JP2006087746A - Evaluation method of hypotensor and apparatus therefor - Google Patents
Evaluation method of hypotensor and apparatus thereforDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006087746A JP2006087746AJP2004278382AJP2004278382AJP2006087746AJP 2006087746 AJP2006087746 AJP 2006087746AJP 2004278382 AJP2004278382 AJP 2004278382AJP 2004278382 AJP2004278382 AJP 2004278382AJP 2006087746 AJP2006087746 AJP 2006087746A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- blood pressure
- antihypertensive
- data
- difference curve
- area
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription49
- 230000036772blood pressureEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription104
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription17
- 208000001953HypotensionDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 238000013075data extractionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 239000002220antihypertensive agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription123
- 229940030600antihypertensive agentDrugs0.000claimsdescription113
- 230000003276anti-hypertensive effectEffects0.000claimsdescription63
- 238000009530blood pressure measurementMethods0.000claimsdescription44
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription33
- 208000021822hypotensiveDiseases0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000001077hypotensive effectEffects0.000claimsdescription6
- 206010020772HypertensionDiseases0.000abstractdescription14
- 230000002060circadianEffects0.000abstractdescription5
- 230000001631hypertensive effectEffects0.000abstractdescription4
- 230000036543hypotensionEffects0.000abstract4
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000abstract1
- 230000035488systolic blood pressureEffects0.000description37
- 230000035487diastolic blood pressureEffects0.000description21
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description18
- 238000001647drug administrationMethods0.000description18
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000description13
- 229940127088antihypertensive drugDrugs0.000description7
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description6
- 230000001186cumulative effectEffects0.000description6
- QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-NmercuryChemical compound[Hg]QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 229910052753mercuryInorganic materials0.000description6
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description4
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description3
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description3
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000description3
- 229940127291Calcium channel antagonistDrugs0.000description2
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description2
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000000480calcium channel blockerSubstances0.000description2
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description2
- 239000003086colorantSubstances0.000description2
- 238000004040coloringMethods0.000description2
- 230000002950deficientEffects0.000description2
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description2
- 238000002560therapeutic procedureMethods0.000description2
- 206010043268TensionDiseases0.000description1
- 208000005434White Coat HypertensionDiseases0.000description1
- 210000004204blood vesselAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000007796conventional methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000011157data evaluationMethods0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000description1
- 239000010432diamondSubstances0.000description1
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description1
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000description1
- 238000009499grossingMethods0.000description1
- 238000000691measurement methodMethods0.000description1
- 229960001597nifedipineDrugs0.000description1
- HYIMSNHJOBLJNT-UHFFFAOYSA-NnifedipineChemical compoundCOC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(=O)OC)C1C1=CC=CC=C1[N+]([O-])=OHYIMSNHJOBLJNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 238000010606normalizationMethods0.000description1
- WRUUGTRCQOWXEG-UHFFFAOYSA-NpamidronateChemical compoundNCCC(O)(P(O)(O)=O)P(O)(O)=OWRUUGTRCQOWXEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000002085persistent effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000630rising effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000391smoking effectEffects0.000description1
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000description1
- 208000037911visceral diseaseDiseases0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Measuring Pulse, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure Or Blood Flow (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、高血圧等の患者に装着する24時間血圧計測装置であるABPMを用い、医師が降圧剤の降圧効果の定量的評価及び、降圧剤の投与後データから降圧剤の投与前のデータを差し引くことによって得られた差分曲線による降圧効果の日内変動の評価を構成する降圧剤の降圧度の時間積分、最大降圧度、最大降圧時間、T/P比を容易に評価できる降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置に関する改良発明である。 The present invention uses ABPM, which is a 24-hour blood pressure measurement device attached to a patient with high blood pressure or the like, and allows a doctor to quantitatively evaluate the antihypertensive effect of the antihypertensive agent, and to obtain data before administration of the antihypertensive agent from post-administration data Evaluation method of antihypertensive agent that can easily evaluate the time integral, maximum antihypertensive degree, maximum antihypertensive time, and T / P ratio of the antihypertensive agent constituting the evaluation of the daily fluctuation of the antihypertensive effect by the difference curve obtained by subtraction And an improved invention relating to the apparatus.
従来、降圧剤を使用する前後の血圧の測定方法として間接法であるカフ帯で上腕圧迫する方法を始めとして、コロトコフ法、オシロメトリック法等があり、コロトコフ法の場合、主に外来診察においてカフ帯で、上腕を圧迫し、聴診器によって、血管の音を聞きながら水銀柱の目盛りをみて収縮期血圧である最高血圧及び、拡張期血圧である最低血圧の変動を測定して高血圧等の判断を医師が行っていた。 Conventional methods for measuring blood pressure before and after using antihypertensive agents include the indirect method of cuffing the upper arm with the cuff belt, the Korotkoff method, the oscillometric method, etc. In the case of the Korotkoff method, cuffs are mainly used in outpatient examinations. The upper arm is pressed with a band, and a stethoscope is used to observe the sound of the blood vessels while observing the scale of the mercury column to measure changes in systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. The doctor was going.
しかし、外来診療は主として午前中に行うことが多く、人間の血圧は夜間に下降し、早朝に覚醒と共に血圧が上昇する日内変動パターンがあるが外来測定血圧では、患者の日内変動パターンまで評価することができなかった。However, outpatient treatment is often performed mainly in the morning, and human blood pressure falls at night, and there is a circadian variation pattern in which blood pressure increases with awakening in the early morning, but outpatient measured blood pressure evaluates to the patient's circadian variation pattern. I couldn't.
前記日内変動パターンは、昼間活動しているとき血圧が高く、夜間の睡眠中に血圧が低下することであり、夜間の降圧が認められた場合ディッパー型とし、夜間の血圧下降が少なくなる場合ノンディッパー型とし、昼間の血圧よりも、夜間の血圧が高い場合には逆ディッパー型となっている。現状では便宜上、夜間の収縮期血圧が昼間に比べて10%以上下がればディッパー、10%未満の場合をノンディッパーとしている。The diurnal variation pattern is a high blood pressure during daytime activity and a decrease in blood pressure during nighttime sleep. A dipper type is used when nighttime blood pressure is observed. It is a dipper type, and is a reverse dipper type when the blood pressure at night is higher than the blood pressure during the day. At present, for convenience, when the systolic blood pressure at night falls by 10% or more compared to the daytime, the dipper is less than 10% and the non-dipper is used.
また日常生活では正常血圧であるが、診察室内では精神的な緊張等のために患者が高血圧になってしまう白衣高血圧症という症状もあり、外来における1回の血圧測定により血圧の日内変動を考慮した高血圧の診断ならびに高血圧の程度の判断、降圧剤の降圧効果の判定を行うには限界があった。In addition, normal blood pressure is observed in daily life, but there is also a symptom of white coat hypertension that causes the patient to become hypertensive due to mental tension etc. in the examination room. There were limits to the diagnosis of hypertension, the degree of hypertension, and the antihypertensive effect of antihypertensive drugs.
