JP2014153583A - Management method of signature document and signature server - Google Patents
Management method of signature document and signature serverDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2014153583A JP2014153583AJP2013024001AJP2013024001AJP2014153583AJP 2014153583 AJP2014153583 AJP 2014153583AJP 2013024001 AJP2013024001 AJP 2013024001AJP 2013024001 AJP2013024001 AJP 2013024001AJP 2014153583 AJP2014153583 AJP 2014153583A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- document
- signature
- data
- format
- storage unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、署名文書を管理する技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a technique for managing a signature document.
近年企業が管理すべきデータは膨大化してきている。例えば製薬会社では、新薬の申請書類など大量の文書を作成、保管する必要がある。また、企業によっては法令等で長期保管が義務付けられている文書等もあり、文書の効率的な管理が求められている。関連する技術として、所定のタイミングで、ストレージ内のファイル(文書)の内容に対して同一性判定を行い、同一の内容のファイルが複数存在した場合に、そのファイルの実体を有する実体ファイルを1つにし、同一の内容とされた全てのファイルまたは1つを除く全てのファイルを、実体ファイルを参照する仮想ファイルの形式に変更することで、共有ストレージにおけるデータの保持の効率化を行う技術が知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 In recent years, data to be managed by companies has become enormous. For example, pharmaceutical companies need to create and store a large number of documents such as application documents for new drugs. In addition, some companies require documents to be stored for a long period by law, and efficient management of documents is required. As a related technique, the identity of the contents of a file (document) in the storage is determined at a predetermined timing, and when there are a plurality of files having the same contents, one entity file having the entity of the file is determined. A technology that improves the efficiency of data retention in shared storage by changing all files except the one with the same content or all files except one into a virtual file format that refers to the actual file. It is known (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
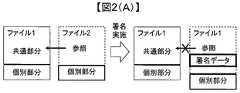
インターネットの普及に伴って、文書の改竄を防止するために、紙文書での手書き署名に相当するものを電子的に実現する電子署名の重要性が高まっている。従来、電子署名は実体のある文書に対して行われるのが一般的であったが、今後、文書の仮想化が進むにつれて、仮想文書に対して電子署名を行うことが考えられる。しかし、実体文書のデータを参照している仮想文書や、仮想文書からデータを参照されている実体文書に対して電子署名を行った場合、仮想化部分や仮想文書から参照されている実体文書のデータに署名データが入り込んでしまう。このため、実体文書と実体文書のデータを参照する仮想文書において、署名データ以外のデータは同内容のデータであっても、仮想文書により参照される実体文書のデータと実体文書のデータを参照する仮想文書のデータとが同じデータとみなせなくなり、仮想文書は実体文書を参照できなくなる場合がある。例えば図2(A)に示すように、実体文書1の一部のデータを参照する仮想文書2に電子署名を行った場合、仮想文書2の仮想化部分に署名データが入り込み、実体文書1の被参照共通部分(実データ)と、署名後の仮想文書2の仮想化部分でデータが異なってしまう。このため、署名後は仮想文書2は、もともと参照していた実体文書1の被参照共通部分を参照できなくなる。従ってこの場合、仮想文書2により参照されていた実体文書1の共通部分を、別途文書2にも持たせるようにする必要があり、管理すべきデータが増大してしまう。 With the spread of the Internet, in order to prevent falsification of documents, the importance of electronic signatures that electronically realize the equivalent of handwritten signatures on paper documents is increasing. Conventionally, an electronic signature is generally applied to a substantial document. However, it is considered that an electronic signature is applied to a virtual document as the virtualization of the document proceeds. However, when an electronic signature is applied to a virtual document that refers to data of an entity document or an entity document that refers to data from a virtual document, the virtual document or the entity document referenced from the virtual document Signature data gets into the data. For this reason, in the virtual document that references the entity document and the data of the entity document, the data of the entity document and the data of the entity document that are referred to by the virtual document are referenced even if the data other than the signature data has the same contents. The virtual document data cannot be regarded as the same data, and the virtual document may not be able to refer to the actual document. For example, as shown in FIG. 2A, when an electronic signature is applied to a
以上を踏まえ、本発明は、仮想文書に電子署名を行う場合でも、管理すべきデータを増大させることなく、実体文書を参照できる署名文書の管理方法、これを実施する署名サーバを提供することを目的とする。 In light of the above, the present invention provides a signature document management method that can refer to an entity document without increasing data to be managed even when an electronic signature is applied to a virtual document, and a signature server that implements this. Objective.
本発明の代表的な一例を示せば以下の通りである。すなわち、本発明は、記憶部と、
文書への署名要求に基づき該文書に署名を行い、署名文書の形式を判断し、前記判断した署名文書の形式が署名対象文書に署名データが挿入される形式で、前記署名対象文書が実体文書を参照する仮想文書の場合、前記署名文書から署名データを除去し、該署名データを前記記憶部に記憶し、前記署名データ除去後の文書を前記記憶部に記憶する制御部と、を有する。A typical example of the present invention is as follows. That is, the present invention includes a storage unit,
The document is signed based on a request to sign the document, the format of the signature document is determined, the format of the determined signature document is a format in which signature data is inserted into the signature target document, and the signature target document is an entity document A control unit that removes the signature data from the signature document, stores the signature data in the storage unit, and stores the document after the signature data removal in the storage unit.
本発明によれば、仮想文書に電子署名を行う場合でも、管理すべきデータを増大させることなく、実体文書を参照することができる。 According to the present invention, even when an electronic signature is applied to a virtual document, it is possible to refer to the actual document without increasing the data to be managed.
以下、本発明の実施の形態について説明する。尚、以下に説明する実施の形態は一例であって、本発明はこれに限定されるものではない。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below. The embodiment described below is an example, and the present invention is not limited to this.
図1〜図8を用いて第1の実施例を説明する。 A first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS.
図1は、本発明の第1の実施例の署名システムのハードウェアおよびソフトウェア構成を示すブロック図である。署名システムは、1以上の署名サーバ101と、1以上の外部サーバ141と、1以上のクライアント端末121a及び121b(以下、これらを総称してクライアント端末121とも記載する)と、を備える。尚外部サーバとは、タイムスタンプサーバや、証明書の失効確認を行うOCSPレスポンダ等であり、これらを備えない構成であってもよい。 FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a hardware and software configuration of the signature system according to the first embodiment of this invention. The signature system includes one or
署名サーバ101、クライアント端末121は、それぞれI/F104、123を介してネットワークに接続される。署名サーバ101は、I/F104を介して、クライアント端末121等の外部機器に対して、操作要求の受付けや操作の指示を行う。 The
署名サーバ101は、CPU(Central Processing Unit)等の制御部103、メモリ等の記憶部102およびI/F104を備える。制御部103は、I/F104を介してクライアント端末121等の外部機器からの操作要求の受信および当該操作の実行や、前記外部機器に対して署名や文書編集等の操作結果の送信などを行う。記憶部102はユーザ連携部105、署名作成部106、署名検証部107、文書管理部108、仮想管理部109、署名文書組立て部110、文書管理情報111、仮想管理情報112、分離管理情報113から構成されており、制御部103、I/F104と接続されている。 The
クライアント端末121は、制御部124、記憶部122およびI/F123を備える。制御部124は、I/F123を介して署名サーバ101等への操作要求や、署名サーバ101等からの操作指示や操作結果の受信を行う。記憶部122はサーバ連携部125、ユーザ連携部126から構成されており、制御部124、I/F123と接続されている。 The client terminal 121 includes a
次に、本実施形態の署名システムのソフトウェア構成の詳細(記憶部102、記憶部122に格納される情報)について説明する。 Next, details of the software configuration of the signature system of the present embodiment (information stored in the
最初に記憶部102に格納されたプログラム以外の情報(111〜113の情報)について説明し、その後、記憶部102に格納されたプログラム情報(105〜110の情報)について説明する。 First, information other than the program stored in the storage unit 102 (information of 111 to 113) will be described, and then program information stored in the storage unit 102 (information of 105 to 110) will be described.
文書管理情報111は、署名サーバ101が管理する文書に関する情報である。図3は、本発明の第1の実施例の文書管理情報111の一例を示す説明図である。文書管理情報111は、項目301、302、303、304の四つのデータ項目を含む。項目301は、署名サーバ101が管理する文書(ファイル)の名称を示す。項目302は、各文書が参照しているデータ、即ち、他の文書と共通のデータについてデータの実体を持たずに参照により実現しているデータを示す。例えば図3において、test/1.pdfは、後述の識別番号401が1-1で示されるデータを参照していることを、test/1.xmlは参照しているデータが無いことを示す。項目303は、項目302の参照データの、各文書内での場所を示す。例えば図3において、test/1.pdfは、自文書のアドレス50に参照データが配置される。尚、この場所情報は、その他の形態、例えば文書の先頭から何行目等で表現されてもよい。項目304は、文書と署名及び署名に関連するデータの分離状況を示す。例えば図3において、test/1.pdfは文書は分離されていないことを、test/2.pdfは、後述の識別番号501が2-1で示される形で、文書と署名及び署名に関する情報が分離されていることを示す。 The
仮想管理情報112は、複数の文書で共通のデータであり、データの実体は一つの文書が保持し、他の文書はそのデータを参照しているものについての情報である。図4は、本発明の第1の実施例の仮想管理情報112の一例を示す説明図である。仮想管理情報112は、項目401、402、403の三つのデータ項目を含む。項目401は、各共通データを識別するための識別番号を示す。項目402は、共通データの実体を持っている文書の名称情報を示す。項目403は、項目402の文書内における、当該共通データの場所情報を示す。例えば図4において、識別番号401が1-1で表される共通データは、名称402がtest/2.pdfで示される文書において、アドレス10からデータ長が50の範囲のデータであることを示す。 The
分離管理情報113は、署名文書から抽出された署名や署名に関する情報及び、署名文書から抽出された文書に関する情報を示す。これら抽出したデータは、もとの署名文書とは別に管理される。尚、署名に関する情報とは、署名データ以外に、署名作成に使用したユーザの公開鍵証明書の情報や、文書の増分更新情報等である。増分更新情報とは、例えばPDF形式の文書では、もとの文書の末尾に加えられる新たな情報である。もとの文書に変更を加えずに、新たな内容の追加や署名の追加を行なう場合に使用される。図5は、本発明の第1の実施例の分離管理情報113の一例を示す説明図である。分離管理情報113は、項目501、502、503、504、505、の五つのデータ項目を含む。項目501は、各分離された署名や署名に関する情報及び抽出された文書に関する情報を識別するための識別番号を示す。項目502は、署名文書からの署名の除去や文書の抽出といった、署名文書と署名や署名に関する情報等との分離状況を示す。項目502が「署名」のものは署名文書から署名データが抽出されて別に管理されていることを、「文書」のものは署名文書から署名データではなく署名対象の文書が抽出されて別に管理されていることを示す。項目503は、署名データの形式を示す。具体的にはpkcs7の形式や、xml署名のenveloping形式(署名データの中に署名対象の文書が含まれている形式)等である。項目504は、抽出された署名や文書のデータのもとの文書での位置情報を示す。外部に文書を転送する際など、抽出されて別に管理されている署名や文書の情報をもとの文書に入れて復元するために使用する。例えば図5において、項目501が2-1のデータは、もとの文書のアドレス100の部分に当該データが入れられる。項目505は項目501の各データの共用可否を示す情報である。データの共用を許可する場合、当該データが他の文書のデータと一致するか否かの判定を行い、一致する場合は、他の文書からデータを参照させる又は他の文書のデータを参照する。例えば図5において、項目501のデータが署名データの場合は各データは固有で他の文書と共通でないと考えられるため他文書のと共用不可(Nと表記)、一方文書データの場合は他の文書と同じデータである可能性もあるため共用可(Yと表記)としている。但し、これに限らず署名データであっても他の文書と共用可能にしてもよい。 The
次に、記憶部102に格納されたプログラム情報について説明する。ユーザ連携部105は、署名サーバ101へ操作要求を行うユーザを認証し、ユーザが要求する操作の実行を許可又は禁止する等の処理を実行する。署名作成部106は、文書への署名を行う。署名処理としては、例えば文書のハッシュ値を生成し、そのハッシュ値を署名者の秘密鍵で暗号化し、この暗号化した値を署名値として文書に付加する。尚、文書のハッシュ値を署名者が使用するクライアント端末に送り、署名者側で当該ハッシュ値をもとに署名値を作成し、署名者から当該署名値を貰って署名サーバで文書に付加するなど、上記以外の処理でもよい。尚、署名作成部106は、必要に応じて外部サーバ141と連携し、タイムスタンプやOCSPレスポンス等の取得を行う。また署名作成部106は、文書に署名を行った際、署名文書の形式を判断し、文書管理情報111や仮想管理情報112をもとに、署名対象が仮想化されているデータ又は共通のデータとして他の文書から参照されているデータを含むか判断し、判断結果に基づき、署名文書から署名や署名に関する情報を抽出、又は署名文書から文書データを抽出し、文書管理部108を通して、もとの署名文書から当該抽出データを除去したデータと、当該抽出データを、署名文書の情報として記憶部102に記憶する。署名検証部107は、文書になされた署名が正当か否かの検証を行う。具体的には、署名文書のハッシュ値から署名値を計算し、当該計算した署名値と署名文書に付加されている署名値を比較して一致する場合は、正当と判断する。文書管理部108は、ユーザからの要求を受けて、文書の編集や記憶、外部への文書の転送や外部からの文書の取込みを行う。仮想管理部109は、複数の文書間で共通のデータを管理し、各文書のデータを比較することで文書間で共通のデータがあるか否か判断し、共通のデータがある場合は、データの実体を一つ保持し、他の文書から当該データの実体を参照させる、即ち、文書を仮想化することを行う。尚、各文書のデータの比較は、文書単位で比較してもよいし、文書のデータを分割し分割単位で比較してもよい。データの分割は均等サイズであっても、任意サイズであってもよい。その他にも、例えばPDF等の場合は文書内においてデータがオブジェクト番号ごとに管理されており、各オブジェクト番号のデータ毎等にデータの一致比較を行うようにしてもよい。署名文書組立て部110は、もとの署名文書から抽出された署名や署名に関する情報又は文書データと、当該署名文書が仮想化されているか否か(他の文書のデータを参照しているか)の情報をもとに、当該抽出が行われる前のもとの署名文書を組立てる。 Next, program information stored in the
次に記憶部122に格納される情報について説明する。サーバ連携部125は、署名サーバ101など外部のサーバと連携し、ユーザからの操作要求(署名作成や文書編集要求など)を外部のサーバに送信、外部のサーバからの応答結果の受信等を行う。ユーザ連携部126は、クライアント端末への操作要求を行うユーザを認証し、ユーザが要求する操作の許可、又は禁止、操作結果の表示等の処理を行う。 Next, information stored in the
以上が本実施例における署名システムのハードウェアおよびソフトウェア構成である。次に、前述したハードウェアおよびソフトウェア構成に基づいて本実施例における文書への署名実施、署名文書の組立て、文書の取込みの処理について説明する。文書への署名実施処理は、ユーザからの要求を受けて署名サーバ101が文書に署名する時などに行う。署名文書の組立て処理は、署名サーバ101が外部に署名文書を転送する時などに行う。文書の取込み処理は、署名サーバ101が外部から文書を受信して記憶部102に記憶する時などに行う。以下に各処理の詳細を示す。
<文書への署名実施処理>
図6は、本発明の第1の実施例の署名サーバ101が実行する、文書への署名実施処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。The above is the hardware and software configuration of the signature system in the present embodiment. Next, a description will be given of processing for signing a document, assembling a signed document, and taking in a document according to the present embodiment based on the hardware and software configurations described above. The signature execution processing for the document is performed when the
<Signature execution processing for documents>
FIG. 6 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a signature execution process for a document executed by the
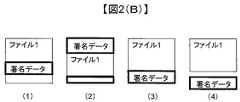
ユーザ連携部105は、ユーザから署名作成の要求を受付ける(601)。具体的には、どの文書に対して署名を行うか等の情報を受信する。上記要求を受け、署名作成部106は、文書に対して署名を行い、署名した文書を記憶部102に記憶する前に、署名文書の形式を判断する(602)。前記署名した文書が、署名対象の文書の中に署名データが挿入される形式の場合(603)、署名作成部106は、さらに署名文書が仮想化されているか否か、即ち、他の文書のデータを参照しているか否か文書管理情報111の情報を見て判断し(604)、仮想化されている場合、前記署名した文書から署名データを取り除き、当該取り除いた署名データを分離管理情報113として別途管理する(605)。尚、署名文書の形式の判断は、例えば署名文書の中身を解析して署名データ部分を特定して判断してもよいし、署名を実施する際に適用した署名のフォーマット情報(例えば署名タイプ303で表されるような情報)をもとに判断してもよい。または各文書の署名の有無を示すフラグを設けて別途管理してもよい。署名文書の形式としては、例えば図2(B)に示すようなものが挙げられる。図2(B)において(1)と(3)は署名対象の文書の中に署名データが挿入される形式である。そのうち(3)は文書の末尾に増分更新(もとの文書に変更を加えずに追加)する特別な場合であり、例えば署名を延長するためにアーカイブ形式で次々と署名を追加していく場合などにこのような形式になりうる。そして(2)は署名データの中に署名対象の文書が含まれている形式であり、(4)は署名データを格納する文書と文書データを格納する文書が別々の形式である場合である。例えば署名対象の文書の中に署名データが挿入される形式の一例としては、図2(C)の(1)に示すPDF文書であり、「<</Type/Sig〜>>」といった形で文書の中に署名データが格納されている。尚、ステップ604は文書が仮想化されているか否かの判断であり、仮想化されている場合にステップ605以降の処理を行う形態だが、その他の形態として、仮想化されていない文書であっても他の仮想化されている文書から参照されている文書の場合については、ステップ605以降の処理を行うようにしてよい。尚、文書が仮想化されているか否かは、参照データ302をもとに判断可能であり、参照データ302の登録がある文書は他の文書の参照により仮想化されている。また、文書が他の文書から参照されているか否かは、仮想管理情報112のデータ項目402をもとに判断可能であり、データ項目402に登録されている文書は他の文書からデータを参照されている。また、署名文書が仮想化されているかの判断に加えて、署名データが仮想化されている部分に入り込むかまで判断するようにしてもよい。そして署名作成部106は、上記処理を行った署名文書、即ち、署名データ除去後の署名文書を記憶部102に記憶し(606)、処理を終了する。一方、前記署名した文書がステップ603の形式ではない場合、署名作成部106は、前記署名した文書が、署名データの中に署名対象の文書が含まれている形式であるか判断し(607)、当該形式である場合は、前記署名した文書から署名対象の文書データを取り除き、当該取り除いた文書データを分離管理情報113として別途管理し(608)、ステップ606に進んで上記処理を行った署名文書を保存し、処理を終了する。例えば署名データの中に署名対象の文書が含まれている形式の一例としては、図2(C)の(2)に示すXML文書であり、<Signature>で表される署名データの中に、<Object Id=”test”>といった形で指定される文書データが格納されている。尚、これらの署名文書の形式は文書の拡張子によって唯一定まるわけではなく、例えばXML文書であっても図2(C)の(1)の形態を取る場合もある。前記署名した文書が、ステップ607の形式でない場合(例えば署名文書と署名対象の文書が別々の文書になっている場合等)はステップ606に進み、前記署名した文書をそのまま保存し、処理を終了する。尚、上記処理においては、単に署名文書から署名データを抽出・除去するのではなく、署名文書の形式に応じて、署名文書から署名データではなく文書データを抽出・除去するようにしている。これは、署名文書から署名データを除去するだけでは、署名文書によっては(例えば図2(C)の(2)のような場合)署名対象のデータまで削除され、データの実体が残らなくなってしまうためである。また、上記処理において、文書に署名する以外に内容を追加してから署名するような場合も考えられるが、その場合も内容を追加した文書から上記処理と同様に署名データや文書データの抽出を行うようにしてもよい。また、上記処理において、署名データや文書データが除去された署名文書を保存する前に、当該除去が行われた署名文書を再度一つの署名文書に組立てて、当該組立てた署名文書の署名を検証して正当と確認してから(正しく復元可能な状態で当該除去が行われたと判断してから)、当該除去が行われた署名文書を保存するようにしてもよい。 The
次に、本実施例における、署名文書の組立て処理について説明する。尚、署名文書の組立て処理は、署名サーバ101が外部(クライアント端末121や外部サーバ141など)に署名文書を転送する時などに行われる。本処理により、署名サーバ101が備えるような署名文書の分離や組立ての仕組みが無い計算機であっても、署名サーバ101から転送された署名文書を正しく認識できるようになる。
<署名文書の組立て処理>
図7は、本発明の第1の実施例の署名サーバ101が実行する、署名文書の組立て処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。Next, a process for assembling a signature document in this embodiment will be described. The signature document assembling process is performed when the
<Assembly processing of signature document>
FIG. 7 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a signature document assembling process executed by the
ユーザ連携部105は、ユーザから文書のexport要求を受付ける(701)。具体的には、どの文書をどこにexportするか等の情報を受信する。上記要求を受け、文書管理部108は、前記export対象の文書が署名を含むか判断し(702)、署名を含まない場合は、仮想化されているか判断する(708)。署名の有無や仮想化の有無の判断は、署名作成処理の場合と同様にして行うことができる。仮想化されていない場合はステップ707に進み、仮想化されている場合は、仮想化されているデータを実データとして文書を構築し、ステップ707に進む。尚、仮想化されているデータを実データにする一例としては、例えば参照しているデータを仮想化されている部分にコピーする等して行う。ステップ702において、前記export対象の文書が署名を含む場合、文書管理部108は前記export対象の文書から署名が除去されているか判断し(703)、除去されてない場合は、ステップ710に進み、除去されている場合は、さらに前記export対象の文書が仮想化されているか判断する(704)。署名が除去されているか否かは、例えば文書管理情報111の項目304及び分離管理情報113の項目402をもとに判断することができ、項目304の登録がある文書で、項目402が署名に関するものである場合は署名が除去されていると判断する。仮想化されてない場合ステップ706に進み、仮想化されている場合、前記export対象の文書の仮想化されている部分を実データとして文書を構築した後(705)、前記除去されている署名データをもとの文書に入れて署名文書を構築する(706)。尚、上記ではまず仮想化されているデータを実データに戻してから文書への署名データの入れ込みを行う。これは、文書への署名データの入れ込みを行ってから仮想化されているデータを実データに戻すと、当該実データによって署名データが上書きされてしまう可能性があるためである。また本処理では、文書への署名データの入れ込みにあたり、入れ込む部分にもともとあった文書のデータは、署名データの下にずらす等配置して文書を保存する。尚、署名対象文書の中に署名データが挿入されている形式において、仮想化されているデータの中に署名データが入り込む場合はあっても、仮想化されているデータが署名データの中に入り込む場合はないため、上記の逆の手順、即ち署名データを入れ込んだ後に、仮想化されているデータを実データに戻して署名データをずらすということは行えない。そして署名サーバ101は文書をexportし(707)、処理を終了する。ステップ703で署名が除去されてない場合、文書管理部108は、前記export対象の文書から文書データが除去されているか判断し(710)、除去されてない場合ステップ707に進み、除去されている場合、前記除去されている文書データをもとの文書に入れて署名文書を構築し(711)、ステップ707に進む。文書データが除去されているか否かは、例えば文書管理情報111の項目304及び分離管理情報113の項目402をもとに判断することができ、項目304の登録がある文書で、項目402が文書に関するものである場合は文書データが除去されていると判断する。尚、上記処理では、署名文書を外部にexportする際に文書を組立ててからexportしているが、別の形態として文書の組立てを行わずに分離したままexportする処理としてもよい。これは例えば署名文書を別の署名や文書管理のシステムに移行するにあたり、移行先が本署名システムと同様の署名作成や文書管理の機能を持つシステムの場合、再度移行先のシステムで後述の文書の取込み処理を行う手間、即ち、適宜署名文書から署名データや文書データの抽出・除去及び、これら抽出したデータを別管理する手間を省くためである。また、署名文書を分離したままexportすることで、例えば署名文書のうち旧システム(移行元)による署名データ部分だけ破棄して、新システム(移行先)による署名データに置き換えて署名文書を保存する等が可能である。例えば分離した形の署名文書を旧システムから受取った新システムは、当該分離した形の署名文書の署名データを検証し、署名データが正当である、即ち、署名文書が旧システムからexportされてから新システムに取込まれる迄の間に改竄されてない、と判断された場合は、当該署名文書の署名データを新システムの署名データに置き換えて文書を保存する等である。尚、署名データの置き換えにあたっては、新システムの署名データを付加する際、もとの文書に変更を加えずに処理してもよいし、新システムに固有のメタデータ等を文書に加えてから処理してもよい。 The
次に、本実施例における、文書の取込み処理について説明する。本処理により、署名サーバ101以外の計算機が作成した署名文書であっても、前述のような署名文書から署名や文書の情報が抽出及び別管理された形で署名サーバ101に保存されるようになる。
<文書の取込み処理>
図8は、本発明の第1の実施例の署名サーバ101が実行する、文書の取込み処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。Next, document fetch processing in the present embodiment will be described. With this processing, even for a signature document created by a computer other than the
<Document import processing>
FIG. 8 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a document fetch process executed by the
ユーザ連携部105は、ユーザから文書の取込み要求を受付ける(801)。具体的には、ユーザから文書のuploadを受けるなどして、取込む文書や取込み先等の情報を受信する。上記要求を受け、文書管理部108は、前記export対象の文書が署名を含むか判断し(802)、署名を含まない場合は、ステップ806に進み、署名を含む場合は、当該文書を保存する前に当該署名文書の形式を判断する(803)。文書管理部は、当該文書が、署名対象の文書の中に署名データが挿入される形式か判断し、当該形式でない場合はステップ810に進み、当該形式の場合は(804)、文書から署名データを抽出して除去し、当該抽出した署名データを別途管理する(805)。尚、署名の有無や形式は署名実施処理と同様にして判断できる。また、抽出したデータは、分離管理情報113として管理する。次に文書管理部108は、当該署名データが除去された文書が署名サーバ101内の共通データと一致するか否か判断する(806)。一致するものがない場合はステップ809に進み、一致するものがある場合は、一致する部分のデータは共通データのデータを参照することで文書を仮想化し(808)、文書を保存する(809)。尚、共通データと一致するか否かの判断は仮想管理情報112に登録されているデータとの一致比較により行う。尚、他の形態として共通データとの一致比較以外に、署名システム内の任意の他の文書とのデータの一致比較を行うようにしてもよい。また、文書を仮想化する場合は、文書管理情報111の項目302に、参照している文書のデータを識別するための識別番号401が登録される。また、仮想化によって新たな共通データが生じる場合は、仮想管理情報112に当該共通データの情報が登録される。取込み対象の文書がステップ804の形式でない場合、文書管理部108は、当該文書が、署名データの中に署名対象の文書が含まれている形式か判断し(810)、当該形式の場合は、文書から、署名データの中に署名対象として含まれている文書データを抽出して除去し、当該抽出した文書データを別途管理し(811)、ステップ809に進んで当該抽出・除去を行った文書を保存する。当該文書がステップ810の形式でない場合(例えば署名文書と文書が別々の文書になっているような場合など)は、ステップ809に進んでこれらの文書を保存する。 The
尚、前述の署名実施処理において、署名した文書に対して、さらに署名サーバ101が別の署名を行う場合、即ち、文書に二個以上の署名を行うような場合、署名対象の署名文書が分離されて管理されているか文書管理情報111の項目304をもとに判断し、分離されている場合は、前述の署名文書の組立て処理と同様にして当該署名文書を一時的に一つの署名文書に組立て、当該組立てた署名文書に対して署名を行い、前述の署名実施の処理の場合と同様にして、適宜前記組立てた署名文書から署名データや文書データを抽出・除去し、分離管理情報113として別途管理する。尚、上記処理において一時的に一つの署名文書を組立ててから署名を行うのは、分離されているものではなく署名文書全体を対象として署名値を算出するためである。 In the signature execution process described above, when the
また、文書間での共通データの有無の比較は、前述の署名実施処理や文書取込み処理を契機として行ってもよいし、これらの処理とは独立して定期的なタイミング等で実施するようにしてもよい。また、署名文書からの署名データの抽出・除去においては、署名データだけを抽出・除去するのではなく、署名データを含む増分更新データ(もとの文書に変更を加えずに追加したデータ)全体を抽出・除去するようにしてもよい。例えばもとの文書に変更を加えずにアーカイブ形式で署名を追加するような場合等であり、例えばPDF文書では%%EOFで括られるデータ等が増分更新データに該当する。尚、上記の第1の実施例においては、文書に署名した際、当該署名文書から適宜署名や文書データを抽出してから署名文書を保存する。本処理を行わない場合、仮想化されている部分や他文書から参照されて利用されている部分に署名データが入り込んだ場合に、参照元と参照先の文書間でデータが一致しなくなり、参照関係を維持できなくなる。本処理を行うことで、署名後も、参照元と参照先の文書は実質的に同内容となるため、データの参照関係を維持したままにすることができる。 In addition, the comparison of the presence or absence of common data between documents may be performed in response to the above-described signature execution processing or document capture processing, or may be performed at regular timing etc. independently of these processing. May be. In addition, when extracting / removing signature data from a signed document, the entire incremental update data including the signature data (data added without changing the original document) is not extracted / removed only from the signature data. May be extracted and removed. For example, the signature is added in the archive format without changing the original document. For example, in the PDF document, the data enclosed in %% EOF corresponds to the incremental update data. In the first embodiment, when a document is signed, the signature document is stored after appropriately extracting the signature and document data from the signed document. If this processing is not performed, when signature data enters a virtualized part or a part that is referenced and used by another document, the data does not match between the reference source and the reference destination document. The relationship cannot be maintained. By performing this processing, the reference source document and the reference destination document have substantially the same content after the signature, and thus the data reference relationship can be maintained.
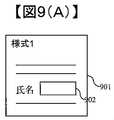
以上が、第1の実施例の文書への署名実施、署名文書の組立て、文書の取込みの処理の説明である。次に、本発明の第1の実施例の変形例を説明する。本変形例では、第1の実施例の処理に加え、署名サーバ101は予めベースとなる文書の様式情報を持ち、当該様式情報をもとに文書の作成、署名を行うことができる。また予め登録されている様式情報以外に、新たに任意の様式情報を追加して使用することも可能である。様式情報について図9(A)を一例として説明する。図9(A)の様式1(901)では、氏名(902)以外の部分には既に定型の文書が記載されており、ユーザはこの様式1のうち空白となっている氏名部分を編集して新たな文書を作成することができる。例えば契約書の文書など、文書の記載内容の殆どが予め固定化されていて、文書の一部分のみ編集する必要がある場合には、このような様式情報を使うことで、毎回同じ内容を逐一入力して文書を作成する手間を省くことができる。 The above is the description of the signature execution process, signature document assembly process, and document capture process of the first embodiment. Next, a modification of the first embodiment of the present invention will be described. In this modification, in addition to the processing of the first embodiment, the
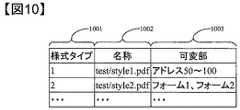
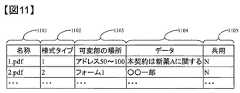
本変形例の署名サーバの記憶部102は、図1の内容と異なり図14(A)に示す要素で構成される。新たな項目114〜116が加わっている。様式管理部114は、様式管理情報115への様式情報の追加や、様式情報の編集等の管理を行う。様式管理情報115は、署名サーバ101が保持している様式情報を示し、事前に登録されている情報以外に新たに様式情報を追加することも可能である。様式管理情報115について図10を一例として説明する。様式管理情報115は、項目1001〜1003の三つのデータ項目を含む。項目1001は、様式情報を識別するための様式タイプを示す。項目1002は、各様式情報の名称を示す。項目1003は、各様式情報における可変部、即ち、各様式において、文書が固定ではなく、ユーザが編集可能な部分を示す。例えば図10において、様式タイプが1の様式は、test/style1.pdfという名称であり、当該様式においてアドレス50〜100の部分のデータは固定ではなくユーザが編集できるようになっている。可変部管理情報116は、様式を使って作成した文書において、当該文書での可変部のデータを管理する情報である。可変部管理情報116について、図11を一例として説明する。可変部管理情報116は、項目1101、1102、1103、1104、1105の五つのデータ項目を持つ。項目1101は、様式を用いて作成した文書の名称名を示す。項目1102は、項目1101の文書で使用された様式のタイプを示す。様式のタイプは項目1001で登録されているものが使用される。項目1103は、項目1101の文書における可変部、即ち、文書が固定ではなく編集が可能な部分の場所情報(例えば当該文書のアドレス50〜100まで等)を示す。項目1104は、項目1101の文書における可変部のデータを示す。例えば図11において、名称1101が1.pdfの文書の可変部には、「本契約は新薬Aに関する」というデータが格納されている。尚、可変部のデータを管理する別の形態として、例えばdocx形式の文書等、複数の文書で一つの文書が構成される文書において、ベースとなる文書の中に、可変部データを記述するための追加文書を埋込んで一つの文書を構成して管理するようにしてもよい。具体的には文書の固定部分を記載した1.docx文書の中に、データの入力等の編集が可能な、各可変部のデータを記述するための文書2.docx、3.docx等を埋込み、この初期(可変部のデータがまだ記述されていない状態)の一つの文書を様式文書とし、ユーザの編集するデータ(可変部のデータ)は2.docx、3.docxとして管理する等である。項目1105は、項目1101の文書の可変部のデータの共用可否を示す情報である。データの共用を許可する場合、当該データが他の文書のデータと一致するか否かの判定を行い、一致する場合は、他の文書からデータを参照させる又は他の文書のデータを参照する。例えば図11において、「N」となっているものは、共用を許可しないことを示す。 Unlike the contents of FIG. 1, the
以下に第1の実施例の変形例での、文書への署名処理を説明する。以下では、第1の実施例と処理の異なる部分についてのみ説明する。本変形例では、第1の実施例とは異なり予め定められた定型の文書をもとに文書の作成及び署名を行う。以下に処理の詳細を示す。
<第1の実施例の変形例での文書への署名処理>
ユーザからの要求を受け、署名サーバ101は、ユーザから指定された様式情報をもとに文書を作成する。具体的には、ユーザに指定された様式タイプ1001の文書を複製するなどして文書を作成し、当該文書の可変部をユーザからの要求を受けて編集する。尚、本手順で作成した文書の情報は可変部管理情報115として登録される。例えば図11において、「1.pdf」の文書は、様式タイプが「1」の文書をベースに作成されており、ユーザが編集した可変部のデータは項目1104として管理され、他のデータとの共用は行わない設定となっている。また、当該作成した文書においては、ベースとした前記様式タイプの文書のデータについては、実データを持たずに前記様式タイプの文書のデータの参照により実現する(当該作成した文書を仮想化する)。但し、これに限らず実データを持つような形式にしてもよい。そして署名サーバ101は、当該作成した文書に署名を行う。この時、作成した署名文書を保存する前に、実施例1と同様にして、前記署名文書が、署名対象の文書の中に署名データが挿入される形式か判断し、当該形式の場合、前記署名文書から署名データを取り除き、当該取り除いた署名データを分離管理情報113として別途管理し、上記処理を行った署名文書を保存する。一方、前記署名文書が上記の形式ではなく、前記署名文書が、署名データの中に署名対象の文書が含まれている形式の場合、前記署名文書から署名対象の文書データを除去し、除去した文書データを分離管理情報113として別途管理し、上記処理を行った署名文書を保存する。尚、前記抽出した文書データが実データではなく、他の文書のデータを参照しているデータの場合は、その参照関係を維持したままデータの抽出を行う。一方、前記署名文書が上記の何れの形式でもない場合、例えば署名対象の文書と署名が別々の文書として作成されるような場合は、前記署名文書をそのまま保存する。In the following, a document signature process according to a modification of the first embodiment will be described. In the following, only the parts that differ from the first embodiment will be described. In this modification, unlike the first embodiment, a document is created and signed based on a predetermined standard document. Details of the processing are shown below.
<Signature Processing for Document in Modification of First Embodiment>
Upon receiving a request from the user, the
以上の処理を行うことで、図9(B)に示すように、様式情報をベースとして文書の作成及び署名が行われ、作成された署名文書は、署名サーバ101の内部においては適宜、様式タイプのデータ、署名のデータ、可変部のデータといった形で分けて管理されることになる。尚、署名文書の組立て処理については、第1の実施例と同様にして、署名文書の仮想化されている部分を実データとして構成し直した後、各署名文書の可変部分のデータと結合させ、上記の抽出や除去が行われた署名データまたは文書データを、前記結合を行った署名文書に入れ込むことで行う。また、文書の取込み処理については、第1の実施例と同様にして、適宜署名文書から署名データまたは文書データを抽出・除去して別途管理し、当該除去が行われた署名文書が上記の各様式タイプの文書のデータと一致するか否か判断し、一致する場合は、一致する部分のデータを上記の様式タイプの文書のデータの参照により構成して文書を保存することで行う。例えば、製薬業界等の業務に特化した形の文書においては、所定のベースとなる定型文書を様式として設けておき、基本は当該定型文書との一致判定を行うということが考えられる。また、上記の一致比較の別の形態として、一致比較を行わずに文書取込みの際にユーザがどの様式タイプを使った文書であるか指定することで様式タイプを判断してもよいし、文書の所定部分の情報をもとに様式タイプを判断してもよいし、文書の構造(例えばdocx形式等の文書の場合、一つの文書内にどんな文書が埋込まれているか等)の情報をもとに様式タイプを判断してもよいし、様式タイプの文書との比較以外に、任意の文書とも比較するようにしてもよい。 By performing the above processing, as shown in FIG. 9B, a document is created and signed based on the format information, and the created signature document is appropriately stored in the
以上が、本発明の第1の実施例およびその変形例の説明である。 The above is the description of the first embodiment of the present invention and its modifications.
次に、本発明の第2の実施例を説明する。第2の実施例では、複数のユーザ間で文書への署名、署名文書の承認といった、一連の署名のワークフローを行う。署名サーバ101はユーザからの要求を受けて署名ワークフローを開始し、各ユーザに文書への署名依頼や、署名文書の承認依頼を行う。ワークフローにおいて承認が得られなかった場合は、一つ前のユーザにワークフローを戻して文書の修正依頼を行う。本実施例での署名のワークフローは、実施例1の署名作成や文書管理方式をベースとする方式である。これにより、仮にワークフローが一つ前のユーザに戻されて署名文書を修正する場合でも、当該ユーザはそのフローの最初の状態から文書を編集し直す必要がない。即ち、署名に関する情報は別に管理されているため、承認依頼する直前の文書(承認依頼した文書から署名に関する情報だけが除かれた文書)を使って、編集し直すことができる。具体的には、例えば一番目のユーザが文書を作成し、次のユーザが当該文書に内容を追加して署名し、三番目のユーザが署名文書を承認するような場合、承認が得られなかった場合、二番目のユーザは、一番目のユーザが作成した文書に再度内容を追加して修正し直すのではなく、三番目のユーザに承認依頼する直前の文書で署名を付ける前のものを使って修正することができる。これは、本実施例の署名ワークフロー方式では、署名に関する情報が署名文書とは別に管理されているために実現することができる。当該方式ではない場合、一旦署名された文書を編集し直そうとしても、署名文書の改竄となってしまうため、承認依頼した文書ではなく、一番目のユーザが作成した文書を再度編集し直す必要がある。その他に変更管理のような仕組みを使って文書をもとに戻すことも考えられるが、その場合、ある一時点の文書(例えばフローにおいて、一番目のユーザの操作が終了した時点の文書のみ等)を管理するのでなく、全ての時点の文書の情報、即ち、文書に対するユーザの操作を逐一記録・管理しなければならず、管理すべき情報や仕組みの複雑性が増す。その他にフローの各フェーズの終了時点ごとに文書を保存する仕組みの場合は、フローのフェーズ数分文書を保存する必要があるため、フェーズ数が多くなるにつれて管理すべき情報が増大してしまう。本方式では、保存が必要なのはある一時点の文書のみであり、上記のような利便性の高い署名ワークフローを行うことができる。本実施例の署名サーバの記憶部102は、図14(A)の内容と異なり図14(B)に示す要素で構成される。新たな項目117、118が加わっている。署名フロー管理部117は、ユーザからの要求を受けて、実施したい署名ワークフローの登録(署名ワークフロー管理情報118に署名ワークフロー内容の登録)、署名ワークフローの開始、実施中の署名ワークフローのステータス管理、ユーザ連携部と連携してユーザへの署名依頼通知等を行う。署名ワークフロー管理情報118は、どの文書に誰にどんな条件で署名や編集させるかといった、署名ワークフローに関する情報を示す。署名ワークフロー管理情報118について図12を一例として説明する。署名ワークフロー管理情報118は、項目1201〜1206の六つのデータ項目を含む。項目1201は、各署名ワークフローを識別するための識別番号を示す。項目1202は、各署名ワークフローにおいて、署名や編集対象となる文書の情報を示す。各署名者は、当該文書に対して順次署名や編集を行う。項目1203は、署名ワークフローの進捗状況を示す。例えば図12において、署名条件ID1201が「1」のものは、項目1203が「1/2」である。これは項目1202で指定された文書に対して全部で二人のユーザに署名や編集や承認等を行わせる予定だが、現在そのうちの一人目のユーザが作業を行なっている途中であることを示す。一人目のユーザの処理が完了すると、項目1203は「2/2」即ち、二人目のユーザが署名ワークフローにおいて依頼されている作業を行うことになる。項目1204は、署名や文書の編集を実施可能な署名者を示す情報である。本情報により、指定した署名者のみ署名可能にする等が可能になる。尚、予め署名者を指定するのでなく、任意のユーザからの署名を可能にする等の設定にしてもよい。項目1205は、署名ワークフローの順序を示す情報である。例えば図12の例では、署名者Aの順序が「1」で署名者Bの順序が「2」である。これは、まず署名者Aが署名や文書の編集、承認等の作業を完了してからでないと署名者Bは作業できないことを示す。本情報により各署名者のワークフローにおける順序を設定可能だが、順序を設定しない、即ち任意の順序での署名や文書の編集等を可能にする設定にしてもよい。例えば項目1205に全て同じ値を設定するなどして、作業の順序制御しないようにしてもよい。項目1206は、各署名者にどんな条件で署名を行わせるか(署名のみ、署名と文書の編集、承認等)についての情報を示す。例えば図12の例では、署名者Aは、文書に署名のみ行うのに対し、署名者Bは署名文書の承認を、署名者Cは文書の編集(コメント追加)と署名の両方を行う。尚、上記以外の条件、例えば署名は行わせず文書の編集や確認のみ行わせるような条件等、を設定してもよい。 Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. In the second embodiment, a series of signature workflows such as document signature and signature document approval is performed between a plurality of users. Upon receiving a request from the user, the
以下に、本実施例での署名ワークフローの処理の詳細について説明する。署名サーバ101は、ユーザに対して署名依頼、署名文書の承認依頼及び、承認が得られなかった署名文書の修正依頼等を行う。
<署名ワークフロー処理>
図13は、本発明の第2の実施例の署名サーバ101が実行する、署名ワークフロー処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。Details of the signature workflow processing in this embodiment will be described below. The
<Signature workflow processing>
FIG. 13 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a signature workflow process executed by the
ユーザ連携部105は、ユーザから署名ワークフローの開始要求を受付け、署名ワークフローを開始する(1301)。具体的には、ユーザが事前に設定するなどして登録した署名ワークフロー(署名ワークフロー管理情報118に登録された署名ワークフロー)について、ユーザから開始要求を受け、当該登録された内容に沿って署名ワークフローを開始する。署名サーバ101は、前記登録された署名ワークフローの情報をもとに、ユーザに署名依頼の通知を行う(1302)。例えば図12において、項目1201が「1」の署名ワークフローについては、最初に署名者Aに「1.pdf」の文書に署名するよう依頼を行う。署名サーバ101は前記ユーザからの要求を受け、文書への署名を行う(1303)。署名サーバ101は署名した文書を保存する前に、署名文書を分析し、署名対象の文書の中に署名データが挿入される形式か判断する(1304)、当該形式でない場合ステップ1307に進み、当該形式の場合、署名された文書から署名データを抽出・除去し、当該抽出した署名データを別途管理し(1305)、文書を保存する(1306)。一方、前記署名した文書がステップ1304の形式ではない場合、署名サーバ101は、前記署名した文書が、署名データの中に署名対象の文書が含まれている形式であるか判断し(1307)、当該形式である場合は、前記署名した文書から署名対象の文書データを取り除き、当該取り除いた文書データを分離管理情報113として別途管理し(1308)、ステップ1306に進んで上記処理を行った署名文書を保存する。前記署名した文書が、ステップ1307の形式でない場合(例えば署名文書と署名対象の文書文書が別々の文書になっている場合等)はステップ1306に進み、前記署名した文書をそのまま保存する。尚、署名文書の形式の判断や署名文書からの署名データや文書データの抽出・除去については、第1の実施例と同様にして行う。 The
次に署名サーバ101は、署名ワークフローを次の段階へ進め、署名ワークフローにおいて順序1305が次のユーザ(例えば承認者等)に、署名文書の承認等の依頼通知を行う(1309)。この時例えば図12において、項目1201が「1」の署名ワークフローの場合、署名者Bに依頼通知が送られ、項目1203のステータスは「2/2」に設定される。署名サーバ101は、当該ユーザに署名文書の提示等を行う場合は、上記の除去され別途管理された署名データ等を組合せて、一つの署名文書を組立てて提示する(1310)。尚、署名文書の組立ては第1の実施例と同様にして行う。当該ユーザに署名文書が承認された場合(1311)、署名サーバ101は、署名ワークフローの開始要求を行ったユーザに、署名ワークフローの終了通知を行い(1312)、署名ワークフロー処理を終了する。ステップ1311において承認されなかった場合、署名サーバ101は、当該ユーザの一つ前のユーザ(署名者)に、署名文書の修正依頼を行う。例えば図12において、項目1201が「1」の署名ワークフローの場合、署名者Aに修正依頼が送られる。署名サーバ101は、当該一つ前のユーザに修正が必要な署名文書の提示を行う場合は、上記の署名文書から当該一つ前のユーザが最初のワークフローの段階(例えば図12において、項目1201が「1」の署名ワークフローの場合、項目1203のステータスが「1/2」の段階)で行った署名のデータを除去して提示する(1314)。署名サーバ101は、当該一つ前のユーザからの要求を受け、前記署名のデータが除去された文書の編集や署名を実施し(1315)、ステップ1309に進む。尚、上記の署名ワークフローにおいて、文書に署名するだけでなく、文書に内容を追加して署名するような場合は、署名ワークローのどのフェーズでの内容追加かといった情報も併せて管理するようにしてもよい。 Next, the
以上が、本発明の第2の実施例の説明である。 The above is the description of the second embodiment of the present invention.
以上の本発明の実施の形態によれば、例えば、署名サーバとクライアント端末を含んで構成される署名システムにおいて、署名サーバは署名や編集対象の文書を格納する文書管理情報と、他の文書から参照される等して一以上の文書間で共有する共通データを管理する仮想管理情報と、署名文書から抽出された文書や署名のデータ等、各文書とは別途管理される情報を管理する分離管理情報とを備える。署名サーバ101はユーザからの指示に基づき、文書への署名を実施し、署名文書の形式や文書の仮想化有無等を判断し、署名文書を保存する前に、適宜署名文書から文書や署名データの抽出及び除去を行い、当該抽出したデータを別途記憶部102に記憶する。署名サーバはさらに、前記署名文書を署名サーバ外部に転送する場合は、適宜前記署名文書の仮想化された部分(他の文書の実データを参照している部分)のデータを実データとして構成し直した後、適宜抽出・除去された署名データを組合せて一つの署名文書として構成し直したものを送信し、署名サーバの外部で作成された署名文書を署名サーバに取込む場合は、当該署名文書の形式等を判断し、署名文書を保存する前に、適宜署名文書から文書や署名データの抽出及び除去を行い、当該抽出したデータを別途記憶部102に記憶し、当該文書や署名データの抽出及び除去が行われた署名文書が署名サーバ内の他の文書と共通のデータを含むか判断し、共通のデータを含む場合は、当該署名文書のデータを実データでなく共通のデータの参照により実現し保存する。署名サーバの他の形態として、署名サーバはさらに、文書の様式についての情報を予め定めた様式管理情報と、当該様式における編集可能な部分についての情報を管理する可変部管理情報とを備え、当該様式をもとに新規文書の作成及び、新規文書への署名を行い、新規文書における様式で固定されている部分のデータの仮想化や、適宜署名文書からの署名データの抽出及び除去を行い、当該抽出したデータと、新規文書における様式で固定されていない可変部分のデータとを、別途記憶部102に記憶する。署名サーバはさらに、複数人でワークフロー形式で文書への署名や署名文書の承認等を行うための署名フロー管理情報を備え、ユーザからの要求をもとに文書への署名を行い、上述の署名作成処理と同様にして、署名文書を保存する前に、署名文書の形式等をもとに適宜、署名文書から文書や署名データの抽出及び除去を行って文書を保存し、あるユーザが作成した署名文書について次のユーザから承認を得られなかった場合は、署名サーバは当該署名文書から前記あるユーザが実施した署名に関するデータを除去し、当該署名に関するデータが除去された、承認を依頼する直前の文書を前記あるユーザに対して提示して署名文書の修正及び署名を受付ける。 According to the above-described embodiment of the present invention, for example, in a signature system including a signature server and a client terminal, the signature server includes document management information for storing a signature and a document to be edited, and other documents. Virtual management information that manages common data that is shared among one or more documents by being referenced, etc., and separation that manages information that is managed separately from each document, such as documents extracted from signature documents and signature data Management information. The
以上説明した本発明の一実施形態によれば、仮想文書に電子署名を行う場合でも、管理すべきデータを増大させることなく、実体文書を参照できる。また、予め文書の様式が定められた定型の文書を用いた場合の署名文書の効率的管理や、署名ワークフローの手戻り発生時における利便性の高い署名文書の修正を行うことができる。 According to the embodiment of the present invention described above, even when an electronic signature is applied to a virtual document, it is possible to refer to an actual document without increasing data to be managed. In addition, it is possible to efficiently manage a signed document when a standard document having a predetermined document format is used, and to correct a highly convenient signed document when a rework of the signature workflow occurs.
以上、本発明の実施の形態について説明したが、本発明はこうした実施の形態に何ら限定されるものではなく、本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲内において様々な形態で実施し得ることは勿論である。 As mentioned above, although embodiment of this invention was described, this invention is not limited to such embodiment at all, Of course, it can implement with various forms within the range which does not deviate from the meaning of this invention. is there.
101…署名サーバ、102、122…記憶部、103,124…制御部、104,123…I/F,121…クライアント端末。101 ... signature server, 102, 122 ... storage unit, 103,124 ... control unit, 104,123 ... I / F, 121 ... client terminal.
Claims (12)
Translated fromJapanese文書への署名要求に基づき該文書への署名を行い、署名文書を記憶部に記録する前に、該署名文書の形式を判断し、
前記判断した署名文書の形式が署名対象文書に署名データが挿入される形式で、前記署名対象文書が実体文書を参照する仮想文書の場合、前記署名文書から前記署名データを除去し、該署名データを前記記憶部に記憶し、
前記署名データ除去後の文書を前記記憶部に記憶する、
ことを特徴とする署名文書の管理方法。A method for managing a signed document in a signature server that signs a document,
Signing the document based on a signature request for the document, and determining the format of the signed document before recording the signed document in the storage unit,
When the determined signature document format is a format in which signature data is inserted into a signature target document and the signature target document is a virtual document that refers to an entity document, the signature data is removed from the signature document, and the signature data Is stored in the storage unit,
Storing the document after the removal of the signature data in the storage unit;
A signed document management method characterized by the above.
前記署名文書の形式が該署名文書の署名データ中に前記署名対象文書が含まれる形式の場合、前記署名文書から前記署名対象の文書データを除去し、該文書データを前記記憶部に記憶し、前記文書データ除去後の文書を前記記憶部に記憶する、
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の署名文書の管理方法。By the signing server,
If the signature document format is a format in which the signature target document is included in the signature data of the signature document, the signature target document data is removed from the signature document, and the document data is stored in the storage unit, Storing the document after removal of the document data in the storage unit;
The signed document management method according to claim 1.
署名ワークフローの開始要求に基づき署名ワークフローを開始し、承認依頼がされた署名文書が承認されなかった場合、前記署名文書から前記署名データを除去し、該署名データが除去された文書の修正依頼を受付ける、
ことを特徴とする請求項2に記載の署名文書の管理方法。By the signing server,
The signature workflow is started based on the request for starting the signature workflow, and when the requested signature document is not approved, the signature data is removed from the signature document, and a correction request for the document from which the signature data is removed is issued. Accept,
The signature document management method according to claim 2, wherein:
文書の取込み要求を受信し、該受信文書について、署名の有無を判断し、署名が有る場合に署名文書の形式を判断し、前記判断した署名文書の形式が署名対象文書に署名データが挿入される形式の場合、前記署名文書から署名データを除去し、該署名データを前記記憶部に記憶し、該署名データ除去後の文書のデータと前記記憶部に記憶されている他の文書のデータと一致しているか否かを判断し、一致している場合、前記署名データ除去後の文書を仮想文書として他の文書データの参照により実現する、
ことを特徴とする請求項3に記載の署名文書の管理方法。By the signing server,
A document capture request is received, the presence / absence of a signature is determined for the received document, the signature document format is determined if a signature is present, and the signature data is inserted into the signature target document. The signature data is removed from the signature document, the signature data is stored in the storage unit, the document data after the signature data is removed, and the other document data stored in the storage unit, It is determined whether or not they match, and if they match, the document after the removal of the signature data is realized by referring to other document data as a virtual document.
The signature document management method according to claim 3.
前記署名サーバにより、
前記様式情報をもとに前記文書の作成と作成文書への署名を行い、該署名文書の前記固定部分について前記様式情報のデータの参照により実現し、前記署名文書の前記可変部分のデータと署名データを前記記憶部に記憶する、
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の署名文書の管理方法。The storage unit further stores format information defining a fixed part and a variable part of the document,
By the signing server,
Creating the document based on the format information and signing the created document, realizing the fixed part of the signed document by referring to the data of the format information, and the data and signature of the variable part of the signature document Storing data in the storage unit;
The signed document management method according to claim 1.
前記署名文書の取出し要求を受信し、前記署名データの除去が行われた署名文書を、
前記除去された署名データと前記署名対象データとを結合してもとの実体文書に戻してから、又は前記結合を行わずに、前記除去された署名データと前記署名対象データとを分離した形で前記署名サーバ外部に送信する、
ことを特徴とする請求項3に記載の署名文書の管理方法。By the signing server,
The signature document from which the signature data removal request has been received,
A form in which the removed signature data and the signature target data are separated from each other after the removed signature data and the signature target data are combined into the original document or without the combination. To send outside the signing server,
The signature document management method according to claim 3.
文書への署名要求に基づき該文書への署名を行い、署名文書を記憶部に記録する前に、該署名文書の形式を判断し、
前記判断した署名文書の形式が署名対象文書に署名データが挿入される形式で、前記署名対象文書が実体文書を参照する仮想文書の場合、前記署名文書から前記署名データを除去し、該署名データを前記記憶部に記憶し、
前記署名データ除去後の文書を前記記憶部に記憶する制御部と、を有する、
ことを特徴とする署名サーバ。A storage unit;
Signing the document based on a signature request for the document, and determining the format of the signed document before recording the signed document in the storage unit,
When the determined signature document format is a format in which signature data is inserted into a signature target document and the signature target document is a virtual document that refers to an entity document, the signature data is removed from the signature document, and the signature data Is stored in the storage unit,
A control unit that stores the document after the signature data removal in the storage unit,
A signature server characterized by that.
ことを特徴とする請求項7に記載の署名サーバ。The control unit removes the document data from the signature document and stores the document data in the storage unit when the format of the signature document is a format in which the signature target document is included in the signature data of the signature document And storing the document after the document data removal in the storage unit,
The signature server according to claim 7.
ことを特徴とする請求項8に記載の署名サーバ。The control unit starts the signature workflow based on the request to start the signature workflow, and when the requested signature document is not approved, the control unit removes the signature data from the signature document, and the signature data is removed. Accept document revision requests,
9. The signature server according to claim 8, wherein
ことを特徴とする請求項9に記載の署名サーバ。The control unit receives a document take-in request, determines the presence or absence of a signature for the received document, determines the format of the signature document if there is a signature, and determines the format of the determined signature document as the signature target document. If the signature data is inserted, the signature data is removed from the signed document, and whether the data of the document after the removal of the signature data matches the data of another document stored in the storage unit If the document matches, the document after removal of the signature data is realized by referring to another document as a virtual document.
The signature server according to claim 9.
前記制御部は、前記様式情報をもとに前記文書の作成と作成文書に署名を行い、該署名文書の前記固定部分について前記様式情報のデータの参照により実現し、前記署名文書の前記可変部分のデータと署名データを前記記憶部に記憶する、
ことを特徴とする請求項7に記載の署名サーバ。The storage unit further stores format information defining a fixed part and a variable part of the document,
The control unit creates the document based on the format information and signs the created document, and realizes the fixed part of the signature document by referring to the data of the format information, and the variable part of the signature document. Data and signature data are stored in the storage unit,
The signature server according to claim 7.
ことを特徴とする請求項9に記載の署名サーバ。The control unit receives the request to retrieve the signature document, and converts the signature document from which the signature data has been removed into an original document obtained by combining the removed signature data and the signature target data. After returning or without performing the combination, the removed signature data and the signature target data are transmitted to the outside of the signature server in a separated form.
The signature server according to claim 9.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013024001AJP2014153583A (en) | 2013-02-12 | 2013-02-12 | Management method of signature document and signature server |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013024001AJP2014153583A (en) | 2013-02-12 | 2013-02-12 | Management method of signature document and signature server |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014153583Atrue JP2014153583A (en) | 2014-08-25 |
Family
ID=51575487
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013024001APendingJP2014153583A (en) | 2013-02-12 | 2013-02-12 | Management method of signature document and signature server |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2014153583A (en) |
Cited By (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111951916A (en)* | 2020-08-11 | 2020-11-17 | 北京天健源达科技股份有限公司 | Method for backspacing signature of electronic medical record |
| JP2021177666A (en)* | 2016-02-23 | 2021-11-11 | エヌチェーン ホールディングス リミテッドNchain Holdings Limited | Exchange using blockchain-based tokenization |
| US11755718B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2023-09-12 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Blockchain implemented counting system and method for use in secure voting and distribution |
| JP2024024656A (en)* | 2021-06-30 | 2024-02-22 | 弁護士ドットコム株式会社 | Program, information processing device, method |
| JP2024027133A (en)* | 2021-06-30 | 2024-02-29 | 弁護士ドットコム株式会社 | Program, information processing apparatus, and method |
| US11936774B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-03-19 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Determining a common secret for the secure exchange of information and hierarchical, deterministic cryptographic keys |
| US11972422B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-04-30 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Registry and automated management method for blockchain-enforced smart contracts |
| US12107952B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-10-01 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Methods and systems for efficient transfer of entities on a peer-to-peer distributed ledger using the blockchain |
| US12182805B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-12-31 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Tokenisation method and system for implementing exchanges on a blockchain |
| US12217224B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-02-04 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Method and system for efficient transfer of cryptocurrency associated with a payroll on a blockchain that leads to an automated payroll method and system based on smart contracts |
| US12248539B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-03-11 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Method and system for securing computer software using a distributed hash table and a blockchain |
| US12294661B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-05-06 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Personal device security using cryptocurrency wallets |
| US12367468B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-07-22 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Blockchain-implemented method for control and distribution of digital content |
| US12406237B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-09-02 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Universal tokenisation system for blockchain-based cryptocurrencies |
- 2013
- 2013-02-12JPJP2013024001Apatent/JP2014153583A/enactivePending
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US12248539B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-03-11 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Method and system for securing computer software using a distributed hash table and a blockchain |
| US12254452B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-03-18 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Method and system for efficient transfer of cryptocurrency associated with a payroll on a blockchain that leads to an automated payroll method and system based on smart contracts |
| US11755718B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2023-09-12 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Blockchain implemented counting system and method for use in secure voting and distribution |
| US12107952B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-10-01 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Methods and systems for efficient transfer of entities on a peer-to-peer distributed ledger using the blockchain |
| US12406237B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-09-02 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Universal tokenisation system for blockchain-based cryptocurrencies |
| US12367468B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-07-22 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Blockchain-implemented method for control and distribution of digital content |
| US11936774B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-03-19 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Determining a common secret for the secure exchange of information and hierarchical, deterministic cryptographic keys |
| US11972422B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-04-30 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Registry and automated management method for blockchain-enforced smart contracts |
| JP2021177666A (en)* | 2016-02-23 | 2021-11-11 | エヌチェーン ホールディングス リミテッドNchain Holdings Limited | Exchange using blockchain-based tokenization |
| US12182805B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-12-31 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Tokenisation method and system for implementing exchanges on a blockchain |
| US12314379B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-05-27 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Agent-based turing complete transactions integrating feedback within a blockchain system |
| US12217224B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-02-04 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Method and system for efficient transfer of cryptocurrency associated with a payroll on a blockchain that leads to an automated payroll method and system based on smart contracts |
| US12294661B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-05-06 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Personal device security using cryptocurrency wallets |
| US12032677B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2024-07-09 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Agent-based turing complete transactions integrating feedback within a blockchain system |
| US12271466B2 (en) | 2016-02-23 | 2025-04-08 | Nchain Licensing Ag | Blockchain implemented counting system and method for use in secure voting and distribution |
| CN111951916A (en)* | 2020-08-11 | 2020-11-17 | 北京天健源达科技股份有限公司 | Method for backspacing signature of electronic medical record |
| CN111951916B (en)* | 2020-08-11 | 2023-09-26 | 北京天健源达科技股份有限公司 | Method for rollback processing of electronic medical record signature |
| JP2024027133A (en)* | 2021-06-30 | 2024-02-29 | 弁護士ドットコム株式会社 | Program, information processing apparatus, and method |
| JP2024024656A (en)* | 2021-06-30 | 2024-02-22 | 弁護士ドットコム株式会社 | Program, information processing device, method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2014153583A (en) | Management method of signature document and signature server | |
| JP7361165B2 (en) | Systems and methods for managing public software component ecosystems using distributed ledgers | |
| CN110495132B (en) | System and method for generating, uploading and executing code blocks within distributed network nodes | |
| JP4602769B2 (en) | Navigate the content space of a document set | |
| JP2021505095A (en) | Blockchain communication and ordering | |
| CN107316239A (en) | A kind of authentification of message and source tracing method and system based on block chain | |
| US20090157987A1 (en) | System and Method for Creating Self-Authenticating Documents Including Unique Content Identifiers | |
| CN110771093A (en) | Method and system for proving existence of digital document and label chain block chain system | |
| JP2010512579A (en) | System and method for file authentication and versioning using unique content identifiers | |
| CN116579295B (en) | Method for dynamically inserting pages, moving bits and hiding and displaying multi-format file subscription | |
| US20230186241A1 (en) | Generation method, storage medium, and information processing device | |
| JP5179319B2 (en) | Electronic document management apparatus and electronic document management method | |
| JP2009284138A (en) | Document processing apparatus and document processing program | |
| WO2019205293A1 (en) | Service permission management method and apparatus, and computer device and storage medium | |
| JP6807239B2 (en) | Timestamp management system, timestamp management method, and timestamp management program | |
| JP2013192125A (en) | Electronic signature system and method for electronic signature and postscript | |
| JP5973604B1 (en) | Electronic loan contract storage system, method and program thereof | |
| JP5525740B2 (en) | Virtual appliance server management method and system | |
| CN114385595A (en) | Data migration method, device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| JP6877294B2 (en) | Program and timestamp management device | |
| JP7556396B2 (en) | Registrant terminal, holder terminal, method and program | |
| CN103129125B (en) | Catalogue method for supervising and device | |
| JP2025072237A (en) | File management program and file management device | |
| CN118862019A (en) | Method and system for confirming ownership of artificial intelligence generated content works | |
| JP7017868B2 (en) | Program and timestamp management device |