JP2016145836A - Mechanisms implemented using geodetic triangulation to determine global positioning of computing devices - Google Patents
Mechanisms implemented using geodetic triangulation to determine global positioning of computing devicesDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2016145836A JP2016145836AJP2016058236AJP2016058236AJP2016145836AJP 2016145836 AJP2016145836 AJP 2016145836AJP 2016058236 AJP2016058236 AJP 2016058236AJP 2016058236 AJP2016058236 AJP 2016058236AJP 2016145836 AJP2016145836 AJP 2016145836A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- computing device
- location information
- location
- triangulation
- computer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Position Fixing By Use Of Radio Waves (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapaneseこの分野は、概してコンピュータデバイスに関し、特にコンピュータデバイスのグローバルポジショニング(global positioning)を判定するための測地学的三角測量(geodetic triangulation)を使用して実現する機構を使用することに関する。 This field relates generally to computing devices, and more particularly to using mechanisms implemented using geodesic triangulation to determine global positioning of computing devices.
現在では、開けた空の視野がない閉じたエリア(室内又は都市峡谷等)でコンピュータデバイスがグローバルな所在地を判定することができるようにする標準的な方法が存在しない。 Currently, there is no standard way to allow a computing device to determine a global location in a closed area (such as a room or urban canyon) that has no open sky field of view.
グローバルポジショニングシステム(GPS:Global Positioning System)に基づくデバイス(例えば、ナビゲーションシステム等)は、衛星が視野に入る場合に室外で動作するが、室内の場合及び/又は開けた衛星の視野がない場合にうまく動作しない。 Devices based on the Global Positioning System (GPS) (eg navigation systems, etc.) operate outdoors when the satellite enters the field of view, but indoors and / or when there is no view of the open satellite Does not work well.
本発明の実施例について、添付図面において限定ではなく一例として説明する。添付図面において、同様の参照符号は同様の要素を示す。 Embodiments of the present invention will now be described by way of example and not limitation in the accompanying drawings. In the accompanying drawings, like reference numerals designate like elements.
本発明の実施例は、本発明の一実施例に従ってコンピュータデバイスのグローバルな所在地を判定するために、動的なクライアント側の測地学的三角測量を実現する機構を提供する。本発明の実施例の方法は、コンピュータデバイスにおいて、静的な無線アクセスポイントに関連する第1の位置情報を検出することを含む。この方法は、コンピュータデバイスにおいて、現在位置に関する第2の位置情報をブロードキャストする移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関連する第2の位置情報を検出し、第1及び第2の位置情報に基づいてコンピュータデバイスの現在位置を動的に判定することを更に含んでもよい。 Embodiments of the present invention provide a mechanism for implementing dynamic client-side geodetic triangulation to determine the global location of computing devices in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention. The method of an embodiment of the present invention includes detecting first location information associated with a static wireless access point at a computing device. The method detects second location information associated with a moving computer device that broadcasts second location information regarding a current location at the computing device, and based on the first and second location information, It may further include dynamically determining the current position.
一実施例では、クライアントコンピュータデバイスが開けた空又は衛星の視野がない場合に(室内、都市峡谷、野球場等)、Wi-Fiインフラストラクチャ及び/又は周辺のWiFi可能なデバイスから取得したGPSデータを使用して、三角測量を行って所在地を見つけることを可能にするクライアント側の対策が提供される。一実施例では、前述の対策は、クライアントデバイスが新規な方法で位置を解釈するために使用することができる重要な情報を含み得る特定の測地学的なアップデート(最新情報)の新たな生成を含む。例えば、測地学的なアップデートは、地球の表面を楕円で近似することができ、表面近くのいずれかの位置が緯度、経度、高度等について記述される測地座標等を使用した、地球上のクライアントデバイスの実際の所在地又は場所に関するアップデートを提供してもよい。更に、新規な対策は、新規なクライアント側の三角測量を促進する際の更なる精度を提供することができるジオ・クラウド(geo cloud)におけるピア・ツー・ピアの関与を提供する。 In one embodiment, GPS data obtained from the Wi-Fi infrastructure and / or surrounding WiFi-capable devices when the client computer device does not have an open sky or satellite view (room, urban canyon, baseball field, etc.) Is used to provide client-side countermeasures that allow triangulation to be found. In one embodiment, the aforementioned measures create a new generation of specific geodetic updates (latest information) that can include important information that client devices can use to interpret the location in a new way. Including. For example, geodetic updates can approximate the earth's surface with an ellipse and clients on the earth using geodetic coordinates etc. where any position near the surface is described in terms of latitude, longitude, altitude, etc. Updates regarding the actual location or location of the device may be provided. Furthermore, the new measures provide peer-to-peer engagement in a geo cloud that can provide further accuracy in facilitating new client-side triangulation.
本発明の実施例は、どのようにクライアントコンピュータシステムがWi-Fiインフラストラクチャと直接接続する必要なしに、ピア・ツー・ピアで(スマートフォン等のような移動中のクライアントコンピュータデバイス等で)及び/又は静的な位置決めデバイス(いずれか所定の期間に静止した所在地にあるコンピュータデバイス又は無線アクセスポイント等)を使用して、その正確な所在地を三角測量することができるかを直接的に概説する。或る実施例では、Wi-Fiアクセスは、ジオ・ピング(geo-ping)要求を見つけてそれに応答することができるため以外に全く必要なくてもよい。一実施例では、Wi-Fiインフラストラクチャ及びいずれかのクライアントコンピュータデバイスは、Wi-Fi接続を認証する必要なく、グローバルポジショニングデータを提供し、グローバルポジショニングの共有に関与することが許可される。この技術は、単にWi-Fi周波数を使用するビーコン応答システム等を有するだけで、Wi-Fiインフラストラクチャなしでも実行可能である。 Embodiments of the present invention can be used peer-to-peer (such as on a moving client computer device such as a smartphone) and / or without requiring the client computer system to connect directly to the Wi-Fi infrastructure. Or, a direct overview of whether the exact location can be triangulated using a static positioning device (such as a computer device or a wireless access point at a stationary location at any given time). In some embodiments, Wi-Fi access may not be required at all except to be able to find and respond to a geo-ping request. In one embodiment, the Wi-Fi infrastructure and any client computing devices are allowed to provide global positioning data and participate in global positioning sharing without having to authenticate the Wi-Fi connection. This technology can be implemented without a Wi-Fi infrastructure by simply having a beacon response system or the like that uses a Wi-Fi frequency.
図1は、本発明の一実施例による動的測地学的三角測量機構を使用するコンピュータデバイスを示している。一実施例では、ホストマシン(例えば、コンピュータデバイス)100は、コンピュータデバイスのグローバルポジショニングの動的且つ自動的な判定を実現するため、動的測地学的三角測量機構(“三角測量機構”)110を有するものとして示されている。コンピュータデバイス100は、スマートフォン(例えば、iPhone(登録商標)、BlackBerry(登録商標)等)を含む携帯電話、ハンドヘルドコンピュータデバイス、パーソナルデジタルアシスタント(PDA)等のようなモバイルコンピュータデバイス、タブレットコンピュータ(例えば、iPad(登録商標)、Samsung Galaxy Tab(登録商標)等)、ラップトップコンピュータ(例えば、ノートブック、ネットブック等)、電子リーダ(例えば、Kindle(登録商標)、Nook(登録商標)等)、GPSナビゲーションシステム等を含んでもよい。コンピュータデバイス100は、セットトップボックス(例えば、インターネットに基づくケーブルテレビ用セットトップボックス等)、更に大きいコンピュータデバイス(デスクトップコンピュータ、サーバコンピュータ、クラスタに基づくコンピュータ等)を更に含んでもよい。 FIG. 1 illustrates a computing device that uses a dynamic geodesic triangulation mechanism according to one embodiment of the present invention. In one embodiment, the host machine (eg, computing device) 100 may use a dynamic geodesic triangulation mechanism (“triangulation mechanism”) 110 to provide dynamic and automatic determination of the global positioning of the computing device. It is shown as having The
コンピュータデバイス100は、コンピュータデバイス100のいずれかのハードウェア又は物理リソースとユーザとの間のインタフェースの役目をするオペレーティングシステム106を含む。コンピュータデバイス100は、1つ以上のプロセッサ102、メモリデバイス104、ネットワークデバイス、ドライバ等と、タッチスクリーン、タッチパネル、タッチパッド、仮想又は通常のキーボード、仮想又は通常のマウス等のような入出力(I/O)ソース108とを更に含む。“コンピュータデバイス”、“ノード”、“コンピュータノード”、“クライアント”、“メモリクライアント”、“ホスト”、“サーバ”、“メモリサーバ”、“マシン(機械)”、“デバイス”、“コンピュータデバイス”、“コンピュータ”、“コンピュータシステム”、“クラスタに基づくコンピュータ”等の用語は、この文献を通じて区別なく同じ意味で使用される点に留意すべきである。 The
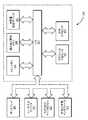
図2は、本発明の一実施例による動的測地学的三角測量機構を示している。図示の実施例では、三角測量機構110は、コンピュータデバイスの地理的位置又は所在地の動的且つ自動的な判定を実現するための様々な構成要素202、204、206、208、210、212、214及び216を含む。一実施例では、三角測量機構110の三角測量ユニット202は、コンピュータデバイスのジオ・ポジショニングの自動的、動的及び効率的な判定を生じるクライアント側の三角測量を実現する。三角測量ユニット202は、コンピュータデバイスがインフラストラクチャ(例えば、Wi-Fiインフラストラクチャ)に接続する必要なく、コンピュータデバイスが位置情報にアクセスすることを可能にするために、グローバル標準の手法を利用する位置サービスセット識別子(SSID:service set identifier)モジュール204を含む。一実施例では、位置SSIDモジュール204は、位置SSIDモジュール204がコンピュータデバイスに対してWi-Fiインフラストラクチャと関連付けを行うことを必要とせずに、その代わりに関与するコンピュータデバイス及び/又はWi-Fiインフラストラクチャによって行われた単純なブロードキャストを受信、リスン(listen)及び関与することを可能にするように、SSID名及びセキュリティ設計を標準化する。SSIDは、特定の802.11無線ローカルエリアネットワーク(LAN:Local Area Network)を識別するために使用されてもよい。例えば、クライアントデバイスは、所定の範囲内でSSIDをアドバタイズする全てのアクセスポイント(AP:access point)からビーコンメッセージを受信してもよい。このクライアントデバイスは、構成に基づいて手動で又は自動的に関連付けを行う無線ネットワークを選択してもよい。位置SSIDモジュール204は、ピア・ツー・ピア位置共有ネットワークを可能にするための特定のSSIDの標準化又は手法を提供する。 FIG. 2 illustrates a dynamic geodesic triangulation mechanism according to one embodiment of the present invention. In the illustrated embodiment, the triangulation mechanism 110 provides
三角測量ユニット202は、静的な構成位置(例えば、アクセスポイント又は固定/静止しているコンピュータデバイス)を有するデバイスと、移動中のコンピュータデバイスとの間を区別するための処理を提供する静的インジケータ206を更に含む。この新規な技術は、関与するコンピュータデバイスが推定の精度を向上させるのに役立てるために使用される。更に、位置(例えば、どこにいるか)を見つけようとしているデバイスが、ブロードキャストモジュール216を介して、どのくらい静的な測地学的位置に近いかを他のコンピュータデバイス及びアクセスポイントに通知又はブロードキャストする機能を有することを可能にする。ブロードキャストモジュール216は、コンピュータデバイスがその信頼度をアドバタイズ又は発行すること等のような如何なる数のブロードキャスト目的に使用されてもよい。これらの“見失った(lost)”デバイスが1つ以上の静的な測地学的位置に近いことを見つけた場合、その精度を向上させるのに役立てるために、移動中のコンピュータデバイスを使用することができる。換言すると、静的インジケータ206は、アドバタイズされているコンピュータデバイスの位置が静的に構成されているか否か、又はコンピュータデバイスが自分の位置を動的に判定したか否かを示すために使用される。静的インジケータ206は、その位置を“学習”したピアコンピュータデバイスと、静的にプログラムされた位置を有するインフラストラクチャに基づくコンピュータデバイスとの間の違いを判定する手法を提供する。
三角測量ユニット202の信号強度予測器208は、コンピュータデバイスから送出された(予想)信号強度を予測するために信号強度予測器208を使用すること等のように、距離を判定するのに役立てるために信号強度を識別して使用する手法を提供する。コンピュータデバイスの電力の出力を知らなければ(ブラックボックスのように)、信号強度は予想が困難である。このことは、距離測定を困難、不正確及び予測不可能にする可能性がある。しかし、一実施例では、信号強度予測器208において信号強度情報を埋め込むことにより、信号をリスンすることができる各コンピュータデバイスは、freespace(登録商標)モデルのような正確な信号予測について知られた長距離サウンドデバイスを使用してその距離をより良く予測するために、この信号強度情報を使用してもよい。更に、例えば、ビーコン送信コンピュータデバイスの送信電力及びアンテナ利得をアドバタイズするために、16進数が使用されてもよい。この技術は、受信ノードが信号に関連する電力及び特定のインジケータ(受信した無線信号に存在する電力の指標を表す受信信号強度表示度数(RSSI:Received Signal Strength Indication)等)をより良く認識又は計算することを可能にする。 The
三角測量ユニット202の信頼度インジケータ210は、ピア・ツー・ピア共有セッションにおけるクライアントコンピュータデバイスの学習した位置の使用のような新規な方法で使用され得る信頼度係数を示してもよい。各クライアントコンピュータデバイスは、位置のその信頼度をアドバタイズし、ネットワーク内の他のコンピュータデバイス(他のクライアントコンピュータデバイスを含む)がこれを聞き取り、自分の学習した位置に信頼度を追加し、他のコンピュータデバイスに同じことを可能にするために、重み付けられた方法でその数を使用することを可能にしてもよい。この技術を使用して、特定の位置のアップデートにおいて100%の信頼度が得られる可能性が低い場合であっても、正確性を向上させるために利用可能な情報を使用する新規なピア・ツー・ピアの対策が取り入れられる。従って、この場合にはその特定のアップデートを与えるための重みが下げられる。更に、16進数は、アドバタイズする位置においてクライアントデバイスが有する信頼度を示すために使用される。それぞれの数字の増加は、例えば、クライアントデバイスがその位置で有し得る信頼度における0.1メートルの変化を示す。 The
一実施例では、三角測量機構110は、経度(例えば、8個の16進文字+1バイト)、緯度(例えば、8個の16進文字+1バイト)等のような地理的位置212を提供する。三角測量機構110は、三角測量機構110がいずれかの種類のコンピュータデバイス(例えば、パーソナルコンピュータ、タブレットコンピュータ、スマートフォン、ビデオゲームコンソール、デジタルオーディオプレイヤ、GPSナビゲーションシステム等のようなWi-Fi可能なコンピュータデバイス)、Wi-Fi又はホットスポットプロバイダ(例えば、電気通信会社、インターネットサービスプロバイダ等)、WLANを実装するための現在知られている標準及び将来の標準(例えば、IEEE(Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)802.11等)等と動的且つ自動的に適合することを可能にする適合モジュール214を更に提供する。これにより、三角測量機構110は、この文献を通じて記載する機能を効率的に実行することが可能になる。 In one embodiment, the triangulation mechanism 110 provides a
コンピュータデバイスの地理的位置又は所在地を検出するために動的且つ自動的なクライアント側の三角測量を実現するために、いずれかの数及び種類の構成要素が動的測地学的三角測量機構110に追加されてもよく、動的測地学的三角測量機構110から削除されてもよいことが考えられる。簡潔、明瞭及び理解を容易にするために、及び三角測量機構110に集中し続けるために、コンピュータデバイスのもののような多くの標準又は既知の構成要素は、ここでは図示又は説明されない。本発明の実施例は、いずれかの特定の技術又は標準に限定されず、変化する技術及び標準を採用して適合するのに十分に動的であることが考えられる。 Any number and type of components can be added to the dynamic geodetic triangulation mechanism 110 to implement dynamic and automatic client-side triangulation to detect the geographic location or location of a computing device. It is contemplated that it may be added or deleted from the dynamic geodesic triangulation mechanism 110. To facilitate brevity, clarity and understanding, and to continue to focus on the triangulation mechanism 110, many standard or known components, such as those of computing devices, are not shown or described herein. Embodiments of the present invention are not limited to any particular technology or standard, but are considered sufficiently dynamic to adopt and adapt to changing technology and standards.
図3A〜3Cは、本発明の一実施例に従って動的測地学的三角測量機構を使用したクライアントに基づく三角測量を実現するためのトランザクション系列を示している。図3Aを参照すると、Wi-Fi可能なクライアントコンピュータデバイス302は、コンピュータデバイス302の所定のエリア又は範囲内で最高の信頼度のいずれかの数の利用可能なWi-Fiアクセスポイント304、306、308のような最高の信頼度にあるいずれか利用可能な位置を認識することにより、及び/又はいずれか利用可能な位置と接続することにより、自分(例えば、自分の地理的位置及び/又は目的地(コーヒーショップ等)を見つける移動中のコンピュータデバイス(例えば、ユーザに属するスマートフォン))を位置決めしようとする。例えば、図示のように、それぞれの円305、307及び309は、それぞれその対応するWi-Fiアクセスポイント304、306及び308の無線範囲を表す。同様に、円303は、クライアントデバイス302の範囲又はアクセスを表し、他の円305、307、309と重複する(又は接触する)ものとして示されている。 3A-3C illustrate a transaction sequence for implementing client-based triangulation using a dynamic geodesic triangulation mechanism in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 3A, a Wi-Fi enabled
クライアントデバイス302がモールにおいて靴屋を見つけようとする個々のユーザに属することを仮定する。一実施例では、クライアントデバイス302がモールのエリアに近づくとすぐに、まず、モール、近くのStarbucks(登録商標)、空港等のような場所にあるWi-Fi AP304、306、308のように、最高の重みを伝達するこれらのAPの位置304、306、308(対応する円305、307、309で示される)のうち1つ以上と接触する。換言すると、最高の信頼度を有するAPの位置304、306、308が高い優先度になり、従って、(図3Bを参照して更に説明する他の移動中のクライアントデバイスのような他の低い信頼度の位置に対して)このクライアント側の三角測量における最高の重みとして最初に使用される。一実施例では、高い重みのAP又は静的なAP304、306、308の1つは、図1の三角測量機構110により予め定められた所定の期間に同じ位置に静止している(例えば、モールのベンチに座っている)ユーザ、及び/又はコンピュータデバイス302を介して三角測量機構110に期間情報を与えるコンピュータデバイス302のユーザ等によるいずれかの関与者に属するクライアントデバイス302と同様のクライアントデバイスからのビーコンを含んでもよい。 Assume that the
次に図3Bを参照すると、高い重みのAP304、306、308が識別され、クライアントデバイス302と接触すると、他の円305、307及び309と重複するように示されているそれぞれ対応するエリア、信号又はアクセスの円315、317及び319により表されるように、低い重みの位置314、316及び318(例えば、移動中のクライアントコンピュータデバイス)が識別され、クライアントデバイス302と接触する。例えば、一実施例では、これらの低い重みの位置314、316、318は、モールの近く又はモール内のようなコンピュータデバイス302の周辺の所定のエリア内にいる他のユーザに属するWi-Fi可能な移動中のクライアントコンピュータデバイスを含む。例えば、これらのWi-Fi可能なコンピュータデバイス314、316、318のユーザは、クライアントデバイス302のユーザと同じ靴屋を見つけようとする他の買い物客又は同じ靴屋に現在いる他の買い物客を含んでもよく、靴屋の近くの他の場所(例えば、コーヒーショップ)を見つけようとする他の買い物客又は他の場所に現在いる他の買い物客を含んでもよい。これは、クライアントデバイス302の地理的所在地のより良い認識に役立ち、より良い認識を生じる。換言すると、まず、静的なAP304、306、308に関連する高い重みの低い信頼度の位置がクライアントデバイス302の近くになって接続し、続いて、(更に)低い重みの(更に)低い信頼度のコンピュータデバイス314、316、318がクライアントデバイス302の近くになり、(モールの靴屋のようなその目的地等に関して)クライアントデバイス302の地理的位置の精度及び信頼度を改善する。 Referring now to FIG. 3B, when the
一実施例では、Wi-Fi可能な移動中のコンピュータデバイス314、316、318のこれらの低い重みの位置は、低い信頼度のビーコン(これらのクライアントデバイス314、316、318から受信した複数の位置又は位置に関するアップデート等(例えば、モールのコーヒーショップにいてFacebook(登録商標)のプロフィールをアップデートしているクライアントデバイス314、316、318の1人以上のユーザ))に基づいて判定されてもよい。この新規なクライアント側の三角測量技術は、ユーザがクライアントデバイス302でインターネットにアクセスする必要なく(Yelp(登録商標)、Where(登録商標)等のようなウェブサイトにアクセスする必要なく)、クライアントデバイス302(従って、クライアントデバイス302のユーザ)が靴屋に関するその正確な位置を判定するのに役立つ。インターネットへのアクセスは、クライアントデバイス302が室内にいるため及び/又は開けた空(従って、衛星)の視野を有さないため等の悪い受信のため可能ではない可能性がある。 In one embodiment, these low weight locations of Wi-Fi enabled
一実施例では、図2の三角測量機構110の位置SSIDモジュール204は、クライアントデバイス302(及び他の関与するクライアントデバイス314、316、318)がWi-Fiインフラストラクチャと接続する必要なく、クライアントデバイス302とAP304、306、308及び他の移動中のクライアントデバイス314、316、318との間でアクセス位置情報を通信する。高い重みの静的に構成された位置304、306、308と低い重みの移動中の位置314、316、318とを区別するのは、図2の静的インジケータ206である。同様に、信号強度予測器208は、クライアントデバイス302、静的なAP304、306、308及び移動中のクライアントデバイス314、316、318がその信号強度を予測することを実現し、信頼度インジケータ210は、クライアントデバイス302、静的なAP304、306、308及び移動中のクライアントデバイス314、316、318が自分の位置に関する信頼度をブロードキャスト又はアドバタイズすることを実現する。自分の位置に関する信頼度は、コンピュータデバイス302、314、316、318(及び静的に構成されたAP304、306、308)により受信され、各信頼度に重み(高い重み、低い重み、中程度の重み等)を割り当てるために使用される。これらの重み付けられた信頼度は、信頼度を各AP又はクライアントデバイスの現在の学習した位置(例えば、モールの靴屋の所望の目的地に関するクライアントデバイス302の現在位置等)に信頼度を追加するために使用される。 In one embodiment, the
図3Cは、クライアントデバイス302がその所在地を他のもの(高い重みのAP304、306、308、低い重みのクライアントデバイス314、316、318等)にビーコン送信していることを示す。これにより、それぞれの関与するAP304、306、308及びクライアントデバイス314、316、318は、クライアントデバイス302によりビーコン送信された情報を使用して自分の位置を較正することが可能になる。クライアントデバイス302によるこのビーコン送信と、関与するAP304、306、308及びクライアントデバイス314、316、318の学習した所在地の共同の信頼度とが、図示の円320により表されている。別の言い方をすれば、クライアントデバイス302が(図3A及び3Bを参照して前述したように)その位置を判定すると、自分の位置をAP304、306、308及びクライアントデバイス314、316、318にブロードキャストする。これにより、これらはこの情報から恩恵を受け、特に移動中のクライアントデバイス314、316、318について自分の所在地の信頼度を獲得する。 FIG. 3C shows that the
図4は、本発明の一実施例に従ってコンピュータデバイスのグローバルポジショニングを判定するために動的なクライアント側の測地学的三角測量を実行する方法を示している。方法400は、ハードウェア(例えば、回路、専用ロジック、プログラム可能ロジック等)、ソフトウェア(処理デバイスで実行する命令等)、又はこれらの組み合わせを有してもよい処理ロジックにより実行されてもよい。一実施例では、方法400は、図1の動的測地学的三角測量機構110により実行されてもよい。 FIG. 4 illustrates a method for performing dynamic client-side geodetic triangulation to determine global positioning of a computing device according to one embodiment of the present invention. The
方法400は、所望の位置(クライアントコンピュータデバイスのユーザが自分の正確な所在地又は現在の地理的位置を知る必要があること等)又は目的地(ユーザが家、店、野球場、道路等を見つけようとすること等)を探しているクライアントコンピュータデバイス(例えば、スマートフォン、タブレットコンピュータ等のようなモバイルコンピュータデバイス)が1つ以上の高い重みの位置(例えば、静的な無線アクセスポイント等)を検出することにより、ブロック405で始まる。ブロック410において、クライアントコンピュータデバイスは、高い重みの位置を検出すると、位置及び/又は高い重みの位置から受信した高い重みの位置に関する他の関連情報(例えば、信頼度、アップデート等)に基づいてその所在地を調整する。 The
ブロック415において、クライアントコンピュータデバイスは、1つ以上の低い重みの位置(例えば、(例えば、Main Street及びFirst Avenueの角のStarbucks等で)自分の位置をブロードキャストする他の関与する移動中のクライアントデバイス及び/又は自分の位置を判定するため等に使用され得る位置に関するアップデートをビーコン送信する他の関与する移動中のクライアントデバイス)を検出する。ブロック420において、クライアントコンピュータデバイスは、低い重みの位置を検出すると、これらの位置及び/又は関連情報(例えば、信頼度、位置に関するアップデート等)に基づいて自分の物理的位置を再調整する。ブロック425において、自分の位置を再調整すると、クライアントコンピュータデバイスは、自分の位置をブロードキャストする。これにより、他のもの(例えば、高い重みのAP及び低い重みのコンピュータデバイス等)がこの情報から恩恵を受け、自分の位置を調整、構成又は較正することが可能になる。ブロック430において、クライアントコンピュータデバイスは、自分の再調整された所在地に基づいて前述の所望の位置又は目的を見つける又は到達する。 At
図5は、本発明の一実施例による動的測地学的三角測量機構を使用して実現するコンピュータシステム500を示している。例示的なコンピュータシステム500は、図1のコンピュータデバイス100及びこの明細書を通じて(図3A〜3C等を参照して)説明した他のコンピュータデバイスのいずれかと同じものでもよく、同様のものでもよい。コンピュータシステム500は、情報を通信するためのバス、リンク、相互接続(以下では“バス”と呼ばれる)又は他の通信手段501と、情報を処理するためにバス501に結合されたマイクロプロセッサ502のような処理手段とを含む。コンピュータシステム500は、並列パイプラインを通じてグラフィックを処理するためのグラフィックプロセッサ503で増強されてもよく、1つ以上の中央プロセッサ502に組み込まれてもよく、1つ以上の別々のプロセッサとして提供されてもよい。 FIG. 5 illustrates a
コンピュータシステム500は、プロセッサ502により実行される命令及び情報を格納するためにバス501に結合されたメインメモリ504(RAM又は他の動的データ記憶デバイス等)を更に含む。メインメモリはまた、プロセッサによる命令の実行中に一時変数又は他の中間情報を格納するために使用されてもよい。コンピュータシステム500はまた、プロセッサのための静的情報及び命令を格納するためにバス501に結合された不揮発性メモリ506(読み取り専用メモリ(ROM)又は他の静的データ記憶デバイス等)を含んでもよい。
大容量メモリ507(磁気ディスク、光ディスク又はソリッドステートアレイ等)及び対応するドライブもまた、情報及び命令を格納するためにコンピュータシステム500のバス501に結合されてもよい。コンピュータシステム500はまた、情報をユーザに表示するために、バスを介してディスプレイデバイス又はモニタ521(液晶ディスプレイ(LCD)又は有機発光ダイオード(OLED)アレイ等)に結合されてもよい。例えば、前述の様々なビュー及びユーザ相互作用に加えて、インストール状態、動作状態及び他の情報のグラフィック表示及びテキスト表示が、ディスプレイデバイス521上にユーザに提示されてもよい。 Mass memory 507 (such as a magnetic disk, optical disk or solid state array) and corresponding drive may also be coupled to bus 501 of
典型的には、ユーザ入力デバイス522(英数字、関数及び他のキー等を有するキーボード等)は、情報及びコマンド選択をプロセッサ502に通信するためにバス501に結合されてもよい。更なるユーザ入力デバイス522は、カーソル制御入力デバイス(マウス、トラックボール、トラックパッド又はカーソル方向キー等)を含んでもよく、方向情報及びコマンド選択をプロセッサ502に通信し、ディスプレイ521上でカーソル移動を制御するためにバスに結合されてもよい。 Typically, a user input device 522 (such as a keyboard with alphanumeric characters, functions and other keys, etc.) may be coupled to bus 501 for communicating information and command selections to processor 502. Additional
カメラ及びマイクロフォンアレイ523は、前述のように、ジェスチャを観測し、オーディオ及びビデオを記録し、ビジュアル及びオーディオコマンドを受信するためにバス501に結合されてもよい。 Camera and microphone array 523 may be coupled to bus 501 to observe gestures, record audio and video, and receive visual and audio commands, as described above.
通信インタフェース525もバス501に結合される。通信インタフェースは、例えばLAN又は広域ネットワーク(WAN)をサポートするために通信リンクを提供する目的のモデム、ネットワークインタフェースカード又は他の周知のインタフェースデバイス(Ethernet(登録商標)、トークンリング、又は他の種類の物理的有線若しくは無線接続に結合するために使用されるもの等)を含んでもよい。このように、コンピュータシステム500はまた、例えばイントラネット又はインターネットを含む従来のネットワークインフラストラクチャを介して、複数の周辺デバイス、他のクライアント、又は操縦面若しくはコンソール、又はサーバに結合されてもよい。ネットワークの例は、LAN、WAN、メトロポリタンエリアネットワーク(MAN)、パーソナルエリアネットワーク(PAN)、イントラネット、インターネット等を含むが、これらに限定されない。 A
実施例は、親ボードを使用して相互接続された1つ以上のマイクロチップ又は集積回路、配線ロジック、メモリデバイスにより格納されてマイクロプロセッサにより実行されるソフトウェア、ファームウェア、特定用途向け集積回路(ASIC)及び/又はフィールドプログラマブルゲートアレイ(FPGA)のいずれか又は組み合わせとして実装されてもよい。“ロジック”という用語は、一例として、ソフトウェア若しくはハードウェア及び/又はソフトウェアとハードウェアとの組み合わせ(ファームウェア等)を含んでもよい。 Embodiments include one or more microchips or integrated circuits interconnected using a parent board, wiring logic, software stored in a memory device and executed by a microprocessor, firmware, application specific integrated circuits (ASICs). ) And / or a field programmable gate array (FPGA). The term “logic” may include, by way of example, software or hardware and / or a combination of software and hardware (such as firmware).
例えば、実施例は、1つ以上の機械(コンピュータシステム500のようなコンピュータ、コンピュータのネットワーク、又は他の電子デバイス等)により実行された場合、1つ以上の機械が本発明の実施例に従って動作を実行することを生じ得る機械実行可能命令を格納した1つ以上の機械読み取り可能な媒体(過渡的でない機械読み取り可能な媒体等)を含んでもよいコンピュータプログラムプロダクトとして提供されてもよい。機械読み取り可能な媒体は、フロッピー(登録商標)ディスク、光ディスク、CD-ROM(Compact Disc-ROM)及び磁気光ディスク、ROM、RAM、消去可能プログラム可能読み取り専用メモリ(EPROM)、電気的消去可能プログラム可能読み取り専用メモリ(EEPROM)、磁気若しくは光学カード、フラッシュメモリ、又は機械実行可能命令を格納するのに適した他の種類の媒体/機械読み取り可能な媒体(ソリッドステート記憶デバイス、高速及び高信頼性DRAMサブシステム等)を含んでもよいが、これらに限定されない。 For example, when an embodiment is performed by one or more machines (such as a computer such as
プログラムコード又は命令は、例えば、揮発性及び/又は不揮発性メモリ(ソリッドステートメモリ、ハードドライブ、フロッピー(登録商標)ディスク、光記憶装置、テープ、フラッシュメモリ、メモリスティック、デジタルビデオディスク、DVD(digital versatile disc)等を含む記憶デバイス及び/又は関連する機械読み取り可能若しくは機械アクセス可能若しくは機械実行可能な媒体、並びに、機械アクセス可能な生物状態保持記憶装置のような更に新型の媒体等)に格納されてもよい。機械読み取り可能な媒体は、機械に読み取り可能な形式で情報を格納、送信又は受信する如何なる機構を含んでもよく、媒体は、プログラムコードを符号化した電気形式、光形式、音響形式又は他の形式の伝搬信号又は搬送波が通過する有形の媒体(アンテナ、光ファイバ、通信インタフェース等)を含んでもよい。プログラムコードは、パケット、シリアルデータ、パラレルデータ、伝搬信号等の形式で送信されてもよく、圧縮フォーマット又は暗号化フォーマットで使用されてもよい。 The program code or instructions may be, for example, volatile and / or non-volatile memory (solid state memory, hard drive, floppy disk, optical storage device, tape, flash memory, memory stick, digital video disk, DVD (digital versatile disc) and / or related machine-readable or machine-accessible or machine-executable media, as well as newer types of media such as machine-accessible biological state storage devices). May be. A machine-readable medium may include any mechanism for storing, transmitting, or receiving information in a machine-readable form, such as an electrical, optical, acoustic, or other form of encoded program code. Or a tangible medium (antenna, optical fiber, communication interface, etc.) through which the propagation signal or carrier wave passes. The program code may be transmitted in the form of a packet, serial data, parallel data, a propagation signal, etc., and may be used in a compressed format or an encrypted format.
プログラムコードは、プロセッサ、プロセッサにより読み取り可能な揮発性及び/又は不揮発性メモリ、少なくとも1つの入力デバイス、及び/又は1つ以上の出力デバイスをそれぞれ含むプログラム可能な機械(モバイルコンピュータ又は静止コンピュータ、パーソナルデジタルアシスタント、セットトップボックス、携帯電話及びページャ、スマートフォン、タブレットコンピュータ、家電機器デバイス(DVDプレイヤ、パーソナルビデオレコーダ、パーソナルビデオプレイヤ、衛星受信機、ステレオ受信機、ケーブルTV受信機を含む)、及び他の電子デバイス等)で実行するプログラムに実装されてもよい。プログラムコードは、記載の実施例を実行して出力情報を生成するために入力デバイスを使用して入力されたデータに適用されてもよい。出力情報は、1つ以上の出力デバイスに適用されてもよい。当業者は、開示の対象の実施例がマルチプロセッサ又はマルチコアプロセッサシステム、ミニコンピュータ、メインフレームコンピュータ、並びに、仮想的にいずれかのデバイスに組み込まれてもよい普及型若しくは小型コンピュータ又はプロセッサを含む様々なコンピュータシステム構成で実行され得ることを認識し得る。開示の対象の実施例はまた、タスク又はその一部が通信ネットワークを通じて連結された遠隔処理デバイスにより実行され得る分散コンピュータ環境で実行されてもよい。 The program code may be a programmable machine (mobile computer or stationary computer, personal computer), each including a processor, volatile and / or nonvolatile memory readable by the processor, at least one input device, and / or one or more output devices. Digital assistants, set-top boxes, mobile phones and pagers, smartphones, tablet computers, consumer electronics devices (including DVD players, personal video recorders, personal video players, satellite receivers, stereo receivers, cable TV receivers), and others Or an electronic device or the like). Program code may be applied to data entered using an input device to perform the described embodiments and generate output information. The output information may be applied to one or more output devices. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the disclosed embodiments include multiprocessor or multicore processor systems, minicomputers, mainframe computers, and popular or small computers or processors that may be virtually incorporated into any device. It can be appreciated that it can be implemented with any computer system configuration. Embodiments of the disclosed subject matter may also be practiced in distributed computing environments where tasks or portions thereof may be performed by remote processing devices that are linked through a communications network.
“一実施例”、“実施例”、“例示的な実施例”、“様々な実施例”等への言及は、記載した本発明の実施例が特定の機能、構成又は特徴を含んでもよいが、必ずしも全ての実施例がこの特定の機能、構成又は特徴を含むとは限らないことを示す。更に、いくつかの実施例は、他の実施例について説明した機能の一部を有してもよく、全部を有してもよく、全く有さなくてもよい。 References to “one embodiment”, “example”, “exemplary embodiment”, “various embodiments”, etc., may include specific functions, configurations or features of the described embodiments of the present invention. However, it is indicated that not all embodiments include this particular function, configuration or feature. Further, some embodiments may have some, all, or none of the functions described for other embodiments.
発明の詳細な説明及び特許請求の範囲において、“結合”及びその派生形が使用されることがある。“結合”は、2つ以上の要素が互いに協調又は相互作用することを示すために使用されるが、これらの間に介在する物理的又は電気的な構成要素を有してもよく、有さなくてもよい。 In the detailed description of the invention and in the claims, “combinations” and its derivatives may be used. “Coupled” is used to indicate that two or more elements cooperate or interact with each other, but may have physical or electrical components intervening between them. It does not have to be.
特に言及しない限り、一般的な要素を記述するために特許請求の範囲で使用される順序の形容詞である“第1”、“第2”、“第3”等の使用は、単に同様の要素の異なるインスタンスが参照されることを示し、このように記載した要素が時間的、空間的、ランク的又は他の方法で所与の系列になければならないことを意味するものではない。 Unless stated otherwise, the use of the "first", "second", "third" etc. in the order adjectives used in the claims to describe a general element is simply a similar element. Does not imply that the elements so described must be in a given sequence in time, space, rank, or otherwise.
図面及び前述の説明は、実施例の例を提供する。当業者は、記載の要素のうち1つ以上が単一の機能要素に結合され得ることを認識する。或いは、特定の要素は複数の機能的要素に分割されてもよい。一実施例からの要素は他の実施例に追加されてもよい。例えば、ここに記載の処理の順序は変更されてもよく、ここに記載の方法に限定されない。更に、いずれかのフローチャートの動作は、図示の順序に実施される必要はなく、全ての動作が必ずしも実行される必要もない。また、他の動作に依存しない動作は、他の動作と並列に実行されてもよい。本発明の実施例は、これらの特定の例により限定されない。明細書に明示的に提供されていても提供されていなくても、構成、大きさ及び素材の使用の違いのように複数の変更が可能である。実施例は、特許請求の範囲により与えられるものと少なくとも同程度に広くなり得る。 The drawings and the foregoing description provide examples of the embodiments. One skilled in the art will recognize that one or more of the described elements can be combined into a single functional element. Alternatively, a specific element may be divided into a plurality of functional elements. Elements from one embodiment may be added to other embodiments. For example, the order of the processes described here may be changed and is not limited to the method described here. Furthermore, the operations of any of the flowcharts do not have to be performed in the order shown, and all the operations need not necessarily be performed. In addition, operations that do not depend on other operations may be executed in parallel with other operations. Embodiments of the invention are not limited by these specific examples. A number of changes are possible, such as differences in configuration, size, and use of materials, whether explicitly provided or not provided in the specification. Embodiments can be at least as broad as given by the claims.
図面に示す技術は、1つ以上の電子デバイス(例えば、エンドステーション、ネットワークエレメント)に格納されて実行されるコード及びデータを使用して実装されてもよい。このような電子デバイスは、過渡的でないコンピュータ読み取り可能な媒体(例えば、磁気ディスク、光ディスク、ランダムアクセスメモリ、読み取り専用メモリ、フラッシュメモリデバイス、相変化メモリ)及び過渡的なコンピュータ読み取り可能な伝送媒体(例えば、電気、光、音響又は他の形式の伝搬信号)のようなコンピュータ読み取り可能な媒体を使用してコード及びデータを(内部で及び/又はネットワーク上で他の電子デバイスと)格納及び通信する。更に、典型的には、このような電子デバイスは、1つ以上の記憶デバイス(過渡的でない機械読み取り可能な記憶媒体等)、ユーザ入出力デバイス(例えば、キーボード、タッチスクリーン、及び/又はディスプレイ)、及びネットワーク接続のような1つ以上の他の構成要素に結合された一式の1つ以上のプロセッサを含む。典型的には、一式のプロセッサと他の構成要素との結合は、1つ以上のバス及びブリッジ(バスコントローラとも呼ばれる)を通じて行われる。従って、所与の電子デバイスの記憶デバイスは、典型的にはその電子デバイスの一式の1つ以上のプロセッサで実行されるコード及び/又はデータを格納する。当然に、本発明の実施例の1つ以上の部分は、ソフトウェア、ファームウェア及び/又はハードウェアの異なる組み合わせを使用して実装されてもよい。 The techniques shown in the drawings may be implemented using code and data stored and executed on one or more electronic devices (eg, end stations, network elements). Such electronic devices include non-transient computer readable media (eg, magnetic disks, optical discs, random access memory, read only memory, flash memory devices, phase change memory) and transient computer readable transmission media ( Store and communicate code and data (internally and / or with other electronic devices on a network) using computer readable media (eg, electrical, optical, acoustic or other types of propagated signals) . Further, typically, such electronic devices include one or more storage devices (such as non-transient machine-readable storage media), user input / output devices (eg, keyboards, touch screens, and / or displays). And a set of one or more processors coupled to one or more other components, such as a network connection. Typically, the combination of a set of processors and other components is done through one or more buses and bridges (also called bus controllers). Thus, the storage device of a given electronic device typically stores code and / or data that is executed by one or more processors of the set of electronic devices. Of course, one or more portions of embodiments of the present invention may be implemented using different combinations of software, firmware and / or hardware.
前述の明細書において、特定の例示的な実施例を参照して本発明について説明した。しかし、ここでの説明に従って様々な変更及び変形が行われてもよいことは明らかである。従って、明細書及び図面は、限定的な意味ではなく、例示的な意味として見なされるべきである。 In the foregoing specification, the invention has been described with reference to specific exemplary embodiments. However, it will be apparent that various changes and modifications may be made in accordance with the description herein. The specification and drawings are, accordingly, to be regarded in an illustrative sense rather than a restrictive sense.
Claims (14)
Translated fromJapanese前記オペレーティングシステムは、測地学的三角測量を実行するために動的測地学的三角測量論理ユニットに通信可能に結合され、
前記動的測地学的三角測量論理ユニット(“三角測量ユニット”)は、
前記装置において、静的な無線アクセスポイントに関連する第1の位置情報と、現在位置に関する第2の位置情報をブロードキャストする移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関連する第2の位置情報とを検出し、
前記第1及び第2の位置情報に基づいて前記装置の現在位置を動的に決定し、
前記第1の位置情報及び前記第2の位置情報に基づいて前記装置の前記現在位置を調整し、
前記三角測量ユニットは、前記無線アクセスポイント及び前記移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関する変化する信頼度にそれぞれ基づいて、前記第1の位置情報に関連する高い重みと、前記第2の位置情報に関連する低い重みとを更に調整する装置。A device having a processor executing on an operating system,
The operating system is communicatively coupled to a dynamic geodesic triangulation logic unit to perform geodesic triangulation,
The dynamic geodesic triangulation logic unit (“triangulation unit”) is
Detecting, in the apparatus, first location information associated with a static wireless access point and second location information associated with a moving computing device that broadcasts second location information relating to a current location;
Dynamically determining the current position of the device based on the first and second position information;
Adjusting the current position of the device based on the first position information and the second position information;
The triangulation unit has a high weight associated with the first location information and a low associated with the second location information based on varying reliability for the wireless access point and the moving computing device, respectively. A device for further adjusting the weight.
前記命令は、前記処理デバイスに対して、
静的な無線アクセスポイントに関連する第1の位置情報を検出させ、前記処理デバイスは、現在位置に関する第2の位置情報をブロードキャストする移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関連する第2の位置情報を更に検出し、
前記第1及び第2の位置情報に基づいて前記コンピュータデバイスの現在位置を動的に決定させ、
前記第1の位置情報及び前記第2の位置情報に基づいて前記コンピュータデバイスの前記現在位置を調整させ、三角測量ユニットは、前記無線アクセスポイント及び前記移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関する変化する信頼度にそれぞれ基づいて、前記第1の位置情報に関連する高い重みと、前記第2の位置情報に関連する低い重みとを更に調整するシステム。A system comprising a computer device having a memory for storing instructions and a processing device for executing the instructions,
The instructions to the processing device;
First position information associated with a static wireless access point is detected, and the processing device further detects second position information associated with a moving computing device that broadcasts second position information regarding a current position. And
Dynamically determining the current location of the computing device based on the first and second location information;
Adjusting the current position of the computer device based on the first position information and the second position information, and the triangulation unit is configured to change the reliability regarding the wireless access point and the moving computer device, respectively. Based on this, the system further adjusts the high weight associated with the first position information and the low weight associated with the second position information.
前記コンピュータデバイスにおいて、現在位置に関する第2の位置情報をブロードキャストする移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関連する第2の位置情報を検出するステップと、
前記第1及び第2の位置情報に基づいて前記コンピュータデバイスの現在位置を動的に決定するステップと、
前記第1の位置情報及び前記第2の位置情報に基づいて前記コンピュータデバイスの前記現在位置を調整するステップであり、三角測量ユニットは、前記無線アクセスポイント及び前記移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関する変化する信頼度にそれぞれ基づいて、前記第1の位置情報に関連する高い重みと、前記第2の位置情報に関連する低い重みとを更に調整するステップと。
を有する方法。Detecting, at a computing device, first location information associated with a static wireless access point;
Detecting at the computing device second location information associated with the moving computing device that broadcasts second location information regarding a current location;
Dynamically determining a current location of the computing device based on the first and second location information;
Adjusting the current location of the computing device based on the first location information and the second location information, wherein the triangulation unit is configured to change the reliability of the wireless access point and the moving computing device. Further adjusting a high weight associated with the first location information and a low weight associated with the second location information based on each degree.
Having a method.
静的な無線アクセスポイントに関連する第1の位置情報を検出させ、
現在位置に関する第2の位置情報をブロードキャストする移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関連する第2の位置情報を検出させ、
前記第1及び第2の位置情報に基づいて前記コンピュータデバイスの現在位置を動的に決定させ、
前記第1の位置情報及び前記第2の位置情報に基づいて前記コンピュータデバイスの前記現在位置を調整させ、三角測量ユニットは、前記無線アクセスポイント及び前記移動中のコンピュータデバイスに関する変化する信頼度にそれぞれ基づいて、前記第1の位置情報に関連する高い重みと、前記第2の位置情報に関連する低い重みとを更に調整するコンピュータプログラム。For computer devices
Detecting first location information associated with a static wireless access point;
Detecting second location information associated with the moving computing device that broadcasts second location information regarding the current location;
Dynamically determining the current location of the computing device based on the first and second location information;
Adjusting the current position of the computer device based on the first position information and the second position information, and the triangulation unit is configured to change the reliability regarding the wireless access point and the moving computer device, respectively. A computer program for further adjusting a high weight associated with the first position information and a low weight associated with the second position information based on the first position information.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016058236AJP2016145836A (en) | 2016-03-23 | 2016-03-23 | Mechanisms implemented using geodetic triangulation to determine global positioning of computing devices |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016058236AJP2016145836A (en) | 2016-03-23 | 2016-03-23 | Mechanisms implemented using geodetic triangulation to determine global positioning of computing devices |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014548769ADivisionJP2015509187A (en) | 2011-12-22 | 2011-12-22 | Mechanisms implemented using geodetic triangulation to determine global positioning of computing devices |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016145836Atrue JP2016145836A (en) | 2016-08-12 |
Family
ID=56686232
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016058236APendingJP2016145836A (en) | 2016-03-23 | 2016-03-23 | Mechanisms implemented using geodetic triangulation to determine global positioning of computing devices |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2016145836A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11224003B2 (en) | 2019-05-31 | 2022-01-11 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Apparatus and control method |
| US11467792B2 (en) | 2019-05-31 | 2022-10-11 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Apparatus and control method |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000244967A (en)* | 1999-02-24 | 2000-09-08 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, MOBILE MACHINE AND BASE STATION COMPOSING THE SYSTEM, AND METHOD OF DETECTING POSITION OF MOBILE MACHINE IN THE SYSTEM |
| WO2003098953A1 (en)* | 2002-05-17 | 2003-11-27 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Method and device for determining a position in a mobile radio system |
| JP2007533968A (en)* | 2003-05-26 | 2007-11-22 | コモンウェルス サイエンティフィック アンド インダストリアル リサーチ オーガナイゼイション | Wireless self-survey location determination method |
| JP2008306532A (en)* | 2007-06-08 | 2008-12-18 | Kddi R & D Laboratories Inc | Mobile terminal, positioning system and positioning method using the same, and its program |
| JP2009536808A (en)* | 2006-05-08 | 2009-10-15 | スカイフック ワイヤレス,インク. | Method and system for estimating user movement attributes in a WLAN positioning system |
| JP2009545934A (en)* | 2006-08-03 | 2009-12-24 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・ドコモ | Method of distinguishing line of sight (LOS) and non-LOS (NLOS) using multipath channel statistics data |
| WO2010027179A2 (en)* | 2008-09-05 | 2010-03-11 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Mobile station assisted location based service |
| US20100246405A1 (en)* | 2009-03-31 | 2010-09-30 | Miodrag Potkonjak | Efficient location discovery |
- 2016
- 2016-03-23JPJP2016058236Apatent/JP2016145836A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000244967A (en)* | 1999-02-24 | 2000-09-08 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | MOBILE COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, MOBILE MACHINE AND BASE STATION COMPOSING THE SYSTEM, AND METHOD OF DETECTING POSITION OF MOBILE MACHINE IN THE SYSTEM |
| WO2003098953A1 (en)* | 2002-05-17 | 2003-11-27 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Method and device for determining a position in a mobile radio system |
| JP2007533968A (en)* | 2003-05-26 | 2007-11-22 | コモンウェルス サイエンティフィック アンド インダストリアル リサーチ オーガナイゼイション | Wireless self-survey location determination method |
| JP2009536808A (en)* | 2006-05-08 | 2009-10-15 | スカイフック ワイヤレス,インク. | Method and system for estimating user movement attributes in a WLAN positioning system |
| JP2009545934A (en)* | 2006-08-03 | 2009-12-24 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・ドコモ | Method of distinguishing line of sight (LOS) and non-LOS (NLOS) using multipath channel statistics data |
| JP2008306532A (en)* | 2007-06-08 | 2008-12-18 | Kddi R & D Laboratories Inc | Mobile terminal, positioning system and positioning method using the same, and its program |
| WO2010027179A2 (en)* | 2008-09-05 | 2010-03-11 | Lg Electronics Inc. | Mobile station assisted location based service |
| US20100246405A1 (en)* | 2009-03-31 | 2010-09-30 | Miodrag Potkonjak | Efficient location discovery |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11224003B2 (en) | 2019-05-31 | 2022-01-11 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Apparatus and control method |
| US11467792B2 (en) | 2019-05-31 | 2022-10-11 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Apparatus and control method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10820138B2 (en) | Generating geofences | |
| US9143894B2 (en) | Method and system for proximity and context based deduction of position for a GPS enable computing device | |
| US10085294B2 (en) | Determining when to establish connection between mobile client and proxy devices | |
| US20090191892A1 (en) | Integrating position-determining and wi-fi functions | |
| US20180332557A1 (en) | New access point setup | |
| EP3025527B1 (en) | Generating geofences | |
| TW201616824A (en) | System and method for calibrating bluetooth low energy signal strengths | |
| US9609470B2 (en) | Data routing for positioning | |
| US11026283B2 (en) | Determining when to establish connection between mobile client and proxy devices | |
| KR101639204B1 (en) | Mechanism for employing and facilitating geodetic triangulation for determining global positioning of computing devices | |
| US20150103738A1 (en) | Selecting an access point for determining position of a device based on traffic load information | |
| US20140244167A1 (en) | Methods, apparatuses and computer program products for providing a location correction cache | |
| US10708880B2 (en) | Electronic device and method for determining entry of region of interest of electronic device | |
| JP2016145836A (en) | Mechanisms implemented using geodetic triangulation to determine global positioning of computing devices | |
| US9161162B2 (en) | Estimating the geographical position of an apparatus based on its proximity to other apparatuses | |
| CN111814824A (en) | Method, device, server and system for acquiring association relationship | |
| CN112438063A (en) | Radio node location and clustering for improved device location |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20170321 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20170620 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20171031 |