JP2019144964A - Tactile force sense presentation device and tactile force sense presentation method - Google Patents
Tactile force sense presentation device and tactile force sense presentation methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2019144964A JP2019144964AJP2018030123AJP2018030123AJP2019144964AJP 2019144964 AJP2019144964 AJP 2019144964AJP 2018030123 AJP2018030123 AJP 2018030123AJP 2018030123 AJP2018030123 AJP 2018030123AJP 2019144964 AJP2019144964 AJP 2019144964A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- haptic
- sense presentation
- unit
- user
- finger
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B06—GENERATING OR TRANSMITTING MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS IN GENERAL
- B06B—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR GENERATING OR TRANSMITTING MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS OF INFRASONIC, SONIC, OR ULTRASONIC FREQUENCY, e.g. FOR PERFORMING MECHANICAL WORK IN GENERAL
- B06B1/00—Methods or apparatus for generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency
- B06B1/02—Methods or apparatus for generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency making use of electrical energy
- B06B1/04—Methods or apparatus for generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency making use of electrical energy operating with electromagnetism
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B06—GENERATING OR TRANSMITTING MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS IN GENERAL
- B06B—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR GENERATING OR TRANSMITTING MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS OF INFRASONIC, SONIC, OR ULTRASONIC FREQUENCY, e.g. FOR PERFORMING MECHANICAL WORK IN GENERAL
- B06B1/00—Methods or apparatus for generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency
- B06B1/02—Methods or apparatus for generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency making use of electrical energy
- B06B1/06—Methods or apparatus for generating mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic, or ultrasonic frequency making use of electrical energy operating with piezoelectric effect or with electrostriction
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R16/00—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for
- B60R16/02—Electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for; Arrangement of elements of electric or fluid circuits specially adapted for vehicles and not otherwise provided for electric constitutive elements
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/26—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00 specially adapted for navigation in a road network
- G01C21/34—Route searching; Route guidance
- G01C21/36—Input/output arrangements for on-board computers
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/03—Arrangements for converting the position or the displacement of a member into a coded form
- G06F3/041—Digitisers, e.g. for touch screens or touch pads, characterised by the transducing means
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/01—Input arrangements or combined input and output arrangements for interaction between user and computer
- G06F3/048—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI]
- G06F3/0487—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI] using specific features provided by the input device, e.g. functions controlled by the rotation of a mouse with dual sensing arrangements, or of the nature of the input device, e.g. tap gestures based on pressure sensed by a digitiser
- G06F3/0488—Interaction techniques based on graphical user interfaces [GUI] using specific features provided by the input device, e.g. functions controlled by the rotation of a mouse with dual sensing arrangements, or of the nature of the input device, e.g. tap gestures based on pressure sensed by a digitiser using a touch-screen or digitiser, e.g. input of commands through traced gestures
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- User Interface Of Digital Computer (AREA)
- Apparatuses For Generation Of Mechanical Vibrations (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、UI(User Interface)への入力操作を行うユーザに触力覚を提示する触力覚提示装置および触力覚提示方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a tactile force sense presentation device and a tactile force sense presentation method for presenting a tactile force sense to a user who performs an input operation to a UI (User Interface).
特許文献1には、タッチパッドであるインタフェース装置の表面への接触入力に基づいて、ユーザの指へ触覚を与える触覚効果対応装置が開示されている。
従来技術に係る触覚効果対応装置を、車両用GUI(Graphic User Interface)に適用した場合、例えばGUIのポインタ位置ごとに操作機能が異なるので、運転中のなぞり動作に基づく位置決定が重要となるが、従来技術ではポインタ位置に応じた触覚を与えるのみで、ポインタの位置決定については視覚による依存度が高いという課題がある。 When the haptic effect compatible device according to the prior art is applied to a vehicle GUI (Graphic User Interface), for example, the operation function differs depending on the pointer position of the GUI, but position determination based on the tracing operation during driving is important. However, the conventional technique only gives a sense of touch according to the position of the pointer, and there is a problem that the position of the pointer is highly dependent on the visual sense.
そこで、本発明は、機器へ操作を入力するときの、視覚による位置決定の依存度を低減することができる触力覚提示装置および触力覚提示方法を提供する。 Therefore, the present invention provides a haptic sense presentation device and a haptic sense presentation method capable of reducing the dependency of visual position determination when an operation is input to a device.
本発明の一態様に係る触力覚提示装置は、ユーザが操作を入力する入力部と、前記入力部を介して前記ユーザに触力覚を提示する触力覚提示部と、前記入力部および前記触力覚提示部と電気的に接続され、前記入力部に入力された操作に基づいて前記触力覚提示部を制御する制御部とを備え、前記制御部は、前記ユーザが前記入力部に触れた接触位置と前記接触位置の移動方向に基づいて前記触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動を制御する。 A tactile sensation presentation device according to an aspect of the present invention includes an input unit through which a user inputs an operation, a haptic presentation unit that presents a haptic sensation to the user via the input unit, the input unit, A control unit that is electrically connected to the haptic sense presentation unit and controls the haptic sense presentation unit based on an operation input to the input unit. The tactile force sensation vibration presented from the tactile force sense presenting unit is controlled based on the contact position touched by and the moving direction of the contact position.
また、本発明の一態様に係る触力覚提示方法は、触力覚提示装置の触力覚提示方法であって、前記触力覚提示装置は、ユーザが操作を入力する入力部と、前記入力部を振動させる触力覚提示部と、前記入力部および前記触力覚提示部と電気的に接続される制御部と、を備え、前記制御部は、前記ユーザが前記入力部に触れた接触位置を検出するステップと、前記接触位置の移動方向を検出するステップと、前記接触位置と前記移動方向に基づいて前記触力覚提示部の触力覚振動を制御するステップとを含む。 A haptic sense presentation method according to an aspect of the present invention is a haptic sense presentation method for a haptic sense presentation device, wherein the haptic sense presentation device includes: an input unit through which a user inputs an operation; A tactile force sense presentation unit that vibrates the input unit; and a control unit that is electrically connected to the input unit and the tactile force sense presentation unit. The control unit touches the input unit by the user Detecting a contact position; detecting a movement direction of the contact position; and controlling haptic vibration of the haptic sense presentation unit based on the contact position and the movement direction.
なお、これらの全般的または具体的な態様は、システム、方法、集積回路、コンピュータプログラムまたはコンピュータ読み取り可能なCD−ROMなどの記録媒体で実現されてもよく、システム、方法、集積回路、コンピュータプログラム及び記録媒体の任意な組み合わせで実現されてもよい。 These general or specific aspects may be realized by a system, a method, an integrated circuit, a computer program, or a recording medium such as a computer-readable CD-ROM. The system, method, integrated circuit, computer program Also, any combination of recording media may be realized.
本発明の触力覚提示装置および触力覚提示方法は、機器へ操作を入力するときの、視覚による位置決定の依存度を低減することができる。 The haptic sense presentation device and the haptic sense presentation method of the present invention can reduce the dependency of visual position determination when an operation is input to a device.
本発明の一態様に係る触力覚提示装置は、ユーザが操作を入力する入力部と、前記入力部を介して前記ユーザに触力覚を提示する触力覚提示部と、前記入力部および前記触力覚提示部と電気的に接続され、前記入力部に入力された操作に基づいて前記触力覚提示部を制御する制御部とを備え、前記制御部は、前記ユーザが前記入力部に触れた接触位置と前記接触位置の移動方向に基づいて前記触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動を制御する。 A tactile sensation presentation device according to an aspect of the present invention includes an input unit through which a user inputs an operation, a haptic presentation unit that presents a haptic sensation to the user via the input unit, the input unit, A control unit that is electrically connected to the haptic sense presentation unit and controls the haptic sense presentation unit based on an operation input to the input unit. The tactile force sensation vibration presented from the tactile force sense presenting unit is controlled based on the contact position touched by and the moving direction of the contact position.
これによれば、ユーザは、指の移動方向に基づいて触力覚提示部から触力覚を提示されるので、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動しているのか否かを認識することができる。したがって、この触力覚提示装置によると、機器へ操作を入力するときの、視覚への位置決定の依存度を低減することができる。これにより、ユーザは、他の作業を行っている場合であっても、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動して、機器の操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる。 According to this, since the user is presented with a tactile force sense from the tactile force sense presenting unit based on the moving direction of the finger, it is recognized whether or not the finger is moving in the intended operation direction or the correct operation direction. can do. Therefore, according to the haptic sense presentation device, it is possible to reduce the dependence of the position determination on the vision when an operation is input to the device. Thereby, even when the user is performing another work, the user can move the finger in the intended operation direction or the correct operation direction, and can easily operate the device with high accuracy.
また、前記制御部は、前記接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、前記触力覚提示部から提示される前記触力覚振動の大きさを制御してもよい。ここで、触力覚振動とは、触力覚提示部が触力覚を提示するための振動のことであると、以下、定義する。 Further, the control unit may control the magnitude of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presenting unit based on a moving direction of the contact position. Here, the tactile force sense vibration is defined below as a vibration for the tactile force sense presenting unit to present a tactile force sense.
これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動が大きいか小さいかによって意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向を認識することができるので、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動することができる。または、物体の実物を触った場合に感じられる触感(形状や質感)を感じることができる。 According to this, since the user can recognize the intended operation direction or the correct operation direction depending on whether the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit is large or small, the intended operation direction or the correct operation direction can be recognized. You can move your finger in the direction. Alternatively, it is possible to feel the tactile sensation (shape and texture) that is felt when the actual object is touched.
また、前記制御部は、前記接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、前記触力覚提示部から提示される前記触力覚振動の周波数を制御してもよい。 Further, the control unit may control the frequency of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit based on a moving direction of the contact position.
これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動の周波数が高いか低いかによって意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向を認識することができるので、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動することができる。または、物体の実物を触った場合に感じられる触感を感じることができる。 According to this, the user can recognize the intended operation direction or the correct operation direction depending on whether the frequency of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit is high or low. The finger can be moved in the correct operation direction. Alternatively, it is possible to feel the tactile sensation that is felt when the actual object is touched.
また、前記制御部は、前記接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、前記触力覚提示部から提示される前記触力覚振動のパターンを制御してもよい。 The control unit may control a pattern of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit based on a moving direction of the contact position.
これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動のパターンの違いによって意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向を認識することができるので、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動することができる。または、物体の実物を触った場合に感じられる触感を感じることができる。 According to this, since the user can recognize the intended operation direction or the correct operation direction by the difference in the pattern of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit, the intended operation direction or the correct operation direction You can move your finger. Alternatively, it is possible to feel the tactile sensation that is felt when the actual object is touched.
また、前記制御部は、前記入力部において前記接触位置を移動させる目標位置を有し、前記接触位置と前記移動方向から、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっているか否かを判断し、判断結果に基づいて前記触力覚提示部から提示される前記触力覚振動を制御してもよい。 The control unit has a target position for moving the contact position in the input unit, and determines whether the contact position is toward the target position from the contact position and the moving direction. The haptic vibration presented from the haptic presentation unit may be controlled based on the result.
これによれば、触力覚提示部は、目標位置の方向に対する指の相対的な移動方向に基づいて触力覚を提示するので、ユーザは、指の移動方向が目標位置に向かっているか否かを認識することができる。これにより、ユーザは、他の作業を行っている場合であっても、目標位置の方向に指を移動して、機器の操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる。 According to this, since the tactile force sense presentation unit presents a tactile force sense based on the direction of movement of the finger relative to the direction of the target position, the user can determine whether or not the direction of movement of the finger is toward the target position. Can be recognized. Thereby, even when the user is performing another work, the user can move the finger in the direction of the target position and easily operate the device with high accuracy.
また、前記制御部は、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっている場合と、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっていない場合とで、前記触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚が異なるように制御してもよい。 In addition, the control unit may detect a haptic sensation presented from the haptic sense presentation unit when the contact position is directed toward the target position and when the contact position is not directed toward the target position. It may be controlled differently.
これによれば、触力覚提示部は、接触位置が目標位置に向かっている場合と向かっていない場合とで異なる触力覚を提示するので、ユーザは、当該触力覚により、接触位置が目標位置に向かっているか否かを認識することができる。 According to this, the tactile force sense presenting unit presents a different tactile force sense depending on whether the contact position is toward the target position or not, and thus the user can determine the contact position based on the tactile force sense. It is possible to recognize whether or not the vehicle is moving toward the target position.
また、前記制御部は、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっている場合よりも前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっていない場合のほうが、前記触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚が大きくなるように制御してもよい。 In addition, the control unit is more sensitive to a tactile force sense presented from the tactile force sense presenting unit when the contact position is not toward the target position than when the contact position is toward the target position. You may control so that it may become large.
これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動が大きいか小さいかによって、接触位置が目標位置に向かっているか否かを認識することができる。 According to this, the user can recognize whether or not the contact position is toward the target position depending on whether the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit is large or small.
また、前記制御部は、前記目標位置と前記接触位置とを結ぶ直線と前記移動方向とから、前記目標位置に対する前記移動方向のズレ角を求め、前記ズレ角が大きいほど前記触力覚提示部から提示される前記触力覚振動が大きくなるように制御してもよい。 Further, the control unit obtains a deviation angle in the movement direction with respect to the target position from a straight line connecting the target position and the contact position and the movement direction, and the haptic sense presentation unit increases as the deviation angle increases. Control may be performed so that the haptic vibration presented from is increased.
これによれば、目標位置の方向と指の移動方向のズレ角に基づいて触力覚振動の大きさが変わるので、ユーザは、指の移動方向と目標位置の方向とがずれているか否かを認識することができる。これにより、ユーザは、他の作業を行っている場合であっても、目標位置の方向に指を移動して、機器の操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる。 According to this, since the magnitude of the tactile sensation vibration changes based on the deviation angle between the direction of the target position and the direction of movement of the finger, the user determines whether the direction of movement of the finger and the direction of the target position are misaligned. Can be recognized. Thereby, even when the user is performing another work, the user can move the finger in the direction of the target position and easily operate the device with high accuracy.
また、前記制御部は、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっている場合よりも前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっていない場合のほうが、前記触力覚提示部から提示される前記触力覚振動の周波数が低くなるように制御してもよい。 In addition, the control unit provides the tactile force sense presented from the tactile force sense presenting unit when the contact position is not toward the target position than when the contact position is toward the target position. You may control so that the frequency of vibration may become low.
これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動の周波数が高いか低いかによって、接触位置が目標位置に向かっているか否かを認識することができる。 According to this, the user can recognize whether or not the contact position is toward the target position depending on whether the frequency of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit is high or low.
また、前記制御部は、前記目標位置と前記接触位置とを結ぶ直線と前記移動方向とから、前記目標位置に対する前記移動方向のズレ角を求め、前記ズレ角が大きいほど前記触力覚提示部から提示される前記触力覚振動の周波数が低くなるように制御してもよい。 Further, the control unit obtains a deviation angle in the movement direction with respect to the target position from a straight line connecting the target position and the contact position and the movement direction, and the haptic sense presentation unit increases as the deviation angle increases. Control may be performed so that the frequency of the haptic vibration presented from is reduced.
これによれば、目標位置の方向と指の移動方向のズレ角に基づいて触力覚振動の周波数が変わるので、ユーザは、指の移動方向と目標位置の方向とがずれているか否かを認識することができる。これにより、ユーザは、他の作業を行っている場合であっても、目標位置の方向に指を移動して、機器の操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる。 According to this, since the frequency of the tactile sensation vibration changes based on the deviation angle between the direction of the target position and the movement direction of the finger, the user can check whether the movement direction of the finger and the direction of the target position are deviated. Can be recognized. Thereby, even when the user is performing another work, the user can move the finger in the direction of the target position and easily operate the device with high accuracy.
また、前記制御部は、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっている場合は前記触力覚提示部から触力覚を提示させず、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっていない場合は、前記触力覚提示部から触力覚を提示させるように制御してもよい。 In addition, the control unit does not present a tactile force sense from the tactile force sense presentation unit when the contact position is toward the target position, and when the contact position is not toward the target position, Control may be performed so that a haptic sense is presented from the haptic sense presentation unit.
これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部から触力覚が提示される場合には指の移動方向が目標位置に向かっておらず、触力覚提示部から触力覚が提示されない場合には指の移動方向が目標位置に向かっていると認識することができる。したがって、ユーザは、触力覚が提示されない方向に指を移動させることにより、容易に目標位置に到達することができる。 According to this, when the haptic sense is presented from the haptic sense presentation unit, the user does not move the finger toward the target position, and the haptic sense presentation unit does not present the haptic sense. It can be recognized that the moving direction of the finger is toward the target position. Therefore, the user can easily reach the target position by moving the finger in a direction in which no tactile force sense is presented.
また、前記入力部は、静電容量式、光学式、または抵抗膜式の入力部であってもよい。 The input unit may be a capacitance type, an optical type, or a resistance type input unit.
これによれば、指と入力部との間の静電容量の変化により、精度よく指の接触位置を検出することができる。または、光を照射したときの指からの反射光または指の影により、簡便に指の接触位置を検出することができる。または、指が接触したことによる入力部の抵抗値の変化により、簡便に指の接触位置を検出することができる。 According to this, the contact position of the finger can be detected with high accuracy by the change in the capacitance between the finger and the input unit. Alternatively, the contact position of the finger can be easily detected based on the reflected light from the finger or the shadow of the finger when the light is irradiated. Alternatively, the contact position of the finger can be easily detected based on a change in the resistance value of the input unit due to the contact of the finger.
また、前記触力覚提示部は、ユーザに与える前記触力覚振動を発生する触力覚発生素子を有し、前記触力覚発生素子は、圧電体で構成されるか、または電磁的に動作する構成を有してもよい。 The tactile force sense presentation unit includes a tactile force sense generating element that generates the tactile force sense vibration to be given to a user, and the tactile force sense generating element includes a piezoelectric body or electromagnetically. You may have the structure which operate | moves.
これによれば、圧電体から発生される振動により、ユーザに触力覚を提示することができる。または、電磁力により発生される振動により、ユーザに触力覚を提示することができる。 According to this, a tactile sensation can be presented to the user by vibration generated from the piezoelectric body. Alternatively, a tactile force sense can be presented to the user by vibration generated by electromagnetic force.
また、前記入力部と前記触力覚提示部との間に導電板を有してもよい。 Moreover, you may have a conductive board between the said input part and the said tactile-force sense presentation part.
これによれば、入力部は、触力覚提示部からの電界により発生するノイズを低減することができる。 According to this, the input unit can reduce noise generated by the electric field from the haptic sense presentation unit.
また、本発明の一態様に係る触力覚提示方法は、触力覚提示装置の触力覚提示方法であって、前記触力覚提示装置は、ユーザが操作を入力する入力部と、前記入力部を振動させる触力覚提示部と、前記入力部および前記触力覚提示部と電気的に接続される制御部と、を備え、前記制御部は、前記ユーザが前記入力部に触れた接触位置を検出するステップと、前記接触位置の移動方向を検出するステップと、前記接触位置と前記移動方向に基づいて前記触力覚提示部の触力覚振動を制御するステップとを含む。 A haptic sense presentation method according to an aspect of the present invention is a haptic sense presentation method for a haptic sense presentation device, wherein the haptic sense presentation device includes: an input unit through which a user inputs an operation; A tactile force sense presentation unit that vibrates the input unit; and a control unit that is electrically connected to the input unit and the tactile force sense presentation unit. The control unit touches the input unit by the user Detecting a contact position; detecting a movement direction of the contact position; and controlling haptic vibration of the haptic sense presentation unit based on the contact position and the movement direction.
これによれば、ユーザは、指の移動方向に基づいて触力覚提示部から触力覚を提示されるので、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動しているのか否かを認識することができる。したがって、機器へ操作を入力するときの、視覚への位置決定の依存度を低減することができる。これにより、ユーザは、他の作業を行っている場合であっても、機器の操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる。 According to this, since the user is presented with a tactile force sense from the tactile force sense presenting unit based on the moving direction of the finger, it is recognized whether or not the finger is moving in the intended operation direction or the correct operation direction. can do. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the dependence of the position determination on the vision when inputting an operation to the device. Thereby, even if the user is performing another work, the user can easily and accurately operate the device.
また、前記制御部は、前記入力部において前記接触位置を移動させる目標位置を決定するステップと、前記接触位置と前記移動方向から、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっているか否かを判断するステップと、前記判断の結果に基づいて前記触力覚提示部の前記触力覚振動を制御するステップとを含んでもよい。 The control unit determines whether or not the contact position is directed toward the target position from the step of determining a target position for moving the contact position in the input unit, and the contact position and the moving direction. And a step of controlling the haptic vibration of the haptic sense presentation unit based on a result of the determination.
これによれば、目標位置の方向に対する指の相対的な移動方向に基づいて触力覚が提示されるので、ユーザは、指の移動方向が目標位置に向かっているか否かを認識することができる。これにより、ユーザは、他の作業を行っている場合であっても、目標位置の方向に指を移動して、機器の操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる。 According to this, since the tactile force sense is presented based on the movement direction of the finger relative to the direction of the target position, the user can recognize whether or not the movement direction of the finger is toward the target position. it can. Thereby, even when the user is performing another work, the user can move the finger in the direction of the target position and easily operate the device with high accuracy.
