JP2005222500A - Ad distribution system - Google Patents
Ad distribution systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005222500A JP2005222500AJP2004032713AJP2004032713AJP2005222500AJP 2005222500 AJP2005222500 AJP 2005222500AJP 2004032713 AJP2004032713 AJP 2004032713AJP 2004032713 AJP2004032713 AJP 2004032713AJP 2005222500 AJP2005222500 AJP 2005222500A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- advertisement
- user
- agent
- category
- evaluation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription78
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000claimsdescription30
- 230000007115recruitmentEffects0.000claimsdescription12
- 238000013209evaluation strategyMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description56
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description26
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000description13
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description12
- 238000013528artificial neural networkMethods0.000description11
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description11
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000description7
- 238000013210evaluation modelMethods0.000description7
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description7
- 210000002569neuronAnatomy0.000description6
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description5
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description5
- 238000012384transportation and deliveryMethods0.000description4
- 235000021152breakfastNutrition0.000description3
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description3
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description3
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description3
- 230000001360synchronised effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000002716delivery methodMethods0.000description2
- 239000000284extractSubstances0.000description2
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description2
- 239000002699waste materialSubstances0.000description2
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description1
- 230000001413cellular effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000007418data miningMethods0.000description1
- 230000006866deteriorationEffects0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 230000010365information processingEffects0.000description1
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000013439planningMethods0.000description1
- 238000012552reviewMethods0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese本発明は広告配信システムに関し、特に、利用者の意図や状況を考慮して適切な広告を利用者に配信する広告配信システムに関するものである。 The present invention relates to an advertisement distribution system, and more particularly to an advertisement distribution system that distributes an appropriate advertisement to a user in consideration of the user's intention and situation.
従来の携帯電話機向けの広告配信システムは、設置式のPC(personal computer)環境で多く用いられているダイレクト電子メールやウェブページを、携帯電話機の画面向けにカスタマイズして利用しているものが多い。携帯電話機は設置型のPCとは異なり、情報を閲覧する場合において、利用者の現在の状況(場所、時間など)が関わる情報が必要となることが多くある。現在の携帯電話機向けの広告を扱う環境には、以下のような特徴がある。
(1)携帯電話機の発達により、小型PC並の性能を持ち、独立したプログラムを動かすことができる。
(2)画面に表示可能な情報量(画面の大きさ、広告数)が限られているため、軽量でシンプルなコンテンツが好まれる。
(3)確立されたビジネスアプリケーションとして認知されており、課金メカニズムが確立している。
また、広告主が、ネットワークで接続されているユーザ端末に宣伝広告を行うべく、広告に関する情報を添付して代理店に広告依頼を行い、広告依頼を受けた代理店が、広告コンテンツを制作し、この広告コンテンツと広告に関する情報とをプロバイダに送信して広告配信依頼を行い、プロバイダが、広告に関する情報に基づいて、広告の配信先の顧客ユーザを選び出して、それらの端末のIPアドレスを記載した配信先リストを作成し、この配信先リストに記載されているIPアドレスに従って広告コンテンツ及び提示制御情報を配信し、これらを受信したユーザ端末が、提示制御情報に基づいて広告コンテンツの表示、音声による提示を行うことにより、広告配信側の無駄を排除しつつ、広告受信側の一般ユーザがより希望する情報を配信し得る広告効率の高い広告配信システムを提供するようにしたものがある(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
(1) Due to the development of mobile phones, it has the same performance as a small PC and can run independent programs.
(2) Since the amount of information (screen size, number of advertisements) that can be displayed on the screen is limited, lightweight and simple content is preferred.
(3) It is recognized as an established business application, and a charging mechanism has been established.
In addition, an advertiser makes an advertisement request to an agency with information related to the advertisement, in order to place an advertisement on a user terminal connected to the network, and the agency that receives the advertisement request produces advertisement content. , This advertisement content and advertisement-related information are transmitted to the provider and an advertisement distribution request is made. The provider selects a customer user to whom the advertisement is distributed based on the advertisement-related information, and describes the IP address of those terminals. The distribution destination list is created, the advertising content and the presentation control information are distributed according to the IP address described in the distribution destination list, and the user terminal that receives them displays the advertising content based on the presentation control information, and the audio By distributing the information that is desired by the general user on the receiving side of the advertisement while eliminating waste on the distributing side, It is obtained by a high advertising efficiency advertising distribution system capable to provide (for example, see Patent Document 1).
しかしながら、従来の携帯電話機向けの広告ビジネスには次のような問題点があった。
(1)広告コンテンツの処理中に、電波状態の悪化などの原因で電話網が切断されることがある。
(2)利用者の状態(場所、時間、意図など)を考慮した質の良い情報をリアルタイムで得ることが難しい。
(3)広告仲介者が質の良い広告を収集することが難しく、クリックスルー率を上げることが難しい。
本発明はこのような状況に鑑みてなされたものであり、携帯電話機への広告コンテンツの配信において、利用者の意図や状況を考慮して、広告主が提供する適切な広告コンテンツを収集、配布するための仕組みを実現するものである。また、広告欄の価値(時価)をリアルタイムに見積もることにより、利用者が欲している情報を広告コンテンツとして入手することができるシステムを実現することができるようにするものである。However, the conventional advertising business for mobile phones has the following problems.
(1) During processing of advertising content, the telephone network may be disconnected due to factors such as deterioration of radio wave conditions.
(2) It is difficult to obtain high-quality information in real time in consideration of the user's condition (location, time, intention, etc.).
(3) It is difficult for advertisement intermediaries to collect high-quality advertisements, and it is difficult to increase the click-through rate.
The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and collects and distributes appropriate advertising content provided by the advertiser in consideration of the user's intention and circumstances in the distribution of advertising content to mobile phones. It realizes a mechanism to do this. In addition, by estimating the value (market price) of the advertisement column in real time, it is possible to realize a system that can obtain information desired by the user as advertisement content.
請求項1に記載の広告配信システムは、利用者に対して広告を配信する広告配信システムであって、利用者の利用者情報を抽出する抽出手段と、利用者情報に基づいて、利用者に対して配信すべき広告のカテゴリを推論するカテゴリ推論手段と、カテゴリ推論手段によって推論されたカテゴリの広告を募集する公告募集手段と、募集に対して所定の広告主による広告を提案する提案手段と、提案手段によって提案された広告を評価する評価手段と、評価手段による評価結果に応じて、広告を利用者に対して配信する配信手段とを備えることを特徴とする。
また、評価手段は、所定の評価戦略に基づいて提案手段によって提案された広告を評価するようにすることができる。
また、提案手段は、カテゴリの広告を検索し、所定の広告主が準備した広報戦略に基づいて、広告の入札価値を見積もり、入札価値に基づいて広告の提案を行うようにすることができる。
また、利用者によってクリックされた広告の種類、クリックされた回数、クリックされた時刻、クリックされた場所を含む情報を取引履歴情報として記憶する記憶手段をさらに備え、取引履歴情報は、広告主の検索または広告の評価に用いられるようにすることができる。
また、評価手段は、取引履歴情報に基づいて広告を評価するようにすることができる。
請求項6に記載の広告配信方法は、利用者に対して広告を配信する広告配信方法であって、利用者の利用者情報を抽出する抽出ステップと、利用者情報に基づいて、利用者に対して配信すべき広告のカテゴリを推論するカテゴリ推論ステップと、カテゴリ推論ステップにおいて推論されたカテゴリの広告を募集する公告募集ステップと、募集に対して所定の広告主による広告を提案する提案ステップと、提案ステップにおいて提案された広告を評価する評価ステップと、評価ステップにおける評価結果に応じて、広告を利用者に対して配信する配信ステップとを備えることを特徴とする。
請求項7に記載の広告配信プログラムは、利用者に対して広告を配信する広告配信システムを制御する広告配信プログラムであって、利用者の利用者情報を抽出する抽出ステップと、利用者情報に基づいて、利用者に対して配信すべき広告のカテゴリを推論するカテゴリ推論ステップと、カテゴリ推論ステップにおいて推論されたカテゴリの広告を募集する公告募集ステップと、募集に対して所定の広告主による広告を提案する提案ステップと、提案ステップにおいて提案された広告を評価する評価ステップと、評価ステップにおける評価結果に応じて、広告を利用者に対して配信する配信ステップとを広告配信システムに実行させることを特徴とする。The advertisement distribution system according to
Moreover, the evaluation means can evaluate the advertisement proposed by the proposal means based on a predetermined evaluation strategy.
Further, the suggestion means can search for advertisements in the category, estimate the bid value of the advertisement based on a public relation strategy prepared by a predetermined advertiser, and propose the advertisement based on the bid value.
Further, the information processing apparatus further comprises storage means for storing information including the type of the advertisement clicked by the user, the number of clicks, the click time, and the clicked place as transaction history information. It can be used for search or advertising evaluation.
Moreover, the evaluation means can evaluate the advertisement based on the transaction history information.
An advertisement delivery method according to
An advertisement distribution program according to
本発明の広告配信システムによれば、携帯電話機と広告仲介システムは、非同期的な通信プロトコルで動作するため、処理途中で通信が切断されてもよい。これによって、広告仲介システムは通信状態を気にすることなく、利用者に広告コンテンツを提供することができる。
また、利用者の状態を監視する「利用者エージェント」を携帯電話機に常駐させることにより、リアルタイムに情報収集が可能となる。これによって、利用者の現在の場所、時間、操作、および動作から推測できる趣味、習慣に関する情報を得ることができる。
また、広告発行システムのビジネスディレクトリを作ることにより、利用者の状態を検索キーとして、広告仲介システムは利用者に適した広告コンテンツを提供することが可能な広告発行システムを即時に検索することができる。
また、広告発行システムが仲介システムに対して、利用者の情報を元に広告欄の価値を評価し、時価を提案することにより、単なる値引き競争になりがちな入札を防ぎ、クリックスルー率の高い広告コンテンツの提供が可能となる。According to the advertisement distribution system of the present invention, since the mobile phone and the advertisement mediation system operate with an asynchronous communication protocol, the communication may be disconnected during the processing. Thereby, the advertisement mediation system can provide the advertisement content to the user without worrying about the communication state.
Further, by making a “user agent” that monitors the user's state resident in the mobile phone, information can be collected in real time. As a result, information on hobbies and habits that can be estimated from the current location, time, operation, and operation of the user can be obtained.
In addition, by creating a business directory for the advertisement issuance system, the advertisement mediation system can immediately search for an advertisement issuance system that can provide advertisement content suitable for the user, using the state of the user as a search key. it can.
In addition, the advertisement issuing system evaluates the value of the advertising column based on the user's information to the brokerage system and proposes the market price, thereby preventing bids that tend to be mere discount competition and high click-through rate Advertisement content can be provided.
図1は、本発明の広告配信システムの一実施の形態の構成例を示すブロック図である。同図に示すように、本実施の形態は、携帯電話機10と、携帯電話機10と携帯電話網100を介して接続される広告仲介サーバ20と、広告仲介サーバ20とインターネット等のネットワークを介して接続される1または複数の広告発行サーバ30とから構成されている。以下では、各広告発行サーバ30を広告発行サーバ30−1,30−2,30−3と記載する。 FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of an embodiment of an advertisement distribution system according to the present invention. As shown in the figure, the present embodiment includes a
携帯電話機10には、携帯電話システム11が実装されている。この携帯電話システム11は、広告欄12と、利用者エージェント13と、利用者情報(職業、国籍、年齢、性別等)を記憶する記憶装置14と、表示ルールを記憶する記憶装置15等により構成されている。 A mobile phone system 11 is mounted on the
利用者エージェント13は、利用者の状態(時間(携帯電話機10のキャリア(携帯電話機会社)が提供するもの等)、場所(携帯電話機10のキャリア(携帯電話機会社)が提供するもの等)、操作、および利用者の習慣等から推測される意図等)を監視するものであり、携帯電話機10の図示せぬ処理装置に常駐し、通信状態に関わらず、利用者の状態を自動収集し、必要に応じて収集した利用者の状態を広告仲介システム21に提供するようになっている。 The user agent 13 determines the state of the user (time (provided by the carrier (mobile phone company)) of the mobile phone 10), location (thing provided by the carrier (mobile phone company) of the mobile phone 10), operation, etc. , And intentions inferred from the user's habits, etc.), resides in a processing device (not shown) of the
広告仲介サーバ20には、広告仲介システム21が実装されている。この広告仲介システム21は、仲介エージェント22と、取引履歴(利用者が過去に受け入れた広告とクリックスルーに関する履歴情報であり、例えば、広告の種類、表示回数、クリックスルーの有無、場所、時間等からなる)を記憶する記憶装置23と、広告主データベース(DB)を記憶する記憶装置24と、評価戦略を記憶する記憶装置25と、利用者情報(利用者が興味のある趣味、分野に関するキーワード、利用者の行動予定(スケジュール)等)を記憶する記憶装置26等により構成されている。 An advertisement mediation system 21 is mounted on the
広告仲介システム21は、利用者に応じた様々な広告コンテンツを収集、選別し、実際の広告コンテンツを提供する広告発行システムを検索するものである。利用者が所持する携帯電話機10に実装された携帯電話システム11と、広告仲介システム21は非同期的に動作するため、通信が途中で切断されてもよい。 The advertisement mediation system 21 collects and sorts various advertisement contents according to users and searches for an advertisement issuance system that provides actual advertisement contents. Since the mobile phone system 11 mounted on the
また、広告仲介システム21の記憶装置24には、広告主の情報(ビジネスディレクトリ(広告主を登録した電話帳、或いは、データベース等))や広告の種類等の情報が登録されている。仲介エージェント22は、利用者情報を元に、ビジネスディレクトリから、広告コンテンツを配信する広告発行システムを検索することにより、幅広い広告コンテンツを入手するようになっている。 In addition, in the
また、最適な広告コンテンツを入手する際に、仲介エージェント22または利用者エージェント13は、匿名化された利用者情報(個人を特定することができないように、通知する必要のない情報を除いた利用者情報であり、利用者の氏名、住所、電話番号、行動予定、趣味等を元に、広告の入札価格決定に必要な指標化された情報)を広告エージェント32に提供する。広告エージェント32は、この情報を後述するクリックスルー率の期待値計算の要素として用いる。 Further, when obtaining the optimal advertising content, the mediating agent 22 or the user agent 13 uses the anonymized user information (use of information excluding information that does not need to be notified so that an individual cannot be specified). Information, which is indexed information necessary for determining the bid price of the advertisement) based on the user's name, address, telephone number, action schedule, hobbies, and the like. The advertisement agent 32 uses this information as an element for calculating the expected value of the click-through rate described later.
広告発行サーバ30−1には、広告発行システム31−1が実装されている。この広告発行システム31−1は、広告エージェント32−1と、広告DBを記憶する記憶装置33−1と、広報戦略を記憶する記憶装置34−1と、取引履歴を記憶する記憶装置35−1等により構成されている。広告エージェント32−1は、広告欄12の評価額を見積もり、広告コンテンツとその価格を仲介エージェント22に提案(入札)するようになっている。広告発行サーバ30−2,30−3も基本的に同様の構成であるので、その説明は省略する。また、以下では、広告発行サーバ30−1,30−2,30−3等を区別する必要がない場合、適宜広告発行サーバ30と記載する。広告発行システム31−1,31−2,31−3およびその構成要素についても同様に、適宜広告発行システム31などと記載する。 An advertisement issuing system 31-1 is installed in the advertisement issuing server 30-1. This advertisement issuing system 31-1 includes an advertisement agent 32-1, a storage device 33-1 for storing an advertisement DB, a storage device 34-1 for storing a public relations strategy, and a storage device 35-1 for storing a transaction history. Etc. The advertisement agent 32-1 estimates the evaluation amount of the advertisement column 12, and proposes (bids) the advertisement content and its price to the mediating agent 22. Since the advertisement issuing servers 30-2 and 30-3 have basically the same configuration, the description thereof is omitted. In the following description, the advertisement issuing servers 30-1, 30-2, 30-3 and the like are appropriately referred to as the advertisement issuing server 30 when it is not necessary to distinguish them. Similarly, the advertisement issuing systems 31-1, 31-2, 31-3 and their components are also appropriately described as the advertisement issuing system 31 and the like.
図2は、広告が表示される手順を示すフローチャートである。利用者は、ステップS1において、表示トリガ(検索や推論などの操作)を利用者エージェント13に提供する。ステップS11において、利用者エージェント13は、記憶装置14から利用者情報の抽出を行い、カテゴリ推論を行う。次に、ステップS12において、携帯電話網100を介して広告仲介システム21に対して、カテゴリ推論によって得たキーワード等を送信し、広告募集を行う。その後、処理を終了し、利用者による表示トリガ待ちの状態となる。 FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing a procedure for displaying an advertisement. In step S1, the user provides a display trigger (operations such as search and inference) to the user agent 13. In step S11, the user agent 13 extracts user information from the
仲介エージェント22は、ステップS31において、利用者エージェント13による広告募集を受け、利用者エージェント13からのキーワードと、記憶装置26に記憶されている利用者情報とに基づいて、記憶装置24に記憶されている広告主DBから広告主を検索し、ステップS32において広告募集を行う。 In step S31, the mediation agent 22 receives an advertisement solicitation by the user agent 13 and is stored in the
広告エージェント32は、ステップS41において、仲介エージェント22からの広告募集を受けると、記憶装置33に記憶されている広告DBから広告の検索を行い、記憶装置34に記憶されている広報戦略(PS)を読み込む。広報戦略(PS)は、広告コンテンツの提案に要する戦略的なルールを定義したものである。例えば、提案基準となる評価額を見積もる見積もり式、場所、時間に応じた提案の振り分けルールなどである。 When the advertisement agent 32 receives an advertisement recruitment from the mediation agent 22 in step S41, the advertisement agent 32 searches for an advertisement from the advertisement DB stored in the
次に、ステップS42において、価値の見積もりを行う。次に、ステップS43において、提案可能か否かが判定される。その結果、提案不可能であると判定された場合、本処理を終了し、仲介エージェント22からの広告募集待ちの状態となる。一方、提案可能であると判定された場合、ステップS44に進む。ステップS44においては、広告の提案を行う。 Next, in step S42, the value is estimated. Next, in step S43, it is determined whether or not proposal is possible. As a result, when it is determined that the proposal cannot be made, this processing is terminated and the state of waiting for advertisement from the mediation agent 22 is entered. On the other hand, if it is determined that the proposal is possible, the process proceeds to step S44. In step S44, an advertisement is proposed.
仲介エージェント22は、ステップS33において、広告の募集結果の評価を行い、ステップS34において、適切な広告の提案があったか否かが判定される。適切な広告の提案がなかったと判定された場合、ステップS32に戻り、ステップS32以降の処理が繰り返し実行される。一方、適切な広告の提案があったと判定された場合、ステップS35に進み、広告エージェント32より提案された広告を利用者エージェント13に対して提案する。 In step S33, the mediation agent 22 evaluates the advertisement solicitation result, and in step S34, it is determined whether or not an appropriate advertisement has been proposed. When it is determined that there has not been an appropriate advertisement proposal, the process returns to step S32, and the processes after step S32 are repeatedly executed. On the other hand, if it is determined that an appropriate advertisement has been proposed, the process proceeds to step S35, and the advertisement proposed by the advertisement agent 32 is proposed to the user agent 13.
利用者エージェント13は、ステップS21において、仲介エージェント22より提案された広告の評価を行い、ステップS22において、この広告を表示するか否かを判定する。その結果、この広告を表示しないと判定した場合、本処理を終了し、仲介エージェント22からの次の広告提案待ちの状態となる。一方、この広告を表示すると判定した場合、ステップS23に進む。 The user agent 13 evaluates the advertisement proposed by the mediation agent 22 in step S21, and determines whether or not to display the advertisement in step S22. As a result, if it is determined that this advertisement is not displayed, this process is terminated and the next advertisement proposal from the mediation agent 22 is awaited. On the other hand, when it determines with displaying this advertisement, it progresses to step S23.
仲介エージェント22は、ステップS36において、ステップS35において提案した広告が利用者エージェント13によって受け入れられたか否かを判定する。その結果、提案が受け入れられず、拒否されたと判定した場合、本処理を終了し、利用者エージェント13からの次の広告募集待ちの状態となる。一方、提案が受け入れられ、許可されたと判定された場合、ステップS37に進む。 In step S36, the mediation agent 22 determines whether or not the advertisement proposed in step S35 has been accepted by the user agent 13. As a result, if it is determined that the proposal has not been accepted and has been rejected, this processing is terminated, and a waiting state for the next advertisement from the user agent 13 is awaited. On the other hand, if it is determined that the proposal has been accepted and allowed, the process proceeds to step S37.
また、広告エージェント32は、ステップS45において、ステップS44において提案した広告が仲介エージェント22によって受け入れられたか否かを判定する。その結果、提案した広告が仲介エージェント22によって受け入れられず、拒否されたと判定した場合、本処理を終了し、仲介エージェント22からの次の広告の募集待ちの状態となる。一方、提案した広告が仲介エージェント22によって受け入れられ、許可されたと判定した場合、ステップS46に進み、広告の格納場所を示すURL(uniform resource locator)を仲介エージェント22に配信する。 In step S45, the advertisement agent 32 determines whether or not the advertisement proposed in step S44 has been accepted by the mediation agent 22. As a result, when it is determined that the proposed advertisement has not been accepted by the mediation agent 22 and has been rejected, this processing is terminated, and a waiting state for a next advertisement from the mediation agent 22 is awaited. On the other hand, if it is determined that the proposed advertisement has been accepted and permitted by the mediation agent 22, the process proceeds to step S <b> 46, and a URL (uniform resource locator) indicating the storage location of the advertisement is distributed to the mediation agent 22.
仲介エージェント22は、ステップS37において、広告エージェント32から配信された広告のURLを利用者エージェント13に配信する。利用者エージェント13は、ステップS23において、仲介エージェント22から配信された広告のURLを受信すると、そのURLにアクセスし、広告を広告欄12に表示する。その後、処理を終了し、仲介エージェント22からの広告の提案待ちの状態となる。利用者は、ステップS2において、携帯電話機10の広告欄12に表示された広告を閲覧する。 In step S <b> 37, the mediation agent 22 distributes the URL of the advertisement distributed from the advertisement agent 32 to the user agent 13. When the user agent 13 receives the URL of the advertisement distributed from the mediation agent 22 in step S23, the user agent 13 accesses the URL and displays the advertisement in the advertisement column 12. Thereafter, the process is terminated, and the system waits for an advertisement proposal from the mediation agent 22. In step S <b> 2, the user browses the advertisement displayed in the advertisement column 12 of the
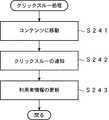
次に、図3のフローチャートを参照して、広告クリックスループロセスについて説明する。利用者は、ステップS51において、携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12に表示された広告を図示せぬボタンを操作してクリックする。次に、ステップS52において、携帯電話機10の画面に、いまクリックした広告に対応するURLに格納されているコンテンツが表示されるので、それを閲覧し、終了する。 Next, the advertisement click-through process will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. In step S51, the user clicks on an advertisement displayed in the advertisement column 12 on the screen of the
利用者エージェント13は、利用者による操作を監視しており、広告がクリックされたことを検出すると、ステップS61において、利用者によってクリックされた広告を示すデータを携帯電話網100を介して仲介エージェント22に送信し、このデータに対応する広告がクリックされたことを通知する。その後、ステップS62に進み、記憶装置14に記憶されている利用者情報の更新を行う。例えば、操作履歴(検索したキーワードの種類、検索回数、キーワードを検索した時刻、場所、クリックした広告の種類、クリックした回数、広告をクリックした時刻、場所等からなる履歴)等の更新を行う。その後、本処理を終了し、利用者のクリック待ちの状態となる。 The user agent 13 monitors the operation by the user, and when detecting that the advertisement has been clicked, in step S61, the user agent 13 transmits the data indicating the advertisement clicked by the user via the
仲介エージェント22は、ステップS71において、利用者エージェント13から送信されてきた、利用者によってクリックされた広告を示すデータを広告エージェント32に送信し、このデータに対応する広告がクリックされたことを通知する。その後、ステップS72に進み、記憶装置23に記憶されている取引履歴を更新する。次に、ステップS73において、広告エージェント32から送信されてきた課金情報に基づいて広告主に対して課金する。その後、本処理を終了し、利用者エージェント13からの通知待ちの状態となる。 In step S71, the mediation agent 22 transmits data indicating the advertisement clicked by the user transmitted from the user agent 13 to the advertisement agent 32, and notifies that the advertisement corresponding to this data has been clicked. To do. Then, it progresses to step S72 and the transaction history memorize | stored in the memory | storage device 23 is updated. Next, in step S73, the advertiser is charged based on the billing information transmitted from the advertisement agent 32. Thereafter, this process is terminated, and a notification from the user agent 13 is awaited.
広告エージェント32は、ステップS81において、仲介エージェント22から送信されてきたデータを受信すると、ステップS82に進み、記憶装置35に記憶されている取引履歴を更新する。次に、ステップS83において、課金情報を仲介エージェント22に送信する。その後、本処理を終了し、仲介エージェント22からの通知待ちの状態となる。 When the advertising agent 32 receives the data transmitted from the mediation agent 22 in step S81, the advertising agent 32 proceeds to step S82 and updates the transaction history stored in the storage device 35. Next, the billing information is transmitted to the mediation agent 22 in step S83. Thereafter, this process is terminated, and a notification waiting state from the mediation agent 22 is awaited.
次に、図4のフローチャートを参照して、各エージェントのイベント通知の関係について説明する。まず、表示イベントについて説明する。利用者は、ステップS101において表示イベントを発生させる。例えば、検索などの操作を行う。利用者エージェント13は、ステップS111において、利用者の操作を検知し、広告要求を仲介エージェント22に対して行う。仲介エージェント22は、ステップS121において、利用者エージェント13からの広告要求を受けると、広告募集を広告エージェント32に対して行う。広告エージェント32は、ステップS131において、仲介エージェント22からの広告募集を受けると、広告の提案を行う。 Next, with reference to the flowchart of FIG. 4, the relationship of event notification of each agent will be described. First, display events will be described. In step S101, the user generates a display event. For example, an operation such as search is performed. In step S <b> 111, the user agent 13 detects a user operation and makes an advertisement request to the mediation agent 22. In step S <b> 121, the mediation agent 22 receives an advertisement request from the user agent 13 and makes an advertisement recruitment to the advertisement agent 32. When the advertisement agent 32 receives an advertisement recruitment from the mediation agent 22 in step S131, the advertisement agent 32 makes an advertisement proposal.
仲介エージェント22は、広告エージェント32から提案された広告を評価し、適切な広告であると判断した場合、利用者エージェント13にその広告を提案する。利用者エージェント13は、仲介エージェント22から提案された広告を評価し、表示すると判断した場合、ステップS132において広告エージェント32から配信されたURLにアクセスし、ステップS112において広告を表示する。 When the mediation agent 22 evaluates the advertisement proposed by the advertisement agent 32 and determines that the advertisement is an appropriate advertisement, the mediation agent 22 proposes the advertisement to the user agent 13. When the user agent 13 evaluates the advertisement proposed by the mediation agent 22 and determines to display it, the user agent 13 accesses the URL distributed from the advertisement agent 32 in step S132, and displays the advertisement in step S112.
次に、クリックスルーイベントについて説明する。利用者は、ステップS102において、画面上でクリック操作をし、クリックスルーイベントを発生させる。ステップS113において、利用者エージェント13は、クリックスルーイベントが発生すると、クリックスルー処理を実行し、仲介エージェント22にクリックスルーイベントの発生を通知する。ステップS122において、仲介エージェント22は、利用者エージェント13からの通知を受け、クリックスルー処理を実行し、広告エージェント32に通知する。ステップS133において、広告エージェント32は、仲介エージェント22からの通知を受け、クリックスルー処理を実行する。 Next, the click-through event will be described. In step S102, the user performs a click operation on the screen to generate a click-through event. In step S113, when the click-through event occurs, the user agent 13 executes a click-through process and notifies the mediation agent 22 of the occurrence of the click-through event. In step S <b> 122, the mediation agent 22 receives the notification from the user agent 13, executes a click-through process, and notifies the advertisement agent 32. In step S133, the advertisement agent 32 receives the notification from the mediation agent 22 and executes a click-through process.
次に、利用者情報設定イベントについて説明する。ステップS103において、利用者が利用者設定を行い、利用者設定イベントが発生すると、ステップS114において、利用者エージェント13により、利用者情報設定が行われる。 Next, a user information setting event will be described. In step S103, when the user performs user setting and a user setting event occurs, user information is set by the user agent 13 in step S114.
次に、広告登録イベントについて説明する。ステップS141において、広告主により広告登録イベントが発生すると、ステップS123において、仲介エージェント22により広告登録が行われる。また、ステップS134において、広告エージェント32により広告登録イベントが発生すると、ステップS123において、仲介エージェント22により、広告登録が行われる。 Next, the advertisement registration event will be described. When an advertisement registration event occurs by the advertiser in step S141, advertisement registration is performed by the mediation agent 22 in step S123. Further, when an advertisement registration event is generated by the advertisement agent 32 in step S134, advertisement registration is performed by the mediation agent 22 in step S123.
次に、図5のフローチャートを参照して、利用者エージェント13によるイベント監視手順について説明する。まず最初に、ステップS211において、利用者エージェントが有効である間、すなわち、利用者エージェントが活性化している間、利用者エージェント13のイベントを監視し、イベント発生時にイベントに応じた処理を割り振り、ステップS212以降の処理が繰り返し実行されるように制御される。ステップS212においては、イベントが発生したか否かが判定される。その結果、イベントが発生したと判定された場合、イベントに応じた処理が実行される。 Next, the event monitoring procedure by the user agent 13 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, in step S211, while the user agent is valid, that is, while the user agent is activated, the event of the user agent 13 is monitored, and processing corresponding to the event is assigned when the event occurs, Control is performed so that the processing after step S212 is repeatedly executed. In step S212, it is determined whether an event has occurred. As a result, when it is determined that an event has occurred, processing corresponding to the event is executed.
利用者のアクションによって広告が表示されるとき、ステップS213において、図6を参照して後述する広告要求処理が実行される。仲介エージェント22から広告が紹介されたとき、ステップS214において、図7を参照して後述する広告表示処理が実行される。利用者が携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12の広告をクリックしたとき、ステップS215において、図8を参照して後述するクリックスルー処理が実行される。利用者が最初にサービスを開始するとき、ステップS216において、図9を参照して後述する利用者情報設定処理が実行される。全てのイベント(利用者のアクション、仲介エージェント22からの広告の紹介、広告のクリック、サービスの開始)は、非同期的に動作するため、不要なイベントの終了を待つ必要がない。また、エージェント間の通信経路を保持する必要がない。 When an advertisement is displayed by the user's action, an advertisement request process described later with reference to FIG. 6 is executed in step S213. When an advertisement is introduced from the mediation agent 22, an advertisement display process described later with reference to FIG. 7 is executed in step S214. When the user clicks on the advertisement in the advertisement column 12 on the screen of the
次に、図6のフローチャートを参照して、利用者エージェント13が、広告要求を行う手順について説明する。まず最初に、ステップS221において、利用者プロファイルから利用者情報の抽出を行う。次に、ステップS222において、利用者情報に基づいて、要求する広告を検索するためのカテゴリまたはキーワードを推論する。次に、ステップS223において、推論したカテゴリまたはキーワードに対して、広告欄12に表示するための広告を仲介エージェント22に要求する。 Next, a procedure for the user agent 13 to make an advertisement request will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, in step S221, user information is extracted from the user profile. Next, in step S222, a category or keyword for searching for the requested advertisement is inferred based on the user information. Next, in step S223, the mediation agent 22 is requested for an advertisement to be displayed in the advertisement column 12 for the inferred category or keyword.
次に、図7のフローチャートを参照して、広告表示の手順について説明する。まず最初に、ステップS231において、利用者エージェント13は、仲介エージェント22から広告を受け取り、表示ルールに従ってその広告を評価する。次に、ステップS232において、評価結果に基づいて、その広告を利用者の携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12に表示するか否かが判定される。その結果、その広告を表示しないと判定された場合、ステップS235に進み、仲介エージェント22および広告エージェント32からの広告のデータおよびURL(uniform resource locator)の受信を拒否する。一方、その広告を表示すると判定された場合、ステップS233に進み、仲介エージェント22または広告エージェント32からの広告のデータまたはURLを受信し、ステップS234において、広告のURLにアクセスし、広告を携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12に表示する。 Next, an advertisement display procedure will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, in step S231, the user agent 13 receives an advertisement from the mediation agent 22, and evaluates the advertisement according to the display rule. Next, in step S232, based on the evaluation result, it is determined whether or not to display the advertisement in the advertisement column 12 on the screen of the user's
次に、図8のフローチャートを参照して、利用者エージェント13のクリックスルー処理について説明する。利用者が、携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12に表示された広告をクリックすると、ステップS241において、利用者エージェント13は、クリックされたその広告にリンクされたコンテンツに移動する。次に、ステップS242において、利用者エージェント13は、仲介エージェント22にクリックスルーを通知する。次に、ステップS243において、クリックスルーした情報を元に、利用者情報を更新する。クリックスルーの情報とは、広告のカテゴリ、クリックスルーの回数、広告主の情報等である。これらの情報は、次回のカテゴリの推論に用いられる。 Next, the click-through process of the user agent 13 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. When the user clicks on the advertisement displayed in the advertisement column 12 on the screen of the
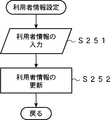
次に、図9のフローチャートを参照して、利用者情報の設定手順について説明する。まず、ステップS251において、利用者は、携帯電話機10の図示しない入力キーを操作して、利用者情報を入力する。利用者情報とは、携帯電話機10の利用者の氏名、住所、年齢、国籍、および職業と、近い将来の行動予定(旅程、訪問スケジュール等)、および広告の表示ルール(一度見た広告は表示しない、特定のカテゴリの広告は表示しない等)などである。 Next, a user information setting procedure will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, in step S251, the user operates the input key (not shown) of the
次に、ステップS252において、利用者エージェント13は、入力された利用者情報を利用者プロファイルとして記憶装置14に記憶させる。既に利用者情報が記憶装置14に記憶されている場合には、その利用者情報が更新される。 Next, in step S252, the user agent 13 stores the input user information in the
次に、図10のフローチャートを参照して、仲介エージェント22によるイベント監視手順について説明する。まず最初に、ステップS261において、仲介エージェント22が有効である間、すなわち、仲介エージェント22が活性化している間、仲介エージェント22のイベントを監視し、イベント発生時にイベントに応じた処理を割り振り、ステップS262以降の処理が繰り返し実行されるように制御される。ステップS262においては、イベントが発生したか否かが判定される。その結果、イベントが発生したと判定された場合、イベントに応じた処理が実行される。 Next, the event monitoring procedure by the mediation agent 22 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, in step S261, while the mediation agent 22 is active, that is, while the mediation agent 22 is activated, the event of the mediation agent 22 is monitored, and processing corresponding to the event is assigned when the event occurs. Control is performed so that the processing after S262 is repeatedly executed. In step S262, it is determined whether an event has occurred. As a result, when it is determined that an event has occurred, processing corresponding to the event is executed.
広告主が登録されるとき、ステップS263において、図13を参照して後述する広告登録処理が実行される。利用者エージェント13から広告が要求されたとき、ステップS264において、図11を参照して後述する広告募集処理が実行される。利用者が携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12の広告をクリックしたとき、ステップS265において、図12を参照して後述するクリックスルー通知処理が実行される。全てのイベント(広告主の登録、利用者エージェント13からの広告の要求、利用者による広告のクリック)は、非同期的に動作するため、不要なイベントの終了を待つ必要がない。また、エージェント間の通信経路を保持する必要がない。 When an advertiser is registered, an advertisement registration process described later with reference to FIG. 13 is executed in step S263. When an advertisement is requested from the user agent 13, an advertisement recruiting process described later with reference to FIG. 11 is executed in step S264. When the user clicks on the advertisement in the advertisement column 12 on the screen of the
次に、図11のフローチャートを参照して、仲介エージェント22による広告募集手順について説明する。ステップS271において、利用者エージェント13から送信されてきた広告要求を受信する。次に、ステップS272において、適切なカテゴリの広告主を検索する。次に、ステップS273において、広告主の広告エージェント32に対して広告を募集する。ステップS274においては、記憶装置25に記憶されている評価戦略に基づいて、募集結果を評価し、広告エージェント32の提案から適切なものを必要な数だけ決定する。ここで、評価戦略とは、適切な提案を選出するためのルールセット(例えば、最も価格の安いものを取るなど)である。 Next, an advertisement solicitation procedure by the mediation agent 22 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. In step S271, the advertisement request transmitted from the user agent 13 is received. Next, in step S272, an advertiser of an appropriate category is searched. Next, in step S273, an advertisement is recruited from the advertisement agent 32 of the advertiser. In step S274, the recruitment result is evaluated based on the evaluation strategy stored in the
次に、ステップS275において、適切な広告の提案があったか否かが判定され、適切な広告の提案がなかったと判定された場合、ステップS273に戻り、ステップS273以降の処理が繰り返し実行される。一方、適切な広告の提案があったと判定された場合、ステップS276に進む。 Next, in step S275, it is determined whether or not there has been an appropriate advertisement proposal. If it is determined that there has not been an appropriate advertisement proposal, the process returns to step S273, and the processes after step S273 are repeatedly executed. On the other hand, if it is determined that an appropriate advertisement has been proposed, the process proceeds to step S276.
ステップS276においては、広告エージェント32から適切な広告の提案があった場合、利用者エージェント13に対してその広告を提案する。ステップS277においては、利用者エージェント13により、提案した広告が受け入れられたか否かが判定される。利用者エージェント13により、提案した広告が受け入れられた(許可された)と判定された場合、ステップS278において、広告エージェント32は広告データに対応するURLを利用者エージェント13に配信する。一方、利用者エージェント13により、提案した広告が受け入れられなかった(拒否された)と判定された場合、そのまま何もせず、処理を終了する。 In step S276, when an appropriate advertisement is proposed by the advertisement agent 32, the advertisement is proposed to the user agent 13. In step S277, the user agent 13 determines whether or not the proposed advertisement has been accepted. If it is determined by the user agent 13 that the proposed advertisement has been accepted (permitted), the advertisement agent 32 delivers a URL corresponding to the advertisement data to the user agent 13 in step S278. On the other hand, when it is determined by the user agent 13 that the proposed advertisement has not been accepted (rejected), nothing is done as it is, and the process is terminated.
次に、図12のフローチャートを参照して、仲介エージェント22によるクリックスルー通知の処理手順について説明する。ステップS281において、利用者エージェント13から、利用者によるクリックスルーの通知を受け取る。次に、ステップS282において、受け取った情報を元に、記憶装置23に記憶されている取引履歴を更新する。取引履歴とは、利用者がクリックした広告の種類、クリック回数、閲覧時間、閲覧場所等の履歴情報である。これらの情報は、広告主の検索や広告の評価に再利用される。次に、ステップS283において、クリックされた広告を提供した広告主に対して、広告料金の課金を行う。 Next, with reference to the flowchart of FIG. 12, the processing procedure of the click-through notification by the mediation agent 22 will be described. In step S281, the user agent 13 receives a click-through notification from the user. Next, in step S282, the transaction history stored in the storage device 23 is updated based on the received information. The transaction history is history information such as the type of advertisement clicked by the user, the number of clicks, the viewing time, and the viewing location. This information is reused for advertiser search and advertisement evaluation. Next, in step S283, an advertising fee is charged to the advertiser who provided the clicked advertisement.
次に、図13のフローチャートを参照して、仲介エージェント22による広告登録の処理手順について説明する。ステップS291において、広告エージェント32または広告主の管理者から、広告情報を受け取る。広告情報とは、利用者エージェント13の要求に応じた広告主を検索するための情報である。例えば、広告主の情報、広告の種類、URL等である。次に、ステップS292において、受け取った広告情報は、記憶装置24に記憶されている広告主DBに保存、更新される。 Next, an advertisement registration processing procedure by the mediation agent 22 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. In step S291, advertisement information is received from the advertisement agent 32 or the manager of the advertiser. The advertising information is information for searching for an advertiser in response to a request from the user agent 13. For example, advertiser information, advertisement type, URL, and the like. Next, in step S292, the received advertisement information is saved and updated in the advertiser DB stored in the
次に、図14のフローチャートを参照して、広告エージェント32によるイベント監視処理手順について説明する。まず最初に、ステップS301において、広告エージェント32が有効である間、すなわち、広告エージェント32が活性化している間、広告エージェント32のイベントを監視し、イベント発生時にイベントに応じた処理を割り振り、ステップS302以降の処理が繰り返し実行されるように制御される。ステップS302においては、イベントが発生したか否かが判定される。その結果、イベントが発生したと判定された場合、イベントに応じた処理が実行される。 Next, an event monitoring process procedure by the advertisement agent 32 will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, in step S301, while the advertising agent 32 is active, that is, while the advertising agent 32 is activated, the event of the advertising agent 32 is monitored, and processing corresponding to the event is assigned when the event occurs. Control is performed so that the processing after S302 is repeatedly executed. In step S302, it is determined whether an event has occurred. As a result, when it is determined that an event has occurred, processing corresponding to the event is executed.
仲介エージェント22から広告募集があったとき、ステップS303において、図15を参照して後述する広告提案処理が実行される。利用者エージェント13に広告を配信するとき、ステップS304において、図16を参照して後述する広告配信処理が実行される。利用者が携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12の広告をクリックしたとき、ステップS305において、図17を参照して後述するクリックスルー通知処理が実行される。全てのイベント(仲介エージェント22からの広告募集、利用者エージェント13に対する広告配信、利用者による広告のクリック)は、非同期的に動作するため、不要なイベントの終了を待つ必要がない。また、エージェント間の通信経路を保持する必要がない。 When there is an advertisement recruitment from the mediation agent 22, an advertisement proposal process described later with reference to FIG. 15 is executed in step S303. When the advertisement is distributed to the user agent 13, an advertisement distribution process described later with reference to FIG. 16 is executed in step S304. When the user clicks on the advertisement in the advertisement field 12 on the screen of the
次に、図15のフローチャートを参照して、広告エージェント32による広告提案の処理手順について説明する。ステップS311において、仲介エージェント22から送信されてきた広告提案の要求(広告募集)を受信する。次に、ステップS312において、適切なカテゴリの広告を検索する。次に、ステップS313において、広告主が広報活動のために準備した広報戦略を読み込む。広報戦略は、ステップS314における入札価値の見積もりで用いられる評価ルールとデータを含んでいる。 Next, with reference to the flowchart of FIG. 15, the processing procedure of the advertisement proposal by the advertisement agent 32 will be described. In step S311, the advertisement proposal request (advertisement solicitation) transmitted from the mediation agent 22 is received. Next, in step S312, an advertisement of an appropriate category is searched. Next, in step S313, the public relation strategy prepared for the public relations by the advertiser is read. The public relations strategy includes evaluation rules and data used in estimating the bid value in step S314.
次に、ステップ314において、広告戦略の内容と、後述する広告エージェント32の評価モデルを使用して、広告の入札価値を見積もる。次に、ステップS315において、入札価値を評価して、広告の提案が可能であるか否かが判定される。その結果、広告の提案が不可能であると判定された場合、処理を終了する。一方、広告の提案が可能であると判定された場合、ステップS316に進む。 Next, in step 314, the bid value of the advertisement is estimated using the contents of the advertising strategy and the evaluation model of the advertising agent 32 described later. Next, in step S315, the bid value is evaluated to determine whether or not an advertisement can be proposed. As a result, when it is determined that the advertisement cannot be proposed, the process is terminated. On the other hand, if it is determined that an advertisement can be proposed, the process proceeds to step S316.
ステップS316においては、仲介エージェント22に対して価格と広告を提案する。次に、ステップS317において仲介エージェント22が提案した価格と広告を受け入れたか否かが判定される。仲介エージェント22が提案した価格と広告を受け入れなかった(拒否した)場合、そのまま処理を終了する。一方、仲介エージェント22が提案した価格と広告を受け入れた(許可した)場合、広告を利用者エージェント13に配信するためのURLを送信する。 In step S316, a price and an advertisement are proposed to the mediation agent 22. Next, in step S317, it is determined whether the price and advertisement proposed by the mediation agent 22 have been accepted. If the mediation agent 22 has not accepted (rejected) the price and advertisement proposed, the processing is terminated. On the other hand, when the price and advertisement proposed by the mediation agent 22 are accepted (permitted), a URL for delivering the advertisement to the user agent 13 is transmitted.
次に、図16のフローチャートを参照して、広告エージェント32による広告配信の処理手順について説明する。ステップS321において、利用者エージェント13から広告の配信依頼(広告要求)を受け取る。次に、ステップS322において、広告を利用者エージェント13に配信する。 Next, with reference to the flowchart of FIG. 16, the procedure of the advertisement delivery process by the advertisement agent 32 will be described. In step S321, an advertisement distribution request (advertisement request) is received from the user agent 13. Next, in step S322, the advertisement is distributed to the user agent 13.
次に、図17のフローチャートを参照して、広告エージェント32によるクリックスルー通知の処理手順について説明する。ステップS331において、仲介エージェント22または利用者エージェント13から、利用者によるクリックスルーの通知を受け取る。次に、ステップS332において、受け取った情報を元に、記憶装置35に記憶されている取引履歴を更新する。取引履歴とは、利用者がクリックした広告の種類、クリック回数、閲覧時間、閲覧場所等の履歴情報である。これらの情報は、広告主の検索や広告入札の価値評価に再利用される。次に、ステップS333において、仲介エージェント22から要求された広告料の課金処理を行う。 Next, with reference to the flowchart of FIG. 17, the processing procedure of the click-through notification by the advertisement agent 32 will be described. In step S331, a notification of a click-through by the user is received from the mediation agent 22 or the user agent 13. Next, in step S332, the transaction history stored in the storage device 35 is updated based on the received information. The transaction history is history information such as the type of advertisement clicked by the user, the number of clicks, the viewing time, and the viewing location. These pieces of information are reused for advertiser search and value evaluation of advertisement bids. Next, in step S333, the advertising fee requested from the mediation agent 22 is charged.
次に、図18のシーケンス図を参照して、利用者、利用者エージェント13、仲介エージェント22、および広告エージェント32間の対話プロトコルについて説明する。利用者、利用者エージェント13、仲介エージェント22、広告エージェント32は、広告表示プロセスと広告クリックスループロセスを通じて、図18に示したシーケンスに従ったメッセージ通信(対話)を行う。後述する同期メッセージとは、相手の返信メッセージを受け取るまで処理を中断(同期処理)するものである。非同期メッセージとは、相手の返信メッセージを待たずに処理を続けて、任意のタイミングで受信(非同期処理)するものである。非同期メッセージの通信では、返信メッセージを受信するまでの空き時間には、通信状態を保持しておく必要はなく、任意に通信を切断することができる。 Next, an interaction protocol between the user, the user agent 13, the mediation agent 22, and the advertisement agent 32 will be described with reference to the sequence diagram of FIG. The user, the user agent 13, the mediation agent 22, and the advertisement agent 32 perform message communication (dialogue) according to the sequence shown in FIG. 18 through the advertisement display process and the advertisement click-through process. The synchronization message described later interrupts the process (synchronization process) until the other party's reply message is received. Asynchronous messages are messages that are received at an arbitrary timing (asynchronous processing) without waiting for the other party's reply message. In the asynchronous message communication, it is not necessary to hold the communication state during the idle time until the reply message is received, and the communication can be arbitrarily disconnected.
まず最初に、ステップS341において、利用者は非同期メッセージにより広告表示を要求する。次に、ステップS342において、利用者エージェント13は、利用者からの広告表示要求に応じて、非同期メッセージにより、仲介エージェント22に対して広告を募集する(例えば、カテゴリとして「レストラン|金融」を指定して非同期メッセージにより仲介エージェント22に対して広告を募集する)。次に、ステップS343において、仲介エージェント22は、同期メッセージにより広告エージェント32に対して広告を募集する。 First, in step S341, the user requests advertisement display using an asynchronous message. Next, in step S342, the user agent 13 recruits advertisements to the mediation agent 22 by an asynchronous message in response to an advertisement display request from the user (for example, “restaurant | finance” is specified as the category). Then, an advertisement is recruited from the mediation agent 22 by an asynchronous message). Next, in step S343, the mediation agent 22 recruits advertisements to the advertisement agent 32 by a synchronization message.
次に、ステップS344において、広告エージェント32は、同期メッセージにより、仲介エージェント22に対して広告提案(例えば、「Aレストラン、朝食メニュー」の提案)を行う。次に、仲介エージェント22は、ステップS345において、同期メッセージにより広告エージェント32に対して提案棄却を行うか、または、ステップS346において、同期メッセージにより広告エージェント32に対して提案受理を行う。 Next, in step S344, the advertisement agent 32 makes an advertisement proposal (for example, a proposal of “A restaurant, breakfast menu”) to the mediation agent 22 by a synchronization message. Next, the mediation agent 22 rejects the proposal with respect to the advertising agent 32 by a synchronous message in step S345, or accepts the proposal to the advertising agent 32 by a synchronous message in step S346.
次に、ステップS347において、仲介エージェント22は、非同期メッセージにより利用者エージェント13に対して広告提案(例えば、「Aレストラン、朝食メニュー」の提案)を行う。次に、利用者エージェント13は、ステップS348において、非同期メッセージにより仲介エージェント22に対して提案棄却を行うか、または、ステップS349において、非同期メッセージにより仲介エージェント22に対して提案受理を行う。提案受理の場合、ステップS350において、利用者エージェント13は、同期メッセージにより仲介エージェント22を介して広告エージェント32に対し、配信要求(例えば、「Aレストラン、朝食メニュー」の配信要求)を行う。 Next, in step S347, the mediation agent 22 makes an advertisement proposal (for example, “A restaurant, breakfast menu” proposal) to the user agent 13 by an asynchronous message. Next, the user agent 13 rejects the proposal to the mediation agent 22 by an asynchronous message in step S348, or accepts the proposal to the mediation agent 22 by an asynchronous message in step S349. In the case of accepting the proposal, in step S350, the user agent 13 makes a distribution request (for example, a distribution request for “A restaurant, breakfast menu”) to the advertising agent 32 via the mediation agent 22 by a synchronous message.
次に、ステップS351において、利用者エージェント13から仲介エージェント22を介して配信要求を受けた広告エージェント32は、同期メッセージにより仲介エージェント22を介して利用者エージェント13に対し、広告配信(広告のURL(例えば、「http://広告URL」)の配信)を行う。 Next, in step S351, the advertisement agent 32 that has received a distribution request from the user agent 13 via the mediation agent 22 sends an advertisement distribution (advertisement URL) to the user agent 13 via the mediation agent 22 by a synchronization message. (For example, distribution of “http: // advertisement URL”)).
次に、ステップS352において、利用者エージェント13は、非同期メッセージにより広告エージェント32から仲介エージェント22を介して配信された広告のURLにアクセスし、その広告を携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12に表示する。ステップS353においては、利用者が携帯電話機10の画面の広告欄12に表示された広告をクリックした場合、非同期メッセージにより利用者エージェント13に対してクリック通知がなされる。すなわち、利用者エージェント13のイベント監視により、利用者が広告欄12に表示されている広告をクリックしたことが検出される。 Next, in step S352, the user agent 13 accesses the URL of the advertisement distributed from the advertisement agent 32 via the mediation agent 22 by an asynchronous message, and displays the advertisement in the advertisement column 12 on the screen of the
次に、ステップS354において、利用者エージェント13は、クリック通知を受けて仲介エージェント22に対して非同期メッセージによりクリック通知を行う。例えば、利用者によってクリックされた広告のURL(例えば、「http://広告URL」)を通知する。次に、ステップS355において、仲介エージェント22は、利用者エージェント13からのクリック通知を受けて、広告エージェント32に対して同期メッセージによりクリック通知を行う。次に、ステップS356において、広告エージェント32は、仲介エージェント22に対して同期メッセージにより課金処理通知を行う。 Next, in step S354, the user agent 13 receives the click notification and sends a click notification to the mediation agent 22 using an asynchronous message. For example, the URL of the advertisement clicked by the user (for example, “http: // advertisement URL”) is notified. Next, in step S355, the mediation agent 22 receives a click notification from the user agent 13 and performs a click notification to the advertisement agent 32 using a synchronization message. Next, in step S356, the advertising agent 32 notifies the mediation agent 22 of a charging process using a synchronization message.
次に、図15のステップS314における広告エージェント32の評価モデルについて説明する。まず、広告エージェント32の概要について説明する。広告エージェント32は、広告主に代わって広告欄12を競売(入札)する。広告エージェント32は、携帯電話機10への広告配信を最適化することを目的にしている。広告エージェント32は、「いつ」、「どの」広告を携帯電話機10に提供するかを決定する。広告エージェント32の動作は、利用者の入力によって決定されるだけでなく、過去の取引履歴をもとに最適化されながら決定される。 Next, the evaluation model of the advertisement agent 32 in step S314 in FIG. 15 will be described. First, the outline of the advertising agent 32 will be described. The advertising agent 32 auctions (bids) the advertising column 12 on behalf of the advertiser. The advertisement agent 32 aims to optimize advertisement distribution to the
広告エージェント32は、広告の競売を要求した仲介エージェント22と対話することができる。入札価格と広告種類の選択には、広告主側の意思決定者(広報担当者)の戦略的決定はもとより、過去の取引履歴も参考とされる。図19は、広告エージェント32の概要を示す図である。同図に示すように、広告エージェント32は、入札依頼に対して広告の入札を行う。その際、意志決定者(広告主の広報担当者)が広告宣伝費や販売戦略をもとに決定した入札価格の決定戦略などの利用者プリファレンス(広報戦略、入札戦略、広報用予算枠等)や、ERPシステム36(一般的なERP(Enterprise Resource Planning)パッケージ、たとえば、商品・在庫データベース、受発注予測パッケージ、管理会計パッケージなど)から提供される過去の取引履歴、発注方法、発注見込み等に基づいて、広告データベース33から提供すべき広告を検索する。 The advertisement agent 32 can interact with the mediation agent 22 that has requested an advertisement auction. The selection of the bid price and advertisement type is based on the past transaction history as well as the strategic decision of the advertiser's decision-maker (public relations person). FIG. 19 is a diagram showing an outline of the advertisement agent 32. As shown in the figure, the advertisement agent 32 bids an advertisement in response to a bid request. At that time, decision-making (advertiser's spokesperson) user preferences such as bid decision strategy determined based on advertising expenses and sales strategy (publicity strategy, bidding strategy, publicity budget, etc.) ) And ERP system 36 (general ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) packages such as merchandise / inventory databases, order forecast packages, management accounting packages, etc.) Based on the above, an advertisement to be provided is searched from the
広告エージェント32は、次のような機能を提供する。
(1)広告欄12をいくらで入札するかを決定する。
(2)広告価格、プロモーション、言語のカスタマイズ(ニーズに合わせて変更)を行う。
(3)過去の取引履歴に基づいて、ルールや動作を見直し、更新する。The advertisement agent 32 provides the following functions.
(1) Decide how much to bid on the advertisement column 12.
(2) Customize advertising prices, promotions, and language (change according to needs).
(3) Review and update rules and actions based on past transaction history.
また、広告エージェント32の動作決定は下記の2種類の技術を応用して行っている。
(1)ルールベース技術:利用者情報に基づいて、ルールによる価値評価とエージェントの動作を予見して決定するもの。
(2)ニューラルネットワーク:ニューラルネットワークは、システムのルール自体を変更することは難しいが、学習によって利用価値のある値(期待値)の見積もりに適したデータマイニング技術である。The operation of the advertising agent 32 is determined by applying the following two types of technologies.
(1) Rule-based technology: A technology that predicts and determines the value evaluation based on rules and the operation of agents based on user information.
(2) Neural network: A neural network is a data mining technique suitable for estimating a value (expected value) that has utility value by learning although it is difficult to change the system rule itself.
次に、入札価格の決定方法について説明する。ここでは、広告エージェント32がニューラルネットワークとルールを使って、どのような手順で適切な入札価格を決定するのかについて説明する。ここでの事例における入札価格決定では、落札成功のために利用者がいくらで入札すべきかを考える。 Next, a method for determining a bid price will be described. Here, the procedure by which the advertising agent 32 determines an appropriate bid price using a neural network and rules will be described. In the bid price determination in the example here, it is considered how much the user should bid for a successful bid.
図20は、入札価格に相当する価値を見積もるための評価モデルの例を示している。この例では、広告エージェント32が、外国人のビジネスマンに対して、東京の日本食レストラン(寿司屋)がどのように広告を提示すべきかを推測し、利用者の携帯電話機10の広告欄12をJPY(日本円)15(円)の価値で入札する意思決定を行うまでの過程を表したものである。 FIG. 20 shows an example of an evaluation model for estimating the value corresponding to the bid price. In this example, the advertising agent 32 guesses how a Japanese restaurant (sushi restaurant) in Tokyo should present an advertisement to a foreign businessman, and sets the advertisement column 12 of the user's
広告エージェント32は、最適な見返り(リターン)を得るために入札額を変更、設定することができる。特徴としては、入札の機能だけでなく、利用者プロファイル(利用者情報)、過去の取引履歴や現在の状態(場所とタイミング)を考慮する機能を持つことである。これらのデータをもとに、広告エージェント32は、以下の「期待値」と「価値」を見積もる。 The advertising agent 32 can change and set the bid amount in order to obtain an optimal return. As a feature, it has not only a bidding function but also a function that considers a user profile (user information), past transaction history, and current state (location and timing). Based on these data, the advertising agent 32 estimates the following “expected value” and “value”.
ニューラルネットワークは、以下の期待値を見積もるために使用される。
(1)落札に対する期待値
この期待値は、入札価格の決定関数のみならず、利用者情報、現在の時間(時刻)、場所に依存した比較関数である。これは次のような関数で表すことができる。
関数f(入札価格,利用者情報,時間,場所)
(2)利用者のクリックスルーに対する期待値(落札したら与えられる)(詳細は後述する)。
(3)商品成約(発注)に対する期待値(クリックスルーしたら与えられる)
入札価格の期待値に類似している。これは次のような関数で表すことができる。
関数f(利用者情報,時間,場所)The neural network is used to estimate the following expected values:
(1) Expected value for successful bid This expected value is a comparison function depending not only on a bid price determination function but also on user information, current time (time), and place. This can be expressed by the following function.
Function f (bid price, user information, time, place)
(2) Expected value for user click-through (given when a successful bid is made) (details will be described later).
(3) Expected value for product closing (ordering) (given after clicking through)
Similar to the expected bid price. This can be expressed by the following function.
Function f (user information, time, place)
ルールベース機構(技術)は、評価モデルの価値ノードを見積もるために使うことができる。
(1)ブランドインパクト(パッシブ):利用者がクリックを行わなかった場合でも、ブランドイメージを与える広告を見たという価値を与える。つまり、意識的もしくは無意識的に、利用者がそのブランドを意識している。
(2)ブランドインパクト(アクティブ):利用者がサイトを訪れるためにクリックした場合、利用者がそのブランドを記憶して、今後も意識する見込みが増える。
(3)カスタマバリュー:利用者が商品を購入することによる利益(利用者による将来的な購入による利益でも可)が広告主に生じる可能性がある。この価値は、それが新規顧客であるかリピート顧客であるかに依存する。Rule-based mechanisms (technologies) can be used to estimate the value node of an evaluation model.
(1) Brand impact (passive): Gives the value of seeing an advertisement that gives a brand image even when the user does not click. In other words, users are consciously or unconsciously aware of the brand.
(2) Brand impact (active): When a user clicks to visit a site, the user remembers the brand and increases the likelihood of being aware of it in the future.
(3) Customer value: There is a possibility that a profit from the purchase of a product by the user (may be profit from a future purchase by the user) is generated in the advertiser. This value depends on whether it is a new customer or a repeat customer.
図20に示した入札価格に相当する価値を見積もるための評価モデルの例では、東京の日本食レストランが外国人のビジネスマンに広告を宣伝した場合、JPY15の入札でJPY8の利益が期待できる。 In the example of the evaluation model for estimating the value corresponding to the bid price shown in FIG. 20, when a Japanese restaurant in Tokyo advertises an advertisement to a foreign businessman, a profit of JPY8 can be expected by bidding for JPY15.
以下の表1は、このシナリオの計算結果をまとめたものである。 Table 1 below summarizes the calculation results for this scenario.
以下では、ニューラルネットワークを使って、どのようにして図20に示した期待ノード(クリックスルー部)を計算するのかについて説明する。その後、価値ノード(カスタマバリュー部)を計算するためのルールの例について説明する。 Hereinafter, how to calculate the expected node (click-through part) shown in FIG. 20 using a neural network will be described. Then, an example of a rule for calculating a value node (customer value part) will be described.
まず、上記評価モデルにおいて、クリックスルー期待値をニューラルネットワークを使って見積もる方法について説明する。図21は、ニューラルネットワークを使ったクリックスルー期待値の計算方法を示す図である。ここでは、外国人のビジネスマンが、東京の日本食レストラン(寿司屋)が出した昼食の広告をクリックする期待値を計算する例を示している。ここで、ニューロン(丸図形)の内部の数値は、出力と、各ニューロンの重みに相当する矢印の値を決定するために使われる。図中の表は、データを処理するためのルールだけでなく、入力値、処理後の値も表している。つまり、それらの入力を0から1の間の数値に変換している。ニューラルネットワークの「入力層」は「隠れ層」に値を渡す際に、シグモイド関数を使った計算を行う。 First, a method for estimating a click-through expectation value using a neural network in the evaluation model will be described. FIG. 21 is a diagram illustrating a method for calculating an expected click-through value using a neural network. Here, an example is shown in which a foreign businessman calculates an expected value for clicking a lunch advertisement from a Japanese restaurant (sushi restaurant) in Tokyo. Here, the numerical value inside the neuron (circular figure) is used to determine the output and the value of the arrow corresponding to the weight of each neuron. The table in the figure represents not only rules for processing data, but also input values and values after processing. That is, these inputs are converted into numerical values between 0 and 1. The “input layer” of the neural network performs calculations using a sigmoid function when passing values to the “hidden layer”.
f(x)=1/(1+e−x)
ここでxは、全ての入力の重みの合計値と等しい。f (x) = 1 / (1 + e−x )
Here, x is equal to the total value of the weights of all inputs.
図21に示したように、ニューラルネットワークは、利用者が広告をクリックする期待値を0.454として計算している。ここで、図21に示した一般的なニューラルネットを使った計算モデルについて簡単に説明しておく。ニューロンの入力(丸の上からの数値(この例では、1,1,1,1,1,1))と閾値(丸の真ん中の数値(1,0,1,1,0.625,1)から、シグモイド関数を使った計算によりニューロンの出力を求める。各出力を定められた重み(weight of output)によって次層のニューロンの入力に割り当てる。次層のニューロンは、入力値の総和にもとづいて先の計算を繰り返すことで出力値を計算する。また、ニューロンによっては入力定数(fixed input)を持つセルがある。この場合、先の計算においてこの定数を用いる。ネットワーク全体の出力値がクリックスルーの期待値(probability of clicking through)となる。 As shown in FIG. 21, the neural network calculates the expected value that the user clicks on the advertisement as 0.454. Here, a calculation model using the general neural network shown in FIG. 21 will be briefly described. Neuron input (number from the top of the circle (1,1,1,1,1,1 in this example)) and threshold (number in the middle of the circle (1,0,1,1,0.625,1 ) To obtain the output of the neuron by calculation using a sigmoid function, assigning each output to the input of the next layer neuron with a predetermined weight (weight of output), which is based on the sum of the input values. The output value is calculated by repeating the previous calculation, and some neurons have a fixed input, and in this case, the constant is used in the previous calculation. The expected value of through (probability of clicking through).
次に、価値ノードの決定と書き換え可能なルールベース(RB)を使った広告のカスタマイズについて説明する。ここでは、広告エージェント32がその行動を決定するために、どのようにしてRBとルールを使うかについて説明する。また、ここでは、図20のカスタマバリューをどのように計算するかという具体例について説明する。 Next, determination of a value node and customization of an advertisement using a rewritable rule base (RB) will be described. Here, how the advertisement agent 32 uses the RB and the rule to determine the action will be described. Here, a specific example of how to calculate the customer value of FIG. 20 will be described.
寿司屋の広告を見ている利用者(外国人)は表2に示すようなプロファイル(属性)を持つ。表2は、アメリカ人ビジネスマンの利用者プロファイルの例を示している。 A user (foreigner) watching an advertisement for a sushi restaurant has a profile (attribute) as shown in Table 2. Table 2 shows an example of a user profile of an American businessman.
同時に、ベンダー(例えば、寿司屋等)は、異なる利用者の期待値の見積もり規準を提供する属性を持つ。例えば、表3に示すような属性値を、手動、またはベンダーの持つERPシステムからウェブサービスを使って得ることができる。表3は、日本食レストラン(寿司屋)のベンダープロファイルの例を示している。 At the same time, vendors (eg, sushi restaurants) have attributes that provide estimates for different users' expected values. For example, attribute values as shown in Table 3 can be obtained manually or from a vendor's ERP system using a web service. Table 3 shows an example of a vendor profile of a Japanese restaurant (sushi restaurant).
利用者もまた、利用者視点からのカスタマバリューの計算を決定する計算ルールを提供する。RBを使うことで、以下のようなルールを更新することができる。
If T in [11.30-14.00] then Lunch Time (LT) = True
If not LT then PL = 0
If T in [17.30-22.00] then Dinner Time (DT) = True
If not DT then PD = 0
If customer is International then Profit New Customer (PN) = 0
If customer is not new then Profit from New Customer (PN) = 0
If customer is not international then Profit International (VI) = 0
SR = SR * Current exchange Rate (100 JPY/USD)Users also provide calculation rules that determine the calculation of customer value from the user's perspective. The following rules can be updated by using RB.
If T in [11.30-14.00] then Lunch Time (LT) = True
If not LT then PL = 0
If T in [17.30-22.00] then Dinner Time (DT) = True
If not DT then PD = 0
If customer is International then Profit New Customer (PN) = 0
If customer is not new then Profit from New Customer (PN) = 0
If customer is not international then Profit International (VI) = 0
SR = SR * Current exchange Rate (100 JPY / USD)
RBを使うことで、ベンダーは利用者から見積もった期待値を決定する計算ルールを徐々に追加、修正することができる。例えば、寿司屋は外国客に対する経験を後々積むことができる可能性がある。その結果、アメリカ人は他国の客に比べて浪費する傾向にあることが分かり、以下のような計算ルールを追加する可能性がある。
If customer is International and American then VI = VI * 1.5By using RBs, vendors can gradually add and modify calculation rules that determine expected values estimated from users. For example, a sushi restaurant may be able to gain experience with foreign customers later. As a result, it turns out that Americans tend to waste compared to customers in other countries, and there is a possibility of adding the following calculation rule.
If customer is International and American then VI = VI * 1.5
次に、期待値の平均化を行う。カスタマバリューは一般に次のように平均化できる。
カスタマバリュー(CV)=PD+PL+PN+VI+Ks(SR−2000)
先の例では、PD=0、PL=220、PN=0、VI=130、Ks=0.0526、SR=USD($)55=JPY5500とすると、以下のように計算できる。
カスタマバリュー=0+220+0+130+0.0526*(5500−2000) =JPY534Next, the expected value is averaged. Customer values can generally be averaged as follows:
Customer value (CV) = PD + PL + PN + VI + Ks (SR-2000)
In the above example, when PD = 0, PL = 220, PN = 0, VI = 130, Ks = 0.0526, SR = USD ($) 55 = JPY5500, the following calculation is possible.
Customer value = 0 + 220 + 0 + 130 + 0.0526 * (5500−2000) = JPY534
これは表2の計算値と一致する。もし、アメリカ人の顧客に関するRBが適用されれば、VI=195(=130*1.5)となるので、カスタマバリューはJPY599に引き上げられる。 This is consistent with the calculated values in Table 2. If RB related to an American customer is applied, VI = 195 (= 130 * 1.5), so the customer value is raised to JPY599.
次に、計算ルールを使った広告のカスタマイゼーションについて説明する。利用者はさらに、どの広告を見せるかを決定するためにもRBを使うことができる。以下は、日本の寿司屋が広告をカスタマイズするためのルールの例を示している。
If Customer Distance > 3 km then do not advertise
If Dinner Time then show Dinner offer
If Lunch Time then show Lunch offer
If customer is International then language = English
このルールの結果、この広告は英語で書かれたお勧め昼食メニューが表示されたものとなる。Next, advertisement customization using calculation rules will be described. The user can also use the RB to determine which advertisements to show. The following are examples of rules for Japanese sushi restaurants to customize advertisements.
If Customer Distance> 3 km then do not advertise
If Dinner Time then show Dinner offer
If Lunch Time then show Lunch offer
If customer is International then language = English
As a result of this rule, the ad will display a recommended lunch menu written in English.
RB技術はベンダーが簡単にルールを追加できる方法を提供する。例えば、もし利用者が外国人で、$50以上の携帯電話の特典プランを持っているときは、スペシャルメニューを勧めるようなルールを追加することができる。 RB technology provides a way for vendors to easily add rules. For example, if the user is a foreigner and has a mobile phone benefit plan of $ 50 or more, a rule that recommends a special menu can be added.
なお、上記実施の形態の構成および動作は例であって、本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で適宜変更することができることは言うまでもない。 It should be noted that the configuration and operation of the above-described embodiment are examples, and it is needless to say that they can be changed as appropriate without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
10 携帯電話機
11 携帯電話システム
12 広告欄
13 利用者エージェント
14,15,23,24,25,26 記憶装置
20 広告仲介サーバ
21 広告仲介システム
22 仲介エージェント
30−1,30−2,30−3 広告発行サーバ
31−1,31−2,31−3 広告発行システム
32−1,32−2,32−3 広告エージェント
33−1,33−2,33−3 記憶装置
34−1,34−2,34−3 記憶装置
35−1,35−2,35−3 記憶装置
36 ERPシステム
100 携帯電話網DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (7)
Translated fromJapanese前記利用者の利用者情報を抽出する抽出手段と、
前記利用者情報に基づいて、前記利用者に対して配信すべき広告のカテゴリを推論するカテゴリ推論手段と、
前記カテゴリ推論手段によって推論された前記カテゴリの広告を募集する公告募集手段と、
前記募集に対して所定の広告主による広告を提案する提案手段と、
前記提案手段によって提案された前記広告を評価する評価手段と、
前記評価手段による評価結果に応じて、前記広告を前記利用者に対して配信する配信手段と
を備えることを特徴とする広告配信システム。An advertisement distribution system for distributing advertisements to users,
Extraction means for extracting user information of the user;
Category inference means for inferring a category of an advertisement to be delivered to the user based on the user information;
Public notice soliciting means for soliciting advertisements of the category inferred by the category inferring means;
Proposing means for proposing an advertisement by a predetermined advertiser for the recruitment;
Evaluation means for evaluating the advertisement proposed by the suggestion means;
An advertisement distribution system comprising: distribution means for distributing the advertisement to the user according to an evaluation result by the evaluation means.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の広告配信システム。The advertisement distribution system according to claim 1, wherein the evaluation unit evaluates the advertisement proposed by the suggestion unit based on a predetermined evaluation strategy.
ことを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の広告配信システム。The proposing means searches for an advertisement of the category, estimates a bid value of the advertisement based on a publicity strategy prepared by the predetermined advertiser, and proposes the advertisement based on the bid value. The advertisement distribution system according to claim 1 or 2.
前記取引履歴情報は、前記広告主の検索または前記広告の評価に用いられる
ことを特徴とする請求項3に記載の広告配信システム。A storage means for storing information including the type of the advertisement clicked by the user, the number of clicks, the click time, and the clicked place as transaction history information;
The advertisement distribution system according to claim 3, wherein the transaction history information is used for searching the advertiser or evaluating the advertisement.
ことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の広告配信システム。The advertisement distribution system according to claim 4, wherein the evaluation unit evaluates the advertisement based on the transaction history information.
前記利用者の利用者情報を抽出する抽出ステップと、
前記利用者情報に基づいて、前記利用者に対して配信すべき広告のカテゴリを推論するカテゴリ推論ステップと、
前記カテゴリ推論ステップにおいて推論された前記カテゴリの広告を募集する公告募集ステップと、
前記募集に対して所定の広告主による広告を提案する提案ステップと、
前記提案ステップにおいて提案された前記広告を評価する評価ステップと、
前記評価ステップにおける評価結果に応じて、前記広告を前記利用者に対して配信する配信ステップと
を備えることを特徴とする広告配信方法。An advertisement distribution method for distributing advertisements to users,
An extraction step of extracting user information of the user;
A category inference step for inferring a category of an advertisement to be delivered to the user based on the user information;
A notice soliciting step for soliciting advertisements of the category inferred in the category inference step;
A proposal step of proposing an advertisement by a predetermined advertiser for the recruitment;
An evaluation step of evaluating the advertisement proposed in the proposal step;
An advertisement distribution method comprising: a distribution step of distributing the advertisement to the user according to an evaluation result in the evaluation step.
前記利用者の利用者情報を抽出する抽出ステップと、
前記利用者情報に基づいて、前記利用者に対して配信すべき広告のカテゴリを推論するカテゴリ推論ステップと、
前記カテゴリ推論ステップにおいて推論された前記カテゴリの広告を募集する公告募集ステップと、
前記募集に対して所定の広告主による広告を提案する提案ステップと、
前記提案ステップにおいて提案された前記広告を評価する評価ステップと、
前記評価ステップにおける評価結果に応じて、前記広告を前記利用者に対して配信する配信ステップとを前記広告配信システムに実行させる
ことを特徴とする広告配信プログラム。
An advertisement distribution program for controlling an advertisement distribution system that distributes advertisements to users,
An extraction step of extracting user information of the user;
A category inference step for inferring a category of an advertisement to be delivered to the user based on the user information;
A notice soliciting step for soliciting advertisements of the category inferred in the category inference step;
A proposal step of proposing an advertisement by a predetermined advertiser for the recruitment;
An evaluation step of evaluating the advertisement proposed in the proposal step;
An advertisement distribution program that causes the advertisement distribution system to execute a distribution step of distributing the advertisement to the user according to an evaluation result in the evaluation step.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004032713AJP2005222500A (en) | 2004-02-09 | 2004-02-09 | Ad distribution system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004032713AJP2005222500A (en) | 2004-02-09 | 2004-02-09 | Ad distribution system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005222500Atrue JP2005222500A (en) | 2005-08-18 |
Family
ID=34998055
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004032713APendingJP2005222500A (en) | 2004-02-09 | 2004-02-09 | Ad distribution system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005222500A (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007323537A (en)* | 2006-06-02 | 2007-12-13 | Navitime Japan Co Ltd | Advertisement distribution system, information distribution server, and terminal device |
| JP2009110466A (en)* | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-21 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Search result presentation method, site search service server, site search service program, and recording medium storing the program |
| JP2010049397A (en)* | 2008-08-20 | 2010-03-04 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Integrated development environment providing system for component cooperation scenario, scenario creation support method, and program |
| JP2010530586A (en)* | 2007-06-20 | 2010-09-09 | エヌエイチエヌ コーポレーション | Ubiquitous presence service method and system for providing various application states based on 3A |
| JP2011511371A (en)* | 2008-02-01 | 2011-04-07 | クゥアルコム・インコーポレイテッド | System and method for auctioning wireless device assets and providing asset allocation options for wireless devices |
| JP2014194806A (en)* | 2009-05-29 | 2014-10-09 | Google Inc | Matching content providers and interested content users |
| JP2016512352A (en)* | 2013-03-07 | 2016-04-25 | フェイスブック,インク. | User identification for advertising opportunities based on paired identifiers |
| KR101751925B1 (en)* | 2016-08-29 | 2017-06-28 | 김연호 | System and method for mediating advertisement marketer |
| CN112308579A (en)* | 2019-07-24 | 2021-02-02 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Information delivery method and device and storage medium |
| JP7440582B1 (en) | 2022-08-18 | 2024-02-28 | 楽天グループ株式会社 | Systems, methods, and programs for advertising distribution |
Citations (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001092743A (en)* | 1999-09-16 | 2001-04-06 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | Method, device and system for information distribution and storage medium with software product distributing information stored therein |
| JP2001352403A (en)* | 2000-06-06 | 2001-12-21 | Nec Planning Research Ltd | Advertisement method and advertisement system utilizing mobile telephone |
| JP2002007462A (en)* | 2000-06-21 | 2002-01-11 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | System and method for advertisement distribution |
| JP2002051024A (en)* | 2000-08-07 | 2002-02-15 | J Planet:Kk | Advertisement delivery system and method for mobile phone |
| JP2002083160A (en)* | 2000-09-06 | 2002-03-22 | Nec Saitama Ltd | Advertisement distribution method, data processing method, communication terminal device, data communication system, information storage medium |
| JP2002183505A (en)* | 2000-12-11 | 2002-06-28 | Uniden Corp | Advertisement invitation distribution system and method of cellular phone |
| JP2002197295A (en)* | 2000-12-27 | 2002-07-12 | Nec Corp | Advertisement space trading system, brokerage method of the advertisement space trading, and record medium which stores advertisement space trading program |
| JP2002216001A (en)* | 2000-11-14 | 2002-08-02 | Masakuni Hirano | One reading guarantee type internet advertisement system |
| JP2002342657A (en)* | 2001-05-22 | 2002-11-29 | Seiko Epson Corp | Advertisement distribution system, portable information terminal used therefor, advertisement distribution method, and portable information terminal control program |
| JP2003067627A (en)* | 2001-08-27 | 2003-03-07 | Victor Co Of Japan Ltd | Network distribution business system |
| JP2003122994A (en)* | 2001-10-12 | 2003-04-25 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Advertising distribution device and program |
| JP2003187148A (en)* | 2001-12-20 | 2003-07-04 | Ntt Data Corp | Processing system of advertisement information by customer |
| JP2003228310A (en)* | 2002-02-06 | 2003-08-15 | Fujitsu Ltd | Advertisement providing device by network, advertisement providing method, and program therefor |
| JP2003345280A (en)* | 2002-05-30 | 2003-12-03 | Hitachi Ltd | Ad distribution method and virtual community system |
| JP2004502187A (en)* | 2000-03-21 | 2004-01-22 | クアック.コム | Internet voice portal advertising system and method |
| JP2004258694A (en)* | 2000-11-21 | 2004-09-16 | Seikoo Insatsu Kk | Method for presenting advertisement using internet |
- 2004
- 2004-02-09JPJP2004032713Apatent/JP2005222500A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001092743A (en)* | 1999-09-16 | 2001-04-06 | Internatl Business Mach Corp <Ibm> | Method, device and system for information distribution and storage medium with software product distributing information stored therein |
| JP2004502187A (en)* | 2000-03-21 | 2004-01-22 | クアック.コム | Internet voice portal advertising system and method |
| JP2001352403A (en)* | 2000-06-06 | 2001-12-21 | Nec Planning Research Ltd | Advertisement method and advertisement system utilizing mobile telephone |
| JP2002007462A (en)* | 2000-06-21 | 2002-01-11 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | System and method for advertisement distribution |
| JP2002051024A (en)* | 2000-08-07 | 2002-02-15 | J Planet:Kk | Advertisement delivery system and method for mobile phone |
| JP2002083160A (en)* | 2000-09-06 | 2002-03-22 | Nec Saitama Ltd | Advertisement distribution method, data processing method, communication terminal device, data communication system, information storage medium |
| JP2002216001A (en)* | 2000-11-14 | 2002-08-02 | Masakuni Hirano | One reading guarantee type internet advertisement system |
| JP2004258694A (en)* | 2000-11-21 | 2004-09-16 | Seikoo Insatsu Kk | Method for presenting advertisement using internet |
| JP2002183505A (en)* | 2000-12-11 | 2002-06-28 | Uniden Corp | Advertisement invitation distribution system and method of cellular phone |
| JP2002197295A (en)* | 2000-12-27 | 2002-07-12 | Nec Corp | Advertisement space trading system, brokerage method of the advertisement space trading, and record medium which stores advertisement space trading program |
| JP2002342657A (en)* | 2001-05-22 | 2002-11-29 | Seiko Epson Corp | Advertisement distribution system, portable information terminal used therefor, advertisement distribution method, and portable information terminal control program |
| JP2003067627A (en)* | 2001-08-27 | 2003-03-07 | Victor Co Of Japan Ltd | Network distribution business system |
| JP2003122994A (en)* | 2001-10-12 | 2003-04-25 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Advertising distribution device and program |
| JP2003187148A (en)* | 2001-12-20 | 2003-07-04 | Ntt Data Corp | Processing system of advertisement information by customer |
| JP2003228310A (en)* | 2002-02-06 | 2003-08-15 | Fujitsu Ltd | Advertisement providing device by network, advertisement providing method, and program therefor |
| JP2003345280A (en)* | 2002-05-30 | 2003-12-03 | Hitachi Ltd | Ad distribution method and virtual community system |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007323537A (en)* | 2006-06-02 | 2007-12-13 | Navitime Japan Co Ltd | Advertisement distribution system, information distribution server, and terminal device |
| JP2010530586A (en)* | 2007-06-20 | 2010-09-09 | エヌエイチエヌ コーポレーション | Ubiquitous presence service method and system for providing various application states based on 3A |
| JP2009110466A (en)* | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-21 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Search result presentation method, site search service server, site search service program, and recording medium storing the program |
| JP2014013580A (en)* | 2008-02-01 | 2014-01-23 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Systems and methods for auctioning wireless device assets and providing wireless devices with asset allocation option |
| JP2011511371A (en)* | 2008-02-01 | 2011-04-07 | クゥアルコム・インコーポレイテッド | System and method for auctioning wireless device assets and providing asset allocation options for wireless devices |
| JP2013058216A (en)* | 2008-02-01 | 2013-03-28 | Qualcomm Inc | Systems and methods for auctioning wireless device assets and providing wireless devices with asset allocation option |
| JP2016136403A (en)* | 2008-02-01 | 2016-07-28 | クゥアルコム・インコーポレイテッドQualcomm Incorporated | Systems and methods for auctioning wireless device assets and providing wireless devices with asset allocation option |
| JP2010049397A (en)* | 2008-08-20 | 2010-03-04 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Integrated development environment providing system for component cooperation scenario, scenario creation support method, and program |
| JP2014194806A (en)* | 2009-05-29 | 2014-10-09 | Google Inc | Matching content providers and interested content users |
| JP2016512352A (en)* | 2013-03-07 | 2016-04-25 | フェイスブック,インク. | User identification for advertising opportunities based on paired identifiers |
| US10559013B2 (en) | 2013-03-07 | 2020-02-11 | Facebook, Inc. | Identifying users for advertising opportunities based on paired identifiers |
| KR101751925B1 (en)* | 2016-08-29 | 2017-06-28 | 김연호 | System and method for mediating advertisement marketer |
| CN112308579A (en)* | 2019-07-24 | 2021-02-02 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Information delivery method and device and storage medium |
| JP7440582B1 (en) | 2022-08-18 | 2024-02-28 | 楽天グループ株式会社 | Systems, methods, and programs for advertising distribution |
| JP2024029780A (en)* | 2022-08-18 | 2024-03-07 | 楽天グループ株式会社 | Systems, methods, and programs for advertising distribution |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI393064B (en) | Device, method, system, and processor readable medium for event communication platform for mobile device users | |
| US8452659B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for connecting consumers with one or more product or service providers | |
| KR101049889B1 (en) | Web site operation method and online system to receive and target advertisements for keyword groups based on behavioral analysis through search | |
| JP4597473B2 (en) | Automatic advertiser notification for a system to provide ranking and price protection in search result lists generated by computer network search engines | |
| US8086541B2 (en) | Systems and methods for generating advertiser recommendations from users of workflow software | |
| US20220277348A1 (en) | Conversion Timing Prediction for Networked Advertising | |
| KR101736597B1 (en) | Service application server, sales management method of service application server and sales management system including the same | |
| US8533038B2 (en) | Offer delivery system | |
| US7945476B2 (en) | Internet contextual advertisement delivery system | |
| US20020120507A1 (en) | Feature rich advertisments including consumer requests for additional information | |
| US20100312691A1 (en) | Loan Quotation System and Method | |
| US7366682B1 (en) | System, method, and code for providing promotions in a network environment | |
| KR20070116243A (en) | Provision to user of history and transaction volume information of content source | |
| JP2010531027A (en) | Dynamic electronic coupons for mobile environments | |
| JP2006504157A (en) | Authorization-based communication and information exchange system. | |
| JP2007531122A (en) | Communication of newly added information via the Internet | |
| Aghazadeh et al. | Digital Marketing Implementation and Practice | |
| JP2005222500A (en) | Ad distribution system | |
| US9928523B2 (en) | System and method for booking an advertisement to an impression using a targeting dimension dictionary | |
| JP7460733B2 (en) | Information and communication system and information and communication method | |
| TWI775687B (en) | Information communication system, and information communication method | |
| US20210097574A1 (en) | Delivering advertisements to mobile applications | |
| US20190026806A1 (en) | System and method of responding to consumer demand to facilitate exchange of goods or services | |
| CN114677155B (en) | Information communication system and information communication method | |
| US20080059294A1 (en) | Systems and methods for displaying targeted advertisements to users of workflow software |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20061228 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20091104 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20091228 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20100427 | |
| A02 | Decision of refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date:20100831 |