JP2019205852A - System for adjusting blood glucose level of person, and method of controlling wirelessly connected eeg monitor and insulin delivery device - Google Patents
System for adjusting blood glucose level of person, and method of controlling wirelessly connected eeg monitor and insulin delivery deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2019205852A JP2019205852AJP2019137416AJP2019137416AJP2019205852AJP 2019205852 AJP2019205852 AJP 2019205852AJP 2019137416 AJP2019137416 AJP 2019137416AJP 2019137416 AJP2019137416 AJP 2019137416AJP 2019205852 AJP2019205852 AJP 2019205852A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- eeg
- insulin
- monitor
- hypoglycemia
- person
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of The Respiration, Hearing Ability, Form, And Blood Characteristics Of Living Organisms (AREA)
- Infusion, Injection, And Reservoir Apparatuses (AREA)
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapaneseこの発明は人の血糖値(血中グルコース・レベル)(blood glucose level)を調整するためのシステムに関する。より詳細にはこの発明は,人の身体にインシュリンを放出する(release)ように構成されるインシュリン投与装置(insulin delivery device)と,EEG電極を備えるEEG検知部を有するEEGモニタとを備えるシステムに関する。EEGモニタは,頭皮において皮下的に配置されるまたは外耳道内に配置されるEEG検知部とともに人の耳領域内に配置されるように構成される。上記EEGモニタは,耳に配置されて低血糖症の発症を識別するように構成されるEEG信号処理装置を備えている。上記システムはさらに上記EEGモニタと上記インシュリン投与装置との間の無線通信リンクを備えている。 The present invention relates to a system for adjusting a person's blood glucose level (blood glucose level). More particularly, the present invention relates to a system comprising an insulin delivery device configured to release insulin into a human body and an EEG monitor having an EEG detector with an EEG electrode. . The EEG monitor is configured to be disposed in a human ear region together with an EEG detection unit disposed subcutaneously in the scalp or disposed in the external auditory canal. The EEG monitor includes an EEG signal processing device that is placed in the ear and configured to identify the onset of hypoglycemia. The system further comprises a wireless communication link between the EEG monitor and the insulin dispensing device.
インシュリン・ポンプのような連続インシュリン注入のためのインシュリン投与装置を,一日のうちで変化する速度でおよび上記人のニーズに応じてインシュリンを投与するために配置することでき,または上記ポンプは上記人によって行われる特定のリクエストに応答して投与することができる。 An insulin dispensing device for continuous insulin infusion, such as an insulin pump, can be arranged to administer insulin at a rate that varies throughout the day and according to the needs of the person, or the pump It can be administered in response to specific requests made by a person.
インシュリン・ポンプを,血糖モニタ(血糖計)(blood glucose monitor)または連続血糖(グルコース)モニタ(連続血糖計)(continuous glucose monitor)(CGM)と組み合わせて,糖尿病患者の血糖値の連続自動制御を行う要望がある。 Combine insulin pump with blood glucose monitor or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) for continuous automatic control of blood glucose levels in diabetic patients There is a request to do.
臨床上重要な課題は人が低血糖状態に近づいている場合に直接的に制御することができないことである。人の脳波を分析することによって低血糖の発症到来(低血糖の発症が近づいていること)(upcoming onset of hypoglycemia)を検出することができる。 A clinically important issue is that one cannot control directly when a person is approaching a hypoglycemic state. By analyzing human brain waves, it is possible to detect the upcoming onset of hypoglycemia.
米国特許第8,348,842B1は,インシュリン・ポンプおよび血糖状態(glycemic state)に関連する出力を生成するように構成されたセンサを含むシステムを開示する。センサの一タイプはEEGを測定するものである。 U.S. Pat. No. 8,348,842 B1 discloses a system that includes an insulin pump and a sensor configured to generate an output related to a glycemic state. One type of sensor measures EEG.
米国特許6,572,542B1は,心電図信号およびEEG信号の結合処理を,低血糖事象を検知するために用いるシステムを開示する。事象によって患者にインシュリンまたはグルカゴンを投与することができる。 US Pat. No. 6,572,542 B1 discloses a system that uses the combined processing of an electrocardiogram signal and an EEG signal to detect a hypoglycemic event. Depending on the event, the patient can be administered insulin or glucagon.
これらの既知のシステムの課題は,EEGモニタリングとインシュリン投与装置とが直接にリンクしていないことであり,したがって低血糖症の発症を予防する機会がない。 The problem with these known systems is that EEG monitoring and insulin delivery devices are not directly linked, so there is no opportunity to prevent the development of hypoglycemia.
上述の課題が,低血糖症の発症到来がEEG信号処理装置によって識別される場合にEEGモニタがインシュリン投与装置に警告信号を送信するシステムによって解決される。上記警告信号によって,上記インシュリン投与装置は所定期間インシュリン投与を制限し,上記警告が上記人または介護者に提供される。 The above problems are solved by a system in which an EEG monitor sends a warning signal to an insulin administration device when the onset of hypoglycemia is identified by the EEG signal processing device. By means of the warning signal, the insulin administration device limits insulin administration for a predetermined period of time and the warning is provided to the person or caregiver.
上記インシュリン投与の制限は,所定の期間インシュリンの投与を完全に停止することを意味するか,またはインシュリンの投与を所定の期間何らかの程度制限する(limiting the insulin delivery to some extend)ことを意味する。インシュリン投与が制限される上記所定期間の長さおよび程度は,警告メッセージ履歴,たとえば複数の警告メッセージが比較的短い時間内に既に送信されたかどうかに応じたものとすることができる。また,制限期間が長すぎる場合には高血糖のリスクも考慮することができる。 The restriction of insulin administration means that the administration of insulin is completely stopped for a predetermined period, or that the insulin administration is limited to some extent for a predetermined period. The length and extent of the predetermined period during which insulin administration is limited can depend on the warning message history, eg, whether multiple warning messages have already been sent within a relatively short time. In addition, if the restriction period is too long, the risk of hyperglycemia can be considered.
この解決手段の利点は,インシュリン投与の自動制限が提供され,これによって上記システムの安全性が高まることである。 The advantage of this solution is that an automatic restriction of insulin administration is provided, which increases the safety of the system.
上記システムの利点は,最適範囲内に血糖値を保持することを目的とするインシュリン投与のより正確な調整を可能にすることである。このより良い調節は,より即効性のインシュリンの使用によって達成することができる。これは,EEGモニタリングによって提供される格別な安全性のために安全に用いることができる。上記システムを利用する者は,長期的に健康状態が向上するメリットを得ることができる。 The advantage of the system is that it allows a more precise adjustment of insulin administration aimed at keeping the blood glucose level within an optimal range. This better regulation can be achieved through the use of more immediate insulin. This can be used safely for the extra safety provided by EEG monitoring. Those who use the above system can obtain the merit of improving their health status over the long term.
一実施態様において上記システムはグルコース(血糖)モニタ(glucose monitor)も備えている。これは,たとえば自動血糖値検出器(automatic blood glucose level detector)または組織液グルコース(tissue fluid glucose)を自動的にモニタリングする連続グルコース(血糖)モニタ(continuous glucose monitor)(CGM)とすることができる。実際のグルコース・レベルを参照してEEG信号から見つけられる結果を評価することが可能になる。このようなグルコース・モニタは標準的な血糖測定値に対して定期的に較正することができる。 In one embodiment, the system also includes a glucose monitor. This can be, for example, an automatic blood glucose level detector or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) that automatically monitors tissue fluid glucose. It is possible to evaluate the results found from the EEG signal with reference to the actual glucose level. Such glucose monitors can be periodically calibrated to standard blood glucose measurements.
一実施態様では,上記インシュリン投与装置が,上記インシュリン投与装置に必要とされるサービスを上記EEGモニタに通知するように構成される。このようなサービスは,たとえば電池の充電または交換の必要性,インシュリン・リザーバへの補充の必要性,修理されるべきなんらかの故障があることである。上記EEGモニタはその後上記システムのユーザに通知することができる。 In one embodiment, the insulin dispensing device is configured to notify the EEG monitor of services required by the insulin dispensing device. Such services include, for example, the need to charge or replace the battery, the need to refill the insulin reservoir, and some failure to be repaired. The EEG monitor can then notify the user of the system.
一実施態様では,上記システムは上記EEGモニタによって制御可能なグルカゴンまたはグルコース投与装置をさらに備えている。これは,上記システムが低血糖症の状態を予防または改善することができるようになることを容易にする。 In one embodiment, the system further comprises a glucagon or glucose administration device that is controllable by the EEG monitor. This facilitates the system becoming able to prevent or ameliorate the hypoglycemic condition.
一実施態様では,上記EEGモニタが機能しておりかつ上記システムを装着している人のEEG信号をキャプチャしているように制御されている場合にだけ,上記インシュリン投与装置はインシュリンを投与するように構成される。たとえ低血糖症の発症が到来しているにもかかわらず,上記EEGモニタの故障によって上記人にインシュリンの継続的投与の結果がもたらされることが防止される。この場合には,上記EEGモニタが機能していないことについて上記人に通知も提供するべきである。実際上は,EEGモニタの故障に応じて,インシュリン・ポンプから上記人に対して血糖値のより頻繁な制御を行うことを指示し,およびインシュリンの投与について幾ばくかの制限を導入することができる。すなわち,低血糖を避ける努力において高血糖に達するリスクは避けなければならない(the risk of ending up with hyperglycemia in the effort to avoid hypoglycemia should be avoided)。 In one embodiment, the insulin dispensing device will dispense insulin only if the EEG monitor is functional and controlled to capture the EEG signal of the person wearing the system. Configured. Despite the onset of hypoglycemia, the failure of the EEG monitor prevents the person from having the result of continuous administration of insulin. In this case, the person should also be notified that the EEG monitor is not functioning. In practice, in response to an EEG monitor failure, the insulin pump can instruct the person to have more frequent control of blood glucose levels and introduce some restrictions on insulin administration. . That is, the risk of ending up with hyperglycemia in the effort to avoid hypoglycemia should be avoided.
一実施態様では,上記EEGモニタが無線通信リンクのためのアンテナを備え,上記アンテナが上記人の皮膚層の外側かつ外耳道の外側に配置されるように構成されている。アンテナのこの位置は,インシュリン投与装置および上記システムの他のユニットとの間の信頼し得る電磁通信のための最適状態を助長にする。 In one embodiment, the EEG monitor comprises an antenna for a wireless communication link, and the antenna is configured to be located outside the person's skin layer and outside the ear canal. This location of the antenna facilitates optimal conditions for reliable electromagnetic communication between the insulin dispensing device and other units of the system.
一実施態様では,自動血糖値検出器(automatic blood glucose level detector)またはCGMが上記EEGモニタまたは上記インシュリン・ポンプに接続されている。これによって,グルコース・レベルに関する連続データが容易に利用可能になり,低血糖の発症到来を検出するシステムの能力を向上させることができる。 In one embodiment, an automatic blood glucose level detector or CGM is connected to the EEG monitor or the insulin pump. This makes continuous data on glucose levels readily available and improves the ability of the system to detect the onset of hypoglycemia.
一実施態様では,上記EEGモニタが,低血糖症の発症到来が識別された事象において血糖値を測定するためのリクエストを送信するように構成される。 In one embodiment, the EEG monitor is configured to send a request to measure a blood glucose level in an event where the onset of hypoglycemia has been identified.
一実施態様では,上記EEG検知部が頭皮において皮下的に配置される。これによって上記EEG電極に組織に対する良好かつ信頼性のある接触が与えられ,クリアなEEG信号を得ることができる。 In one embodiment, the EEG detector is placed subcutaneously in the scalp. As a result, the EEG electrode is given good and reliable contact with the tissue, and a clear EEG signal can be obtained.
一実施態様では,上記EEGモニタが,上記EEGモニタおよび上記インシュリン投与装置の両方からの上記人に対する音声メッセージおよび警告を提供するように構成されるスピーカを備えている。耳領域にEEGモニタを配置することによって上記EEGモニタのスピーカが聞き取りやすくなり,上記システムを装着している人の周囲の人には何らのメッセージまたは警告が聞こえない。 In one embodiment, the EEG monitor comprises a speaker configured to provide voice messages and warnings to the person from both the EEG monitor and the insulin dispensing device. Placing the EEG monitor in the ear region makes it easier to hear the speaker of the EEG monitor, and people around the person wearing the system cannot hear any message or warning.
