JP2005352754A - Information navigation apparatus, method, program, and recording medium - Google Patents
Information navigation apparatus, method, program, and recording mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005352754A JP2005352754AJP2004172683AJP2004172683AJP2005352754AJP 2005352754 AJP2005352754 AJP 2005352754AJP 2004172683 AJP2004172683 AJP 2004172683AJP 2004172683 AJP2004172683 AJP 2004172683AJP 2005352754 AJP2005352754 AJP 2005352754A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information
- content
- user
- viewing
- viewing tendency
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
- Two-Way Televisions, Distribution Of Moving Picture Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese本発明は、情報ナビゲーション装置、方法、プログラム、及び記録媒体に関し、より詳細には、ユーザのデジタルコンテンツに対する視聴傾向を分析し、その分析結果に基づいてユーザの視聴に適したコンテンツ情報を出力するための情報ナビゲーション装置、情報ナビゲーション方法、プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体に関する。 The present invention relates to an information navigation apparatus, method, program, and recording medium. More specifically, the present invention analyzes a viewing tendency of a user with respect to digital content, and outputs content information suitable for viewing by the user based on the analysis result. The present invention relates to an information navigation device, an information navigation method, a program, and a computer-readable recording medium on which the program is recorded.
昨今、パーソナルコンピュータ(以下、PCと略す)やDVDプレーヤ等のデジタル機器が普及し、ブロードバンドの普及による高速ネットワーク化が進み、さらには、デジタル放送が本格的に開始されつつある状況で、デジタルコンテンツ提供サービスを利用するにあたって、ユーザを取り巻く環境が大きく変化しようとしている。 In recent years, digital devices such as personal computers (hereinafter abbreviated as “PCs”) and DVD players have become widespread, high-speed networks have been promoted due to the spread of broadband, and digital broadcasting has started in earnest. The environment surrounding users is about to change drastically when using the provided services.
これまでユーザは、例えば、アナログTV受像機でTV放送を視聴し、オーディオ機器で音楽コンテンツ等を視聴し、ビデオデッキでビデオコンテンツを視聴しており、これらはそれぞれ異なる種類のコンテンツとして認識されていた。ところが、現在、これらのコンテンツは揃ってデジタル化されており、また、一般家庭でのPCやホームネットワーク,家庭内LAN等の普及により、様々な種類及び内容のデジタルコンテンツを同じシステムで取り扱うことが可能となっている。 Until now, for example, users have been watching TV broadcasts on analog TV receivers, viewing music content and the like on audio devices, and viewing video content on video decks, which are recognized as different types of content. It was. However, these contents are currently digitized together, and various types and contents of digital contents can be handled by the same system by the spread of PCs, home networks, home LANs, etc. in ordinary homes. It is possible.
すなわち、各種デジタル放送からの映像・音声コンテンツ、デジタルビデオやCD/MD/DVDプレーヤなどのデジタル機器から再生される映像・音声コンテンツ、PCのハードディスクなどから再生される映像・音声コンテンツ、インターネットを通じてオンライン配信される映像・音声コンテンツなど、多種多様なソースからのデジタルコンテンツを同一のシステムにおいて記録したり視聴したりすることが可能となっている。 That is, video / audio content from various digital broadcasts, video / audio content played from digital devices such as digital video and CD / MD / DVD players, video / audio content played from PC hard disks, etc., online via the Internet It is possible to record and view digital content from various sources such as video / audio content to be distributed in the same system.
例えば、IEEE1394やIEEE802.bなどの通信規格により高速通信可能な家庭内ネットワークを構成し、このネットワークを通じてデジタルAV機器やパーソナルコンピュータを相互に接続し、連携して動作させるHAVi(Home Audio Video Interoperability)システムなどが提案されている。 For example, IEEE 1394 or IEEE 802. HAV (Home Audio Video Interoperability) system that configures a home network capable of high-speed communication according to communication standards such as “b”, connects digital AV devices and personal computers to each other through this network, and operates in cooperation with each other has been proposed. Yes.
上述のごときデジタルコンテンツ視聴環境において、ユーザは、リアルタイムで提供されているものと記録装置に記録されているものとを含めた膨大な量のデジタルコンテンツの中から、好みのコンテンツを選択して視聴することになる。 In the digital content viewing environment as described above, the user selects and views a favorite content from a huge amount of digital content including what is provided in real time and what is recorded on the recording device. Will do.
このとき、単に利用可能なデジタルコンテンツを列挙するのみでは、デジタルコンテンツがあまりに膨大な数存在するため、ユーザが好みのコンテンツを検索し選択するのに大変な時間がかかってしまい、操作も極めて煩雑になってしまう。これは、あたかも、コンピュータの発達に伴って、あらゆる分野で電子データのデータベースが形成・蓄積されたため、どのようなデータがどこに保存されているかをユーザが容易に把握することができなくなったことに相似している。 At this time, simply enumerating the available digital contents has an enormous number of digital contents, so it takes a long time for the user to search for and select the desired contents, and the operation is extremely complicated. Become. This is because the database of electronic data has been formed and accumulated in every field with the development of computers, making it impossible for users to easily understand what data is stored where. It is similar.
そこで、各デジタルコンテンツの種類(ジャンル)に注目した分類をしておき、ユーザはこの分類情報をもとにコンテンツ検索を行うようにすることが提案されている。例えば、デジタルコンテンツを、映画,音楽,アニメ,スポーツなどといった大きな区分で分類し、さらに、映画であればアドベンチャー映画,SF映画などといった小さい区分で分類するような階層構造の分類体系を用いることができる。これにより、例えば、ユーザが特定の映画を視聴しようとした場合には、大分類で映画を選択した後、小分類でSF映画を選択し、表示されたSF映画のタイトル一覧から視聴しようとしているタイトルを選択することができる。 Therefore, it has been proposed to classify each digital content by focusing on the type (genre) and to perform a content search based on this classification information. For example, it is possible to use a hierarchical classification system that classifies digital content into large categories such as movies, music, animation, sports, etc., and further classifies digital content into small categories such as adventure movies and SF movies. it can. Thereby, for example, when the user intends to view a specific movie, after selecting a movie with a large classification, an SF movie is selected with a small classification, and the user intends to view the title from the displayed SF movie title list. A title can be selected.
上述のごとく、デジタルコンテンツの視聴に対しては、従来のテレビジョン受像機において、EPG(電子番組プログラム)を手掛かりに視聴するチャンネルを選局していたのとは全く異なる視聴環境を形成することになる。 As described above, for the viewing of digital contents, a viewing environment completely different from that in which a conventional television receiver selects a channel for viewing an EPG (electronic program program) is formed. become.
また、情報をその分類に従った階層構造としてデータベースに記憶しておくことにより、ユーザに好適な情報検索環境を提供する情報ナビゲーション装置が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1を参照)。特許文献1には、情報の分類による階層構造の形式が示されている。 In addition, an information navigation apparatus has been proposed that provides an information search environment suitable for a user by storing information in a database as a hierarchical structure according to the classification (see, for example, Patent Document 1). Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2004-228561 shows a hierarchical structure format based on information classification.
上述のごとく、膨大な量のデジタルコンテンツをジャンルごとに分類をしておき、ユーザはこの分類情報をもとにコンテンツ検索を行うようすれば、ユーザが膨大なコンテンツの中から目当てのコンテンツをどのようにして探し出せばいいのか分からなくなるといった問題はなくなるものの、目当てのコンテンツを探し当てるまでの操作はコンテンツ量に比例して煩雑で時間のかかるものとなる。特許文献1に記載の装置を含め、例えば大分類,小分類などと分類分けすることで分類に従った検索を実行する装置にあっては、ユーザは、コンテンツを視聴しようとする度に、コンテンツの大分類,小分類,タイトルの選択といった手順を踏まねばならないことになる。 As described above, if a huge amount of digital content is classified by genre, and the user performs a content search based on this classification information, the user can select the target content from the huge content. Although there is no problem of not knowing whether or not it should be found in this way, the operation until finding the target content becomes complicated and time-consuming in proportion to the amount of content. In an apparatus that executes a search according to classification by classifying it into, for example, a major classification, a minor classification, etc., including the apparatus described in
そこで、ユーザにとってコンテンツ選択の煩わしさを軽減させるため、ユーザが行ったコンテンツ選択の履歴情報を記憶しておき、この履歴情報からユーザのコンテンツに対する視聴を分析して、特に視聴度の高いコンテンツについては、より簡易な操作で選択できる嗜好データ管理方法が提案されている(例えば、特許文献2を参照)。 Therefore, in order to reduce the burden of content selection for the user, the history information of the content selection performed by the user is stored, and the viewing of the user's content is analyzed from the history information, and the content with particularly high audience rating is analyzed. Has proposed a preference data management method that can be selected by a simpler operation (see, for example, Patent Document 2).
特許文献2に記載のデジタル放送における嗜好データ管理方法では、ユーザが番組を視聴した履歴から番組興味度を算出し、この番組興味度と、コンテンツに付与されたコンテンツ属性とを用いて、全てのコンテンツに対する視聴得点を算出し、最も視聴得点の高いコンテンツを最適コンテンツとして選択する。また、特許文献2に記載の嗜好データ管理方法や、他の従来技術における例では、ユーザの視聴の履歴をデータとして予め記憶しておき、これを元にユーザのコンテンツ選択を補助することが行われている。
しかしながら、デジタルコンテンツは、多種多様な映像・音声コンテンツを含んでいるものであり、その性質を客観的、定量的に定義することは容易ではなく、特許文献2をはじめとする従来技術では、これらの多種多様なコンテンツからユーザの視聴に合致したものを客観的な基準で横断検索することはできない。 However, digital contents include a wide variety of video and audio contents, and it is not easy to define their characteristics objectively and quantitatively. In the prior art including
また、従来技術によれば、視聴傾向は、一般に、情報の選択履歴に基づき、情報の選択頻度の、全情報の項目との比率として算出される。この視聴傾向の算出は、ユーザの積極的支援が得られれば、少ない情報選択履歴からでも、かなり的確に割り出すことは可能であるが、一般的には、ユーザは何を選択しようと勝手であり、その選択履歴から選択の根拠や理由を推論することができるとは限らない。 Further, according to the prior art, the viewing tendency is generally calculated as a ratio of the information selection frequency to the items of all information based on the information selection history. This viewing tendency can be calculated fairly accurately from a small information selection history if the user's active support is obtained, but in general, the user is free to choose what to select. It is not always possible to infer the basis and reason for selection from the selection history.
また、単純な全情報の項目の頻度の考慮では、よく出演する脇役が、好みの出演者として判断されてしまい、ユーザの視聴傾向を精度良く推定することができない。更に、ユーザ自身のその日,その時の気分で、視聴したいと思うコンテンツの視聴傾向は絶えず変動する。 Further, in consideration of the frequency of all items of simple information, a supporting role that often appears is determined as a favorite performer, and the viewing tendency of the user cannot be accurately estimated. Furthermore, the viewing tendency of the content that the user wants to view constantly changes according to the feeling of the user himself / herself on that day.
本発明は、上述のごとき実情に鑑みてなされたものであり、膨大な量のデジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向をできるだけ客観的な尺度で把握し、これに基づきユーザのコンテンツ選択の補助となるようなコンテンツ情報を出力することが可能な、情報ナビゲーション装置、情報ナビゲーション方法、プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体を提供することをその目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the circumstances as described above, and grasps a user's viewing tendency with respect to an enormous amount of digital content on an objective scale as much as possible, and based on this, assists the user in selecting content. An object of the present invention is to provide an information navigation device, an information navigation method, a program, and a computer-readable recording medium on which the program is recorded.
また、本発明は、膨大な量のデジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向をできるだけ客観的な尺度で把握し、これに基づきユーザのコンテンツ選択の補助となるようなコンテンツ情報を出力すると共に、ユーザ自身のその時点での視聴傾向をリアルタイムに反映させることが可能な、情報ナビゲーション装置、情報ナビゲーション方法、プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体を提供することを他の目的とする。 In addition, the present invention grasps a user's viewing tendency with respect to an enormous amount of digital content on an objective scale as much as possible, and based on this, outputs content information that assists the user in selecting content, Another object of the present invention is to provide an information navigation device, an information navigation method, a program, and a computer-readable recording medium on which the program is recorded, which can reflect the viewing tendency at that time in real time.
本発明は、上述のごとき課題を解決するために、以下の各技術手段により構成される。
第1の技術手段は、デジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向を分析し、該ユーザによるデジタルコンテンツ選択を支援する情報ナビゲーション装置であって、デジタルコンテンツのコンテンツ情報を記憶するコンテンツ情報記憶手段と、ユーザがデジタルコンテンツを選択した履歴であるコンテンツ選択履歴を記憶するコンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段と、前記コンテンツ情報記憶手段で記憶されたコンテンツ情報と、前記コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段で記憶されたユーザのコンテンツ選択履歴とから、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析する視聴傾向分析手段と、該視聴傾向分析手段によるユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果を出力する出力手段と、を備えたことを特徴としたものである。The present invention is constituted by the following technical means in order to solve the above-described problems.
A first technical means is an information navigation device that analyzes a user's viewing tendency with respect to digital content and assists the user in selecting digital content. The content information storage means stores content information of the digital content; Content selection history storage means for storing a content selection history that is a history of selecting digital content; content information stored in the content information storage means; and user content selection history stored in the content selection history storage means; The viewing tendency analyzing means for analyzing the viewing tendency of the user and the output means for outputting the analysis result of the viewing tendency of the user by the viewing tendency analyzing means.
第2の技術手段は、第1の技術手段において、前記出力手段として、前記分析結果を表示する表示手段を備えることを特徴としたものである。 According to a second technical means, in the first technical means, the output means includes a display means for displaying the analysis result.
第3の技術手段は、第1又は第2の技術手段において、前記コンテンツ情報は、各デジタルコンテンツの分類情報を含むことを特徴としたものである。 A third technical means is the first or second technical means, wherein the content information includes classification information of each digital content.
第4の技術手段は、第3の技術手段において、前記コンテンツ情報は、さらに、各デジタルコンテンツの内容に関する情報を含むことを特徴としたものである。 According to a fourth technical means, in the third technical means, the content information further includes information on the contents of each digital content.
第5の技術手段は、第4の技術手段において、前記各デジタルコンテンツの内容に関する情報は、製作者,出演者,対象者年齢層,原作者,配給元,製作国のうち1以上を含んでいることを特徴としたものである。 A fifth technical means is the fourth technical means, wherein the information relating to the contents of each digital content includes at least one of a producer, a performer, a target age group, an original author, a distributor, and a production country. It is characterized by being.
第6の技術手段は、第4の技術手段において、前記各デジタルコンテンツの内容に関する情報のうち、製作者,出演者,対象者年齢層,原作者,配給元,製作国の共通した内容を、1以上のカテゴリに分類することを特徴としたものである。 Sixth technical means, in the fourth technical means, out of the information about the contents of each digital content, the contents common to the producer, performer, target age group, original author, distributor, country of production, It is characterized by being classified into one or more categories.
第7の技術手段は、第4乃至第6のいずれかの技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、各デジタルコンテンツの分類情報及び内容に関する情報のうち1以上の情報を用いて、ユーザの視聴傾向の分析することを特徴としたものである。 A seventh technical means is any one of the fourth to sixth technical means, wherein the viewing tendency analyzing means uses one or more pieces of information regarding classification information and contents of each digital content to view the user. It is characterized by analyzing trends.
第8の技術手段は、第4乃至第6のいずれかの技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、各デジタルコンテンツの分類情報及び内容に関する情報のうち、各分類情報の分布情報とヒストグラム情報のいずれか1以上の情報を用いて、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することを特徴としたものである。 The eighth technical means is any one of the fourth to sixth technical means, wherein the viewing tendency analyzing means includes distribution information and histogram information of each classification information among classification information and contents information of each digital content. One or more pieces of information are used to analyze the viewing tendency of the user.
第9の技術手段は、第4乃至第6のいずれかの技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、各デジタルコンテンツの分類情報及び内容に関する情報のうち、各分類情報の分布情報とヒストグラム情報から得られる値を掛け合わせて、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することを特徴としたものである。 Ninth technical means is any one of the fourth to sixth technical means, wherein the viewing tendency analyzing means is based on distribution information and histogram information of each classification information among classification information and contents information of each digital content. It is characterized by analyzing the user's viewing tendency by multiplying the obtained values.
第10の技術手段は、第4乃至第6のいずれかの技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、各デジタルコンテンツの視聴履歴に関する情報のうち、視聴していない時刻及び視聴していない時間帯の視聴履歴を前後の視聴履歴に関する情報から補完し、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することを特徴としたものである。 According to a tenth technical means, in any one of the fourth to sixth technical means, the viewing tendency analyzing means includes a time of non-viewing and a time zone of non-viewing of information relating to the viewing history of each digital content. Is supplemented with information about previous and subsequent viewing histories, and a user's viewing tendency is analyzed.
第11の技術手段は、第4又は第5の技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、各デジタルコンテンツの視聴履歴に関する情報のうち、時間的に古い視聴履歴に関する情報を削除した結果から、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することを特徴としたものである。 According to an eleventh technical means, in the fourth or fifth technical means, the viewing tendency analyzing means determines that the user deletes information related to the viewing history of each digital content from the result of deleting information related to the oldest viewing history. It is characterized by analyzing the viewing tendency.
第12の技術手段は、第1乃至第11のいずれかの技術手段において、前記出力手段は、前記視聴傾向分析手段によるユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果に従って、ユーザの視聴傾向に合致した利用可能なデジタルコンテンツの一覧を出力する手段をさらに有することを特徴としたものである。 In a twelfth technical means according to any one of the first to eleventh technical means, the output means can be used in conformity with the viewing tendency of the user according to the analysis result of the viewing tendency of the user by the viewing tendency analysis means. It further has means for outputting a list of digital contents.
第13の技術手段は、第1乃至第12のいずれかの技術手段において、前記出力手段により出力したユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果をユーザに修正させる修正手段をさらに備えたことを特徴としたものである。 In a thirteenth technical means according to any one of the first to twelfth technical means, the technical means further comprises correction means for correcting the analysis result of the viewing tendency of the user output by the output means. It is.
第14の技術手段は、第13の技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、前記修正させた分析結果に基づいて、再度、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することを特徴としたものである。 The fourteenth technical means is characterized in that, in the thirteenth technical means, the viewing tendency analyzing means analyzes the viewing tendency of the user again based on the corrected analysis result.
第15の技術手段は、第14の技術手段において、前記出力手段は、前記視聴傾向分析手段で再分析したユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果を、所定の回数だけ出力することを特徴としたものである。 A fifteenth technical means is characterized in that, in the fourteenth technical means, the output means outputs the analysis result of the viewing tendency of the user reanalyzed by the viewing tendency analysis means for a predetermined number of times. is there.
第16の技術手段は、第1乃至第15のいずれかの技術手段において、前記コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段は、前記コンテンツ選択履歴として、視聴時刻,コンテンツを特定するID,視聴時間又は放送・収録時間に対する視聴割合に加えて、視聴した時刻の環境要因を同時に記憶する手段を有することを特徴としたものである。 In a sixteenth technical means according to any one of the first to fifteenth technical means, the content selection history storage means includes, as the content selection history, a viewing time, an ID for identifying the content, a viewing time, or a broadcast / recording time. In addition to the viewing ratio for the above, there are means for simultaneously storing environmental factors of viewing time.
第17の技術手段は、第1乃至第16のいずれかの技術手段において、前記出力手段は、前記コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段において予め登録されたユーザの個人情報、或いは視聴傾向分析手段による分析結果、或いは前記個人情報及び分析結果双方を統合した情報に基づいて、ユーザの視聴傾向に合致したユーザによるコンテンツ選択を支援する情報を出力することを特徴としたものである。 The seventeenth technical means is any one of the first to sixteenth technical means, wherein the output means is personal information of a user registered in advance in the content selection history storage means, or an analysis result by the viewing tendency analysis means, Alternatively, based on information obtained by integrating both the personal information and the analysis result, information for supporting content selection by the user that matches the viewing tendency of the user is output.
第18の技術手段は、第1乃至第17のいずれかの技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、デジタルコンテンツが持つ感性情報に基づき、感性情報を基準とした視聴傾向の分析を行うことを特徴としたものである。 In an eighteenth technical means according to any one of the first to seventeenth technical means, the viewing tendency analyzing means analyzes a viewing tendency based on the sensitivity information based on the sensitivity information possessed by the digital content. It is a feature.
第19の技術手段は、第1乃至第18のいずれかの技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、複数のジャンル若しくは複数のサブジャンルが持つメタ情報、又は、1つのジャンル内若しくは1つのサブジャンル内のコンテンツが持つメタ情報が同一の内容を持つ場合、それをまとめて1つに表現した標準コンテンツ属性により、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することを特徴としたものである。 In a nineteenth technical means according to any one of the first to eighteenth technical means, the viewing tendency analyzing means includes meta information possessed by a plurality of genres or a plurality of sub-genres, or within one genre or one sub-subordinate. When the meta information of the content in the genre has the same content, the viewing tendency of the user is analyzed based on the standard content attributes that are collectively expressed as one.
第20の技術手段は、第1乃至第18のいずれかの技術手段において、前記視聴傾向分析手段は、複数のジャンル若しくは複数のサブジャンルが持つメタ情報、又は、1つのジャンル内若しくは1つのサブジャンル内のコンテンツが持つメタ情報が同一の内容を持つ場合、それを品詞の意味的な面を基準にまとめて1つに表現した標準コンテンツ属性により、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することを特徴としたものである。 A twentieth technical means is any one of the first to eighteenth technical means, wherein the viewing tendency analyzing means includes meta information possessed by a plurality of genres or a plurality of sub-genres, or within one genre or one sub-subordinate. When the meta information of the content in the genre has the same content, it is characterized by analyzing the user's viewing tendency by standard content attributes that are expressed as a single unit based on the semantic aspects of parts of speech. It is a thing.
第21の技術手段は、第1乃至第20のいずれかの技術手段において、デジタル放送,インターネット,外部接続デジタル機器,ハードディスク,デジタル記録媒体のうちいずれかからデジタルコンテンツを取得するコンテンツ取得手段をさらに備えたことを特徴としたものである。 The twenty-first technical means further includes content acquisition means for acquiring digital content from any one of digital broadcasting, the Internet, an externally connected digital device, a hard disk, and a digital recording medium in any of the first to twentieth technical means. It is characterized by having provided.
第22の技術手段は、デジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向を分析し、該ユーザによるデジタルコンテンツ選択を支援する情報ナビゲーション方法であって、デジタルコンテンツのコンテンツ情報を記憶するステップと、ユーザがデジタルコンテンツを選択した履歴であるコンテンツ選択履歴を記憶するステップと、前記コンテンツ情報と、前記ユーザのコンテンツ選択履歴とから、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析するステップと、該分析した結果である前記ユーザの視聴傾向を表示するステップと、を含んでなることを特徴としたものである。 A twenty-second technical means is an information navigation method for analyzing a user's viewing tendency with respect to the digital content and supporting the digital content selection by the user, the step of storing the content information of the digital content, A step of storing a content selection history that is a selected history, a step of analyzing a user's viewing tendency from the content information and the content selection history of the user, and a viewing tendency of the user as a result of the analysis are stored. And a step of displaying.
第23の技術手段は、第22の技術手段において、前記表示したユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果に対して、ユーザの修正を受け付けるステップと、該修正を実行するステップと、該修正を前記表示に反映させるステップと、をさらに含んでなることを特徴としたものである。 In a twenty-third technical means, in the twenty-second technical means, a step of accepting a user's correction for the displayed analysis result of the viewing tendency of the user, a step of executing the correction, and the correction in the display And a step of reflecting.
第24の技術手段は、第23の技術手段において、前記反映した後、前記分析するステップで再分析するステップと、再分析したユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果を、所定の回数だけ表示するステップと、をさらに含んでなることを特徴としたものである。 The twenty-fourth technical means includes the step of re-analyzing in the analyzing step after the reflection in the twenty-third technical means, and the step of displaying the analyzed analysis result of the viewing tendency of the user a predetermined number of times. , Is further included.
第25の技術手段は、第22乃至第24のいずれかの技術手段において、デジタルコンテンツが持つ感性情報に基づき、感性情報を基準とした視聴傾向の分析を行うことを特徴としたものである。 A twenty-fifth technical means is characterized in that, in any one of the twenty-second to twenty-fourth technical means, a viewing tendency is analyzed based on the sensitivity information based on the sensitivity information possessed by the digital content.
第26の技術手段は、第1乃至第21のいずれかの技術手段における情報ナビゲーション装置における各手段として、コンピュータを機能させるためのプログラムである。 A twenty-sixth technical means is a program for causing a computer to function as each means in the information navigation apparatus according to any one of the first to twenty-first technical means.
第27の技術手段は、第26の技術手段におけるプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体である。 The twenty-seventh technical means is a computer-readable recording medium on which the program according to the twenty-sixth technical means is recorded.