なお、これらの全般的または具体的な態様は、システム、方法、集積回路、コンピュータプログラムまたはコンピュータ読み取り可能なCD−ROMなどの記録媒体で実現されてもよく、システム、方法、集積回路、コンピュータプログラム及び記録媒体の任意な組み合わせで実現されてもよい。 These general or specific aspects may be realized by a system, a method, an integrated circuit, a computer program, or a recording medium such as a computer-readable CD-ROM. The system, method, integrated circuit, computer program Also, any combination of recording media may be realized.
以下、本発明の一態様に係る触力覚提示装置及び触力覚提示方法について、図面を参照しながら具体的に説明する。 Hereinafter, a tactile force sense presentation device and a tactile force sense presentation method according to an aspect of the present invention will be specifically described with reference to the drawings.
なお、以下で説明する実施の形態は、いずれも本発明の一具体例を示すものである。以下の実施の形態で示される数値、形状、材料、構成要素、構成要素の配置位置及び接続形態、ステップ、ステップの順序などは、一例であり、本発明を限定する主旨ではない。また、以下の実施の形態における構成要素のうち、最上位概念を示す独立請求項に記載されていない構成要素については、任意の構成要素として説明される。 Note that each of the embodiments described below shows a specific example of the present invention. The numerical values, shapes, materials, constituent elements, arrangement positions and connecting forms of the constituent elements, steps, order of steps, and the like shown in the following embodiments are merely examples and are not intended to limit the present invention. In addition, among the constituent elements in the following embodiments, constituent elements that are not described in the independent claims indicating the highest concept are described as optional constituent elements.
(実施の形態1)
[1−1.触力覚提示装置の構成]
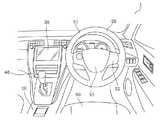
まず、図1を参照しながら、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10及び触力覚提示装置10が配置されている車両の車室の構成について説明する。図1は、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10及び触力覚提示装置10が配置されている車両の車室の構成の一例を示す図である。なお、以下では、車両の走行方向を基準として、前方向、後方向、右方向、及び左方向を規定する。また、車両の車輪が地面に付いている状態において、上方向、下方向、水平方向、及び垂直方向を規定する。(Embodiment 1)
[1-1. Configuration of haptic presentation device]
First, with reference to FIG. 1, a configuration of a haptic
図1に示す自動車1(車両の一例)の車室には、車載機器(図示せず)と、触力覚提示装置10とが搭載されている。また、自動車1の車室には、さらに、シフトレバー40ステアリング50およびシート60が配置されている。 An in-vehicle device (not shown) and a tactile
車載機器は、自動車1などの車両に搭載される機器であり、例えば、カーナビゲーションシステムや、光ディスクを再生するためのオーディオ機器または映像再生機器などである。車載機器は、表示部30を有している。表示部30は、カーナビゲーションを行うための地図、再生された映像、車載機器を操作するためのUI、他の車載機器を制御するためのUIなどを表示する。表示部30は、例えば、液晶ディスプレイ、有機EL(Electro Luminescence)ディスプレイなどにより実現される。また、車載機器は、スピーカ(図示せず)に接続され、音声をスピーカに出力する構成としてもよい。なお、他の車載機器としては、例えば、空調機器などがあり、触力覚提示装置を用いて操作の入力を行うことによって、当該空調機器の動作が制御されるように構成されていてもよい。 The in-vehicle device is a device mounted on a vehicle such as the
触力覚提示装置10は、車載機器の表示部30が表示するUI(User Interface)を操作するための入力を行う装置であり、かつ、操作中のユーザに、入力内容に応じた刺激を与える装置である。 The tactile
触力覚提示装置10は、タッチパッド11を有する入力部12と、触力覚発生素子21が発生する刺激によりユーザに触力覚を与える触力覚提示部20と、触力覚提示部20の動作を制御する制御部25とを有している。 The haptic
触力覚提示装置10において、入力部12は、表示部30に表示されているUIを操作するための入力インタフェースである。ユーザは、入力部12を用いてUIを操作することで、自動車1に搭載されている車載機器を制御することができる。なお、触力覚提示装置10の詳細な構成については、後に詳述する。 In the haptic
自動車1の車室において、触力覚提示装置10は、自動車1に搭乗しているユーザがシート60に座っている状態で、当該ユーザの手が届く範囲の位置であって、ステアリング50を除く位置に配置されている。例えば、触力覚提示装置10は、図1に示すように、シフトレバー40の後方に配置されている。ユーザである運転者は、左手でシフトレバー40の後方に配置されている触力覚提示装置10の入力部12に対して入力を行うことにより、車載機器を操作する。なお、触力覚提示装置10は、当該ユーザの手が届く範囲の位置であって、ステアリング50を除く位置に配置されていれば、上記の位置に配置されていなくてもよい。 In the passenger compartment of the
なお、図1では、右ハンドルの自動車1を例としているが、左ハンドルの自動車であっても左右が反対になるだけであるため、右ハンドルの自動車1の場合と同様のことが言える。 In FIG. 1, the right-
ステアリング50は、自動車1を操舵するためのものであり、リング形状を有するリム51と、リム51の内周面に一体的に形成された略T字状のスポーク52と、スポーク52の中央部に配置されたホーンスイッチ(図示せず)を覆うホーンスイッチカバー53とを有している。 The steering 50 is for steering the
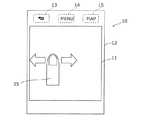
次に、触力覚提示装置10の構成について説明する。図2は、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10を平面視したときの外観斜視図である。 Next, the configuration of the haptic
触力覚提示装置10は、ユーザが操作を入力する入力部12と、ユーザの触力覚に刺激を与える触力覚提示部20(図3参照)と、入力部12に入力された操作に基づいて触力覚提示部20を制御する制御部25(図3参照)とを備えている。 The haptic
図2に示すように、触力覚提示装置10の入力部12は、外観視したときに、タッチパッド11と、タッチスイッチ13〜15を有している。ユーザは、タッチパッド11またはタッチスイッチ13〜15への入力を行うことにより、車載機器の表示部30に表示されているUIを操作することができる。 As shown in FIG. 2, the
タッチパッド11は、ユーザによるタッチを受け付ける入力部である。タッチパッド11は、後述するように、ユーザがタッチする面と反対側の面に静電IC(Integrated Circuit)18(図4参照)を有している。静電IC18は、当該タッチパッド11の検出領域における位置であって、ユーザの身体の一部(例えば指)によりタッチされた位置を検出する。なお、タッチパッド11は、ユーザによる複数のタッチ、つまり、マルチタッチを受け付けるセンサであってもよい。つまり、タッチパッド11は、1本指によるタッチ位置の他にも、同じタイミングにおいて、2本指による2箇所のタッチ位置、3本指による3箇所のタッチ位置を受け付ける構成であってもよい。 The
タッチスイッチ13〜15は、タッチパッド11の前方に配置され、左右方向に並んで配置される。タッチスイッチ13〜15のそれぞれは、タッチスイッチ13〜15が配置されている領域にタッチがされたか否かを検出するスイッチである。 The touch switches 13 to 15 are arranged in front of the
タッチスイッチ13は、例えば、戻るスイッチである。タッチスイッチ13へのタッチが検出されると、表示部30に表示されているUIは、前に表示していたUIに変更される。 The
タッチスイッチ14は、例えば、メニュースイッチである。タッチスイッチ14へのタッチが検出されると、表示部30に表示されているUIには、メニューが表示される。 The
タッチスイッチ15は、例えば、マップスイッチである。タッチスイッチ15へのタッチが検出されると、表示部30に表示されているUIには、マップが表示される。 The
タッチスイッチ13〜15への入力は、例えば、タッチスイッチ13〜15に重なる領域であって、ユーザがタッチする面と反対側の面に配置され感圧センサ(図示せず)によって検出される。感圧センサは、タッチスイッチ13〜15への押し込みによる押圧力の変化を検出するセンサである。例えば、感圧センサへの、所定の押圧力よりも大きい押圧力の入力は、決定を示す入力として受け付けられる。 The input to the touch switches 13 to 15 is, for example, a region that overlaps the touch switches 13 to 15 and is disposed on a surface opposite to the surface that the user touches, and is detected by a pressure-sensitive sensor (not shown). The pressure-sensitive sensor is a sensor that detects a change in pressing force due to pressing into the touch switches 13 to 15. For example, an input of a pressing force greater than a predetermined pressing force to the pressure sensor is accepted as an input indicating determination.
なお、入力部12は、タッチスイッチ13〜15を備えない構成であってもよいし、1つまたは複数のタッチスイッチを備える構成であってもよい。タッチスイッチ13〜15は、タッチパッド11の前方に限らず、タッチパッド11の後方に配置されていてもよい。また、タッチスイッチ13〜15は、例えば、カスタマイズスイッチであってもよい。この場合、ユーザは、当該タッチスイッチ13〜15に予めショートカット入力を割り当てておくことができる。そして、当該タッチスイッチ13〜15へのタッチが検出されると、ユーザにより割り当てられたショートカットに基づくアプリが起動されたり、当該ショートカットが示す所定の操作が実行されたりするとしてもよい。 The
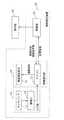
図3は、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10の機能的な構成の一例を示すブロック図である。図4は、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10の構成を示す概略構成図である。 FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating an example of a functional configuration of the haptic
図3に示すように、触力覚提示装置10は、入力部12と、触力覚提示部20と、制御部25とを備える。 As shown in FIG. 3, the haptic
入力部12は、上述したように、タッチパッド11と、静電IC18とを備えている。
タッチパッド11は、ユーザが指などにより接触することにより入力操作を行う入力部である。タッチパッド11は、例えば静電容量式のタッチパッドであり、静電IC18に接続されている。タッチパッド11は、導電膜を有している。静電IC18は、ユーザがタッチパッド11上の導電膜に接触したときの静電容量の変化により、ユーザの指が接触した接触した位置を検出するセンサである。これによれば、ユーザの指と導電膜との間の静電容量の変化により、精度よく指の接触位置を検出することができる。また、ユーザの指と導電膜との間の静電容量の変化が検出できるのであれば、非接触でも指の位置を検出することができる。As described above, the
The
なお、タッチパッド11は、上述した静電容量式の入力部に限らず、例えば、ユーザの指に光を照射して指の接触位置を検出する光学式の入力部であってもよい。これによれば、光を照射したときの指からの反射光または指の影により、簡便に指の接触位置を検出することができる。また、タッチパッド11は、タッチパッド11上に設けられた抵抗膜を用いて接触位置を検出する抵抗膜式であってもよい。これによれば、指が接触したことによるタッチパッド11の抵抗膜の抵抗値の変化により、簡便に指の接触位置を検出することができる。 Note that the
また、タッチパッド11は、これらに限らず、超音波式、電磁誘導式などその他の方式を用いたものであってもよい。また、非接触のタッチパッド11として、超音波式や光学式(例えば、カメラなど)のものを用いてもよい。また、タッチパッド11は、後述するように、入力部と表示部の機能を兼ね備えたタッチパネルであってもよい。 In addition, the
なお、入力部12は、上述したように、タッチスイッチ13〜15を有していてもよい。ユーザがタッチパッド11に入力を行ったことが静電IC18で検出されると、当該入力を示す入力信号が、後述する触力覚提示部20のマイコン22を介して制御部25に出力される。 Note that the
触力覚提示部20は、触力覚発生素子21と、マイコン22とを備えている。 The tactile force
触力覚発生素子21は、ユーザの入力に応じて、ユーザに与える触力覚の発生源となる素子である。触力覚発生素子21は、マイコン22から入力された振動波形に基づいて、ユーザに触力覚を提示する。 The tactile force
触力覚発生素子21は、タッチパッド11に接触したユーザに振動により直接触力覚を与える振動子であってもよいし、非接触で触力覚を与える素子であってもよい。また、触力覚発生素子21は、振動に限らず、ユーザに他の力覚または摩擦感などの触力覚を与える素子であってもよいし、電流刺激など感覚神経に触力覚を与える素子であってもよい。 The tactile force
例えば、振動子は、圧電体で構成された圧電素子であってもよいし、モータ、ソレノイド、ボイスコイルなど、電磁的に動作する構成であってもよい。また、振動子は、リニアレゾナントアクチュエータ、人工筋肉、形状記憶アクチュエータなどであってもよい。 For example, the vibrator may be a piezoelectric element formed of a piezoelectric body, or may be configured to operate electromagnetically, such as a motor, a solenoid, or a voice coil. The vibrator may be a linear resonant actuator, an artificial muscle, a shape memory actuator, or the like.
また、非接触で触力覚を与える素子は、超音波または空気流を発生する素子などであってもよい。感覚神経に触力覚を与える素子は、静電方式の摩擦感を発生する素子などであってもよい。 Further, the element that gives a tactile sensation without contact may be an element that generates ultrasonic waves or airflow. The element that gives a sense of tactile force to the sensory nerve may be an element that generates an electrostatic friction feeling.
制御部25は、入力部12からマイコン22を介して入力された入力信号より、タッチパッド11においてユーザが接触した位置情報を得て、入力信号に応じて車載機器を制御する。また、制御部25は、入力信号に応じて触力覚提示部20を制御し、ユーザに触力覚を与える。 The
具体的には、制御部25は、操作画面を含む表示画面を、車載機器の表示部30に表示させる。また、制御部25は、メニューを表示させることを示す入力信号が入力部12により入力されると、メニューを表示部30の操作画面に表示させる。また、制御部25は、ユーザが入力部12のタッチパッド11に触れた接触位置と接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、触力覚提示部20の触力覚発生素子21から提示される触力覚振動を制御する。具体的には、制御部25は、マイコン22に車載機器の制御状況および表示部30の画面条件などを送信し、触力覚発生素子21に所定の大きさ、周波数またはパターンの触力覚振動を発生させる。 Specifically, the
制御部25は、例えば、所定のプログラムを実行するプロセッサと、当該所定のプログラムを記憶しているメモリとにより実現されてもよいし、専用回路により実現されてもよい。制御部25は、例えば、ECU(Electronic Control Unit)により実現されてもよい。制御部25による制御の詳細については、後に詳述する。 The
また、図4は、触力覚提示装置10のタッチパッド11の構成を断面図で示している。図4に示すように、タッチパッド11の下には、触力覚発生素子21が機械的に固定されている。また、触力覚発生素子21は、ホルダー27に支持されている。ホルダー27は、箱状の本体28に収容されている。また、本体28の内部の底面には、マイコン22が配置された制御ボード26が設けられている。制御ボード26には、外部電源などに接続される端子その他配線などが設けられている。 FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view showing the configuration of the
なお、タッチパッド11と触力覚発生素子21の間には、導電板が設けられていてもよい。タッチパッド11と触力覚発生素子21の間に導電板を設けることにより、タッチパッド11は、触力覚発生素子21から受ける電界によるノイズを低減することができる。なお、図4では導電板を図示していない。 A conductive plate may be provided between the
さらに、タッチパッド11の、ユーザが入力操作を行う面と反対側の面には、静電IC18が配置されている。タッチパッド11は、配線29aにより制御ボード26に接続されている。触力覚発生素子21は、配線29bにより制御ボード26に接続されている。静電IC18および触力覚発生素子21は、制御部25に接続される。 Furthermore, an
[1−2.触力覚提示装置の動作]
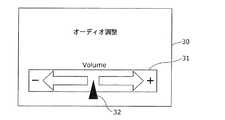
次に、触力覚提示装置10の動作について説明する。図5Aは、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10の入力部12を介して、車載機器に対して行う操作の一例を示す図である。図5Bは、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10の入力部12に対してユーザが行う操作の一例を示す図である。[1-2. Operation of the haptic presentation device]
Next, the operation of the haptic
ユーザは、触力覚提示装置10の入力部12により、例えば車載機器のうちオーディオの音量を調整することができる。この場合、図5Aに示すように、表示部30には、音量調節用の調節ゲージ31が示される。ユーザは、図5Bに示すように、入力部12のタッチパッド11に指35を接触させて左右に移動させることにより、表示部30の調節ゲージ31のつまみ32を左右に移動させる。これにより、ユーザはオーディオの音量を調節することができる。 The user can adjust the audio volume of the in-vehicle device, for example, with the
このとき、制御部25は、ユーザの指35の移動方向に基づいて触力覚発生素子21を制御して振動などの所定の触力覚を発生させ、タッチパッド11を介してユーザの指35に触力覚を与える。例えば、制御部25は、調節ゲージ31が設けられた領域内において、ユーザが調節ゲージ31に沿って指35を移動させているときには振動による触力覚(触力覚振動)を与えず、ユーザの指35の移動方向が調節ゲージ31が設けられた領域から外れる方向であるときには触力覚振動を与えることとしてもよい。 At this time, the
図6は、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10の動作の一例を示すフローチャートである。図7Aおよび図7Bは、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10において、ユーザの指35の接触位置の移動方向と触力覚との関係の例を示す図である。 FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing an example of the operation of the haptic
ユーザが、入力部12のタッチパッド11に指35を接触させて移動させた場合、タッチパッド11に配置された静電IC18は、指35が接触したことによるタッチパッド11の静電容量の変化から、タッチパッド11において指35が接触した位置を検出する。これにより、ユーザがタッチパッド11に接触した指35の接触位置が検出される(ステップS10)。なお、検出された指35の接触位置の情報は、静電IC18から制御ボード26に配置されたマイコン22を介して、制御部25へ出力される。 When the user moves the
指35の接触位置の検出は、定期的に行われる。そして、制御部25は、指35の接触位置の時間的な変化から、タッチパッド11への指35の接触位置の移動方向を検出する(ステップS11)。 The detection of the contact position of the
さらに、制御部25は、指35の移動方向に基づいて、触力覚提示部20の触力覚発生素子21の動作を制御する(ステップS12)。 Further, the
触力覚発生素子21の制御は、例えば、図7Aに示すように、指35が±X方向の成分を含む方向に移動したときには触力覚発生素子21の動作を大きくし、指35が±Y方向にのみ移動したときには触力覚発生素子21の動作を小さくするまたは触力覚発生素子21を動作させない制御を行ってもよい。 For example, as shown in FIG. 7A, when the
また、制御部25は、図7Bに示すように、指35が+Y方向に移動する場合には、触力覚発生素子21の動作を小さくし、指35の移動方向と+Y方向との間の角度(ズレ角)が大きくなるにしたがって触力覚発生素子21の動作を大きくする制御を行ってもよい。この場合、制御部25は、指35の移動方向と+Y方向との間の角度が最大(180°)となる−Y方向へ指35が移動する場合に、触力覚発生素子21の動作が最大となるように制御を行ってもよい。 Further, as shown in FIG. 7B, when the
また、制御部25は、指35の移動方向が、例えば音量などの調節ゲージに沿った方向の場合に触力覚発生素子21の動作を小さくし、指35の移動方向が調節ゲージに直交する方向の場合に触力覚発生素子21の動作を大きくする制御を行ってもよい。なお、指35の移動方向と触力覚発生素子21の制御の態様については、後に詳述する。 Further, the
なお、図6に示したフローチャートは、一例であり、触力覚提示装置10は、触力覚提示装置の機能構成の欄で説明した処理を行えばよく、必ずしも図6のような順番で各ステップを行わなくてもよいし、全てのステップを必ずしも行わなくてもよい。また、指35の移動方向および調節ゲージ31のつまみ32の移動方向は、X方向またはY方向などの直線的な方向に限らず、時計回りの方向または反時計回りの方向などの回転方向または曲線方向であってもよい。 Note that the flowchart shown in FIG. 6 is an example, and the haptic
[1−3.実施例]
以下、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10による触力覚提示動作の具体例について説明する。なお、図8〜11、13、14、18における矢印A、B、C、Dは、表示部30に対して、指を操作する方向を示すものであり、実際には表示部30に表示されない。[1-3. Example]
Hereinafter, a specific example of the haptic sense presentation operation by the haptic
[1−3−1.実施例1]
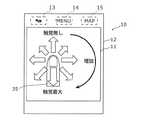
図8は、実施例1に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、ユーザは、図8に示すように車載機器の表示部30に表示されたダイヤル式の調節ゲージ31aを時計回りの方向または反時計回りの回転方向になぞることにより、車載装置の操作を行う。例えば、調節ゲージ31aがオーディオの音量を調節するゲージである場合、図8に示すように、調節ゲージ31aをAの方向になぞることにより音量は大きくなり、調節ゲージ31aをBの方向になぞることにより音量は小さくなる。[1-3-1. Example 1]
FIG. 8 is a diagram for explaining the haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
ユーザは、タッチパッド11において、調節ゲージ31aをAの方向またはBの方向に回転させるように、指を移動させる。このとき、制御部25は、ユーザの指が、音量が大きくなるAの方向に移動した場合と、音量が小さくなるBの方向に移動した場合とで触力覚提示部20が異なる触力覚を提示するように、触力覚発生素子21を制御してもよい。例えば、制御部25は、タッチパッド11におけるユーザの指の接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、触力覚振動の振幅の大きさを制御する。具体的には、制御部25は、ユーザの指がAの方向に移動した場合には触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を大きくし、ユーザの指がBの方向に移動した場合には触力覚振動の振幅を小さくする。これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動が大きいか小さいかによって意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向を認識することができるので、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動することができる。 The user moves the finger on the
なお、制御部25は、ユーザの指の移動距離に応じて触力覚振動の振幅を徐々に大きく、または、徐々に小さくしてもよい。また、制御部25は、ユーザの指の移動速度に応じて、触力覚振動の振幅を徐々に大きく、または、徐々に小さくしてもよい。 The
また、制御部25は、触力覚振動の振幅に限らず、タッチパッド11におけるユーザの指の接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、触力覚振動の周波数を制御してもよい。具体的には、制御部25は、ユーザの指がAの方向に移動した場合には触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の周波数を高くし、ユーザの指がBの方向に移動した場合には当該振動の周波数を低くする。これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動の周波数が高いか低いかによって意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向を認識することができるので、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動することができる。 Further, the
また、制御部25は、触力覚振動の振幅及び周波数に限らず、タッチパッド11におけるユーザの指の接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、触力覚振動のパターンを制御してもよい。具体的には、制御部25は、ユーザの指がAの方向に移動した場合には触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動のパターンを「トン、トン、トン」というパターン1、ユーザの指がBの方向に移動した場合には触力覚振動のパターンを「トトトン、トトトン、トトトン」というパターン2としてもよい。これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動のパターンの違いによって意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向を認識することができるので、意図した操作方向または正しい操作方向に指を移動することができる。 The
また、制御部25は、振動による触力覚に限らず、電流刺激などの他の種類の触力覚をユーザの指に与えることとしてもよい。 Moreover, the
[1−3−2.実施例2]
図9は、実施例2に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、触力覚提示部20は、ユーザの指の接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、車載機器の表示部30に表示された画像などのテクスチャーに応じた触力覚を提示する。ここで、テクスチャーとは、画像などに表された物体の表面の粗さまたは滑らかさなど、物体の実物を触った場合に感じるであろう触感(形状や質感)をいう。[1-3-2. Example 2]
FIG. 9 is a diagram for explaining the haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
図9に示すように、車載機器の表示部30にはハリネズミ31bの画像が表示されている。ここで、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、触力覚提示部20は、ユーザがタッチパッド11を介して、表示されたハリネズミ31bに触れるときに、ユーザの指がハリネズミ31bの毛の流れに沿う方向に移動する場合とハリネズミ31bの毛の流れに逆らう方向に移動する場合とで、異なる触力覚を提示する。 As shown in FIG. 9, the image of the
例えば、制御部25は、ユーザの指がハリネズミ31bの毛の流れに逆らうAの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を大きくし、ユーザが摩擦感を覚える触力覚を与えてもよい。また、ユーザの指がハリネズミ31bの毛の流れに沿うBの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を小さくし、ユーザが摩擦感を覚えない程度の触力覚を与えてもよい。 For example, when the user's finger moves in the direction A against the flow of the hair of the
なお、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10においても、実施例1に示した触力覚提示装置10と同様、触力覚振動の振幅の大きさに限らず、触力覚振動の周波数、パターンまたは触力覚の種類などを制御してユーザの指に提示してもよい。 In addition, in the haptic
[1−3−3.実施例3]
図10Aおよび図10Bは、実施例3に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、ユーザは、ユーザは、図10Aに示すように車載機器の表示部30に表示された調節ゲージ31cを上下方向に移動させることにより、車載装置の操作を行う。例えば、調節ゲージ31cがオーディオの音量を調節するゲージである場合、調節ゲージ31cを図10Aに示すAの方向に移動させることにより音量は大きくなり、調節ゲージ31aを図10Aに示すBの方向に移動させることにより音量は小さくなる。また、ユーザの指が調節ゲージ31cにおいてCの方向またはDの方向に移動した場合には、ユーザはオーディオの音量を調節することはできない。[1-3-3. Example 3]
10A and 10B are diagrams for explaining the haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
ここで、制御部25は、ユーザの指が調節ゲージ31cの領域内にある場合と調節ゲージ31cの領域からはみ出した場合とで、触力覚提示部20が異なる触力覚を提示するように触力覚発生素子21を制御してもよい。例えば、制御部25は、ユーザの指が調節ゲージ31cの領域内においてAの方向またはBの方向に移動した場合には、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を小さく、または、触力覚発生素子21が触力覚振動を発生しないように制御を行う。また、制御部25は、図10Bに示すように、ユーザの指がCの方向またはDの方向に移動し、調節ゲージ31cの領域からはみ出す場合には、触力覚発生素子21が、ユーザの指がAの方向およびBの方向に移動する場合よりも大きな振幅の触力覚振動を発生するように制御を行う。 Here, the
これにより、ユーザは、表示部30またはタッチパッド11を目視により確認しながら指を移動させなくても、調節ゲージ31cから指が調節ゲージ31cの領域からはみ出したか否かを認識することができる。 Accordingly, the user can recognize whether or not the finger has protruded from the region of the
なお、制御部25は、ユーザの指が調節ゲージ31cの領域からはみ出したときに限らず、Cの方向またはDの方向に移動したときに、触力覚発生素子21が、ユーザの指がAの方向およびBの方向に移動する場合よりも大きな振幅の触力覚振動を発生するように制御を行ってもよい。これにより、ユーザの指が調節ゲージ31cの領域からはみ出す前に、ユーザの指が調節ゲージ31cからはみ出すおそれがあることをユーザに認識させることができる。 Note that the
また、制御部25は、さらに、ユーザの指が調節ゲージ31cの領域内においてAの方向に移動する場合とBの方向に移動する場合とで、触力覚発生素子21が異なる触力覚振動を発生するように制御してもよい。例えば、ユーザの指がAの方向に移動する場合には触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を大きくし、ユーザの指がBの方向に移動する場合には触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を小さくしてもよい。また、ユーザの指がAの方向に移動する場合とBの方向に移動する場合では、触力覚振動の周波数は同一とし、ユーザの指がCの方向またはDの方向に移動する場合には、触力覚発生素子21が、ユーザの指がAの方向またはBの方向に移動する場合と異なる周波数の触力覚振動を発生するように制御を行ってもよい。 Further, the
これにより、ユーザは、表示部30またはタッチパッド11を目視により確認しながら指を移動させなくても、調節ゲージ31cから指が調節ゲージ31cの領域からはみ出すか否かを認識するとともに、調整の方向を認識することができる。 Accordingly, the user can recognize whether or not the finger protrudes from the
なお、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10においても、ユーザの指の移動距離に応じて触力覚振動の振幅を徐々に大きく、または、徐々に小さくしてもよい。また、ユーザの指の移動速度に応じて、触力覚振動の振幅を徐々に大きく、または、徐々に小さくしてもよい。また、制御部25は、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅または周波数に限らず、触力覚振動のパターンまたは触力覚の種類を制御してもよい。 Note that, also in the haptic
[1−3−4.実施例4]
図11は、実施例4に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。[1-3-4. Example 4]
FIG. 11 is a diagram for explaining a haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、触力覚提示部20は、ユーザの指の接触位置の移動方向に基づいて、車載機器の表示部30に表示された物体の凹凸、立体形状、または、力の入れやすさなどに応じた触力覚を提示する。 In the haptic
図11に示すように、車載機器の表示部30には立体形状を有する球31dの画像が表示されている。ここで、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、触力覚提示部20は、ユーザがタッチパッド11を介して球31dに触れるときに、ユーザの指が重力に沿った鉛直方向に移動する場合と鉛直方向と直交する水平方向に移動する場合とで、異なる触力覚を提示する。 As shown in FIG. 11, an image of a
例えば、制御部25は、ユーザの指が重力の方向に逆らうAの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を大きくし、ユーザの指が重力の方向に沿うBの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を小さくする。また、制御部25は、ユーザの指が水平方向であるCの方向またはDの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を、ユーザの指がAの方向に移動する場合とBの方向に移動する場合の中間の大きさに制御する。 For example, when the user's finger moves in the direction A against the direction of gravity, the
また、制御部25は、球31dの形状に合わせて、球31dの高さの中央付近から球31dの天頂または底部のほうへ移動するにつれて触力覚振動の振幅の変化の勾配が大きくなるように、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を制御してもよい。 Further, the
なお、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10においても、実施例1に示した触力覚提示装置10と同様、触力覚振動の振幅の大きさに限らず、触力覚振動の周波数、パターンまたは触力覚の種類などを制御してユーザの指に提示してもよい。 In addition, in the haptic
[1−3−5.実施例5]
図12Aおよび図12Bは、実施例5に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、ユーザは、図12Aおよび図12Bに示すように、タッチパッド11に接触させた2本の指35の間隔を広げる動作(ピンチイン)または狭める動作(ピンチアウト)により、車載機器の操作を行う。触力覚提示装置10において、制御部25は、ユーザがタッチパッド11に接触させた2本の指35の間隔を広げるときと狭めるときで、触力覚提示部20が提示する触力覚が異なるように、触力覚発生素子21の制御を行う。[1-3-5. Example 5]
12A and 12B are diagrams for explaining the haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
具体的には、制御部25は、図12Aに示すように、ユーザの2本の指35が間隔を広げるEの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を大きくする。また、制御部25は、図12Aに示すように、ユーザの2本の指35が間隔を広げるFの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を小さくする。 Specifically, as shown in FIG. 12A, the
なお、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10においても、実施例1に示した触力覚提示装置10と同様、触力覚振動の振幅の大きさに限らず、触力覚振動の周波数、パターンまたは触力覚の種類などを制御してユーザの指に提示してもよい。 In addition, in the haptic
[1−3−6.実施例6]
図13Aおよび図13Bは、実施例6に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、ユーザは、車載機器の表示部30に表示された画像が移動しているときに、画像の移動方向に沿う方向または画像の移動方向に逆らう方向に指を移動させることにより、車載機器の操作を行う。[1-3-6. Example 6]
13A and 13B are diagrams for explaining the haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
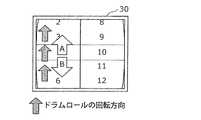
このとき、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、触力覚提示部20は、車載機器の表示部30に表示された画像の移動方向に対するユーザの指の接触位置の相対的な移動方向に基づいて、触力覚を提示する。例えば、ユーザの指の接触位置が画像の移動方向に沿った方向に移動するときには、触力覚提示部20は、振幅の小さい触力覚振動を提示する。また、ユーザの指の接触位置が画像の移動方向に逆らう方向に移動するときには、触力覚提示部20は、振幅の大きい触力覚振動を提示する。 At this time, in the haptic
具体的には、図13Aに示すように、車載機器の表示部30には下方向に回転することができるドラムロールの画像が表示されている。制御部25は、ユーザの指がドラムロールの回転方向に逆らうAの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を大きくし、ユーザが摩擦感を覚える触力覚を与える。また、ユーザの指がドラムロールの回転方向に沿うBの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を小さくし、ユーザが摩擦感を覚えない程度の触力覚を与える。 Specifically, as shown in FIG. 13A, an image of a drum roll that can rotate downward is displayed on the
同様に、図13Bに示すように、車載機器の表示部30に上方向に回転することができるドラムロールが表示されている場合には、制御部25は、ユーザの指がドラムロールの回転方向に沿うAの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を小さくし、ユーザが摩擦感を覚えない程度の触力覚を与える。また、ユーザの指がドラムロールの回転方向に逆らうBの方向に移動するときには、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅を大きくし、ユーザが摩擦感を覚える触力覚を与える。 Similarly, as shown in FIG. 13B, when a drum roll that can be rotated upward is displayed on the
なお、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10においても、実施例1に示した触力覚提示装置10と同様、触力覚振動の振幅の大きさに限らず、画像の移動方向に対するユーザの指の相対的な移動方向に基づいて、触力覚振動の周波数、パターンまたは触力覚の種類などを制御してユーザの指に提示してもよい。 Note that, in the haptic
[1−3−7.実施例7]
図14は、実施例7に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10においても、実施例6に示した触力覚提示装置10と同様、触力覚提示部20は、画像の移動方向に対するユーザの指の相対的な移動方向に基づいて、ユーザの指に触力覚を提示する。[1-3-7. Example 7]
FIG. 14 is a diagram for explaining the haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
具体的には、本実施例において、車載機器はカーナビゲーションシステムであり、図14に示すように、表示部30には地図が表示されている。当該地図は、図14に示すように左斜め下に移動している。ここで、ユーザの指の接触位置が地図の移動方向に逆らうAの方向の成分を持つ方向に移動するときには、触力覚提示部20は、振幅の大きい触力覚振動を提示する。また、ユーザの指が、地図の移動方向に沿ったBの方向の成分を持つ方向に移動するときには、触力覚提示部20は、振幅の小さい触力覚振動を提示する。また、ユーザの指が地図の移動方向と直交するCの方向またはDの方向に移動するときには、触力覚提示部20は、触力覚振動を提示しない。これにより、ユーザは、いずれの方向に地図を移動させているのかを認識することができる。 Specifically, in this embodiment, the in-vehicle device is a car navigation system, and a map is displayed on the
なお、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10においても、実施例1に示した触力覚提示装置10と同様、触力覚振動の振幅の大きさに限らず、画像の移動方向に対するユーザの指の相対的な移動方向に基づいて、触力覚振動の周波数、パターンまたは触力覚の種類などを制御してユーザの指に提示してもよい。 Note that, in the haptic
[1−4.効果など]
以上、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10によれば、ユーザは、指の移動方向に基づいて触力覚提示部20から触力覚を提示されるので、意図した操作方向や正しい操作方向に指を移動しているのか否かを認識することができる。したがって、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置によると、車載装置などの機器へ操作を入力するときの、視覚への位置決定の依存度を低減することができる。[1-4. Effect etc.]
As described above, according to the haptic
(実施の形態2)
[2−1.触力覚提示装置の構成]
次に、実施の形態2に係る触力覚提示装置10について説明する。本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10が実施の形態1に係る触力覚提示装置10と異なる点は、制御部25が、タッチパッド11においてユーザの指35を移動させる目標位置を有し、タッチパッド11に対するユーザの指35の接触位置と移動方向から、接触位置が所定目標位置に向かっているか否かを判断し、当該判断結果に基づいて触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動を制御する点である。なお、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10の構成については、実施の形態1に示した触力覚提示装置10と同様であるため、詳細な説明は省略する。(Embodiment 2)
[2-1. Configuration of haptic presentation device]
Next, the haptic
[2−2.触力覚提示装置の動作]
次に、触力覚提示装置10の動作について説明する。図15Aおよび図15Bは、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10における、ユーザの指35の接触位置の移動方向の例を示す図である。[2-2. Operation of the haptic presentation device]
Next, the operation of the haptic
図15Aおよび図15Bに示すように、ユーザは、車載機器の操作を行うために、タッチパッド11においてユーザの指35を所定の目標位置37まで移動させる操作を行う。目標位置とは、例えば、車載機器の表示部30に表示された目標位置に対応する、タッチパッド11における目標位置37である。表示部30に表示された目標位置とは、例えば、車載機器がカーナビゲーションシステムであり表示部30に地図が表示されている場合に行き先として入力された目的地、または、宝探しゲームにおいて宝物が配置された位置などである。 As shown in FIGS. 15A and 15B, the user performs an operation of moving the user's
本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10では、触力覚提示部20は、図15Aに示すようにユーザの指35が目標位置37の方向に向かって移動している場合と、図15Bに示すようにユーザの指35が目標位置37の方向と異なる方向に移動している場合とで、異なる触力覚を提示する。 In the haptic
より詳細には、制御部25は、タッチパッド11におけるユーザの指35の接触位置と指35の移動方向から、タッチパッド11における指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっているか否かを判断する。そして、制御部25は、当該判断結果に基づいて触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動を制御する。このとき、制御部25は、ユーザの指35が目標位置37の方向に向かって移動している場合と、ユーザの指35が目標位置37の方向と異なる方向に移動している場合とで、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚が異なるように制御する。制御部25は、判断結果に基づいて、触力覚提示部20に設けられた触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅の大きさ、周波数、パターンまたは触力覚の種類が異なるものとなるように制御する。 More specifically, the
これにより、触力覚提示部20は、目標位置37の方向に対する指35の相対的な移動方向に基づいて触力覚を提示するので、ユーザは、指35の移動方向が目標位置に向かっているか否かを認識することができる。よって、ユーザは、他の作業を行っている場合であっても、目標位置37の方向に指35を移動して、機器の操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる。 Thereby, the tactile force
例えば、制御部25は、タッチパッド11においてユーザの指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっている場合よりも、ユーザの指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっていない場合のほうが、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動の振幅が大きくなるように触力覚提示部20を制御する。より具体的には、制御部25は、タッチパッド11においてユーザの指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっている場合よりも、ユーザの指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっていない場合のほうが、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚振動の振幅が大きくなるように制御する。これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動が大きいか小さいかによって、接触位置が目標位置37に向かっているか否かを認識することができる。 For example, the
なお、制御部25は、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動の振幅に限らず、触力覚振動の周波数を制御してもよい。例えば、制御部25は、タッチパッド11においてユーザの指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっている場合よりも、ユーザの指35の接触位置が目標位置に向かっていない場合のほうが、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動の周波数が小さくなるように制御してもよい。これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動の周波数が高いか低いかによって、接触位置が目標位置37に向かっているか否かを認識することができる。 Note that the
また、制御部25は、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動の振幅、周波数に限らず、触力覚振動のパターンまたは触力覚の種類を制御してもよい。また、制御部25は、タッチパッド11においてユーザの指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっている場合は、触力覚提示部20から触力覚を提示させず、ユーザの指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっていない場合は、触力覚提示部20から触力覚を提示させるように制御してもよい。これによれば、ユーザは、触力覚提示部20から触力覚が提示される場合には指35の移動方向が目標位置37に向かっておらず、触力覚提示部20から触力覚が提示されない場合には指35の移動方向が目標位置37に向かっていると認識することができる。したがって、ユーザは、触力覚が提示されない方向に指35を移動させることにより、容易に目標位置に到達することができる。 Further, the
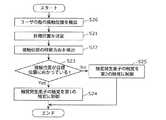
図16は、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10の動作の一例を示すフローチャートである。ユーザが、入力部12のタッチパッド11に指35を接触させて移動させた場合、タッチパッド11に配置された静電IC18は、指35が接触したことによるタッチパッド11の静電容量の変化から、タッチパッド11において指35が接触した位置を検出する。これにより、ユーザがタッチパッド11に接触した指35の接触位置が検出される(ステップS20)。なお、検出された指35の接触位置の情報は、静電IC18から制御ボード26に配置されたマイコン22を介して、制御部25へ出力される。 FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing an example of the operation of the haptic
次に、制御部25により、目標位置37の決定が行われる(ステップS21)。目標位置37は、例えば車載機器がカーナビゲーションシステムである場合には、ユーザにより行き先として入力された目的地、宝探しゲームの場合には宝物の位置、ナビゲーション中のカーナビゲーションシステムにおいては、現在走行している道路が続く方向、などである。制御部25は、目標位置37として、入力された表示部30における目標位置、または予想される表示部30における目標位置の、タッチパッド11における位置を計算して決定する。 Next, the
次に、ユーザの指35の接触位置の検出が行われる。指35の接触位置の検出は、定期的に行われる。そして、制御部25は、指35の接触位置の時間的な変化から、タッチパッド11への指35の接触位置の移動方向を検出する(ステップS22)。 Next, the contact position of the user's
さらに、制御部25は、検出された指35の接触位置が、目標位置37の方向に向かっているか否かを判断する(ステップS23)。指35の接触位置が目標位置37の方向に向かっている場合には(ステップS23においてYes)、制御部25は、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚を第1の触力覚に制御する(ステップS24)。また、指35の接触位置が目標位置37の方向に向かっていない場合には(ステップS23においてNo)、制御部25は、触力覚発生素子21が発生する触力覚を第2の触力覚に制御する(ステップS25)。 Further, the
ここで、第1の触力覚は、例えば、触力覚発生素子21が振動を発生する圧電素子の場合、振動の周波数が第2の触力覚と同一の周波数であり、振動の振幅が第2の触力覚よりも小さい振動である。なお、制御部25は、指35の接触位置が目標位置37に向かっているときは、第1の触力覚を提示しないとしてもよい。 Here, the first tactile force sense is, for example, when the tactile force
[2−3.実施例]
以下、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10による触力覚提示動作の具体例について説明する。[2-3. Example]
Hereinafter, a specific example of the haptic sense presentation operation by the haptic
[2−3−1.実施例8]
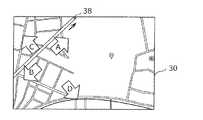
図17は、実施例8に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、ユーザは、タッチパッド11において、目標位置38の方向に向かって相対的に指35を移動させることにより、車載機器の操作を行う。図17に示す触力覚提示装置10では、目標位置38として、宝探しゲームの宝物の位置を示している。したがって、ユーザは、目標位置38がどの位置であるか分からない状態である。[2-3-1. Example 8]
FIG. 17 is a diagram for explaining the haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
触力覚提示装置10は、タッチパッド11においてユーザの指35の位置を移動させることにより、触力覚提示部20から触力覚を提示される。このとき、制御部25は、ユーザの指35の移動方向が目標位置38に近づいている場合には、触力覚提示部20に触力覚を提示させず、ユーザの指35の移動方向が目標位置38から遠ざかる場合には、触力覚提示部20に触力覚を提示させる制御を行う。より具体的には、制御部25は、ユーザの指35の移動方向が目標位置38に近づくAの方向である場合には、触力覚発生素子21に触力覚振動を発生させず、ユーザの指35の移動方向が目標位置38の方向と異なるBの方向、Cの方向およびDの方向である場合には、触力覚発生素子21に触力覚振動を発生させる。 The haptic
したがって、ユーザは、触力覚提示部20から触力覚を提示されないAの方向に指35を移動させることにより、目標位置38に到達することができる。 Therefore, the user can reach the
なお、制御部25は、ユーザの指35の移動方向が目標位置38に近づいている場合には、触力覚発生素子21に振幅の小さい触力覚振動を発生させ、ユーザの指35の移動方向が目標位置38から遠ざかる場合には、触力覚発生素子21に振幅の大きい触力覚振動を発生させることとしてもよい。また、制御部25は、触力覚振動の振幅に限らず、触力覚振動の周波数、パターンまたは触力覚の種類を制御してもよい。 In addition, when the moving direction of the user's
[2−3−2.実施例9]
図18は、実施例9に係る触力覚提示装置10の触力覚提示動作を説明するための図である。本実施例では、車載機器がカーナビゲーションシステムである場合に、ユーザは、表示部30に表示された地図において現在走行している道路の続く方向を表示する操作を行う。本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10では、表示部30にまだ表示されていない道路の続く方向が分からないが、触力覚提示装置10は、ユーザの指を道路の続く方向に誘導するように触力覚を提示する。[2-3-2. Example 9]
FIG. 18 is a diagram for explaining the haptic sense presentation operation of the haptic
本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10では、目標位置として、現在走行中の道路と表示部30の端部とが交わる位置を目標位置38とする。実施例8に示した触力覚提示装置10と同様、本実施例に係る触力覚提示装置10では、ユーザは、タッチパッド11においてユーザの指の位置を移動させることにより、触力覚提示部20から触力覚を提示される。このとき、制御部25は、ユーザの指の移動方向が目標位置38に近づいている場合には、触力覚提示部20に触力覚を提示させず、ユーザの指の移動方向が目標位置38から遠ざかる場合には、触力覚提示部20に触力覚を提示させる制御を行う。具体的には、制御部25は、ユーザの指の移動方向が目標位置38に近づいている場合には、触力覚発生素子21に触力覚振動を発生させず、ユーザの指の移動方向が目標位置38から遠ざかる場合には、触力覚発生素子21に触力覚振動を発生させる。 In the haptic
したがって、ユーザは、触力覚提示部20から触力覚を提示されない方向に指を移動させることにより、目標位置38に到達することができる。これにより、ユーザは、現在走行中の道路が続く方向に地図を移動させることができる。 Therefore, the user can reach the
なお、制御部25は、ユーザの指の移動方向が目標位置38に近づいている場合には、触力覚発生素子21に振幅の小さい触力覚振動を発生させ、ユーザの指の移動方向が目標位置38から遠ざかる場合には、触力覚発生素子21に振幅の大きい触力覚振動を発生させることとしてもよい。また、制御部25は、触力覚振動の振幅に限らず、触力覚振動の周波数、パターンまたは触力覚の種類を制御してもよい。 When the moving direction of the user's finger is approaching the
[2−4.効果など]
このように、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置10によれば、ユーザは、指35が目標位置37の方向に向かっているか否かにより、触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚を異なるものとするので、ユーザは、意図した操作方向や正しい操作方向に指35を移動しているのか否かを認識することができる。したがって、本実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置によると、車載装置などの機器へ操作を入力するときの、視覚への位置決定の依存度を低減することができる。また、ユーザが目標位置を認識していない場合であっても、ユーザの指を正しい方向に誘導することにより、ユーザに正しい操作を行わせることができる。[2-4. Effect etc.]
As described above, according to the haptic
(実施の形態2の変形例)
なお、上述した実施の形態2に係る触力覚提示装置10では、ユーザの指の移動方向が目標位置に向かっているか否かにより、触力覚提示部20は異なる触力覚を提示するものとしたが、これに限らず、触力覚提示部20は、目標位置の方向とユーザの指の移動方向とのズレ角に応じて異なる触力覚を提示してもよい。(Modification of Embodiment 2)
In the haptic
例えば、制御部25は、目標位置37とタッチパッド11におけるユーザの指35の接触位置とを結ぶ直線と、ユーザの指35の移動方向とから、図15Bに示したように、目標位置37に対するユーザの指35の移動方向のズレ角θを求める。そして、ズレ角θが大きいほど触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動の振幅が大きくなるように、触力覚提示部20を制御してもよい。これによれば、目標位置37の方向と指の移動方向のズレ角に基づいて触力覚振動の大きさが変わるので、ユーザは、指の移動方向と目標位置37の方向とがずれているか否かを認識することができる。これにより、ユーザは、他の作業を行っている場合であっても、目標位置の方向に指を移動して、機器の操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる。 For example, as illustrated in FIG. 15B, the
また、制御部25は、目標位置37とタッチパッド11におけるユーザの指35の接触位置とを結ぶ直線と、ユーザの指35の移動方向とから、図15Bに示したように、目標位置37に対するユーザの指35の移動方向のズレ角θを求める。そして、ズレ角θが大きいほど触力覚提示部20から提示される触力覚振動の周波数が小さくなるように、触力覚提示部20を制御してもよい。これによれば、目標位置37の方向と指35の移動方向のズレ角に基づいて触力覚振動の周波数が変わるので、ユーザは、指の移動方向と目標位置の方向とがずれているか否かを認識することができる。よって、触力覚提示装置10は、より正確にユーザの指35を正しい方向に誘導することができる。 Further, the
(その他の実施の形態)
以上、本発明の実施の形態に係る触力覚提示装置および触力覚提示方法について説明したが、触力覚提示装置および触力覚提示方法は上述した実施の形態に限らず、変更を加えてもよい。(Other embodiments)
As described above, the haptic sense presentation device and the haptic sense presentation method according to the embodiment of the present invention have been described. However, the haptic sense presentation device and the haptic sense presentation method are not limited to the above-described embodiments, and are modified. May be.
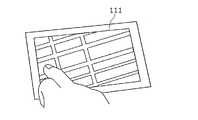
例えば、上述した実施の形態では、触力覚提示装置は、入力部にタッチパッドを設けた構成としたが、タッチパッドに限らず、図19に示すように、入力部と表示部の機能を兼ね備えたタッチパネル111を備えてもよい。なお、図19は、触力覚提示装置の入力部の一例を示す図である。 For example, in the above-described embodiment, the tactile sensation presentation device has a configuration in which a touch pad is provided in the input unit. However, the function of the input unit and the display unit is not limited to the touch pad, as illustrated in FIG. A
また、上述した実施の形態では、入力部として静電容量式のタッチパッドを用いたが、静電容量式に限らず、光学式、抵抗膜式、超音波式、電磁誘導式など他の方式を用いた入力部を用いてもよい。また、静電容量式も含め、非接触で検出できる構成のタッチパッドを用いてもよい。 In the above-described embodiment, the capacitive touch pad is used as the input unit. However, the input unit is not limited to the capacitive type, and other methods such as an optical type, a resistive film type, an ultrasonic type, and an electromagnetic induction type. An input unit using may be used. Moreover, you may use the touchpad of the structure which can be detected non-contacting also including an electrostatic capacitance type.
また、触力覚発生素子は、圧電素子で構成される振動子であってもよいし、モータ、ソレノイド、ボイスコイルなど、電磁的に動作する振動子、リニアレゾナントアクチュエータ、人工筋肉、形状記憶アクチュエータなどであってもよい。また、触力覚発生素子は、は、超音波または空気流を発生する素子など非接触で触力覚を与える素子であってもよいし、静電方式の摩擦感を発生する素子など感覚神経に触力覚を与える素子であってもよい。 Further, the tactile force sense generating element may be a vibrator composed of a piezoelectric element, or may be an electromagnetically operated vibrator such as a motor, a solenoid, or a voice coil, a linear resonant actuator, an artificial muscle, or a shape memory actuator. It may be. Further, the tactile force sense generating element may be a non-contact element that gives a tactile force sense such as an element that generates ultrasonic waves or airflow, or a sensory nerve such as an element that generates an electrostatic friction feeling. It may be an element that gives a sense of tactile force.
また、触力覚提示装置において、制御部は、触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動の大きさを制御するものであってもよいし、触力覚振動の周波数、パターン、触力覚の種類などを制御するものであってもよい。また、制御部は、触力覚振動を発生させない制御を行ってもよい。 In the haptic sense presentation device, the control unit may control the magnitude of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit, and the frequency, pattern, and touch of the haptic vibration. The type of force sense may be controlled. The control unit may perform control that does not generate haptic vibration.
また、上述した実施の形態では、触力覚提示装置は、車両の車室内においてシフトレバーの後方に配置されているとしたが、これに限らず、触力覚提示装置は、当該ユーザの手が届く範囲の位置に配置されていればよい。 In the above-described embodiment, the haptic sense presentation device is disposed behind the shift lever in the vehicle interior of the vehicle. It should just be arrange | positioned in the position of the range which reaches.
また、上述した実施の形態では、触力覚提示装置を例えば、カーナビゲーションシステムや、光ディスクを再生するためのオーディオ機器または映像再生機器などの車載機器の操作入力に用いたが、当該触力覚提示装置は、空調機器など他の車載機器に用いてもよい。また、触力覚提示装置は、車載機器に限らず、ユーザが他の動作を行いながら操作を行う他の機器の操作入力に用いてもよい。 In the above-described embodiments, the haptic sense presentation device is used for operation input of a car navigation system, an in-vehicle device such as an audio device or a video reproduction device for reproducing an optical disc, but the haptic sensation is used. You may use a presentation apparatus for other vehicle equipment, such as an air-conditioner. The tactile sensation presentation device is not limited to the in-vehicle device, and may be used for operation input of other devices that the user performs operations while performing other operations.
以上、本発明の一つまたは複数の態様に係る触力覚提示装置及び触力覚提示方法について、実施の形態に基づいて説明したが、本発明は、この実施の形態に限定されるものではない。本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない限り、当業者が思いつく各種変形を本実施の形態に施したものや、異なる実施の形態における構成要素を組み合わせて構築される形態も、本発明の一つまたは複数の態様の範囲内に含まれてもよい。 As described above, the haptic sense presentation device and the haptic sense presentation method according to one or more aspects of the present invention have been described based on the embodiment. However, the present invention is not limited to this embodiment. Absent. Unless it deviates from the gist of the present invention, one or more of the present invention may be applied to various modifications that can be conceived by those skilled in the art, or forms constructed by combining components in different embodiments. It may be included within the scope of the embodiments.
本発明は、ユーザが他の作業を行っている場合であっても操作を精度よく容易に行うことができる入力装置、車載機器用の入力装置などとして有用である。 INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention is useful as an input device that can be easily and accurately operated even when the user is performing other work, an input device for in-vehicle devices, and the like.
1 自動車
10 触力覚提示装置
11 タッチパッド
12 入力部
13、14、15 タッチスイッチ
18 静電IC
20 触力覚提示部
21 触力覚発生素子
22 マイコン
25 制御部
26 制御ボード
27 ホルダー
28 本体
29a、29b 配線
30 表示部
31、31a、31c 調節ゲージ
31b ハリネズミ
31d 球
32 つまみ
35 指
40 シフトレバー
50 ステアリング
51 リム
52 スポーク
53 ホーンスイッチカバー
60 シート
111 タッチパネルDESCRIPTION OF
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (16)
Translated fromJapanese前記入力部を介して前記ユーザに触力覚を提示する触力覚提示部と、
前記入力部および前記触力覚提示部と電気的に接続され、前記入力部に入力された操作に基づいて前記触力覚提示部を制御する制御部とを備え、
前記制御部は、前記ユーザが前記入力部に触れた接触位置と前記接触位置の移動方向に基づいて前記触力覚提示部から提示される触力覚振動を制御する
触力覚提示装置。An input unit for a user to input an operation;
A tactile sensation presentation unit that presents a tactile sensation to the user via the input unit;
A controller that is electrically connected to the input unit and the haptic sense presentation unit, and that controls the haptic sense presentation unit based on an operation input to the input unit;
The control unit is configured to control a haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit based on a contact position where the user touches the input unit and a moving direction of the contact position.
請求項1に記載の触力覚提示装置。The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 1, wherein the control unit controls the magnitude of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit based on a moving direction of the contact position.
請求項1または2に記載の触力覚提示装置。The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 1, wherein the control unit controls a frequency of the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit based on a moving direction of the contact position.
請求項1〜3のいずれか1項に記載の触力覚提示装置。The tactile force according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the control unit controls a pattern of the tactile sensation vibration presented from the tactile force sense presentation unit based on a moving direction of the contact position. Sense presentation device.
請求項1に記載の触力覚提示装置。The control unit has a target position for moving the contact position in the input unit, determines whether the contact position is toward the target position from the contact position and the moving direction, and determines the determination result. The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 1, wherein the haptic sense vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit is controlled based on the haptic sense vibration.
請求項5に記載の触力覚提示装置。The controller is configured such that the haptic sensation presented by the haptic sensation presentation unit differs between when the contact position is toward the target position and when the contact position is not toward the target position. The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 5.
請求項5に記載の触力覚提示装置。In the control unit, the haptic sensation presented from the haptic sense presentation unit is greater when the contact position is not toward the target position than when the contact position is toward the target position. The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 5.
請求項7に記載の触力覚提示装置。The control unit obtains a deviation angle in the movement direction with respect to the target position from a straight line connecting the target position and the contact position and the movement direction, and presents from the tactile force sense presentation unit as the deviation angle increases. The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 7, wherein the haptic sense vibration is controlled to be increased.
請求項5に記載の触力覚提示装置。The control unit detects the haptic vibration presented from the haptic sense presentation unit when the contact position is not toward the target position than when the contact position is toward the target position. The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 5, wherein the haptic sense presentation device is controlled so as to reduce a frequency.
請求項9に記載の触力覚提示装置。The control unit obtains a deviation angle in the movement direction with respect to the target position from a straight line connecting the target position and the contact position and the movement direction, and presents from the tactile force sense presentation unit as the deviation angle increases. The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 9, wherein the haptic sense vibration frequency is controlled to be low.
請求項5に記載の触力覚提示装置。When the contact position is toward the target position, the control unit does not present a tactile force sense from the tactile force sense presenting unit, and when the contact position is not toward the target position, the tactile force The tactile force sense presentation device according to claim 5, wherein the tactile force sense unit is controlled to present a tactile force sense.
請求項1〜11のいずれか1項に記載の触力覚提示装置。The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 1, wherein the input unit is a capacitance type, optical type, or resistive type input unit.
前記触力覚発生素子は、圧電体で構成されるか、または電磁的に動作する構成を有する
請求項1〜12のいずれか1項に記載の触力覚提示装置。The haptic sense presentation unit includes a haptic sense generating element that generates the haptic vibration given to a user,
The haptic sense presentation device according to any one of claims 1 to 12, wherein the haptic sense generating element is configured by a piezoelectric body or electromagnetically operated.
請求項1〜13のいずれか1項に記載の触力覚提示装置。The haptic sense presentation device according to claim 1, further comprising a conductive plate between the input unit and the haptic sense presentation unit.
前記触力覚提示装置は、
ユーザが操作を入力する入力部と、
前記入力部を振動させる触力覚提示部と、
前記入力部および前記触力覚提示部と電気的に接続される制御部と、を備え、
前記制御部は、
前記ユーザが前記入力部に触れた接触位置を検出するステップと、
前記接触位置の移動方向を検出するステップと、
前記接触位置と前記移動方向に基づいて前記触力覚提示部の触力覚振動を制御するステップとを含む
触力覚提示方法。A tactile sensation presentation method for a haptic presentation device,
The haptic sense presentation device includes:
An input unit for a user to input an operation;
A tactile sensation presentation unit that vibrates the input unit;
A control unit electrically connected to the input unit and the haptic sense presentation unit,
The controller is
Detecting a contact position where the user touches the input unit;
Detecting a moving direction of the contact position;
Controlling a haptic vibration of the haptic sense presentation unit based on the contact position and the moving direction.
前記入力部において前記接触位置を移動させる目標位置を決定するステップと、
前記接触位置と前記移動方向から、前記接触位置が前記目標位置に向かっているか否かを判断するステップと、
前記判断の結果に基づいて前記触力覚提示部の前記触力覚振動を制御するステップとを含む
請求項15に記載の触力覚提示方法。The controller is
Determining a target position for moving the contact position in the input unit;
Determining from the contact position and the movement direction whether the contact position is toward the target position;
The haptic sense presentation method according to claim 15, further comprising: controlling the haptic sense vibration of the haptic sense presentation unit based on the determination result.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018030123AJP2019144964A (en) | 2018-02-22 | 2018-02-22 | Tactile force sense presentation device and tactile force sense presentation method |
| PCT/JP2018/038788WO2019163196A1 (en) | 2018-02-22 | 2018-10-18 | Haptic sensation presentation device and haptic sensation presentation method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018030123AJP2019144964A (en) | 2018-02-22 | 2018-02-22 | Tactile force sense presentation device and tactile force sense presentation method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019144964Atrue JP2019144964A (en) | 2019-08-29 |
Family
ID=67686957
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018030123APendingJP2019144964A (en) | 2018-02-22 | 2018-02-22 | Tactile force sense presentation device and tactile force sense presentation method |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2019144964A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2019163196A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7535163B1 (en) | 2023-08-07 | 2024-08-15 | レノボ・シンガポール・プライベート・リミテッド | Information Processing System |
| JP7627801B1 (en)* | 2024-04-19 | 2025-02-06 | レノボ・シンガポール・プライベート・リミテッド | Information processing system, information processing method, and program |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11789538B2 (en)* | 2019-12-26 | 2023-10-17 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Tactile presentation control apparatus, tactile presentation panel, tactile presentation touch panel, and tactile presentation touch display |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20150062458A1 (en)* | 2012-03-29 | 2015-03-05 | Kyocera Corporation | Input device, display device, and electronic device |
| JP2014071687A (en)* | 2012-09-28 | 2014-04-21 | Panasonic Corp | Display device |
| US10365119B2 (en)* | 2015-03-16 | 2019-07-30 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Map display control device and method for controlling operating feel aroused by map scrolling |
| CN107430455A (en)* | 2015-04-09 | 2017-12-01 | 富士通株式会社 | Drive dynamic control device, electronic equipment, drive control program and drive control method |
| JP6645517B2 (en)* | 2016-01-08 | 2020-02-14 | 富士通株式会社 | Electronic device and method of driving electronic device |
| JP2017138737A (en)* | 2016-02-02 | 2017-08-10 | 富士通テン株式会社 | INPUT DEVICE, DISPLAY DEVICE, AND INPUT DEVICE CONTROL METHOD |
- 2018
- 2018-02-22JPJP2018030123Apatent/JP2019144964A/enactivePending
- 2018-10-18WOPCT/JP2018/038788patent/WO2019163196A1/ennot_activeCeased
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7535163B1 (en) | 2023-08-07 | 2024-08-15 | レノボ・シンガポール・プライベート・リミテッド | Information Processing System |
| JP2025024415A (en)* | 2023-08-07 | 2025-02-20 | レノボ・シンガポール・プライベート・リミテッド | Information Processing System |
| JP7627801B1 (en)* | 2024-04-19 | 2025-02-06 | レノボ・シンガポール・プライベート・リミテッド | Information processing system, information processing method, and program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2019163196A1 (en) | 2019-08-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11625145B2 (en) | Automotive touchscreen with simulated texture for the visually impaired | |
| US10579252B2 (en) | Automotive touchscreen with simulated texture for the visually impaired | |
| US10394375B2 (en) | Systems and methods for controlling multiple displays of a motor vehicle | |
| RU2676043C2 (en) | System for managing touchscreen display in vehicle | |
| US10642381B2 (en) | Vehicular control unit and control method thereof | |
| US9983672B2 (en) | Electrostatic haptic actuator and user interface with an electrostatic haptic actuator | |
| JP5754596B2 (en) | Operation input device | |
| CN106502555B (en) | Vehicle and control method thereof | |
| WO2019163196A1 (en) | Haptic sensation presentation device and haptic sensation presentation method | |
| CN109564469B (en) | Display operation device | |
| CN107209635A (en) | Device and method for controlling a motor vehicle | |
| US20130154972A1 (en) | Tactile presentation device | |
| KR102263593B1 (en) | Vehicle, and control method for the same | |
| WO2021132334A1 (en) | Tactile presentation device and tactile presentation method | |
| JP2017090993A (en) | Haptic feedback device | |
| JP5870689B2 (en) | Operation input system | |
| US11402951B2 (en) | Input device and vehicle | |
| US12073069B2 (en) | Control value setting device and control value setting program | |
| JP6941798B2 (en) | Input device | |
| KR101033954B1 (en) | Interface device control method for tactile display | |
| CN117369626A (en) | User interface device, vehicle, and method of controlling vehicle | |
| JP2019079409A (en) | Input device | |
| JP2014048684A (en) | Information presentation device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A80 | Written request to apply exceptions to lack of novelty of invention | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A80 Effective date:20180322 |