JP2009244916A - Rehabilitation plan updating system - Google Patents
Rehabilitation plan updating systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2009244916A JP2009244916AJP2008087053AJP2008087053AJP2009244916AJP 2009244916 AJP2009244916 AJP 2009244916AJP 2008087053 AJP2008087053 AJP 2008087053AJP 2008087053 AJP2008087053 AJP 2008087053AJP 2009244916 AJP2009244916 AJP 2009244916A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- patient
- rehabilitation
- exercise
- plan
- calculation unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、患者のリハビリプランを更新するリハビリプラン更新システムに関する。 The present invention relates to a rehabilitation plan update system for updating a patient's rehabilitation plan.
従来から、ケガや病気などで入院している患者に対して、術後の経過期間や、健康状態、歩行器およびペースメーカーといった補助具の使用などに応じたリハビリプランが作成されている。通常、リハビリプランには、「1日に100歩以上、歩く」「階段の上り下りをする」などといった運動目標に加えて、「介護付きで入浴する」「自分でトイレに行く」などといった自立・介護目標が設定されている。 Conventionally, rehabilitation plans have been created for patients who are hospitalized due to injury or illness, depending on the postoperative period, health status, use of assistive devices such as walker and pacemaker. Usually, rehabilitation plans are self-supporting, such as “take a bath with care” or “go to the toilet yourself” in addition to exercise goals such as “walk 100 steps a day” or “go up and down stairs”.・ Nursing care goals are set.
ところで、リハビリプランは、医師などが経験に基づいて作成していることが一般的であり、リハビリプランに従って運動や介護が行われた後、患者の感想や要望、目標の達成度、補助具の変更などに基づいてリハビリプランが更新される。しかし、看護師等が常に1人の患者に付き添うことはできないため、リハビリ目標の達成度は、患者自身からの報告によって確認されている。このため、実際に患者が運動などを行ったのか否かは不確実であり、経験が少ない医師では、患者の身体状態を正確に把握して効果的にリハビリプランを更新することが困難である。 By the way, rehabilitation plans are generally created by doctors based on their experiences, and after exercise and care are performed according to the rehabilitation plan, the patient's impressions and requests, the degree of achievement of goals, Rehabilitation plan is updated based on changes. However, since a nurse or the like cannot always accompany one patient, the degree of achievement of the rehabilitation goal is confirmed by a report from the patient himself. For this reason, it is uncertain whether or not the patient actually exercised, and it is difficult for doctors with little experience to accurately grasp the patient's physical condition and effectively update the rehabilitation plan. .
この点に関し、特許文献1には、歩数計の計測値に基づいてユーザの歩行距離などを算出し、ウェブサイト上で仮想的にウォーキングを行うウォーキング仮想旅システムについて記載されている。この技術によると、病院外に出られない患者であっても、病院内を歩くことによって仮想的に旅行している気分を味わうことができ、リハビリに対する意欲を向上させることができる。
しかし、上述した技術では、医師は、患者が1日に何歩くらい歩いたのかを確認することはできても、それが現在の患者の身体状態にとってどの程度の負担なのかを把握することはできない。また、歩行以外の運動や、「自分でトイレに行く」などといった自立作業については正確には把握することができず、結局は、患者の回復度に応じて効果的にリハビリプランを更新するためには、十分な経験が必要となってしまう。 However, with the technology described above, a doctor can determine how many steps a patient has walked in a day, but it does not know how much it is burdening the current patient's physical condition. Can not. In addition, it is not possible to accurately grasp independence work such as exercise other than walking and “going to the toilet by yourself”. In the end, the rehabilitation plan is effectively updated according to the patient's recovery level. Enough experience is required.
上記事情に鑑み、経験を必要とせずに、患者の回復に合わせてリハビリプランを更新することができるリハビリプラン更新システムを提供する。 In view of the above circumstances, a rehabilitation plan update system capable of updating a rehabilitation plan in accordance with the recovery of a patient without requiring experience is provided.
上記目的を達成するリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態は、
患者のリハビリプランを取得するプラン取得部と、
プラン取得部で取得されたリハビリプランから運動量を算出するリハビリ運動量算出部と、
患者によって携帯される携帯機器を用い該患者の動きを計測することで患者の運動量を算出する患者運動量算出部と、
リハビリ運動量算出部および患者運動量算出部のそれぞれで算出された各運動量を互いに比較し、その比較の結果に基づいてリハビリプランを更新するプラン更新部とを備えたことを特徴とする。The basic form of the rehabilitation plan renewal system that achieves the above objective is
A plan acquisition unit for acquiring a patient's rehabilitation plan;
A rehabilitation exercise amount calculation unit for calculating the amount of exercise from the rehabilitation plan acquired by the plan acquisition unit;
A patient exercise amount calculation unit for calculating a patient's exercise amount by measuring the movement of the patient using a portable device carried by the patient; and
And a plan update unit that compares the exercise amounts calculated by the rehabilitation exercise amount calculation unit and the patient exercise amount calculation unit with each other and updates the rehabilitation plan based on a result of the comparison.
このリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態によると、予め作成されたリハビリプランから目標の運動量が算出されるとともに、実際に患者の動きが計測されて患者の運動量が算出され、それら目標の運動量と患者の運動量との比較結果に基づいてリハビリプランが更新される。このため、目標の運動量に対して実際にどの程度動いたかという達成度を容易に確認することができ、経験を必要とせずに、患者の回復に応じて効果的にリハビリプランを更新することができる。 According to the basic form of this rehabilitation plan update system, the target momentum is calculated from the rehabilitation plan created in advance, the patient's movement is actually measured, and the patient's momentum is calculated. The rehabilitation plan is updated based on the comparison result with the amount of exercise. For this reason, it is possible to easily check the degree of achievement of the actual amount of movement with respect to the target momentum, and it is possible to effectively update the rehabilitation plan according to the patient's recovery without requiring experience. it can.
以上説明したように、リハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態によると、経験を必要とせずに、患者の回復に合わせてリハビリプランを更新することができる。 As described above, according to the basic form of the rehabilitation plan update system, the rehabilitation plan can be updated in accordance with the recovery of the patient without requiring experience.
以下、図面を参照して、上記説明した基本形態に対する具体的な実施形態を説明する。 Hereinafter, with reference to the drawings, a specific embodiment for the basic mode described above will be described.
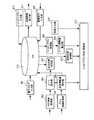
図1は、リハビリ実施システムの概略構成図である。 FIG. 1 is a schematic configuration diagram of a rehabilitation execution system.
図1に示すリハビリ実施システム1は、病院内に構築され、患者のリハビリを支援するとともに、患者の回復度に応じてリハビリプランを更新するためのものである。このリハビリ実施システム1は、患者が腕に装着する、各患者を識別する患者IDが記憶された電子タグ510と、患者が携帯する、歩数を計測するとともに振動強度を検出する歩数計520と、病院内の複数箇所に設置されたタグリーダ101,102,103と、各患者が使用するベットの脇に設置され、患者が自分の診療予定などを表示したり、娯楽に利用するためのベットサイド端末301,302,303と、看護師が携帯し、患者の歩数計520が接続されて歩数計520の計測結果を取得するPDA400と、タグリーダ101,102,103、ベットサイド端末301,302,303、およびPDA400と接続され、電子カルテなどが登録されたサーバ装置200とで構成されている。 A rehabilitation execution system 1 shown in FIG. 1 is constructed in a hospital, supports rehabilitation of a patient, and updates a rehabilitation plan according to the degree of recovery of the patient. The rehabilitation execution system 1 includes an
図2は、サーバ装置200の機能ブロック図である。 FIG. 2 is a functional block diagram of the server device 200.
サーバ装置200には、患者の身体状態などといった患者情報が患者を識別する患者IDと対応付けられた電子カルテが入力される電子カルテ入力部201と、自立作業や介護などの指示(以下では、この指示を看護指示と称する)が入力される看護指示入力部202と、患者のリハビリプランが入力されるリハビリプラン入力部214と、図1に示すタグリーダ101,102,103で読み取られたタグ情報が取得されるタグ情報取得部203と、図1に示すPDA400を介して、患者の歩数計520の計測結果が取得される歩数計情報取得部204と、タグ情報取得部203で取得されたタグ情報に基づいて、患者が移動したルートなどを算出するルート算出部205と、歩数計情報取得部204で取得された計測結果と、ルート算出部205で算出されたルートとに基づいて、患者の運動量を算出する患者運動量算出部206と、ルート算出部205で算出されたルートに基づいて、看護指示が実行されたか否かを判定する自立作業判定部207と、電子カルテ、リハビリプラン、看護指示などが登録されるデータベース(DB)213と、DB213に登録された電子カルテに基づいて、患者の身体状態を取得する身体状態取得部215と、DB213に登録されたリハビリプランを取得するリハビリプラン取得部208と、リハビリプランを実行したときの運動量を算出するリハビリ運動量算出部209と、ベットサイド端末301,302,303やPDA400などを使って、患者がリハビリプランに従ってリハビリを実行した感想などが入力される問診入力部210と、患者運動量算出部206で算出された運動量とリハビリ運動量算出部209で算出された運動量とを比較し、比較結果に基づいてリハビリプランを更新するリハビリプラン作成・更新部212と、患者運動量算出部206で算出された運動量に相当する移動経路を地図上に表示する地図情報表示部211とを備えている。 The server apparatus 200 includes an electronic medical
リハビリプラン取得部208は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態におけるプラン取得部の一例にあたり、リハビリ運動量算出部209は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態におけるリハビリ運動量算出部の一例に相当する。また、患者運動量算出部206は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態における患者運動量算出部の一例にあたり、リハビリプラン作成・更新部212は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態におけるプラン更新部の一例に相当する。 The rehabilitation
図3は、リハビリプランを更新する一連の処理の流れを示すフローチャート図である。 FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a flow of a series of processes for updating the rehabilitation plan.
リハビリプランを更新する元となる最初のリハビリプランは、患者の手術後の経過期間や、手術内容や、使用している治療器具などに基づいて、医師や看護師が手動で作成することがある。この場合、作成されたリハビリプランは、図2に示すリハビリプラン入力部214で入力され、DB213に登録される。ただし、以下では、最初のリハビリプランも自動で作成する場合について説明する。 The first rehabilitation plan from which the rehabilitation plan is updated may be created manually by a doctor or nurse based on the patient's post-surgery time course, the details of the surgery, the treatment instrument being used, etc. . In this case, the created rehabilitation plan is input by the rehabilitation
患者が診察を受けると、医師や看護師などによって、各患者の身体情報などが入力されて電子カルテが作成される。サーバ装置200のキーボードなどを使って患者の情報が入力されると、図2に示す電子カルテ入力部201において、各患者に患者IDが割り当てられ、患者IDが入力内容と対応付けられて電子カルテが作成される。作成された電子カルテは、DB213に保存される。 When a patient is examined, a doctor or a nurse inputs physical information of each patient and creates an electronic medical record. When patient information is input using the keyboard of the server device 200 or the like, a patient ID is assigned to each patient in the electronic medical
DB213に電子カルテが保存されると、身体状態取得部215において、電子カルテ中の患者の身体的な情報が取得され(図3のステップS11)、取得された情報に基づいて身体状態ランクが算出される(図3のステップS12)。 When the electronic medical record is stored in the
図4は、電子カルテの一例を示す図であり、図5は、リハビリ実施システム1において使用される各種テーブルの一例を示す図である。 FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of an electronic medical record, and FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an example of various tables used in the rehabilitation implementation system 1.
図4に示すように、電子カルテには、患者の身長、体重、BMI、血液型といった身体情報や、被爆歴、自立度、障害情報、使用している治療器具(歩行器、杖、ペースメーカー等)などが各患者の患者IDと対応付けて登録されている。 As shown in FIG. 4, the electronic medical record includes physical information such as the patient's height, weight, BMI, blood type, exposure history, independence, disability information, and treatment equipment used (walker, cane, pacemaker, etc.) ) And the like are registered in association with the patient ID of each patient.
図5のパート(A)には、電子カルテ中の一部の情報が抽出された身体情報テーブルが示されている。この身体情報テーブルには、図4に示す電子カルテから取得された、障害情報(嗅覚、触覚、聴覚、師や、色覚、明暗、全盲、運動機能障害など)、および使用している治療器具(杖、松葉杖、歩行器、義肢、コルセット、ペースメーカーなど)が登録されている。身体状態テーブルを構成する各項目には、予めリハビリの困難さを示す点数が用意されており(例えば、杖は「1」、松葉杖は「2」、歩行器は「3」など)、身体状態取得部215では、患者の電子カルテに基づいて身体状態テーブルが作成されるとともに、身体状態テーブルに基づいて各項目の点数の合計(身体状態ランク)が算出される。算出された身体状態ランクは、リハビリプラン作成・更新部212に伝えられる。 Part (A) of FIG. 5 shows a physical information table from which a part of information in the electronic medical record is extracted. In this physical information table, the failure information (olfaction, tactile sensation, hearing, teacher, color vision, light and darkness, blindness, motor dysfunction, etc.) obtained from the electronic medical chart shown in FIG. Canes, crutches, walker, artificial limbs, corsets, pacemakers, etc.) are registered. Each item constituting the physical condition table is prepared in advance with a score indicating difficulty in rehabilitation (for example, “1” for a cane, “2” for a crutch, “3” for a walker), etc. The
リハビリプラン作成・更新部212では、身体状態取得部215から取得された身体状態ランクに基づいて、最初のリハビリプランが作成される(図4のステップS13)。 In the rehabilitation plan creation /
図5のパート(B)には、リパビリプランのマスターテーブルの一例が示されている。 Part (B) of FIG. 5 shows an example of the master table of the rehab plan.
DB213には、リハビリの運動量を示すリハビリランクごとの、運動時間、歩数、距離、階段数、ルート候補といったリハビリプランが登録されたマスターテーブルが予め記憶されている。最初のリハビリプランを作成する際には、リハビリプラン作成・更新部212において、DB213に登録されているマスターテーブルのうち、リハビリランクが患者の身体状態ランクと一致するマスターテーブルが取得されて、そのマスターテーブル中のリハビリプランが患者のリハビリプランとして決定される。 The DB 213 stores in advance a master table in which rehabilitation plans such as exercise time, number of steps, distance, number of steps, and route candidates are registered for each rehabilitation rank indicating the amount of rehabilitation exercise. When creating the first rehabilitation plan, the rehabilitation plan creation /
図5のパート(C)には、患者のリハビリプランを示すリハビリプランテーブルの一例が示されている。このリハビリプランテーブルには、マスターテーブルから抽出されたリハビリプランが患者IDおよび患者名と対応付けて登録されており、リハビリプランの開始日および終了日の項目も用意されている。作成されたリハビリプランテーブルは、DB213に保存される。 Part (C) of FIG. 5 shows an example of a rehabilitation plan table showing a patient's rehabilitation plan. In this rehabilitation plan table, the rehabilitation plan extracted from the master table is registered in association with the patient ID and the patient name, and items for the start date and end date of the rehabilitation plan are also prepared. The created rehabilitation plan table is stored in the DB 213.
また、医師や看護師がサーバ装置200のキーボードなどを使って、患者の自立作業の目標を入力すると、図2に示す看護指示入力部202において看護指示が生成され(図3のステップS3)、看護指示が患者IDと対応付けてDB213に記憶される。 Further, when the doctor or nurse inputs the target of the patient's self-sustaining work using the keyboard of the server device 200 or the like, a nursing instruction is generated in the nursing
以上のようにして、リハビリプランおよび看護指示が決定されると、それらリハビリプランおよび看護指示が用紙上にプリントアウトされて患者に提供される。 As described above, when the rehabilitation plan and the nursing instruction are determined, the rehabilitation plan and the nursing instruction are printed out on a sheet and provided to the patient.
図6は、リハビリプランが印刷された用紙の一例を示す図であり、図7は、看護指示が印刷された用紙の一例を示す図である。 FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example of a sheet on which a rehabilitation plan is printed, and FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example of a sheet on which a nursing instruction is printed.
図6に示す例では、リハビリプランとして、運動時間の目標「30分」、目標歩行数「1000歩」、目標歩行距離「500m」、目標階段昇降数「50段」、モデル歩行ルート「南病棟1階→南病棟3階」が提示されている。また、図7に示す例では、看護指示として、「入浴」「トイレ」「歩行訓練」が提示されている。 In the example shown in FIG. 6, as a rehabilitation plan, an exercise time target “30 minutes”, a target walk number “1000 steps”, a target walk distance “500 m”, a target stair lift number “50 steps”, a model walk route “South Ward” 1st floor → South ward 3rd floor "is presented. In the example shown in FIG. 7, “bathing”, “toilet”, and “walking training” are presented as nursing instructions.
患者は、図6に示すリハビリプランに従ってリハビリを実行するとともに、図7に示す看護指示を実行する。 The patient executes the rehabilitation according to the rehabilitation plan shown in FIG. 6 and also executes the nursing instruction shown in FIG.
上述したように、患者は、腕時計型の電子タグ510と、歩数計520とを携帯している。患者が歩行すると、歩数計520によって歩数と振動強度が計測されるとともに、病院内に設置されたタグリーダ101,102,103によって、電子タグ510に記憶された患者IDが読み取られる。 As described above, the patient carries the wristwatch-type
1日のうちの決められた時間に、各タグリーダ101,102,103からサーバ装置200に、1日の間で読み取られた患者IDとその読取時刻とが送られる。タグリーダ101,102,103から送られてきたタグ情報は、図2に示すタグ情報取得部203で取得される。 At a predetermined time of the day, the patient ID read during one day and the reading time are sent from the
また、看護師は、1日のうちの決められた時間に、PDA400を各患者の計測計520に接続して計測結果をPDA400に取り込み、さらに、PDA400をサーバ装置200に接続する。その結果、患者IDと計測計520の計測結果がPDA400を介してサーバ装置200に伝えられる(図3のステップS15)。 Further, the nurse connects the
タグ情報取得部203で取得された患者IDと読取時刻は、ルート算出部205に伝えられ、PDA情報取得部204で取得された患者IDと計測結果は、患者運動量算出部206に伝えられる。 The patient ID and reading time acquired by the tag
ルート算出部205では、病院内に設置された各タグリーダ101,102,103で読み取られた患者IDと読取時刻とに基づいて、各患者の移動ルート、移動距離、運動時間、および階段の昇降数が算出される(図3のステップS16)。 In the
ここで、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態に対して、
上記携帯機器が、携帯機器を携帯している患者を特定する患者情報を無線で通信するタグであり、
上記患者運動量算出部が、
患者がリハビリを行う場所に設置されてタグと患者情報を無線で通信することで患者情報で特定される患者の移動経路を検知するタグリーダと、
タグリーダによって検知された移動経路上の移動に要した運動量を算出する算出部とを備えたものであるという応用形態は好ましい。Here, for the basic form of the rehabilitation plan update system described above,
The mobile device is a tag that wirelessly communicates patient information that identifies a patient carrying the mobile device,
The patient exercise amount calculation unit
A tag reader that is installed in a place where the patient performs rehabilitation and wirelessly communicates the tag and patient information to detect the movement path of the patient specified by the patient information;
An application form that includes a calculation unit that calculates a momentum required for movement on the movement path detected by the tag reader is preferable.
このリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態によると、患者が歩いた歩数や距離だけではなく、患者が移動した移動経路も把握することができるため、患者がリハビリを行ったことを確実に確認することができるとともに、患者がどこで何をしたのかを大まかに掴むことができる。電子タグ510は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態におけるタグの一例にあたり、タグリーダ101,102,103は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態におけるタグリーダの一例に相当する。また、ルート算出部205は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態における算出部の一例に相当する。 According to the application form of this rehabilitation plan update system, it is possible to grasp not only the number of steps and distance the patient walks but also the movement route that the patient has moved, so it is possible to reliably confirm that the patient has performed rehabilitation. Along with this, you can get a rough idea of where and what the patient did. The
本実施形態においては、まず、各タグリーダ101,102,103から伝えられた読取時刻が患者IDごとにまとめられ、それら読取時刻が早い順にタグリーダ101,102,103の経由順番が決定されることによって、各患者の移動ルートが検出される。続いて、移動距離、運動時間、および階段の昇降数が算出される。 In the present embodiment, first, the reading times transmitted from the
移動距離は、タグリーダ101,102,103の経由順番に従って、隣接するタグリーダ間の距離が加算されることによって算出される。また、最初に経由したタグリーダにおける読取時刻と、最後に経由したタグリーダにおける読取時刻との差分が運動時間として算出される。 The moving distance is calculated by adding the distance between adjacent tag readers in the order of passing through the
図8は、患者が階段を昇った場合に患者IDが読み取られるタグリーダを示す図であり、図9は、エレベータを使った場合に患者IDが読み取られるタグリーダを示す図である。 FIG. 8 is a diagram showing a tag reader whose patient ID is read when the patient climbs the stairs, and FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a tag reader whose patient ID is read when an elevator is used.
図8に示すように、患者が階段を使って移動する場合、患者が装着している電子タグ510に記憶された患者IDは、ルート上に設置されたタグリーダ601に加えて、階段の下段近くに設置されたタグリーダ601、階段の上段近くに設置されたタグリーダ603、および上のエレベータの手前に設置されたタグリーダ604で検出される。また、図9に示すように、患者がエレベータを使って移動する場合、患者が装着している電子タグ510に記憶された患者IDは、ルート上に設置されたタグリーダ601に加えて、階段の下段近くに設置されたタグリーダ601、および下のエレベータの手前に設置されたタグリーダ605に検出される。 As shown in FIG. 8, when the patient moves using the stairs, the patient ID stored in the
ルート算出部205では、患者の患者IDが、階段の下段近くに設置されたタグリーダ601、階段の上段近くに設置されたタグリーダ603、および上のエレベータの手前に設置されたタグリーダ604の順で検出された場合には、その患者が階段を昇ったと判断され、階段の段数が昇降数として決定される。また、患者の患者IDが、階段の下段近くに設置されたタグリーダ601、および下のエレベータの手前に設置されたタグリーダ605の順で検出された場合には、その患者がエレベータを使ったと判断され、階段の昇降数は「0」と決定される。 The
以上のように算出された移動ルートは、自立作業判定部207に伝えられ、移動距離、運動時間、および階段の昇降数は患者運動量算出部206に伝えられる。 The movement route calculated as described above is transmitted to the independent
患者運動量算出部206では、PDA情報取得部204から伝えられた歩数計520の計測結果と、ルート算出部205で算出された移動距離、運動時間、および階段の昇降数とに基づいて、患者の運動量が算出される(図3のステップS17)。 In the patient exercise
ここで、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態に対し、
上記携帯機器が、携帯機器を携帯している患者の歩数を計測する歩数計であり、
上記患者運動量算出部が、
歩数計から患者の歩数を取得し、その歩数に基づいて運動量を算出する算出部を備えたものであるという応用形態は好ましい。Here, for the basic form of the rehabilitation plan update system described above,
The portable device is a pedometer that measures the number of steps of a patient carrying the portable device,
The patient exercise amount calculation unit
An application form in which a calculation unit that acquires the number of steps of the patient from the pedometer and calculates the amount of exercise based on the number of steps is preferable.
このリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態によると、市販の歩数計を使って患者の運動量を容易に算出することができる。歩数計520は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態における歩数計の一例にあたり、患者運動量算出部206は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態における算出部の一例に相当する。 According to the application form of the rehabilitation plan update system, the patient's exercise amount can be easily calculated using a commercially available pedometer. The
患者運動量算出部206では、まず、取得された計測結果および算出結果がまとめられて、図5のパート(D)に示すような運動量テーブルが生成される。この運動量テーブルには、患者ID、ルート算出部205で算出された移動距離、ルート算出部205で算出された階段の昇降数、歩数計520で計測された歩数、歩数計520で計測された振動強度、およびルート算出部205で算出された運動時間が登録されている。運動量テーブル中の各項目には、予め運動量を示す点数がつけられており、患者運動量算出部206では、運動量テーブルに登録された各項目中の点数の合計に基づいて運動量が算出される。尚、健康状態が低い患者の場合、歩くときにすり足になっていることが多く、歩数計520で計測される振動強度は低いと考えられる。歩数計520で振動強度を検出することによって、歩数だけではなく、「楽に歩けたか」「歩くのがつらいか」といったことも把握することができる。 In the patient exercise
算出された運動量は、リハビリプラン作成・更新部212に伝えられるとともに、DB213に保存される。 The calculated amount of exercise is transmitted to the rehabilitation plan creation /
また、自立作業判定部207では、DB213から患者の看護指示が取得され、ルート算出部205から伝えられた移動ルートに基づいて、患者が看護指示を実行したか否かが判定される(図3のステップS19)。まず、看護指示に基づいて、その看護指示を実行する際に経由する場所(例えば、入浴であれば入浴場、歩行訓練であればリハビリ室など)が取得され、ルート算出部205で算出された移動ルート上に取得された経由場所が含まれている場合には、看護指示が実行されたと判定され、算出された移動ルート上に取得された経由場所が含まれていない場合には、看護指示が実行されなかったと判定される。判定結果は、リハビリプラン作成・更新部212に伝えられる。 In addition, in the independent
ここで、ベットサイド端末301,302,303では、患者の運動量に相当する移動経路を地図上に表示することができる。看護師や患者がベットサイド端末301,302,303の操作子を使って患者IDを入力すると、図2に示す地図情報表示部211では、DB213から入力された患者IDと対応する運動量が取得され、取得された運動量が距離に換算される。さらに、予め用意されている地図上に換算された距離に相当する移動経路が記されて、ベットサイド端末301,302,303に表示される(図3のステップS19)。 Here, the
上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態に対して、地図を表した地図情報を用いて地図を表示し、患者運動量算出部で算出された運動量に相当する移動経路を地図上に描く地図表示部を備えたという応用形態は好ましい。 In contrast to the basic form of the rehabilitation plan update system described above, a map display unit that displays a map using map information representing a map and draws a movement path corresponding to the exercise amount calculated by the patient exercise amount calculation unit on the map is provided. The application form of providing is preferable.
このリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態によると、リハビリによる運動量を見た目に確認することができるとともに、目標を立ててリハビリ意欲を高めることができる。 According to the application form of the rehabilitation plan update system, it is possible to visually check the amount of exercise by rehabilitation, and to increase the motivation for rehabilitation by setting a target.
図10は、ベットサイド端末301,302,303に表示された地図を示す図である。 FIG. 10 is a diagram showing a map displayed on the
図10のパート(A)には、建物内を示す平面地図上に移動経路が記された例が示されており、パート(B)には、建物内を示す立体地図上に移動経路が記された例が示されており、パート(C)には、街中の地図上に移動経路が記された例が示されている。このように、病院内でリハビリを行い、その運動量に相当する移動経路が地図上に表示されることによって、仮想的に病院外を散歩している気分になれるとともに、リハビリの努力を見た目に確認することができる。 Part (A) of FIG. 10 shows an example in which a movement route is recorded on a planar map showing the inside of the building, and part (B) shows a movement route on a three-dimensional map showing the inside of the building. Part (C) shows an example in which a travel route is marked on a city map. In this way, by performing rehabilitation in the hospital and displaying the movement route corresponding to the amount of exercise on the map, you can feel like you are virtually taking a walk outside the hospital and visually check the rehabilitation efforts can do.
また、看護師は、患者にリハビリの感想(楽だった、困難だった)を問診して、問診結果をPDA400やベットサイド端末301,302,303に入力する。入力された問診結果は、問診入力部210を介してリハビリプラン作成・更新部212に伝えられる(図3のステップS20)。 In addition, the nurse asks the patient about his rehabilitation feeling (easy and difficult) and inputs the inquiry result to the
以上のようにして、1日のリハビリが終了すると、リハビリプランの更新が行われる。まず、看護師などによって、図4に示す電子カルテ中の、使用する治療用具などが更新される(図3のステップS11)。電子カルテが更新されると、身体状態取得部215において、更新された新たな情報に基づいて身体状態ランクが算出され(図3のステップS12)、算出された身体状態ランクがリハビリプラン作成・更新部212に伝えられる。 As described above, when the daily rehabilitation is completed, the rehabilitation plan is updated. First, a treatment tool or the like used in the electronic medical chart shown in FIG. 4 is updated by a nurse or the like (step S11 in FIG. 3). When the electronic medical record is updated, the physical
また、リハビリプラン取得部208では、DB208から患者のリハビリプランが取得され、取得されたリハビリプランがリハビリ運動量算出部209に伝えられる。 The rehabilitation
リハビリ運動量算出部209では、図5のパート(C)に示すリハビリプランテーブルに従ってリハビリを実行したときの運動量が算出される。リハビリプランテーブル中の各項目には、図5のパート(D)に示す運動量テーブル中の各項目と同様に、予め運動量を示す点数がつけられており、リハビリ運動量算出部209では、運動量テーブルに登録された各項目中の点数の合計に基づいて運動量が算出される。算出された運動量は、リハビリプラン作成・更新部212に伝えられる。 The rehabilitation exercise amount calculation unit 209 calculates the exercise amount when rehabilitation is executed according to the rehabilitation plan table shown in part (C) of FIG. Each item in the rehabilitation plan table is given a score indicating the amount of exercise in advance, similarly to each item in the amount of exercise table shown in Part (D) of FIG. 5. The momentum is calculated based on the total score in each registered item. The calculated amount of exercise is transmitted to the rehabilitation plan creation /
リハビリプラン作成・更新部212では、身体状態取得部215から伝えられた更新された身体状態ランク、リハビリ運動量算出部209から伝えられたリハビリプランの運動量、患者運動量算出部206から伝えられた患者の1日分の運動量、自立作業判定部207から伝えられた看護指示の実行状態、および問診入力部210から伝えられたリハビリプランに対する患者の感想に基づいて、リハビリプランが更新される(図3のステップS13)。 In the rehabilitation plan creation /
ここで、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態に対して、
患者の身体的状態を知得する状態知得部を備え、
上記プラン更新部が、各運動量の比較結果とともに、状態知得部で知得された身体的状態も考慮してリハビリプランを更新するものであるという応用形態は好ましい。Here, for the basic form of the rehabilitation plan update system described above,
Provided with a state acquisition unit for acquiring the physical state of the patient,
An application mode in which the plan update unit updates the rehabilitation plan in consideration of the physical state acquired by the state acquisition unit together with the comparison result of each amount of exercise is preferable.
このリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態によると、患者の回復状態に応じて効果的なリハビリプランを提供することができる。身体状態取得部215は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態における状態知得部の一例に相当する。 According to the application form of this rehabilitation plan update system, an effective rehabilitation plan can be provided according to the recovery state of the patient. The body
また、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの基本形態に対して、
患者に対して求められている自立作業を知得する作業知得部と、
上記タグリーダによって検知された移動経路に基づいて、作業知得部で知得された自立作業が達成されたか否かを判定する判定部とを備え、
上記プラン更新部が、各運動量の比較結果とともに、判定部による判定結果も考慮してリハビリプランを更新するものであるという応用形態は好適である。In addition, for the basic form of the rehabilitation plan update system described above,
A work acquisition unit to learn the independence work required for the patient;
A determination unit that determines whether or not the self-supporting work acquired by the work acquisition unit has been achieved based on the movement path detected by the tag reader;
An application mode in which the plan update unit updates the rehabilitation plan in consideration of the determination result by the determination unit together with the comparison result of each amount of exercise is preferable.
リハビリの運動量に加えて、自立作業の達成結果も考慮されることによって、患者の回復度により適合したリハビリプランを提供することができる。看護指示入力部202は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態における作業知得部の一例にあたり、自立作業判定部207は、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムの応用形態における判定部の一例に相当する。 In addition to the amount of exercise for rehabilitation, the achievement result of the self-supporting work is also taken into consideration, so that a rehabilitation plan that is more suitable for the degree of recovery of the patient can be provided. The nursing
本実施形態においては、リハビリプラン作成・更新部212では、まず、患者の1日分の運動量と、身体状態ランクと、看護指示の実行状態と、患者の感想とに基づいて、実行されたリハビリに対するリハビリランクが算出される。例えば、運動量と身体状態ランクとが加算され、さらに、看護指示の実行状態(実行した場合にはプラス、実行しなかった場合にはマイナス)、および患者の感想(楽だった場合にはプラス、適度であった場合には「0」、困難であった場合にはマイナス)を点数化したものをさらに加算した合計がリハビリランクとして算出される。 In the present embodiment, the rehabilitation plan creation /
続いて、算出されたリハビリランクと、リハビリ運動量算出部209から伝えられたリハビリプランの運動量とが比較される。算出されたリハビリランクがリハビリプランの運動量よりも大きい場合、患者は目標の運動量を達成しているため、DB213に記憶されているリパビリプランのマスターテーブルのうち、リハビリランクが算出されたリハビリランクよりも大きいマスタテーブルが選択され、選択されたマスタテーブル中のリハビリプランが新たなリハビリプランとして更新される。また、算出されたリハビリランクがリハビリプランの運動量と同じである場合、リハビリプランが患者の回復状態に対して適度であると考えられ、現在のリハビリプランが維持される。さらに、算出されたリハビリランクがリハビリプランの運動量よりも小さい場合、リハビリプランが患者の回復状態に対して困難であると考えられるため、DB213に記憶されているリパビリプランのマスターテーブルのうち、リハビリランクが算出されたリハビリランクよりも小さいマスタテーブルが選択され、選択されたマスタテーブル中のリハビリプランが新たなリハビリプランとして更新される。 Subsequently, the calculated rehabilitation rank is compared with the rehabilitation plan exercise amount transmitted from the rehabilitation exercise amount calculation unit 209. If the calculated rehabilitation rank is larger than the rehabilitation plan exercise amount, the patient has achieved the target exercise amount, and therefore, among the rehab plan master tables stored in the
さらに、看護師などによって看護指示が更新され(図3のステップS14)、新たなリハビリプランおよび看護指示に従ってリハビリが実行される(図3のステップS15)。 Further, the nursing instruction is updated by a nurse or the like (step S14 in FIG. 3), and the rehabilitation is executed according to the new rehabilitation plan and the nursing instruction (step S15 in FIG. 3).
このように、本実施形態によると、患者の運動量や、看護指示を実行したか否かを確実に把握することができ、経験を必要とせずに、患者の回復に合わせてリハビリプランを更新することができる。 As described above, according to the present embodiment, it is possible to reliably grasp the amount of exercise of the patient and whether or not the nursing instruction has been executed, and update the rehabilitation plan according to the recovery of the patient without requiring experience. be able to.
ここで、上記では、リハビリプラン更新システムを病院内で適用する例について説明したが、このリハビリプラン更新システムは、例えば、老人ホームなどで適用してもよい。 Here, although the example which applies the rehabilitation plan update system in a hospital was demonstrated above, you may apply this rehabilitation plan update system in a nursing home etc., for example.
また、上記では、電子タグとタグリーダとを使って患者の移動経路を検出する例について説明したが、上述したリハビリプラン更新システムでは、例えば、携帯電話機の利用が許可された場所であれば、携帯電話機のGPS機能などを利用して患者の移動経路を検出してもよい。 In the above description, an example in which a moving path of a patient is detected using an electronic tag and a tag reader has been described. However, in the above-described rehabilitation plan update system, for example, if a mobile phone is permitted to be used, The movement path of the patient may be detected using the GPS function of the telephone.
1 リハビリ実施システム
101,102,103 タグリーダ
200 サーバ装置
301,302,303 ベットサイド端末
400 PDA
510 電子タグ
520 歩数計
201 電子カルテ入力部
202 看護指示入力部
203 タグ情報取得部
204 歩数計情報取得部
205 ルート算出部
206 患者運動量算出部
207 自立作業判定部
208 リハビリプラン取得部
209 リハビリ運動量算出部
210 問診入力部
211 地図情報表示部
212 リハビリプラン作成・更新部
213 DB
214 リハビリプラン入力部2141
510
214 Rehabilitation
Claims (7)
Translated fromJapanese前記プラン取得部で取得されたリハビリプランから運動量を算出するリハビリ運動量算出部と、
前記患者によって携帯される携帯機器を用いて該患者の動きを計測することで患者の運動量を算出する患者運動量算出部と、
前記リハビリ運動量算出部および前記患者運動量算出部のそれぞれで算出された各運動量を互いに比較し、その比較の結果に基づいて前記リハビリプランを更新するプラン更新部とを備えたことを特徴とするリハビリプラン更新システム。A plan acquisition unit for acquiring a patient's rehabilitation plan;
A rehabilitation exercise amount calculation unit for calculating the amount of exercise from the rehabilitation plan acquired by the plan acquisition unit;
A patient exercise amount calculation unit for calculating the patient's exercise amount by measuring the movement of the patient using a portable device carried by the patient; and
A rehabilitation exercise amount calculating unit and a patient exercise amount calculation unit that compare each other's exercise amounts with each other and update the rehabilitation plan based on a result of the comparison; Plan update system.
前記プラン更新部が、前記各運動量の比較結果とともに、前記状態知得部で知得された身体的状態も考慮して前記リハビリプランを更新するものであることを特徴とする請求項1記載のリハビリプラン更新システム。A state acquisition unit for acquiring the physical state of the patient;
The said plan update part updates the said rehabilitation plan in consideration of the physical state acquired by the said state acquisition part with the comparison result of each said momentum, The said rehabilitation plan is characterized by the above-mentioned. Rehabilitation plan update system.
前記患者運動量算出部が、
前記患者がリハビリを行う場所に設置されて前記タグと前記患者情報を無線で通信することで該患者情報で特定される患者の移動経路を検知するタグリーダと、
前記タグリーダによって検知された移動経路上の移動に要した運動量を算出する算出部とを備えたものであることを特徴とする請求項1または2記載のリハビリプラン更新システム。The portable device is a tag that wirelessly communicates patient information that identifies a patient carrying the portable device,
The patient exercise amount calculation unit,
A tag reader installed in a place where the patient performs rehabilitation and wirelessly communicating the tag and the patient information to detect a movement path of the patient specified by the patient information;
The rehabilitation plan update system according to claim 1, further comprising a calculation unit that calculates an amount of exercise required for movement on the movement path detected by the tag reader.
前記タグリーダによって検知された移動経路に基づいて、前記作業知得部で知得された自立作業が達成されたか否かを判定する判定部とを備え、
前記プラン更新部が、前記各運動量の比較結果とともに、前記判定部による判定結果も考慮して前記リハビリプランを更新するものであることを特徴とする請求項3項記載のリハビリプラン更新システム。A work acquisition unit for acquiring the self-supporting work required for the patient;
A determination unit that determines whether or not the self-supporting work acquired by the work acquisition unit has been achieved based on the movement path detected by the tag reader;
4. The rehabilitation plan update system according to claim 3, wherein the plan update unit updates the rehabilitation plan in consideration of a determination result by the determination unit together with a comparison result of the exercise amounts.
前記患者運動量算出部が、
前記歩数計から前記患者の歩数を取得し、その歩数に基づいて運動量を算出する算出部を備えたものであることを特徴とする請求項1から4のうちいずれか1項記載のリハビリプラン更新システム。The portable device is a pedometer for measuring the number of steps of a patient carrying the portable device;
The patient exercise amount calculation unit,
The rehabilitation plan update according to any one of claims 1 to 4, further comprising a calculation unit that acquires the number of steps of the patient from the pedometer and calculates an amount of exercise based on the number of steps. system.
前記患者運動量算出部が、
前記歩数計から前記患者の歩数と振動強度とを取得し、それら歩数と振動強度とに基づいて運動量を算出する算出部を備えたものであることを特徴とする請求項1から5のうちいずれか1項記載のリハビリプラン更新システム。The portable device is a pedometer that measures the number of steps of a patient carrying the portable device and the vibration intensity of the portable device,
The patient exercise amount calculation unit,
6. The apparatus according to claim 1, further comprising a calculation unit that acquires the number of steps and the vibration intensity of the patient from the pedometer and calculates an amount of exercise based on the number of steps and the vibration intensity. The rehabilitation plan update system according to claim 1.
。2. A map display unit which displays the map using map information representing a map and draws a movement path corresponding to the amount of exercise calculated by the patient exercise amount calculation unit on the map. The rehabilitation plan update system according to any one of 5 to 5.
.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008087053AJP5200623B2 (en) | 2008-03-28 | 2008-03-28 | Rehabilitation plan update system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008087053AJP5200623B2 (en) | 2008-03-28 | 2008-03-28 | Rehabilitation plan update system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009244916Atrue JP2009244916A (en) | 2009-10-22 |
| JP5200623B2 JP5200623B2 (en) | 2013-06-05 |
Family
ID=41306771
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008087053AExpired - Fee RelatedJP5200623B2 (en) | 2008-03-28 | 2008-03-28 | Rehabilitation plan update system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5200623B2 (en) |
Cited By (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011243203A (en)* | 2010-05-17 | 2011-12-01 | Iizuka Yoshinori | Rehabilitation plan creation system, rehabilitation plan creation method, and rehabilitation plan creation program |
| JP2015132957A (en)* | 2014-01-10 | 2015-07-23 | フクダ電子株式会社 | Rehabilitation support device and rehabilitation report |
| KR101763066B1 (en)* | 2016-04-14 | 2017-07-31 | 인하대학교 산학협력단 | Pedestrian Navigation Method and System with Reconfigurable Multi Modal Interface |
| JP2018032120A (en)* | 2016-08-23 | 2018-03-01 | 株式会社Msd | Treatment evaluation system and program |
| JP2020149321A (en)* | 2019-03-13 | 2020-09-17 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | Rehabilitation support device, rehabilitation support method, and rehabilitation support program |
| JP2020166835A (en)* | 2019-03-29 | 2020-10-08 | 株式会社Rehab for JAPAN | Rehabilitation plan creation support device, rehabilitation plan creation support system, rehabilitation plan creation support method, and rehabilitation plan creation support computer program |
| JP2020204569A (en)* | 2019-06-18 | 2020-12-24 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Up-down direction determining device and up-down direction determining system |
| JP2021016763A (en)* | 2019-07-17 | 2021-02-15 | 株式会社ニューロスペースNeurospace Inc. | Remote cognitive training system |
| JPWO2021075017A1 (en)* | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-22 | ||
| WO2021075018A1 (en)* | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-22 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing method |
| JP2022024766A (en)* | 2020-07-28 | 2022-02-09 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Training systems, training methods and programs |
| JP2022024767A (en)* | 2020-07-28 | 2022-02-09 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Training system, training method, and program |
| CN114420235A (en)* | 2022-01-26 | 2022-04-29 | 上海微创医疗机器人(集团)股份有限公司 | Postoperative recovery plan generation system, generation method and storage medium |
| CN115634439A (en)* | 2022-10-19 | 2023-01-24 | 武汉大学 | Shelter patient isolation fitness management system |
| JP7344622B1 (en)* | 2022-05-09 | 2023-09-14 | 株式会社Utヘルステック | A telemedicine support system to assist in the selection and implementation of rehabilitation programs for orthopedic patients. |
| WO2023219056A1 (en)* | 2022-05-09 | 2023-11-16 | 株式会社Utヘルステック | Telemedicine assisstance system for assisting selection and execution of rehabilitation program for orthopedic patients |
| JP2025048958A (en)* | 2023-09-21 | 2025-04-03 | ソフトバンクグループ株式会社 | system |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0852244A (en)* | 1994-08-12 | 1996-02-27 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Training device |
| JP2002291952A (en)* | 2001-03-29 | 2002-10-08 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Exercise support device, portable electronic device, exercise management system, and program |
| WO2004030540A1 (en)* | 2002-10-02 | 2004-04-15 | Suzuken Co., Ltd. | Health management system, measurement device, and data processing device |
| JP2004136105A (en)* | 1995-09-13 | 2004-05-13 | Seiko Epson Corp | Health condition management device |
| JP2005287708A (en)* | 2004-03-31 | 2005-10-20 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Exercise evaluation device |
| JP2006236128A (en)* | 2005-02-25 | 2006-09-07 | Matrix:Kk | Behavior detection system |
| JP2006302122A (en)* | 2005-04-22 | 2006-11-02 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Exercise support system, user terminal device thereof, and exercise support program |
- 2008
- 2008-03-28JPJP2008087053Apatent/JP5200623B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0852244A (en)* | 1994-08-12 | 1996-02-27 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | Training device |
| JP2004136105A (en)* | 1995-09-13 | 2004-05-13 | Seiko Epson Corp | Health condition management device |
| JP2002291952A (en)* | 2001-03-29 | 2002-10-08 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Exercise support device, portable electronic device, exercise management system, and program |
| WO2004030540A1 (en)* | 2002-10-02 | 2004-04-15 | Suzuken Co., Ltd. | Health management system, measurement device, and data processing device |
| JP2005287708A (en)* | 2004-03-31 | 2005-10-20 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Exercise evaluation device |
| JP2006236128A (en)* | 2005-02-25 | 2006-09-07 | Matrix:Kk | Behavior detection system |
| JP2006302122A (en)* | 2005-04-22 | 2006-11-02 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Exercise support system, user terminal device thereof, and exercise support program |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| JPN6012028470; 尾関 拓也: 'ITを用いた運動指導とは?' 肥満と糖尿病 Vol.6 No.3, 20070510, pp.493-496* |
Cited By (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011243203A (en)* | 2010-05-17 | 2011-12-01 | Iizuka Yoshinori | Rehabilitation plan creation system, rehabilitation plan creation method, and rehabilitation plan creation program |
| JP2015132957A (en)* | 2014-01-10 | 2015-07-23 | フクダ電子株式会社 | Rehabilitation support device and rehabilitation report |
| KR101763066B1 (en)* | 2016-04-14 | 2017-07-31 | 인하대학교 산학협력단 | Pedestrian Navigation Method and System with Reconfigurable Multi Modal Interface |
| JP2018032120A (en)* | 2016-08-23 | 2018-03-01 | 株式会社Msd | Treatment evaluation system and program |
| CN113518649A (en)* | 2019-03-13 | 2021-10-19 | 欧姆龙健康医疗事业株式会社 | Rehabilitation support device, rehabilitation support method, and rehabilitation support program |
| JP2020149321A (en)* | 2019-03-13 | 2020-09-17 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | Rehabilitation support device, rehabilitation support method, and rehabilitation support program |
| WO2020184119A1 (en)* | 2019-03-13 | 2020-09-17 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | Rehabilitation assistance device, rehabilitation assistance method, and rehabilitation assistance program |
| US11875888B2 (en) | 2019-03-13 | 2024-01-16 | Omron Healthcare Co., Ltd. | Rehabilitation assistance device, rehabilitation assistance method, and non-transient storage medium storing rehabilitation assistance program |
| JP7279428B2 (en) | 2019-03-13 | 2023-05-23 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | Rehabilitation support device, rehabilitation support method, and rehabilitation support program |
| JP2020166835A (en)* | 2019-03-29 | 2020-10-08 | 株式会社Rehab for JAPAN | Rehabilitation plan creation support device, rehabilitation plan creation support system, rehabilitation plan creation support method, and rehabilitation plan creation support computer program |
| JP7338257B2 (en) | 2019-06-18 | 2023-09-05 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Lifting direction determination device and lifting direction determination system |
| JP2020204569A (en)* | 2019-06-18 | 2020-12-24 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Up-down direction determining device and up-down direction determining system |
| JP2021016763A (en)* | 2019-07-17 | 2021-02-15 | 株式会社ニューロスペースNeurospace Inc. | Remote cognitive training system |
| JP7327498B2 (en) | 2019-10-17 | 2023-08-16 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing method |
| JPWO2021075018A1 (en)* | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-22 | ||
| WO2021075018A1 (en)* | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-22 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing method |
| US12419565B2 (en) | 2019-10-17 | 2025-09-23 | Nec Corporation | Information processing method |
| WO2021075017A1 (en)* | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-22 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing method |
| JP7367767B2 (en) | 2019-10-17 | 2023-10-24 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing method |
| JPWO2021075017A1 (en)* | 2019-10-17 | 2021-04-22 | ||
| JP2022024767A (en)* | 2020-07-28 | 2022-02-09 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Training system, training method, and program |
| JP7322831B2 (en) | 2020-07-28 | 2023-08-08 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | TRAINING SYSTEM, TRAINING PLAN GENERATION METHOD AND PROGRAM |
| JP2022024766A (en)* | 2020-07-28 | 2022-02-09 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Training systems, training methods and programs |
| CN114420235A (en)* | 2022-01-26 | 2022-04-29 | 上海微创医疗机器人(集团)股份有限公司 | Postoperative recovery plan generation system, generation method and storage medium |
| JP7344622B1 (en)* | 2022-05-09 | 2023-09-14 | 株式会社Utヘルステック | A telemedicine support system to assist in the selection and implementation of rehabilitation programs for orthopedic patients. |
| WO2023219056A1 (en)* | 2022-05-09 | 2023-11-16 | 株式会社Utヘルステック | Telemedicine assisstance system for assisting selection and execution of rehabilitation program for orthopedic patients |
| CN115634439A (en)* | 2022-10-19 | 2023-01-24 | 武汉大学 | Shelter patient isolation fitness management system |
| JP2025048958A (en)* | 2023-09-21 | 2025-04-03 | ソフトバンクグループ株式会社 | system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5200623B2 (en) | 2013-06-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5200623B2 (en) | Rehabilitation plan update system | |
| JP6351978B2 (en) | Motion information processing apparatus and program | |
| JP6289165B2 (en) | Rehabilitation support device | |
| US20170352288A1 (en) | Method and system for physical training and rehabilitation | |
| JP2001517115A (en) | Systems and methods for monitoring training programs | |
| JP6864460B2 (en) | Disease prediction device | |
| JP2002345994A (en) | Walking training equipment | |
| CN112231539B (en) | Search device, system, method and program | |
| JP2005352686A (en) | Rehabilitation management device | |
| JP2025003015A (en) | Rehabilitation support system, rehabilitation support method and program | |
| JP7584858B2 (en) | An exercise status understanding support device and an exercise status understanding support program. | |
| JP2006102462A (en) | Fall prevention guidance support device, fall prevention guidance support system, fall prevention guidance support program, fall prevention guidance support system program, storage medium storing fall prevention guidance support program, and storage medium storing fall prevention guidance support system program | |
| JP6995737B2 (en) | Support device | |
| CN112153100B (en) | Resident device presenting apparatus, resident device presenting system, resident device presenting method, resident device presenting program, and resident | |
| Roque et al. | Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies: 12th International Joint Conference, BIOSTEC 2019, Prague, Czech Republic, February 22–24, 2019, Revised Selected Papers | |
| JP2005192647A (en) | Cognitive dysfunction ameliorate system | |
| CN113996013A (en) | Training system, training method, and program | |
| CN113996014A (en) | Training systems, training methods and procedures | |
| JP7435363B2 (en) | Training system, training plan generation method and program | |
| CN113995627B (en) | Presentation system, presentation method, and program | |
| Abdullah | Design and Development of Biofeedback Stick Technology (BfT) to Improve the Quality of Life of Walking Stick Users | |
| Bieber et al. | Determination of the healing corridor of patients with knee arthroplasty by a motor-powered rollator | |
| JP2024064541A (en) | Dangerous area information generating device, dangerous area information generating system, and dangerous area information generating method | |
| WO2024261996A1 (en) | Information generation device, information provision system, information generation method, and recording medium | |
| WO2024261997A1 (en) | Information generating device, information providing system, information providing method, and recording medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20101216 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20120525 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20120605 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20120806 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20121016 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20121214 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20130115 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20130128 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160222 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |