JP2005329018A - Medical appliance - Google Patents
Medical applianceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005329018A JP2005329018AJP2004150056AJP2004150056AJP2005329018AJP 2005329018 AJP2005329018 AJP 2005329018AJP 2004150056 AJP2004150056 AJP 2004150056AJP 2004150056 AJP2004150056 AJP 2004150056AJP 2005329018 AJP2005329018 AJP 2005329018A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- catheter
- guide wire
- medical instrument
- coil spring
- pigtail
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 229920005989resinPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 239000011347resinSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 239000003550markerSubstances0.000claimsdescription11
- 238000005452bendingMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000003780insertionMethods0.000abstractdescription6
- 230000037431insertionEffects0.000abstractdescription6
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000010998test methodMethods0.000description4
- 229910045601alloyInorganic materials0.000description3
- 239000000956alloySubstances0.000description3
- 238000009434installationMethods0.000description3
- 229910001000nickel titaniumInorganic materials0.000description3
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000description3
- 238000005219brazingMethods0.000description2
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description2
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description2
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description2
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description2
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-NplatinumChemical compound[Pt]BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000description2
- 229920005992thermoplastic resinPolymers0.000description2
- 239000004698PolyethyleneSubstances0.000description1
- 239000004433Thermoplastic polyurethaneSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002272anti-calculusEffects0.000description1
- 230000002785anti-thrombosisEffects0.000description1
- 239000003146anticoagulant agentSubstances0.000description1
- 229920001971elastomerPolymers0.000description1
- 239000000806elastomerSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001747exhibiting effectEffects0.000description1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-NgoldChemical compound[Au]PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910052737goldInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000010931goldSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001771impaired effectEffects0.000description1
- 229910052741iridiumInorganic materials0.000description1
- GKOZUEZYRPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-Niridium atomChemical compound[Ir]GKOZUEZYRPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052697platinumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000013001point bendingMethods0.000description1
- 229920006122polyamide resinPolymers0.000description1
- -1polyethylenePolymers0.000description1
- 229920000573polyethylenePolymers0.000description1
- 229920002635polyurethanePolymers0.000description1
- 239000004814polyurethaneSubstances0.000description1
- 229920003225polyurethane elastomerPolymers0.000description1
- 239000002994raw materialSubstances0.000description1
- 229920002050silicone resinPolymers0.000description1
- 239000007779soft materialSubstances0.000description1
- 229920002725thermoplastic elastomerPolymers0.000description1
- 229920002803thermoplastic polyurethanePolymers0.000description1
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-NtungstenChemical compound[W]WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910052721tungstenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000010937tungstenSubstances0.000description1
- 238000003466weldingMethods0.000description1
- 238000004804windingMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Media Introduction/Drainage Providing Device (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromJapanese本発明は医療器具に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a medical device.
カテーテルは様々な用途で利用され、使用される目的、症例、体の部位によってその形状も様々である。カテーテルを体内に留置する際、カテーテルの留置位置移動を防止するために、端部に固定手段を有するカテーテルも多く、その固定手段としてマレコット状またはピッグテール状に成形したり、カテーテルを複数のルーメンからなるマルチルーメンチューブとして端部にバルーンを取り付けたりする方法が好んで用いられる。 Catheters are used in various applications, and their shapes vary depending on the purpose, case, and body part used. In order to prevent the indwelling position of the catheter from moving when the catheter is placed in the body, there are many catheters having a fixing means at the end, and the fixing means is formed into a malecot shape or a pigtail shape, or the catheter is divided into a plurality of lumens As a multi-lumen tube, a method of attaching a balloon to the end is preferably used.
カテーテルを体内に留置する際には、一般的にはガイドワイヤーをまず体内に留置し、そのガイドワイヤーに沿わせてカテーテルを体内に挿入していく場合が多い。
マレコットカテーテルやバルーンカテーテルである場合、カテーテルの固定手段部分はカテーテル挿入時には直線状であるため、体内に挿入する際に大きな抵抗となることは少ないが、ピッグテールカテーテルの場合、ガイドワイヤーを挿入してもピッグテール部分が十分に直線状にならず、挿入が困難となってしまう場合が多い。When placing a catheter in the body, in general, a guide wire is first placed in the body, and the catheter is often inserted into the body along the guide wire.
In the case of a malecot catheter or balloon catheter, the fixing means of the catheter is straight when inserted, so there is little resistance when inserted into the body, but in the case of a pigtail catheter, a guide wire is inserted. In many cases, however, the pigtail portion is not sufficiently linear, making insertion difficult.
カテーテルのピッグテール部分をできるだけ直線状にするためには、カテーテルに使用する樹脂の硬度を下げ、柔らかいものを原材料として使用することが考えられるが、樹脂硬度を下げた場合、カテーテルのコシが弱くなり、挿入しにくくなる。
よって、ピッグテール部のみを他部より樹脂硬度が低く、柔軟な樹脂で製造することが考えられているが、カテーテルの固定機能が損なわれるという問題点がある。
また、カテーテルを体内に挿入する際に使用されるガイドワイヤーとして、芯線をNiTi合金から形成し、折れ曲がりにくくしたガイドワイヤーがよく使用されるが、NiTi合金は従来からガイドワイヤーの芯線に使用されるステンレス鋼と比較して曲げ剛性が低く、ピッグテールカテーテルに挿入した場合、ピッグテール部分を十分に直線化できないという問題点がある。(例えば特許文献1)
Therefore, it is considered that only the pigtail part is made of a soft resin having a lower resin hardness than the other parts, but there is a problem that the fixing function of the catheter is impaired.
In addition, as a guide wire used when inserting a catheter into the body, a guide wire that is made of a NiTi alloy and is not easily bent is often used. However, a NiTi alloy is conventionally used as a guide wire core wire. There is a problem in that the bending rigidity is low compared to stainless steel, and when inserted into a pigtail catheter, the pigtail portion cannot be sufficiently straightened. (For example, Patent Document 1)
本発明は、上記問題点を解決することを目的とし、確実に体内で固定でき、挿入を容易とする医療器具を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a medical instrument that can be reliably fixed in the body and can be easily inserted.
このような目的は、下記(1)〜(11)に記載の本発明により達成される。
(1)カテーテルと前記カテーテル内に挿入されるガイドワイヤーとを有する医療器具であって、前記カテーテルを構成する樹脂の樹脂硬度は80〜100[A]であり、かつ前記ガイドワイヤーの曲げ荷重は7.0[N]以上であることを特徴とする医療器具。
(2)前記カテーテルの少なくとも一方の端部がピッグテール状に形成されているものである上記(1)に記載の医療器具。
(3)前記カテーテルには、目盛が設置されているものである上記(1)または(2)に記載の医療器具。
(4)前記カテーテルには、他部よりもX線不透過性が高い物質から形成されているマーカーが設置されているものである上記(1)ないし(3)のいずれかに記載の医療器具。
(5)前記マーカーは、前記カテーテルのピッグテール部と本体部の境界部に設置されているものである上記(4)に記載の医療器具。
(6)前記カテーテルの端部に糸が設置されている上記(1)ないし(5)のいずれかに記載の医療器具。
(7)前記カテーテルのピッグテール状に形成されている端部を直線化できる手段が設置されている上記(2)ないし(6)のいずれかに記載の医療器具。
(8)前記カテーテルのピッグテール状に形成されている端部を直線化できる手段は、前記カテーテルの外径より大きな内径を持ち、かつ前記カテーテルよりも硬質な筒状体である上記(7)に記載の医療器具。
(9)前記ガイドワイヤーは芯線と、該芯線の外周を被覆するコイルスプリングから構成され、少なくとも一部のコイルスプリングのピッチが他部と比較して大きいものである上記(1)ないし(8)のいずれかに記載の医療器具。
(10)前記コイルスプリングのピッチが他部と比較して大きいのは、前記ガイドワイヤーの先端部である上記(9)に記載の医療器具。
(11)前記芯線と前記コイルスプリングは先端部、後端部および、先端部と後端部の間の少なくとも1ヶ所以上で固定されているものである上記(9)または(10)に記載の医療器具。Such an object is achieved by the present invention described in the following (1) to (11).
(1) A medical instrument having a catheter and a guide wire inserted into the catheter, wherein the resin constituting the catheter has a resin hardness of 80 to 100 [A], and the bending load of the guide wire is A medical instrument characterized by being 7.0 [N] or more.
(2) The medical instrument according to (1), wherein at least one end of the catheter is formed in a pigtail shape.
(3) The medical instrument according to (1) or (2), wherein the catheter is provided with a scale.
(4) The medical device according to any one of (1) to (3), wherein the catheter is provided with a marker made of a substance having a higher radiopacity than other portions. .
(5) The medical instrument according to (4), wherein the marker is installed at a boundary portion between the pigtail portion and the main body portion of the catheter.
(6) The medical device according to any one of (1) to (5), wherein a thread is installed at an end of the catheter.
(7) The medical instrument according to any one of (2) to (6), wherein means for straightening an end portion of the catheter formed in a pigtail shape is installed.
(8) In the above (7), the means capable of straightening the end of the catheter formed into a pigtail shape is a cylindrical body having an inner diameter larger than the outer diameter of the catheter and harder than the catheter. The medical device described.
(9) Said guide wire is comprised from the core wire and the coil spring which coat | covers the outer periphery of this core wire, The pitch of at least one part coil spring is large compared with the other part (1) thru | or (8). The medical instrument in any one of.
(10) The medical instrument according to (9), wherein a pitch of the coil spring is larger than that of the other portion at a distal end portion of the guide wire.
(11) The core wire and the coil spring are fixed at at least one or more positions between a front end portion, a rear end portion, and a front end portion and a rear end portion, as described in (9) or (10) above. Medical instrument.
本発明により、確実に体内で固定でき、挿入を容易とする医療器具を提供することが出来る。
また、端部がピッグテール状に形成されたカテーテルであっても、ガイドワイヤー挿入時にピッグテール部が十分に直線化し、カテーテルを容易に体内に挿入できる医療器具を提供することが出来る。According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a medical instrument that can be reliably fixed in the body and can be easily inserted.
Moreover, even if the end portion of the catheter is formed into a pigtail shape, the pigtail portion is sufficiently straightened when the guide wire is inserted, and a medical instrument that can be easily inserted into the body can be provided.
以下、本発明の医療器具を添付図面に示す好適な実施の形態に基づいて詳細に説明する。
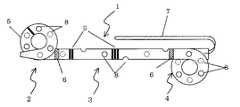
図1は本発明の一実施例であるカテーテル(1)の概略図である。図2は本発明の一実施例であるガイドワイヤーの断面を示す概略図である。図3は、比較例として従来のガイドワイヤーを示す概略図である。図4は、カテーテルの戻り角度を示す概略図である。Hereinafter, the medical device of the present invention will be described in detail based on preferred embodiments shown in the accompanying drawings.
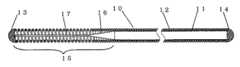
FIG. 1 is a schematic view of a catheter (1) according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a schematic view showing a cross section of a guide wire according to an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3 is a schematic view showing a conventional guide wire as a comparative example. FIG. 4 is a schematic view showing the return angle of the catheter.
図1に示すように、本発明の医療器具に用いられるカテーテル(1)は、腎盂内固定部(2)、本体部(3)、膀胱内固定部(4)、目盛(5)、X線造影マーカー(6)、糸(7)からなる。腎盂内固定部(2)と膀胱内固定部(4)がピッグテール部である。X線造影マーカー(6)が、他部よりもX線不透過性が高い物質である。腎盂内固定部(2)、本体部(3)、膀胱内固定部(4)は一体に成形された、特に限定はされないが、外径0.5〜20mm、肉厚0.1〜3.0mmのチューブからなり、樹脂硬度80〜100[A]、好ましくは85〜98[A]の熱可塑性樹脂、シリコーン樹脂等からなり、好ましくは熱可塑性ポリウレタンエラストマーからなる。樹脂硬度が、上記上限値を超えるとカテーテルが硬くなり、ガイドワイヤーを挿入してもピッグテール部が十分に直線化できなくなり、前記下限値未満ではカテーテルのコシがなくなり、体内への挿入が困難となるため、好ましくない。 As shown in FIG. 1, the catheter (1) used in the medical device of the present invention includes an intrarenal fixation part (2), a main body part (3), an intravesical fixation part (4), a scale (5), and an X-ray. Consists of contrast marker (6) and thread (7). The intrarenal fixation part (2) and the intravesical fixation part (4) are pigtail parts. The X-ray contrast marker (6) is a substance having higher radiopacity than other parts. The intrarenal fixation part (2), the main body part (3), and the intravesical fixation part (4) are integrally formed. Although not particularly limited, the outer diameter is 0.5 to 20 mm, and the wall thickness is 0.1 to 3. It consists of a 0 mm tube, and consists of a thermoplastic resin, silicone resin, etc. with a resin hardness of 80 to 100 [A], preferably 85 to 98 [A], preferably a thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer. If the resin hardness exceeds the above upper limit, the catheter becomes hard, and even if a guide wire is inserted, the pigtail part cannot be sufficiently straightened, and if the resin hardness is less than the lower limit, the stiffness of the catheter is lost and insertion into the body is difficult. Therefore, it is not preferable.
腎盂内固定部(2)、膀胱内固定部(4)は、特に限定はされないが、外径5〜30mmの略円形状に丸められており、側面に外径0.5〜2mmの側孔(8)が設置されていることが好ましい。本体部(3)は、特に限定はされないが、長さ10〜400mmであり、外径0.5〜2mmの側孔(8)が5〜20mm間隔で60〜120°づつ回転しながら螺旋状に全体にわたって設置されていることが好ましい。目盛(5)は、特に限定はされないが、印刷等により、カテーテル(1)の遠位端から50mm毎に設置されることが好ましい。目盛(5)の数は特に限定はされないが、カテーテル(1)の本体部(3)の長さによって、1〜10個で適宜選択する。目盛(5)の形式は特に限定されないが、5cm地点は1本線、10cm地点は2本線というように、挿入深度が判別できるように区別しておくことが好ましい。 The intrarenal fixation part (2) and the intravesical fixation part (4) are not particularly limited, but are rounded into a substantially circular shape having an outer diameter of 5 to 30 mm, and side holes having an outer diameter of 0.5 to 2 mm are formed on the side surfaces. (8) is preferably installed. The main body (3) is not particularly limited, but has a length of 10 to 400 mm, and the side holes (8) having an outer diameter of 0.5 to 2 mm are spirally rotated by 60 to 120 ° at intervals of 5 to 20 mm. It is preferable to be installed throughout. The scale (5) is not particularly limited, but is preferably installed every 50 mm from the distal end of the catheter (1) by printing or the like. The number of scales (5) is not particularly limited, but is appropriately selected from 1 to 10 depending on the length of the main body (3) of the catheter (1). The format of the scale (5) is not particularly limited, but it is preferable that the 5 cm point is a single line and the 10 cm point is a double line so that the insertion depth can be distinguished.
X線造影マーカー(6)は、特に限定はされないが、金、白金、イリジウム、タングステン、これらの合金等のX線高不透過性物質からなる厚さ0.01〜0.5mm板状部材を略円筒状に丸めた物、もしくは環状部材である。X線造影マーカー(6)の設置方法は問わないが、例えば延伸することや、熱収縮チューブを収縮させることによって設置部分の外径を縮小させ、縮小させた部分にはめ込んで接着することや、チューブ内に埋め込むことが考えられる。X線造影マーカー(6)を設置した部分の外径は本体部の外径と略同等であることが好ましい。X線造影マーカー(6)の設置位置は、特に限定はされないが、ピッグテール部(2)(4)と本体部(3)の境界部に設置することが好ましい。 The X-ray contrast marker (6) is not particularly limited, but a plate member having a thickness of 0.01 to 0.5 mm made of an X-ray highly opaque material such as gold, platinum, iridium, tungsten, and alloys thereof. It is a product rounded into a substantially cylindrical shape or an annular member. The installation method of the X-ray contrast marker (6) is not limited. For example, the outer diameter of the installation part is reduced by stretching or contracting the heat-shrinkable tube, and it is fitted and adhered to the reduced part. It is conceivable to embed in the tube. The outer diameter of the portion where the X-ray contrast marker (6) is installed is preferably substantially equal to the outer diameter of the main body. The installation position of the X-ray contrast marker (6) is not particularly limited, but it is preferably installed at the boundary between the pigtail (2) (4) and the main body (3).
糸(7)は、特に限定はされないが、外径0.05〜1mm、長さ600〜1500mmであり、膀胱側固定部(4)に設置された最も基端側にある側孔(8)に通して設置され、末端を結び合わせて環状になっていることが好ましい。 The thread (7) is not particularly limited, but has an outer diameter of 0.05 to 1 mm and a length of 600 to 1500 mm, and is the most proximal side hole (8) installed in the bladder side fixing portion (4). It is preferable that it is installed through and the end is connected to form a ring.
このカテーテル(1)には親水性樹脂、抗結石物質、抗血栓物質などを被覆する場合もある。カテーテル(1)にガイドワイヤー(10)を挿入する際に、カテーテル(1)のピッグテール部(2)(4)を直線化し、ガイドワイヤー(10)の挿入を容易にする手段として、カテーテル(1)の本体部(3)に筒状体を設置してもよい。この筒状体は熱可塑性樹脂からなり、好ましくはフッ素樹脂、ポリエチレン等からなり、カテーテル(1)に使用される樹脂よりも硬質であることが好ましく、樹脂硬度60[D]以上であることがより好ましい。この筒状体の寸法は組み合わされるカテーテル(1)の外径、長さにもよるが、外径2〜50mm、長さ5〜350mmである。 The catheter (1) may be coated with a hydrophilic resin, an anticalculus substance, an antithrombotic substance, or the like. When inserting the guide wire (10) into the catheter (1), as a means for straightening the pigtail portions (2) and (4) of the catheter (1) and facilitating insertion of the guide wire (10), the catheter (1 A cylindrical body may be installed in the main body (3). This cylindrical body is made of a thermoplastic resin, preferably made of fluororesin, polyethylene or the like, preferably harder than the resin used for the catheter (1), and has a resin hardness of 60 [D] or more. More preferred. The dimensions of this cylindrical body are 2 to 50 mm in outer diameter and 5 to 350 mm in length, although depending on the outer diameter and length of the combined catheter (1).
ガイドワイヤー(10)は、芯線(11)、コイルスプリング(12)、先端固定部(13)、後端固定部(14)からなる。芯線(11)は、特に限定はされないが、全長200〜5000mm、外径0.1〜1.0mmのステンレス線または超弾性の性質を示す金属からなり、その先端部分(15)には先端に向かって徐々に柔軟性が増加するようにテーパー部(16)と細径部(17)が形成されていることが好ましい。ガイドワイヤーに剛性を持たせるためには、芯線(11)の外径は可能な限り大きい方が好ましく、コイルスプリング(12)の内径と同径であることが好ましい。The guide wire (10) includes a core wire (11), a coil spring (12), a tip fixing portion (13), and a rear end fixing portion (14). The core wire (11) is not particularly limited, but is composed of a stainless steel wire having a total length of 200 to 5000 mm and an outer diameter of 0.1 to 1.0 mm or a metal exhibiting superelasticity, and has a tip portion (15) at the tip. It is preferable that the taper portion (16) and the small diameter portion (17) are formed so that the flexibility gradually increases. In order to give rigidity to the guide wire, the outer diameter of the core wire (11) is preferably as large as possible, and is preferably the same as the inner diameter of the coil spring (12).
コイルスプリング(12)は、特に限定はされないが、直径0.05〜0.3mmのステンレス線または超弾性の性質を示す金属からなり、ガイドワイヤー全体が直径0.2〜2.0mmとなるように芯線(11)を被覆していることが好ましい。芯線(11)とコイルスプリング(12)はその両端で、溶接、ロウ付け、かしめ等の方法によって固定されており、先端固定部(13)、後端固定部(14)は共に半球状に形状付けられている。芯線(11)とコイルスプリング(12)は両端以外の部分で1ヶ所以上ロウ付け等で固定されてもよい。コイルスプリング(12)はカテーテルや、体組織等との滑り性を良くするためにフッ素樹脂等でコーティングされてあってもよい。コイルスプリング(12)の本体部は密巻、つまりコイルの間隔が0に近い状態で巻かれており、コイルスプリング(12)の先端部はガイドワイヤー(10)の先端から10〜100mmにわたって本体部よりも疎巻に巻かれており、コイル間の間隔は0.0005〜0.02mmであることが好ましい。即ち、コイルスプリング(12)の先端部のピッチが本体部よりも大きい状態となっている。 The coil spring (12) is not particularly limited, but is made of a stainless wire having a diameter of 0.05 to 0.3 mm or a metal having superelasticity, and the entire guide wire has a diameter of 0.2 to 2.0 mm. It is preferable to coat the core wire (11). The core wire (11) and the coil spring (12) are fixed at both ends by welding, brazing, caulking or the like, and the tip fixing portion (13) and the rear end fixing portion (14) are both hemispherical. It is attached. The core wire (11) and the coil spring (12) may be fixed by brazing or the like at one or more places other than both ends. The coil spring (12) may be coated with a fluororesin or the like in order to improve slipperiness with a catheter, body tissue, or the like. The main body of the coil spring (12) is closely wound, that is, wound in a state where the coil interval is close to 0, and the distal end of the coil spring (12) extends from 10 to 100 mm from the distal end of the guide wire (10). The coil is wound more loosely, and the distance between the coils is preferably 0.0005 to 0.02 mm. That is, the pitch of the tip of the coil spring (12) is larger than that of the main body.
ガイドワイヤーの曲げ荷重は組み合わされるカテーテルの樹脂硬度にもよるが7.0[N]以上であることが好ましく、8.0[N]以上であることがより好ましい。前記曲げ加重が、前記下限値未満では、カテーテルのピッグテール部分を十分に直線化することが難しく、好ましくない。
前記カテーテルに前記ガイドワイヤーを挿入するとき、カテーテルの戻り角度は150°以上であることが好ましく、160°以上であることがより好ましい。前記戻り角度が、前記下限値未満ではカテーテルを体内に挿入しづらく、好ましくない。Although the bending load of the guide wire depends on the resin hardness of the combined catheter, it is preferably 7.0 [N] or more, and more preferably 8.0 [N] or more. If the bending load is less than the lower limit value, it is difficult to sufficiently straighten the pigtail portion of the catheter, which is not preferable.
When the guide wire is inserted into the catheter, the return angle of the catheter is preferably 150 ° or more, and more preferably 160 ° or more. If the return angle is less than the lower limit, it is difficult to insert the catheter into the body.
(実施例1)
カテーテル(1)は樹脂硬度98[A]のポリウレタンエラストマーから成形され、ピッグテール部巻径22mm、本体部全長260mm、外径2.0mm、内径1.2mmであり、本体部に径1.1mmの側孔(8)が10mm間隔で90度づつ回転しながら螺旋状に全体にわたって設置され、ピッグテール部に径1.1mmの側孔(8)が60度毎に表裏交互に設置されている。ガイドワイヤー(10)は全長1500mm、外径0.97mmである。芯線(11)は外径0.65mmの超弾性の性質を示すニッケルチタン合金であり、その先端部は先端に向かって縮径されている。芯線(11)のテーパー部(16)長さは100mm、細径部(17)外径0.17mm、長さ20mmである。コイルスプリング(12)は外径0.13mmのステンレス鋼である。このガイドワイヤーの曲げ荷重は、8.0[N]である。(Example 1)
The catheter (1) is molded from a polyurethane elastomer having a resin hardness of 98 [A] and has a pigtail winding diameter of 22 mm, a main body length of 260 mm, an outer diameter of 2.0 mm, and an inner diameter of 1.2 mm. The side holes (8) are spirally installed over the whole while rotating 90 degrees at 10 mm intervals, and the side holes (8) with a diameter of 1.1 mm are alternately installed on the pigtail portion every 60 degrees. The guide wire (10) has a total length of 1500 mm and an outer diameter of 0.97 mm. The core wire (11) is a nickel titanium alloy having a superelastic property with an outer diameter of 0.65 mm, and its tip portion is reduced in diameter toward the tip. The length of the taper portion (16) of the core wire (11) is 100 mm, the thin diameter portion (17) has an outer diameter of 0.17 mm, and a length of 20 mm. The coil spring (12) is stainless steel having an outer diameter of 0.13 mm. The bending load of this guide wire is 8.0 [N].
(比較例1)
全長、外径等の寸法は実施例1と同等であるが、芯線(11)の径は0.45mmであり、芯線(11)をポリアミド樹脂からなる被覆(18)で覆っている。このガイドワイヤーの曲げ荷重は、2.2[N]である。
実施例および比較例で得られた医療器具について、戻り角度について評価を行った。得られた結果を表1に示す。
The overall length, outer diameter, and other dimensions are the same as in Example 1, but the diameter of the core wire (11) is 0.45 mm, and the core wire (11) is covered with a coating (18) made of polyamide resin. The bending load of this guide wire is 2.2 [N].
About the medical instrument obtained by the Example and the comparative example, it evaluated about the return angle. The obtained results are shown in Table 1.
(試験方法1)
曲げ荷重は、ガイドワイヤーの、支点間距離60mmにて3点曲げ試験を行い、たわみ3mm時の荷重をもって曲げ荷重とした。
(試験方法2)
戻り角度は、カテーテルにガイドワイヤーを挿入し、カテーテルの戻り角度を測定した。
(試験方法3)
樹脂硬度はJISK7311ポリウレタン系熱可塑性エラストマーの試験方法に従い測定した。(Test method 1)
The bending load was a three-point bending test with a guide wire distance of 60 mm between fulcrums, and the bending load was defined as the load at the time of deflection of 3 mm.
(Test method 2)
The return angle was measured by inserting a guide wire into the catheter and measuring the return angle of the catheter.
(Test method 3)
The resin hardness was measured according to the test method for JISK7311 polyurethane-based thermoplastic elastomer.
本発明の医療器具は、確実に体内で固定でき、挿入を容易とすることが出来る。より具体的には、端部がピッグテール状に形成された尿管用カテーテルであっても、ガイドワイヤー挿入時にピッグテール部が十分に直線化し、カテーテルを容易に体内に挿入できる。 The medical device of the present invention can be reliably fixed in the body and can be easily inserted. More specifically, even if the end portion is a ureteral catheter formed in a pigtail shape, the pigtail portion is sufficiently straightened when the guide wire is inserted, and the catheter can be easily inserted into the body.
1.尿管ステント
2.腎盂内固定部
3.本体部
4.膀胱内固定部
5.目盛
6.X線造影マーカー
7.糸
8.側孔
10.ガイドワイヤー
11.芯線
12.コイルスプリング
13.先端固定部
14.後端固定部
15.芯線先端部
16.テーパー部
17.最径部
18.被覆
20.戻り角度
1. 1. Ureteral stent 2. Intrarenal fixation
Claims (11)
Translated fromJapaneseThe medical device according to claim 9 or 10, wherein the core wire and the coil spring are fixed at a tip portion, a rear end portion, and at least one place between the tip portion and the rear end portion.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004150056AJP2005329018A (en) | 2004-05-20 | 2004-05-20 | Medical appliance |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004150056AJP2005329018A (en) | 2004-05-20 | 2004-05-20 | Medical appliance |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005329018Atrue JP2005329018A (en) | 2005-12-02 |
Family
ID=35484041
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004150056APendingJP2005329018A (en) | 2004-05-20 | 2004-05-20 | Medical appliance |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005329018A (en) |
- 2004
- 2004-05-20JPJP2004150056Apatent/JP2005329018A/enactivePending
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN100469398C (en) | Guiding wire | |
| US7744545B2 (en) | Guide wire | |
| EP2982406A1 (en) | Guide wire | |
| US7747314B2 (en) | Distal assembly for a medical device | |
| JP2007236472A (en) | Catheter | |
| EP3434309B1 (en) | Catheter | |
| EP2163276A1 (en) | Guide wire | |
| US20160361520A1 (en) | Guide wire for medical devices | |
| EP2338555A2 (en) | Guidewire | |
| US20040087876A1 (en) | Medical device having flexible distal tip | |
| US20120245488A1 (en) | Guidewire | |
| EP1088568A1 (en) | Guiding aid for a medical instrument | |
| EP2505225A2 (en) | Guide wire | |
| US8585680B2 (en) | Endovascular device tip assembly incorporating a marker device and method for making the same | |
| JP2000116788A (en) | Catheter | |
| JP4790349B2 (en) | catheter | |
| JP2012029872A (en) | Catheter | |
| JP4754843B2 (en) | catheter | |
| JP5280263B2 (en) | Guide wire | |
| JP2005329018A (en) | Medical appliance | |
| JP2017164200A (en) | Guide wire | |
| JP3179894U (en) | catheter | |
| JP2006271901A (en) | Coiled contrast marker, method for manufacturing the same, and catheter | |
| JP4402814B2 (en) | Medical guidewire | |
| JP2007075531A (en) | Medical guide wire |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20061025 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20081222 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20090106 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20090512 |