JP2021089219A - Image inspection system and image inspection method - Google Patents
Image inspection system and image inspection methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2021089219A JP2021089219AJP2019220123AJP2019220123AJP2021089219AJP 2021089219 AJP2021089219 AJP 2021089219AJP 2019220123 AJP2019220123 AJP 2019220123AJP 2019220123 AJP2019220123 AJP 2019220123AJP 2021089219 AJP2021089219 AJP 2021089219A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- artificial
- inspection
- actual
- defective product
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000007689inspectionMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription214
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription51
- 238000010801machine learningMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription33
- 230000002950deficientEffects0.000claimsdescription338
- 238000003860storageMethods0.000claimsdescription88
- 238000013528artificial neural networkMethods0.000claimsdescription24
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000002194synthesizing effectEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description24
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description16
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description11
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000description3
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000011179visual inspectionMethods0.000description2
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000004065semiconductorSubstances0.000description1
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Investigating Materials By The Use Of Optical Means Adapted For Particular Applications (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、検査対象物が良品であるか否かを判定する画像処理技術に関する。 The present invention relates to an image processing technique for determining whether or not an inspection object is a non-defective product.
従来、検査対象物が良品であるか否かを判定する画像処理技術において、検査対象物を撮影して得られた検査画像と、予め準備された検査対象物の良品の画像とを比較することで欠点などを検出し、その検出結果にもとづき良品であるか否かの判定が行われている。
この際、検査対象物である製品が良品であると判定し得る良品の範囲には、ある程度の幅が存在するために、この良品の範囲を網羅する様々な良品画像を準備して、これらを検査画像と比較することが必要であった。Conventionally, in an image processing technique for determining whether or not an inspection object is a non-defective product, an inspection image obtained by photographing the inspection object is compared with an image of a non-defective product of the inspection object prepared in advance. Detects defects and the like, and determines whether or not the product is a good product based on the detection result.
At this time, since there is a certain range in the range of non-defective products that can be determined that the product to be inspected is a non-defective product, various non-defective product images covering the range of this non-defective product are prepared and these are used. It was necessary to compare with the inspection image.
ところが、製品には、その製造工程における様々な要因によってバラツキが生じ得るため、製品の種類ごとに良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を準備することは、非常に困難であるという問題があった。
また、このような良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を準備できても、製品のデザインが変更されると再度良品画像を準備する必要があり、良品画像の準備は、大変煩雑な作業であった。However, there is a problem that it is very difficult to prepare a non-defective image that covers the range of non-defective products for each type of product because the products may vary due to various factors in the manufacturing process.
Moreover, even if a non-defective image that covers the range of such a non-defective product can be prepared, it is necessary to prepare the non-defective image again when the design of the product is changed, and the preparation of the non-defective image is a very complicated work. ..
具体的には、例えば、製造された容器の品質を検査するための画像検査システムにおいては、その容器の画像について少しの色の違いなどで本来は不良品ではないもの(良品範囲のバラツキを有するもの)が不良品として検出された場合、今後そのような検出がなされないように、その画像を画像検査システムに入力して良品画像を手作業で更新する必要があった。
そこで、本発明者らは、このような問題を解消するために、製品の良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を容易に得ることができ、これを用いて検査対象物が良品であるか否かの判定を行うことが可能な画像検査システムを研究して、本発明を完成させた。Specifically, for example, in an image inspection system for inspecting the quality of a manufactured container, the image of the container is not originally a defective product due to a slight difference in color, etc. (there is a variation in the range of non-defective products). When the product was detected as a defective product, it was necessary to manually update the non-defective product image by inputting the image into the image inspection system so that such detection would not be performed in the future.
Therefore, in order to solve such a problem, the present inventors can easily obtain a non-defective product image covering the range of non-defective products of the product, and use this to determine whether or not the inspection target is a non-defective product. The present invention has been completed by studying an image inspection system capable of making a determination of.
具体的には、非特許文献1に示される敵対的生成ネットワーク(GAN:Generative Adversarial Nets)の技術を応用することにより、製品の良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を人工的に生成し、これを良品画像に含めて検査画像と比較することにより、良品画像の準備における上記の問題を解消することができた。 Specifically, by applying the technology of the Generative Adversarial Nets (GAN) shown in Non-Patent
ここで、敵対的生成ネットワークを用いた技術としては、特許文献1に記載の生成モデル学習方法を挙げることができる。
しかしながら、この技術は、検査対象物が良品であるか否かの判定を行うために用いられるものでなかった。Here, as a technique using the hostile generation network, the generation model learning method described in
However, this technique has not been used to determine whether an object to be inspected is a non-defective product.
また、検査対象物が良品であるか否かの判定を行うために用いられる技術としては、特許文献2に記載の外観検査装置を挙げることができる。この外観検査装置はオードエンコーダの技術を用いてリアルタイムで生成された人工的な良品画像を検査画像と比較することで、検査対象物が良品であるか否かの判定が行われている。
しかしながら、このような構成の場合、リアルタイムで人工的な良品画像と検査画像を比較し、その違いを平均二乗誤差などの判定式を用いて良品と不良品を判定するために、良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を事前に準備して判定式の閾値を決定する必要があることから、不確実性が高いという問題があった。また、GANを用いる場合に比較して、画像処理のアルゴリズムにもとづき生成される画像の品質が劣るという問題があった。Further, as a technique used for determining whether or not the inspection object is a non-defective product, the visual inspection apparatus described in Patent Document 2 can be mentioned. This visual inspection device compares an artificial non-defective product image generated in real time with an inspection image using the technology of an ode encoder to determine whether or not the inspection target is a non-defective product.
However, in the case of such a configuration, in order to compare the artificial non-defective product image and the inspection image in real time and judge the difference between the non-defective product and the defective product by using a judgment formula such as mean square error, the range of the non-defective product is set. Since it is necessary to prepare a non-defective image to cover in advance and determine the threshold value of the judgment formula, there is a problem that the uncertainty is high. Further, there is a problem that the quality of the image generated based on the image processing algorithm is inferior as compared with the case of using GAN.
本発明は、上記事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、製品の良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を容易に得ることができ、これを用いて検査対象物が良品であるか否かの判定を行うことが可能な画像検査システムの提供を目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and a non-defective product image covering the range of non-defective products of a product can be easily obtained, and using this, it is determined whether or not the inspection target is a non-defective product. The purpose is to provide an image inspection system that can be performed.
上記目的を達成するため、画像検査を行う画像検査システムであって、所定の入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成する生成器、複数の実際の良品画像を入力すると共に、前記生成器から前記人工的な良品画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品画像及び前記複数の実際の良品画像が、実際の良品画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力する識別器、前記人工的な良品画像を記憶する人工的良品画像記憶部、及び、前記複数の実際の良品画像を記憶する実良品画像記憶部を備え、前記生成器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、前記識別器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行うニューラルネットワーク部と、前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき人工的な良品画像を生成する画像生成部と、検査画像を入力して、当該検査画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する検査部とを有する構成としてある。 An image inspection system that performs image inspection in order to achieve the above object, a generator that generates an artificial non-defective product image based on predetermined input information, a plurality of actual non-defective product images, and the generation. The artificial good product image is input from the vessel, and the probability indicating whether or not the artificial good product image and the plurality of actual good product images are recognized as actual good product images is calculated, and one or more of them are calculated. A classifier that outputs the probability or its error for each image to the generator, an artificial non-defective image storage unit that stores the artificial non-defective image, and a real non-defective image that stores the plurality of actual non-defective images. A storage unit is provided, the generator performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product image is recognized as an actual good product image, and the discriminator performs machine learning so that the artificial good product image is an actual good product image. Instead, it is determined by a neural network unit that performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the plurality of actual non-defective images are recognized as actual non-defective images, and a trained generator obtained by the neural network unit. An image generation unit that generates an artificial non-defective product image based on the input information and an inspection image are input, and the inspection image is compared with the artificial non-defective product image or the actual non-defective product image generated by the image generation unit. It is configured to have an inspection unit for determining whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product.
また、本発明の画像検査システムは、画像検査を行う画像検査システムであって、所定の入力情報にもとづいて、基準画像との差分を表す人工的な良品の差分画像を生成する生成器、前記人工的な良品の差分画像と基準画像とを合成して、人工的な良品画像を生成する基準画像合成部、複数の実際の良品画像を入力すると共に、前記基準画像合成部により生成された前記人工的な良品画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品画像及び前記実際の良品画像が、実際の良品画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力する識別器、前記人工的な良品画像を記憶する人工的良品画像記憶部、及び、前記複数の実際の良品画像を記憶する実良品画像記憶部を備え、前記生成器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、前記識別器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行うニューラルネットワーク部と、前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき人工的な良品画像を生成する画像生成部と、検査画像を入力して、当該検査画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する検査部とを有する構成としてある。 Further, the image inspection system of the present invention is an image inspection system that performs image inspection, and is a generator that generates an artificial non-defective difference image representing a difference from a reference image based on predetermined input information. A reference image compositing unit that synthesizes an artificial non-defective product difference image and a reference image to generate an artificial non-defective product image, a plurality of actual non-defective product images are input, and the reference image compositing unit is generated. An artificial non-defective product image is input, the probability indicating whether or not the artificial non-defective product image and the actual non-defective product image are recognized as an actual non-defective product image is calculated, and the said for each one or a plurality of images. A classifier that outputs a probability or its error to the generator, an artificial good product image storage unit that stores the artificial good product image, and a real good product image storage unit that stores the plurality of actual good product images are provided. The generator performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product image is recognized as an actual good product image, and the classifier performs machine learning so that the artificial good product image is not an actual good product image but a plurality of the above. An artificial image based on predetermined input information by a neural network unit that performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the actual non-defective image of the image is recognized as an actual non-defective image, and a trained generator obtained by the neural network unit. An image generation unit that generates a good product image and an inspection image are input, and the inspection image is compared with an artificial good product image or an actual good product image generated by the image generation unit to obtain the inspection image. It is configured to have an inspection unit for determining whether or not the product is a non-defective product.
さらに、本発明の画像検査システムは、画像検査を行う画像検査システムであって、所定の入力情報にもとづいて、基準画像との差分を表す人工的な良品の差分画像を生成する生成器、複数の実際の良品画像を入力して、基準画像との差分を抽出し、実際の良品の差分画像を生成する実良品差分画像生成部、前記実際の良品の差分画像を入力すると共に、前記生成器から前記人工的な良品の差分画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品の差分画像及び前記実際の良品の差分画像が、実際の良品の差分画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力する識別器、前記人工的な良品の差分画像を記憶する人工的良品差分画像記憶部、及び、前記複数の実際の良品の差分画像を記憶する実良品差分画像記憶部を備え、前記生成器が前記人工的な良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、前記識別器が前記人工的な良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行うニューラルネットワーク部と、前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき基準画像との差分を表す人工的な良品の差分画像を生成する画像生成部と、検査画像を入力して、基準画像との差分を抽出し、検査画像の差分画像を生成する検査差分画像生成部、及び、前記検査画像の差分画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品の差分画像又は実際の良品の差分画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する良品判定部を備えた検査部とを有する構成としてある。 Further, the image inspection system of the present invention is an image inspection system that performs image inspection, and is a plurality of generators that generate an artificial non-defective difference image representing a difference from a reference image based on predetermined input information. The actual non-defective product image is input, the difference from the reference image is extracted, and the actual non-defective product difference image is generated. The difference image of the artificial good product is input from, and the probability indicating whether or not the difference image of the artificial good product and the difference image of the actual good product are recognized as the difference image of the actual good product is calculated. A classifier that outputs the probability or its error for each one or a plurality of images to the generator, an artificial good product difference image storage unit that stores the artificial good product difference image, and the plurality of actual products. A real good product difference image storage unit that stores a good product difference image is provided, and the generator performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product difference image is recognized as an actual good product difference image. The classifier is machine-learned to increase the probability that the artificial difference image of a good product is not an actual difference image of a good product and the plurality of actual difference images of a good product are recognized as an actual difference image of a good product. An image generator that generates an artificial non-defective difference image that represents the difference from the reference image based on predetermined input information by the neural network unit that performs the above and the trained generator obtained by the neural network unit, and an inspection. An inspection difference image generation unit that inputs an image, extracts the difference from the reference image, and generates a difference image of the inspection image, and an artificial non-defective product that generates the difference image of the inspection image by the image generation unit. It is configured to have an inspection unit provided with a non-defective product determination unit for determining whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product by comparing with the difference image of the above or an actual difference image of a non-defective product.
また、本発明の画像検査方法は、画像検査を行う画像検査方法であって、
ニューラルネットワーク部における生成器が、所定の入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成して人工的良品画像記憶部に記憶させ、ニューラルネットワーク部における識別器が、実良品画像記憶部に記憶されている複数の実際の良品画像を入力すると共に、前記生成器から前記人工的な良品画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品画像及び前記実際の良品画像が、実際の良品画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力し、前記生成器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、前記識別器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、画像生成部が、前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき人工的な良品画像を生成し、検査部が、検査画像を入力して、当該検査画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する方法としてある。Further, the image inspection method of the present invention is an image inspection method for performing an image inspection.
The generator in the neural network unit generates an artificial non-defective image based on the predetermined input information and stores it in the artificial non-defective image storage unit, and the discriminator in the neural network unit stores it in the actual non-defective image storage unit. A plurality of actual non-defective product images are input, and the artificial non-defective product image is input from the generator, and the artificial non-defective product image and the actual non-defective product image are recognized as actual non-defective product images. The probability indicating whether or not the image is obtained is calculated, the probability or the error thereof for each one or a plurality of images is output to the generator, and the generator recognizes that the artificial good product image is an actual good product image. Machine learning is performed so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product image is not an actual good product image, and the plurality of actual good product images are recognized as actual good product images. The image generation unit generates an artificial non-defective image based on the predetermined input information by the trained generator obtained by the neural network unit, and the inspection unit inputs the inspection image. This is a method of comparing the inspection image with an artificial non-defective product image generated by the image generation unit or an actual non-defective product image to determine whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product.
また、本発明の画像検査プログラムは、画像検査を行う画像検査プログラムであって、コンピュータを、所定の入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成する生成器、複数の実際の良品画像を入力すると共に、前記生成器から前記人工的な良品画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品画像及び前記複数の実際の良品画像が、実際の良品画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力する識別器、前記人工的な良品画像を記憶する人工的良品画像記憶部、及び、前記複数の実際の良品画像を記憶する実良品画像記憶部として機能させ、前記生成器に前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行わせ、前記識別器に前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行わせ、さらに、前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき人工的な良品画像を生成する画像生成部、並びに、検査画像を入力して、当該検査画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する検査部として機能させる構成としてある。 Further, the image inspection program of the present invention is an image inspection program that performs image inspection, and uses a computer to generate an artificial non-defective image based on predetermined input information, a generator, and a plurality of actual non-defective images. At the same time, the artificial good product image is input from the generator, and the probability indicating whether or not the artificial good product image and the plurality of actual good product images are recognized as actual good product images is determined. A classifier that calculates and outputs the probability or its error for each one or a plurality of images to the generator, an artificial good product image storage unit that stores the artificial good product image, and the plurality of actual good product images. The generator is made to function as a real good product image storage unit, machine learning is performed so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product image is recognized as an actual good product image, and the classifier is made to perform the artificial good product image. Machine learning is performed so as to increase the probability that the good good product image is not the actual good product image and the plurality of actual good product images are the actual good product images, and further, the learning obtained by the neural network unit is performed. An image generation unit that generates an artificial non-defective product image based on predetermined input information by the completed generator, and an artificial non-defective product image or an artificial non-defective product image generated by the image generation unit by inputting an inspection image and producing the inspection image. It is configured to function as an inspection unit for determining whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product as compared with an actual non-defective product image.
本発明によれば、製品の良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を容易に得ることができ、これを用いて検査対象物が良品であるか否かの判定を行うことのできる画像検査システムの提供が可能となる。 According to the present invention, there is provided an image inspection system capable of easily obtaining a non-defective product image covering the range of non-defective products of a product and using this to determine whether or not the inspection target is a non-defective product. Is possible.
以下、本発明の画像検査システム、及び画像検査方法の実施形態について詳細に説明する。ただし、本発明は、以下の実施形態の具体的な内容に限定されるものではない。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the image inspection system and the image inspection method of the present invention will be described in detail. However, the present invention is not limited to the specific contents of the following embodiments.
[第一実施形態]
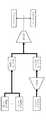
まず、本発明の第一実施形態に係る画像検査システム、及び画像検査方法について、図1〜図5を参照して説明する。図1は、本実施形態の画像検査システムにおける敵対的生成ネットワークの概要を示す説明図である。図2は、本実施形態の画像検査システムの構成を示すブロック図であり、図3は、同システムによる処理手順を示すフローチャートである。また、図4は、同システムによる処理手順における生成器の更新を含む生成器学習工程の概要を示す説明図であり、図5は、同システムによる処理手順における識別器の更新を含む識別器学習工程の概要を示す説明図である。[First Embodiment]
First, the image inspection system and the image inspection method according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 5. FIG. 1 is an explanatory diagram showing an outline of a hostile generation network in the image inspection system of the present embodiment. FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the image inspection system of the present embodiment, and FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure by the system. Further, FIG. 4 is an explanatory diagram showing an outline of the generator learning process including the update of the generator in the processing procedure by the system, and FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram including the update of the classifier in the processing procedure by the system. It is explanatory drawing which shows the outline of a process.
まず、図1を参照して、本実施形態の画像検査システムにおける敵対的生成ネットワークの概要について説明する。
本実施形態の画像検査システムにおける敵対的生成ネットワークは、GAN(Generative Adversarial Nets)を応用したものであり、ニューラルネットワークで構成された生成器と識別器を備え、これらが互いに競い合うように機械学習を行うことによって、生成器と識別器の機能を向上させるものである。
最終的には、学習済み生成器により生成される画像が、識別器によって本物(リアル、実際のもの)を示す画像であるか、あるいは偽物(フェイク、人工的なもの)を示す画像であるかの判定がつかないレベルに到達する。この判定がつかないレベルでは、リアルの確率(以下、リアル確率)が0.5で、フェイクの確率(以下、フェイク確率)が0.5となる。First, with reference to FIG. 1, an outline of a hostile generation network in the image inspection system of the present embodiment will be described.
The hostile generation network in the image inspection system of the present embodiment is an application of GAN (Generative Adversarial Nets), includes a generator and a classifier composed of a neural network, and performs machine learning so that they compete with each other. By doing so, the functions of the generator and the classifier are improved.
Ultimately, is the image produced by the trained generator an image showing the real (real, real) or fake (fake, artificial) by the discriminator? Reach a level that cannot be judged. At a level where this determination cannot be made, the real probability (hereinafter, real probability) is 0.5, and the fake probability (hereinafter, fake probability) is 0.5.
具体的には、生成器は、所定の入力情報(ランダムデータ)にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成する。また、これとは別個に、製品の実際の良品画像を準備する。
識別器は、人工的な良品画像と実際の良品画像を入力して、これらがそれぞれリアルであるか、フェイクであるかを判定する。このとき、識別器は、入力された画像がリアルである確率(及び/又はフェイクである確率)等を計算し、この計算結果を一又は複数の画像ごとに生成器に出力する。Specifically, the generator generates an artificial non-defective image based on predetermined input information (random data). Also, separately from this, an actual non-defective image of the product is prepared.
The classifier inputs an artificial non-defective image and an actual non-defective image, and determines whether these are real or fake, respectively. At this time, the classifier calculates the probability that the input image is real (and / or the probability that it is fake), and outputs the calculation result to the generator for each one or a plurality of images.
生成器は、入力した一又は複数の画像ごとの計算結果にもとづいて、識別器がリアルであると判定する確率を高めるように、よりリアルに近い人工的な良品画像を生成するように学習を行い、所定の入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成する。
これに対して、識別器は、人工的な良品画像をフェイクであるとより正確に判定できるように学習を行い、計算結果を一又は複数の画像ごとに生成器に出力する。
このように、生成器と識別器とが切磋琢磨するように交互に学習を行い、生成器と識別器を更新することによって、最終的には、精度の高い人工的な良品画像を生成可能な学習済み生成器を得ることができる。The generator learns to generate a more realistic artificial good image so as to increase the probability that the classifier will determine that it is real, based on the calculation results for each of the input images. Then, an artificial good product image is generated based on the predetermined input information.
On the other hand, the discriminator performs learning so that an artificial non-defective image can be more accurately determined to be a fake, and outputs the calculation result to the generator for each one or a plurality of images.
In this way, learning is possible so that the generator and the classifier alternately learn to work hard, and by updating the generator and the classifier, it is finally possible to generate a highly accurate artificial good image. You can get a finished generator.
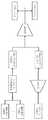
図2に示すように、本実施形態の画像検査システム1は、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10と、画像生成部20と、検査部30とから構成される。これらの各部は、同一の装置に備えられていても良く、別個の装置に備えられていても良い。例えば、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10をコンピュータに備えて、GANによる学習を実行して学習済み生成器を生成し、得られた学習済み生成器を別個のコンピュータへ備えて人工的良品画像を生成し、得られた人工的良品画像を別個の検査装置に備えて、検査を実施することができる。これは、以下の実施形態においても同様である。 As shown in FIG. 2, the
敵対的生成ネットワーク部(ニューラルネットワーク部)10は、情報入力部11、生成器12、人工的良品画像記憶部13、実良品画像記憶部14、及び識別器15を備えている。
情報入力部11は、ランダムデータを生成して、生成器12へ出力する。ランダムデータとしては、n次元の潜在変数(例えば、n次元乱数ベクトル)などを用いることができる。The hostile generation network unit (neural network unit) 10 includes an information input unit 11, a generator 12, an artificial good product
The information input unit 11 generates random data and outputs it to the generator 12. As the random data, an n-dimensional latent variable (for example, an n-dimensional random number vector) or the like can be used.
生成器12は、情報入力部11から入力したランダムデータにもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成し、これを人工的良品画像記憶部13に記憶させる。
また、生成器12は、識別器15から一又は複数の画像ごとに計算された確率(リアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率)を入力し、これにもとづきリアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率の誤差をバックプロパゲーション(逆伝播)することで当該生成器12を更新する。
また、識別器15において、当該確率の誤差を計算して、計算された確率の誤差を生成器12に入力する構成とすることも好ましい。以下の実施形態においても同様である。The generator 12 generates an artificial non-defective product image based on the random data input from the information input unit 11, and stores this in the artificial non-defective product
Further, the generator 12 inputs the probability (real probability and / or fake probability) calculated for each one or a plurality of images from the classifier 15, and backpropagates the error of the real probability and / or the fake probability based on this. The generator 12 is updated by gaiting (backpropagation).
It is also preferable that the classifier 15 calculates the error of the probability and inputs the calculated error of the probability to the generator 12. The same applies to the following embodiments.
具体的には、バックプロパゲーションする値として、「出力とラベルの差(=誤差)」が用いられる。「出力」は、確率(リアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率)である。また、「ラベル」は、確率の教師データであり、実良品画像ではリアル確率が「1」で、フェイク確率が「0」となり、人工的良品画像ではリアル確率が「0」で、フェイク確率が「1」となる。
生成器12は、バックプロパゲーションする値(誤差)を、「出力(real)−ラベル(fake)」、「出力(fake−ラベル(real)」として計算する。すなわち、生成器12は、騙せなかった値を誤差として更新される。Specifically, the "difference between output and label (= error)" is used as the value to be backpropagated. "Output" is a probability (real probability and / or fake probability). Further, the "label" is the teacher data of the probability, and the real probability is "1" and the fake probability is "0" in the real good product image, and the real probability is "0" and the fake probability is "0" in the artificial good product image. It becomes "1".
The generator 12 calculates the backpropagated value (error) as "output (real) -label (fake)" and "output (fake-label (real)". That is, the generator 12 cannot be deceived. The value is updated as an error.
このように、生成器12は、人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行う。
すなわち、生成器12において、識別器15をだます(人工的な良品画像をリアルと判定させる(実際の良品画像であると認められる)確率を高める)ために、識別器15から入力される確率が、リアル確率=1.0(フェイク確率=0.0)になるように機械学習が行われる。なお、初期は、リアル確率が低く、フェイク確率が高くなる。In this way, the generator 12 performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial non-defective image is recognized as an actual non-defective image.
That is, in the generator 12, the probability of being input from the classifier 15 in order to trick the classifier 15 (increasing the probability that the artificial good product image is judged to be real (it is recognized as an actual non-defective product image)) However, machine learning is performed so that the real probability = 1.0 (fake probability = 0.0). Initially, the real probability is low and the fake probability is high.
人工的良品画像記憶部13は、生成器12により生成された人工的な良品画像を識別情報ごとに記憶する。
実良品画像記憶部14は、予め準備された実際の良品画像を識別情報ごとに記憶する。The artificial non-defective product
The actual non-defective product
識別器15は、入力された画像が、リアルであるか又はフェイクであるかの確率を計算する。画像は、人工的良品画像記憶部13と実良品画像記憶部14から入力される。識別器15には、畳込層が備えられ、リアルとフェイクとを見分けるため特徴量を圧縮したネットワークが構成され、そのように判断した理由が重み係数として記録されている。そして、これらが学習によって更新されることにより、識別器15による判定の精度が向上する。 The classifier 15 calculates the probability that the input image is real or fake. The image is input from the artificial good product
ここで、生成器12の学習が進むと、識別器15は人工的な良品画像を「リアル確率が高く、フェイク確率が低い」ことを示す確率を出力するようになる。識別器15は、この確率の誤差をバックプロパゲーションすることにより、当該識別器15を更新する。
具体的には、バックプロパゲーションする値として、「出力とラベルの差(=誤差)」が用いられる。「出力」は、確率(リアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率)である。また、「ラベル」は、確率の教師データであり、実良品画像ではリアル確率が「1」で、フェイク確率が「0」となり、人工的良品画像ではリアル確率が「0」で、フェイク確率が「1」となる。
識別器15は、バックプロパゲーションする値(誤差)を、「出力(real)−ラベル(real)」、「出力(fake)−ラベル(fake)」として計算する。すなわち、識別器15は、騙された値を誤差として更新される。Here, as the learning of the generator 12 progresses, the classifier 15 comes to output the probability indicating that the artificial good product image has "high real probability and low fake probability". The classifier 15 updates the classifier 15 by backpropagating this probability error.
Specifically, the "difference between output and label (= error)" is used as the value to be backpropagated. "Output" is a probability (real probability and / or fake probability). Further, the "label" is the teacher data of the probability, and the real probability is "1" and the fake probability is "0" in the real good product image, and the real probability is "0" and the fake probability is "0" in the artificial good product image. It becomes "1".
The classifier 15 calculates the backpropagation value (error) as "output (real) -label (real)" and "output (fake) -label (fake)". That is, the classifier 15 is updated with the deceived value as an error.
このように、識別器15は、人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行う。
すなわち、識別器15において、生成器12により作成された偽物を見破る(人工的な良品画像をフェイクと判定させる(実際の良品画像でないと認められる)確率を高める)ために、計算される確率がリアル確率=0.0(フェイク確率=1.0)になるように機械学習が行われる。In this way, the classifier 15 performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial non-defective image is not the actual non-defective image but the actual non-defective image is the actual non-defective image.
That is, in the classifier 15, the probability calculated in order to detect the fake created by the generator 12 (increasing the probability that the artificial non-defective image is judged as fake (it is recognized as not the actual non-defective image)) is calculated. Machine learning is performed so that the real probability = 0.0 (fake probability = 1.0).
このようにして、生成器12と識別器15とを交互に更新していくことで、最終的には、生成器12において、当該生成器12により生成される画像について識別器15により出力される確率が、リアル確率=0.5(フェイク確率=0.5)となるように学習が行われる。
そして、このような学習済み生成器を用いることで、製品の種類ごとに良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を生成することが可能になる。By alternately updating the generator 12 and the classifier 15 in this way, the generator 12 finally outputs the image generated by the generator 12 by the classifier 15. Learning is performed so that the probability is real probability = 0.5 (fake probability = 0.5).
Then, by using such a trained generator, it becomes possible to generate a non-defective image that covers the range of non-defective products for each product type.
例えば、製品Aについて実際の良品画像aと実際の良品画像bが存在した場合、GANにより2つの実際の良品画像の間を埋めるような人工的な良品画像cを生成できることで、良品を網羅することが可能となっている。
また、ある製品Aについて学習した結果を、別の製品Bに対して転移学習することにより、製品Bについて準備する実際の良品画像を減らしたうえで、製品Aと同じように良品の範囲を網羅することも可能である。For example, when an actual non-defective product image a and an actual non-defective product image b exist for the product A, the non-defective product is covered by being able to generate an artificial non-defective product image c that fills the space between the two actual non-defective product images by GAN. It is possible.
In addition, by transferring the result of learning about one product A to another product B, the actual non-defective product image prepared for product B is reduced, and the range of non-defective products is covered in the same way as product A. It is also possible to do.
画像生成部20は、情報入力部21、学習済み生成器22、及び人工的良品画像記憶部23を備えている。
情報入力部21は、ランダムデータを生成して、学習済み生成器22へ出力する。ランダムデータとしては、n次元の潜在変数(例えば、n次元乱数ベクトル)などを用いることができる。The image generation unit 20 includes an
The
学習済み生成器22は、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10において実行されたGANによる学習の結果得られた学習済みの生成器12の複製により構成される。
この学習済み生成器22は、情報入力部21から入力したランダムデータにもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成し、人工的良品画像記憶部23に記憶させる。
人工的良品画像記憶部23は、学習済み生成器22によって生成された人工的な良品画像を識別情報ごとに記憶する。The trained
The learned
The artificial non-defective product
検査部30は、検査画像記憶部31、良品画像記憶部32、及び良品判定部33を備えている。
検査画像記憶部31は、検査の対象製品を撮影して得られた検査画像を識別情報ごとに記憶する。
良品画像記憶部32は、実良品画像記憶部14に記憶された実際の良品画像の複製と、人工的良品画像記憶部23に記憶された人工的な良品画像の複製を記憶することができる。なお、良品画像記憶部32において、人工的な良品画像の複製のみを記憶させることもできる。The inspection unit 30 includes an inspection
The inspection
The non-defective product
良品判定部33は、検査画像記憶部31に記憶された検査画像を、良品画像記憶部32に記憶された良品画像と比較することによって、当該検査画像が良品のものであるか否かを判定する。
このとき、良品判定部33は、検査画像と人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像を差分することにより、検査画像に存在する欠点などを検出することができる。すなわち、その差分が一定の閾値を超える場合に、検査画像に欠点などが存在すると検出することができる。
差分する方法としては、具体的には、例えば以下の式を好適に用いることができる。
At this time, the non-defective
Specifically, for example, the following formula can be preferably used as the method of difference.
また、良品判定部33は、検査画像と人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像の平均二乗誤差や平均二乗誤差平方根などの評価値を用いることで、画像が良品のものであるか否かを判定することもできる。すなわち、評価値が一定の閾値を上回る場合に、検査画像が良品のものでないと判定することができる。 Further, the non-defective
また、良品判定部33は、検査画像と人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像の類似度にもとづいて、検査画像が良品のものであるか否かを判定することもできる。すなわち、類似度が一定の閾値を下回る場合に、検査画像が良品のものでないと判定することができる。 Further, the non-defective
次に、図3を参照して、本実施形態の画像検査システムによる処理手順について説明する。
まず、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10において、生成器12を更新するまでの工程(生成器学習工程:ステップ10〜13)と、識別器15を更新するまでの工程(識別器学習工程:ステップ14〜17)とが行われ、これらの工程を所定回数繰り返し実行することにより、学習が完了し、学習済み生成器12が完成する。学習の完了の条件は、例えばリアル確率とフェイク確率が0.5になったときなどとすることができる。Next, the processing procedure by the image inspection system of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
First, in the hostile generation network unit 10, a step up to updating the generator 12 (generator learning step: steps 10 to 13) and a step up to updating the classifier 15 (discriminator learning step: steps 14 to 14). 17) is performed, and by repeating these steps a predetermined number of times, learning is completed and the learned generator 12 is completed. The condition for completing the learning can be, for example, when the real probability and the fake probability become 0.5.
生成器学習工程では、識別器15を固定して(更新を実施しない)、人工的な良品画像が識別器15でリアルと識別されるように生成器12の学習が行われる。生成器学習工程における処理の流れを、図4において太線で示す。
具体的には、情報入力部11により入力情報が生成され(ステップ10)、生成器12が、生成された入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成する(ステップ11)。
次に、識別器15が、人工的な良品画像を入力して、これがリアルであるか、フェイクであるかの確率を計算して出力する(ステップ12)。なお、識別器15による当該処理を識別と称する場合がある。
そして、生成器12の更新が行われる(ステップ13)。
ここで、前述のとおり、生成器12は、識別器15から一又は複数の画像ごとに計算された確率(リアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率)等を入力し、これにもとづきリアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率の誤差をバックプロパゲーションすることで当該生成器12を更新する。In the generator learning step, the classifier 15 is fixed (update is not performed), and the generator 12 is learned so that the artificial non-defective image is identified as real by the classifier 15. The processing flow in the generator learning process is shown by a thick line in FIG.
Specifically, input information is generated by the information input unit 11 (step 10), and the generator 12 generates an artificial non-defective image based on the generated input information (step 11).
Next, the classifier 15 inputs an artificial non-defective image, calculates the probability of whether this is real or fake, and outputs it (step 12). The process performed by the classifier 15 may be referred to as identification.
Then, the generator 12 is updated (step 13).
Here, as described above, the generator 12 inputs the probability (real probability and / or fake probability) calculated for each one or a plurality of images from the classifier 15, and based on this, the real probability and / or the fake. The generator 12 is updated by backpropagating the probability error.
識別器学習工程では、生成器12を固定して(更新を実施しない)、人工的な良品画像と実際の良品画像を識別できるように識別器15の学習が行われる。識別器学習工程における処理の流れを、図5において太線で示す。
具体的には、情報入力部11により入力情報が生成され(ステップ14)、生成器12が、生成された入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成する(ステップ15)。
次に、識別器15が、人工的な良品画像と実際の良品画像を入力して、これらがリアルであるか、フェイクであるかの確率を計算して出力する(ステップ16)。In the classifier learning step, the generator 12 is fixed (update is not performed), and the classifier 15 is learned so that the artificial non-defective image and the actual non-defective image can be discriminated. The processing flow in the classifier learning process is shown by a thick line in FIG.
Specifically, input information is generated by the information input unit 11 (step 14), and the generator 12 generates an artificial non-defective image based on the generated input information (step 15).
Next, the classifier 15 inputs an artificial non-defective image and an actual non-defective image, calculates and outputs the probability of whether these are real or fake (step 16).
このとき、識別器15は、以下の(1)と(2)を用いて、バックプロパゲーションする誤差を計算する。
(1)人工的な良品画像を入力として識別器から出力されたリアルorフェイクであるという確率と画像のフェイクというラベル
(2)実際の良品画像を入力として識別器から出力されたリアルorフェイクであるという確率と画像のリアルというラベルAt this time, the classifier 15 calculates the backpropagation error using the following (1) and (2).
(1) Probability that it is a real or fake output from the classifier by inputting an artificial non-defective image and a label called fake of the image.
(2) Probability that it is real or fake output from the classifier with the actual non-defective image as input and the label that the image is real
そして、識別器15の更新が行われる(ステップ17)。
ここで、前述のとおり、生成器12の学習が進むと、識別器15は人工的な良品画像に対して、「リアル確率が高く、フェイク確率が低い」ことを示す確率を出力するようになる。識別器15は、その確率の誤差をバックプロパゲーションすることにより、当該識別器15を更新する。
なお、実際の良品画像に対しても、識別器15は「リアル確率が高く、フェイク確率が低い」ことを示す確率をより正確に出力するようになる。
また、生成器学習工程と識別器学習工程の実行順序を入れ替えてもよい。Then, the classifier 15 is updated (step 17).
Here, as described above, as the learning of the generator 12 progresses, the classifier 15 outputs a probability indicating that "the real probability is high and the fake probability is low" for the artificial good product image. .. The classifier 15 updates the classifier 15 by backpropagating the error of the probability.
It should be noted that the classifier 15 will more accurately output the probability indicating that "the real probability is high and the fake probability is low" even for the actual non-defective image.
Further, the execution order of the generator learning process and the discriminator learning process may be exchanged.
そして、生成器学習工程と識別器学習工程とが、所定の条件を満たすまで繰り返し実行される(ステップ18)。所定の条件としては、リアル確率とフェイク確率が一定の値(例えば0.5)になることや、所定の実行回数などを用いることができる。
学習済みの生成器12は、画像生成部20へ送信されて記憶され、画像生成部20における学習済み生成器22として構成される(ステップ19)。Then, the generator learning step and the discriminator learning step are repeatedly executed until a predetermined condition is satisfied (step 18). As a predetermined condition, a constant value (for example, 0.5) for the real probability and the fake probability, a predetermined number of executions, and the like can be used.
The trained generator 12 is transmitted to the image generation unit 20 and stored, and is configured as the trained
次に、画像生成部20において、情報入力部21により入力情報が生成され(ステップ20)、学習済み生成器22が、生成された入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成し(ステップ21)、これを人工的良品画像記憶部23に記憶させる。
生成された人工的な良品画像は、検査部30へ送信されて(ステップ22)、良品画像記憶部32に記憶される。Next, in the image generation unit 20, input information is generated by the information input unit 21 (step 20), and the trained
The generated artificial non-defective product image is transmitted to the inspection unit 30 (step 22) and stored in the non-defective product
次に、検査部30において、良品判定部33は、検査画像記憶部31から検査画像を入力すると共に、良品画像記憶部32から良品画像(人工的な良品画像と実際の良品画像)を入力して、検査画像を良品画像と比較して、検査画像に係る製品が良品であるか否かを判定する(ステップ31)。 Next, in the inspection unit 30, the non-defective
本実施形態の画像検査システム、及び画像検査方法をこのようにすれば、実際の良品画像に非常に近い人工的な良品画像を自動的に大量に生成することができ、また製品の種類ごとに良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を準備することができる。
このため、良品画像を容易に十分に得ることができ、これを用いて効率的に、検査対象物が良品であるか否かの判定を行うことが可能となる。By using the image inspection system and the image inspection method of the present embodiment in this way, it is possible to automatically generate a large number of artificial non-defective images that are very close to the actual non-defective images, and for each product type. It is possible to prepare a non-defective image that covers the range of non-defective products.
Therefore, a good image can be easily and sufficiently obtained, and it is possible to efficiently determine whether or not the inspection target is a good product by using the image.
[第二実施形態]
次に、本発明の第二実施形態に係る画像検査システム、及び画像検査方法について、図6〜図8を参照して説明する。図6は、本実施形態の画像検査システムの概要を示す説明図であり、図7は、同システムの構成を示すブロック図であり、図8は、同システムによる処理手順を示すフローチャートである。[Second Embodiment]
Next, the image inspection system and the image inspection method according to the second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 6 to 8. FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing an outline of the image inspection system of the present embodiment, FIG. 7 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the system, and FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure by the system.
まず、図6を参照して、本実施形態の画像検査システムの特徴について説明する。
本実施形態の画像検査システムは、生成器が基準画像との差分を表す人工的な良品差分画像(色、形状等の差分画像)を生成し、得られた人工的な良品差分画像に基準画像を合成することにより、人工的な良品画像を生成する点で第一実施形態と相違する。その点については、第一実施形態と同様の構成とすることができる。First, the features of the image inspection system of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
In the image inspection system of the present embodiment, the generator generates an artificial non-defective product difference image (difference image of color, shape, etc.) showing the difference from the reference image, and the obtained artificial non-defective product difference image is used as a reference image. Is different from the first embodiment in that an artificial non-defective image is generated by synthesizing. In that respect, the configuration can be the same as that of the first embodiment.
すなわち、図7に示すように、本実施形態の画像検査システム1aは、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10aと、画像生成部20aと、検査部30aとから構成される。
敵対的生成ネットワーク部10aは、情報入力部11a、生成器12a、人工的良品画像記憶部13a、実良品画像記憶部14a、識別器15a、人工的良品差分画像記憶部16a、基準画像合成部17aを備えている。That is, as shown in FIG. 7, the image inspection system 1a of the present embodiment includes a hostile generation network unit 10a, an image generation unit 20a, and an inspection unit 30a.
The hostile generation network unit 10a includes an information input unit 11a, a
情報入力部11a、人工的良品画像記憶部13a、実良品画像記憶部14a、及び識別器15aは、第一実施形態における同一番号が付された対応する構成と同様の構成のものとすることができる。
生成器12aは、第一実施形態と異なり、情報入力部11aから入力したランダムデータにもとづいて、人工的な良品差分画像を生成し、これを人工的良品差分画像記憶部16aに記憶させる。The information input unit 11a, the artificial non-defective product
Unlike the first embodiment, the
生成器12aは、識別器15aから一又は複数の画像ごとに計算された確率(リアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率)等を入力し、これにもとづきリアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率の誤差をバックプロパゲーションすることで当該生成器12aを更新する。
そして、最終的に得られた学習済み生成器が、画像生成部20aに送信されて、当該画像生成部20aおける学習済み生成器22aを構成する。The
Then, the finally obtained learned generator is transmitted to the image generation unit 20a to form the trained
人工的良品差分画像記憶部16aは、生成器12aにより生成された人工的な良品差分画像を識別情報ごとに記憶する。
基準画像合成部17aは、人工的良品差分画像記憶部16aから人工的な良品差分画像を入力して、当該人工的な良品差分画像に基準画像を合成し、人工的な良品画像を生成して、人工的良品画像記憶部13aに識別情報ごとに記憶させる。
基準画像としては、デザイン図面や実際の良品画像の平均画像等を用いることができる。The artificial non-defective product difference
The reference
As the reference image, a design drawing, an average image of an actual non-defective product image, or the like can be used.
次に、図8を参照して、本実施形態の画像検査システムによる処理手順について説明する。
まず、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10aにおいて、生成器12aを更新するまでの工程(生成器学習工程:ステップ40〜44)と、識別器15aを更新するまでの工程(識別器学習工程:ステップ45〜49)とが行われ、これらの工程を所定回数繰り返し実行することにより、学習が完了し、学習済み生成器12aが完成する。学習の完了の条件は、例えばリアル確率とフェイク確率が0.5になったときなどとすることができる。Next, the processing procedure by the image inspection system of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
First, in the hostile generation network unit 10a, a step up to updating the
生成器学習工程では、識別器15aを固定して(更新を実施しない)、人工的な良品画像が識別器15aでリアルと識別されるように生成器12aの学習が行われる。
具体的には、情報入力部11aにより入力情報が生成され(ステップ40)、生成器12aが、生成された入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品差分画像を生成する(ステップ41)。
次に、基準画像合成部17aが、人工的な良品差分画像を基準画像と合成して、人工的な良品画像を生成する(ステッ42)。In the generator learning step, the
Specifically, input information is generated by the information input unit 11a (step 40), and the
Next, the reference
次に、識別器15aが、人工的な良品画像を入力して、これがリアルであるか、フェイクであるかの確率等を計算して出力する(ステップ43)。
そして、生成器12aの更新が行われる(ステップ44)。Next, the
Then, the
識別器学習工程では、生成器12aを固定して(更新を実施しない)、人工的な良品画像と実際の良品画像を識別できるように識別器15aの学習が行われる。
具体的には、情報入力部11aにより入力情報が生成され(ステップ45)、生成器12aが、生成された入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品差分画像を生成する(ステップ46)。
次に、基準画像合成部17aが、人工的な良品差分画像を基準画像と合成して、人工的な良品画像を生成する(ステッ47)。In the classifier learning step, the
Specifically, input information is generated by the information input unit 11a (step 45), and the
Next, the reference
次に、識別器15aが、人工的な良品画像と実際の良品画像を入力して、これらがリアルであるか、フェイクであるかの確率を計算して出力する(ステップ48)。
そして、識別器15aの更新が行われる(ステップ49)。Next, the
Then, the
そして、生成器学習工程と識別器学習工程とが、所定の条件を満たすまで繰り返し実行される(ステップ50)。所定の条件としては、リアル確率とフェイク確率が一定の値(例えば0.5)になることや、所定の実行回数などを用いることができる。
学習済みの生成器12aは、画像生成部20aへ送信されて記憶され、当該画像生成部20aにおける学習済み生成器22aとして構成される(ステップ51)。
以降の処理は、第一実施形態における同一番号が付された対応する構成による処理と同様のものとすることができる。Then, the generator learning step and the discriminator learning step are repeatedly executed until a predetermined condition is satisfied (step 50). As a predetermined condition, a constant value (for example, 0.5) for the real probability and the fake probability, a predetermined number of executions, and the like can be used.
The trained
Subsequent processing can be the same as the processing according to the corresponding configuration with the same number in the first embodiment.
本実施形態の画像検査システム、及び画像検査方法をこのようにすれば、デザイン図面が異なる場合などにおいて、人工的な良品差分画像を用いることにより、ある程度デザインの違いをキャンセルすることが可能になる。すなわち、キズなどの不良箇所とデザインなどの模様を分離した画像を検査対象とすることができ、生成器はデザインを除いた良品範囲のバラツキを含んだ画像を生成するネットワークを構築することができる。
このため、デザイン図面が異なる場合などにおいて、同一の人工的な良品差分画像を用いることが可能になり、ある程度デザインの違いがある製品に対して同じ画像生成部と検査部を用いることが可能になる。By using the image inspection system and the image inspection method of the present embodiment in this way, it is possible to cancel the difference in design to some extent by using an artificial non-defective difference image when the design drawings are different. .. That is, it is possible to inspect an image in which a defective part such as a scratch and a pattern such as a design are separated, and the generator can construct a network that generates an image including a variation in the non-defective range excluding the design. ..
Therefore, when the design drawings are different, it is possible to use the same artificial non-defective product difference image, and it is possible to use the same image generation unit and inspection unit for products having a certain degree of design difference. Become.
[第三実施形態]
次に、本発明の第三実施形態に係る画像検査システム、及び画像検査方法について、図9〜図11を参照して説明する。図9は、本実施形態の画像検査システムの概要を示す説明図であり、図10は、同システムの構成を示すブロック図であり、図11は、同システムによる処理手順を示すフローチャートである。[Third Embodiment]
Next, the image inspection system and the image inspection method according to the third embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 9 to 11. 9 is an explanatory diagram showing an outline of the image inspection system of the present embodiment, FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the system, and FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure by the system.
まず、図9を参照して、本実施形態の画像検査システムの特徴について説明する。
本実施形態の画像検査システムは、生成器が基準画像との差分を表す人工的な良品差分画像(色、形状等の差分画像)を生成すると共に、これとは別個に製品の良品画像から基準との差分を抽出して、実際の良品差分画像を生成し、識別器がこれらを入力して、リアルであるか又はフェイクであるかの確率を計算する点で第一実施形態と相違する。その他の点については、第一実施形態と同様の構成とすることができる。First, the features of the image inspection system of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
In the image inspection system of the present embodiment, the generator generates an artificial non-defective product difference image (difference image of color, shape, etc.) showing the difference from the reference image, and separately from this, the reference is performed from the non-defective product image of the product. It differs from the first embodiment in that the difference between the two is extracted to generate an actual non-defective image, and the classifier inputs these to calculate the probability of being real or fake. Other points can be the same as that of the first embodiment.
すなわち、図10に示すように、本実施形態の画像検査システム1bは、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10bと、画像生成部20bと、検査部30bとから構成される。
敵対的生成ネットワーク部10bは、情報入力部11b、生成器12b、実良品画像記憶部14b、識別器15b、人工的良品差分画像記憶部16b、実良品差分画像生成部18b、実良品差分画像記憶部19bを備えている。That is, as shown in FIG. 10, the image inspection system 1b of the present embodiment includes a hostile generation network unit 10b, an image generation unit 20b, and an inspection unit 30b.
The hostile generation network unit 10b includes an
情報入力部11b、及び実良品画像記憶部14bは、第一実施形態における同一番号が付された対応する構成と同様の構成のものとすることができる。
生成器12bは、第一実施形態と異なり、情報入力部11bから入力したランダムデータにもとづいて、人工的な良品差分画像を生成し、これを人工的良品差分画像記憶部16bに記憶させる。The
Unlike the first embodiment, the
生成器12bは、識別器15bから一又は複数の画像ごとに計算された確率(リアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率)等を入力し、これにもとづきリアル確率及び/又はフェイク確率の誤差をバックプロパゲーションすることで当該生成器12bを更新する。
このとき、生成器12bは、人工的な良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行う。
そして、最終的に得られた学習済み生成器が、画像生成部20bに送信されて、当該画像生成部20bおける学習済み生成器22bを構成する。The
At this time, the
Then, the finally obtained learned generator is transmitted to the image generation unit 20b to form the trained
人工的良品差分画像記憶部16bは、生成器12bにより生成された人工的な良品差分画像を識別情報ごとに記憶する。
実良品差分画像生成部18bは、実良品画像記憶部14bから実際の良品画像を入力して、基準画像との差分を表す実際の良品差分画像(色、形状等の差分画像)を生成し、これを実良品差分画像記憶部19bに識別情報ごとに記憶させる。The artificial non-defective product difference
The real good product difference
識別器15bは、入力された画像が、リアルであるか又はフェイクであるかの確率を計算する。画像は、人工的良品差分画像記憶部16bと実良品差分画像記憶部19bから入力される。また、識別器15bは、計算した確率の差をバックプロパゲーションすることにより、当該識別器15bを更新する。
このとき、識別器15bは、人工的な良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像でなく、実際の良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行う。The
At this time, the
画像生成部20bは、情報入力部21b、学習済み生成器22b、及び人工的良品差分画像記憶部24bを備えている。
学習済み生成器22bは、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10bにおいて実行されたGANによる学習の結果得られた学習済みの生成器12bの複製により構成される。
この学習済み生成器22bは、情報入力部21bから入力したランダムデータにもとづいて、人工的な良品差分画像を生成し、人工的良品差分画像記憶部24bに記憶させる。
人工的良品差分画像記憶部24bは、学習済み生成器22bによって生成された人工的な良品差分画像を識別情報ごとに記憶する。The image generation unit 20b includes an
The trained
The learned
The artificial non-defective product difference
検査部30bは、検査画像記憶部31b、良品判定部33b、良品差分画像記憶部34b、検査差分画像生成部35b、及び検査差分画像記憶部36bを備えている。
検査画像記憶部31bは、検査の対象製品を撮影して得られた検査画像を識別情報ごとに記憶する。
良品差分画像記憶部34bは、実良品差分画像記憶部19bに記憶された実際の良品差分画像の複製と、人工的良品差分画像記憶部24bに記憶された人工的な良品差分画像の複製を記憶することができる。なお、良品差分画像記憶部34bにおいて、人工的な良品差分画像の複製のみを記憶させることもできる。The inspection unit 30b includes an inspection
The inspection
The non-defective product difference
検査差分画像生成部35bは、検査画像記憶部31bから検査画像を入力して、基準画像との差分を表す検査差分画像(色、形状等の差分画像,検査画像の差分画像)を生成し、これを検査差分画像記憶部36bに識別情報ごとに記憶させる。 The inspection difference
良品判定部33bは、検査差分画像記憶部36bに記憶された検査差分画像を、良品差分画像記憶部34bに記憶された良品差分画像と比較することによって、当該検査差分画像が良品のものであるか否かを判定する。
このとき、良品判定部33bは、検査差分画像と人工的な良品差分画像又は実際の良品差分画像を差分することにより、検査差分画像に存在する欠点などを検出することができる。すなわち、その差分が一定の閾値を超える場合に、検査差分画像に欠点などが存在すると検出することができる。The non-defective
At this time, the non-defective
また、良品判定部33bは、検査差分画像と人工的な良品差分画像又は実際の良品差分画像の平均二乗誤差や平均二乗誤差平方根などの評価値を用いることで、画像が良品のものであるか否かを判定することもできる。すなわち、評価値が一定の閾値を上回る場合に、検査差分画像が良品のものでないと判定することができる。 Further, the non-defective
また、良品判定部33bは、検査差分画像と人工的な良品差分画像又は実際の良品差分画像の類似度にもとづいて、検査差分画像が良品のものであるか否かを判定することもできる。すなわち、類似度が一定の閾値を下回る場合に、検査差分画像が良品のものでないと判定することができる。 Further, the non-defective
次に、図11を参照して、本実施形態の画像検査システムによる処理手順について説明する。
まず、敵対的生成ネットワーク部10bにおいて、生成器12bを更新するまでの工程(生成器学習工程:ステップ60〜63)と、識別器15bを更新するまでの工程(識別器学習工程:ステップ64〜68)とが行われ、これらの工程を所定回数繰り返し実行することにより、学習が完了し、学習済み生成器12bが完成する。学習の完了の条件は、例えばリアル確率とフェイク確率が0.5になったときなどとすることができる。Next, the processing procedure by the image inspection system of the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
First, in the hostile generation network unit 10b, a step up to updating the
生成器学習工程では、識別器15bを固定して(更新を実施しない)、人工的な良品画像が識別器15bでリアルと識別されるように生成器12bの学習が行われる。
具体的には、情報入力部11bにより入力情報が生成され(ステップ60)、生成器12bが、生成された入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品差分画像を生成する(ステップ61)。In the generator learning step, the
Specifically, input information is generated by the
次に、識別器15bが、人工的な良品差分画像を入力して、これがリアルであるか、フェイクであるかの確率等を計算して出力する(ステップ62)。
そして、生成器12bの更新が行われる(ステップ63)。Next, the
Then, the
識別器学習工程では、生成器12bを固定して(更新を実施しない)、人工的な良品差分画像と実際の良品差分画像を識別できるように識別器15bの学習が行われる。
具体的には、情報入力部11bにより入力情報が生成され(ステップ64)、生成器12bが、生成された入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品差分画像を生成する(ステップ65)。In the classifier learning step, the
Specifically, input information is generated by the
一方、実良品差分画像生成部18bが、実良品画像記憶部14bから実際の良品画像を入力して、基準画像との差分を表す実際の良品差分画像(色、形状等の差分画像)を生成する(ステップ66)。
なお、ステップ64、65と、ステップ66の実行順序は入れ替えても良い。On the other hand, the actual non-defective product difference
The execution order of steps 64 and 65 and step 66 may be interchanged.
次に、識別器15bが、人工的な良品差分画像と実際の良品差分画像を入力して、これらがリアルであるか、フェイクであるかの確率を計算して出力する(ステップ67)。
そして、識別器15bの更新が行われる(ステップ68)。Next, the
Then, the
そして、生成器学習工程と識別器学習工程とが、所定の条件を満たすまで繰り返し実行される(ステップ69)。所定の条件としては、リアル確率とフェイク確率が一定の値(例えば0.5)になることや、所定の実行回数などを用いることができる。
学習済みの生成器12bは、画像生成部20bへ送信されて記憶され、当該画像生成部20bにおける学習済み生成器22bとして構成される(ステップ70)。
以降の処理は、第一実施形態における同一番号が付された対応する構成による処理と同様のものとすることができる。Then, the generator learning step and the discriminator learning step are repeatedly executed until a predetermined condition is satisfied (step 69). As a predetermined condition, a constant value (for example, 0.5) for the real probability and the fake probability, a predetermined number of executions, and the like can be used.
The trained
Subsequent processing can be the same as the processing according to the corresponding configuration with the same number in the first embodiment.
本実施形態の画像検査システム、及び画像検査方法をこのようにすれば、キズなどの不良箇所とデザインなどの模様を分離した画像を検査対象とすることができ、生成器はデザインを除いた良品範囲のバラツキを含んだ画像を生成するネットワークを構築することができる。
このため、デザイン図面が異なる場合などにおいて、同一の人工的な良品差分画像を用いることが可能になり、ある程度デザインの違いがある製品に対して同じ画像生成部と検査部を用いることが可能になる。By using the image inspection system and the image inspection method of the present embodiment in this way, it is possible to inspect an image in which defective parts such as scratches and patterns such as designs are separated, and the generator is a non-defective product excluding the design. It is possible to construct a network that generates an image including a variation in the range.
Therefore, when the design drawings are different, it is possible to use the same artificial non-defective product difference image, and it is possible to use the same image generation unit and inspection unit for products having a certain degree of design difference. Become.
上記実施形態の画像検査システムは、本発明の画像処理プログラムに制御されたコンピュータを用いて実現することができる。コンピュータのCPUは、画像処理プログラムにもとづいてコンピュータの各構成要素に指令を送り、画像検査システムの動作に必要となる所定の処理、例えば、入力情報の生成処理、人工的な良品(差分)画像生成処理、実際の良品差分画像生成処理、検査差分画像生成処理、識別器による識別処理、生成器の更新処理、識別器の更新処理、良品判定処理等を行わせる。このように、本発明の画像検査システムにおける各処理、動作は、プログラムとコンピュータとが協働した具体的手段により実現できるものである。 The image inspection system of the above embodiment can be realized by using a computer controlled by the image processing program of the present invention. The CPU of the computer sends a command to each component of the computer based on the image processing program, and performs predetermined processing necessary for the operation of the image inspection system, for example, input information generation processing, artificial good product (difference) image. The generation process, the actual non-defective product difference image generation process, the inspection difference image generation process, the identification process by the classifier, the generator update process, the classifier update process, the non-defective product determination process, and the like are performed. As described above, each process and operation in the image inspection system of the present invention can be realized by concrete means in which the program and the computer cooperate.
プログラムは予めROM,RAM等の記録媒体に格納され、コンピュータに実装された記録媒体から当該コンピュータにプログラムを読み込ませて実行されるが、例えば通信回線を介してコンピュータに読み込ませることもできる。
また、プログラムを格納する記録媒体は、例えば半導体メモリ、磁気ディスク、光ディスク、その他任意のコンピュータで読取り可能な任意の記録手段により構成できる。The program is stored in a recording medium such as ROM or RAM in advance, and the program is read by the computer from the recording medium mounted on the computer and executed. However, the program can also be read by the computer via a communication line, for example.
Further, the recording medium for storing the program can be configured by, for example, a semiconductor memory, a magnetic disk, an optical disk, or any other recording means that can be read by any computer.
以上説明したように、本発明の実施形態に係る画像検査システムによれば、実際の良品画像に非常に近い人工的な良品画像を自動的に大量に生成することができ、また製品の種類ごとに良品の範囲を網羅する良品画像を準備することができる。
このため、良品画像を容易に十分に得ることができ、これを用いて効率的に、検査対象物が良品であるか否かの判定を行うことが可能となる。As described above, according to the image inspection system according to the embodiment of the present invention, a large number of artificial non-defective images that are very close to the actual non-defective images can be automatically generated, and for each product type. It is possible to prepare a non-defective image that covers the range of non-defective products.
Therefore, a good image can be easily and sufficiently obtained, and it is possible to efficiently determine whether or not the inspection target is a good product by using the image.
また、デザイン図面が異なる場合などにおいて、人工的な良品差分画像を用いることにより、キズなどの不良箇所とデザインなどの模様を分離した画像を検査対象とすることができ、デザイン図面が異なる場合などにおいて、同一の人工的な良品差分画像を用いることが可能になる。このため、ある程度デザインの違いがある製品に対して同じ画像生成部と検査部を用いることが可能になる。 In addition, when the design drawings are different, by using an artificial non-defective product difference image, it is possible to inspect an image in which defective parts such as scratches and patterns such as designs are separated, and when the design drawings are different, etc. In, it becomes possible to use the same artificial non-defective product difference image. Therefore, it is possible to use the same image generation unit and inspection unit for products having a certain degree of design difference.
本発明は、以上の実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の範囲内において、種々の変更実施が可能であることは言うまでもない。
例えば、上記のGANに代えて、例えば入力ノイズとして与えたベクトルを元にDeepCNNを介して画像を生成するDCGANや、入力する画像と共にラベル情報を追加することで、狙った条件の画像を生成できるcGAN、あるいは「ウマ」⇔「シマウマ」のように画像のドメインを変換することができるcycleGAN、又はその他のGANの亜種を用いるなど適宜変更することが可能である。It goes without saying that the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and various modifications can be made within the scope of the present invention.
For example, instead of the above GAN, DCGAN that generates an image via DeepCNN based on a vector given as input noise, or by adding label information together with the input image, an image of the target condition can be generated. It can be appropriately changed by using cGAN, cycleGAN capable of converting the domain of the image such as "horse" ⇔ "shimauma", or other variants of GAN.
本発明は、製品や設備等を画像データにもとづき検査するために、様々な良品画像を網羅的に準備することが必要な画像検査システムなどにおいて、好適に利用することが可能である。 INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention can be suitably used in an image inspection system or the like in which it is necessary to comprehensively prepare various non-defective image images in order to inspect a product, equipment, or the like based on image data.
1,1a,1b 画像検査システム
10,10a,10b 敵対的生成ネットワーク部
11,11a,11b 情報入力部
12,12a,12b 生成器
13,13a 人工的良品画像記憶部
14,14a,14b 実良品画像記憶部
15,15a,15b 識別器
16a,16b 人工的良品差分画像記憶部
17a 基準画像合成部
18b 実良品差分画像生成部
19b 実良品差分画像記憶部
20,20a,20b 画像生成部
21,21a,21b 情報入力部
22,22a,22b 学習済み生成器
23,23a 人工的良品画像記憶部
24b 人工的良品差分画像記憶部
30,30a,30b 検査部
31,31a,31b 検査画像記憶部
32,32a 良品画像記憶部
33,33a,33b 良品判定部
34b 良品差分画像記憶部
35b 検査差分画像生成部
36b 検査差分画像記憶部
1,1a, 1b Image inspection system 10,10a, 10b Hostile
Claims (12)
Translated fromJapanese所定の入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成する生成器、
複数の実際の良品画像を入力すると共に、前記生成器から前記人工的な良品画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品画像及び前記複数の実際の良品画像が、実際の良品画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力する識別器、
前記人工的な良品画像を記憶する人工的良品画像記憶部、及び、
前記複数の実際の良品画像を記憶する実良品画像記憶部を備え、
前記生成器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、前記識別器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行うニューラルネットワーク部と、
前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき人工的な良品画像を生成する画像生成部と、
検査画像を入力して、当該検査画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する検査部と、を有する
ことを特徴とする画像検査システム。An image inspection system that performs image inspection
A generator that generates an artificial good image based on the specified input information,
A plurality of actual non-defective product images are input, and the artificial non-defective product image is input from the generator, and the artificial non-defective product image and the plurality of actual non-defective product images are recognized as actual non-defective product images. A classifier that calculates the probability indicating whether or not the image is present and outputs the probability or its error for each one or a plurality of images to the generator.
An artificial good product image storage unit that stores the artificial good product image, and
A real good product image storage unit for storing the plurality of actual good product images is provided.
The generator performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product image is recognized as an actual good product image, and the discriminator performs machine learning so that the artificial good product image is not an actual good product image but a plurality of the above. A neural network unit that performs machine learning to increase the probability that the actual good product image is recognized as an actual good product image.
An image generator that generates an artificial non-defective image based on predetermined input information by the trained generator obtained by the neural network unit, and an image generator.
An inspection unit that inputs an inspection image and compares the inspection image with an artificial non-defective product image generated by the image generation unit or an actual non-defective product image to determine whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product. An image inspection system characterized by having,.
所定の入力情報にもとづいて、基準画像との差分を表す人工的な良品の差分画像を生成する生成器、
前記人工的な良品の差分画像と基準画像とを合成して、人工的な良品画像を生成する基準画像合成部、
複数の実際の良品画像を入力すると共に、前記基準画像合成部により生成された前記人工的な良品画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品画像及び前記実際の良品画像が、実際の良品画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力する識別器、
前記人工的な良品画像を記憶する人工的良品画像記憶部、及び、
前記複数の実際の良品画像を記憶する実良品画像記憶部を備え、
前記生成器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、前記識別器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行うニューラルネットワーク部と、
前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき人工的な良品画像を生成する画像生成部と、
検査画像を入力して、当該検査画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する検査部と、を有する
ことを特徴とする画像検査システム。An image inspection system that performs image inspection
A generator that generates an artificial non-defective difference image that represents the difference from the reference image based on the predetermined input information.
A reference image synthesizer that generates an artificial non-defective image by synthesizing the difference image of the artificial non-defective product and the reference image.
A plurality of actual non-defective product images are input, and the artificial non-defective product image generated by the reference image compositing unit is input, and the artificial non-defective product image and the actual non-defective product image are actual non-defective product images. A classifier that calculates the probability indicating whether or not it is recognized and outputs the probability or its error for each one or a plurality of images to the generator.
An artificial good product image storage unit that stores the artificial good product image, and
A real good product image storage unit for storing the plurality of actual good product images is provided.
The generator performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product image is recognized as an actual good product image, and the discriminator performs machine learning so that the artificial good product image is not an actual good product image but a plurality of the above. A neural network unit that performs machine learning to increase the probability that the actual good product image is recognized as an actual good product image.
An image generator that generates an artificial non-defective image based on predetermined input information by the trained generator obtained by the neural network unit, and an image generator.
An inspection unit that inputs an inspection image and compares the inspection image with an artificial non-defective product image generated by the image generation unit or an actual non-defective product image to determine whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product. An image inspection system characterized by having,.
所定の入力情報にもとづいて、基準画像との差分を表す人工的な良品の差分画像を生成する生成器、
複数の実際の良品画像を入力して、基準画像との差分を抽出し、実際の良品の差分画像を生成する実良品差分画像生成部、
前記実際の良品の差分画像を入力すると共に、前記生成器から前記人工的な良品の差分画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品の差分画像及び前記実際の良品の差分画像が、実際の良品の差分画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力する識別器、
前記人工的な良品の差分画像を記憶する人工的良品差分画像記憶部、及び、
前記複数の実際の良品の差分画像を記憶する実良品差分画像記憶部を備え、
前記生成器が前記人工的な良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、前記識別器が前記人工的な良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品の差分画像が実際の良品の差分画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行うニューラルネットワーク部と、
前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき基準画像との差分を表す人工的な良品の差分画像を生成する画像生成部と、
検査画像を入力して、基準画像との差分を抽出し、検査画像の差分画像を生成する検査差分画像生成部、及び、前記検査画像の差分画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品の差分画像又は実際の良品の差分画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する良品判定部を備えた検査部と、を有する
ことを特徴とする画像検査システム。An image inspection system that performs image inspection
A generator that generates an artificial non-defective difference image that represents the difference from the reference image based on the predetermined input information.
A real good product difference image generator that inputs multiple actual good product images, extracts the difference from the reference image, and generates the actual good product difference image.
The difference image of the actual non-defective product is input, and the difference image of the artificial non-defective product is input from the generator, and the difference image of the artificial non-defective product and the difference image of the actual non-defective product are the actual non-defective products. A classifier that calculates the probability indicating whether or not it is recognized as a difference image and outputs the probability or its error for each one or a plurality of images to the generator.
An artificial non-defective product difference image storage unit that stores the artificial non-defective product difference image, and
A real good product difference image storage unit for storing the plurality of actual good product difference images is provided.
The generator performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the difference image of the artificial good product is recognized as the difference image of the actual good product, and the discriminator performs machine learning so that the difference image of the artificial good product is the actual good product. A neural network unit that performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the plurality of actual good product difference images are recognized as actual good product difference images instead of the difference images of the above.
An image generator that generates an artificial non-defective difference image that represents the difference from the reference image based on predetermined input information by the trained generator obtained by the neural network unit.
An inspection difference image generation unit that inputs an inspection image, extracts a difference from the reference image, and generates a difference image of the inspection image, and an artificial artificial difference image generated by the image generation unit. An image inspection system including an inspection unit including a non-defective product determination unit for determining whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product by comparing with a non-defective product difference image or an actual non-defective product difference image.
ことを特徴とする請求項1〜4のいずれかに記載の画像検査システム。Any of claims 1 to 4, wherein the inspection unit detects defects existing in the inspection image by differentiating the inspection image from the artificial non-defective product image or the actual non-defective product image. The image inspection system described in.
ことを特徴とする請求項1〜4のいずれかに記載の画像検査システム。Claim 1 is characterized in that the inspection unit determines whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product by calculating an evaluation value of the inspection image and the artificial non-defective product image or the actual non-defective product image. The image inspection system according to any one of 4 to 4.
ことを特徴とする請求項1〜4のいずれかに記載の画像検査システム。Claims 1 to 1, wherein the inspection unit determines whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product based on the similarity between the inspection image and the artificial non-defective product image or the actual non-defective product image. The image inspection system according to any one of 4.
ニューラルネットワーク部における生成器が、所定の入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成して人工的良品画像記憶部に記憶させ、
ニューラルネットワーク部における識別器が、実良品画像記憶部に記憶されている複数の実際の良品画像を入力すると共に、前記生成器から前記人工的な良品画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品画像及び前記実際の良品画像が、実際の良品画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力し、
前記生成器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、前記識別器が前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行い、
画像生成部が、前記ニューラルネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき人工的な良品画像を生成し、
検査部が、検査画像を入力して、当該検査画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する
ことを特徴とする画像検査方法。It is an image inspection method that performs image inspection.
The generator in the neural network unit generates an artificial non-defective image based on the predetermined input information and stores it in the artificial non-defective image storage unit.
The classifier in the neural network unit inputs a plurality of actual non-defective product images stored in the real non-defective product image storage unit, and also inputs the artificial non-defective product image from the generator to obtain the artificial non-defective product image and the artificial non-defective product image. The probability indicating whether or not the actual non-defective product image is recognized as the actual non-defective product image is calculated, and the probability or its error for each one or a plurality of images is output to the generator.
The generator performs machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product image is recognized as an actual good product image, and the discriminator performs machine learning so that the artificial good product image is not an actual good product image but a plurality of the above. Machine learning is performed to increase the probability that the actual good product image of is recognized as the actual good product image.
The image generation unit generates an artificial non-defective image based on predetermined input information by the trained generator obtained by the neural network unit.
The inspection unit inputs an inspection image and compares the inspection image with an artificial non-defective product image generated by the image generation unit or an actual non-defective product image to determine whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product. An image inspection method characterized by doing so.
コンピュータを、
所定の入力情報にもとづいて、人工的な良品画像を生成する生成器、
複数の実際の良品画像を入力すると共に、前記生成器から前記人工的な良品画像を入力し、前記人工的な良品画像及び前記複数の実際の良品画像が、実際の良品画像であると認められるか否かを示す確率を計算し、一又は複数の画像ごとの前記確率又はその誤差を前記生成器へ出力する識別器、
前記人工的な良品画像を記憶する人工的良品画像記憶部、及び、
前記複数の実際の良品画像を記憶する実良品画像記憶部として機能させ、
前記生成器に前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行わせ、前記識別器に前記人工的な良品画像が実際の良品画像でなく、前記複数の実際の良品画像が実際の良品画像であると認められる確率を高めるように機械学習を行わせ、さらに、
前記敵対的生成ネットワーク部により得られた学習済み生成器によって、所定の入力情報にもとづき人工的な良品画像を生成する画像生成部、並びに、
検査画像を入力して、当該検査画像を前記画像生成部により生成された人工的な良品画像又は実際の良品画像と比較して、前記検査画像が良品であるか否かを判定する検査部として機能させる
ことを特徴とする画像検査プログラム。An image inspection program that performs image inspection
Computer,
A generator that generates an artificial good image based on the specified input information,
A plurality of actual non-defective product images are input, and the artificial non-defective product image is input from the generator, and the artificial non-defective product image and the plurality of actual non-defective product images are recognized as actual non-defective product images. A classifier that calculates the probability indicating whether or not the image is present and outputs the probability or its error for each one or a plurality of images to the generator.
An artificial good product image storage unit that stores the artificial good product image, and
It functions as a real good product image storage unit that stores the plurality of actual good product images.
The generator is made to perform machine learning so as to increase the probability that the artificial good product image is recognized as an actual good product image, and the classifier is made to perform the artificial good product image instead of the actual good product image. Machine learning is performed to increase the probability that multiple actual good product images are recognized as actual good product images, and further.
An image generator that generates an artificial non-defective image based on predetermined input information by the trained generator obtained by the hostile generation network unit, and
As an inspection unit that inputs an inspection image and compares the inspection image with an artificial non-defective product image generated by the image generation unit or an actual non-defective product image to determine whether or not the inspection image is a non-defective product. An image inspection program characterized by making it work.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019220123AJP2021089219A (en) | 2019-12-05 | 2019-12-05 | Image inspection system and image inspection method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019220123AJP2021089219A (en) | 2019-12-05 | 2019-12-05 | Image inspection system and image inspection method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2021089219Atrue JP2021089219A (en) | 2021-06-10 |
Family
ID=76220325
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019220123APendingJP2021089219A (en) | 2019-12-05 | 2019-12-05 | Image inspection system and image inspection method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2021089219A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023135089A (en)* | 2022-03-15 | 2023-09-28 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Inspection equipment and inspection method |
| WO2024261856A1 (en)* | 2023-06-20 | 2024-12-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing method, and recording medium |
| WO2024261964A1 (en)* | 2023-06-22 | 2024-12-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Learning device, information processing device, learning method, and recording medium |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005156334A (en)* | 2003-11-25 | 2005-06-16 | Nec Tohoku Sangyo System Kk | Pseudo defective image automatic creation device and imaging inspection device |
| JP2017054239A (en)* | 2015-09-08 | 2017-03-16 | 株式会社Screenホールディングス | Image classification apparatus and image classification method |
| US20170200260A1 (en)* | 2016-01-11 | 2017-07-13 | Kla-Tencor Corporation | Accelerating semiconductor-related computations using learning based models |
| JP6241576B1 (en)* | 2016-12-06 | 2017-12-06 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Inspection apparatus and inspection method |
| JP2019087181A (en)* | 2017-11-10 | 2019-06-06 | アズビル株式会社 | Image inspection apparatus and method |
| CN109916906A (en)* | 2018-10-11 | 2019-06-21 | 乐人株式会社 | Defect detecting device and method |
| US20190197358A1 (en)* | 2017-12-21 | 2019-06-27 | International Business Machines Corporation | Generative Adversarial Network Medical Image Generation for Training of a Classifier |
| JP2019530117A (en)* | 2016-09-14 | 2019-10-17 | ケーエルエー コーポレイション | Convolutional neural network based mode selection and defect classification for image fusion |
- 2019
- 2019-12-05JPJP2019220123Apatent/JP2021089219A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005156334A (en)* | 2003-11-25 | 2005-06-16 | Nec Tohoku Sangyo System Kk | Pseudo defective image automatic creation device and imaging inspection device |
| JP2017054239A (en)* | 2015-09-08 | 2017-03-16 | 株式会社Screenホールディングス | Image classification apparatus and image classification method |
| US20170200260A1 (en)* | 2016-01-11 | 2017-07-13 | Kla-Tencor Corporation | Accelerating semiconductor-related computations using learning based models |
| JP2019530117A (en)* | 2016-09-14 | 2019-10-17 | ケーエルエー コーポレイション | Convolutional neural network based mode selection and defect classification for image fusion |
| JP6241576B1 (en)* | 2016-12-06 | 2017-12-06 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Inspection apparatus and inspection method |
| JP2019087181A (en)* | 2017-11-10 | 2019-06-06 | アズビル株式会社 | Image inspection apparatus and method |
| US20190197358A1 (en)* | 2017-12-21 | 2019-06-27 | International Business Machines Corporation | Generative Adversarial Network Medical Image Generation for Training of a Classifier |
| CN109916906A (en)* | 2018-10-11 | 2019-06-21 | 乐人株式会社 | Defect detecting device and method |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023135089A (en)* | 2022-03-15 | 2023-09-28 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Inspection equipment and inspection method |
| JP7639744B2 (en) | 2022-03-15 | 2025-03-05 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Inspection device and inspection method |
| WO2024261856A1 (en)* | 2023-06-20 | 2024-12-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing method, and recording medium |
| WO2024261964A1 (en)* | 2023-06-22 | 2024-12-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Learning device, information processing device, learning method, and recording medium |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10997711B2 (en) | Appearance inspection device | |
| US11774859B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for evaluating an unknown effect of defects of an element of a photolithography process | |
| CN109741268B (en) | Damaged image complement method for wall painting | |
| JP2021089219A (en) | Image inspection system and image inspection method | |
| JP5441728B2 (en) | Sensory inspection device and sensory inspection method | |
| CN113554636B (en) | Chip defect detection method based on generation of countermeasure network and calculation hologram | |
| KR102428740B1 (en) | Point Cloud Completion Network Creation and Point Cloud Data Processing | |
| CN117173461A (en) | Multi-visual task filling container defect detection method, system and medium | |
| Eastwood et al. | Generation and categorisation of surface texture data using a modified progressively growing adversarial network | |
| TW202100951A (en) | Image matching method and calculation system for performing image matching processing | |
| CN117726576A (en) | Image enhancement for machine learning based defect inspection | |
| JP5218084B2 (en) | Inspection method | |
| Elmquist et al. | A performance contextualization approach to validating camera models for robot simulation | |
| CN116818891A (en) | Ultrasonic defect detection and classification system using machine learning | |
| JP7070308B2 (en) | Estimator generator, inspection device, estimator generator method, and estimator generator | |
| WO2022202456A1 (en) | Appearance inspection method and appearance inspection system | |
| KR20220136883A (en) | Point cloud data completion and point cloud data processing | |
| EP3997574B1 (en) | Method for simulation assisted data generation and deep learning intelligence creation in non-destructive evaluation systems | |
| Avola et al. | Real-Time GAN-Based model for underwater image enhancement | |
| JP7581811B2 (en) | Image processing system and image processing program | |
| YOUCEFA et al. | Using Convolutional Neural Networks to detect defects in manufacturing | |
| CN119169038B (en) | A generative edge trace reduction method based on diffusion model | |
| CN120509325B (en) | Fatigue crack growth identification method for aero-engine components based on machine vision | |
| KR102855690B1 (en) | Wafer defect pattern classification method using topological data analysis | |
| CN118887244B (en) | Multi-mode image-based multi-task defect segmentation method and system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20221128 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20230531 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20230606 | |
| A601 | Written request for extension of time | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date:20230731 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20231005 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20231121 | |
| A601 | Written request for extension of time | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date:20240115 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20240611 |