JP2006093986A - Moving picture recording apparatus - Google Patents
Moving picture recording apparatusDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006093986A JP2006093986AJP2004275445AJP2004275445AJP2006093986AJP 2006093986 AJP2006093986 AJP 2006093986AJP 2004275445 AJP2004275445 AJP 2004275445AJP 2004275445 AJP2004275445 AJP 2004275445AJP 2006093986 AJP2006093986 AJP 2006093986A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- file
- recording
- moving image
- capacity
- moving picture
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000description4
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description3
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description3
- 102100037709Desmocollin-3Human genes0.000description2
- 101000968042Homo sapiens Desmocollin-2Proteins0.000description2
- 101000880960Homo sapiens Desmocollin-3Proteins0.000description2
- 230000006835compressionEffects0.000description2
- 238000007906compressionMethods0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 230000002596correlated effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000875corresponding effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 238000003384imaging methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000005070samplingMethods0.000description1
- 230000005236sound signalEffects0.000description1
- 230000001360synchronised effectEffects0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Television Signal Processing For Recording (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は動画記録装置に係り、特にレンズから入射した光を電気信号に変換する撮像素子又は外部入力のいずれか、又は両方を兼ね備え、そこから得られた動画像信号を記録媒体に記録する動画記録装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a moving image recording apparatus, and in particular, a moving image which has either an image pickup element for converting light incident from a lens into an electric signal, an external input, or both, and records a moving image signal obtained therefrom on a recording medium. The present invention relates to a recording apparatus.
レンズから入射した光を電気信号に変換する撮像素子又は外部入力のいずれか、又は両方を兼ね備え、そこから得られた動画像信号を記録媒体に記録する動画記録装置として、従来より知られているビデオカメラにおいて、動画像を記録した記録媒体の編集作業を行う場合は、その記録媒体よりも大容量の記録媒体を持ったパーソナルコンピュータ(以下、パソコンという)などの機器に一旦移し、そこで編集を行った後にビデオカメラの記録媒体に戻すことが通常行われる。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally known as a moving image recording apparatus that has either an image pickup element that converts light incident from a lens into an electric signal, an external input, or both, and records a moving image signal obtained therefrom on a recording medium. When editing a recording medium on which a moving image is recorded with a video camera, the recording medium is temporarily moved to a device such as a personal computer (hereinafter referred to as a personal computer) having a recording medium having a larger capacity than the recording medium, and editing is performed there. Usually, the recording is returned to the recording medium of the video camera.
これは、動画像を記録した記録媒体の編集作業を行う場合、編集対象のファイルと同等の容量の作業領域を同一のメディア内若しくは別にメモリを搭載する必要があるが、モバイル的な使い方をする小型の民生用機器であるビデオカメラでは、大容量の記録媒体を搭載することが難しく、特に記録媒体に長時間連続的に記録した動画像信号の記録ファイルは容量が大きくなり、編集することが困難であるからである。 This means that when editing a recording medium that records moving images, it is necessary to install a work area of the same capacity as the file to be edited in the same medium or separately, but use it as a mobile device. A video camera, which is a small consumer device, is difficult to mount a large-capacity recording medium. Especially, a moving image signal recording file recorded continuously for a long time on a recording medium has a large capacity and can be edited. It is difficult.
しかし、大容量の記録媒体を内蔵または装着しなくても、ビデオカメラ内で編集を行いたいという要求がある。また、ビデオカメラの記録媒体とパソコンとの間での記録データファイルの受け渡しの際の、ファイルが壊れるなど不測の事態を最小限に抑えたいからである。 However, there is a demand for editing within a video camera without incorporating or mounting a large capacity recording medium. Another reason is that it is desirable to minimize unforeseen circumstances such as file corruption when the recording data file is transferred between the recording medium of the video camera and the personal computer.
一方、受信される動画像などのデジタル・データ・ストリームをデジタル・ビデオ・ディスクのような記録媒体に、記録集合体単位で区切りながら記録する記録方法が従来より知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。この特許文献1記載の記録方法では、上記の記録集合体単位で記録された記録集合体のサーチのための時間情報が、各記録情報単位に対応させて記録される。 On the other hand, a recording method for recording a received digital data stream such as a moving image on a recording medium such as a digital video disc while being divided in units of recording aggregates is known (for example, Patent Documents). 1). In the recording method described in
しかるに、従来の動画記録装置では、撮影した動画像を記録した記録媒体の編集の際は、前述したようにパソコンの大容量の記録媒体を利用するために、動画記録装置との間での記録ファイルの受け渡しの際に記録ファイルが壊れるなどの不測の事態が発生する場合があり、長時間撮影した動画像の記録ファイルほど被害が大きくなってしまい、また、動画記録装置内の容量の少ない記録媒体において動画編集が容易にできないという問題がある。 However, in the conventional moving picture recording apparatus, when editing the recording medium on which the captured moving image is recorded, since the large capacity recording medium of the personal computer is used as described above, recording with the moving picture recording apparatus is performed. Unexpected situations such as recording file corruption may occur during file delivery, and the longer the video recording file shot for a long time, the greater the damage, and the less recording in the video recording device. There is a problem that moving image editing cannot be easily performed on a medium.
一方、特許文献1記載の動画記録方法をビデオカメラのような動画記録装置に適用した場合は、記録媒体に所定の記録集合単位で区切りながら撮影動画像が記録されると共に時間情報も記録され、その時間情報を利用して高速でサーチすることができるだけであり、容量の少ない記録媒体での動画編集が容易にできない。 On the other hand, when the moving image recording method described in
本発明は以上の点に鑑みなされたもので、容量の少ない記録媒体でも動画編集が容易に行い得るような動画記録を記録媒体に行う動画記録装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above points, and an object of the present invention is to provide a moving image recording apparatus that performs moving image recording on a recording medium so that moving image editing can be easily performed even on a recording medium with a small capacity.
また、本発明の他の目的は、記録媒体の記録ファイルが壊れるなどの不測の事態による被害を最小限にし得る動画記録装置を提供することにある。 Another object of the present invention is to provide a moving picture recording apparatus capable of minimizing damage caused by an unexpected situation such as a recording file on a recording medium being broken.
上記の目的を達成するため、第1の発明は、記録開始時から記録終了時までの期間、撮像された動画像信号を圧縮符号化する符号化手段と、符号化手段により圧縮符号化された動画像信号を、予め設定した時間単位又は容量単位でファイル分割して、記録媒体に記録する記録手段とを有することを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above object, the first aspect of the invention is an encoding means for compressing and encoding a captured moving image signal during a period from the start of recording to the end of recording, and is compressed and encoded by the encoding means. Recording means for dividing a moving image signal into files by a preset time unit or capacity unit and recording the divided video file on a recording medium.
この発明では、圧縮符号化された動画像信号は、予め設定した時間単位又は容量単位でファイル分割されて記録媒体に記録されるため、記録時間に依存することなく1ファイル当りの容量を小さくできる。 In the present invention, since the compression-coded moving image signal is divided into files by a preset time unit or capacity unit and recorded on the recording medium, the capacity per file can be reduced without depending on the recording time. .
また、上記の目的を達成するため、第2の発明は、予め設定した時間単位又は容量単位を任意の値に設定する設定手段を有し、記録手段は、圧縮符号化された動画像信号をファイル分割して記録媒体に記録するに際し、設定手段により設定された時間単位又は容量単位毎にファイルクローズした後、次のファイルの記録を開始することを繰り返すことを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above object, the second invention has setting means for setting a predetermined time unit or capacity unit to an arbitrary value, and the recording means stores the compression-coded moving image signal. When the file is divided and recorded on the recording medium, the file is closed for each time unit or capacity unit set by the setting unit, and then recording of the next file is repeated.
本発明によれば、圧縮符号化された動画像信号を、予め設定した時間単位又は容量単位でファイル分割して記録媒体に記録することにより、記録時間に依存することなく1ファイル当りの容量を小さくするようにしたため、モバイル的な用途のビデオカメラにおいて動画記録用記録媒体として使用するメモリカード等の低容量記録媒体でも編集作業が容易に行える。 According to the present invention, a compression-coded moving image signal is divided into files by a preset time unit or capacity unit and recorded on a recording medium, so that the capacity per file can be reduced without depending on the recording time. Since the size is reduced, editing work can be easily performed even with a low-capacity recording medium such as a memory card used as a recording medium for moving image recording in a video camera for mobile use.
また、本発明によれば、記録媒体には動画像信号が複数のファイルに分割して記録されているため、ファイルが壊れたときの被害を最小限に抑えることができ、また、一度に扱うデータ量が1つの分割ファイル分で少ないため、記録動画像データが扱い易く、更に、頭出しのポイントが増え、見たいところを探し易い。 In addition, according to the present invention, since a moving image signal is divided and recorded in a plurality of files on the recording medium, damage when the file is broken can be minimized and handled at a time. Since the amount of data is small for one divided file, the recorded moving image data is easy to handle, and further, the number of cue points increases, making it easy to search for a desired place.
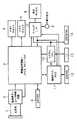
図1は本発明になる動画記録装置の一実施の形態のブロック図、図2は本発明の動作説明用フローチャートを示す。図1は動画記録装置の一実施の形態のデジタルビデオカメラであり、光学系1でフォーカスやアイリス等が調整されて入射した動きのある被写体からの光は、撮像素子/カメラ制御回路2内の撮像素子の撮像面上で光学像を結像して光電変換され、動画に関する撮像信号とされる。この撮像信号は、撮像素子/カメラ制御回路2内のカメラ制御回路で相関二重サンプリング(CDS)によるS/N改善、自動利得制御(AGC)による利得調整、A/D変換によるデジタル変換などの処理が施された後、画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DEC3に供給される。 FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an embodiment of a moving picture recording apparatus according to the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the present invention. FIG. 1 shows a digital video camera according to an embodiment of a moving image recording apparatus. Light from a moving subject that is incident after the focus, iris, etc. are adjusted by an
画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DSC3は、画像処理回路とJPEGエンコーダ(ENC)とDSC(デジタル・スチル・カメラシステム)とからなり、その画像処理回路において、例えば撮像素子/カメラ制御回路2の出力撮像信号が2chの画像データの場合は、1枚の画像データに合成したり、撮像素子/カメラ制御回路2に必要なクロックなどを生成した後、そのJPEGエンコーダ(ENC)にてズーム、モザイクなどの電子画像処理を行い、最終的に例えばデジタルビデオカメラ(DVC)の規格に合う所定有効画素数の画像サイズを変換した動画像の画像データを出力する。なお、画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DSC3は、シンクロナス・ダイナミック・ランダム・アクセス・メモリ(SDRAM)4との間で、必要なデータのやり取りを行う。 The image processing circuit / JPEG ENC / DSC 3 includes an image processing circuit, a JPEG encoder (ENC), and a DSC (digital still camera system). In the image processing circuit, for example, output imaging of the image sensor /
また、画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DSC3のJPEGエンコーダ(ENC)にて得られた動画像の画像データは、動画ENC/DEC11に供給される。動画ENC/DEC11は、動画エンコーダ(ENC)と動画デコーダ(DEC)とからなり、上記の動画像の画像データをそのままアナログインタフェース(I/F)7を通して表示デバイス8に供給し、ここで表示させる。外部入出力端子9にモニタ装置が接続されている場合は、そのモニタ装置にも表示させる。 Also, the image data of the moving image obtained by the JPEG encoder (ENC) of the image processing circuit / JPEG ENC / DSC 3 is supplied to the moving image ENC /
また、上記の動画ENC/DEC11の動画ENCは、上記の動画像の画像データを例えばMPEG2の方式で圧縮符号化し、得られた圧縮符号化動画像データを、画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DSC3を通してメモリスロット5に装着されている第1の記録媒体(例えばSDメモリカード)に記録する。また、これと同時に、メモリスロット6に装着されている第2の記録媒体に圧縮された動画像データを記録することも可能である。 In addition, the moving image ENC of the moving image ENC / DEC11 is obtained by compressing and coding the image data of the moving image by, for example, the MPEG2 system, and the obtained compressed and encoded moving image data through the image processing circuit / JPEG ENC / DSC3. Recording is performed on a first recording medium (for example, an SD memory card) mounted in the memory slot 5. At the same time, the compressed moving image data can be recorded on the second recording medium mounted in the
なお、外部入出力端子9にマイクが接続されている場合は、マイクで収音した音声信号を、上記の圧縮された動画像信号とまとめて1つのファイルとして、メモリスロット5、6にそれぞれ装着されているSDメモリカード等に記録することも可能である。 If a microphone is connected to the external input /
システムCPU(中央処理装置)10は、ユーザインタフェース(UI)13からの入力データに基づいて、このデジタルビデオカメラの各ブロックへ各種の制御信号を出力する。SDRAM12は動画ENC/DEC11の動作に必要な作業領域として用いられる。電気的に消去可能な不揮発性メモリであるEEPROM14は、例えば後述する時間情報が予め格納されている。 A system CPU (central processing unit) 10 outputs various control signals to each block of the digital video camera based on input data from a user interface (UI) 13. The
次に、本実施の形態の動作について、図2のフローチャートを併せ参照して説明する。まず、ビデオカメラの電源をオン(ON)すると、光学系1から入射した光は、前述したように撮像素子/カメラ制御回路2で撮像信号に変換された後、画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DSC3により画像処理された後、アナログI/F7を経由して表示デバイス8で被写体の動画像が表示される。 Next, the operation of the present embodiment will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, when the power of the video camera is turned on, the light incident from the
この状態で使用者によりUI13及びシステムCPU10を介してEEPROM14に、ファイル化時間情報(1分、5分、10分又は無制限)が設定される(ステップS1)。続いて、使用者により動画のSDメモリカードへの記録開始操作を行うと(ステップS2)、その操作信号がUI13を介してシステムCPU10に供給される。 In this state, the file time information (1 minute, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, or unlimited) is set in the
これにより、システムCPU10は、EEPROM14に事前に格納されている時間情報(例えば、10分)を読み出して、内蔵のファイル化時計による計時を開始すると共に(ステップS3)、動画ENC/DEC11によるMPEG2のエンコード動作を開始させ、得られたMPEG2で圧縮符号化された動画像データのSDメモリカードへの記録を開始させる(ステップS4)。 As a result, the
すなわち、動画ENC/DEC11は、画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DSC3により画像処理されて取り出された撮影されている動画像データを入力として受け、MPEG2方式で圧縮符号化を開始し、その圧縮符号化された動画像データを画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DSC3内のDSCをそのまま通してメモリスロット5に装着されているSDメモリカードに記録させる。なお、ここでは、説明の便宜上、メモリスロット5に装着されているSDメモリカードへの記録について説明するが、メモリスロット6に装着されている他の記録媒体への記録も同様にして行うことが可能である。 That is, the moving image ENC / DEC11 receives as input the moving image data that has been taken and is processed by the image processing circuit / JPEG ENC / DSC3, starts compression encoding in the MPEG2 system, and the compression encoding The recorded moving image data is passed through the DSC in the image processing circuit / JPEG ENC / DSC 3 as it is and is recorded on the SD memory card mounted in the memory slot 5. Here, for convenience of explanation, recording to an SD memory card mounted in the memory slot 5 will be described, but recording to another recording medium mounted to the
このSDメモリカードへの動画像データの記録が、EEPROM14から読み出された時間情報(ここでは、10分)だけ継続して行われたかどうか、システムCPU10が判定し(ステップS5)、記録開始から10分経過すると、システムCPU10は動画ENC/DEC11を制御して、MPEG2で規定されているGOP(group of picture)単位で上記時間情報の10分間のファイルクローズを行い(ステップS6)、メモリスロット5に装着されているSDメモリカードにファイルを作成する(ステップS7)。 The
このファイルは、例えばSD_VIDEOという名称のフォルダ内に、「PRG001」という名称のファイルの下に、「MOV001.MOD」という名称の動画像データ用ファイルと、「MOV001.MOI」という名称の管理情報用ファイルとが対で作成される。 This file is, for example, in a folder named SD_VIDEO, under a file named “PRG001”, for a moving image data file named “MOV001.MOD”, and for management information named “MOV001.MOD”. A file is created in pairs.
上記のファイル作成後に、システムCPU10はUI13から撮影停止操作情報が入力されたかどうかチェックし(ステップS8)、撮影停止操作情報が入力されていないときには、ステップS3に再び戻って、内蔵の時計にリセットをかけて計時を再び最初から開始する。 After creating the file, the
このようにして、使用者が撮影停止操作をすることにより、システムCPU10がUI13から撮影停止操作情報が入力されたことを確認するまでは、ステップS3からS8までの処理が繰り返され、動画ENC/DEC11はエンコードを継続し、10分間毎に撮影動画像の圧縮符号化データがGOP単位でファイルクローズし、メモリスロット5に装着されているSDメモリカードにファイルが作成されていく。 In this way, the processing from step S3 to S8 is repeated until the
従って、SDメモリカードには、上記のSD_VIDEOという名称のフォルダ内に、「PRG001」という名称のファイルの下に、「MOV00i.MOD」という名称の動画像データ用ファイルと、「MOV00i.MOI」という名称の管理情報用ファイル(ただし、i=2,3,・・・,n)とが対で順次作成されていく。なお、動画像データ用ファイルと管理情報用ファイルの数が所定数に達した場合は、続いて、次の「PRG002」という名称のファイルの下に、上記と同様にして動画像データ用ファイルと管理情報用ファイルの対が順次作成されていく。 Therefore, in the SD memory card, a moving image data file named “MOV00i.MOD” and a file named “MOV00i.MOD” are located under the file named “PRG001” in the folder named SD_VIDEO. Name management information files (where i = 2, 3,..., N) are sequentially created in pairs. When the number of moving image data files and management information files reaches a predetermined number, the moving image data file and the file named “PRG002” are subsequently recorded in the same manner as described above. Management information file pairs are created sequentially.
その後、システムCPU10がステップS8でUI13から撮影停止操作情報が入力されたことを確認すると、システムCPU10は、動画ENC/DEC11に動作停止情報を供給して、それまで継続してエンコード動作をしていた動画ENC/DEC11のエンコード動作を停止させ、ファイルクローズし、メモリスロット5に装着されているSDメモリカードへの書き込みを終了させる(ステップS9)。このようにして、メモリスロット5に装着されているSDメモリカードには、所望の撮影動画像が連続して、撮影時間に応じた数の小容量のファイルに分割して記録される。 Thereafter, when the
ここで、従来は記録される動画像信号のファイルは、連続した一つのファイルで保存されるため、記録時間が長くなれば、自ずとファイル容量が大きくなり、編集する際にはそれと同等の空き容量を持っている記録媒体を用いないと編集できないことがあり、通常はパソコンなどの大容量の記録媒体を持った機器に記録情報を一旦移して編集を行う必要がある。 Here, conventionally, a moving image signal file to be recorded is saved as a single continuous file. Therefore, if the recording time becomes longer, the file capacity will naturally increase, and when editing it will have an equivalent free space. Editing may not be possible without using a recording medium having a recording medium. Usually, it is necessary to transfer recording information to a device having a large-capacity recording medium such as a personal computer for editing.
しかし、本実施の形態では、使用者の操作により連続的に記録を行うが、SDメモリカード内では、ある一定時間単位に分割してファイル化して記録することにより、1ファイル当りの容量を少なく抑えているため、編集作業を行うときには、SDメモリカード等に別に1ファイルと同等の容量を編集用に用意すればよいので、大容量の記録媒体が不要であり、よって、編集作業がモバイル機器であるデジタルカメラ内で容易に行うことができる。 However, in this embodiment, recording is performed continuously by the user's operation, but the capacity per file is reduced by dividing the SD memory card into a certain unit of time and recording it as a file. Therefore, when the editing work is performed, a capacity equivalent to one file may be prepared for editing on the SD memory card or the like, so that a large-capacity recording medium is not required. This can be done easily in a digital camera.
また、ファイルが分割されているので、ファイルが壊れた時の被害を最小限に抑えることができる。また、一度に扱うデータ量は、1ファイル分であり少ないので、扱い易い。更に、SDメモリカードには複数のファイルが分割して記録されているので、頭出しのポイントが増え、見たいところを探し易いという効果もある。 Moreover, since the file is divided, damage when the file is broken can be minimized. Also, the amount of data handled at one time is as small as one file, so it is easy to handle. Furthermore, since a plurality of files are divided and recorded on the SD memory card, there is an effect that the point of cueing increases and it is easy to find a place to see.
なお、本発明は上記の実施の形態に限定されるものではなく、例えば、EEPROM14に記憶するファイルクローズの設定は、上記の実施の形態の1分、5分、10分といった時間設定のほかに、1Mバイト、10Mバイトなどの容量で設定させることも可能であり、また使用者が任意に設定することも可能である。 The present invention is not limited to the above embodiment. For example, the file close setting stored in the
1 光学系
2 撮像素子/カメラ制御回路
3 画像処理回路/JPEG ENC/DSC
5、6 メモリスロット
7 アナログインタフェース(I/F)
8 表示デバイス
9 外部入出力端子
10 システムCPU(中央処理装置)
11 動画ENC/DEC
13 UI(ユーザインタフェース)
14 時間情報格納用EEPROM
DESCRIPTION OF
5, 6
8
11 Video ENC / DEC
13 UI (user interface)
14 Time information storage EEPROM
Claims (2)
Translated fromJapanese前記符号化手段により圧縮符号化された動画像信号を、予め設定した時間単位又は容量単位でファイル分割して、記録媒体に記録する記録手段と
を有することを特徴とする動画記録装置。Encoding means for compressing and encoding the captured moving image signal during a period from the start of recording to the end of recording;
A moving image recording apparatus comprising: a recording unit configured to divide a moving image signal compressed and encoded by the encoding unit into a file by a preset time unit or capacity unit and record the file on a recording medium.
A setting unit configured to set the preset time unit or capacity unit to an arbitrary value, and the recording unit divides the compressed and encoded moving image signal into a file and records the file on the recording medium; 2. The moving image recording apparatus according to claim 1, wherein after the file is closed for each time unit or capacity unit set by the setting means, recording of the next file is repeatedly started.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004275445AJP2006093986A (en) | 2004-09-22 | 2004-09-22 | Moving picture recording apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004275445AJP2006093986A (en) | 2004-09-22 | 2004-09-22 | Moving picture recording apparatus |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006093986Atrue JP2006093986A (en) | 2006-04-06 |
Family
ID=36234554
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004275445APendingJP2006093986A (en) | 2004-09-22 | 2004-09-22 | Moving picture recording apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006093986A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010154506A (en)* | 2008-11-28 | 2010-07-08 | Nikon Corp | Image file generation device, camera, and image file generation program |
- 2004
- 2004-09-22JPJP2004275445Apatent/JP2006093986A/enactivePending
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010154506A (en)* | 2008-11-28 | 2010-07-08 | Nikon Corp | Image file generation device, camera, and image file generation program |
| US8953066B2 (en) | 2008-11-28 | 2015-02-10 | Nikon Corporation | Image file generation device, camera and image file generation method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101264389B1 (en) | Imaging device and method | |
| US20110142410A1 (en) | Reproducing apparatus for video data | |
| JP4958758B2 (en) | Recording apparatus, reproducing apparatus, recording method, reproducing method, and program | |
| JP4359773B2 (en) | Image compression processing apparatus, image compression processing method, and image compression processing program | |
| CN107079131A (en) | Image processing device and image processing method | |
| JP2009147549A (en) | Moving picture recording apparatus, moving picture reproducing apparatus, and program | |
| JP4560422B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP2004088567A (en) | Device and method for picking-up image, recording medium, and program | |
| CN102547086B (en) | Image capturing apparatus, image capturing control method, and storage medium storing program for image capturing | |
| JP2009147743A (en) | Recording apparatus, reproducing apparatus, recording method, reproducing method, and program | |
| CN107079130A (en) | Image processing device and image processing method | |
| RU2518173C2 (en) | Apparatus for recording image data | |
| US20070047918A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for recording moving picture | |
| TW201008275A (en) | Video recording device and method | |
| JP5118465B2 (en) | Recording apparatus, reproducing apparatus, recording method, reproducing method, and program | |
| KR101480407B1 (en) | Digital image processing apparatus, control method thereof, and recording medium recording the control method | |
| JP2009152672A (en) | Recording apparatus, reproducing apparatus, recording method, reproducing method, and program | |
| JP2006093986A (en) | Moving picture recording apparatus | |
| JP6278353B2 (en) | RECORDING DEVICE, RECORDING METHOD, PROGRAM, AND IMAGING DEVICE | |
| JP4785460B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging method | |
| KR101332299B1 (en) | Image recording apparatus and method thereof | |
| JP5561044B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program | |
| JP2010147531A (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging method | |
| JP4234662B2 (en) | Electronic device and data recording method thereof | |
| JPH07236110A (en) | Digital still camera |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20061227 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20080408 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20080603 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20080624 |