第2の観点において,この発明は人の血糖値を調節する方法に関するものであり,
インシュリンを人の身体に放出するように構成されるインシュリン投与装置を提供し,
上記人の耳領域にEEGモニタを配置し,ここで上記EEGモニタがEEG電極を含むEEG検知部を有している。上記EEG検知部は頭皮において皮下的に配置されまたは外耳道内に配置され,上記EEGモニタは耳に配置され,かつ低血糖の発症を識別するように構成されるEEG信号処理装置を備えており,
上記EEGモニタと上記インシュリン投与装置との間に無線通信リンクを確立し,
低血糖症の発症到来を識別するために上記EEG検知部によってサンプリングされるEEG信号を分析するように上記EEG信号処理装置を構成し,
低血糖症の発症到来が識別された場合に警告信号を上記インシュリン投与装置に送るように上記EEGモニタを構成する。上記警告信号によって,上記インシュリン投与装置に所定時間上記インシュリン投与を制限させることができる。上記EEGモニタはさらに警告を上記人または介護者に提供する。In a second aspect, the present invention relates to a method for regulating a person's blood glucose level,
Providing an insulin administration device configured to release insulin into a human body;
An EEG monitor is disposed in the human ear region, and the EEG monitor has an EEG detection unit including an EEG electrode. The EEG detector is placed subcutaneously in the scalp or in the ear canal, the EEG monitor is placed in the ear and comprises an EEG signal processor configured to identify the onset of hypoglycemia;
Establishing a wireless communication link between the EEG monitor and the insulin delivery device;
Configuring the EEG signal processing device to analyze the EEG signal sampled by the EEG detector to identify the onset of hypoglycemia;
The EEG monitor is configured to send a warning signal to the insulin administration device when the onset of hypoglycemia is identified. The insulin administration device can restrict the insulin administration for a predetermined time by the warning signal. The EEG monitor further provides a warning to the person or caregiver.
以下,図面を参照してこの発明の実施態様をより詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the drawings.
図1は,EEGモニタ1,インシュリン投与装置(insulin delivery device)またはインシュリン・ポンプ2,および血糖モニタ(blood glucose monitor)またはCGMの形態のグルコース・モニタ(血糖モニタ)3を備えるシステムを示している。上記EEGモニタ1および上記インシュリン・ポンプ2は無線接続6によって接続されている。上記グルコース・モニタ3は手動または自動のものとすることができ,測定されたグルコース・レベルを上記インシュリン・ポンプ2に与えることができる。 FIG. 1 shows a system comprising an EEG monitor 1, an insulin delivery device or
上記EEGモニタ1はモニタされる人の耳領域に配置されるように構成されている。上記EEGモニタ1は2つの主要部,すなわちEEG検知(感知)部12およびEEG信号処理装置11を備えている。これに加えて上記EEGモニタは警告またはメッセージを提供するための構成要素,たとえばスピーカ13も備えている。上記EEGモニタ1は,たとえば電源を電池の形態で備えることもできる。 The EEG monitor 1 is configured to be arranged in the ear region of a person to be monitored. The EEG monitor 1 includes two main parts, that is, an EEG detection (sensing)
上記EEG検知部12はEEG信号を検出するための電極(複数)を有している。上記EEG検知部12はEEG電極(複数)を備え,これを頭皮において皮下的に,好ましくは耳の後ろから延在する領域に配置することができる。上記EEG電極は外耳道内における表皮電極(surface skin electrodes)として配置することもできる。上記EEG電極は組織または皮膚への直接電気接続(direct electric connection)を有するタイプのものとすることでき,または上記電極の電導部と上記組織もしくは皮膚との間に誘電物質が配置される静電容量タイプのものとすることができる。皮下または外耳道内のいずれかに上記EEG電極を有することの利点は,良好かつクリアなEEG信号を受信することができ,かつこのような位置における電極は,頭皮外側の位置に比べて周囲からの電磁雑音をピックアップすることからより保護されることである。 The
上記EEG電極の皮下配置または外耳道配置は美容の観点からも好ましい。上記皮下配置または外耳道配置はさらに信頼性の観点からも好ましく,それはこれらの位置は組織または皮膚のいずれかへの信頼性のある安定的な接触を助長し,すなわち接触不良のリスクおよびこれによるEEG信号が検出できなくなることを,たとえば運動その他日常活動中に接触不良を起こしやすい外部電極に比べて,非常に少なくする。 The subcutaneous placement or the external auditory canal placement of the EEG electrode is also preferable from the viewpoint of beauty. The subcutaneous or external auditory canal placement is also preferred from a reliability point of view, as these locations facilitate reliable and stable contact with either tissue or skin, ie the risk of poor contact and the resulting EEG It makes the signal undetectable much less, for example, compared to external electrodes that are prone to contact failure during exercise and other daily activities.
上記EEG信号処理装置11は上記EEGセンサからEEG信号を受信し,上記信号を処理して上記測定EEG信号から特定の特徴を抽出するように構成されている。この特徴抽出は,たとえばEEG信号中の特定周波数および振幅に関連付けることができる。この抽出された特徴を分類して,それが低血糖の発症到来(比較的近い将来の低血糖発症)の特定(identifying an upcoming onset of hypoglycemia)に関連しているかどうかを決定することができる。上記EEG信号処理装置は好ましくはスピーカに接続され,上記システムのユーザに対して低血糖症の発症到来の警告が提供される。 The
識別される低血糖症の発症到来に関する警告信号は,上記EEGモニタが有する無線接続6から上記インシュリン・ポンプ2に送信することもできる。 The identified warning signal regarding the onset of hypoglycemia can also be transmitted to the
上記無線接続6には任意の形態を用いることができるが,多くの場合,好ましくは,電磁ベースの,または無線の(radio)接続が選択される。上記接続のためのプロトコルはブルートゥースに基づくものとすることができ,好ましくは低電力ブルートゥース接続とされる。 Any form of wireless connection 6 can be used, but in many cases, preferably an electromagnetic-based or radio connection is selected. The protocol for the connection can be based on Bluetooth, preferably a low power Bluetooth connection.
上記インシュリン・ポンプ2は,上記システムのユーザへ皮下注入によってインシュリンを投与(管理)する。上記インシュリン・ポンプは典型的には連続的にベーザルドーズ(basal dose)(基礎用量)を投与し,食事や高血糖レベルに関連したボーラスドーズ(bolus dose)(増用量)を補充することができる。ベーザルレートおよびボーラスの両方のインシュリン投与は個々のユーザにニーズに合わせることができる。グルコース・モニタリングからの入力は投与されるインシュリンドーズの進行調整に用いられる。 The
異なるタイプのグルコース・モニタ3を用いてもよい。一のタイプはフィンガースティック測定(finger stick measurement)であり,これは指の小さい刺し傷(small prick)からの血液の液滴を得ることに基づくもので,小さいストリップ上にこれを置き,血糖値計で解析される。その結果は,無線で,または上記結果を上記インシュリン・ポンプにユーザが入力することで,直接に上記インシュリン・ポンプに転送することができる。 Different types of glucose monitor 3 may be used. One type is finger stick measurement, which is based on obtaining a drop of blood from a small prick of the finger, placing it on a small strip, Analyzed in total. The result can be transferred directly to the insulin pump wirelessly or by the user inputting the result to the insulin pump.
これに代わる直接血糖モニタリングが上述したCGMであり,これは組織液(tissue fluid)中のグルコース・レベルを計測するものである。これはたとえば皮膚に穿刺される針によって皮下的に配置されるセンサを含み,上記針および貫通スポット(penetration spot)は定期的に交換される。グルコース・センサをより恒久的に皮下に埋め込むこともできる。この埋込グルコース・センサは,分離部分とすることが可能な,または上記インシュリン・ポンプの一部とすることが可能な外部装置と好ましくは無線で接続することができる。 An alternative direct blood glucose monitoring is the CGM described above, which measures the glucose level in tissue fluid. This includes, for example, a sensor placed subcutaneously by a needle punctured into the skin, and the needle and penetration spot are periodically replaced. The glucose sensor can also be implanted more permanently subcutaneously. This implanted glucose sensor can be preferably connected wirelessly to an external device that can be a separate part or can be part of the insulin pump.
図1のシステムが動作しているとき,上記インシュリン・ポンプ2は,通常,ボーラスドーズを補充したベーゼルドーズを投与し,上記ボーラスドーズはユーザのリクエスト(要求)によって投与することができる。グルコース・レベルは選択時(selected times)にまたは連続的に検査され,それに応じてインシュリン・ポンプからのドーズを調整することができる。上記EEGモニタ1はEEG信号を連続的にモニタリングし,低血糖の発症到来が検出された場合に,警告信号が上記インシュリン・ポンプに送信され,好ましくはスピーカを使用してユーザに直接警告が提供される。自動グルコース・モニタが上記システムの一部である場合には,低血糖症の発症到来の上記EEGモニタからの警告は,グルコース測定の要求をもたらすものとすべきである。 When the system of FIG. 1 is operating, the
上記EEGモニタが低血糖症の発症が近づいていることを示しているが,上記自動グルコース・モニタが正常なグルコース・レベルを示している場合には,マニュアルによるフィンガースティック・タイプの血糖値測定をコントロールとして要求することができる。 If the EEG monitor indicates the onset of hypoglycemia, but the automatic glucose monitor indicates normal glucose levels, manual fingerstick-type blood glucose measurement should be performed. Can be requested as a control.
上記インシュリン・ポンプは,警告メッセージまたは信号を受信すると,ユーザへのインシュリンの投与を制限するように設定される。好ましくは,ユーザの糖尿病に見識を有する医師が,任意の警告信号に対する応答のプログラミングを含むインシュリン・ポンプの正確なプログラミングに対してアドバイスを提供するか,または決定をする。インシュリン・ポンプへの警告信号と同時に,警告がユーザに提供される。そのような警告にどのように反応するかについて,たとえば,血糖値の速やかな測定および/または血糖値を上昇させる何らかの特定の栄養素の速やかな取得を,事前にユーザに知らせておくべきである。 The insulin pump is set to limit the administration of insulin to the user upon receipt of a warning message or signal. Preferably, a physician with knowledge of the user's diabetes will provide advice or make decisions on the correct programming of the insulin pump, including programming the response to any warning signal. A warning is provided to the user simultaneously with a warning signal to the insulin pump. The user should be informed in advance of how to react to such warnings, for example, prompt measurement of blood glucose levels and / or rapid acquisition of any specific nutrient that increases blood glucose levels.
インシュリン投与の正確な制限はまた,上記インシュリン・ポンプに接続されたCGMからの入力にも依存させることができる。ユーザの糖尿病の履歴に応じて,低血糖が発症に近いことをEEGモニタまたはCGM測定値のいずれかが示す場合に,インシュリンの投与の制限を導入することができる。上記制限のレベルは,上記EEGモニタによって検出されるEEG信号中の特徴および上記CGMによる正確な測定に基づいて決定することもできる。これは,上記EEGモニタが,EEG信号処理装置によって抽出される特徴に関する情報を,警告メッセージとともに上記インシュリン・ポンプに送信すべきであることを意味する。 The exact limit of insulin administration can also depend on input from the CGM connected to the insulin pump. Depending on the user's history of diabetes, a restriction on insulin administration can be introduced when either the EEG monitor or CGM measurements indicate that hypoglycemia is close to onset. The level of restriction can also be determined based on features in the EEG signal detected by the EEG monitor and accurate measurements by the CGM. This means that the EEG monitor should send information about the features extracted by the EEG signal processor to the insulin pump along with a warning message.
図2はグルカゴン・ポンプ4が追加された図1のシステムを示している。グルカゴン・ポンプは,上記システムが低血糖の発症を予防または克服することができるようにすることを助長する。これはグルカゴン・ポンプを自動的にアクティベーションする(起動する)ことによって行うことができ,その結果として血糖値を上昇させるグルカゴン・ドーズが投与される。EEGモニタが低血糖状態を検出すると,この自動アクティベーションがトリガされる。グルカゴン・ポンプはまた,上記システムを持ち運ぶ(所持する)人によって制御することもできる。これによって上記人は,実際の血糖値が制御される前に,上記EEGモニタが低血糖症の発症到来の警告を送信する状況においてグルカゴン・ドーズを投与することができる。 FIG. 2 shows the system of FIG. 1 with the addition of the glucagon pump 4. Glucagon pumps help the system to prevent or overcome the development of hypoglycemia. This can be done by automatically activating (activating) the glucagon pump, resulting in a glucagon dose that raises the blood glucose level. This automatic activation is triggered when the EEG monitor detects a hypoglycemic condition. The glucagon pump can also be controlled by the person carrying the system. This allows the person to administer glucagon doses in a situation where the EEG monitor sends a warning of the onset of hypoglycemia before the actual blood sugar level is controlled.
上記グルカゴン・ポンプに加えて,これとは独立して,上記システムに外部ユニット5を設けることができる。この外部ユニットはいくつかの機能,たとえばユーザ・インタフェース,データの格納,インターネット接続,および上記システムを持ち運ぶ人に関連する習慣(relevant habits)の追跡および記憶を備えることができる。関連する習慣は,いつ上記人がボーラスを投与するか,いつ食事をとるか,いつ運動するか,またはいつマニュアルで血糖値を測定するかとすることができ,その測定値を,上記外部装置を介して入力させかつ上記インシュリン・ポンプに送ることができる。上記外部装置は,上記目的のためのソフトウェアを備える上記人の携帯電話,腕時計または任意の小型ポータブル・コンピュータ装置とすることができる。上記システムの一または複数の構成要素への接続は無線,たとえばブルートゥース接続とされるべきである。 In addition to the glucagon pump, an
このように外部ユニット5をユーザと上記システムの構成要素との間のインターフェースとして用いることができる。ユーザは,マニュアルで測定された血糖値,食事に関する情報,またはユーザが食べるもの,警告に対する応答もしくは警告のキャンセル,または上記システムに対するユーザの選択調整のような関連情報を入力することができる。 Thus, the
上記外部ユニット5を,上記システムの一または複数の構成要素からのユーザに対する情報を提示するために用いることもできる。これは上記人に,たとえばスピーカを通じて与えられる警報に関連するさらなる詳細とすることができる。この詳細を,上記人がとるべき行動に関する指示とすることができる。また外部ユニット5に接続された上記システム内の任意のユニットの動作状態に関する情報を,上記外部ユニットを通じて上記ユーザに提供してもよい。この例は,電池の充電レベルまたはインシュリン・ポンプもしくはグルカゴン・ポンプのリザーバのレベルとすることができる。 The
上記外部ユニット5をデータの記憶のために用いてもよい。これは警告をトリガするEEG信号の事象に関連するサンプリングされたEEG信号とすることができる。警告のトリガに関連するEEG信号のサンプリングおよび収集は,上記EEG信号からの特定の特徴の抽出およびこれらの特徴の分類のために用いられるアルゴリズムを改善するために用いることができる。特に警告に関連するEEG信号のサンプルは,警告が供給されるべきレベルまたは閾値を調整するために用いることができる。この目的のために警告のときの測定血糖値を関連づけ,自動血糖値モニタまたはCGMから上記外部ユニット5に送信することができ,または上記ユニットから上記外部ユニットに入力されたフィンガースティック計測の結果を送信することができる。 The
上記外部ユニット5はまたインターネット接続を有してもよく,EEG信号サンプルを医師に直接にアップロードするために用いることができ,医師はこのインターネット接続を通じて上記システムの設定を調整することもできる。警告はまた,インターネットを通じて,親戚やヘルパーに送信してもよく,または警報を一または複数のあらかじめ選択された電話番号,ウェブページまたはIPアドレスに直接に送信することもできる。 The
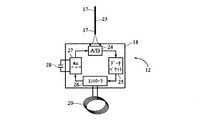
図3は上記システム内のEEGモニタの一例をより詳細に示している。EEGモニタ1は外部EEG信号処理装置11および埋込み型EEG検知部12を備えている。EEG検知部12は,人の耳の後ろに皮下的に配置されるのに適するもので,電子モジュール60に接続された皮下EEG電極(複数)17を含む。上記EEG電極の数は少なくとも2つである。多くの場合,少なくとも3つ以上の電極が望まれる。図4により詳細に示す電子モジュール18は,多くの場合A/D変換器24,通信コントローラ26および電圧レギュレータ27を備えている。電極17はA/D変換器に接続され,上記通信コントローラが誘導リンク19の第1のコイル20に接続される。 FIG. 3 shows an example of the EEG monitor in the system in more detail. The EEG monitor 1 includes an external EEG
上記EEG信号処理装置11は上記誘導リンク19の第2のコイル21に接続されたコントローラ(図示略)を有する信号処理装置10を備えている。上記信号処理装置10はさらに電源用の電池(図示略)に接続され,かつ低血糖症の発症到来が識別されたときに音響信号,たとえば警告を提供するためのスピーカ13に接続されている。上記EEG信号処理装置部11はまたデータのロギングのためのメモリ16,上記システム内の他のユニット,たとえば上記外部ユニットとの無線通信のためのアンテナ14を備える無線機15を備えている。 The EEG
使用時において,上記EEG信号処理装置11は,EEG信号のモニタリングが望まれる人の耳の後ろであって,皮下的に埋込み可能なEEG検知部12の近くに配置することができ,上記EEG検知部12は好ましくは皮膚の直下でかつユーザの耳のすぐ後ろに埋め込まれ,これによって信頼性のある電気EEG信号が上記電極17によって検出されるように配置される。 In use, the
図4にさらに詳細に示すように,上記EEG検知部12の電極17は,ワイヤ23に沿う限定領域において組織に接触して配置された電極17を有する1本のワイヤ23に配置することができる。 As shown in more detail in FIG. 4, the
上記電極17はEEG信号を電圧電位の変化としてピックアップし,変化電圧を電子モジュール18内の上記A/D変換器24に供給する。上記A/D変換器24は上記変化電圧をデジタル信号に変換し,このデジタル信号を上記電子モジュール18の一部であるデータパケット・コントローラ25に提示する。上記データパケット・コントローラ25は所定の通信プロトコルにしたがって上記デジタル信号をデータパケットのストリームに編成し,得られたデータパケットのストリームを通信コントローラ26に供給する。 The
上記通信コントローラ26は,上記第1のコイル20によって上記外部EEG信号処理装置11の第2のコイル21からエネルギーを受け取ることによって電磁的に電子モジュール18を励磁する(energize)ように構成される。上記第1のコイル20において受け取られた電磁エネルギーは電圧レギュレータ27に転送され,セラミック・コンデンサ28とともに電子モジュール18の電源として用いられる。 The
さらに上記通信コントローラ26は,上記電極17からのEEG信号を表すデータパケットを取り込み,第1のコイル20において受信された第2のコイル21からの電力負荷を変調することによって,誘導リンクを介してEEG検知部からのデジタル化されたEEG信号を伝達する。この変調された負荷はEEG信号処理装置11から検出可能であり,ここで上記負荷変調が上記信号処理装置10によって連続的に復号されかつ分析されるのに適する電気信号に変換される。 Furthermore, the
低血糖症の発症到来を識別するためのEEG信号の分析は,様々なアルゴリズムに基づくことができる。この分析をどのように実施することができるかの一例が,WO2006/069549 A1に示されている。 The analysis of the EEG signal to identify the onset of hypoglycemia can be based on various algorithms. An example of how this analysis can be performed is shown in WO 2006/069549 A1.
EEG信号の分析の結果に応じて低血糖症の発症到来が確認された場合に,上記信号処理装置10によって警告音を発するようにスピーカ13を作動させることができる。 When the onset of hypoglycemia is confirmed according to the result of the analysis of the EEG signal, the
図3に示す実施形態のEEG電極17は,上記EEG検知部12の電子モジュールによる検出に適する信号を提供するために,ユーザの耳の後ろに皮下的に埋め込まれるように配置される。EEG電極からの典型的な出力信号は約1μV〜100μVの範囲の大きさを持つ。筋肉収縮は通常10mVの大きさの電圧レベルを生成するが,そのような信号は上記システムによってフィルタ・アウトされる。上記電極の固有ノイズ・レベルは0.1〜100Hzの帯域幅で測定して約1μV RMSであり,上記出力信号の使用可能帯域幅は0.1〜40Hzである。 The
上記EEG検知部12はセラミックなどの生体適合性材料(図示略)に収納される。電極も白金−イリジウム合金のような生体適合性金属から作られる。上記EEG信号処理装置11が,上記埋込み部が配置されている耳の後ろ側に(耳かけ型補聴器のように)装着されると,上記EEG信号処理装置11の第2のコイル21は上記EEG検知部12の第1のコイル20から数ミリメートルとなる。これによってEEG信号処理装置11と上記EEG検知部12との間の通信および電力転送が助長される。2つのコイルは好ましくは密接に整列されるべきであり,これによって電力のより効率的な転送およびより信頼できる通信を達成することができる。 The
上記EEGモニタの上記EEG検知部は,図3および図4に関して埋込み可能なものとして説明した。しかしながら上記EEG検知部を,外耳道の皮膚表面からのEEG信号を検出する電極とともに外耳道内に配置することもできる。この目的のための電極を備えるイヤプラグの一例が,WO2011/000383A1(たとえばこの公報の図2を参照)に示されている。 The EEG detector of the EEG monitor has been described as being embeddable with respect to FIGS. However, the EEG detector can be arranged in the ear canal together with an electrode for detecting an EEG signal from the skin surface of the ear canal. An example of an earplug with electrodes for this purpose is shown in WO2011 / 000383A1 (see eg FIG. 2 of this publication).
図5は上記システム用のインシュリン・ポンプ2の一例を示している。上記インシュリン・ポンプは上記ユーザとのコミュニケーションのためのディスプレイ31,および上記インシュリン・ポンプを装着している人へのインシュリンの投与を制御するコントローラ32を有している。インシュリン・ポンプはまた,上記システムの他のユニットとの通信のためのアンテナ34を備える無線機33を備えている。さらにインシュリン・ポンプは,インシュリン用のリザーバ36,およびカニューレ35を含む注入セットを通じてインシュリンを投与するためにピストンを動かすモータ37を備えている。 FIG. 5 shows an example of an
上記EEGモニタとインシュリン・ポンプとの間の無線接続は,通信における高い信頼性を保証するプロトコルを有するべきである。上記プロトコルは,定期的な時間間隔で,たとえば1秒おきに接続が存在することを確認するべきであり,たとえば接続が15秒以上失われた場合には,上記システムを装着している人または介護者に通知を提供することができる。無線接続が失われた状況において,上記インシュリン・ポンプおよび上記EEGモニタの両方は,プログラムされた設定にしたがって機能し続けなければならない。この場合,上記システムを使用している人に明確に通知するべきであり,介護者にも通知するべきである。上記無線接続が失われた状況において上記EEGモニタが低血糖症の発症到来を検出した場合,上記人および/または介護者に提供される警告は,インシュリン・ポンプから投与されるインシュリンの自動制限(たとえば休止または制限)を実行することができないことを,明確に強調すべきである。 The wireless connection between the EEG monitor and the insulin pump should have a protocol that ensures high reliability in communication. The protocol should check that a connection exists at regular time intervals, for example every other second, eg if the connection is lost for more than 15 seconds or if the person wearing the system or Notifications can be provided to caregivers. In situations where the wireless connection is lost, both the insulin pump and the EEG monitor must continue to function according to the programmed settings. In this case, the person using the system should be clearly notified and the caregiver should also be notified. If the EEG monitor detects the onset of hypoglycemia in a situation where the wireless connection has been lost, the warning provided to the person and / or caregiver will automatically limit the insulin administered from the insulin pump ( It should be clearly emphasized that it is not possible to perform (eg pauses or restrictions).
上記インシュリン・ポンプと上記EEGモニタとの間の接続が失われた場合,インシュリン・ポンプが実行するようにプログラムされる任意の動作は,自動的かつ連続的な血糖測定またはCGMの利用可能性に依存するべきである。オプションの一つは,ボーラスドーズが,通知およびユーザによる確認の後にのみ投与されることである。また,上記システムが,上記EEGモニタが完全に機能接続を有し続けているグルカゴン・ポンプを含む場合には,低血糖症の発症到来が識別されたときに上記EEGモニタがグルカゴンの投与を制御することができれば,このグルカゴン・ポンプを安全に提供することができる。このようなプログラミングは個々のユーザのニーズに基づくべきであり,したがって上記人の糖尿病状態を認識している医師との協議に基づくべきである。 If the connection between the insulin pump and the EEG monitor is lost, any action that the insulin pump is programmed to perform will automatically and continuously measure blood glucose or CGM availability. Should depend. One option is that the bolus dose is administered only after notification and user confirmation. Also, if the system includes a glucagon pump where the EEG monitor continues to have a fully functional connection, the EEG monitor controls the administration of glucagon when the onset of hypoglycemia is identified. If possible, this glucagon pump can be provided safely. Such programming should be based on the needs of individual users and therefore should be based on consultation with a physician who is aware of the person's diabetic condition.
上記システム内の任意の装置からの音声メッセージまたは通知を,上記EEGモニタを通じて上記システムを使用している人に提供することができる。これには,インシュリンのリザーバが再充填が推奨されるレベルに達したこと,または上記インシュリン・ポンプの電池が再充電もしくは交換を要することといった上記インシュリン・ポンプからの情報を含ませることができる。安全上の理由から,上記インシュリン・ポンプは,上記EEGモニタとインシュリン・ポンプとの間の無線接続が失われた場合であっても,警告を提供するための別個の警告手段を有することが好ましい。 Voice messages or notifications from any device in the system can be provided to the person using the system through the EEG monitor. This may include information from the insulin pump that the insulin reservoir has reached a recommended refill level or that the battery of the insulin pump needs to be recharged or replaced. For safety reasons, the insulin pump preferably has a separate warning means for providing a warning even if the wireless connection between the EEG monitor and the insulin pump is lost. .
Claims (11)
Translated fromJapaneseEEG電極(17)を備えるEEG検知部(12)を有し,頭皮において皮下的に配置されるまたは外耳道内に配置される上記EEG検知部(12)とともに上記人の耳領域に配置されるように構成され,上記耳に配置されかつ低血糖の発症を識別するように構成されるEEG信号処理装置(11)を備えるEEGモニタ(1),および
上記EEGモニタ(1)と上記インシュリン投与装置との間の無線通信リンクであって,定期的な時間間隔で無線接続が存在することが確認される無線通信リンクを備え,
上記EEGモニタ(1)が,上記EEG信号処理装置(11)によって低血糖症の発症到来が識別された場合に警告信号を上記インシュリン投与装置に送信するように構成されており,上記警告信号によって上記インシュリン投与装置が所定時間の間インシュリンの投与を制限し,低血糖症の発症到来が識別された場合および上記無線接続が所定時間にわたって失われた状況において,上記EEGモニタ(1)によって警告が上記人または介護者に提供され,
上記無線接続が失われた状況において低血糖の発症到来が識別された場合に上記EEGモニタ(1)によって上記人または介護者に提供される上記警告は,上記インシュリン投与装置から投与されるインシュリンの自動制限が実行できないことが強調される,
人の血糖値を調整するためのシステム。An insulin administration device configured to release insulin into the human body,
It has an EEG detector (12) having an EEG electrode (17) and is arranged in the human ear region together with the EEG detector (12) arranged subcutaneously in the scalp or in the ear canal An EEG monitor (1) comprising an EEG signal processing device (11) arranged in the ear and configured to identify the onset of hypoglycemia, and the EEG monitor (1) and the insulin administration device, Comprising a wireless communication linkbetween which the wireless connection is confirmed to be present at regular time intervals ,
The EEG monitor (1) is configured to transmit a warning signal to the insulin administration device when the onset of hypoglycemia is identified by the EEG signal processing device (11). In the case where the insulin administration device restricts insulin administration for a predetermined timeand the onset of hypoglycemia is identified and the wireless connection is lost for a predetermined time, the EEG monitor (1) warns theuser. Provided to the above person or caregiver,
The warning provided to the person or caregiver by the EEG monitor (1) when the onset of hypoglycemia is identified in a situation where the wireless connection has been lost, is the indication of the insulin administered from the insulin administration device. Emphasizes that automatic restriction cannot be performed,
A system for adjusting a person's blood sugar level.
上記EEG信号処理装置(11)によって上記人の低血糖症の発症到来が識別された場合に,上記EEGモニタ(1)が,上記無線通信リンクを通じて警告信号を上記インシュリン投与装置に送信して,所定時間の間インシュリンの放出を制限するように上記インシュリン投与装置を制御し,When the EEG signal processor (11) identifies the onset of the person's hypoglycemia, the EEG monitor (1) sends a warning signal to the insulin administration device via the wireless communication link; Controlling the insulin administration device to limit the release of insulin for a predetermined time;
低血糖症の発症到来が識別された場合および上記無線接続が所定時間にわたって失われた状況において,上記EEGモニタ(1)が警告を上記人または介護者に提供し,The EEG monitor (1) provides a warning to the person or caregiver when the onset of hypoglycemia is identified and in situations where the wireless connection has been lost for a predetermined time;
上記無線接続が失われた状況において低血糖の発症到来が識別された場合に,上記EEGモニタ(1)が,上記インシュリン投与装置から投与されるインシュリンの自動制限が実行できないことを強調した警告を上記人または介護者に提供する,When the onset of hypoglycemia is identified in the situation where the wireless connection is lost, the EEG monitor (1) warns that it cannot execute the automatic restriction of insulin administered from the insulin administration device. Provide to the above person or caregiver,
無線接続されたEEGモニタおよびインシュリン投与装置を制御する方法。A method for controlling a wirelessly connected EEG monitor and insulin dispensing device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019137416AJP2019205852A (en) | 2019-07-26 | 2019-07-26 | System for adjusting blood glucose level of person, and method of controlling wirelessly connected eeg monitor and insulin delivery device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019137416AJP2019205852A (en) | 2019-07-26 | 2019-07-26 | System for adjusting blood glucose level of person, and method of controlling wirelessly connected eeg monitor and insulin delivery device |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017537476ADivisionJP2018507016A (en) | 2015-01-19 | 2015-01-19 | System and method for adjusting a person's blood glucose level |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019205852Atrue JP2019205852A (en) | 2019-12-05 |
Family
ID=68767157
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019137416APendingJP2019205852A (en) | 2019-07-26 | 2019-07-26 | System for adjusting blood glucose level of person, and method of controlling wirelessly connected eeg monitor and insulin delivery device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2019205852A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023530781A (en)* | 2021-05-08 | 2023-07-19 | バイオリンク インコーポレイテッド | Fault detection for microneedle array-based persistent analyte monitoring devices |
| US11872055B2 (en) | 2020-07-29 | 2024-01-16 | Biolinq Incorporated | Continuous analyte monitoring system with microneedle array |
| US12109032B1 (en) | 2017-03-11 | 2024-10-08 | Biolinq Incorporated | Methods for achieving an isolated electrical interface between an anterior surface of a microneedle structure and a posterior surface of a support structure |
| US12336816B2 (en) | 2023-02-02 | 2025-06-24 | Biolinq Incorporated | Method for improved sensor sensitivity of a microneedle-based continuous analyte monitoring system |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6572542B1 (en)* | 2000-03-03 | 2003-06-03 | Medtronic, Inc. | System and method for monitoring and controlling the glycemic state of a patient |
| JP2007307359A (en)* | 2006-03-31 | 2007-11-29 | Lifescan Inc | Drug delivery system and method |
| JP2013517856A (en)* | 2010-02-01 | 2013-05-20 | ヴェーデクス・アクティーセルスカプ | Portable EEG monitor system with wireless communication |
- 2019
- 2019-07-26JPJP2019137416Apatent/JP2019205852A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6572542B1 (en)* | 2000-03-03 | 2003-06-03 | Medtronic, Inc. | System and method for monitoring and controlling the glycemic state of a patient |
| JP2007307359A (en)* | 2006-03-31 | 2007-11-29 | Lifescan Inc | Drug delivery system and method |
| JP2013517856A (en)* | 2010-02-01 | 2013-05-20 | ヴェーデクス・アクティーセルスカプ | Portable EEG monitor system with wireless communication |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12109032B1 (en) | 2017-03-11 | 2024-10-08 | Biolinq Incorporated | Methods for achieving an isolated electrical interface between an anterior surface of a microneedle structure and a posterior surface of a support structure |
| US12369830B2 (en) | 2017-03-11 | 2025-07-29 | Biolinq Incorporated | Methods for achieving an isolated electrical interface between an anterior surface of a microneedle structure and a posterior surface of a support structure |
| US11872055B2 (en) | 2020-07-29 | 2024-01-16 | Biolinq Incorporated | Continuous analyte monitoring system with microneedle array |
| US12011294B2 (en) | 2020-07-29 | 2024-06-18 | Biolinq Incorporated | Continuous analyte monitoring system with microneedle array |
| US12279888B2 (en) | 2020-07-29 | 2025-04-22 | Biolinq Incorporated | Continuous analyte monitoring system with microneedle array |
| US12285271B2 (en) | 2020-07-29 | 2025-04-29 | Biolinq Incorporated | Continuous analyte monitoring system with microneedle array |
| JP2023530781A (en)* | 2021-05-08 | 2023-07-19 | バイオリンク インコーポレイテッド | Fault detection for microneedle array-based persistent analyte monitoring devices |
| JP7341583B2 (en) | 2021-05-08 | 2023-09-11 | バイオリンク インコーポレイテッド | Fault detection for microneedle array-based continuous analyte monitoring devices |
| JP7341583B6 (en) | 2021-05-08 | 2023-09-29 | バイオリンク インコーポレイテッド | Fault detection for microneedle array-based continuous analyte monitoring devices |
| JP2023155323A (en)* | 2021-05-08 | 2023-10-20 | バイオリンク インコーポレイテッド | Fault detection for microneedle array based continuous analyte monitoring device |
| US11857344B2 (en) | 2021-05-08 | 2024-01-02 | Biolinq Incorporated | Fault detection for microneedle array based continuous analyte monitoring device |
| US12336816B2 (en) | 2023-02-02 | 2025-06-24 | Biolinq Incorporated | Method for improved sensor sensitivity of a microneedle-based continuous analyte monitoring system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11445974B2 (en) | System and method for adjusting the blood glucose level of a person | |
| JP2019205852A (en) | System for adjusting blood glucose level of person, and method of controlling wirelessly connected eeg monitor and insulin delivery device | |
| RU2756426C2 (en) | Method and system for obtaining and analyzing physiological data | |
| KR101335740B1 (en) | Method and system for eeg monitoring and portable monitoring device with hearing aid and eeg monitor | |
| EP1841476B1 (en) | Fluid delivery device with integrated monitoring of physiological characteristics | |
| CA2669294C (en) | Analyte sensing apparatus for hospital use | |
| US8849368B2 (en) | Implantable electronic devices for detecting hypoglycaemia using EEG signals | |
| KR20120086324A (en) | Method and apparatus for alerting a person carrying an eeg assembly | |
| CN101534704A (en) | Adaptive hypoglycaemia alert system and method | |
| JP6467530B2 (en) | EEG monitor | |
| WO2009070675A2 (en) | Device to monitor glucose levels and ischemia | |
| WO2010104978A2 (en) | System and method for delivery of physician notifications | |
| WO2020232121A1 (en) | Ear-worn devices for communication with medical devices | |
| CN106667437A (en) | System for predicting postoperative complication of implantable medical device | |
| CN118369136A (en) | Modular defibrillator system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20190726 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20200619 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20200714 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20210224 |