JP2015154920A - Body condition management program and body condition management system - Google Patents
Body condition management program and body condition management systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2015154920A JP2015154920AJP2014251408AJP2014251408AJP2015154920AJP 2015154920 AJP2015154920 AJP 2015154920AJP 2014251408 AJP2014251408 AJP 2014251408AJP 2014251408 AJP2014251408 AJP 2014251408AJP 2015154920 AJP2015154920 AJP 2015154920A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- physical condition
- subject
- terminal device
- biological state
- biological
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription229
- 230000002159abnormal effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription34
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 230000036760body temperatureEffects0.000claimsdescription32
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000claimsdescription12
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000abstractdescription17
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000abstractdescription5
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description53
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description25
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description12
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description10
- 230000000747cardiac effectEffects0.000description7
- 206010019345Heat strokeDiseases0.000description6
- 230000005856abnormalityEffects0.000description4
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000description3
- 230000001133accelerationEffects0.000description2
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 230000010365information processingEffects0.000description2
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description2
- 210000000707wristAnatomy0.000description2
- 241000283690Bos taurusSpecies0.000description1
- 241000282472Canis lupus familiarisSpecies0.000description1
- 241000283086EquidaeSpecies0.000description1
- 241000282326Felis catusSpecies0.000description1
- 125000002066L-histidyl groupChemical group[H]N1C([H])=NC(C([H])([H])[C@](C(=O)[*])([H])N([H])[H])=C1[H]0.000description1
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000description1
- 241001494479PecoraSpecies0.000description1
- 241000282887SuidaeSpecies0.000description1
- 238000007792additionMethods0.000description1
- 238000004378air conditioningMethods0.000description1
- 238000012217deletionMethods0.000description1
- 230000037430deletionEffects0.000description1
- 230000006866deteriorationEffects0.000description1
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000description1
- 239000011521glassSubstances0.000description1
- 238000002156mixingMethods0.000description1
- 210000004165myocardiumAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000029058respiratory gaseous exchangeEffects0.000description1
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description1
- 238000010792warmingMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Measuring And Recording Apparatus For Diagnosis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、工事現場等における作業者等の体調を生体状態から随時把握し、作業者等の体調の異変の早期発見と警告を行うための体調管理プログラム及び体調管理システムに関する。 The present invention relates to a physical condition management program and a physical condition management system for ascertaining the physical condition of a worker or the like at a construction site or the like from the state of a living body at any time, and for early detection and warning of an abnormality in the physical condition of the worker or the like.
近年、地球温暖化等により、熱中症を発症する例が多発している。特に、空調の効かない屋外での作業となる作業現場等においては熱中症が発生する場合が多い。そのため、作業者等の熱中症等による体調異変を早期に把握して熱中症等の発生を未然に防止することが求められている。
また、従来より、例えば、患者の体調を生体状態から把握し、必要に応じて警告音を発する病院のベッド脇に設置する生体情報処理装置は広く使用されてきた。
例えば、特許文献1には、各病室の患者用に設けられた生体状態獲得装置からの各種生体状態を集中的にモニタリングするモニタ装置を備えた生体情報処理装置に関する発明が開示されている。In recent years, heat stroke has frequently occurred due to global warming and the like. In particular, heat stroke often occurs at work sites where work is performed outdoors where air conditioning is not effective. Therefore, it is required to grasp the physical condition change due to heat stroke etc. of the workers at an early stage and prevent the occurrence of heat stroke etc. in advance.
Conventionally, for example, a biological information processing apparatus installed beside a hospital bed that grasps a patient's physical condition from a biological state and emits a warning sound as necessary has been widely used.
For example, Patent Document 1 discloses an invention related to a biological information processing apparatus including a monitor device that intensively monitors various biological states from a biological state acquisition device provided for patients in each hospital room.
特に熱中症の場合、本人が体調の異変に気づいたときにはすでに手遅れになって動けなくなっている場合がある。
また、同じ環境においても、体調異変となる作業者等には個人差があるため、作業環境そのものを計測する装置ではなく、個人差のある個々の作業者等の生体状態を計測することにより、個々の作業者等の体調を把握し、体調異変を防止する必要がある。
しかし、特許文献1に記載のモニタ装置では、装置が大型になってしまい携帯不可能なため、作業者等の病院外における種々の作業中に、作業者等の体調を把握することはできない。
本発明は、このような点に鑑みて創案されたものであり、屋外の作業者等にも適用可能であり、屋外の作業者等の体調の異変の早期発見と警告を行うことが可能であり、作業事故を未然に防止し、作業者等の健康と安全を確保することができる体調管理プログラム及び体調管理システムを提供することを課題とする。Especially in the case of heat stroke, when the person notices a change in physical condition, it may be too late to be able to move.
In addition, even in the same environment, because there are individual differences in workers etc. who are in abnormal physical condition, by measuring the biological state of individual workers etc. with individual differences, rather than a device that measures the work environment itself, It is necessary to grasp the physical condition of each worker and prevent the physical condition from changing.
However, since the monitor device described in Patent Document 1 becomes large and cannot be carried, the physical condition of the worker or the like cannot be grasped during various operations outside the hospital.
The present invention was devised in view of these points, and can be applied to outdoor workers, etc., and can detect and warn of an abnormal change in physical condition of an outdoor worker. It is an object to provide a physical condition management program and a physical condition management system capable of preventing work accidents and ensuring the health and safety of workers and the like.
上記課題を解決するため、本発明に係る体調管理プログラムは次の手段をとる。
まず、本発明の第1の発明は、単数または複数の対象者のそれぞれに装着されて、装着された対象者の生体状態を検出し、検出した生体状態に関する生体状態検出情報を、対象者端末装置に送信する生体状態検出装置と、それぞれの前記生体状態検出装置毎に用意された前記対象者端末装置、あるいは複数の前記生体状態検出装置に対応させて用意された前記対象者端末装置と、を備えた体調管理システムにおける前記対象者端末装置を、前記生体状態検出装置から送信された前記生体状態検出情報を受信する受信手段、受信した前記生体状態検出情報を、当該生体状態検出情報に対応する対象者の体調として認識可能とする生体情報データに変換するデータ変換手段、変換した前記生体情報データが所定の体調異変状態となった前記生体状態検出情報に対応する対象者である体調異変者を抽出する体調異変者抽出手段、体調異変者が抽出されたことを報知する注意喚起手段、として機能させるための、体調管理プログラムである。In order to solve the above problems, the physical condition management program according to the present invention takes the following means.
First, according to a first aspect of the present invention, a biological state detection information relating to a detected biological state is detected by detecting the biological state of the attached target person attached to each of one or a plurality of subjects. A biological state detection device to be transmitted to the device, the subject terminal device prepared for each of the biological state detection devices, or the subject terminal device prepared corresponding to a plurality of the biological state detection devices, The subject terminal device in the physical condition management system comprising: receiving means for receiving the biological state detection information transmitted from the biological state detection device; and the received biological state detection information corresponding to the biological state detection information Data converting means for converting into biological information data that can be recognized as the physical condition of the subject to be subjected to, the biological state in which the converted biological information data is in a predetermined physical condition abnormal state Health accident who extracting means for extracting a physical condition accident who is the subject corresponding to the detection information, alerting means for informing that the physical condition accident individual is extracted, to function as a physical condition management program.
この第1の発明によれば、各対象者個々の生体状態検出情報を生体状態検出装置により取得して、対象者端末装置において体調異変者を抽出し、当該体調異変者等に注意喚起を行うことができる。
したがって、屋外における作業現場等においても、作業者等が容易に作業者自身の、あるいは他の作業者の体調の異変を早期に把握することができる。これにより、作業事故を未然に防止し、作業者等の健康と安全を確保することができる。According to the first aspect of the invention, the biological state detection information of each subject person is acquired by the biological state detection device, the physical condition abnormal person is extracted in the target person terminal device, and the physical condition abnormal person or the like is alerted. be able to.
Therefore, even at an outdoor work site or the like, it is possible for the worker or the like to easily grasp an abnormality in the physical condition of the worker himself or another worker. As a result, work accidents can be prevented and the health and safety of workers and the like can be ensured.
次に、本発明の第2の発明は、上記第1の発明に係る体調管理プログラムであって、前記対象者端末装置を、前記体調異変者抽出手段にて体調異変者が抽出された場合、体調異変者が発見されたことを含む体調異変者発見情報を、予め設定された送信先に向けて送信する通報手段、として機能させるための、体調管理プログラムである。 Next, the second invention of the present invention is the physical condition management program according to the first invention, wherein the subject person terminal device is extracted by the physical condition abnormal person extraction means, It is a physical condition management program for functioning as a reporting means for transmitting physical condition stranger discovery information including the discovery of a physical condition stranger to a preset destination.
この第2の発明によれば、体調異変者や周囲の作業者等に加えて、予め設定された送信先の管理者等にも体調異変者が発生したことを通報することができる。
これにより、作業事故を未然に防止し、作業者等の健康と安全を確保することができる。According to the second aspect of the present invention, it is possible to report to the manager of the transmission destination set in advance that the physical condition has changed, in addition to the physical condition change person and surrounding workers.
As a result, work accidents can be prevented and the health and safety of workers and the like can be ensured.
次に、本発明の第3の発明は、上記第1の発明または第2の発明に係る体調管理プログラムであって、前記対象者端末装置は、少なくとも過去の所定期間の前記生体情報データをそれぞれの対象者に対応させて記憶しており、前記体調異変者抽出手段における前記所定の体調異変状態の判定を、前記所定期間におけるそれぞれの対象者に対応する過去の前記生体情報データに基づいて算出した対象者毎の閾値あるいは予め入力された対象者毎の閾値と、前記データ変換手段にて変換した前記生体情報データと、に基づいて行う、体調管理プログラムである。 Next, a third invention of the present invention is the physical condition management program according to the first invention or the second invention, wherein the subject terminal device stores the biological information data of at least a past predetermined period, respectively. And the determination of the predetermined abnormal state of the physical condition in the physical condition abnormal person extraction means is calculated based on the past biological information data corresponding to each target person in the predetermined period. The physical condition management program is performed based on the threshold value for each subject person or the threshold value for each subject person input in advance and the biological information data converted by the data conversion means.
この第3の発明によれば、過去の生体情報データに基づいて算出した対象者毎の閾値あるいは予め入力した対象者毎の閾値に基づいて体調異変者を抽出する。
これにより、作業者等の個人差に応じた体調の異変を早期に発見及び警告することができる。According to the third aspect of the invention, the physical condition anomaly is extracted based on the threshold for each subject calculated based on the past biological information data or the threshold for each subject inputted in advance.
Thereby, the abnormality of the physical condition according to individual differences, such as an operator, can be discovered and warned at an early stage.
次に、本発明の第4の発明は、上記第1の発明〜第3の発明のいずれか1つに係る体調管理プログラムであって、前記生体状態検出装置は、装着された対象者の心拍状態、脈拍状態、体温状態、体の傾倒状態、心電位状態、の少なくとも1つを検出可能である、体調管理プログラムである。 Next, 4th invention of this invention is a physical condition management program which concerns on any one of the said 1st invention-3rd invention, Comprising: The said biological condition detection apparatus is a heartbeat of the mounted subject. It is a physical condition management program capable of detecting at least one of a state, a pulse state, a body temperature state, a body tilt state, and a cardiac potential state.
この第4の発明によれば、心拍状態、脈拍状態、体温状態、体の傾倒状態、心電位状態等を検出して体調異変者を抽出することで、熱中症を含む作業者等の体調の異変を適切に発見することができる。 According to the fourth aspect of the present invention, by detecting a heartbeat state, a pulse state, a body temperature state, a body tilt state, a cardiac potential state, etc. Anomalies can be detected appropriately.
次に、本発明の第5の発明は、スマートフォン、タブレット型コンピュータ、ウェアラブル端末、ノート型コンピュータの少なくとも1つであって上記第1の発明〜第4の発明のいずれか1つに係る体調管理プログラムを搭載した前記対象者端末装置と、前記生体状態検出装置と、を備えた体調管理システムである。 Next, a fifth aspect of the present invention is a physical condition management according to any one of the first to fourth aspects of the present invention, which is at least one of a smartphone, a tablet computer, a wearable terminal, and a notebook computer. It is a physical condition management system provided with the said subject person terminal device carrying the program and the said biological condition detection apparatus.
この第5の発明によれば、対象者端末装置として、スマートフォン、タブレット型コンピュータ、ウェアラブル端末、ノート型コンピュータのうち少なくとも1つを利用することで、体調管理システムを、比較的容易に実現することができる。 According to the fifth invention, the physical condition management system can be realized relatively easily by using at least one of a smartphone, a tablet computer, a wearable terminal, and a notebook computer as the target person terminal device. Can do.
次に、本発明の第6の発明は、上記第5の発明に係る体調管理システムであって、前記生体状態検出装置毎に前記対象者端末装置が用意されており、前記生体状態検出装置と前記対象者端末装置は有線にて接続され、前記生体状態検出装置は変調手段を有し、前記対象者端末装置は音声入力端子と復調手段を有し、前記生体状態検出装置は生体状態検出情報を前記変調手段で変調した変調信号を前記有線を介して前記対象者端末装置へ出力し、前記対象者端末装置は前記有線を介して前記音声入力端子から入力された変調信号を前記復調手段にて復調することで前記生体状態検出情報を受信する体調管理システムである。 Next, a sixth aspect of the present invention is the physical condition management system according to the fifth aspect, wherein the subject terminal device is prepared for each of the biological state detection devices, and the biological state detection device The subject terminal device is connected by wire, the biological state detection device has a modulation unit, the subject terminal device has a voice input terminal and a demodulation unit, and the biological state detection device is biological state detection information The modulated signal modulated by the modulating means is output to the subject terminal device via the wire, and the subject terminal device receives the modulated signal input from the audio input terminal via the wire to the demodulating means. The physical condition management system receives the biological state detection information by demodulating the information.
この第6の発明によれば、生体状態検出装置における通信手段(有線での通信手段)を、例えばUSB用の通信手段よりもより安価な従来のモデム用の通信手段で実現することができるので、生体状態検出装置をより低コストで実現することができる。 According to the sixth aspect of the invention, the communication means (wired communication means) in the biological state detection device can be realized by a conventional modem communication means that is cheaper than, for example, a USB communication means. Thus, the biological state detection device can be realized at a lower cost.
以下に本発明を実施するための形態を図面を用いて説明する。
●[体調管理システムの第1の実施の形態(図1(A))]
図1(A)は、本発明の体調管理システムを構成する生体状態検出装置10と対象者端末装置20の第1の実施の形態及び、生体状態検出装置10の構成の例を説明する図である。本実施形態における生体状態検出装置10は、単数または複数の対象者のそれぞれに装着されて、装着された対象者の生体状態を検出し、検出した生体状態に関する生体状態検出情報を、対象者端末装置20に送信する。
生体状態検出装置10は、例えば生体情報センサユニットである。この生体状態検出装置10は、例えば心拍状態を検出可能な検出手段(例えば心拍検出用センサ121)と検出プログラムを備えている。またこの生体状態検出装置10は、例えば脈拍状態を検出可能な検出手段(例えば脈拍検出用センサ122)と検出プログラムを備えている。またこの生体状態検出装置10は、例えば体温状態を検出可能な検出手段(例えば体温検出用センサ123)と検出プログラムを備えている。またこの生体状態検出装置10は、例えば体の傾倒状態を検出可能な検出手段(例えば加速度センサ124)と検出プログラムを備えている。またこの生体状態検出装置10は、例えば心電位状態(例えば心筋の動きに伴う電位の変化)を検出可能な検出手段(例えば心電位検出用センサ125)と検出プログラム等を備えている。
また、生体状態検出装置10は、検出した生体状態に関する生体状態検出情報を対象者端末装置20に送信する送信プログラムと送信手段(例えば送信回路111)とアンテナ113、各プログラムを実行するCPU101、受信手段(例えば受信回路112)等を備えている。EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION Below, the form for implementing this invention is demonstrated using drawing.
● [First embodiment of physical condition management system (FIG. 1A)]
FIG. 1A is a diagram for explaining an example of the configuration of the first embodiment of the biological
The biological
In addition, the biological
●[体調管理システムの第2の実施の形態(図1(B))]
図1(B)は、生体状態検出装置10と対象者端末装置20とで構成された体調管理システムの第2の実施の形態及び、生体状態検出装置10の構成の例を説明する図である。第2の実施の形態の体調管理システムでは、生体状態検出装置の少なくとも一部のセンサから電極等の検出部が分離され、センサと検出部とが配線にて接続されている。図1(B)に示す生体状態検出装置10は図1(A)に示す生体状態検出装置10に対して、心電位検出用センサ125から分離した電極等の検出部131、132、133をリード線により延長して対象者の適切な個所に装着できるように構成されている。例えば心電位検出用のセンサ125は、検出部133を基準とした検出部131の電位、及び検出部133を基準とした検出部132の電位を計測する。なお、分離された検出部が配線にて接続された構成は、心電位検出用センサ125に限定されるものではなく、図1(B)に示す検出手段(この場合、符号121〜125)の少なくとも1つが、分離された検出部が配線にて接続される構成となっていればよい。[Second embodiment of physical condition management system (FIG. 1B)]
FIG. 1B is a diagram for explaining an example of the configuration of the second embodiment of the physical condition management system configured by the biological
●[体調管理システムを対象者に装着する第1の装着方法(図2(A))]
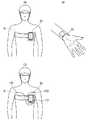
図2(A)は、対象者の胸部に図1(A)に示す生体状態検出装置10を装着し、対象者端末装置20を対象者の衣類等のポケットに収容した例を示す図である。生体状態検出装置10は、ベルト等で皮膚に接触して装着される。この際、生体状態検出装置10の各検出手段が皮膚に接するように配置されている。また、当該生体状態検出装置10は、上述のように、無線または有線の通信手段により、検知した生体状態検出情報を対象者端末装置20に対して送信する。● [First Wearing Method for Wearing Physical Condition Management System to Subject (FIG. 2 (A))]
FIG. 2A is a diagram showing an example in which the biological
●[体調管理システムを対象者に装着する第2の装着方法(図2(B))]
図2(B)は、対象者の手首に図1(A)に示す生体状態検出装置10を装着した例を説明する図である。この例の場合も、当該生体状態検出装置10は、各検出手段が皮膚に接するように装着され、無線または有線の通信手段により、検知した生体状態検出情報を対象者端末装置20に対して送信する。● [Second method of wearing physical condition management system on subject (Fig. 2 (B))]
FIG. 2B is a diagram illustrating an example in which the biological
●[体調管理システムを対象者に装着する第3の装着方法(図2(C))]
図2(C)は、図2(A)に対して、図1(B)に示す生体状態検出装置10及び検出部131〜133を対象者に装着した例を示している。
この場合、各生体状態の検出に適切な位置が離れている場合であっても、検出部が分離されているので、生体状態の検出に適切な位置に適切な検出部を取り付けることができるので、より精度よく生体状態を検出することができる。
また、対象者の皮膚に接触させるべき検出部の全てを分離すれば、生体状態検出装置10を対象者の衣類のポケット等に収容することができるので便利である。
また、分離された検出部が、予め所定位置に取り付けられた肌着を用意して、当該肌着を対象者に着用させるようにしてもよい。
このように、検出部を分離した生体状態検出装置を用いて、分離した検出部を対象者の所定位置に取り付けて(皮膚に接触させて)、生体状態検出装置を衣類のポケット等に収容した場合も、「対象者に生体状態検出装置を装着する」という概念に含む。● [Third method of wearing physical condition management system on subject (Fig. 2 (C))]
FIG. 2C illustrates an example in which the biological
In this case, since the detection unit is separated even when the appropriate position for detection of each biological state is separated, an appropriate detection unit can be attached at an appropriate position for detection of the biological state. Thus, the biological state can be detected with higher accuracy.
Further, if all of the detection units to be brought into contact with the subject's skin are separated, it is convenient because the biological
Moreover, the separated detection part may prepare the underwear previously attached to the predetermined position, and may make it make the subject wear the said underwear.
In this way, using the biological state detection device with the detection unit separated, the separated detection unit is attached to a predetermined position of the subject (in contact with the skin), and the biological state detection device is housed in a clothing pocket or the like. This is also included in the concept of “wearing the subject with the biological state detection device”.
●[体調管理システムを作業現場に適用した第1の利用方法(図3)]
図3は、本発明の体調管理システム1の作業現場での使用例、及び動作の概略を説明する第1の利用方法を説明する図である。この第1の利用方法では、各対象者は、1つの生体状態検出装置10を装着し、かつ1つの対象者端末装置20を携帯して作業を行う。つまり、第1の利用方法は、生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置とを、1対1で利用する方法である。本発明の体調管理プログラムが対象者端末装置20上で動作することにより、各対象者の体調が対象者端末装置20上で把握されている。また、対象者端末装置20上で対象者に体調異変が発生したことを把握したときは、対象者に対して注意喚起が行われると共に、必要に応じて別の場所に居る管理者の管理者用パソコン30に電子メール等により体調異変者が発見されたことが通報される。当該管理者は、通報された電子メール等を確認して体調異変者に休息を取らせて体調を回復させ、作業事故を未然に防止することができる。また、当該管理者は、体調異変者が発生した作業現場の衛生環境について問題が発生しそうな場合は、必要に応じて作業現場に注意喚起を行うことができる。● [First method of using physical condition management system at work site (Fig. 3)]
FIG. 3 is a diagram for explaining a usage example of the physical condition management system 1 according to the present invention and a first usage method for explaining an outline of the operation. In this first usage method, each subject wears one living body
●[体調管理システムを作業現場に適用した第2の利用方法(図4)]
図4は、本発明の体調管理システム1の作業現場での使用例、及び動作の概略を説明する第2の利用方法を説明する図である。この第2の利用方法では、各対象者は1つの生体状態検出装置10を装着し、1つの対象者端末装置20を数人の対象者で共有して作業を行う。つまり、第2の利用方法は、生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置とを、多対1で利用する方法である。本発明の体調管理プログラムが対象者端末装置20上で動作することにより、各対象者の体調が対象者端末装置20上で把握されている。また、対象者端末装置20上で対象者に体調異変が発生したことを把握したときは、対象者に対して注意喚起が行われると共に、必要に応じて別の場所に居る管理者の管理者用パソコン30に電子メール等により体調異変者が発見されたことが通報される。当該管理者は、通報された電子メール等を確認して体調異変者に休息を取らせて体調を回復させ、作業事故を未然に防止することができる。また、当該管理者は、体調異変者が発生した作業現場の衛生環境について問題が発生しそうな場合は、必要に応じて作業現場に注意喚起を行うことができる。● [Second method of using physical condition management system at work site (Fig. 4)]
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining a usage example of the physical condition management system 1 of the present invention at the work site and a second usage method for explaining an outline of the operation. In this second usage method, each subject wears one biological
●[生体状態検出装置10と対象者端末装置20とが送受信する情報(図5)]
図5は、本発明の体調管理システム1を構成する生体状態検出装置10と対象者端末装置20が送受信する情報の概略を説明する図である。生体状態検出装置10により検知された生体状態検出情報は、生体状態検出装置10に備わっている送信用バッファとアンテナ113を介して、対象者端末装置20に送信される。対象者端末装置20で受信した生体状態検出情報は、対象者端末装置20に備わっている受信用バッファを介して、対象者端末装置20で体調管理プログラムにより生体情報データにデータ変換され、対象者が体調異変者か否かの診断に用いられる。なお、体調異変者であるか否かの判断の元となる生体情報データの例は図7及び図8に示すとおりである。なお、図7に示す生体情報データ201における符号201Aにて示す生体情報データは、体調異変時の生体情報データの例を示しており、この例では、対象者の体温が閾値の例である37.5℃を超えている。また、対象者端末装置20は、体調異変者を抽出した場合には、対象者に対して注意喚起を行うと共に、必要に応じてメールを管理者へ送信することにより、診断結果を管理者に通報する。[Information transmitted and received between the biological
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining an outline of information transmitted and received between the biological
●[対象者端末装置20の処理手順(図6〜図8)]
図6は、本発明の体調管理プログラムを説明する図であり、対象者端末装置20の処理手順を説明するフローチャートである。
ステップS10にて、対象者端末装置20は、生体状態検出装置10により対象者から取得した生体状態検出情報を、生体状態検出装置10から受信する。このステップS10にて、前記対象者端末装置20は前記生体状態検出装置10から送信された前記生体状態検出情報を受信する受信手段として機能する。
なお、生体状態検出装置10は、自身の識別情報とともに生体状態検出情報を送信する。
また、対象者端末装置20には、生体状態検出装置10の識別情報に対応させて、対象者を識別可能な氏名等(Aさん、Bさん等)が登録されている。[Processing procedure of the target person terminal device 20 (FIGS. 6 to 8)]
FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining the physical condition management program of the present invention, and is a flowchart for explaining the processing procedure of the subject
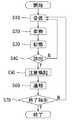
In step S <b> 10, the subject
The biological
In addition, in the subject
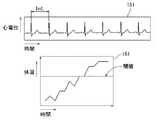
ステップS20にて、対象者端末装置20は、受信した生体状態検出情報のデータ変換を行って生体情報データ(図7、図8参照)を作成する。これにより、対象者端末装置20は、データ変換後の生体情報データとしての、心電図、体温等、有意なデータを体調管理に利用できる。このステップS20にて、対象者端末装置20は受信した生体状態検出情報を、生体状態検出情報に対応する対象者の体調として認識可能とする生体情報データに変換するデータ変換手段として機能する。ステップS20で、対象者端末装置20は生体状態検出情報から例えばCSV形式の生体情報データ201にデータ変換を行う。図7の例では、このCSV形式のデータを表計算ソフト等で表示させた例が示されており、この生体情報データ201は、心拍数および体温の(図示した例では心拍と体温のみだが、他の生体情報データを記録しても良い)時系列のデータとなっている。また、CSV形式のファイルに含まれるデータや、受信した生体状態検出情報から図8に示されるような心電図151や体温161等のグラフを作成することもできる。 In step S20, the subject
ステップS30にて、対象者端末装置20は、データ変換後の生体情報データを対象者端末装置20の不揮発性メモリ等に保存して、後の体調管理の診断基準として用いる。このステップS30において、前記対象者端末装置は、少なくとも過去の所定期間の前記生体情報データをそれぞれの対象者に対応させて記憶する手段として機能する。 In step S <b> 30, the subject
ステップS40にて、対象者端末装置20は、対象者が体調異変を起こしているか否かの診断を行う。このステップS40にて体調異変者が抽出された場合(Y)には、次のステップ(S50)へ進み抽出されなかった場合(N)は、ステップS10に戻り、再び生体状態検出装置10からの生態情報データの受信準備態勢のまま待機する。このステップS40にて、対象者端末装置20は変換した生体情報データが所定の体調異変状態である生体状態検出情報に対応する対象者である体調異変者を抽出する体調異変者抽出手段として機能する。例えば、体調異変者抽出作業において、心電位のピーク電位の間隔の変化が所定値以上の場合、心拍数が所定値以上(例えば130拍/分以上)の場合、脈拍が所定値以上(例えば130拍/分以上)の場合、体温が所定閾値以上(例えば37.5℃以上)の場合、体が傾倒した状態が所定時間以上(例えば5分以上)継続した場合等、体調に異変が発生した場合(体調異変が始まったと推定されるできるだけ早い段階)に、対象者端末装置20が体調異変者を抽出する。 In step S <b> 40, the subject
ステップS50にて、対象者端末装置20は、対象者に注意喚起を行う。なお、注意喚起の具体的な例は、図9、図10を用いて後述する。このステップS50にて、対象者端末装置20は体調異変者が抽出されたことを報知する注意喚起手段として機能する。 In step S50, the target person
ステップS60にて、対象者端末装置20は、図5に示すようなデータを含む電子メールにより管理者に対して通報を行う。メールの文面の例は、図5の符号301に示すように、例えば、対象者名(この例ではAさん)、体調異変内容(この例では体温異常)、場所(対象者端末装置20が予め備えているGPSユニットからのGPSデータ等に基づいた場所)、時刻等である。このステップS60にて、前記対象者端末装置20は、前記体調異変者抽出手段にて体調異変者が抽出された場合、体調異変者が発見されたことを含む体調異変者発見情報を、予め設定された送信先(この例ではメールアドレス)に向けて送信する通報手段、として機能する。 In step S60, the target person
ステップS70にて、対象者端末装置20は、対象者からの入力指示による本体調管理プログラムの終了判定を行い、終了する場合(Y)には終了の手順を実施し、継続する場合(N)にはステップS10に戻り、再び生体状態検出装置10からの生態情報データの受信準備態勢のまま待機する。 In step S <b> 70, the subject
例えば、対象者端末装置20は、少なくとも過去の所定期間の生体情報データをそれぞれの対象者に対応させて記憶している。
そして対象者端末装置20は、体調管理プログラムにより、体調異変者抽出手段における所定の体調異変状態の判定を、所定期間におけるそれぞれの対象者に対応する過去の生体情報データに基づいて算出した対象者毎の閾値あるいは予め入力された対象者毎の閾値と、データ変換手段にて変換した生体情報データと、に基づいて行う。
対象者端末装置20は、図7の生体情報データを用いて、当該データの対象者の閾値を求めることができる。例えば、Aさんに固有の体温の閾値を求める場合、対象者端末装置20は、図7に示す生体情報データ201の中から、所定期間内のAさんの体温のデータから、Aさんの所定期間内の体温の中央値と標準偏差を求める。そして、対象者端末装置20は、求めた中央値から、標準偏差に基づいた値だけ離れた値をAさんに固有の体温の閾値とする。あるいは、当該対象者に固有の体温用の閾値を設定して、対象者端末装置20に入力するようにしても良い。なお、体温以外の心拍、脈拍等も同様に対象者端末装置20が閾値を設定することができる。また、例えば心電位の場合、対象者端末装置20が、対象者の所定期間のピーク電圧のインターバル(図8中のInt.)から当該対象者に対する中央値と標準偏差を求め、求めた中央値から標準偏差に基づいた値だけ離れた値を当該対象者の心電位の閾値とすることもできる。For example, the subject
Then, the subject
The subject
●[第1の利用方法(図3)における注意喚起方法(図9)]
図9は、第1の利用方法(図3)において、注意喚起を行う様子の例を説明する図である。この例では、対象者は、1つの生体状態検出装置10を装着し、1つの対象者端末装置20を保持している。対象者端末装置20を体調管理手段として機能させる体調管理プログラムにより、対象者端末装置20は、例えば、体温が閾値を越えたと判断した場合には、対象者端末装置20から音声出力や発光や振動等の注意喚起を行う。この注意喚起により体調異変が発生した対象者だけでなく対象者の近くに居る他の作業者にも周知されるので、対象者が動けなくなっている状態であっても、近くに居る作業者が救助を手配することにより、対象者が適切な処置を受けることが可能となる。● [Attention method in the first usage method (Fig. 3) (Fig. 9)]
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating an example of a state of alerting in the first usage method (FIG. 3). In this example, the subject wears one biological
●[第2の利用方法(図4)における注意喚起方法(図10)]
図10は、第2の利用方法(図4)において、注意喚起を行う様子の例を説明する図である。この例では、各対象者が、それぞれ1つの生体状態検出装置10を装着し、3名の対象者で対象者端末装置20を共有する場合の例を示している。各生体状態検出装置10は、検出した生体状態検出情報を対象者端末装置20に送信し、体調管理プログラムにより、該対象者端末装置20がまとめて3人分の体調管理手段として機能している。この例では対象者端末装置20は、Aさん、Bさんに体調異変はないと判定し、Cさんの体温が閾値を超えて上昇していると判定し、体調異変者としてCさんを抽出し、Cさんに体調異変が発生しているという注意喚起(音、光、振動等)を行う。● [Awareness method in the second usage method (FIG. 4) (FIG. 10)]
FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a state of alerting in the second usage method (FIG. 4). In this example, each subject person wears one living body
以上の説明は生体状態検出装置10と対象者端末装置20との間の通信が無線通信の場合を説明したが、生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置との間の通信を有線通信で実現することも可能である。以下、生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置との間の通信を有線通信で実現する例について説明する。なお、以下の説明では、有線通信の例としてモデムを利用した例を説明するが、USBを用いてもよい。 In the above description, the communication between the biological
●[体調管理システムの第3の実施の形態(図11(A))]
図11(A)に示す第3の実施の形態の体調管理システム1Aは、図1(A)の生体状態検出装置10と対象者端末装置20との間の通信が無線通信の場合の第1の実施の形態を、有線通信で実現した第3の実施の形態の体調管理システム1Aの構成及び、生体状態検出装置10Aの構成の例を説明する図である。図11(A)におけるセンサ121〜125は、それぞれ図1(A)におけるセンサ121〜125と同じであるのでここでは説明を省略する。また、符号111Aは送信回路(通信手段)に相当し、変調手段等を備えており、符号101AはCPUである。また、対象者端末装置20には有線による入力手段20Mが設けられているものとする。本実施形態の生体状態検出装置10Aは有線通信の送信機能のみを備えたものであるため、図1(A)の受信回路112およびアンテナ113は必要としない。また対象者端末装置が例えばスマートフォンである場合、入力手段20Mは、マイク入力端子(音声入力端子に相当)を利用することが可能である。このため、従来のモデム用の手段で通信手段を実現できるため生体状態検出装置10Aを含む体調管理システム1Aを低コストで実現できる。
そして生体状態検出装置10Aは、生体状態検出情報を変調手段(送信回路111A)にて(少なくとも周波数を)変調した変調信号を、有線を介して対象者端末装置20に送信する。
また、対象者端末装置20は、有線を介して入力手段20M(音声入力端子に相当)から入力された変調信号を、復調プログラム(復調手段に相当)にて復調することで、生体状態検出情報を受信する。なお、変調手段、及び復調手段は、周波数変調と振幅変調と位相変調のいずれか又は複数を組み合わせて変調、及び復調を行うようにしてもよい。● [Third embodiment of physical condition management system (FIG. 11A)]
The physical
Then, the biological
In addition, the subject
●[体調管理システムの第4の実施の形態(図11(B))]
図11(B)に示す第4の実施の形態の体調管理システム1Bは、図1(B)の生体状態検出装置10と対象者端末装置20との間の通信が無線通信の場合の第2の実施の形態を、有線通信で実現した第4の実施の形態の体調管理システム1Bの構成及び、生体状態検出装置10Bの構成の例を説明する図である。図11(B)におけるセンサ121〜125は、それぞれ図1(A)におけるセンサ121〜125と同じであるのでここでは説明を省略する。図11(B)に示す第4の実施の形態の生体状態検出装置10Bは、図11(A)に示す第3の実施の形態の生体状態検出装置10Aに対して、(図1(B)に示す第2の実施の形態と同様に)検出部131〜133が分離されている。
また、送信回路111A、入力手段20M、生体状態検出装置10Bの動作、対象者端末装置20の動作、等は、図11(A)に示す第3の実施の形態と同様であるので、説明を省略する。
これらにより、第3の実施の形態の生体情報検出装置10Aを含む体調管理システム1Aと同様に、第4の実施の形態の生体情報検出装置10Bを含む体調管理システム1Bを、低コストで実現できる。[Fourth embodiment of physical condition management system (FIG. 11B)]
The physical
Further, the operation of the
As a result, the physical
●[体調管理システムの第4の実施の形態の他の例(図11(C))]
図11(C)に示す第4の実施の形態の他の例の体調管理システム1Cの生体状態検出装置10Cは、図11(B)に示す生体状態検出装置10Bに対して、体温検出用センサ123から分離された電極等の検出部134、135が追加されている。また、心音検出用センサ126及び心音検出用センサ126から分離された電極等の検出部136が追加されている。そしてCPUが、符号101Aから符号101Cに変更されている。また、図11(C)におけるセンサ121〜125は、それぞれ図11(B)におけるセンサ121〜125と同じである。
図11(C)に示す第4の実施の形態の他の例(第4の実施の形態(その2)に相当)の体調管理システム1Cでは、検出部134、135のそれぞれを、例えば対象者の耳の穴および脇の下等に取り付けることで、対象者の体温を、より精度よく検出することができる。また、検出部136を、例えば対象者の心臓のより近傍に取付けることで、対象者の心音を、より精度よく検出することができる。
なお、図1(A)に示す第1の実施の形態の生体状態検出装置10や図11(A)に示す第3の実施の形態の生体状態検出装置10Aに心音検出用センサ126を追加してもよい。また、図1(B)に示す第2の実施の形態の生体状態検出装置10や図11(B)に示す第4の実施の形態の生体状態検出装置10Bに心音検出用センサ126と検出部136を追加してもよい。[Another example of the fourth embodiment of the physical condition management system (FIG. 11C)]
A living body state detection device 10C of a physical condition management system 1C of another example of the fourth embodiment shown in FIG. 11C is a body temperature detection sensor compared to the living body
In the physical condition management system 1C of another example of the fourth embodiment shown in FIG. 11C (corresponding to the fourth embodiment (part 2)), each of the
A heart
●[体調管理システムの第2の実施の形態の他の例(図11(D))]
図11(D)に示す第2の実施の形態の他の例の体調管理システム1Dの生体状態検出装置10Dは、図1(B)に示す生体状態検出装置10に対して、体温検出用センサ123から分離された電極等の検出部134、135が追加されている。また、心音検出用センサ126及び心音検出用センサ126から分離された電極等の検出部136が追加されている。そしてCPUが、符号101から符号101Dに変更されている。また、図11(D)におけるセンサ121〜125は、それぞれ図1(B)におけるセンサ121〜125と同じである。
図11(D)に示す第2の実施の形態の他の例の体調管理システムでは、図11(C)に示す第4の実施の形態の他の例の効果と同様に、検出部134、135のそれぞれを、例えば対象者の耳の穴および脇の下等に取り付けることで、対象者の体温をより精度よく検出することができる。また、検出部136を、例えば対象者の心臓のより近傍に取り付けることで、対象者の心音を、より精度よく検出することができる。● [Another example of the second embodiment of the physical condition management system (FIG. 11D)]
The biological condition detection device 10D of the physical condition management system 1D of another example of the second embodiment shown in FIG. 11D is a body temperature detection sensor compared to the biological
In the physical condition management system according to another example of the second embodiment illustrated in FIG. 11D, the
●[体調管理システムを対象者に装着する第4の装着方法(図12)]
図12は、図11(C)に示す生体状態検出装置10C及び検出部131〜136を対象者に装着した第4の装着方法を示している。
図12に示す第4の装着方法は、図2(C)に示す第3の装着方法に対して、新たな検出部134、135(体温検出用センサから分離した検出部)のそれぞれが、耳の穴、脇の下に取り付けられ、新たな検出部136(心音検出用センサから分離した検出部)が、心臓の近傍に取り付けている点が異なる。また、生体状態検出装置10Cが、対象者の耳の近傍となるヘルメットに取り付けられている点も異なる。● [Fourth Wearing Method for Wearing Physical Condition Management System to Subject (Fig. 12)]
FIG. 12 shows a fourth attachment method in which the biological state detection device 10C and the
The fourth wearing method shown in FIG. 12 is different from the third wearing method shown in FIG. 2C in that each of the
第4の装着方法では、各生体状態の検出に適切な位置が離れている場合であっても、検出部が分離されているので、生体状態の検出に適切な位置に適切な検出部を取り付けることができるので、より精度よく生体状態を検出することができる。
また、対象者の皮膚に接触させるべき検出部の全てを分離すれば、生体状態検出装置10Cを対象者の皮膚に接触させる必要が無いので、対象者の衣類のポケット等に収容することが可能であり、例えばヘルメットに装着することもできるので便利である。
このように、検出部を分離した生体状態検出装置10C(図11(C)参照)を用いて、分離した検出部を対象者の所定位置に取り付けて(皮膚に接触させて)、生体状態検出装置をヘルメットに装着した場合も、「対象者に生体状態検出装置を装着する」という概念に含む。
なお、生体状態検出装置10Cをヘルメットに装着することにより、耳の穴に設けた体温の検出部134からの距離がわずかなため、検出信号への雑音の混入や検出信号の減衰による検出精度の劣化が防止できる。In the fourth mounting method, the detection unit is separated even when the positions appropriate for the detection of each biological state are separated, so that an appropriate detection unit is attached at a position appropriate for the detection of the biological state. Therefore, the biological state can be detected with higher accuracy.
Further, if all of the detection units to be brought into contact with the subject's skin are separated, it is not necessary to bring the living body state detection device 10C into contact with the subject's skin, so that it can be accommodated in the subject's clothing pocket or the like. For example, it is convenient because it can be attached to a helmet.
In this way, using the biological state detection device 10C (see FIG. 11C) from which the detection unit is separated, the separated detection unit is attached to a predetermined position of the subject (in contact with the skin) to detect the biological state. The case where the device is mounted on the helmet is also included in the concept of “wearing the subject with the biological state detection device”.
By attaching the biological state detection device 10C to the helmet, the distance from the body
●[体調管理システムを作業現場に適用した第1の利用方法の他の例(図13)]
図13に示す第1の利用方法(生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置が1対1の利用方法)の他の例は、図11(C)に示す第4の実施の形態の他の例の体調管理システム1Cを、図12に示す第4の装着方法にて対象者に装着して、作業現場で利用する例を示している。そして、図3に示す第1の利用方法と同様に、本発明の体調管理プログラムが対象者端末装置20上で動作することにより、各対象者の体調が対象者端末装置20上で把握されている。また、対象者端末装置20上で対象者に体調異変が発生したことを把握したときは、対象者に対して注意喚起が行われると共に、必要に応じて別の場所に居る管理者の管理者用パソコン30に電子メール等により体調異変者が発見されたことが通報される。当該管理者は、通報された電子メール等を確認して体調異変者に休息を取らせて体調を回復させ、作業事故を未然に防止することができる。また、当該管理者は、体調異変者が発生した作業現場の衛生環境について問題が発生しそうな場合は、必要に応じて作業現場に注意喚起を行うことができる。
なお、生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置とを1対1で利用する第1の利用方法は、第1の実施の形態の体調管理システム1(図1(A))、第2の実施の形態の体調管理システム1(図1(B))、第3の実施の形態の体調管理システム1A(図11(A))、第4の実施の形態の体調管理システム1B(図11(B))、第4の実施の形態の他の例の体調管理システム1C(図11(C))、第2の実施の形態の他の例の体調管理システム1D(図11(D))、のいずれの体調管理システムでも利用することができる。● [Another example of the first usage method applying the physical condition management system to the work site (FIG. 13)]
Another example of the first usage method shown in FIG. 13 (one-to-one usage method between the biological state detection device and the subject terminal device) is another example of the fourth embodiment shown in FIG. The physical condition management system 1 </ b> C is attached to a subject by the fourth wearing method shown in FIG. 12 and is used at a work site. As in the first usage method shown in FIG. 3, the physical condition management program of the present invention operates on the target person
In addition, the 1st utilization method which utilizes a biological condition detection apparatus and a subject person's terminal device 1: 1 is the physical condition management system 1 (FIG. 1 (A)) of 1st Embodiment, 2nd implementation. Physical condition management system 1 (FIG. 1B), physical
●[体調管理システムを作業現場に適用した第2の利用方法の他の例(図14)]
図14に示す第2の利用方法(生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置が多対1の利用方法)の他の例は、図11(D)に示す第2の実施の形態の他の例の体調管理システム1Dを、図12に示す第4の装着方法にて対象者に装着して、作業現場で利用する例を示している。なお、生体状態端末装置10Dの構成については、上述したとおりであり、生体状態検出装置10Dと対象者端末装置20間の通信は無線通信により行う。そして、図4に示す第2の利用方法と同様に、本発明の体調管理プログラムが対象者端末装置20上で動作することにより、各対象者の体調が対象者端末装置20上で把握されている。また、対象者端末装置20上で対象者に体調異変が発生したことを把握したときは、対象者に対して注意喚起が行われると共に、必要に応じて別の場所に居る管理者の管理者用パソコン30に電子メール等により体調異変者が発見されたことが通報される。当該管理者は、通報された電子メール等を確認して体調異変者に休息を取らせて体調を回復させ、作業事故を未然に防止することができる。また、当該管理者は、体調異変者が発生した作業現場の衛生環境について問題が発生しそうな場合は、必要に応じて作業現場に注意喚起を行うことができる。
なお、生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置とを多対1で利用する第2の利用方法は、生体状態検出装置と対象者端末装置との間の通信が無線通信である、第1の実施の形態の体調管理システム1(図1(A))、第2の実施の形態の体調管理システム1(図1(B))、第2の実施の形態の他の例の体調管理システム1D(図11(D))にて利用することができる。● [Another example of the second usage method applying the physical condition management system to the work site (FIG. 14)]
Another example of the second usage method shown in FIG. 14 (a method in which the biological state detection device and the target person's terminal device are many-to-one) is another example of the second embodiment shown in FIG. The physical condition management system 1D is attached to the subject by the fourth wearing method shown in FIG. 12, and is used at the work site. The configuration of the biological state terminal device 10D is as described above, and communication between the biological state detection device 10D and the subject
In addition, the 2nd utilization method using a biological condition detection apparatus and a subject person terminal device in many-to-one is 1st implementation whose communication between a biological condition detection apparatus and a subject person terminal device is wireless communication. Physical condition management system 1 (FIG. 1 (A)) of the form of the second embodiment, physical condition management system 1 (FIG. 1 (B)) of the second embodiment, physical condition management system 1D of another example of the second embodiment ( It can be used in FIG.
なお、本実施の形態の説明では、検出する生体状態として、心拍状態、脈拍状態、体温状態、体の傾倒状態、または心電位状態を検出する例を説明したが、これらのうち少なくとも1つを検出すればよく、また、他の生体情報データ(例えば、1分間の呼吸回数や心音等)を検出しても良い。 In the description of the present embodiment, an example in which a heartbeat state, a pulse state, a body temperature state, a body tilt state, or an electrocardiographic state is detected as a biological state to be detected is described. At least one of these is detected. What is necessary is just to detect, and other biometric information data (For example, the number of breathing per minute, a heart sound, etc.) may be detected.
本発明の体調管理プログラム及び体調管理システムは、本実施の形態で説明した外観、構成、処理、表示例等に限定されず、本発明の要旨を変更しない範囲で種々の変更、追加、削除が可能である。例えば対象者としての車両等を運転中の運転者の心拍数や体の傾倒状態から居眠り運転を検知して注意喚起を行うことも可能である。
また、GPSユニットは対象者端末装置20でなく生体状態検出装置10、10A、10B、10C、10Dに備えていてもよい。
また、スマートフォン、タブレット型コンピュータ、ウェアラブル端末(眼鏡タイプ、腕時計タイプ等、身につけることができる端末)、ノート型コンピュータの少なくとも1つに体調管理プログラムを搭載した対象者端末装置20と、生体状態検出装置10、10A、10B、10C、10Dと、を備えた体調管理システムとして構成することもできる。
また、対象者の体の傾倒状態とは、鉛直方向に対する対象者の体の傾斜状態や、対象者の活動状態(体が動いているか否か)を含む。
また、以上(≧)、以下(≦)、より大きい(>)、未満(<)等は、等号を含んでも含まなくても良い。
また、本実施の形態の説明に用いた数値は一例であり、この数値に限定されるものではない。The physical condition management program and physical condition management system of the present invention are not limited to the appearance, configuration, processing, display examples, etc. described in the present embodiment, and various changes, additions, and deletions can be made without changing the gist of the present invention. Is possible. For example, it is also possible to alert the driver by detecting a drowsy driving from the heart rate of the driver who is driving the vehicle or the like as the subject or the tilted state of the body.
Further, the GPS unit may be provided not in the subject
In addition, a subject
The tilted state of the subject's body includes the tilted state of the subject's body relative to the vertical direction and the subject's activity state (whether or not the body is moving).
Further, the above (≧), the following (≦), the larger (>), the less (<), etc. may or may not include an equal sign.
The numerical values used in the description of the present embodiment are examples, and are not limited to these numerical values.
例えば本発明の体調管理プログラム及び体調管理システムは、例えば体温や心拍数や心音等の異常から判定できる工事現場における作業者の熱中症等の体調管理だけでなく、乗り物の運転者の居眠り運転検知や、地下の作業者の体調管理に適用することも可能である。
また、対象者にはヒト以外の生物、例えば牛、馬、羊、豚等の家畜や、犬、猫、等のペットを含み、本発明は、これらの生物の体調管理に適用することもできる。For example, the physical condition management program and the physical condition management system of the present invention can detect not only the physical condition management such as heat stroke of the worker at the construction site, which can be determined from abnormalities such as body temperature, heart rate, heart sound, etc. It can also be applied to the physical condition management of underground workers.
In addition, the subjects include non-human organisms, for example, domestic animals such as cows, horses, sheep, and pigs, and pets such as dogs, cats, etc., and the present invention can also be applied to the physical condition management of these organisms. .
1、1A、1B、1C、1D 体調管理システム
10、10A、10B、10C、10D 生体状態検出装置(生体情報センサユニット)
20 対象者端末装置
30 管理者用パソコン
101、101A、101C、101D CPU
111、111A 送信回路
112 受信回路
113 アンテナ
121 心拍検出用センサ
122 脈拍検出用センサ
123 体温検出用センサ
124 加速度センサ
125 心電位状態検出用センサ
126 心音検出用センサ
131〜133、134、135、136 検出部
201 生体情報データ
1, 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D Physical
20
111,
Claims (6)
Translated fromJapaneseそれぞれの前記生体状態検出装置毎に用意された前記対象者端末装置、あるいは複数の前記生体状態検出装置に対応させて用意された前記対象者端末装置と、を備えた体調管理システムにおける前記対象者端末装置を、
前記生体状態検出装置から送信された前記生体状態検出情報を受信する受信手段、
受信した前記生体状態検出情報を、当該生体状態検出情報に対応する対象者の体調として認識可能とする生体情報データに変換するデータ変換手段、
変換した前記生体情報データが所定の体調異変状態となった前記生体状態検出情報に対応する対象者である体調異変者を抽出する体調異変者抽出手段、
体調異変者が抽出されたことを報知する注意喚起手段、として機能させるための、
体調管理プログラム。A biological state detection device that is attached to each of one or more subjects, detects a biological state of the attached subjects, and transmits biological state detection information related to the detected biological state to the subject terminal device;
The subject person in a physical condition management system comprising: the subject person terminal device prepared for each of the biological state detection devices; or the subject person terminal device prepared corresponding to a plurality of the biological state detection devices. Terminal device
Receiving means for receiving the biological state detection information transmitted from the biological state detection device;
Data conversion means for converting the received biological state detection information into biological information data that can be recognized as the physical condition of the subject corresponding to the biological state detection information;
A physical condition anomaly extraction means for extracting a physical condition anomaly who is a subject corresponding to the biological condition detection information in which the converted biological information data is in a predetermined physical anomaly state;
In order to function as an alerting means for notifying that an abnormal person has been extracted,
Physical condition management program.
前記対象者端末装置を、
前記体調異変者抽出手段にて体調異変者が抽出された場合、体調異変者が発見されたことを含む体調異変者発見情報を、予め設定された送信先に向けて送信する通報手段、として機能させるための、
体調管理プログラム。The physical condition management program according to claim 1,
The target terminal device
When the physical condition abnormal person is extracted by the physical condition abnormal person extraction means, it functions as a reporting means for transmitting physical condition abnormal person discovery information including that the physical condition abnormal person has been discovered to a preset destination To make
Physical condition management program.
前記対象者端末装置は、少なくとも過去の所定期間の前記生体情報データをそれぞれの対象者に対応させて記憶しており、
前記体調異変者抽出手段における前記所定の体調異変状態の判定を、前記所定期間におけるそれぞれの対象者に対応する過去の前記生体情報データに基づいて算出した対象者毎の閾値あるいは予め入力された対象者毎の閾値と、前記データ変換手段にて変換した前記生体情報データと、に基づいて行う、
体調管理プログラム。The physical condition management program according to claim 1 or 2,
The target person terminal device stores at least the biological information data of a predetermined period in the past corresponding to each target person,
A threshold for each subject calculated based on the past biological information data corresponding to each subject in the predetermined period, or a pre-input subject, for the determination of the prescribed state of strangeness in the physical condition anomaly extracting means Based on a threshold for each person and the biological information data converted by the data conversion means,
Physical condition management program.
前記生体状態検出装置は、装着された対象者の心拍状態、脈拍状態、体温状態、体の傾倒状態、心電位状態、の少なくとも1つを検出可能である、
体調管理プログラム。The physical condition management program according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The biological state detection device is capable of detecting at least one of a heartbeat state, a pulse state, a body temperature state, a body tilted state, and an electrocardiographic state of a wearing subject.
Physical condition management program.
前記生体状態検出装置と、を備えた、
体調管理システム。The target person terminal device that is at least one of a smartphone, a tablet computer, a wearable terminal, and a notebook computer and is equipped with the physical condition management program according to any one of claims 1 to 4,
The biological state detection device,
Physical condition management system.
前記生体状態検出装置毎に前記対象者端末装置が用意されており、
前記生体状態検出装置と前記対象者端末装置は有線にて接続され、
前記生体状態検出装置は変調手段を有し、
前記対象者端末装置は音声入力端子と復調手段を有し、
前記生体状態検出装置は生体状態検出情報を前記変調手段で変調した変調信号を前記有線を介して前記対象者端末装置へ出力し、
前記対象者端末装置は前記有線を介して前記音声入力端子から入力された変調信号を前記復調手段にて復調することで前記生体状態検出情報を受信する、
体調管理システム。
The physical condition management system according to claim 5,
The subject terminal device is prepared for each biological state detection device,
The biological state detection device and the subject terminal device are connected by wire,
The biological state detection device has a modulation means,
The target person terminal device has a voice input terminal and a demodulating means,
The biological state detection device outputs a modulation signal obtained by modulating biological state detection information by the modulation means to the subject terminal device via the wire,
The subject terminal device receives the biological state detection information by demodulating a modulation signal input from the voice input terminal via the wire with the demodulation means,
Physical condition management system.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014251408AJP2015154920A (en) | 2014-01-20 | 2014-12-12 | Body condition management program and body condition management system |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014007502 | 2014-01-20 | ||
| JP2014007502 | 2014-01-20 | ||
| JP2014251408AJP2015154920A (en) | 2014-01-20 | 2014-12-12 | Body condition management program and body condition management system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015154920Atrue JP2015154920A (en) | 2015-08-27 |
Family
ID=54774644
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014251408APendingJP2015154920A (en) | 2014-01-20 | 2014-12-12 | Body condition management program and body condition management system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2015154920A (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106504469A (en)* | 2016-10-27 | 2017-03-15 | 广东小天才科技有限公司 | Heatstroke reminding method and device and mobile terminal |
| JP2017131256A (en)* | 2016-01-25 | 2017-08-03 | 日本Did株式会社 | Digital signage system |
| JP2017533794A (en)* | 2014-10-17 | 2017-11-16 | ガードハット インコーポレイテッド | State-responsive indicating assembly and method |
| JP2019033832A (en)* | 2017-08-10 | 2019-03-07 | スターライト工業株式会社 | Mobile information terminal, holding member for the same, and user management system comprising the same |
| WO2019078308A1 (en)* | 2017-10-18 | 2019-04-25 | 学校法人東京理科大学 | Head-mounted device, heat stroke prevention system, and rehydration alarm system |
| JP2021090518A (en)* | 2019-12-09 | 2021-06-17 | 株式会社辰巳菱機 | Notification apparatus |
| JP2021122581A (en)* | 2020-02-06 | 2021-08-30 | 国立大学法人大阪大学 | Biometric information processing method and biometric information processing system |
| JP2022112060A (en)* | 2021-01-21 | 2022-08-02 | 日立建機株式会社 | Construction site management system |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010218126A (en)* | 2009-03-16 | 2010-09-30 | Toshiba Mitsubishi-Electric Industrial System Corp | Wearable sensor and behavior analyzing/monitoring device including the same |
| JP2010279498A (en)* | 2009-06-03 | 2010-12-16 | Kddi Corp | Sensor device, system and conversion device for outputting measurement signal as audio signal |
| JP2013022217A (en)* | 2011-07-21 | 2013-02-04 | Hitachi Engineering & Services Co Ltd | Heat illness detection system |
- 2014
- 2014-12-12JPJP2014251408Apatent/JP2015154920A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010218126A (en)* | 2009-03-16 | 2010-09-30 | Toshiba Mitsubishi-Electric Industrial System Corp | Wearable sensor and behavior analyzing/monitoring device including the same |
| JP2010279498A (en)* | 2009-06-03 | 2010-12-16 | Kddi Corp | Sensor device, system and conversion device for outputting measurement signal as audio signal |
| JP2013022217A (en)* | 2011-07-21 | 2013-02-04 | Hitachi Engineering & Services Co Ltd | Heat illness detection system |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017533794A (en)* | 2014-10-17 | 2017-11-16 | ガードハット インコーポレイテッド | State-responsive indicating assembly and method |
| JP2017131256A (en)* | 2016-01-25 | 2017-08-03 | 日本Did株式会社 | Digital signage system |
| CN106504469A (en)* | 2016-10-27 | 2017-03-15 | 广东小天才科技有限公司 | Heatstroke reminding method and device and mobile terminal |
| JP2019033832A (en)* | 2017-08-10 | 2019-03-07 | スターライト工業株式会社 | Mobile information terminal, holding member for the same, and user management system comprising the same |
| JP2022179706A (en)* | 2017-08-10 | 2022-12-02 | スターライト工業株式会社 | Portable information terminal and user management system having portable information terminal |
| WO2019078308A1 (en)* | 2017-10-18 | 2019-04-25 | 学校法人東京理科大学 | Head-mounted device, heat stroke prevention system, and rehydration alarm system |
| US11122849B2 (en) | 2017-10-18 | 2021-09-21 | Tokyo University Of Science Foundation | Head-mounted device, heatstroke prevention system, and rehydration alarm system |
| JP2021090518A (en)* | 2019-12-09 | 2021-06-17 | 株式会社辰巳菱機 | Notification apparatus |
| JP7170277B2 (en) | 2019-12-09 | 2022-11-14 | 株式会社辰巳菱機 | Reporting device |
| JP2021122581A (en)* | 2020-02-06 | 2021-08-30 | 国立大学法人大阪大学 | Biometric information processing method and biometric information processing system |
| JP2022112060A (en)* | 2021-01-21 | 2022-08-02 | 日立建機株式会社 | Construction site management system |
| JP7579156B2 (en) | 2021-01-21 | 2024-11-07 | 日立建機株式会社 | Construction site management system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2015154920A (en) | Body condition management program and body condition management system | |
| JP6039453B2 (en) | Medical monitor system | |
| EP3175781B1 (en) | Use of a body area network for monitoring a fall protection harness and the person wearing the same | |
| EP2777493B1 (en) | Methods, systems, and devices for monitoring and displaying medical parameters for a patient | |
| US8081082B2 (en) | Monitoring patterns of motion | |
| KR101638408B1 (en) | Wearable motion sensor device for detecting falls, fall detection system, and fall detection method | |
| KR101584090B1 (en) | Mirror device, wearable device and exercise management system | |
| JP2005253609A (en) | Bioinformation processing system | |
| CN105023392A (en) | Intelligent bracelet with life alarm function and system thereof | |
| EP3079088A1 (en) | User behavior safety monitoring method and device | |
| CN105380593A (en) | Method and system FOR PATIENT ACTIVITY MONITORING, and portable telemetry device | |
| JP2014230207A (en) | Fall-down case report system, and program for fall-down case report system | |
| RU2015155952A (en) | MEDICAL DEVICE ALARM PROCESSING | |
| JP2012230610A (en) | Living body location monitoring device and system | |
| US11172861B2 (en) | Detection devices and monitoring systems including detection devices | |
| CN110660492A (en) | Dynamic physiological parameter monitoring method, system, monitoring equipment and medium | |
| KR20150101892A (en) | Electrocardiography measuring system and the measuring method | |
| JP2019144730A (en) | Watching support system | |
| US20200294638A1 (en) | Mobile information terminal, physiological information management method, and non-transitory computer readable storage medium | |
| JP2014092946A (en) | Personal information disclosure system and personal information disclosure method | |
| JP2014092945A (en) | Physical condition determination system and physical condition determination method | |
| Ohashi et al. | Safe patient transfer system with monitoring of location and vital signs | |
| CN211628375U (en) | Tumble alarm system | |
| JP2015100568A (en) | Biotelemetry system | |
| US20230336947A1 (en) | Data Analysis System, Server Device, Data Analysis Method and Data Analysis Program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20151130 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20151208 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20160419 |