリ実行部151は、情報管理サーバ20が管理するポイントを消費するか否かを判定する。例えば、健康アプリ実行部151は、健康アプリにおいて、ユーザからのポイントの消費の指示操作を受け付けた場合に、ポイントを消費する。ポイントを消費する場合は、ステップS19においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS20に進む。一方で、ポイントを消費しない場合は、ステップS19においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS21に進む。
ステップS20において、健康アプリ実行部151は、情報管理サーバ20の管理処理実行部251と連携することにより、ポイントを消費すると共に、このポイントと引き換えにユーザに対して何らかの利益を与える。In step S19, the health
In step S<b>20 , the health
ステップS21において、健康アプリ実行部151は、情報管理処理を終了するか否かを判定する。例えば、健康アプリ実行部151は、ユーザからの情報管理処理の終了の指示操作を受け付けた場合に、情報管理処理を終了する。情報管理処理を終了する場合は、ステップS21においてYesと判定され、処理は一度終了する。一方で、情報管理処理を終了しない場合は、ステップS21においてNoと判定され、処理は再度ステップS11から繰り返される。 In step S21, health
[情報管理サーバ20の動作]
図7は、情報管理サーバ20が実行する、情報管理処理時の動作の流れを示すフローチャートである。
情報管理サーバ20における動作は、情報管理サーバ20の起動に伴い管理処理実行部251が機能すると共に開始される。[Operation of information management server 20]
FIG. 7 is a flow chart showing the flow of operations during information management processing executed by the
The operation of the
ステップS31において、管理処理実行部251は、閲覧者に関連するユーザの健康情報を、閲覧装置30に対して送信するか否かを判定する。例えば、管理処理実行部251は、ユーザ端末10から新たな健康情報を受信した場合に、健康情報を閲覧装置30に対して送信する。健康情報を送信する場合は、ステップS31においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS32に進む。一方で、健康情報を送信しない場合は、ステップS31においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS32に進む。
ステップS32において、管理処理実行部251は、閲覧者に関連するユーザの健康情報を、閲覧装置30に対して送信する。In step S<b>31 , the management
In step S<b>32 , the management
ステップS33において、分析部252は、健康情報記憶部271に記憶されている各ユーザの健康情報に基づいて、各ユーザの健康に関する分析を行うか否かを判定する。例えば、分析部252は、ユーザ端末10から新たな健康情報を受信した場合に、分析を行う。分析を行う場合は、ステップS33においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS34に進む。一方で、分析を行わない場合は、ステップS33においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS36に進む。
ステップS34において、分析部252は、各ユーザの健康情報に基づいて、各ユーザの健康に関する分析を行う。In step S<b>33 , the
In step S34, the
ステップS35において、提示制御部253は、第1の分析結果をユーザ端末10のユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、第2の分析結果をユーザ端末10のユーザ以外の、閲覧装置30を利用する閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う。 In step S35, the
ステップS36において、情報提示部254は、各分析結果を、情報管理サーバ20を利用する事業者(例えば、情報管理システムSを運用する事業者)に対して提示するか否かを判定する。例えば、情報提示部254は、提示を行うタイミングが到来した場合に、各分析結果を提示する。各分析結果を提示する場合は、ステップS36においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS37に進む。一方で、各分析結果を提示しない場合は、ステップS36においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS38に進む。
ステップS37において、情報提示部254は、各分析結果を、情報管理サーバ20を利用する事業者に対して提示する。In step S36, the
In step S<b>37 , the
ステップS38において、提示制御部253は、ユーザが解決すべき、健康を増進するための課題をユーザ端末10のユーザに対して提示する制御を行うか否かを判定する。例えば、提示制御部253は、情報処理システムSを運営する事業者の設定等に基づいて、新たな課題が発生した場合に、課題を提示する制御を行う。課題を提示する制御を行う場合は、ステップS38においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS39に進む。一方で、課題を提示する制御を行わない場合は、ステップS38においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS40に進む。
ステップS39において、提示制御部253は、ユーザが解決すべき、健康を増進するための課題をユーザ端末10のユーザに対して提示する制御を行う。In step S<b>38 , the
In step S<b>39 , the
ステップS40において、分析部252は、受信した健康情報に基づいて、ユーザにより課題が解決されたか否かを分析するか否かを判定する。例えば、分析部252は、ユーザ端末10から健康情報を受信した場合に、分析を行う。分析を行う場合は、ステップS40においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS41に進む。一方で、分析を行わない場合は、ステップS40においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS42に進む。
ステップS41において、分析部252は、健康情報に基づいて、ユーザにより課題が解決されたか否かを分析する。In step S40, the
In step S41, the
ステップS42において、課題管理部255は、分析部252の分析に応じてユーザにより課題が解決されたか否かを判定する。課題が解決された場合は、ステップS42においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS43に進む。一方で、課題が解決されていない場合は、ステップS42においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS44に進む。
ステップS43において、課題管理部255は、ユーザに対して所定の対価を付与する。In step S<b>42 , the
In step S43, the
ステップS44において、管理処理実行部251は、ポイントを消費するか否かを判定する。例えば、管理処理実行部251は、ユーザ端末10の健康アプリ実行部151が健康アプリにおいて、ユーザからのポイントの消費の指示操作を受け付けた場合に、ポイントを消費する。ポイントを消費する場合は、ステップS44においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS45に進む。一方で、ポイントを消費しない場合は、ステップS44においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS46に進む。
ステップS45において、管理処理実行部251は、ユーザ端末10の健康アプリ実行部151と連携することにより、ポイントを消費すると共に、このポイントと引き換えにユーザに対して何らかの利益を与える。In step S44, the management
In step S<b>45 , the management
ステップS46において、管理処理実行部251は、情報管理処理を終了するか否かを判定する。例えば、管理処理実行部251は、情報管理サーバ20を利用する事業者(例えば、情報管理システムSを運用する事業者)からの情報管理処理の終了の指示操作を受け付けた場合に、情報管理処理を終了する。情報管理処理を終了する場合は、ステップS46においてYesと判定され、処理は一度終了する。一方で、情報管理処理を終了しない場合は、ステップS46においてNoと判定され、処理は再度ステップS31から繰り返される。 In step S46, the management
[閲覧装置30の動作]
図8は、閲覧装置30が実行する、情報管理処理時の動作の流れを示すフローチャートである。
閲覧装置30における動作は、閲覧装置30の起動に伴い閲覧処理実行部351が機能すると共に開始される。[Operation of viewing device 30]
FIG. 8 is a flow chart showing the flow of operations during information management processing executed by the
The operation of the
ステップS51において、情報提示部352は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した第2の分析結果を、閲覧者に対して提示するか否かを判定する。例えば、情報提示部352は、提示を行うタイミングが到来した場合に、第2の分析結果を提示する。第2の分析結果を提示する場合は、ステップS51においてYesと判定され、処理はステップS52に進む。一方で、第2の分析結果を提示しない場合は、ステップS51においてNoと判定され、処理はステップS53に進む。
ステップS52において、情報提示部352は、情報管理サーバ20から受信した第2の分析結果を、閲覧者に対して提示する。In step S51, the
In step S52, the
ステップS53において、閲覧処理実行部351は、情報管理処理を終了するか否かを判定する。例えば、閲覧処理実行部351は、閲覧者からの情報管理処理の終了の指示操作を受け付けた場合に、情報管理処理を終了する。情報管理処理を終了する場合は、ステップS53においてYesと判定され、処理は一度終了する。一方で、情報管理処理を終了しない場合は、ステップS53においてNoと判定され、処理は再度ステップS51から繰り返される。 In step S53, the browsing
以上説明した、情報管理システムSに含まれる各装置それぞれにおける、情報管理処理時の動作によれば、複数の提示先において、それぞれ異なる分析結果が提示される。そのため、ユーザや閲覧者は、ユーザや閲覧者によってそれぞれ異なる、各ユーザや閲覧者にとって好適な分析結果を閲覧することができる。 According to the operation during information management processing in each device included in the information management system S described above, different analysis results are presented to a plurality of presentation destinations. Therefore, users and viewers can view analysis results suitable for each user and viewer, which are different for each user and viewer.
これにより、ユーザや閲覧者は、ユーザの健康状態を適切に把握し、例えば、ユーザが病状の発生する前の段階(すなわち、未病の段階)にあることを早期に発見することができる。また、ユーザの日々の健康状態の変化を継続的に観察することができる。
したがって、本発明の実施形態に係る情報管理システムSによれば、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用することができる。As a result, the user and viewers can appropriately grasp the user's health condition, and can, for example, quickly discover that the user is in a pre-disease stage (i.e., pre-disease stage). In addition, it is possible to continuously observe changes in the user's daily health condition.
Therefore, according to the information management system S according to the embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to further utilize the information regarding the user.
[表示例]
次に、情報管理システムSにおいて表示される、各種情報及びユーザインタフェースを含んだ表示画面の例について説明する。
図9は、第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果の提示時(図6のステップS18や、図8のステップS52に相当)に、ユーザ端末10や閲覧装置30において表示される分析結果提示画面60の一例を示す模式図である。図9に示すように、分析結果提示画面60は、書誌情報表示領域61と、画像表示領域62と、テキスト表示領域63を、表示領域として含む。[Display example]
Next, an example of a display screen including various information and a user interface displayed in the information management system S will be described.
FIG. 9 shows an analysis result presentation displayed on the
書誌情報表示領域61には、分析結果に対応するユーザの氏名等の属性や、健康情報の測定日といった書誌的な事項が表示される。
画像表示領域62には、第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果に対応する値や所定の指標に基づいた分類が、単にテキストの形式で表示されるのみならず、棒グラフや円グラフといった画像の形式でも表示される。これにより、ユーザや閲覧者は、各分析結果をより直感的に把握することができる。なお、図中でハッチングを用いて表現しているように、グラフ等において、情報ごとに適宜色分けをしたりすることにより、より直感的な把握を可能とすることができる。In the bibliographic
In the
テキスト表示領域63には、第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果の解説や、分析結果を踏まえたアドバイスがテキストの形式で表示される。この場合、分析結果の解説は、例えば、値やグラフから読み取れる内容を、より具体的に表現したものである。例えば、ユーザと同年代の平均値との比較や、そのような健康状態となっている原因と想定される生活習慣等である。また、分析結果を踏まえたアドバイスは、例えば、ユーザが取り入れやすいような新たな生活習慣の提案や、お勧めできる栄養補助食品やサプリメント等の提案である。これにより、ユーザや閲覧者は、値やグラフから読み取れる内容を、より具体的に把握することができると共に、ユーザの健康状態に応じたより健康を増進するための方法等を把握することができる。 In the
また、例えば、第2の分析結果の閲覧者が、医療従事者であるような場合には、この閲覧者がユーザに対して健康情報に基づいた健康に関する指導を行う場合がある。あるいは、第2の分析結果の閲覧者が、医療従事者でなくとも、ユーザに対して健康情報に基づいた健康に関する指導を行う部署の人間や、所定の健康アドバイザー等であることもある。そこで、このような、健康情報に基づいた健康に関する指導を支援するための情報が、第2の分析結果に含まれるようにしてもよい。例えば、指導を行う場合に説明すべき事項や、病院でのより精密な検査を促す説明や、第1の分析結果における分析結果よりも医学的に高度な分析結果等に対応するテキストが、第2の分析結果としてテキスト表示領域63に表示されるようにするとよい。
これにより、第2の分析結果の閲覧者(例えば、ユーザの所属する企業や団体や自治体や、ユーザを診察等する医療従事者)による、ユーザへの健康に関する指導を支援することができる。Also, for example, if the viewer of the second analysis result is a medical professional, the viewer may provide health-related guidance to the user based on the health information. Alternatively, the viewer of the second analysis result may not be a medical professional, but may be a person in a department that provides health-related guidance to the user based on health information, a predetermined health advisor, or the like. Therefore, the second analysis result may include information for supporting health guidance based on such health information. For example, texts that correspond to items that should be explained when providing guidance, explanations that encourage more detailed examinations at hospitals, and analysis results that are medically more advanced than the analysis results in the first analysis result, etc. It is preferable that the analysis result of 2 is displayed in the
Accordingly, it is possible to support health-related guidance to users by viewers of the second analysis results (for example, companies, organizations, and local governments to which users belong, and medical professionals who examine users, etc.).
図10は、第1の分析結果や第2の分析結果の提示時(図6のステップS16や、図8のステップS52に相当)に、ユーザ端末10や閲覧装置30において表示される分析結果提示画面の、他の一例である分析結果提示画面70を示す模式図である。図10に示すように、分析結果提示画面70は、書誌情報表示領域71と、画像表示領域72と、テキスト表示領域73を、表示領域として含む。これら各表示領域の概略は、上述した、書誌情報表示領域61と、画像表示領域62と、テキスト表示領域63同等なので、重複する説明は省略する。 FIG. 10 shows an analysis result presentation displayed on the
分析結果提示画面70は、分析結果提示画面60を表示した後に、新たに取得された健康情報に基づいて分析された分析結果を表示する表示例であり、健康情報の変化に応じた分析結果の変化を特に強調して示すものである。例えば、画像表示領域72の動脈血管弾性度の値が、画像表示領域62にて示した値「69」から「98」に変化したことを、これとは異なる態様(ここでは、異なる文字サイズ)で強調して示している。またこれに対応して、棒グラフにおいても、「69」を示す棒グラフに重ねて、これとは異なる態様(ここでは、異なるハッチング)で「98」を示す棒グラフを強調して示している。また、他の分析結果の値等においても同様の変化したことを強調して示している。
このように、分析結果の変化を強調して示すことにより、ユーザや閲覧者は、前回の健康情報取得時から、今回の健康情報取得時において、どのように健康状態が変化しているのかを、容易に把握することができる。そのため、健康状態の変化を継続的に観察することができる。The analysis
In this way, by emphasizing the changes in the analysis results, users and viewers can see how their health conditions have changed since the last health information was obtained. , can be easily grasped. Therefore, changes in health conditions can be continuously observed.
この場合に、例えば、健康情報取得部152がユーザによる所定の行為の前後それぞれにおいて、健康情報を取得し、分析部252が所定の行為の前後それぞれにおいて取得された健康情報の変化に基づいて分析を行うようにしてもよい。この所定の行為は特に限定されず、例えば、ユーザが行う運動やストレッチ等の動作であってもよいし、ユーザに対して行われる、手技や医療機器を用いた施術や治療であってもよい。
これにより、これら所定の行為が、ユーザにどのような効果をもたらすのかを、健康情報の分析結果という客観的な指標でエビデンスとして示すことができる。したがって、例えば、所定の手技を用いた施術の有用性を、客観性をもって宣伝広告等することが可能となる。In this case, for example, the health
As a result, it is possible to show what kind of effect these predetermined actions have on the user as evidence in the form of an objective index, which is the analysis result of the health information. Therefore, for example, it is possible to objectively advertise the usefulness of a treatment using a predetermined procedure.
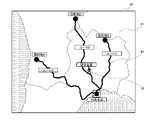
図11は、ユーザが解決すべき、健康を増進するための課題の提示時(図6のステップS18に相当)に、ユーザ端末10において表示される課題提示画面80の一例を示す模式図である。図11に示すように、課題提示画面80は、地図表示領域81を表示領域として含む。本例では、課題として、ユーザが徒歩での移動を行うことが提示される場面を想定する。 FIG. 11 is a schematic diagram showing an example of a
地図表示領域81には、或る地域の地図が表示される。また、地図表示領域81には、地図上に、ルート表示82と、現在位置アイコン83と、が表示される。
ルート表示82は、ユーザが移動すべきルートに対応するものであり、例えば、図中にルートA、ルートB、ルートCとして示すように、複数ルートが表示されてもよい。この場合、ユーザは、自身が移動するルートを、自身の好みに応じて選択することができる。A map of a certain area is displayed in the
The
現在位置アイコン83は、課題が提示されてから、ユーザが出発点から目的地に向かってルート上を徒歩で移動した距離を示すものである。移動した距離は、分析部252による健康情報の分析結果に基づいて、リアルタイムに算出することができる。
このようにして、課題を提示することにより、ユーザは自身が移動することにより、実際に地図上のルートを移動している感覚を得ることができるので、移動に対する興味を抱くことができる。したがって、単にテキストで課題を提示するような場合と比べて、ユーザによる課題を解決することについてのモチベーションを高めることができる。この場合に、よりユーザに興味を抱かせるために、地図に対応する地域を実際に存在する地域として、ルートを実際に存在するハイキングロード等にしてもよい。ほかにも、よりユーザに興味を抱かせるために、現在位置に対応する、ハイキングロード上の画像等を併せて表示するようにしてもよい。The
By presenting the tasks in this way, the user can feel that he or she is actually moving along the route on the map, and thus can develop an interest in movement. Therefore, it is possible to increase the user's motivation to solve the problem, compared to simply presenting the problem in text form. In this case, in order to make the user more interested, the area corresponding to the map may be an area that actually exists, and the route may be a hiking road that actually exists. In addition, in order to make the user more interested, an image of the hiking road corresponding to the current position may be displayed together.
図12は、ユーザが解決すべき、健康を増進するための課題の提示時(図6のステップS18に相当)に、ユーザ端末10において表示される課題提示画面の、他の一例である課題提示画面90を示す模式図である。図12に示すように、課題提示画面90は、背景表示領域91を表示領域として含む。本例では、課題として、ユーザがダンスを行うことが提示される場面を想定する。 FIG. 12 shows another example of a task presentation screen displayed on the
背景表示領域91には、キャラクタ画像92と、テキスト93と、それらの背景となる背景画像と、が表示される。
キャラクタ画像92は、例えば、人型の画像であり、課題提示画面90の表示と共に出力される音楽に合わせてダンスを行う。例えば、図中(A)から図中(B)のように、ダンスに対応して体を動かすような表示がなされる。
テキスト93は、出力される音楽に対応する歌詞や、ダンスの解説等に対応したテキストである。In the
The
The
このようにして、課題を提示することにより、ユーザは、このキャラクタ画像92の動きを模して、音楽に合わせたダンスを行うことができる。これにより、ユーザは、ダンスの振り付けを予め覚える必要なく、容易にダンスを行うことができるので、ダンスに対する興味を抱くことができる。したがって、図11のような表示と同様に、単にテキストで課題を提示するような場合と比べて、ユーザによる課題を解決することについてのモチベーションを高めることができる。この場合に、よりユーザに興味を抱かせるために、ユーザが自身の好みに合わせて、ダンスに対応する曲を選択できるようにしてもよい。 By presenting the task in this way, the user can imitate the movement of the
なお、図9から図11を参照して説明した表示はあくまで一例であり、本実施形態における表示は、これらに限定されない。 The displays described with reference to FIGS. 9 to 11 are merely examples, and the displays in the present embodiment are not limited to these.
[変形例]
本発明は、上述の実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の目的を達成できる範囲での変形、改良等は本発明に含まれるものである。この場合に、上述の実施形態及びその変形、改良等は、本明細書等に記載された発明の範囲及び要旨に含まれると共に、特許請求の範囲に記載された発明とその均等の範囲に含まれる。
一例として、以上説明した本発明の実施形態を、以下のようにして変形してもよい。[Modification]
The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, but includes modifications, improvements, etc. within the scope of achieving the object of the present invention. In this case, the above-described embodiments and their modifications, improvements, etc. are included in the scope and gist of the invention described in this specification, etc., and are included in the scope of the invention described in the claims and their equivalents. be
As an example, the embodiments of the present invention described above may be modified as follows.
[変形例1]
上述した実施形態における、情報管理システムSの構成や運用方法は一例に過ぎず、これに限らない。例えば、上述した実施形態では、情報管理サーバ20の機能を単体の装置で実現することを想定していたが、これに限らず複数の装置(例えば、クラウドサーバ)が協働して情報管理サーバ20の機能を実現してもよい。他にも、例えば、上述した実施形態では、情報管理システムSを運営する事業者が情報管理サーバ20を利用し、この事業者とは異なる閲覧者が閲覧装置30を利用することを想定していたが、これに限らず、この事業者と閲覧者が同一の主体であってもよい。例えば、或る企業が情報管理システムSを運営し、自社の社員をユーザ端末10のユーザとしてもよい。[Modification 1]
The configuration and operation method of the information management system S in the above-described embodiment are merely examples, and are not limited to these. For example, in the above-described embodiment, it was assumed that the functions of the
[変形例2]
上述した実施形態では、各ユーザから健康情報を取得し、各ユーザそれぞれについて健康情報の分析を行っていた。すなわち、一人のユーザを単位として分析を行っていた。これに限らず、複数のユーザから取得した健康情報に基づいて、複数のユーザを、1つ又は複数の母集団とした分析を行うようにしてもよい。[Modification 2]
In the above-described embodiment, health information is obtained from each user, and health information is analyzed for each user. That is, the analysis was performed with one user as a unit. Not limited to this, analysis may be performed with a plurality of users as one or a plurality of populations based on health information acquired from a plurality of users.
例えば、或る企業それぞれを単位として分析を行うようにする。この場合、例えば、或る企業に所属する複数のユーザの健康情報が母集団となり、母集団での健康情報の平均値や分布や偏差等を分析することが可能となる。これにより、母集団となった複数のユーザ全体での(すなわち、或る企業に所属する社員全員での)健康状態の傾向等を把握することができる。 For example, an analysis is performed with each company as a unit. In this case, for example, the health information of a plurality of users belonging to a certain company becomes a population, and the average value, distribution, deviation, etc. of the health information in the population can be analyzed. As a result, it is possible to comprehend trends in the state of health of the entire population of users (that is, of all employees belonging to a certain company).
また、このような分析を例えば、複数の企業それぞれについて行うようにしてもよい。すなわち、母集団を複数としてそれぞれ分析を行うようにしてもよい。これにより、各企業間での健康状態の比較等を行うことできる。
このように、本変形例によれば、一人のユーザに関する分析のみならず、例えば、ユーザの所属する企業や団体や自治体を単位とした分析や、これら企業や団体や自治体ごとの比較といった分析を行うことができる。したがって、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用することができる。Also, such an analysis may be performed for each of a plurality of companies, for example. That is, analysis may be performed for each of a plurality of populations. As a result, it is possible to compare health conditions between companies.
As described above, according to this modification, not only the analysis of one user but also the analysis of the company, organization, or municipality to which the user belongs, or the comparison of each company, organization, or municipality can be performed. It can be carried out. Therefore, the information about the user can be used more effectively.
[変形例3]
上述した実施形態では、何れのユーザの第2の分析結果を、何れの閲覧者に対して提示するのか(すなわち、何れの閲覧者の閲覧装置30に第2の分析結果を送信するのか)が、予め定まっていた。これに限らず、所定の条件に応じて、第2の分析結果を提示する閲覧者(すなわち、第2の分析結果の送信先となる閲覧装置30)を異ならせるようにしてもよい。[Modification 3]
In the above-described embodiment, which user's second analysis result is presented to which viewer (that is, to which viewer's
例えば、第2の分析結果の内容に応じて、第2の分析結果を提示する閲覧者を異ならせるようにする。この場合、例えば、第2の分析結果に対応するユーザの健康状態が通常であり、健康である場合には、例えば、このユーザが所属する企業を閲覧者として第2の分析結果を提示する。一方で、第2の分析結果に対応するユーザの健康状態に異常が生じており、何らかの症状が疑われる場合には、このユーザが所属する企業を閲覧者とするのみならず、さらに診察等の支援を行うために医療従事者も閲覧者として第2の分析結果を提示する。
これにより、第2の分析結果を適切な閲覧者に対して提示することができる。したがって、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用することができる。For example, depending on the contents of the second analysis result, different viewers are presented with the second analysis result. In this case, for example, if the health condition of the user corresponding to the second analysis result is normal and healthy, the second analysis result is presented with the company to which the user belongs as a viewer. On the other hand, if the health condition of the user corresponding to the second analysis result is abnormal and some symptom is suspected, not only the company to which this user belongs is regarded as the viewer, but also medical examination or the like is performed. A second analysis result is also presented by a medical professional as a viewer to provide assistance.
Thereby, the second analysis result can be presented to appropriate viewers. Therefore, the information about the user can be used more effectively.
なお、同様の考えで、第1の分析結果を提示するユーザ(すなわち、第1の分析結果の送信先となるユーザ端末10)を異ならせるようにしてもよい。例えば、健康情報の取得元となったユーザと関係の深い他のユーザ(例えば、家族)に対して、第1の分析結果を、送信するようにしてもよい。他にも、例えば、分析結果の内容に応じて、第1の分析結果をユーザに提示するが、第2の分析結果の閲覧者への提示は行わないようにしてもよい。また、第2の分析結果を閲覧者に提示するが、第1の分析結果のユーザへの提示は行わないようにしてもよい。 Based on the same idea, the user who presents the first analysis result (that is, the
[構成例]
以上のように、本実施形態に係る情報管理システムSは、ユーザ端末10と、当該ユーザ端末10と通信可能に接続された情報管理サーバ20と、を備える。また、ユーザ端末10は、健康情報取得部152、を備える。さらに、情報管理サーバ20は、分析部252と、提示制御部253と、を備える。
健康情報取得部152は、ユーザの健康に関する情報である健康情報を、ユーザから取得する。
分析部252は、健康情報取得部152が取得した健康情報に基づいて、ユーザの健康に関する分析を行う。
提示制御部253は、分析部252による第1の分析結果をユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、分析部252による第1の分析結果とは少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果である第2の分析結果をユーザ以外の閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う。[Configuration example]
As described above, the information management system S according to this embodiment includes the
The health
The
The
このように、情報管理システムSによれば、複数の提示先において、それぞれ異なる分析結果が提示される。そのため、ユーザや閲覧者は、ユーザや閲覧者によってそれぞれ異なる、各ユーザや閲覧者にとって好適な分析結果を閲覧することができる。
これにより、ユーザや閲覧者は、ユーザの健康状態を適切に把握し、例えば、ユーザが病状の発生する前の段階(すなわち、未病の段階)にあることを早期に発見することができる。また、ユーザの日々の健康状態の変化を継続的に観察することができる。
したがって、本発明の実施形態に係る情報管理システムSによれば、ユーザに関する情報を、より一層活用することができる。Thus, according to the information management system S, different analysis results are presented to a plurality of presentation destinations. Therefore, users and viewers can view analysis results suitable for each user and viewer, which are different for each user and viewer.
As a result, the user and viewers can appropriately grasp the user's health condition, and can, for example, quickly discover that the user is in a pre-disease stage (i.e., pre-disease stage). In addition, it is possible to continuously observe changes in the user's daily health condition.
Therefore, according to the information management system S according to the embodiment of the present invention, it is possible to further utilize the information regarding the user.
提示制御部253は、ユーザ端末10に第1の分析結果を提示させることにより、ユーザに対する第1の分析結果を提示する制御を実現すると共に、ユーザ端末10以外の他の装置に第2の分析結果を提示させることにより、閲覧者に対する第2の分析結果を提示する制御を実現する。
これにより、ユーザは、ユーザ端末10を健康情報の取得に利用できるのみならず、自身にとって好適な分析結果である第1の分析結果を閲覧することができる。一方で、閲覧者は、ユーザが利用するユーザ端末10以外の装置において、自身にとって好適な分析結果である第2の分析結果を閲覧することができる。By causing the
Thereby, the user can not only use the
分析部252は、閲覧者からユーザに対して行われる、健康情報に基づいた健康に関する指導を支援する情報を第2の分析結果に含ませる。
これにより、閲覧者(例えば、ユーザの所属する企業や団体や自治体や、ユーザを診察等する医療従事者)による、ユーザへの健康に関する指導を支援することができる。The
Accordingly, it is possible to assist health-related guidance to users by viewers (for example, companies, organizations, and local governments to which users belong, and medical professionals who examine users, etc.).
健康情報取得部152は、ユーザによる所定の行為の前後それぞれにおいて、健康情報を取得する。
分析部252は、所定の行為の前後それぞれにおいて取得された健康情報の変化に基づいて分析を行う。
これにより、所定の行為(例えば、ユーザによる所定の動作や、ユーザに対して行われる、手技や医療機器を用いた施術や治療)が、ユーザにどのような効果をもたらすのかを、健康情報の分析結果という客観的な指標でエビデンスとして示すことができる。The health
The
As a result, the effect of a predetermined action (for example, a predetermined action by the user, or a procedure or treatment using a medical device performed on the user) on the user can be displayed in the health information. It can be shown as evidence in the objective index of the analysis result.
情報管理サーバ20は、課題管理部255をさらに備える。
提示制御部253は、ユーザが解決すべき、健康を増進するための課題をユーザに対して提示する制御を行う。
分析部252は、課題が提示された後に健康情報取得部152が取得した健康情報に基づいて、ユーザによって課題が解決されたか否かを分析する。
課題管理部255は、課題が解決されたか否かに応じて、ユーザに対して所定の利益と引き換えることが可能な対価を付与する。
これにより、ユーザに対して単に課題を提示するのみでなく、この課題が解決されたか否かを、健康情報に基づいて、客観的に分析することができる。また、課題を解決することができたユーザに対して、所定の対価という報酬を付与することで、ユーザによる課題を解決することについてのモチベーションを高めることができる。The
The
The
The
Thereby, it is possible not only to simply present the problem to the user, but also to objectively analyze whether or not the problem has been solved based on the health information. In addition, by giving a predetermined compensation as a reward to the user who has successfully solved the problem, it is possible to increase the user's motivation to solve the problem.
分析部252は、複数のユーザから取得した健康情報に基づいて、複数のユーザを、1つ又は複数の母集団とした分析を行う。
これにより、一人のユーザに関する分析のみならず、例えば、ユーザの所属する企業や団体や自治体を単位とした分析や、これら企業や団体や自治体ごとの比較といった分析を行うことができる。The
As a result, it is possible not only to analyze one user, but also to perform analysis for each company, organization, or local government to which the user belongs, or for comparison of each company, organization, or local government.
提示制御部253は、分析部252による分析結果に基づいて、当該分析結果の提示先を異ならせる。
これにより、分析結果の内容に応じた提示先に対して提示を行うことができる。例えば、通常の健康結果であればユーザの所属する企業等にのみ提示をするが、治療等の必要性が生じるような健康結果であれば医療従事者に対しても提示するようなことができる。The
Thereby, presentation can be performed to a presentation destination according to the content of the analysis result. For example, if it is a normal health result, it is presented only to the user's company, etc., but if it is a health result that requires treatment, etc., it is possible to present it to medical professionals. .
上述した一連の処理は、ハードウェアにより実行させることもできるし、ソフトウェアにより実行させることもできる。
換言すると、上述の実施形態における機能的構成は例示に過ぎず、特に限定されない。すなわち、上述した一連の処理を全体として実行できる機能が情報管理システムSを構成するいずれかのコンピュータに備えられていれば足り、この機能を実現するためにどのような機能ブロックを用いるのかは特に示した例に限定されない。
また、1つの機能ブロックは、ハードウェア単体で構成してもよいし、ソフトウェア単体で構成してもよいし、それらの組み合わせで構成してもよい。The series of processes described above can be executed by hardware or by software.
In other words, the functional configurations in the above-described embodiments are merely examples and are not particularly limited. That is, it is sufficient that any one of the computers constituting the information management system S has a function capable of executing the above-described series of processes as a whole, and what kind of functional block is used to realize this function does not particularly matter. It is not limited to the examples shown.
Also, one functional block may be composed of hardware alone, software alone, or a combination thereof.
また、上述した一連の処理を実行するためのプログラムを含む記録媒体は、ユーザにプログラムを提供するために装置本体とは別に配布されるリムーバブルメディア(例えば、リムーバブルメディア831)により構成されるだけでなく、装置本体に予め組み込まれた状態でユーザに提供される記録媒体(例えば、ROM812や記憶部817)等で構成される。 Also, the recording medium containing the program for executing the series of processes described above is simply configured by a removable medium (for example, removable medium 831) that is distributed separately from the main body of the apparatus in order to provide the program to the user. Instead, it consists of a recording medium (for example, the
また、上述した実施形態に記載された効果は、本発明から生じる最も好適な効果を列挙したに過ぎず、本発明による効果は、本実施形態に記載されたものに限定されるものではない。 Moreover, the effects described in the above-described embodiments are merely enumerations of the most suitable effects produced by the present invention, and the effects of the present invention are not limited to those described in the present embodiment.
10 ユーザ端末、20 情報管理サーバ、30 閲覧装置、151 健康アプリ実行部、152 健康情報取得部、153,254,352 情報提示部、171,271,371 分析結果記憶部、172 第1の分析結果記憶部、251 管理処理実行部、252 分析部、253 提示制御部、255 課題管理部、272 各分析結果記憶部、273 ポイント情報記憶部、351 閲覧処理実行部、472 第2の分析結果記憶部、800 情報処理装置、811 CPU、812 ROM、813 RAM、814 バス、815 入力部、816 出力部、817 記憶部、818 通信部、819 ドライブ、820 センサ部、831 リムーバブルメディア、N ネットワーク、S 情報管理システム10 user terminal, 20 information management server, 30 browsing device, 151 health application execution unit, 152 health information acquisition unit, 153, 254, 352 information presentation unit, 171, 271, 371 analysis result storage unit, 172 first analysis
Claims (10)
Translated fromJapanese前記端末は、
ユーザの健康に関する情報である健康情報を、前記ユーザから取得する情報取得手段、
を備え、
前記サーバは、
前記情報取得手段が取得した前記健康情報に基づいて、前記ユーザの健康に関する分析を行う分析手段と、
前記分析手段による第1の分析結果を前記ユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、前記分析手段による前記第1の分析結果とは少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果である第2の分析結果を前記ユーザ以外の閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う提示制御手段と、
を備える、
ことを特徴とする情報管理システム。An information management system comprising a terminal and a server communicably connected to the terminal,
The terminal is
Information acquiring means for acquiring health information, which is information about the user's health, from the user;
with
The server is
analysis means for analyzing the user's health based on the health information acquired by the information acquisition means;
controlling presentation of a first analysis result by the analysis means to the user, and presenting a second analysis result, which is an analysis result at least partially different from the first analysis result by the analysis means, to the Presentation control means for controlling presentation to viewers other than the user;
comprising
An information management system characterized by:
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の情報管理システム。The presentation control means realizes control for presenting the first analysis result to the user by causing the terminal to present the first analysis result, and presents the second analysis result to a device other than the terminal. Realizing the control of presenting the second analysis result to the viewer by presenting the analysis result of
The information management system according to claim 1, characterized by:
ことを特徴とする請求項1又は2に記載の情報管理システム。The analysis means includes, in the second analysis result, information that supports health-related guidance given by the viewer to the user based on the health information.
3. The information management system according to claim 1 or 2, characterized by:
前記分析手段は、前記所定の行為の前後それぞれにおいて取得された健康情報の変化に基づいて分析を行う、
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至3の何れか1項に記載の情報管理システム。The information acquisition means acquires health information before and after a predetermined action by the user,
The analysis means analyzes based on changes in health information acquired before and after the predetermined action, respectively.
4. The information management system according to any one of claims 1 to 3, characterized by:
前記分析手段は、前記課題が提示された後に前記情報取得手段が取得した前記健康情報に基づいて、前記ユーザによって前記課題が解決されたか否かを分析し、
前記課題が解決されたか否かに応じて、前記ユーザに対して所定の利益と引き換えることが可能な対価を付与する課題管理手段をさらに備える、
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至4の何れか1項に記載の情報管理システム。The presentation control means performs control to present to the user a problem to be solved by the user for promoting health,
The analysis means analyzes whether the task has been solved by the user based on the health information acquired by the information acquisition means after the task has been presented;
Further comprising task management means for giving consideration that can be exchanged for a predetermined profit to the user depending on whether the task is solved,
5. The information management system according to any one of claims 1 to 4, characterized by:
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至5の何れか1項に記載の情報管理システム。The analysis means performs analysis based on the health information acquired from the plurality of users, with the plurality of users as one or more populations.
6. The information management system according to any one of claims 1 to 5, characterized by:
ことを特徴とする請求項1乃至6の何れか1項に記載の情報管理システム。The presentation control means changes the presentation destination of the analysis result based on the analysis result by the analysis means;
7. The information management system according to any one of claims 1 to 6, characterized by:
前記端末が、ユーザの健康に関する情報である健康情報を、前記ユーザから取得する情報取得ステップと、
前記サーバが、前記情報取得ステップにて取得した前記健康情報に基づいて、前記ユーザの健康に関する分析を行う分析ステップと、
前記サーバが、前記分析ステップによる第1の分析結果を前記ユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、前記分析ステップによる前記第1の分析結果とは少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果である第2の分析結果を前記ユーザ以外の閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う提示制御ステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする情報管理方法。An information management method performed by an information management system comprising a terminal and a server communicably connected to the terminal,
an information acquisition step in which the terminal acquires, from the user, health information, which is information relating to the user's health;
an analysis step in which the server analyzes the user's health based on the health information acquired in the information acquisition step;
The server performs control to present a first analysis result from the analysis step to the user, and presents a second analysis result that is at least partially different from the first analysis result from the analysis step. a presentation control step of performing control to present the analysis result to a viewer other than the user;
An information management method comprising:
前記端末がユーザから取得した前記ユーザの健康に関する情報である健康情報に基づいて、前記ユーザの健康に関する分析を行う分析手段と、
前記分析手段による第1の分析結果を前記ユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、前記分析手段による前記第1の分析結果とは少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果である第2の分析結果を前記ユーザ以外の閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う提示制御手段と、
を備えることを特徴とするサーバ。A server communicably connected to a terminal,
analysis means for analyzing the user's health based on health information, which is information about the user's health acquired from the user by the terminal;
controlling presentation of a first analysis result by the analysis means to the user, and presenting a second analysis result, which is an analysis result at least partially different from the first analysis result by the analysis means, to the Presentation control means for controlling presentation to viewers other than the user;
A server characterized by comprising:
前記端末がユーザから取得した前記ユーザの健康に関する情報である健康情報に基づいて、前記ユーザの健康に関する分析を行う分析機能と、
前記分析機能による第1の分析結果を前記ユーザに対して提示する制御を行うと共に、前記分析機能による前記第1の分析結果とは少なくとも一部が異なる分析結果である第2の分析結果を前記ユーザ以外の閲覧者に対して提示する制御を行う提示制御機能と、
実現させることを特徴とするプログラム。on a computer that is communicatively connected to the terminal,
an analysis function that analyzes the user's health based on health information, which is information about the user's health acquired by the terminal from the user;
controlling presentation of a first analysis result by the analysis function to the user, and presenting a second analysis result that is an analysis result at least partially different from the first analysis result by the analysis function; a presentation control function for controlling presentation to viewers other than the user;
A program characterized by realizing
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021009925AJP2022113593A (en) | 2021-01-25 | 2021-01-25 | Information management system, information management method, server, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021009925AJP2022113593A (en) | 2021-01-25 | 2021-01-25 | Information management system, information management method, server, and program |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2022113593Atrue JP2022113593A (en) | 2022-08-04 |
Family
ID=82658118
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021009925APendingJP2022113593A (en) | 2021-01-25 | 2021-01-25 | Information management system, information management method, server, and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2022113593A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2025049012A (en)* | 2023-09-21 | 2025-04-03 | ソフトバンクグループ株式会社 | system |
| JP2025049010A (en)* | 2023-09-21 | 2025-04-03 | ソフトバンクグループ株式会社 | system |
| WO2025105350A1 (en)* | 2023-11-17 | 2025-05-22 | Flora株式会社 | Analysis system, analysis method, and computer program |
- 2021
- 2021-01-25JPJP2021009925Apatent/JP2022113593A/enactivePending
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2025049012A (en)* | 2023-09-21 | 2025-04-03 | ソフトバンクグループ株式会社 | system |
| JP2025049010A (en)* | 2023-09-21 | 2025-04-03 | ソフトバンクグループ株式会社 | system |
| WO2025105350A1 (en)* | 2023-11-17 | 2025-05-22 | Flora株式会社 | Analysis system, analysis method, and computer program |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102427508B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for mental healthcare based on artificial intelligence | |
| Califf | Future of personalized cardiovascular medicine: JACC state-of-the-art review | |
| JP2022113593A (en) | Information management system, information management method, server, and program | |
| US20180211730A1 (en) | Health information (data) medical collection, processing and feedback continuum systems and methods | |
| Colucci et al. | A “matter of communication”: A new classification to compare and evaluate telehealth and telemedicine interventions and understand their effectiveness as a communication process | |
| Feller et al. | Judgment and decision-making in clinical dentistry | |
| Aboelmaged et al. | Mobile apps use for wellness and fitness and university students’ subjective wellbeing | |
| Adami et al. | Monitoring health parameters of elders to support independent living and improve their quality of life | |
| EP4610989A1 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method, and program | |
| JP6342095B1 (en) | Health management system, health management method, program, and recording medium | |
| Jimison et al. | The role of human computer interaction in consumer health applications: current state, challenges and future | |
| Connor et al. | Reflections on vital sign measurement in nursing practice | |
| JP6450986B1 (en) | HEALTHCARE SUPPORT SERVER, HEALTHCARE SUPPORT METHOD, AND COMPUTER-READABLE PROGRAM | |
| JP2020194346A (en) | Medical institution selection supporting device | |
| JP7393518B2 (en) | Teacher data collection device, teacher data collection method and recording medium | |
| Chousiadas et al. | Advancing quantified-self applications utilizing visual data analytics and the internet of things | |
| Flores-Vaquero et al. | A product-service system approach to telehealth application design | |
| JP2019212263A (en) | Information processor and program | |
| Singh et al. | Enhancing patient well-being in healthcare through the integration of IoT and neural network | |
| Canally et al. | Using integrated bio-physiotherapy informatics in home health-care settings: A qualitative analysis of a point-of-care decision support system | |
| Aniko et al. | Use of the Usability Scale System as a Monitoring Dashboard Test for Inpatient Covid-19 Patients in Hospitals | |
| Tesanovic et al. | eHealth personalization in the next generation RPM systems | |
| Jiménez Garcia et al. | An integrated patient-centric approach for situated research on total hip replacement: ESTHER | |
| Nwagwu et al. | Use of mobile technologies for care of internal medicine clients in Nigeria’s premier teaching hospital | |
| Almansour et al. | A quantitative and qualitative exploration of critical factors in the IAI-CGM framework: the perspective of Saudi patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus |