JP2012248021A - Information processing unit, asset information managing method and program - Google Patents
Information processing unit, asset information managing method and programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2012248021A JP2012248021AJP2011119583AJP2011119583AJP2012248021AJP 2012248021 AJP2012248021 AJP 2012248021AJP 2011119583 AJP2011119583 AJP 2011119583AJP 2011119583 AJP2011119583 AJP 2011119583AJP 2012248021 AJP2012248021 AJP 2012248021A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information
- user
- heir
- identification information
- asset
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
- Financial Or Insurance-Related Operations Such As Payment And Settlement (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、情報処理装置、資産情報管理方法、及びプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to an information processing apparatus, an asset information management method, and a program.
近年、画像データ、音楽データ、画像データをレイアウト編集したアルバムデータなどのコンテンツをクライアント装置がネットワークを介してコンテンツ管理サーバ装置にアップロードし、コンテンツがコンテンツ管理サーバ装置で保管されている。
このような場合、クライアント装置のユーザ以外は、コンテンツがコンテンツ管理サーバ装置に保管してあることを知ることができなかったり、たとえ知っていてもアクセス制限のためにコンテンツを参照できなかったりした。したがって、ユーザが死亡してしまうと、他のユーザがコンテンツを相続して管理することができなかった。
ここで、ユーザの相続の原因が発生したことがシステムに入力されると、データベースに登録済みの処理方法およびコンテンツに基づき、処理を行うことが開示されている(特許文献1参照)。なお、コンテンツの譲渡(相続)を行うために、ユーザによりコンテンツの処理方法とコンテンツとが関連付けられて予めデータベースに登録されている。
この仕組よれば、相続の原因が入力されることで、事前に登録された処理方法とコンテンツとの関連付けに基づいて、そのコンテンツを他のユーザに譲渡することができる。In recent years, content such as image data, music data, and album data obtained by editing the layout of image data is uploaded to a content management server device by a client device via a network, and the content is stored in the content management server device.
In such a case, other than the user of the client device cannot know that the content is stored in the content management server device, or even if it knows, the content cannot be referred due to access restriction. Therefore, if the user dies, other users cannot inherit and manage the content.
Here, it is disclosed that when a cause of user inheritance is input to the system, processing is performed based on a processing method and content registered in a database (see Patent Document 1). In order to transfer (inherit) content, the content processing method is associated with the content by the user and registered in advance in the database.
According to this structure, when the cause of inheritance is input, the content can be transferred to another user based on the association between the processing method registered in advance and the content.
ここで、従来の仕組みでは、ユーザの所有するコンテンツをユーザの死後に参照するためには、管理者に問い合わせて法的な手続きをとるなど、複雑な手順を踏まなければならなかった。
他方、特許文献1に記載の方法では、事前に処理方法とコンテンツとを関連付けてデータベースに登録しておき、相続の原因の入力が他のユーザを介して行われることで、他のユーザにコンテンツを譲渡することができる。しかしながら、このような方法では、相続の原因の入力が他のユーザに起因しているので、相続の原因の入力が行われないことがあり、コンテンツ等の資産情報が譲渡されない事態が生じ、資産情報が適切に管理できないおそれがある。Here, in the conventional mechanism, in order to refer to the contents owned by the user after the death of the user, it has been necessary to take a complicated procedure such as inquiring the administrator and taking a legal procedure.
On the other hand, in the method described in
本発明はこのような問題点に鑑みなされたもので、資産情報をより適切に管理することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such problems, and an object thereof is to more appropriately manage asset information.
そこで、本発明に係る情報処理装置は、ユーザが利用するユーザ端末および前記ユーザの資産情報と前記ユーザを識別する識別情報とが関連付けられて記憶され、更に、前記ユーザの識別情報と前記ユーザの相続人を識別する識別情報とが関連付けられて記憶された記憶部と通信可能に接続された情報処理装置であって、前記ユーザが生きているかを確認する確認情報を前記ユーザ端末に送信し、前記確認情報に対する返答情報を前記ユーザ端末から受信する通信手段と、前記通信手段で一定の時間内に前記返答情報が受信されていないと判断すると、前記ユーザの識別情報をもとに前記記憶部から前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを読み出し、前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを関連付けて前記記憶部に格納する制御手段と、を有することを特徴とする。 Therefore, the information processing apparatus according to the present invention stores the user terminal used by the user and the asset information of the user in association with the identification information for identifying the user, and further stores the identification information of the user and the user's identification information. An information processing apparatus that is communicably connected to a storage unit that is associated with identification information that identifies an heir, and transmits confirmation information to the user terminal to confirm whether the user is alive, Communication means for receiving response information for the confirmation information from the user terminal; and determining that the response information has not been received within a predetermined time by the communication means, the storage unit based on the identification information of the user Control means for reading out the asset information and the identification information of the heir from and storing the asset information and the identification information of the heir in the storage unit in association with each other; Characterized in that it has.
また、本発明は、資産情報管理方法、プログラム等としてもよい。 Further, the present invention may be an asset information management method, a program, or the like.
本発明によれば、資産情報をより適切に管理することができる。 According to the present invention, asset information can be managed more appropriately.
以下、本発明の実施形態について図面に基づいて説明する。なお、実施形態は、本発明を限定するものではなく、また、実施形態で説明されている全ての構成が本発明の課題を解決するための手段に必須であるとは限らない。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. The embodiments do not limit the present invention, and all the configurations described in the embodiments are not necessarily essential to the means for solving the problems of the present invention.
<第1の実施形態>
(システム全体の説明)
本実施形態に係る資産情報管理システムについて図1を参照して説明する。図1は、資産情報管理システムの構成の一例を示す図である。
資産情報管理システムは、ユーザ端末101、サーバ装置104、及び相続人端末105を含んで構成される。ユーザ端末101、サーバ装置104、及び相続人端末105は、情報処理装置(コンピュータ)の一例であり、ネットワーク(インターネット103等)を介して通信可能に接続されている。<First Embodiment>
(Description of the entire system)
An asset information management system according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an example of the configuration of an asset information management system.
The asset information management system includes a
ユーザ端末101は、被相続人(以下ではユーザと適宜称する。)が利用する情報処理装置の一例であり、デジタルカメラ102で撮影された画像情報(画像)を取り込み、保持している。サーバ装置104は、ユーザ端末101からインターネット103を経由してアップロードされた画像を格納する。また、サーバ装置104は、ユーザ端末101から要求があると、要求に従って画像を取得してユーザ端末101に送信する。
ここで、ユーザ端末101は、複数設けられていてもよい。この場合、サーバ装置104は、複数のユーザ端末101と通信可能である。また、この場合、画像のアップロード元のユーザ端末と画像の送信先のユーザ端末とは、異なっていてもよい。The
Here, a plurality of
また、サーバ装置104は、ユーザ端末101から入力された被相続人の情報と相続人の情報との続柄をもとに相続人の階層構造を作成する。また、サーバ装置104は、認証に用いられるユーザID等の認証情報がユーザにより入力されてサーバ装置104にログインしたユーザ端末101からのアクセスが一定期間ない場合、ユーザの死活を確認する処理を行う。そして、サーバ装置104は、処理結果に基づいて、相続人端末105にユーザの資産(資産情報)を譲渡するために(相続人に相続させるために)、ユーザの資産および相続人に関するデータの更新を行う。
相続人端末105は、相続人が利用する情報処理装置の一例であり、サーバ装置104と通信し、例えばユーザ端末101のユーザが保有していたアルバムなどの資産をサーバ装置104から受理する。Further, the
The
(情報処理装置の説明)
ユーザ端末101、サーバ装置104、相続人端末105等として適用可能な情報処理装置200の構成について図2を参照して説明する。図2は、情報処理装置200の構成の一例を示す図である。
なお、情報処理装置200については、それぞれ単一の情報処理装置で実現してもよいし、必要に応じた複数の情報処理装置に各機能を分散して実現するようにしてもよい。また、例えば、ユーザ端末101と相続人端末105とを一の情報処理装置で実現してもよい。複数の情報処理装置で構成される場合は、互いに通信可能なようにLocal Area Network(LAN)などで接続されている。
Central Processing Unit(CPU)201は、情報処理装置200全体を制御する制御部の一例である。Read Only Memory(ROM)202は、変更を必要としないプログラム、パラメータ等を格納する。Random Access Memory(RAM)203は、外部登録装置またはインターネット214などから供給されるプログラム、データ等を一時記憶する。外部記憶装置204は、情報処理装置200に固定して設置されたハードディスク、メモリカード、情報処理装置200から着脱可能な光ディスク、磁気カード、光カード、ICカードなどである。ROM202、RAM203、及び外部記憶装置204は、記憶部の一例である。(Description of information processing device)
A configuration of the
The
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) 201 is an example of a control unit that controls the entire
操作入力インターフェイス(操作入力IF)205は、操作者(被相続人、相続人、管理者等)の操作を受け付ける、各種のデータを入力するポインティングデバイス209、キーボード210などの入力デバイスとのインターフェイスである。表示インターフェイス(表示IF)206は、情報処理装置200の保持するデータ、供給されたデータ等を表示するためのディスプレイ211などの表示装置とのインターフェイスである。
ネットワークインターフェイス(ネットワークIF)207は、インターネット214などのネットワーク回線に接続するためのインターフェイスである。画像入力インターフェイス(画像入力IF)208は、画像入力デバイス213とのインターフェイスである。システムバス212は、各デバイス(201〜208)を通信可能に接続するバスである。なお、情報処理装置200の機能および後述のフローチャートに係る処理は、CPU201が外部記憶装置204またはインターネット214などから供給されるプログラムを読み出して実行し、上述の各デバイスを適時に制御することにより実現される。An operation input interface (operation input IF) 205 is an interface with an input device such as a
A network interface (network IF) 207 is an interface for connecting to a network line such as the
(ユーザ端末の動作の説明)
ユーザ端末101は、ユーザ端末用のプログラムを実行し、所定のURLを設定しておくことで、サーバ装置104と通信し、画像を包含したアルバム(資産の一例)、ユーザの相続人などを表示し、各種の設定を受け付ける。
ユーザ端末101を利用するためには、ログインするユーザ(被相続人)についての登録が事前に必要であるので、ユーザの情報(ユーザ情報)の登録について図3を参照して説明する。なお、図3は、ユーザ情報を登録する画面の一例(画面301)を示す図である。(Description of user terminal operation)
The
In order to use the
画面301は、ユーザ情報を登録するときにディスプレイ211に表示される画面である。なお、画面301は、ユーザ端末用のプログラムが実行されることにより起動される資産を管理するアプリケーションによりディスプレイ211に表示される。画面301には、ユーザ情報を入力するための入力欄(ユーザ名302、生年月日303、与信情報としてのクレジットカード番号304、E−Mail305)、及び任意に相続人を選択するための相続人を選択するボタン306が表示されている。
ユーザによる入力デバイスの操作(ユーザ操作)により相続人を選択するボタン306が押下されると、相続人のユーザ情報を選択などする画面(例えば後述の画面501)を表示する。また、ユーザ操作により顔写真を追加するボタン308が押下され、ユーザの顔写真が選択されると、ユーザ情報として指定され、顔写真が領域307に表示される。
また、ユーザ操作に応答して、ユーザ情報が入力され、追加するボタン310が押下されると、ユーザ端末101からサーバ装置104にユーザ情報が送信され、サーバ装置104にログインするユーザのレコードとして保管される。なお、ユーザ操作により閉じるボタン309が押下されると、画面301が閉じられる。A
When a
In addition, when user information is input in response to a user operation and the
次に、ユーザ端末101のユーザが資産情報管理システム(サーバ装置104)にログインしたときにディスプレイ211表示される画面について図4を参照して説明する。図4は、画面の一例(画面401、画面411、画面421)を示す図である。なお、各画面は、上記アプリケーションによりディスプレイ211に表示される。
図4(A)に示す画面401は、トップページの画面である。領域402には、無効化されているトップページボタン404、有効化されているアルバムを参照するボタン405、及び有効化されている相続人を参照するボタン406が表示されている。例えば、ユーザ操作により、アルバムを参照するボタン405が押下されると、図4(B)のようなアルバム一覧の画面411に画面が遷移し、相続人を参照するボタン406が押下されると、図4(C)のような相続人一覧の画面421に画面が遷移する。なお、トップページボタン404は、トップページの画面401を表示している間は無効となっている。
領域403では、画面毎の目的に応じて表示が切り替えられる。領域403には、トップページの画面401ではシステムの概要407が表示され、アルバム一覧の画面411ではアルバムの一覧が表示され、相続人一覧の画面421では相続人の一覧が表示される。Next, a screen displayed on the
A
In the
また、図4(B)に示すように、アルバム一覧の画面411の領域402では、有効化されているトップページボタン412、無効化されているアルバムを参照するボタン413、及び有効化されている相続人を参照するボタン406が表示されている。また、領域403には、ログインしているユーザの保有するアルバムの情報がサーバ装置104から受信されて表示される。
例えば、アルバム414からアルバム416までは、サーバ装置104に登録されているアルバムである。例えば、ユーザ操作により、アルバムが選択され、画像を参照するボタン417が押下されると、アルバムの画像の一覧表示画面(図示せず。)に画面が遷移する。
また、例えば、ユーザ操作により、アルバムが選択され、削除するボタン418が押下されると、選択されたアルバムの削除の要求がサーバ装置104に送信され、サーバ装置104では選択されたアルバムが削除される。また、例えば、ユーザ操作により、追加するボタン419が押下されてアルバムが指定されると、アルバムの追加の要求がサーバ装置104に送信され、サーバ装置104ではアルバムが追加される。Also, as shown in FIG. 4B, in the
For example,
In addition, for example, when an album is selected by a user operation and the
また、図4(C)に示すように、相続人一覧の画面421の領域402では、有効化されているトップページボタン412、有効化されているアルバムを参照するボタン405、及び無効化されている相続人を参照するボタン422が表示されている。また、領域403には、相続人を選択するボタン423が押下されることで開かれる後述の図5の画面で選択されたユーザ情報、及び指定された続柄の情報(相続人情報)が表示される。
領域425には、相続人情報に関する項目が表示される。例えば、相続人の属性を入力するための入力欄(優先度426、適用開始年齢427、適用終了年齢428)の値が編集され、更新するボタン431が押下されると、サーバ装置104にその更新情報が送信される。これにより、優先度426、適用開始年齢427、及び適用終了年齢428のぞれぞれの規定値が更新される。
また、相続人が複数人存在し、画面に表示することができない場合には、ユーザは、スクロールバー429を利用して、表示されていない相続人情報に関する項目を表示することができる。また、ユーザ操作により、チェックボックス424が選択された状態にされ、削除するボタン430が押下されると、サーバ装置104にログインしているユーザと相続人との関連を削除するための要求(削除要求)が送信される。そして、サーバ装置104では、削除要求が受信されると、前記ユーザの資産の譲渡の対象から選択された相続人に関する情報が削除される。Also, as shown in FIG. 4C, in the
In the
Further, when there are a plurality of heirs and they cannot be displayed on the screen, the user can use the
次に、相続人一覧の画面421の相続人を選択するボタン423が押下された場合に開かれる相続人を特定する画面について図5を参照して説明する。図5は、ディスプレイ211に表示される画面の一例(画面501)を示す図である。
画面501は、相続人情報を入力するための画面である。ユーザ操作により、入力欄502に相続人を検索のための条件が入力され、相続人を検索するボタン503が押下されると、検索結果が領域505に表示される。より具体的には、領域505には、相続人の候補のユーザ名、年齢など、相続人のユーザ情報が表示される。また、領域505では、リストボタン506によりユーザとの続柄が指定可能である。相続人の候補が複数存在し、画面に表示することができない場合には、ユーザは、スクロールバー507を利用して、表示されていない相続人のユーザ情報を表示することができる。Next, a screen for specifying an heir to be opened when the
A
また、ユーザ操作により、チェックボックス504が選択された状態にされ、選択するボタン509が押下されると、選択された相続人の候補がユーザの相続人として設定される。また、ユーザ操作により閉じるボタン508が押下されると、画面501が閉じられる。
また、ユーザがユーザ端末101などを介してサーバ装置104に一定期間アクセスしていない場合は、ユーザ端末101は、サーバ装置104からメールを受信する。このときに受信されるメールは、ユーザの死活確認用メール(ユーザが生きているかを確認する確認情報の一例)であり、メールには、ユーザに関する情報、確認済みの通知先へのリンクが含まれる。なお、確認済みの通知先へのリンクには後述する死活確認の対象のユーザを特定するためのユーザIDが関連付けられている。
ここで、ユーザ操作により、確認済みの通知先へのリンクが押下されると、ユーザ端末101は、ユーザが活動中であることを示すメッセージ(返答情報の一例)をサーバ装置104に送信する。When the
When the user has not accessed the
Here, when a link to a confirmed notification destination is pressed by a user operation, the
(相続人端末の動作の説明)
相続人端末105は、相続人端末用のプログラムを実行してアプリケーションを起動する。そして、所定のURLを設定しておくことで、相続人端末105は、サーバ装置104と通信し、サーバ装置104で保有されていたアルバムなどのユーザの資産を受理する。
相続人端末105を利用するためには、ログインする相続人の登録が事前に必要であるが、この登録は、ユーザ端末101におけるユーザの登録の画面301での操作と同じように行われる。なお、この相続人のユーザ情報については、ユーザ端末101のユーザのユーザ情報と同様にレコードとしてサーバ装置104に保管されて管理される。(Explanation of operation of heir terminal)
The
In order to use the
ここで、相続人端末105は、相続人が資産情報管理システムにログインした後に、サーバ装置104からの資産相続メールを受信することがある。資産相続メールは、ユーザの死後に資産の相続を承認するか放棄するかを確認する問合情報の一例である。相続人端末105は、資産相続メールを受信した場合、ユーザ情報、相続を承認する旨の通知先へのリンク、相続を放棄する旨の通知先へのリンクを表示する。なお、これらのリンクには、ユーザを特定するためのユーザIDが関連付けられている。
例えば、相続を承認する旨の通知先へのリンクが押下されると、相続人端末105は、ユーザが保有しているアルバムなどの資産を相続することを示すメッセージ(承認情報の一例)をサーバ装置104に送信する。なお、ユーザの資産を相続することを示すメッセージが相続人端末105からサーバ装置104に送信されることで、相続人は、ユーザの資産を相続することになる。
また、相続を放棄する旨の通知先へのリンクが押下され、ユーザの資産を相続しないことを示すメッセージ(放棄情報の一例)がサーバ装置104に送信されることで、相続人は、ユーザの資産の相続を放棄することになる。Here, the
For example, when a link to a notification destination for approving inheritance is pressed, the
In addition, a link to a notification destination to abandon inheritance is pressed, and a message (an example of abandonment information) indicating that the user's asset is not inherited is transmitted to the
(サーバ装置の動作の説明)
図6、図7、及び図8は、サーバ装置104が管理する情報を格納する管理形態の一例(ユーザ・テーブル601、続柄・テーブル621、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801等)を示す図である。なお、各テーブルは、外部記憶装置204に設けられているものとして説明する。
図6(A)に示すように、ユーザ・テーブル601には、ユーザを表現するレコードが格納される。ここでのユーザには、被相続人および相続人が含まれる。ユーザ・テーブル601については、ユーザID602、ユーザ名603、生年月日604、与信情報605、最終アクセス時間606、状態607、E−Mail608、及び顔情報609のデータを格納するための属性が定義されている。
ユーザID602は、レコードを特定するための識別子(ユーザを識別可能な識別情報)の一例である。ユーザ名603は、ユーザの名前を示す。生年月日604は、ユーザの生年月日を示す。与信情報605は、ユーザのクレジットカード番号などの与信情報を示す。最終アクセス時間606は、ユーザがサーバ装置104に最後にアクセスした時間(最終アクセス時間)を示す。状態607は、ユーザに死活確認用メールを送信済みであるか否かを示す。E−Mail608は、ユーザの所在を示す所在情報の一例であり、E−Mailを示す。顔情報609は、ユーザの顔情報(顔の画像)を示す。(Explanation of server device operation)
6, 7, and 8 are examples of management forms for storing information managed by the server device 104 (user table 601, relationship table 621, user heir table 701, user album table 801, etc.). FIG. Each table is described as being provided in the
As shown in FIG. 6A, the user table 601 stores a record representing a user. The users here include a decedent and an heir. For the user table 601, attributes for storing data of
The
また、レコード610は、ユーザ・テーブル601のレコードの一例である。ユーザ端末101、相続人端末105等からのユーザの登録要求に従ってレコードが追加される。なお、レコード611は、サーバ装置104の管理者のアカウント(管理用ユーザ)の情報を示し、ユーザ端末101、相続人端末105等をユーザが利用するのに先立って、管理者によって事前に登録されているレコードである。
図6(B)に示すように、続柄・テーブル621には、続柄を表現するレコードが格納される。続柄・テーブル621については、続柄ID622、続柄名623、優先度624、適用開始年齢625、及び適用終了年齢626のデータを格納するための属性が定義されている。続柄ID622は、レコードを特定するための識別子の一例である。続柄名623は、続柄名を示す。優先度624は、続柄の優先度を示す。適用開始年齢625は、続柄が適用開始される年齢を示す。適用終了年齢626は、続柄が適用終了される年齢を示す。
また、レコード627は、続柄・テーブル621のレコードの一例である。例えば、続柄・テーブル621には、父、母、祖父母、息子、娘など、あるユーザを本人として見た場合の続柄に関するレコードが事前に登録されている。なお、レコード628は、サーバ装置104で利用される管理用の続柄を示すレコードである。A
As shown in FIG. 6B, the relationship / table 621 stores a record expressing the relationship. In the relationship / table 621, attributes for storing data of the
The
図7に示すように、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701には、ユーザと相続人との関係を表現するレコードが格納される。ユーザ相続人・テーブル701については、ユーザID702、相続人ID703、続柄ID704、優先度・上書き705、適用開始年齢・上書き706、及び適用終了年齢・上書き707のデータを格納するための属性が定義されている。ユーザID702は、ユーザを特定する識別子の一例である。相続人ID703は、相続人を特定する識別子の一例である。続柄ID704は、ユーザと相続人との続柄を特定する識別子の一例である。
優先度・上書き705では、続柄・テーブル621の優先度624に格納されている値を任意に上書きするための値を示す。適用開始年齢・上書き706では、続柄・テーブル621の適用開始年齢625に格納されている値を任意に上書きするための値を示す。適用終了年齢・上書き707では、続柄・テーブル621の適用終了年齢626に格納されている値を任意に上書きするための値を示す。As shown in FIG. 7, the user heir / table 701 stores a record expressing the relationship between the user and the heir. The user heir / table 701 defines attributes for storing data of
The priority /
また、レコード708は、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701のレコードの一例である。なお、レコード709は、サーバ装置104で利用される管理用のレコードを示す。ユーザID702および相続人ID703は、ユーザ・テーブル601のユーザID602の値と関連付けられている。本実施形態では、サーバ装置104は、ユーザのユーザID602の値をユーザID702に設定し、ユーザの相続人のユーザID602の値を相続人ID703に設定したレコードを作成することで、ユーザと相続人とを関連付ける。故に、サーバ装置104は、ユーザのユーザIDをもとに、ユーザの相続人のレコードを取得することができる。
また、続柄ID704は、続柄・テーブル621の続柄ID622の値と関連付けられている。例えば、サーバ装置104は、あるユーザのユーザID702と、ある相続人の相続人ID703との続柄については、この続柄ID704に関連する続柄ID622の続柄・テーブル621のレコードを特定することで取得することができる。換言するならば、ユーザと相続人との関係は、ユーザIDと相続人IDとその続柄IDによって決定される。A
The
また、優先度624および優先度・上書き705の値、生年月日604、適用開始年齢625および適用開始年齢・上書き706の値、並びに適用終了年齢626および適用終了年齢・上書き707の値から、ユーザにとっての相続人(優先度)が確定される。例えば、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701の優先度・上書き705の値が「なし」である場合、ユーザにとっての相続人の優先度は、続柄・テーブル621の優先度624の優先度が適用される。
また、続柄・テーブル621には、相続人の続柄が実際に適用開始される相続人の年齢が設定されているが、これを、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701の適用開始年齢・上書き706の値で上書きすることができる。また、続柄・テーブル621には、相続人の続柄が実際に適用終了される相続人の年齢が設定されているが、これを、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701の適用終了年齢・上書き707の値で上書きすることができる。
即ち、優先度624および優先度・上書き705の値、生年月日604、適用開始年齢625および適用開始年齢・上書き706の値、並びに適用終了年齢626および適用終了年齢・上書き707の値は、相続を許可するかを判定するための条件情報の一例である。Further, from the values of the
In addition, the age of the heir who actually starts application of the successor's relationship is set in the relationship / table 621, and this is expressed by the value of the application start age / overwrite 706 of the user heir / table 701. Can be overwritten. In addition, the age of the heir to which the inheritance of the heir is actually applied is set in the relationship / table 621, and this is the value of the application end age / overwrite 707 of the user heir / table 701. Can be overwritten.
That is, the values of
本実施形態では、ユーザID702にはユーザのユーザIDが関連付けられているので、サーバ装置104は、ユーザのユーザIDをもとに相続人のレコードを取得できる。この際、サーバ装置104は、レコード間の優先度が高いレコード順にソートすることで、ユーザから見た場合の相続人の階層関係を取得することができる。
なお、管理用のレコード709は、優先度が必ず最下位になる。よって、サーバ装置104は、ユーザ端末101から登録された相続人のレコードを検索し、1件も見つからなかった場合、管理用のレコード709の管理用ユーザを最終的な相続人として設定する。管理用ユーザは、資産の譲渡先(相続人)が見つからない場合に、最終的な相続人としての資産に対する処理を実行するためのユーザである。In this embodiment, since the user ID of the user is associated with the
The
図8は、サーバ装置104が管理する資産の一例であるアルバムおよび画像の情報を格納する管理形態の一例を示す図である。
図8(A)に示すように、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801には、ユーザが保有するアルバムを表現するレコードが格納される。ユーザアルバム・テーブル801については、ユーザを特定する識別子の一例であるユーザID802、アルバムを特定する識別子の一例であるアルバムID803のデータを格納するための属性が定義されている。FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating an example of a management form for storing information on albums and images, which are examples of assets managed by the
As shown in FIG. 8A, the user album table 801 stores records representing albums held by the user. The user album table 801 defines attributes for storing data of a
また、レコード804は、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801のレコードの一例である。ユーザID802の値は、ユーザ・テーブル601のユーザID602の値と関連付けられている。アルバムID803の値は、後述するアルバム・テーブル811のアルバムID812の値と関連付けられている。サーバ装置104は、これらの関連付けによってユーザが保有するアルバムを特定することができる。
図8(B)に示すように、アルバム・テーブル811には、アルバム自体を表現するレコードが格納される。アルバム・テーブル811については、アルバムを特定する識別子の一例であるアルバムID812、アルバムの名前を示すアルバム名813のデータを格納するための属性が定義されている。また、レコード814は、アルバム・テーブル811のレコードの一例である。A
As shown in FIG. 8B, the album table 811 stores records representing the album itself. The album table 811 defines attributes for storing data of an
図8(C)に示すように、アルバム構成画像・テーブル821には、アルバムが包含している画像を表現するレコードが格納される。アルバム構成画像・テーブル821については、アルバムを特定する識別子の一例であるアルバムID822、アルバムに包含される画像を特定する識別子の一例である画像ID823のデータを格納するための属性が定義されている。
また、レコード824は、アルバム構成画像・テーブル821のレコードの一例である。アルバムID822の値は、アルバム・テーブル811のアルバムID812の値と関連付けられている。また、画像ID823の値は、後述する画像・テーブル831の画像ID832の値と関連付けられている。サーバ装置104は、これらの関連付けによってアルバムが包含する画像を特定することができる。
図8(D)に示すように、画像・テーブル831には、画像自体を表現するレコードが格納される。画像・テーブル831については、画像を特定する識別子の一例である画像ID832、画像の名前を示す画像名833、画像の保管先を示すパス834のデータを格納するための属性が定義されている。また、レコード835は、画像・テーブル831のレコードの一例である。As shown in FIG. 8C, the album composition image / table 821 stores records representing images included in the album. The album composition image / table 821 defines attributes for storing data of an
A
As shown in FIG. 8D, the image / table 831 stores a record representing the image itself. In the image / table 831, attributes for storing data of an
例えば、サーバ装置104は、登録されたユーザに対応するユーザ・テーブル601のレコードからユーザID602(ユーザID602の値)を取得する。そして、サーバ装置104は、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801、アルバム・テーブル811、アルバム構成画像・テーブル821、画像・テーブル831と順に辿ることで、ユーザの保有するアルバムおよび画像を取得することができる。
ここで取得されたアルバム、画像などについては、サーバ装置104は、ユーザ端末101の取得要求に従って送信する。また、ユーザ端末101は、アルバム、画像などの情報を受信すると、アルバム一覧の画面411、アルバムの画像の一覧表示画面などにそれぞれ表示する。For example, the
The
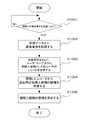
次に、ユーザ端末101における画面301での追加するボタン310の押下によって、サーバ装置104がユーザの登録要求を受信したときの動作について図9を参照して説明する。図9は、ユーザ登録時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。以下では、登録要求に、画面301で入力された情報(ユーザのユーザ情報、相続人情報など)が含まれているものとして説明をする。なお、以下の処理は、サーバ装置104のCPU201が外部記憶装置204からプログラムを実行し、各種デバイスを制御することにより実現される。
まず、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101からユーザの登録要求を受信したかを判定する(S901)。このとき、CPU201は、ユーザの登録要求を受信したと判定した場合、S902に処理を進め、他方、受信していないと判定した場合、受信したと判定するまでS901の処理を継続する。Next, an operation when the
First, the
S902では、CPU201は、受信した登録要求(受信データ)からユーザ情報を取得する。続いて、CPU201は、取得したユーザ情報をもとにユーザ・テーブル601のレコードを作成し、作成したレコードをユーザ・テーブル601に登録する(S903)。
例えば、CPU201は、ユーザ・テーブル601の新規レコードには、自動採番号の値をユーザID602に設定し、画面301のユーザ名302の値をユーザ名603に設定し、生年月日303の値を生年月日604に設定する。また、CPU201は、クレジットカード番号304の値を与信情報605に設定し、E−Mail305の値をE−Mail608に設定し、顔写真の領域307に設定された写真を顔情報609に設定する。また、CPU201は、最終アクセス時間606には現在の時間を設定し、状態607には規定値として「なし」を設定する。In step S902, the
For example, the
続いて、CPU201は、受信データから相続人情報を取得し(S904)、取得した相続人情報から配列SOZOKUを作成する(S905)。続いて、CPU201は、ユーザ・テーブル601から管理用のユーザのレコード611を取得し(S906)、続柄・テーブル621から管理用の続柄のレコード628を取得する(S907)。
続いて、CPU201は、S905で作成した配列SOZOKUに、S905およびS906で取得した管理用のユーザのレコードおよび続柄のレコードから管理用の相続人情報を作成し、配列SOZOKUの要素として追加する(S908)。続いて、CPU201は、変数I、相続人情報が格納された配列SOZOKUの要素数を格納するための変数SIZEを作成し、それぞれ、0(ゼロ)、配列SOZOKUの要素数で初期化する(S909)。Subsequently, the
Subsequently, the
なお、受信する相続人情報には、画面301の相続人を選択するボタン306の押下によって起動する画面501で選択された相続人のユーザ情報が含まれる。より具体的には、相続人を検索するボタン503の押下によって、画面501の検索の条件の値をもとに、ユーザ・テーブル601から相続人の候補となるレコードが取得され、画面501に表示されることになる。そして、選択するボタン509が押下されたときに選択されている相続人のレコードの値が相続人のユーザ情報として扱われる。
また、画面501には、続柄・テーブル621から管理用のレコード628を除いた全てのレコードが表示され、画面501での続柄の選択によって、登録されるユーザと相続人との続柄が決定される。配列SOZOKUでは、このようにして取得された相続人のユーザ情報と続柄の情報とを含む相続人情報が要素となっている。
例えば、配列SOZOKUには、相続人のユーザID、登録されるユーザとの続柄に対応する続柄IDとが格納されている。相続人の検索および続柄の取得に関する詳細については図10、及び図11を用いて後述する。The received heir information includes the user information of the heir selected on the
The
For example, the array SOZOKU stores the user ID of the heir and the relationship ID corresponding to the relationship with the registered user. Details regarding the search for the heir and the acquisition of the relationship will be described later with reference to FIGS. 10 and 11.
続いて、CPU201は、変数Iの値と変数SIZEの値とを比較し、変数Iの値が変数SIZEの値より小さいかを判定する(S910)。このとき、CPU201は、変数Iの値が変数SIZEの値よりも小さいと判定した場合、S911に処理を進め、他方、変数Iの値が変数SIZEの値以上であると判定した場合、処理を終了する。
S911では、CPU201は、配列SOZOKU[I]の要素である相続人情報を取得し、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701のレコードとして登録する。
この際、CPU201は、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701の新規レコードのユーザID702には被相続人となるユーザのユーザIDを設定し、相続人ID703には相続人となるユーザのユーザIDを設定する。また、CPU201は、続柄IDには相続人情報の続柄IDの値(被相続人と相続人というユーザ間の続柄に対応する続柄・テーブル621の続柄ID622の何れかの値)を設定する。また、CPU201は、優先度・上書き705、適用開始年齢・上書き706、及び適用終了年齢・上書き707には、それぞれ規定値(「なし」等)を設定する。Subsequently, the
In step S <b> 911, the
At this time, the
なお、優先度・上書き705、適用開始年齢・上書き706、適用終了年齢・上書き707については、ユーザ端末101の画面421を介して更新され得る。例えば、優先度426、適用開始年齢427、適用終了年齢428の値が相続人の更新情報とされ、サーバ装置104は、更新するボタン431の押下によって更新情報を受信した場合に更新するが、この処理の詳細については後述する。続いて、CPU201は、変数Iを1だけカウントアップし(S912)、S910からの処理を継続する。
なお、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701の新規レコードの作成方法は、上述の内容に限られるものではない。例えば、ユーザ端末101の画面501の選択するボタン509の押下によって、サーバ装置104は、ユーザの相続人情報および相続人の登録要求を受信する構成とすることもできる。この場合、サーバ装置104のCPU201は、サーバ装置104にログインしているユーザのユーザIDに関連付けて、S905からS912までと同様の処理を実行する。CPU201は、このように処理を実行し、相続人情報をユーザ相続人・テーブル701のレコードとして登録する。Note that the priority /
Note that the method for creating a new record of the user heir / table 701 is not limited to the above-described content. For example, the
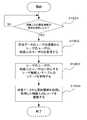
次に、ユーザ端末101における画面501での相続人を検索するボタン503の押下によって、サーバ装置104が相続人の検索要求を受信したときの動作について図10を参照して説明する。図10は、相続人検索時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101から、画面501での相続人を検索するボタン503の押下によって、被相続人としてのユーザに関係する相続人の検索要求を受信したかを判定する(S1001)。このとき、CPU201は、検索要求を受信したと判定した場合、S1202に処理を進め、他方、検索要求を受信していないと判定した場合、検索要求を受信するまでS1001の処理を継続する。
続いて、CPU201は、受信した検索要求(受信データ)から検索条件を取得する(S1002)。なお、S1002で取得される検索条件としては、相続人としてのユーザを特定するためのユーザ名、生年月日などが考えられる。Next, an operation when the
First, the
Subsequently, the
続いて、CPU201は、ユーザ名、生年月日などの検索条件をもとに、ユーザ・テーブル601から相続人の候補となるユーザのレコードを取得する(S1003)。続いて、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101の画面501に表示させるための相続人のユーザ情報を作成する(S1004)。続いて、CPU201は、S1004で作成した相続人のユーザ情報をユーザ端末101に送信(返却)する(S1005)。
なお、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101の画面421に表示される相続人情報については、検索条件として被相続人のユーザIDを用いて、上述とは異なる方法で取得する。例えば、CPU201は、被相続人のユーザIDに対応するユーザ相続人・テーブル701のレコードを特定し、特定したレコードの相続人IDに対応するユーザ・テーブル601のレコードを特定し、特定したこれらのレコードから被相続人情報を作成する。Subsequently, the
Note that the
次に、ユーザ端末101が画面501を表示するときに、サーバ装置104がユーザ端末101からの続柄の取得要求を受信したときの動作について図11を参照して説明する。図11は、続柄取得時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101から続柄の取得要求を受信したかを判定する(S1101)。このとき、CPU201は、続柄の取得要求を受信したと判定した場合、S1102に処理を進め、他方、続柄の取得要求を受信していないと判定した場合、続柄の取得要求を受信するまでS1101の処理を継続する。
S1102では、CPU201は、続柄・テーブル621から管理用のレコード628を除いた全てのレコードを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、S1102で取得した続柄・テーブル621のレコードからユーザ端末101に返却するための続柄の情報を作成する(S1103)。続いて、CPU201は、作成した続柄の情報を、ユーザ端末101の画面501の続柄に表示する情報として送信(返却)する(S1104)。Next, an operation when the
First, the
In step S1102, the
次に、一定期間、サーバ装置104にユーザ端末101からアクセスがない場合、サーバ装置104がユーザ端末101にユーザの死活確認のメッセージ(死活確認用メール等)を送信するときの動作について図12を参照して説明する。図12は、状態確認時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、サーバ装置104に事前に設定されているタイマーによって、被相続人としてのユーザに死活確認のメッセージを送信する時間となったかを判定する(S1201)。このとき、CPU201は、送信する時間となったと判定した場合、S1202に処理を進め、他方、送信する時間になっていないと判定した場合、送信する時間となるまでS1201の処理を継続する。S1202では、CPU201は、ユーザ・テーブル601の与信情報605を参照し、与信情報を管理している第三者に問い合わせを行い、死亡している可能性のあるユーザのレコードを取得する。
なお、S1201で使用するタイマーについては、ファイル、データベース等に設定情報を格納して管理してもよいし、OS(オペレーティングシステム)などのタイマーを利用してもよい。また、与信情報を管理している第三者としては、金融機関、保険会社など、クレジットカード番号などを利用し、ユーザの死活を確認できる機関、個人等のシステムを採用することができる。Next, when the
First, the
Note that the timer used in S1201 may be managed by storing setting information in a file, database, or the like, or a timer such as an OS (Operating System) may be used. As a third party managing credit information, a system such as a financial institution, an insurance company, etc. that uses a credit card number or the like and can confirm the life and death of a user can be adopted.
続いて、CPU201は、ユーザ・テーブル601の最終アクセス時間606を参照し、最後にアクセスしてから現在までの時間が一定期間を超える場合は、死亡している可能性があると判定し、該当するユーザのレコードを取得する(S1203)。続いて、CPU201は、S1202およびS1203で取得したレコードをマージし(S1204)、死活確認の対象となるユーザ情報の配列RECEIVERを作成する(S1205)。なお、S1203の判定に使用する期間の情報については、サーバ装置104に、ファイル、データベースなどとして事前に設定されているものとする。
続いて、CPU201は、変数I、死活確認の対象となるユーザ情報の配列RECEIVERの要素数を格納するための変数SIZEを作成し、それぞれ、0(ゼロ)、配列RECEIVERの要素数で初期化する(S1206)。続いて、CPU201は、変数Iの値と変数SIZEの値とを比較し、変数Iの値が変数SIZEの値よりも小さいかを判定する(S1207)。このとき、CPU201は、変数Iの値が変数SIZEの値よりも小さいと判定した場合、S1208に処理を進め、他方、変数Iの値が変数SIZEの値以上であると判定した場合、処理を終了する。Subsequently, the
Subsequently, the
S1208では、CPU201は、配列RECEIVER[I]の情報からユーザのユーザID、ユーザ名、E−Mailを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、S1208で取得したユーザID、ユーザ名を関連付けて死活確認用メールを作成する(S1209)。例えば、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101が受信する死活確認用メールにユーザ名、確認済みの通知先へのリンクにユーザIDを関連付けることで、ユーザ端末101の死活確認用メールに死活確認するユーザのユーザ名が表示される。また、確認済みの通知先へのリンクの押下時には、サーバ装置104のCPU201は、死活確認の対象となったユーザのユーザIDを受信することができる。 In step S1208, the
続いて、CPU201は、S1209で作成した死活確認用メールをS1208で取得したE−Mailの宛先に送信する(S1210)。続いて、CPU201は、メールを送信したユーザのユーザIDに対応するユーザ・テーブル601のレコードの状態607を「譲渡確認中」に更新し(S1211)、変数Iを1だけカウントアップし(S1212)、S1207からの処理を継続する。 Subsequently, the
次に、ユーザ端末101での死活確認用メールのリンクの押下によって、サーバ装置104が、ユーザが活動中であること(ユーザの有効)を示すメッセージを受信したときの動作について図13を参照して説明する。図13は、状態更新時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101での死活確認用メールのリンクの押下によって、死活確認中のユーザの有効を示すメッセージを受信したかを判定する(S1301)。このとき、CPU201は、メッセージを受信したと判定した場合、S1302に処理を進め、他方、受信していないと判定した場合、受信するまでS1301の処理を継続する。
S1302では、CPU201は、受信したメッセージ(受信データ)からユーザIDを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、S1302で取得したユーザIDの値に対応するユーザ・テーブル601のレコードの状態607をS1211で更新した「譲渡確認中」から「なし」に更新する(S1303)。このようにすることで、CPU201は、死活確認中のユーザが有効であり、資産の譲渡の対象から外すことができる。Next, referring to FIG. 13, the operation when the
First, the
In step S1302, the
次に、サーバ装置104から相続人端末105に資産を譲渡、即ちユーザから相続人に資産が相続されるときの動作について図14を参照して説明する。図14は、相続確認時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、サーバ装置104に事前に設定されているタイマーによって、相続人としてのユーザに対して、被相続人のユーザの資産の相続(遺産相続)に関するメッセージを送信する時間となったか(一定の時間内であるか)を判定する(S1401)。このとき、CPU201は、送信する時間となったと判定した場合、S1402に処理を進め、他方、送信する時間になっていないと判断した場合、送信する時間となるまでS1401の処理を継続する。Next, an operation when assets are transferred from the
First, the
S1402では、CPU201は、ユーザ・テーブル601の状態607を参照して「譲渡確認中」のユーザのレコードを取得する。
なお、S1401で使用するタイマーについては、ファイル、データベース等に設定情報を格納して管理してもよいし、OSなどのタイマーを利用してもよい。
また、S1402で抽出の対象となるユーザ・テーブル601のレコードは、S1211で「譲渡確認中」に状態607が更新され、死活確認中の状態が開始してから一定期間が経過してもS1303で状態607が「なし」に更新されなかったレコードである。ここで、死活確認中の状態が開始した時間は、最終アクセス時間であってもよいし、「譲渡確認中」に更新された時間(図示せず。)であってもよい。In step S <b> 1402, the
Note that the timer used in S1401 may be managed by storing setting information in a file, database, or the like, or a timer such as an OS may be used.
In addition, the record of the user table 601 to be extracted in S1402 is updated in the
続いて、CPU201は、S1402で取得したレコードから配列USERを作成する(S1403)。続いて、CPU201は、変数I、変数SIZEを作成し、それぞれ、0(ゼロ)、配列USERの要素数で初期化する(S1404)。続いて、CPU201は、変数Iの値と変数S1ZEの値とを比較し、変数Iの値が変数S1ZEの値よりも小さいかを判定する(S1405)。このとき、CPU201は、変数Iの値が変数SIZEの値よりも小さいと判定した場合、S1406に処理を進め、他方、変数Iの値が変数SIZEの値以上であると判定した場合、処理を終了する。
S1406では、CPU201は、配列USER[I]の情報からユーザIDを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、取得したユーザIDをもとに、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701のユーザIDに関連付けられている相続人のレコードを取得する(S1407)。Subsequently, the
In step S1406, the
続いて、CPU201は、S1407で取得した相続人のレコードから、優先度の最も高いレコードを抽出し、抽出したレコードの値が格納された配列RECEIVERを作成する(S1408)。ここで、相続人の優先度は、上述したように優先度624および優先度・上書き705の値、生年月日604、適用開始年齢625および適用開始年齢・上書き706の値、並びに、適用終了年齢626および適用終了年齢・上書き707の値から決定される。続いて、CPU201は、変数J、変数RSIZEを作成し、それぞれ、0(ゼロ)、配列RECEIVERの要素数で初期化する(S1409)。
続いて、CPU201は、変数Jの値と変数RSIZEの値とを比較し、変数Jの値が変数RSIZEの値よりも小さいかを判定する(S1410)。このとき、CPU201は、変数Jの値が変数RSIZEの値よりも小さいと判定した場合、S1411に処理を進め、他方、変数Jの値が変数RSIZEの値以上であると判定した場合、続いてS1414の処理を行う。Subsequently, the
Subsequently, the
S1411では、CPU201は、配列RECEIVER[J]から相続人のユーザIDを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、S1411で取得したユーザIDの値に対応するユーザ・テーブル601のレコードのユーザに対し、資産の相続の確認処理を実行する(S1412)。
資産の相続の確認処理には、幾つかのパターンがある。1つは、S1412で取得したユーザの情報から、相続人端末105が受信する資産相続メールを作成し、相続人端末105に送信するパターンである。このパターンでは、資産相続メールには、被相続人のユーザ情報、相続を承認する旨の通知先へのリンク、相続を放棄する旨の通知先へのリンクには相続人のユーザIDを関連付けておく。そして、相続人端末105からこれらのリンクの押下によって、サーバ装置104は、被相続人のユーザID、相続人のユーザIDを受信し、資産を相続人に譲渡したり、しなかったりする制御を行うことができる。In step S1411, the
There are several patterns in the asset inheritance confirmation process. One is a pattern in which an asset inheritance mail received by the
また、他には、被相続人と相続人との続柄が、続柄・テーブル621の管理用のレコード818の続柄であるパターンである。このパターンでは、サーバ装置104のCPU201は、資産相続メールを作成せずに、被相続人のユーザIDに関連するアルバム、画像を全て、ユーザ・テーブル601の管理用のレコード610の管理用ユーザに譲渡する。
例えば、CPU201は、資産に関連する被相続人のユーザIDを管理用ユーザのユーザIDに変更する。そして、CPU201は、被相続人に関連するレコードをユーザ・テーブル601、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801から全て削除する。In addition, there is a pattern in which the relationship between the decedent and the heir is the relationship of the record 818 for management in the relationship / table 621. In this pattern, the
For example, the
なお、CPU201は、被相続人としてのユーザが保有するアルバム、画像を相続人としてのユーザに譲渡するために、被相続人のユーザIDを取得し、このユーザIDに関連付けられたユーザアルバム・テーブル801のレコードを取得する。そして、CPU201は、アルバム・テーブル811、アルバム構成画像・テーブル821、画像・テーブル831と順に辿り、ユーザの保有するアルバムおよび画像を取得し、これらのレコードをコピーし、相続人のユーザIDに関連付けることで譲渡を行う。この処理の詳細については、図15を用いて後述する。
続いて、CPU201は、変数Jの値を1だけカウントアップし(S1413)、S1410からの処理を継続する。S1614では、CPU201は、変数Iの値を1だけカウントアップし、S1405からの処理を継続する。Note that the
Subsequently, the
次に、相続人端末105での資産相続メールの相続を承認する旨の通知先へのリンク押下によって、サーバ装置104が資産の相続を承認することを示すメッセージを受信したときの動作について図15を参照して説明する。図15は、相続承認時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、相続人端末105での資産相続メールの相続を承認する旨の通知先へのリンクの押下によって、相続人からの資産の相続を承認することを示すメッセージを受信したかを判定する(S1501)。このとき、CPU201は、メッセージを受信したと判定した場合、S1502に処理を進め、他方、受信していないと判定した場合、受信するまでS1501の処理を継続する。
S1502では、CPU201は、受信したメッセージ(受信データ)から被相続人のユーザID、及び相続人のユーザIDを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、S1502で取得した被相続人のユーザIDに対応するユーザアルバム・テーブル801のレコードからアルバムIDを取得する(S1503)。Next, the operation when the
First, the
In step S1502, the
続いて、CPU201は、S1503で取得したアルバムIDから、アルバム・テーブル811、アルバム構成画像・テーブル821、画像・テーブル831と順に辿ることで、ユーザの保有するアルバムおよび画像を取得する。そして、CPU201は、これらのレコードをコピーし、相続人のユーザIDに関連付け、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801にレコードを登録する(S1504)。
続いて、CPU201は、被相続人のユーザIDとユーザ相続人・テーブル701のユーザID702とを用いて、被相続人のユーザIDに関連付けられている相続人のレコードをユーザ相続人・テーブル701から取得する(S1505)。Subsequently, the
Subsequently, the
続いて、CPU201は、取得したレコードの中から最も優先度の高いレコードを抽出する(S1506)。続いて、CPU201は、S1506で取得した相続人のレコードに対応するユーザに対してアルバムという資産の相続に係る処理を実行する(S1507)。
ここで、相続に係る処理とは、被相続人から相続人への資産の引渡しに係る最終的な処理である。被相続人に関係する最も優先度の高い全ての相続人が相続の承認、又は相続の放棄を完了している場合は、被相続人の情報は不要となる。よって、相続に係る処理では、CPU201は、被相続人のユーザIDに関連するレコードをユーザ・テーブル601、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801から全て削除する処理を実行する。
なお、ユーザ・テーブル601から相続人のユーザIDに対応するレコードの顔情報808を参照し、その顔情報を分析し、被相続人の保有するアルバムの画像内容と比較して(画像処理などの技術を用いて解析して)譲渡の配分を決定する構成を採用してもよい。Subsequently, the
Here, the process related to inheritance is the final process related to the delivery of assets from the inheritor to the heir. If all heirs with the highest priority related to the deceased have completed the approval of inheritance or abandonment of the inheritance, the information of the deceased is not required. Therefore, in the process related to inheritance, the
The face information 808 of the record corresponding to the user ID of the heir is referred to from the user table 601, the face information is analyzed, and compared with the image content of the album held by the heir (such as image processing). A configuration may be adopted in which the allocation of the transfer is determined (analyzed using technology).
次に、ユーザ端末101での資産相続メールの相続を放棄する旨の通知先へのリンク押下によって、サーバ装置104が資産の相続を放棄することを示すメッセージを受信したときの動作について図16を参照して説明する。図16は、相続放棄時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、相続人端末105での資産相続メールの相続を放棄する旨の通知先へのリンクの押下によって、相続人からの資産の相続を放棄することを示すメッセージを受信したかを判定する(S1601)。このとき、CPU201は、メッセージを受信したと判定した場合、S1602に処理を進め、他方、受信していないと判定した場合、受信するまでS1601の処理を継続する。Next, FIG. 16 shows the operation when the
First, the
S1602では、CPU201は、受信したメッセージ(受信データ)から被相続人のユーザID、相続人のユーザIDを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、被相続人のユーザIDとユーザ相続人・テーブル701のユーザID702とを用いて、被相続人のユーザIDに関連付けられている相続人のレコードをユーザ相続人・テーブル701から取得する(S1603)。続いて、CPU201は、取得したレコードの中から最も優先度の高いレコードを抽出する(S1604)。
続いて、CPU201は、S1604で取得した相続人のレコードに対応するユーザに対してアルバムという資産の相続に係る処理を実行する(S1605)。
上述したように、相続に係る処理では、CPU201は、被相続人のユーザIDに関連するレコードをユーザ・テーブル601、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801から全て削除する処理を実行する。In S <b> 1602, the
Subsequently, the
As described above, in the process related to inheritance, the
なお、CPU201は、最も高い優先度の全ての相続人が相続を放棄することとなっている場合、次に高い優先度の相続人のユーザを検索し、そのユーザをその時点で最も優先度の高い相続人として資産相続メールを作成し、相続人端末105に送信する。また、このとき、CPU201は、相続人が管理用のユーザの場合は、S1412で管理用ユーザを見つけたときと同様の処理を実行する。 Note that if all heirs with the highest priority are to give up inheritance, the
次に、管理用ユーザが資産を保有したときのサーバ装置104の動作について図17を参照して説明する。図17は、管理処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、サーバ装置104に事前に設定しておいたタイマーによって、管理用ユーザに係る処理が実行される時間となったかを判定する(S1701)。このとき、CPU201は、実行する時間となったと判定した場合、S1702に処理を進め、他方、時間となっていないと判定した場合、実行可能な時間となるまでS1701を継続する。Next, the operation of the
First, the
S1702では、CPU201は、ユーザ・テーブル601の管理用ユーザのユーザIDに関連するアルバム、画像を全て取得する。続いて、CPU201は、それらに対して、事前に設定情報に設定されていた管理用ユーザの処理を実行する(S1703)。
例えば、設定情報が管理用ユーザのユーザIDに関連するテーブルのレコードおよび画像を削除することを示す情報であった場合について説明する。この場合、CPU201は、ユーザ・テーブル601、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701、ユーザアルバム・テーブル801から、管理用ユーザのユーザIDに対応するレコードおよび画像を全て削除する。
なお、S1701で使用するタイマーについては、ファイル、データベース等に設定情報を格納して管理してもよいし、OSなどのタイマーを利用してもよい。In step S <b> 1702, the
For example, a case where the setting information is information indicating that a record and an image in a table related to the user ID of the management user are deleted will be described. In this case, the
Note that the timer used in S1701 may be managed by storing setting information in a file, database, or the like, or a timer such as an OS may be used.
次に、ユーザ端末101での相続人一覧の画面421の削除するボタン430の押下によって、サーバ装置104がユーザと相続人の関係の削除要求を受信したときの動作について図18を参照して説明する。図18は、関係削除時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101での画面421の削除するボタン430の押下による相続人の削除要求を受信したかを判定する(S1801)。このとき、CPU201は、受信したと判定した場合、S1802に処理を進め、他方、受信していないと判定した場合、受信するまでS1801の処理を継続する。
S1802では、CPU201は、受信した削除要求(受信データ)から被相続人のユーザID、及び相続人のユーザIDを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、被相続人のユーザIDおよび相続人のIDに関連付けられているユーザ相続人・テーブル701のレコードを削除する(S1803)。Next, an operation when the
First, the
In step S1802, the
次に、ユーザ端末101での相続人一覧の画面421の更新するボタン431の押下によって、サーバ装置104がユーザと相続人の関係の更新要求を受信したときの動作について図19を参照して説明する。図19は、関係更新時処理に係るフローチャートの一例を示す図である。
まず、CPU201は、ユーザ端末101での画面421の更新するボタン431の押下による相続人の更新要求を受信したかを判定する(S1901)。このとき、CPU201は、受信したと判定した場合、S1902に処理を進め、他方、受信していないと判定した場合、受信するまでS1901の処理を継続する。
S1902では、CPU201は、受信した更新要求(受信データ)から被相続人のユーザID、及び相続人のユーザIDを取得する。続いて、CPU201は、被相続人のユーザIDおよび相続人のIDに関連付けられているユーザ相続人・テーブル701のレコードを取得する(S1903)。続いてCPU201は、更新要求(更新情報)に含まれる優先度、適用開始年齢、適用終了年齢を、ユーザ相続人・テーブル701の優先度・上書き705、適用開始年齢・上書き706、適用終了年齢・上書き707に設定して更新処理を実行する(S1904)。Next, the operation when the
First, the
In S1902, the
上述の構成によれば、ユーザの親族、友人といった関係性に基づき、譲渡先のユーザの存在が確認できないような場合でも、その譲渡先の関係性を辿って、譲渡先を決めることができる。また、上述の構成によれば、譲渡先の優先順位付けを行ったり、ユーザの年齢といった時間軸によって、譲渡先を切り替えたりすることができる。
また、上述の構成によれば、ユーザの死亡について相続人がサーバ装置104に手動で入力する必要がなくなるので、ユーザの資産を相続人に譲渡することができなくなる事態を低減できる。また、上述の構成によれば、譲渡先が特定できないことにより、死亡したユーザの資産(コンテンツ)がサーバ装置104に保存されたままの状態となることを回避できるようになる。According to the above-described configuration, even when the presence of the transfer destination user cannot be confirmed based on the relationship between the user's relatives and friends, the transfer destination can be determined by following the transfer destination relationship. Further, according to the above-described configuration, it is possible to prioritize transfer destinations and to switch transfer destinations according to a time axis such as a user's age.
Further, according to the above-described configuration, since it is not necessary for the heir to manually input the death of the user to the
<その他の実施形態>
本実施形態は、上述した構成に限られるものではない。例えば、サーバ装置104が一定時間内に資産相続メールに対する返答がなかった場合は、CPU201は、S1402からの処理を行ってもよい。この構成によれば、資産相続メールの送信が再度行われるので、より確実に資産情報を管理できるようになる。
また、本発明は、以下の処理を実行することによっても実現される。即ち、上述した実施形態の機能を実現するソフトウェア(プログラム)を、ネットワーク又は各種記憶媒体を介してシステム或いは装置に供給し、そのシステム或いは装置のコンピュータ(又はCPUやMPU等)がプログラムを読み出して実行する処理である。<Other embodiments>
The present embodiment is not limited to the configuration described above. For example, if the
The present invention can also be realized by executing the following processing. That is, software (program) that realizes the functions of the above-described embodiments is supplied to a system or apparatus via a network or various storage media, and a computer (or CPU, MPU, etc.) of the system or apparatus reads the program. It is a process to be executed.
上述した実施形態の構成によれば、資産情報をより適切に管理することができる。 According to the configuration of the above-described embodiment, asset information can be managed more appropriately.
以上、本発明の好ましい実施形態について詳述したが、本発明は係る特定の実施形態に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲に記載された本発明の要旨の範囲内において、種々の変形・変更が可能である。 The preferred embodiments of the present invention have been described in detail above, but the present invention is not limited to such specific embodiments, and various modifications can be made within the scope of the gist of the present invention described in the claims.・ Change is possible.
Claims (10)
Translated fromJapanese前記ユーザが生きているかを確認する確認情報を前記ユーザ端末に送信し、前記確認情報に対する返答情報を前記ユーザ端末から受信する通信手段と、
前記通信手段で一定の時間内に前記返答情報が受信されていないと判断すると、前記ユーザの識別情報をもとに前記記憶部から前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを読み出し、前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを関連付けて前記記憶部に格納する制御手段と、
を有することを特徴とする情報処理装置。The user terminal used by the user and the asset information of the user are stored in association with the identification information for identifying the user, and the identification information for identifying the user and the identification information for identifying the heir of the user are further associated with each other. An information processing apparatus communicably connected to the storage unit stored in the memory,
Communication means for transmitting confirmation information for confirming whether the user is alive to the user terminal, and receiving response information for the confirmation information from the user terminal;
If the communication means determines that the response information has not been received within a certain time, the asset information and the heir identification information are read from the storage unit based on the user identification information, and the asset Control means for associating information and identification information of the heir in the storage unit;
An information processing apparatus comprising:
前記記憶部には、更に、前記相続人の識別情報と前記相続人の所在情報とが関連付けられて記憶され、
前記通信手段は、前記相続人の識別情報をもとに前記相続人の所在情報を読み出し、相続について承認するか放棄するかを問い合わせる問合情報を、前記所在情報をもとに送信し、
前記制御手段は、前記通信手段で前記問合情報に対する承認する旨の承認情報が受信されたと判断した場合、前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを関連付けて前記記憶部に格納することを特徴とする請求項1記載の情報処理装置。Connected to the heir terminal used by the heir;
The storage unit further stores the identification information of the heir and the location information of the heir in association with each other,
The communication means reads out the location information of the heir based on the identification information of the heir, and transmits inquiry information asking whether to approve or abandon the inheritance based on the location information,
When the control means determines that the approval information for approving the inquiry information is received by the communication means, the control means associates the asset information and the identification information of the heir and stores them in the storage unit. The information processing apparatus according to claim 1.
前記制御手段は、前記相続人の識別情報をもとに前記相続人の条件情報を読み出し、読み出した条件情報より相続を許可すると判定した相続人の識別情報と前記資産情報とを関連付けて前記記憶部に格納することを特徴とする請求項1又は2記載の情報処理装置。In the storage unit, further, identification information of the heir and condition information for determining whether to permit the inheritance are associated and stored,
The control means reads out the condition information of the heir based on the identification information of the heir and associates the identification information of the heir determined to permit inheritance from the read condition information and the asset information in association with the storage The information processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the information processing apparatus is stored in a unit.
前記制御手段は、前記相続人の識別情報が前記記憶部に存在しないと判断した場合、前記ユーザの資産情報が関連付けられている前記ユーザの識別情報を前記管理用のユーザの識別情報に変更することを特徴とする請求項1乃至3の何れか1項記載の情報処理装置。The storage unit further includes identification information for identifying a management user,
When the control means determines that the heir identification information does not exist in the storage unit, the control means changes the user identification information associated with the user asset information to the management user identification information. The information processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the information processing apparatus is an information processing apparatus.
前記制御手段は、前記管理用のユーザの識別情報が関連付けられた資産情報を前記設定情報に従って処理することを特徴とする請求項4記載の情報処理装置。The storage unit further stores setting information indicating handling of the asset information,
The information processing apparatus according to claim 4, wherein the control unit processes asset information associated with identification information of the management user according to the setting information.
前記記憶部には、更に、前記相続人の識別情報と前記相続人を示す画像情報とが関連付けられて記憶され、
前記制御手段は、前記相続人の識別情報をもとに前記相続人の画像情報を読み出し、前記相続人の画像情報および前記資産情報の画像情報を解析し、前記相続人の識別情報に関連付ける前記資産情報の画像情報を決定することを特徴とする請求項1乃至7の何れか1項記載の情報処理装置。The asset information is image information,
In the storage unit, further, identification information of the heir and image information indicating the heir are associated and stored,
The control means reads the heir image information based on the heir identification information, analyzes the heir image information and the asset information image information, and associates the heir image information with the heir identification information. 8. The information processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein image information of asset information is determined.
通信手段が、前記ユーザが生きているかを確認する確認情報を前記ユーザ端末に送信し、前記確認情報に対する返答情報を前記ユーザ端末から受信する通信工程と、
制御手段が、前記通信工程で一定の時間内に前記返答情報が受信されていないと判断すると、前記ユーザの識別情報をもとに前記記憶部から前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを読み出し、前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを関連付けて前記記憶部に格納する制御工程と、
を有することを特徴とする資産情報管理方法。The user terminal used by the user and the asset information of the user are stored in association with the identification information for identifying the user, and the identification information for identifying the user and the identification information for identifying the heir of the user are further associated with each other. An asset information management method in an information processing apparatus communicably connected to a storage unit stored in a
A communication step of transmitting confirmation information for confirming whether the user is alive to the user terminal, and receiving response information for the confirmation information from the user terminal;
When the control means determines that the response information has not been received within a certain time in the communication step, the control unit obtains the asset information and the heir identification information from the storage unit based on the user identification information. A control step of reading and associating and storing the asset information and the identification information of the heir in the storage unit;
An asset information management method characterized by comprising:
前記ユーザが生きているかを確認する確認情報を前記ユーザ端末に送信し、前記確認情報に対する返答情報を前記ユーザ端末から受信する通信手段、
前記通信手段で一定の時間内に前記返答情報が受信されていないと判断すると、前記ユーザの識別情報をもとに前記記憶部から前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを読み出し、前記資産情報と前記相続人の識別情報とを関連付けて前記記憶部に格納する制御手段、
として機能させるプログラム。The user terminal used by the user and the asset information of the user are stored in association with the identification information for identifying the user, and the identification information for identifying the user and the identification information for identifying the heir of the user are further associated with each other. A computer that is communicably connected to the storage unit
Communication means for transmitting confirmation information for confirming whether the user is alive to the user terminal, and receiving response information for the confirmation information from the user terminal;
If the communication means determines that the response information has not been received within a certain time, the asset information and the heir identification information are read from the storage unit based on the user identification information, and the asset Control means for associating information and identification information of the heir in the storage unit;
Program to function as.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011119583AJP2012248021A (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2011-05-27 | Information processing unit, asset information managing method and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011119583AJP2012248021A (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2011-05-27 | Information processing unit, asset information managing method and program |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012248021Atrue JP2012248021A (en) | 2012-12-13 |
Family
ID=47468403
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011119583APendingJP2012248021A (en) | 2011-05-27 | 2011-05-27 | Information processing unit, asset information managing method and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2012248021A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014050159A1 (en)* | 2012-09-28 | 2014-04-03 | 株式会社 東芝 | Information processing device, data return method, and program |
| JP2019149789A (en)* | 2018-02-27 | 2019-09-05 | 株式会社Digtus | Takeover target information processing system |
| JP2020030504A (en)* | 2018-08-21 | 2020-02-27 | 宗教法人 證大寺 | Information management device and information management processing program |
| JP2021117558A (en)* | 2020-01-23 | 2021-08-10 | 株式会社エータイ | Succession information processing method, succession information processing device, succession information processing program and recording medium |
| WO2023013115A1 (en)* | 2021-08-04 | 2023-02-09 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002373247A (en)* | 2001-06-14 | 2002-12-26 | Daiwa Securities Group Inc | Payment system and program for system products |
| JP2004110651A (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2004-04-08 | Bank Of Tokyo-Mitsubishi Ltd | Device and method used for communication from banking establishment to customer, program for implementing method in computer, and record medium recording the program |
| JP2004295751A (en)* | 2003-03-28 | 2004-10-21 | Bank Of Tokyo-Mitsubishi Ltd | Personal information management system and personal information management method |
| US20080167994A1 (en)* | 2005-07-22 | 2008-07-10 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics, N.V. | Digital Inheritance |
| JP2009175790A (en)* | 2008-01-21 | 2009-08-06 | Nec Corp | Content asset management system, method and control program |
| JP2009177719A (en)* | 2008-01-28 | 2009-08-06 | Nec Corp | System and method for executing contact in occurrence of emergency situation |
- 2011
- 2011-05-27JPJP2011119583Apatent/JP2012248021A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002373247A (en)* | 2001-06-14 | 2002-12-26 | Daiwa Securities Group Inc | Payment system and program for system products |
| JP2004110651A (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2004-04-08 | Bank Of Tokyo-Mitsubishi Ltd | Device and method used for communication from banking establishment to customer, program for implementing method in computer, and record medium recording the program |
| JP2004295751A (en)* | 2003-03-28 | 2004-10-21 | Bank Of Tokyo-Mitsubishi Ltd | Personal information management system and personal information management method |
| US20080167994A1 (en)* | 2005-07-22 | 2008-07-10 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics, N.V. | Digital Inheritance |
| JP2009175790A (en)* | 2008-01-21 | 2009-08-06 | Nec Corp | Content asset management system, method and control program |
| JP2009177719A (en)* | 2008-01-28 | 2009-08-06 | Nec Corp | System and method for executing contact in occurrence of emergency situation |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| JPN6015013278; 月刊e・コロンブス 第36巻,第1版, 20101028, 第83頁, 東方通信社* |
| JPN6015013279; '今こそ知りたいウィンドウズ7' 日経PC21 第16巻,第7号, 20110324, 第36-41頁, 日経BP社* |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014050159A1 (en)* | 2012-09-28 | 2014-04-03 | 株式会社 東芝 | Information processing device, data return method, and program |
| JP2019149789A (en)* | 2018-02-27 | 2019-09-05 | 株式会社Digtus | Takeover target information processing system |
| JP7129691B2 (en) | 2018-02-27 | 2022-09-02 | 株式会社Digtus | Information processing system to be transferred |
| JP2020030504A (en)* | 2018-08-21 | 2020-02-27 | 宗教法人 證大寺 | Information management device and information management processing program |
| JP7193950B2 (en) | 2018-08-21 | 2022-12-21 | 宗教法人 證大寺 | Information management device and information management processing program |
| JP2021117558A (en)* | 2020-01-23 | 2021-08-10 | 株式会社エータイ | Succession information processing method, succession information processing device, succession information processing program and recording medium |
| JP7503910B2 (en) | 2020-01-23 | 2024-06-21 | 株式会社エータイ | Inheritance information processing method, inheritance information processing device, inheritance information processing program, and recording medium |
| WO2023013115A1 (en)* | 2021-08-04 | 2023-02-09 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6725715B2 (en) | Determining presence in applications that access shared and synchronized content | |
| US10019136B1 (en) | Image sharing device, apparatus, and method | |
| US8352581B2 (en) | Data transmission apparatus indicating transmission status, transmission control method indicating transmission status, and program thereof | |
| US10027726B1 (en) | Device, apparatus, and method for facial recognition | |
| US10027727B1 (en) | Facial recognition device, apparatus, and method | |
| US20210383370A1 (en) | Enhanced multi-party user data deletion | |
| JP6706637B2 (en) | Document creation program and information processing device | |
| US20180330428A1 (en) | Enterprise data marketplace system and method | |
| KR20170032448A (en) | Data information transaction method and system | |
| CN102918535A (en) | Content-processing device, content-processing method, content-processing program, and integrated circuit | |
| KR101475335B1 (en) | Enhancing an inquiry for a search of a database | |
| US11736449B2 (en) | System and method to allow anonymous users to contribute multimedia content across multiple digital workspaces | |
| JPWO2009125571A1 (en) | Content search system and content search method | |
| JP2012248021A (en) | Information processing unit, asset information managing method and program | |
| JP2009282938A (en) | Conference support method and conference support device | |
| US20190043020A1 (en) | Generating and enhancing meeting-related objects based on image data | |
| CN103019534B (en) | Mobile terminal and method to set up | |
| JP4543761B2 (en) | Content sharing system and content container creation method | |
| WO2023007867A1 (en) | Ticket management system, program, and method | |
| JP2021103592A (en) | Document management device and method for managing document | |
| US10657139B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus and non-transitory computer readable medium for distributed resource management | |
| US11074365B2 (en) | Event-based directory and contact management | |
| JP2017068778A (en) | Information processing device | |
| JP6398368B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing system, and program | |
| JP5865551B2 (en) | Content display method, program, and content display system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20140520 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20150227 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20150407 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20150804 |