JP2010173739A - Binding band and molded object having hinge structure - Google Patents
Binding band and molded object having hinge structureDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010173739A JP2010173739AJP2010064237AJP2010064237AJP2010173739AJP 2010173739 AJP2010173739 AJP 2010173739AJP 2010064237 AJP2010064237 AJP 2010064237AJP 2010064237 AJP2010064237 AJP 2010064237AJP 2010173739 AJP2010173739 AJP 2010173739A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- polyamide resin
- hinge structure
- carbon atoms
- binding band
- band
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Package Frames And Binding Bands (AREA)
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、結束バンドまたはヒンジ構造部を有する成形品に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a molded product having a binding band or a hinge structure.
ポリアミド樹脂は、自動車、電気・電子分野の部品類をはじめとする種々の用途に使用されている。充填材やガラス繊維などが配合されていない未強化ポリアミド樹脂組成物の主用途としては、結束バンド(後記、図1および図2参照)、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品(後記、図3および図4参照)、特に自動車、電気・電子分野で使用されるコネクターが挙げられる。 Polyamide resins are used in various applications including parts for automobiles and electrical / electronic fields. The main application of the unreinforced polyamide resin composition in which no filler, glass fiber, or the like is blended is a molded product having a binding band (see FIG. 1 and FIG. 2) and a hinge structure (see FIG. 3, FIG. 3 and FIG. 3). 4), and particularly connectors used in the automobile and electrical / electronic fields.
原料樹脂が剛直性の高いポリアミド樹脂であり、成形品が肉厚の薄い結束バンド部や、ヒンジ構造部を有する場合には、肉薄部を折り曲げ変形するときに折れ易いので、原料樹脂に吸水処理を施して柔軟化する工夫がなされてきた。しかし、吸水処理を施しても低温環境下で使用するときは柔軟性が不十分で、ヒンジ構造部などの薄い部分で折損するというトラブルが発生していた。 If the raw material resin is a polyamide resin with high rigidity and the molded product has a thin binding band part or hinge structure part, it is easy to bend when the thin part is bent and deformed. It has been devised to make it flexible. However, even when the water absorption treatment is performed, when used in a low temperature environment, the flexibility is insufficient, and there has been a problem that the thin portion such as the hinge structure breaks.
ヒンジ構造部などの薄い部分の折損防止のため、剛直性の高いポリアミド6・6、または難燃グレードなどの改良検討がなされてきた。原料樹脂に柔軟性を付与するため、剛直性の高いポリアミド樹脂に、柔軟性を付与する成分を共重合化させる方法、ポリオレフィン系樹脂や柔軟なポリアミド樹脂を配合する方法などが提案されている。 In order to prevent breakage of a thin portion such as a hinge structure portion, improvement studies have been made on
また、結束バンドの低温折損性の改善を目的として、変性ポリオレフィンを添加した樹脂組成物(特許文献1参照)、ヨウ化カリウムを添加した樹脂組成物(特許文献2参照)、好ましくはポリアミド6・6とポリアミド6の混合物に、滑剤と結晶核剤とを配合したポリアミド樹脂組成物(特許文献3参照)などが提案されている。 In addition, for the purpose of improving the low-temperature breakability of the binding band, a resin composition to which modified polyolefin is added (see Patent Document 1), a resin composition to which potassium iodide is added (see Patent Document 2), preferably
また、結束バンド部や、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品は、ヒンジ構造部と成形品の他の部分との間に肉厚差があるので、成形品製造時に成形品を金型から離型する際にトラブル(離型性不良)が発生することがある。このような離型性不良の改良は、これまで縷々試みられてきた。例えば、ステアリン酸バリウム、ラウリン酸バリウム、ステアリン酸アルミニウムよりなる群より選ばれた一種以上の化合物を配合した樹脂組成物とする方法、炭索数10〜20の脂肪族カルボン酸の塩、および炭素数22以上の脂肪族カルボン酸、またはその誘導体を配合した樹脂組成物とする方法のほか、粒径が10μ以下の窒化ホウ素の粉末と、炭素数15以上の脂肪族カルボン酸の誘導体とを配合したポリアミド樹脂組成物(特許文献4参照)。さらに分子末端に炭素数6〜22の炭化水素基を有するポリアミド樹脂(特許文献5参照)、などが提案されている。 In addition, the molded product having the binding band part and the hinge structure part has a thickness difference between the hinge structure part and the other part of the molded product, so that the molded product is released from the mold when the molded product is manufactured. Trouble (deformation failure) may occur. Many attempts have been made to improve such releasability. For example, a method of preparing a resin composition containing one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of barium stearate, barium laurate, and aluminum stearate, a salt of an aliphatic carboxylic acid having 10 to 20 carbon cords, and carbon In addition to a method of preparing a resin composition containing an aliphatic carboxylic acid having a number of 22 or more, or a derivative thereof, a powder of boron nitride having a particle size of 10 μm or less and a derivative of an aliphatic carboxylic acid having a carbon number of 15 or more Polyamide resin composition (see Patent Document 4). Furthermore, a polyamide resin having a hydrocarbon group having 6 to 22 carbon atoms at the molecular end (see Patent Document 5) has been proposed.
本発明は、上記従来の諸欠点を解決するために、鋭意検討の結果完成したものである。すなわち、本発明の目的は、製造時の離型性に優れて折損が発生し難い結束バンド、または、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品を提供することにある。 The present invention has been completed as a result of intensive studies in order to solve the above-described conventional drawbacks. That is, an object of the present invention is to provide a molded article having a binding band or a hinge structure part that is excellent in releasability during manufacture and hardly breaks.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明では、射出成形により得られた、バンド部及びバンド部挿入穴を有する結束バンドであって、前記結束バンドは、ポリアミド樹脂に、炭素数12〜22の脂肪族カルボン酸のアルミニウム塩が配合されてなるポリアミド樹脂組成物からなり、前記ポリアミド樹脂が、末端に炭素数6〜22の炭化水素基を有し、この炭化水素基の数が前記ポリアミド樹脂の全末端基の40〜100%であることを特徴とする、結束バンドを提供する。また、さらに、本発明ではさらに、射出成形により得られた、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品であって、前記成形品は、ポリアミド樹脂に、炭素数12〜22の脂肪族カルボン酸のアルミニウム塩が配合されてなるポリアミド樹脂組成物からなり、前記ポリアミド樹脂が、末端に炭素数6〜22の炭化水素基を有し、この炭化水素基の数が前記ポリアミド樹脂の全末端基の40〜100%であることを特徴とする、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品を提供する。 In order to solve the above-described problems, the present invention provides a binding band having a band part and a band part insertion hole obtained by injection molding, wherein the binding band is made of a polyamide resin and a fat having 12 to 22 carbon atoms. The polyamide resin has a hydrocarbon group having 6 to 22 carbon atoms at the terminal, and the number of hydrocarbon groups is the total number of the polyamide resin. A binding band is provided, characterized in that it is 40-100% of the end groups. Furthermore, in the present invention, it is a molded article having a hinge structure part obtained by injection molding, wherein the molded article is made of a polyamide resin and an aluminum salt of an aliphatic carboxylic acid having 12 to 22 carbon atoms. It is composed of a blended polyamide resin composition, and the polyamide resin has a hydrocarbon group having 6 to 22 carbon atoms at the terminal, and the number of the hydrocarbon groups is 40 to 100% of all the terminal groups of the polyamide resin. A molded article having a hinge structure part is provided.
本発明は以下に詳細に説明するとおりであり、次のような特別に有利な効果を奏し、その産業上の利用価値は極めて大である。
1.本発明に係るポリアミド樹脂組成物は、肉薄部を有する結束バンド、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品などの製造時離型性に優れて折損が発生し難い。
2.本発明に係るポリアミド樹脂組成物から得られる、結束バンド、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品は、薄肉部が優れた低温折損防止効果を発揮する。
3.本発明に係るポリアミド樹脂組成物から得られる、結束バンド、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品は、自動車、電気・電子分野で使用される製品の品質を化させ、部品の高機能化に寄与する。The present invention is as described in detail below, and has the following particularly advantageous effects, and its industrial utility value is extremely large.
1. The polyamide resin composition according to the present invention is excellent in releasability during production of a binding band having a thin portion, a molded product having a hinge structure portion, and the like, and hardly breaks.
2. A molded product having a binding band and a hinge structure part obtained from the polyamide resin composition according to the present invention exhibits a low-temperature breakage preventing effect with an excellent thin part.
3. A molded product having a binding band and a hinge structure obtained from the polyamide resin composition according to the present invention improves the quality of products used in the automobile and electrical / electronic fields, and contributes to the enhancement of the functions of parts.
以下、本発明につき詳細に説明する。
本発明に係る樹脂組成物を構成するポリアミド樹脂は、3員環以上のラクタム、重合可能なω−アミノ酸、二塩基酸とジアミンなどの重縮合によって得られるポリアミド類を言う。具体的には、ε−カプロラクタム、アミノカプロン酸、エナントラクタム、7−アミノヘプタン酸、11−アミノウンデカン酸、9−アミノノナン酸、α−ピロリドン、α−ピベリドンなどの重合体、ヘキサメチレンジアミン、ノナメチレンジアミン、ウンデカメチレンジアミン、ドデカメチレンジアミン、メタキシリレンジアミンなどのジアミンと、テレフタル酸、イソフタル酸、アジピン酸、セバチン酸、ドデカン二塩基酸、グルタール酸などのジカルボン酸とを重縮合させて得られる重合体、または、これらの共重合体、例えば、ポリアミド4、6、7、8、11、12、6・6、6・9、6・10、6・11、6・12、6T、6/6・6、6/12、6/6Tなどが挙げられる。ここで「・」は単量体の組合せを意味し、「/」は共重合体を意味する。この中で特にポリアミド6、ポリアミド6・6またはこれらの共重合体が好ましく、とりわけポリアミド6が好ましい。ポリアミド樹脂の好ましい粘度数は、ISO 307に準拠して測定した値で90〜190ml/gの範囲であり、特に好ましいのは99〜138ml/gの範囲である。Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail.
The polyamide resin constituting the resin composition according to the present invention refers to polyamides obtained by polycondensation of a lactam having three or more members, a polymerizable ω-amino acid, a dibasic acid and a diamine. Specifically, polymers such as ε-caprolactam, aminocaproic acid, enanthractam, 7-aminoheptanoic acid, 11-aminoundecanoic acid, 9-aminononanoic acid, α-pyrrolidone, α-piberidone, hexamethylenediamine, nonamethylene Obtained by polycondensation of diamines such as diamine, undecamethylenediamine, dodecamethylenediamine, and metaxylylenediamine with dicarboxylic acids such as terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid, adipic acid, sebacic acid, dodecane dibasic acid, and glutaric acid. Polymers, or copolymers thereof, such as
上記原料ポリアミド樹脂は、末端に炭素数6〜22の炭化水素基を有し、この炭化水素基の数が前記ポリアミド樹脂の全末端基の40〜100%であるポリアミド樹脂である。このようなポリアミド系樹脂は、炭素数7〜23のモノカルボン酸類と、炭素数6〜22のモノアミン類、および/または、炭素数2〜22のジアミン類、あるいは、炭素数6〜22のモノアミン類と炭素数3〜24のジカルボン酸類とを組合せて存在させ、重合して得られる末端が封止されたポリアミド樹脂である。これらの末端基封止剤の組合せとしては、ステアリン酸とオクタデシルアミン、ステアリン酸とヘキサメチレンジアミン、ステアリン酸とアジピン酸とステアリルアミンなどの組合せが好ましい。全末端基中の炭素数6〜22の炭化水素基の比率は50%以上が好ましく、より好ましいのは70%以上である。 The raw material polyamide resin is a polyamide resin having a hydrocarbon group having 6 to 22 carbon atoms at the terminal, and the number of hydrocarbon groups is 40 to 100% of the total terminal groups of the polyamide resin. Such polyamide resins include monocarboxylic acids having 7 to 23 carbon atoms, monoamines having 6 to 22 carbon atoms, and / or diamines having 2 to 22 carbon atoms, or monoamines having 6 to 22 carbon atoms. It is a polyamide resin having a terminal end capped obtained by polymerizing it and a dicarboxylic acid having 3 to 24 carbon atoms in combination. As a combination of these end group blocking agents, a combination of stearic acid and octadecylamine, stearic acid and hexamethylenediamine, stearic acid, adipic acid and stearylamine is preferable. The ratio of the hydrocarbon group having 6 to 22 carbon atoms in all terminal groups is preferably 50% or more, more preferably 70% or more.
上記ポリアミド樹脂には、炭素数12〜22の脂肪族カルボン酸のアルミニウム塩を配合する。脂肪族カルボン酸のアルミニウム塩の中で好ましいのは、ステアリン酸アルミニウム、ラウリン酸アルミニウムである。脂肪族カルボン酸のアルミニウム塩の配合量は、ポリアミド樹脂組成物の0.01〜1重量%の範囲とする。配合量が0.01重量%未満であると、成形品薄肉部の低温折損性の改良効果が発揮されないし、配合量が1重量%より多いと、機械的性質が低下し、低温折損性も低下する。上記範囲で好ましいのは、0.03〜0.7重量%であり、とりわけ好ましいのは0.05〜0.5重量%である。 The polyamide resin is blended with an aluminum salt of an aliphatic carboxylic acid having 12 to 22 carbon atoms. Among the aluminum salts of aliphatic carboxylic acids, aluminum stearate and aluminum laurate are preferred. The amount of the aliphatic carboxylic acid aluminum salt is in the range of 0.01 to 1% by weight of the polyamide resin composition. If the blending amount is less than 0.01% by weight, the effect of improving the low-temperature fracture property of the thin part of the molded product is not exhibited. If the blending amount is more than 1% by weight, the mechanical properties are lowered and the low-temperature fracture property is also low. descend. In the above range, 0.03 to 0.7% by weight is preferable, and 0.05 to 0.5% by weight is particularly preferable.
脂肪族カルボン酸アルミニウム塩の離型性の改良効果を補足するために、上記ポリアミド樹脂に、他の離型剤を0.005〜0.5重量%、より好ましくは0.01〜0.2重量%の範囲で配合することができる。他の離型剤としては、パラフィンワックス、ポリエチレンワックス、脂肪酸類、脂肪酸エステル類、ビス脂肪酸アミド類などであり、ポリアミドとの相溶性の観点から肪肪酸アミド類が特に好ましい。ビス脂肪酸アミド類の具体例としては、エチレンビスステアリン酸アミド、メチレンビスステアリン酸アミドが挙げられる。 In order to supplement the effect of improving the release property of the aliphatic carboxylic acid aluminum salt, another release agent is added to the polyamide resin in an amount of 0.005 to 0.5% by weight, more preferably 0.01 to 0.2%. It can mix | blend in the range of weight%. Other mold release agents include paraffin wax, polyethylene wax, fatty acids, fatty acid esters, bisfatty acid amides and the like, and fatty acid amides are particularly preferred from the viewpoint of compatibility with polyamide. Specific examples of the bis fatty acid amides include ethylene bis stearic acid amide and methylene bis stearic acid amide.
また、上記ポリアミド樹脂組成物には、本発明の目的を損なわない範囲で、他種の樹脂や各種樹脂添加剤を、配合することができる。他の樹脂としては、ポリオレフィン系樹脂、変性ポリオレフィン系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ポリエステルエラストマー、ポリアミドエラストマー、ポリスチレン系樹脂などが挙げられる。樹脂添加剤としては、ヒンダードフェノ一ル類などの安定剤、ハロゲン化銅化合物などの耐熱性改良剤、シアヌル酸メラミンなどの難燃剤、顔料、染料、帯電防止剤などが挙げられる。しかし、結晶化を促進する核剤や無機充填剤は、特別な目的がない限り配合しない。このような著しい結晶化促進効果があり配合するのに好ましくない核剤や無機充填材としては、タルク、ワラストナイト、カオリン、焼成カオリン、マイカ、ゼオオライト、ボロンナイトライドなどが挙げられる。 In addition, other types of resins and various resin additives can be blended with the polyamide resin composition as long as the object of the present invention is not impaired. Examples of other resins include polyolefin resins, modified polyolefin resins, polyester resins, polyester elastomers, polyamide elastomers, and polystyrene resins. Examples of the resin additive include stabilizers such as hindered phenols, heat resistance improvers such as copper halide compounds, flame retardants such as melamine cyanurate, pigments, dyes, and antistatic agents. However, nucleating agents and inorganic fillers that promote crystallization are not blended unless there is a special purpose. Examples of such nucleating agents and inorganic fillers that have a remarkable crystallization promoting effect and are not preferable for blending include talc, wollastonite, kaolin, calcined kaolin, mica, zeolite, and boron nitride.
本発明に係るポリアミド樹脂組成物を調製する方法としては、(1)原料ポリアミド樹脂と炭素数12〜22の脂肪族カルボン酸アルミニウム塩とを所定量秤量し、要すれば、他の樹脂、樹脂添加剤などを追加配合し、ブレンダーなどで混合し、ドライブレンド物とする方法、(2)炭素数12〜22の脂肪族カルボン酸アルミニウム塩が多く配合されたマスターバッチを調整し、このマスターバッチを原料ポリアミド樹脂にドライブレンドする方法、または、(3)上記(1)または(2)のドライブレンド物を押出機などの溶融混練機によって溶融してペレット化する方法、などによればよい。ドライブレンド物またはペレットは、射出成形法によって目的の結束バンド(後記、図1および図2参照)や、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品(後記、図3および図4参照)などを製造する際の原料樹脂材料として使用できる。 As a method for preparing the polyamide resin composition according to the present invention, (1) a predetermined amount of a raw material polyamide resin and an aliphatic carboxylic acid aluminum salt having 12 to 22 carbon atoms are weighed and, if necessary, other resins and resins. A method of adding additional additives, etc., and mixing with a blender to make a dry blend, (2) preparing a masterbatch containing a large number of aliphatic carboxylic acid aluminum salts having 12 to 22 carbon atoms, this masterbatch Or a method of dry blending the raw material polyamide resin into a raw material polyamide resin, or (3) a method of melting and pelletizing the dry blend of (1) or (2) with a melt kneader such as an extruder. The dry blended product or pellet is produced by producing an intended binding band (see below, FIG. 1 and FIG. 2), a molded product having a hinge structure (see below, FIG. 3 and FIG. 4), etc. by an injection molding method. It can be used as a raw material resin material.
以下、本発明を実施例により更に詳細に説明するが、本発明はその要旨を越えない限り、以下の記載例に制限されるものではない EXAMPLES Hereinafter, although an Example demonstrates this invention further in detail, this invention is not restrict | limited to the following description examples, unless the summary is exceeded.
実施例および比較例で使用した成分の種類と特性は、以下のとおりである。
1.ポリアミド樹脂:
(1)PA−1:ポリアミド6であって、全末端基の85%がステアリン酸とオクタデシルアミンを導入することによって封止され、粘度数118ml/gのものである。
(2)PA−2:ポリアミド6であって、全末端基の40%が酢酸を導入して封止され、粘度数118ml/gのものである。The types and characteristics of the components used in the examples and comparative examples are as follows.
1. Polyamide resin:
(1) PA-1:
(2) PA-2:
2.脂肪酸金属塩または滑剤
(3)Al:ステアリン酸アルミニウム(日本油脂社製)である。
(4)Ca:ステアリン酸カルシウム(日本油脂社製)である。
(5)Ba:ステアリン酸バリウム(日本油脂社製)である。
(6)Mg:ステアリン酸マグネシウム(日本油脂社製)である。
(7)EBS:チレンビスステアリン酸アミド(花王社製)である。2. Fatty acid metal salt or lubricant (3) Al: Aluminum stearate (manufactured by NOF Corporation).
(4) Ca: calcium stearate (manufactured by NOF Corporation).
(5) Ba: Barium stearate (manufactured by NOF Corporation).
(6) Mg: Magnesium stearate (manufactured by NOF Corporation).
(7) EBS: Tylene bis stearamide (manufactured by Kao Corporation).
実施例および比較例における樹脂組成物と成形品の評価試験は、以下に記載のとおりである。
(a)離型試験:射出成形機(日精樹脂工業社製、形式:PS40)を使用して、図1および図2に示した構造を有する結束バンドと、図3および図4に示した構造を有する成形品を、以下に記載の方法で120ショット連続して成形して成形品を得た。得られた成形品について、結束バンドの肉薄部(図1参照)またはヒンジ構造部(図3参照)の折損、割れなどの離型トラブル発生の有無を目視観察して評価する方法である。離型トラブルの発生が認められなかったものを○、認められたものを×と判定し、評価結果を表−2に示した。Evaluation tests of resin compositions and molded products in Examples and Comparative Examples are as described below.
(A) Mold release test: Using an injection molding machine (manufactured by Nissei Plastic Industry Co., Ltd., model: PS40), a binding band having the structure shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 and the structure shown in FIGS. 3 and 4 A molded product having a shape was obtained by continuously molding 120 shots by the method described below. The obtained molded product is evaluated by visually observing the occurrence of mold release troubles such as breakage and cracking of the thin portion (see FIG. 1) or the hinge structure portion (see FIG. 3) of the binding band. The case where the occurrence of the release trouble was not recognized was judged as “◯”, and the case where the trouble was found was judged as “X”, and the evaluation results are shown in Table 2.
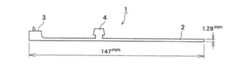
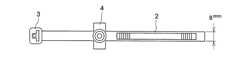
なお、図1は実施例、比較例で製造した結束バンドの側面略図であり、図2は平面略図である。図3は、結束バンドの低温折損性試験の実施状態を説明する際の側面略図であり、図4は実施例、比較例で製造したヒンジ構造部を有する成形品の略図であり、図5は図4に示した成形品のヒンジ構造部の拡大略図であり、図6はヒンジ構造部の低温折損性の実施状態を説明する際の側面略図である。図1ないし図3において、1は結束バンド、2はバンド部、3はバンド部挿入穴、4は突起、5は結束部であり、図4ないし図5において、6は成形品、7は厚さが0.4mmのフィルムによって構成されているヒンジ構造部である。 1 is a schematic side view of a binding band manufactured in Examples and Comparative Examples, and FIG. 2 is a schematic plan view. FIG. 3 is a schematic side view for explaining an implementation state of a low-temperature breakability test for a binding band, FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of a molded product having a hinge structure manufactured in Examples and Comparative Examples, and FIG. FIG. 6 is an enlarged schematic view of the hinge structure portion of the molded product shown in FIG. 4, and FIG. 6 is a schematic side view for explaining an implementation state of the cold breakability of the hinge structure portion. 1 to 3, 1 is a binding band, 2 is a band portion, 3 is a band portion insertion hole, 4 is a protrusion, 5 is a binding portion, in FIGS. 4 to 5, 6 is a molded product, and 7 is a thickness. It is a hinge structure part comprised with a 0.4 mm film.
(b)低温折損性(バンド):上記(a)に記載の方法で製造された図1および図2に示した結束バンドを、−25℃の恒温槽内で8時間以上放置した後、図3に側面略図として示したように、バンド部2をバンド挿入穴3に通し、バンド挿入穴3を片手で保持しながら、バンド部2の先端を図3の矢印方向に強く引っ張り、結束バンド1への割れ発生の有無を目視観察する方法である。試験は20本の結束バンドについて行い、割れが認められた数を表−2に示す。結束バンド1の割れは、ほとんど結束部5に発生する。(B) Low temperature breakability (band): After the binding band shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 manufactured by the method described in (a) above is left in a thermostatic bath at −25 ° C. for 8 hours or more, 3, the
(c)低温折損性(ヒンジ):図3および図4に示したヒンジ構造部を有する成形品(絶乾品)20個を、−35℃雰囲気下で8時間以上放置した後、図4に点線で示したように、角度90度の一回折り曲げ、ヒンジ構造部の折損の有無を目視観察する方法である。20個の成形品の中で、ヒンジ構造部に割れが認められた数を表−2に示す。(C) Low temperature breakage (hinge): After 20 pieces of molded products (absolutely dried products) having the hinge structure shown in FIGS. 3 and 4 were left in an atmosphere of −35 ° C. for 8 hours or longer, FIG. As indicated by the dotted line, this is a method of visually observing whether the hinge structure part is bent once or bent at an angle of 90 degrees. Table 20 shows the number of cracks observed in the hinge structure portion among the 20 molded products.
[実施例1〜実施例2、比較例1〜比較例7]
ポリアミド系樹脂、脂肪酸金属塩およびその他の添加剤を、表−1に掲げた割合で秤量し、ブレンダーで混合した。得られたドライブレンド物を原料とし、図1および図2に示した結束バンド1と、図4および図5に示したヒンジ構造部を有する成形品6を、射出成形機(日精樹脂工業社製、型式:PS40)によって、樹脂温度250℃、射出時間3秒、冷却時間7秒、全サイクル10秒の条件で、120シヨット以上連続成形した。得られた結束バンド1とヒンジ構造部を有する成形品6につき、上記の評価方法に準拠して、成形品製造時の離型性と、成形品の低温時折損性を評価した。評価結果を、表−2に示す。[Example 1 to Example 2, Comparative Example 1 to Comparative Example 7]
Polyamide-based resin, fatty acid metal salt and other additives were weighed in the proportions listed in Table 1 and mixed with a blender. Using the obtained dry blend as a raw material, a molded
表−1および表−2より、つぎのことが明らかになる。
1.本発明に係るポリアミド樹脂組成物は、結束バンド、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品製造時の離型性に優れて折損が発生し難い(実施例1〜実施例2参照)。
2.本発明に係るポリアミド樹脂組成物から得られる、結束バンド、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品の薄肉部は、優れた低温折損防止効果を発揮する(実施例1〜実施例2参照)。
3.これに対してポリアミド樹脂が請求項1の要件を満たすものであっても、炭素数6〜22の脂肪族カルボン酸のアルミニウム塩を配合しないものは、離型性および低温折損防止性の双方が劣る(比較例1参照)。
4.ポリアミド樹脂が請求項1の要件を満たしても、満たさなくても、炭素数6〜22の脂肪族カルボン酸のアルミニウム塩を配合しないものは、離型性および低温折損防止性の双方が劣る(比較例2、比較例3参照)。
5.これに対してポリアミド樹脂が、請求項1の要件を満たすものであっても、炭素数6〜22の脂肪族カルボン酸のアルミニウム塩以外の脂肪酸金属塩または滑剤を配合したものは、離型性は改良されるが低温折損防止性が劣る(比較例4〜比較例7参照)。The following becomes clear from Table-1 and Table-2.
1. The polyamide resin composition according to the present invention is excellent in releasability at the time of producing a molded product having a binding band and a hinge structure, and hardly breaks (see Examples 1 to 2).
2. The thin-walled part of the molded article having a binding band and a hinge structure part obtained from the polyamide resin composition according to the present invention exhibits an excellent low-temperature breakage preventing effect (see Examples 1 to 2).
3. On the other hand, even if the polyamide resin satisfies the requirements of
4). Even if the polyamide resin satisfies the requirement of
5). On the other hand, even if the polyamide resin satisfies the requirements of
本発明に係る成形品は、優れた薄肉部の低温折れ防止効果を有しているので、自動車、電気電子分野に使用される結束バンドや、ヒンジ構造部を有する成形品として使用され、その品質に対する信頼性向上が図られる。 Since the molded product according to the present invention has an excellent effect of preventing the low temperature breakage of the thin-walled portion, it is used as a molded product having a binding band and a hinge structure portion used in the automobile and electric / electronic fields, and its quality. The reliability is improved.
1:結束バンド
2:バンド部
3:バンド部挿入穴
4:突起
5:結束部
6:成形品
7:ヒンジ構造部
1: Bundling band 2: Band part 3: Band part insertion hole 4: Projection 5: Bundling part 6: Molded product 7: Hinge structure part
Claims (2)
Translated fromJapaneseA molded article having a hinge structure obtained by injection molding, wherein the molded article is made from a polyamide resin composition in which an aluminum salt of an aliphatic carboxylic acid having 12 to 22 carbon atoms is blended with a polyamide resin. The polyamide resin has a hydrocarbon group having 6 to 22 carbon atoms at the terminal, and the number of the hydrocarbon groups is 40 to 100% of the total terminal group of the polyamide resin. Molded product with structural part.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010064237AJP2010173739A (en) | 2010-03-19 | 2010-03-19 | Binding band and molded object having hinge structure |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010064237AJP2010173739A (en) | 2010-03-19 | 2010-03-19 | Binding band and molded object having hinge structure |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004163959ADivisionJP5080718B2 (en) | 2004-06-02 | 2004-06-02 | Polyamide resin composition |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010173739Atrue JP2010173739A (en) | 2010-08-12 |
Family
ID=42705090
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010064237APendingJP2010173739A (en) | 2010-03-19 | 2010-03-19 | Binding band and molded object having hinge structure |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2010173739A (en) |
Cited By (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014500372A (en)* | 2010-12-21 | 2014-01-09 | ビーエーエスエフ ソシエタス・ヨーロピア | Thermoplastic molding material |
| JP2017060863A (en)* | 2011-02-24 | 2017-03-30 | スパイナル・エレメンツ・インコーポレーテッド | Method and apparatus for stabilizing bone |
| US9721695B2 (en) | 2010-12-21 | 2017-08-01 | Basf Se | Thermoplastic molding composition |
| US10022161B2 (en) | 2011-02-24 | 2018-07-17 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Vertebral facet joint fusion implant and method for fusion |
| US10085776B2 (en) | 2004-02-06 | 2018-10-02 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Vertebral facet joint prosthesis and method of fixation |
| USD834194S1 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2018-11-20 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Interbody bone implant |
| US10194955B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2019-02-05 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Method of placing an implant between bone portions |
| US10251679B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2019-04-09 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Apparatus for bone stabilization and distraction and methods of use |
| US10426524B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2019-10-01 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Apparatus for spinal fixation and methods of use |
| US10624680B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2020-04-21 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Device and method for reinforcement of a facet |
| US10758361B2 (en) | 2015-01-27 | 2020-09-01 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Facet joint implant |
| US11304733B2 (en) | 2020-02-14 | 2022-04-19 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie methods |
| US11457959B2 (en) | 2019-05-22 | 2022-10-04 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie and bone tie inserter |
| US11464552B2 (en) | 2019-05-22 | 2022-10-11 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie and bone tie inserter |
| US11478275B2 (en) | 2014-09-17 | 2022-10-25 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Flexible fastening band connector |
| US12369952B2 (en) | 2021-12-10 | 2025-07-29 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie and portal |
| US12440242B2 (en) | 2024-04-29 | 2025-10-14 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Flexible fastening band connector |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61163935A (en)* | 1985-01-14 | 1986-07-24 | Mitsubishi Chem Ind Ltd | Polyamide resin and production thereof |
| JPS61236828A (en)* | 1985-04-15 | 1986-10-22 | Mitsubishi Chem Ind Ltd | Automotive underhood parts |
| JPS61296030A (en)* | 1985-06-25 | 1986-12-26 | Mitsubishi Chem Ind Ltd | Polyamide resin and production thereof |
| JPH0782474A (en)* | 1993-09-13 | 1995-03-28 | Asahi Chem Ind Co Ltd | Polyamide resin composition |
| JPH0873736A (en)* | 1994-08-31 | 1996-03-19 | Mitsubishi Eng Plast Kk | Polyamide resin composition suitable for binding band |
- 2010
- 2010-03-19JPJP2010064237Apatent/JP2010173739A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61163935A (en)* | 1985-01-14 | 1986-07-24 | Mitsubishi Chem Ind Ltd | Polyamide resin and production thereof |
| JPS61236828A (en)* | 1985-04-15 | 1986-10-22 | Mitsubishi Chem Ind Ltd | Automotive underhood parts |
| JPS61296030A (en)* | 1985-06-25 | 1986-12-26 | Mitsubishi Chem Ind Ltd | Polyamide resin and production thereof |
| JPH0782474A (en)* | 1993-09-13 | 1995-03-28 | Asahi Chem Ind Co Ltd | Polyamide resin composition |
| JPH0873736A (en)* | 1994-08-31 | 1996-03-19 | Mitsubishi Eng Plast Kk | Polyamide resin composition suitable for binding band |
Cited By (31)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10085776B2 (en) | 2004-02-06 | 2018-10-02 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Vertebral facet joint prosthesis and method of fixation |
| JP2016117913A (en)* | 2010-12-21 | 2016-06-30 | ビーエーエスエフ ソシエタス・ヨーロピアBasf Se | Thermoplastic molding material |
| JP2014500372A (en)* | 2010-12-21 | 2014-01-09 | ビーエーエスエフ ソシエタス・ヨーロピア | Thermoplastic molding material |
| US9721695B2 (en) | 2010-12-21 | 2017-08-01 | Basf Se | Thermoplastic molding composition |
| US12343048B2 (en) | 2011-02-24 | 2025-07-01 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for stabilizing bone |
| JP2017060863A (en)* | 2011-02-24 | 2017-03-30 | スパイナル・エレメンツ・インコーポレーテッド | Method and apparatus for stabilizing bone |
| US10022161B2 (en) | 2011-02-24 | 2018-07-17 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Vertebral facet joint fusion implant and method for fusion |
| US10368921B2 (en) | 2011-02-24 | 2019-08-06 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for stabilizing bone |
| US11464551B2 (en) | 2011-02-24 | 2022-10-11 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for stabilizing bone |
| USD926982S1 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2021-08-03 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Interbody bone implant |
| USD834194S1 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2018-11-20 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Interbody bone implant |
| USD857900S1 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2019-08-27 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Interbody bone implant |
| USD958366S1 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2022-07-19 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Interbody bone implant |
| USD884896S1 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2020-05-19 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Interbody bone implant |
| USD979062S1 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2023-02-21 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Interbody bone implant |
| US10251679B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2019-04-09 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Apparatus for bone stabilization and distraction and methods of use |
| US11272961B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2022-03-15 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Apparatus for bone stabilization and distraction and methods of use |
| US10426524B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2019-10-01 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Apparatus for spinal fixation and methods of use |
| US10194955B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2019-02-05 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Method of placing an implant between bone portions |
| US11517354B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2022-12-06 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Method of placing an implant between bone portions |
| US11918258B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2024-03-05 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Device and method for reinforcement of a facet |
| US10624680B2 (en) | 2013-09-27 | 2020-04-21 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Device and method for reinforcement of a facet |
| US11478275B2 (en) | 2014-09-17 | 2022-10-25 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Flexible fastening band connector |
| US11998240B2 (en) | 2014-09-17 | 2024-06-04 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Flexible fastening band connector |
| US10758361B2 (en) | 2015-01-27 | 2020-09-01 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Facet joint implant |
| US11457959B2 (en) | 2019-05-22 | 2022-10-04 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie and bone tie inserter |
| US11464552B2 (en) | 2019-05-22 | 2022-10-11 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie and bone tie inserter |
| US11304733B2 (en) | 2020-02-14 | 2022-04-19 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie methods |
| US12232778B2 (en) | 2020-02-14 | 2025-02-25 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie methods |
| US12369952B2 (en) | 2021-12-10 | 2025-07-29 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Bone tie and portal |
| US12440242B2 (en) | 2024-04-29 | 2025-10-14 | Spinal Elements, Inc. | Flexible fastening band connector |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2010173739A (en) | Binding band and molded object having hinge structure | |
| US10364339B2 (en) | Polyamide resin composition and molded article produced therefrom | |
| JPWO2020040282A1 (en) | Polyamide and polyamide composition | |
| CN101772550A (en) | polyamide composition | |
| CN102906164B (en) | Masterbatch pellets, process for producing same, and polyamide resin composition containing the masterbatch pellets | |
| JP2012062417A (en) | Polyamide resin composition and method for molding the same | |
| TWI644977B (en) | Thermoplastic resin composition and molded article formed by molding the same | |
| CN114502656B (en) | Polyamide composition and articles thereof | |
| CN102482491A (en) | Semi-aromatic polyamide resin composition, its production method and its products | |
| JPH11222553A (en) | Aromatic polyamide resin composition | |
| JP5516265B2 (en) | Molding method of polyamide resin composition | |
| CN107298852B (en) | Polyamide resin composition and molded article | |
| CN106554616A (en) | Amilan polyamide resin composition and its molded body | |
| WO2019155982A1 (en) | Thermoplastic resin composition, and molded article obtained by molding same | |
| JP5854564B2 (en) | Polyamide resin composition and molded product | |
| JP5080718B2 (en) | Polyamide resin composition | |
| CN112930372B (en) | Polyamide composition | |
| JP5818184B2 (en) | High melting point polyamide resin composition with excellent vibration and appearance at the time of water absorption | |
| JP6210217B2 (en) | Carbon fiber reinforced polyamide resin composition | |
| JP7079139B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing polyamide resin composition | |
| CN112592582B (en) | Polyamide resin composition, molded article comprising same, and in-vehicle camera component | |
| JP2024074668A (en) | Polyamide resin composition and molded body | |
| TWI869372B (en) | Carbon fiber reinforced polyamide resin composition and molded product thereof | |
| TW202246471A (en) | Flame-retardant polyamide resin composition and molded article comprising same | |
| JP2018193437A (en) | Thermoplastic resin composition and molded article obtained by molding the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date:20100924 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20100928 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20120221 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20120306 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20120710 |