JP2014522066A - Interoperation of I/O devices with computing hosts - Google Patents
Interoperation of I/O devices with computing hostsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2014522066A JP2014522066AJP2014525104AJP2014525104AJP2014522066AJP 2014522066 AJP2014522066 AJP 2014522066AJP 2014525104 AJP2014525104 AJP 2014525104AJP 2014525104 AJP2014525104 AJP 2014525104AJP 2014522066 AJP2014522066 AJP 2014522066A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- command
- data
- map
- standard
- computing host
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0655—Vertical data movement, i.e. input-output transfer; data movement between one or more hosts and one or more storage devices
- G06F3/0659—Command handling arrangements, e.g. command buffers, queues, command scheduling
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/0604—Improving or facilitating administration, e.g. storage management
- G06F3/0607—Improving or facilitating administration, e.g. storage management by facilitating the process of upgrading existing storage systems, e.g. for improving compatibility between host and storage device
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/061—Improving I/O performance
- G06F3/0611—Improving I/O performance in relation to response time
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0668—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems adopting a particular infrastructure
- G06F3/0671—In-line storage system
- G06F3/0673—Single storage device
- G06F3/0679—Non-volatile semiconductor memory device, e.g. flash memory, one time programmable memory [OTP]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/08—Addressing or allocation; Relocation in hierarchically structured memory systems, e.g. virtual memory systems
- G06F12/10—Address translation
- G06F12/1027—Address translation using associative or pseudo-associative address translation means, e.g. translation look-aside buffer [TLB]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0668—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems adopting a particular infrastructure
- G06F3/067—Distributed or networked storage systems, e.g. storage area networks [SAN], network attached storage [NAS]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Techniques For Improving Reliability Of Storages (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
- Signal Processing For Digital Recording And Reproducing (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese 関連出願の相互参照
本出願の優先権利益の主張を、(それがある場合には、適宜)添付の出願データシート、請求、または送達状において行う。本出願の種類によって許容される範囲内で、本出願はこの参照によりあらゆる目的で以下の出願を組み込むものであり、以下の出願はすべて、発明がなされた時点において本出願と所有者を同じくするものである。 CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS A claim to priority benefit of this application, if any, is made in the attached Application Data Sheet, claim, or transmittal letter, as appropriate. To the extent permitted by the nature of this application, this application incorporates by this reference for all purposes the following applications, all of which are commonly owned with this application at the time the invention was made:
2011年8月9日付で出願された、Earl T.COHENを筆頭発明者とする、「I/O DEVICE AND COMPUTING HOST INTEROPERATION」という名称の、米国仮出願(整理番号第SF−11−15号および出願番号第61/521,739号);2011年9月6日付で出願された、Earl T.COHENを筆頭発明者とする、「I/O DEVICE AND COMPUTING HOST INTEROPERATION」という名称の、米国仮出願(整理番号第SF−11−15A号および出願番号第61/531,551号);および2011年10月5日付で出願された、Earl T.COHENを筆頭発明者とする、「I/O DEVICE AND COMPUTING HOST INTEROPERATION」という名称の、米国仮出願(整理番号第SF−11−15B号および出願番号第61/543,666号)。U.S. Provisional Application No. SF-11-15 and Application No. 61/521,739, filed August 9, 2011, entitled "I/O DEVICE AND COMPUTSING HOST INTEROPERATION," with Earl T. COHEN as lead inventor; U.S. Provisional Application No. SF-11-15A and Application No. 61/531,551, filed September 6, 2011, entitled "I/O DEVICE AND COMPUTSING HOST INTEROPERATION," with Earl T. COHEN as lead inventor; and U.S. Provisional Application No. SF-11-15A and Application No. 61/531,551, filed October 5, 2011, entitled "I/O DEVICE AND COMPUTSING HOST INTEROPERATION," with Earl T. COHEN as lead inventor. U.S. Provisional Application No. SF-11-15B and Application No. 61/543,666, entitled "I/O DEVICE AND COMPUTSING HOST INTEROPERATION," with COHEN as lead inventor.
分野:コンピューティングホストおよび入出力デバイスの技術の進歩が、使用の性能、効率、及び有用性の改善を提供するために必要とされる。Area: Advances in computing host and input/output device technology are needed to provide improved performance, efficiency, and usability of use.
関連技術:公知である、または周知であるものとして明記されない限り、コンテキスト、定義、または比較を目的とするものを含む本明細書における技法および概念の言及は、そのような技法または概念が以前から公知であり、あるいは先行技術の一部であることの容認と解釈すべきではない。特許、特許出願、および出版物を含む、本明細書で引用されるあらゆる参照文献は(それがある場合には)、具体的に組み込まれているか否かを問わず、あらゆる目的で、この参照によりその全体が本明細書に組み込まれるものである。Related Art: Unless expressly stated as known or well known, reference to techniques and concepts herein, including for purposes of context, definition, or comparison, should not be construed as an admission that such techniques or concepts were previously known or part of the prior art. All references cited herein, including patents, patent applications, and publications, if any, are hereby incorporated by this reference in their entirety for all purposes, whether or not specifically incorporated.
本発明は多くの方法で実施されてよく、例えば、プロセス、製造品、装置、システム、組成物、ならびに、コンピュータ可読記憶媒体(ディスクといった光学的大容量記憶装置および/または磁気的大容量記憶装置、フラッシュストレージといった不揮発性記憶を有する集積回路など)や、プログラム命令が光通信リンクまたは電子通信リンク上で送られるコンピュータネットワークといったコンピュータ可読媒体として実施されてよい。詳細な説明では、上記の分野における使用のコスト、収益性、性能、効率、および有用性の改善を可能にする本発明の1つ若しくはそれ以上の実施形態の説明を行う。詳細な説明は、詳細な説明の残りの部分の理解を容易にするための概説を含む。概説は、本明細書で説明する概念に従うシステム、方法、製造品、およびコンピュータ可読媒体の1つ若しくはそれ以上の例示的実施形態を含む。結論の項でより詳細に論じるように、本発明は、発行される特許請求の範囲内のあらゆる可能な改変形態および変形形態を包含するものである。The present invention may be implemented in many ways, for example, as a process, an article of manufacture, an apparatus, a system, a composition of matter, and a computer readable medium, such as an optical mass storage device such as a disk and/or a magnetic mass storage device, an integrated circuit having non-volatile storage such as flash storage, and a computer network in which program instructions are transmitted over optical or electronic communication links. The detailed description provides a description of one or more embodiments of the present invention that enable improvements in cost, profitability, performance, efficiency, and usefulness of use in the above fields. The detailed description includes an overview to facilitate understanding of the remainder of the detailed description. The overview includes one or more exemplary embodiments of systems, methods, articles of manufacture, and computer readable media according to the concepts described herein. As discussed in more detail in the concluding section, the present invention is intended to embrace all possible modifications and variations within the scope of the issued claims.
図面の参照符号の一覧
本発明の1つ若しくはそれ以上の実施形態の詳細な説明を、以下で、本発明の選択された詳細を図示する添付の図を併用して行う。本発明を実施形態との関連で説明する。実施形態は、本明細書では、単なる例示であると理解されるものであり、本発明は、明確に、本明細書中の実施形態のいずれか若しくは全部に、またはいずれか若しくは全部によって限定されるものではなく、本発明は、多数の代替形態、改変形態、および均等物を包含するものである。説明が単調にならないように、様々な言葉によるラベル(これに限定されるものではないが、最初の、最後の、ある一定の、様々な、別の、他の、特定の、選択の、いくつかの、目立ったなど)が実施形態のセットを区別するために適用される場合がある。本明細書で使用する場合、そのようなラベルは、明確に、質を伝えるためのものでも、いかなる形の好みや先入観を伝えるためのものでもなく、単に、別々のセットを都合よく区別するためのものにすぎない。開示するプロセスのいくつかの動作の順序は本発明の範囲内で変更可能である。多様な実施形態がプロセス、方法、および/またはプログラム命令の各特徴の差異を説明するのに使用される場合は常に、所定の、または動的に決定される基準に従って、複数の多様な実施形態にそれぞれ対応する複数の動作モードの1つの静的選択および/または動的選択を行う他の実施形態が企図されている。以下の説明では、本発明の十分な理解を提供するために、多数の具体的詳細を示す。それらの詳細は例として示すものであり、本発明は、それらの詳細の一部または全部がなくても、特許請求の範囲に従って実施されうる。わかりやすくするために、本発明に関連した技術分野で公知の技術資料は、本発明が不必要に曖昧になることのないように詳細に説明していない。A detailed description of one or more embodiments of the present invention is provided below in conjunction with the accompanying figures illustrating selected details of the invention. The present invention is described in connection with the embodiments. The embodiments are understood herein to be merely exemplary, and the present invention is not expressly limited to or by any or all of the embodiments herein, and the present invention encompasses numerous alternatives, modifications, and equivalents. To avoid monotony in the description, various worded labels (including but not limited to first, last, certain, various, another, other, particular, selection, several, prominent, etc.) may be applied to distinguish sets of embodiments. As used herein, such labels are not intended to expressly convey a quality or any form of preference or prejudice, but merely to conveniently distinguish between separate sets. The order of some operations of the disclosed processes may be changed within the scope of the present invention. Whenever various embodiments are used to describe differences in the respective features of a process, method, and/or program instructions, other embodiments are contemplated that statically and/or dynamically select one of a plurality of operating modes, each corresponding to a plurality of various embodiments, according to predetermined or dynamically determined criteria. In the following description, numerous specific details are set forth to provide a thorough understanding of the invention. These details are provided by way of example, and the invention may be practiced according to the claims without some or all of these details. For the sake of clarity, technical materials known in the art related to the invention have not been described in detail so as not to unnecessarily obscure the invention.
概説
この概説は、詳細な説明のより迅速な理解を助けるために含まれるにすぎず、本発明は、(それがある場合には、明示的な例を含む)この概説で提示される概念だけに限定されるものではなく、どんな概説の段落も、必然的に、主題全体の縮約された見方であり、網羅的な、または限定的な記述であることを意味するものではない。例えば、以下の概説は、スペースおよび編成によりある一定の実施形態だけに限定される概要情報を提供するものである。特許請求の範囲が究極的にそこに導かれることになる実施形態を含む多くの他の実施形態があり、それらを本明細書の残りの部分にわたって論じる。 Overview This overview is included merely to aid in a quicker comprehension of the detailed description, and the present invention is not limited to only the concepts presented in this overview (including explicit examples, if any), and any overview paragraph is necessarily a condensed view of the entire subject matter and is not meant to be an exhaustive or limiting description. For example, the following overview provides summary information that is limited to only certain embodiments due to space and organization. There are many other embodiments, including those to which the claims will ultimately be directed, which are discussed throughout the remainder of this specification.
頭字語
ここで定義される様々な縮めた表現の略語(例えば、頭字語)の少なくとも一部が本明細書において使用される特定の要素を指す。 Acronyms At least some of the various contraction abbreviations (eg, acronyms) defined herein refer to particular elements used herein.
ある実施形態では、ソリッドステートディスク(SSD)といった入出力デバイスが、ホストインターフェースを介して、本明細書では単にホストとも呼ぶホスト・コンピューティング・システムに接続される。様々な実施形態によれば、接続は、PCIe、SATA、SAS、USB、イーサネット(登録商標)、ファイバチャネル、または2台の電子デバイスを接続するのに適した任意の他のインターフェースを含む1若しくはそれ以上のホストインターフェースを介したものである。別の実施形態では、ホストインターフェースは、電気信号インターフェースおよびホストプロトコルを含む。ホストプロトコルは、入出力デバイスにデータを送り、入出力デバイスからデータを受け取るコマンドを含む、入出力デバイスと通信するための標準コマンドを定義する。In one embodiment, an I/O device, such as a solid state disk (SSD), is connected to a host computing system, also referred to herein simply as a host, via a host interface. According to various embodiments, the connection is through one or more host interfaces, including PCIe, SATA, SAS, USB, Ethernet, Fibre Channel, or any other interface suitable for connecting two electronic devices. In another embodiment, the host interface includes an electrical signal interface and a host protocol. The host protocol defines standard commands for communicating with the I/O device, including commands for sending data to and receiving data from the I/O device.
ホスト・コンピューティング・システムは、本明細書でコンピューティングホストと呼ぶ(または単に「ホスト」と呼ぶ場合もある)1若しくはそれ以上の処理要素を含む。様々な実施形態によれば、コンピューティングホストは、オペレーティングシステムおよび/またはハイパーバイザといった監視ソフトウェア、監視ソフトウェアと入出力デバイスとの間で通信するためのドライバ、アプリケーションソフトウェア、ならびにBIOS、のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を実行する。別の実施形態では、ドライバの一部分の一部または全部またはコピーがBIOS、オペレーティングシステム、ハイパーバイザ、およびアプリケーションのうちの1若しくはそれ以上に組み込まれる。さらに別の実施形態では、アプリケーションは、バイパスモードでドライバを介してコマンドを送ることによって、および/または入出力デバイスとの直接通信を有することによって、入出力デバイスとより直接的に通信することができるようになっている。入出力デバイスとの直接通信を有するアプリケーションの一例は、PCIe入出力デバイスの仮想機能(VF)によって提供される。ドライバは入出力デバイスの一次機能と通信して入出力デバイスを全体にわたって構成し、1若しくはそれ以上のアプリケーションが、それぞれの仮想機能によって入出力デバイスと直接通信する。仮想機能は、アプリケーションの各々が入出力デバイスの少なくとも一部分をアプリケーションの専用入出力デバイスとして扱うことを可能にする。A host computing system includes one or more processing elements, referred to herein as a computing host (or sometimes simply as a "host"). According to various embodiments, the computing host executes one or more of the following: monitoring software, such as an operating system and/or a hypervisor, drivers for communicating between the monitoring software and the I/O devices, application software, and a BIOS. In another embodiment, some or all of a portion of the driver or a copy is incorporated into one or more of the BIOS, the operating system, the hypervisor, and the application. In yet another embodiment, an application is able to communicate more directly with an I/O device by sending commands through the driver in a bypass mode and/or by having direct communication with the I/O device. One example of an application having direct communication with an I/O device is provided by a virtual function (VF) of a PCIe I/O device. A driver communicates with a primary function of the I/O device to configure the I/O device throughout, and one or more applications communicate directly with the I/O device through their respective virtual functions. The virtual functions allow each of the applications to treat at least a portion of the I/O device as the application's dedicated I/O device.
ホストプロトコルの標準コマンドは、ホストプロトコルが標準化される時点の入出力デバイスの特徴および機能のセットを提供する。入出力デバイスの中には、標準ホストプロトコルでサポートされていない特徴および/または機能を有し、よって、コンピューティングホストが標準ホストプロトコルを使用して制御することができないものがある。したがって、ある実施形態では、非標準の特徴および/または機能が、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を含む技術によってホストプロトコルに追加される:予約コマンドコードを使用すること;ベンダ特有のコマンドを使用すること;既存のコマンド内の予約フィールドを使用すること;不使用のアドレスビットといった、特定の入出力デバイスによって使用されないコマンドのある特定のフィールド内のビットを使用すること;SATAにおけるSET FEATURESコマンドによるものと同様に、機能レジスタに新しい特徴を追加すること;コマンドを集約し、および/または融合することによるもの;ならびに当分野で公知の他の技術。非標準の特徴および/または機能の使用は、任意選択で、入出力デバイスと通信することができるようにした非標準のドライバおよび/またはアプリケーションの使用と組み合わされる。The standard commands of the host protocol provide a set of features and functions of the I/O device at the time the host protocol is standardized. Some I/O devices have features and/or functions that are not supported by the standard host protocol and therefore cannot be controlled by a computing host using the standard host protocol. Thus, in some embodiments, non-standard features and/or functions are added to the host protocol by techniques including one or more of the following: using reserved command codes; using vendor-specific commands; using reserved fields in existing commands; using bits in certain fields of the command that are not used by a particular I/O device, such as unused address bits; adding new features to a feature register, similar to the SET FEATURES command in SATA; by aggregating and/or fusing commands; and other techniques known in the art. The use of non-standard features and/or functions is optionally combined with the use of non-standard drivers and/or applications that are capable of communicating with the I/O device.
本明細書において、標準コマンドの非標準修飾子とは、上記の技術のいずれかを使用して、標準ホストプロトコルでサポートされていない非標準の特徴および/または機能で標準コマンドを拡張することを指す。様々な実施形態では、非標準修飾子(またはその部分)を、任意選択で、(標準)コマンドによって使用され、または(標準)コマンドと共に提供されるヒントと呼ぶ。第1の例では、非標準修飾子は、ホストプロトコル内でコマンドの一部として符号化され、もっぱらそのコマンドのみに影響を及ぼす(「一度に1つ」のヒントなど)。第2の例では、非標準修飾子は、ホストプロトコル内でコマンドの一部として符号化され、例えば後続のコマンドのうちの1つに対する別の非標準修飾子によって一時的に使用不可とされない限り、または、例えば別のコマンドに対する別の非標準修飾子によって、すべてのそれ以後のコマンドについて使用不可とされない限り、後続のコマンドに対して有効のままである(「スティッキーな」ヒントなど)。第3の例では、非標準修飾子は、SATAにおけるSET FEATURESコマンドによるものと同様に、モード設定コマンドによって構成レジスタにおいて使用可能とされ、例えば別のモード設定コマンドによって明示的に使用不可とされない限り有効のままである。これらの例の多くの組み合わせおよび変形が可能である。As used herein, a non-standard modifier of a standard command refers to extending a standard command with non-standard features and/or functionality not supported by the standard host protocol using any of the techniques described above. In various embodiments, the non-standard modifier (or a portion thereof) is optionally referred to as a hint used by or provided with the (standard) command. In a first example, the non-standard modifier is encoded as part of the command in the host protocol and affects only that command (e.g., a "one at a time" hint). In a second example, the non-standard modifier is encoded as part of the command in the host protocol and remains in effect for subsequent commands (e.g., a "sticky" hint) unless it is temporarily disabled, e.g., by another non-standard modifier for one of the subsequent commands, or disabled for all subsequent commands, e.g., by another non-standard modifier for another command. In a third example, non-standard modifiers are enabled in the configuration register by a mode set command, similar to the SET FEATURES command in SATA, and remain in effect unless explicitly disabled, e.g., by another mode set command. Many combinations and variations of these examples are possible.
様々な実施形態によれば、非標準の特徴および/または機能は、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上に影響を及ぼす:コマンドの実行;コマンドの能力および/または性能;コマンドと関連付けられたデータの扱いおよび/または処理;複数のコマンド間の関係;複数のコマンドのデータ間の関係;コマンドのデータが切り捨てられるという指示;コマンドのデータが訂正不能であるという指示;コマンドのデータタイプの仕様;コマンドのデータのデータアクセスタイプの仕様;複数のコマンドのデータについてのデータ順序付けの仕様;複数のコマンドのデータ間のデータ関係の仕様;任意の他のデータ値、データタイプ、データシーケンス、データ関係、データ宛先、またはデータプロパティの仕様;能力および/または性能といった入出力デバイスのプロパティ;ならびに、入出力デバイスの動作および/またはコマンドおよび/若しくはデータの処理、および/またはデータの記憶、取得および/若しくは再利用に影響を及ぼす任意の他の特徴および/または機能。According to various embodiments, the non-standard features and/or functions affect one or more of the following: execution of a command; the capabilities and/or performance of a command; the handling and/or processing of data associated with a command; relationships between multiple commands; relationships between data of multiple commands; an indication that data of a command is to be truncated; an indication that data of a command is uncorrectable; a specification of a data type for a command; a specification of a data access type for the data of the command; a specification of data ordering for data of multiple commands; a specification of data relationships between data of multiple commands; a specification of any other data value, data type, data sequence, data relationship, data destination, or data property; properties of the I/O device, such as capabilities and/or performance; and any other features and/or functions that affect the operation of the I/O device and/or the processing of commands and/or data, and/or the storage, retrieval, and/or reuse of data.
ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、コマンドが複数のLBAのうちの1つを含み、マップが、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、コマンドのLBAをマップの複数のエントリのうちの1つと関連付ける。マップのエントリの各々は、入出力デバイスのNVM内の位置、および/またはLBAと関連付けられたデータがNVMに存在しない(割り当てられていない、割り当て解除されている、削除されている、NVMから切り捨てられているなど)という指示を含む。様々な実施形態によれば、コマンドを受け取ったことに応答して、入出力デバイスは以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を実行する:LBAと関連付けられたマップのエントリにアクセスする;LBAと関連付けられたマップのエントリにコマンドの非標準修飾子の指示を記憶する;LBAと関連付けられたマップのエントリから前のコマンドの非標準修飾子の指示を取得する;およびコマンドを受け取ったことに応答して入出力デバイスによって実行される他の動作。マップのエントリからの非標準修飾子を記憶し、および/または取得することにより、非標準修飾子の影響を、LBAのうちの特定のものと関連付け、および/または複数のコマンドにわたって持続させることが可能になる。例えば、コマンドは、複数のデータバンドのうちの1固定データバンドであるデータ宛先を指定する特定の非標準修飾子を含む。指定の固定データバンドにコマンドのデータを記憶することに加えて、特定の非標準修飾子の指示も、コマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップのエントリに記憶される。コマンドのデータのその後の再利用動作では、コマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップのエントリにアクセスし、特定の非標準修飾子の指示に従って、再利用動作にデータを再利用して指定の固定データバンド戻させることが可能になる。In certain embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the command includes one of a plurality of LBAs, and the map optionally and/or selectively associates the LBA of the command with one of a plurality of entries in the map. Each of the entries in the map includes a location in the NVM of the I/O device and/or an indication that the data associated with the LBA is not present in the NVM (not allocated, deallocated, deleted, truncated from the NVM, etc.). According to various embodiments, in response to receiving the command, the I/O device performs one or more of the following: accesses the entry in the map associated with the LBA; stores an indication of the command's non-standard qualifier in the entry in the map associated with the LBA; retrieves an indication of the non-standard qualifier of a previous command from the entry in the map associated with the LBA; and other actions performed by the I/O device in response to receiving the command. Storing and/or retrieving the non-standard qualifier from the entry in the map allows the effect of the non-standard qualifier to be associated with a particular one of the LBAs and/or to persist across multiple commands. For example, the command includes a particular non-standard modifier that specifies a data destination that is a fixed data band of multiple data bands. In addition to storing the command's data in the specified fixed data band, an indication of the particular non-standard modifier is also stored in an entry of the map associated with the command's LBA. A subsequent reclamation operation of the command's data can access the entry of the map associated with the command's LBA and follow the indication of the particular non-standard modifier to cause the reclamation operation to reclaim the data back into the specified fixed data band.
データのタイプを指定する非標準修飾子の例には、圧縮不能といったデータの圧縮性の仕様(specification)や、データベースジャーナルとしての使用といったデータの使用モデルの仕様が含まれる。場合によっては、(仕様や、マップに記録されている以前に提供された仕様といった)特定のタイプのものであると(例えば、入出力デバイスおよび/またはホストによって)識別されたデータは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスによってより効率よく処理される。ある使用シナリオでは、例えば、データベース・ジャーナル・タイプのものであると識別されたデータは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、複数のデータバンドのうちの、データベース・ジャーナルの類型データのために確保されたデータベース・ジャーナル用データバンドに記憶される。様々な実施形態において、データベース・ジャーナル用データバンドは、固定サイズのものであり、一杯になると、データベース・ジャーナル用データバンド内の最も古いデータは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、自動削除される。Examples of non-standard qualifiers for specifying a type of data include a specification of the compressibility of the data, such as incompressible, or a specification of a usage model of the data, such as use as a database journal. In some cases, data identified (e.g., by the I/O device and/or host) as being of a particular type (such as a specification or a previously provided specification recorded in a map) is optionally and/or selectively processed more efficiently by the I/O device. In one usage scenario, for example, data identified as being of a database journal type is optionally and/or selectively stored in a database journal data band of multiple data bands reserved for database journal type data. In various embodiments, the database journal data band is of a fixed size, and when full, the oldest data in the database journal data band is optionally and/or selectively automatically deleted.
データアクセスタイプを指定する非標準修飾子の例には、読み出し/書き込みアクセスタイプの仕様、略読み出しアクセスタイプ(read−mostly access type)の仕様、略書き込みアクセスタイプの仕様(write−mostly access type)、追記型(読み出し専用ともいう)アクセスタイプの仕様、および一時アクセスタイプの仕様が含まれる。場合によっては、(仕様や、マップに記録されている以前に提供された仕様といった)特定のアクセスタイプを有するものであると(例えば、入出力デバイスおよび/またはホストによって)識別されたデータは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスによってより効率よく処理される。第1の例では、データが読み取られ、または書き込まれる相対頻度を特定することは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスが、データの書き込み、アクセス、読み出し、および/または再利用をより効率よく可能にするようなやり方で、および/またはそのような位置にデータを都合よく記憶することを可能にする。第2の例では、入出力デバイスによって追記型であると識別されているデータへの標準書き込みアクセスが、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、誤りとして扱われる。Examples of non-standard qualifiers that specify data access types include a read/write access type specification, a read-mostly access type specification, a write-mostly access type specification, a write-only access type specification, and a temporary access type specification. In some cases, data identified (e.g., by the I/O device and/or host) as having a particular access type (such as a specification or a previously provided specification recorded in a map) is optionally and/or selectively processed more efficiently by the I/O device. In a first example, identifying the relative frequency at which data is read or written optionally and/or selectively allows the I/O device to conveniently store the data in a manner and/or location that allows the data to be written, accessed, read, and/or reused more efficiently. In a second example, standard write accesses to data that is identified by the I/O device as being write-once are optionally and/or selectively treated as an error.
ある実施形態では、一時アクセスタイプの仕様は、データが入出力デバイスによって記憶されることを可能にし、さらに、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスが、コンピューティングホストからそうするよう求めるコマンドを受け取っていなくても、データを削除し、および/または削減すること(「自動削減」など)を可能にする。例えば、ストレージの特定の部分が一時的であると識別することが、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスが、ストレージのその部分を再利用するのではなく削減することを可能にする。様々な実施形態によれば、入出力デバイスによって削除され、または削減された一時データへのコンピューティングホストによるその後のアクセスは、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を返す:データが削除され、または削減されたという指示;誤り指示;特定のパターンおよび/または値を含むデータ;ならびにデータが入出力デバイスによって削除され、または削減されたというコンピューティングへの任意の他の指示。In some embodiments, the specification of a temporary access type allows the data to be stored by the I/O device and further, optionally and/or selectively, allows the I/O device to delete and/or reduce the data (e.g., "auto-reducing") even without receiving a command from the computing host to do so. For example, identifying a particular portion of storage as temporary may optionally and/or selectively allow the I/O device to reduce rather than reclaim that portion of storage. According to various embodiments, subsequent access by the computing host to the temporary data deleted or reduced by the I/O device returns one or more of the following: an indication that the data has been deleted or reduced; an error indication; data containing a particular pattern and/or value; and any other indication to the computing host that the data has been deleted or reduced by the I/O device.
様々な実施形態において、リセット後一時アクセスタイプの仕様は、データが入出力デバイスによって記憶されることを可能にし、さらに、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスが、コンピューティングホストからそうするよう求めるコマンドを受け取っていなくても、ただし、入出力デバイスおよび/または入出力デバイスを含むシステムの後続の電源サイクルおよび/またはリセットの後に限って、データを削除し、および/または削減すること(「自動切り捨て」など)を可能にする。例えば、ページファイルといったある特定のオペレーティング・システム・データおよび/またはメムキャッシュディー(memcached)アプリケーションのデータといった特定のアプリケーションのデータは、システムの電源サイクルおよび/またはリセットの後で無効になる。ある実施形態では、リセット後一時アクセスタイプの指示は、2ビットカウンタといったカウンタを含む。グローバルカウンタの値を使用して、リセット後一時アクセスタイプの指示のカウンタが初期化される。グローバルカウンタは、入出力デバイスおよび/またはシステムの電源サイクルおよび/またはリセットごとに増分される。リセット後一時アクセスタイプの指示を有する、入出力デバイスのNVMの一部分といったストレージの特定の部分が、リセット後一時アクセスタイプの指示のカウンタがグローバルカウンタと一致するかどうかに従って、再利用のためにストレージのその特定の部分を処理するときに、選択的に切り捨てられる。さらに別の実施形態では、複数のグローバルカウンタがあり、グローバルカウンタの各々は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、独立に増分され、リセット後一時アクセスタイプの指示は、グローバルカウンタの個々のカウンタの仕様をさらに含む。ビットマスクや固定値といったカウンタ以外の技術が、様々な実施形態において、ストレージの特定の部分が再利用されるときに選択的に切り捨てられるべきであるかどうか識別するのに使用される。In various embodiments, the specification of the temporary access type after reset allows the data to be stored by the I/O device and, optionally and/or selectively, allows the I/O device to delete and/or reduce (e.g., "auto-truncate") the data even if it has not received a command to do so from the computing host, but only after a subsequent power cycle and/or reset of the I/O device and/or the system including the I/O device. For example, certain operating system data, such as a page file, and/or certain application data, such as memcached application data, are invalidated after a power cycle and/or reset of the system. In one embodiment, the indication of temporary access type after reset includes a counter, such as a two-bit counter. The value of the global counter is used to initialize the counter of indications of temporary access type after reset. The global counter is incremented for each power cycle and/or reset of the I/O device and/or the system. A particular portion of storage, such as a portion of an I/O device's NVM, having an indication of a temporary access type after reset is selectively truncated when processing the particular portion of storage for reclamation according to whether a counter in the indication of the temporary access type after reset matches a global counter. In yet another embodiment, there are multiple global counters, each of which is optionally and/or selectively incremented independently, and the indication of the temporary access type after reset further includes a specification of an individual counter of the global counters. Techniques other than counters, such as bit masks or fixed values, are used in various embodiments to identify whether a particular portion of storage should be selectively truncated when reclaimed.
さらに別の実施形態では、電源サイクルおよび/またはリセットの指示は、リセット後一時アクセスタイプの指示を有するストレージの部分が後で再利用のために処理されるときにストレージのその部分が切り捨てられることが可能であることを指示するためにコンピューティングホストから提供される信号である。第1の例では、仮想機械を用いる環境において、コンピューティングホストから提供される信号は、仮想機械のリセットおよび/または終了の指示である。第2の例では、メムキャッシュディーアプリケーションを用い、コンピューティングホストから提供される信号は、メムキャッシュディーアプリケーションのリセットおよび/または終了の指示である。第3の例では、電源サイクルおよび/またはリセットの指示は、入出力デバイスの仮想機能の機能レベルのリセットである。ある使用シナリオでは、LBAの特定の範囲といった、仮想機能と関連付けられた入出力デバイスのNVMの部分だけが、機能レベルのリセットによる影響を受ける。In yet another embodiment, the power cycle and/or reset indication is a signal provided from a computing host to indicate that the portion of storage having a reset temporary access type indication may be truncated when that portion of storage is subsequently processed for reclamation. In a first example, in an environment using a virtual machine, the signal provided from the computing host is an indication to reset and/or terminate the virtual machine. In a second example, using a memcache-dee application, the signal provided from the computing host is an indication to reset and/or terminate the memcache-dee application. In a third example, the power cycle and/or reset indication is a function-level reset of a virtual function of an I/O device. In one usage scenario, only the portion of the NVM of the I/O device associated with the virtual function, such as a particular range of LBAs, is affected by the function-level reset.
データ順序付けを指定する非標準修飾子の例には、順次データ順序付けの仕様、およびアトミックデータ順序付けの仕様が含まれる。場合によっては、(仕様や、マップに記録されている以前に提供された仕様といった)特定のデータ順序付けのものであると(例えば、入出力デバイスおよび/またはホストによって)識別されたデータは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスによってより効率よく処理される。第1の例では、データが順次データ順序付けに属すると特定することは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスが、データの書き込み、アクセス、読み出し、および/または再利用をより効率よく可能にするようなやり方で、および/またはそのような位置にデータを都合よく記憶することを可能にする。第2の例では、データがアトミックデータ順序付けに属すると特定することは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスが、アトミックデータ順序付けのデータを1単位として都合よく扱うことを可能にし、アトミックデータ順序付けのデータの全部がコンピューティングホストによって識別可能であるように正常に書き込まれること、またはアトミックデータ順序付けのデータが全く書き込まれないことを保証することを可能にする。ある実施形態では、データのアトミックシーケンスを書き込むことは、シーケンスの開始および/または終了を指示するログ情報といったメタデータを書き込むことを含む。Examples of non-standard qualifiers that specify data ordering include a sequential data ordering specification and an atomic data ordering specification. In some cases, data identified (e.g., by the I/O device and/or host) as being of a particular data ordering (such as a specification or a previously provided specification recorded in a map) is optionally and/or selectively processed more efficiently by the I/O device. In a first example, identifying data as belonging to a sequential data ordering optionally and/or selectively allows the I/O device to conveniently store the data in a manner and/or location that allows the data to be written, accessed, read, and/or reused more efficiently. In a second example, identifying data as belonging to an atomic data ordering optionally and/or selectively allows the I/O device to conveniently treat the atomic data ordering data as a unit and ensure that either all of the atomic data ordering data is successfully written as identifiable by the computing host, or none of the atomic data ordering data is written. In one embodiment, writing an atomic sequence of data includes writing metadata, such as log information, that indicates the start and/or end of the sequence.
データ関係を指定する非標準修飾子の例には、複数のデータ項目間の読み出しおよび/または書き込みの関連付けの仕様が含まれる。場合によっては、(仕様や、マップに記録されている以前に提供された仕様といった)特定のデータ関係のものであると(例えば、入出力デバイスおよび/またはホストによって)識別されたデータは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスによってより効率よく処理される。例えば、2つのデータ項目間の読み出しデータ関係を特定することは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスが、データ項目のうちの第1の項目が読み取られるときに、データ項目のうちの第2の項目を都合よくプリフェッチすることを可能にする。ある使用例および/またはシナリオでは、第1のデータ項目はファイルシステム内のファイルのラベルであり、第2のデータ項目はファイルの対応する範囲である。様々な実施形態によれば、データ関係は以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である:1対1;1対多;多対1;多対多;書き込みコマンドと比較すると読み出しコマンドについては異なるなど、コマンドによって異なるデータ関係;およびデータ項目間の任意の他の関係。Examples of non-standard qualifiers for specifying data relationships include the specification of a read and/or write association between multiple data items. In some cases, data identified (e.g., by an I/O device and/or host) as being of a particular data relationship (such as a specification or a previously provided specification recorded in a map) is optionally and/or selectively processed more efficiently by an I/O device. For example, identifying a read data relationship between two data items optionally and/or selectively allows an I/O device to advantageously pre-fetch a second one of the data items when a first one of the data items is read. In one use case and/or scenario, the first data item is a label of a file in a file system and the second data item is a corresponding range of the file. According to various embodiments, the data relationship is one or more of the following: one-to-one; one-to-many; many-to-one; many-to-many; a data relationship that varies by command, such as different for a read command compared to a write command; and any other relationship between data items.
データ宛先を指定する非標準修飾子の例には、(特定のフラッシュ記憶要素や、例えばNVMの要素間でのデータ拡散を可能にするためのフラッシュ記憶要素の集合体といった)NVMの特定の部分の仕様、階層型ストレージ層の仕様、ストレージのタイプの仕様、および複数のデータバンドのうちの1つの仕様が含まれる。場合によっては、(仕様や、マップに記録されている以前に提供された仕様といった)特定のデータ宛先のものであると(例えば、入出力デバイスおよび/またはホストによって)識別されたデータは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスによってより効率よく処理される。第1の例では、データが指定のタイプのストレージに優先的に記憶されていることを特定することは、入出力デバイスが、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、SLCフラッシュ対MLCフラッシュ、フラッシュ対MRAM、あるいは揮発性メモリ対NVMといった、異なる特性の複数のメモリのうちの1つにデータを都合よく記憶することを可能にする。メモリの異なる特性は以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を含む:揮発性;アクセス時間、待ち時間、および/またはバンド幅といった性能;読み出し、書き込み、または消去の時間;能力;信頼性;寿命;低レベル誤り訂正および/または冗長性機能;高レベル誤り訂正および/または冗長性機能;ならびに他のメモリ特性。第2の例では、データが複数のデータバンドのうちの指定のデータバンドに記憶されるべきであることを特定することは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスが、データを指定のデータバンドに都合よく記憶して、書き込み速度、再利用速度、再利用頻度、書き込み増幅、およびデータストレージの他の特性のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を改善することを可能にする。Examples of non-standard qualifiers specifying data destinations include the specification of a particular portion of the NVM (such as a particular flash storage element or a collection of flash storage elements to allow data spreading among elements of the NVM), the specification of a hierarchical storage tier, the specification of a type of storage, and the specification of one of multiple data bands. In some cases, data identified (e.g., by the I/O device and/or host) as being of a particular data destination (such as a specification or a previously provided specification recorded in a map) is optionally and/or selectively processed more efficiently by the I/O device. In a first example, identifying that the data is preferentially stored in a specified type of storage allows the I/O device to optionally and/or selectively store the data advantageously in one of multiple memories of different characteristics, such as SLC flash vs. MLC flash, flash vs. MRAM, or volatile memory vs. NVM. The different characteristics of the memory include one or more of the following: volatility; performance such as access time, latency, and/or bandwidth; read, write, or erase time; capacity; reliability; lifetime; low level error correction and/or redundancy capabilities; high level error correction and/or redundancy capabilities; and other memory characteristics. In a second example, identifying that the data should be stored in a specified data band of the multiple data bands optionally and/or selectively enables an input/output device to advantageously store the data in the specified data band to improve one or more of write speed, reuse speed, reuse frequency, write amplification, and other characteristics of data storage.
コマンド関係を指定する非標準修飾子の例には、コマンド間の好ましい、または必要とされる相対順序を課すコマンド優先順位の仕様、および少なくともいくつかのタイプのコマンド間の境界を課すコマンドバリアの仕様が含まれる。例えば、書き込みコマンド・バリア・タイプのコマンドバリアは、読み出しコマンドに対しては透過的であるが、書き込みコマンドに対しては非透過的であり、書き込みコマンドバリアが、すべての以前に実行依頼された書き込みコマンドが書き込みコマンドバリアの完了の前に完了するよう保証することを可能にする。Examples of non-standard qualifiers that specify command relationships include the specification of command priority, which imposes a preferred or required relative order between commands, and the specification of command barriers, which impose boundaries between at least some types of commands. For example, a write command barrier type of command barrier is transparent to read commands but opaque to write commands, allowing the write command barrier to ensure that all previously submitted write commands complete before the completion of the write command barrier.
集約され、および/または融合されたコマンドの例は、1単位として扱われ、実行されないかまとめて実行されるかのどちらかである、2若しくはそれ以上のコマンドの組み合わせである。例えば、非標準修飾子は、融合コマンドシーケンスの開始、継続、または終了を指定する。融合コマンドシーケンスのコマンドは、すべてのコマンドが正常に完了しない限り、コマンドのいずれの影響も現れないようなアトミックなやり方で実行される。融合コマンドシーケンスの一例が比較−書き込みシーケンスであり、このシーケンスでは、後続の書き込みコマンドの影響は、先行する比較コマンドが、例えば比較が等しいことによって正常に行われた場合に限って現れる。様々な実施形態によれば、融合コマンドシーケンスのコマンドは、順次に、並列に、ホストプロトコルの順序付け規則によって決定される順序で、コマンドが入出力デバイスによって受け取られる順序で、および任意の順序で、のうちの1若しくはそれ以上のとして実行される。An example of an aggregated and/or fused command is a combination of two or more commands that are treated as a unit and are either not executed or executed together. For example, non-standard modifiers specify the beginning, continuation, or end of a fused command sequence. The commands of the fused command sequence are executed in an atomic manner such that the effect of any of the commands is not seen unless all of the commands complete successfully. An example of a fused command sequence is a compare-write sequence, where the effect of a subsequent write command is seen only if the preceding compare command was successful, e.g., by comparing equal. According to various embodiments, the commands of the fused command sequence are executed as one or more of: sequentially, in parallel, in an order determined by the ordering rules of the host protocol, in the order in which the commands are received by the I/O device, and in any order.
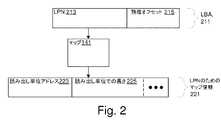
一部の実施形態では、SSDといった入出力装置がSSDコントローラを含む。SSDコントローラはホストインターフェースとSSDのNVMとの間のブリッジとして働き、SSDのホストインターフェースを介してコンピューティングホストから送られるホストプロトコルのコマンドを実行する。コマンドの少なくとも一部は、SSDに、コンピューティングホストから送られたデータおよびコンピューティングホストに送られるデータについて、それぞれ、NVMの書き込みおよび読み出しを行うよう指図する。別の実施形態では、SSDコントローラは、マップを使用してホストプロトコルのLBAとNVM内の物理的記憶アドレスとを変換することができるようになっている。別の実施形態では、マップの少なくとも一部分が、入出力装置の専用記憶(コンピューティングホストからは見えない)に使用される。例えば、コンピューティングホストからアクセスできないLBAの部分が、入出力装置によって、ログ、統計、または他の専用データへのアクセスを管理するのに使用される。In some embodiments, an I/O device, such as an SSD, includes an SSD controller. The SSD controller acts as a bridge between the host interface and the SSD's NVM, and executes host protocol commands sent from the computing host through the SSD's host interface. At least some of the commands instruct the SSD to write and read the NVM for data sent from and to the computing host, respectively. In another embodiment, the SSD controller is capable of translating between host protocol LBAs and physical storage addresses in the NVM using a map. In another embodiment, at least a portion of the map is used for the I/O device's private storage (not visible to the computing host). For example, portions of the LBAs that are not accessible to the computing host are used by the I/O device to manage access to logs, statistics, or other private data.
様々な実施形態によれば、マップは、1レベルマップ、2レベルマップ、マルチレベルマップ、直接マップ、連想マップ、およびホストプロトコルのLBAをNVM内の物理的記憶アドレスと関連付ける他の手段のうち1若しくはそれ以上である。例えば、ある実施形態では、2レベルマップは、LBAの第1の関数を、複数の第2レベル・マップ・ページのうち1つのNVM内のそれぞれのアドレスと関連付ける第1レベルマップを有し、第2レベル・マップ・ページの各々は、LBAの第2の関数をLBAに対応するデータのNVM内のそれぞれのアドレスと関連付ける。別の実施形態では、LBAの第1の関数およびLBAの第2の関数の例は、第2レベル・マップ・ページの各々に含まれる固定数のエントリによって除算されるときに得られる商および余りである。複数の第2レベル・マップ・ページをまとめて第2レベルマップと呼ぶ。本明細書では、マップの1若しくはそれ以上のエントリという場合、それは、1レベルマップ、2レベルマップの第1レベル、2レベルマップの第2レベル、マルチレベルマップの任意のレベル、またはエントリを有する任意の他の種類のマップを含む、任意の種類のマップの1若しくはそれ以上のエントリをいう。According to various embodiments, the map is one or more of a one-level map, a two-level map, a multi-level map, a direct map, an associative map, and other means of associating LBAs of the host protocol with physical storage addresses in the NVM. For example, in one embodiment, the two-level map has a first level map that associates a first function of the LBA with a respective address in the NVM of one of a plurality of second level map pages, each of which associates a second function of the LBA with a respective address in the NVM of data corresponding to the LBA. In another embodiment, examples of the first function of the LBA and the second function of the LBA are the quotient and remainder obtained when divided by a fixed number of entries contained in each of the second level map pages. The plurality of second level map pages are collectively referred to as the second level map. As used herein, a reference to one or more entries of a map refers to one or more entries of any type of map, including a one-level map, a first level of a two-level map, a second level of a two-level map, any level of a multi-level map, or any other type of map having entries.
様々な実施形態によれば、第2レベルマップ(またはマルチレベルマップの低レベル)のマップページの各々は、マップページの他のものと同数のエントリを含む、マップページの少なくとも他のいくつかと異なる数のエントリを含む、マップページの他のものと同じ粒度のエントリを含む、マップページの他のものと異なる粒度のエントリを含む、すべて同じ粒度ものであるエントリを含む、複数の粒度のものであるエントリを含む、マップページの内容の書式および/またはレイアウトを指定するそれぞれのヘッダを含む、ならびにマップページのエントリを表す任意の他の書式、レイアウト、または編成を有する、のうち1若しくはそれ以上である。例えば、第1の第2レベル・マップ・ページは、1エントリ当たり4KBの粒度の仕様を有し、第2の第2レベル・マップ・ページは、1エントリ当たり8KBの粒度、および第1の第2レベル・マップ・ページの半数だけのエントリの仕様を有する。According to various embodiments, each of the map pages of the second level map (or a lower level of a multi-level map) includes one or more of: the same number of entries as the others of the map page; a different number of entries than at least some of the others of the map page; entries of the same granularity as the others of the map page; entries of a different granularity than the others of the map page; entries that are all of the same granularity; entries that are of multiple granularities; includes a respective header that specifies the format and/or layout of the contents of the map page; and has any other format, layout, or organization that represents the entries of the map page. For example, a first second level map page has a specification of 4KB granularity per entry, and a second second level map page has a specification of 8KB granularity per entry and half as many entries as the first second level map page.
別の実施形態では、高レベルマップのエントリは、対応する低レベル・マップページの書式および/またはレイアウト情報を含む。例えば、第1レベルマップ内のエントリの各々は、関連付けられた第2レベル・マップ・ページ内のエントリについての粒度仕様を含む。In another embodiment, the entries of the higher level map include format and/or layout information for the corresponding lower level map page. For example, each entry in the first level map includes granularity specifications for entries in the associated second level map page.
ある実施形態では、マップは複数のエントリを有し、エントリの各々は、1若しくはそれ以上のLBAを、LBAのデータが記憶されているNVM内のそれぞれの位置を選択的に含む情報と関連付ける。例えば、LBAは512Bのセクタを指定し、マップ内の各エントリは、LBAの並んだ8セクタ(4KB)領域と関連付けられている。In one embodiment, the map has multiple entries, each of which associates one or more LBAs with information that optionally includes a respective location within the NVM where the data at the LBA is stored. For example, an LBA may specify a 512B sector, and each entry in the map may be associated with an aligned 8-sector (4KB) region of the LBA.
様々な実施形態によれば、マップのエントリの情報は、NVM内の位置、NVM内の読み出し単位のアドレス、NVMに記憶された関連付けられたLBAのデータを取得するために読み出すべき読み出し単位の数、NVMに記憶された関連付けられたLBAのデータのサイズであって、任意選択で、および/または選択的に1バイトより大きい粒度を有するサイズ、関連付けられたLBAのデータが切り捨てられているといった理由で、関連付けられたLBAのデータがNVMに存在しないという表示、関連付けられたLBAのデータに適用された任意の非標準修飾子を含む、関連付けられたLBAのデータの属性、および関連付けられたLBAのデータの任意の他のメタデータ、属性、または性質のうち1若しくはそれ以上を含む。According to various embodiments, the information in the map entry includes one or more of a location in the NVM, an address of the read unit in the NVM, a number of read units to read to obtain the associated LBA's data stored in the NVM, a size of the associated LBA's data stored in the NVM, optionally and/or selectively having a granularity greater than one byte, an indication that the associated LBA's data is not present in the NVM, such as because the associated LBA's data has been truncated, attributes of the associated LBA's data, including any non-standard modifiers applied to the associated LBA's data, and any other metadata, attributes, or properties of the associated LBA's data.
ある実施形態では、NVM内のアドレスは、アドレスのうち1つを表すのに必要とされるビット数を低減させるために領域へグループ化される。例えば、入出力装置のLBAが64領域に分割され、NVMが、LBA領域の各々に1つずつ、64領域に分割される場合には、特定のLBAと関連付けられたマップエントリは、必要とするアドレスビット数が6少なくて済む。というのは、NVM内の領域のうち1つが特定のLBAの領域によって決定されうるからである。様々な実施形態によれば、LBAの領域とNVMの領域との間の関連付けは、同等性、1対1数値関数といった直接的関連付け、表ルックアップ、動的マッピング、および2セットの数を関連付ける任意の他の方法のうち1若しくはそれ以上によるものである。In some embodiments, addresses in the NVM are grouped into regions to reduce the number of bits required to represent one of the addresses. For example, if the LBAs of an I/O device are divided into 64 regions and the NVM is divided into 64 regions, one for each of the LBA regions, then a map entry associated with a particular LBA will require 6 fewer address bits because one of the regions in the NVM can be determined by the region of a particular LBA. According to various embodiments, the association between the region of the LBA and the region of the NVM is by one or more of the following: equality, a direct association such as a one-to-one numeric function, a table lookup, dynamic mapping, and any other method of associating two sets of numbers.
様々な実施形態では、NVM内の位置は、複数の読み出し単位のうち1つのアドレス、ならびに読み出し単位での長さおよび/または範囲を含む。長さは、NVMに記憶された複数のデータ項目のうち特定の1つのサイズであり、マップのエントリと関連付けられた特定のデータ項目は長さを含む。様々な実施形態によれば、長さは、1バイト、1より大きいバイト、1読み出し単位、読み出し単位の指定された小部分、データ項目のうち1つの最大許容圧縮率に従った粒度、および記憶使用量を追跡するのに使用される任意の他の粒度のうち1若しくはそれ以上の粒度を有する。範囲は、特定のデータ項目のそれぞれの部分を記憶する、整数の読み出し単位といった読み出し単位の数である。別の実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、読み出し単位の範囲内の最初の読み出し単位および/または読み出し単位の範囲内の最後の読み出し単位は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、データ項目のうち複数のデータ項目の一部または全部を記憶する。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、長さおよび/または範囲は、例えば、長さ(長さおよび/または範囲が符号化されるコンテキストではサイズともいう)を範囲からのオフセットとして記憶することによって、符号化されて記憶される。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、長さおよび/または範囲の未使用の符号化が、非標準修飾子の指示や、関連付けられたデータ項目がNVMに存在するかどうかについての指示といった追加情報を符号化する。In various embodiments, the location in the NVM includes an address of one of the read units, and a length and/or range in read units. The length is the size of a particular one of the data items stored in the NVM, and the particular data item associated with the entry of the map includes the length. According to various embodiments, the length has one or more of the following granularities: one byte, more than one byte, one read unit, a specified fraction of a read unit, a granularity according to the maximum allowable compression ratio of one of the data items, and any other granularity used to track storage usage. The range is the number of read units, such as an integer number of read units, that store respective portions of the particular data item. In another embodiment and/or usage scenario, the first read unit in the range of read units and/or the last read unit in the range of read units optionally and/or selectively store some or all of the data items of the data items. In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the length and/or range are stored encoded, for example, by storing the length (also called size in contexts where the length and/or range are encoded) as an offset from the range. In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, unused encodings of the length and/or range encode additional information, such as an indication of non-standard modifiers or an indication of whether the associated data item is present in NVM.
NVM内の位置をアドレスおよび長さとして符号化することにより、NVMに記憶されたデータをサイズ変更することが可能になる。例えば、第1の4KB領域は400Bのサイズに圧縮され、全体が単一の読み出し単位に記憶され、1読み出し単位の長さを有し、他方第2の4KB領域は圧縮不能であり、1より大の読み出し単位にまたがり、1より大の読み出し単位の長さを有する。別の実施形態では、LBAの領域と関連付けられた記憶の読み出し単位での長さおよび/または範囲を有することにより、NVMの必要な部分だけを読み出すことでLBAの領域のデータを検索することを可能にする。By encoding locations in the NVM as addresses and lengths, it is possible to resize the data stored in the NVM. For example, a first 4KB region may be compressed to a size of 400B and stored entirely in a single read unit and have a length of 1 read unit, while a second 4KB region is not compressible, spans more than 1 read unit, and has a length of more than 1 read unit. In another embodiment, having a length and/or range in read units of storage associated with an LBA region allows data in an LBA region to be retrieved by reading only the required portion of the NVM.
ある実施形態では、マップのエントリの各々は、エントリと関連付けられたLBAの領域の属性を指定する、メタデータともいう情報を含む。別の実施形態では、メタデータの少なくとも一部は、例えば、領域の複数のLBAの各々について別々のメタデータ仕様を有することによって、領域の粒度より細かい粒度ものである。様々な実施形態によれば、メタデータは、領域と関連付けられたNVM内のデータに適用可能な、および/または領域と関連付けられたNVM内のデータの書き込み、データへのアクセス、データの読み出し、および/若しくはデータの再利用を変更し、および/または制御するのに使用されるべき1若しくはそれ以上の非標準修飾子を含む。In one embodiment, each of the map's entries includes information, also referred to as metadata, that specifies attributes of the region of the LBA associated with the entry. In another embodiment, at least a portion of the metadata is at a finer granularity than the granularity of the region, for example, by having separate metadata specifications for each of the region's multiple LBAs. According to various embodiments, the metadata includes one or more non-standard qualifiers that are applicable to data in the NVM associated with the region and/or that are to be used to modify and/or control writing, accessing, reading, and/or reusing data in the NVM associated with the region.
コマンドの非標準修飾子に応答してメタデータをマップのエントリに記憶することの一例として、拡張書き込みコマンドは、LBA、および書き込みコマンドのデータが一時的であることを指定する非標準修飾子を含む。書き込みコマンドのデータがNVMに記憶され、LBAと関連付けられたマップの特定のエントリが、書き込みコマンドのデータのNVM内の位置、およびLBAと関連付けられたデータの一時指定の指示を含むように更新される。マップのその特定のエントリにアクセスする、後続のコマンドや、再利用などの内部動作といった後続の動作は、LBAと関連付けられたデータの一時指定の指示を決定し、LBAと関連付けられたデータの一時指定の指示が存在する場合には異なるやり方で実行することができる。例えば、LBAと関連付けられたデータの一時指定の指示を有するLBAの再利用は、ある実施形態では、LBAと関連付けられたデータを再利用するのではなく、LBAと関連付けられたデータを削減することができるようになっている。As an example of storing metadata in an entry of a map in response to a non-standard modifier of a command, an extended write command includes an LBA and a non-standard modifier that specifies that the data of the write command is temporary. The data of the write command is stored in the NVM, and a particular entry of the map associated with the LBA is updated to include the location in the NVM of the data of the write command and an indication of the temporary designation of the data associated with the LBA. Subsequent operations, such as a subsequent command or internal operation such as reclamation, that access that particular entry of the map may determine the indication of the temporary designation of the data associated with the LBA and may be performed differently if an indication of the temporary designation of the data associated with the LBA is present. For example, reclaiming an LBA with an indication of the temporary designation of the data associated with the LBA may, in one embodiment, reduce the data associated with the LBA rather than reclaiming the data associated with the LBA.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスは、DRAMといった外部メモリを含み、外部メモリは、例えばDDR2またはDDR3インターフェースを介して、入出力デバイスの要素に直接接続される。様々な実施形態によれば、外部メモリは、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上のために使用される:入出力デバイスのマップの一部または全部を記憶するため;入出力デバイスのマルチレベルマップのレベルのうちの1若しくはそれ以上を記憶するため;入出力デバイスに送られた書き込みデータをバッファするため;入出力デバイスの内部状態を記憶するため;および入出力デバイスの任意の他のメモリストレージ。例えば、外部メモリは、マップへのアクセスを提供するのに使用されるが、外部メモリが揮発性である場合には、更新がNVM内のマップに選択的に記憶される。様々な実施形態および/または使用シナリオにおいて、更新は、任意選択で、条件付きで、および/または選択的に、即時に記憶され、および/または遅延される。別の実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、すべての更新が記憶される。別の実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、更新のうちの一部が(例えば、より古い更新が、そのより古い更新を記憶する前により新しい更新に取って代わられているために、または更新のうちの1若しくはそれ以上の記憶を省略することを可能にする回復技術のために)記憶されない。様々な実施形態によれば、外部メモリは以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である:SRAMである;DRAMである;MRAMまたは他のNVMである;DDRインターフェースを有する;DDR2またはDDR3インターフェースを有する;任意の他のメモリインターフェースを有する;および任意の他の揮発性または不揮発性の外部メモリデバイスである。In some embodiments, the I/O device includes an external memory, such as a DRAM, that is directly connected to elements of the I/O device, for example, via a DDR2 or DDR3 interface. According to various embodiments, the external memory is used for one or more of the following: to store some or all of the map of the I/O device; to store one or more of the levels of the multi-level map of the I/O device; to buffer write data sent to the I/O device; to store the internal state of the I/O device; and any other memory storage of the I/O device. For example, the external memory is used to provide access to the map, but if the external memory is volatile, updates are selectively stored to the map in the NVM. In various embodiments and/or usage scenarios, updates are optionally, conditionally, and/or selectively stored immediately and/or delayed. In other embodiments and/or usage scenarios, all updates are stored. In other embodiments and/or usage scenarios, some of the updates are not stored (e.g., because an older update has been superseded by a newer update before the older update was stored, or because of a recovery technique that allows for the storage of one or more of the updates to be omitted). According to various embodiments, the external memory is one or more of the following: SRAM; DRAM; MRAM or other NVM; has a DDR interface; has a DDR2 or DDR3 interface; has any other memory interface; and is any other volatile or non-volatile external memory device.
マルチレベルマップを有するいくつかの実施形態といった別の実施形態では、マップの下位レベルが、入出力デバイスのLBAと関連付けられたデータといったコンピューティングホストからのデータと共に入出力デバイスのNVMに記憶され、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、直接接続されたDRAMを利用しない。マップの下位レベルのエントリへのアクセスは、少なくともときどきは、NVMを使用して行われる。In other embodiments, such as some embodiments having a multi-level map, the lower levels of the map are stored in the I/O device's NVM along with data from the computing host, such as data associated with the I/O device's LBAs, and the I/O device optionally and/or selectively does not utilize directly attached DRAM. Access to the lower level entries of the map is, at least sometimes, performed using the NVM.
ある実施形態では、マップのシャドウコピーがコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶される。様々な実施形態において、入出力デバイスは、マップのシャドウコピーや内部状態といった情報を、コンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する。様々な実施形態によれば、コンピューティングホストのメモリは、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である:プロセッサに接続されたDRAMメモリといったコンピューティングホストのメインメモリ;コンピューティングホストのシステムアクセス可能メモリ;コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリ;コンピューティングホストのPCIeアドレス指定可能メモリ;DRAMメモリやSRAMメモリといった揮発性メモリ;フラッシュメモリやMRAMメモリといったNVM;入出力デバイスからアクセス可能であり、入出力デバイスに直接接続されていない任意のメモリ;および入出力デバイスとコンピューティングホストの両方からアクセス可能な任意のメモリ。In one embodiment, a shadow copy of the map is stored in the memory of the computing host. In various embodiments, the I/O device stores information, such as a shadow copy of the map and internal state, in the memory of the computing host. According to various embodiments, the memory of the computing host is one or more of the following: the main memory of the computing host, such as DRAM memory connected to the processor; the system accessible memory of the computing host; the I/O space memory of the computing host; the PCIe addressable memory of the computing host; volatile memory, such as DRAM memory or SRAM memory; NVM, such as flash memory or MRAM memory; any memory accessible to the I/O device and not directly connected to the I/O device; and any memory accessible to both the I/O device and the computing host.
様々な実施形態によれば、マップのシャドウコピーは、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を含む:マップのエントリのうちの少なくともいくつか;マップのすべてのエントリ;マップの対応するエントリのサブセットを含むエントリ;マップの対応するエントリに従った情報を含むエントリ;マップのエントリに存在しない有効な指示および/または他の情報を含むエントリ;2レベルマップの第2レベルのエントリに対応するエントリのみ;マルチレベルマップの最低レベルのエントリに対応するエントリのみ;2レベルマップの第2レベルのページに対応するページ構造といったマップのページ構造に対応するページ構造;ならびにマップと論理的に整合性を有する任意の構造。According to various embodiments, the shadow copy of the map includes one or more of the following: at least some of the entries of the map; all of the entries of the map; entries that include a subset of the corresponding entries of the map; entries that include information according to the corresponding entries of the map; entries that include valid instructions and/or other information not present in the entries of the map; only the entries that correspond to the second level entries of a two-level map; only the entries that correspond to the lowest level entries of a multi-level map; page structures that correspond to the page structures of the map, such as page structures that correspond to the second level pages of a two-level map; and any structures that are logically consistent with the map.
別の実施形態では、マップのシャドウコピーは、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する:マップの対応するエントリと同じ書式を有するエントリ;マップの対応するエントリと類似した書式を有するエントリ;およびマップの対応するエントリと異なる書式を有するエントリ。第1の例では、2レベルマップの第2レベルのページがNVMに圧縮形式で記憶され、マップの第2レベルのシャドウコピーが非圧縮形式で記憶される。第2の例では、マップのシャドウコピーのエントリのうちの1若しくはそれ以上を含むマップのシャドウコピーの複数の部分の各々が、マップに存在しない有効な指示を有する。有効な指示は、それらの部分が独立に初期化され、および/または更新されることを可能にする。第3の例では、マップのシャドウコピーのエントリの各々が、エントリと関連付けられたLBAのデータが1若しくはそれ以上の記憶層のうちのどれに存在するか指示する、マップに存在しない情報を有する。第4の例では、マップのエントリの各々が、エントリと関連付けられたLBAのデータのアーカイブ状態を指示する、マップのシャドウコピーに存在しない情報を有する。第5の例では、マップのシャドウコピーおよび/またはマップは、各エントリと関連付けられたLBAのデータのストレージ層を指示することができるようになっている。第6の例では、マップのシャドウコピーおよび/またはマップは、ホストによって読み出し可能な、および/または書き込み可能な、1エントリ当たり1若しくはそれ以上のビットを含む。第7の例では、マップのエントリの各々が、それぞれの長さおよびそれぞれの範囲を含み、マップのシャドウコピーの対応するエントリの各々が、それぞれの範囲を含み、それぞれの長さを含まない。In another embodiment, the shadow copy of the map has one or more of the following: entries having the same format as the corresponding entries of the map; entries having a similar format as the corresponding entries of the map; and entries having a different format than the corresponding entries of the map. In a first example, the second level pages of the two-level map are stored in the NVM in a compressed format and the second level shadow copy of the map is stored in an uncompressed format. In a second example, each of a plurality of portions of the shadow copy of the map that includes one or more of the entries of the shadow copy of the map has a valid indication not present in the map. The valid indication allows the portions to be initialized and/or updated independently. In a third example, each of the entries of the shadow copy of the map has information not present in the map that indicates in which of one or more storage layers the data of the LBA associated with the entry resides. In a fourth example, each of the entries of the map has information not present in the shadow copy of the map that indicates the archive state of the data of the LBA associated with the entry. In a fifth example, the shadow copy of the map and/or the map can indicate the storage layer of the data of the LBA associated with each entry. In a sixth example, the shadow copy of the map and/or the map includes one or more bits per entry that are readable and/or writable by the host. In a seventh example, each of the entries of the map includes a respective length and a respective range, and each of the corresponding entries of the shadow copy of the map includes a respective range and does not include a respective length.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスの電源オンやリセットといったリセットイベント時に、マップの初期シャドウコピーがコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶される。様々な実施形態によれば、マップの初期シャドウコピーは、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である:すべて無効;マップのコピー;マルチレベルマップの1つ若しくは複数のレベルのコピー;最初に使用されるものとして識別された部分といった、マップの少なくとも一部分のコピー;およびマップと整合性を有する任意の状態。別の実施形態では、マップのシャドウコピーは、LBAが参照される際に動的に更新される。第1の例では、LBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリが、LBAが最初にアクセスされるときに、初期状態から更新される。第2の例では、LBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピーの一部分が、LBAが最初にアクセスされるときに、初期状態から更新される。引き続き第2の例では、この部分は、LBAと関連付けられたエントリを含む第2レベルのマップページに対応するエントリといった、マップのシャドウコピーの複数のエントリを含む。In some embodiments, upon a reset event, such as a power-on or reset of an I/O device, an initial shadow copy of the map is stored in the memory of the computing host. According to various embodiments, the initial shadow copy of the map is one or more of the following: a fully invalidated copy of the map; a copy of one or more levels of a multi-level map; a copy of at least a portion of the map, such as a portion identified as being used for the first time; and any state consistent with the map. In another embodiment, the shadow copy of the map is dynamically updated as an LBA is referenced. In a first example, an entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the LBA is updated from an initial state when the LBA is first accessed. In a second example, a portion of the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the LBA is updated from an initial state when the LBA is first accessed. Continuing with the second example, this portion includes multiple entries of the shadow copy of the map, such as an entry corresponding to a second level map page that includes an entry associated with the LBA.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスによって受け取られる1若しくはそれ以上のコマンドの各々は、入出力デバイスがコマンドの実行の少なくとも一部分としてマップを更新することを可能にする。これら1若しくはそれ以上のコマンドを、本明細書では、マップ更新コマンドと呼ぶ。様々な実施形態によれば、マップ更新コマンドは、書き込みコマンド、切り捨てコマンド、マップの少なくとも一部分を無効にするコマンド、およびマップを変更することができるようにした任意の他のコマンド、のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を含む。In some embodiments, each of the one or more commands received by the I/O device enables the I/O device to update the map as at least a portion of the execution of the command. These one or more commands are referred to herein as map update commands. According to various embodiments, the map update commands include one or more of a write command, a truncate command, a command to invalidate at least a portion of the map, and any other command that allows the map to be modified.
ある実施形態では、書き込みコマンドといったマップ更新コマンドは、LBAを含み、LBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリを無効にする。様々な実施形態によれば、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である:無効化はマップ更新コマンドを発行するときにコンピューティングホストによって行われる;無効化はマップ更新コマンドを受け取り、および/または実行するときに入出力デバイスによって行われる;無効化は、LBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリ内の有効な指示をオフにすることを含む;および無効化は、LBAに対応するエントリを含むマップのシャドウコピーの複数のエントリを含むマップのシャドウコピーの一部分内の有効な指示をオフにすることを含む。マップ更新コマンドに応答してマップ更新コマンドのLBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリを無効にすることは、マップのシャドウコピー内のエントリへのその後のアクセスが、マップのシャドウコピー内のエントリの情報が無効であると決定することを可能にする。In some embodiments, a map update command, such as a write command, includes an LBA and invalidates an entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the LBA. According to various embodiments, one or more of the following: the invalidation is performed by the computing host when issuing the map update command; the invalidation is performed by the I/O device when receiving and/or executing the map update command; the invalidation includes turning off a valid indication in an entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the LBA; and the invalidation includes turning off a valid indication in a portion of the shadow copy of the map that includes multiple entries of the shadow copy of the map that includes the entry that corresponds to the LBA. Invalidating the entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the LBA of the map update command in response to the map update command allows a subsequent access to the entry in the shadow copy of the map to determine that the information in the entry in the shadow copy of the map is invalid.
ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスによって受け取られる書き込みコマンドが、書き込みコマンドのデータが入出力デバイスのNVMに書き込まれることを可能にする。入出力デバイスは、書き込みコマンドのデータが書き込まれるNVM内の位置を決定し、書き込みコマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップ内のエントリを、NVM内の位置を含むように更新する。別の実施形態では、コンピューティングホストのメモリ内のマップのシャドウコピーも、書き込みコマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリがNVM内の位置を含むように更新される。In one embodiment and/or usage scenario, a write command received by an I/O device causes data of the write command to be written to an NVM of the I/O device. The I/O device determines a location in the NVM to which the data of the write command will be written and updates an entry in a map associated with the LBA of the write command to include the location in the NVM. In another embodiment, a shadow copy of the map in the memory of the computing host is also updated such that an entry in the shadow copy of the map associated with the LBA of the write command includes the location in the NVM.
ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、切り捨てコマンドを受け取ったことに応答して、入出力デバイスは、切り捨てコマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップ内のエントリを、LBAと関連付けられたデータがNVMに存在しないという指示を含むように更新する。別の実施形態では、コンピューティングホストのメモリ内のマップのシャドウコピーも、切り捨てコマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリがLBAと関連付けられたデータがNVMに存在しないという指示を含むように更新される。In one embodiment and/or usage scenario, in response to receiving the truncate command, the I/O device updates an entry in the map associated with the LBA of the truncate command to include an indication that data associated with the LBA is not present in the NVM. In another embodiment, a shadow copy of the map in the computing host's memory is also updated such that an entry in the shadow copy of the map associated with the LBA of the truncate command includes an indication that data associated with the LBA is not present in the NVM.
様々な実施形態によれば、マップのシャドウコピーの更新は、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上によって行われる:マップ更新コマンドといった特定のタイプのコマンドを発行したことに応答したコンピューティングホスト;入出力デバイスから更新情報を受け取ったことに応答したコンピューティングホスト;最近の更新を求めて入出力デバイスをポーリングし、更新情報を有する応答を受け取ったことに応答したコンピューティングホスト;PCIeアドレス空間内のマップのシャドウコピーにアクセスすることによってなど、コンピューティングホストのメモリ内のマップのシャドウコピーにアクセスすることによる入出力デバイス;ならびにコンピューティングホストおよび入出力デバイスを含むシステムの別のエージェント。更新情報は、マップの1若しくはそれ以上のエントリの少なくともいくつかのコンテンツに従った情報、および/または1若しくはそれ以上のエントリと関連付けられたそれぞれのLBAといった1若しくはそれ以上のエントリの指示を含む。様々な実施形態において、更新情報は、任意の書式で、または1若しくはそれ以上の入出力デバイスと1若しくはそれ以上のコンピューティングホストとの間で情報を伝える任意の技術によって伝えられる。第1の例では、SATAホストプロトコルを使用して、更新情報は、コンピューティングホストが読み出し可能なログページで伝えられる。第2の例では、NVM ExpressといったPCIeベースのホストプロトコルを使用して、更新情報は、少なくとも部分的に入出力デバイスがコンピューティングホストのメモリ内の領域を書き込み、コンピューティングホストに割り込みで知らせることによって伝えられる。According to various embodiments, the update of the shadow copy of the map is performed by one or more of the following: the computing host in response to issuing a particular type of command, such as a map update command; the computing host in response to receiving update information from an I/O device; the computing host in response to polling the I/O device for recent updates and receiving a response with the update information; the I/O device by accessing a shadow copy of the map in the computing host's memory, such as by accessing a shadow copy of the map in a PCIe address space; and another agent of the system, including the computing host and the I/O device. The update information includes information according to the content of at least some of the one or more entries of the map, and/or an indication of the one or more entries, such as the respective LBAs associated with the one or more entries. In various embodiments, the update information is conveyed in any format or by any technique that conveys information between one or more I/O devices and one or more computing hosts. In a first example, using a SATA host protocol, the update information is conveyed in a log page that is readable by the computing host. In a second example, using a PCIe-based host protocol such as NVM Express, updates are communicated at least in part by the I/O device writing to a location in the computing host's memory and notifying the computing host via an interrupt.
ある実施形態では、マップ更新コマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップ内のエントリは、LBAと関連付けられ、NVMに記憶されたデータの長さおよび/または範囲を指定する情報をさらに含む。というのは、LBAと関連付けられ、NVMに記憶されたデータの長さおよび/または範囲を指定する情報がデータの圧縮率に応じて変動するからである。別の実施形態では、マップ更新コマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、LBAと関連付けられ、NVMに記憶されたデータの長さおよび/または範囲をさらに含む。様々な実施形態によれば、LBAと関連付けられ、NVMに記憶されたデータの長さおよび/または範囲は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、さらに、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を符号化することができるようになっている:LBAと関連付けられたデータの一部および/または全部が切り捨てられるという指示;LBAと関連付けられたデータの一部および/または全部が訂正不能であるという指示;ならびに、LBAと関連付けられたデータの一部および/または全部の任意の他のプロパティ。In one embodiment, the entry in the map associated with the LBA of the map update command further includes information specifying the length and/or range of the data associated with the LBA and stored in the NVM, since the information specifying the length and/or range of the data associated with the LBA and stored in the NVM varies depending on the compressibility of the data. In another embodiment, the entry in the shadow copy of the map associated with the LBA of the map update command optionally and/or selectively further includes the length and/or range of the data associated with the LBA and stored in the NVM. According to various embodiments, the length and/or range of the data associated with the LBA and stored in the NVM may optionally and/or selectively further encode one or more of the following: an indication that some and/or all of the data associated with the LBA is truncated; an indication that some and/or all of the data associated with the LBA is uncorrectable; and any other properties of some and/or all of the data associated with the LBA.
ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、LBAと関連付けられ、NVMに記憶されたデータの長さを、マップ更新コマンドのLBAと関連付けられたマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリに記憶することは、マップ更新コマンドのLBAのデータを上書きするときなどに、後続のマップ更新コマンドにおいてLBAと関連付けられ、NVMに記憶されたデータの長さを提供するためのマップのシャドウコピーの使用を可能にする。LBAと関連付けられ、NVMに記憶されたデータの長さは、後続のマップ更新コマンドによってマップ更新コマンドのLBAのデータを上書きするときに、マップ更新コマンドのLBAのデータを含むNVMの領域における使用空間統計を調整するのに使用される。例えば、マップ更新コマンドのLBAのデータを含むNVMの領域についての使用空間統計が、後続のマップ更新コマンドによってマップ更新コマンドのLBAのデータを上書きするときに、LBAと関連付けられ、NVMに記憶されたデータの長さの分だけ減分される。In certain embodiments and/or usage scenarios, storing the length of the data associated with the LBA and stored in the NVM in an entry in the shadow copy of the map associated with the LBA of the map update command enables use of the shadow copy of the map to provide the length of the data associated with the LBA and stored in the NVM in a subsequent map update command, such as when overwriting the data at the LBA of the map update command. The length of the data associated with the LBA and stored in the NVM is used to adjust the used space statistics for the region of the NVM that includes the data at the LBA of the map update command when the data at the LBA of the map update command is overwritten by a subsequent map update command. For example, the used space statistics for the region of the NVM that includes the data at the LBA of the map update command is decremented by the length of the data associated with the LBA and stored in the NVM when the data at the LBA of the map update command is overwritten by a subsequent map update command.
ある実施形態では、LBAのところのデータを要求する読み出しコマンドといったマップ読み出し要求が、LBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリにアクセスすることができるようになっている。様々な実施形態によれば、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である:アクセスは読み出しコマンドを発行するときにコンピューティングホストによって行われる;アクセスは読み出しコマンドを受け取り、および/または実行するときに入出力デバイスによって行われる;およびアクセスはLBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリの少なくとも一部分を読み取ることを含む。読み出しコマンドのLBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリにアクセスすることにより、マップにアクセスしなくても、マップの対応するエントリに従った情報が提供される。マルチレベルマップの下位レベルといったマップが入出力デバイスのNVMに記憶されるある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、マップのシャドウコピーへのアクセスは、より待ち時間が短く、LBAのところのデータにアクセスする待ち時間を都合よく向上させる。In some embodiments, a map read request, such as a read command requesting data at an LBA, may access an entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the LBA. According to various embodiments, one or more of the following: the access is made by a computing host when issuing the read command; the access is made by an I/O device when receiving and/or executing the read command; and the access includes reading at least a portion of an entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the LBA. Accessing an entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the LBA of the read command provides information according to the corresponding entry of the map without accessing the map. In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios in which a map, such as a lower level of a multi-level map, is stored in the NVM of the I/O device, accessing the shadow copy of the map has lower latency and advantageously improves the latency of accessing data at the LBA.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスからの特定のLBAに対応するデータを読み取るよう求める読み出し要求に応答して、コンピューティングホストは、特定のLBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピーのエントリの少なくとも一部分を読み取る。コンピューティングホストは、入出力デバイスに予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを送り、予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドは、入出力デバイスのNVM内の位置といったマップのシャドウコピーのエントリの情報を含む。様々な実施形態において、予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドは特定のLBAを提供しない。別の実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、NVM内の位置はNVM内のそれぞれの範囲を含む。In one embodiment, in response to a read request from an I/O device to read data corresponding to a particular LBA, the computing host reads at least a portion of an entry in the shadow copy of the map corresponding to the particular LBA. The computing host sends a pre-mapped read command to the I/O device, where the pre-mapped read command includes information of the entry in the shadow copy of the map, such as a location in the NVM of the I/O device. In various embodiments, the pre-mapped read command does not provide a particular LBA. In another embodiment and/or usage scenario, the location in the NVM includes a respective range in the NVM.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスからの特定のLBAに対応するデータを読み取るよう求める読み出し要求に応答して、コンピューティングホストは、特定のLBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピーのエントリの少なくとも一部分を読み取ることができるようになっている。マップのシャドウコピーのエントリが有効でないことが、例えば有効指示によって指示される場合、コンピューティングホストは入出力デバイスに、特定のLBAを含む読み出しコマンドを送る。マップのシャドウコピーのエントリが有効であることが、例えば有効指示によって指示される場合、コンピューティングホストは入出力デバイスに、入出力デバイスのNVM内の位置といった、マップのシャドウコピーのエントリの情報を含む予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを送る。様々な実施形態において、予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドは特定のLBAを提供しない。別の実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、NVM内の位置はNVM内のそれぞれの範囲を含む。In some embodiments, in response to a read request from an I/O device to read data corresponding to a particular LBA, the computing host is adapted to read at least a portion of the entry in the shadow copy of the map corresponding to the particular LBA. If the entry in the shadow copy of the map is not valid, e.g., the validity indication indicates, the computing host sends a read command to the I/O device that includes the particular LBA. If the entry in the shadow copy of the map is valid, e.g., the validity indication indicates, the computing host sends a pre-mapped read command to the I/O device that includes information about the entry in the shadow copy of the map, such as a location in the NVM of the I/O device. In various embodiments, the pre-mapped read command does not provide a particular LBA. In other embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the location in the NVM includes a respective range in the NVM.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスが入出力デバイスのNVM内の位置を含む予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを受け取ったことに応答して、入出力デバイスは、その位置のところのNVMにアクセスして読み出しデータを取得することができるようになっている。入出力デバイスは、予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを受け取ったことに応答してマップにアクセスすることを省略する。予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドに応答して、読み出しデータおよび/またはその処理済みバージョンが返される。In one embodiment, in response to an I/O device receiving a pre-mapped read command that includes a location in the I/O device's NVM, the I/O device can access the NVM at the location to obtain the read data. The I/O device omits accessing the map in response to receiving the pre-mapped read command. In response to the pre-mapped read command, the read data and/or a processed version thereof is returned.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスが特定のLBAに対応する入出力デバイスからのデータを読み取るよう求める読み出しコマンドを受け取ったことに応答して、入出力デバイスは、特定のLBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピーのエントリの少なくとも一部分を読み取ることができるようになっている。入出力デバイスは、マップにアクセスせずに、マップのシャドウコピーのエントリから特定のLBAのデータに対応するNVM内の位置を取得する。入出力デバイスは、NVM内のその位置のところのNVMにアクセスして読み出しデータを取得する。読み出しコマンドに応答して、読み出しデータおよび/またはその処理済みバージョンが返される。In one embodiment, in response to an I/O device receiving a read command requesting that the I/O device read data from the I/O device that corresponds to a particular LBA, the I/O device is adapted to read at least a portion of an entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the particular LBA. The I/O device obtains a location in the NVM that corresponds to the data at the particular LBA from the entry in the shadow copy of the map without accessing the map. The I/O device accesses the NVM at the location in the NVM to obtain the read data. In response to the read command, the read data and/or a processed version thereof is returned.
ある実施形態では、特定のLBAに対応する入出力デバイスからのデータを読み取るよう求める読み出しコマンドの受け取りに応答して、入出力デバイスは、特定のLBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピーのエントリの少なくとも一部分を読み取ることができるようになっている。マップのシャドウコピーのエントリが有効でないことが、例えば有効指示によって指示される場合、入出力デバイスはマップにアクセスして、特定のLBAのデータに対応するNVM内の位置を決定する。マップのシャドウコピーのエントリが有効であることが、例えば有効指示によって指示される場合、入出力デバイスは、マップにアクセスせずに、マップのシャドウコピーのエントリから特定のLBAのデータに対応するNVM内の位置を取得する。入出力デバイスは、NVM内の位置のところのNVMにアクセスして読み出しデータを取得する。読み出しコマンドに応答して、読み出しデータおよび/または処理済みバージョンが返される。In one embodiment, in response to receiving a read command to read data from the I/O device corresponding to a particular LBA, the I/O device is adapted to read at least a portion of an entry in the shadow copy of the map corresponding to the particular LBA. If the entry in the shadow copy of the map is not valid, e.g., indicated by a valid indication, the I/O device accesses the map to determine a location in the NVM corresponding to the data at the particular LBA. If the entry in the shadow copy of the map is valid, e.g., indicated by a valid indication, the I/O device obtains the location in the NVM corresponding to the data at the particular LBA from the entry in the shadow copy of the map without accessing the map. The I/O device accesses the NVM at the location in the NVM to obtain the read data. In response to the read command, the read data and/or a processed version are returned.
上記の実施形態の変形を含む別の実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスのNVM内の位置は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、特定のLBAに対応するデータが入出力デバイスのNVMに存在するかどうかの指示を符号化することができるようになっている。例えば、削減されたデータまたは入出力デバイスが書式設定されて以来書き込まれたことのないデータは入出力デバイスのNVMに存在しない。In other embodiments and/or usage scenarios, including variations of the above embodiments, the locations in the NVM of the I/O device may optionally and/or selectively encode an indication of whether data corresponding to a particular LBA is present in the NVM of the I/O device. For example, reduced data or data that has not been written since the I/O device was formatted is not present in the NVM of the I/O device.
コンピューティングホストがNVM内の位置を、マップのシャドウコピーにアクセスすることによってなど、入出力デバイスからデータを読み取ろうと試みることの一部として決定する変形形態では、コンピューティングホストは、入出力デバイスにコマンドを送らずに、特定のLBAに対応するデータが入出力デバイスのNVMに存在しないと決定することができるようになっている。様々な実施形態によれば、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である:コンピューティングホストは入出力デバイスにコマンドを送らずに読み出し要求への応答を返す;コンピューティングホストは入出力デバイスに特定のLBAを含むコマンドを送る;およびコンピューティングホストは入出力デバイスに、特定のLBAに対応するマップのシャドウコピーのエントリから取得される情報を含むコマンドを送る。In a variation in which the computing host determines the location in the NVM as part of attempting to read data from the I/O device, such as by accessing a shadow copy of the map, the computing host is able to determine that data corresponding to a particular LBA is not present in the NVM of the I/O device without sending a command to the I/O device. According to various embodiments, one or more of the following: the computing host returns a response to the read request without sending a command to the I/O device; the computing host sends a command to the I/O device that includes the particular LBA; and the computing host sends a command to the I/O device that includes information obtained from an entry in the shadow copy of the map that corresponds to the particular LBA.
入出力デバイスがNVM内の位置を、マップのシャドウコピーにアクセスすることによってなど、読み出しコマンドを実行することの一部として決定する変形形態では、入出力デバイスは、NVMにアクセスして読み出しデータを取得せずに、読み出しコマンドへの応答を返すことができるようになっている。In a variation in which the I/O device determines the location in the NVM as part of executing the read command, such as by accessing a shadow copy of the map, the I/O device is able to return a response to the read command without accessing the NVM to obtain the read data.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスは、NVMの領域を再利用するときにマップのシャドウコピーを使用することができるようになっている。再利用は、マップにシャドウコピーのエントリによって、再利用のためにNVMの領域から読み取られたデータがまだ有効であるかどうかを、例えば、マップのシャドウコピーのエントリのうちの1つにおいて最新であることによって決定ことができるようになっている。様々な実施形態において、最新であるデータは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、データをNVM内の新しい位置に書き込み、マップのエントリを、新しい位置を指定するように更新することによって再利用される。様々な実施形態によれば、マップのシャドウコピーのエントリのうちの対応する1つは、無効にされ、または新しい位置で更新される。別の実施形態では、NVM内の特定の位置のところのNVMから読み取られたデータは、データと関連付けられ、NVMから読み取られたヘッダがLBAの少なくとも一部分を含み、LBAの少なくとも一部分と関連付けられたマップのシャドウコピー内のエントリがNVM内の特定の位置を含む場合に、最新である。In one embodiment, the I/O device can use the shadow copy of the map when reclaiming a region of the NVM. Reclaiming can be determined by the shadow copy of the map entries whether data read from a region of the NVM for reclamation is still valid, e.g., by being up-to-date in one of the shadow copy of the map entries. In various embodiments, data that is up-to-date is optionally and/or selectively reclaimed by writing the data to a new location in the NVM and updating the entry of the map to specify the new location. According to various embodiments, a corresponding one of the shadow copy of the map entries is invalidated or updated with the new location. In another embodiment, data read from the NVM at a particular location in the NVM is up-to-date if a header associated with the data and read from the NVM includes at least a portion of an LBA, and an entry in the shadow copy of the map associated with at least a portion of the LBA includes the particular location in the NVM.
ある実施形態では、無効化または更新は、(例えば、書き込み後比較的すぐの)再利用と関連付けられた書き込みに応答したものである。別の実施形態では、無効化または更新は、入出力デバイスが(例えば、書き込みが行われてから任意の長さの時間経過後に)領域を消去した(あるいは消去しようとしている)ことに応答したものである。データの自動切り捨てを提供するある実施形態では、再利用は自動切り捨てを含み、その場合、最新のデータは、新しい位置に書き込まれるのではなく、マップ内で切り捨て済みとマークされる。コンピューティングホストはデータまたはデータ切り捨ての指示を受け取ることができるようになっているため、様々な実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、(たとえ削減されたとしても)最新のデータが提供され、あるいは切り捨ての指示が提供され、書き込みに応答して、または消去に応答して再利用関連の更新が行われるかどうかにかからわらず、マップのシャドウコピーの使用を可能にする。In some embodiments, the invalidation or update is in response to a write associated with the reclamation (e.g., relatively soon after the write). In other embodiments, the invalidation or update is in response to an I/O device erasing (or attempting to erase) the region (e.g., any length of time after the write). In some embodiments that provide automatic truncation of data, the reclamation includes automatic truncation, where the most recent data is marked as truncated in the map rather than being written to a new location. Because the computing host is capable of receiving data or an indication of data truncation, various embodiments and/or usage scenarios allow the use of a shadow copy of the map to provide the most recent data (even if reduced) or an indication of truncation, regardless of whether the reclamation-related update occurs in response to a write or in response to an erase.
例えば、入出力デバイスはコンピューティングホストに、再利用によって更新されている第2レベルのマップエントリおよび/またはマップ部分(第2レベルのマップページなど)のリストの更新を伝える。伝達は、ログメッセージ、予約LBA空間、またはマップ情報を提供するのに適した任意の技術のうちの任意の1若しくはそれ以上によるものである。更新は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、マップのシャドウコピーの1若しくはそれ以上のエントリの無効化を指示し、および/またはマップのシャドウコピーの影響を受けたエントリの1若しくはそれ以上の新しい値を含む。入出力デバイスはコンピューティングホストに、更新が利用可能であることを以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上によって通知する:コマンド状況内の予約ビット、入出力デバイスからコンピューティングホストへの任意の1若しくはそれ以上のタイプの応答内の予約ビット、誤り報告、割り込み、および入出力デバイスとコンピューティングホストとの間で通信するための他の技術。ある使用シナリオでは、更新された第2レベルのマップエントリによって参照されたデータの消去は、更新が(例えば、マップのシャドウコピーに対して)適用されているというコンピューティングホストからの確認を受け取ることに依存したものである。For example, the I/O device communicates to the computing host updates to the list of second level map entries and/or map portions (e.g., second level map pages) that have been updated by reclamation. The communication may be by any one or more of log messages, reserved LBA space, or any technique suitable for providing map information. The updates may optionally and/or selectively indicate invalidation of one or more entries in the shadow copy of the map and/or include one or more new values of the affected entries in the shadow copy of the map. The I/O device notifies the computing host that updates are available by one or more of the following: reserved bits in a command status, reserved bits in any one or more types of responses from the I/O device to the computing host, error reports, interrupts, and other techniques for communicating between the I/O device and the computing host. In one usage scenario, the erasure of data referenced by the updated second level map entries is dependent on receiving confirmation from the computing host that the updates have been applied (e.g., to the shadow copy of the map).
様々な実施形態において、マップのシャドウコピーは、CRCやチェックサムといった1若しくはそれ以上の誤り検出コードを含む。誤り検出コードの各々は、マップのシャドウコピーの1若しくはそれ以上のエントリを含むそれぞれの部分を保護する。例えば、ある実施形態では、それぞれの部分は第2レベルのマップページに対応する。様々な実施形態によれば、それぞれの部分のうちの1つの完全性は以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上によって検証される:それぞれの部分と関連付けられた誤り検出コードを再計算し、検証すること;それぞれの部分と関連付けられた誤り検出コードを、マップの対応する部分に従って計算された誤り検出コードと比較すること;およびそれぞれの部分をマップの対応する部分と共に直接検証すること。様々な実施形態によれば、それぞれの部分のうちの1つの完全性は以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上として検証される:入出力デバイスおよび/または入出力デバイスを含むシステムのリセットおよび/または電源サイクルの都度;入出力デバイスおよび/または入出力デバイスを含むシステムが低電力および/または休眠状態(低電力動作状態など)を終了する都度;指定の間隔後に;ならびに指定の頻度に従って周期的に。In various embodiments, the shadow copy of the map includes one or more error detection codes, such as a CRC or a checksum. Each of the error detection codes protects a respective portion of the shadow copy of the map that includes one or more entries. For example, in one embodiment, each portion corresponds to a second level map page. According to various embodiments, the integrity of one of the respective portions is verified by one or more of the following: recalculating and verifying the error detection code associated with each portion; comparing the error detection code associated with each portion to an error detection code calculated according to the corresponding portion of the map; and directly verifying each portion with the corresponding portion of the map. According to various embodiments, the integrity of one of the respective portions is verified as one or more of the following: upon each reset and/or power cycle of the I/O device and/or the system including the I/O device; upon each exit of the I/O device and/or the system including the I/O device from a low power and/or dormant state (e.g., a low power operating state); after a specified interval; and periodically according to a specified frequency.
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスは、コンピューティングホストのメモリを使用して入出力デバイスの状態を保存することができるようになっている。様々な実施形態によれば、入出力デバイスの状態は以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を含む:マップのシャドウコピー;入出力デバイスのマップのキャッシュ;入出力デバイスのマルチレベルマップの1若しくはそれ以上のレベルのキャッシュ;入出力デバイスの2レベルマップの第1レベル;入出力デバイスのマルチレベルマップの上位レベル;入出力デバイスの揮発状態;NVMのアクセスおよび/または挙動に従った統計といった入出力デバイスによって維持される統計;入出力デバイスが低電力状態を開始するときに失われる入出力デバイスの内部状態;ならびに入出力デバイスの他の状態。様々な実施形態において、入出力デバイスの保存された状態のすべての部分または任意の部分が、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、保存されるときに暗号化され、復元されるときに解読される。In some embodiments, the I/O device is adapted to use the memory of the computing host to save the state of the I/O device. According to various embodiments, the state of the I/O device includes one or more of the following: a shadow copy of the map; a cache of the map of the I/O device; a cache of one or more levels of the multi-level map of the I/O device; a first level of a two-level map of the I/O device; a top level of the multi-level map of the I/O device; a volatile state of the I/O device; statistics maintained by the I/O device, such as statistics according to NVM access and/or behavior; an internal state of the I/O device that is lost when the I/O device enters a low power state; and other states of the I/O device. In various embodiments, all or any portions of the saved state of the I/O device are optionally and/or selectively encrypted when saved and decrypted when restored.
ある実施形態では、通常モード(高電力動作状態など)で動作している入出力デバイスは、例えば、低電力状態を開始するよう求める要求を受け取ったことに応答して、または入出力デバイスの非アクティビティ期間に応答して、入出力デバイスの構成設定に従って、低電力および/または休眠状態(低電力動作状態など)を開始することを決定することができるようになっている。低電力状態を開始することを決定したことに応答して、入出力デバイスは、入出力デバイスの状態の少なくとも1つの第1の部分をコンピューティングホストのメモリに保存することができるようになっている。入出力デバイスは次いで、低電力状態を開始することができるようになっており、入出力デバイスの状態の少なくとも1つの第1の部分は、例えば、入出力デバイスの少なくとも一部分への電力が除去されることによって失われる。その後に、入出力デバイスは、例えば、低電力状態を終了するよう求める要求を受け取ることによって、低電力状態を終了することを決定することができるようになっている。低電力状態を終了することを決定したことに応答して、入出力デバイスは、低電力状態を終了することができるようになっている。入出力デバイスは次いで、コンピューティングホストのメモリから入出力デバイス状態の少なくとも1つの第1の部分を復元し、通常モードでの動作を再開することができるようになっている。様々な実施形態によれば、低電力状態は、待機状態、休眠状態、休止状態、遊休状態、および入出力デバイスの電力管理プロトコルにおける任意の状態、のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である。In some embodiments, an input/output device operating in a normal mode (e.g., a high-power operating state) may determine to enter a low-power and/or dormant state (e.g., a low-power operating state) in accordance with a configuration setting of the input/output device, e.g., in response to receiving a request to enter a low-power state or in response to a period of inactivity of the input/output device. In response to determining to enter the low-power state, the input/output device may save at least a first portion of the state of the input/output device to a memory of the computing host. The input/output device may then enter the low-power state, and at least a first portion of the state of the input/output device is lost, e.g., by removing power to at least a portion of the input/output device. Thereafter, the input/output device may determine to exit the low-power state, e.g., by receiving a request to exit the low-power state. In response to determining to exit the low-power state, the input/output device may exit the low-power state. The input/output device may then restore at least a first portion of the state of the input/output device from the memory of the computing host and resume operation in the normal mode. According to various embodiments, the low power state is one or more of a standby state, a dormant state, a hibernate state, an idle state, and any state in the power management protocol of the I/O device.
別の実施形態では、低電力状態を開始することを決定したことに応答して、入出力デバイスの状態の少なくとも1つの第2の部分が入出力デバイスのNVMに保存される。さらに別の実施形態では、低電力状態を終了することを決定したことに応答して、入出力デバイスは、NVMから入出力デバイスの状態の少なくとも1つの第3の部分を復元することができるようになっている。例えば、ある使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスの状態の少なくとも1つの第1の部分は第1レベルのマップを含み、入出力デバイスの状態の少なくとも1つの第2の部分は入出力デバイスの状態のチェックポイントを含み、入出力デバイスの状態の少なくとも1つの第3の部分は入出力デバイスのプロセッサの実行可能コードを含む。In another embodiment, in response to determining to enter the low power state, at least a second portion of the state of the I/O device is saved to the NVM of the I/O device. In yet another embodiment, in response to determining to exit the low power state, the I/O device is adapted to restore at least a third portion of the state of the I/O device from the NVM. For example, in one usage scenario, at least a first portion of the state of the I/O device includes a first level map, at least a second portion of the state of the I/O device includes a checkpoint of the state of the I/O device, and at least a third portion of the state of the I/O device includes executable code of a processor of the I/O device.
様々な実施形態において、入出力記憶デバイスは、1若しくはそれ以上の非標準統計を計算することができるようになっている。非標準統計の例は、ストレージ使用状況、ストレージ使用パーセンテージ、書き込み増幅、ならびに入出力記憶デバイスの不揮発性記憶の1若しくはそれ以上のバンドのサイズおよび/または使用状況である。ある実施形態および/使用シナリオでは、入出力記憶デバイスのストレージの少なくとも一部分を実施するNVMに書き込まれるべきデータが、NVMでの書き込みの前にサイズを低減される。非標準統計の別の例は、少なくとも部分的にサイズ低減に基づく、および/または過去および/若しくは現在のサイズ低減に基づく将来のサイズ低減の予測に基づくストレージ使用状況および/またはストレージ使用パーセンテージである。非標準統計値の返しを要求する(例えばコンピューティングホストからの)コマンドを受け取ったことに応答して、入出力記憶デバイスは、要求された非標準統計を(例えばコンピューティングホストに)返す。(例えば非標準統計のうちの1若しくはそれ以上の全部または任意の部分の)計算の結果は、任意選択で、任意のサイズ低減の影響を受ける。サイズ低減は、例えば、圧縮および/またはデータ重複排除によるものである。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、非標準統計のうちの1若しくはそれ以上(例えば、NVMの使用状況といったストレージ使用状況)が、以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上に従って変動する:サイズ低減の質、(例えばコンピューティングホストから受け取られる)切り捨てコマンドの数および/またはサイズ、(例えばコンピューティングホストから)受け取られる一時データの量、ならびに(例えば入出力記憶デバイスによって)削減された一時データの量。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、非標準統計のうちの1若しくはそれ以上(例えばバンドの使用状況)が、サイズ低減の質に従って変動する。In various embodiments, the I/O storage device is adapted to calculate one or more non-standard statistics. Examples of non-standard statistics are storage usage, storage usage percentage, write amplification, and size and/or usage of one or more bands of non-volatile storage of the I/O storage device. In certain embodiments and/or usage scenarios, data to be written to an NVM implementing at least a portion of the storage of the I/O storage device is reduced in size prior to writing at the NVM. Another example of a non-standard statistic is storage usage and/or storage usage percentage based at least in part on size reduction and/or a prediction of future size reduction based on past and/or current size reduction. In response to receiving a command (e.g., from a computing host) requesting the return of a non-standard statistic, the I/O storage device returns (e.g., to the computing host) the requested non-standard statistics. The results of the calculation (e.g., of all or any portion of one or more of the non-standard statistics) are optionally subject to any size reduction. The size reduction is due to, for example, compression and/or data deduplication. In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, one or more of the non-standard statistics (e.g., storage usage, such as NVM usage) vary according to one or more of the following: quality of size reduction, number and/or size of truncate commands (e.g., received from a computing host), amount of temporary data received (e.g., from a computing host), and amount of temporary data reduced (e.g., by an I/O storage device). In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, one or more of the non-standard statistics (e.g., band usage) vary according to quality of size reduction.
一部の実施形態では、NVM内の様々なサイズの量の圧縮データにアクセスすることにより、ある使用シナリオでは記憶効率が改善される。例えば、SSDコントローラは、コンピューティングホストから(例えばディスク書き込みコマンドに関連した)(圧縮されていない)データを受け取り、データを圧縮し、データをフラッシュメモリへ記憶する。コンピューティングホストからの(例えばディスク読み出しコマンドに関連した)その後の要求に応答して、SSDコントローラはフラッシュメモリから圧縮データを読み出し、圧縮データを解凍し、解凍されたデータをコンピューティングホストに提供する。圧縮データは、様々なサイズの量に従ってフラッシュメモリに記憶され、各量のサイズは、例えば、圧縮アルゴリズム、動作モード、様々なデータに関する圧縮有効性により変動する。SSDコントローラは、一部は、含まれるマップ表を調べて(1つまたは複数の)ヘッダがフラッシュメモリのどこに記憶されているか確認することによってデータを解凍する。SSDコントローラは、適切な(圧縮)データがフラッシュメモリのどこに記憶されているか確認するためにフラッシュメモリから得た(1つまたは複数の)ヘッダをパースする。SSDコントローラは、コンピューティングホストに提供すべき解凍データを生成するために、フラッシュメモリからの適切なデータを解凍する。本出願では、「解凍する(uncompress)」(およびその変形)は、「伸張する(decompress)」(およびその変形)と同義である。In some embodiments, accessing the various sized quantities of compressed data in the NVM improves storage efficiency in certain usage scenarios. For example, the SSD controller receives (uncompressed) data from a computing host (e.g., associated with a disk write command), compresses the data, and stores the data in flash memory. In response to a subsequent request from the computing host (e.g., associated with a disk read command), the SSD controller reads the compressed data from the flash memory, decompresses the compressed data, and provides the decompressed data to the computing host. The compressed data is stored in the flash memory according to various sized quantities, the size of each quantity varying depending on, for example, the compression algorithm, the mode of operation, and the compression effectiveness for various data. The SSD controller decompresses the data, in part, by consulting an included map table to ascertain where the header(s) are stored in the flash memory. The SSD controller parses the header(s) from the flash memory to ascertain where the appropriate (compressed) data is stored in the flash memory. The SSD controller decompresses the appropriate data from the flash memory to generate decompressed data to be provided to the computing host. In this application, "uncompress" (and variations thereof) is synonymous with "decompress" (and variations thereof).
様々な実施形態では、SSDコントローラは、コンピューティングホストとインターフェースするためのホストインターフェースと、フラッシュメモリといったNVMとインターフェースするためのインターフェースと、各インターフェースを制御し、圧縮および解凍と共に、低レベル誤り訂正、高レベル誤り訂正、ならびに独立シリコン素子を用いた動的高レベル冗長性モード管理を行う(および/または行うことの様々な態様を制御する)ための回路とを含む。In various embodiments, the SSD controller includes a host interface for interfacing with a computing host, an interface for interfacing with an NVM such as flash memory, and circuitry for controlling each interface and for performing (and/or controlling various aspects of performing) low-level error correction, high-level error correction, and dynamic high-level redundancy mode management using independent silicon devices, along with compression and decompression.
様々な実施形態によれば、あるホストインターフェースは、USBインターフェース規格、CFインターフェース規格、MMCインターフェース規格、SDインターフェース規格、メモリ・スティック・インターフェース規格、xDピクチャ・カード・インターフェース規格、IDEインターフェース規格、SATAインターフェース規格、SCSIインターフェース規格、SASインターフェース規格、およびPCIeインターフェース規格のうちの1つ若しくはそれ以上と適合する。様々な実施形態によれば、コンピューティングホストは、コンピュータ、ワークステーションコンピュータ、サーバコンピュータ、ストレージサーバ、PC、ラップトップコンピュータ、ノートブックコンピュータ、ネットブックコンピュータ、PDA、メディアプレーヤ、メディアレコーダ、ディジタルカメラ、セルラハンドセット、コードレス電話機ハンドセット、および電子ゲームのうちの全部または任意の部分である。一部の実施形態では、インターフェースホスト(SAS/SATAブリッジなど)は、コンピューティングホストおよび/またはコンピューティングホストへのブリッジとして動作する。According to various embodiments, a host interface is compatible with one or more of the USB interface standard, the CF interface standard, the MMC interface standard, the SD interface standard, the Memory Stick interface standard, the xD Picture Card interface standard, the IDE interface standard, the SATA interface standard, the SCSI interface standard, the SAS interface standard, and the PCIe interface standard. According to various embodiments, the computing host is all or any part of a computer, a workstation computer, a server computer, a storage server, a PC, a laptop computer, a notebook computer, a netbook computer, a PDA, a media player, a media recorder, a digital camera, a cellular handset, a cordless telephone handset, and an electronic game. In some embodiments, the interface host (e.g., a SAS/SATA bridge) acts as the computing host and/or a bridge to the computing host.
様々な実施形態では、SSDコントローラは、1つ若しくはそれ以上のプロセッサを含む。プロセッサは、SSDコントローラの動作を制御し、および/または行うためにファームウェアを実行する。SSDコントローラは、コマンドおよび/または状況ならびにデータを送り、受け取るためにコンピューティングホストと通信する。コンピューティングホストは、オペレーティングシステム、ドライバ、およびアプリケーションのうちの1つ若しくはそれ以上を実行する。コンピューティングホストによるSSDコントローラとの通信は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ドライバおよび/またはアプリケーションによるものである。第1の例では、SSDコントローラへのすべての通信がドライバによるものであり、アプリケーションは、ドライバに高レベルコマンドを提供し、ドライバがそれをSSDコントローラのための特定のコマンドに変換する。第2の例では、ドライバはバイパスモードを実施し、アプリケーションは、ドライバを介してSSDコントローラに特定のコマンドを送ることができるようになっている。第3の例では、PCIe SSDコントローラが1つ若しくはそれ以上の仮想機能(Virtual Functions:VFs)をサポートし、アプリケーションが、一度構成されると、ドライバをバイパスしてSSDコントローラを直接通信することを可能にする。In various embodiments, the SSD controller includes one or more processors. The processor executes firmware to control and/or perform the operation of the SSD controller. The SSD controller communicates with a computing host to send and receive commands and/or status and data. The computing host executes one or more of an operating system, a driver, and an application. Communication with the SSD controller by the computing host is optionally and/or selectively through the driver and/or the application. In a first example, all communication to the SSD controller is through the driver, and the application provides high-level commands to the driver, which the driver translates into specific commands for the SSD controller. In a second example, the driver implements a bypass mode, allowing the application to send specific commands to the SSD controller through the driver. In a third example, the PCIe SSD controller supports one or more Virtual Functions (VFs), allowing the application, once configured, to bypass the driver and communicate directly with the SSD controller.
様々な実施形態によれば、あるSSDは、HDD、CDドライブ、DVDドライブといった磁気的不揮発性記憶および/または光学的不揮発性記憶によって使用されるフォームファクタ、電気的インターフェース、および/またはプロトコルと適合する。様々な実施形態では、SSDは、0以上のパリティ符号、0以上のRS符号、0以上のBCH符号、0以上のビタビ符号または他のトレリス符号、および0以上のLDPC符号の様々な組み合わせを使用する。According to various embodiments, an SSD is compatible with form factors, electrical interfaces, and/or protocols used by magnetic and/or optical non-volatile storage such as HDDs, CD drives, DVD drives, etc. In various embodiments, the SSD uses various combinations of zero or more parity codes, zero or more RS codes, zero or more BCH codes, zero or more Viterbi codes or other trellis codes, and zero or more LDPC codes.
例示的な実施形態
詳細な記載に対する導入を締めくくる際に続くものは、「ECs」(例示的な組み合わせ)として明示的に列挙される少なくとも一部の例示的な実施形態を含む例示的な実施形態を集めたものであり、本明細書において記載される概念に従った様々な実施形態の種類の追加的な記載を提供する。これらの例は、互いに排他的、網羅的、又は制限的であることを意味せず、本発明はこれらの例示的な実施形態には限定されるものでなく、特許請求の範囲の範囲内の全ての可能な改変形態及び変化形態を含む。 Exemplary Embodiments In concluding the introduction to the detailed description, what follows is a collection of exemplary embodiments, including at least some exemplary embodiments explicitly listed as "ECs" (exemplary combinations), to provide additional descriptions of various embodiment types consistent with the concepts described herein. These examples are not meant to be mutually exclusive, exhaustive, or limiting, and the invention is not limited to these exemplary embodiments, but includes all possible modifications and variations within the scope of the claims.
EC1)方法であって、
標準コマンドと非標準修飾子の仕様とを有する拡張コマンドを入出力デバイスで受け取る工程と、
前記非標準修飾子に従って前記標準コマンドを実行する工程と
を有し、
前記非標準修飾子を使用して前記標準コマンドの実行を変更することによりシステムレベルの性能が改善されるものである
方法。 EC1) A method comprising:
receiving an extension command at an input/output device, the extension command having a standard command and a specification of a non-standard modifier;
executing the standard command according to the non-standard modifier;
The method wherein the non-standard modifiers are used to modify the execution of the standard commands to improve system level performance.
EC2)方法であって、
非標準修飾子を有効にする仕様を有するモード設定コマンドを入出力デバイスで受け取る工程と、
標準コマンドを前記入出力デバイスで受け取る工程と、
前記非標準修飾子に従って前記標準コマンドを実行する工程と
を有し、
前記非標準修飾子を使用して前記標準コマンドの実行を変更することによりシステムレベルの性能が改善されるものである
方法。 EC2) A method comprising:
receiving a mode set command at an input/output device having a specification for enabling a non-standard modifier;
receiving a standard command at said input/output device;
executing the standard command according to the non-standard modifier;
The method wherein the non-standard modifiers are used to modify the execution of the standard commands to improve system level performance.
EC3)EC1またはEC2記載の方法において、さらに、
前記非標準修飾子を前記標準コマンドのデータと関連付ける工程を有するものである方法。 EC3) The method according to EC1 or EC2, further comprising:
The method further comprising the step of associating the non-standard modifier with data of the standard command.
EC4)EC3記載の方法において、さらに、
前記標準コマンドの前記データと共に後で取得するために前記非標準修飾子の指示を記憶する工程を有するものである方法。 EC4) The method according to EC3, further comprising:
storing an indication of the non-standard modifier for later retrieval along with the data of the standard command.
EC5)EC4記載の方法において、前記記憶する工程は不揮発的である方法。EC5) The method according to EC4, wherein the storing step is non-volatile.
EC6)EC4記載の方法において、さらに、
前記非標準修飾子の前記指示をマップの複数のエントリのうちの特定の1つに記憶する工程であって、前記特定のエントリは前記標準コマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)によって前記標準コマンドの前記データと関連付けられている、記憶する工程を有するものである方法。 EC6) The method according to EC4, further comprising:
Storing the indication of the non-standard modifier in a particular one of a plurality of entries of a map, the particular entry being associated with the data of the standard command by a logical block address (LBA) of the standard command.
EC7)EC4記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、さらに、
前記書き込みコマンドの前記データへのアクセスを指定する後続の読み出しコマンドに応答して、前記非標準修飾子の前記指示に従って前記後続の読み出しコマンドの実行を変更する工程を有するものである方法。 EC7) The method of EC4, wherein the standard command is a write command, and further comprising:
in response to a subsequent read command specifying access to the data of the write command, modifying execution of the subsequent read command in accordance with the indication of the non-standard modifier.
EC8)EC4記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは第1のコマンドであり、さらに、
前記第1のコマンドの前記データへのアクセスを指定する後続のコマンドに応答して、前記非標準修飾子の前記指示に従って前記後続のコマンドの実行を変更する工程を有するものである方法。 EC8) The method of EC4, wherein the standard command is a first command, further comprising:
in response to a subsequent command specifying access to the data of the first command, modifying execution of the subsequent command in accordance with the indication of the non-standard modifier.
EC9)EC8記載の方法において、
前記第1のコマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、
前記非標準修飾子は、前記書き込みコマンドの前記データが読み出し専用であるという指示を有し、
前記後続のコマンドの実行を変更する前記工程は、前記後続のコマンドが標準書き込みコマンドである場合に誤り指示を返す工程を有する方法。 EC9) In the method according to EC8,
the first command is a write command;
the non-standard qualifier comprises an indication that the data in the write command is read-only;
The method, wherein the step of modifying execution of the subsequent command comprises returning an error indication if the subsequent command is a standard write command.
EC10)EC4記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、さらに、
前記書き込みコマンドの前記データが再利用されるべきであると決定する工程と、
前記非標準修飾子の前記指示にアクセスする工程と、
前記非標準修飾子の前記指示に応答して、前記書き込みコマンドの前記データを削減する工程と
を有し、それによって、前記書き込みコマンドの前記データは再利用されるのではなく切り捨てられる方法。 EC10) The method of EC4, wherein the standard command is a write command, and further comprising:
determining that the data of the write command should be reused;
accessing the indication of the non-standard modifier;
and pruning the data of the write command in response to the indication of the non-standard qualifier, whereby the data of the write command is truncated rather than reused.
EC11)EC1またはEC2記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは読み出しコマンドである方法。EC11) The method according to EC1 or EC2, wherein the standard command is a read command.
EC12)EC1またはEC2記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは読み出しコマンドまたは書き込みコマンドの一方である方法。EC12) The method according to EC1 or EC2, wherein the standard command is either a read command or a write command.
EC13)EC1またはEC2記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドはデータ移動コマンドである方法。EC13) The method according to EC1 or EC2, wherein the standard command is a data movement command.
EC14)EC1またはEC2記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは切り捨てコマンドである方法。EC14) The method of EC1 or EC2, wherein the standard command is a truncate command.
EC15)EC14記載の方法において、前記非標準修飾子は、前記切り捨てコマンドが必須であるかそれとも任意選択であるか選択的に決定する方法。EC15) The method of EC14, wherein the non-standard modifier selectively determines whether the truncation command is required or optional.
EC16)EC1またはEC2記載の方法において、前記非標準修飾子は、少なくとも部分的に前記標準コマンドの予約フィールドによって指定される方法。EC16) The method of EC1 or EC2, wherein the non-standard modifier is specified, at least in part, by a reserved field of the standard command.
EC17)EC1またはEC2記載の方法において、前記非標準修飾子は、少なくとも部分的に前記標準コマンドの複数のアドレスビットのうちの少なくともいくつかによって指定される方法。EC17) The method of EC1 or EC2, wherein the non-standard modifier is specified, at least in part, by at least some of a plurality of address bits of the standard command.
EC18)EC17記載の方法において、前記アドレスビットのうちの前記少なくともいくつかは、前記入出力デバイスによってそれ以外に使用されない方法。EC18) The method of EC17, wherein at least some of the address bits are not otherwise used by the I/O device.
EC19)EC1またはEC2記載の方法において、前記非標準修飾子は、
データタイプの仕様、
データアクセスタイプの仕様、
データ順序付けの仕様、
データ関係の仕様、
データ宛先の仕様、および
コマンド関係の仕様
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である方法。 EC19) The method according to EC1 or EC2, wherein the non-standard modifier is:
Data type specifications,
Data access type specifications,
Data ordering specifications,
Data related specifications,
The method being one or more of: a data destination specification; and a command relation specification.
EC20)EC19記載の方法において、前記データタイプの前記仕様は圧縮率指示を有する方法。EC20) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data type includes a compression ratio indication.
EC21)EC20記載の方法において、前記データタイプの前記仕様は、前記データタイプが圧縮不能であるという指示を有する方法。EC21) The method of EC20, wherein the specification of the data type includes an indication that the data type is incompressible.
EC22)EC19記載の方法において、前記データタイプの前記仕様はデータベース・ジャーナル・タイプの指示を有する方法。EC22) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data type includes an indication of a database journal type.
EC23)EC19記載の方法において、前記データアクセスタイプの前記仕様は、読み出し/書き込みデータアクセスタイプの指示、略読み出しデータアクセスタイプの指示、および略書き込みデータアクセスタイプの指示のうちの2若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。EC23) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data access type includes two or more of an indication of a read/write data access type, an indication of a mostly read data access type, and an indication of a mostly write data access type.
EC24)EC19記載の方法において、前記データアクセスタイプの前記仕様は、読み出し/書き込みデータアクセスタイプの指示、略読み出しデータアクセスタイプの指示、略書き込みデータアクセスタイプの指示および一時データアクセスタイプの指示のうちの2若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。EC24) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data access type includes two or more of an indication of a read/write data access type, an indication of a mostly read data access type, an indication of a mostly write data access type, and an indication of a temporary data access type.
EC25)EC19記載の方法において、前記データアクセスタイプの前記仕様は一時データアクセスタイプの指示を有する方法。EC25) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data access type includes an indication of a temporary data access type.
EC26)EC25記載の方法において、
前記標準コマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、前記非標準修飾子は前記一時データアクセスタイプの指示を有し、さらに、
前記書き込みコマンドのデータを不揮発的に記憶する工程と、
前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが再利用されるべきであると決定したことに応答し、前記非標準修飾子に従って、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データを削減する工程と
を有するものである方法。 EC26) In the method according to EC25,
the standard command is a write command, the non-standard qualifier has an indication of the temporary data access type, and
storing the write command data in a non-volatile manner;
in response to determining that the data stored by the write command should be reused, pruning the data stored by the write command in accordance with the non-standard qualifier.
EC27)EC26記載の方法において、さらに、
前記削減する工程に続く前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データの読み出しに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが切り捨てられるという指示を返す工程を有するものである方法。 EC27) The method according to EC26, further comprising:
In response to reading the data stored by the write command following the reducing step, returning an indication that the data stored by the write command is truncated.
EC28)EC26記載の方法において、さらに、
前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データの読み出しに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが切り捨てられるという指示、または前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データを選択的に返す工程を有するものである方法。 EC28) The method according to EC26, further comprising:
In response to reading the data stored by the write command, selectively returning an indication that the data stored by the write command is truncated or the data stored by the write command.
EC29)EC27またはEC28記載の方法において、さらに、
前記読み出しに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが切り捨てられるという前記指示を非データ応答として返す工程を有するものである方法。 EC29) The method according to EC27 or EC28, further comprising:
In response to the read, returning the indication that the data stored by the write command is truncated as a non-data response.
EC30)EC27またはEC28記載の方法において、さらに、
前記読み出しに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが切り捨てられるという前記指示を返されるデータにおいて特定のパターンとして返す工程を有するものである方法。 EC30) The method according to EC27 or EC28, further comprising:
in response to the read, returning the indication that the data stored by the write command is truncated as a particular pattern in returned data.
EC31)EC19記載の方法において、前記データアクセスタイプの前記仕様は読み出し専用データアクセスタイプの指示を有する方法。EC31) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data access type includes an indication of a read-only data access type.
EC32)EC31記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは第1の書き込みコマンドであり、前記非標準修飾子は前記読み出し専用データアクセスタイプの指示を有し、さらに、
前記第1の書き込みコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)に従って前記第1の書き込みコマンドのデータを不揮発的に記憶する工程と、
前記第1の書き込みコマンドの前記論理ブロックアドレスに書き込もうとする後続の書き込みコマンドに応答して、誤り指示を返す工程と
を有するものである方法。 EC32) The method of EC31, wherein the standard command is a first write command and the non-standard qualifier comprises an indication of the read-only data access type, further comprising:
non-volatilely storing data of the first write command according to a logical block address (LBA) of the first write command;
returning an error indication in response to a subsequent write command attempting to write to the logical block address of the first write command.
EC33)EC19記載の方法において、前記データ順序付けの前記仕様はアトミックシーケンスの指示を有する方法。EC33) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data ordering comprises an indication of an atomic sequence.
EC34)EC19記載の方法において、前記データ順序付けの前記仕様は、順次シーケンスの指示およびアトミックシーケンスの指示のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。EC34) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data ordering comprises one or more of an indication of a sequential sequence and an indication of an atomic sequence.
EC35)EC19記載の方法において、さらに、
前記データ関係を前記標準コマンドのデータと関連付ける工程を有するものである方法。 EC35) The method according to EC19, further comprising:
The method further comprising the step of associating the data relationship with data of the standard command.
EC36)EC35記載の方法において、さらに、
前記データ関係および前記標準コマンドの前記データを不揮発的に記憶する工程を有するものである方法。 EC36) The method according to EC35, further comprising:
storing said data relationship and said data of said standard command in a non-volatile manner.
EC37)EC36記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは第1の標準コマンドであり、さらに、
続いて、前記データ関係を後続の標準コマンドのデータと関連付ける工程を有するものである方法。 EC37) The method of EC36, wherein the standard command is a first standard command and further comprising:
The method further comprises the step of: subsequently associating the data relationship with data of a subsequent standard command.
EC38)EC37記載の方法において、さらに、
前記データ関係に従ってデータを取得する工程を有するものである方法。 EC38) The method according to EC37, further comprising:
The method comprising obtaining data according to the data relationship.
EC39)EC19記載の方法において、前記データ宛先の前記仕様は複数のデータバンドのうちの1つを指定する方法。EC39) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the data destination specifies one of a plurality of data bands.
EC40)EC39記載の方法において、前記データバンドはホットバンドとコールドバンドとを有する方法。EC40) The method of EC39, wherein the data band has a hot band and a cold band.
EC41)EC19記載の方法において、前記コマンド関係の前記仕様はコマンド優先順位を有する方法。EC41) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the command relationship includes a command priority.
EC42)EC19記載の方法において、前記コマンド関係の前記仕様はコマンド順序付け従属関係を有する方法。EC42) The method of EC19, wherein the specification of the command relationship includes a command ordering dependency relationship.
EC43)EC42記載の方法において、前記コマンド順序付け従属関係はコマンドバリアである方法。EC43) The method of EC42, wherein the command ordering dependency is a command barrier.
EC44)EC2記載の方法において、前記標準コマンドは2若しくはそれ以上の標準コマンドのシーケンスである方法。EC44) The method of EC2, wherein the standard command is a sequence of two or more standard commands.
EC45)EC2記載の方法において、
前記モード設定コマンドは第1のモード設定コマンドであり、さらに、
前記標準コマンドを受け取る前記工程に続いて、前記非標準修飾子を使用不可にする仕様を有する第2のモード設定コマンドを受け取る工程を有するものである方法。 EC45) In the method according to EC2,
the mode setting command is a first mode setting command,
Following said step of receiving said standard command, the method further comprises the step of receiving a second mode setting command having a specification that disables said non-standard modifier.
EC46)方法であって、
入出力デバイスで、外部インターフェースを介してコマンドを受け取る工程と、
前記コマンドのタイプを確認する工程と、
前記コマンドのタイプが読み出しコマンドである場合、マップにアクセスして前記コマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を変換し、不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置を選択的に有する変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報を取得する工程と、
前記コマンドのタイプが予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドである場合、当該予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドの情報から、前記マップを使用せずに前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置を決定する工程と、
前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置に対応するデータを返す工程と
を有し、
前記予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドの前記情報は、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の少なくとも一部分を有するものである、
方法。 EC46) A method comprising the steps of:
receiving a command via an external interface at an input/output device;
determining the type of the command;
if the type of the command is a read command, accessing a map to translate a logical block address (LBA) of the command and obtain translated logical block address information selectively having a predetermined location in a non-volatile memory (NVM);
if the command type is a pre-mapped read command, determining the location in the non-volatile memory from information in the pre-mapped read command without using the map;
returning data corresponding to the location in the non-volatile memory;
the information in the pre-mapped read command comprises at least a portion of the translated logical block address information.
method.
EC47)EC46記載の方法において、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報は、前記不揮発性メモリ内の位置または前記コマンドの前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないという指示を選択的に有するものである方法。EC47) The method of EC46, wherein the converted logical block address information selectively includes a location within the non-volatile memory or an indication that the logical block address of the command does not exist in the non-volatile memory.
EC48)EC46記載の方法において、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報は、前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位のうちの第1の読み出し単位のアドレスおよび読み出し単位での長さを選択的に有する方法。EC48) The method of EC46, wherein the converted logical block address information selectively includes an address and a length in read units of a first read unit of one or more read units of the non-volatile memory.
EC49)EC48記載の方法において、前記1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位の各々のサイズは少なくとも512バイトである方法。EC49) The method of EC48, wherein the size of each of the one or more read units is at least 512 bytes.
EC50)EC46記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップのシャドウコピーにアクセスして前記論理ブロックアドレスを変換して、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分を取得する工程と、
前記入出力デバイスに前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分を含む前記予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを送る工程と
を有するものである方法。 EC50) The method of EC46, further comprising:
accessing a shadow copy of the map to translate the logical block addresses to obtain the at least a portion of the translated logical block address information;
sending the pre-mapped read command including the at least a portion of the translated logical block address information to the I/O device.
EC51)EC50記載の方法において、前記アクセスする工程はコンピューティングホストにおけるものである方法。EC51) The method of EC50, wherein the accessing step is in a computing host.
EC52)EC50記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは複数のエントリを有し、前記エントリの各々は有効性の指示を有する方法。EC52) The method of EC50, wherein the shadow copy of the map has a plurality of entries, each of the entries having a validity indication.
EC53)EC52記載の方法において、
前記論理ブロックアドレスは複数の論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)のうちの1つであり、
前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報は複数の変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報のうちの1つであり、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は、前記論理ブロックアドレスのうちの1若しくはそれ以上を、前記複数の変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報のそれぞれの情報と関連付ける方法。 EC53) The method according to EC52,
the logical block address is one of a plurality of logical block addresses (LBAs);
the translated logical block address information is one of a plurality of translated logical block address information;
Each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map associates one or more of the logical block addresses with respective information of the plurality of translated logical block address information.
EC54)EC53記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は、前記複数の変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記それぞれの情報の少なくとも一部分を有する方法。EC54) The method of EC53, wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map has at least a portion of the respective information of the plurality of translated logical block address information.
EC55)EC53記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリのうちの少なくとも1つは、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを選択的に指定する方法。EC55) The method of EC53, wherein at least one of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively specifies that the logical block address associated with the at least one of the valid entries is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC56)EC55記載の方法において、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記論理ブロックアドレスは切り捨てられるものである方法。EC56) The method of EC55, wherein the logical block address associated with at least one of the valid entries is truncated.
EC57)EC52記載の方法において、
前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置は前記不揮発性メモリ内の複数の位置のうちの1つであり、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は前記不揮発性メモリ内のそれぞれの位置を選択的に指定する方法。 EC57) The method according to EC52,
the location in the non-volatile memory is one of a plurality of locations in the non-volatile memory;
Each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively designates a respective location within the non-volatile memory.
EC58)EC57記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は、前記エントリと関連付けられたデータが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを選択的に指定する方法。EC58) The method of EC57, wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively specifies that data associated with the entry is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC59)EC52記載の方法において、さらに、
最初に前記マップの前記シャドウコピーのすべてのエントリを無効とマークする工程を有するものである方法。 EC59) The method of EC52, further comprising:
The method includes the step of first marking all entries of the shadow copy in the map as invalid.
EC60)EC52記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスに書き込みコマンドを送ったことに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と関連付けられた前記マップの前記シャドウコピーのエントリを無効とマークする工程を有するものである方法。 EC60) The method of EC52, further comprising:
In response to sending a write command to the I/O device, marking an entry in the shadow copy of the map associated with a logical block address (LBA) of the write command as invalid.
EC61)EC60記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスで、前記外部インターフェースを介して前記書き込みコマンドを受け取る工程と、
前記書き込みコマンドを受け取る前記工程に続いて、前記書き込みコマンドの前記論理ブロックアドレスに対応するシャドウマップ更新を送る工程と
を有するものである方法。 EC61) The method of EC60, further comprising:
receiving, at the input/output device, the write command via the external interface;
following said step of receiving said write command, sending a shadow map update corresponding to the logical block address of said write command.
EC62)EC61記載の方法において、さらに、
前記シャドウマップ更新に従って前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを更新する工程を有するものであり、
前記更新する工程は、前記書き込みコマンドの前記論理ブロックアドレスと関連付けられた前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリを有効とマークする方法。 EC62) The method according to EC61, further comprising:
updating the shadow copy of the map in accordance with the shadow map updates;
The method wherein the updating step marks the entry of the shadow copy of the map associated with the logical block address of the write command as valid.
EC63)EC62記載の方法において、前記更新する工程は前記入出力デバイスによるものである方法。EC63) The method of EC62, wherein the updating step is performed by the input/output device.
EC64)EC50記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを前記入出力デバイスに接続されたコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する工程を有するものである方法。 EC64) The method of EC50, further comprising:
Storing the shadow copy of the map in a memory of a computing host connected to the I/O device.
EC65)EC64記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストに送る工程を有するものである方法。 EC65) The method according to EC64, further comprising:
Sending the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the computing host.
EC66)EC64記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有する方法。EC66) The method of EC64, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises a main memory of the computing host.
EC67)EC64記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有する方法。EC67) The method of EC64, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC68)EC67記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能である方法。EC68) The method of EC67, wherein the memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC69)EC64記載の方法において、前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに不揮発的に記憶される方法。EC69) The method of EC64, wherein the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory.
EC70)EC69記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有する方法。EC70) The method of EC69, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC71)EC46記載の方法において、前記マップは2レベルマップを有する方法。EC71) The method of EC46, wherein the map comprises a two-level map.
EC72)EC71記載の方法において、
前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応する方法。 EC72) The method according to EC71,
the map has a first level and a second level;
The method wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map.
EC73)方法であって、
入出力デバイスで、外部インターフェースを介して書き込みコマンドを受け取る工程と、
前記書き込みコマンドのデータを不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置に書き込む工程と、
前記書き込みコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)とマップ内の前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置との関連付けを記憶する工程と、
前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置に基づいた情報を有する更新情報を前記マップのシャドウコピーに送る工程と
を有する方法。 EC73) A method comprising the steps of:
receiving a write command at an input/output device via an external interface;
writing data of the write command to a predetermined location in a non-volatile memory (NVM);
storing an association between a logical block address (LBA) of the write command and the location in the non-volatile memory in a map;
sending updates to a shadow copy of the map with information based on the location in the non-volatile memory.
EC74)EC73記載の方法において、前記マップは2レベルマップを有する方法。EC74) The method of EC73, wherein the map comprises a two-level map.
EC75)EC74記載の方法において、
前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応する方法。 EC75) The method according to EC74,
the map has a first level and a second level;
The method wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map.
EC76)EC73記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置に従った前記情報は、前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位のうちの第1の読み出し単位のアドレスおよび読み出し単位での長さを有する方法。EC76) The method of EC73, wherein the information according to the location in the non-volatile memory includes an address of a first read unit of one or more read units of the non-volatile memory and a length in read units.
EC77)EC73記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを前記入出力デバイスに接続されたコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する工程を有するものである方法。 EC77) The method according to EC73, further comprising:
Storing the shadow copy of the map in a memory of a computing host connected to the I/O device.
EC78)EC77記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストに送る工程を有するものである方法。 EC78) The method according to EC77, further comprising:
Sending the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the computing host.
EC79)EC77記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有する方法。EC79) The method of EC77, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises a main memory of the computing host.
EC80)EC77記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有する方法。EC80) The method of EC77, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC81)EC80記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能である方法。EC81) The method of EC80, wherein the memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC82)EC80記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリに送る工程を有するものである方法。 EC82) The method of EC80, further comprising:
Sending the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the I/O space memory of the computing host.
EC83)EC82記載の方法において、前記更新を送る前記工程はPCIe書き込み要求を送る工程を有する方法。EC83) The method of EC82, wherein the step of sending the update includes the step of sending a PCIe write request.
EC84)EC82記載の方法において、前記更新を送る前記工程は前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの読み出し−変更−書き込みを有する方法。EC84) The method of EC82, wherein the step of sending the updates comprises reading-modifying-writing the shadow copy of the map.
EC85)EC82記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスが読み出しコマンドを実行する前に、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーから前記読み出しコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)の変換をフェッチする工程を有するものである方法。 EC85) The method according to EC82, further comprising:
The method comprising fetching a logical block address (LBA) translation of the read command from the shadow copy of the map before the I/O device executes the read command.
EC86)EC85記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程は前記入出力デバイスによるものである方法。EC86) The method of EC85, wherein the fetching step is performed by the input/output device.
EC87)EC86記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程はPCIe読み出し要求を送る工程を有する方法。EC87) The method of EC86, wherein the fetching step includes sending a PCIe read request.
EC88)EC85記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程は前記コンピューティングホストによるものであり、前記読み出しコマンドは予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドである方法。EC88) The method of EC85, wherein the fetching is by the computing host and the read command is a pre-mapped read command.
EC89)EC77記載の方法において、前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに不揮発的に記憶される方法。EC89) The method of EC77, wherein the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory.
EC90)EC89記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有する方法。EC90) The method of EC89, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC91)方法であって、
入出力デバイスのマップのシャドウコピーを初期化して、当該マップのシャドウコピーの複数のエントリのすべてを無効とマークする工程と、
前記入出力デバイスから前記マップの前記シャドウコピーに対する更新を受け取る工程と、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーに対する更新に従って、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーのエントリのうちの少なくとも1つを有効とマークする工程と
を有する方法。 EC91) A method comprising the steps of:
initializing a shadow copy of a map of I/O devices and marking all of a plurality of entries in the shadow copy of the map as invalid;
receiving updates to the shadow copy of the map from the input/output device;
marking at least one of the entries of the shadow copy of the map as valid according to updates to the shadow copy of the map.
EC92)EC91記載の方法において、前記更新に従ってマークする前記工程は、前記更新の変換論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)情報を前記エントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付ける工程をさらに有するものである方法。EC92) The method of EC91, wherein the step of marking according to the update further comprises the step of associating translated logical block address (LBA) information of the update with the at least one of the entries.
EC93)EC92記載の方法において、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報は前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の位置を有する方法。EC93) The method of EC92, wherein the converted logical block address information has a location within a non-volatile memory (NVM) of the I/O device.
EC94)EC91記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は、前記入出力デバイスの少なくとも1つの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を、前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の位置と選択的に関連付ける方法。EC94) The method of EC91, wherein each of the entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively associates at least one logical block address (LBA) of the I/O device with a location within a non-volatile memory (NVM) of the I/O device.
EC95)EC91記載の方法において、前記入出力デバイスの前記マップは2レベルマップを有する方法。EC95) The method of EC91, wherein the map of the input/output device comprises a two-level map.
EC96)EC95記載の方法において、
前記入出力デバイスの前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記入出力デバイスの前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応する方法。 EC96) The method according to EC95,
the map of the input/output device has a first level and a second level;
The method wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map of the I/O device.
EC97)EC91記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを前記入出力デバイスに接続されたコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する工程を有するものである方法。 EC97) The method of EC91, further comprising:
Storing the shadow copy of the map in a memory of a computing host connected to the I/O device.
EC98)EC97記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストに送る工程を有するものである方法。 EC98) The method of EC97, further comprising:
Sending the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the computing host.
EC99)EC97記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有する方法。EC99) The method of EC97, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises main memory of the computing host.
EC100)EC97記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有する方法。EC100) The method of EC97, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC101)EC100記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能である方法。EC101) The method of EC100, wherein the memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC102)EC100記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリに送る工程を有するものである方法。 EC102) The method of EC100, further comprising:
Sending the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the I/O space memory of the computing host.
EC103)EC102記載の方法において、前記更新を送る前記工程はPCIe書き込み要求を送る工程を有する方法。EC103) The method of EC102, wherein sending the update comprises sending a PCIe write request.
EC104)EC102記載の方法において、前記更新を送る前記工程は前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの読み出し−変更−書き込みを有する方法。EC104) The method of EC102, wherein the step of sending the updates comprises reading-modifying-writing the shadow copy of the map.
EC105)EC102記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスが読み出しコマンドを実行する前に、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーから前記読み出しコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)の変換をフェッチする工程を有するものである方法。 EC105) The method according to EC102, further comprising:
The method comprising fetching a logical block address (LBA) translation of the read command from the shadow copy of the map before the I/O device executes the read command.
EC106)EC105記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程は前記入出力デバイスによるものである方法。EC106) The method of EC105, wherein the fetching step is performed by the input/output device.
EC107)EC106記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程はPCIe読み出し要求を送る工程を有する方法。EC107) The method of EC106, wherein the fetching step includes sending a PCIe read request.
EC108)EC105記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程は前記コンピューティングホストによるものであり、前記読み出しコマンドは予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドである方法。EC108) The method of EC105, wherein the fetching is by the computing host and the read command is a pre-mapped read command.
EC109)EC97記載の方法において、前記マップは前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)に不揮発的に記憶される方法。EC109) The method of EC97, wherein the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in non-volatile memory (NVM) of the input/output device.
EC110)EC109記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有する方法。EC110) The method of EC109, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC111)方法であって、
入出力デバイスに対する要求が読み出し要求であるかどうかを決定する工程であって、
前記入出力デバイスは複数のエントリを有するマップを有し、当該マップの複数のエントリのうちの少なくともいくつかのエントリの各々は、前記入出力デバイスの各論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を、前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置を選択的に有する各変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報にマップするものであり、
前記マップのシャドウコピーは対応する複数のエントリを有するものである、
前記決定する工程と、
前記要求が読み出し要求である場合、当該読み出し要求の論理ブロックアドレスと関連付けられた前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリのうちの特定の1つが有効であるかどうかを決定する工程と、
前記特定のエントリが有効である場合、前記特定のエントリに基づいた、前記各変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の少なくとも一部分を有する予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを前記入出力デバイスに選択的に送る工程と
を有する方法。 EC111) A method comprising the steps of:
determining whether the request to the I/O device is a read request,
the I/O device has a map having a plurality of entries, at least some of the plurality of entries of the map each mapping a respective logical block address (LBA) of the I/O device to a respective translated logical block address information selectively having a predetermined location within a non-volatile memory (NVM) of the I/O device;
The shadow copy of the map has a corresponding number of entries.
the determining step;
if the request is a read request, determining whether a particular one of the entries in the shadow copy of the map associated with the logical block address of the read request is valid;
and if the particular entry is valid, selectively sending a pre-mapped read command to the I/O device having at least a portion of the respective translated logical block address information based on the particular entry.
EC112)EC111記載の方法において、
前記マップのシャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は前記マップ内のそれぞれのエントリに対応し、
前記マップの前記エントリのうちの前記少なくともいくつかのエントリ各々は、前記各論理ブロックアドレスによってマップされた前記各変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報を有し、
前記マップの前記エントリのうちの前記少なくともいくつかのうちの1つに対応する前記マップのシャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は、前記各変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の少なくとも一部分を有するものである方法。 EC112) The method according to EC111,
each of the entries in the shadow copy of the map corresponds to a respective entry in the map;
each of the at least some of the entries of the map having the respective translated logical block address information mapped by the respective logical block address;
wherein each of the entries of a shadow copy of the map corresponding to one of the at least some of the entries of the map comprises at least a portion of the respective translated logical block address information.
EC113)EC111記載の方法において、前記マップの前記複数のエントリは第2レベルのマップである方法。EC113) The method of EC111, wherein the plurality of entries of the map are a second level map.
EC114)EC113記載の方法において、前記入出力デバイスは第1レベルのマップをさらに有するものである方法。EC114) The method of EC113, wherein the input/output device further comprises a first level map.
EC115)EC111記載の方法において、前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分は、前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置または前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないという指示を選択的に有する方法。EC115) The method of EC111, wherein the at least a portion of the respective converted logical block address information selectively includes an indication that the location in the non-volatile memory or the respective logical block address is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC116)EC115記載の方法において、前記選択的に送る工程は、前記特定のエントリに従った前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分が、前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを指示するかどうか決定する工程を有する方法。EC116) The method of EC115, wherein the selectively sending step includes determining whether the at least a portion of the respective translated logical block address information according to the particular entry indicates that the logical block address of the read request is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC117)EC116記載の方法において、前記選択的に送る工程は、前記特定のエントリに従った前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分が、前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在することを指示する場合に、単に前記入出力デバイスに前記予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを送る工程をさらに有するものである方法。EC117) The method of EC116, wherein the selectively sending step further comprises sending the pre-mapped read command to the I/O device only if the at least a portion of the respective translated logical block address information according to the particular entry indicates that the logical block address of the read request is present in the non-volatile memory.
EC118)EC117記載の方法において、前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスが切り捨てられる場合には、前記特定のエントリに従った前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分は、前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを指示する方法。EC118) The method of EC117, wherein if the logical block address of the read request is truncated, the at least a portion of the translated logical block address information according to the particular entry indicates that the logical block address of the read request is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC119)EC111記載の方法において、前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分は、前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位のうちの第1の読み出し単位のアドレスおよび読み出し単位での長さを選択的に有する方法。EC119) The method of EC111, wherein the at least one portion of each converted logical block address information selectively has an address and length in read units of a first read unit of one or more read units of the non-volatile memory.
EC120)EC119記載の方法において、前記1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位の各々のサイズは少なくとも512バイトである方法。EC120) The method of EC119, wherein the size of each of the one or more read units is at least 512 bytes.
EC121)EC111記載の方法において、さらに、
前記特定のエントリが無効である場合に、前記入出力デバイスに前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスを有する標準読み出しコマンドを送る工程を有するものである方法。 EC121) The method according to EC111, further comprising:
If the particular entry is invalid, sending a standard read command to the I/O device having the logical block address of the read request.
EC122)EC111記載の方法において、さらに、
前記要求が書き込み要求である場合に、前記書き込み要求の論理ブロックアドレスと関連付けられた前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリのうちの1つを無効とマークする工程を有するものである方法。 EC122) The method according to EC111, further comprising:
If the request is a write request, marking one of the entries in the shadow copy of the map associated with a logical block address of the write request as invalid.
EC123)EC111記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの各エントリは、有効性指示、および前記マップの対応するエントリからの少なくともいくつかのコンテンツのコピーを有する方法。EC123) The method of EC111, wherein each entry of the shadow copy of the map has a validity indication and a copy of at least some of the content from a corresponding entry of the map.
EC124)EC123記載の方法において、前記特定のエントリが有効である場合に、前記マップ内の前記対応するエントリからの少なくともいくつかのコンテンツの前記コピーは、前記マップの前記対応するエントリからの前記少なくともいくつかのコンテンツと同じである方法。EC124) The method of EC123, wherein if the particular entry is valid, the copy of at least some of the content from the corresponding entry in the map is the same as the at least some of the content from the corresponding entry in the map.
EC125)EC123記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの有効なエントリは前記マップの有効なエントリの部分集合である方法。EC125) The method of EC123, wherein the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map are a subset of the valid entries of the map.
EC126)EC125記載の方法において、前記部分集合は真部分集合である方法。EC126) The method of EC125, wherein the subset is a proper subset.
EC127)EC111記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は、無効であり、または前記マップの対応するエントリに従った情報を有する方法。EC127) The method of EC111, wherein each of the entries of the shadow copy of the map is invalid or has information in accordance with a corresponding entry of the map.
EC128)EC111記載の方法において、前記入出力デバイスの前記マップは2レベルマップを有する方法。EC128) The method of EC111, wherein the map of the input/output device has a two-level map.
EC129)EC128記載の方法において、
前記入出力デバイスの前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記入出力デバイスの前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応する方法。 EC129) The method according to EC128,
the map of the input/output device has a first level and a second level;
The method wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map of the I/O device.
EC130)EC111記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は有効性の指示を有する方法。EC130) The method of EC111, wherein each of the entries of the shadow copy of the map has a validity indication.
EC131)EC130記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は、前記論理ブロックアドレスのうちのそれぞれの1若しくはそれ以上を、前記不揮発性メモリ内のそれぞれの位置と選択的に関連付ける方法。EC131) The method of EC130, wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively associates a respective one or more of the logical block addresses with a respective location in the non-volatile memory.
EC132)EC131記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリのうちの少なくとも1つは、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスのうちの少なくとも1つが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを選択的に指定する方法。EC132) The method of EC131, wherein at least one of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively specifies that at least one of the respective logical block addresses associated with the at least one of the valid entries is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC133)EC132記載の方法において、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスのうちの前記少なくとも1つは切り捨てられる方法。EC133) The method of EC132, wherein the at least one of the respective logical block addresses associated with the at least one of the valid entries is truncated.
EC134)EC130記載の方法において、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は前記不揮発性メモリ内のそれぞれの位置を選択的に指定する方法。EC134) The method of EC130, wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively designates a respective location within the non-volatile memory.
EC135)EC130記載の方法において、さらに、
最初に前記マップの前記シャドウコピーのすべての前記エントリを無効とマークする工程を有するものである方法。 EC135) The method of EC130, further comprising:
The method comprising the step of first marking all of the entries in the shadow copy of the map as invalid.
EC136)EC111記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを前記入出力デバイスに接続されたコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する工程を有するものである方法。 EC136) The method according to EC111, further comprising:
Storing the shadow copy of the map in a memory of a computing host connected to the I/O device.
EC137)EC136記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスから前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの更新を受け取る工程を有するものである方法。 EC137) The method according to EC136, further comprising:
The method comprising receiving updates to the shadow copy of the map from the input/output device.
EC138)EC136記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有する方法。EC138) The method of EC136, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises a main memory of the computing host.
EC139)EC136記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有する方法。EC139) The method of EC136, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC140)EC139記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能である方法。EC140) The method of EC139, wherein the memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC141)EC139記載の方法において、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリに送る工程を有するものである方法。 EC141) The method according to EC139, further comprising:
Sending the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the I/O space memory of the computing host.
EC142)EC141記載の方法において、前記更新を送る前記工程はPCIe書き込み要求を送る工程を有する方法。EC142) The method of EC141, wherein sending the update comprises sending a PCIe write request.
EC143)EC141記載の方法において、前記更新を送る前記工程はマップのシャドウコピーの読み出し−変更−書き込みを有する方法。EC143) The method of EC141, wherein the step of sending the updates comprises reading-modifying-writing a shadow copy of the map.
EC144)EC141記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスが特定のコマンドを実行する前に、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーから前記特定のコマンドの論理ブロックアドレスの変換をフェッチする工程を有するものである方法。 EC144) The method according to EC141, further comprising:
The method comprising the step of fetching a translation of a logical block address of a particular command from the shadow copy of the map before the I/O device executes the particular command.
EC145)EC144記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程は前記入出力デバイスによるものである方法。EC145) The method of EC144, wherein the fetching step is performed by the input/output device.
EC146)EC145記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程はPCIe読み出し要求を送る工程を有する方法。EC146) The method of EC145, wherein the fetching step includes sending a PCIe read request.
EC147)EC144記載の方法において、前記フェッチする工程は前記コンピューティングホストによるものである方法。EC147) The method of EC144, wherein the fetching step is performed by the computing host.
EC148)EC147記載の方法において、前記特定のコマンドは予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドである方法。EC148) The method of EC147, wherein the specific command is a pre-mapped read command.
EC149)EC136記載の方法において、前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに不揮発的に記憶される方法。EC149) The method of EC136, wherein the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory.
EC150)EC149記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有する方法。EC150) The method of EC149, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC151)方法であって、
低電力状態を開始するという指示を入出力デバイスで受け取る工程と、
前記入出力デバイスの内部状態をコンピューティングホストのシステムアクセス可能メモリに保存する工程と、
前記低電力状態を終了するという指示を前記入出力デバイスで受け取る工程と、
前記システムアクセス可能メモリから前記入出力デバイスの前記内部状態を復元する工程と
を有する方法。 EC151) A method comprising the steps of:
receiving an indication at an input/output device to initiate a low power state;
saving an internal state of said input/output device in a system accessible memory of a computing host;
receiving an indication at the input/output device to exit the low power state;
and restoring the internal state of the input/output device from the system accessible memory.
EC152)EC151記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記システムアクセス可能メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有する方法。EC152) The method of EC151, wherein the system accessible memory of the computing host comprises main memory of the computing host.
EC153)EC151記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記システムアクセス可能メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有する方法。EC153) The method of EC151, wherein the system accessible memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC154)EC153記載の方法において、前記コンピューティングホストの前記システムアクセス可能メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能である方法。EC154) The method of EC153, wherein the system accessible memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC155)システムであって、
コンピューティングホストに接続された入出力デバイスと、
前記入出力デバイスの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置と選択的に関連付ける前記入出力デバイスのマップと、
前記コンピューティングホストのメモリ内の前記マップのシャドウコピーと
を有し、
前記マップのシャドウコピーにアクセスするために前記入出力デバイスを対象とする少なくともいくつかの動作が有効化され、それにより、前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ内の所定の位置が決定されるものである、
システム。 EC155) A system comprising:
an input/output device connected to a computing host;
a map of the I/O device that selectively associates logical block addresses (LBAs) of the I/O device with predetermined locations within a non-volatile memory (NVM) of the I/O device;
a shadow copy of the map in a memory of the computing host;
at least some operations directed to the I/O device are enabled to access a shadow copy of the map, thereby determining a predetermined location in a non-volatile memory of the I/O device;
system.
EC156)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、前記少なくともいくつかの動作は前記マップにアクセスために有効化されていないものであるシステム。EC156) The system of EC155, wherein at least some of the actions are not enabled for accessing the map.
EC157)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは複数のエントリを有し、当該エントリの各々は前記論理ブロックアドレスの各々のうちの1つと関連付けられており、当該エントリの各々は有効性の指示を有し、
前記マップのシャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリのうちの少なくとも1つは、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記各論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを選択的に特定するシステム。 EC157) The system according to EC155,
the shadow copy of the map has a plurality of entries, each of the entries being associated with one of the respective logical block addresses, each of the entries having a validity indication;
The system selectively identifies that at least one of the valid entries of a shadow copy of the map is not present in the non-volatile memory for the respective logical block address associated with the at least one of the valid entries.
EC158)EC157記載のシステムにおいて、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスは切り捨てられるシステム。EC158) The system of EC157, wherein the respective logical block addresses associated with the at least one of the valid entries are truncated.
EC159)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有するシステム。EC159) The system of EC155, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises a main memory of the computing host.
EC160)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有するシステム。EC160) The system of EC155, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC161)EC160記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能であるシステム。EC161) The system of EC160, wherein the I/O space memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC162)EC161記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスと前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリとを含む入出力カードを有するものであるシステム。 EC162) The system of EC161, further comprising:
A system having an I/O card including the I/O device and the I/O space memory of the computing host.
EC163)EC162記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力デバイスは、前記入出力カード上の複数の入出力デバイスのうちの第1の入出力デバイスであり、前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリは前記複数の入出力デバイス間で共用されるシステム。EC163) The system of EC162, wherein the I/O device is a first I/O device of a plurality of I/O devices on the I/O card, and the I/O space memory of the computing host is shared among the plurality of I/O devices.
EC164)EC162記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力カードは前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリを有するシステム。EC164) The system of EC162, wherein the input/output card comprises the memory of the computing host.
EC165)EC162記載のシステムにおいて、
前記入出力カードはスイッチを有し、
前記入出力デバイスと前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリとは各々前記スイッチに接続されているシステム。 EC165) The system according to EC162,
The input/output card has a switch;
The input/output devices and the memory of the computing host are each connected to the switch.
EC166)EC165記載のシステムにおいて、
前記入出力デバイスは複数の入出力デバイスのうちの第1の入出力デバイスであり、
前記入出力デバイスの各々は前記スイッチに接続されているシステム。 EC166) The system according to EC165,
the input/output device is a first input/output device of a plurality of input/output devices;
The system wherein each of said input/output devices is connected to said switch.
EC167)EC165記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記スイッチに直接接続されているシステム。EC167) The system of EC165, wherein the memory of the computing host is directly connected to the switch.
EC168)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは前記入出力デバイスに直接接続されているシステム。EC168) A system according to EC155, wherein the map is directly connected to the input/output device.
EC169)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに記憶されるシステム。EC169) A system as described in EC155, in which the map is stored in the non-volatile memory.
EC170)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記入出力デバイスに直接接続されていないシステム。EC170) The system of EC155, wherein the shadow copy of the map is not directly connected to the I/O device.
EC171)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは2レベルマップを有するシステム。EC171) A system as described in EC155, wherein the map comprises a two-level map.
EC172)EC171記載のシステムにおいて、
前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応するシステム。 EC172) The system according to EC171,
the map has a first level and a second level;
The system, wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map.
EC173)EC155記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに不揮発的に記憶されるシステム。EC173) A system according to EC155, in which the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory.
EC174)EC173記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有するシステム。EC174) The system of EC173, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC175)システムであって、
コンピューティングホストに接続された入出力デバイスと、
前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能なメモリであって、当該メモリは前記入出力デバイスに直接接続されていないものである、前記メモリと
を有し、
前記入出力デバイスの状態は、前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能な前記メモリに記憶されるものである、
システム。 EC175) system, comprising:
an input/output device connected to a computing host;
a memory accessible by the computing host, the memory not directly connected to the input/output device;
the state of the input/output devices is stored in the memory accessible by the computing host;
system.
EC176)EC175記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置と選択的に関連付ける入出力デバイスのマップを有するものであり、
前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能な前記メモリに記憶された前記入出力デバイスの前記状態は、前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能な前記メモリに記憶された前記マップのシャドウコピーを有し、
前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに不揮発的に記憶されるものであるシステム。 EC176) The system of EC175, further comprising:
a map of the I/O device that selectively associates logical block addresses (LBAs) of the I/O device with predetermined locations within a non-volatile memory (NVM) of the I/O device;
the state of the I/O device stored in the memory accessible by the computing host comprises a shadow copy of the map stored in the memory accessible by the computing host;
The map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory.
EC177)EC176記載のシステムにおいて、
前記マップのシャドウコピーは複数のエントリを有し、当該エントリの各々は前記論理ブロックアドレスの各々のうちの1つと関連付けられており、当該エントリの各々は有効性の指示を有し、
前記マップのシャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリのうちの少なくとも1つは、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記各論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを選択的に特定するものであるシステム。 EC177) In the system according to EC176,
the shadow copy of the map has a plurality of entries, each of the entries being associated with one of the respective logical block addresses, each of the entries having a validity indication;
The system wherein at least one of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively identifies that the respective logical block address associated with the at least one of the valid entries is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC178)EC175記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能な前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有するシステム。EC178) The system of EC175, wherein the memory accessible by the computing host comprises main memory of the computing host.
EC179)EC175記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能な前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有するシステム。EC179) The system of EC175, wherein the memory accessible by the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC180)EC179記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能であるシステム。EC180) The system of EC179, wherein the I/O space memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC181)EC175記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能な前記メモリに記憶された前記入出力デバイスの前記状態は前記入出力デバイスの内部状態を有するシステム。EC181) The system of EC175, wherein the state of the input/output device stored in the memory accessible by the computing host comprises an internal state of the input/output device.
EC182)EC181記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力デバイスの前記内部状態は、前記入出力デバイスが低電力状態を開始するときに失われる状態を有するシステム。EC182) The system of EC181, wherein the internal state of the input/output device is lost when the input/output device enters a low power state.
EC183)EC182記載のシステムにおいて、前記低電力状態を開始するよう求める要求に応答して、前記入出力デバイスは、前記入出力デバイスが前記低電力状態を開始するときに失われる前記状態を、前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能な前記メモリに記憶することができるようにしたシステム。EC183) The system of EC182, wherein in response to a request to initiate the low power state, the input/output device is capable of storing in the memory accessible by the computing host the state that is lost when the input/output device initiates the low power state.
EC184)EC175記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストによってアクセス可能な前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有するシステム。EC184) The system of EC175, wherein the memory accessible by the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC185)方法であって、
ストレージにアクセスするよう求めるコマンドを受け取る工程であって、前記コマンドはアクセスタイプを指定し、1若しくはそれ以上のパラメータを有するものである、前記受け取る工程と、
前記ストレージの位置を決定する工程と
を有し、前記決定する工程は、含まれるデータ構造を条件付きで参照して前記位置を確認する工程を有し、前記参照する工程は、前記パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上が前記位置の仕様を有する場合は省略されるものである、
方法。 EC185) A method comprising the steps of:
receiving a command to access storage, the command specifying an access type and having one or more parameters;
determining a location of said storage, said determining step including a step of conditionally referencing an included data structure to verify said location, said referencing step being omitted if one or more of said parameters include a specification of said location.
method.
EC186)EC185記載の方法において、前記仕様は、
前記ストレージの領域の指示、
前記ストレージの物理的アドレスの指示、
前記ストレージのデータの長さ、および
前記ストレージのデータの範囲
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC 186) The method according to EC 185, wherein the specifications are:
An indication of an area of said storage;
An indication of a physical address of said storage;
The method comprises one or more of: a length of data in said storage; and a range of data in said storage.
EC187)EC185記載の方法において、前記含まれるデータ構造は、それぞれの1若しくはそれ以上の論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と関連付けられたデータが前記ストレージ内のどこに位置するかを各々が記述する1若しくはそれ以上のエントリを有する方法。EC187) The method of EC185, wherein the included data structure has one or more entries, each describing where data associated with a respective one or more logical block addresses (LBAs) is located within the storage.
EC188)EC187記載の方法において、前記エントリの各々は、前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスと関連付けられた1若しくはそれ以上の属性をさらに選択的に記述するものである方法。EC188) The method of EC187, wherein each of the entries further selectively describes one or more attributes associated with the respective logical block address.
EC189)EC187記載の方法において、前記エントリの各々は、前記ストレージの1若しくはそれ以上の領域と関連付けられた1若しくはそれ以上の属性をさらに記述するものである方法。EC189) The method of EC187, wherein each of the entries further describes one or more attributes associated with one or more regions of the storage.
EC190)EC185記載の方法において、さらに、
前記受け取る工程の前に、前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する工程を有するものである方法。 EC190) The method of EC185 further comprising:
The method further comprising, prior to said receiving step, providing updates describing changes to said included data structures.
EC191)EC190記載の方法において、前記コマンドはコンピューティングホストによって提供され、前記更新は前記コンピューティングホストに提供される方法。EC191) The method of EC190, wherein the command is provided by a computing host and the update is provided to the computing host.
EC192)EC190記載の方法において、前記更新は前記位置の前記仕様を有する方法。EC192) The method of EC190, wherein the update includes the specification of the position.
EC193)EC192記載の方法において、前記コマンドは論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)に従ったものであり、前記提供する工程は前記論理ブロックアドレスに書き込みコマンドを提供したことに応答したものである方法。EC193) The method of EC192, wherein the command is according to a logical block address (LBA) and the providing step is in response to providing a write command to the logical block address.
EC194)EC192記載の方法において、前記提供する工程は、前記ストレージの少なくともいくらかを実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)の1若しくはそれ以上の部分を再利用し、および/または再配置したことに応答したものである方法。EC194) The method of EC192, wherein the providing step is in response to reclaiming and/or reallocating one or more portions of non-volatile memory (NVM) that implements at least some of the storage.
EC195)EC185記載の方法において、前記受け取る工程および前記決定する工程は、入出力記憶デバイスによるものである方法。EC195) The method of EC185, wherein the receiving and determining steps are performed by an input/output storage device.
EC196)EC185記載の方法において、前記コマンドはコンピューティングホストによって提供される方法。EC196) The method of EC185, wherein the command is provided by a computing host.
EC197)EC185記載の方法において、前記パラメータは標準パラメータおよび非標準パラメータを有し、前記標準パラメータは規格によって定義され、前記非標準パラメータは前記規格によって定義されず、前記非標準パラメータは、前記仕様を有する前記パラメータを有する方法。EC197) A method according to EC185, wherein the parameters include standard parameters and non-standard parameters, the standard parameters being defined by a standard, the non-standard parameters being not defined by the standard, and the non-standard parameters being the parameters having the specification.
EC198)EC185記載の方法において、前記コマンドは規格によって定義され、前記仕様を有する前記パラメータは前記規格によって定義されない方法。EC198) A method according to EC185, in which the command is defined by a standard and the parameter having the specification is not defined by the standard.
EC199)EC197またはEC198記載の方法において、前記仕様を有する前記パラメータは、
予約コマンドコード、
ベンダ特有のパラメータ、
予約フィールド、
不使用フィールド、および
機能レジスタ内の値
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC 199) In the method according to EC 197 or EC 198, the parameter having the specification is
Reservation command code,
Vendor specific parameters,
Reserved fields,
The method includes one or more of: an unused field; and a value in a capability register.
EC200)EC185記載の方法において、さらに、
前記アクセスタイプおよび前記位置に従って前記ストレージのアクセスを実行する工程を有するものである方法。 EC200) The method of EC185, further comprising:
performing an access of the storage according to the access type and the location.
EC201)EC200記載の方法において、前記アクセスタイプは読み出しアクセスタイプであり、前記アクセスは読み出しアクセスである方法。EC201) The method of EC200, wherein the access type is a read access type and the access is a read access.
EC202)EC201記載の方法において、前記パラメータは前記仕様を有する方法。EC202) The method of EC201, wherein the parameters have the specifications.
EC203)EC202記載の方法において、前記コマンドは予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドである方法。EC203) The method of EC202, wherein the command is a pre-mapped read command.
EC204)EC185記載の方法において、前記位置は第1の位置であり、さらに、
前記アクセスタイプおよび第2の位置に従って前記ストレージのアクセスを行う工程を有するものである方法。 EC204) The method of EC185, wherein the position is a first position and further comprising:
accessing the storage according to the access type and the second location.
EC205)EC204記載の方法において、前記アクセスタイプは書き込みアクセスタイプであり、前記アクセスは書き込みアクセスである方法。EC205) The method of EC204, wherein the access type is a write access type and the access is a write access.
EC206)EC205記載の方法において、さらに、
前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する工程であって、前記更新は前記第2の位置の指定を有するものである、提供する工程を有するものである方法。 EC206) The method according to EC205, further comprising:
providing an update describing a change to the included data structure, the update including a specification of the second location.
EC207)EC205記載の方法において、さらに、
前記仕様に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正する工程を有するものである方法。 EC207) The method according to EC205, further comprising:
modifying said storage usage calculation in accordance with said specification.
EC208)EC185記載の方法において、前記コマンドは切り捨てコマンドであり、前記アクセスタイプは切り捨てアクセスタイプである方法。EC208) The method of EC185, wherein the command is a truncate command and the access type is a truncate access type.
EC209)EC208記載の方法において、さらに、
前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する工程であって、前記更新は、前記コマンドを受け取る前記工程の前に前記位置にマップされた論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)の属性の仕様を有するものである、提供する工程を有するものである方法。 EC209) The method according to EC208, further comprising:
providing an update describing changes to the included data structure, the update including a specification of attributes of a logical block address (LBA) that was mapped to the location prior to the step of receiving the command.
EC210)EC209記載の方法において、前記属性は、前記論理ブロックアドレスが削減されたことを指示する方法。EC210) The method of EC209, wherein the attribute indicates that the logical block address has been reduced.
EC211)EC208記載の方法において、さらに、
前記仕様に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正する工程を有するものである方法。 EC211) The method according to EC208, further comprising:
modifying said storage usage calculation in accordance with said specification.
EC212)方法であって、
コマンドを受け取る工程であって、当該コマンドは複数のコマンドタイプのうちの1つであり、当該コマンドタイプは第1のタイプおよび第2のタイプを有するものである、前記受け取る工程と、
前記コマンドが前記コマンドタイプのうちのどのコマンドであるかを決定する工程と、
前記コマンドが前記第1のタイプのコマンドである場合、第1の処理を行い、次いで第2の処理を行う工程と、
前記コマンドが前記第2のタイプのコマンドである場合、前記第1の処理を行わずに前記第2の処理を行う工程と
を有し、
前記第2の処理は、前記コマンドが前記第1のタイプのものである場合、前記第1の処理によって生成される情報を使用し、前記コマンドが前記第2のタイプのものである場合、当該コマンドによって提供される情報を使用するものである、
方法。 EC212) A method comprising the steps of:
receiving a command, the command being one of a plurality of command types, the command type having a first type and a second type;
determining which of said command types said command is;
performing a first operation if the command is a command of the first type, and then performing a second operation;
if the command is the second type command, performing the second processing without performing the first processing;
the second process uses information generated by the first process if the command is of the first type, and uses information provided by the command if the command is of the second type.
method.
EC213)EC212記載の方法において、前記コマンドは入出力記憶デバイスのストレージにアクセスするものである方法。EC213) The method of EC212, wherein the command accesses storage of an input/output storage device.
EC214)EC213記載の方法において、前記第1の処理は、含まれるデータ構造にアクセスして前記情報を生成する工程を有する方法。EC214) The method of EC213, wherein the first process includes accessing an included data structure to generate the information.
EC215)EC214記載の方法において、前記含まれるデータ構造は、論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と前記ストレージの少なくともいくらかを実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)の物理アドレスとの間のマッピングを記述するマップであり、前記情報は前記マッピングのうちの1つの少なくとも一部を有する方法。EC215) The method of EC214, wherein the included data structure is a map describing mappings between logical block addresses (LBAs) and physical addresses of a non-volatile memory (NVM) implementing at least some of the storage, and the information comprises at least a portion of one of the mappings.
EC216)EC215記載の方法において、前記第1のタイプのコマンドは前記論理ブロックアドレスのうちの少なくとも1つを指定する方法。EC216) The method of EC215, wherein the first type command specifies at least one of the logical block addresses.
EC217)EC216記載の方法において、前記第2のタイプのコマンドは前記論理ブロックアドレスのうちのいずれも指定しない方法。EC217) The method of EC216, wherein the second type command does not specify any of the logical block addresses.
EC218)EC214記載の方法において、さらに、
前記受け取る工程の前に、前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する工程を有するものである方法。 EC218) The method according to EC214, further comprising:
The method further comprising, prior to said receiving step, providing updates describing changes to said included data structures.
EC219)EC218記載の方法において、前記更新は前記情報の指定を有する方法。EC219) The method of EC218, wherein the update comprises specifying the information.
EC220)EC219記載の方法において、前記仕様は、
前記ストレージの領域の指示、
前記ストレージの物理アドレスの指示、
前記ストレージのデータの長さ、および
前記ストレージのデータの範囲
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC220) The method according to EC219, wherein the specifications are:
An indication of an area of said storage;
An indication of a physical address of the storage;
The method comprises one or more of: a length of data in said storage; and a range of data in said storage.
EC221)EC219記載の方法において、前記提供する工程は、前記コマンドタイプのうちの書き込みコマンドタイプを受け取ったことに応答したものである方法。EC221) The method of EC219, wherein the providing step is in response to receiving a write command type among the command types.
EC222)EC219記載の方法において、前記提供する工程は、前記ストレージの少なくともいくらかを実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)の一部分を再利用し、および/または再配置したことに応答したものである方法。EC222) The method of EC219, wherein the providing step is in response to reclaiming and/or reallocating a portion of non-volatile memory (NVM) that implements at least some of the storage.
EC223)EC218記載の方法において、前記コマンドはコンピューティングホストによって提供され、前記更新は前記コンピューティングホストに提供される方法。EC223) The method of EC218, wherein the command is provided by a computing host and the update is provided to the computing host.
EC224)EC213記載の方法において、前記受け取る工程、前記決定する工程、および前記2つの行う動作は、前記入出力記憶デバイスによるものである方法。EC224) The method of EC213, wherein the receiving step, the determining step, and the two actions taken are performed by the input/output storage device.
EC225)EC213記載の方法において、前記コマンドはコンピューティングホストによって提供される方法。EC225) The method of EC213, wherein the command is provided by a computing host.
EC226)EC212記載の方法において、前記第1のタイプの前記コマンドは規格によって定義され、前記第2のタイプの前記コマンドは前記規格によって定義されない方法。EC226) The method of EC212, wherein the commands of the first type are defined by a standard and the commands of the second type are not defined by the standard.
EC227)EC212記載の方法において、前記コマンドが前記第2のタイプのものであるときに、前記情報は、
予約コマンドコード、
ベンダ特有のパラメータ、
予約フィールド、
不使用フィールド、および
機能レジスタ内の値
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上によって提供される方法。 EC227) The method of EC212, wherein when the command is of the second type, the information comprises:
Reservation command code,
Vendor specific parameters,
Reserved fields,
the method being provided by one or more of: an unused field; and a value in a capability register.
EC228)EC214記載の方法において、前記第1のタイプは読み出しタイプを有し、前記第2のタイプは予めマッピングされた読み出しタイプを有する方法。EC228) The method of EC214, wherein the first type has a read type and the second type has a pre-mapped read type.
EC229)EC228記載の方法において、前記ストレージの前記アクセスは読み出しアクセスであり、前記情報は前記ストレージの位置を有し、前記第2の処理は前記位置を読み取る工程を有する方法。EC229) The method of EC228, wherein the access of the storage is a read access, the information includes a location of the storage, and the second process includes a step of reading the location.
EC230)EC214記載の方法において、前記第1のタイプは第1の書き込みタイプを有し、前記第2のタイプは第2の書き込みタイプを有し、前記第2の書き込みタイプは、前記第1の書き込みタイプが前記情報を提供しない間に前記情報を提供する方法。EC230) The method of EC214, wherein the first type has a first write type and the second type has a second write type, and the second write type provides the information while the first write type does not provide the information.
EC231)EC230記載の方法において、前記ストレージの前記アクセスは書き込みアクセスであり、前記情報は前記ストレージの第1の位置を有し、前記第2の処理は、前記ストレージの第2の位置を書き込む工程と、前記第1の位置に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正する工程とを有する方法。EC231) The method of EC230, wherein the access of the storage is a write access, the information has a first location of the storage, and the second process includes writing a second location of the storage and modifying a calculation of the usage status of the storage according to the first location.
EC232)EC231記載の方法において、さらに、
前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する工程であって、前記更新は前記第2の位置の指定を有するものである、提供する工程を有するものである方法。 EC232) The method according to EC231, further comprising:
providing an update describing a change to the included data structure, the update having a specification of the second location.
EC233)EC214記載の方法において、前記第1のタイプは第1の切り捨てタイプを有し、前記第2のタイプは第2の切り捨てタイプを有し、前記第2の切り捨てタイプは、前記第1の切り捨てタイプが前記情報を提供しない間に前記情報を提供する方法。EC233) The method of EC214, wherein the first type has a first truncation type and the second type has a second truncation type, the second truncation type providing the information while the first truncation type does not provide the information.
EC234)EC233記載の方法において、前記ストレージの前記アクセスは切り捨てアクセスであり、前記情報は前記ストレージの位置を有し、前記第2の処理は、前記位置に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正する工程を有する方法。EC234) The method of EC233, wherein the access of the storage is a truncated access, the information includes a location of the storage, and the second process includes modifying a calculation of the usage of the storage according to the location.
EC235)EC234記載の方法において、さらに、
前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する工程であって、前記更新は、前記コマンドを受け取る前記工程の前に、前記含まれるデータ構造に従って前記位置にマップされた論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)の属性の仕様を有するものである、提供する工程を有するものである方法。 EC235) The method according to EC234, further comprising:
providing an update describing changes to the included data structure, the update including a specification of attributes of a logical block address (LBA) mapped to the location according to the included data structure prior to the step of receiving the command.
EC236)EC235記載の方法において、前記属性は、前記論理ブロックアドレスが削減されたことを指示する方法。EC236) The method of EC235, wherein the attribute indicates that the logical block address has been reduced.
EC237)方法であって、
コンピューティングホストからコマンドを受け取る工程であって、前記コマンドは0若しくはそれ以上の標準パラメータおよび1若しくはそれ以上の非標準パラメータを有するものである、前記受け取る工程と、
前記標準パラメータに従って前記コマンドを実行する工程と
を有し、
前記受け取る工程および前記実行する工程は入出力記憶デバイスを介して行われるものであり、当該入出力記憶デバイスは、前記非標準パラメータを使用することにより、前記非標準パラメータを使用しない場合よりも高い効率で動作可能である
方法。 EC237) A method comprising the steps of:
receiving a command from a computing host, the command having zero or more standard parameters and one or more non-standard parameters;
and executing the command according to the standard parameters;
The steps of receiving and executing are performed via an input/output storage device, the input/output storage device being capable of operating at a higher efficiency using the non-standard parameters than if the non-standard parameters were not used.
EC238)EC237記載の方法において、前記入出力記憶デバイスはストレージを前記コンピューティングホストにインターフェースさせるものである方法。EC238) The method of EC237, wherein the input/output storage device interfaces storage to the computing host.
EC239)EC237記載の方法において、前記入出力記憶デバイスは、前記非標準パラメータを使用することにより、前記非標準パラメータを使用しない場合よりも高い効率で前記コマンドを実行するように動作可能である方法。EC239) The method of EC237, wherein the I/O storage device is operable to execute the command with greater efficiency by using the non-standard parameters than if the non-standard parameters were not used.
EC240)EC239記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスのストレージの少なくとも一部分を実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)を管理する工程を有するものである方法。 EC240) The method of EC239, further comprising:
A method comprising managing a non-volatile memory (NVM) that implements at least a portion of the storage of the I/O storage device.
EC241)EC240記載の方法において、前記コマンドは読み出しコマンドであり、前記非標準パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に前記不揮発性メモリ内の物理位置を指定し、さらに、
前記物理位置を読み取る工程を有するものである方法。 EC241) The method of EC240, wherein the command is a read command, and one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, a physical location within the non-volatile memory; and
The method comprising the step of reading the physical location.
EC242)EC241記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが含まれる入出力デバイスマップへのマッピング更新を行う工程と、前記マッピング更新のうちの少なくともいくつかを前記コンピューティングホストに提供して、前記コンピューティングホストがコンピューティング・ホスト・マップを更新することができるようにする工程とを有するものであり、前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップおよび前記入出力デバイスマップは、各々、論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と前記不揮発性メモリの位置との間のマッピングを記述するそれぞれのエントリを有し、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1つは、少なくとも部分的に前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップにアクセスすることによって決定される方法。 EC242) The method according to EC241, further comprising:
11. A method for determining whether a non-standard parameter is determined, at least in part, by accessing a computing host map, the method comprising: making mapping updates to an I/O device map in which the I/O storage device is included; and providing at least some of the mapping updates to the computing host to enable the computing host to update the computing host map, the computing host map and the I/O device map each having respective entries that describe mappings between logical block addresses (LBAs) and locations of the non-volatile memory, the non-standard parameters being determined, at least in part, by accessing the computing host map.
EC243)EC242記載の方法において、前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップにアクセスするための待ち時間は、前記入出力デバイスマップにアクセスするための待ち時間よりも短く、より前記高い効率はより低い待ち時間を有する方法。EC243) The method of EC242, wherein the latency for accessing the computing host map is less than the latency for accessing the I/O device map, and the higher the efficiency, the lower the latency.
EC244)EC240記載の方法において、前記コマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、前記非標準パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に前記不揮発性メモリ内の第1の物理位置を指定し、さらに、
前記不揮発性メモリ内の第2の物理位置を書き込む工程と、前記第1の物理位置に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正する工程とを有するものである方法。 EC244) The method of EC240, wherein the command is a write command, one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, a first physical location within the non-volatile memory, and further comprising:
A method comprising: writing a second physical location in the non-volatile memory; and modifying the storage usage calculation according to the first physical location.
EC245)EC244記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが含まれる入出力デバイスマップへのマッピング更新を行う工程と、前記マッピング更新のうちの少なくともいくつかを前記コンピューティングホストに提供して、前記コンピューティングホストがコンピューティング・ホスト・マップを更新することができるようにする工程とを有するものであり、前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップおよび前記入出力デバイスマップは、各々、論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と前記不揮発性メモリの位置との間のマッピングを記述するそれぞれのエントリを有し、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1つは、少なくとも部分的に前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップにアクセスすることによって決定される方法。 EC245) The method according to EC244, further comprising:
11. A method for determining whether a non-standard parameter is determined, at least in part, by accessing a computing host map, the method comprising: making mapping updates to an I/O device map in which the I/O storage device is included; and providing at least some of the mapping updates to the computing host to enable the computing host to update the computing host map, the computing host map and the I/O device map each having respective entries that describe mappings between logical block addresses (LBAs) and locations of the non-volatile memory, the non-standard parameters being determined, at least in part, by accessing the computing host map.
EC246)EC245記載の方法において、前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップにアクセスするための待ち時間は、前記入出力デバイスマップにアクセスするための待ち時間よりも短く、より前記高い効率はより低い待ち時間を有する方法。EC246) The method of EC245, wherein the latency for accessing the computing host map is less than the latency for accessing the I/O device map, and the higher the efficiency, the lower the latency.
EC247)EC237記載の方法において、前記コマンドは第1のコマンドであり、前記入出力記憶デバイスは、前記非標準パラメータに従って、前記非標準パラメータを使用しない場合よりも高い効率で、前記第1のコマンドの後で受け取られる第2のコマンドを実行するように動作可能である方法。EC247) The method of EC237, wherein the command is a first command, and the I/O storage device is operable to execute a second command received after the first command in accordance with the non-standard parameters with greater efficiency than would be achieved without the non-standard parameters.
EC248)EC247記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスのストレージの少なくとも一部分を実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)を管理する工程を有するものである方法。 EC248) The method of EC247 further comprising:
A method comprising managing a non-volatile memory (NVM) that implements at least a portion of the storage of the I/O storage device.
EC249)EC248記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と前記不揮発性メモリの位置との間のマッピングを記述するエントリを有する含まれるマップを管理する工程を有するものである方法。 EC249) The method according to EC248, further comprising:
The method, wherein the I/O storage device comprises managing a contained map having entries describing mappings between logical block addresses (LBAs) and locations in the non-volatile memory.
EC250)EC249記載の方法において、前記標準パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上の少なくとも一部分は特定の論理ブロックアドレスを有し、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記非標準パラメータから決定される少なくともいくらかの情報を、前記エントリのうちの少なくとも1つの選択されるエントリに記憶する工程を有するものであり、前記選択されるエントリは、少なくとも部分的に前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスによって選択される方法。 EC250) The method of EC249, wherein at least a portion of one or more of the standard parameters comprises a specific logical block address, and further comprising:
The method further comprising the step of: said I/O storage device storing at least some information determined from said non-standard parameters in at least one selected one of said entries, said selected entry being selected at least in part by said particular logical block address.
EC251)EC250記載の方法において、前記第2のコマンドは前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスに従ったものである方法。EC251) The method of EC250, wherein the second command is in accordance with the specific logical block address.
EC252)EC250記載の方法において、前記情報は複数のデータバンドのうちの特定の1つの識別を有し、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスがマップされている前記不揮発性メモリの部分を、前記特定のデータバンド内に留まるように再利用する工程を有するものである方法。 EC252) The method of EC250, wherein the information comprises an identification of a particular one of a plurality of data bands, and further comprising:
The method, wherein the I/O storage device includes the step of reclaiming the portion of the non-volatile memory to which the particular logical block address is mapped so as to remain within the particular data band.
EC253)EC248記載の方法において、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータタイプのうちの1つを指定し、前記複数のデータタイプは、
圧縮可能データタイプ、
圧縮不能データタイプ、および
使用モデル・データ・タイプ
のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC253) The method of EC248, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters at least partially specify one of a plurality of data types, the plurality of data types comprising:
compressible data types,
A method comprising any two or more of: an incompressible data type; and a usage model data type.
EC254)EC253記載の方法において、前記使用モデル・データ・タイプはデータベース・ジャーナル・データ・タイプを有し、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記データベース・ジャーナル・データ・タイプと関連付けられたデータを複数のデータバンドのうちのデータベース・ジャーナル用データバンドに記憶するように前記不揮発性メモリを管理する工程と、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記データベース・ジャーナル用データバンドを、前記データベース・ジャーナル・バンド内のデータの量が閾値を超えるときに、前記データベース・ジャーナル・バンドのより古いデータが選択的に削除されるように管理する工程とを有するものである方法。 EC254) The method of EC253, wherein the usage model data type comprises a database journal data type, and further comprising:
managing the non-volatile memory such that the I/O storage device stores data associated with the database journal data type in a database journal data band among a plurality of data bands;
and wherein the I/O storage device manages the data bands for the database journal such that older data in the database journal bands is selectively deleted when the amount of data in the database journal bands exceeds a threshold.
EC255)EC254記載の方法において、さらに、
前記より古いデータが再利用されるときに前記より古いデータを削除する工程を有するものである方法。 EC255) The method according to EC254, further comprising:
Deleting the older data when the older data is reused.
EC256)EC248記載の方法において、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータアクセスタイプのうちの1つを指定し、前記データアクセスタイプは、
読み出し/書き込みデータアクセスタイプ、
略読み出しデータアクセスタイプ、
略書き込みデータアクセスタイプ、および
一時データアクセスタイプ
のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC256) The method of EC248, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, one of a plurality of data access types, the data access types including:
Read/write data access type,
Short read data access type,
A method having any two or more of: a mostly-write data access type; and a temporary data access type.
EC257)EC256記載の方法において、前記第2のコマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記書き込みコマンドに応答して前記不揮発性メモリの特定の部分を書き込む工程であって、前記特定の部分は、少なくとも部分的に前記データアクセスタイプによって決定されるものである、書き込む工程を有するものである方法。 EC257) The method of EC256, wherein the second command is a write command, and further comprising:
The method further comprising the step of: the I/O storage device writing a specific portion of the non-volatile memory in response to the write command, the specific portion being determined at least in part by the data access type.
EC258)EC257記載の方法において、前記データアクセスタイプは読み出し/書き込みデータアクセスタイプであり、前記特定の部分は、相対的に多数のプログラム/消去サイクルに耐えたことがなく、相対的に少数のプログラム/消去サイクルに耐えたことがないものである方法。EC258) The method of EC257, wherein the data access type is a read/write data access type, and the particular portion has not endured a relatively large number of program/erase cycles and has not endured a relatively small number of program/erase cycles.
EC259)EC257記載の方法において、前記データアクセスタイプは略読み出しデータアクセスタイプであり、前記特定の部分は、相対的に多数のプログラム/消去サイクルに耐えたことがあるものである方法。EC259) The method of EC257, wherein the data access type is mostly read data access type and the particular portion has endured a relatively large number of program/erase cycles.
EC260)EC257記載の方法において、前記データアクセスタイプは略書き込みデータアクセスタイプであり、前記特定の部分は、相対的に少数のプログラム/消去サイクルに耐えたことがあるものである方法。EC260) The method of EC257, wherein the data access type is a mostly write data access type and the particular portion has endured a relatively small number of program/erase cycles.
EC261)EC258、EC259、またはEC260記載の方法において、前記より高い効率はより高い信頼性を有する方法。EC261) A method according to EC258, EC259, or EC260, wherein the higher efficiency has higher reliability.
EC262)EC258、EC259、またはEC260記載の方法において、前記より高い効率はより長い寿命を有する方法。EC262) A method according to EC258, EC259, or EC260, wherein the higher efficiency has a longer life.
EC263)EC256記載の方法において、前記標準パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上の少なくとも一部分は特定の論理ブロックアドレスを有し、前記データアクセスタイプは前記一時データアクセスタイプであり、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、特定のイベントに応答して、前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスに対応する前記不揮発性メモリ内の位置のところに記憶されたデータを削除する工程を有するものである方法。 EC263) The method of EC256, wherein at least a portion of one or more of the standard parameters comprises a specific logical block address, the data access type is the temporary data access type, and further comprising:
The method further comprising the step of: said I/O storage device deleting data stored at a location in said non-volatile memory corresponding to said particular logical block address in response to a particular event.
EC264)EC263記載の方法において、前記データを削除する前記工程は、前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスに従った前記マップのエントリのところの前記入出力記憶デバイスのマップを、前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスに対応するデータが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを指定するように更新する工程を有する方法。EC264) The method of EC263, wherein the step of deleting the data includes updating a map of the I/O storage device at an entry in the map according to the particular logical block address to specify that data corresponding to the particular logical block address is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC265)EC263記載の方法において、前記データを削除する前記工程は、前記データを削減する工程を有する方法。EC265) The method of EC263, wherein the step of deleting the data includes the step of reducing the data.
EC266)EC263記載の方法において、前記特定のイベントは、
前記入出力記憶デバイスの不揮発性メモリ管理動作、
前記入出力記憶デバイスの不揮発性メモリ再利用動作、
前記入出力記憶デバイスの電源サイクル、
前記入出力記憶デバイスのリセット、
仮想入出力記憶デバイスの仮想機械電源サイクル、
仮想入出力記憶デバイスの仮想機械リセット、
前記コンピューティングホストからの明示的要求、および
メムキャッシュディーアプリケーションからの要求
のうちの任意の1若しくはそれ以上である方法。 EC266) The method of EC263, wherein the specific event is:
non-volatile memory management operations of said I/O storage device;
a non-volatile memory reclamation operation of the input/output storage device;
power cycling said I/O storage device;
resetting said input/output storage device;
Virtual machine power cycle of virtual I/O storage devices;
Virtual machine reset of virtual I/O storage devices,
The method may be any one or more of: an explicit request from the computing host; and a request from a memcache application.
EC267)EC248記載の方法において、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータ順序付けのうちの1つを指定し、前記データ順序付けは、順次順序付けおよびアトミック順序付けのうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。EC267) The method of EC248, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters at least partially specify one of a plurality of data orderings, the data orderings including any two or more of sequential ordering and atomic ordering.
EC268)EC248記載の方法において、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータ関係のうちの1つを指定し、前記データ関係は、複数のデータ項目間の読み出しおよび/または書き込み関連付け、ならびにプリフェッチデータ関係のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。EC268) The method of EC248, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, one of a plurality of data relationships, the data relationships including any two or more of a read and/or write association between a plurality of data items and a prefetch data relationship.
EC269)EC248記載の方法において、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータ宛先のうちの1つを指定し、前記データ宛先は、
前記不揮発性メモリの特定の部分、
階層型ストレージ層、
ストレージのタイプ、および特定のデータバンド
のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC269) The method of EC248, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, one of a plurality of data destinations, the data destinations including:
A particular portion of the non-volatile memory;
Hierarchical storage tiers,
The type of storage and the method of having any two or more of the specified data bands.
EC270)EC269記載の方法において、ストレージの前記タイプは、
シングルレベルセル(SLC)、
マルチレベルセル(MLC)、
磁気ランダム・アクセス・メモリ(MRAM)、
揮発性、および
不揮発性
のうちの任意の1若しくはそれ以上である方法。 EC270) The method of EC269, wherein the type of storage is:
Single Level Cell (SLC),
Multi-Level Cell (MLC),
Magnetic Random Access Memory (MRAM),
The method may be any one or more of: volatile; and non-volatile.
EC271)EC269記載の方法において、前記データ宛先のうちの前記1つの仕様は、
書き込み速度、
再利用速度、
再利用頻度、および
書き込み増幅
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上の改善を可能にする方法。 EC271) The method according to EC269, wherein the specification of one of the data destinations comprises:
Write speed,
Reuse rate,
A method that allows for improvements in one or more of: reuse frequency; and write amplification.
EC272)EC248記載の方法において、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のコマンド処理特性のうちの1つを指定し、前記コマンド処理特性は、
コマンド優先順位、
コマンド順序付け、
特定のタイプのコマンドに対するバリア、
特定のタイプのコマンド間の境界、
コマンドの集約、
コマンドの融合、および
コマンドのアトミック動作
のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC272) The method of EC248, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters at least partially specify one of a plurality of command processing characteristics, the command processing characteristics including:
Command priority,
Command Sequencing,
Barriers to certain types of commands,
The boundaries between certain types of commands,
Command aggregation,
A method comprising any two or more of: command fusion; and command atomic operation.
EC273)EC239またはEC247記載の方法において、前記より高い効率はより高い性能を有する方法。EC273) A method according to EC239 or EC247, wherein the higher efficiency means higher performance.
EC274)EC273記載の方法において、前記より高い性能は、
より高いバンド幅、
より低い待ち時間、および
より低い電力
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC274) The method of EC273, wherein the higher performance is
Higher bandwidth,
The method has one or more of: lower latency; and lower power.
EC275)EC239またはEC247記載の方法において、前記より高い効率はより高い信頼性を有する方法。EC275) A method according to EC239 or EC247, wherein the higher efficiency is a method with higher reliability.
EC276)EC275記載の方法において、前記より高い信頼性は、より低い誤り率およびより長い寿命のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。EC276) The method of EC275, wherein the higher reliability comprises one or more of a lower error rate and a longer lifetime.
EC277)方法であって、
コンピューティングホストから非標準統計値の返しを要求するコマンドを受け取る工程と、
前記コンピューティングホストに前記非標準統計値を返す工程と
を有し、
前記受け取る工程および前記返す工程は、前記非標準統計を計算するように動作可能な入出力記憶デバイスを介して実行されるものである、
方法。 EC277) A method comprising the steps of:
receiving a command from a computing host requesting return of a non-standard statistic;
returning the non-standardized statistics to the computing host;
the receiving and returning steps being performed via an input/output storage device operable to calculate the non-standard statistics.
method.
EC278)EC277記載の方法において、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスのストレージの少なくとも一部分を実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)に書き込まれるべきデータのサイズを低減させる工程を有するものであり、
前記計算は、少なくとも一部は前記低減させる工程に基づくものである方法。 EC278) The method of EC277, further comprising:
reducing a size of data to be written to a non-volatile memory (NVM) implementing at least a portion of the storage of the I/O storage device;
The method, wherein said calculating is based at least in part on said reducing step.
EC279)EC278記載の方法において、前記低減させる工程は圧縮を有する方法。EC279) A method according to EC278, wherein the reducing step comprises compression.
EC280)EC278記載の方法において、前記低減させる工程はデータ重複排除を有する方法。EC280) The method of EC278, wherein the reducing step comprises data deduplication.
EC281)EC278記載の方法において、前記非標準統計は前記不揮発性メモリの使用状況に従ったものである方法。EC281) The method of EC278, wherein the non-standard statistics are based on usage of the non-volatile memory.
EC282)EC281記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリの前記使用状況は、前記低減させる工程の質に従って変動する方法。EC282) A method according to EC281, in which the usage status of the non-volatile memory varies according to the quality of the reducing process.
EC283)EC281記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリの前記使用状況は、前記コンピューティングホストから受け取られる切り捨てコマンドの数および/またはサイズに従って変動する方法。EC283) The method of EC281, wherein the usage of the non-volatile memory varies according to the number and/or size of truncation commands received from the computing host.
EC284)EC281記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリの前記使用状況は、前記コンピューティングホストから受け取られる一時データの量に従って変動する方法。EC284) The method of EC281, wherein the usage of the non-volatile memory varies according to an amount of temporary data received from the computing host.
EC285)EC284記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリの前記使用状況は、前記入出力記憶デバイスによって削減された前記一時データの量に従って変動する方法。EC285) The method of EC284, wherein the usage status of the non-volatile memory varies according to the amount of temporary data reduced by the input/output storage device.
EC286)EC281記載の方法において、前記非標準統計は前記不揮発性メモリの使用状況パーセンテージに従ったものである方法。EC286) The method of EC281, wherein the non-standard statistics are according to a usage percentage of the non-volatile memory.
EC287)EC281記載の方法において、前記非標準統計は、前記入出力記憶デバイスの書き込み増幅に従ったものである方法。EC287) The method of EC281, wherein the non-standard statistics are in accordance with write amplification of the I/O storage device.
EC288)EC278記載の方法において、前記非標準統計は前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上のバンドのサイズである方法。EC288) The method of EC278, wherein the non-standard statistic is the size of one or more bands of the non-volatile memory.
EC289)EC278記載の方法において、前記非標準統計は前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上のバンドの使用状況である方法。EC289) The method of EC278, wherein the non-standard statistics are the usage of one or more bands of the non-volatile memory.
EC290)EC289記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリの前記1若しくはそれ以上のバンドの前記使用状況は前記低減させる工程の質に従って変動する方法。EC290) The method of EC289, wherein the usage of the one or more bands of the non-volatile memory varies according to the quality of the reducing process.
EC291)EC195、EC213、EC238、またはEC277記載の方法において、前記入出力記憶デバイスは、前記コマンドの前記受け取りを行うことができるようにしたソリッドステートディスク(SSD)コントローラを有する方法。EC291) A method as described in EC195, EC213, EC238, or EC277, wherein the input/output storage device has a solid-state disk (SSD) controller that is capable of performing the receiving of the command.
EC292)EC291記載の方法において、前記SSDコントローラは単一の集積回路(IC)において実装される方法。EC292) The method of EC291, wherein the SSD controller is implemented in a single integrated circuit (IC).
EC293)EC292記載の方法において、前記ストレージの少なくとも一部分は不揮発性メモリ(NVM)によって実施される方法。EC293) The method of EC292, wherein at least a portion of the storage is implemented by non-volatile memory (NVM).
EC294)EC293記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリは1若しくはそれ以上のフラッシュメモリを有する方法。EC294) The method of EC293, wherein the non-volatile memory comprises one or more flash memories.
EC295)EC293記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリの少なくとも一部分は、
NANDフラッシュ技術記憶セル、および
NORフラッシュ技術記憶セル
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC295) The method of EC293, wherein at least a portion of the non-volatile memory comprises:
A method comprising one or more of: a NAND flash technology storage cell; and a NOR flash technology storage cell.
EC296)EC293記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリの少なくとも一部分は、
シングルレベルセル(SLC)フラッシュ技術記憶セル、および
マルチレベルセル(MLC)フラッシュ技術記憶セル
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有する方法。 EC296) The method of EC293, wherein at least a portion of the non-volatile memory is:
A method having one or more of: a single level cell (SLC) flash technology storage cell; and a multi-level cell (MLC) flash technology storage cell.
EC297)EC293記載の方法において、前記ソリッドステートディスクコントローラは、前記不揮発性メモリに対してデータを通信するように動作可能な不揮発性メモリインターフェースを有し、前記データのうちの少なくとも一部は前記コマンドのうちの少なくともいくつかと関連付けられているものである方法。EC297) The method of EC293, wherein the solid state disk controller has a non-volatile memory interface operable to communicate data to the non-volatile memory, at least some of the data being associated with at least some of the commands.
EC298)EC297記載の方法において、前記不揮発性メモリインターフェースは、
オープンNANDフラッシュインターフェース(ONFI)、
トグルモードインターフェース、
デュアル・データ・レート(DDR)同期インターフェース、
同期インターフェース、および
非同期インターフェース
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上と適合する方法。 EC298) The method of EC297, wherein the non-volatile memory interface further comprises:
Open NAND Flash Interface (ONFI),
Toggle mode interface,
Dual Data Rate (DDR) synchronous interface;
A method that conforms to one or more of a synchronous interface and an asynchronous interface.
EC299)EC293記載の方法において、前記ソリッドステートディスクコントローラおよび前記不揮発性メモリはソリッドステートディスクに具備される方法。EC299) The method of EC293, wherein the solid state disk controller and the non-volatile memory are provided on a solid state disk.
EC300)EC291記載の方法において、前記ソリッドステートディスクコントローラは、ストレージインターフェース規格と適合し、前記ストレージインターフェースを介して前記コマンドを提供するコンピューティングホストに接続するよう動作可能なストレージインターフェースを有するものである方法。EC300) The method of EC291, wherein the solid-state disk controller has a storage interface that conforms to a storage interface standard and is operable to connect to a computing host that provides the commands via the storage interface.
EC301)EC300記載の方法において、さらに、
前記コマンドを提供するように前記コンピューティングホストを動作させる工程を有するものである方法。 EC301) The method of EC300, further comprising:
The method comprising operating the computing host to provide the command.
EC302)方法であって、
外部インターフェースを介してコンピューティングホストから入出力デバイスでコマンドを受け取る工程と、
前記コマンドのタイプを確認する工程と、
前記コマンドのタイプが読み出しコマンドであることに応答して、マップにアクセスして前記コマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を変換し、不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置を選択的に含む変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報を取得する工程と、
前記コマンドタイプが予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドであることに応答して、前記予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドの情報から、前記マップを使用せずに前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置を決定する工程と、
前記位置に対応するデータを返す工程と
を有し、
前記情報は、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の少なくとも一部分を有するものである、
方法。 EC302) A method comprising:
receiving a command at the input/output device from a computing host via an external interface;
determining the type of the command;
in response to the command type being a read command, accessing a map to translate a logical block address (LBA) of the command to obtain translated logical block address information selectively including a predetermined location within a non-volatile memory (NVM);
in response to the command type being a pre-mapped read command, determining the location within the non-volatile memory from information in the pre-mapped read command without using the map;
and returning data corresponding to the location;
the information comprising at least a portion of the translated logical block address information.
method.
EC303)EC302記載の方法において、前記位置は第1の位置であり、前記情報は第1の情報であり、当該方法は、さらに、
前記コマンドのタイプが書き込みコマンドであることに応答して、
前記書き込みコマンドのデータを前記不揮発性メモリ内の第2の位置に書き込む工程と、
前記書き込みコマンドの論理ブロックアドレスと前記マップの不揮発性メモリ内の前記第2の位置との関連付けを記憶する工程と、
前記第2の位置に基づいた第2の情報を含む更新情報を前記マップのシャドウコピーに送る工程と
を有し、
前記第1の情報は、少なくとも部分的に前記シャドウコピーから取得され、前記シャドウコピーは、少なくとも部分的に前記コンピューティングホストに接続された入出力カードのメモリデバイスに記憶されるものである方法。 EC303) The method of EC302, wherein the location is a first location and the information is first information, the method further comprising:
In response to the command type being a write command,
writing data of the write command to a second location in the non-volatile memory;
storing an association between a logical block address of the write command and the second location in the non-volatile memory of the map;
sending updates to the shadow copy of the map including second information based on the second position;
The method, wherein the first information is obtained at least in part from the shadow copy, the shadow copy being stored at least in part in a memory device of an input/output card connected to the computing host.
EC304)システムであって、
標準コマンドと非標準修飾子の仕様とを有する拡張コマンドを受け取る手段と、
前記非標準修飾子に従って前記標準コマンドを実行する手段と
を有し、
前記非標準修飾子を使用して前記標準コマンドの実行を変更することによりシステムレベルの性能が改善されるものである
システム。 EC304) A system comprising:
means for receiving an extension command having a standard command and a specification of a non-standard modifier;
and means for executing the standard command according to the non-standard modifier;
The non-standard modifiers are used to modify the execution of the standard commands to improve system level performance.
EC305)システムであって、
非標準修飾子を有効にする仕様を有するモード設定コマンドを入出力デバイスで受け取る手段と、
前記入出力デバイスで、標準コマンドを受け取る手段と、
前記非標準修飾子に従って前記標準コマンドを実行する手段と
を有し、
前記非標準修飾子を使用して前記標準コマンドの実行を変更することによりシステムレベルの性能が改善されるものである
システム。 EC305) system, comprising:
means for receiving a mode setting command at an input/output device having a specification for enabling a non-standard modifier;
means for receiving standard commands at said input/output device;
and means for executing the standard command according to the non-standard modifier;
The non-standard modifiers are used to modify the execution of the standard commands to improve system level performance.
EC306)EC304またはEC305記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記非標準修飾子を前記標準コマンドのデータと関連付ける手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC306) The system of EC304 or EC305, further comprising:
The system further comprising means for associating said non-standard modifier with data of said standard command.
EC307)EC306記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記標準コマンドの前記データと共に後で取得するために前記非標準修飾子の指示を記憶する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC307) The system of EC306, further comprising:
means for storing an indication of said non-standard modifier for later retrieval along with said data of said standard command.
EC308)EC307記載のシステムにおいて、前記記憶は不揮発的であるシステム。EC308) A system according to EC307, in which the memory is non-volatile.
EC309)EC307記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記非標準修飾子の前記指示をマップの複数のエントリのうちの特定の1つに記憶する手段であって、前記特定のエントリは前記標準コマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)によって前記標準コマンドの前記データと関連付けられている、記憶する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC309) The system of EC307, further comprising:
A system having a means for storing the indication of the non-standard modifier in a particular one of a plurality of entries of a map, the particular entry being associated with the data of the standard command by a logical block address (LBA) of the standard command.
EC310)EC307記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、さらに、
前記書き込みコマンドの前記データへのアクセスを指定する後続の読み出しコマンドに応答して、前記非標準修飾子の前記指示に従って前記後続の読み出しコマンドの実行を変更する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC310) The system of EC307, wherein the standard command is a write command, and further comprising:
means for, in response to a subsequent read command specifying access to said data of said write command, modifying execution of said subsequent read command in accordance with said indication of said non-standard modifier.
EC311)EC307記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドは第1のコマンドであり、さらに、
前記第1のコマンドの前記データへのアクセスを指定する後続のコマンドに応答して、前記非標準修飾子の前記指示に従って前記後続のコマンドの実行を変更する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC311) The system of EC307, wherein the standard command is a first command, and further comprising:
means for, in response to a subsequent command specifying access to said data of said first command, modifying execution of said subsequent command in accordance with said indication of said non-standard modifier.
EC312)EC311記載のシステムにおいて、
前記第1のコマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、
前記非標準修飾子は、前記書き込みコマンドの前記データが読み出し専用であるという指示を有し、
前記後続のコマンドの実行の前記変更は、前記後続のコマンドが標準書き込みコマンドである場合に誤り指示を返すことを有するシステム。 EC312) The system according to EC311,
the first command is a write command;
the non-standard qualifier comprises an indication that the data in the write command is read-only;
The alteration of the execution of the subsequent command comprises returning an error indication if the subsequent command is a standard write command.
EC313)EC307記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、さらに、
前記書き込みコマンドの前記データが再利用されるべきであると決定する手段と、
前記非標準修飾子の前記指示にアクセスする手段と、
前記非標準修飾子の前記指示に応答して、前記書き込みコマンドの前記データを削減する手段と
を有し、それによって、前記書き込みコマンドの前記データは再利用されるのではなく切り捨てられるシステム。 EC313) The system of EC307, wherein the standard command is a write command, and further comprising:
means for determining that the data of the write command should be reused;
means for accessing said indication of said non-standard modifier;
means for reducing the data of the write command in response to the indication of the non-standard qualifier, whereby the data of the write command is truncated rather than reused.
EC314)EC304またはEC305記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドは読み出しコマンドであるシステム。EC314) A system according to EC304 or EC305, in which the standard command is a read command.
EC315)EC304またはEC305記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドは読み出しコマンドまたは書き込みコマンドの一方であるシステム。EC315) A system according to EC304 or EC305, in which the standard command is either a read command or a write command.
EC316)EC304またはEC305記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドはデータ移動コマンドであるシステム。EC316) A system according to EC304 or EC305, in which the standard command is a data movement command.
EC317)EC304またはEC305記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドは切り捨てコマンドであるシステム。EC317) A system according to EC304 or EC305, wherein the standard command is a truncate command.
EC318)EC317記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準修飾子は、前記切り捨てコマンドが必須であるかそれとも任意選択であるか選択的に決定するシステム。EC318) A system according to EC317, wherein the non-standard modifier selectively determines whether the truncation command is required or optional.
EC319)EC304またはEC305記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準修飾子は、少なくとも部分的に前記標準コマンドの予約フィールドによって指定されるシステム。EC319) A system as described in EC304 or EC305, wherein the non-standard modifier is specified, at least in part, by a reserved field of the standard command.
EC320)EC304またはEC305記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準修飾子は、少なくとも部分的に前記標準コマンドの複数のアドレスビットのうちの少なくともいくつかによって指定されるシステム。EC320) A system according to EC304 or EC305, in which the non-standard modifier is specified at least in part by at least some of a plurality of address bits of the standard command.
EC321)EC320記載のシステムにおいて、前記アドレスビットのうちの前記少なくともいくつかは、前記入出力デバイスによってそれ以外に使用されないシステム。EC321) The system of EC320, wherein at least some of the address bits are not otherwise used by the I/O device.
EC322)EC304またはEC305記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準修飾子は、
データタイプの仕様、
データアクセスタイプの仕様、
データ順序付けの仕様、
データ関係の仕様、
データ宛先の仕様、および
コマンド関係の仕様
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上であるシステム。 EC322) In the system according to EC304 or EC305, the non-standard modifier is
Data type specifications,
Data access type specifications,
Data ordering specifications,
Data related specifications,
A system that is one or more of: a data destination specification; and a command related specification.
EC323)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データタイプの前記仕様は圧縮率指示を有するシステム。EC323) A system according to EC322, wherein the specifications for the data type include a compression ratio indication.
EC324)EC323記載のシステムにおいて、前記データタイプの前記仕様は、前記データタイプが圧縮不能であるという指示を有するシステム。EC324) The system of EC323, wherein the specification of the data type includes an indication that the data type is incompressible.
EC325)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データタイプの前記仕様はデータベース・ジャーナル・タイプの指示を有するシステム。EC325) The system of EC322, wherein the specification of the data type includes an indication of a database journal type.
EC326)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データアクセスタイプの前記仕様は、読み出し/書き込みデータアクセスタイプの指示、略読み出しデータアクセスタイプの指示、および略書き込みデータアクセスタイプの指示のうちの2若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。EC326) The system of EC322, wherein the specification of the data access type includes two or more of an indication of a read/write data access type, an indication of a mostly read data access type, and an indication of a mostly write data access type.
EC327)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データアクセスタイプの前記仕様は、読み出し/書き込みデータアクセスタイプの指示、略読み出しデータアクセスタイプの指示、略書き込みデータアクセスタイプの指示、および一時データアクセスタイプの指示のうちの2若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。EC327) In the system described in EC322, the specification of the data access type includes two or more of an indication of a read/write data access type, an indication of a mostly read data access type, an indication of a mostly write data access type, and an indication of a temporary data access type.
EC328)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データアクセスタイプの前記仕様は一時データアクセスタイプの指示を有するシステム。EC328) The system of EC322, wherein the specification of the data access type includes an indication of a temporary data access type.
EC329)EC328記載のシステムにおいて、
前記標準コマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、前記非標準修飾子は前記一時データアクセスタイプの指示を有し、さらに、
前記書き込みコマンドのデータを不揮発的に記憶する手段と、
前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが再利用されるべきであると決定したことに応答し、前記非標準修飾子に従って、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データを削減する手段と
を有するものであるシステム。 EC329) The system according to EC328,
the standard command is a write command, the non-standard qualifier has an indication of the temporary data access type, and
means for non-volatilely storing data of the write command;
and means for pruning the data stored by the write command in accordance with the non-standard qualifier in response to determining that the data stored by the write command should be reused.
EC330)EC329記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記切り捨てに続く前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データの読み出しに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが切り捨てられるという指示を返す手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC330) The system of EC329, further comprising:
means for returning an indication that the data stored by the write command is truncated in response to a read of the data stored by the write command following the truncation.
EC331)EC329記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データの読み出しに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが切り捨てられるという指示、または前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データを選択的に返す手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC331) The system of EC329, further comprising:
means for selectively returning, in response to reading the data stored by the write command, an indication that the data stored by the write command is truncated or the data stored by the write command.
EC332)EC330またはEC331記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記読み出しに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが切り捨てられるという前記指示を非データ応答として返す手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC332) The system of EC330 or EC331, further comprising:
means for returning, in response to the read, the indication that the data stored by the write command is truncated as a non-data response.
EC333)EC330またはEC331記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記読み出しに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドによって記憶された前記データが切り捨てられるという前記指示を返されるデータにおいて特定のパターンとして返す手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC333) The system of EC330 or EC331, further comprising:
means, in response to said read, for returning as a particular pattern in returned data said indication that said data stored by said write command is truncated.
EC334)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データアクセスタイプの前記仕様は読み出し専用データアクセスタイプの指示を有するシステム。EC334) The system of EC322, wherein the specification of the data access type includes an indication of a read-only data access type.
EC335)EC334記載のシステムにおいて、
前記標準コマンドは第1の書き込みコマンドであり、前記非標準修飾子は前記読み出し専用データアクセスタイプの指示を有し、さらに、
前記第1の書き込みコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)に従って前記第1の書き込みコマンドのデータを不揮発的に記憶する手段と、
前記第1の書き込みコマンドの前記論理ブロックアドレスに書き込もうとする後続の書き込みコマンドに応答して、誤り指示を返す手段と
を有するものであるシステム。 EC335) In the system according to EC334,
the standard command is a first write command, the non-standard qualifier having an indication of the read-only data access type, and
means for non-volatilely storing data of the first write command according to a logical block address (LBA) of the first write command;
means for returning an error indication in response to a subsequent write command attempting to write to the logical block address of the first write command.
EC336)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データ順序付けの前記仕様はアトミックシーケンスの指示を有するシステム。EC336) The system of EC322, wherein the specification of the data ordering includes an indication of an atomic sequence.
EC337)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データ順序付けの前記仕様は、順次シーケンスの指示およびアトミックシーケンスの指示のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。EC337) The system of EC322, wherein the specification of the data ordering comprises one or more of a sequential sequence indication and an atomic sequence indication.
EC338)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記データ関係を前記標準コマンドのデータと関連付ける手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC338) The system of EC322, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for associating said data relationship with data of said standard command.
EC339)EC338記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記データ関係および前記標準コマンドの前記データを不揮発的に記憶する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC339) The system of EC338, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for non-volatilely storing said data relations and said data of said standard commands.
EC340)EC339記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドは第1の標準コマンドであり、さらに、
続いて、前記データ関係を後続の標準コマンドのデータと関連付ける手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC340) The system of EC339, wherein the standard command is a first standard command, and further comprising:
The system then has means for associating said data relationship with data of a subsequent standard command.
EC341)EC340記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記データ関係に従ってデータを取得する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC341) The system of EC340, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for obtaining data according to the data relationship.
EC342)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記データ宛先の前記仕様は複数のデータバンドのうちの1つを指定するシステム。EC342) In the system of EC322, the specification of the data destination specifies one of a plurality of data bands.
EC343)EC342記載のシステムにおいて、前記データバンドはホットバンドとコールドバンドとを有するシステム。EC343) A system according to EC342, wherein the data band comprises a hot band and a cold band.
EC344)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンド関係の前記仕様はコマンド優先順位を有するシステム。EC344) In the system described in EC322, the specification of the command relationship has a command priority.
EC345)EC322記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンド関係の前記仕様はコマンド順序付け従属関係を有するシステム。EC345) A system according to EC322, wherein the specification of the command relationship has a command ordering dependency relationship.
EC346)EC345記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンド順序付け従属関係はコマンドバリアであるシステム。EC346) The system of EC345, wherein the command ordering dependency is a command barrier.
EC347)EC305記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準コマンドは2若しくはそれ以上の標準コマンドのシーケンスであるシステム。EC347) A system as described in EC305, wherein the standard command is a sequence of two or more standard commands.
EC348)EC305記載のシステムにおいて、
前記モード設定コマンドは第1のモード設定コマンドであり、さらに、
前記標準コマンドの前記受け取りに続いて、前記非標準修飾子を使用不可にする仕様を有する第2のモード設定コマンドを受け取る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC348) In the system according to EC305,
the mode setting command is a first mode setting command,
subsequent to said receiving said standard command, a second mode setting command having a specification for disabling said non-standard modifiers.
EC349)システムであって、
外部インターフェースを介して入出力デバイスでコマンドを受け取る手段と、
前記コマンドのタイプを確認する手段と、
前記コマンドのタイプが読み出しコマンドである場合、マップにアクセスして前記コマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を変換し、不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置を選択的に含む変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報を取得する手段と、
前記コマンドの前記タイプが予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドである場合、前記予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドの情報から、前記マップを使用せずに前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置を決定する手段と、
前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置に対応するデータを返す手段と
を有し、
前記予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドの前記情報は、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の少なくとも一部分を有するものである、
システム。 EC349) system, comprising:
means for receiving commands at the input/output device via an external interface;
means for determining the type of the command;
means for translating a logical block address (LBA) of the command by accessing a map if the type of the command is a read command, and obtaining translated logical block address information that selectively includes a predetermined location in a non-volatile memory (NVM);
means for determining, if the type of the command is a pre-mapped read command, the location in the non-volatile memory from information in the pre-mapped read command without using the map;
and means for returning data corresponding to said location in said non-volatile memory;
the information in the pre-mapped read command comprises at least a portion of the translated logical block address information.
system.
EC350)EC349記載のシステムにおいて、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報は、前記不揮発性メモリ内の位置または前記コマンドの前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないという指示を選択的に有するシステム。EC350) The system of EC349, wherein the converted logical block address information selectively includes a location within the non-volatile memory or an indication that the logical block address of the command does not exist in the non-volatile memory.
EC351)EC349記載のシステムにおいて、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報は、前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位のうちの第1の読み出し単位のアドレスおよび読み出し単位での長さを選択的に有するシステム。EC351) A system according to EC349, in which the converted logical block address information selectively includes an address and a length in read units of a first read unit of one or more read units of the non-volatile memory.
EC352)EC351記載のシステムにおいて、前記1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位の各々のサイズは少なくとも512バイトであるシステム。EC352) The system of EC351, wherein the size of each of the one or more read units is at least 512 bytes.
EC353)EC349記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップのシャドウコピーにアクセスして前記論理ブロックアドレスを変換して、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分を取得する手段と、
前記入出力デバイスに前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分を含む前記予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを送る手段と
を有するものであるシステム。 EC353) The system of EC349, further comprising:
means for accessing a shadow copy of said map to translate said logical block addresses and obtaining said at least a portion of said translated logical block address information;
means for sending said pre-mapped read command including said at least a portion of said translated logical block address information to said input/output device.
EC354)EC353記載のシステムにおいて、前記アクセスはコンピューティングホストにおけるものであるシステム。EC354) The system of EC353, wherein the access is at a computing host.
EC355)EC353記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは複数のエントリを有し、前記エントリの各々は有効性の指示を有するシステム。EC355) The system of EC353, wherein the shadow copy of the map has a plurality of entries, each of the entries having a validity indication.
EC356)EC355記載のシステムにおいて、
前記論理ブロックアドレスは複数の論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)のうちの1つであり、
前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報は複数の変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報のうちの1つであり、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は、前記論理ブロックアドレスのうちの1若しくはそれ以上を、前記複数の変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報のそれぞれの情報と関連付けるシステム。 EC356) In the system of EC355,
the logical block address is one of a plurality of logical block addresses (LBAs);
the translated logical block address information is one of a plurality of translated logical block address information;
Each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map associates one or more of the logical block addresses with a respective one of the plurality of translated logical block address information.
EC357)EC356記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は、前記複数の変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記それぞれの情報の少なくとも一部分を有するシステム。EC357) The system of EC356, wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map has at least a portion of the respective information of the plurality of translated logical block address information.
EC358)EC356記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリのうちの少なくとも1つは、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを選択的に指定するシステム。EC358) The system of EC356, wherein at least one of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively specifies that the logical block address associated with the at least one of the valid entries is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC359)EC358記載のシステムにおいて、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記論理ブロックアドレスは切り捨てられるシステム。EC359) The system of EC358, wherein the logical block address associated with at least one of the valid entries is truncated.
EC360)EC355記載のシステムにおいて、
前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置は前記不揮発性メモリ内の複数の位置のうちの1つであり、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は前記不揮発性メモリ内のそれぞれの位置を選択的に指定するシステム。 EC360) In the system described in EC355,
the location in the non-volatile memory is one of a plurality of locations in the non-volatile memory;
The system wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively designates a respective location within the non-volatile memory.
EC361)EC360記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は、前記エントリと関連付けられたデータが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを選択的に指定するシステム。EC361) The system of EC360, wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively specifies that data associated with the entry is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC362)EC355記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
最初に前記マップの前記シャドウコピーのすべてのエントリを無効とマークする手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC362) The system of EC355, further comprising:
The system includes a means for initially marking all entries of the shadow copy in the map as invalid.
EC363)EC355記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスに書き込みコマンドを送ったことに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と関連付けられた前記マップの前記シャドウコピーのエントリを無効とマークする手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC363) The system of EC355, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for, in response to sending a write command to the I/O device, marking as invalid an entry in the shadow copy of the map associated with a logical block address (LBA) of the write command.
EC364)EC363記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスで、前記外部インターフェースを介して前記書き込みコマンドを受け取る手段と、
前記書き込みコマンドの前記受け取りに続いて、前記書き込みコマンドの前記論理ブロックアドレスに対応するシャドウマップ更新を送る手段と
を有するものであるシステム。 EC364) The system of EC363, further comprising:
means for receiving, at said input/output device, said write command via said external interface;
means for sending a shadow map update corresponding to the logical block address of the write command following the receipt of the write command.
EC365)EC364記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記シャドウマップ更新に従って前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを更新する手段を有するものであり、
前記更新する手段は、前記書き込みコマンドの前記論理ブロックアドレスと関連付けられた前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリを有効とマークするシステム。 EC365) The system of EC364, further comprising:
means for updating the shadow copy of the map in accordance with the shadow map updates;
The system wherein the means for updating marks the entry in the shadow copy of the map associated with the logical block address of the write command as valid.
EC366)EC365記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新は前記入出力デバイスによるものであるシステム。EC366) A system according to EC365, wherein the update is performed by the input/output device.
EC367)EC353記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを前記入出力デバイスに接続されたコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC367) The system of EC353, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for storing said shadow copy of said map in a memory of a computing host connected to said I/O device.
EC368)EC367記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストに送る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC368) The system of EC367, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for transmitting the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the computing host.
EC369)EC367記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有するシステム。EC369) The system of EC367, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises the main memory of the computing host.
EC370)EC367記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有するシステム。EC370) The system of EC367, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC371)EC370記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能であるシステム。EC371) The system of EC370, wherein the memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC372)EC367記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに不揮発的に記憶されるシステム。EC372) A system according to EC367, in which the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory.
EC373)EC372記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有するシステム。EC373) The system of EC372, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC374)EC349記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは2レベルマップを有するシステム。EC374) A system as described in EC349, wherein the map comprises a two-level map.
EC375)EC374記載のシステムにおいて、
前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応するシステム。 EC375) In the system according to EC374,
the map has a first level and a second level;
The system, wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map.
EC376)システムであって、
入出力デバイスで、外部インターフェースを介して書き込みコマンドを受け取る手段と、
前記書き込みコマンドのデータを不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の位置に書き込む手段と、
前記書き込みコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)とマップの前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置との関連付けを記憶する手段と、
前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置に従った情報を有する更新を前記マップのシャドウコピーに送る手段と
を有するシステム。 EC376) system,
a means for receiving a write command via an external interface at an input/output device;
means for writing data of the write command to a location in a non-volatile memory (NVM);
means for storing an association between a logical block address (LBA) of the write command and the location in the non-volatile memory of a map;
means for sending updates to a shadow copy of the map having information according to the location in the non-volatile memory.
EC377)EC376記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは2レベルマップを有するシステム。EC377) A system according to EC376, wherein the map comprises a two-level map.
EC378)EC377記載のシステムにおいて、
前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応するシステム。 EC378) In the system according to EC377,
the map has a first level and a second level;
The system, wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map.
EC379)EC376記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置に従った前記情報は、前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位のうちの第1の読み出し単位のアドレスおよび読み出し単位での長さを有するシステム。EC379) The system of EC376, wherein the information according to the location in the non-volatile memory includes an address and a length in read units of a first read unit of one or more read units of the non-volatile memory.
EC380)EC376記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを前記入出力デバイスに接続されたコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC380) The system of EC376, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for storing said shadow copy of said map in a memory of a computing host connected to said I/O device.
EC381)EC380記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストに送る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC381) The system of EC380, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for transmitting the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the computing host.
EC382)EC380記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有するシステム。EC382) The system of EC380, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises the main memory of the computing host.
EC383)EC380記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有するシステム。EC383) The system of EC380, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC384)EC383記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能であるシステム。EC384) The system of EC383, wherein the memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC385)EC383記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリに送る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC385) The system of EC383, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for transmitting the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the I/O space memory of the computing host.
EC386)EC385記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新を送る前記手段はPCIe書き込み要求を送る手段を有するシステム。EC386) The system of EC385, wherein the means for sending the update includes means for sending a PCIe write request.
EC387)EC385記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新を送る前記手段は前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの読み出し−変更−書き込みの手段を有するシステム。EC387) The system of EC385, wherein the means for sending the updates includes means for reading-modifying-writing the shadow copy of the map.
EC388)EC385記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスが読み出しコマンドを実行する前に、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーから前記読み出しコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)の変換をフェッチする手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC388) The system of EC385, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for fetching a logical block address (LBA) translation of the read command from the shadow copy of the map before the I/O device executes the read command.
EC389)EC388記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチは前記入出力デバイスによるものであるシステム。EC389) The system of EC388, wherein the fetch is performed by the input/output device.
EC390)EC389記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチする手段はPCIe読み出し要求を送る手段を有するシステム。EC390) The system of EC389, wherein the fetching means includes means for sending a PCIe read request.
EC391)EC388記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチは前記コンピューティングホストによるものであり、前記読み出しコマンドは予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドであるシステム。EC391) The system of EC388, wherein the fetch is by the computing host and the read command is a pre-mapped read command.
EC392)EC380記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに不揮発的に記憶されるシステム。EC392) A system according to EC380, in which the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory.
EC393)EC392記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有するシステム。EC393) The system of EC392, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC394)システムであって、
入出力デバイスのマップのシャドウコピーを初期化して、当該マップのシャドウコピーの複数のエントリのすべてを無効とマークする手段と、
前記入出力デバイスから前記マップの前記シャドウコピーに対する更新を受け取る手段と、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーに対する更新に従って、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーのエントリのうちの少なくとも1つを有効とマークする手段と
を有するシステム。 EC394) system,
means for initializing a shadow copy of a map of I/O devices and marking all of a plurality of entries in the shadow copy of the map as invalid;
means for receiving updates to the shadow copy of the map from the input/output device;
means for marking at least one of the entries of the shadow copy of the map as valid according to updates to the shadow copy of the map.
EC395)EC394記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新に従って前記マークする手段は、前記更新の変換論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)情報を前記エントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付ける手段をさらに有するものであるシステム。EC395) The system of EC394, wherein the means for marking according to the update further comprises means for associating translated logical block address (LBA) information of the update with the at least one of the entries.
EC396)EC395記載のシステムにおいて、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報は前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の位置を有するシステム。EC396) The system of EC395, wherein the converted logical block address information has a location within a non-volatile memory (NVM) of the I/O device.
EC397)EC394記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は、前記入出力デバイスの少なくとも1つの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を、前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の位置と選択的に関連付けるシステム。EC397) The system of EC394, wherein each of the entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively associates at least one logical block address (LBA) of the I/O device with a location within a non-volatile memory (NVM) of the I/O device.
EC398)EC394記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力デバイスの前記マップは2レベルマップを有するシステム。EC398) A system as described in EC394, wherein the map of the input/output device has a two-level map.
EC399)EC398記載のシステムにおいて、
前記入出力デバイスの前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記入出力デバイスの前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応するシステム。 EC399) In the system according to EC398,
the map of the input/output device has a first level and a second level;
The system, wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map of the input/output devices.
EC400)EC394記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを前記入出力デバイスに接続されたコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC400) The system according to EC394, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for storing said shadow copy of said map in a memory of a computing host connected to said I/O device.
EC401)EC400記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストに送る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC401) The system of EC400, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for transmitting the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the computing host.
EC402)EC400記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有するシステム。EC402) In the system described in EC400, the memory of the computing host comprises the main memory of the computing host.
EC403)EC400記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有するシステム。EC403) In the system described in EC400, the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC404)EC403記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能であるシステム。EC404) The system of EC403, wherein the memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC405)EC403記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリに送る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC405) The system of EC403, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for transmitting the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the I/O space memory of the computing host.
EC406)EC405記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新を送る前記手段はPCIe書き込み要求を送る手段を有するシステム。EC406) The system of EC405, wherein the means for sending the update includes means for sending a PCIe write request.
EC407)EC405記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新を送る前記手段は前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの読み出し−変更−書き込みの手段を有するシステム。EC407) The system of EC405, wherein the means for sending the updates includes means for reading-modifying-writing the shadow copy of the map.
EC408)EC405記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスが読み出しコマンドを実行する前に、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーから前記読み出しコマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)の変換をフェッチする手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC408) The system of EC405, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for fetching a logical block address (LBA) translation of the read command from the shadow copy of the map before the I/O device executes the read command.
EC409)EC408記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチは前記入出力デバイスによるものであるシステム。EC409) The system of EC408, wherein the fetch is performed by the input/output device.
EC410)EC409記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチする手段はPCIe読み出し要求を送る手段を有するシステム。EC410) The system of EC409, wherein the fetching means includes means for sending a PCIe read request.
EC411)EC408記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチは前記コンピューティングホストによるものであり、前記読み出しコマンドは予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドであるシステム。EC411) The system of EC408, wherein the fetch is by the computing host and the read command is a pre-mapped read command.
EC412)EC400記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)に不揮発的に記憶されるシステム。EC412) A system according to EC400, in which the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory (NVM) of the input/output device.
EC413)EC412記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有するシステム。EC413) The system of EC412, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC414)システムであって、
入出力デバイスに対する要求が読み出し要求であるかどうかを決定する手段であって、
前記入出力デバイスは複数のエントリを有するマップを有し、当該マップの複数のエントリのうちの少なくともいくつかの各々は、前記入出力デバイスの各論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を、前記入出力デバイスの不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置を選択的に有する各変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報にマップするものであり、
前記マップのシャドウコピーは対応する複数のエントリを有するものである、
前記決定する手段と、
前記要求が読み出し要求である場合、当該読み出し要求の論理ブロックアドレスと関連付けられた前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリのうちの特定の1つが有効であるかどうかを決定する手段と、
前記特定のエントリが有効である場合、前記特定のエントリに基づいた、前記各変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の少なくとも一部分を有する予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを前記入出力デバイスに選択的に送る手段と
を有するシステム。 EC414) system, comprising:
means for determining whether a request to an input/output device is a read request, comprising:
the I/O device has a map having a plurality of entries, each of at least some of the plurality of entries of the map mapping a respective logical block address (LBA) of the I/O device to a respective translated logical block address information selectively having a predetermined location within a non-volatile memory (NVM) of the I/O device;
The shadow copy of the map has a corresponding number of entries.
The determining means;
if the request is a read request, means for determining whether a particular one of the entries in the shadow copy of the map associated with the logical block address of the read request is valid;
and if the particular entry is valid, means for selectively sending a pre-mapped read command to the I/O device having at least a portion of the respective translated logical block address information based on the particular entry.
EC415)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は前記マップ内のそれぞれのエントリに対応し、
前記マップの前記エントリのうちの前記少なくともいくつかの各々は、前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスによってマップされた前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報を有し、
前記マップの前記エントリのうちの前記少なくともいくつかのうちの1つに対応する前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は、前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の少なくとも一部分を有するシステム。 EC415) The system of EC414,
each of the entries of the shadow copy of the map corresponds to a respective entry in the map;
each of said at least some of said entries of said map having said respective translated logical block address information mapped by said respective logical block address;
The system wherein each of the entries of the shadow copy of the map corresponding to one of the at least some of the entries of the map has at least a portion of the respective translated logical block address information.
EC416)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記複数のエントリは第2レベルのマップであるシステム。EC416) The system of EC414, wherein the plurality of entries of the map are a second level map.
EC417)EC416記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力デバイスは第1レベルのマップをさらに有するものであるシステム。EC417) The system of EC416, wherein the input/output device further comprises a first level map.
EC418)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分は、前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置または前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないという指示を選択的に有するシステム。EC418) The system of EC414, wherein the at least a portion of the respective converted logical block address information selectively includes an indication that the location in the non-volatile memory or the respective logical block address is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC419)EC418記載のシステムにおいて、前記選択的に送る手段は、前記特定のエントリに従った前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分が、前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを指示するかどうか決定する手段を有するシステム。EC419) In the system of EC418, the selectively sending means includes means for determining whether the at least a portion of the respective translated logical block address information according to the particular entry indicates that the logical block address of the read request is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC420)EC419記載のシステムにおいて、前記選択的に送る手段は、前記特定のエントリに従った前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分が、前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在することを指示する場合に、単に前記入出力デバイスに前記予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを送る手段をさらに有するものであるシステム。EC420) In the system of EC419, the selective sending means further comprises means for only sending the pre-mapped read command to the I/O device if the at least a portion of the respective translated logical block address information according to the particular entry indicates that the logical block address of the read request is present in the non-volatile memory.
EC421)EC420記載のシステムにおいて、前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスが切り捨てられる場合には、前記特定のエントリに従った前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分は、前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを指示するシステム。EC421) The system of EC420, wherein if the logical block address of the read request is truncated, the at least a portion of the translated logical block address information according to the particular entry indicates that the logical block address of the read request is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC422)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、前記それぞれの変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の前記少なくとも一部分は、前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位のうちの第1の読み出し単位のアドレスおよび読み出し単位での長さを選択的に有するシステム。EC422) The system of EC414, wherein the at least a portion of each converted logical block address information selectively includes an address and length in read units of a first read unit of one or more read units of the non-volatile memory.
EC423)EC422記載のシステムにおいて、前記1若しくはそれ以上の読み出し単位の各々のサイズは少なくとも512バイトであるシステム。EC423) The system of EC422, wherein the size of each of the one or more read units is at least 512 bytes.
EC424)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記特定のエントリが無効である場合に、前記入出力デバイスに前記読み出し要求の前記論理ブロックアドレスを有する標準読み出しコマンドを送る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC424) The system of EC414, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for sending a standard read command to said I/O device having said logical block address of said read request if said particular entry is invalid.
EC425)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記要求が書き込み要求である場合に、前記書き込み要求の論理ブロックアドレスと関連付けられた前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリのうちの1つを無効とマークする手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC425) The system of EC414, further comprising:
If the request is a write request, then means for marking as invalid one of the entries in the shadow copy of the map associated with a logical block address of the write request.
EC426)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの各エントリは、有効性指示、および前記マップの対応するエントリからの少なくともいくつかのコンテンツのコピーを有するシステム。EC426) The system of EC414, wherein each entry of the shadow copy of the map has a validity indication and a copy of at least some of the content from a corresponding entry of the map.
EC427)EC426記載のシステムにおいて、前記特定のエントリが有効である場合に、前記マップ内の前記対応するエントリからの少なくともいくつかのコンテンツの前記コピーは、前記マップの前記対応するエントリからの前記少なくともいくつかのコンテンツと同じであるシステム。EC427) The system of EC426, wherein when the particular entry is valid, the copy of at least some of the content from the corresponding entry in the map is the same as the at least some of the content from the corresponding entry in the map.
EC428)EC426記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの有効なエントリは前記マップの有効なエントリの部分集合であるシステム。EC428) The system of EC426, wherein the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map are a subset of the valid entries of the map.
EC429)EC428記載のシステムにおいて、前記部分集合は真部分集合であるシステム。EC429) A system according to EC428, wherein the subset is a proper subset.
EC430)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は、無効であり、または前記マップの対応するエントリに従った情報を有するシステム。EC430) The system of EC414, wherein each of the entries in the shadow copy of the map is invalid or has information in accordance with the corresponding entry in the map.
EC431)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力デバイスの前記マップは2レベルマップを有するシステム。EC431) A system as described in EC414, in which the map of the input/output device has a two-level map.
EC432)EC431記載のシステムにおいて、
前記入出力デバイスの前記マップは第1レベルおよび第2レベルを有し、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーは前記入出力デバイスの前記マップの前記第2レベルに対応するシステム。 EC432) The system according to EC431,
the map of the input/output device has a first level and a second level;
The system, wherein the shadow copy of the map corresponds to the second level of the map of the input/output devices.
EC433)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記エントリの各々は有効性の指示を有するシステム。EC433) The system of EC414, wherein each of the entries of the shadow copy of the map has a validity indication.
EC434)EC433記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は、前記論理ブロックアドレスのうちのそれぞれの1若しくはそれ以上を、前記不揮発性メモリ内のそれぞれの位置と選択的に関連付けるシステム。EC434) The system of EC433, wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively associates a respective one or more of the logical block addresses with a respective location in the non-volatile memory.
EC435)EC434記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリのうちの少なくとも1つは、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスのうちの少なくとも1つが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを選択的に指定するシステム。EC435) The system of EC434, wherein at least one of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively specifies that at least one of the respective logical block addresses associated with the at least one of the valid entries is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC436)EC435記載のシステムにおいて、前記有効なエントリのうちの前記少なくとも1つと関連付けられた前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスのうちの前記少なくとも1つは切り捨てられるシステム。EC436) The system of EC435, wherein at least one of the respective logical block addresses associated with at least one of the valid entries is truncated.
EC437)EC433記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの前記有効なエントリの各々は前記不揮発性メモリ内のそれぞれの位置を選択的に指定するシステム。EC437) The system of EC433, wherein each of the valid entries of the shadow copy of the map selectively designates a respective location within the non-volatile memory.
EC438)EC433記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
最初に前記マップの前記シャドウコピーのすべての前記エントリを無効とマークする手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC438) The system of EC433, further comprising:
The system includes means for initially marking all of the entries in the shadow copy of the map as invalid.
EC439)EC414記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーを前記入出力デバイスに接続されたコンピューティングホストのメモリに記憶する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC439) The system of EC414, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for storing said shadow copy of said map in a memory of a computing host connected to said I/O device.
EC440)EC439記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスから前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの更新を受け取る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC440) The system of EC439, further comprising:
The system further comprising means for receiving updates to the shadow copy of the map from the input/output device.
EC441)EC439記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有するシステム。EC441) The system of EC439, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises the main memory of the computing host.
EC442)EC439記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有するシステム。EC442) The system of EC439, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC443)EC442記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能であるシステム。EC443) The system of EC442, wherein the memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in a PCIe address space.
EC444)EC442記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記マップの前記シャドウコピーへの前記更新を前記入出力デバイスから前記コンピューティングホストの前記入出力空間メモリに送る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC444) The system of EC442, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for transmitting the updates to the shadow copy of the map from the I/O device to the I/O space memory of the computing host.
EC445)EC444記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新を送る前記手段はPCIe書き込み要求を送る手段を有するシステム。EC445) The system of EC444, wherein the means for sending the update includes means for sending a PCIe write request.
EC446)EC444記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新を送る前記手段は前記マップの前記シャドウコピーの読み出し−変更−書き込みの手段を有するシステム。EC446) The system of EC444, wherein the means for sending the updates includes means for reading-modifying-writing the shadow copy of the map.
EC447)EC444記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力デバイスが特定のコマンドを実行する前に、前記マップの前記シャドウコピーから前記特定のコマンドの論理ブロックアドレスの変換をフェッチする手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC447) The system of EC444, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for fetching a translation of a logical block address of a particular command from the shadow copy of the map before the I/O device executes the particular command.
EC448)EC447記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチは前記入出力デバイスによるものであるシステム。EC448) The system of EC447, wherein the fetch is performed by the input/output device.
EC449)EC448記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチする手段はPCIe読み出し要求を送る手段を有するシステム。EC449) The system of EC448, wherein the fetching means includes means for sending a PCIe read request.
EC450)EC447記載のシステムにおいて、前記フェッチは前記コンピューティングホストによるものであるシステム。EC450) The system of EC447, wherein the fetch is performed by the computing host.
EC451)EC450記載のシステムにおいて、前記特定のコマンドは予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドであるシステム。EC451) A system according to EC450, in which the specific command is a pre-mapped read command.
EC452)EC439記載のシステムにおいて、前記マップは前記不揮発性メモリに不揮発的に記憶されるシステム。EC452) A system according to EC439, in which the map is stored in a non-volatile manner in the non-volatile memory.
EC453)EC452記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記メモリは揮発性メモリを有するシステム。EC453) The system of EC452, wherein the memory of the computing host comprises volatile memory.
EC454)システムであって、
低電力状態を開始するという指示を入出力デバイスで受け取る手段と、
前記入出力デバイスの内部状態をコンピューティングホストのシステムアクセス可能メモリに保存する手段と、
前記低電力状態を終了するという指示を前記入出力デバイスで受け取る手段と、
前記システムアクセス可能メモリから前記入出力デバイスの前記内部状態を復元する手段と
を有するシステム。 EC454) system, comprising:
means for receiving an indication at an input/output device to initiate a low power state;
means for storing an internal state of said input/output device in a system accessible memory of a computing host;
means for receiving an indication at the input/output device to exit the low power state;
and means for restoring said internal state of said input/output device from said system accessible memory.
EC455)EC454記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記システムアクセス可能メモリは前記コンピューティングホストのメインメモリを有するシステム。EC455) The system of EC454, wherein the system accessible memory of the computing host comprises main memory of the computing host.
EC456)EC454記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記システムアクセス可能メモリは前記コンピューティングホストの入出力空間メモリを有するシステム。EC456) The system of EC454, wherein the system accessible memory of the computing host comprises an input/output space memory of the computing host.
EC457)EC456記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティングホストの前記システムアクセス可能メモリは、PCIeアドレス空間において前記入出力デバイスによってアクセス可能であるシステム。EC457) The system of EC456, wherein the system accessible memory of the computing host is accessible by the I/O device in PCIe address space.
EC458)システムであって、
ストレージにアクセスするよう求めるコマンドを受け取る手段であって、前記コマンドはアクセスタイプを指定し、1若しくはそれ以上のパラメータを有するものである、前記受け取る手段と、
前記ストレージの位置を決定する手段と
を有し、
前記決定する手段は、含まれるデータ構造を条件付きで参照して前記位置を確認する手段を有し、前記参照は、前記パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上が前記位置の仕様を有する場合は省略されるものである、
システム。 EC458) system, comprising:
means for receiving a command requesting access to storage, the command specifying an access type and having one or more parameters;
and means for determining a location of the storage;
said determining means having means for conditionally referencing an included data structure to ascertain said location, said reference being omitted if one or more of said parameters includes a specification of said location;
system.
EC459)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、前記指定は、
前記ストレージの領域の指示、
前記ストレージの物理アドレスの指示、
前記ストレージのデータの長さ、および
前記ストレージのデータの範囲
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC459) The system of EC458, wherein the specification is:
An indication of an area of said storage;
An indication of a physical address of the storage;
The system has one or more of: a length of data in said storage; and a range of data in said storage.
EC460)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、前記含まれるデータ構造は、それぞれの1若しくはそれ以上の論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と関連付けられたデータが前記ストレージ内のどこに位置するかを各々が記述する1若しくはそれ以上のエントリを有するシステム。EC460) The system of EC458, wherein the included data structure has one or more entries, each describing where data associated with a respective one or more logical block addresses (LBAs) is located within the storage.
EC461)EC460記載のシステムにおいて、前記エントリの各々は、前記それぞれの論理ブロックアドレスと関連付けられた1若しくはそれ以上の属性をさらに選択的に記述するものであるシステム。EC461) The system of EC460, wherein each of the entries further selectively describes one or more attributes associated with the respective logical block address.
EC462)EC460記載のシステムにおいて、前記エントリの各々は、前記ストレージの1若しくはそれ以上の領域と関連付けられた1若しくはそれ以上の属性をさらに記述するものであるシステム。EC462) The system of EC460, wherein each of the entries further describes one or more attributes associated with one or more areas of the storage.
EC463)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記受け取りの前に、前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC463) The system of EC458, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for providing updates describing changes to the included data structures prior to said receiving.
EC464)EC463記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドはコンピューティングホストによって提供され、前記更新は前記コンピューティングホストに提供されるシステム。EC464) The system of EC463, wherein the command is provided by a computing host and the update is provided to the computing host.
EC465)EC463記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新は前記位置の前記仕様を有するシステム。EC465) A system as described in EC463, wherein the update includes the specification of the position.
EC466)EC465記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドは論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)に従ったものであり、前記提供は前記論理ブロックアドレスに書き込みコマンドを提供したことに応答したものであるシステム。EC466) The system of EC465, wherein the command is according to a logical block address (LBA) and the providing is in response to providing a write command to the logical block address.
EC467)EC465記載のシステムにおいて、前記提供する手段は、前記ストレージの少なくともいくらかを実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)の1若しくはそれ以上の部分を再利用し、および/または再配置したことに応答するものであるシステム。EC467) The system of EC465, wherein the providing means is responsive to reclaiming and/or relocating one or more portions of a non-volatile memory (NVM) implementing at least some of the storage.
EC468)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、前記受け取りおよび前記決定は、入出力記憶デバイスによるものであるシステム。EC468) The system of EC458, wherein the receiving and the determining are performed by an input/output storage device.
EC469)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドはコンピューティングホストによって提供されるシステム。EC469) The system of EC458, wherein the command is provided by a computing host.
EC470)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、前記パラメータは標準パラメータおよび非標準パラメータを有し、前記標準パラメータは規格によって定義され、前記非標準パラメータは前記規格によって定義されず、前記非標準パラメータは、前記仕様を有する前記パラメータを有するシステム。EC470) A system according to EC458, wherein the parameters include standard parameters and non-standard parameters, the standard parameters being defined by a standard, the non-standard parameters being not defined by the standard, and the non-standard parameters being the parameters having the specification.
EC471)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドは規格によって定義され、前記仕様を有する前記パラメータは前記規格によって定義されないシステム。EC471) A system according to EC458, in which the command is defined by a standard and the parameter having the specification is not defined by the standard.
EC472)EC470またはEC471記載のシステムにおいて、前記仕様を有する前記パラメータは、
予約コマンドコード、
ベンダ特有のパラメータ、
予約フィールド、
不使用フィールド、および
機能レジスタ内の値
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC472) The system of EC470 or EC471, wherein the parameter having the specification is:
Reservation command code,
Vendor specific parameters,
Reserved fields,
A system having one or more of the following: an unused field; and a value in a capability register.
EC473)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記アクセスタイプおよび前記位置に従って前記ストレージのアクセスを行う手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC473) The system of EC458, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for accessing said storage in accordance with said access type and said location.
EC474)EC473記載のシステムにおいて、前記アクセスタイプは読み出しアクセスタイプであり、前記アクセスは読み出しアクセスであるシステム。EC474) A system according to EC473, wherein the access type is a read access type and the access is a read access.
EC475)EC474記載のシステムにおいて、前記パラメータは前記仕様を有するシステム。EC475) A system according to EC474, wherein the parameters have the above specifications.
EC476)EC475記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドは予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドであるシステム。EC476) A system according to EC475, wherein the command is a pre-mapped read command.
EC477)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、前記位置は第1の位置であり、さらに、
前記アクセスタイプおよび第2の位置に従って前記ストレージのアクセスを行う手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC477) The system of EC458, wherein the location is a first location and further comprising:
The system further comprises means for accessing said storage according to said access type and said second location.
EC478)EC477記載のシステムにおいて、前記アクセスタイプは書き込みアクセスタイプであり、前記アクセスは書き込みアクセスであるシステム。EC478) A system according to EC477, wherein the access type is a write access type and the access is a write access.
EC479)EC478記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する手段であって、前記更新は前記第2の位置の仕様を有するものである、提供する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC479) The system of EC478, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for providing an update describing a change to the included data structure, the update including a specification of the second location.
EC480)EC478記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記仕様に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC480) The system of EC478, further comprising:
The system further comprising means for modifying said storage usage calculations in accordance with said specifications.
EC481)EC458記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドは切り捨てコマンドであり、前記アクセスタイプは切り捨てアクセスタイプであるシステム。EC481) A system as described in EC458, in which the command is a truncation command and the access type is a truncation access type.
EC482)EC481記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する手段であって、前記更新は、前記コマンドの受け取りの前に前記位置にマップされた論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)の属性の仕様を有するものである、提供する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC482) The system of EC481, further comprising:
A system having means for providing an update describing a change to the included data structure, the update including a specification of attributes of a logical block address (LBA) that was mapped to the location prior to receipt of the command.
EC483)EC482記載のシステムにおいて、前記属性は、前記論理ブロックアドレスが削減されたことを指示するシステム。EC483) A system according to EC482, in which the attribute indicates that the logical block address has been reduced.
EC484)EC481記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記仕様に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC484) The system of EC481, further comprising:
The system further comprising means for modifying said storage usage calculations in accordance with said specifications.
EC485)システムであって、
コマンドを受け取る手段であって、当該コマンドは複数のコマンドタイプのうちの1つであり、当該コマンドタイプは第1のタイプおよび第2のタイプを有するものである、前記受け取る手段と、
前記コマンドが前記コマンドのタイプのうちのどれであるか決定する手段と、
前記コマンドが前記第1のタイプのものである場合、第1の処理を行い、次いで第2の処理を行う手段と、
前記コマンドが前記第2のタイプのものである場合、前記第1の処理を行わずに前記第2の処理を行う手段と
を有し、
前記第2の処理は、前記コマンドが前記第1のタイプのものである場合、前記第1の処理によって生成される情報を使用し、前記コマンドが前記第2のタイプのものである場合、当該コマンドによって提供される情報を使用するものである、
システム。 EC485) system,
means for receiving a command, the command being one of a plurality of command types, the command type having a first type and a second type;
means for determining which of said command types said command is;
means for performing a first operation and then a second operation if the command is of the first type;
means for performing the second processing without performing the first processing if the command is of the second type;
the second process uses information generated by the first process if the command is of the first type, and uses information provided by the command if the command is of the second type.
system.
EC486)EC485記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドは入出力記憶デバイスのストレージにアクセスするものであるシステム。EC486) A system as described in EC485, in which the command accesses storage of an input/output storage device.
EC487)EC486記載のシステムにおいて、前記第1の処理は、含まれるデータ構造にアクセスして前記情報を生成することを有するシステム。EC487) The system of EC486, wherein the first process includes accessing an included data structure to generate the information.
EC488)EC487記載のシステムにおいて、前記含まれるデータ構造は、論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と前記ストレージの少なくともいくらかを実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)の物理アドレスとの間のマッピングを記述するマップであり、前記情報は前記マッピングのうちの1つの少なくとも一部を有するシステム。EC488) The system of EC487, wherein the included data structure is a map describing mappings between logical block addresses (LBAs) and physical addresses of a non-volatile memory (NVM) implementing at least some of the storage, and the information comprises at least a portion of one of the mappings.
EC489)EC488記載のシステムにおいて、前記第1のタイプのコマンドは前記論理ブロックアドレスのうちの少なくとも1つを指定するシステム。EC489) The system of EC488, wherein the first type command specifies at least one of the logical block addresses.
EC490)EC489記載のシステムにおいて、前記第2のタイプのコマンドは前記論理ブロックアドレスのうちのいずれも指定しないシステム。EC490) The system of EC489, wherein the second type command does not specify any of the logical block addresses.
EC491)EC487記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記受け取りの前に、前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC491) The system of EC487, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for providing updates describing changes to the included data structures prior to said receiving.
EC492)EC491記載のシステムにおいて、前記更新は前記情報の仕様を有するシステム。EC492) A system according to EC491, wherein the update has a specification of the information.
EC493)EC492記載のシステムにおいて、前記仕様は、
前記ストレージの領域の指示、
前記ストレージの物理アドレスの指示、
前記ストレージのデータの長さ、および
前記ストレージのデータの範囲
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC493) The system of EC492, wherein the specifications are:
An indication of an area of said storage;
An indication of a physical address of the storage;
The system has one or more of: a length of data in said storage; and a range of data in said storage.
EC494)EC492記載のシステムにおいて、前記提供する手段は、前記コマンドのタイプのうちの書き込みコマンドを受け取ったことに応答するものであるシステム。EC494) A system according to EC492, wherein the providing means is responsive to receiving a write command among the command types.
EC495)EC492記載のシステムにおいて、前記提供する手段は、前記ストレージの少なくともいくらかを実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)の一部分を再利用し、および/または再配置したことに応答するものであるシステム。EC495) The system of EC492, wherein the providing means is responsive to reclaiming and/or reallocating a portion of non-volatile memory (NVM) that implements at least some of the storage.
EC496)EC491記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドはコンピューティングホストによって提供され、前記更新は前記コンピューティングホストに提供されるシステム。EC496) The system of EC491, wherein the command is provided by a computing host and the update is provided to the computing host.
EC497)EC486記載のシステムにおいて、前記受け取り、前記決定、および前記2つの行う動作は、前記入出力記憶デバイスによるものであるシステム。EC497) A system as described in EC486, in which the receiving, determining, and performing of the two actions are performed by the input/output storage device.
EC498)EC486記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドはコンピューティングホストによって提供されるシステム。EC498) The system of EC486, wherein the command is provided by a computing host.
EC499)EC485記載のシステムにおいて、前記第1のタイプの前記コマンドは前記規格によって定義され、前記第2のタイプの前記コマンドは前記規格によって定義されないシステム。EC499) A system according to EC485, in which the commands of the first type are defined by the standard and the commands of the second type are not defined by the standard.
EC500)EC485記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドが前記第2のタイプのものであるときに、前記情報は、
予約コマンドコード、
ベンダ特有のパラメータ、
予約フィールド、
不使用フィールド、および
機能レジスタ内の値
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上によって提供されるシステム。 EC500) In the system of EC485, when the command is of the second type, the information is:
Reservation command code,
Vendor specific parameters,
Reserved fields,
the system provided by one or more of the following: an unused field; and a value in a capability register.
EC501)EC487記載のシステムにおいて、前記第1のタイプは読み出しタイプを有し、前記第2のタイプは予めマッピングされた読み出しタイプを有するシステム。EC501) A system as described in EC487, wherein the first type has a read type and the second type has a pre-mapped read type.
EC502)EC501記載のシステムにおいて、前記ストレージの前記アクセスは読み出しアクセスであり、前記情報は前記ストレージの位置を有し、前記第2の処理は前記位置を読み取ることを有するシステム。EC502) The system of EC501, wherein the access of the storage is a read access, the information includes a location of the storage, and the second process includes reading the location.
EC503)EC487記載のシステムにおいて、前記第1のタイプは第1の書き込みタイプを有し、前記第2のタイプは第2の書き込みタイプを有し、前記第2の書き込みタイプは、前記第1の書き込みタイプが前記情報を提供しない間に前記情報を提供するシステム。EC503) In the system described in EC487, the first type has a first write type and the second type has a second write type, and the second write type provides the information while the first write type does not provide the information.
EC504)EC503記載のシステムにおいて、前記ストレージの前記アクセスは書き込みアクセスであり、前記情報は前記ストレージの第1の位置を有し、前記第2の処理は、前記ストレージの第2の位置を書き込むことと、前記第1の位置に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正することとを有するシステム。EC504) The system of EC503, wherein the access of the storage is a write access, the information has a first location of the storage, and the second process includes writing a second location of the storage and modifying a calculation of the usage status of the storage according to the first location.
EC505)EC504記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する手段であって、前記更新は前記第2の位置の仕様を有するものである、提供する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC505) The system of EC504, further comprising:
The system further comprising: means for providing an update describing a change to the included data structure, the update including a specification of the second location.
EC506)EC487記載のシステムにおいて、前記第1のタイプは第1の切り捨てタイプを有し、前記第2のタイプは第2の切り捨てタイプを有し、前記第2の切り捨てタイプは、前記第1の切り捨てタイプが前記情報を提供しない間に前記情報を提供するシステム。EC506) The system of EC487, wherein the first type has a first truncation type and the second type has a second truncation type, and the second truncation type provides the information while the first truncation type does not provide the information.
EC507)EC506記載のシステムにおいて、前記ストレージの前記アクセスは切り捨てアクセスであり、前記情報は前記ストレージの位置を有し、前記第2の処理は、前記位置に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正する工程を有するシステム。EC507) The system of EC506, wherein the access of the storage is a truncated access, the information includes a location of the storage, and the second process includes modifying a calculation of the usage status of the storage according to the location.
EC508)EC507記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記含まれるデータ構造への変更を記述する更新を提供する手段であって、前記更新は、前記コマンドの前記受け取りの前に前記含まれるデータ構造に従って前記位置にマップされた論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)の属性の仕様を有するものである、提供する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC508) The system of EC507, further comprising:
A system having means for providing an update describing a change to the included data structure, the update including a specification of attributes of a logical block address (LBA) that was mapped to the location according to the included data structure prior to the receipt of the command.
EC509)EC508記載のシステムにおいて、前記属性は、前記論理ブロックアドレスが削減されたことを指示するシステム。EC509) In the system described in EC508, the attribute indicates that the logical block address has been reduced.
EC510)システムであって、
コンピューティングホストからコマンドを受け取る手段であって、前記コマンドは0若しくはそれ以上の標準パラメータおよび1若しくはそれ以上の非標準パラメータを有するものである、前記受け取る手段と、
前記標準パラメータに従って前記コマンドを実行する手段と
を有し、
前記受け取りおよび前記実行は、前記非標準パラメータを使用して、入出力記憶デバイスを介して行われるものであり、当該入出力記憶デバイスは、前記非標準パラメータを使用することにより、前記非標準パラメータを使用しない場合よりも高い効率で動作可能である、
システム。 EC510) system, comprising:
means for receiving a command from a computing host, the command having zero or more standard parameters and one or more non-standard parameters;
means for executing the command according to the standard parameters;
said receiving and said executing being performed via an input/output storage device using said non-standard parameters, said input/output storage device being operable with said non-standard parameters at a greater efficiency than if said non-standard parameters were not used;
system.
EC511)EC510記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力記憶デバイスは前記コンピューティングホストへのストレージにインターフェースするシステム。EC511) The system of EC510, wherein the I/O storage device interfaces with storage to the computing host.
EC512)EC510記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力記憶デバイスは、前記非標準パラメータを使用することにより、前記非標準パラメータを使用しない場合よりも高い効率で前記コマンドを実行するように動作可能であるシステム。EC512) The system of EC510, wherein the input/output storage device is operable to execute the command with greater efficiency by using the non-standard parameters than if the non-standard parameters were not used.
EC513)EC512記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスのストレージの少なくとも一部分を実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)を管理する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC513) The system of EC512, further comprising:
A system comprising means for managing a non-volatile memory (NVM) implementing at least a portion of the storage of said I/O storage device.
EC514)EC513記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドは読み出しコマンドであり、前記非標準パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に前記不揮発性メモリ内の物理位置を指定し、さらに、
前記物理位置を読み取る手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC514) The system of EC513, wherein the command is a read command, and one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, a physical location within the non-volatile memory; and
A system having means for reading said physical location.
EC515)EC514記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、含まれる入出力デバイスマップへのマッピング更新を行い、前記マッピング更新のうちの少なくともいくつかを前記コンピューティングホストに提供して、前記コンピューティングホストがコンピューティング・ホスト・マップを更新することができるようにする手段を有するものであり、前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップおよび前記入出力デバイスマップは、各々、論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と不揮発性メモリの前記位置との間のマッピングを記述するそれぞれのエントリを有し、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1つは、少なくとも部分的に前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップにアクセスすることによって決定されるシステム。 EC515) The system of EC514, further comprising:
A system in which the I/O storage device has means for providing mapping updates to an I/O device map included therein and for providing at least some of the mapping updates to the computing host to enable the computing host to update the computing host map, the computing host map and the I/O device map each having respective entries describing mappings between logical block addresses (LBAs) and the locations of non-volatile memory, and at least one of the non-standard parameters being determined, at least in part, by accessing the computing host map.
EC516)EC515記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップにアクセスするための待ち時間は、前記入出力デバイスマップにアクセスするための待ち時間よりも短く、前記より高い効率はより低い待ち時間を有するシステム。EC516) The system of EC515, wherein the latency for accessing the computing host map is less than the latency for accessing the I/O device map, and the higher efficiency has a lower latency.
EC517)EC513記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、前記非標準パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に前記不揮発性メモリ内の第1の物理位置を指定し、さらに、
前記不揮発性メモリ内の第2の物理位置を書き込むことと、前記第1の物理位置に従って前記ストレージの使用状況の計算を修正することとを有するものであるシステム。 EC517) The system of EC513, wherein the command is a write command, and one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, a first physical location within the non-volatile memory; and
writing a second physical location in the non-volatile memory; and modifying the storage usage calculation according to the first physical location.
EC518)EC517記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、含まれる入出力デバイスマップへのマッピング更新を行い、前記マッピング更新のうちの少なくともいくつかを前記コンピューティングホストに提供して、前記コンピューティングホストがコンピューティング・ホスト・マップを更新することを可能にする手段を有するものであり、前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップおよび前記入出力デバイスマップは、各々、論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と前記不揮発性メモリの位置との間のマッピングを記述するそれぞれのエントリを有し、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1つは、少なくとも部分的に前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップにアクセスすることによって決定されるシステム。 EC518) The system of EC517, further comprising:
A system in which the I/O storage device has means for making mapping updates to an I/O device map included therein and providing at least some of the mapping updates to the computing host to enable the computing host to update the computing host map, the computing host map and the I/O device map each having respective entries describing mappings between logical block addresses (LBAs) and locations of the non-volatile memory, and at least one of the non-standard parameters being determined, at least in part, by accessing the computing host map.
EC519)EC518記載のシステムにおいて、前記コンピューティング・ホスト・マップにアクセスするための待ち時間は、前記入出力デバイスマップにアクセスするための待ち時間よりも短く、前記より高い効率はより低い待ち時間を有するシステム。EC519) The system of EC518, wherein the latency for accessing the computing host map is less than the latency for accessing the I/O device map, and the higher efficiency has a lower latency.
EC520)EC510記載のシステムにおいて、前記コマンドは第1のコマンドであり、前記入出力記憶デバイスは、前記非標準パラメータに従って、前記非標準パラメータを使用しない場合よりも高い効率で、前記第1のコマンドの後で受け取られる第2のコマンドを実行するように動作可能であるシステム。EC520) The system of EC510, wherein the command is a first command, and the input/output storage device is operable to execute a second command received after the first command in accordance with the non-standard parameters with greater efficiency than if the non-standard parameters were not used.
EC521)EC520記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスのストレージの少なくとも一部分を実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)を管理する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC521) The system of EC520, further comprising:
A system comprising means for managing a non-volatile memory (NVM) implementing at least a portion of the storage of said I/O storage device.
EC522)EC521記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)と前記不揮発性メモリの位置との間のマッピングを記述するエントリを有する含まれるマップを管理する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC522) The system of EC521, further comprising:
A system in which said I/O storage device has means for managing a contained map having entries describing mappings between logical block addresses (LBAs) and locations in said non-volatile memory.
EC523)EC522記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上の少なくとも一部分は特定の論理ブロックアドレスを有し、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記非標準パラメータから決定される少なくともいくらかの情報を、前記エントリのうちの少なくとも1つの選択されるエントリに記憶することを有するものであり、前記選択されるエントリは、少なくとも部分的に前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスによって選択されるシステム。 EC523) The system of EC522, wherein at least a portion of one or more of the standard parameters comprises a specific logical block address, and further comprising:
The system further comprising: said input/output storage device storing at least some information determined from said non-standard parameters in at least one selected one of said entries, said selected entry being selected at least in part by said particular logical block address.
EC524)EC523記載のシステムにおいて、前記第2のコマンドは前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスに従ったものであるシステム。EC524) A system according to EC523, wherein the second command is in accordance with the specific logical block address.
EC525)EC523記載のシステムにおいて、前記情報は複数のデータバンドのうちの特定の1つの識別を有し、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスがマップされている前記不揮発性メモリの部分を、前記特定のデータバンド内に留まるように再利用する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC525) The system of EC523, wherein the information comprises an identification of a particular one of a plurality of data bands, and further comprising:
A system in which the I/O storage device has means for reclaiming the portion of the non-volatile memory to which the particular logical block address is mapped so as to remain within the particular data band.
EC526)EC521記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータタイプのうちの1つを指定し、前記複数のデータタイプは、
圧縮可能データタイプ、
圧縮不能データタイプ、および
使用モデル・データ・タイプ
のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC526) The system of EC521, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, one of a plurality of data types, the plurality of data types including:
compressible data types,
A system having any two or more of: an incompressible data type; and a usage model data type.
EC527)EC526記載のシステムにおいて、前記使用モデル・データ・タイプはデータベース・ジャーナル・データ・タイプを有し、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記データベース・ジャーナル・データ・タイプと関連付けられたデータを複数のデータバンドのうちのデータベース・ジャーナル用データバンドに記憶するように前記不揮発性メモリを管理する手段と、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記データベース・ジャーナル用データバンドを、前記データベース・ジャーナル・バンド内のデータの量が閾値を超えるときに、前記データベース・ジャーナル・バンドのより古いデータが選択的に削除されるように管理する手段と
を有するものであるシステム。 EC527) The system of EC526, wherein the usage model data type comprises a database journal data type, and further comprising:
means for managing said non-volatile memory such that said I/O storage device stores data associated with said database journal data type in a database journal data band among a plurality of data bands;
and means for managing the data bands for the database journal such that older data in the database journal bands is selectively deleted when the amount of data in the database journal bands exceeds a threshold.
EC528)EC527記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記より古いデータが再利用されるときに前記より古いデータを削除する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC528) The system of EC527, further comprising:
Means for deleting said older data as said older data is reused.
EC529)EC521記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータアクセスタイプのうちの1つを指定し、前記複数のデータアクセスタイプは、
読み出し/書き込みデータアクセスタイプ、
略読み出しデータアクセスタイプ、
略書き込みデータアクセスタイプ、および
一時データアクセスタイプ
のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC529) The system of EC521, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, one of a plurality of data access types, the plurality of data access types including:
Read/write data access type,
Short read data access type,
A system having any two or more of: a mostly-write data access type; and a temporary data access type.
EC530)EC529記載のシステムにおいて、前記第2のコマンドは書き込みコマンドであり、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、前記書き込みコマンドに応答して前記不揮発性メモリの特定の部分を書き込む手段であって、前記特定の部分は、少なくとも部分的に前記データアクセスタイプによって決定されるものである、書き込む手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC530) The system of EC529, wherein the second command is a write command, and further comprising:
The system wherein the input/output storage device has means for writing a specific portion of the non-volatile memory in response to the write command, the specific portion being determined at least in part by the data access type.
EC531)EC530記載のシステムにおいて、前記データアクセスタイプは読み出し/書き込みデータアクセスタイプであり、前記特定の部分は、相対的に多数のプログラム/消去サイクルに耐えたことがなく、相対的に少数のプログラム/消去サイクルに耐えたことがないものであるシステム。EC531) The system of EC530, wherein the data access type is a read/write data access type, and the particular portion has not endured a relatively large number of program/erase cycles and has not endured a relatively small number of program/erase cycles.
EC532)EC530記載のシステムにおいて、前記データアクセスタイプは略読み出しデータアクセスタイプであり、前記特定の部分は、相対的に多数のプログラム/消去サイクルに耐えたことがあるものであるシステム。EC532) The system of EC530, wherein the data access type is mostly read data access type, and the particular portion has endured a relatively large number of program/erase cycles.
EC533)EC530記載のシステムにおいて、前記データアクセスタイプは略書き込みデータアクセスタイプであり、前記特定の部分は、相対的に少数のプログラム/消去サイクルに耐えたことがあるものであるシステム。EC533) The system of EC530, wherein the data access type is a mostly write data access type and the particular portion has endured a relatively small number of program/erase cycles.
EC534)EC531、EC532、またはEC533記載のシステムにおいて、前記より高い効率はより高い信頼性を有するシステム。EC534) A system according to EC531, EC532, or EC533, wherein the higher efficiency means a higher reliability.
EC535)EC531、EC532、またはEC533記載のシステムにおいて、前記より高い効率はより長い寿命を有するシステム。EC535) A system according to EC531, EC532, or EC533, wherein the higher efficiency has a longer life.
EC536)EC529記載のシステムにおいて、前記標準パラメータのうちの1若しくはそれ以上の少なくとも一部分は特定の論理ブロックアドレスを有し、前記データアクセスタイプは前記一時データアクセスタイプであり、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスが、特定のイベントに応答して、前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスに対応する前記不揮発性メモリ内の位置のところに記憶されたデータを削除する手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC536) The system of EC529, wherein at least a portion of one or more of the standard parameters comprises a specific logical block address, the data access type is the temporary data access type, and further comprising:
A system in which the I/O storage device has means for deleting data stored at a location in the non-volatile memory corresponding to the particular logical block address in response to a particular event.
EC537)EC536記載のシステムにおいて、前記データを削除する前記手段は、前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスに対応するデータが前記不揮発性メモリに存在しないことを指定するために、前記特定の論理ブロックアドレスに従って前記マップのエントリのところの前記入出力記憶デバイスのマップを更新する手段を有するシステム。EC537) In the system described in EC536, the means for deleting the data includes means for updating a map of the I/O storage device at an entry of the map according to the specific logical block address to specify that data corresponding to the specific logical block address is not present in the non-volatile memory.
EC538)EC536記載のシステムにおいて、前記データを削除する前記手段は、前記データを削減する手段を有するシステム。EC538) A system according to EC536, wherein the means for deleting the data includes a means for reducing the data.
EC539)EC536記載のシステムにおいて、前記特定のイベントは、
前記入出力記憶デバイスの不揮発性メモリ管理動作、
前記入出力記憶デバイスの不揮発性メモリ再利用動作、
前記入出力記憶デバイスの電源サイクル、
前記入出力記憶デバイスのリセット、
仮想入出力記憶デバイスの仮想機械電源サイクル、
仮想入出力記憶デバイスの仮想機械リセット、
前記コンピューティングホストからの明示的要求、および
メムキャッシュディーアプリケーションからの要求
のうちの任意の1若しくはそれ以上であるシステム。 EC539) The system of EC536, wherein the particular event is:
non-volatile memory management operations of said I/O storage device;
a non-volatile memory reclamation operation of the input/output storage device;
power cycling said I/O storage device;
resetting said I/O storage device;
Virtual machine power cycle of virtual I/O storage devices;
Virtual machine reset of virtual I/O storage devices,
The system may be configured to receive a cache from any one or more of the following: an explicit request from the computing host; and a request from a memcache application.
EC540)EC521記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータ順序付けのうちの1つを指定し、前記データ順序付けは、順次順序付けおよびアトミック順序付けのうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。EC540) The system of EC521, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters at least partially specify one of a plurality of data orderings, the data orderings including any two or more of sequential ordering and atomic ordering.
EC541)EC521記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータ関係のうちの1つを指定し、前記データ関係は、複数のデータ項目間の読み出しおよび/または書き込み関連付け、ならびにプリフェッチデータ関係のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。EC541) The system of EC521, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, one of a plurality of data relationships, the data relationships including any two or more of a read and/or write association between a plurality of data items and a prefetch data relationship.
EC542)EC521記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のデータ宛先のうちの1つを指定し、前記データ宛先は、
前記不揮発性メモリの特定の部分、
階層型ストレージ層、
ストレージのタイプ、および
特定のデータバンド
のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC542) The system of EC521, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, one of a plurality of data destinations, the data destinations including:
A particular portion of the non-volatile memory;
Hierarchical storage tiers,
A system having any two or more of a type of storage, and a particular data band.
EC543)EC542記載のシステムにおいて、ストレージの前記タイプは、
シングルレベルセル(SLC)、
マルチレベルセル(MLC)、
磁気ランダム・アクセス・メモリ(MRAM)、
揮発性、および
不揮発性
のうちの任意の1若しくはそれ以上であるシステム。 EC543) The system of EC542, wherein the type of storage is:
Single Level Cell (SLC),
Multi-Level Cell (MLC),
Magnetic Random Access Memory (MRAM),
A system that is any one or more of volatile and non-volatile.
EC544)EC542記載のシステムにおいて、前記データ宛先のうちの前記1つの前記仕様は、
書き込み速度、
再利用速度、
再利用頻度、および
書き込み増幅
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上の改善を可能にするシステム。 EC544) The system of EC542, wherein the specification of the one of the data destinations comprises:
Write speed,
Reuse rate,
A system that enables improvements in one or more of: reuse frequency; and write amplification.
EC545)EC521記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準パラメータのうちの少なくとも1若しくはそれ以上は、少なくとも部分的に複数のコマンド処理特性のうちの1つを指定し、前記コマンド処理特性は、
コマンド優先順位、
コマンド順序付け、
特定のタイプのコマンドに対するバリア、
特定のタイプのコマンド間の境界、
コマンドの集約、
コマンドの融合、および
コマンドのアトミック動作
のうちの任意の2若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC545) The system of EC521, wherein at least one or more of the non-standard parameters specify, at least in part, one of a plurality of command processing characteristics, the command processing characteristics including:
Command priority,
Command Sequencing,
Barriers to certain types of commands,
The boundaries between certain types of commands,
Command aggregation,
A system having any two or more of: command fusion; and command atomic actions.
EC546)EC512またはEC520記載のシステムにおいて、前記より高い効率はより高い性能を有するシステム。EC546) A system according to EC512 or EC520, wherein the higher efficiency means a system with higher performance.
EC547)EC546記載のシステムにおいて、前記より高い性能は、
より高いバンド幅、
より低い待ち時間、および
より低い電力
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC547) The system of EC546, wherein the higher performance is
Higher bandwidth,
A system having one or more of: lower latency; and lower power.
EC548)EC512またはEC520記載のシステムにおいて、前記より高い効率はより高い信頼性を有するシステム。EC548) A system according to EC512 or EC520, wherein the higher efficiency means a higher reliability.
EC549)EC548記載のシステムにおいて、前記より高い信頼性は、より低い誤り率およびより長い寿命のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。EC549) The system of EC548, wherein the higher reliability comprises one or more of a lower error rate and a longer lifetime.
EC550)システムであって、
コンピューティングホストからコマンドを受け取る手段であって、前記コマンドは、非標準統計値の返しを要求するものである、前記受け取る手段と、
前記コンピューティングホストに前記非標準統計値を返す手段と
を有し、
前記受け取る工程および前記返す工程は、前記非標準統計を計算するように動作可能な入出力記憶デバイスを介して実行されるものである、
システム。 EC550) system,
means for receiving a command from a computing host, the command requesting return of a non-standard statistic;
and means for returning the non-standard statistics to the computing host;
the receiving and returning steps being performed via an input/output storage device operable to calculate the non-standard statistics.
system.
EC551)EC550記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記入出力記憶デバイスのストレージの少なくとも一部分を実施する不揮発性メモリ(NVM)に書き込まれるべきデータのサイズを低減させる手段を有するものであり、
前記計算は、少なくとも一部は前記低減に基づくものであるシステム。 EC551) The system of EC550, further comprising:
means for reducing a size of data to be written to a non-volatile memory (NVM) implementing at least a portion of the storage of said I/O storage device;
The system, wherein the calculation is based at least in part on the reduction.
EC552)EC551記載のシステムにおいて、前記低減させる手段は圧縮の手段を有するシステム。EC552) A system according to EC551, in which the reducing means comprises a compressing means.
EC553)EC551記載のシステムにおいて、前記低減させる手段は重複排除の手段を有するシステム。EC553) A system according to EC551, in which the reduction means includes a deduplication means.
EC554)EC551記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準統計は前記不揮発性メモリの使用状況に従ったものであるシステム。EC554) The system of EC551, wherein the non-standard statistics are based on usage of the non-volatile memory.
EC555)EC554記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリの前記使用状況は、前記低減の質に従って変動するシステム。EC555) A system according to EC554, in which the usage status of the non-volatile memory varies according to the quality of the reduction.
EC556)EC554記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリの前記使用状況は、前記コンピューティングホストから受け取られる切り捨てコマンドの数および/またはサイズに従って変動するシステム。EC556) The system of EC554, wherein the usage of the non-volatile memory varies according to the number and/or size of truncation commands received from the computing host.
EC557)EC554記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリの前記使用状況は、前記コンピューティングホストから受け取られる一時データの量に従って変動するシステム。EC557) The system of EC554, wherein the usage of the non-volatile memory varies according to the amount of temporary data received from the computing host.
EC558)EC557記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリの前記使用状況は、前記入出力記憶デバイスによって削減された前記一時データの量に従って変動するシステム。EC558) In the system described in EC557, the usage status of the non-volatile memory varies according to the amount of temporary data reduced by the input/output storage device.
EC559)EC554記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準統計は前記不揮発性メモリの使用状況パーセンテージに従ったものであるシステム。EC559) The system of EC554, wherein the non-standard statistics are based on a usage percentage of the non-volatile memory.
EC560)EC554記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準統計は前記入出力記憶デバイスの書き込み増幅に従ったものであるシステム。EC560) The system of EC554, wherein the non-standard statistics are according to write amplification of the I/O storage device.
EC561)EC551記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準統計は前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上のバンドのサイズであるシステム。EC561) The system of EC551, wherein the non-standard statistic is the size of one or more bands of the non-volatile memory.
EC562)EC551記載のシステムにおいて、前記非標準統計は前記不揮発性メモリの1若しくはそれ以上のバンドの使用状況であるシステム。EC562) The system of EC551, wherein the non-standard statistics are usage of one or more bands of the non-volatile memory.
EC563)EC562記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリの前記1若しくはそれ以上のバンドの前記使用状況は前記低減の質に従って変動するシステム。EC563) The system of EC562, wherein the usage of the one or more bands of the non-volatile memory varies according to the quality of the reduction.
EC564)EC468、EC486、EC511、またはEC550記載のシステムにおいて、前記入出力記憶デバイスは前記コマンドを受け取る前記手段であるソリッドステートディスク(SSD)コントローラを有するシステム。EC564) A system according to EC468, EC486, EC511, or EC550, wherein the input/output storage device has a solid-state disk (SSD) controller which is the means for receiving the command.
EC565)EC564記載のシステムにおいて、前記ソリッドステートディスクコントローラは単一の集積回路(IC)において実装されるシステム。EC565) A system according to EC564, wherein the solid-state disk controller is implemented in a single integrated circuit (IC).
EC566)EC565記載のシステムにおいて、前記ストレージの少なくとも一部分は不揮発性メモリ(NVM)によって実施されるシステム。EC566) The system of EC565, wherein at least a portion of the storage is implemented by non-volatile memory (NVM).
EC567)EC566記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリは1若しくはそれ以上のフラッシュメモリを有するシステム。EC567) The system of EC566, wherein the non-volatile memory comprises one or more flash memories.
EC568)EC566記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリの少なくとも一部分は、
NANDフラッシュ技術記憶セル、および
NORフラッシュ技術記憶セル
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC568) The system of EC566, wherein at least a portion of the non-volatile memory is:
A system having one or more of: NAND flash technology storage cells; and NOR flash technology storage cells.
EC569)EC566記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリの少なくとも一部分は、
シングルレベルセル(SLC)フラッシュ技術記憶セル、および
マルチレベルセル(MLC)フラッシュ技術記憶セル
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するシステム。 EC569) The system of EC566, wherein at least a portion of the non-volatile memory is:
A system having one or more of: single level cell (SLC) flash technology storage cells; and multi-level cell (MLC) flash technology storage cells.
EC570)EC566記載のシステムにおいて、前記ソリッドステートディスクコントローラは、前記不揮発性メモリに対してデータを通信するように動作可能な不揮発性メモリインターフェースを有し、前記データのうちの少なくとも一部は前記コマンドのうちの少なくともいくつかと関連付けられているものであるシステム。EC570) The system of EC566, wherein the solid state disk controller has a non-volatile memory interface operable to communicate data to the non-volatile memory, at least some of the data being associated with at least some of the commands.
EC571)EC570記載のシステムにおいて、前記不揮発性メモリインターフェースは、
オープンNANDフラッシュインターフェース(ONFI)、
トグルモードインターフェース、
デュアル・データ・レート(DDR)同期インターフェース、
同期インターフェース、および
非同期インターフェース
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上と適合するシステム。 EC571) The system of EC570, wherein the non-volatile memory interface:
Open NAND Flash Interface (ONFI),
Toggle mode interface,
Dual Data Rate (DDR) synchronous interface;
A system that conforms to one or more of the following: a synchronous interface; and an asynchronous interface.
EC572)EC566記載のシステムにおいて、前記ソリッドステートディスクコントローラおよび前記不揮発性メモリはソリッドステートディスクに具備されるシステム。EC572) The system of EC566, wherein the solid state disk controller and the non-volatile memory are provided on a solid state disk.
EC573)EC564記載のシステムにおいて、前記ソリッドステートディスクコントローラは、ストレージインターフェース規格と適合し、前記ストレージインターフェースを介して前記コマンドを提供するコンピューティングホストに接続するように動作可能なストレージインターフェースを有するシステム。EC573) The system of EC564, wherein the solid state disk controller has a storage interface that conforms to a storage interface standard and is operable to connect to a computing host that provides the commands via the storage interface.
EC574)EC573記載のシステムにおいて、さらに、
前記コマンドを提供するように前記コンピューティングホストを動作させる手段を有するものであるシステム。 EC574) The system of EC573, further comprising:
The system further comprises means for operating said computing host to provide said command.
EC575)少なくとも1つのストレージインターフェース規格を有するか、又は参照する上記ECのうちのいずれかのECであって、前記ストレージインターフェース規格は、
ユニバーサル・シリアル・バス(Universal Serial Bus:USB)インターフェース規格と、
コンパクトフラッシュ(登録商標)(Compact Flash:CF)インターフェース規格と、
マルチメディアカード(MultiMediaCard:MMC)インターフェース規格と、
セキュアデジタル(Secure Digital:SD)インターフェース規格と、
メモリ・スティック・インターフェース規格と、
xDピクチャ・カード・インターフェース規格と、
内蔵ドライブエレクトロニクス(Integrated Drive Electronics:IDE)インターフェース規格と、
シリアル・アドバンスト・テクノロジー・アタッチメント(Serial Advanced Technology Attachment:SATA)インターフェース規格と、
エクスターナルSATA(eSATA)インターフェース規格と、
スモール・コンピュータ・システム・インターフェース(SCSI)インターフェース規格と、
シリアル接続スモール・コンピュータ・システム・インターフェース(SAS)インターフェース規格と、
ファイバー・チャンネル・インターフェース規格と、
イーサネット(登録商標)インターフェース規格と、
ペリフェラル・コンポーネント・インターコネクト・エキスプレス(Peripheral Component Interconnect express:PCIe)インターフェース規格と
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するものであるストレージインターフェース規格を有するか、又は参照する上記ECのうちのいずれかのEC。 EC575) Any of the above ECs having or referencing at least one storage interface standard, the storage interface standard being:
the Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface standard;
The Compact Flash (CF) interface standard;
MultiMediaCard (MMC) interface standard;
The Secure Digital (SD) interface standard;
The Memory Stick interface standard;
xD Picture Card Interface Standard;
The Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface standard;
the Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) interface standard;
The external SATA (eSATA) interface standard;
the Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) interface standard;
the Serial Attached Small Computer System Interface (SAS) interface standard;
Fibre Channel interface standards;
an Ethernet interface standard;
Any of the above ECs having or referencing a storage interface standard having one or more of the following: a Peripheral Component Interconnect express (PCIe) interface standard; and
EC146)少なくとも1つの計算ホストを有するか、又は参照する上記のECのうちのいずれかのECであって、前記計算ホストは、
コンピュータと、
ワークステーションコンピュータと、
サーバコンピュータと、
ストレージサーバと、
パーソナルコンピュータ(Personal Computer:PC)と、
ラップトップコンピュータと、
ノートブックコンピュータと、
ネットブックコンピュータと、
携帯端末(Personal Digital Assistant:PDA)と、
メディアプレイヤと、
メディアレコーダと、
デジタルカメラと、
セル方式送受話器と、
コードレス電話の送受話器と、
電子ゲームと
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するものである、上記ECのうちのいずれかのEC。 EC146) Any of the above ECs having or referencing at least one computing host, the computing host comprising:
A computer,
A workstation computer;
A server computer;
A storage server;
A personal computer (PC);
A laptop computer;
A notebook computer;
A netbook computer
A mobile terminal (Personal Digital Assistant: PDA),
A media player and
A media recorder
A digital camera,
A cellular handset;
A cordless telephone handset;
Any of the above ECs comprising one or more of the following: an electronic game; and
システム
図1Aに、(コンピューティングホストなどの)ホストと相互動作する(入出力記憶デバイスなどの)入出力デバイス内で動作可能であるSSDコントローラを有するSSD101の実施形態の選択された詳細を図示する。SSDコントローラは、NVM素子(フラッシュメモリなど)によって実施されるような不揮発性記憶を管理するためのものである。SSDコントローラ100は1若しくはそれ以上の外部インターフェース110を介してホスト(不図示)に通信可能に接続されている。様々な実施形態によれば、外部インターフェース110は、SATAインターフェース、SASインターフェース、PCIeインターフェース、ファイバ・チャネル・インターフェース、イーサネット(登録商標)(Ethernet(登録商標))インターフェース(10ギガビットイーサネット(登録商標)など)、上記のインターフェースのいずれかの非標準バージョン、カスタムインターフェース、またはストレージおよび/若しくは通信および/若しくはコンピューティング機器を相互接続するのに使用される任意の他の種類のインターフェースのうち1若しくはそれ以上である。例えば、ある実施形態では、SSDコントローラ100は、SATAインターフェースおよびPCIeインターフェースを有する。 SYSTEM FIG. 1A illustrates selected details of an embodiment of an
SSDコントローラ100は、さらに、1若しくはそれ以上のデバイスインターフェース190を介して、フラッシュデバイス192の1若しくはそれ以上のインスタンスといった、1若しくはそれ以上の記憶デバイスを有するNVM199に通信可能に接続されている。様々な実施形態によれば、デバイスインターフェース190は、非同期インターフェース、同期インターフェース、DDR同期インターフェース、ONFI2.2やONFI3.0互換インターフェースといったONFI互換インターフェース、トグルモード互換フラッシュインターフェース、上記のインターフェースのいずれかの非標準バージョン、カスタムインターフェース、または記憶デバイスに接続するのに使用される任意の他の種類のインターフェースのうち1若しくはそれ以上である。
フラッシュデバイス192の各々は、ある実施形態では、1若しくはそれ以上の個々のフラッシュダイ194を有する。フラッシュデバイス192のうち特定のフラッシュデバイスの種類に従って、特定のフラッシュデバイス192内の複数のフラッシュダイ194に、並列に、任意選択で、および/または選択的にアクセスすることができる。フラッシュデバイス192は、単に、SSDコントローラ100に通信可能に接続することが可能な記憶デバイスの一種を表しているにすぎない。様々な実施形態では、SLC NANDフラッシュメモリ、MLC NANDフラッシュメモリ、NORフラッシュメモリ、読み出し専用メモリ、スタティック・ランダム・アクセス・メモリ、ダイナミック・ランダム・アクセス・メモリ、強磁性メモリ、相変化メモリ、レーストラックメモリ、または任意の他の種類のメモリデバイス若しくは記憶媒体といった、任意の種類の記憶デバイスを使用することができる。Each of the flash devices 192, in some embodiments, includes one or more individual flash dies 194. Depending on the particular flash device type of the flash devices 192, multiple flash dies 194 within a particular flash device 192 may be accessed in parallel, optionally and/or selectively. The flash devices 192 merely represent one type of storage device that may be communicatively connected to the
様々な実施形態によれば、デバイスインターフェース190は、1つのバスにつきフラッシュデバイス192の1若しくはそれ以上のインスタンスを有する1若しくはそれ以上のバス;グループ内のバスにおおむね並列にアクセスさせる、1つのバスにつきフラッシュデバイス192の1若しくはそれ以上のインスタンスを有する1若しくはそれ以上のバスグループ;またはデバイスインターフェース190上へのフラッシュデバイス192の1若しくはそれ以上のインスタンスの任意の他の編成として編成される。According to various embodiments,
引き続き図1Aにおいて、SSDコントローラ100は、ホストインターフェース111、データ処理121、バッファ131、マップ141、リサイクラ151、ECC161、デバイスインターフェース論理191、CPU171といった1若しくはそれ以上のモジュールを有する。図1Aに図示する具体的なモジュールおよび相互接続は、単に、一実施形態を表すにすぎず、これらのモジュールの一部または全部、および図示されていないさらに別のモジュールの多くの配置および相互接続が考えられる。第1の例として、ある実施形態では、デュアルポーティングを提供するための2つ以上のホストインターフェース111がある。第2の例として、ある実施形態では、データ処理121および/またはECC161がバッファ131と組み合わされている。第3の例として、ある実施形態では、ホストインターフェース111がバッファ131に直接接続されており、データ処理121が、バッファ131に記憶されたデータに任意選択で、および/または選択的に作用する。第4の例として、ある実施形態では、デバイスインターフェース論理191がバッファ131に直接接続されており、ECC161が、バッファ131に記憶されたデータに任意選択で、および/または選択的に作用する。Continuing with FIG. 1A,
ホストインターフェース111は、外部インターフェース110を介してコマンドおよび/またはデータを送受信し、ある実施形態では、タグ追跡113によって個々のコマンドの進捗を追跡する。例えば、コマンドは、読み出すべきアドレス(LBAなど)およびデータの量(LBA量、例えばセクタの数など)を指定する読み出しコマンドを含み、これに応答してSSDは、読み出し状況および/または読み出しデータを提供する。別の例では、コマンドは、NVM199内の位置を指定する予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンド、ならびに読み出し単位量での長さおよび/または範囲を含む。さらに別の例では、コマンドは、書き込むべきアドレス(LBAなど)およびデータの量(LBA量、例えばセクタの数など)を指定する書き込みコマンドを含み、これに応答してSSDは、書き込み状況を提供し、および/または書き込みデータを要求し、任意選択でその後に書き込み状況を提供する。さらに別の例では、コマンドは、もはや割り当てられる必要のなくなった1つ若しくはそれ以上のアドレス(1つ若しくはそれ以上のLBAなど)を指定する割り当て解除コマンド(切り捨てコマンドなど)を含み、これに応答してSSDは、マップをしかるべく変更し、任意選択で割り当て解除状況を提供する。あるコンテキストでは、ATA互換TRIMコマンドが割り当て解除コマンドの例である。さらに別の例では、コマンドは、超コンデンサ・テスト・コマンドまたはデータハーデニング成功問い合わせを含み、これに応答してSSDは、適切な状況を提供する。ある実施形態では、ホストインターフェース111は、SATAプロトコルと適合し、NCQコマンドを使用して、最高32までの未処理のコマンドを有することができるようになっており、各コマンドは0から31までの数として表された一意のタグを有する。ある実施形態では、タグ追跡113は、外部インターフェース110を介して受け取ったコマンドのための外部タグを、SSDコントローラ100による処理の間にコマンドを追跡するのに使用される内部タグと関連付けることができるようになっている。The host interface 111 sends and receives commands and/or data via the
様々な実施形態によれば、データ処理121は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、バッファ131と外部インターフェース110との間で送られる一部または全部のデータを処理する、およびデータ処理121は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、バッファ131に記憶されたデータを処理する、以下のうち1若しくはそれ以上が行われる。ある実施形態では、データ処理121は、1若しくはそれ以上のエンジン123を使用して、書式設定、書式設定の変更、符号変換、ならびに他のデータ処理および/または動作タスクのうち1若しくはそれ以上を行う。According to various embodiments, data processing 121 optionally and/or selectively processes some or all of the data sent between buffer 131 and
バッファ131は、外部インターフェース110からデバイスインターフェース190へ/デバイスインターフェース190から外部インターフェース110へ送られたデータを記憶する。ある実施形態では、バッファ131は、さらに、SSDコントローラ100によってフラッシュデバイス192の1若しくはそれ以上のインスタンスを管理するのに使用される、一部または全部のマップ表といったシステムデータも記憶する。様々な実施形態では、バッファ131は、データの一時記憶に使用されるメモリ137、バッファ131への、および/またはバッファ131からのデータの移動を制御するのに使用されるDMA133、ならびに高レベル誤り訂正および/または冗長性機能と、他のデータ移動および/または動作機能とを提供するのに使用されるECC−X135のうち1若しくはそれ以上を有する。高レベル冗長性機能の一例がRAID様の能力であり、ディスクレベルではなく、フラッシュ・デバイス・レベル(フラッシュデバイス192のうち複数のものなど)および/またはフラッシュダイ・レベル(フラッシュダイ194など)の冗長性を備える。Buffer 131 stores data sent from
様々な実施形態によれば、以下のうち1若しくはそれ以上である。ECC161は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、バッファ131とデバイスインターフェース190との間で送られる一部または全部のデータを処理する;およびECC161は、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、バッファ131に記憶されたデータを処理する。ある実施形態では、ECC161は、例えば1若しくはそれ以上のECC技法に従った低レベル誤り訂正および/または冗長性機能を提供するのに使用される。ある実施形態では、ECC161は、CRC符号、ハミング符号、RS符号、BCH符号、LDPC符号、ビタビ符号、トレリス符号、硬判定符号、軟判定符号、消去ベースの符号、任意の誤り検出および/または訂正符号、ならびに上記の任意の組み合わせのうち1若しくはそれ以上を実施する。ある実施形態では、ECC161は、1若しくはそれ以上の復号器(LDPC復号器など)を有する。According to various embodiments, one or more of the following:
デバイスインターフェース論理191は、デバイスインターフェース190を介してフラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスを制御する。デバイスインターフェース論理191は、フラッシュデバイス192のプロトコルに従ってフラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスへ/からデータを送ることができるようになっている。デバイスインターフェース論理191は、デバイスインターフェース190を介したフラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスの制御を選択的に配列するスケジューリング193を有する。例えば、ある実施形態では、スケジューリング193は、フラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスへの動作を待ち行列に入れ、フラッシュデバイス192(またはフラッシュダイ194)のインスタンスの個々のインスタンスへの動作を、フラッシュデバイス192(またはフラッシュダイ194)のインスタンスの個々のインスタンスが利用可能になるに従って選択的に送ることができるようになっている。Device interface logic 191 controls instances of flash device 192 via
マップ141は、外部インターフェース110上で使用されるデータアドレス仕様と、デバイスインターフェース190上で使用されるデータアドレス仕様との間の変換を行い、表143を使用して外部データアドレスからNVM199内の位置へマップする。例えば、ある実施形態では、マップ141は、外部インターフェース110上で使用されるLBAを、表143によって提供されるマッピングにより、1若しくはそれ以上のフラッシュダイ194を対象とするブロックおよび/またはページアドレスに変換する。ドライブ製造または割り当て解除以来一度も書き込まれていないLBAでは、マップは、LBAが読み出された場合に返すべきデフォルト値を指し示す。例えば、割り当て解除コマンドを処理するときに、マップは、割り当て解除されたLBAに対応するエントリがデフォルト値のうち1つを指し示すように変更される。様々な実施形態では、様々なデフォルト値があり、各々が対応するポインタを有する。複数のデフォルト値は、ある(例えば第1の範囲内の)割り当て解除されたLBAを1つのデフォルト値として読み出し、ある(例えば第2の範囲内の)割り当て解除されたLBAを別のデフォルト値として読み出すことを可能にする。デフォルト値は、様々な実施形態では、フラッシュメモリ、ハードウェア、ファームウェア、コマンドおよび/若しくはプリミティブ引数および/若しくはパラメータ、プログラマブルレジスタ、またはそれらの様々な組み合わせによって定義される。
ある実施形態では、マップ141は、表143を使用して、外部インターフェース110上で使用されるアドレスと、デバイスインターフェース190上で使用されるデータアドレス仕様との間の変換を行い、および/またはルックアップする。様々な実施形態によれば、表143は、1レベルマップ、2レベルマップ、マルチレベルマップ、マップキャッシュ、圧縮マップ、あるアドレス空間から別のアドレス空間への任意の種類のマッピング、および上記の任意の組み合わせのうち1若しくはそれ以上である。様々な実施形態によれば、表143は、スタティック・ランダム・アクセス・メモリ、ダイナミック・ランダム・アクセス・メモリ、NVM(フラッシュメモリなど)、キャッシュメモリ、オンチップメモリ、オフチップメモリ、および上記の任意の組み合わせのうち1若しくはそれ以上を有する。In one embodiment, map 141 uses table 143 to translate and/or look up between addresses used on
ある実施形態では、リサイクラ151は、不要部分の整理を行う。例えば、ある実施形態では、フラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスは、ブロックが書き換え可能になる前に消去されなければならないブロックを有する。リサイクラ151は、例えば、マップ141によって維持されるマップをスキャンすることによって、フラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスのどの部分が実際に使用されているか(例えば、割り当て解除されているのではなく割り当てられていること)を決定し、フラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスの未使用の(例えば割り当て解除された)部分を、未使用の部分を消去することによって書き込みに利用できるようにすることができるようになっている。別の実施形態では、リサイクラ151は、フラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスのより大きい連続した部分を書き込みに利用できるようにするために、フラッシュデバイス192のインスタンス内に記憶されたデータを移動することができるようになっている。In one embodiment, recycler 151 performs eviction. For example, in one embodiment, an instance of flash device 192 has blocks that must be erased before they can be rewritten. Recycler 151 can determine, e.g., by scanning a map maintained by
ある実施形態では、フラッシュデバイス192のインスタンスは、異なる種類および/または属性のデータを記憶するための1若しくはそれ以上のバンドを保持するように、選択的に、および/または動的に構成され、管理され、および/または使用される。バンドの数、配置、サイズ、および種類は、動的に変更可能である。例えば、コンピューティングホストからのデータはホット(アクティブな)バンドに書き込まれ、リサイクラ151からのデータはコールド(あまりアクティブではない)バンドに書き込まれる。ある使用シナリオでは、コンピューティングホストが長い順次のストリームを書き込む場合には、ホットバンドのサイズが増大し、コンピューティングホストがランダムな書き込みを行い、またはわずかな書き込みしか行わない場合には、コールドバンドのサイズが増大する。In one embodiment, an instance of flash device 192 is selectively and/or dynamically configured, managed, and/or used to hold one or more bands for storing different types and/or attributes of data. The number, placement, size, and type of bands can be dynamically changed. For example, data from a computing host is written to a hot (active) band, and data from recycler 151 is written to a cold (less active) band. In one usage scenario, the size of the hot band increases when the computing host writes long sequential streams, and the size of the cold band increases when the computing host writes randomly or performs few writes.
CPU171は、SSDコントローラ100の様々な部分を制御する。CPU171は、CPUコア172を有する。CPUコア172は、様々な実施形態によれば、1若しくはそれ以上のシングルコアプロセッサまたはマルチコアプロセッサである。CPUコア172内の個々のプロセッサコアは、ある実施形態では、マルチスレッド化されている。CPUコア172は、命令および/またはデータのキャッシュおよび/またはメモリを有する。例えば、命令メモリは、CPUコア172が、SSDコントローラ100を制御するためのプログラム(ファームウェアとも呼ばれるソフトウェアなど)を実行することを可能にする命令を有する。ある実施形態では、CPUコア172によって実行されるファームウェアの一部または全部が、(例えば、図1BのNVM199のファームウェア106として図示されている)フラッシュデバイス192のインスタンス上に記憶される。
様々な実施形態では、CPU171は、外部インターフェース110を介して受け取られるコマンドを、コマンドが進行している間に追跡し、制御するコマンド管理173、バッファ131の割り当ておよび使用を制御するバッファ管理175、マップ141を制御する変換管理177、データアドレス指定の整合性を制御し、例えば、外部データアクセスと再利用データアクセスとの間の矛盾を回避するコヒーレンシ管理179、デバイスインターフェース論理191を制御するデバイス管理181、識別情報の変更および通信を制御する識別情報管理182、ならびに、任意選択で、他の管理部をさらに有する。CPU171によって果たされる管理機能は、そのいずれか、若しくは全部が、ハードウェア、ソフトウェア(CPUコア172上や、外部インターフェース110を介して接続されたホスト上で実行されるファームウェアなど)、またはそれらの任意の実施形態によって制御され、および/または管理され、あるいは、そのどれも、制御も管理もされないものである。In various embodiments,
ある実施形態では、CPU171は、性能統計の収集および/または報告、SMARTの実施、電源逐次開閉機構の制御、電力消費の制御および/または調整、電源障害への応答、クロック速度の制御および/またはモニタリングおよび/または調整、ならびに他の管理タスクのうち1若しくはそれ以上といった、他の管理タスクを行うことができるようになっている。In some embodiments,
様々な実施形態は、SSDコントローラ100と同様の、例えば、ホストインターフェース111および/または外部インターフェース110の適応による、様々なコンピューティングホストを用いた動作と適合するコンピューティングホスト・フラッシュ・メモリ・コントローラを有する。様々なコンピューティングホストは、コンピュータ、ワークステーションコンピュータ、サーバコンピュータ、ストレージサーバ、PC、ラップトップコンピュータ、ノートブックコンピュータ、ネットブックコンピュータ、PDA、メディアプレーヤ、メディアレコーダ、ディジタルカメラ、セルラハンドセット、コードレス電話機ハンドセット、および電子ゲームのうち1つまたはそれらの任意の組み合わせを有する。Various embodiments have a computing host flash memory controller that is compatible with operation with a variety of computing hosts, similar to
様々な実施形態では、SSDコントローラ(またはコンピューティングホスト・フラッシュ・メモリ・コントローラ)の全部または任意の部分が、単一のIC、マルチダイICの単一のダイ、マルチダイICの複数のダイ、または複数のIC上で実施される。例えば、バッファ131は、SSDコントローラ100の他の要素と同じダイ上に実施される。別の例では、バッファ131は、SSDコントローラ100の他の要素と異なるダイ上に実施される。In various embodiments, all or any portion of the SSD controller (or computing host flash memory controller) is implemented on a single IC, a single die of a multi-die IC, multiple dies of a multi-die IC, or multiple ICs. For example, buffer 131 is implemented on the same die as other elements of
図1Bに、図1AのSSDの1若しくはそれ以上のインスタンスを有するシステムの様々な実施形態の選択された詳細を図示する。SSD101は、デバイスインターフェース190を介してNVM199に接続されたSSDコントローラ100を有する。図には、様々な種別の実施形態、すなわち、ホストに直接接続された単一のSSD、各々がそれぞれの外部インターフェースを介してホストに直接それぞれ接続されている複数のSSD、および様々な相互接続要素を介してホストに間接的に接続された1若しくはそれ以上のSSDが示されている。FIG. 1B illustrates selected details of various embodiments of a system having one or more instances of the SSD of FIG. 1A.
ホストに直接接続された単一のSSDの例示的実施形態としては、SSD101の1つのインスタンスが、外部インターフェース110を介してホスト102に直接接続される(例えば、スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103が省かれ、バイパスされ、またはパススルーされる)。各々がそれぞれの外部インターフェースを介してホストに直接接続されている複数のSSDの例示的実施形態としては、SSD101の複数のインスタンスの各々が、外部インターフェース110のそれぞれのインスタンスを介してホスト102に直接それぞれ接続される(例えば、スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103が省かれ、バイパスされ、またはパススルーされる)。様々な相互接続要素を介してホストに間接的に接続された1若しくはそれ以上のSSDの例示的実施形態としては、SSD101の1若しくはそれ以上のインスタンスの各々が、ホスト102に間接的にそれぞれ接続される。各間接接続は、スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103に接続された外部インターフェース110のそれぞれのインスタンス、およびホスト102に接続する中間インターフェース104を介したものである。In an exemplary embodiment of a single SSD directly connected to a host, one instance of
スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103を有する実施形態の一部は、メモリインターフェース180を介して接続された、SSDによってアクセス可能なカードメモリ112Cも有する。様々な実施形態では、SSD、スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ、および/またはカードメモリのうち1若しくはそれ以上が、物理的に識別可能なモジュール、カード、または差し込み可能な要素(入出力カード116など)上に含まれる。ある実施形態では、SSD101(またはその変形)は、ホスト102として動作するイニシエータ(開始プログラム)に接続されたSASドライブまたはSATAドライブに対応する。Some embodiments having a switch/fabric/intermediate controller 103 also have a
ホスト102は、OS105、ドライバ107、アプリケーション109、マルチデバイス管理ソフトウェア114の様々な組み合わせといった、ホストソフトウェア115の様々な要素を実行することができるようになっている。点線矢印107Dは、ホストソフトウェア←→入出力装置通信、例えば、SSD101のインスタンスのうち1若しくはそれ以上から/へ、ドライバ107を介したOS105、ドライバ107、および、ドライバ107を介して、またはVFとして直接アプリケーション109のうち任意の1若しくはそれ以上へ/から送られ/受け取られるデータを表す。Host 102 is capable of executing various elements of host software 115, such as various combinations of
OS105は、SSDとインターフェースするための(概念的にはドライバ107によって図示されている)ドライバを有し、および/またはそのようなドライバを用いて動作することができるようになっている。Windows(登録商標)の様々なバージョン(95、98、ME、NT、XP、2000、サーバ、Vista、および7など)、Linux(登録商標)の様々なバージョン(Red Hat、Debian、およびUbuntuなど)、ならびにMacOSの様々なバージョン(8、9およびXなど)がOS105の例である。様々な実施形態では、ドライバは、SATA、AHCI、NVM Expressといった標準のインターフェースおよび/またはプロトコルを用いて動作する標準のドライバおよび/または汎用のドライバ(「シュリンクラップされた(市販の)」または「プリインストールされた」ともいう)であり、あるいは、任意選択で、SSD101に特有のコマンドの使用を可能にするようにカスタマイズされており、および/またはベンダ特有のものである。あるドライブおよび/またはドライバは、アプリケーションレベルのプログラム、例えば最適化NANDアクセス(Optimized NAND Access)(ONAともいう)または直接NANDアクセス(Direct NAND Access)(DNAともいう)の各技法によるアプリケーション109などが、コマンドをSSD101に直接伝えることを可能にするパススルーモードを有し、カスタマイズされたアプリケーションが、汎用ドライバとでさえもSSD101に特有のコマンドを使用することを可能にする。ONAの技法は、非標準修飾子(hints)の使用、ベンダ特有のコマンドの使用、非標準の統計の通信、例えば圧縮可能性に従った実際のNVMの使用、および他の技法のうち1若しくはそれ以上を有する。DNAの技法は、NVMへのマップされていない読み出し、書き込み、および/または消去アクセスを提供する非標準のコマンドまたはベンダ特有の(コマンド)の使用、例えば、入出力装置が通常は行うはずのデータの書式設定をバイパスすることによる、NVMへのより直接的なアクセスを提供する非標準の、またはベンダ特有のコマンドの使用、および他の技法のうち1若しくはそれ以上を有する。ドライバの例は、ONAまたはDNAサポートなしのドライバ、ONA使用可能ドライバ、DNA使用可能ドライバ、ONA/DNA使用可能ドライバである。ドライバの別の例は、ベンダ提供ドライバ、ベンダ開発ドライバ、および/またはベンダ拡張ドライバ、ならびにクライアント提供ドライバ、クライアント開発ドライバ、および/またはクライアント拡張ドライバである。The
アプリケーションレベルのプログラムの例は、ONAまたはDNAサポートなしのアプリケーション、ONA使用可能アプリケーション、DNA使用可能アプリケーション、およびONA/DNA使用可能アプリケーションである。点線矢印109Dは、アプリケーション←→入出力装置通信(ドライバによるバイパスや、アプリケーションのためのVFによるバイパスなど)、例えば、OSを仲介として使用するアプリケーションなしでSSDと通信するONA使用可能アプリケーションおよびONA使用可能ドライバなどを表す。点線矢印109Vは、アプリケーション←→入出力装置通信(アプリケーションのためのVFによるバイパスなど)、例えば、OSまたはドライバを仲介として使用するアプリケーションなしでSSDと通信するDNA使用可能アプリケーションおよびDNA使用可能ドライバなどを表す。Examples of application level programs are applications without ONA or DNA support, ONA enabled applications, DNA enabled applications, and ONA/DNA enabled applications. Dotted
NVM199の1若しくはそれ以上の部分が、ある実施形態では、ファームウェア記憶、例えばファームウェア106に使用される。ファームウェア記憶は、1若しくはそれ以上のファームウェアイメージ(またはその部分)を有する。ファームウェアイメージは、例えばSSDコントローラ100のCPUコア172によって実行される、例えばファームウェアの1若しくはそれ以上のイメージを有する。ファームウェアイメージは、別の例では、例えばファームウェア実行時にCPUコアによって参照される、定数、パラメータ値、NVMデバイス情報の1若しくはそれ以上のイメージを有する。ファームウェアのイメージは、例えば、現在のファームウェアイメージおよび0以上の(ファームウェア更新に対して)前のファームウェアイメージに対応する。様々な実施形態では、ファームウェアは、汎用動作モード、標準動作モード、ONA動作モード、および/またはDNA動作モードを提供する。ある実施形態では、ファームウェア動作モードのうち1若しくはそれ以上が、ドライバによって任意選択で伝えられ、および/または提供される、鍵または様々なソフトウェア技法によって使用可能とされる(例えば、1若しくはそれ以上のAPIが「ロック解除」される)。One or more portions of
ある実施形態では、ホスト102はシャドウマップ108を別個のハードウェアリソースとして含み、別の実施形態では、シャドウマップは、一部または全部がホストメモリ112Hによって実施される。シャドウマップ108、ホストメモリ112H、およびカードメモリ112Cの例は、DRAM、SRAM、および/またはフラッシュデバイスによって実施されるような1若しくはそれ以上の揮発性素子および/またはNVM素子である。ホストメモリのさらに別の例は、システムメモリ、ホスト・メイン・メモリ、ホスト・キャッシュ・メモリ、ホストアクセス可能メモリ、および入出力デバイスアクセス可能メモリである。In one embodiment, the host 102 includes the shadow map 108 as a separate hardware resource, while in another embodiment, the shadow map is implemented in part or in whole by the host memory 112H. Examples of the shadow map 108, the host memory 112H, and the
本明細書で別により詳細に説明するように、様々な実施形態において、ホスト102および/またはSSD101のインスタンスのうちの1若しくはそれ以上は、シャドウマップ108にアクセスして、LBAを、NVM199のインスタンスのうちの1若しくはそれ以上の要素といった、入出力デバイスNVMのうちの1若しくはそれ以上の部分を対象とするブロックアドレスおよび/またはページアドレスに変換するのに使用可能なマッピング情報の全部または任意の部分を保存し、取得することができるようになっている。概念的には、シャドウマップは、マップ141のインスタンスのうちの1若しくはそれ以上に含まれる情報に従う(例えば情報を追尾する)。シャドウマップ内の情報は、ホスト102のうちの1若しくはそれ以上によって(例えば、SSDにコマンドを発行することと連動して)、またSSD101のインスタンスのうちの1若しくはそれ以上によって(ホストからのコマンドを処理することと連動して)更新される。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオ(例えば、入出力カード116を有し、図1Bの(任意選択の)カードメモリ112Cをシャドウマップのストレージとして使用するいくつかの実施形態)では、1若しくはそれ以上の入出力デバイス、例えばSSDはシャドウマップにアクセスし、ホストはシャドウマップにアクセスしない。やはり本明細書で別により詳細に説明するように、様々な実施形態において、SSD101のインスタンスのうちの1若しくはそれ以上は、カードメモリ112Cおよび/またはホストメモリ112Hにアクセスして、例えば、休眠状態を開始し、終了するときに、それぞれのSSDインスタンスの内部の状態情報を保存し、復元することができるようになっている。As described in more detail elsewhere herein, in various embodiments, one or more of the host 102 and/or
スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラを欠くある実施形態では、SSDは、外部インターフェース110を介して直接ホストに接続される。様々な実施形態では、SSDコントローラ100は、RAIDコントローラといった他のコントローラの1若しくはそれ以上の中間レベルを介してホストに接続される。ある実施形態では、SSD101(またはその変形)は、SASドライブまたはSATAドライブに対応し、スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103は、イニシエータにさらに接続されたエキスパンダに対応し、あるいは、スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103は、エキスパンダを介してイニシエータに間接的に接続されたブリッジに対応する。ある実施形態では、スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103は、1若しくはそれ以上のPCIeスイッチおよび/またはファブリックを有する。In some embodiments lacking a switch/fabric/intermediate controller, the SSD is connected to the host directly through the
様々な実施形態、例えば、コンピューティングホストとしてのホスト102(コンピュータ、ワークステーションコンピュータ、サーバコンピュータ、ストレージサーバ、PC、ラップトップコンピュータ、ノートブックコンピュータ、および/またはネットブックコンピュータなど)を有する実施形態のあるものでは、コンピューティングホストは、任意選択で、1若しくはそれ以上のローカルサーバおよび/またはリモートサーバ(例えば、任意選択のサーバ118)と(例えば、任意選択の入出力装置/リソースおよび記憶装置/リソース117および任意選択のLAN/WAN119を介して)通信することができるようになっている。通信は、例えば、SSD101要素のうち任意の1若しくはそれ以上のローカルおよび/またはリモートのアクセス、管理、および/または使用を可能にする。ある実施形態では、通信は、全部または一部がイーサネット(登録商標)(Ethernet(登録商標))によるものである。ある実施形態では、通信は、全部または一部がファイバチャネルによるものである。LAN/WAN119は、様々な実施形態では、1若しくはそれ以上のローカル・エリア・ネットワークおよび/または広域ネットワーク、例えば、サーバファーム内のネットワーク、サーバファームを接続するネットワーク、メトロエリアネットワーク、およびインターネットのうち任意の1若しくはそれ以上を表す。In various embodiments, e.g., some embodiments having a host 102 (e.g., a computer, a workstation computer, a server computer, a storage server, a PC, a laptop computer, a notebook computer, and/or a netbook computer) as a computing host, the computing host can optionally communicate (e.g., via optional I/O devices/resources and storage devices/
様々な実施形態では、1若しくはそれ以上のNVMと組み合わされたSSDコントローラおよび/またはコンピューティングホスト・フラッシュ・メモリ・コントローラが、USB記憶コンポーネント、CF記憶コンポーネント、MMC記憶コンポーネント、SD記憶コンポーネント、メモリスティック記憶コンポーネント、xDピクチャカード記憶コンポーネントといった不揮発性記憶コンポーネントとして実施される。In various embodiments, the SSD controller and/or computing host flash memory controller in combination with one or more NVMs is implemented as a non-volatile storage component, such as a USB storage component, a CF storage component, an MMC storage component, an SD storage component, a memory stick storage component, an xD picture card storage component, etc.
様々な実施形態では、SSDコントローラ(またはコンピューティングホスト・フラッシュ・メモリ・コントローラ)の全部またはいずれかの部分、またはその機能が、コントローラが接続されるべきホスト(図1Bのホスト102など)において実施される。様々な実施形態では、SSDコントローラ(若しくはコンピューティングホスト・フラッシュ・メモリ・コントローラ)の全部またはいずれかの部分、またはその機能が、ハードウェア(論理回路など)、ソフトウェアおよび/若しくはファームウェア(ドライバソフトウェアおよび/若しくはSSD制御ファームウェアなど)、またはそれらの任意の組み合わせによって実施される。例えば、(例えば図1AのECC161および/またはECC−X135と同様の)ECC部の、またはECC部と関連付けられた機能が、一部はホスト上のソフトウェアによって、一部はSSDコントローラ内のファームウェアとハードウェアとの組み合わせによって実施される。別の例として、(例えば図1Aのリサイクラ151と同様の)リサイクラ部の、またはリサイクラ部と関連付けられた機能が、一部はホスト上のソフトウェアによって、一部はコンピューティングホスト・フラッシュ・メモリ・コントローラ内のハードウェアによって実施される。In various embodiments, all or any part of the SSD controller (or computing host flash memory controller), or its functions, are implemented in a host (such as host 102 in FIG. 1B) to which the controller is to be connected. In various embodiments, all or any part of the SSD controller (or computing host flash memory controller), or its functions, are implemented by hardware (such as logic circuits), software and/or firmware (such as driver software and/or SSD control firmware), or any combination thereof. For example, the ECC portion (e.g., similar to
マッピングの動作
図2に、LBAのLPN部分のマッピングの実施形態の選択された詳細を図示する。ある実施形態では、読み出し単位は、NVMのページの部分といった、独立に読み出すことのできるNVMの最も細かい粒度である。別の実施形態では、読み出し単位は、検査ビットによって保護されるすべてのデータに(低レベル)誤り訂正符号の検査ビット(冗長性ともいう)を加えたものに対応する。例えば、図1AのECC161は、検査ビットによる、例えばLDPC符号による誤り訂正を実施し、読み出し単位は、LDPC符号化ビットによって保護されるデータビットにLDPC符号を加えたものを実施する符号化ビットに対応する。 Mapping Operation FIG. 2 illustrates selected details of an embodiment of a mapping of the LPN portion of an LBA. In one embodiment, a read unit is the finest granularity of the NVM that can be read independently, such as a portion of a page of the NVM. In another embodiment, a read unit corresponds to all data protected by check bits plus check bits (also called redundancy) of a (low-level) error correction code. For example,
ある実施形態では、マップ141は、LBA211のLPN213部分を、例えば(図1Aに図示される)表143によって、LPNのためのマップ情報221にマップする。LPNのためのマップ情報(例えばLPNのためのマップ情報221)をマップエントリともいう。マップ141は、LPNを対応するマップエントリと関連付けるといわれる。様々な実施形態では、マッピングは、1若しくはそれ以上の連想ルックアップ、1若しくはそれ以上の非連想ルックアップ、および/または1若しくはそれ以上の他の技法によるものである。In one embodiment, map 141 maps the
ある実施形態では、SSDコントローラ100は、潜在的に、および/またはアクティブに使用されているLPNごとに1つのマップエントリを維持する。In one embodiment,
ある実施形態では、LPNのためのマップ情報221は、それぞれの読み出し単位アドレス223および読み出し単位での長さ225を有する。ある実施形態では、長さおよび/または範囲は、例えば、読み出し単位での長さ225の全部またはいずれかの部分において、例えば、長さを範囲からのオフセットとして記憶することによって、符号化して記憶される。別の実施形態では、第1のLPNは第1のマップエントリと関連付けられており、(第1のLPNと異なるが、第1のLPNによって参照される論理ページと同サイズの論理ページを参照する)第2のLPNは第2のマップエントリと関連付けられており、第1のマップエントリのそれぞれの読み出し単位での長さは、第2のマップエントリのそれぞれの読み出し単位での長さと異なる。In one embodiment,
様々な実施形態では、同じ時点において、第1のLPNは第1のマップエントリと関連付けられており、(第1のLPNと異なる)第2のLPNは第2のマップエントリと関連付けられており、第1のマップエントリのそれぞれの読み出し単位アドレスは、第2のマップエントリのそれぞれの読み出し単位アドレスと同じである。別の実施形態では、第1のLPNと関連付けられたデータおよび第2のLPNと関連付けられたデータは、どちらも、NVM199内の同じデバイスの同じ物理ページに記憶されている。In various embodiments, at the same point in time, a first LPN is associated with a first map entry, a second LPN (different from the first LPN) is associated with a second map entry, and the respective read unit addresses of the first map entry are the same as the respective read unit addresses of the second map entry. In another embodiment, the data associated with the first LPN and the data associated with the second LPN are both stored in the same physical page of the same device in
様々な実施形態によれば、読み出し単位アドレス223は、NVM内の開始アドレス、NVM内の終了アドレス、上記のいずれかのオフセット、およびLPN213と関連付けられたNVMの部分を特定するための任意の他の技法のうち1若しくはそれ以上と関連付けられている。According to various embodiments, the read unit address 223 is associated with one or more of a starting address within the NVM, an ending address within the NVM, an offset of any of the above, and any other technique for identifying the portion of the NVM associated with the
図3に、読み出し単位の量で測った長さを総体として有する、様々な読み出し単位として編成された読み出しデータを生成するための、読み出し単位アドレスのところのNVMへのアクセスの実施形態の選択された詳細を図示する。様々な実施形態によれば、最初の読み出し単位313は、NVMのアドレス空間における最低のアドレスを有する読み出しデータ311内の読み出し単位のうち1つ、読み出し単位のうち固定された1つ、読み出し単位のうちのいずれか1つ、読み出し単位のうち可変の1つ、および任意の他の技法によって選択される読み出し単位のうち1つのうち1若しくはそれ以上である。様々な実施形態では、SSDコントローラ100は、NVM199にアクセスし、読み出し単位での長さ225によって指定される数以下の数の読み出し単位を読み出すことによって読み出しデータ311を生成することができるようになっている。3 illustrates selected details of an embodiment of accessing the NVM at read unit addresses to generate read data organized as various read units collectively having lengths measured in read units. According to various embodiments, the
図4Aに、(図3の読み出し単位313や読み出し単位315といった)読み出し単位の実施形態の選択された詳細を読み出し単位401Aとして図示する。様々な実施形態および使用シナリオにおいて、ヘッダ1 411AからヘッダN 419Aは連続しており、ヘッダの各々によって(例えばそれぞれのオフセットにより)特定されるそれぞれのデータ領域は、ヘッダの最後のものに後に続いて連続している。各データ領域は総体としてデータバイト421Aを形成している。各データ領域は、各ヘッダが記憶される位置順と一致した位置順で記憶される。例えば、読み出し単位の先頭のところの第1のヘッダを考えると、第2のヘッダおよび第3のヘッダは、第1のヘッダのすぐ後に続く。(第1のヘッダ内の第1のオフセットによって特定される)第1のデータ領域は第3のヘッダのすぐ後に続く。(第2のヘッダ内の第2のオフセットによって特定される)第2のデータ領域は第1のデータ領域のすぐ後に続く。同様に、(第3のヘッダ内によって特定される)第3データ領域も第2のデータ領域のすぐ後に続く。4A illustrates selected details of an embodiment of a read unit (such as
図4Bに、(図3の読み出し単位313や読み出し単位315といった)読み出し単位の別の実施形態の選択された詳細を読み出し単位401Bとして図示する。様々な実施形態および/または使用シナリオにおいて、ヘッダマーカ(HM)410Bは、後に続く連続したヘッダ(ヘッダ1 411B、ヘッダ2 412B...ヘッダN 419B)の数を指示する任意選択の最初のフィールド(例えば1バイトのフィールド)である。データ領域(データバイト421B、データバイト422B...データバイト429B)は、それぞれ、ヘッダ(ヘッダ1 411B、ヘッダ2 412B...ヘッダN 419B)によって特定され、ヘッダが記憶される位置順とは逆の位置順で記憶される。ヘッダは読み出し単位の先頭から開始し、対応するデータ領域は読み出し単位の末尾から開始する。ある実施形態では、データ領域内のデータバイト(例えば、データバイト421B、データバイト422B...データバイト429B)は、前方順(位置順と一致するバイト順)に配置され、別の実施形態では、データバイトは、逆順(位置順に対して反転されたバイト順)に配置される。ある実施形態では、ヘッダマーカが、(例えば図4Aに示すように)ヘッダおよびデータバイトが同じ位置順で記憶されている読み出し単位で使用される。4B illustrates selected details of another embodiment of a read unit (such as
ある実施形態では、任意選択のパディングバイト431A(または431B)は、特定のLPNと関連付けられたデータの粒度に従ったものである。例えば、ある実施形態では、データバイト421A(またはデータバイト421B、データバイト422B...データバイト429Bの総体)が、ヘッダ1 411AからヘッダN 419Aまで(またはヘッダ1 411B、ヘッダ2 412B...ヘッダN 419B)の最後のヘッダを除くすべてのヘッダと関連付けられたデータを記憶した後で、決まった量、例えば8バイトより少ない残りのスペースを有する場合には、最後のヘッダと関連付けられたLPNのデータは後続の読み出し単位において開始する。別の実施形態では、最後のヘッダ内の特定のオフセット値(例えばすべて1)が、最後のヘッダと関連付けられたLPNのデータが後続の読み出し単位において開始することを指示する。In one embodiment, the optional padding bytes 431A (or 431B) are according to the granularity of the data associated with a particular LPN. For example, in one embodiment, if data bytes 421A (or data bytes 421B, data bytes 422B, ... data bytes 429B collectively) have less than a fixed amount of remaining space, e.g., 8 bytes, after storing data associated with all headers except the last header from
図5に、いくつかのフィールドを有するヘッダ(例えば、図4Aのヘッダ1 411AからヘッダN 419Aまでや、図4Bのヘッダ1 411Bからヘッダ 419Bまでのいずれか)の実施形態の選択された詳細を図示する。ある実施形態では、ヘッダは固定長である(例えば、各ヘッダは同じバイト数の長さである)。ヘッダ501は、種類511、最終標識513、フラグ515、LPN517、長さ519、およびオフセット521の各フィールドを有する。種類フィールドは、データバイトのカテゴリを特定する。例えば、種類フィールドは、データバイトのカテゴリが、ホストデータ(論理ページデータなど)またはシステムデータ(マップ情報やチェックポイント情報など)の1つであることを指示する。最終フィールドは、ヘッダがデータバイトの前の最終ヘッダであることを指示する。ヘッダマーカを用いるある実施形態では、最終フィールドは任意選択で割愛される。LPNフィールドは、ヘッダが関連付けられているLPNである。LPNフィールドは、特定のLPNと関連付けられたヘッダのうち特定のヘッダを、例えば、特定のLPNと一致するLPNフィールドを有するヘッダを求めてヘッダをサーチすることによって決定するためのヘッダのパーシングを可能にする。長さフィールドは、データバイトのバイト単位の長さ(例えば、ヘッダ501と関連付けられたデータバイト421Aに何バイトのデータがあるか)である。ある実施形態では、オフセットフィールド内のオフセットは、特定の粒度(8バイトの粒度など)に従って丸められる。エポックフィールドは、同じストリームまたは異なるストリームの他のオブジェクトに関連してヘッダがその一部であるオブジェクトの書き込み順を特定するタイムマーカである。5 illustrates selected details of an embodiment of a header having several fields (e.g., either
様々な実施形態では、特定のLPNと関連付けられた一部または全部の情報が、特定のLPNと関連付けられたマップエントリ、特定のLPNと関連付けられたヘッダ、またはその両方に記憶される。例えば、ある実施形態では、長さ519の一部または全部が、ヘッダではなくマップエントリに記憶される。In various embodiments, some or all of the information associated with a particular LPN is stored in a map entry associated with the particular LPN, in a header associated with the particular LPN, or both. For example, in one embodiment, some or all of the length 519 is stored in a map entry rather than in the header.
コマンド操作
図6に、入出力デバイスコマンド処理600として、入出力デバイス(記憶デバイスなど)におけるコマンドおよび任意選択のヒント情報の処理の一実施形態の選択された詳細の流れ図を示す。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスコマンド処理600は、「一度に1つ」のヒント処理を可能にし、この処理では、明示的ヒントモードを有する特定のコマンドが入出力デバイスに送られ、入出力デバイスは付随するヒントに従って特定のコマンドを処理する。後続のコマンドの処理はヒントによる影響を受けない(が、後続のコマンドのうちの1若しくはそれ以上は、任意選択で、それぞれの処理に影響を及ぼすそれぞれの付随するヒントを有する)。 Command Operation Figure 6 illustrates a flow diagram of selected details of one embodiment of the processing of commands and optional hint information in an I/O device (such as a storage device) as I/O
入出力デバイスの例が、図1Aおよび図1Bに示すSSD101のインスタンスである。処理は、電源投入されていない、休眠モードの、リセット状態の、といった入出力デバイスの非アクティブ状態から開始する(入出力デバイス電源オフまたはリセット状態601)。処理は、電源投入される、動作状態および/またはアクティブ状態に遷移する、リセットを終了する、といった、入出力デバイスがアクティブになるときに次に進む(アクティブ化する601A)。入出力デバイスは次いで、内部データ構造およびハードウェア要素を初期化することによって、例えば、初期値を記憶し、以前に保存された値を復元し、および/またはアクティブな動作と適合する状態値を作成することによって、動作の準備を行う(入出力デバイス初期化611)。An example of an I/O device is the instance of
動作の準備を行った後で、入出力デバイスはホストからのコマンドの受け取りを待つ(「コマンドを受け取るか?621」および「いいえ621N」)。コマンドを受け取り次第(はい621Y)、入出力デバイスは、コマンドがヒントと共に提供され、またはコマンドがヒントを使用するか否か決定する(コマンドはヒントありか、またはヒントを使用するか?631)。そうである場合(はい631Y)には、入出力デバイスは、ヒントと共に、および/またはヒントを使用してコマンドを処理する(ヒントを使用してコマンドを処理する641)。そうでない場合(いいえ631N)には、入出力デバイスは、ヒントなしでコマンドを処理する(コマンドを処理する(ヒントなし)651)。(ヒントありまたはヒントなしの)コマンドの処理の後で、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ホストに結果情報を返す(コマンド状況を送る661)。入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで折り返して別のコマンドを待つ(コマンドを受け取るか?621)。After preparing for operation, the I/O device waits to receive a command from the host ("Command Accepted? 621" and "No 621N"). Upon receiving a command (Yes 621Y), the I/O device determines whether the command was provided with or uses a hint (Command with Hint or with Hint? 631). If so (Yes 631Y), the I/O device processes the command with and/or using the hint (Process Command with Hint 641). If not (No 631N), the I/O device processes the command without the hint (Process Command (No Hint) 651). After processing the command (with or without hint), the I/O device optionally and/or selectively returns result information to the host (Send Command Status 661). Processing within the I/O device then loops back to wait for another command (Command Accepted? 621).
図7に、入出力デバイスコマンド処理700として、入出力デバイス(記憶デバイスなど)におけるコマンドおよび任意選択のヒント情報の処理の別の実施形態の流れ図を示す。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスコマンド処理700は「スティッキーな」ヒント処理を可能にし、この処理では、ヒントモードを開始するコマンドが入出力デバイスに送られ、その後に続いてヒントモードで処理される1若しくはそれ以上のコマンドが送られる。次いで、ヒントモードを終了するコマンドが、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、入出力デバイスに送られ、ヒントモードを終了するコマンドが送られる場合には、後続のコマンドはヒントなしで処理される。Figure 7 illustrates a flow diagram of another embodiment of processing commands and optional hint information in an I/O device (e.g., a storage device) as I/O
図6の場合と同様に、入出力デバイスの例は、図1Aおよび図1Bに示すSSD101のインスタンスである。やはり図6の場合と同様に、処理は入出力デバイスの非アクティブ状態から開始し(入出力デバイス電源オフまたはリセット状態701)、続いて入出力デバイスがアクティブになり(アクティブ化する701A)、動作の準備を行う(入出力デバイス初期化711)。As in FIG. 6, an example I/O device is an instance of
動作の準備を行った後で、入出力デバイスはホストからのコマンドの受け取りを待つ(「コマンドを受け取るか?721」および「いいえ721N」)。コマンドを受け取り次第(はい721Y)、入出力デバイスは、コマンドがヒントモードに関連したものであるか否か決定する(コマンドはヒントモードのものか?731)。そうである場合(はい731Y)には、入出力デバイスはヒントモードを開始する(またはコマンドに応じて、ヒントモードを終了する)(ヒントモードを開始/終了する741)。そうでない場合(いいえ731N)には、入出力デバイスは、ヒントモードを開始せずに(または終了せずに)、現在のモードでコマンドを処理する(現在のモードでコマンドを処理する751)。(ヒントモードに関連したものであるにせよ、そうでないにせよ)コマンドの処理の後で、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ホストに結果情報を返す(コマンド状況を送る761)。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、例えば、コマンドおよび/または結果情報に応じて、入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで、折り返して別のコマンドを待ち(コマンドを受け取るか?721)、または条件付きで、かつ/若しくは選択的に(例えば、コマンドおよび/または結果情報に応じて)、入出力デバイスは次いで、ヒントモードを終了すべきか否か決定する(ヒントモードを終了するか?771)。そうである場合(はい771Y)には、入出力デバイスはヒントモードを終了し(ヒントモードを終了する781)、入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで、折り返して別のコマンドを待つ(コマンドを受け取るか?721)。そうでない場合(いいえ771N)には、入出力デバイス内の処理は、ヒントモードを終了せずに、折り返して別のコマンドを待つ(コマンドを受け取るか?721)。ある実施形態では、単一のコマンドの処理の間に、入出力デバイスは、ヒントモードを開始し、単一のコマンドに基づいて、さらに、コマンドを実行して(読み出し動作、書き込み動作、切り捨て動作といった)特定の動作を実行する。例えば、いくつかのコマンドについては、処理は、741から751へ、次いで761へ進む。After preparing for operation, the I/O device waits to receive a command from the host ("Receive command? 721" and "No 721N"). Upon receiving a command (Yes 721Y), the I/O device determines whether the command is associated with hint mode (Is command for hint mode? 731). If so (Yes 731Y), the I/O device starts hint mode (or, depending on the command, ends hint mode) (Start/Exit hint mode 741). If not (No 731N), the I/O device processes the command in the current mode without starting (or ending) hint mode (Process command in current mode 751). After processing the command (whether associated with hint mode or not), the I/O device optionally and/or selectively returns result information to the host (Send command status 761). In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, e.g., depending on the command and/or result information, the processing in the I/O device then loops back to wait for another command (command received? 721), or conditionally and/or selectively (e.g., depending on the command and/or result information), the I/O device then determines whether to exit hint mode (exit hint mode? 771). If so (yes 771Y), the I/O device exits hint mode (exit hint mode 781) and the processing in the I/O device then loops back to wait for another command (command received? 721). If not (no 771N), the processing in the I/O device does not exit hint mode and loops back to wait for another command (command received? 721). In some embodiments, during the processing of a single command, the I/O device enters hint mode and, based on the single command, further executes the command to perform a specific operation (such as a read operation, a write operation, a truncate operation). For example, for some commands, the processing proceeds from 741 to 751 and then to 761.
図8に、入出力デバイスコマンド処理800として、入出力デバイス(記憶デバイスなど)におけるコマンドおよび任意選択のヒント情報の処理の別の実施形態の流れ図を示す。概念的には、図8には、1若しくはそれ以上の実施形態において同時に利用可能な図6および図7で表された機能が表されている。様々な実施形態および/または使用シナリオにおいて、入出力デバイスコマンド処理800は、一度に1つの、スティッキーなヒント処理を可能にし、この処理では、同時に使用可能な1若しくはそれ以上のヒントおよび/またはヒントモードがある。ヒントおよび/またはヒントモードは、任意選択で、選択的に、および/または条件付きで、コマンドのタイプ、LBA、データバンド、あるいは他のアドレス、データおよび/またはコマンド関連のパラメータ若しくは条件といった、1若しくはそれ以上の要因に依存する。FIG. 8 illustrates a flow diagram of another embodiment of processing commands and optional hint information in an I/O device (such as a storage device) as I/O
図6および図7の場合と同様に、入出力デバイスの例は、図1Aおよび図1Bに示すSSD101のインスタンスである。やはり図6および図7の場合と同様に、処理は入出力デバイスの非アクティブ状態から開始し(入出力デバイス電源オフまたはリセット状態801)、続いて入出力デバイスがアクティブになり(アクティブ化する801A)、動作の準備を行う(入出力デバイス初期化811)。As in Figures 6 and 7, an example I/O device is an instance of
動作の準備を行った後で、入出力デバイスはホストからのコマンドの受け取りを待つ(「コマンドを受け取るか?821」および「いいえ821N」)。コマンドを受け取り次第(はい821Y)、入出力デバイスは、コマンドが、明示的にヒントと共に提供され、またはコマンドが明示的にヒントを使用するか否か決定する(ヒントありか、またはヒントを使用するか?831)。そうである場合(はい831Y)には、入出力デバイスは、現在のモードに従って明示的なヒントと共に、および/または明示的なヒントを使用してコマンドを処理する(現在のモードでヒントを用いて処理する832)。様々な実施形態において、現在のモードは、コマンド、コマンドを有するLBA、(例えば、コマンドを有するLBA、マップ情報、またはデータバンドとモードとの他の関係から決定される)データバンド、他のアドレス、データおよび/若しくはコマンド関連のパラメータ若しくは条件、または1若しくはそれ以上の以前に提供された明示的ヒントおよび/若しくは暗黙的ヒントのうちの1若しくはそれ以上に依存する。After preparing for operation, the I/O device waits to receive a command from the host ("Receive Command? 821" and "No 821N"). Upon receiving a command (Yes 821Y), the I/O device determines whether the command was provided with or uses an explicit hint (With Hint or With Hint? 831). If so (Yes 831Y), the I/O device processes the command with and/or with the explicit hint according to the current mode (Process with Hint in Current Mode 832). In various embodiments, the current mode depends on one or more of the command, the LBA with the command, the data band (e.g., determined from the LBA with the command, map information, or other relationship between the data band and the mode), other address, data, and/or command related parameters or conditions, or one or more previously provided explicit hints and/or implicit hints.
コマンドが明示的なヒントを有しておらず、明示的なヒントを使用しない場合(いいえ831N)には、入出力デバイスは、コマンドが特定のヒントモードを開始すべきであるか否か決定する(ヒントモードを開始するか?841)。そうである場合(はい841Y)には、入出力デバイスは特定のヒントモードを開始する(特定のヒントモードを開始する(現在のモード+=特定のモード)842)。単一のヒントモードがある実施形態では、単一のヒントモードを開始することは、概念的には、現在のモードに、単一のヒントモードに対応する値を割り当てることに対応する。2若しくはそれ以上のヒントモードがある実施形態では、特定のヒントモードを開始することは、概念的には、現在のモードに、特定のヒントモードと共に(例えばこれを加えた)現在のモードに対応する値を割り当てることに対応する。様々な実施形態において、特定のヒントモードは、1若しくはそれ以上のLBA、LBAの1若しくはそれ以上の範囲、および1若しくはそれ以上のデータバンドのうちの1若しくはそれ以上と関連付けられている。明示的なヒントを有する、または使用するコマンドの処理は、一度に1つのヒント処理を可能にする。If the command does not have an explicit hint and does not use an explicit hint (No 831N), the I/O device determines whether the command should initiate a specific hint mode (Initiate Hint Mode? 841). If so (Yes 841Y), the I/O device initiates the specific hint mode (Initiate Specific Hint Mode (Current Mode +=Specific Mode) 842). In embodiments with a single hint mode, initiating the single hint mode conceptually corresponds to assigning to the current mode a value corresponding to the single hint mode. In embodiments with two or more hint modes, initiating the specific hint mode conceptually corresponds to assigning to the current mode a value corresponding to the current mode along with (e.g., in addition to) the specific hint mode. In various embodiments, the specific hint mode is associated with one or more of one or more LBAs, one or more ranges of LBAs, and one or more data bands. Processing commands with or using explicit hints allows for one hint processing at a time.
コマンドが特定のヒントモードを開始すべきでない場合(いいえ841N)には、入出力デバイスは、コマンドが特定のヒントモードを終了すべきであるか否か決定する(ヒントモードを終了するか?851)。そうである場合(はい851Y)には、入出力デバイスは特定のヒントモードを終了する(特定のヒントモードを終了する(現在のモード−=特定のモード)852)。単一のヒントモードがある実施形態では、単一のヒントモードを終了することは、概念的には、現在のモードに、単一のヒントモードが非アクティブであることに対応するデフォルト値を割り当てることに対応する。2若しくはそれ以上のヒントモードがある実施形態では、特定のヒントモードを終了することは、概念的には、現在のモードに、特定のヒントモードなしで(例えばこれを差し引いた)現在のモードに対応する値を割り当てることに対応する。様々な実施形態において、特定のヒントモードは、1若しくはそれ以上のLBA、LBAの1若しくはそれ以上の範囲、および1若しくはそれ以上のデータバンドのうちの1若しくはそれ以上と関連付けられている。If the command should not start the specific hint mode (No 841N), the I/O device determines whether the command should exit the specific hint mode (Exit Hint Mode? 851). If so (Yes 851Y), the I/O device exits the specific hint mode (Exit Specific Hint Mode (Current Mode -=Specific Mode) 852). In embodiments with a single hint mode, exiting the single hint mode conceptually corresponds to assigning the current mode a default value that corresponds to the single hint mode being inactive. In embodiments with two or more hint modes, exiting the specific hint mode conceptually corresponds to assigning the current mode a value that corresponds to the current mode without (e.g., minus) the specific hint mode. In various embodiments, the specific hint mode is associated with one or more of one or more LBAs, one or more ranges of LBAs, and one or more data bands.
コマンドが特定のヒントモードを終了すべきでない場合(いいえ851N)には、入出力デバイスは、コマンドが特定のヒントモードを終了すべきであるか否か決定する(すべてのヒントモードを終了するか?861)。そうである場合(はい861Y)には、入出力デバイスはすべてのヒントモードを終了する(すべてのヒントモードを終了する(現在のモード=デフォルトモード)862)。単一のヒントモードがある実施形態(または2若しくはそれ以上ヒントモードがある実施形態)では、すべてのヒントモードを終了することは、概念的には、現在のモードに、単一のヒントモード(またはすべてのヒントモード)が非アクティブであることに対応するデフォルト値を割り当てることに対応する。If the command should not exit the particular hint mode (No 851N), the I/O device determines whether the command should exit the particular hint mode (Exit All Hint Modes? 861). If so (Yes 861Y), the I/O device exits all hint modes (Exit All Hint Modes (Current Mode = Default Mode) 862). In embodiments where there is a single hint mode (or embodiments where there are two or more hint modes), exiting all hint modes conceptually corresponds to assigning the current mode a default value that corresponds to the single hint mode (or all hint modes) being inactive.
コマンドがすべてのヒントモードを終了すべきでない場合(いいえ861N)には、コマンドは、現在のモードで処理され(現在のモードで処理する(ヒントなし)872)、現在のモードは、例えば、以前に受け取られたヒント開始/終了に関連したコマンドに基づく現在のモードへのあらゆる以前の変更を含むが、コマンドはヒントを提供しないと決定されているため、いかなる追加のヒント情報も含まない。特定のヒントモードを開始するコマンドおよび特定のヒントモードまたはすべてのヒントモードを終了するコマンドの処理は、スティッキーなヒント処理を可能にする。If the command should not exit all hint modes (No 861N), the command is processed in the current mode (Process in Current Mode (No Hints) 872), which includes any previous changes to the current mode based, for example, on previously received hint start/end related commands, but does not include any additional hint information since the command was determined not to provide a hint. Processing of commands to enter specific hint modes and commands to exit specific hint modes or all hint modes allows for sticky hint processing.
(それぞれ、832、842、852、862、および872に対応する、明示的に提供されたヒントありの、または明示的に提供されたヒントを使用した、特定のヒントモードを開始する、または終了する、すべてのヒントモードを終了する、あるいは現在のモードだけに基づいた)コマンドの処理の後で、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ホストに結果情報を返す(状況を送る881)。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、例えば、コマンドおよび/または結果情報に応じて、入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで、折り返して別のコマンドを待ち(コマンドを受け取るか?821)、または任意選択で、条件付きで、かつ/若しくは選択的に(例えば、コマンドおよび/または結果情報に応じて)、入出力デバイスは次いで、1若しくはそれ以上のヒントモードを終了し((1若しくはそれ以上の)ヒントモードを終了する882)、入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで折り返して別のコマンドを待つ(コマンドを受け取るか?821)。After processing the command (entering or exiting a particular hint mode, exiting all hint modes, or based only on the current mode, with or using an explicitly provided hint, corresponding to 832, 842, 852, 862, and 872, respectively), the I/O device optionally and/or selectively returns result information to the host (send status 881). In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, for example, depending on the command and/or result information, processing within the I/O device then loops back to wait for another command (command received? 821), or, optionally, conditionally, and/or selectively (e.g., depending on the command and/or result information), the I/O device then exits one or more hint modes (exit (one or more) hint modes 882), and processing within the I/O device then loops back to wait for another command (command received? 821).
決定831、841、851、および861の順序付けは例示にすぎず、他の順序付けを有する別の実施形態、ならびに決定のうちの1若しくはそれ以上が並列に行われ、または決定の「はい」パスのうちの複数が、任意選択で、および/または選択的に評価される実施形態も企図されている。例えば、ある実施形態では、特定のコマンドがその特定のコマンドおよび後続のコマンドに影響を及ぼすスティッキーなヒントを使用する。The ordering of
マップ操作
図9に、入出力デバイスコマンド処理900として、入出力デバイス(記憶デバイスなど)におけるコマンドおよび任意選択のシャドウマップ情報の処理の一実施形態の流れ図を示す。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスコマンド処理900は、入出力デバイスが、通常は特定の処理によって取得されるはずのホスト提供情報に基づいて特定の処理を省略する(例えば、図1Aおよび図1Bのマップ141といったマップへのアクセスをスキップする)ことを可能にする。ホストは、少なくとも部分的に入出力デバイスから伝えられるマップ更新によって管理されるシャドウマップにアクセスすることによって情報を提供することができるようになっている。 9 illustrates a flow diagram of one embodiment of processing of commands and optional shadow map information in an I/O device (such as a storage device) as I/O
図6から図8の場合と同様に、入出力デバイスの例は、図1Aおよび図1Bに示すSSD101のインスタンスである。やはり図6から図8の場合と同様に、処理は入出力デバイスの非アクティブ状態から開始し(入出力デバイス電源オフまたはリセット状態901)、続いて入出力デバイスがアクティブになり(アクティブ化する901A)、動作の準備を行う(入出力デバイス初期化911)。As in Figures 6-8, an example I/O device is an instance of
動作の準備を行った後で、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ホストに開始マップ情報を伝える(ホストに初期マップを転送する921)。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスは、概念的「フェッチ・オン・デマンド」技術に従って開始マップ情報の全部または任意の部分の伝達を省略する。伝達は、任意選択で、バックグラウンド動作として行われる。ホストは伝えられたマップ情報をシャドウマップ(図1Bのシャドウマップ108など)において保持する。入出力デバイスは次いで、ホストからのコマンドの受け取りを待つ(「コマンドを受け取るか?931」および「いいえ931N」)。After preparing for operation, the I/O device optionally and/or selectively communicates the starting map information to the host (transfer initial map to host 921). In certain embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the I/O device omits communicating all or any part of the starting map information in accordance with a conceptual "fetch-on-demand" technique. The communication is optionally performed as a background operation. The host maintains the communicated map information in a shadow map (such as shadow map 108 in FIG. 1B). The I/O device then waits to receive a command from the host ("Receive command? 931" and "No 931N").
コマンドを受け取り次第(はい931Y)、入出力デバイスは、コマンドが、図1Aのフラッシュダイ194のうちの1若しくはそれ以上のブロック/ページといった、入出力デバイスNVMの特定の部分の特定のブロックアドレスおよび/またはページアドレスを対象とする位置情報を含み、または有するか否か決定する(位置は提供されたか?941)。そうでない場合(いいえ941N)には、入出力デバイスは、例えば、マップにアクセスすることによって、特定のブロックアドレスおよび/またはページアドレスならびに入出力デバイスNVMの特定の部分を決定する(位置を決定する951)。入出力デバイスは、決定した位置を使用してコマンドを処理する(コマンドを処理する961)。コマンドが位置情報を含み、または有する場合(はい941Y)には、位置決定は省略され、入出力デバイスは、提供された位置情報を使用してコマンドを処理する(コマンドを処理する961)。Upon receiving the command (Yes 931Y), the I/O device determines whether the command includes or has location information (Location Provided? 941) that targets a specific block address and/or page address of a specific portion of the I/O device NVM, such as one or more blocks/pages of the flash die 194 of FIG. 1A. If not (No 941N), the I/O device determines the specific block address and/or page address and the specific portion of the I/O device NVM (Determine Location 951), e.g., by accessing a map. The I/O device processes the command using the determined location (Process Command 961). If the command includes or has location information (Yes 941Y), then the location determination is omitted and the I/O device processes the command using the provided location information (Process Command 961).
コマンドの処理の後で、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ホストに結果情報を返し(コマンド状況を送る971)、結果情報は任意選択で1つ若しくは複数のマップ更新を含み、例えば、コマンドが書き込みコマンドである場合には、入出力デバイスはホストに、特定のブロックアドレスおよび/またはページアドレスを対象とする位置情報など、書き込みコマンドのLBAと入出力デバイスNVMの特定の部分との間のマッピングを記述するマップ更新を伝える。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、例えば、コマンドおよび/または結果情報に応じて、入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで、折り返して別のコマンドを待ち(コマンドを受け取るか?931)、または条件付きで、かつ/若しくは選択的に(例えば、コマンドおよび/または結果情報に応じて)、入出力デバイスは次いで、ホストにマップ更新を伝えるべきか否か決定する(マップ更新を送るべきか?981)。そうでない場合(いいえ981N)には、入出力デバイス内の処理は、折り返して別のコマンドを待つ(コマンドを受け取るか?931)。そうである場合(はい981Y)には、入出力デバイスはホストに1若しくはそれ以上のマップ更新を伝える(ホストに(1若しくはそれ以上の)マップ更新を転送する991)。ある実施形態では、マップ更新はバックグラウンド動作として伝えられる。ある実施形態では、マップ更新は累積され、グループとして、任意選択でバックグラウンド動作として転送される。入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで折り返して別のコマンドを待つ(コマンドを受け取るか?931)。After processing the command, the I/O device optionally and/or selectively returns result information to the host (send command status 971), which optionally includes one or more map updates, e.g., if the command is a write command, the I/O device communicates to the host a map update that describes the mapping between the LBA of the write command and a particular portion of the I/O device NVM, such as location information for a particular block address and/or page address. In certain embodiments and/or usage scenarios, e.g., depending on the command and/or result information, processing within the I/O device then loops back and waits for another command (command received? 931), or conditionally and/or selectively (e.g., depending on the command and/or result information), the I/O device then determines whether to communicate a map update to the host (should I send a map update? 981). If not (no 981N), processing within the I/O device loops back and waits for another command (command received? 931). If so (Yes 981Y), the I/O device communicates one or more map updates to the host (Transfer (one or more) map updates to host 991). In some embodiments, the map updates are communicated as a background operation. In some embodiments, the map updates are accumulated and transferred as a group, optionally as a background operation. Processing within the I/O device then loops back to wait for another command (Command received? 931).
ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスは、初期化またはコマンドの直接関連したものではない入出力デバイスによる処理に応答して、ホストに1若しくはそれ以上の更新を伝える。例えば、入出力デバイスが入出力デバイスNVMの領域を再利用するときに、LBAと入出力デバイスNVM内の位置との間のマッピングへの0若しくはそれ以上の変更が生じる。入出力デバイスは、ある場合、マッピング変更を、981/991の場合と同様に、1若しくはそれ以上のマップ更新としてホストに伝える。In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the I/O device communicates one or more updates to the host in response to processing by the I/O device that is not directly related to an initialization or command. For example, when the I/O device reclaims space in the I/O device NVM, zero or more changes to the mapping between LBAs and locations within the I/O device NVM occur. The I/O device communicates the mapping changes, in some cases, to the host as one or more map updates, similar to the 981/991 case.
(カードメモリを備える入出力カード、例えば、図1Bの(任意選択の)カードメモリ112Cをシャドウマップ用のストレージとして使用する入出力カード116などを有するある実施形態といった)ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、1若しくはそれ以上の入出力デバイスは、ホストの関与なしで、シャドウマップとしてカードメモリを使用する。ホストにマップ更新を伝えるのではなく、入出力デバイスは、マップ更新に従ってシャドウマップを変更する。In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios (such as some embodiments having an I/O card with card memory, such as I/O card 116 in FIG. 1B, which uses (optional)
図10に、ホスト・シャドウ・マップ処理1000として、コンピューティングホストにおけるシャドウマップ情報の維持の一実施形態の流れ図を示す。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、ホスト・シャドウ・マップ処理1000は、入出力デバイスが、通常は特定の処理によって取得されるはずのホスト提供情報に基づいて特定の処理を省略する(例えば、図1Aおよび図1Bのマップ141といったマップへのアクセスをスキップする)ことを可能にする。ホストは、少なくとも部分的に入出力デバイスから伝えられるマップ更新によって管理されるシャドウマップにアクセスすることによって情報を提供することができるようになっている。Figure 10 illustrates a flow diagram of one embodiment of maintaining shadow map information in a computing host as host
ホストの例は図1Bに示すホスト102である。図6から図9場合と同様に、処理は入出力デバイスの非アクティブ状態から開始し(入出力デバイス電源オフまたはリセット状態1001)、続いて入出力デバイスがアクティブになる(アクティブ化する1001A)。ホストは次いで、図1Bのシャドウマップ108といったシャドウマップのすべてのエントリを情報がないとマークする(シャドウマップをすべて無効として初期化する1011)。ホストの処理は次いで、入出力デバイスから伝えられる1若しくはそれ以上のマップ更新の受け取りを待つ(「初期マップまたは更新を受け取るか?1021」および「いいえ1021N」)。マップ更新を受け取り次第(はい1021Y)、ホストは、受け取ったマップ更新に従ってシャドウマップを更新する(シャドウマップを更新する1031)。An example of a host is host 102 shown in FIG. 1B. As in FIGS. 6-9, the process starts with the I/O device inactive (I/O device power off or reset state 1001), followed by the I/O device becoming active (activate 1001A). The host then marks all entries in a shadow map, such as shadow map 108 in FIG. 1B, as empty (initialize all shadow maps as invalid 1011). The host process then waits to receive one or more map updates communicated from the I/O device ("Receive initial map or update? 1021" and "No 1021N"). Upon receiving a map update (
様々な実施形態において、入出力デバイスから伝えられるマップ更新は、初期化に関連した入出力デバイス処理(図9のホストに初期マップを転送する921など)の結果、書き込みに関連した入出力デバイス処理(図9のコマンド状況を送る(任意選択で、書き込みのためのマップ更新と共に)971)の結果、マップ更新の入出力デバイス累積(図9のホストに(1若しくはそれ以上の)マップ更新を転送する991)の結果、またはこれらの任意の組み合わせである。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、マップ更新のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を無視する。例えば、ホストは、再利用アクティビティに起因して生じる特定のマップ更新を、例えば、特定のマップ更新が、ホストが特定のマップ更新を処理する前の書き込みが原因でホストが無効にするシャドウ・マップ・エントリに対応するときなどに無視する。In various embodiments, the map updates communicated from the I/O device are the result of an initialization-related I/O device operation (e.g., forwarding initial map to host 921 in FIG. 9), a write-related I/O device operation (send command status (optionally with map updates for write) 971 in FIG. 9), an I/O device accumulation of map updates (forwarding (one or more) map updates to host 991 in FIG. 9), or any combination thereof. In certain embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the host optionally and/or selectively ignores one or more of the map updates. For example, the host may ignore a particular map update that occurs due to reclamation activity, such as when the particular map update corresponds to a shadow map entry that the host invalidates due to a write before the host processed the particular map update.
ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオ(例えば、入出力カード116を有し、図1Bの(任意選択の)カードメモリ112Cをシャドウマップのストレージとして使用するいくつかの実施形態)では、1若しくはそれ以上の入出力デバイス、例えばSSDはシャドウマップを使用し、ホストはシャドウマップを使用しない。入出力デバイスは、図10に示す処理の全部または任意の部分を実行し、例えば、入出力デバイスは、シャドウマップ初期化および更新を行う。In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios (e.g., some embodiments having an I/O card 116 and using the (optional)
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスは、ホストコマンドから独立して、および/またはホストコマンドに応答してではあるが、ホストコマンド内で参照されないLBAにおいて、または読み出しコマンドといった、通常はマップを更新しないはずのホストコマンド内のLBAにおいてマップを更新する。第1の例では、再利用(不要部分の整理など)に起因してNVM内のデータが再配置され、マップは任意のそうした再配置データの新しい位置を反映するように更新される。第2の例では、読み出しコマンドに応答して、過剰な読み出し回数を有する(例えば、データは読み出し妨害誤りを冒す可能性が高い)という決定に起因してデータが再配置される。入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ホストに、例えば、割り込みによって、あるいは状況情報によって、独立の入出力デバイスアクティビティに起因したマップへの未処理の更新があることを知らせる。様々な実施形態によれば、独立の入出力デバイスアクティビティに起因したマップへの更新は以下のうちの1若しくはそれ以上である:ホストコマンドに応答したものであるマップの他の更新と共にホストに伝えられる;ホストへの別個の通信としてホストに伝えられる;ホストが要求した独立の更新に応答して、例えば独立の更新のログを読み取ることによってホストに伝えられる;入出力デバイスによってシャドウマップに直接書き込まれる;および他の技術。別の実施形態では、再利用され、および/または再配置されたNVMの部分が、NVMのその部分のあらゆるマップ更新がホストに伝えられ、および/またはシャドウマップにおいて更新されるまで消去されない。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、シャドウマップ更新後まで消去を遅延させることは、(再利用および/または再配置の前の)シャドウマップ内の以前の位置情報がホストによって使用されることを可能にし、よって、そうでなければ、更新エントリが新しい位置情報で更新されるまで更新エントリの使用を不可能にするはずのシャドウマップの更新エントリの無効化による性能の不利益を回避する。In some embodiments, the I/O device updates the map independent of and/or in response to a host command, but at LBAs not referenced in the host command, or at LBAs in a host command that would not normally update the map, such as a read command. In a first example, data in the NVM is relocated due to reclamation (e.g., garbage collection), and the map is updated to reflect the new location of any such relocated data. In a second example, data is relocated in response to a read command due to a determination that it has an excessive number of reads (e.g., the data is likely to suffer read disturb errors). The I/O device optionally and/or selectively informs the host, e.g., by interrupt or by status information, that there are pending updates to the map due to independent I/O device activity. According to various embodiments, updates to the map due to independent I/O device activity are one or more of the following: communicated to the host along with other updates to the map in response to a host command; communicated to the host as a separate communication to the host; communicated to the host in response to an independent update requested by the host, e.g., by reading a log of the independent updates; written directly to the shadow map by the I/O device; and other techniques. In another embodiment, a portion of the NVM that has been reclaimed and/or relocated is not erased until any map updates for that portion of the NVM have been communicated to the host and/or updated in the shadow map. In certain embodiments and/or usage scenarios, delaying the erase until after the shadow map update allows previous location information in the shadow map (before the reclaiming and/or relocation) to be used by the host, thus avoiding a performance penalty due to invalidation of the update entry in the shadow map that would otherwise make the update entry unusable until the update entry is updated with the new location information.
図11に、ホストコマンド発行1100として、コンピューティングホストにおけるコマンドおよび任意選択のシャドウマップ情報の発行の一実施形態の流れ図を示す。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、ホストコマンド発行1100は、入出力デバイスが、通常は特定の処理によって取得されるはずのホスト提供情報に基づいて特定の処理を省略する(例えば、図1Aおよび図1Bのマップ141といったマップへのアクセスをスキップする)ことを可能にする。ホストは、少なくとも部分的にホストからの変更(ならびに入出力デバイスから伝えられるマップ更新)によって管理されるシャドウマップにアクセスすることによって情報を提供することができるようになっている。Figure 11 illustrates a flow diagram of one embodiment of issuing commands and optional shadow map information in a computing host as
ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、書き込みコマンドを発行することと併せて、ホストは、書き込みが変更するLBAについてのシャドウ・マップ・エントリを無効にする。というのは、書き込みコマンドを処理するときに、LBAについてのマッピングが入出力デバイスによって変更されるからである。続いて、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、書き込まれたLBAに関連した1若しくはそれ以上のマップ更新を伝え、ホストは次いで、マップ更新に従ってシャドウマップを変更する。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、切り捨てコマンドを発行することと併せて、ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、切り捨てが関連するLBAについてのシャドウ・マップ・エントリを切り捨て済みとマークする。というのは、切り捨てコマンドを処理するときに、LBAについてのマッピングが入出力デバイスによって切り捨て済みとマークされるからである。入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、削減されたLBAに関連したマップ更新を伝えることを省略する。というのは、ホストはすでにそれらのLBAを切り捨て済みとマークしているからである。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、読み出しコマンドを発行することと併せて、ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、読み出しコマンドがアクセスするLBAについてのシャドウマップ内に有効なエントリがあるかどうか検査する。有効なエントリが見つかる場合には、ホストは、予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを、有効なエントリからの位置情報と共に発行し、任意選択で、コマンドを発行するときにLBAを省略する。位置情報は、入出力デバイスが、通常はLBAから位置情報を決定するために行われるはずのマップルックアップを省略することを可能にする。有効なエントリが見つからない場合には、ホストは、LBAと共に、位置情報なしで読み出しコマンドを発行する。入出力デバイスは次いで、一部は、読み取ったLBAに基づいてマップルックアップを実行することによって読み出しコマンドを処理して位置情報を決定する、
より具体的には、ホストの例は図1Bに示すホスト102である。図6から図10場合と同様に、処理は入出力デバイスの非アクティブ状態から開始し(入出力デバイス電源オフまたはリセット状態1101)、続いて入出力デバイスがアクティブになる(アクティブ化する1101A)。ホストの処理は次いで、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、すべてのシャドウ・マップ・エントリを空とマークし、ホスト上で実行されているソフトウェア要素(例えば、図1BのOS105、ドライバ107、およびアプリケーション109の様々な組み合わせ)によって生成されるコマンドといったコマンドを待つ(「コマンドは?1111」および「いいえ1111N」)。コマンドが生成され次第(はい1111Y)、ホストは、生成されたコマンドがどのコマンドか、あるいはどのコマンドタイプか決定する(コマンドを復号する1121)。 In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, in conjunction with issuing a write command, the host invalidates shadow map entries for LBAs that the write modifies, since the mapping for the LBAs is modified by the I/O device when processing the write command. The I/O device then optionally communicates one or more map updates associated with the written LBAs, and the host then modifies the shadow map according to the map updates. In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, in conjunction with issuing a truncate command, the host optionally and/or selectively marks shadow map entries for LBAs to which the truncation is associated as truncated, since the mapping for the LBAs is marked as truncated by the I/O device when processing the truncate command. The I/O device optionally omits communicating map updates associated with the reduced LBAs, since the host has already marked those LBAs as truncated. In one embodiment and/or usage scenario, in conjunction with issuing a read command, the host optionally and/or selectively checks whether there is a valid entry in the shadow map for the LBA accessed by the read command. If a valid entry is found, the host issues a pre-mapped read command with location information from the valid entry, and optionally omits the LBA when issuing the command. The location information allows the I/O device to omit a map lookup that would normally be performed to determine location information from the LBA. If a valid entry is not found, the host issues a read command with the LBA but without the location information. The I/O device then processes the read command to determine location information, in part, by performing a map lookup based on the read LBA.
More specifically, an example of a host is host 102 shown in Figure IB. As in Figures 6-10, the process starts with an inactive state of the I/O device (I/O device power off or reset state 1101), followed by the I/O device becoming active (activate 1101A). The host process then optionally and/or selectively marks all shadow map entries as empty and waits for a command ("What's the command? 1111" and "No 1111N"), such as a command generated by a software element (e.g., various combinations of
コマンドが書き込みコマンド、あるいは書き込みコマンドタイプ(書き込み1121W)である場合には、ホストは、書き込みが変更するLBAについてのシャドウ・マップ・エントリを空とマークし(例えば無効にし)(シャドウマップ内のLBAを無効とマークする1131)、入出力デバイスに書き込みを発行する(コマンドを発行する1161)。コマンドが切り捨てコマンド、あるいは切り捨てコマンドタイプ(切り捨て1121T)である場合には、ホストは、切り捨てが関連するLBAについてのシャドウ・マップ・エントリを切り捨て済みとマークし(シャドウマップ内のLBAを切り捨て済みとマークする1141)、入出力デバイスに切り捨てを発行する(コマンドを発行する1161)。コマンドが読み出しコマンド、あるいは読み出しコマンドタイプ(読み出し1121R)である場合には、ホストは、読み出しがアクセスするLBAについてのシャドウマップ内に有効なエントリがあるかどうか検査する(LBAはシャドウマップ内で有効か?1151)。有効なエントリが見つかる場合(はい1151Y)には、ホストは入出力デバイスに、有効なエントリからの位置情報と共に予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを発行し、任意選択で、コマンドを発行するときにLBAを省略する(コマンドを(シャドウマップからの位置と共に)予めマッピングされた読み出しとして発行する1171)。有効なエントリが見つからない場合(いいえ1151N)には、ホストは入出力デバイスに、LBAと共に、位置情報なしで読み出しコマンドを発行する(コマンドを発行する1161)。コマンドが書き込み、切り捨て、または読み出し以外、あるいは、書き込みタイプ、切り捨てタイプ、または読み出し種類以外である場合(その他1121O)には、ホストは入出力デバイスにコマンドを発行し(コマンドを発行する1161)、任意選択で、コマンドと関連付けられた任意のLBAを含める。If the command is a write command or a write command type (Write 1121W), the host marks the shadow map entry for the LBAs that the write modifies as empty (e.g., invalidates) (Mark LBAs in Shadow Map Invalid 1131) and issues the write to the I/O device (Issue Command 1161). If the command is a truncate command or a truncate command type (Truncate 1121T), the host marks the shadow map entry for the LBAs that the truncate is associated with as truncated (Mark LBAs in Shadow Map As Truncated 1141) and issues the truncate to the I/O device (Issue Command 1161). If the command is a read command or a read command type (
ある実施形態では、ホストが入出力デバイスにコマンドを発行する(コマンドを発行する1161)ときに、ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、コマンドが関連するLBAについてのシャドウマップの(ある場合)有効なエントリから取得される情報を含める。例えば、書き込みコマンドのLBAについてのシャドウマップ内に有効なエントリがある場合には、ホストは、入出力デバイスにその書き込みコマンドを発行するときに、有効なエントリからの位置および/または長さ情報を提供する。入出力デバイスは、例えば、その位置および/または長さ情報を使用して、使用空間の記帳を更新する(例えば、使用空間[位置]−=長さなど)。ある実施形態では、ホストが予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドを発行する(コマンドを(シャドウマップからの位置と共に)予めマッピングされた読み出しとして発行する1171)ときに、ホストは、長さおよび/または範囲情報を含むシャドウマップからの位置情報を提供し、入出力デバイスが、マップにアクセスせずに、(その長さおよび/または範囲に基づいて)どれだけのデータを読み取るべきか決定することを可能にする。In some embodiments, when the host issues a command to the I/O device (issue command 1161), the host optionally and/or selectively includes information obtained from a valid entry (if any) in the shadow map for the LBA to which the command pertains. For example, if there is a valid entry in the shadow map for the LBA of a write command, the host provides the location and/or length information from the valid entry when issuing the write command to the I/O device. The I/O device, for example, uses the location and/or length information to update its bookkeeping of used space (e.g., used space [location] -= length, etc.). In some embodiments, when the host issues a premapped read command (issue command as premapped read (with location from shadow map) 1171), the host provides the location information from the shadow map, including the length and/or range information, allowing the I/O device to determine how much data to read (based on the length and/or range) without accessing the map.
ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、コマンドのサイズに基づいてシャドウマップを無視する。相対的に長い長さを有するコマンド、例えば、各々がそれぞれのマップエントリと関連付けられている複数のLBA単位にまたがるデータを参照するコマンドなどは、場合によっては、追加の位置情報(例えば、1LBA単位当たり1つの位置情報など)を有し、コマンドのサイズを増大させる。相対的に長い長さを有するコマンドは、入出力デバイスの順次マップエントリにアクセスし、マップアクセスのコストは複数の単位にわたってならされる。例えば、ホストは4KBを上回るデータを参照する読み出しコマンドのシャドウマップを無視する。ある実施形態では、ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、相対的に中程度の長さを有するコマンドを複数のコマンドに分割する。例えば、ホストは、8KB(または16KB)のデータを参照する読み出しコマンドを、各々4KBのデータを参照する2つの(または4つの)読み出しコマンドに分割する。ある実施形態では、予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンド(またはその変形)は、複数の位置情報要素を指定することができるようになっており、別の実施形態では、予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンド(およびその変形)は、単一の位置情報要素を指定するだけに制限される。ある実施形態では、下位部分(入出力デバイスNVMの4KB部分の1つの特定のSATAセクタなど)へのアクセスは、その特定のセクタを識別する追加の位置情報を使用する。The host optionally and/or selectively ignores the shadow map based on the size of the command. Commands with a relatively long length, such as commands that reference data across multiple LBA units, each associated with a respective map entry, may have additional location information (e.g., one location information per LBA unit), increasing the size of the command. Commands with a relatively long length access sequential map entries of the I/O device, and the cost of map access is smoothed across multiple units. For example, the host ignores the shadow map for read commands that reference more than 4 KB of data. In some embodiments, the host optionally and/or selectively splits commands with a relatively medium length into multiple commands. For example, the host splits a read command that references 8 KB (or 16 KB) of data into two (or four) read commands, each referencing 4 KB of data. In some embodiments, the pre-mapped read command (or variants thereof) is capable of specifying multiple location information elements, while in other embodiments, the pre-mapped read command (or variants thereof) is limited to specifying only a single location information element. In some embodiments, accesses to a lower portion (such as one particular SATA sector of a 4KB portion of the I/O device NVM) use additional location information that identifies that particular sector.
(カードメモリを備える入出力カード、例えば、図1Bの(任意選択の)カードメモリ112Cをシャドウマップ用のストレージとして使用する入出力カード116などを有するある実施形態といった)ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、1若しくはそれ以上の入出力デバイスはシャドウマップを使用し、ホストはシャドウマップを使用しない。入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、図11に示す処理の全部または任意の部分を実行する。例えば、入出力デバイスはシャドウマップ内の特定のエントリを、書き込みコマンドを処理するときには無効とマークし、切り捨てコマンドを処理するときには切り捨て済みとマークする。In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios (such as an embodiment having an I/O card with card memory, such as I/O card 116 in FIG. 1B using (optional)
低電力動作
図12に、入出力デバイス休眠開始/終了1200として、入出力デバイス(記憶デバイスなど)の休眠状態の開始および終了の一実施形態の流れ図を示す。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイス休眠開始/終了1200は、入出力デバイスの電力ダウンまたは電源オフを可能にすることによって、例えば、休眠状態を開始することによって、内部状態の全部または任意の部分を入出力デバイスとは別個の(あるいは、入出力デバイスに対して別個の電力制御を受ける)保存/復元メモリに記憶することによって、電力低減を可能にする。入出力デバイスが休眠状態を終了するときに、内部状態の全部または一部が保存/復元メモリから復元される。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、保存/復元メモリから内部状態を復元することは、保存/復元メモリ以外に保持された情報から内部状態を再構築すること(例えば、入出力デバイスのNVMの読み出しから取得されるマップ情報からマップ情報のキャッシュを再構築することなど)よりも効率がよい(例えば、より低い待ち時間および/またはより低電力である)。 LOW POWER OPERATION FIG. 12 illustrates a flow diagram of one embodiment of entering and exiting a hibernation state for an I/O device (such as a storage device) as I/O Device Hibernation Entry/
内部状態の例は、入出力デバイスの任意の揮発性状態(入出力デバイスが休眠状態で動作するときに失われる状態など)、マップ情報(図1Aおよび図1Bのマップ141で維持されるキャッシュマップ情報、シャドウマップ情報、マルチレベルマップの任意の1若しくはそれ以上のレベルなど)、ならびに入出力デバイスによって維持される統計である。保存/復元メモリの例は、入出力デバイスにアクセス可能で、入出力デバイスにとって相対的にローカルであるメモリ((任意選択の)カードメモリ112Cなど)、および入出力デバイスからアクセス可能なホストメモリ(ホストメモリ112H、およびシャドウマップ108など)である。Examples of internal state are any volatile state of the I/O device (such as state lost when the I/O device operates in a dormant state), map information (such as cache map information maintained in
図6から図9の場合と同様に、入出力デバイスの例は、図1Aおよび図1Bに示すSSD101のインスタンスである。やはり図6から図9の場合と同様に、処理は入出力デバイスの非アクティブ状態から開始し(入出力デバイス電源オフまたはリセット状態1201)、続いて入出力デバイスがアクティブになり(アクティブ化する1201A)、動作の準備を行う(入出力デバイス初期化1211)。As in Figures 6-9, an example I/O device is an instance of
動作の準備を行った後で、入出力デバイスは、コマンドを受け取り、処理し、電源投入せずに他のアクティビティを実行することができるようにした高電力動作状態になる(アクティブな動作状態1221)。低電力動作状態を開始するよう求める要求を待つ間(「休眠状態を開始するか?1231」および「いいえ1231N」)、入出力デバイスは高電力動作状態(アクティブな動作状態1221)のままであり、ある場合、受け取ったコマンドを実行する(図示せず)。入出力デバイスのインターフェースを介して受け取られる明示的要求や、非アクティビティの期間に応答して入出力デバイスによって生成される暗黙的要求といった、低電力動作状態を開始するよう求める要求を受け取り次第(はい1231Y)、入出力デバイスは内部状態の全部または任意の部分を保存/復元メモリに記憶する(内部状態を保存/復元メモリに記憶する1241)。入出力デバイスは次いで、低電力動作状態を開始する(休眠状態1251)。様々な実施形態において、入出力デバイスは、内部状態の全部または任意の部分を、例えば、複数の暗号化技術のうちのいずれか1つにより暗号化することによって、暗号化された形で保存する。After preparing for operation, the I/O device enters a high-power operating state (active operating state 1221) that allows it to receive and process commands and perform other activities without powering up. While waiting for a request to enter a low-power operating state ("Enter Dormant State? 1231" and "No 1231N"), the I/O device remains in the high-power operating state (active operating state 1221) and executes received commands, if any (not shown). Upon receiving a request to enter a low-power operating state (Yes 1231Y), such as an explicit request received through an interface of the I/O device or an implicit request generated by the I/O device in response to a period of inactivity, the I/O device stores all or any part of its internal state in a save/restore memory (Store Internal State in Save/Restore Memory 1241). The I/O device then enters a low-power operating state (Dormant State 1251). In various embodiments, the I/O device stores all or any part of its internal state in encrypted form, for example by encrypting it with any one of a number of encryption techniques.
低電力動作状態を終了するよう求める要求を待つ間(「休眠状態を終了するか?1261」および「いいえ1261N」)、入出力デバイスは低電力動作状態(休眠状態1251)のままである。低電力動作状態を終了するよう求める要求を受け取り次第(はい1261Y)、入出力デバイスは、保存/復元メモリから保存/復元メモリに保存された内部状態の全部または任意の部分を復元する(保存/復元メモリから内部状態を復元する1271)。入出力デバイスは次いで、高電力動作状態を開始し、入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで折り返して戻る(アクティブな動作状態1221)。様々な実施形態において、入出力デバイスは、例えば、暗号化技術のうちのいずれか1つにより解読することによって、暗号化された形から内部状態の全部または任意の部分を復元する。The I/O device remains in the low-power operating state (dormant state 1251) while waiting for a request to exit the low-power operating state ("Exit Dormant State? 1261" and "No 1261N"). Upon receiving a request to exit the low-power operating state (Yes 1261Y), the I/O device restores all or any portion of the internal state saved in the Save/Restore memory from the Save/Restore memory (Restore Internal State from Save/Restore Memory 1271). The I/O device then enters a high-power operating state, and processing within the I/O device then wraps around (active operating state 1221). In various embodiments, the I/O device restores all or any portion of the internal state from the encrypted form, for example, by decrypting it with any one of the encryption techniques.
様々な実施形態において、休眠状態は、電源オフ状態、電力ダウン状態、低減電力状態、低電力状態、低めの電力状態、休止状態、入出力デバイスの全部または任意の部分が電源オフされ、若しくは電力ダウンされた状態、または入出力デバイスが完全に(例えばアクティブに)動作しているときよりも少ない電力を消費する任意の動作状態のうちの任意の1若しくはそれ以上である。様々な実施形態において、休眠状態を終了することは、例えば、NVMへのアクセスによる情報の再構築に起因する待ち時間の代償(および/または電力コスト)を課し、(NVMへのアクセスによる再構築の代わりに)保存/復元メモリから読み取ることにより情報を復元することは、待ち時間の代償(および/または電力コスト)を低減させる。様々な実施形態において、内部状態の全部または任意の部分は(例えば、「内部状態を保存/復元メモリに保存する1241」と関連付けられた処理によって)保存される。ある実施形態では、ドライバが、ホストメモリの一部分を、保存/復元メモリとして使用されるように割り当てる。In various embodiments, the dormant state is any one or more of a power off state, a power down state, a reduced power state, a low power state, a lower power state, a hibernation state, a state in which all or any portion of an I/O device is powered off or down, or any operating state in which an I/O device consumes less power than when fully (e.g., actively) operating. In various embodiments, exiting a dormant state imposes a latency cost (and/or power cost) due, for example, to reconstructing information by accessing the NVM, and restoring information by reading from the save/restore memory (instead of reconstructing by accessing the NVM) reduces the latency cost (and/or power cost). In various embodiments, all or any portion of the internal state is saved (e.g., by an operation associated with "Save Internal State to Save/Restore Memory 1241"). In some embodiments, the driver allocates a portion of host memory to be used as the save/restore memory.
組み合わせ動作
図13Aおよび図13Bに、それぞれ、入出力デバイスとコンピューティングホストとの相互運用1300Aおよび1300Bとして、入出力デバイス(記憶デバイスなど)とコンピューティングホストとの相互運用の一実施形態の流れ図をまとめて示す。本明細書の別の箇所では、これら2つの図をまとめて記述し、入出力デバイスとコンピューティングホストとの相互運用1300と呼ぶ。入出力デバイスとコンピューティングホストとの相互運用1300は、概念的には、一度に1つのスティッキーなヒント、ホスト提供の位置情報、ホスト・シャドウ・マップ情報のホストおよび入出力デバイスの更新、ならびに入出力デバイス内部状態の保存および復元といった、図6から図12によって示される1若しくはそれ以上の機能を組み合わせた様々な実施形態を示すものである。 Combined Operation Figures 13A and 13B collectively show flow diagrams of one embodiment of I/O device (e.g., storage device) interoperation with a computing host as I/O device interoperation with a
やはり本明細書の別の箇所では、ホスト動作1310Aおよびホスト動作1310Bをまとめてホスト動作1310と呼び、デバイス動作1320Aおよびデバイス動作1320Bをまとめてデバイス動作1320と呼ぶ。ホスト動作1310は、図1Bのホスト102といったコンピューティングホストによって行われる動作を記述している。デバイス動作1320は、図1BのSSD101のインスタンスのうちのいずれか1つといった入出力デバイス(記憶デバイスなど)によって行われる動作を記述している。Also elsewhere in this specification, host operations 1310A and 1310B are collectively referred to as host operations 1310, and device operations 1320A and 1320B are collectively referred to as device operations 1320. Host operations 1310 describe operations performed by a computing host, such as host 102 of FIG. 1B. Device operations 1320 describe operations performed by an input/output device (e.g., a storage device), such as any one of the instances of
処理は(図6などの場合と同様に)入出力デバイスの非アクティブ状態から開始する(入出力デバイス電源オフ/休眠またはリセット状態1301)。処理は、入出力デバイスが、例えば、電源オンされ、動作および/またはアクティブ状態に遷移し、あるいはリセットを終了することによってアクティブになるときに次に進む。次いでホスト(アクティブ化する1301H)は、図1Bのシャドウマップ108といったシャドウマップのすべてのエントリを情報がないとマークする(シャドウマップをすべて無効として初期化する1311)。入出力デバイス(アクティブ化する1301D)は動作の準備を行う(入出力デバイス初期化、およびメモリからの条件付き状態復元1321)。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、準備は、任意選択で、および/または条件付きで、保存/復元メモリ(図1Bの(任意選択の)カードメモリ112Cなど)から内部状態の全部または一部を復元することを含む。様々な実施形態において、入出力デバイスは、例えば、複数の暗号化技術のうちのいずれか1つにより解読することによって、暗号化された形から内部状態の全部または任意の部分を復元する。ある実施形態では、ホストは解読の全部または任意の部分を行う。The process starts with the I/O device in an inactive state (I/O device powered off/sleep or reset state 1301) (as in FIG. 6, etc.). The process proceeds when the I/O device becomes active, for example by being powered on and transitioning to an operational and/or active state, or by coming out of reset. The host (activate 1301H) then marks all entries in a shadow map, such as shadow map 108 of FIG. 1B, as empty (initialize all shadow maps as invalid 1311). The I/O device (activate 1301D) prepares for operation (I/O device initialization and conditional state restore from memory 1321). In certain embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the preparation includes optionally and/or conditionally restoring all or a portion of the internal state from a save/restore memory (such as the (optional)
次いで入出力デバイスは、ホストがシャドウマップをさらに初期化し、および/または更新する(シャドウマップを初期化/更新する1312)ために、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、(ホストへ1322Hとして)ホストに、ある場合、更新されたマップ情報を伝える(ホストにローカルマップ(全部または更新)を送る1322)。場合によっては、入出力デバイスに電源投入した後の1322/1312までの最初のパスは、概念的には、ローカルマップ(図1Bのマップ141など)の全イメージを送ることによりシャドウマップを初期化することに対応し、1322/1312までの後続のパスは、概念的には、入出力デバイスによるコマンドの実行、および/または再利用といった入出力デバイスの独立のアクティビティの結果としてシャドウマップを(増分的に)更新することに対応する。場合によっては、シャドウマップは、LBAがホストによって参照された結果として更新される。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、マップ更新のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を無視する。例えば、ホストは、再利用アクティビティに起因して生じる特定のマップ更新を、例えば、特定のマップ更新が、ホストが特定のマップ更新を処理する前の書き込みに起因してホストが無効にするシャドウ・マップ・エントリに対応するときなどに無視する。The I/O device then optionally and/or selectively communicates updated map information, if any, to the host (as To Host 1322H) for the host to further initialize and/or update the shadow map (Initialize/Update Shadow Map 1312). In some cases, the first pass to 1322/1312 after powering up the I/O device conceptually corresponds to initializing the shadow map by sending a full image of the local map (such as
ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスは、初期化またはコマンドの直接関連したものではない入出力デバイスによる処理に応答して、ホストに1若しくはそれ以上の更新を伝える。例えば、入出力デバイスが入出力デバイスNVMの領域を再利用するときに、LBAと入出力デバイスNVM内の位置との間のマッピングへの0若しくはそれ以上の変更が生じる。入出力デバイスは、ある場合、マッピング変更を、1322の場合と同様に、1若しくはそれ以上のマップ更新としてホストに伝える。In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the I/O device communicates one or more updates to the host in response to processing by the I/O device that is not directly related to an initialization or command. For example, when the I/O device reclaims space in the I/O device NVM, zero or more changes to the mapping between LBAs and locations within the I/O device NVM occur. The I/O device communicates the mapping changes, if any, to the host as one or more map updates, similar to those in 1322.
入出力デバイス内の処理は次いで、入出力デバイスが低電力動作状態を開始するよう求める要求(休眠1322S)を受け取るか、それともコマンド(コマンド1322C)を受け取るかに応じて進む。低電力動作状態を開始するよう求める要求を受け取り次第、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、内部状態の全部または任意の部分を保存/復元メモリに保存する(休眠要求を受け取る、およびメモリに状態を保存する1323)。様々な実施形態において、入出力デバイスは、内部状態の全部または任意の部分を、例えば、暗号化技術のうちのいずれかにより暗号化することによって、暗号化された形で保存する。ある実施形態では、ホストは暗号化の全部または任意の部分を行う。入出力デバイスは次いで、低電力動作状態を開始し、戻ってアクティブ化を待つ(入出力デバイス電源オフ/休眠またはリセット状態1301)。コマンドの受け取りは、以下で、(コマンド/(ヒント)(およびシャドウマップ情報)を受け取る1325)に関連して説明する。Processing within the I/O device then proceeds depending on whether the I/O device receives a request (sleep 1322S) or a command (
シャドウマップの初期化を完了した後で、ホストは、例えば、図1BのOS105、ドライバ107、およびアプリケーション109のうちの任意の1若しくはそれ以上により、コマンドを生成し(生成する1312G)、任意選択でヒントと共に、またはヒントを使用して生成する(コマンドを生成する(任意選択のヒント)1313)。ホストは次いで、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、コマンドは、ホストが、ある場合、シャドウマップから入出力デバイスに有効な情報を提供することに有用性があるようなものであるかどうか決定する(シャドウマップを参照するか?1314R)。いいえ(いいえ1314RN)である場合には、ホストは、いかなるシャドウマップ情報もなしで入出力デバイスに(任意選択でヒントと共に、またはヒントを使用して)コマンドを提供する(コマンド/(ヒント)を、シャドウマップ情報なしで送る1315N)。例えば、ある実施形態では、コマンドが読み出しである場合には、場合によっては、ホストが位置情報を提供することに有用性があり、よって、入出力デバイスが、位置情報を決定することを省略し、読み出しデータを低減された待ち時間で提供することが可能になる。引き続きこの例について、コマンドが書き込みである場合には、場合によっては、ホストが位置情報を提供することにほとんど、または全く有用性がない。というのは、入出力デバイスに位置情報を提供することはほとんどまたは全く性能上の利益をもたらさず、位置情報は、書き込み処理の性能にとって相対的に重要でないからである。別の例として、ある実施形態では、コマンドが単一のLBAを参照する場合には、場合によっては、ホストが位置情報を提供することに有用性があり、よって、入出力デバイスが、位置情報を決定することを省略し、コマンドの待ち時間を低減させることを可能にする。引き続き別の例について、コマンドが複数の連続したLBAを参照する場合には、場合によっては、ホストが位置情報を提供することにほとんど有用性がない。というのは、入出力デバイスに位置情報を提供することはほとんどまたは全く性能上の利益をもたらさず、コマンドの平均待ち時間は、入出力デバイスが位置情報を決定するか否かの影響を相対的に受けにくいからである。After completing the initialization of the shadow map, the host, e.g., by any one or more of
ホストが入出力デバイスに有効なシャドウマップ情報を提供することに有用性がある場合(はい1314RY)には、ホストは、コマンドが関連するLBAについてシャドウマップ内に有効なエントリがあるかどうか検査する(シャドウマップの有効なエントリか?1314V)。有効なエントリが見つからない(いいえ1314VN)場合には、ホストは入出力デバイスに、LBAと共に(任意選択でヒントと共に、またはヒントを使用して)、シャドウマップ情報なしでコマンドを発行する(コマンド/(ヒント)を、シャドウマップ情報なしで送る1315N)。有効なエントリが見つかる(はい1314VY)場合には、ホストは入出力デバイスに、有効なエントリからのシャドウマップ情報と共にコマンドを発行し、任意選択で、コマンドを発行するときにLBAを省略する(コマンド/(ヒント)およびシャドウマップ情報を送る1315M)。ある実施形態では、1314Rが省略され、シャドウマップは、有効なエントリの有無について非選択的に検査され(例えば、処理は1313から1314Vに進み)、あるいは、シャドウマップは有効なエントリの有無について全く検査されない(例えば、処理は1313から1315Nに進む)。If it would be useful for the host to provide valid shadow map information to the I/O device (Yes 1314RY), the host checks whether there is a valid entry in the shadow map for the LBA to which the command pertains (Valid Entry in Shadow Map? 1314V). If no valid entry is found (No 1314VN), the host issues the command to the I/O device with the LBA (optionally with or using a hint) and without the shadow map information (Send Command/(Hint) Without Shadow Map Info 1315N). If a valid entry is found (Yes 1314VY), the host issues the command to the I/O device with the shadow map information from the valid entry, optionally omitting the LBA when issuing the command (Send Command/(Hint) and Shadow Map Info 1315M). In some embodiments, 1314R is omitted and the shadow map is non-selectively checked for valid entries (e.g., processing proceeds from 1313 to 1314V), or the shadow map is not checked for valid entries at all (e.g., processing proceeds from 1313 to 1315N).
コマンド、任意選択のLBA、および任意選択のヒント情報は、1315Mに関連した処理からにせよ、1315Nに関連した処理からにせよ、ホストから入出力デバイスに(デバイスへ1315D)提供される(送る1315S)。コマンドが入出力デバイスに提供された後で、ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、コマンドおよび/または他の基準に従ってコマンドに関連したLBAについてのシャドウ・マップ・エントリをマークする(シャドウマップ情報を選択的に変更する1316)。ホストの処理は次いで、入出力デバイスからの状況を待つ。The command, optional LBA, and optional hint information are provided (send 1315S) from the host to the I/O device (to
コマンドを、LBAのうちの0若しくはそれ以上、シャドウマップ(位置など)、および任意選択のヒント情報と共に受け取り次第(コマンド/(ヒント)(およびシャドウマップ情報)を受け取る1325)、入出力デバイスは、シャドウマップ情報の関連性および存在を決定する(シャドウマップ情報は?1326)。シャドウマップ情報が受け取ったコマンドに関して利益を提供しない場合(不要1326U)には、入出力デバイスは現在のモードで任意選択のヒント情報と共に、または任意選択のヒント情報を使用してコマンドを処理する(現在のモードでコマンド/(ヒント)を処理する1328)。ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスは、ホストからは利用できない情報を有し、入出力デバイスは、ホストがシャドウマップからの情報を提供するときでさえも、ローカルマップにアクセスする。例えば、シャドウマップは完全には初期化されず、デバイスは、ホストにない切り捨て情報を有する。別の例では、入出力デバイスは、入出力デバイスNVMの一部分の再利用および消去などが原因で、シャドウマップ情報が不完全である(例えば、あるLBAの情報が欠けている)と決定する。例えば、入出力デバイスは、予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンド内の位置情報により、入出力デバイスNVMの対応する部分が消去されていると決定し、その位置情報を使用する代わりに、入出力デバイスはローカルマップにアクセスして位置情報を取得する。現在のモードは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、コマンドが(ある場合)どのLBAに関連するかの関数であり、さらに任意選択で、および/または選択的に、以前に受け取った特定のヒントモードを開始/終了するコマンドの関数である。Upon receiving a command along with zero or more of the LBAs, the shadow map (e.g., location), and optional hint information (Receive Command/(Hint) (and Shadow Map Information) 1325), the I/O device determines the relevance and presence of the shadow map information (Shadow Map Information? 1326). If the shadow map information does not provide any benefit with respect to the received command (Not Required 1326U), the I/O device processes the command along with or using the optional hint information in the current mode (Process Command/(Hint) in Current Mode 1328). In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios, the I/O device has information that is not available from the host, and the I/O device accesses a local map even when the host provides information from the shadow map. For example, the shadow map is not fully initialized and the device has truncated information that is not in the host. In another example, the I/O device determines that the shadow map information is incomplete (e.g., information for certain LBAs is missing), such as due to the reuse and erasure of portions of the I/O device NVM. For example, the I/O device may determine that the corresponding portion of the I/O device NVM has been erased due to location information in a pre-mapped read command, and instead of using that location information, the I/O device accesses a local map to obtain the location information. The current mode is optionally and/or selectively a function of which LBA (if any) the command relates to, and further optionally and/or selectively a function of a previously received command to enter/exit a particular hint mode.
シャドウマップ情報が受け取ったコマンドに関して有用であり、シャドウマップ情報がホストによって提供された場合(はい1326Y)には、入出力デバイスは、現在のモードでの任意選択のヒント情報および提供されたシャドウマップ情報と共に、またはそれらを使用してコマンドを処理する(現在のモードでコマンド/(ヒント)を処理する1328)。シャドウマップ情報がホストによって提供されておらず、コマンドの処理がマップ情報に依存する場合(いいえ1326N)には、入出力デバイスは、ローカルマップ(図1Bのマップ141など)にアクセスして、コマンドを実行するときに使用すべき位置情報といった情報を決定する(ローカルマップを参照する1327)。次いで入出力デバイスは、現在のモードでの任意選択のヒント情報およびローカルマップからのマップ情報と共に、またはそれらを使用してコマンドを処理する(現在のモードでコマンド/(ヒント)を処理する1328)。If shadow map information is useful for the received command and shadow map information was provided by the host (
コマンドを処理した後で、入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ホストに(ホストへ1329H)結果情報を返す(状況を送る1329)。次いで入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、ホストに、ある場合、更新されたマップ情報を伝え(ホストにローカルマップ(全部または更新)を送る1322)、低電力動作状態を開始するよう求める要求またはコマンドを待つ。ホストの処理は、状況を待って、状況を受け取り(状況を受け取る1319)、次いで、ある場合、(「ホストへ1322H」として)入出力デバイスからシャドウマップへのマップ更新を待つ(シャドウマップを初期化/更新する1312)。After processing the command, the I/O device optionally and/or selectively returns result information (send status 1329) to the host (To
(カードメモリを有する入出力カード、例えば、図1Bの(任意選択の)カードメモリ112Cをシャドウマップ用のストレージとして使用する入出力カード116などを有するある実施形態といった)ある実施形態および/または使用シナリオでは、入出力デバイスは、ホストの関与なしで、シャドウマップとしてカードメモリを使用する。入出力デバイスは、シャドウマップを初期化し、シャドウマップに、ある場合、マップ更新を適用する。入出力デバイスは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、(ローカルマップの代わりに、および/またはローカルマップに加えて)シャドウマップにアクセスして位置情報を取得する。In some embodiments and/or usage scenarios (such as some embodiments having an I/O card with card memory, such as I/O card 116 in FIG. 1B that uses (optional)
図6から図13A/図13Bのうちの1若しくはそれ以上によって全部または一部が説明される実施形態といった様々な実施形態において、様々なホストコマンドは、以下の表で記載するように、シャドウ・マップ・エントリ状態に応じたホスト処理をもたらす。表では、シャドウ・マップ・エントリ状態が「有効」であるときの「書き込み」コマンドのコマンドパラメータとしての「位置、長さ、範囲」といった、イタリック体表記の要素は任意選択である。In various embodiments, such as those described in whole or in part by one or more of Figures 6 through 13A/13B, various host commands result in host processing depending on the shadow map entry state, as described in the following table. In the table, elements in italics are optional, such as "position, length, range" as command parameters for a "write" command when the shadow map entry state is "valid."
表に関連した例として、LBAが切り捨てられていないことを指示する有効なシャドウ・マップ・エントリを有するLBAに関連した読み出しコマンドを考える。ホストは、有効なシャドウ・マップ・エントリからの「位置」のパラメータと共に「予めマッピングされた読み出し」コマンドによって有効なシャドウ・マップ・エントリからの情報を伝える。任意選択で、ホストは、有効なシャドウ・マップ・エントリからの「長さ」および/または「範囲」情報も伝える。入出力デバイスに「位置」、「長さ」、および/または「範囲」の情報を提供することにより、通常は行われるはずのローカルマップへのアクセスが省略されるため、入出力デバイス内の処理が低減される。別の例として、LBAが削減されたことを指示する有効なシャドウ・マップ・エントリを有するLBAに関連した読み出しコマンドを考える。(データが切り捨てられているために)読み取るべき有用なデータがないため、ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスにコマンドが送られず(「動作なし」)、よって、入出力デバイスによる無益な処理が低減され、および/または省かれる。別の実施形態では、たとえLBAが削減されたことをシャドウ・マップ・エントリが指示していても、読み出しコマンドが入出力デバイスに送られる(「読み出し(LBA)」)。入出力デバイスに読み出しコマンドを送ることにより、(ホストではなく)入出力デバイスが、削減されたLBAの読み出しのために返すべきデータを決定することをできるようになる。別の実施形態では、読み出しコマンドは、シャドウ・マップ・エントリからの「長さ」および/または「範囲」の情報と共に提供される。「長さ」および/または「範囲」の情報は、複数の切り捨てタイプのうちの1つを符号化しており、入出力デバイスは、少なくとも一部は符号化に基づいて読み出しのために返すべきデータを決定する。As an example related to the table, consider a read command associated with an LBA that has a valid shadow map entry indicating that the LBA has not been truncated. The host conveys information from the valid shadow map entry via a "premapped read" command along with a "location" parameter from the valid shadow map entry. Optionally, the host also conveys "length" and/or "range" information from the valid shadow map entry. By providing the I/O device with "location", "length", and/or "range" information, processing within the I/O device is reduced because accesses to the local map that would normally be made are omitted. As another example, consider a read command associated with an LBA that has a valid shadow map entry indicating that the LBA has been truncated. Since there is no useful data to read (because the data has been truncated), in one embodiment, no command is sent to the I/O device ("no action"), thereby reducing and/or eliminating futile processing by the I/O device. In another embodiment, a read command is sent to the I/O device ("Read (LBA)") even though the shadow map entry indicates that the LBA has been pruned. Sending the read command to the I/O device allows the I/O device (rather than the host) to determine the data to return for a read of the pruned LBA. In another embodiment, the read command is provided along with "length" and/or "extent" information from the shadow map entry. The "length" and/or "extent" information encodes one of a number of truncation types, and the I/O device determines the data to return for the read based at least in part on the encoding.
以上の説明において、コマンドはホストから入出力デバイスに送られる(例えば発行される)ものとして説明され(例えば、図6の621、図7の721、図8の821、図9の931、図11の1161、および図13A/図13Bの1315S/1325)、結果は入出力デバイスからホストに返されるものとして説明されている(例えば、図6の661、図7の761、図8の881、図9の971および991、図10の1021、ならびに図13A/図13Bの1329/1319および1322/1312)。様々な実施形態および/または使用シナリオにおいて、コマンドはプログラムされた入出力、DMA、エントリによって作業待ち行列に送られ、1若しくはそれ以上のコマンド、モード、ならびに/または入出力デバイスの構成レジスタおよび/若しくは構成ページに書き込まれ、ホストから入出力デバイスに「プッシュされ」、ホストから入出力デバイスによって、また、ホストから入出力デバイスへのコマンドの通信を可能にする他の技術によって「プルされる」。様々な実施形態および/または使用シナリオにおいて、結果は、ホストメモリ、DMA、エントリへの入出力デバイスアクセスによって完了待ち行列に送られ、入出力デバイスの1若しくはそれ以上の状況レジスタおよび/またはログページから読み取られ、入出力デバイスからホストに「プッシュされ」、入出力デバイスからホストによって、また、入出力デバイスからホストへの結果の通信を可能にする他の技術によって「プルされる」。ある実施形態では、複数の結果が完了待ち行列へとグループ化され、ホストは、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、(例えば、割り込み機構によって)一度に1コマンドよりも大きい粒度で結果を知らされる。ある実施形態では、ホストがマップ更新を要求したことに応答して、例えば、ホストが入出力デバイスのログページを読み出し、それに応答して入出力デバイスがホストに1若しくはそれ以上のマップ更新を送ることによって、更新マップ情報が入出力デバイスによってホストに提供される。
以上で説明した実施形態のうちのいくつかでは、(例えば、図7の741および/または781、図8の842、852、および/または872、ならびに図13A/図13Bの1328のうちの任意の1若しくはそれ以上の処理に際して、および/またはこれに関連して)いくつかのスティッキーなヒントが、任意選択で、および/または選択的に、1若しくはそれ以上のマップエントリに、また任意選択で、1若しくはそれ以上のシャドウ・マップ・エントリに記録される。例えば、あるデータタイプのヒントはスティッキーなヒントとして使用され、ヒントと共に供給されるLBAのマップエントリに記録され、対応するシャドウマップ更新が、任意選択で、および/または選択的に提供される。後続のそのLBAの参照は、LBAのマップエントリに記録されたそのデータタイプのヒントに従って処理される。スティッキーなヒントとして使用可能なヒントの別の例は、データアクセスタイプのヒント、データ順序付けのヒント、データ関係のヒント、およびデータ宛先のヒントである。In some of the embodiments described above (e.g., during and/or in conjunction with processing any one or more of 741 and/or 781 of FIG. 7, 842, 852, and/or 872 of FIG. 8, and 1328 of FIG. 13A/FIG. 13B), some sticky hints are optionally and/or selectively recorded in one or more map entries and optionally in one or more shadow map entries. For example, a data type hint is used as a sticky hint and recorded in the map entry of the LBA provided with the hint, and a corresponding shadow map update is optionally and/or selectively provided. Subsequent references to that LBA are processed according to the data type hint recorded in the map entry of the LBA. Other examples of hints that can be used as sticky hints are data access type hints, data ordering hints, data relationship hints, and data destination hints.
様々な実施形態では、例えば、図6から図13A/13Bで説明した動作および/または機能の全部またはいずれかの部分が、例えば、1若しくはそれ以上の状態機械によって実施される。状態機械の実施態様の例には、ハードウェア(論理ゲートおよび/若しくは回路、専用状態機械回路、配線制御回路など)、ソフトウェア(ファームウェアやマイクロコードなど)、またはハードウェアとソフトウェアの組み合わせが含まれる。一部の実施形態では、状態機械のうち1若しくはそれ以上が、少なくとも部分的にファームウェア、ドライバ、および/またはアプリケーションによって実施される。様々な実施形態において、状態機械のうち1若しくはそれ以上が、一部が図1AのSSDコントローラ100によって、一部がCPUコア172によって実行されるファームウェアによって、一部が図1Bのファームウェア106によって、一部がドライバ107によって、および/または一部がアプリケーション109によって実施される。In various embodiments, all or any portion of the operations and/or functions described, for example, in FIGS. 6 through 13A/13B are implemented, for example, by one or more state machines. Examples of state machine implementations include hardware (e.g., logic gates and/or circuits, dedicated state machine circuits, hardwired control circuits, etc.), software (e.g., firmware and microcode), or a combination of hardware and software. In some embodiments, one or more of the state machines are implemented, at least in part, by firmware, drivers, and/or applications. In various embodiments, one or more of the state machines are implemented, in part, by
様々な実施形態では、図6から図13A/13B説明した動作および/または機能の全部またはいずれかの部分が、ハードウェアおよび/またはファームウェアの技法の任意の組み合わせにより、例えば、図1Aのコマンド管理173、変換管理177、および/またはマップ141のうちいずれか1若しくはそれ以上によって、その制御下で、および/またはそれに従って実施される。In various embodiments, all or any portion of the operations and/or functionality described in Figures 6 through 13A/13B are performed by any combination of hardware and/or firmware techniques, such as by, under the control of, and/or in accordance with any one or more of
様々な実施形態において、HBAはホストの要素(1若しくはそれ以上のプロセッサおよび1若しくはそれ以上のメモリなど)を、入出力デバイス、例えばSATAドライブといった入出力記憶デバイスなどに接続する。HBAのプロセッサおよび/またはメモリへの接続は、少なくとも部分的に1若しくはそれ以上の入出力デバイス通信インターフェース、バス、および/またはチャネル(PCIeインターフェースなど)を介したものである。プロセッサのうちのあるものは、入出力デバイスと通信するOS、ドライバ、および/またはアプリケーションのソフトウェア要素を実行する。ある実施形態では、ホストの要素とHBAとの間のトランスポートはAHCIに準拠し、T13準拠ATAコマンドがHBAを介して入出力デバイスのSSDのSATAまたはPCIeインターフェースに渡される。別の実施形態では、ホストの要素とHBAとの間のトランスポートはNVMエクスプレスに準拠し、T13準拠ATAコマンドと類似した少なくともいくつかの属性を有するコマンドがHBAを介して入出力デバイスのSSDのPCIeインターフェースに渡される。ある実施形態ではHBAはホストに含まれ、別の実施形態ではHBAは入出力デバイスに含まれる。ある実施形態ではHBAは省かれ、入出力デバイスは(明示的なHBAなしで)1若しくはそれ以上の入出力デバイス通信インターフェース、バス、および/またはチャネル(PCIeインターフェースなど)に接続される。In various embodiments, the HBA connects host elements (e.g., one or more processors and one or more memories) to I/O devices, such as I/O storage devices, e.g., SATA drives. The HBA's connection to the processors and/or memory is at least partially via one or more I/O device communication interfaces, buses, and/or channels (e.g., PCIe interfaces). Some of the processors execute software elements of the OS, drivers, and/or applications that communicate with the I/O devices. In one embodiment, the transport between the host elements and the HBA is AHCI compliant, with T13 compliant ATA commands being passed through the HBA to the SATA or PCIe interface of the SSD of the I/O device. In another embodiment, the transport between the host elements and the HBA is NVM Express compliant, with commands having at least some attributes similar to T13 compliant ATA commands being passed through the HBA to the PCIe interface of the SSD of the I/O device. In one embodiment, the HBA is included in the host, and in another embodiment, the HBA is included in the I/O device. In some embodiments, the HBA is omitted and the I/O devices are connected (without an explicit HBA) to one or more I/O device communication interfaces, buses, and/or channels (e.g., PCIe interfaces).
例えば、図1Bのコンテキストでは、ホスト102は、ホスト上で走っているソフトウェア(例えばOS105、ドライバ107、および/またはアプリケーション109)と(例えば、ホストインターフェース111に含まれるSATA互換ホストインターフェースを有する)SSD101との間の通信を可能にするHBAを含む。通信は、ソフトウェアからSSDへのコマンドの受け渡しを含む。コマンドのトランスポートはAHCIを介したものであり、T13準拠ATAコマンドがSSDのSATAインターフェースに提供される。よって、図6から図13A/図13Bに関して説明したようなコマンドおよび/または結果は、AHCIトランスポートによって受け渡される。For example, in the context of FIG. 1B, host 102 includes an HBA that enables communication between software running on the host (e.g.,
別の例として、図1Bのコンテキストでは、ホスト102は、スイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103との通信を可能にするチップセットを含み、中間インターフェース104および外部インターフェース110はPCIe互換である(例えば、SSD101はホストインターフェース111に含まれるPCIeインターフェースを有する)。チップセットおよびスイッチ/ファブリック/中間コントローラ103は、ホストのOS、ドライバ、および/またはアプリケーションソフトウェアとSSD101との間の、コマンドの受け渡しを含む通信を可能にする。コマンドのトランスポートはNVMエクスプレスを介したものであり、T13準拠ATAコマンドに類似した少なくともいくつかの属性を有するコマンドがSSDのPCIeインターフェースに提供される。よって、図6から図13A/図13Bに関して説明したようなコマンドおよび/または結果は、NVMエクスプレストランスポートによって受け渡される。As another example, in the context of FIG. 1B, the host 102 includes a chipset that enables communication with the switch/fabric/intermediate controller 103, and the intermediate interface 104 and
実施技法の例
ある実施形態では、入出力デバイスまたはその一部、例えば、(コンピューティングホストなどの)ホスト、例えば、フラッシュメモリ、コンピューティングホスト・フラッシュ・メモリ・コントローラ、および/またはSSDコントローラ(例えば図1AのSSDコントローラ100)、ならびにプロセッサ、マイクロプロセッサ、システム・オン・チップ、特定用途向け集積回路、ハードウェアアクセラレータ、または前述の動作の全部または部分を提供する他の回路と相互動作する入出力デバイスのSSDコントローラよって行われる動作の全部またはいずれかの部分の様々な組み合わせが、コンピュータシステムによる処理と適合する仕様によって指定される。仕様は、様々な記述、例えば、ハードウェア記述言語、回路記述、ネットリスト記述、マスク記述、またはレイアウト記述に従ったものである。記述の例には、Verilog、VHDL、SPICE、SPICEの変形、例えば、PSpice、IBIS、LEF、DEF、GDS−II、OASIS、または他の記述が含まれる。様々な実施形態では、処理は、1若しくはそれ以上の集積回路上に含めるのに適する論理および/または回路を生成し、検証し、または指定するための解釈、コンパイル、シミュレーション、および合成の任意の組み合わせを含む。各集積回路は、様々な実施形態によれば、様々な技法に従って設計することができ、および/または製造することができる。技法には、プログラマブルな技法(例えば、フィールド若しくはマスク・プログラマブル・ゲート・アレイ集積回路)、セミカスタムの技法(例えば、全部若しくは一部がセルベースの集積回路)、およびフルカスタムの技法(例えば、実質的に専門化された集積回路)、それらの任意の組み合わせ、または集積回路の設計および/若しくは製造と適合する任意の他の技法が含まれる。 Example Implementation Techniques In an embodiment, various combinations of all or any portion of operations performed by an I/O device or a portion thereof, e.g., a host (such as a computing host), e.g., a flash memory, a computing host flash memory controller, and/or an SSD controller (e.g.,
ある実施形態では、命令のセットを記憶しているコンピュータ可読媒体によって記述される動作の全部または部分の様々な組み合わせが、1若しくはそれ以上のプログラム命令の実行および/若しくは解釈によって、1若しくはそれ以上のソースおよび/若しくはスクリプト言語命令文の解釈および/若しくはコンパイルによって、または、プログラミングおよび/若しくはスクリプティング言語命令文で表現された情報をコンパイルし、変換し、および/または解釈することによって生成されるバイナリ命令の実行によって実行される。命令文は任意の標準のプログラミングまたはスクリプティング言語(例えば、C、C++、Fortran、Pascal、Ada、Java(登録商標)、VBscript、Shell)と適合する。プログラム命令、言語命令文、またはバイナリ命令のうち1若しくはそれ以上が、任意選択で、1若しくはそれ以上のコンピュータ可読記憶媒体要素上に記憶される。様々な実施形態では、プログラム命令の一部、全部、または様々な部分が、1若しくはそれ以上の関数、ルーチン、サブルーチン、インラインルーチン、プロシージャ、マクロ、またはそれらの部分として実現される。In some embodiments, various combinations of all or portions of the operations described by the computer readable medium storing a set of instructions are performed by executing and/or interpreting one or more program instructions, by interpreting and/or compiling one or more source and/or scripting language statements, or by executing binary instructions generated by compiling, translating, and/or interpreting information expressed in programming and/or scripting language statements. The statements are compatible with any standard programming or scripting language (e.g., C, C++, Fortran, Pascal, Ada, Java, VBscript, Shell). One or more of the program instructions, language statements, or binary instructions are optionally stored on one or more computer readable storage medium elements. In various embodiments, some, all, or various portions of the program instructions are implemented as one or more functions, routines, subroutines, inline routines, procedures, macros, or portions thereof.
結論
ある特定の選択が、説明において、テキストおよび図面を作成するに際の単なる便宜のためになされており、別の指示がない限り、それらの選択は、それ自体で、前述の実施形態の構造または動作に関する追加情報を伝えるものと解釈すべきではない。選択の例には、図の符番に使用される呼称の特定の編成または割り当て、および実施形態の特徴および要素を識別し、参照するのに使用される要素識別子(コールアウトや数値識別子など)の特定の編成または割り当てが含まれる。 Conclusion Certain choices have been made in the description merely for convenience in producing text and figures, and unless otherwise indicated, those choices should not, in themselves, be construed as conveying additional information regarding the structure or operation of the described embodiments. Examples of choices include the particular organization or assignment of designations used in the figure numbers, and the particular organization or assignment of element identifiers (such as callouts or numeric identifiers) used to identify and reference features and elements of the embodiments.
「includes」または「including」という語は、開放型範囲の論理集合を記述する抽象概念として解釈されるべきことが明確に意図されており、後に続けて「within」という語が明示されない限り物理的包含を伝えるためのものではない。
前述の実施形態は、説明および理解の明確さのためにある程度詳細に説明されているが、本発明は提示した詳細だけに限定されるものではない。本発明の多くの実施形態がある。開示の実施形態は例示であり、限定ではない。 The words "includes" or "including" are expressly intended to be interpreted as an abstraction describing a logical collection of open-ended scope, and are not intended to convey physical inclusion unless explicitly followed by the word "within."
Although the foregoing embodiments have been described in some detail for clarity of explanation and understanding, the present invention is not limited to the details presented. There are many embodiments of the present invention. The disclosed embodiments are illustrative and not limiting.
説明と整合性を有する、構成、配置、および使用における多くの変形が可能であり、それらの変形は、発行される特許の特許請求の範囲内にあることが理解されるであろう。例えば、相互接続および機能ユニットのビット幅、クロック速度、および使用される技術の種類は、各構成要素ブロックにおける様々な実施形態に従って変わりうる。相互接続および論理に与えられた名称は、単なる例であり、説明した概念を限定するものと解釈すべきではない。フローチャートおよび流れ図のプロセス、動作、および機能要素の順序および配置は、様々な実施形態に従って変わりうる。また、特に別に指定しない限り、指定される値範囲、使用される最大値および最小値、または他の特定の仕様(例えば、フラッシュメモリ技術の種類、レジスタおよびバッファ内のエントリまたは段の数)は、単に前述の実施形態のものにすぎず、実施技術の改善および変更を追跡することが見込まれるものであり、限定として解釈すべきではない。It will be understood that many variations in configuration, arrangement, and use are possible that are consistent with the description, and that are within the scope of the claims of the patent to be issued. For example, the bit widths, clock speeds, and types of technology used of the interconnects and functional units may vary according to various embodiments in each component block. The names given to the interconnects and logic are merely examples and should not be construed as limiting the concepts described. The order and arrangement of the processes, operations, and functional elements of the flow charts and diagrams may vary according to various embodiments. Also, unless otherwise specified, any value ranges specified, maximum and minimum values used, or other specific specifications (e.g., type of flash memory technology, number of entries or stages in registers and buffers) are merely those of the embodiments described above, are expected to track improvements and changes in the implementation technology, and should not be construed as limitations.
当分野で公知の機能的に等価の技法を、様々なコンポーネント、サブシステム、動作、関数、ルーチン、サブルーチン、インラインルーチン、プロシージャ、マクロ、またはそれらの部分を実施するのに、前述の技法の代わりに用いることができる。また、実施形態の多くの機能的態様を、より高速な処理(以前にハードウェアにあった機能のソフトウェアへの移行を円滑化する)およびより高い集積密度(以前にソフトウェアにあった機能のハードウェアへの移行を円滑化する)の実施形態に依存する設計制約条件および技術傾向に応じて、選択的に、ハードウェア(おおむね専用の回路など)で、またはソフトウェアで(例えば、プログラムされたコントローラ若しくはプロセッサのある方式によって)実現できることも理解される。様々な実施形態の具体的な変形は、これに限定されるものではないが、分割の違い、フォームファクタおよび構成の違い、異なるオペレーティングシステムおよび他のシステムソフトウェアの使用、異なるインターフェース規格、ネットワークプロトコル、または通信リンクの使用、本明細書で説明した概念を、特定の用途の固有の技術的業務的制約条件に従って実施するときに予期されるべき他の変形を含む。Functionally equivalent techniques known in the art may be substituted for the techniques described above to implement various components, subsystems, operations, functions, routines, subroutines, in-line routines, procedures, macros, or portions thereof. It is also understood that many functional aspects of the embodiments may be selectively implemented in hardware (such as largely dedicated circuitry) or software (e.g., by some manner of programmed controller or processor) depending on design constraints and technology trends that depend on the embodiment for faster processing (facilitating the migration of functions previously in hardware to software) and higher integration density (facilitating the migration of functions previously in software to hardware). Specific variations of the various embodiments include, but are not limited to, different partitioning, different form factors and configurations, use of different operating systems and other system software, use of different interface standards, network protocols, or communication links, and other variations that should be expected when implementing the concepts described herein according to the unique technical and business constraints of a particular application.
各実施形態は、前述の各実施形態の多くの態様の最小限の実施に必要とされるものを大きく超えた詳細および環境的コンテキストと共に説明されている。ある実施形態は、残りの要素間での基本的協働を変更せずに開示の構成要素または機能を割愛することを当業者は理解するであろう。よって、開示の詳細の多くが前述の実施形態の様々な態様を実施するのに必要ではないことが理解される。残りの要素が先行技術と区別できる範囲内で、割愛される構成要素および特徴は本明細書で説明した概念を限定するものではない。Each embodiment is described with details and environmental context that go far beyond what is required for the minimal implementation of many aspects of each of the foregoing embodiments. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that certain embodiments omit disclosed components or features without altering the basic cooperation between the remaining elements. Thus, it will be appreciated that many of the disclosed details are not necessary to implement various aspects of the foregoing embodiments. To the extent that the remaining elements are distinguishable from the prior art, the omitted components and features are not intended to limit the concepts described herein.
設計におけるすべてのそのような変形は、前述の実施形態によって伝えられる教示に対する実質的な変更ではない。また、本明細書で説明した実施形態は、他のコンピューティング用途およびネットワーキング用途に幅広い適用性を有し、前述の実施形態の特定の用途または産業だけに限定されるものではないことも理解される。よって本発明は、発行される特許の特許請求の範囲内に包含されるあらゆる可能な改変形態および変形形態を含むものと解釈すべきである。Any such variations in design are not substantive changes to the teachings conveyed by the previously described embodiments. It is also understood that the embodiments described herein have broad applicability to other computing and networking applications and are not limited to the specific application or industry of the previously described embodiments. Thus, the present invention should be construed as including all possible modifications and variations encompassed within the scope of the claims of the issued patent.
Claims (32)
Translated fromJapaneseコンピューティングホストから送信された、仕様(specification)を有するコマンドを入出力デバイスで受け取る工程であって、当該仕様は複数の非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つを有し、当該非標準仕様は1若しくはそれ以上の非標準コマンド修飾子を有するものである、前記受け取る工程と、
前記仕様が前記非標準コマンド修飾子のうちの特定の1つを有することに応答して、前記特定の非標準コマンド修飾子に従って前記コマンドを実行する工程と
を有し、
前記非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つは複数のデータ宛先のうちの特定の1つを識別し、前記データ宛先は複数のデータバンドを有するものである、
方法。 1. A method comprising:
receiving, at an input/output device, a command having a specification sent from a computing host, the specification comprising at least one of a plurality of non-standard specifications, the non-standard specification comprising one or more non-standard command modifiers;
in response to the specification having a particular one of the non-standard command modifiers, executing the command in accordance with the particular non-standard command modifier;
At least one of the non-standard specifications identifies a particular one of a plurality of data destinations, the data destination having a plurality of data bands.
method.
コンピューティングホストで、入出力デバイスに仕様を有するコマンドを提供する工程であって、当該仕様は複数の非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つを有し、当該非標準仕様は1若しくはそれ以上の非標準コマンド修飾子を有するものである、前記提供する工程を有し、
前記仕様が前記非標準コマンド修飾子のうちの特定の1つを有することに応答して、前記入出力デバイスは前記特定の非標準コマンド修飾子に従って前記コマンドを実行し、
前記非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つは複数のデータ宛先のうちの特定の1つを識別し、前記データ宛先は複数のデータバンドを有するものである、
方法。 1. A method comprising:
providing, at a computing host, a command having a specification to an input/output device, the specification comprising at least one of a plurality of non-standard specifications, the non-standard specification having one or more non-standard command modifiers;
in response to the specification having a particular one of the non-standard command modifiers, the input/output device executes the command in accordance with the particular non-standard command modifier;
At least one of the non-standard specifications identifies a particular one of a plurality of data destinations, the data destination having a plurality of data bands.
method.
コンピュータ、
ワークステーションコンピュータ、
サーバコンピュータ、
ストレージサーバ、
パーソナルコンピュータ(PC)、
ラップトップコンピュータ、
ノートブックコンピュータ、
ネットブックコンピュータ、
携帯情報端末(PDA)、
メディアプレーヤ、
メディアレコーダ、
デジタルカメラ、
セルラハンドセット、
コードレス電話機ハンドセット、および
電子ゲーム
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を有するものである方法。 7. The method of claim 6, wherein the computing host comprises:
computer,
Workstation computers,
Server computer,
Storage servers,
Personal computers (PCs),
Laptop computers,
Notebook computers,
Netbook Computer,
Personal digital assistants (PDAs),
Media player,
Media Recorder,
Digital cameras,
Cellular handsets,
The method comprises one or more of: a cordless telephone handset; and an electronic game.
コンピューティングホストから送信された、仕様を有するコマンドを入出力デバイスで受け取る工程であって、当該仕様は複数の非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つを有し、当該非標準仕様は1若しくはそれ以上の非標準コマンド修飾子を有するものである、前記受け取る工程と、
前記仕様が前記非標準コマンド修飾子のうちの特定の1つを有することに応答して、前記特定の非標準コマンド修飾子に従って前記コマンドを実行する工程であって、前記コマンドのデータと共に前記非標準コマンド修飾子の指示を記憶する工程を有するものである、前記コマンドを実行する工程と、
前記指示にアクセスして、前記データの全部または任意の部分を、再利用するのではなく削減することを決定する工程と
を有する方法。 1. A method comprising:
receiving, at an input/output device, a command having a specification sent from a computing host, the specification comprising at least one of a plurality of non-standard specifications, the non-standard specification comprising one or more non-standard command modifiers;
in response to the specification having a particular one of the non-standard command modifiers, executing the command in accordance with the particular non-standard command modifier, the executing the command comprising storing an indication of the non-standard command modifier along with data for the command;
and accessing the instructions to determine to reduce, rather than reuse, all or any portion of the data.
データタイプ、
データアクセスタイプ、
データ順序付け、
データ関係、および
コマンド関係
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を指定する方法。 11. The method of claim 1, 2, or 10, wherein at least one of the non-standard specifications comprises:
Data type,
Data access type,
Data ordering,
A method for specifying one or more of a data relation and a command relation.
コンピューティングホストから仕様を有するコマンドを受け取る手段を有する入出力デバイスであって、当該仕様は複数の非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つを有し、当該非標準仕様は1若しくはそれ以上の非標準コマンド修飾子を有するものである、前記入出力デバイスを有し、
前記入出力デバイスは、さらに、前記仕様が前記非標準コマンド修飾子のうちの特定の1つを有することに応答して、前記特定の非標準コマンド修飾子に従って前記コマンドを実行する手段を有するものであり、
前記非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つは複数のデータ宛先のうちの特定の1つを識別し、前記データ宛先は複数のデータバンドを有するものである、
システム。 1. A system comprising:
an input/output device having means for receiving a command having a specification from a computing host, the specification comprising at least one of a plurality of non-standard specifications, the non-standard specification comprising one or more non-standard command modifiers;
the input/output device further comprising means for, in response to the specification having a particular one of the non-standard command modifiers, executing the command in accordance with the particular non-standard command modifier;
At least one of the non-standard specifications identifies a particular one of a plurality of data destinations, the data destination having a plurality of data bands.
system.
入出力デバイスに仕様を有するコマンドを提供する手段を有するコンピューティングホストであって、当該仕様は複数の非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つを有し、当該非標準仕様は1若しくはそれ以上の非標準コマンド修飾子を有するものである、前記コンピューティングホストを有し、
前記仕様が前記非標準コマンド修飾子のうちの特定の1つを有することに応答して、前記入出力デバイスは前記特定の非標準コマンド修飾子に従って前記コマンドを実行し、
前記非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つは複数のデータ宛先のうちの特定の1つを識別し、前記データ宛先は複数のデータバンドを有するものである、
システム。 1. A system comprising:
a computing host having means for providing a command having a specification to an input/output device, the specification comprising at least one of a plurality of non-standard specifications, the non-standard specification comprising one or more non-standard command modifiers;
in response to the specification having a particular one of the non-standard command modifiers, the input/output device executes the command in accordance with the particular non-standard command modifier;
At least one of the non-standard specifications identifies a particular one of a plurality of data destinations, the data destination having a plurality of data bands.
system.
コンピュータ、
ワークステーションコンピュータ、
サーバコンピュータ、
ストレージサーバ、
パーソナルコンピュータ(PC)、
ラップトップコンピュータ、
ノートブックコンピュータ、
ネットブックコンピュータ、
携帯情報端末(PDA)、
メディアプレーヤ、
メディアレコーダ、
デジタルカメラ、
セルラハンドセット、
コードレス電話機ハンドセット、および
電子ゲーム
のうちのいずれか1つであるシステム。 20. The system of claim 19, wherein the computing host comprises:
computer,
Workstation computers,
Server computer,
Storage servers,
Personal computers (PCs),
Laptop computers,
Notebook computers,
Netbook Computer,
Personal digital assistants (PDAs),
Media player,
Media Recorder,
Digital cameras,
Cellular handsets,
A system that is one of the following: a cordless telephone handset; and an electronic game.
コンピューティングホストから仕様を有するコマンドを受け取る手段を有する入出力デバイスであって、当該仕様は複数の非標準仕様のうちの少なくとも1つを有し、当該非標準仕様は1若しくはそれ以上の非標準コマンド修飾子を有するものであり、
当該入出力デバイスは、さらに、前記仕様が前記非標準コマンド修飾子のうちの特定の1つを有することに応答して、前記特定の非標準コマンド修飾子に従って前記コマンドを実行する手段を有し、当該手段は、前記コマンドのデータと共に前記非標準コマンド修飾子の指示を記憶する手段を有するものである、
前記入出力デバイスと、
前記指示にアクセスして、前記データの全部または任意の部分を、再利用するのではなく削減することを決定する手段と
を有するシステム。 1. A system comprising:
1. An input/output device having means for receiving a command having a specification from a computing host, the specification comprising at least one of a plurality of non-standard specifications, the non-standard specification having one or more non-standard command modifiers;
the input/output device further comprising means for, in response to the specification including a particular one of the non-standard command modifiers, executing the command in accordance with the particular non-standard command modifier, the means comprising means for storing an indication of the non-standard command modifier along with data for the command.
The input/output device;
and means for accessing said instructions to determine to reduce, rather than reuse, all or any portion of said data.
データタイプ、
データアクセスタイプ、
データ順序付け、
データ関係、および
コマンド関係
のうちの1若しくはそれ以上を指定するシステム。 24. The system of claim 14, 15, or 23, wherein at least one of the non-standard specifications comprises:
Data type,
Data access type,
Data ordering,
A system for specifying one or more of data relations and command relations.
外部インターフェースを介してコンピューティングホストからコマンドを入出力デバイスで受け取る手段と、
前記コマンドのタイプを確認する手段と、
前記コマンドのタイプが読み出しコマンドであることに応答して、マップにアクセスして前記コマンドの論理ブロックアドレス(LBA)を変換(translate)し、不揮発性メモリ(NVM)内の所定の位置を選択的に含む変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報を取得する手段と、
前記コマンドのタイプが予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドであることに応答して、当該予めマッピングされた読み出しコマンドの情報から、前記マップを使用せずに前記不揮発性メモリ内の前記位置を決定する手段と、
前記位置に対応するデータを返す手段と
を有し、
前記情報は、前記変換された論理ブロックアドレス情報の少なくとも一部分を有するものである、
システム。 1. A system comprising:
means for receiving commands at the input/output device from a computing host via an external interface;
means for determining the type of the command;
means for responsively translating a logical block address (LBA) of the command by accessing a map to obtain translated logical block address information selectively including a predetermined location within a non-volatile memory (NVM) in response to the command being a type of read command;
means for determining, in response to the command type being a pre-mapped read command, from information in the pre-mapped read command, the location within the non-volatile memory without using the map;
and means for returning data corresponding to said location;
the information comprising at least a portion of the translated logical block address information.
system.
前記コマンドのタイプが書き込みコマンドであることに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドのデータを前記不揮発性メモリ内の第2の位置に書き込む手段と、
前記コマンドのタイプが書き込みコマンドであることに応答して、前記書き込みコマンドの論理ブロックアドレスと前記マップ内の前記第2の位置との関連付けを記憶する手段と、
前記コマンドのタイプが書き込みコマンドであることに応答して、前記第2の位置に基づいた第2の情報を含む更新情報を前記マップのシャドウコピーに送る手段と
を有し、
前記第1の情報は、少なくとも部分的に前記シャドウコピーから取得され、前記シャドウコピーは、少なくとも部分的に前記コンピューティングホストに接続された入出力カードのメモリデバイスに記憶されるものであるシステム。 28. The system of claim 27, wherein the location is a first location and the information is first information, the system further comprising:
means for, in response to the command type being a write command, writing data of the write command to a second location within the non-volatile memory;
means for storing, in response to the command type being a write command, an association between a logical block address of the write command and the second location in the map;
means for sending an update to a shadow copy of the map, the update including second information based on the second location, in response to the command type being a write command;
The system, wherein the first information is obtained at least in part from the shadow copy, the shadow copy being stored at least in part in a memory device of an input/output card connected to the computing host.
低電力状態を開始するという指示を入出力デバイスで受け取る手段と、
前記入出力デバイスの内部状態をコンピューティングホストのシステムアクセス可能メモリに保存する手段と、
前記低電力状態を終了するという指示を前記入出力デバイスで受け取る手段と、
前記システムアクセス可能メモリから前記入出力デバイスの前記内部状態を復元する手段と
を有するシステム。 1. A system comprising:
means for receiving an indication at an input/output device to initiate a low power state;
means for storing an internal state of said input/output device in a system accessible memory of a computing host;
means for receiving an indication at the input/output device to exit the low power state;
and means for restoring said internal state of said input/output device from said system accessible memory.
標準コマンドと非標準修飾子の仕様とを有する拡張コマンドを入出力デバイスで受け取る手段と、
前記非標準修飾子に従って前記標準コマンドを実行する手段と
を有し、
前記非標準修飾子を使用して前記標準コマンドの実行を変更することによりシステムレベルの性能が改善されるものである
システム。 1. A system comprising:
means for receiving at an input/output device an extended command having a standard command and a specification of a non-standard modifier;
and means for executing the standard command according to the non-standard modifier;
The non-standard modifiers are used to modify the execution of the standard commands to improve system level performance.
Applications Claiming Priority (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201161521739P | 2011-08-09 | 2011-08-09 | |
| US61/521,739 | 2011-08-09 | ||
| US201161531551P | 2011-09-06 | 2011-09-06 | |
| US61/531,551 | 2011-09-06 | ||
| US201161543666P | 2011-10-05 | 2011-10-05 | |
| US61/543,666 | 2011-10-05 | ||
| PCT/US2012/049905WO2013022915A1 (en) | 2011-08-09 | 2012-08-08 | I/o device and computing host interoperation |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014522066Atrue JP2014522066A (en) | 2014-08-28 |
Family
ID=47668897
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014525104APendingJP2014522066A (en) | 2011-08-09 | 2012-08-08 | Interoperation of I/O devices with computing hosts |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (4) | US9389805B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP2742429A4 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2014522066A (en) |
| KR (2) | KR101438716B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN103858116B (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI584125B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2013022915A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017162066A (en)* | 2016-03-08 | 2017-09-14 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | Storage system, information processing system, and control method |
| US11481157B2 (en) | 2020-09-17 | 2022-10-25 | Kioxia Corporation | Electronic apparatus and transfer method |
Families Citing this family (151)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8782434B1 (en) | 2010-07-15 | 2014-07-15 | The Research Foundation For The State University Of New York | System and method for validating program execution at run-time |
| JP2014522066A (en) | 2011-08-09 | 2014-08-28 | エルエスアイ コーポレーション | Interoperation of I/O devices with computing hosts |
| WO2013164869A1 (en)* | 2012-05-02 | 2013-11-07 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Storage system and control method therefor |
| US20140047210A1 (en)* | 2012-08-08 | 2014-02-13 | Lsi Corporation | Trim mechanism using multi-level mapping in a solid-state media |
| US9207749B2 (en)* | 2012-08-28 | 2015-12-08 | Intel Corporation | Mechanism for facilitating efficient operations paths for storage devices in computing systems |
| US9122873B2 (en) | 2012-09-14 | 2015-09-01 | The Research Foundation For The State University Of New York | Continuous run-time validation of program execution: a practical approach |
| US9069782B2 (en) | 2012-10-01 | 2015-06-30 | The Research Foundation For The State University Of New York | System and method for security and privacy aware virtual machine checkpointing |
| US9395924B2 (en) | 2013-01-22 | 2016-07-19 | Seagate Technology Llc | Management of and region selection for writes to non-volatile memory |
| US9071281B2 (en)* | 2013-03-10 | 2015-06-30 | Intel Corporation | Selective provision of error correction for memory |
| US9585008B2 (en)* | 2013-04-19 | 2017-02-28 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Apparatus and methods for signaling out-of-standard capability in wireless communication networks |
| US9882984B2 (en)* | 2013-08-02 | 2018-01-30 | International Business Machines Corporation | Cache migration management in a virtualized distributed computing system |
| US9507404B2 (en)* | 2013-08-28 | 2016-11-29 | Via Technologies, Inc. | Single core wakeup multi-core synchronization mechanism |
| KR101547317B1 (en)* | 2013-09-30 | 2015-08-26 | 주식회사 유니테스트 | System for detecting fail block using logic block address and data buffer address in storage test device |
| TWI516921B (en)* | 2013-10-02 | 2016-01-11 | 群聯電子股份有限公司 | Data processing method, memory storage device and memory controlling circuit unit |
| US9612773B2 (en)* | 2013-11-21 | 2017-04-04 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | User device having a host flash translation layer (FTL), a method for transferring an erase count thereof, a method for transferring reprogram information thereof, and a method for transferring a page offset of an open block thereof |
| KR102103543B1 (en)* | 2013-11-28 | 2020-05-29 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | All-in-one data storage device having internal hardware filter, method thereof, and system having the data storage device |
| US10013344B2 (en) | 2014-01-14 | 2018-07-03 | Avago Technologies General Ip (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. | Enhanced SSD caching |
| US9509769B2 (en)* | 2014-02-28 | 2016-11-29 | Sap Se | Reflecting data modification requests in an offline environment |
| US9990298B2 (en) | 2014-05-12 | 2018-06-05 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc | System and method for caching solid state device read request results |
| CN106063227B (en)* | 2014-05-29 | 2019-10-18 | 华为技术有限公司 | Business processing method, related equipment and system |
| US9652415B2 (en) | 2014-07-09 | 2017-05-16 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Atomic non-volatile memory data transfer |
| TWI540582B (en)* | 2014-07-10 | 2016-07-01 | 群聯電子股份有限公司 | Data management method, memory control circuit unit and memory storage apparatus |
| US9904621B2 (en) | 2014-07-15 | 2018-02-27 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Methods and systems for flash buffer sizing |
| US9645744B2 (en) | 2014-07-22 | 2017-05-09 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Suspending and resuming non-volatile memory operations |
| KR102249810B1 (en)* | 2014-07-23 | 2021-05-11 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Storage device and operating method of storage device |
| US20160034185A1 (en)* | 2014-07-30 | 2016-02-04 | Lsi Corporation | Host-based device driver splitting of input/out for redundant array of independent disks systems |
| JP6547135B2 (en) | 2014-08-21 | 2019-07-24 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Recording medium, adapter and information processing apparatus |
| CN104281533B (en)* | 2014-09-18 | 2018-03-20 | 深圳市中博科创信息技术有限公司 | A kind of method and device of data storage |
| US9952978B2 (en) | 2014-10-27 | 2018-04-24 | Sandisk Technologies, Llc | Method for improving mixed random performance in low queue depth workloads |
| US9558125B2 (en)* | 2014-10-27 | 2017-01-31 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Processing of un-map commands to enhance performance and endurance of a storage device |
| US9753649B2 (en) | 2014-10-27 | 2017-09-05 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Tracking intermix of writes and un-map commands across power cycles |
| US9824007B2 (en) | 2014-11-21 | 2017-11-21 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Data integrity enhancement to protect against returning old versions of data |
| US9817752B2 (en) | 2014-11-21 | 2017-11-14 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Data integrity enhancement to protect against returning old versions of data |
| US10423339B2 (en)* | 2015-02-02 | 2019-09-24 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Logical block address mapping for hard disk drives |
| CN106164888A (en)* | 2015-02-26 | 2016-11-23 | 斯特拉托斯卡莱有限公司 | An ordering scheme for network and storage I/O requests to minimize workload idle time and inter-workload interference |
| US9647697B2 (en) | 2015-03-16 | 2017-05-09 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Method and system for determining soft information offsets |
| US9652175B2 (en) | 2015-04-09 | 2017-05-16 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Locally generating and storing RAID stripe parity with single relative memory address for storing data segments and parity in multiple non-volatile memory portions |
| US10437747B2 (en) | 2015-04-10 | 2019-10-08 | Rambus Inc. | Memory appliance couplings and operations |
| US9864545B2 (en) | 2015-04-14 | 2018-01-09 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Open erase block read automation |
| US9753653B2 (en) | 2015-04-14 | 2017-09-05 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | High-priority NAND operations management |
| US10372529B2 (en) | 2015-04-20 | 2019-08-06 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Iterative soft information correction and decoding |
| US9778878B2 (en) | 2015-04-22 | 2017-10-03 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Method and system for limiting write command execution |
| CN106155812A (en) | 2015-04-28 | 2016-11-23 | 阿里巴巴集团控股有限公司 | Method, device, system and the electronic equipment of a kind of resource management to fictitious host computer |
| US9959206B2 (en) | 2015-05-19 | 2018-05-01 | Toshiba Memory Corporation | Memory system and method of controlling cache memory |
| US9690517B2 (en)* | 2015-05-22 | 2017-06-27 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Dual-mode error-correction code/write-once memory codec |
| US9870149B2 (en) | 2015-07-08 | 2018-01-16 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Scheduling operations in non-volatile memory devices using preference values |
| US11983138B2 (en) | 2015-07-26 | 2024-05-14 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Self-configuring SSD multi-protocol support in host-less environment |
| US10127968B2 (en)* | 2015-08-03 | 2018-11-13 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for completing pending write requests to volatile memory prior to transitioning to self-refresh mode |
| JP6460940B2 (en)* | 2015-08-06 | 2019-01-30 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | Storage device and data saving method |
| US9715939B2 (en) | 2015-08-10 | 2017-07-25 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Low read data storage management |
| US10055142B1 (en)* | 2015-10-13 | 2018-08-21 | Maxlinear Asia Singapore Pte Ltd. | Apparatus and method for command processing for a fast block input/output device |
| US9886196B2 (en) | 2015-10-21 | 2018-02-06 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Method and system for efficient common processing in memory device controllers |
| US10108340B2 (en)* | 2015-10-21 | 2018-10-23 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Method and system for a common processing framework for memory device controllers |
| KR101728864B1 (en)* | 2015-10-30 | 2017-04-20 | (주)에프씨아이 | Method, Apparatus and Computer Program for Management of Flash Memory |
| US10228990B2 (en) | 2015-11-12 | 2019-03-12 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Variable-term error metrics adjustment |
| US11762764B1 (en) | 2015-12-02 | 2023-09-19 | Pure Storage, Inc. | Writing data in a storage system that includes a first type of storage device and a second type of storage device |
| US9760479B2 (en)* | 2015-12-02 | 2017-09-12 | Pure Storage, Inc. | Writing data in a storage system that includes a first type of storage device and a second type of storage device |
| US10126970B2 (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2018-11-13 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Paired metablocks in non-volatile storage device |
| CN105512007B (en)* | 2015-12-17 | 2018-12-04 | 英业达科技有限公司 | A kind of control method and system of PCIE disk state lamp |
| US9959046B2 (en)* | 2015-12-30 | 2018-05-01 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Multi-streaming mechanism to optimize journal based data storage systems on SSD |
| US9837146B2 (en) | 2016-01-08 | 2017-12-05 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Memory system temperature management |
| US9875811B2 (en)* | 2016-01-13 | 2018-01-23 | Macronix International Co., Ltd. | Method and device for reading a memory |
| TWI621125B (en)* | 2016-01-26 | 2018-04-11 | 旺宏電子股份有限公司 | Method and device for reading a memory |
| US10025727B2 (en)* | 2016-02-05 | 2018-07-17 | Honeywell International Inc. | Relay mechanism to facilitate processor communication with inaccessible input/output (I/O) device |
| US10732856B2 (en) | 2016-03-03 | 2020-08-04 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Erase health metric to rank memory portions |
| KR102514388B1 (en) | 2016-03-25 | 2023-03-28 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Memory system and operating method of memory system |
| US10156999B2 (en)* | 2016-03-28 | 2018-12-18 | Seagate Technology Llc | Dynamic bandwidth reporting for solid-state drives |
| US20170285975A1 (en)* | 2016-04-01 | 2017-10-05 | Sanjeev N. Trika | Technologies for managing immutable data on a data storage device |
| TWI622923B (en)* | 2016-05-04 | 2018-05-01 | 群聯電子股份有限公司 | Trim commands processing method, memory control circuit unit and memory storage apparatus |
| JP2017224113A (en) | 2016-06-14 | 2017-12-21 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | Memory device |
| CN107506135B (en)* | 2016-06-14 | 2022-05-06 | 杭州海康威视数字技术股份有限公司 | Data processing method, device and system |
| US11133042B2 (en) | 2016-06-27 | 2021-09-28 | SK Hynix Inc. | Semiconductor memory system and semiconductor memory device, which can be remotely initialized |
| KR102592359B1 (en) | 2016-06-27 | 2023-10-20 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Semiconductor device |
| US10181346B2 (en) | 2016-08-02 | 2019-01-15 | SK Hynix Inc. | Semiconductor devices and operations thereof |
| US10147471B2 (en) | 2016-08-02 | 2018-12-04 | SK Hynix Inc. | Semiconductor devices and semiconductor systems |
| US11217286B2 (en) | 2016-06-27 | 2022-01-04 | SK Hynix Inc. | Semiconductor memory device with power down operation |
| US10481830B2 (en) | 2016-07-25 | 2019-11-19 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Selectively throttling host reads for read disturbs in non-volatile memory system |
| US11144496B2 (en) | 2016-07-26 | 2021-10-12 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Self-configuring SSD multi-protocol support in host-less environment |
| US10372659B2 (en) | 2016-07-26 | 2019-08-06 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Multi-mode NMVE over fabrics devices |
| US11461258B2 (en) | 2016-09-14 | 2022-10-04 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Self-configuring baseboard management controller (BMC) |
| US10210123B2 (en) | 2016-07-26 | 2019-02-19 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | System and method for supporting multi-path and/or multi-mode NMVe over fabrics devices |
| US10346041B2 (en) | 2016-09-14 | 2019-07-09 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method for using BMC as proxy NVMeoF discovery controller to provide NVM subsystems to host |
| US12424253B2 (en) | 2016-08-02 | 2025-09-23 | SK Hynix Inc. | Semiconductor device with power-down signal generation |
| US9747039B1 (en) | 2016-10-04 | 2017-08-29 | Pure Storage, Inc. | Reservations over multiple paths on NVMe over fabrics |
| CN106708441B (en)* | 2016-12-29 | 2019-06-21 | 至誉科技(武汉)有限公司 | A kind of operating method for reducing solid-state storage read latency |
| JP2018120439A (en) | 2017-01-25 | 2018-08-02 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | Memory system and control method |
| US10579273B2 (en)* | 2017-05-03 | 2020-03-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Maintaining correct I/O statistics for altered data migrated within a tiered storage environment |
| US9905294B1 (en)* | 2017-05-03 | 2018-02-27 | Seagate Technology Llc | Writing logically offset pages of data to N-level memory cells coupled to a common word line |
| US10191911B2 (en)* | 2017-05-27 | 2019-01-29 | Plesk International Gmbh | Permanent website hosting on mobile devices |
| US10990291B2 (en)* | 2017-06-12 | 2021-04-27 | Dell Products, L.P. | Software assist memory module hardware architecture |
| US10275162B2 (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2019-04-30 | Dell Products L.P. | Methods and systems for managing data migration in solid state non-volatile memory |
| US10339073B2 (en)* | 2017-06-29 | 2019-07-02 | Keysight Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for reducing write latency |
| CN109213425B (en)* | 2017-06-30 | 2023-10-31 | 北京忆恒创源科技股份有限公司 | Processing atomic commands in solid state storage devices using distributed caching |
| US10908998B2 (en) | 2017-08-08 | 2021-02-02 | Toshiba Memory Corporation | Managing function level reset in an IO virtualization-enabled storage device |
| US10446197B2 (en) | 2017-08-31 | 2019-10-15 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Optimized scan interval |
| CN107391049B (en)* | 2017-09-08 | 2023-05-26 | 南宁磁动电子科技有限公司 | Storage connection device and storage system |
| CN109558271B (en)* | 2017-09-26 | 2023-02-24 | 深圳大心电子科技有限公司 | Data backup method, data recovery method and storage controller |
| CN107479938B (en)* | 2017-09-27 | 2024-03-29 | 北京忆芯科技有限公司 | Electronic devices and methods of starting them |
| US10754580B2 (en) | 2017-10-23 | 2020-08-25 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Virtual partition management in a memory device |
| KR102543059B1 (en) | 2017-11-22 | 2023-06-14 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method of decoding low density parity check (LDPC) code, decoder and system performing the same |
| KR20200096613A (en) | 2017-12-11 | 2020-08-12 | 마이크론 테크놀로지, 인크. | Technique for Improving Garbage Collection Efficiency in Cached Flash Transformation Layer |
| KR20190090268A (en)* | 2018-01-24 | 2019-08-01 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Memory controller and memory system having the same |
| US10365854B1 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2019-07-30 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Tracking data temperatures of logical block addresses |
| KR102583592B1 (en)* | 2018-03-27 | 2023-10-06 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Memory controller and memory system having the same |
| US10534551B1 (en)* | 2018-06-22 | 2020-01-14 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Managing write operations during a power loss |
| US10725941B2 (en) | 2018-06-30 | 2020-07-28 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Multi-device storage system with hosted services on peer storage devices |
| US10409511B1 (en) | 2018-06-30 | 2019-09-10 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Multi-device storage system with distributed read/write processing |
| US11115490B2 (en)* | 2018-07-31 | 2021-09-07 | EMC IP Holding Company LLC | Host based read cache for san supporting NVMEF with E2E validation |
| US10592144B2 (en) | 2018-08-03 | 2020-03-17 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Storage system fabric with multichannel compute complex |
| JP6995723B2 (en)* | 2018-09-19 | 2022-01-17 | キオクシア株式会社 | Memory system, storage system, and control method |
| US10726865B2 (en) | 2018-10-11 | 2020-07-28 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Zoned block command to stream command translator |
| US11221768B2 (en) | 2018-10-29 | 2022-01-11 | International Business Machines Corporation | Safe shared volume access |
| KR102686917B1 (en) | 2018-10-31 | 2024-07-19 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method of operating storage device, storage device performing the same and method of operating storage system using the same |
| US10922178B2 (en)* | 2018-10-31 | 2021-02-16 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Masterless raid for byte-addressable non-volatile memory |
| KR102672193B1 (en)* | 2018-12-12 | 2024-06-07 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Electronic device |
| KR102795556B1 (en)* | 2018-12-14 | 2025-04-15 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Controller and operating method thereof |
| KR102735042B1 (en) | 2018-12-19 | 2024-11-28 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Memory controller and operating method thereof |
| KR102811446B1 (en) | 2019-01-15 | 2025-05-22 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Storage device and operating method thereof |
| KR102787556B1 (en) | 2019-02-15 | 2025-03-31 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Memory controller and operating method thereof |
| KR102659832B1 (en)* | 2019-03-05 | 2024-04-22 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Data storage device and system |
| US11151063B2 (en) | 2019-04-19 | 2021-10-19 | EMC IP Holding Company LLC | Host system directly connected to internal switching fabric of storage system |
| US11500549B2 (en)* | 2019-04-19 | 2022-11-15 | EMC IP Holding Company LLC | Secure host access to storage system resources via storage system interface and internal switching fabric |
| US10698844B1 (en)* | 2019-04-19 | 2020-06-30 | EMC IP Holding Company LLC | Intelligent external storage system interface |
| US10782906B1 (en)* | 2019-07-17 | 2020-09-22 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory subsystem interface to relate data and to retrieve related data |
| US11210010B2 (en)* | 2019-07-30 | 2021-12-28 | International Business Machines Corporation | Data migration in a multi-tiered storage system |
| US11074182B2 (en) | 2019-08-22 | 2021-07-27 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Three tiered hierarchical memory systems |
| US11295806B2 (en) | 2019-08-28 | 2022-04-05 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Large file integrity techniques |
| US11210024B2 (en) | 2019-12-16 | 2021-12-28 | International Business Machines Corporation | Optimizing read-modify-write operations to a storage device by writing a copy of the write data to a shadow block |
| TWI730600B (en) | 2020-01-21 | 2021-06-11 | 群聯電子股份有限公司 | Data writing method, memory controlling circuit unit and memory storage device |
| US11500747B2 (en)* | 2020-01-30 | 2022-11-15 | Dell Products L.P. | Computer initialization debug message display system |
| KR20210097353A (en)* | 2020-01-30 | 2021-08-09 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | Memory system, memory controller, and operating method of memory system |
| CN113535616B (en)* | 2020-04-13 | 2023-09-22 | 慧荣科技股份有限公司 | Computer readable storage medium, method and device for controlling access of flash memory device |
| CN111813345A (en)* | 2020-07-17 | 2020-10-23 | 济南浪潮数据技术有限公司 | Data transmission method, device, server and readable storage medium |
| US12271752B2 (en)* | 2020-07-31 | 2025-04-08 | EMC IP Holding Company LLC | Techniques for managing cores for storage |
| DE102021121105A1 (en)* | 2020-09-28 | 2022-03-31 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | SMART STORAGE STORAGE DEVICE |
| KR102827119B1 (en)* | 2020-10-14 | 2025-06-27 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Memory device, host device and memory system comprising the memory device and host device |
| US11775210B2 (en)* | 2020-10-14 | 2023-10-03 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Storage system and method for device-determined, application-specific dynamic command clustering |
| TWI789650B (en)* | 2020-11-26 | 2023-01-11 | 神雲科技股份有限公司 | Integrated control management system |
| US11468202B2 (en) | 2020-12-15 | 2022-10-11 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Hardware-based security authentication |
| KR20220101349A (en) | 2021-01-11 | 2022-07-19 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method of writing data in storage device and storage device performing the same |
| WO2022177945A1 (en)* | 2021-02-16 | 2022-08-25 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Controller for managing multiple types of memory |
| US11500548B2 (en)* | 2021-03-04 | 2022-11-15 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Memory physical presence security identification |
| JP2022137811A (en)* | 2021-03-09 | 2022-09-22 | キオクシア株式会社 | Information processing systems, storage devices and hosts |
| CN113326001B (en)* | 2021-05-20 | 2023-08-01 | 锐掣(杭州)科技有限公司 | Data processing method, device, apparatus, system, medium, and program |
| US20230015697A1 (en)* | 2021-07-13 | 2023-01-19 | Citrix Systems, Inc. | Application programming interface (api) authorization |
| JP2023045867A (en) | 2021-09-22 | 2023-04-03 | キオクシア株式会社 | memory system |
| TWI805505B (en)* | 2022-10-11 | 2023-06-11 | 慧榮科技股份有限公司 | Method and computer program product and apparatus for scheduling and executing host data-update commands |
| CN117909251A (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2024-04-19 | 慧荣科技股份有限公司 | Storage medium, method and device for scheduling and executing host data update commands |
| TWI818762B (en)* | 2022-10-11 | 2023-10-11 | 慧榮科技股份有限公司 | Method and computer program product and apparatus for scheduling and executing host data-update commands |
| CN117909252A (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2024-04-19 | 慧荣科技股份有限公司 | Storage medium, method and device for scheduling and executing host data update commands |
| CN120578619A (en)* | 2025-08-05 | 2025-09-02 | 上海壁仞科技股份有限公司 | PCIE device and operating method thereof |
Family Cites Families (67)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4942552A (en)* | 1986-11-20 | 1990-07-17 | Allen-Bradley Company, Inc. | Method and apparatus for saving and performing industrial control commands |
| US5210660A (en) | 1990-01-17 | 1993-05-11 | International Business Machines Corporation | Sectored servo independent of data architecture |
| US5278703A (en) | 1991-06-21 | 1994-01-11 | Digital Equipment Corp. | Embedded servo banded format for magnetic disks for use with a data processing system |
| JP3212787B2 (en) | 1993-12-02 | 2001-09-25 | 日本電気株式会社 | Transfer data management method and data transfer method between host and terminal |
| JPH1153235A (en) | 1997-08-08 | 1999-02-26 | Toshiba Corp | Disk storage device data updating method and disk storage control system |
| KR100544177B1 (en)* | 2000-01-18 | 2006-01-23 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method of controlling portable device having facilities of storing and playing digital contents by computer and portable device operation method thereby |
| US6427198B1 (en)* | 2000-02-15 | 2002-07-30 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method, system, and program for determining system configuration |
| US6763424B2 (en) | 2001-01-19 | 2004-07-13 | Sandisk Corporation | Partial block data programming and reading operations in a non-volatile memory |
| AU2002326752A1 (en) | 2001-08-24 | 2003-03-10 | Intel Corporation (A Delaware Corporation) (A Delawware Corporation) | A general input/output architecture protocol and related methods to manage data integrity |
| JP2003087348A (en)* | 2001-09-14 | 2003-03-20 | Matsushita Graphic Communication Systems Inc | Communication control method, communication controller, and adsl communication device |
| KR100445134B1 (en) | 2002-01-31 | 2004-08-21 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Host equipped with stabilizing function for flash memory and the method thereof |
| US7406587B1 (en)* | 2002-07-31 | 2008-07-29 | Silicon Graphics, Inc. | Method and system for renaming registers in a microprocessor |
| US6968439B2 (en) | 2002-08-29 | 2005-11-22 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Single segment data object management |
| EP1465116A1 (en)* | 2003-03-31 | 2004-10-06 | STMicroelectronics Limited | Computer graphics |
| JP4175185B2 (en) | 2003-06-06 | 2008-11-05 | 日本電気株式会社 | Network information recording device |
| CN1670701A (en) | 2004-03-17 | 2005-09-21 | 德鑫科技股份有限公司 | Compressed Data Storage Method |
| US20060174067A1 (en) | 2005-02-03 | 2006-08-03 | Craig Soules | Method of caching data |
| US20060200612A1 (en)* | 2005-03-02 | 2006-09-07 | Laurence Hamid | Method and protocol for transmitting extended commands to USB devices |
| CN101390043A (en) | 2005-07-01 | 2009-03-18 | 美国日本电气实验室公司 | Storage architecture for embedded systems |
| CN100361094C (en) | 2005-07-01 | 2008-01-09 | 华为技术有限公司 | A Method of Saving Global Variable Memory Space |
| US7159082B1 (en) | 2005-10-03 | 2007-01-02 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | System and method for throttling memory accesses |
| US7844877B2 (en) | 2005-11-15 | 2010-11-30 | Ramot At Tel Aviv University Ltd. | Method and device for multi phase error-correction |
| US20070168668A1 (en)* | 2005-12-08 | 2007-07-19 | Chang Robert C | Media card with command pass through mechanism |
| US7719983B2 (en) | 2006-01-06 | 2010-05-18 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method for autonomic system management using adaptive allocation of resources |
| JP4855102B2 (en) | 2006-02-23 | 2012-01-18 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Computer system, management computer, storage system, and storage area allocation control method |
| US7639531B2 (en) | 2006-05-15 | 2009-12-29 | Apple Inc. | Dynamic cell bit resolution |
| US7613043B2 (en) | 2006-05-15 | 2009-11-03 | Apple Inc. | Shifting reference values to account for voltage sag |
| US7594073B2 (en) | 2006-09-29 | 2009-09-22 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for caching memory content on a computing system to facilitate instant-on resuming from a hibernation state |
| CN100504830C (en)* | 2007-01-08 | 2009-06-24 | 中国信息安全产品测评认证中心 | Composite device of smart card and U disk and method for communicating with computer |
| US7721040B2 (en) | 2007-01-18 | 2010-05-18 | Sandisk Il Ltd. | Method and system for facilitating fast wake-up of a flash memory system |
| US7596643B2 (en)* | 2007-02-07 | 2009-09-29 | Siliconsystems, Inc. | Storage subsystem with configurable buffer |
| JP2009026296A (en) | 2007-06-21 | 2009-02-05 | Toshiba Corp | Electronic device, memory device, host device |
| US8078787B2 (en) | 2007-06-22 | 2011-12-13 | Apple Inc. | Communication between a host device and an accessory via an intermediate device |
| US8429358B2 (en)* | 2007-08-14 | 2013-04-23 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and data storage device for processing commands |
| US8473707B2 (en) | 2008-03-27 | 2013-06-25 | Open Invention Network, Llc | Method for achieving sequential I/O performance from a random workload |
| US7769919B2 (en) | 2008-05-15 | 2010-08-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Protecting computer memory from simultaneous direct memory access operations using active and inactive translation tables |
| TW201007734A (en) | 2008-08-06 | 2010-02-16 | Genesys Logic Inc | Flash memory control apparatus having signal-converting module |
| US7925925B2 (en) | 2008-12-30 | 2011-04-12 | Intel Corporation | Delta checkpoints for a non-volatile memory indirection table |
| CN101576834B (en) | 2009-05-08 | 2012-05-30 | 西安蓝海本立信息科技有限公司 | Continuous data protection system and method for establishing data view based on timestamp |
| TWI400707B (en) | 2009-07-09 | 2013-07-01 | Phison Electronics Corp | Logical block management method for a flash memory and control circuit and storage system using the same |
| US8479080B1 (en) | 2009-07-12 | 2013-07-02 | Apple Inc. | Adaptive over-provisioning in memory systems |
| JP5377182B2 (en)* | 2009-09-10 | 2013-12-25 | 株式会社東芝 | Control device |
| US9753847B2 (en) | 2009-10-27 | 2017-09-05 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Non-volatile semiconductor memory segregating sequential, random, and system data to reduce garbage collection for page based mapping |
| US8156304B2 (en)* | 2009-12-04 | 2012-04-10 | Oracle International Corporation | Dynamic data storage repartitioning |
| US8677054B1 (en) | 2009-12-16 | 2014-03-18 | Apple Inc. | Memory management schemes for non-volatile memory devices |
| JP2011128998A (en)* | 2009-12-18 | 2011-06-30 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor storage device |
| TWI484334B (en) | 2009-12-24 | 2015-05-11 | Univ Nat Taiwan | Method for region-based management of non-volatile memory |
| US8327226B2 (en) | 2010-02-03 | 2012-12-04 | Seagate Technology Llc | Adjustable error correction code length in an electrical storage device |
| JP2011203916A (en) | 2010-03-25 | 2011-10-13 | Toshiba Corp | Memory controller and semiconductor storage device |
| US8621141B2 (en) | 2010-04-01 | 2013-12-31 | Intel Corporations | Method and system for wear leveling in a solid state drive |
| US9183134B2 (en) | 2010-04-22 | 2015-11-10 | Seagate Technology Llc | Data segregation in a storage device |
| US8489855B2 (en) | 2010-05-07 | 2013-07-16 | Ocz Technology Group Inc. | NAND flash-based solid state drive and method of operation |
| US8966176B2 (en)* | 2010-05-27 | 2015-02-24 | Sandisk Il Ltd. | Memory management storage to a host device |
| US8368564B2 (en) | 2010-08-24 | 2013-02-05 | Allen Ku | Wireless keyboard having waterproof mechanism |
| CN101930404B (en) | 2010-08-27 | 2012-11-21 | 威盛电子股份有限公司 | Storage device and method of operation thereof |
| US20120059976A1 (en)* | 2010-09-07 | 2012-03-08 | Daniel L. Rosenband | Storage array controller for solid-state storage devices |
| US9063663B2 (en) | 2010-09-21 | 2015-06-23 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Semiconductor storage device and data control method thereof |
| US8560648B2 (en) | 2010-11-10 | 2013-10-15 | Microsoft Corporation | Location control service |
| WO2012099937A2 (en) | 2011-01-18 | 2012-07-26 | Lsi Corporation | Higher-level redundancy information computation |
| CN102023818A (en) | 2010-12-06 | 2011-04-20 | 成都市华为赛门铁克科技有限公司 | Method and device for regulating capacity of storage equipment, and storage equipment |
| KR101467941B1 (en) | 2011-04-26 | 2014-12-02 | 엘에스아이 코포레이션 | Variable over provisioning for non-volatile storage |
| US8793429B1 (en)* | 2011-06-03 | 2014-07-29 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Solid-state drive with reduced power up time |
| JP2014522066A (en) | 2011-08-09 | 2014-08-28 | エルエスアイ コーポレーション | Interoperation of I/O devices with computing hosts |
| US8661196B2 (en) | 2011-08-15 | 2014-02-25 | International Business Machines Corporation | Optimizing locations of data accessed by client applications interacting with a storage system |
| KR101562781B1 (en) | 2011-10-05 | 2015-10-23 | 엘에스아이 코포레이션 | Self-journaling and hierarchical consistency for non-volatile storage |
| US9037820B2 (en) | 2012-06-29 | 2015-05-19 | Intel Corporation | Optimized context drop for a solid state drive (SSD) |
| US9395924B2 (en) | 2013-01-22 | 2016-07-19 | Seagate Technology Llc | Management of and region selection for writes to non-volatile memory |
- 2012
- 2012-08-08JPJP2014525104Apatent/JP2014522066A/enactivePending
- 2012-08-08KRKR1020147006222Apatent/KR101438716B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2012-08-08CNCN201280049511.1Apatent/CN103858116B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2012-08-08EPEP12821517.5Apatent/EP2742429A4/ennot_activeWithdrawn
- 2012-08-08KRKR1020147009043Apatent/KR101798036B1/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
- 2012-08-08USUS14/237,331patent/US9389805B2/enactiveActive
- 2012-08-08WOPCT/US2012/049905patent/WO2013022915A1/enactiveApplication Filing
- 2012-08-09TWTW101128817Apatent/TWI584125B/ennot_activeIP Right Cessation
- 2013
- 2013-07-05USUS13/936,010patent/US20130297894A1/ennot_activeAbandoned
- 2017
- 2017-07-27USUS15/661,079patent/US10514864B2/enactiveActive
- 2019
- 2019-11-14USUS16/684,027patent/US10936251B2/enactiveActive
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017162066A (en)* | 2016-03-08 | 2017-09-14 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | Storage system, information processing system, and control method |
| CN107168639A (en)* | 2016-03-08 | 2017-09-15 | 东芝存储器株式会社 | The control method of storage system, information processing system and nonvolatile memory |
| US10162749B2 (en) | 2016-03-08 | 2018-12-25 | Toshiba Memory Corporation | Storage system and information processing system for controlling nonvolatile memory |
| CN107168639B (en)* | 2016-03-08 | 2020-04-07 | 东芝存储器株式会社 | Storage system, information processing system, and method for controlling nonvolatile memory |
| US12124370B2 (en) | 2016-03-08 | 2024-10-22 | Kioxia Corporation | Storage system and information processing system for controlling nonvolatile memory |
| US11481157B2 (en) | 2020-09-17 | 2022-10-25 | Kioxia Corporation | Electronic apparatus and transfer method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US9389805B2 (en) | 2016-07-12 |
| US20170322751A1 (en) | 2017-11-09 |
| KR101438716B1 (en) | 2014-09-11 |
| TW201314464A (en) | 2013-04-01 |
| CN103858116B (en) | 2015-09-02 |
| TWI584125B (en) | 2017-05-21 |
| CN103858116A (en) | 2014-06-11 |
| US10514864B2 (en) | 2019-12-24 |
| EP2742429A1 (en) | 2014-06-18 |
| US10936251B2 (en) | 2021-03-02 |
| KR20140061498A (en) | 2014-05-21 |
| WO2013022915A1 (en) | 2013-02-14 |
| US20130297894A1 (en) | 2013-11-07 |
| EP2742429A4 (en) | 2015-03-25 |
| US20140181327A1 (en) | 2014-06-26 |
| US20200081660A1 (en) | 2020-03-12 |
| KR20140044933A (en) | 2014-04-15 |
| KR101798036B1 (en) | 2017-11-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10936251B2 (en) | I/O device and computing host interoperation | |
| JP6082389B2 (en) | Managing the impact of device firmware updates from the host perspective | |
| KR101467939B1 (en) | Variable over provisioning for non-volatile storage | |
| JP6265746B2 (en) | Mapping / conversion between storage address space and non-volatile memory address, range, and length | |
| KR102155191B1 (en) | Management of and region selection for writes to non-volatile memory | |
| US9092160B2 (en) | Selective enablement of operating modes or features via host transfer rate detection | |
| US9396104B1 (en) | Accessing compressed data of varying-sized quanta in non-volatile memory |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20150808 |