本発明によれば、膨大な量のデジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向をできるだけ客観的な尺度で把握し、これに基づきユーザのコンテンツ選択の補助となるようなコンテンツ情報を出力することが可能となる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to grasp a user's viewing tendency with respect to an enormous amount of digital content on an objective scale as much as possible, and to output content information that assists the user in selecting content based on this. .
また、本発明によれば、膨大な量のデジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向をできるだけ客観的な尺度で把握し、これに基づきユーザのコンテンツ選択の補助となるようなコンテンツ情報を出力すると共に、ユーザ自身のその時点での視聴傾向をリアルタイムに反映させることが可能となる。 Further, according to the present invention, the user's viewing tendency with respect to a huge amount of digital content is grasped by an objective scale as much as possible, and based on this, content information that assists the user's content selection is output, and the user It becomes possible to reflect the viewing tendency at that time in real time.
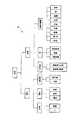
図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る情報ナビゲーション装置の内部構成を概略的に示す機能ブロック図で、図中、1は情報ナビゲーション装置、10は制御手段、11は表示手段、12は入力手段、13は視聴傾向分析手段、14はコンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段、15はコンテンツ情報データベース(以下、コンテンツ情報DBと略す)、16は外部接続端子、17はネットワークインターフェイス(以下、ネットワークI/Fと略す)、18はチューナ、19はハードディスクである。 FIG. 1 is a functional block diagram schematically showing an internal configuration of an information navigation apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. In the figure, 1 is an information navigation apparatus, 10 is control means, 11 is display means, and 12 is input. Means 13, viewing tendency analysis means 14, content selection history storage means 15, content information database (hereinafter abbreviated as content information DB), 16 external connection terminals, 17 network interface (hereinafter referred to as network I / F) 18 is a tuner, and 19 is a hard disk.
本発明の一実施形態に係る情報ナビゲーション装置(しばしば、本装置と略す)1は、少なくともコンテンツ情報記憶手段,コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14,視聴傾向分析手段13,出力手段を備えるものとする。出力手段は、表示手段11で例示しているが、本装置1は、表示手段11を装置内に備えなくとも、少なくとも表示装置に接続され出力手段で出力する各種情報やデジタルコンテンツがユーザに対して表示できる環境にある必要がある。また、コンテンツ情報記憶手段は、コンテンツ情報DB15で例示する。また、図1で例示する情報ナビゲーション装置は、入力手段12、外部接続端子16、ネットワークインターフェイス17、チューナ18、ハードディスク19、及び本装置1における制御を行う制御手段11を備えた構成とする。 An information navigation apparatus (often abbreviated as this apparatus) 1 according to an embodiment of the present invention includes at least content information storage means, content selection history storage means 14, viewing tendency analysis means 13, and output means. Although the output unit is exemplified by the display unit 11, the
本装置1は、デジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向を分析し、そのユーザによるデジタルコンテンツの選択を支援する情報ナビゲーション装置であり、支援の方法として、そのユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果として、好ましくはそのユーザの視聴傾向に合致したデジタルコンテンツのコンテンツ情報を出力してユーザに提示することで、ユーザの視聴に合致したユーザの情報選択(コンテンツ選択)を支援する。従って、本装置1はコンテンツ選択支援装置とも謂える。 The
制御手段10は、一般的なオーディオビジュアル(AV)装置に用いられるマイクロコンピュータ等の演算処理装置であり、情報ナビゲーション装置1の各構成部分の動作及び各構成部分間のデータ伝送を制御する。 The control means 10 is an arithmetic processing device such as a microcomputer used in a general audio visual (AV) device, and controls the operation of each component of the
表示手段11は、映像コンテンツを再生するモニタまたは音声コンテンツを再生するスピーカを含んでおり、ユーザは表示手段11によりデジタルコンテンツを視聴することができる。モニタは、また、本装置1の設定情報やデジタルコンテンツに付随する情報などをOSD(On Screen Display)表示することができるものとする。本発明に係る後述の視聴傾向分析手段13によるユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果を出力する出力手段としても、この表示手段11を流用でき、特に、OSD機能で分析結果を出力して、ユーザによるコンテンツ選択を支援するようにすればよい。 The display unit 11 includes a monitor that reproduces video content or a speaker that reproduces audio content, and the user can view digital content through the display unit 11. The monitor is also capable of OSD (On Screen Display) display of setting information of the
本装置1には、このように、出力手段として、後述の視聴傾向分析手段13による分析結果を表示する表示手段を備えることが好ましく、以下、この表示手段を表示手段11として説明する。また、出力手段は、視聴傾向分析手段13によるユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果に従って、ユーザの視聴傾向に合致した利用可能なデジタルコンテンツのコンテンツ情報(特に利用可能なデジタルコンテンツの一覧)を出力する手段をさらに有することが、ユーザ支援がより良く実施できるという点で好ましい。 As described above, the
出力手段は、コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14において予め登録されたユーザの個人情報(年齢・性別,好み,キーワード等)、或いは視聴傾向分析手段による分析結果、或いは個人情報及び分析結果双方を統合した情報に基づいて、ユーザの視聴傾向に合致したユーザによるコンテンツ選択を支援する情報を出力してもよい。ユーザの個人情報を予め登録する場合には、コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14に記憶しておけばよい。このようなナビゲーション機能を採用することで、よりユーザに合致したコンテンツの推薦が可能となる。尚、本発明に係る視聴傾向分析によれば、上述のごときユーザの個人情報を予め登録しなくても、視聴傾向を算出することができ、視聴傾向に合致したコンテンツを推薦できる。 The output means is the user's personal information (age / gender, preference, keyword, etc.) registered in advance in the content selection history storage means 14, the analysis result by the viewing tendency analysis means, or the information integrating both personal information and analysis results On the basis of the information, information that assists the user in selecting content that matches the viewing tendency of the user may be output. When the user's personal information is registered in advance, it may be stored in the content selection
入力手段12は、ユーザからの操作を受け付けるものであり、例えば、赤外線方式のリモートコントローラ(以下、「リモコン」と略する)や、本装置1表面に設けた操作パネル,マウス,キーボードなどからの操作が入力される。 The
視聴傾向分析手段13は、後述するコンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14,コンテンツ情報記憶手段(コンテンツ情報DB15で例示)に記憶されている情報(それぞれコンテンツ情報,コンテンツ選択履歴)に基づいて、ユーザのコンテンツに対する視聴傾向を分析する。視聴傾向分析手段13は、例えば、所定のプログラムを含んだROM(Read Only Memory)などにより構成することができる。 The viewing tendency analysis means 13 is based on information (content information and content selection history, respectively) stored in a content selection history storage means 14 and content information storage means (illustrated in the content information DB 15) to be described later. Analyze viewing trends. The viewing tendency analysis means 13 can be configured by a ROM (Read Only Memory) including a predetermined program, for example.
コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14は、ユーザが視聴したコンテンツの情報を、コンテンツ選択履歴として記憶する。すなわち、コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14は、ユーザがデジタルコンテンツを選択した履歴であるコンテンツ選択履歴を記憶する。例えば、各コンテンツについて、ユーザが視聴した日時,視聴時間,視聴回数,コンテンツの取得元(ソース)などを記憶しておくことができる。また、コンテンツ再生の途中で視聴を中断したことなども情報として記憶しておいてもよい。 The content selection
コンテンツ情報DB15は、本装置1において利用可能な各種コンテンツに関する様々な情報(コンテンツ情報)を記憶している。例えば、各種コンテンツの分類情報や、コンテンツのメタ情報(後述する)などを記憶しておくことができる。尚、コンテンツ情報DB15の一部は、本装置1外部に蓄積されている情報を利用するものであってもよい。例えば、コンテンツ配信元のサーバに記憶されているコンテンツ情報を取得するようにしてもよい。 The
ここで、コンテンツ情報は、上述のごとく各デジタルコンテンツの分類情報を含むことが好ましく、さらに、各デジタルコンテンツの内容に関する情報を含むことが好ましい。また、各デジタルコンテンツの内容に関する情報は、製作者,出演者,対象者年齢層,原作者,配給元,製作国のうち1以上を含んでいることが好ましい。また、各デジタルコンテンツの内容に関する情報のうち、製作者,出演者,対象者年齢層,原作者,配給元,製作国の共通した内容を、1以上のカテゴリに分類してもよい。 Here, the content information preferably includes the classification information of each digital content as described above, and further preferably includes information regarding the contents of each digital content. Moreover, it is preferable that the information regarding the contents of each digital content includes at least one of the producer, performer, target age group, original author, distributor, and country of production. Moreover, you may classify | categorize the common content of a producer, a performer, a target person age group, an original author, a distributor, and a production country among the information regarding the content of each digital content into one or more categories.
そして、コンテンツ情報に関するこれらの形態にあっては、視聴傾向分析手段13は、各デジタルコンテンツの分類情報及び内容に関する情報のうち1以上の情報を用いて、ユーザの視聴傾向の分析するとよい。若しくは、視聴傾向分析手段13は、各デジタルコンテンツの分類情報及び内容に関する情報のうち、各分類情報の分布情報とヒストグラム情報のいずれか1以上の情報を用いて、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することがより好ましい。より好ましくは、視聴傾向分析手段13は、各デジタルコンテンツの分類情報及び内容に関する情報のうち、各分類情報の分布情報とヒストグラム情報から得られる値を掛け合わせて、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析するとよい。また、視聴傾向分析手段13は、各デジタルコンテンツの視聴履歴に関する情報のうち、視聴していない時刻及び視聴していない時間帯の視聴履歴を前後の視聴履歴に関する情報から補完し、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析するようにしてもよい。さらに、各デジタルコンテンツの視聴履歴に関する情報が製作者,出演者,対象者年齢層,原作者,配給元,製作国のうち1以上を含んでいる形態にあっては、視聴傾向分析手段13は、各デジタルコンテンツの視聴履歴に関する情報のうち、時間的に古い視聴履歴に関する情報を削除した結果から、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することが好ましい。 In these forms relating to the content information, the viewing tendency analyzing means 13 may analyze the viewing tendency of the user by using one or more pieces of information regarding the classification information and contents of each digital content. Alternatively, the viewing tendency analyzing means 13 analyzes the viewing tendency of the user by using one or more of distribution information and histogram information of each classification information among the classification information and contents information of each digital content. Is more preferable. More preferably, the viewing tendency analyzing means 13 may analyze the viewing tendency of the user by multiplying the distribution information of each classification information and the value obtained from the histogram information among the classification information and contents information of each digital content. . In addition, the viewing tendency analysis means 13 complements the viewing history at the time of non-viewing and the non-viewing time zone from the information about the viewing history before and after the viewing history of each digital content, and the viewing trend of the user You may make it analyze. Furthermore, when the information regarding the viewing history of each digital content includes one or more of the producer, performer, target age group, original author, distributor, and production country, the viewing tendency analysis means 13 It is preferable to analyze the viewing tendency of the user from the result of deleting the information related to the viewing history that is older in time among the information regarding the viewing history of each digital content.
また、本装置1は、デジタル放送,インターネット,外部接続デジタル機器,ハードディスク,デジタル記録媒体のうちいずれかからデジタルコンテンツを取得するコンテンツ取得手段をさらに備えることが好ましい。具体的には、次に例示する外部接続端子16,ネットワークI/F17,チューナ18,ハードディスク19等がそれに該当する。 The
外部接続端子16は、外部のデジタル機器と接続するための端子であり、例えば、IEEE1394やUSBなどの通信規格を利用することができる。本装置1に接続するデジタル機器としては、デジタルビデオ,DVDプレーヤ,ハードディスクレコーダ,CDプレーヤ,MDプレーヤなどが挙げられる。 The
ネットワークI/F17は、本装置1をインターネット等の外部ネットワークに接続しデータ通信を行うためのインターフェイスである。例えば、Ethernet(登録商標)規格に準じたNIC(Network Interface Card)などを用いてLAN(Local Area Network)などに接続することができる。 The network I /
チューナ18は、主に放送を受信するためのものであり、例えば、BS/CSデジタル放送用混合チューナや、ケーブルテレビジョン用チューナなどを用いることができる。また、チューナ18は、本装置外部に設置したアンテナ(図示せず)より放送信号を受信し、本装置内で利用可能な放送信号に変換するものである。また、図示しないが、チューナ18は、放送信号のデコーダを備えているものとする。現在、BSデジタル放送や地上デジタル放送では、MPEG2形式のデジタルデータをTS(Transport Stream)パケットに分割して放送しており、このMPEG2−TS方式のパケットを受信側で再構成し、MPEG2形式のデジタルデータを取得するようなシステムが採用されている。 The
ハードディスク19は、磁気ディスク等の不揮発性記憶装置であり、本装置1で利用する各種デジタルコンテンツなど大容量のデータを記憶しておくことができる。また、デジタルコンテンツ以外にも、本装置1の制御に必要なプログラムやデータ(コンテンツ選択履歴やコンテンツ情報等)などを記憶しておくこともできる。 The hard disk 19 is a non-volatile storage device such as a magnetic disk, and can store a large amount of data such as various digital contents used in the
次に、上述のごとく構成された本実施形態に係る情報ナビゲーション装置1の動作について説明する。 Next, the operation of the
ユーザは、外部接続端子16により外部接続されたデジタル機器、ネットワークI/F17を通じて接続されたインターネット等、チューナ18を通じて受信されるデジタル放送などから取得されるデジタルコンテンツ、並びに本装置1内のハードディスク19に記憶されているデジタルコンテンツから、好みのコンテンツを選択して、表示手段11に出力させることにより視聴をすることができる。 The user can use digital devices externally connected through the
ここで、これらのデジタルコンテンツは、本装置1内では、所定の共通のデータ形式で扱われるようになっている。具体的には、現在デジタル放送やDVDなどに広く利用されているデジタルデータの圧縮方式であるMPEG方式などを利用することができる。特に、映像コンテンツには、MPEG2方式を利用すれば、映像・音声合わせて4〜15Mbps程度のデータ転送速度でS−VHSビデオ並みの画質で再生することができる。 Here, these digital contents are handled in a predetermined common data format in the
ユーザがこれらのデジタルコンテンツから好みのコンテンツを選択するにあたっては、まず、コンテンツの選択画面が表示手段11にOSD表示される。ここで、デジタル放送コンテンツについては、従来のEPG(Electronic Programming Guide)表示を行うことができ、インターネットコンテンツについては、当該WEBサイトのタイトル一覧をそのまま表示することができ、外部接続機器としてDVDプレーヤを利用している場合には、既定のDVDメニュー画面が表示されることになる。また、ハードディスク19内に記憶されたデジタルコンテンツについては、所定のコンテンツリスト表示プログラムなどにより、コンテンツ選択画面の表示を行うことができる。尚、本装置1内において、これら異なるコンテンツソースから利用可能なデジタルコンテンツを検索し、まとめてリスト表示することができるようなプログラムを備えていてもよい。 When the user selects a favorite content from these digital contents, first, a content selection screen is OSD-displayed on the display means 11. Here, conventional EPG (Electronic Programming Guide) display can be performed for digital broadcasting content, and a title list of the WEB site can be displayed as it is for Internet content, and a DVD player can be used as an external connection device. If it is used, a default DVD menu screen is displayed. For digital contents stored in the hard disk 19, a content selection screen can be displayed by a predetermined content list display program or the like. It should be noted that the
ユーザがいずれかのコンテンツを選択すると、制御手段10はそのコンテンツを表示手段11に出力する。このとき、制御手段10は、当該コンテンツの情報をコンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14に記憶させる。 When the user selects any content, the
ここで、本発明の情報ナビゲーション装置における特徴部分である、ユーザの視聴傾向に合わせたコンテンツ情報の表示について説明する。 Here, the display of the content information in accordance with the viewing tendency of the user, which is a characteristic part in the information navigation apparatus of the present invention, will be described.
ユーザの操作に応じて、視聴傾向分析手段13は、コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14に記憶されているユーザのコンテンツ選択履歴(基本的に視聴のための選択とする)を参照すると共に、コンテンツ情報DB15に分析の時点で既に記憶されているコンテンツに関する情報を参照して、ユーザのコンテンツ視聴傾向を割り出す。 In response to the user's operation, the viewing
以下に、コンテンツに関する情報とその利用方法について述べる。図2及び図3は、本発明において利用するデジタルコンテンツの分類構造(オントロジー)を例示する概念図である。また、図4乃至図6は、デジタルコンテンツに関連付けられるメタ情報を説明するための概念図で、図4は図2及び図3に例示するコンテンツ分類構造に対応するメタ情報を示す概念図で、図5は品詞を意味的な側面から分類するという基準を用いた標準コンテンツ属性を示す概念図、図6は名詞の分類例を示す概念図である。 The following describes information related to content and how to use it. 2 and 3 are conceptual diagrams illustrating a digital content classification structure (ontology) used in the present invention. FIGS. 4 to 6 are conceptual diagrams for explaining meta information associated with digital content. FIG. 4 is a conceptual diagram illustrating meta information corresponding to the content classification structure illustrated in FIGS. FIG. 5 is a conceptual diagram showing standard content attributes using a standard for classifying parts of speech from semantic aspects, and FIG. 6 is a conceptual diagram showing an example of noun classification.
図2及び図3で例示するオントロジー2のように、全てのデジタルコンテンツ20は、大分類(ジャンル)21及び小分類(サブジャンル)23により分類されており、コンテンツ自体はコンテンツID24により識別されるようになっている。例えば、大分類21は、エンターテイメント,ニュース,ライフスタイル,カルチャーとラーニング,その他にジャンル分けし、そのうち例えばエンターテイメントには項目22として、映画,アニメ,音楽,スポーツ,その他といったように分類するとよい。それらの項目22は、小分類23にジャンル分け(すなわちサブジャンル分け)される項目やされない項目があってもよい。映画とアニメ,音楽,スポーツ,グルメ,趣味といった項目(小分類23有りの項目)22のうち、例えばスポーツに関しては、サッカー,野球,ゴルフ,テニス,・・・,その他といった項目23に小分類するとよい。また、各コンテンツID24には、後述するが図4のようにコンテンツのメタ情報25が関連付けられている。本発明の情報ナビゲーション装置のコンテンツ情報DB15では、これらのデジタルコンテンツ分類情報を記憶している。 As shown in
このようなデジタルコンテンツの分類方法は、コンテンツを選択する際の重要な指標になることから、できるだけ標準化し、その基準に基づく統一的な分類を行うのが望ましい。例えば、既に国際標準化として策定されているISO/SC29のMPEG−7や、標準作成中のMPEG−21などに準拠したオントロジーを利用することができる。また、日本国内では、コンテンツIDフォーラム(cIDf)という、産学共同でデジタルコンテンツにユニークなコードと、コンテンツのメタ情報をペアにした、コンテンツIDの付与基準を作成している組織がある。 Since such a digital content classification method is an important index when selecting content, it is desirable to standardize as much as possible and perform uniform classification based on the standard. For example, it is possible to use an ontology that conforms to MPEG-7 of ISO /
また、WEB上の各種情報の分類体系としては、ウェブオントロジー言語(OWL)がW3Cにより策定されている。OWLは、RDF(Resource Description Framework)モデルとRDFスキーマによるリソースの叙述を行うことにより、WEB上に存在する各種情報の分類体系(クラス)やそれらの関係、さらにはそれを推論していくためのルールを定義するものである。これにより、各地で独自に定義されている語彙を関連づけ、相互運用できるようになったり、オントロジーで表現された知識を利用して、エージェントが高度な検索などを行ったりすることが期待されている。 In addition, as a classification system for various types of information on the WEB, a web ontology language (OWL) is formulated by the W3C. OWL uses RDF (Resource Description Framework) model and RDF schema to describe resources, so that the classification system (class) of various information existing on the WEB and their relations, as well as their inference Define rules. As a result, it is expected that vocabularies that are uniquely defined in each region will be linked and interoperable, and that agents will perform advanced searches using knowledge expressed in ontology. .
ここで、図2及び図3に示すコンテンツ分類構造2に対応する図4の「メタ情報」25とは、情報に関する情報のことであり、例えば、情報の使い方に関する情報や、情報の性質に関する情報などをいうものである。すなわち、各コンテンツに関する情報(製作者,出演者,対象者年齢層,原作者,配給元,製作国等)であり、これらの情報は、上述した標準に従ってコンテンツデータに付随して配信されるものである。 Here, the “meta information” 25 in FIG. 4 corresponding to the
デジタルコンテンツの配信元が提供するこのようなメタ情報を利用することにより、テキストデータとは異なり機械的な意味処理が困難であるデジタルコンテンツに対して、その形式や内容に関連するオントロジーから確実な探索を行うことが可能となる。 By using such meta information provided by digital content distributors, digital content that is difficult to process mechanically, unlike text data, can be reliably identified from the ontology related to its format and content. Search can be performed.
また、ユーザが所有するハードディスク19などの記憶装置の記憶容量増大により、膨大な量の多種多様なデジタルコンテンツが蓄積されているような場合であっても、オントロジーを用いて異なる種類・形式のコンテンツを横断検索することが可能となる。 Even if a huge amount of various digital contents are accumulated due to an increase in the storage capacity of a storage device such as the hard disk 19 owned by the user, contents of different types and formats using ontologies Can be cross-searched.
さらには、予め登録しておいたユーザの視聴と現在利用可能なコンテンツとを照らし合わせた上で、ユーザの好みに合ったコンテンツを推奨(リコメンド)するメニューやランク付けなどを提示することができる。 Furthermore, it is possible to present a menu, ranking, etc. for recommending (recommending) content that matches the user's preference after checking the user's viewing registered in advance with the currently available content. .
このメタ情報25は、「映画&ドラマ」,「スポーツ」,「音楽」等の異なる小分類において、「出演」,「選手」,「歌手or出演者」等のようにメタ情報名が異なっても同様の内容を指し示すことがある。この場合、このような同一の情報はまとめて、表記若しくは管理することが好ましい。そして、視聴傾向分析手段13は、複数のジャンル若しくは複数のサブジャンルが持つメタ情報、又は、1つのジャンル内若しくは1つのサブジャンル内のコンテンツが持つメタ情報が同一の内容を持つ場合、それをまとめて1つに表現した標準コンテンツ属性により、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することが好ましい。特に、メタ情報が同一の内容を持つ場合、それを品詞の意味的な面を基準にまとめて1つに表現した標準コンテンツ属性により、ユーザの視聴傾向を分析することが好ましい。すなわち、図6における名詞の分類29で例示するような、名詞(を参照)等の品詞を意味的な側面から分類するという基準を用いて、図5の標準コンテンツ属性26を設定するとよい。図5において、27は標準コンテンツ属性名、28は各標準コンテンツ属性に含まれるメタ情報を指す。 The meta information 25 has different meta information names such as “appearance”, “player”, “singer or performer” in different sub-categories such as “movie & drama”, “sports”, “music”, etc. May point to the same content. In this case, it is preferable that such identical information is collectively written or managed. Then, the viewing tendency analyzing means 13, when meta information possessed by a plurality of genres or a plurality of sub-genres, or meta-information possessed by contents within one genre or one sub-genre has the same content, It is preferable to analyze the viewing tendency of the user based on the standard content attributes expressed collectively. In particular, when the meta information has the same content, it is preferable to analyze the viewing tendency of the user based on standard content attributes that are expressed as a single item based on the semantic aspects of the part of speech. That is, the
この標準コンテンツ属性26は、1つのコンテンツが持つメタ情報に基づいて、例えば、「ジャンル」,「タイトル」,「制作(人)」,「音楽(人)」,「出演(人)」,「原作/脚本(人)」,「制作(組織)」,「音楽(音響)」,「字幕/音声」,「時間」,「時刻」,「場所」,「音楽(曲)」,「あらすじ」の各属性に情報が設定される。例えば「制作(人)」では、コンテンツ情報の「制作総指揮」,「監督」,「撮影者」が相当する。「場所」27aのように開催場所,収録場所,施設,地域といった情報28を含む標準コンテンツ属性もあれば、「あらすじ」27bのように情報28を含まない標準コンテンツ属性もある。 This
ここで、図5における標準コンテンツ属性名27、若しくは標準コンテンツ属性名27に含まれる情報28(キーワード)を、視聴因子と定義する。すなわち、前者の場合、ジャンル,タイトル,製作(人),・・・といった標準コンテンツ属性名を視聴因子とし、後者の場合、例えば「制作(人)」に含まれる監督名,撮影者名,・・・といったキーワードを視聴因子とする。 Here, the standard
本発明に係る情報ナビゲーション装置1は、視聴傾向として割り出された視聴因子の、例えば上位5項目等をグラフ表示することができ、さらに好ましくは、ユーザ自身が必要に応じてそのグラフ表示を直接修正することができることを特徴としている。 The
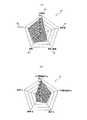
図7は、図1の情報ナビゲーション装置において、ユーザの視聴傾向をグラフ表示する一例を説明するための図で、図7(A)は標準コンテンツ属性に関する視聴因子グラフの一例を、図7(B)は図7(A)の中の出演者に関するキーワードに関して上位5つの出演者キーワードをグラフ化した例を示している。図中、5項目のメタ情報から構成されたレーダチャートによりユーザの視聴傾向を示しているが、表示方法はこれに限定されるものではなく、例えば、表形式やテキスト形式で表示しても構わない。 FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining an example in which a user's viewing tendency is displayed in a graph in the information navigation apparatus of FIG. 1, and FIG. 7 (A) is an example of a viewing factor graph regarding standard content attributes. ) Shows an example in which the top five performer keywords are graphed with respect to the keywords related to performers in FIG. In the figure, the user's viewing tendency is shown by a radar chart composed of five items of meta information. However, the display method is not limited to this, and for example, it may be displayed in a table format or a text format. Absent.
図7(A)は、ユーザからの操作に応じて視聴傾向分析手段13が割り出したユーザの視聴傾向を示すレーダチャートである。図7(A)中の5項目は、「出演者」31が90、「ジャンル」32が80、「音楽」33が70、「原作・脚本」34が50、「製作者」35が20と、この順にスコアが高く表示されている。これは、ユーザが「出演者」31というメタ情報に対しては最も強い視聴傾向を有しているが、「制作者」35に対しては視聴傾向が最も弱いということを意味している。 FIG. 7A is a radar chart showing the viewing tendency of the user determined by the viewing tendency analysis means 13 according to the operation from the user. The five items in FIG. 7A are “performer” 31 is 90, “genre” 32 is 80, “music” 33 is 70, “original / screenplay” 34 is 50, and “producer” 35 is 20. In this order, the score is displayed higher. This means that the user has the strongest viewing tendency with respect to the meta information “performer” 31, but the viewing tendency with respect to “producer” 35 is the weakest.
図7(A)に示す視聴傾向をユーザが承認すると、本発明に係る情報ナビゲーション装置1は、この視聴傾向に基づいて、現在利用可能なコンテンツを検索し、いくつかのコンテンツをユーザに推奨する画面を表示する。 When the user approves the viewing tendency shown in FIG. 7A, the
また、図7で説明する視聴因子グラフは、図7(A)における例えば出演者31を選択することで図7(B)の表示を可能とするような階層の構造を取っている。従って、ユーザの希望により、詳細に見ることが可能となっている。 In addition, the audience factor graph described in FIG. 7 has a hierarchical structure that enables the display of FIG. 7B by selecting, for example, the
一方、ユーザが図7(A)に示す視聴傾向を変更したい場合には、入力手段12からカーソル等(カーソルの他、タッチパネル、音声入力を含む)を操作することにより、レーダチャートの各項目のスコアを自由に変更することができるようになっている。例えば、出演者31の値を90から60に、ジャンル32の値を80から20に修正するなどである。また、図7(B)に示す出演者31における各出演者の視聴傾向を修正することも可能とするとよい。尚、視聴傾向の修正に関しては、図11等を参照して他の実施形態でその詳細を説明する。 On the other hand, when the user wants to change the viewing tendency shown in FIG. 7A, by operating a cursor or the like (including the cursor, touch panel, and voice input) from the
次に、視聴履歴に基づく視聴傾向分析について説明する。
図8は、図1の情報ナビゲーション装置におけるコンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段で記憶される視聴履歴の一例を示す図で、図中、36は視聴履歴である。Next, viewing tendency analysis based on viewing history will be described.
FIG. 8 is a diagram showing an example of the viewing history stored in the content selection history storage means in the information navigation apparatus of FIG. 1, in which 36 is the viewing history.
図7で例示した視聴因子グラフは、図8で例示するコンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14に記憶された視聴履歴を元に、視聴傾向分析手段13で分析される。図8で例示する視聴履歴36は、視聴時間及びコンテンツIDと共に、各コンテンツの収録時間(若しくは、放送される時間)と、その収録時間に対する視聴時間の比率(割合)が記録されている。これは、最後まで視聴したのか、最初だけ視聴したのか等の視聴比率を記録することで、単純にチャンネルを合わせたという履歴だけでなく、より詳細に視聴形態を把握するためのものである。ここで、勿論10分や30分といった特定の時間の閾値を用いても可能である。しかし、コンテンツの収録時間は様々であり、一様に閾値を決めることは難しいと思われる。例えば、「野球のプロ野球選手Aが出場した試合を番組の最後まで見た場合は、視聴比率1.0、ちょうど半分までしか見なかった場合は、0.5となり、標準コンテンツ属性の出演者及び出演者に含まれる「プロ野球選手A」という視聴因子の値は、それぞれ、1.0、0.5と加算される。 The viewing factor graph illustrated in FIG. 7 is analyzed by the viewing
また、コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14は、コンテンツ選択履歴として、視聴時刻,コンテンツを特定するID,視聴時間又は放送・収録時間に対する視聴割合に加えて、視聴した時刻の環境要因を同時に記憶する手段を備えることが、よりユーザが好むコンテンツを推薦できるので好ましい。ここでの環境要因としては天気の変化(例えば雨から晴れになったなど)や様々な要因が挙げられる。さらに、視聴傾向分析手段13は、デジタルコンテンツが持つ感性情報に基づき、感性情報を基準とした視聴傾向の分析を行うようにしてもよい。コンテンツメタデータに感性的な情報が含まれている場合、コンテンツが持つ感性情報(テーマ)に基づいて、感性を基準とした視聴傾向を抽出し、ユーザに提示するなど、感性情報に沿ったコンテンツの推薦が可能となる。 Further, the content selection history storage means 14 includes means for simultaneously storing, as the content selection history, the viewing time, the ID for specifying the content, the viewing time or the viewing ratio with respect to the broadcast / recording time, as well as the environmental factor of the viewing time. It is preferable to provide the content because the content that the user prefers can be recommended. The environmental factors here include changes in the weather (for example, it has become clear from rain) and various factors. Further, the viewing tendency analysis means 13 may analyze the viewing tendency based on the sensitivity information based on the sensitivity information of the digital content. If the content metadata contains emotional information, the content in line with the emotional information, such as extracting the viewing tendency based on the sensitivity based on the emotional information (theme) of the content and presenting it to the user Can be recommended.
図9は、視聴因子に含まれるキーワードの分布の違いによる視聴傾向を説明するための図で、図中、41は出演者の種類の分布が少ない場合の出現頻度値のグラフ、42は出演者の種類の分布がやや大きい場合の出現頻度値のグラフ、43は出演者の種類の分布が大きい場合の出現頻度値のグラフである。 FIG. 9 is a diagram for explaining a viewing tendency due to a difference in distribution of keywords included in viewing factors. In the figure, 41 is a graph of appearance frequency values when there is little distribution of performer types, and 42 is a performer. The graph of the appearance frequency value when the distribution of the type of is slightly larger, and the
図9で例示するように、視聴因子に含まれるキーワードの分布の違いによって視聴傾向が分かる。視聴因子に含まれるキーワードの分布の分散が小さい場合(グラフ41を参照)、例えば出演者名のキーワードの種類が少ない場合、ユーザはある特定の人が出演するコンテンツを視聴していると謂える。また、視聴因子に含まれるキーワードの分布の分散が大きい場合(グラフ43を参照)、例えば出演者名のキーワードの種類の種類が特定のキーワードの偏っていなくて平坦な場合、ユーザはいろんな人が出演するコンテンツを見ていると謂える。グラフ42はそれらの中間であり、視聴因子に含まれるキーワードの分布の分散があまり大きくない場合、例えば出演者名のキーワードの種類が少ないとは謂えない場合、ユーザはある特定の人たちが出演するコンテンツを視聴している、換言すると、ユーザはいろんな人が出演する番組を視聴しているが特定の人たちに偏っていると謂える。 As illustrated in FIG. 9, the viewing tendency can be understood by the difference in the distribution of keywords included in the viewing factor. When the distribution of keywords included in the viewing factor is small (see graph 41), for example, when there are few types of keywords for performer names, it can be said that the user is viewing content in which a specific person appears. . In addition, when the distribution of the keyword included in the audience factor is large (see graph 43), for example, when the type of the keyword type of the performer name is not biased with a specific keyword and is flat, various users are used. You can say that you are watching the content to appear. The
図10は、図1の情報ナビゲーション装置における視聴傾向分析手段の分析方法を説明するための図で、図中、51は視聴因子iのキーワード統計分布、52は視聴因子iのキーワードヒストグラム、53は統計値及び係数群、54はεiとσiとの関係を表すグラフ、55はお薦め度の算出式、56は確率群、57はあるコンテンツをユーザが視聴する確率の算出式である。 10 is a diagram for explaining an analysis method of the viewing tendency analysis means in the information navigation apparatus of FIG. 1, in which 51 is a keyword statistical distribution of the viewing factor i, 52 is a keyword histogram of the viewing factor i, 53 is A statistical value and coefficient group, 54 is a graph showing the relationship between εi and σi, 55 is a recommendation calculation formula, 56 is a probability group, and 57 is a calculation formula for the probability that a user views a certain content.
視聴傾向分析手段13では、図9で例示した、視聴因子に含まれるキーワードの分布を考慮した分析を行う。今、あるコンテンツCが与えられた時、ユーザWがそのコンテンツを気に入る確率を求めると仮定する。つまり、P(W|C)をあるコンテンツをユーザが視聴する確率、すなわちコンテンツがユーザの嗜好に一致している確率とする。P(C|W)を視聴傾向分析から得られるコンテンツのお薦め度、すなわち視聴傾向モデルから得られる新規コンテンツのお薦めランキングとする。P(C)をコンテンツが存在する確率と定義し、P(W)を、ユーザがコンテンツを視聴する際の他の要因により、言い換えるとユーザの個人内要因,環境要因などにより、ユーザがコンテンツを視聴すること自体の確率(ユーザが視聴するコンテンツの妥当性)と定義する。ここで、ユーザの個人内要因,環境要因とは、「元々野球が好きであるということ」や「流行の映画情報」などが該当し、それぞれ個人内因子,環境因子とも謂える。このように、P(W)は、抽出されたコンテンツを更に他の因子を用いて再順位付けするための関数である。 The viewing tendency analysis means 13 performs analysis in consideration of the distribution of keywords included in the viewing factor exemplified in FIG. Assume that when a certain content C is given, the probability that the user W likes the content is obtained. That is, let P (W | C) be the probability that the user views a certain content, that is, the probability that the content matches the user's preference. Let P (C | W) be the recommended degree of content obtained from the viewing tendency analysis, that is, the recommended ranking of new content obtained from the viewing tendency model. P (C) is defined as the probability that the content exists, and P (W) is determined by the user because of other factors when the user views the content, in other words, the user's internal factors, environmental factors, etc. It is defined as the probability of viewing itself (the validity of the content viewed by the user). Here, the intra-personal factors and environmental factors of the user correspond to “originally like baseball”, “fashionable movie information”, and the like, which can be referred to as individual factors and environmental factors, respectively. As described above, P (W) is a function for re-ranking the extracted content by using another factor.
この時、ベイズの確率より、P(W|C)は、式57より、P(C|W)*P(W)/P(C)と変形できる。ここで、P(C)は、コンテンツが存在する確率と考えられるため、計算上無視できる。すると、あるコンテンツCが与えられたという条件の下で、ユーザWが気に入るかどうかの確率P(W|C)は、ユーザWという条件の下で、これまでの視聴傾向分析結果によりコンテンツCを見た確率P(C|W)と、ユーザWの個人内要因,環境要因P(W)との積で表現できる。 At this time, P (W | C) can be transformed to P (C | W) * P (W) / P (C) from Equation 57 based on the Bayesian probability. Here, P (C) can be ignored in calculation because it is considered as the probability that the content exists. Then, under the condition that a certain content C is given, the probability P (W | C) of whether or not the user W likes the content C is determined based on the viewing tendency analysis results so far under the condition of the user W. It can be expressed by the product of the probability P (C | W) seen, the personal factor of the user W, and the environmental factor P (W).
コンテンツのお薦め度P(C|W)を、式55(下式(1))に示す。ここで、αiは、視聴因子iにおけるキーワードの分散を修正するための係数(視聴傾向をグラフ化したものをユーザが修正した場合に設定される)であり、通常は1.0である。また、εiは、視聴因子iのキーワードの分散値σiを引数に取る視聴寄与度である。分散値が小さい時、視聴寄与度εiは大きな値をとり、分散値が大きい場合は、視聴寄与度εiは小さな値となる。例えば、εi=1/(1+σi)のような式となる(グラフ54を参照)。これは指数関数の逆数のような形でσiが増加するにつれて、小さな値を取る関数であるが、他の定義でもかまわない。γkj,iは、視聴因子iにおけるキーワードの正規化頻度値である。つまり、視聴因子のキーワードヒストグラムの累積値が1.0になるように各要素を正規化した値であり、「プロ野球選手A」の出現頻度は、0.8というような形になる。γkj,iは、視聴因子iにおいて、新規コンテンツjのメタデータが持つk個の属性情報のヒストグラムにおける値である。お薦め度P(C|W)は、このようにσi,εi,γkj,i,αiの各値53より計算される。The recommendation level P (C | W) of content is shown in Formula 55 (Formula (1) below). Here, αi is a coefficient (set when the user corrects the graph of the viewing tendency) for correcting the distribution of the keyword in the viewing factor i, and is usually 1.0. Further, εi is a viewing contribution degree that takes a variance value σi of the keyword of the viewing factori as an argument. When the variance value is small, the viewing contribution εi takes a large value, and when the variance value is large, the viewing contribution εi becomes a small value. For example, an expression such as εi = 1 / (1 + σi ) is obtained (see graph 54). This is a function that takes a smaller value as σi increases in the form of the reciprocal of an exponential function, but other definitions may be used. γkj, i is a keyword normalization frequency value in the viewing factor i. That is, each element is normalized so that the cumulative value of the audience factor keyword histogram is 1.0, and the appearance frequency of “professional baseball player A” is 0.8. γkj, i is a value in a histogram of k pieces of attribute information possessed by the metadata of the new content j in the viewing factor i. The recommendation degree P (C | W) is thus calculated from the
図11は、本発明の他の実施形態に係る情報ナビゲーション装置を説明するための概念図で、ユーザによる視聴傾向の修正の様子を示す図である。 FIG. 11 is a conceptual diagram for explaining an information navigation apparatus according to another embodiment of the present invention, and is a diagram illustrating how a viewing tendency is corrected by a user.
本発明は、上述したように、ユーザの希望により視聴傾向の修正ができるようになっていることが好ましい。修正を可能とするために、本発明に係る他の実施形態に係る情報ナビゲーション装置として、出力手段により出力したユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果をユーザに修正させる修正手段をさらに備えるとよい。この修正手段を備えることにより、よりユーザの嗜好に合ったコンテンツを提示(コンテンツ一覧の出力)することが可能となるので好ましい。さらに、修正させた分析結果に基づいて、再度、視聴傾向分析手段13による分析を実行し、その結果を出力(表示手段11で表示)するようにすることが、同様の理由から好ましい。また、出力手段は、視聴傾向分析手段13で再分析したユーザの視聴傾向の分析結果を、所定の回数だけ出力するようにしてもよい。例えば、次回だけ出力、或いは次回以降の特定回数だけ出力するようにすればよい。勿論、次回以降全ての出力の際にこの再分析結果が反映された形でのデジタルコンテンツ表示を実行するようにしてもよい。 As described above, in the present invention, it is preferable that the viewing tendency can be corrected according to the desire of the user. In order to enable correction, the information navigation apparatus according to another embodiment of the present invention may further include correction means for allowing the user to correct the analysis result of the viewing tendency of the user output by the output means. By providing this correcting means, it is possible to present content (content list output) more suited to the user's preference. Furthermore, based on the corrected analysis result, it is preferable to execute the analysis by the viewing
これにより、ユーザは、視聴傾向分析手段13が割り出したユーザの視聴傾向に対して、その日その時の気分に応じた修正を加えることにより、より視聴に適したコンテンツの検索を行い、又は推奨を受けることが可能となる。 As a result, the user performs a search for content more suitable for viewing or receives a recommendation by making corrections according to the mood at that time on the viewing trend of the user determined by the viewing trend analysis means 13. It becomes possible.
図11を参照して、ユーザによる視聴傾向の修正の様子を説明する。図11において、グラフ30は、標準コンテンツ属性に基づいて得られた視聴傾向に大きく寄与する視聴因子、例えば上位5種類の視聴因子をグラフ化したものである。また、グラム30aは、この中の出演者31に関する視聴因子内のキーワード、例えば上位5種類をグラフ化したものである。ここでは、各視聴因子の寄与度の大きさをレーダチャートを用いて表しているが、勿論、棒グラフや折れ線グラフなど他の方法を採用してもよい。 With reference to FIG. 11, the manner in which the viewing tendency is corrected by the user will be described. In FIG. 11, a
グラフ30では、ユーザは、出演者31とジャンル32に重点を置いていることが読みとれる。また、出演者31では、プロ野球選手A,プロ野球選手Bに重点を置いて見ていることが分かる。この時、ユーザがグラフ30内の視聴因子の寄与度を変更(分散値への係数を変更)し、グラフ30aのようにした場合、変更後の寄与度ε’iは、下式(2),(3)で与えられる。ここで、εiは、更新前の寄与度である。尚、視聴因子のキーワードヒストグラムの変更に際しては、頻度値そのものを直接変更する。ただし、再度ヒストグラム全体を正規化する必要がある。変更された視聴因子を使って、新しいコンテンツをユーザが視聴する確率を計算する(図10を参照)。In the
このようにして、例えば、出演者に関する寄与度、すなわち視聴因子(出演者)のキーワード統計分布51で例示するキーワードの分散や視聴因子(出演者)のキーワードヒストグラム52で例示するキーワードヒストグラムを求める。尚、全ての寄与度を0とすると、初期登録のみの寄与度により順位付けがなされ、全ての寄与度をノーマライズすると、全ての因子が等しく寄与するような順位付けがなされる。 In this way, for example, the degree of contribution related to the performer, that is, the keyword distribution exemplified by the keyword
図12及び図13は、図1の情報ナビゲーション装置におけるコンテンツ推薦の一連の流れを説明するための図で、図12(A)は標準コンテンツ属性と自己申告との時間経過による割合の変化を表す図で、図12(B)はコンテンツ推薦の流れを説明するためのフロー図である。特に、図13は、視聴データ収集からコンテンツ推薦までの流れを説明するためのフロー図である。ここでは、簡略化のため、ユーザによる修正も含めた形態を説明するが、「ユーザによる修正」を含めない形態にあってはその部分を除けばよい。 12 and 13 are diagrams for explaining a series of content recommendation flow in the information navigation apparatus of FIG. 1, and FIG. 12 (A) shows a change in the ratio of the standard content attribute and self-report over time. FIG. 12B is a flowchart for explaining the flow of content recommendation. In particular, FIG. 13 is a flowchart for explaining the flow from viewing data collection to content recommendation. Here, for the sake of simplification, a mode including correction by the user will be described. However, if the mode does not include “correction by the user”, that portion may be omitted.
まず、視聴履歴が全くない場合、すなわち購入したばっかりで、全く視聴傾向の分析ができない場合、若しくは、分析するにはデータが少なすぎる場合は、ユーザが予め自己申告した(登録した)キーワードを用いて、視聴傾向の分析を行うと仮定している。この自己申告と標準コンテンツ属性との比率は、時間経過により視聴傾向の分析に必要なデータが収集されるので、図12(A)に示すような形が上げられる。つまり、最初は、自己申告のキーワードを視聴因子として用い、時間が経過するにつれて、ユーザがコンテンツを視聴した際に得られた標準コンテンツ属性の視聴因子を用いるように、配分比率を変えるという方法がある。 First, if there is no viewing history at all, that is, if you have just purchased and cannot analyze the viewing tendency at all, or if there is too little data to analyze, use the keywords that the user self-reported (registered) in advance Therefore, it is assumed that the viewing tendency is analyzed. The ratio between the self-report and the standard content attribute is increased as shown in FIG. 12A because data necessary for analyzing the viewing tendency is collected over time. That is, at first, the self-declared keyword is used as a viewing factor, and as time passes, the distribution ratio is changed so that the viewing factor of the standard content attribute obtained when the user views the content is used. is there.
図12(B)を参照して説明すると、まずは、コンテンツ全体(母集団)61から、自己申告されたキーワードを用いた検索65を実行してランキングを算出し、コンテンツ順位別の一覧62を求め、個人内因子・慣用因子による再ランキング(P(W)に相当)67を行い、最終的なランキングを算出する。若しくは、コンテンツ全体(母集団)61から、コンテンツ属性によるコンテンツのランキング66を実行し、コンテンツ順位別の一覧62を求め、個人内因子・慣用因子による再ランキング(P(W)に相当)67を行い、最終的なランキングを算出する。 Referring to FIG. 12B, first, a
そして、その結果であるコンテンツ一覧63を、ユーザに視聴傾向のグラフ化表示64により提示する。ユーザが、視聴傾向のグラフ化されたものを表示し修正した場合には、自己申告キーワードを用いた検索65若しくは標準コンテンツ属性によるコンテンツのランキング66を再度行う。 Then, the
図13を参照して、視聴データ収集からコンテンツ推薦までの流れを説明すると、ユーザによるコンテンツ視聴(ステップS11)が行われた後、その視聴されたコンテンツとコンテンツに付随するメタデータが視聴履歴データとして収集される(ステップS12)。すなわち、ステップS12では、コンテンツ選択履歴が記憶される。 Referring to FIG. 13, the flow from viewing data collection to content recommendation will be described. After content viewing by the user (step S11), the viewed content and metadata associated with the content are viewed history data. (Step S12). That is, in step S12, the content selection history is stored.
次に、分析に移る。メタデータに含まれるキーワード抽出のために、形態素解析が行われ、複数のキーワードが抽出される(ステップS13)。その後、キーワード分布の分散値計算(ステップS14)、キーワードヒストグラムの作成(ステップS15)が、正規化と共に計算が行われる。このキーワード分布の分散値と、ヒストグラムから視聴因子別の寄与度の計算が行われる(ステップS16)。これが視聴傾向結果となる。 Next, move on to analysis. To extract keywords included in the metadata, morphological analysis is performed, and a plurality of keywords are extracted (step S13). Thereafter, calculation of the variance value of the keyword distribution (step S14) and creation of the keyword histogram (step S15) are performed together with normalization. The degree of contribution for each audience factor is calculated from the variance value of the keyword distribution and the histogram (step S16). This is the viewing tendency result.
この視聴傾向結果を元に、新規に推薦するコンテンツのために、複数のコンテンツメタデータを使って、推薦候補コンテンツの計算が行われ(ステップS16)。この時の複数コンテンツメタデータは、その時点で視聴できるコンテンツのものであったり、既に録画済みのコンテンツのメタデータであることが多い。勿論、全ての視聴可能なコンテンツのメタデータの計算を行うことは非現実である場合が殆どであるため、視聴傾向結果から上位のコンテンツに絞って、計算が行われる場合もある。この視聴因子別寄与度計算が行われた後に、寄与度の値から順位付けされたコンテンツがユーザに推薦されることとなる(ステップS17)。また、ユーザの修正があった場合には、再度、ステップS16の計算及びステップS17における推薦及び表示を実行し、ユーザの修正を反映すればよい(図12(B)を参照)。 Based on this viewing tendency result, the recommended candidate content is calculated using a plurality of content metadata for the newly recommended content (step S16). The multiple content metadata at this time is often content that can be viewed at that time, or metadata of content that has already been recorded. Of course, since it is almost unrealistic to calculate the metadata of all viewable contents, the calculation may be performed by narrowing down to the upper content from the viewing tendency result. After the audience factor-specific contribution calculation is performed, the content ranked based on the contribution value is recommended to the user (step S17). If there is a user correction, the calculation in step S16 and the recommendation and display in step S17 may be executed again to reflect the user correction (see FIG. 12B).
図14及び図15は、図1の情報ナビゲーション装置におけるコンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段の記憶処理例を説明するための図で、図14は視聴履歴データの記録例を、図15は図14の視聴履歴データを時系列で記録する例を説明するための図である。 14 and 15 are diagrams for explaining a storage processing example of the content selection history storage means in the information navigation apparatus of FIG. 1, FIG. 14 is a recording example of viewing history data, and FIG. 15 is a viewing history of FIG. It is a figure for demonstrating the example which records data in time series.
コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14の記録方法の例を、図14中、符号70で例示する。ここでは、ユーザ視聴結果として得られた標準コンテンツ属性71(標準コンテンツ属性名71の標準コンテンツ属性)のキーワードの分散値の大小により、すなわち、寄与度計算の元になる分散値によって、重要度が異なることを示している(図14中、符号72を参照)。分散が小さい場合は視聴寄与度へ与える影響も大きいことを示している。同様に分散が大きい場合は、視聴寄与度へ与える影響が小さいことを示している。ここで例示したように、コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14における1つのコンテンツ選択履歴(視聴データ)は、各標準コンテンツ属性71を分散値の大小と共に記憶すればよいが、この方法に限ったものではない。 An example of a recording method of the content selection
コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段14では実際には時系列や集計によって記録されることとなる。図15で例示するように、図14で例示したような標準コンテンツ属性のキーワードの分散値の集計は、ユーザの視聴開始からこの機能を搭載した機器の使用停止(破棄するまで)まで、1つの結果として集計する場合や、各時間間隔毎(24時間毎,1ヶ月毎等)に集計する場合(視聴履歴データ71a,71b,71c,71d,・・・)がある。 In the content selection history storage means 14, it is actually recorded in time series or totalization. As illustrated in FIG. 15, the aggregation of the standard content attribute keywords as illustrated in FIG. 14 is counted from the start of user viewing until the use of the device equipped with this function is stopped (until it is discarded). As a result, there are cases where data is aggregated, and data is aggregated every time interval (every 24 hours, every month, etc.) (
ユーザの行動として、朝見る番組は決まっており、夜見る番組は、その都度面白いものを見るといった場合、1つの結果として集計するよりも、時間間隔毎(朝,昼,夜等)に集計する方が、推薦コンテンツの精度を上げる点で好ましい。しかしながら、時間間隔毎に集計した場合には、該当する時間帯に視聴履歴がない場合、コンテンツを推薦することができなくなってしまう。つまり、朝と夜にコンテンツは視聴するが、昼は見ないといった場合、ある時昼にコンテンツを見ようと思っても集計データがないために、コンテンツを推薦することができない。 As the user's behavior, the program to watch in the morning is decided, and the program to watch at night is counted every time interval (morning, noon, night, etc.) rather than summing up as one result when watching interesting programs each time. This is preferable in terms of increasing the accuracy of recommended content. However, when counting is performed for each time interval, it becomes impossible to recommend content if there is no viewing history in the corresponding time zone. In other words, if you watch the content in the morning and at night but do not watch it at noon, you cannot recommend the content because there is no aggregate data even if you try to watch the content at noon.
このような場合には、朝と夜の集計結果から、若しくは集計の元となる視聴履歴から、昼の視聴傾向を補間(補完)する方法が考えられる。例えば、ユーザはある出演者のファンであり、朝でも夜でも、コンテンツが放送していれば若しくは視聴可能であれば見るというケースに、たまたま昼にも放送されることがわかり、見ようと思った場合、朝と夜の視聴履歴データ、若しくは、視聴傾向結果から、昼にもある出演者の視聴因子の寄与度を補完することが可能になる。また、補完する方法についても、線形(単純に朝と夜を足して2で割るというような、1次式で表現できる場合)に補完する場合や、2次式で補完する場合、スプライン関数など、若しくは、朝や夜のどちらか一方と同じにするといった方法など、時間的推移を考慮した方法も考えられる。 In such a case, a method of interpolating (complementing) the daytime viewing tendency from the morning and night totaling results or from the viewing history that is the basis of the totaling can be considered. For example, the user is a fan of a performer, and in the morning or at night, if the content is broadcast or if it can be viewed, it will be seen that it will be broadcast in the afternoon, so I wanted to watch it In this case, it is possible to supplement the contribution of the viewing factors of the performers who are also in the daytime from the morning and evening viewing history data or the viewing tendency result. As for the method of complementation, when complementing linearly (when it can be expressed by a linear expression such as simply adding morning and night and dividing by 2), when complementing with a quadratic expression, a spline function, etc. Alternatively, a method that considers temporal transition, such as a method of making it the same as either morning or night, can be considered.
そして、ユーザの履歴データを機器購入してからの最初の使用開始から、機器廃棄までの使用停止まで、全て保存できる場合や、記憶容量の関係から、過去の古いものから削除していき、一定の容量に抑えるという場合も考えられる。この場合、単純に実際に記録した視聴履歴データを削除して、次の実際に記録した視聴履歴データから始めるという場合だけでなく、その間を補完した視聴履歴データ、若しくは視聴履歴結果、視聴傾向結果を保持するということも考えられる。これは、ユーザの最新情報を常に優先度を高く評価するような場合に相当し、現在時刻のものほど視聴履歴データを高く評価し、過去の古い視聴履歴データを低く評価するということに相当する。勿論、時系列パラメータとして、現在を1.0、過去にさかのぼるほど0.0に近づけた値を、視聴因子の寄与度計算に反映する(掛け算若しくは、逆数の引き算等)方法もある。 And if you can save everything from the first use of the user's history data after purchasing the device to the end of use until the device is discarded, or because of the storage capacity, it will be deleted from the oldest ones. It is also conceivable that the capacity is limited to. In this case, not only simply deleting the actually recorded viewing history data and starting from the next actually recorded viewing history data, but also complementing the viewing history data or viewing history results, viewing trend results It is also conceivable to hold This corresponds to a case where the latest information of the user is always evaluated with a high priority, and is equivalent to evaluating the viewing history data higher for the current time and lowering the past old viewing history data. . Of course, as a time series parameter, there is also a method of reflecting a value that approaches 1.0 at the present time and 0.0 as it goes back in the past in the calculation of the contribution degree of the viewing factor (multiplication or subtraction of the reciprocal number).
更に、環境情報として世相・流行の情報を視聴因子の寄与度計算に反映する方法も考えられる。つまり、音楽CD売り上げランキングやDVDレンタルランキング、映画等の興業収益ランキングなどのランキング情報を、環境情報として取り込む(例えば、P(W)のキーワードとして利用など)方法である。しかし、ランキング情報がないニュースなどでは、「今日のトピック」などの情報を利用するか、時事そのものを推定する方法をとらなければならない。例えば、時事を推定する方法としては、ニュースの各記事(社会,スポーツ,政治,経済,文化・芸能等)の内容、若しくは見出しのキーワード抽出を行い、直接利用する場合や、各時刻におけるニュースタイトル・記事のキーワード分布の頻度及び時系列変化を用いる場合がある。つまり、急激に頻度が高くなったキーワードが一定時間持続するもの時事(若しくは、世相・流行)とする場合がある。この場合、突発的に頻度の高いキーワード、常に頻度の高いキーワード、単純に頻度の低いキーワードは世相・流行とは見なさないなどの処理が必要になる。また、ニュースのタイトルではなく、記事内容から直接キーワードを求める場合は、TF/IDF(Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequancy)手法等による重要語抽出方法が挙げられる。 Furthermore, there may be a method of reflecting social and fashion information as environmental information in the contribution factor calculation. That is, it is a method of taking in ranking information such as music CD sales ranking, DVD rental ranking, and industry profit ranking of movies and the like as environmental information (for example, using it as a keyword of P (W)). However, for news that does not have ranking information, information such as “Today's topic” should be used, or a method of estimating the current affair itself must be taken. For example, as a method of estimating current events, the content of each news article (society, sports, politics, economy, culture, performing arts, etc.) or keyword extraction of headlines is extracted and used directly, or the news title at each time・ The frequency of the keyword distribution of articles and time-series changes may be used. In other words, there is a case where a keyword whose frequency has suddenly increased lasts for a certain period of time (or social situation / trend). In this case, it is necessary to perform processing such as suddenly high-frequency keywords, always high-frequency keywords, and simply low-frequency keywords are not regarded as social trends / trends. In addition, when a keyword is directly obtained from an article content instead of a news title, an important word extraction method using a TF / IDF (Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequency) method or the like can be used.
本発明に係る情報ナビゲーション装置及び方法によれば、膨大な量のデジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向をできるだけ客観的な尺度で把握し、これに基づきユーザのコンテンツ選択の補助となるようなコンテンツ情報を出力することが可能となる。すなわち、ユーザのデジタルコンテンツに対する視聴傾向を定量的に分析し、その分析結果に基づいてユーザの視聴に適したコンテンツ情報を出力(表示)できる。特に、多様化、複雑化しているデジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向を分析し、その分析結果に基づいて、ユーザが直感的に認識できるようなコンテンツ情報の出力を行うことにより、具体的には、コンテンツの視聴回数や頻度だけではなくコンテンツ属性に含まれるキーワード間のばらつきも考慮してユーザの視聴傾向を分析し、分析された視聴傾向をレーダチャートなどの図やリスト等を用いてユーザに提示することにより、効果的な情報ナビゲーション機能を提供することができる。また、このような情報分析方法だけでも有用である。また、本発明は、基本的に、ユーザの個人情報(年齢・性別,好み,キーワード等)を予め登録しなくても、視聴傾向を算出することができ、視聴傾向に合致したコンテンツを推薦できる。 According to the information navigation apparatus and method of the present invention, content information that assists the user in selecting content based on the user's viewing tendency with respect to an enormous amount of digital content is ascertained on an objective scale as much as possible. It becomes possible to output. That is, it is possible to quantitatively analyze the viewing tendency of the user with respect to the digital content, and output (display) content information suitable for the user's viewing based on the analysis result. In particular, by analyzing the user's viewing tendency for diversified and complicated digital content, and by outputting content information that can be intuitively recognized by the user based on the analysis result, specifically, Analyzes the user's viewing tendency considering not only the number and frequency of content viewing but also the variation among keywords included in the content attribute, and presents the analyzed viewing tendency to the user using a chart or list such as a radar chart By doing so, an effective information navigation function can be provided. Also, such an information analysis method alone is useful. In addition, according to the present invention, it is possible to calculate a viewing tendency without registering user's personal information (age / gender, preference, keyword, etc.) in advance, and to recommend content that matches the viewing tendency. .
また、本発明を適用することで、コンテンツの視聴時刻が重なった時でもユーザの視聴傾向に基づいて視聴及び録画の有線選択を自動的に行うこと、ユーザに指示されていなくても視聴傾向に基づいて自動的に録画すること、視聴している番組の終わりの時に次のお薦めコンテンツを視聴傾向に基づいて推薦すること(例えば、お薦めコンテンツの放送開始時間が近づいたら、ユーザに知らせること)、及び、ユーザが何か面白い番組がないかチャンネルを頻繁に切り替えて、コンテンツを探している場合には自動的にオススメコンテンツを推薦することなど、様々なメリットをユーザは享受できる。 In addition, by applying the present invention, even when the viewing time of content overlaps, wired selection for viewing and recording is automatically performed based on the viewing tendency of the user, and even if the user is not instructed, the viewing tendency is increased. Automatically record based on, recommend the next recommended content based on viewing tendency at the end of the program being watched (for example, notify the user when the recommended content starts to broadcast), In addition, the user can enjoy various merits such as frequently recommending recommended content when the user is searching for content by frequently switching channels for any interesting program.
さらに、ユーザ修正が可能な形態にあっては、単に過去のコンテンツ選択履歴から分析される視聴傾向に基づいてコンテンツ選択の補助を行うのみではなく、膨大な量のデジタルコンテンツに対するユーザの視聴傾向をできるだけ客観的な尺度で把握し、これに基づきユーザのコンテンツ選択の補助となるなコンテンツ情報を表示すると共に、提示された視聴傾向(視聴履歴の分析と計算により算出されたユーザの視聴傾向)に対してユーザがその場で修正を行うことにより、具体的にはユーザが図やリストを直接変更することにより、ユーザ自身のその時点での視聴傾向をリアルタイムに反映させることができる。また、ユーザは、反映させた結果で改めて、推薦コンテンツを求めることもできる。従って、その日その時の気分に左右されるユーザの視聴により視聴に適したコンテンツの検索を行って再度推奨することや、その場でユーザからの視聴傾向の直感的な修正を取り入れたコンテンツの推奨が可能となる。 Furthermore, in a form in which the user can be modified, not only the content selection is assisted based on the viewing tendency analyzed from the past content selection history but also the user's viewing tendency with respect to a huge amount of digital content. Understand as much as possible with an objective scale, and display content information that will assist users in selecting content based on this, and show the viewing tendency (user viewing tendency calculated by analysis and calculation of viewing history). On the other hand, when the user makes corrections on the spot, specifically, when the user directly changes the diagram or list, the viewing tendency of the user himself / herself at that time can be reflected in real time. In addition, the user can obtain the recommended content again with the reflected result. Therefore, it is recommended to search again for the content suitable for viewing by the user's viewing that depends on the mood at that time and to recommend it again, or to recommend content that incorporates intuitive correction of viewing tendency from the user on the spot. It becomes possible.
以上、本発明に係る情報ナビゲーション装置及びその方法について説明してきたが、本発明は、各実施形態における情報ナビゲーション装置における各手段として、コンピュータ(PC等)を機能させるためのプログラムとしての形態も採用できる。これら各手段のうち記憶手段は、例えばコンピュータにおける記憶装置及びそれを制御する手段となる。本発明は、さらに、このプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体としての形態も採用できる。本発明による情報ナビゲーションの機能を実現するためのプログラムやデータを記憶した記録媒体の実施形態を説明する。記録媒体としては、具体的には、CD−ROM、光磁気ディスク、DVD−ROM、FD、フラッシュメモリ、及びその他各種ROMやRAM等が想定でき、上述した本発明の各実施形態に係る情報ナビゲーションプログラムを、これら記録媒体に記録して流通させることにより、当機能の実現を容易にする。そして、CPU,メモリ等を備えたコンピュータなどの情報処理装置に、上述のごとくの記録媒体を装着して情報処理装置によりプログラムを読み出すか、若しくは情報処理装置が備えている記録媒体に当プログラムを記憶させておき、必要に応じて読み出すことにより、本発明に係わる情報ナビゲーションの機能を実行することができる。 As described above, the information navigation apparatus and the method thereof according to the present invention have been described. However, the present invention also adopts a form as a program for causing a computer (PC or the like) to function as each means in the information navigation apparatus according to each embodiment. it can. Of these means, the storage means is, for example, a storage device in a computer and a means for controlling it. The present invention can also adopt a form as a computer-readable recording medium on which the program is recorded. An embodiment of a recording medium storing a program and data for realizing an information navigation function according to the present invention will be described. Specifically, a CD-ROM, a magneto-optical disk, a DVD-ROM, an FD, a flash memory, and other various ROMs and RAMs can be assumed as the recording medium. The information navigation according to each embodiment of the present invention described above. This function is facilitated by recording and distributing the program on these recording media. Then, the information processing apparatus such as a computer having a CPU and a memory is loaded with the recording medium as described above, and the program is read by the information processing apparatus, or the program is loaded on the recording medium provided in the information processing apparatus. The information navigation function according to the present invention can be executed by storing it and reading it out as necessary.
尚、本発明に係る情報ナビゲーション機能について、具体的な実施の形態を示して説明したが、本発明はこれらに限定されるものではない。当業者であれば、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲内において、上記各実施形態又は他の実施形態にかかる発明の構成及び機能に様々な変更・改良を加えることが可能である。 The information navigation function according to the present invention has been described with reference to specific embodiments, but the present invention is not limited to these. A person skilled in the art can make various changes and improvements to the configurations and functions of the invention according to the above-described embodiments or other embodiments without departing from the gist of the present invention.
本発明は、上述のごとき情報ナビゲーション装置を、ネットショッピングや広告配信等に対しても応用し、同様の情報ナビゲーション処理を実行することが可能である。これは、ネットショッピングで閲覧及び/又は購入する商品に関する情報や、配信される広告情報が、デジタルコンテンツであると謂えることを鑑みれば容易に理解し、応用することができる。 The present invention can apply the information navigation apparatus as described above to online shopping, advertisement distribution, etc., and execute the same information navigation processing. This can be easily understood and applied in view of the fact that information regarding products to be browsed and / or purchased through online shopping and distributed advertisement information are digital contents.
1…情報ナビゲーション装置、10…制御手段、11…表示手段、12…入力手段、13…視聴傾向分析手段、14…コンテンツ選択履歴記憶手段、15…コンテンツ情報データベース、16…外部接続端子、17…ネットワークインターフェイス、18…チューナ、19…ハードディスク。DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (27)
Translated fromJapanesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004172683AJP2005352754A (en) | 2004-06-10 | 2004-06-10 | Information navigation apparatus, method, program, and recording medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004172683AJP2005352754A (en) | 2004-06-10 | 2004-06-10 | Information navigation apparatus, method, program, and recording medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005352754Atrue JP2005352754A (en) | 2005-12-22 |
Family
ID=35587190
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004172683APendingJP2005352754A (en) | 2004-06-10 | 2004-06-10 | Information navigation apparatus, method, program, and recording medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005352754A (en) |
Cited By (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006339693A (en)* | 2005-05-31 | 2006-12-14 | Sony Corp | Information processing apparatus, processing method thereof, and program for making computer execute the method |
| JP2007200104A (en)* | 2006-01-27 | 2007-08-09 | Toshiba Corp | Display control system, display control method, and display control program |
| JP2007208965A (en)* | 2006-01-04 | 2007-08-16 | Hitachi Ltd | Video system and video selection method thereof |
| JP2007233515A (en)* | 2006-02-28 | 2007-09-13 | Sony Corp | Information processor and information processing method, information providing apparatus and information providing method, and program |
| WO2008004576A1 (en)* | 2006-07-06 | 2008-01-10 | Pioneer Corporation | Content evaluation/search device |
| JP2008141416A (en)* | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-19 | Fujitsu Ltd | Program search device |
| JP2008306655A (en)* | 2007-06-11 | 2008-12-18 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Viewing history storage device, digital broadcast receiving device, and recommended program search device |
| JP2009237676A (en)* | 2008-03-26 | 2009-10-15 | Softbank Mobile Corp | Web page retrieval program and web page retrieval system |
| US7620964B2 (en) | 2005-12-26 | 2009-11-17 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Recommended program search device and recommended program search method |
| WO2010089961A1 (en)* | 2009-02-06 | 2010-08-12 | パナソニック株式会社 | Video search and playback system, video search device, and video playback device |
| JP2011527049A (en)* | 2008-06-28 | 2011-10-20 | マイクロソフト コーポレーション | Playlists suitable for rental jukebox media content services and personal media players |
| JP2013097554A (en)* | 2011-10-31 | 2013-05-20 | Jvc Kenwood Corp | Information processor, information processing method and information processing program |
| JP2014502392A (en)* | 2010-11-25 | 2014-01-30 | サムスン エレクトロニクス カンパニー リミテッド | Content providing method and system |
| JP2014518583A (en)* | 2011-04-25 | 2014-07-31 | アリババ・グループ・ホールディング・リミテッド | Determination of recommended data |
| KR20150101340A (en)* | 2014-02-26 | 2015-09-03 | 에스케이플래닛 주식회사 | Method of generating category preference for each user, method of recommending products using the same and apparatus for the same |
| JP2015177526A (en)* | 2014-03-18 | 2015-10-05 | Necパーソナルコンピュータ株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing apparatus control method, and program |
| JP2015177525A (en)* | 2014-03-18 | 2015-10-05 | Necパーソナルコンピュータ株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing apparatus control method, and program |
| KR20160044278A (en)* | 2014-10-15 | 2016-04-25 | 주식회사 케이티 | Method for making theme of contents, apparatus and system |
| JP2020057406A (en)* | 2016-04-22 | 2020-04-09 | グーグル エルエルシー | Viewing time clustering for video search |
| JP2022051090A (en)* | 2020-09-18 | 2022-03-31 | Tvs Regza株式会社 | Data acquisition equipment, programs and information processing systems |
| JP2022158864A (en)* | 2021-03-31 | 2022-10-17 | 株式会社ビデオリサーチ | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
| JP7741942B1 (en)* | 2024-08-23 | 2025-09-18 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | Information processing device and information processing method |
- 2004
- 2004-06-10JPJP2004172683Apatent/JP2005352754A/enactivePending
Cited By (31)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006339693A (en)* | 2005-05-31 | 2006-12-14 | Sony Corp | Information processing apparatus, processing method thereof, and program for making computer execute the method |
| US7620964B2 (en) | 2005-12-26 | 2009-11-17 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Recommended program search device and recommended program search method |
| JP2007208965A (en)* | 2006-01-04 | 2007-08-16 | Hitachi Ltd | Video system and video selection method thereof |
| JP2007200104A (en)* | 2006-01-27 | 2007-08-09 | Toshiba Corp | Display control system, display control method, and display control program |
| JP2007233515A (en)* | 2006-02-28 | 2007-09-13 | Sony Corp | Information processor and information processing method, information providing apparatus and information providing method, and program |
| JPWO2008004576A1 (en)* | 2006-07-06 | 2009-12-03 | パイオニア株式会社 | Content evaluation device, content search device, content evaluation method, content search method, and first and second computer programs |
| WO2008004576A1 (en)* | 2006-07-06 | 2008-01-10 | Pioneer Corporation | Content evaluation/search device |
| JP2008141416A (en)* | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-19 | Fujitsu Ltd | Program search device |
| JP2008306655A (en)* | 2007-06-11 | 2008-12-18 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Viewing history storage device, digital broadcast receiving device, and recommended program search device |
| JP2009237676A (en)* | 2008-03-26 | 2009-10-15 | Softbank Mobile Corp | Web page retrieval program and web page retrieval system |
| JP2011527049A (en)* | 2008-06-28 | 2011-10-20 | マイクロソフト コーポレーション | Playlists suitable for rental jukebox media content services and personal media players |
| WO2010089961A1 (en)* | 2009-02-06 | 2010-08-12 | パナソニック株式会社 | Video search and playback system, video search device, and video playback device |
| US9465863B2 (en) | 2010-11-25 | 2016-10-11 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Content-providing method and system |
| JP2014502392A (en)* | 2010-11-25 | 2014-01-30 | サムスン エレクトロニクス カンパニー リミテッド | Content providing method and system |
| JP2014518583A (en)* | 2011-04-25 | 2014-07-31 | アリババ・グループ・ホールディング・リミテッド | Determination of recommended data |
| US9047623B2 (en) | 2011-04-25 | 2015-06-02 | Alibaba Group Holding Limited | Determination of recommendation data |
| JP2013097554A (en)* | 2011-10-31 | 2013-05-20 | Jvc Kenwood Corp | Information processor, information processing method and information processing program |
| KR102210442B1 (en)* | 2014-02-26 | 2021-02-02 | 에스케이플래닛 주식회사 | Method of generating category preference for each user, method of recommending products using the same and apparatus for the same |
| KR20150101340A (en)* | 2014-02-26 | 2015-09-03 | 에스케이플래닛 주식회사 | Method of generating category preference for each user, method of recommending products using the same and apparatus for the same |
| WO2015129988A1 (en)* | 2014-02-26 | 2015-09-03 | 에스케이플래닛 주식회사 | Method for generating category preference for each user, method for product recommendation using same, and device for same |
| JP2015177526A (en)* | 2014-03-18 | 2015-10-05 | Necパーソナルコンピュータ株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing apparatus control method, and program |
| JP2015177525A (en)* | 2014-03-18 | 2015-10-05 | Necパーソナルコンピュータ株式会社 | Information processing apparatus, information processing apparatus control method, and program |
| KR20160044278A (en)* | 2014-10-15 | 2016-04-25 | 주식회사 케이티 | Method for making theme of contents, apparatus and system |
| KR101616788B1 (en) | 2014-10-15 | 2016-04-29 | 주식회사 케이티 | Method for making theme of contents, apparatus and system |
| JP2020057406A (en)* | 2016-04-22 | 2020-04-09 | グーグル エルエルシー | Viewing time clustering for video search |
| US11570512B2 (en) | 2016-04-22 | 2023-01-31 | Google Llc | Watch-time clustering for video searches |
| JP2022051090A (en)* | 2020-09-18 | 2022-03-31 | Tvs Regza株式会社 | Data acquisition equipment, programs and information processing systems |
| JP7248633B2 (en) | 2020-09-18 | 2023-03-29 | Tvs Regza株式会社 | Data collection device, program and information processing system |
| JP2022158864A (en)* | 2021-03-31 | 2022-10-17 | 株式会社ビデオリサーチ | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
| JP7534718B2 (en) | 2021-03-31 | 2024-08-15 | 株式会社ビデオリサーチ | Information processing device, information processing method, and program |
| JP7741942B1 (en)* | 2024-08-23 | 2025-09-18 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | Information processing device and information processing method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101142935B1 (en) | Method and device for generating a user profile on the basis of playlists | |
| JP2005352754A (en) | Information navigation apparatus, method, program, and recording medium | |
| CN1659882B (en) | Method and system for completing content augmentation of personal profiles | |
| JP4363806B2 (en) | Audiovisual program management system and audiovisual program management method | |
| US7657907B2 (en) | Automatic user profiling | |
| RU2524840C2 (en) | Adaptive implicit examination for recommendation systems | |
| JP7514892B2 (en) | SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR IDENTIFYING AUDIO CONTENT USING INTERACTIVE MEDIA GUIDANCE | |
| US8782533B2 (en) | Collaborative device for enabling users to select collaborative content, and method thereof | |
| JP4370850B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus and method, program, and recording medium | |
| JP2005539307A (en) | Adapting media system interest profiles | |
| KR20060125523A (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program | |
| CN102265276A (en) | Context-based recommender system | |
| JP2005056361A (en) | Information processor and method, program, and storage medium | |
| JP2005509965A (en) | Creating an agent used to recommend media content | |
| WO2011101527A1 (en) | Method for providing a recommendation to a user | |
| CN102084645A (en) | Related scene addition device and related scene addition method | |
| CN1666519A (en) | Context and time-sensitive profile builder | |
| JP2005018269A (en) | Information navigation device | |
| JP5008250B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus and method, program, and recording medium | |
| JP5757886B2 (en) | Television broadcast recording reservation method, apparatus and system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20060912 | |
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date:20060922 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20090609 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20090807 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20091020 | |
| A521 | Written amendment | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20100107 | |
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date:20100201 | |
| A912 | Re-examination (zenchi) completed and case transferred to appeal board | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date:20100219 |