患者の高血圧等の程度、血圧の日内変動、年齢、性別又は、内臓疾患や喫煙等のように危険因子の有無を医師が勘案して適切な降圧強度及び降圧持続時間を有する降圧剤を処方し、膨大なABPM等のデータを医師が勘案することによって適切な降圧剤の選択、降圧剤療法が適切であるかの判断は困難であった。Doctors prescribe antihypertensive agents with appropriate antihypertensive strength and duration of antihypertensive, taking into account the degree of hypertension, circadian variation of blood pressure, age, sex, or the presence of risk factors such as visceral disease or smoking It has been difficult for doctors to consider the selection of an appropriate antihypertensive agent and to determine whether an antihypertensive agent therapy is appropriate by taking into account a huge amount of data such as ABPM.
なお、その他の降圧剤の評価方法としては下記のように第1から第4まで評価方法がある。第1の降圧剤の評価方法として、臨床開発時に治験薬の降圧効果を評価する場合に使用する<累積降圧率>があり、降圧度を評価した後、(1)下降(2)下降傾向(3)不変のいずれかであった患者の割合を%で示す場合がある。As other methods for evaluating antihypertensive agents, there are first to fourth evaluation methods as described below. The first antihypertensive evaluation method includes <cumulative antihypertensive rate> used when evaluating the antihypertensive effect of a study drug during clinical development. After evaluating the antihypertensive degree, (1) downward (2) downward trend ( 3) The percentage of patients who were either unchanged may be indicated in%.
前記累積降圧率の降圧度は(1)の下降の場合、(収縮期血圧≦20,DBP≦−0)で示すことができ、(2)の下降傾向の場合、(収縮期血圧−19から−10、拡張期血圧−9から−5)で示すことができ、(3)の不変の場合、(収縮期血圧±9、拡張期血圧±4)で示すことができる。なお、患者が重症である場合、累積降下率が低くなる。In the case of a decrease in (1), the degree of decrease in the cumulative antihypertensive rate can be expressed as (systolic blood pressure ≦ 20, DBP ≦ −0), and in the case of a decreasing tendency in (2), from (systolic blood pressure−19) −10, diastolic blood pressure −9 to −5), and in the case of no change in (3), it can be indicated by (systolic blood pressure ± 9, diastolic blood pressure ± 4). In addition, when a patient is serious, a cumulative fall rate becomes low.
第2の降圧剤の評価方法として<血圧正常化率(降圧達成率)>があり、ある薬剤を投与した際の高血圧ガイドラインなどの降圧目標値(たとえばJSHの一般の高血患者では、140/90)以下にコントロールできた患者の割合を用いて製薬会社等は評価を行っていた。As a second method for evaluating antihypertensive agents, there is <blood pressure normalization rate (hypertensive achievement rate)>, and an antihypertensive target value such as a hypertension guideline when a certain drug is administered (for example, 140 / 90) Pharmaceutical companies etc. evaluated using the ratio of patients who were able to control below.
第3の降圧剤の評価方法として<血圧平均値>として、平均血圧値=(収縮期血圧+2×拡張期血圧)/3で薬剤の降圧度(投与前と投与後の平均血圧の差)を評価することがある。なお、第4の降圧剤の評価方法として<平均降圧度(単位:mmHg)>がある。
これは、ABPMを使用して、日内の多数の測定値の平均値で評価するものである。As an evaluation method of the third antihypertensive agent, as <blood pressure mean value>, mean blood pressure value = (systolic blood pressure + 2 × diastolic blood pressure) / 3, and the antihypertensive level of the drug (difference between mean blood pressure before and after administration) May be evaluated. In addition, there exists <average antihypertensive degree (unit: mmHg)> as a 4th evaluation method of an antihypertensive agent.
This uses ABPM to evaluate the average value of a large number of measurements during the day.
また、従来の発明では、「血圧測定装置、血圧測定方法、及び血圧測定処理プログラムを記録した記録媒体」がある。かかる発明は、血圧測定装置にあって、測定された血圧関連データの信頼性を評価することを可能にし血圧を測定する血圧測定手段と、この血圧測定手段による血圧の測定の際における、脈の発生間隔を測定する脈間隔測定手段と、この脈間隔測定手段により測定された脈の発生間隔と予め定められた式データに基づき、前記血圧測定手段により測定された血圧測定値を評価する測定血圧評価手段とを具備したことを特徴とする血圧測定装置であるが、脈の発生間隔を計測することを手段とする従来発明では医師が降圧剤の降圧効果を定量的に投与時期を判断することは不可能である。
本発明は、高血圧患者に対して降圧剤を処方する際、患者の日内変動パターンを数値、図表化等からなる定量的に評価していなかった問題や、患者が降圧剤を使用している場合等のように、膨大なABPM等のデータから降圧剤の24時間に亘る降圧効果を定量的に活用、抽出できなかった問題、各種の降圧剤の24時間の降圧効果を定量的に比較できなかったために降圧剤の強弱が医師の経験あるいは、定性的な判断によって行われていた欠点、そして、患者が降圧剤を服用しても効果を得られない場合に医師が他の種類の降圧剤に変更する等医師が即座に患者への有効な降圧剤を推定できなかった問題を解決することである。 When prescribing an antihypertensive agent to a hypertensive patient, the present invention has a problem that the patient's diurnal variation pattern has not been quantitatively evaluated consisting of numerical values, charts, etc., or the patient is using an antihypertensive agent As mentioned above, it is not possible to quantitatively compare the 24-hour antihypertensive effect of various antihypertensive agents, such as the problem that the antihypertensive agent's 24-hour antihypertensive effect could not be quantitatively utilized and extracted from a huge amount of ABPM data, etc. Therefore, the strength of the antihypertensive agent is due to the doctor's experience or qualitative judgment, and when the patient does not get the effect even if the patient takes the antihypertensive agent, The problem is that doctors could not immediately estimate effective antihypertensive drugs for patients, such as changing.
本発明は、上記の課題を解決するために、24時間血圧計測装置と、前記24時間血圧計測装置から血圧データ等を入出力できるコンピュータにおいて、前記コンピュータに蓄積した血圧データ等から同一患者における特定の降圧剤の投与前と投与後のデータを自動的に抽出する又は、ある特定の降圧剤を使用した患者の降圧剤の使用前と使用後のデータを自動的に抽出できるデータ抽出手段、前記データ抽出手段によって抽出したデータを基に降圧剤の投与前と投与後の差分曲線を定量的かつ日内変動パターンとして算出及び表示する差分曲線算出手段、差分曲線と基準血圧0mmHgとの間で囲まれた降圧面積を算出する降圧面積算出手段、算出した前記差分曲線と前記降圧面積から自動的に降圧ピーク値等の評価をディスプレイ上に表示できる評価表示手段とからなることを特徴とする降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置の構成とした。 In order to solve the above problems, the present invention provides a 24-hour blood pressure measurement device and a computer capable of inputting / outputting blood pressure data from the 24-hour blood pressure measurement device, and specifying the same patient from the blood pressure data accumulated in the computer. Data extracting means capable of automatically extracting data before and after administration of the antihypertensive agent, or automatically extracting data before and after use of the antihypertensive agent of a patient using a specific antihypertensive agent, The difference curve calculation means for calculating and displaying the difference curve before and after administration of the antihypertensive agent as a quantitative and diurnal variation pattern based on the data extracted by the data extraction means, surrounded by the difference curve and the reference blood pressure of 0 mmHg The step-down area calculation means for calculating the step-down area, and the evaluation such as the step-down peak value is automatically displayed on the display from the calculated difference curve and the step-down area. It consists of an evaluation display means can have a structure of the evaluation method and apparatus antihypertensive agent characterized.
第1に本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置は、医師は患者各々の降圧剤の効果を降圧面積及び差分曲線を算出し、斜線等で降圧面積全体を着色する等のディスプレイ表示により、個々の患者が持っている特有の血圧日内変動パターンを把握できた上で、前記患者の日内変動パターンに適合した降圧剤を定量的かつ視覚的に評価できるため、患者に対して最も適した降圧剤の投与が可能となる。 First, the method and apparatus for evaluating an antihypertensive agent according to the present invention is that a doctor calculates the hypotensive area and difference curve for the effect of each hypotensive agent, and displays the display such as coloring the entire antihypertensive area with diagonal lines etc. Because it is possible to quantitatively and visually evaluate antihypertensive drugs that match the patient's diurnal variation pattern after grasping the peculiar blood pressure diurnal variation pattern possessed by each patient, it is most suitable for the patient Allows administration of antihypertensive agents.
第2に医師は、膨大なABPMである24時間血圧計測装置のデータを数値として活用することで、抽出できなかった問題を解決し、降圧効果の判定及び降圧療法の判定を医師が容易にできるようになった。 Secondly, the doctor can solve the problem that could not be extracted by using the data of the 24-hour blood pressure measurement device, which is a huge ABPM, as a numerical value, and the doctor can easily determine the antihypertensive effect and determine the antihypertensive therapy. It became so.
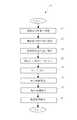
図1は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置の内部構成図、図2は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置の全体図、図3は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置の流れ図である。FIG. 1 is an internal configuration diagram of an evaluation method and apparatus for an antihypertensive agent according to the present invention, FIG. 2 is an overall view of the evaluation method and apparatus for an antihypertensive agent according to the present invention, and FIG. 3 is an evaluation of an antihypertensive agent according to the present invention. 2 is a flowchart of a method and apparatus thereof.
図1及び図2に示したように、本発明である「降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置1」は、医師が降圧剤を使用する患者に携帯させる24時間血圧計測装置2と、前記24時間血圧計測装置2から血圧データ等を記憶装置3eで入出力できるコンピュータ3において、
前記コンピュータ3の記憶装置3eに蓄積した同一患者の血圧データ等から同一の患者における特定の降圧剤の投与前と投与後のデータを自動的に抽出する又は、ある特定の降圧剤を使用した患者の降圧剤の使用前と使用後のデータを自動的に抽出できるデータ抽出手段、前記データ抽出手段によって抽出したデータを基に、特定の降圧剤の投与前と投与後のデータからなる差分曲線を定量的かつ日内変動パターンとして算出及び表示する差分曲線算出手段、差分曲線と基準血圧0mmHgとの間で囲まれた面積である降圧度mmHgと、降圧時間(分)の積分量である降圧面積を算出する降圧面積算出手段によって算出した前記差分曲線と前記降圧面積から自動的に降圧ピーク値等の評価をディスプレイ上に表示できる評価表示手段とからなることを特徴とする降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置である。As shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the “evaluation method and
Patients who automatically extract data before and after administration of a specific antihypertensive agent in the same patient from blood pressure data etc. of the same patient stored in the
24時間血圧計測装置2とは、カフ帯2aと、患者毎にある特定の降圧剤の投与前と投与後の血圧等データを記録する測定装置2bと、前記カフ帯2aにエアを送気し測定装置2bとを接続する接続ケーブル2cとからなり、前記測定装置2bは、前記エアの流入量、流出量を制御する制御装置と、血圧等のデータを記録するメモリを備え、更にエアの流入量、流出量を調節する自動開放弁や、カフ帯2aの圧力を制御する圧力センサーや、加圧ポンプを備えた装置である。なお、本発明で使用する24時間血圧計測装置2の血圧の測定方法は、コロトコフ法、オシロメトリック法等のいずれかの測定方法を選択することが可能である。The 24-hour blood
なお、前記24時間血圧計測装置2を装着する患者は、主に高血圧の者を対象とし、高血圧の定義としてWHOの基準となる収縮期血圧140mmHg以上、又は、拡張期血圧90mmHg以上を基準とする。なお、収縮期血圧130mmHg以下、かつ拡張期血圧85mmHg以下を正常とする。The patient wearing the 24-hour blood
そして、24時間血圧計測装置2で測定した患者の血圧等のデータは、USBケーブル等のデータを出力するケーブル等から、前記測定装置2b内に設けた送受信装置を利用して、クライアントのコンピュータ3まで血圧等のデータを送信する仕組みである。 Then, data such as the blood pressure of the patient measured by the blood
クライアントのコンピュータ3は、24時間血圧計測装置2で得た血圧等のデータを送受信できる装置であり、前記血圧等のデータを構成する患者名、収縮期血圧等の各データ毎に手入力することもできるキーボード3fを備えた入力装置3b、膨大なABPM等のデータから正しい血圧値及び血圧日内変動を視覚化して表示できるディスプレイ3hである出力装置3c、血圧等のデータを送受信できる送受信装置3dと、血圧等のデータを構成し、使用降圧剤名、患者毎、投与降圧剤毎に分けると共に、使用降圧剤名、収縮期血圧、拡張期血圧、心拍数、記録時間等からなる薬剤データ3i、血圧測定データ3j、患者別データ3kとからなる記憶装置3eと、前記薬剤データ3i、血圧測定データ3j、患者別データ3kのそれぞれから抽出データを自動判断し、自動判断の結果である降圧剤等の薬投与後の血圧等のデータから、薬投与前の血圧等のデータを差し引いて描いた
各降圧剤毎の平均の収縮期血圧、拡張期血圧、心拍数などの差分曲線等を演算できるCPU3aとからなることを特徴とする。The
前記CPU3aは、記憶装置3e等に蓄積した血圧データ等から抽出データを自動的に判断するデータ抽出手段によって抽出し、その抽出したデータを基に複数の差分曲線を算出する差分曲線算出手段、前記差分曲線と基準血圧0mmHgとの間で囲まれた算出した降圧部分面積の合計を降圧面積として黄色等の斜線で着色する降圧面積算出手段、算出した差分曲線と前記降圧部分面積から自動的に降圧ピーク値、降圧トラフ値等の評価を前記降圧面積の下部に表等で示すことができる評価表示手段とからなること特徴とする。The CPU 3a extracts the extracted data from the blood pressure data stored in the
前記評価表示手段によって得た結果は、コンピュータ3を構成する前記入力装置3bの接続部3gまでUSBケーブル等のケーブルで接続し、MO等の記録媒体を備えた制御装置3lに保管するか、若しくは出力装置17を構成するプリンター17aに紙データとして出力することができる。The result obtained by the evaluation display means is connected to the
なお、前記制御装置3lは、前記CPU3aに対し、降圧剤の投与前と投与後の差分曲線や降圧面積を算出するデータ抽出が足りているがどうかを判断すると共に抽出データが欠損した場合、患者個人毎のデータの平均値をサーバーとなるコンピュータ5から適宜データを抽出することができる。Note that the
そして前記コンピュータ3は、インターネット通信回線4又はLAN等(図示せず)を介して接続したサーバーとなるコンピュータ5と接続している。コンピュータ5は、前記クライアントのコンピュータ3同様、外部の病院等で測定した24時間血圧計測装置2等の血圧等のデータを集計できるCPU5aと、前記血圧等のデータを構成する患者名等の各データ毎に手入力できるキーボード5fを備えた入力装置5b、血圧等のデータを視覚化して表示できるディスプレイ5gである出力装置5c、血圧等のデータを送受信できる送受信装置5dと、血圧等のデータを各データ毎に分けてデータベースとして機能する薬剤データ6、血圧測定データ7、患者別データ8とからなる記憶装置5eとからなることを特徴とする。The
前記CPU5aは、記録紙やカルテ等9bにも記録することができるプリンター9a等の出力装置9を備え、前記制御装置3lと同様の機能を有した制御装置5hをコンピュータ5の外部に備えていることを特徴とする。The
コンピュータ5の記憶装置5eは、前記クライアント側であるコンピュータ3の記憶装置3eに一旦格納した膨大な薬剤データ6、血圧測定データ7、患者別データ8をマスターデータとして保管することができる。また制御装置5hは、コンピュータ3を構成する制御装置3lと同様の機能を有すると共にサーバーのコンピュータ5の記憶装置5e全体の正誤性を確認するための装置で、前記入力装置5bまでUSBケーブル等のケーブルで接続している。次に、図3で本発明を構成する降圧剤の評価方法について詳細を説明する。The
図3に示した本発明を構成する降圧剤の評価方法1aは、医師は高血圧のように疾患にかかった薬剤投与患者の選定S1と、選定した患者に対し、薬剤投与前の血圧測定S2をすることから始める。The method 1a for evaluating the antihypertensive agent constituting the present invention shown in FIG. 3 is that the doctor selects S1 of a drug-administered patient suffering from a disease such as hypertension, and performs blood pressure measurement S2 before drug administration on the selected patient. Start by doing.
薬剤投与前の血圧測定S2は、降圧剤の服用を開始する前に予め各患者毎に前記24時間血圧計測装置2を上腕に装着し、血圧等のデータを図1及び図2に示した測定装置2b内部のメモリーに一時的に正確に記録する仕組みである。そして、薬剤投与前の血圧測定S2が終了した後に、薬剤投与後の血圧測定S3となる。なお、患者の血圧の測定方法については、薬剤投与前の血圧測定S2、薬剤投与後の血圧測定S3共に同一とする。The blood pressure measurement S2 before drug administration is performed by previously mounting the 24-hour blood
次に、前記血圧測定S3手段によって測定した血圧等のデータは自動的に図1及び図2に示した24時間血圧計測装置2からクライアントであるコンピュータ3までUSB等のケーブルで送信する。なお、USB、R232C等のケーブルが使用できない場合の手動式データ入力の手段として、測定した血圧データを手入力S4する手段を設けた。よって前記24時間血圧計測装置2で得た記録用紙等の血圧等のデータをキーボード3fを使用し手入力でも行うことができる。Next, data such as blood pressure measured by the blood pressure measurement S3 means is automatically transmitted from the 24-hour blood
データ抽出S5手段は、コンピュータ3が自動的に薬剤データ3i、血圧測定データ3j、患者別データ3kとからなる記憶装置3eにアクセスし、特定の降圧剤の投与前と投与後のデータであるデータ抽出S5する条件となる薬剤の種類や、収縮期血圧・拡張期血圧、心拍数などのパラメータ及び、コロトコフ、オシロメトリック等の測定方法等に沿ってコンピュータ3のCPU3aまで送信する手段である。Data extraction S5 means that the
差分曲線算出S6手段は、コンピュータ3のCPU3a又はコンピュータ5のCPU5aを用いて、各種降圧剤毎の降圧剤の投与後データから、各種降圧剤毎の降圧剤の投与前データを差し引く差引手段と、差し引いた後の各値に基づいて、各種降圧剤毎の差分値の平均値から降圧剤毎に差分曲線を差し引き、定量的かつ日内変動パターンとして出力する手段である。The difference curve calculation S6 means uses the CPU 3a of the
本発明は、前記複数の差分曲線で、個々の患者が持っている特有の血圧日内変動パターンを表示できると共に、降圧剤の最大降圧度及び最大降圧時間を評価することでき、なおかつ、降圧剤投与後の経過時間により、どれほどの降圧度が得られるのかについての評価を行うこともできる。The present invention is capable of displaying a peculiar blood pressure diurnal variation pattern possessed by each patient with the plurality of difference curves, and evaluating the maximum antihypertensive degree and the maximum antihypertensive time of the antihypertensive agent, and administering the antihypertensive agent It is also possible to evaluate how much the degree of pressure reduction can be obtained by the elapsed time later.
また、前記差分曲線の最下点となる最大降圧度(降圧ピーク値、単位:mmHg)及び、差分曲線の最上点となる最小降圧度(降圧トラフ値、単位:mmHg)のそれぞれを求めることができると共に、前記最大降圧度、最小降圧度からなるT/P比を評価できることを特徴とする。詳細は図5で説明をする。In addition, each of the maximum step-down degree (step-down peak value, unit: mmHg) serving as the lowest point of the difference curve and the minimum step-down degree (step-down trough value, unit: mmHg) serving as the top point of the difference curve may be obtained. In addition, it is possible to evaluate a T / P ratio composed of the maximum and minimum pressure reduction degrees. Details will be described with reference to FIG.
降圧面積算出S7手段は、降圧度mmHgと、降圧時間(分)の積分量である。即ち、前記差分曲線を構成する縦軸のmmHgを上底及び下底とし、横軸の時間を高さとして略台形状の降圧部分面積を演算し、前記降圧部分面積を30分毎の積分を行い、その合計である降圧面積を算出及び表示する手段であるThe step-down area calculation S7 means is an integrated amount of the step-down degree mmHg and the step-down time (minutes). That is, the vertical axis mmHg constituting the difference curve is set as the upper and lower bases, the horizontal time is set as the height, the substantially trapezoidal step-down partial area is calculated, and the step-down partial area is integrated every 30 minutes. This is a means to calculate and display the total step-down area.
また前記降圧面積評価手段S7は、降圧剤の投与後データから降圧剤の投与前データを差し引き、各降圧剤毎の差分値の平均値から差分曲線を算出して降圧部分面積を演算し、前記降圧面積をディスプレイ3h上に表示できることを特徴とする。The antihypertensive area evaluation means S7 subtracts the data before administration of the antihypertensive agent from the post-administration data of the antihypertensive agent, calculates a differential curve from the average value of the difference values for each antihypertensive agent, calculates the antihypertensive partial area, The step-down area can be displayed on the
降圧評価表示S8手段は、ディスプレイ3h上に表示した差分曲線上に、降圧剤を投与したポイントは、三角形や菱形などの記号や符号等を用いて医師に視覚的にわかりやすく表示でき、なおかつ、次回の薬剤投与時間などの表示をディスプレイ3h上に表示することができる。次に図4及び図5にて、前記差分曲線の詳細と降圧面積の詳細について説明をする。The antihypertensive evaluation display S8 means, on the difference curve displayed on the
図4は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置で出力した差分値データ表の降圧部分面積を示した正面図、図5は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置で患者の24時間血圧計測装置2の血圧等のデータから正しい血圧値及び血圧の日内変動を抽出し、出力した差分値データ表の降圧面積を示した正面図である。FIG. 4 is a front view showing the antihypertensive partial area of the differential value data table output by the method and apparatus for evaluating antihypertensive agents according to the present invention, and FIG. It is the front view which showed the pressure | voltage fall area of the difference value data table | surface which extracted the correct blood pressure value and the diurnal variation of the blood pressure from data, such as a blood pressure of the 24-hour blood
なお、図4及び図5に示した差分値データ表10は、前記差分曲線算出S6手段、前記降圧面積算出S7手段、前記降圧評価表示S8手段からなり、医師が降圧剤等の薬剤である降圧剤Xを使用している患者から得た24時間血圧計測装置2のデータから、前記差分曲線算出S6手段により、薬剤投与後の血圧等のデータから、薬剤投与前の血圧等のデータを差引くことで各血圧等のデータ毎に差分曲線に変え、降圧面積算出S7で降圧部分面積を算出し、降圧評価表示S8で、前記降圧部分面積の合計である降圧面積全体を黄色等の斜線で着色することである。The difference value data table 10 shown in FIGS. 4 and 5 includes the difference curve calculation S6 means, the antihypertensive area calculation S7 means, and the antihypertensive evaluation display S8 means. Subtract data such as blood pressure before drug administration from data such as blood pressure after drug administration from the data of the 24-hour blood
本発明で使用する差分曲線は、第1差分曲線10c、第2差分曲線10d、第3差分曲線10eからなり、余弦曲線の最上点である降圧ピーク値と最小値である降圧トラフ値の差の1/2と、余弦曲線の最下点を示す時刻の3要素からなることを特徴とする。The difference curve used in the present invention includes a
本発明の場合、各患者毎に対応する血圧等のデータに欠損が生じた場合でも、前記サーバーのコンピュータ5から、各患者毎に対応した平均値データから前記欠損データ得ることができる。なお、本発明では、24時間の単一周期のみから降圧面積を算出しているが、12時間周期、8時間周期、48時間周期のように周期時間を変動しても降圧面積を自由に算出することができる。In the case of the present invention, even when data such as blood pressure corresponding to each patient is deficient, the deficient data can be obtained from the average value data corresponding to each patient from the
前記差分曲線は、コサイナー法を構成するコサインフィティング法等(cosinefitting)を用いて時系列データを最適余弦曲線等で回帰するもでき、かつ、前記コサインフィティング法(cosinefitting)に限定せず、シングルコサイナー法(single cosinor)、ポピュレイションミーンコサイナー法(population−mean cosinor)、そして、24時間に亘る時系列データを周期回帰する場合に血圧日内変動の中の12時間、8時間等のより短い周期までデータのとして取り込むことができる離散フーリエ変換(DFT)法等を取り込むことでより最適な差分曲線とすることもできる。The difference curve may be obtained by regressing time series data with an optimal cosine curve or the like using a cosine fitting method or the like (cosine fitting) constituting the cosigner method, and is not limited to the cosine fitting method (cosine fitting). Single-cosinor method, population-mean-cosinor method, and 12 hours, 8 hours, etc. in the blood pressure circadian variation when time series data over 24 hours is periodically regressed A more optimal difference curve can be obtained by capturing a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) method or the like that can be captured as data up to a shorter period.
また、平滑化手法として、前記差分曲線を構成する各点に関し、隣接する3点又は4点の平均値を求め、これを1時点のデータとして置き換える移動平均法などで、
各患者毎、各降圧剤のデータ毎の平均値を求めることができる。Further, as a smoothing method, for each point constituting the difference curve, an average value of three or four points adjacent to each other is obtained, and this is replaced with data at one time point.
The average value for each patient and for each data of each antihypertensive agent can be obtained.
図4に示した差分値データ表10の縦軸は、収縮期血圧10c、拡張期血圧10d、心拍数10eの差分値10aを10毎に6区分に分けて表示した±30(単位:mmHg、或いは心拍数/分)の範囲で表示し、横軸は、患者が降圧剤を投与した直後で単位:mmHg、或いは(心拍数/分)である0:00から30分毎に24時間分である48区分を構成する時間軸10bを設けた。 The vertical axis of the difference value data table 10 shown in FIG. 4 indicates ± 30 (unit: mmHg, in which the
本発明において、前記差分値10aの範囲及び、時間軸10bについて各範囲を限定せず、自由に変更することができる。時間軸10bは、降圧剤投与後からの累計時間のみならず、時計等のように10時、14時等のように現在時刻の表示と投与後の累計時間の表示を併せて行うこともできる。また降圧剤を投与したポイントは、三角形や菱形などの記号や符号を用いて、視覚的にわかりやすく表示できる。In the present invention, the range of the
図4の上部に示した縦軸の基準血圧10lとなる0mmHg以下は、赤色等で収縮期血圧であるSYSの数値や第1差分曲線10cを示し、以下同様に青色等で拡張期血圧であるDIAの数値や第2差分曲線10dを示し、緑色等で心拍数であるPRの数値や第3差分曲線10eを示した。なお、前記SYS:10c、DIA:10d、PR:10eの数値及び曲線に付す色は自由に変更ができる。Below 0 mmHg, which is the reference blood pressure 10 l on the vertical axis shown in the upper part of FIG. 4, shows the numerical value of SYS, which is systolic blood pressure in red and the like, and the
図4に示した略台形状のA’、B’、C’・・A、B、Cの面積は降圧部分面積15である。前記降圧部分面積15は、緩やかに右上方向に上昇していく収縮期血圧(SYS)を構成する第1差分曲線10cと、縦軸の基準血圧10lの0mmHgとの間の面積となる。The areas of the substantially trapezoidal shapes A ′, B ′, C ′... A, B, C shown in FIG. The hypotensive
収縮期血圧の場合の降圧面積:10gは、第1差分曲線10cと横軸の基準線0mmHgとの間に囲まれた降圧部分面積の合計となる。降圧剤Xは、前記収縮血圧の降圧面積は、−25140(単位:mmHg・分)と図4の上部に表示する。The pressure reduction area in the case of systolic blood pressure: 10 g is the sum of the pressure reduction partial areas surrounded between the
なお、収縮期血圧の降圧面積15が−25140mmHg分であるということは、即ち、1日では1440分となり、−25140を前記1440分で除すると平均−17.46mmHgの降圧効果が得られることを示している。また拡張期血圧であるDIA10h、心拍数/分であるPR10iも同様に算出できる。It should be noted that the systolic blood
拡張期血圧の場合の降圧面積:10hは、第2差分曲線10dと縦軸の基準である0mmHgとの間に囲まれた降圧部分面積の合計となり、心拍数であるPR:10iは、第3差分曲線10eと縦軸にある基準血圧0mmHgとの間に囲まれた心拍数部分面積の合計となる。Decreased area in the case of diastolic blood pressure: 10h is the sum of the hypotensive partial areas enclosed between the
本発明は、収縮期血圧であるSYS:10gの降圧部分面積15から降圧面積15aを自動的に算出できることで前記降圧部分面積の集合体である降圧面積の色分けを行うと共に、降圧面積の大きさによって、医師が降圧剤の効果の大きさを視覚的に判断でき、更に患者の日内変動パターンまでを考慮して使用中の降圧剤の評価を行うことができる。According to the present invention, the
また降圧面積15aの基準となる面積値は、降圧剤X以外の各製薬メーカー等の降圧剤の種類毎に異なる。よって、降圧面積15aの大きさとなる基準血圧は限定をしない。なお降圧面積15aの基準血圧をより多く得るために、前記インターネット通信回線4を経て、サーバーのコンピュータ5から、1種類の降圧剤毎に20人前後の患者データから検出し、平均値を、クライアントのコンピュータ3の降圧面積の基準血圧とすることができる。Moreover, the area value used as the reference | standard of the
図5に示したのは、前記図4に示した降圧部分面積15の合計となる降圧面積である。図5は収縮期血圧である第1差分曲線10cと降圧面積15aの詳細を中心に説明する。本発明を構成する前記第1差分曲線10c及び降圧面積15aは、1日1回服用の持続性のカルシウム拮抗薬等で生じるT/P比となるトラフ/ピーク比を自動的に算出し、前記降圧面積15aに隣接して表示できることを特徴としている。FIG. 5 shows the step-down area that is the sum of the step-down
トラフ/ピーク比は、1988年にFDA(米国食品医薬局)の降圧薬評価ガイドライン中で提唱された降圧剤の持続性を評価する指標で、降圧剤服用後の降下度の最大値(降圧ピーク値)から、次回の降圧剤服用前の降圧度の最小値(降圧トラフ値)との比率である。尚、理想は100%であるが(日内変動全くなし)だが、実際の降圧薬では、50%以上あることが望ましい。The trough / peak ratio is an index for evaluating the sustainability of antihypertensive drugs proposed in 1988 by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) antihypertensive drug evaluation guidelines. Value) to the minimum value of the antihypertensive level (antihypertensive trough value) before taking the next antihypertensive agent. Although the ideal is 100% (no daily fluctuation), it is desirable that the actual antihypertensive drug is 50% or more.
本発明は降圧剤Xとしてカルシウム拮抗薬であるニフェジピンを用い、血圧日内変動の中で第1差分曲線10c上に降圧トラフ値10jと降圧ピーク値10fの各々を示し、次回降圧剤を服用する直前等に多く見られる降圧効果が最小となる最小降圧度となる降圧トラフ値10jをX軸方向に対して時間軸10b毎に示した表上に数字で示すと共に、逆正三角形等の図形とトラフの頭文字であるTの文字を組み合わせた文字図形でX軸上に自動的に示すことができる。The present invention uses nifedipine, which is a calcium antagonist, as the antihypertensive X, and shows each of the
また降圧剤を投与したとき、血中濃度が上昇して降圧効果が最大となる最大降圧度を構成する降圧ピーク値10fをX軸方向に対して時間軸10b毎に示した表上に数字で示すと共に、正三角形等の図形とピークの頭文字であるPの文字を組み合わせた文字図形でX軸上に自動的に示すことができる。In addition, when an antihypertensive agent is administered, the
よって差分曲線から、患者の最大降圧度及び、最大降圧時間を評価できると共に、降圧剤投与後の経過時間や降圧剤を投与してからの累計時間(図示せず)を図4及び図5のディスプレイ上に表示することができる。さらにまた前記降圧トラフ値と降圧トラフ値との双方からなるトラフ/ピーク比については、前記第心拍数であるPR10iに隣接して、T/P比10k、44.0(%)として自動的に表示することができる。Therefore, from the difference curve, the maximum antihypertensive degree and the maximum antihypertensive time of the patient can be evaluated, and the elapsed time after administration of the antihypertensive agent and the cumulative time after administration of the antihypertensive agent (not shown) are shown in FIG. 4 and FIG. Can be displayed on the display. Further, the trough / peak ratio composed of both the step-down trough value and the step-down trough value is automatically set as a T / P ratio of 10k, 44.0 (%) adjacent to the PR10i as the heart rate. Can be displayed.
前記T/P比10kの算出方法は、収縮期血圧の場合、SYS10gの降圧トラフ値10jの値である−11、降圧ピーク値10fの値である−25で割り、百分率に直すことで前記T/P比10kを算出することができる。In the case of systolic blood pressure, the calculation method of the T /
なお、24時間血圧計測装置2で、24時間の計測をしたが<領域Y>のように、計測忘れ、若しくはデータ不十分等のように、血圧等のデータ等のデータの欠損を生じた場合、
各降圧剤毎、各患者毎のデータを参照し、時間毎に隣接するデータを自動的に前記欠損データとして補完することができる。In addition, when 24-hour blood
By referring to the data of each antihypertensive agent and each patient, the adjacent data can be automatically supplemented as the missing data every time.
図6は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置の薬剤投与前のデータ表の正面図、図7は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置の薬剤投与後のデータ表の正面図、図8は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置の差分値データ表の降圧部分面積の拡大図である。FIG. 6 is a front view of a data table before drug administration of the antihypertensive evaluation method and apparatus according to the present invention, and FIG. 7 is a front view of the data table after drug administration of the antihypertensive evaluation method and apparatus according to the present invention. FIG. 8 is an enlarged view of the hypotensive partial area of the difference value data table of the hypotensive agent evaluation method and apparatus according to the present invention.
図6及び図7のデータ表11、12に示したように、縦軸である収縮期血圧(SYS)及び拡張期血圧(DIA)については、水銀柱ミリメートル11a、12aであるmmHgを単位とした。なお、横軸である心拍数(PR)については、心拍数/分とした。
前記図4及び図5と同様に横軸は、患者が降圧剤を投与した直後である0:00から30分毎に24時間分の48枠を構成する時間軸11b、12bとし、符号11c、12cは、SYSである収縮期血圧曲線であり、符号11d、12dは、DIAである拡張期血圧曲線、符号11e、12eは、PRである心拍数曲線とする。As shown in the data tables 11 and 12 of FIGS. 6 and 7, the systolic blood pressure (SYS) and the diastolic blood pressure (DIA) which are the vertical axis are expressed in mmHg which are millimeters of
Similar to FIGS. 4 and 5, the horizontal axis represents time axes 11b and 12b constituting 48 frames for 24 hours every 30 minutes from 0:00, which is immediately after the patient has administered the antihypertensive agent.
図8に示した第1差分曲線10cは、基準血圧10lである0mmHgとの間に設けた複数の略台形状の降圧部分面積15の合計である降圧面積15aからなることを特徴とする。なお、図8に示したAの部分降圧面積を算出する場合には、上底、下底を各L1、L2等のL*とし、時間軸をT1、T2とするT*とする場合、降圧部分面積は((L1+L2)×T1))/2となり、次のBの降圧部分面積を((L2+L3)×T2)/2)とし、以下、A、B、C・・・のように順次面積を合計することで、患者の24時間血圧計測装置を装着した際の全体の降圧面積15aを表示することができる。The
なお、図9は、本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置で、本発明で使用する降圧剤等の薬剤データ等を入力するための入力画面13の正面図である。図9に示したように入力画面13には、タイトル13aとなる「血圧測定データグラフ表示」と表示され、表示画面内の構成を、データ選択ボタン13b、薬剤・患者選択ボタン13c、そして血圧等のデータを、各差分曲線に変換し、基準との間に囲まれた面積である降圧面積に変換できるデータ変換ボタン13dを備えている。FIG. 9 is a front view of an
図10に示したのは、本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置の第2実施例である。図1に示した構成との相違点は、クライアントであるコンピュータ3の外部接続装置としてICカード14aの読み取り、書き込みを可能としたカードリーダー14を設けたことを特徴とするものである。FIG. 10 shows a second embodiment of the antihypertensive evaluation method and apparatus according to the present invention. The difference from the configuration shown in FIG. 1 is that a
クライアントのコンピュータ3は、24時間血圧計測装置2で得た血圧等のデータを外部装置のカードリーダー14に送ることで、診察券となるICカード14a内部に前記血圧等のデータ、本発明で算出した降圧面積等の評価・判定結果となるデータを記録することができる。The
カードリーダー14は、前記ICカード14aに内部から血圧等のデータを読み取ることのみならず、書き込みである記録もできる装置である。なお、前記入力装置3bの接続部3gまでUSBケーブルのみならず、R232Cケーブル等のデータを出力するケーブル等で接続している。The
即ち、担当医が変更になった場合や、外出先で事後に遭遇した場合でも、本発明を構成する降圧面積等の評価・判定の結果を患者毎の固有のデータとして所持できるようになるため、急遽、担当医以外の医師が降圧剤を投与しなければならない場合でも、クライアントのコンピュータ3、サーバーのコンピュータ5の記憶装置にアクセスできる送受信装置を備え、かつ、カードリーダ14等を備えたデスクトップ型コンピュータ、ノートブック型のコンピュータ、PDA型端末装置等のようにコンピュータさえあれば、降圧剤を投与する時期の見極や、降圧剤の持続性の有無を医師は迅速にかつ簡単に判断することができる。In other words, even if the doctor in charge changes or encounters later on the go, it is possible to have the results of evaluation / determination of the pressure-lowering area etc. constituting the present invention as unique data for each patient Urgently, even if a doctor other than the attending physician has to administer the antihypertensive agent, the desktop is provided with a transmission / reception device that can access the storage device of the
図11は本発明である降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置で出力した降圧剤Xを服用した後
の24時間血圧を予測を示したデータ表16である。今データ表16は、縦軸である収縮期血圧(SYS)及び拡張期血圧(DIA)を水銀柱ミリメートル16aとし、横軸に時間軸等16b及び、服用前収縮期血圧16c、服用後収縮期血圧16d、及び、差分収縮期血圧16eの数値一覧を表示できることとした。FIG. 11 is a data table 16 showing the prediction of blood pressure for 24 hours after taking the antihypertensive agent X output by the method for evaluating antihypertensive agents and the device according to the present invention. The present data table 16 shows that the vertical axis is systolic blood pressure (SYS) and diastolic blood pressure (DIA) 16 millimeters of mercury, the horizontal axis is
前記図1等に示した24時間血圧計測装置2で計測した患者の血圧データから、当該降圧剤の前記差分曲線値を差し引くことで、当該降圧剤をその患者に処方した場合の日内血圧データを予測できることを特徴とする。By subtracting the difference curve value of the antihypertensive agent from the blood pressure data of the patient measured by the 24-hour blood
データ表を出力する装置の構成は、実施例1の装置構成を示した図1及び図2に示した24時間血圧計測装置2と前記24時間血圧計測装置2から血圧データ等を記憶装置3eで入出力できるコンピュータ3、及びデータ抽出手段等を使用する。また元データとして図6及び図7に示した薬剤投与前のデータ表の曲線である符号11c、薬剤投与後のデータ表の曲線である符号12cをそのまま使用することができる。The configuration of the device for outputting the data table is the 24-hour blood
即ち、本発明では従来24時間血圧計測装置2で得た膨大な血圧データを活用できなかった問題を、グラフや数値等のように定量的かつ視覚的に表示できるため、降圧剤Xの効果を予め降圧面積として予想できると共に、患者に直接降圧剤を投与しなくても患者に処方する降圧剤の効果及び日内血圧データを容易に予測することができる。That is, in the present invention, the problem that the vast blood pressure data obtained by the conventional 24-hour blood
1 降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置
1a 降圧剤の評価方法
2 24時間血圧計測装置
2a カフ帯
2b 測定装置
2c 接続ケーブル
3 コンピュータ
3a CPU
3b 入力装置
3c 出力装置
3d 送受信装置
3e 記憶装置
3f キーボード
3g 接続部
3h ディスプレイ
3i 薬剤データ
3j 血圧測定データ
3k 患者別データ
3l 制御装置
4 インターネット通信回線
5 コンピュータ
5a CPU
5b 入力装置
5c 出力装置
5d 送受信装置
5e 記憶装置
5f キーボード
5g ディスプレイ
5h 制御装置
6 薬剤データ
7 血圧測定データ
8 患者別データ
9 出力装置
9a プリンター
9b カルテ等
10 差分値データ表
10a 差分値
10b 時間軸
10c 第1差分曲線
10d 第2差分曲線
10e 第3差分曲線
10f 降圧ピーク値
10g SYS
10h DIA
10i PR
10j 降圧トラフ値
10k T/P比
10l 基準血圧
11 データ表
11a 水銀柱mmHg
11b 時間軸
11c 符号
11d 符号
11e 符号
12 データ表
12a 水銀柱mmHg
12b 時間軸
12c 符号
12d 符号
13 入力画面
13a タイトル
13b データ選択ボタン
13c 薬剤・患者選択ボタン
13d データ変換ボタン
14
カードリーダー
14a ICカード
15 降圧部分面積
15a 降圧面積
16 データ表
16a 水銀柱ミリメートル
16b 時間軸等
16c 服用前収縮期血圧
16d 服用後収縮期血圧
16e 差分収縮期血圧
17 出力装置
17a プリンター
S1 薬剤投与患者の選定
S2 薬剤投与前の血圧測定
S3 薬剤投与後の血圧測定
S4 測定した血圧データを入力
S5 データ抽出
S6 差分曲線算出
S7 降圧面積算出
S8 降圧評価表示
DESCRIPTION OF
10h DIA
10i PR
10j Blood
Claims (7)
Translated fromJapanese前記コンピュータに蓄積した血圧データ等から同一患者における特定の降圧剤の投与前と投与後のデータを自動的に抽出するデータ抽出手段、データ抽出手段によって抽出したデータを基に降圧剤の投与前と投与後の差分曲線を定量的かつ日内変動パターンとして算出及び表示する差分曲線算出手段、差分曲線と基準血圧0mmHgとの間で囲まれた降圧面積を算出する降圧面積算出手段、算出した前記差分曲線と前記降圧面積から自動的に降圧ピーク値等の評価をディスプレイ上に表示できる評価表示手段とからなることを特徴とする降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置。In a computer capable of inputting / outputting blood pressure data and the like from the 24-hour blood pressure measurement device and the 24-hour blood pressure measurement device,
Data extraction means for automatically extracting data before and after administration of a specific antihypertensive agent in the same patient from blood pressure data and the like stored in the computer, before administration of the antihypertensive agent based on the data extracted by the data extraction means Difference curve calculation means for calculating and displaying a difference curve after administration as a quantitative and diurnal variation pattern, an antihypertensive area calculation means for calculating an antihypertensive area enclosed between the difference curve and a reference blood pressure of 0 mmHg, and the calculated difference curve And an evaluation display means capable of automatically displaying an evaluation of the peak value of the anti-hypertensity on the display from the anti-hypertensive area and an apparatus for evaluating the anti-hypertensive agent.
各降圧剤毎の差分値の平均値から差分曲線を算出して降圧部分面積を演算し、前記降圧面積をディスプレイ上に表示できることを特徴とする請求項1項に記載の降圧剤の評価方法及びその装置The antihypertensive area evaluation means subtracts pre-administration data of antihypertensive agents from post-administration data of antihypertensive agents,
The method for evaluating an antihypertensive agent according to claim 1, wherein a difference curve is calculated from an average value of the difference values for each antihypertensive agent, a hypotensive partial area is calculated, and the antihypertensive area can be displayed on a display. The device
請求項1項又は、請求項2項に記載の降圧剤の効果の評価方法The method for evaluating the effect of an antihypertensive agent according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the antihypertensive area calculating means can quantitatively evaluate the antihypertensive effect of the antihypertensive agent.
The daily blood pressure data when the antihypertensive agent is used for the patient can be predicted by subtracting the difference curve value of the antihypertensive agent from the blood pressure data of the patient measured by the 24-hour blood pressure measuring device. The method for evaluating an antihypertensive agent according to any one of claims 1 to 6.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004278382AJP2006087746A (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2004-09-24 | Evaluation method of hypotensor and apparatus therefor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004278382AJP2006087746A (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2004-09-24 | Evaluation method of hypotensor and apparatus therefor |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006087746Atrue JP2006087746A (en) | 2006-04-06 |
Family
ID=36229251
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004278382APendingJP2006087746A (en) | 2004-09-24 | 2004-09-24 | Evaluation method of hypotensor and apparatus therefor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006087746A (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE112007000508T5 (en) | 2006-03-28 | 2009-01-29 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Kadoma-shi | Method for determining a mounting condition |
| JP2010142273A (en)* | 2008-12-16 | 2010-07-01 | Omron Healthcare Co Ltd | Biomarker management apparatus |
| JP2010279399A (en)* | 2009-06-02 | 2010-12-16 | Nikkiso Co Ltd | Patient data management device |
| JP2016095653A (en)* | 2014-11-13 | 2016-05-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing system, information processing apparatus, information processing method, and information processing program |
| JP2016093314A (en)* | 2014-11-13 | 2016-05-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing system, information processing apparatus, information processing method, and information processing program |
| CN111226285A (en)* | 2017-10-18 | 2020-06-02 | 佳能医疗系统株式会社 | Hospital Information System and Image Data Generation Program |
| JPWO2021210172A1 (en)* | 2020-04-17 | 2021-10-21 | ||
| CN117247329A (en)* | 2023-09-19 | 2023-12-19 | 苏州泽厚生物科技有限公司 | Preparation method of amino-protected benzocyclone compounds |
- 2004
- 2004-09-24JPJP2004278382Apatent/JP2006087746A/enactivePending
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE112007000508T5 (en) | 2006-03-28 | 2009-01-29 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Kadoma-shi | Method for determining a mounting condition |
| JP2010142273A (en)* | 2008-12-16 | 2010-07-01 | Omron Healthcare Co Ltd | Biomarker management apparatus |
| JP2010279399A (en)* | 2009-06-02 | 2010-12-16 | Nikkiso Co Ltd | Patient data management device |
| JP2016095653A (en)* | 2014-11-13 | 2016-05-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing system, information processing apparatus, information processing method, and information processing program |
| JP2016093314A (en)* | 2014-11-13 | 2016-05-26 | 日本電気株式会社 | Information processing system, information processing apparatus, information processing method, and information processing program |
| CN111226285A (en)* | 2017-10-18 | 2020-06-02 | 佳能医疗系统株式会社 | Hospital Information System and Image Data Generation Program |
| JPWO2021210172A1 (en)* | 2020-04-17 | 2021-10-21 | ||
| WO2021210172A1 (en)* | 2020-04-17 | 2021-10-21 | 日本電気株式会社 | Data processing device, system, data processing method, and recording medium |
| JP7409486B2 (en) | 2020-04-17 | 2024-01-09 | 日本電気株式会社 | Data processing device, system, data processing method, and program |
| CN117247329A (en)* | 2023-09-19 | 2023-12-19 | 苏州泽厚生物科技有限公司 | Preparation method of amino-protected benzocyclone compounds |
| CN117247329B (en)* | 2023-09-19 | 2025-09-19 | 苏州泽厚生物科技有限公司 | Preparation method of amino-protected benzocyclic ketone compound |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7124453B2 (en) | Medication management device, medication management method and medication management program | |
| JP4025220B2 (en) | Blood pressure monitor and cardiovascular disease risk analysis program | |
| JP3668843B2 (en) | Electronic blood pressure monitor and blood pressure measurement data processing system | |
| Imai et al. | The Japanese Society of Hypertension guidelines for self-monitoring of blood pressure at home | |
| USRE41236E1 (en) | Method and apparatus for multiple patient parameter variability analysis and display | |
| TWI303985B (en) | A blood pressure measuring device and a method for operating a blood pressure measuring device | |
| US20080294021A1 (en) | System and Method for the Management or Control of Cardiovascular Related Diseases, Such as Hypertension | |
| US20110009714A1 (en) | Hemodynamic monitors and alarms | |
| US20040111034A1 (en) | System for measuring at least one body parameter, a blood pressure monitor and a medical thermometer | |
| JP7076967B2 (en) | Data processing equipment, data processing method and data processing program | |
| Head et al. | Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring | |
| US20210118539A1 (en) | Medication management device, medication management method, and non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing medication management program | |
| WO2007116635A1 (en) | Blood pressure meter where variation in blood pressure value can be known | |
| Islam | Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension | |
| WO2018235652A1 (en) | HEALTH MANAGEMENT DEVICE, HEALTH MANAGEMENT METHOD, AND HEALTH MANAGEMENT PROGRAM | |
| JP2006087746A (en) | Evaluation method of hypotensor and apparatus therefor | |
| TWI328439B (en) | A system and method for hypertension management | |
| WO2023112779A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and program | |
| US7678060B1 (en) | Method of monitoring a state of health, and a wellness/emotional state monitor implementing the method | |
| Zuspan et al. | Blood pressure self-monitoring during pregnancy: practical considerations | |
| US6878116B2 (en) | Blood pressure analyzer | |
| Janicki-Deverts et al. | Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring | |
| De Lusignan et al. | Measuring blood pressure at the wrist: more comfortable for patients and more convenient for doctors? | |
| JP6926399B2 (en) | Diagnostic support device, diagnostic support method, and diagnostic support program | |
| RAYBURN et al. | Portable blood pressure monitoring for borderline or mild hypertension during pregnancy |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20060310 | |
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date:20070202 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20070411 | |
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date:20070508 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20070511 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20070703 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20070913 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20071112 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20080130 |