JP2015137938A - Adsorption energy measurement method - Google Patents
Adsorption energy measurement methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2015137938A JP2015137938AJP2014009707AJP2014009707AJP2015137938AJP 2015137938 AJP2015137938 AJP 2015137938AJP 2014009707 AJP2014009707 AJP 2014009707AJP 2014009707 AJP2014009707 AJP 2014009707AJP 2015137938 AJP2015137938 AJP 2015137938A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- capacitance
- parallel plate
- adsorption
- adsorption energy
- plate electrodes
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Investigating Or Analyzing Materials By The Use Of Electric Means (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、新規な吸着エネルギーの測定方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a novel method for measuring adsorption energy.
潤滑油に配合される油性剤は金属表面に吸着して吸着膜を作ることで、境界潤滑状態にある金属間の直接接触を妨げて摩擦、摩耗を減少させる働きをする。
油性剤としては、例えば高級脂肪酸、高級アルコール、アミン、エステル、金属せっけん等の各種分子の中から金属表面に対して最適な吸着力を有するものが選択して使用される。The oil-based agent blended in the lubricating oil is adsorbed on the metal surface to form an adsorbed film, thereby preventing direct contact between metals in the boundary lubrication state and reducing friction and wear.
As the oily agent, for example, those having an optimum adsorptive power to the metal surface are selected from various molecules such as higher fatty acids, higher alcohols, amines, esters, and metal soaps.
そのため油性剤として適した新規物質を開発したり、あるいは既知の油性剤の性能を評価したりするためにはその吸着エネルギーを把握することが肝要である。
従来、油性剤等の分子の吸着エネルギーを求めるためには下記の方法が採用されてきた。
ます吸着エネルギーを求めたい分子を溶剤に溶解して特定の濃度Cを有する溶液を調製する。Therefore, it is important to grasp the adsorption energy in order to develop a new substance suitable as an oily agent or to evaluate the performance of a known oily agent.
Conventionally, the following method has been employed to determine the adsorption energy of molecules such as oily agents.
First, a molecule having a specific concentration C is prepared by dissolving a molecule for which adsorption energy is desired in a solvent.
次いでこの溶液に、吸着対象としての金属片を浸漬したのち引き上げて単分子膜が形成されたか否かを判定する。すなわち分子が吸着して単分子膜が形成されると引き上げた金属片の表面は溶液をはじくのに対し、単分子膜が形成されていない場合には溶液に濡れることから、引き上げた金属片の表面の濡れの状態を目視によって確認することで、単分子膜の形成の有無を判定できる。 Next, a metal piece as an object to be adsorbed is immersed in this solution and then pulled up to determine whether a monomolecular film has been formed. In other words, when the molecule is adsorbed and the monomolecular film is formed, the surface of the metal piece pulled up repels the solution, whereas when the monomolecular film is not formed, the surface of the metal piece is lifted. The presence or absence of monomolecular film formation can be determined by visually confirming the wet state of the surface.
そこで上記の操作を、溶液の温度を少しずつ上昇させながら繰り返し実施して金属片が溶液に濡れ始める温度を臨界温度TWとして求める。そして式(1): Therefore, the above operation is repeated while increasing the temperature of the solution little by little, and the temperature at which the metal piece begins to get wet with the solution is determined as the critical temperature TW. And equation (1):
〔式中、Rは気体定数、Cは溶液の濃度、TWは臨界温度を示す。〕
によってその分子の吸着エネルギーUを求めることができる。
ところが上記の方法では、分子と固体(金属片)の吸着が可逆的に脱着を繰り返す物理吸着であることを前提として吸着エネルギーを求めており、不可逆的な化学吸着の吸着エネルギーを求めることはできない。[Wherein R is a gas constant, C is the concentration of the solution, and TW is the critical temperature. ]
Thus, the adsorption energy U of the molecule can be obtained.
However, in the above method, the adsorption energy is obtained on the assumption that the adsorption of the molecule and the solid (metal piece) is reversibly repeated, and the adsorption energy of irreversible chemical adsorption cannot be obtained. .
また浸漬→引き上げ→判定の操作を繰り返す必要があることから測定に時間と労力を有する上、目視による判定を含むことから測定者による誤差等を生じやすく結果がばらつきやすいという問題もある。
化学吸着、物理吸着を問わず分子の吸着エネルギーを簡単かつ正確に求めることができる測定方法は確立されていないのが現状である。In addition, since it is necessary to repeat the operation of dipping → pickup → determination, there are problems that time and labor are required for measurement, and that determination by visual observation is included, so that an error or the like is likely to occur by a measurer and results are likely to vary.
At present, no measurement method has been established that can easily and accurately determine the adsorption energy of molecules regardless of chemical adsorption or physical adsorption.
例えば特許文献1には、振動子上に一対の電極を設けた上に感応膜を被覆し、検出したい分子を当該感応膜に吸着させた際の振動子の振動数の変化、および電極間の抵抗または導電率の変化からその分子の濃度等を求めるセンサと、それを用いた物質検出方法が開示されている。
しかしかかるセンサおよび方法は、感応膜として二酸化チタン粒子の凝集体からなる多孔質膜を使用しているなど、ガス中のガス分子の検出に特化されている。そのため油性剤等として機能する分子の、溶液(潤滑剤の再現)中での金属表面への吸着の際の吸着エネルギーの測定に、上記のセンサと方法を適用することは困難である。For example, Patent Document 1 discloses a change in vibration frequency of a vibrator when a pair of electrodes is provided on a vibrator, a sensitive film is coated, and a molecule to be detected is adsorbed on the sensitive film, and between the electrodes. A sensor for obtaining the concentration of a molecule from a change in resistance or conductivity and a substance detection method using the sensor are disclosed.
However, such sensors and methods are specialized in the detection of gas molecules in a gas, such as using a porous membrane made of aggregates of titanium dioxide particles as a sensitive membrane. Therefore, it is difficult to apply the above-described sensor and method to the measurement of adsorption energy at the time of adsorption of a molecule functioning as an oily agent or the like on a metal surface in a solution (reproduction of a lubricant).
本発明の目的は、化学吸着、物理吸着を問わず分子の吸着エネルギーを簡単かつ正確に求めるための新規な吸着エネルギー測定方法を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a novel adsorption energy measuring method for easily and accurately obtaining the adsorption energy of molecules regardless of chemical adsorption or physical adsorption.
上記課題を解決するため、本発明は吸着エネルギーを求めたい分子を溶剤に溶解して溶液を調製する第一工程、
調製した溶液を2枚の平行平板電極間に満たして、当該平行平板電極の表面に溶液中の分子を吸着させる第二工程、および
第二工程で分子を吸着させる前後の平行平板電極間の静電容量を、当該平行平板電極間の距離を200μm以下に設定した状態で測定して、当該静電容量の変化から分子の吸着エネルギーを求める第三工程
を含むことを特徴とする吸着エネルギー測定方法(請求項1)である。In order to solve the above problems, the present invention is a first step of preparing a solution by dissolving a molecule for which adsorption energy is desired in a solvent,
Fill the prepared solution between two parallel plate electrodes and adsorb molecules in the solution on the surface of the parallel plate electrode, and static between the parallel plate electrodes before and after adsorbing molecules in the second step An adsorption energy measurement method comprising a third step of measuring the electric capacity in a state where the distance between the parallel plate electrodes is set to 200 μm or less and obtaining the adsorption energy of the molecule from the change in the capacitance. (Claim 1).
上記第三工程では、平行平板電極間の距離を50μm以上に設定して静電容量を測定するのが好ましい(請求項2)。
また上記第三工程では、周波数10MHz以下の電圧を平行平板電極間に印加して静電容量を測定するのが好ましい(請求項3)。
さらに上記第三工程では、溶剤を除去した乾燥状態で静電容量を測定するのが好ましい(請求項4)。In the third step, it is preferable to measure the capacitance by setting the distance between the parallel plate electrodes to 50 μm or more.
In the third step, it is preferable to measure a capacitance by applying a voltage having a frequency of 10 MHz or less between the parallel plate electrodes.
Further, in the third step, it is preferable to measure the capacitance in a dry state from which the solvent is removed.
請求項1記載の発明においては、吸着エネルギーを求めたい分子の溶液を2枚の平行平板電極間に満たして加熱等することで、当該平行平板電極の互いに対向する表面に、溶液中に含まれる分子を化学吸着もしくは物理吸着させて分子膜を形成すると、かかる表面の表面エネルギーが変化するとともに電気的特性も変化する。
そこでこの電気的特性の変化を、2枚の平行平板電極間の静電容量の変化として定量的に測定すると化学吸着、物理吸着を問わず分子の吸着エネルギーを簡単かつ正確に求めることが可能となる。In the first aspect of the present invention, a solution of a molecule for which adsorption energy is to be obtained is filled between two parallel plate electrodes and heated, so that they are contained in the solution on the surfaces of the parallel plate electrodes facing each other. When a molecular film is formed by chemical adsorption or physical adsorption of molecules, the surface energy of the surface changes and the electrical characteristics also change.
Therefore, if this change in electrical characteristics is quantitatively measured as the change in capacitance between two parallel plate electrodes, it is possible to easily and accurately determine the adsorption energy of molecules regardless of chemical adsorption or physical adsorption. Become.
すなわち測定した静電容量Cから、下記式(2)(3)によって、目的とする分子の吸着エネルギーEaを求めることができる。 That is, from the measured capacitance C, the adsorption energy Ea of the target molecule can be obtained by the following formulas (2) and (3).
〔式中、fは静電容量の測定時に平行平板電極間に印加する電圧の周波数[MHz]、Cは静電容量[F]を示す。〕[In the formula, f represents the frequency [MHz] of the voltage applied between the parallel plate electrodes when measuring the capacitance, and C represents the capacitance [F]. ]
〔式中、Vは静電容量Cの測定時に平行平板電極間に印加する電圧[V]、Z(吸着)は分子を吸着させた状態での式(2)の結果、Z(未吸着)は吸着させる前の式(2)の結果、tは測定時間[秒]、Sは平行平板電極の表面積[mm2]、aは分子1モルの占める面積[mm2]を示す。〕
なお第三工程で、平行平板電極間の距離を200μm以下に限定しているのは、当該距離が200μmを超える場合には、分子膜形成による静電容量Cの変化を検出できないためである。[Where V is the voltage [V] applied between the parallel plate electrodes when measuring the capacitance C, and Z (adsorption) is the result of equation (2) with molecules adsorbed, Z (unadsorbed) Is the measurement time [second], S is the surface area [mm2 ] of the parallel plate electrode, and a is the area [mm2 ] occupied by 1 mol of the molecule. ]
The reason why the distance between the parallel plate electrodes is limited to 200 μm or less in the third step is that when the distance exceeds 200 μm, the change in the capacitance C due to the formation of the molecular film cannot be detected.
また第三工程において平行平板電極間の距離を、上記の範囲でも50μm以上に設定すると、静電容量Cをより正確に精度よく測定できる。
同様に第三工程において平行平板電極間に印加する電圧の周波数fを10MHz以下に設定すると、静電容量Cをより正確に精度よく測定できる。
さらに第三工程において溶剤を除去した乾燥状態にすると、静電容量Cをより正確に精度よく測定できる。Further, when the distance between the parallel plate electrodes in the third step is set to 50 μm or more even in the above range, the capacitance C can be measured more accurately and accurately.
Similarly, when the frequency f of the voltage applied between the parallel plate electrodes in the third step is set to 10 MHz or less, the capacitance C can be measured more accurately and accurately.
Furthermore, when it is made into the dry state which removed the solvent in the 3rd process, the electrostatic capacitance C can be measured more correctly and accurately.
本発明の吸着エネルギー測定方法は、
吸着エネルギーEaを求めたい分子を溶剤に溶解して溶液を調製する第一工程、
調製した溶液を2枚の平行平板電極間に満たして、当該平行平板電極の表面に溶液中の分子を吸着させる第二工程、および
第二工程で分子を吸着させる前後の平行平板電極間の静電容量Cを、当該平行平板電極間の距離dを200μm以下に設定した状態で測定して、当該静電容量Cの変化から分子の吸着エネルギーEaを求める第三工程
を含んでいる。The adsorption energy measuring method of the present invention is
A first step of preparing a solution by dissolving the molecule for which the adsorption energy Ea is desired in a solvent;
Fill the prepared solution between two parallel plate electrodes and adsorb molecules in the solution on the surface of the parallel plate electrode, and static between the parallel plate electrodes before and after adsorbing molecules in the second step A third step is included in which the capacitance C is measured in a state where the distance d between the parallel plate electrodes is set to 200 μm or less, and the molecular adsorption energy Ea is determined from the change in the capacitance C.
上記各工程を含む本発明の測定方法は、先に説明したように潤滑油の油性剤として機能する高級脂肪酸、高級アルコール、アミン、エステル、金属せっけん等の各種分子など、種々の分子の吸着エネルギーEaの測定に適用することができる。
(第一工程)
第一工程で分子を溶解して溶液を調製するための溶剤としては、吸着エネルギーEaを求めたい分子の溶解性に優れた種々の溶剤が使用可能である。As described above, the measurement method of the present invention including each of the steps described above is the adsorption energy of various molecules such as higher fatty acids, higher alcohols, amines, esters, metal soaps and the like that function as lubricants for lubricating oils. It can be applied to the measurement of Ea.
(First step)
As a solvent for preparing a solution by dissolving molecules in the first step, various solvents excellent in the solubility of molecules for which the adsorption energy Ea is desired can be used.
特に分子が油性剤である場合には、潤滑油中での油性剤の吸着挙動を再現することや、吸着時の加熱によって気化しにくいこと等を考慮して分子量がある程度大きい上、第三工程で静電容量Cの測定に先立って容易に乾燥除去するために分子量が一定であることが好ましい。
かかる条件を満足する溶剤としては、これに限定されないが例えばヘキサデカン等の炭素数8以上、20以下のアルカン類などが挙げられる。またアルコール、アセトンなどの揮発性の高い溶剤も使用可能である。In particular, when the molecule is an oily agent, the molecular weight is somewhat large in consideration of reproducing the adsorption behavior of the oily agent in the lubricating oil and being difficult to vaporize by heating during adsorption. Therefore, it is preferable that the molecular weight is constant so that it can be easily removed by drying prior to the measurement of the capacitance C.
Examples of the solvent that satisfies such conditions include, but are not limited to, alkanes having 8 to 20 carbon atoms such as hexadecane. A highly volatile solvent such as alcohol or acetone can also be used.
溶液の濃度は任意に設定できる。ただし静電容量Cをより正確に精度よく測定することを考慮すると、平行平板電極の表面により多くの分子を吸着させるために、例えば室温での分子の最大溶解濃度に設定するのが好ましい。
(第二工程)
2枚の平行平板電極としては、吸着対象である特定表面に対する分子の吸着挙動を再現するために、少なくとも互いに対向する表面が上記特定表面と同じ、または近時の材料からなるものを用いるのが好ましい。The concentration of the solution can be set arbitrarily. However, considering that the capacitance C is measured more accurately and accurately, in order to adsorb more molecules on the surface of the parallel plate electrode, it is preferable to set the maximum dissolved concentration of molecules at room temperature, for example.
(Second step)
As two parallel plate electrodes, in order to reproduce the adsorption behavior of molecules on a specific surface to be adsorbed, at least the surfaces facing each other are made of the same material as the specific surface or made of a recent material. preferable.
平行平板電極の全体を上記吸着対象と同じまたは近時の材料で形成してもよいし、分子を吸着させる表面に上記材料からなるコーティングを形成したものを平行平板電極として用いてもよい。
例えば分子が油性剤であり、軸受鋼等の鋼材に対する吸着エネルギーEaを求める場合には、平行平板電極として、少なくともその表面が鉄系の材料からなるものを用いるのが好ましい。The entire parallel plate electrode may be formed of the same material as the adsorption target or a material close to that of the adsorption target, or a parallel plate electrode in which a coating made of the above material is formed on the surface on which molecules are adsorbed may be used.
For example, when the molecule is an oily agent and the adsorption energy Ea for a steel material such as bearing steel is obtained, it is preferable to use a parallel plate electrode having at least a surface made of an iron-based material.
第二工程では、調製した溶液を平行平板電極間に満たした状態で、例えば加熱等して、溶液中の分子を平行平板電極の表面に吸着させる。
この際、溶液を良好に保持するため2枚の平行平板電極は互いに対向する表面を水平に保持した状態とするのが好ましい。
加熱の温度は任意に設定できる。例えば分子が油性剤である場合には、潤滑油中での油性剤の吸着挙動を再現するために、加熱の温度を当該潤滑油の想定される使用温度付近に設定するのが好ましい。In the second step, in a state where the prepared solution is filled between parallel plate electrodes, for example, heating is performed to adsorb molecules in the solution to the surface of the parallel plate electrodes.
At this time, in order to hold the solution satisfactorily, the two parallel plate electrodes are preferably in a state where the surfaces facing each other are held horizontally.
The heating temperature can be arbitrarily set. For example, when the molecule is an oily agent, in order to reproduce the adsorption behavior of the oily agent in the lubricating oil, it is preferable to set the heating temperature in the vicinity of the expected use temperature of the lubricating oil.
また吸着の時間も任意に設定できる。ただし静電容量Cをより正確に精度よく測定することを考慮すると、平行平板電極の表面に十分な厚みを有する分子膜を形成するために、吸着の時間は1時間以上、特に5時間以上に設定するのが好ましい。また吸着エネルギー測定の効率化を図ることを考慮すると、吸着の時間は12時間以下、特に10時間以下に設定するのが好ましい。 The adsorption time can also be set arbitrarily. However, in consideration of measuring the capacitance C more accurately and accurately, the adsorption time is 1 hour or more, particularly 5 hours or more in order to form a molecular film having a sufficient thickness on the surface of the parallel plate electrode. It is preferable to set. In consideration of increasing the efficiency of adsorption energy measurement, the adsorption time is preferably set to 12 hours or less, particularly 10 hours or less.
上記加熱により、平行平板電極の表面への分子の吸着を促進するとともに、吸着させた分子の配向性を向上できる。
(第三工程)
第三工程では、第二工程で分子を吸着させる前後の平行平板電極間の静電容量Cを、当該平行平板電極間の距離dを200μm以下に設定した状態で測定する。距離dが上記の範囲を超える場合には、平行平板電極間の空気の影響で、分子膜形成による静電容量Cの変化を検出できないためである。The heating can promote the adsorption of molecules to the surface of the parallel plate electrode and improve the orientation of the adsorbed molecules.
(Third process)
In the third step, the capacitance C between the parallel plate electrodes before and after the molecules are adsorbed in the second step is measured in a state where the distance d between the parallel plate electrodes is set to 200 μm or less. This is because when the distance d exceeds the above range, the change in the capacitance C due to the formation of the molecular film cannot be detected due to the influence of air between the parallel plate electrodes.
これに対し距離dを上記の範囲とすることで、分子膜形成による静電容量Cの変化を検出することが可能となる。
なお平行平板電極間の距離dは、上記の範囲でも50μm以上に設定するのが好ましい。距離dがこの範囲未満では、読み取り誤差やごくわずかな平行平板電極の傾斜等の影響よって、静電容量Cを正確に精度よく測定できないおそれがある。On the other hand, by setting the distance d within the above range, it is possible to detect a change in the capacitance C due to the formation of the molecular film.
The distance d between the parallel plate electrodes is preferably set to 50 μm or more even in the above range. If the distance d is less than this range, there is a possibility that the capacitance C cannot be measured accurately and accurately due to the influence of reading errors and a slight inclination of the parallel plate electrode.
これに対し距離dを上記の範囲とすることで、かかる読み取り誤差や傾斜等の影響を排除して、静電容量Cをより正確に精度よく測定できる。
また分子を吸着させる前と後で平行平板電極間の距離dを同じにして静電容量Cを測定するのが、当然ながら静電容量Cの変化を正確に測定する上で好ましい。ただし距離dと静電容量Cとの関係が明確である場合は、分子を吸着させる前と後で距離dを変化させてもよい。On the other hand, by setting the distance d within the above range, it is possible to eliminate the influence of the reading error and the inclination, and to measure the capacitance C more accurately and accurately.
In addition, it is naturally preferable to measure the capacitance C with the same distance d between the parallel plate electrodes before and after adsorbing molecules in order to accurately measure the change in the capacitance C. However, when the relationship between the distance d and the capacitance C is clear, the distance d may be changed before and after the molecules are adsorbed.
また平行平板電極間に印加する電圧の周波数fは10MHz以下に設定するのが好ましい。周波数fがこの範囲を超える電圧を印加した場合には、回路のコイル成分の影響によって、静電容量Cを正確に精度よく測定できないおそれがある。
これに対し印加電圧の周波数fを上記の範囲とすることで、かかるコイル成分の影響を排除して静電容量Cをより正確に精度よく測定できる。上記10MHz以下の全周波数域で測定が可能である。The frequency f of the voltage applied between the parallel plate electrodes is preferably set to 10 MHz or less. When a voltage whose frequency f exceeds this range is applied, there is a possibility that the capacitance C cannot be measured accurately and accurately due to the influence of the coil component of the circuit.
On the other hand, by setting the frequency f of the applied voltage within the above range, the influence of the coil component can be eliminated and the capacitance C can be measured more accurately and accurately. Measurement is possible in the entire frequency range of 10 MHz or less.
また溶剤の影響を排除して静電容量Cをより正確に精度よく測定するためには、溶液を除去するとともに溶剤を乾燥除去した乾燥状態として、当該静電容量Cを測定するのが好ましい。
また、特に第二工程での吸着時に加熱した場合は、形成した分子膜への空気中の水分等の吸着を防止して、当該吸着成分の影響を排除しながら静電容量Cを測定するために、平行平板電極を、溶液の除去から静電容量Cの測定までの間、吸着時と同程度の温度に加熱し続けるのが好ましい。In order to eliminate the influence of the solvent and measure the capacitance C more accurately and accurately, it is preferable to measure the capacitance C in a dry state in which the solution is removed and the solvent is removed by drying.
In particular, when heating is performed at the time of adsorption in the second step, the capacitance C is measured while preventing the adsorption of moisture in the air to the formed molecular film and eliminating the influence of the adsorbed component. In addition, it is preferable that the parallel plate electrode is continuously heated to the same temperature as that during the adsorption from the removal of the solution to the measurement of the capacitance C.
測定後の平行平板電極は、表面に吸着させた分子膜を除去すれば何度でも測定に使用できるため経済的である。
上記の各工程を経る本発明の吸着エネルギー測定方法によれば、平行平板電極に接続した、例えばLCRメータ等の機器によって測定した静電容量Cから吸着エネルギーEaを求めることができる。そのため、測定者による誤差等を生じることなく常に正確な吸着エネルギーEaを求めることができる。また従来法のように測定を繰り返す必要がなく、短時間で効率よく吸着エネルギーEaを求めることができる。The parallel plate electrode after measurement is economical because it can be used for measurement any number of times as long as the molecular film adsorbed on the surface is removed.
According to the adsorption energy measuring method of the present invention through the above steps, the adsorption energy Ea can be obtained from the capacitance C measured by a device such as an LCR meter connected to the parallel plate electrode. Therefore, the accurate adsorption energy Ea can always be obtained without causing an error or the like by the measurer. Further, it is not necessary to repeat the measurement as in the conventional method, and the adsorption energy Ea can be obtained efficiently in a short time.
〈平行平板電極間の距離検討I〉
(第一工程)
分子のサンプルとしてのステアリン酸を、溶剤としてのヘキサデカンに溶解して溶液を調製した。濃度は室温でのステアリン酸の最大溶解濃度に設定した。
(平行平板電極)
平行平板電極としては、互いに対向する表面が鉄系材料からなるアジレント・テクノロジー(株)製の誘電体測定用電極(φ=38mm)を用意した。<Distance study between parallel plate electrodes I>
(First step)
A solution was prepared by dissolving stearic acid as a molecular sample in hexadecane as a solvent. The concentration was set to the maximum dissolution concentration of stearic acid at room temperature.
(Parallel plate electrode)
As the parallel plate electrodes, dielectric measurement electrodes (φ = 38 mm) manufactured by Agilent Technologies, whose surfaces facing each other were made of an iron-based material were prepared.
(第二工程)
上記平行平板電極の互いに対向する表面を水平に保持した状態で、当該平行平板電極間に先の溶液を満たし、50℃に設定した恒温槽中で8時間加熱して、当該溶液中のステアリン酸を平行平板電極の表面に吸着させた。
(第三工程)
平行平板電極間の溶液を除去し、さらに溶剤を乾燥除去して乾燥状態としたのち、平行平板電極間の距離dを100μmから1000μmまで増加させながら、印可電圧の周波数fを5MHzに設定して静電容量Cを測定した。(Second step)
In a state where the surfaces of the parallel plate electrodes facing each other are held horizontally, the above solution is filled between the parallel plate electrodes and heated in a thermostatic bath set at 50 ° C. for 8 hours to obtain stearic acid in the solution. Was adsorbed on the surface of the parallel plate electrode.
(Third process)
After removing the solution between the parallel plate electrodes and further removing the solvent by drying, the frequency d of the applied voltage was set to 5 MHz while increasing the distance d between the parallel plate electrodes from 100 μm to 1000 μm. The capacitance C was measured.
平行平板電極の温度は、溶液の除去から静電容量Cの測定までの間50℃に維持した。
そしてそれぞれの測定結果と、ステアリン酸を吸着させる前の未吸着状態の同じ距離dでの静電容量Cの測定値との差を、当該静電容量Cの変化量ΔCとして、各距離dごとに算出した。結果を図1に示す。
(評価)
図1より、距離dが200μmを超える場合にはステアリン酸を吸着させる前後での静電容量Cの変化量ΔCがほぼ0に近くなってしまっていることから、平行平板電極間の空気の影響で、分子膜形成による静電容量Cの変化を検出できないことが判った。The temperature of the parallel plate electrode was maintained at 50 ° C. from the removal of the solution to the measurement of the capacitance C.
The difference between each measurement result and the measured value of the capacitance C at the same distance d in the non-adsorbed state before the stearic acid is adsorbed is defined as the change amount ΔC of the capacitance C for each distance d. Calculated. The results are shown in FIG.
(Evaluation)
As shown in FIG. 1, when the distance d exceeds 200 μm, the change amount ΔC of the capacitance C before and after the stearic acid is adsorbed is almost zero. Thus, it was found that the change in the capacitance C due to the formation of the molecular film could not be detected.
これに対し距離dを200μm以下とすることで上記空気の影響を排除し、ステアリン酸を吸着させる前後での静電容量Cの変化量ΔCを大きくとって、分子膜形成による静電容量Cの変化を良好に検出できることが判った。
〈平行平板電極間の距離検討II〉
上記検討Iと同様にして互いに対向する未吸着状態の平行平板電極間の距離dを300μmから10μmまで減少させながら、印可電圧の周波数fを5MHzに設定して静電容量Cを測定した。On the other hand, by setting the distance d to 200 μm or less, the influence of the air is eliminated, and the change amount ΔC of the capacitance C before and after the stearic acid is adsorbed is increased so that the capacitance C due to the formation of the molecular film is reduced. It was found that the change can be detected well.
<Examination of distance between parallel plate electrodes II>
The capacitance C was measured by setting the frequency f of the applied voltage to 5 MHz while reducing the distance d between the non-adsorbed parallel plate electrodes facing each other from 300 μm to 10 μm in the same manner as in Study I above.
平行平板電極の温度は50℃に維持した。
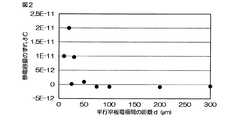
そしてそれぞれの測定結果と、空気中の静電容量Cの理論値との差を測定値のずれδCとして、各距離dごとに算出した。結果を図2に示す。
図2より、距離dが50μm未満では理論値とのずれδCのばらつきが大きいことから、読み取り誤差やごくわずかな平行平板電極の傾斜等の影響によって静電容量Cを正確に精度よく測定できない傾向があることが判った。The temperature of the parallel plate electrode was maintained at 50 ° C.
The difference between each measurement result and the theoretical value of the capacitance C in the air was calculated for each distance d as a measurement value deviation δC. The results are shown in FIG.
As shown in FIG. 2, when the distance d is less than 50 μm, the deviation δC from the theoretical value is large. Therefore, the capacitance C tends not to be measured accurately and accurately due to the influence of reading error and a slight inclination of the parallel plate electrode. It turns out that there is.
これに対し距離dを50μm以上とすると理論値とのずれδCをほぼ0にでき、上記読み取り誤差や傾斜等の影響を排除して静電容量Cをできるだけ正確に精度よく測定できることが判った。
〈印加電圧の周波数検討〉
上記検討Iと同様にして互いに対向する未吸着状態の平行平板電極間の距離dを100μmに設定して、印可電圧の周波数fを100kHzから30MHzまで増加させながら静電容量Cを測定した。On the other hand, it was found that when the distance d is 50 μm or more, the deviation δC from the theoretical value can be made substantially zero, and the capacitance C can be measured as accurately and accurately as possible without the influence of the reading error and inclination.
<Examination of applied voltage frequency>
The capacitance C was measured while increasing the applied voltage frequency f from 100 kHz to 30 MHz by setting the distance d between the non-adsorbed parallel plate electrodes facing each other to 100 μm in the same manner as in Study I above.
平行平板電極の温度は50℃に維持した。
そしてそれぞれの測定結果を図3に示した。なお図3中の太線は、空気中の静電容量Cの理論値を示している。
図3より、印加電圧の周波数が10MHzを超える場合には理論値とのずれが大きいことから、回路のコイル成分の影響によって、静電容量Cを正確に精度よく測定できない傾向があることが判った。The temperature of the parallel plate electrode was maintained at 50 ° C.
The measurement results are shown in FIG. In addition, the thick line in FIG. 3 has shown the theoretical value of the electrostatic capacitance C in the air.
From FIG. 3, it can be seen that when the frequency of the applied voltage exceeds 10 MHz, the deviation from the theoretical value is large, so that the capacitance C tends to be measured accurately and accurately due to the influence of the coil component of the circuit. It was.
これに対し周波数を10MHz以下とすることで理論値とのずれをほぼ0にでき、上記コイル成分の影響を排除して静電容量Cをできるだけ正確に精度よく測定できることが判った。
〈測定結果の再現性検討〉
上記検討Iと同様にして互いに対向する表面にステアリン酸を吸着させた平行平板電極間の距離dを100μmに設定し、印可電圧の周波数fを5MHzに設定して静電容量Cを測定した。On the other hand, it was found that by setting the frequency to 10 MHz or less, the deviation from the theoretical value can be almost zero, and the influence of the coil component can be eliminated and the capacitance C can be measured as accurately and accurately as possible.
<Examination of reproducibility of measurement results>
In the same manner as in Study I above, the capacitance d was measured by setting the distance d between parallel plate electrodes having stearic acid adsorbed on the surfaces facing each other to 100 μm and the frequency f of the applied voltage to 5 MHz.
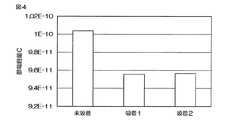
かかるステアリン酸の吸着から静電容量Cの測定までの各工程を2回実施した(吸着1、吸着2)。測定結果を、ステアリン酸を吸着させる前の状態の同じ距離dでの静電容量Cの測定結果(未吸着)と併せて図4に示す。
図4より、本発明によればステアリン酸等の分子の静電容量Cを再現性良く測定でき、吸着エネルギーEaを精度よく求められることが判った。Each process from the adsorption of stearic acid to the measurement of the capacitance C was performed twice (Adsorption 1, Adsorption 2). The measurement result is shown in FIG. 4 together with the measurement result (non-adsorption) of the capacitance C at the same distance d in the state before the stearic acid is adsorbed.
FIG. 4 shows that according to the present invention, the electrostatic capacity C of molecules such as stearic acid can be measured with good reproducibility, and the adsorption energy Ea can be obtained with high accuracy.
Claims (4)
Translated fromJapanese調製した溶液を2枚の平行平板電極間に満たして、当該平行平板電極の表面に溶液中の分子を吸着させる第二工程、および
第二工程で分子を吸着させる前後の平行平板電極間の静電容量を、当該平行平板電極間の距離を200μm以下に設定した状態で測定して、当該静電容量の変化から分子の吸着エネルギーを求める第三工程
を含むことを特徴とする吸着エネルギー測定方法。The first step of preparing a solution by dissolving the molecule for which adsorption energy is desired in a solvent,
Fill the prepared solution between two parallel plate electrodes and adsorb molecules in the solution on the surface of the parallel plate electrode, and static between the parallel plate electrodes before and after adsorbing molecules in the second step An adsorption energy measurement method comprising a third step of measuring the electric capacity in a state where the distance between the parallel plate electrodes is set to 200 μm or less and obtaining the adsorption energy of the molecule from the change in the capacitance. .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014009707AJP2015137938A (en) | 2014-01-22 | 2014-01-22 | Adsorption energy measurement method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014009707AJP2015137938A (en) | 2014-01-22 | 2014-01-22 | Adsorption energy measurement method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015137938Atrue JP2015137938A (en) | 2015-07-30 |
Family
ID=53769026
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014009707APendingJP2015137938A (en) | 2014-01-22 | 2014-01-22 | Adsorption energy measurement method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2015137938A (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5245996A (en)* | 1975-10-06 | 1977-04-12 | Kabi Ab | Inspection method of biochemical reaction |
| JP2000509507A (en)* | 1997-02-06 | 2000-07-25 | イー.ヘラー アンド カンパニー | Small volume in vitro analyte sensor |
| JP2001033412A (en)* | 1999-05-14 | 2001-02-09 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Adsorption amount sensor |
| JP2004298783A (en)* | 2003-03-31 | 2004-10-28 | Kitakyushu Foundation For The Advancement Of Industry Science & Technology | Chemical substance separation membrane, method for producing the same, chemical substance detection method and chemical substance detection device |
| JP2013024648A (en)* | 2011-07-19 | 2013-02-04 | Nippon Dempa Kogyo Co Ltd | Detection device and detection method |
- 2014
- 2014-01-22JPJP2014009707Apatent/JP2015137938A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5245996A (en)* | 1975-10-06 | 1977-04-12 | Kabi Ab | Inspection method of biochemical reaction |
| US4072576A (en)* | 1975-10-06 | 1978-02-07 | Ab Kabi | Method for studying enzymatic and other biochemical reactions |
| JP2000509507A (en)* | 1997-02-06 | 2000-07-25 | イー.ヘラー アンド カンパニー | Small volume in vitro analyte sensor |
| JP2001033412A (en)* | 1999-05-14 | 2001-02-09 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Adsorption amount sensor |
| JP2004298783A (en)* | 2003-03-31 | 2004-10-28 | Kitakyushu Foundation For The Advancement Of Industry Science & Technology | Chemical substance separation membrane, method for producing the same, chemical substance detection method and chemical substance detection device |
| JP2013024648A (en)* | 2011-07-19 | 2013-02-04 | Nippon Dempa Kogyo Co Ltd | Detection device and detection method |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| GULSEN AVCI: "Inhibitor effect of N,N'-methylenediacrylamide on corrosion behavior of mild steel in 0.5 M HCl", MATERIALS CHEMISTRY AND PHYSICS, vol. 112, JPN6017037997, 2008, pages 234 - 238, ISSN: 0003657037* |
| NIKOLAY A. ROGOZHNIKOV ET AL.: "Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption of cyanide ions on silver. Part I", JOURNAL OF ELECTROANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY, vol. 434, JPN6017037999, 1997, pages 19 - 30, ISSN: 0003657038* |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102667461B (en) | Measuring method and measuring device for deterioration and deterioration degree of lubricating oil | |
| Singh et al. | Investigation of the effect of disulfiram on corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution | |
| Khanmohammadi et al. | Ionic liquids as additives in water-based lubricants: from surface adsorption to tribofilm formation | |
| Bhushan et al. | AFM-based nanotribological and electrical characterization of ultrathin wear-resistant ionic liquid films | |
| TWI490490B (en) | A method for measuring deterioration of lubricating oil and a measuring device thereof, and a lubricating oil monitoring system for a machine and a device | |
| JP2005529333A (en) | Working fluid analysis method using impedance spectroscopy | |
| JP2017538128A (en) | Sample composition detection based on thermal properties | |
| Raphael et al. | Corrosion inhibition investigations of 3-acetylpyridine semicarbazone on carbon steel in hydrochloric acid medium | |
| NL1019186C2 (en) | Method for determining the glass transition temperature of a polymer component during use. | |
| JP2007502411A (en) | Deconvolution method of impedance spectrum | |
| WO2019151295A1 (en) | Oil condition determination system, oil condition determination method, and oil condition determination program | |
| Sturdy et al. | Quartz crystal rheometry: A quantitative technique for studying curing and aging in artists' paints | |
| Crespo et al. | Methodology to characterize rheology, surface forces and friction of confined liquids at the molecular scale using the ATLAS apparatus | |
| JP2015137938A (en) | Adsorption energy measurement method | |
| JP6319195B2 (en) | Method of measuring plating thickness of plating material, method of measuring corrosion amount of plating material, and corrosion sensor of plating material | |
| JP6704331B2 (en) | Viscosity measuring device and viscosity measuring method | |
| CN114184596B (en) | Synchronous thermogravimetry-Raman characterization method | |
| Farajpour et al. | Measuring trapped DNA at the liquid-air interface for enhanced single molecule sensing | |
| US6459280B1 (en) | Capacitance devices for film thickness mapping, measurement methods using same | |
| Dittes et al. | Dielectric thermoscopy characterization of water contaminated grease | |
| RU2630545C1 (en) | Appliance for lubricating media boundary layers thickness measurement | |
| Nakano et al. | Breakdown processes of boundary films formed by oiliness additives | |
| JP3577268B2 (en) | Fluid component and property change detection method and detector | |
| CN109374485B (en) | A magnetorheological fluid sedimentation velocity detection device, method and system | |
| Matveevsky et al. | The effect of the nature of friction surfaces and lubricant on the adsorption and temperature stability of lubricant layers |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20161213 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20170928 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20171005 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20180405 |