JP2008250507A - Information processing apparatus, and method and program for starting the same - Google Patents
Information processing apparatus, and method and program for starting the sameDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008250507A JP2008250507AJP2007089158AJP2007089158AJP2008250507AJP 2008250507 AJP2008250507 AJP 2008250507AJP 2007089158 AJP2007089158 AJP 2007089158AJP 2007089158 AJP2007089158 AJP 2007089158AJP 2008250507 AJP2008250507 AJP 2008250507A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information
- slot
- storage means
- shared disk
- information processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription43
- 230000010365information processingEffects0.000titleclaimsdescription35
- 238000012790confirmationMethods0.000claimsdescription28
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000claimsdescription12
- 230000002093peripheral effectEffects0.000claimsdescription12
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsdescription8
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description13
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description7
- 238000004904shorteningMethods0.000description4
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 238000007796conventional methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000002699waste materialSubstances0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Stored Programmes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、情報処理装置、情報処理装置の起動方法、及び情報処理装置の起動プログラムに関し、特に、起動時間を短縮する技術に関する。 The present invention relates to an information processing apparatus, an information processing apparatus activation method, and an information processing apparatus activation program, and more particularly to a technique for shortening an activation time.
従来のコンピュータシステムの立ち上げでは、全てのI/Oスロットを対象に、I/Oスロットの若番から、順次I/Oカードの実装状況を確認し、さらに、I/Oカードに接続しているデバイス装置の確認を行っている。 In the start-up of a conventional computer system, for all I / O slots, check the mounting status of the I / O cards sequentially from the lowest numbered I / O slot, and then connect to the I / O card. Checking the device device.
ところが、I/Oカードがないスロットでは、応答がなく、I/Oタイムアウトになるまで待ち状態となるため、カードがないスロットが増えると、大幅に確認時間が増加してしまうという問題がある。 However, in a slot without an I / O card, there is no response and a waiting state is reached until an I / O time-out occurs. Therefore, there is a problem that the confirmation time significantly increases when the number of slots without a card increases.
また、大規模なシステムでは、I/Oスロットの数が多くなるため、I/Oスロットの増加で確認時間が増える上に、空きスロットも増加すると、さらに、大幅に確認時間が伸びてしまい、システムの立ち上げ時間の増加の要因になっている。しかしながら、一般に、大規模なシステムほど、システムの重要度が高く、立ち上げ時間を短くしたいと要求があるものの、これと相反しているのが現状である。 In a large-scale system, since the number of I / O slots increases, the confirmation time increases as the number of I / O slots increases, and if the number of empty slots also increases, the confirmation time further increases. This is a factor in increasing system startup time. However, in general, the larger the system, the higher the importance of the system, and there is a demand to shorten the start-up time, but there is a conflict with this.
また、システム立ち上げ時間の増加要因として、I/Oカードに接続しているデバイスの確認がある。すなわち、I/Oカードに接続しているディスク(論理ディスク)の数が多ければ多いほど、確認の回数が増加するため、確認時間が伸びてしまうという問題がある。 Further, as a factor for increasing the system start-up time, there is confirmation of a device connected to the I / O card. That is, as the number of disks (logical disks) connected to the I / O card increases, the number of times of confirmation increases, and there is a problem that the confirmation time increases.
また、複数のコンピュータシステムから共有されるディスク装置の場合、それぞれのコンピュータシステムの立ち上げ時において、共有ディスクの確認を行うようになっているため、共有ディスクが既に他のコンピュータで使用されている状態であっても、共有ディスクの確認を行っている。このため、共有ディスクでは、既に他のコンピュータシステムで確認済みのディスクの確認を、各コンピュータシステムの立ち上げ時に、重複して行うという無駄が発生している。 In the case of a disk device shared by a plurality of computer systems, since the shared disk is checked when each computer system is started up, the shared disk is already used by another computer. The shared disk is being checked even in the state. For this reason, in the shared disk, there is a waste that the confirmation of the disk that has already been confirmed by another computer system is duplicated when each computer system is started up.
コンピュータの起動時間を短縮する技術分野においては、例えば、特許文献1や特許文献2に記載の従来技術がある。特許文献1に記載の従来技術は、通信制御処理装置におけるプログラムの実行時間の高速化を図ったものである。また、特許文献2に記載の従来技術は、例えば段落0012によると、BIOSの起動処理を簡略化することで起動時間を高速化するものである。
しかしながら、上記従来技術は、上記の問題すべてに解決を与える技術ではない。 However, the above prior art is not a technique that provides a solution to all the above problems.
そこで本発明は、上記の実情に鑑みて、システム立ち上げ時に掛かる時間を短縮することを目的とする。 In view of the above circumstances, an object of the present invention is to reduce the time required for system startup.
上記目的を達成するための請求項1記載の発明は、装置の起動を制御する制御手段と、周辺機器を装置に接続するためのインターフェースであるI/Oスロットと、装置に関する各種設定を記憶する不揮発性の第1の記憶手段と、を備え、前記第1の記憶手段は、装置が高速起動するか否かの情報を示すブートモードフラグと、前記I/Oスロットの接続情報を示すI/Oスロット情報と、を記憶し、前記制御手段は、前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記I/Oスロットのうち周辺機器が接続されていないスロットのスキャンをバイパスし、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記I/Oスロット情報に基づいて起動する制御を行うことを特徴とする情報処理装置である。 In order to achieve the above object, the invention according to claim 1 stores control means for controlling activation of the apparatus, an I / O slot which is an interface for connecting peripheral devices to the apparatus, and various settings relating to the apparatus. Non-volatile first storage means, wherein the first storage means is a boot mode flag indicating information indicating whether or not the apparatus is to be started at high speed, and an I / O indicating connection information of the I / O slot. O slot information is stored, and when the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at high speed, the control means bypasses scanning of the I / O slot to which no peripheral device is connected. Then, the information processing apparatus is configured to perform control to be activated based on the I / O slot information stored in the first storage unit.
請求項2記載の発明は、請求項1記載の情報処理装置において、前記I/Oスロットは、他の情報処理装置もアクセス可能な共有ディスクを有する第2の記憶手段と、前記共有ディスクへのアクセスが可能になるよう接続し、前記第1の記憶手段は、前記共有ディスクへの接続情報を示す共有ディスク情報を記憶し、前記制御手段は、前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記第2の記憶手段が行う前記共有ディスクの確認動作をバイパスし、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記共有ディスク情報に基づいて起動する制御を行うことを特徴とする。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the information processing apparatus according to the first aspect, the I / O slot includes a second storage unit having a shared disk that can be accessed by other information processing apparatuses, and the shared disk. The first storage means stores shared disk information indicating connection information to the shared disk, and the control means indicates that the boot mode flag causes the apparatus to start at high speed. In this case, the second storage unit bypasses the operation of checking the shared disk and performs control to start up based on the shared disk information stored in the first storage unit. To do.
請求項3記載の発明は、請求項1又は2記載の情報処理装置において、前記制御手段は、前記ブートモードフラグが装置の通常起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記I/Oスロットの接続情報を収集し、収集した情報を前記第1の記憶手段に、前記I/Oスロット情報として記憶させることを特徴とする。 According to a third aspect of the present invention, in the information processing device according to the first or second aspect, when the control means indicates that the boot mode flag indicates normal startup of the device, the connection information of the I / O slot And the collected information is stored in the first storage means as the I / O slot information.
請求項4記載の発明は、請求項1から3のいずれか1項記載の情報処理装置において、前記第1の記憶手段は、前記I/Oスロットごとにデバイスの存在情報を保持するデバイス情報を記憶し、前記制御手段は、前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記デバイス情報に基づいて、存在しないデバイスのスキャンをバイパスして起動する制御を行うことを特徴とする。 According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, in the information processing apparatus according to any one of the first to third aspects, the first storage unit stores device information for holding device presence information for each I / O slot. Storing, and when the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at high speed, the control means performs control to bypass scanning of a non-existing device based on the device information. To do.
請求項5記載の発明は、請求項4記載の情報処理装置において、前記デバイス情報は、SCSI規格のデバイスの存在情報を保持し、SCSIターゲットとLUNデバイスの状態を保持することを特徴とする。 According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, in the information processing apparatus according to the fourth aspect, the device information holds presence information of a SCSI standard device and holds states of a SCSI target and a LUN device.
請求項6記載の発明は、装置の起動を制御する制御手段と、周辺機器を装置に接続するためのインターフェースであるI/Oスロットと、装置に関する各種設定を記憶する不揮発性の第1の記憶手段と、を備え、前記第1の記憶手段は、装置が高速起動するか否かの情報を示すブートモードフラグと、前記I/Oスロットの接続情報を示すI/Oスロット情報と、を記憶する情報処理装置の起動方法であって、前記制御手段による、前記ブートモードフラグを参照するステップと、前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を確認するステップと、前記I/Oスロットのうち周辺機器が接続されていないスロットのスキャンをバイパスするステップと、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記I/Oスロット情報に基づいて起動するステップと、を含むことを特徴とする情報処理装置の起動方法である。 According to a sixth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a control means for controlling activation of the apparatus, an I / O slot that is an interface for connecting peripheral devices to the apparatus, and a first nonvolatile memory for storing various settings relating to the apparatus. And the first storage means stores a boot mode flag indicating information indicating whether or not the apparatus is to be started at high speed, and I / O slot information indicating connection information of the I / O slot. An information processing apparatus start-up method comprising: a step of referring to the boot mode flag by the control means; a step of confirming that the boot mode flag starts the apparatus at a high speed; The step of bypassing the scan of the slot to which the peripheral device is not connected and the activation based on the I / O slot information stored in the first storage means A step, a starting method of an information processing apparatus, which comprises a.
請求項7記載の発明は、請求項6記載の情報処理装置の起動方法において、前記情報処理装置が、他の情報処理装置もアクセス可能な共有ディスクを有する第2の記憶手段と、前記共有ディスクへのアクセスが可能になるよう接続されていて、前記第1の記憶手段による、前記共有ディスクへの接続情報を示す共有ディスク情報を記憶するステップと、前記第2の記憶手段による前記共有ディスクの確認動作を、前記制御手段によりバイパスするステップと、前記制御手段による、前記共有ディスク情報に基づいて起動するステップと、を含むことを特徴とする。 According to a seventh aspect of the present invention, in the information processing apparatus activation method according to the sixth aspect, the information processing apparatus includes a second storage unit having a shared disk that can be accessed by other information processing apparatuses, and the shared disk. Storing shared disk information indicating connection information to the shared disk by the first storage means, and connecting the shared disk by the second storage means. The confirmation operation includes a step of bypassing by the control means and a step of starting based on the shared disk information by the control means.
請求項8記載の発明は、装置の起動を制御する制御手段と、周辺機器を装置に接続するためのインターフェースであるI/Oスロットと、装置に関する各種設定を記憶する不揮発性の第1の記憶手段と、を備える情報処理装置に、前記第1の記憶手段が、装置が高速起動するか否かの情報を示すブートモードフラグと、前記I/Oスロットの接続情報を示すI/Oスロット情報と、を記憶する処理と、前記制御手段が、前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記I/Oスロットのうち周辺機器が接続されていないスロットのスキャンをバイパスし、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記I/Oスロット情報に基づいて起動する制御を行う処理と、を実行させることを特徴とする情報処理装置の起動プログラムである。 According to an eighth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a control means for controlling the activation of the apparatus, an I / O slot which is an interface for connecting peripheral devices to the apparatus, and a first nonvolatile memory for storing various settings relating to the apparatus. An information processing apparatus comprising: a boot mode flag indicating whether the first storage means is activated at high speed; and I / O slot information indicating connection information of the I / O slot. When the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at high speed, the control unit bypasses scanning of the I / O slot to which no peripheral device is connected. And a process for performing a control to be activated based on the I / O slot information stored in the first storage means. A.
請求項9記載の発明は、請求項8記載の情報処理装置の起動プログラムにおいて、前記I/Oスロットが、他の情報処理装置もアクセス可能な共有ディスクを有する第2の記憶手段と、前記共有ディスクへのアクセスが可能になるよう接続している前記情報処理装置に、前記第1の記憶手段が、前記共有ディスクへの接続情報を示す共有ディスク情報を記憶する処理と、前記制御手段が、前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記第2の記憶手段が行う前記共有ディスクの確認動作をバイパスし、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記共有ディスク情報に基づいて起動する制御を行う処理と、を実行させることを特徴とする。 According to a ninth aspect of the present invention, in the information processing apparatus startup program according to the eighth aspect, the I / O slot has a second storage unit having a shared disk accessible to other information processing apparatuses, and the shared A process in which the first storage unit stores shared disk information indicating connection information to the shared disk in the information processing apparatus connected so as to enable access to a disk; The shared disk information stored in the first storage means, bypassing the shared disk confirmation operation performed by the second storage means when the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at high speed. And a process of performing control to be activated based on the above.
本発明によれば、システム立ち上げ時に掛かる時間を短縮することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to reduce the time required for system startup.
以下、本発明の実施の形態について図面を参照して説明する。まず、第1の実施の形態の構成及び動作について説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. First, the configuration and operation of the first embodiment will be described.
図1は、第1の実施の形態の構成を示すブロック図である。本実施形態の立ち上げ時間短縮方法が適用されるコンピュータシステムは、サーバ1,2とディスク装置30で構成される。サーバ1は、プロセッサ11、メインメモリ13、メインメモリ13を制御するメモリ制御部12、I/Oスロット15に実装されるI/Oカードの制御を行うI/O制御部14、ブート方法を設定,記憶するブードモードフラグ16、ブートモードフラグ16がセットされている時に、I/Oスロットの確認を行わないI/Oスロット情報を記憶するI/Oスロット情報17、I/Oデバイスの確認を行わない共有ディスクの情報を記憶する共有ディスク情報18を有して構成される。そして、ブートモードフラグ16,I/Oスロット情報17,共有ディスク情報18は、不揮発性メモリで構成されている。なお、サーバ2についてもサーバ1と同様である。 FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the first embodiment. A computer system to which the startup time shortening method of this embodiment is applied includes
また、図1のサーバ1,2では、I/Oスロット番号“00”,“01”にSCSI(Small Computer System Interface)カードが実装され、I/Oスロット番号“02”,“03”は空きスロットになっている。 Further, in the
各サーバのI/Oスロット“00”のカードからSCSIインターフェースにより、ディスク装置30のディスク制御部31のポートに接続され、各サーバのI/Oスロット“01”のカードからSCSIインターフェースにより、ディスク装置30のディスク制御部32のポートに接続されている。 Each server is connected to the port of the
また、ディスク装置30の論理ディスクである、LUN1からLUN4までは、共有ディスク33として設定され、サーバ1,2から論理ディスクが見えるようになっている。LUN5,6は、ローカルディスク34として設定され、LUN5はサーバ1から見え、LUN6はサーバ2から見えるようになっている。 In addition,
ディスク装置30のディスク制御部31,32の各ポートのSCSI IDは、全て“00”に設定され、サーバ1,2のI/Oスロット“00”,“01”のSCSI IDは、全て“07”に設定されている。 The SCSI IDs of the ports of the
次に、図1の構成図、図2、図3の動作フローチャートを参照して、第1の実施の形態の動作を説明する。 Next, the operation of the first embodiment will be described with reference to the configuration diagram of FIG. 1 and the operation flowcharts of FIGS.
図2は、1回目の立ち上げ等、ブートモードフラグ16がセットされていない時の動作(第1の実施の形態の第1の動作例)を示すフローチャートである。本動作例は、立ち上げのためのI/O確認とI/Oスロット情報17に保存する情報の収集を行うものである。 FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing an operation (first operation example of the first embodiment) when the
図3は、2回目以降の立ち上げ等、ブートモードフラグ16がセットされている時の動作フローチャートを示したもので、高速立ち上げの処理を説明するためのフローチャートである。 FIG. 3 shows an operation flowchart when the
まず、最初は、1回目の立ち上げなので、図1と図2の動作フローチャートを使用して、I/Oスロット情報の収集と保存を説明する。 First, since it is the first startup, the collection and storage of I / O slot information will be described using the operation flowcharts of FIGS. 1 and 2.
電源ON(ステップS201)の後、プロセッサ11がブートモードフラグ16を読み(ステップS202)、フラグ16がセットされていないことを確認すると(ステップS203)、I/Oスロット番号を“00”にセットする(ステップS204)。 After the power is turned on (step S201), the
次に、このI/Oスロット番号のI/Oスロットに実装されたカードの確認を行う(ステップS205)。図1のサーバ2では、I/Oスロット番号“00”は、カードが実装されているので、ステップS206で定められた時間内に応答があり、I/Oカードがあったと判断して、該当するI/Oスロット番号“00”のI/Oスロット情報17をリセットする(ステップS207)。 Next, the card mounted in the I / O slot of this I / O slot number is confirmed (step S205). In the
次に、I/Oカードの種類を判断し、SCSI系カードであるので(ステップS208)、次にSCSIに接続されるターゲットとデバイスの確認を行う。SCSI ID番号を“00”にセットし(ステップS210)、このSCSI ID番号のSCSIターゲットの確認を行い(ステップS211)、定められた時間内に応答があったかを判断する(ステップS212)。 Next, the type of the I / O card is determined, and since it is a SCSI card (step S208), the target and device connected to the SCSI are checked next. The SCSI ID number is set to “00” (step S210), the SCSI target of this SCSI ID number is confirmed (step S211), and it is determined whether there is a response within a predetermined time (step S212).
SCSI ID“00”のターゲットがあるので、定められた時間内に応答があり、SCSIターゲットと判断して(ステップS212)、次にSCSIデバイスの確認を行う。LUN番号に“00”をセットし(ステップS213)、このLUN番号のデバイスを確認する(ステップS214)。 Since there is a target with the SCSI ID “00”, there is a response within a predetermined time, it is determined as a SCSI target (step S212), and then the SCSI device is confirmed. “00” is set in the LUN number (step S213), and the device of this LUN number is confirmed (step S214).
ステップS214でデバイスを確認後、LUN番号が最大値になったかを判断し(ステップS215)、最大値になっていない場合は、LUN番号を+1して(ステップS216)、最大値になるまでデバイスの確認を繰り返し行い(ステップS215)、この結果、サーバ2は、LUN1,2,3,4,6があったことを認識する。 After checking the device in step S214, it is determined whether the LUN number has reached the maximum value (step S215). If the LUN number has not reached the maximum value, the LUN number is incremented by 1 (step S216), and the device is used until it reaches the maximum value. Are repeatedly confirmed (step S215), and as a result, the
LUN番号が最大値になると、SCSI ID番号が最大になったかを判断する(ステップS217)。SCSI IDの最大値は、通常“15”であるので、“00”は最大値でなく、ステップS219に進む。 When the LUN number reaches the maximum value, it is determined whether the SCSI ID number has reached the maximum (step S217). Since the maximum value of the SCSI ID is normally “15”, “00” is not the maximum value, and the process proceeds to step S219.
SCSI ID番号を+1して、SCSI ID“01”となり(ステップS219)、次のSCSI ID番号のターゲットを確認しに行くため、ステップS211へ進む。 The SCSI ID number is incremented by 1 to become SCSI ID “01” (step S219), and the process proceeds to step S211 to check the target of the next SCSI ID number.
SCSI ID番号“01”のSCSIターゲットスキャンを行い(ステップS211)、SCSI ID“01”がないので、定められた時間内に応答がなく(ステップS212)、ステップS217へ進み、再びSCSI IDが最大値であるかを判断していく(ステップS217)。 A SCSI target scan with the SCSI ID number “01” is performed (step S211), and since there is no SCSI ID “01”, there is no response within a predetermined time (step S212), the process proceeds to step S217, and the SCSI ID is maximized again. Whether it is a value or not is determined (step S217).
そして、SCSI IDが“15”になるまで繰り返し、SCSI IDのターゲットとデバイスの確認が行われていく。SCSI IDが“15”になったので、最大値と判断して(ステップS217)、ステップS218へ進む。I/Oスロット番号を+1して、I/Oスロット番号が“01”となる(ステップS218)。 Then, the SCSI ID target and device are checked repeatedly until the SCSI ID becomes “15”. Since the SCSI ID has become “15”, the maximum value is determined (step S217), and the process proceeds to step S218. The I / O slot number is incremented by 1, and the I / O slot number becomes “01” (step S218).
ステップS220では、I/Oスロット番号が最大値を超えたかを判断する。I/Oスロット番号“01”は、最大値ではないので、ステップS205へ進み、I/Oスロットの確認を行う(ステップS205)。I/Oスロット番号“01”は、カードが実装されているので、I/Oスロット番号“00”の時と同様の処理が行われていく。 In step S220, it is determined whether the I / O slot number exceeds the maximum value. Since the I / O slot number “01” is not the maximum value, the process proceeds to step S205 to check the I / O slot (step S205). Since the card is mounted on the I / O slot number “01”, the same processing as that for the I / O slot number “00” is performed.
次に、I/Oスロット番号が“02”になったとき、再びステップS205でI/Oスロットの確認を行う。I/Oスロット番号“02”は、カードが実装されていないので、定められた時間内に応答がなく(ステップS206)、I/Oカードがないと判断して、I/Oスロット番号“02”のI/Oスロット情報17をセットして(ステップS209)、ステップS218へ進んで、先ほどと同様に、ステップS218でI/Oスロット番号に+1して、I/Oスロット番号が“03”となり、I/Oスロット番号“02”の時と同様にステップS205へ進んで、I/Oスロットの確認を行っていく。 Next, when the I / O slot number becomes “02”, the I / O slot is confirmed again in step S205. Since the I / O slot number “02” is not mounted, no response is made within a predetermined time (step S206), it is determined that there is no I / O card, and the I / O slot number “02”. "I /
この結果、I/Oスロット情報17では、図6のように、I/Oスロット番号“02”,“03”のところがセットされる。最後に、ステップS218でI/Oスロット番号に+1して、I/Oスロット番号が“04”となると、ステップS220で、I/Oスロット番号が最大値を超えたことを判断して、立ち上げ時のI/O確認処理が終了する(ステップS221)。 As a result, in the I /
このように、立ち上げ時のI/O確認処理では、I/Oスロットの若番から実装されているカードの種類を判断し、SCSIカードである場合は、SCSI下に接続されているLUNデバイスの確認を順次行っていき、1回目のI/O確認処理では、I/Oスロットにカードが実装されていないとき、I/Oスロット情報17のビットがセットされていく。 In this way, in the I / O confirmation process at the time of start-up, the type of card mounted from the lowest number in the I / O slot is determined. If it is a SCSI card, the LUN device connected under the SCSI In the first I / O confirmation processing, when no card is mounted in the I / O slot, the bit of the I /
次に、2回目以降の立ち上げ等、ブートモードフラグ16がセットされている時の動作(第1の実施の形態の第2の動作例)を図3のフローチャートで説明する。 Next, the operation (second operation example of the first embodiment) when the
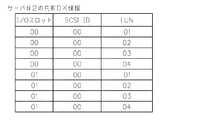
なお、以下では、予め、ブートモードフラグ16がセットされ、I/Oスロット情報17が1回目の立ち上げ処理で図6に例示される設定になり、さらに、共有ディスク情報18が図4と図5に例示される設定であるとする。 In the following description, the
電源ON(ステップS301)の後、プロセッサ11がブートモードフラグ16を読み(ステップS302)、フラグ16がセットされていることを確認すると(ステップS303)、I/Oスロット番号を“00”にセットする(ステップS304)。 After the power is turned on (step S301), the
次に、I/Oスロット情報17でI/Oスロット番号“00”のところを参照する(ステップS305)。図6を見ると、値は“0”になっており、空きスロットでないと判断する(ステップS306)。I/Oスロット番号“00”のI/Oスロットの確認を行う(ステップS307)。 Next, the I /
次に、I/Oカードの種類を判断し、SCSI系カードであるので(ステップS308)、次にSCSIに接続されるターゲットとデバイスの確認を行う。SCSI ID番号を“00”にセットし(ステップS309)、このSCSI ID番号のSCSIターゲットの確認を行い(ステップS310)、定められた時間内に応答があったかを判断する(ステップS311)。 Next, the type of the I / O card is determined, and since it is a SCSI card (step S308), the target and device connected to the SCSI are checked next. The SCSI ID number is set to “00” (step S309), the SCSI target of this SCSI ID number is confirmed (step S310), and it is determined whether there is a response within a predetermined time (step S311).
SCSI ID“00”のターゲットがあるので、定められた時間内に応答があり、SCSIターゲットと判断して(ステップS311)、次にSCSIデバイスの確認を行う。 Since there is a target with the SCSI ID “00”, there is a response within a predetermined time, and it is determined as a SCSI target (step S311), and then the SCSI device is confirmed.
LUN番号に“00”をセットし(ステップS312)、共有ディスク情報でLUN番号“00”のところを確認する(ステップS313)。図5を見ると、I/Oスロット番号“00”,SCSI ID“00”,LUN番号“00”がないので、共有ディスクの対象でないことを判断し(ステップS314)、LUN番号“00”のデバイス確認を行い、デバイスがないことを確認する(ステップS316)。 “00” is set in the LUN number (step S312), and the location of the LUN number “00” is confirmed in the shared disk information (step S313). Referring to FIG. 5, since there is no I / O slot number “00”, SCSI ID “00”, and LUN number “00”, it is determined that the disk is not a shared disk target (step S314). Device confirmation is performed to confirm that there is no device (step S316).
次に、LUN番号が最大値であるかを判断し(ステップS317)、LUN番号“00”が最大値でないので、LUN番号を+1して(ステップS318)、LUN番号が“01”となり、再びステップS313からデバイスの確認を行う。共有ディスク情報でLUN番号“01”のところを確認し(ステップS313)、図5を見ると、LUN番号“01”があるので、共有ディスクの対象であると判断し(ステップS314)、該当LUN番号のデバイスの確認をバイパスする(ステップS315)。 Next, it is determined whether the LUN number is the maximum value (step S317). Since the LUN number “00” is not the maximum value, the LUN number is incremented by 1 (step S318), and the LUN number becomes “01”. The device is confirmed from step S313. The location of the LUN number “01” is confirmed in the shared disk information (step S313). As shown in FIG. 5, since there is the LUN number “01”, it is determined that it is a target of the shared disk (step S314), and the corresponding LUN. The confirmation of the device with the number is bypassed (step S315).
ステップS317でLUN番号が最大値かを判断し、最大値になるまで、ステップS313からデバイスの確認を繰り返し行う。この結果、サーバ2では、LUN1,2,3,4のデバイス確認をバイパスし、LUN6のデバイス確認を行う。 In step S317, it is determined whether the LUN number is the maximum value, and device confirmation is repeated from step S313 until the LUN number reaches the maximum value. As a result, the
LUN番号が最大値になると、SCSI ID番号が最大になったことを判断し(ステップS317)、SCSI IDの最大値は、通常“15”であるので、“00”は最大値でなく、ステップS321に進む。 When the LUN number reaches the maximum value, it is determined that the SCSI ID number has become the maximum (step S317). Since the maximum value of the SCSI ID is normally “15”, “00” is not the maximum value, but the step The process proceeds to S321.
SCSI ID番号を+1して、SCSI ID“01”となり(ステップS321)、次のSCSI ID番号のターゲットを確認しに行くため、ステップS310へ進む。SCSI ID番号“01”のSCSIターゲットスキャンを行い(ステップS310)、SCSI ID“01”がないので、定められた時間内に応答がなく(ステップS311)、ステップS319へ進み、再びSCSI IDが最大値であるかを判断していく(ステップS319)。 The SCSI ID number is incremented by 1 to become SCSI ID “01” (step S321), and the process proceeds to step S310 to check the target of the next SCSI ID number. A SCSI target scan with the SCSI ID number “01” is performed (step S310), and since there is no SCSI ID “01”, there is no response within a predetermined time (step S311), the process proceeds to step S319, and the SCSI ID is maximized again. Whether the value is a value is determined (step S319).
そして、SCSI IDが“15”になるまで繰り返し、SCSI IDのターゲットとデバイスの確認が行われていく。SCSI IDが“15”になると最大値と判断して(ステップS319)、ステップS320へ進む。I/Oスロット番号を+1して、I/Oスロット番号が“01”となる(ステップS320)。 Then, the SCSI ID target and device are checked repeatedly until the SCSI ID becomes “15”. When the SCSI ID becomes “15”, the maximum value is determined (step S319), and the process proceeds to step S320. The I / O slot number is incremented by 1, and the I / O slot number becomes “01” (step S320).
ステップS322では、I/Oスロット番号が最大値を超えたかを判断する。I/Oスロット番号“01”は、最大値ではないので、ステップS305へ進み、再びI/Oスロット情報のI/Oスロット番号“01”のところを参照する(ステップS305)。I/Oスロット番号“01”は、カードが実装されているので、I/Oスロット番号“00”の時と同様の処理が行われていく。 In step S322, it is determined whether the I / O slot number exceeds the maximum value. Since the I / O slot number “01” is not the maximum value, the process proceeds to step S305, and the I / O slot number “01” in the I / O slot information is referred again (step S305). Since the card is mounted on the I / O slot number “01”, the same processing as that for the I / O slot number “00” is performed.
次にI/Oスロット番号が“02”になったとき、ステップS205でI/Oスロット番号“02”のところを参照する。I/Oスロット番号“02”は、ビットがセットされている空きスロット状態なので(ステップS306、Yes)、I/Oスロットの確認を行わないでステップS320へ進む。 Next, when the I / O slot number becomes “02”, the I / O slot number “02” is referred to in step S205. Since the I / O slot number “02” is an empty slot state in which a bit is set (step S306, Yes), the process proceeds to step S320 without checking the I / O slot.
先ほどと同様に、ステップS320でI/Oスロット番号に+1して、I/Oスロット番号が“03”となり、I/Oスロット番号“02”の時と同様にステップS305へ進んで、I/Oスロットの確認を行っていく。ステップS320でI/Oスロット番号に+1して、I/Oスロット番号が“04”となると、ステップS322で、I/Oスロット番号が最大値を超えたことを判断して、立ち上げ時のI/O確認処理が終了する(ステップS323)。 As before, the I / O slot number is incremented by 1 in step S320, the I / O slot number becomes “03”, and the process proceeds to step S305 as in the case of the I / O slot number “02”. Check the O slot. When the I / O slot number is incremented by one in step S320 and the I / O slot number becomes "04", it is determined in step S322 that the I / O slot number has exceeded the maximum value, The I / O confirmation process ends (step S323).
このように、2回目の立ち上げ時のI/O確認処理では、1回目の立ち上げで、空きスロットとなったI/Oスロットの確認を行わない。さらに、他のサーバと共有されている論理ディスクの確認を行わないように動作していく。 As described above, in the I / O confirmation processing at the second startup, the I / O slot that has become an empty slot at the first startup is not checked. Further, the operation is performed so as not to check the logical disk shared with other servers.
次に、上記実施形態の作用効果について説明する。 Next, the effect of the said embodiment is demonstrated.
コンピュータシステムにおいて、1回目の立ち上げで、I/Oスロットの各スロットでI/Oカードが有るか無いかの確認を行い、この確認情報と各サーバで共有される論理ディスクの情報を保存しておく。そして、2回目以降の立ち上げでは、保存情報を参照して、I/Oカードがないスロットの確認をバイパスし、また、他サーバで使用している共有される論理ディスクの確認をバイパスするようにした。 In the computer system, at the first start-up, it is confirmed whether or not an I / O card is present in each slot of the I / O slot, and this confirmation information and information on the logical disk shared by each server are stored. Keep it. In the second and subsequent startups, the confirmation of the slot without the I / O card is bypassed with reference to the stored information, and the confirmation of the shared logical disk used by another server is bypassed. I made it.
このため、従来、立ち上げ時に時間が掛かっていた未実装I/Oスロットの確認を行わず、加えて、他サーバで確認できない、I/Oカードからディスク装置までのインターフェースの確認を行いつつ、共有される論理ディスクの確認を行わないので、システムの立ち上げ時間を短縮することができる。 For this reason, while confirming the interface from the I / O card to the disk device that cannot be confirmed by other servers, in addition to confirming the unmounted I / O slot, which conventionally took time at startup, Since the shared logical disk is not checked, the system startup time can be shortened.
大規模なシステムになればなるほど、I/Oスロットの数量,共有ディスクの数量も多くなるため、さらに立ち上げ時間の短縮の効果が高くなる。 The larger the system, the greater the number of I / O slots and the number of shared disks, which further increases the effect of shortening the startup time.
また、上記実施形態を使用した、現用/待機のコールドスタンバイのシステムでは、待機サーバの立ち上げ時間が短くなるので、待機への切り替え時間が短くできるという効果があり、システム全体の稼動性をより高めることができる。 In addition, in the active / standby cold standby system using the above embodiment, the startup time of the standby server is shortened, so that the time for switching to standby can be shortened, and the operability of the entire system is further improved. Can be increased.
次に、図7、図8、図9を参照して、本発明の第2の実施の形態の構成及び動作について説明する。 Next, the configuration and operation of the second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. 7, FIG. 8, and FIG.
図7は、第2の実施の形態の構成例を示すブロック図である。図1と対応する部分については同じ符号を付して煩雑化を避けるため適宜説明を省略するが、図7には、図1と比較して、I/Oスロット毎にSCSIターゲットとLUNデバイスの状態を記憶するデバイス情報19が新たに追加されている。 FIG. 7 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of the second embodiment. The portions corresponding to those in FIG. 1 are denoted by the same reference numerals and description thereof will be omitted as appropriate to avoid complication, but in FIG. 7, the SCSI target and LUN device for each I / O slot are compared with those in FIG.
1回目の立ち上げで、SCSIターゲットとLUNデバイスが有るか無いかの確認を行い、この確認情報を保存しておき、2回目以降の立ち上げで、この保存情報を参照して、SCSIターゲットやLUNデバイスがないところの確認をバイパスするようにする。 Check if there is a SCSI target and LUN device at the first start-up, save this confirmation information, and refer to this saved information at the second and subsequent start-ups Bypass confirmation where there is no LUN device.
図8は、1回目の立ち上げ等、ブートモードフラグ16がセットされていない時の動作(第2の実施の形態の第1の動作例)を示すフローチャートである。また、図9は、2回目以降の立ち上げ等、ブートモードフラグ16がセットされている時の動作(第2の実施の形態の第2の動作例)を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing an operation when the
まず、1回目の立ち上げについて、図8を参照して説明する。なお、以下の説明においては、図2と異なっている部分(ステップS812〜819)を中心に説明する。 First, the first startup will be described with reference to FIG. In the following description, the description will focus on portions that differ from FIG. 2 (steps S812 to 819).
ステップS812では、SCSIターゲットの確認を行っている際、規定時間内に応答があった場合、すなわち、ターゲットがあるときには、デバイス情報19に該当するSCSIターゲットの情報をリセットする(ステップS813)。 In step S812, when the SCSI target is being confirmed, if there is a response within the specified time, that is, if there is a target, the SCSI target information corresponding to the
一方、規定時間内に応答がない場合、すなわち、ターゲットがないとき、デバイス情報19で該当するSCSIターゲットの情報をセットし(ステップS814)、ステップS822へ進んで、次のSCSIターゲットの確認を行う。ステップS813の後、ステップS815に進み、LUN Noに“00”をセットし、LUNデバイスの確認を行う(ステップS816)。 On the other hand, when there is no response within the specified time, that is, when there is no target, information on the corresponding SCSI target is set in the device information 19 (step S814), and the process proceeds to step S822 to confirm the next SCSI target. . After step S813, the process proceeds to step S815, where “00” is set in LUN No, and the LUN device is confirmed (step S816).
ステップS817で、規定時間内に応答があった場合、すなわちデバイスがあるときには、デバイス情報19に該当するLUNデバイスの情報をリセットし(ステップS818)、ステップS819へ進み、LUN Noが最大値になるまで、LUNデバイスの確認を行っていく。 If there is a response within the specified time in step S817, that is, if there is a device, the information on the LUN device corresponding to the
ステップS817で、規定時間内に応答がない場合、すなわちデバイスがないときには、デバイス情報19に該当するLUNデバイスの情報をセットし(ステップS820)、ステップS819へ進み、LUN Noが最大値になるまで、LUNデバイスの確認を行っていく。 If there is no response within the specified time in step S817, that is, if there is no device, information on the LUN device corresponding to the
以上の動作により、SCSI IDの若番から、SCSIターゲットとLUNデバイスの確認を行い、ターゲットとデバイスがない場合には、デバイス情報19の該当情報をセットしていく。 With the above operation, the SCSI target and LUN device are confirmed from the lowest SCSI ID, and if there is no target and device, the corresponding information of the
次に、2回目の立ち上げについて、図9を参照して説明する。なお、以下の説明においては、図3と異なっている部分(ステップS910〜915)を中心に説明する。 Next, the second startup will be described with reference to FIG. In the following description, the description will focus on the parts (steps S910 to 915) that are different from FIG.
ステップS910では、デバイス情報19を参照し、該当するSCSI IDターゲットの情報がセットされているか?(ターゲットはないか?)を確認する。情報がリセットされている時、ターゲットありと判断し(ステップS911、Yes)、SCSIターゲットの確認を行う(ステップS912)。一方、情報がセットされている時、ターゲットなしと判断し(ステップS911、No)、ステップS922へ進み、次のSCSI IDのターゲットの確認を行っていく(ステップS922,925)。 In step S910, the
ステップS912の後、LUN Noを“00”にセットし(ステップS913)、デバイス情報19を参照し(ステップS914)、該当するLUNデバイスの情報がセットされているか?(リセットされているか?)を確認する(ステップS915)。 After step S912, LUN No is set to “00” (step S913), the
情報がリセットされている時、デバイスありと判断し、共有ディスク情報の参照して(ステップS916)、共有ディスクの場合、LUNデバイスの確認をバイパスし(ステップS918)、共有ディスクでない場合、LUNデバイスの確認を行っていく(ステップS921)。 When the information is reset, it is determined that there is a device, and the shared disk information is referred to (step S916). If it is a shared disk, the LUN device confirmation is bypassed (step S918). (Step S921).
ステップS915で、情報がセットされている時、デバイスなしと判断し、ステップS919へ進み、LUN Noが最大値になるまで、ステップS914〜919を繰り返していく。 When information is set in step S915, it is determined that there is no device, and the process proceeds to step S919, and steps S914 to 919 are repeated until the LUN No reaches the maximum value.
以上の動作により、1回目の立ち上げで、存在していないSCSIターゲットとLUNデバイスの確認を行わないようにしたので、さらに、立ち上げ時のI/O確認に掛かる時間を短縮することができる。 With the above operation, since the SCSI target and LUN device that do not exist are not checked at the first startup, the time required for I / O check at startup can be further reduced. .
次に、本発明を起動プログラムとして実施する態様について説明する。上記の実施の形態の動作を情報処理装置(サーバ、ワークステーション、パーソナルコンピュータ等を含む)に実行させるプログラムは、本発明の一実施形態に該当する。このプログラムは、アプリケーション、オペレーティングシステム、BIOSプログラム(Basic Input/Output System:基本入出力システム。)のいずれであっても、また、いずれかの一部であってもよい。上記実施形態の各手順を実行させるプログラムを構成することで、コンピュータシステムの可搬性や拡張性が高まる。 Next, an embodiment in which the present invention is implemented as a startup program will be described. A program that causes an information processing apparatus (including a server, a workstation, a personal computer, and the like) to execute the operation of the above embodiment corresponds to an embodiment of the present invention. This program may be any of an application, an operating system, and a BIOS program (Basic Input / Output System: basic input / output system), or may be a part of any of them. By configuring a program that executes each procedure of the above-described embodiment, the portability and expandability of the computer system are enhanced.
1,2 サーバ
11,21 プロセッサ
12,22 メモリ制御部
13,23 メインメモリ
14,24 I/O制御部
15,25 I/Oスロット
16,26 ブートモードフラグ
17,27 I/Oスロット情報
18,28 共有DK情報
19,29 デバイス情報
30 ディスク装置
31,32 DK制御部
33 共有ディスク
34 ローカルディスク
35 SCSIインターフェース1, 2
Claims (9)
Translated fromJapanese周辺機器を装置に接続するためのインターフェースであるI/Oスロットと、
装置に関する各種設定を記憶する不揮発性の第1の記憶手段と、を備え、
前記第1の記憶手段は、
装置が高速起動するか否かの情報を示すブートモードフラグと、
前記I/Oスロットの接続情報を示すI/Oスロット情報と、を記憶し、
前記制御手段は、
前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記I/Oスロットのうち周辺機器が接続されていないスロットのスキャンをバイパスし、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記I/Oスロット情報に基づいて起動する制御を行うことを特徴とする情報処理装置。Control means for controlling the activation of the device;
An I / O slot which is an interface for connecting peripheral devices to the device;
Nonvolatile first storage means for storing various settings relating to the device,
The first storage means is
A boot mode flag indicating information on whether or not the device starts at high speed; and
Storing I / O slot information indicating connection information of the I / O slot;
The control means includes
When the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at high speed, the scan of the I / O slot to which no peripheral device is connected is bypassed and stored in the first storage means An information processing apparatus that performs start-up control based on I / O slot information.
他の情報処理装置もアクセス可能な共有ディスクを有する第2の記憶手段と、前記共有ディスクへのアクセスが可能になるよう接続し、
前記第1の記憶手段は、
前記共有ディスクへの接続情報を示す共有ディスク情報を記憶し、
前記制御手段は、
前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記第2の記憶手段が行う前記共有ディスクの確認動作をバイパスし、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記共有ディスク情報に基づいて起動する制御を行うことを特徴とする請求項1記載の情報処理装置。The I / O slot is
A second storage means having a shared disk that can be accessed by other information processing apparatuses, and connected so as to enable access to the shared disk;
The first storage means is
Storing shared disk information indicating connection information to the shared disk;
The control means includes
The shared disk information stored in the first storage means, bypassing the shared disk confirmation operation performed by the second storage means when the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at high speed. The information processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the control is performed based on the control.
前記ブートモードフラグが装置の通常起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記I/Oスロットの接続情報を収集し、収集した情報を前記第1の記憶手段に、前記I/Oスロット情報として記憶させることを特徴とする請求項1又は2記載の情報処理装置。The control means includes
When the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is normally started, the I / O slot connection information is collected, and the collected information is stored in the first storage means as the I / O slot information. The information processing apparatus according to claim 1 or 2.
前記I/Oスロットごとにデバイスの存在情報を保持するデバイス情報を記憶し、
前記制御手段は、
前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記デバイス情報に基づいて、存在しないデバイスのスキャンをバイパスして起動する制御を行うことを特徴とする請求項1から3のいずれか1項記載の情報処理装置。The first storage means is
Storing device information holding device presence information for each I / O slot;
The control means includes
4. The control according to claim 1, wherein when the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at a high speed, a control for starting by bypassing a scan for a non-existing device is performed based on the device information. The information processing apparatus according to claim 1.
周辺機器を装置に接続するためのインターフェースであるI/Oスロットと、
装置に関する各種設定を記憶する不揮発性の第1の記憶手段と、を備え、
前記第1の記憶手段は、
装置が高速起動するか否かの情報を示すブートモードフラグと、
前記I/Oスロットの接続情報を示すI/Oスロット情報と、を記憶する情報処理装置の起動方法であって、
前記制御手段による、
前記ブートモードフラグを参照するステップと、
前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を確認するステップと、
前記I/Oスロットのうち周辺機器が接続されていないスロットのスキャンをバイパスするステップと、
前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記I/Oスロット情報に基づいて起動するステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする情報処理装置の起動方法。Control means for controlling the activation of the device;
An I / O slot which is an interface for connecting peripheral devices to the device;
Nonvolatile first storage means for storing various settings relating to the device,
The first storage means is
A boot mode flag indicating information on whether or not the device starts at high speed; and
An information processing apparatus activation method for storing I / O slot information indicating connection information of the I / O slot,
By the control means,
Referring to the boot mode flag;
Confirming that the boot mode flag is for fast startup of the device;
Bypassing a scan of the I / O slot to which a peripheral device is not connected;
Starting based on the I / O slot information stored in the first storage means;
A method for starting an information processing apparatus, comprising:
他の情報処理装置もアクセス可能な共有ディスクを有する第2の記憶手段と、前記共有ディスクへのアクセスが可能になるよう接続されていて、
前記第1の記憶手段による、前記共有ディスクへの接続情報を示す共有ディスク情報を記憶するステップと、
前記第2の記憶手段による前記共有ディスクの確認動作を、前記制御手段によりバイパスするステップと、
前記制御手段による、前記共有ディスク情報に基づいて起動するステップと、
を含むことを特徴とする請求項6記載の情報処理装置の起動方法。The information processing apparatus is
A second storage means having a shared disk accessible to other information processing devices, and connected to the shared disk so as to be accessible;
Storing shared disk information indicating connection information to the shared disk by the first storage means;
Bypassing the checking operation of the shared disk by the second storage means by the control means;
Starting based on the shared disk information by the control means;
The method for starting an information processing apparatus according to claim 6, further comprising:
周辺機器を装置に接続するためのインターフェースであるI/Oスロットと、
装置に関する各種設定を記憶する不揮発性の第1の記憶手段と、を備える情報処理装置に、
前記第1の記憶手段が、
装置が高速起動するか否かの情報を示すブートモードフラグと、
前記I/Oスロットの接続情報を示すI/Oスロット情報と、を記憶する処理と、
前記制御手段が、
前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記I/Oスロットのうち周辺機器が接続されていないスロットのスキャンをバイパスし、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記I/Oスロット情報に基づいて起動する制御を行う処理と、
を実行させることを特徴とする情報処理装置の起動プログラム。Control means for controlling the activation of the device;
An I / O slot which is an interface for connecting peripheral devices to the device;
A non-volatile first storage means for storing various settings related to the apparatus;
The first storage means
A boot mode flag indicating information on whether or not the device starts up at high speed; and
Processing for storing I / O slot information indicating connection information of the I / O slot;
The control means is
When the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at high speed, the scan of the I / O slot to which no peripheral device is connected is bypassed and stored in the first storage means A process for performing control based on the I / O slot information;
An information processing apparatus start program for executing
他の情報処理装置もアクセス可能な共有ディスクを有する第2の記憶手段と、前記共有ディスクへのアクセスが可能になるよう接続している前記情報処理装置に、
前記第1の記憶手段が、
前記共有ディスクへの接続情報を示す共有ディスク情報を記憶する処理と、
前記制御手段が、
前記ブートモードフラグが装置の高速起動をする旨を示す場合に、前記第2の記憶手段が行う前記共有ディスクの確認動作をバイパスし、前記第1の記憶手段に記憶されている前記共有ディスク情報に基づいて起動する制御を行う処理と、
を実行させることを特徴とする請求項8記載の情報処理装置の起動プログラム。The I / O slot is
A second storage means having a shared disk accessible to other information processing apparatuses, and the information processing apparatus connected so as to enable access to the shared disk;
The first storage means
Storing shared disk information indicating connection information to the shared disk;
The control means is
The shared disk information stored in the first storage means, bypassing the shared disk confirmation operation performed by the second storage means when the boot mode flag indicates that the apparatus is to be started at high speed. A process of performing control based on
The information processing apparatus startup program according to claim 8, wherein:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007089158AJP5029095B2 (en) | 2007-03-29 | 2007-03-29 | Information processing apparatus, activation method thereof, and activation program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007089158AJP5029095B2 (en) | 2007-03-29 | 2007-03-29 | Information processing apparatus, activation method thereof, and activation program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008250507Atrue JP2008250507A (en) | 2008-10-16 |
| JP5029095B2 JP5029095B2 (en) | 2012-09-19 |
Family
ID=39975409
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007089158AExpired - Fee RelatedJP5029095B2 (en) | 2007-03-29 | 2007-03-29 | Information processing apparatus, activation method thereof, and activation program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5029095B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9974563B2 (en) | 2014-05-28 | 2018-05-22 | Cook Medical Technologies Llc | Medical devices having a releasable member and methods of using the same |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04273356A (en)* | 1991-02-28 | 1992-09-29 | Nec Corp | Input/output controller |
| JPH04370844A (en)* | 1991-06-19 | 1992-12-24 | Fujitsu Ltd | Multi-board system and its slave board recognition method |
| JPH09282262A (en)* | 1996-04-09 | 1997-10-31 | Ekushingu:Kk | Interface device |
| JP2001147888A (en)* | 1999-11-22 | 2001-05-29 | Nec Corp | Method for recognizing connecting device |
| JP2003084981A (en)* | 2001-09-11 | 2003-03-20 | Seiko Epson Corp | Starting method of information processing device |
| JP2005234872A (en)* | 2004-02-19 | 2005-09-02 | Seiko Epson Corp | Computer, computer startup method, BIOS program, and information storage medium |
| JP2006236058A (en)* | 2005-02-25 | 2006-09-07 | Toshiba Corp | Information processing apparatus and system activation method |
- 2007
- 2007-03-29JPJP2007089158Apatent/JP5029095B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04273356A (en)* | 1991-02-28 | 1992-09-29 | Nec Corp | Input/output controller |
| JPH04370844A (en)* | 1991-06-19 | 1992-12-24 | Fujitsu Ltd | Multi-board system and its slave board recognition method |
| JPH09282262A (en)* | 1996-04-09 | 1997-10-31 | Ekushingu:Kk | Interface device |
| JP2001147888A (en)* | 1999-11-22 | 2001-05-29 | Nec Corp | Method for recognizing connecting device |
| JP2003084981A (en)* | 2001-09-11 | 2003-03-20 | Seiko Epson Corp | Starting method of information processing device |
| JP2005234872A (en)* | 2004-02-19 | 2005-09-02 | Seiko Epson Corp | Computer, computer startup method, BIOS program, and information storage medium |
| JP2006236058A (en)* | 2005-02-25 | 2006-09-07 | Toshiba Corp | Information processing apparatus and system activation method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5029095B2 (en) | 2012-09-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10042664B2 (en) | Device remote access method, thin client, and virtual machine | |
| EP2483799B1 (en) | Portable desktop device and method of host computer system hardware recognition and configuration | |
| CN100474247C (en) | Method for updating firmware in computer server systems | |
| US9557791B2 (en) | Computer device and method for converting working mode of universal serial bus connector of the computer device | |
| JP5821393B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, activation method, program | |
| CN101923473B (en) | Embedded electronic device and method for updating firmware thereof | |
| CN102439557A (en) | Hybrid storage device | |
| CN117785311B (en) | Server startup method and device, storage medium and electronic device | |
| CN102592073B (en) | Anti-malware scanning system and method thereof | |
| CN107391120A (en) | One kind starts control method, electronic equipment and computer-readable recording medium | |
| JP5029095B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus, activation method thereof, and activation program | |
| US10466916B2 (en) | System and method of dynamic write protect of storage devices exposed by baseboard management controller (BMC) | |
| KR20190113614A (en) | Information processing apparatus, and information processing method | |
| EP2835737A1 (en) | Data terminal running mode switching method, device, and data terminal | |
| EP2813947B1 (en) | Electronic device and method for mounting file system using virtual block device | |
| JP2012194675A (en) | Information apparatus and emergency access method for information apparatus | |
| JP7103804B2 (en) | User interface control device, user interface control method, and user interface control program | |
| CN113721993A (en) | System starting method, device, equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| JP7609469B2 (en) | Processing device, processing system, processing method, and program | |
| CN110532040A (en) | Loading method and device, the storage medium and electronic equipment of firmware program | |
| US10095589B2 (en) | System and method for optimization of operating system restore | |
| CN114528147B (en) | Fingerprint deleting method and device in dual operating system | |
| JP4597032B2 (en) | Computer system, basic program startup method, and loader program | |
| JP5104320B2 (en) | Computer system, computer main body, startup method, and initialization program | |
| JPH09146651A (en) | Computer remote start system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20100302 | |
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date:20110919 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20120307 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20120313 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20120508 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20120529 | |
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20120611 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150706 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |