JP2004038247A - License management method, license management system, license management program - Google Patents
License management method, license management system, license management programDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2004038247A JP2004038247AJP2002190454AJP2002190454AJP2004038247AJP 2004038247 AJP2004038247 AJP 2004038247AJP 2002190454 AJP2002190454 AJP 2002190454AJP 2002190454 AJP2002190454 AJP 2002190454AJP 2004038247 AJP2004038247 AJP 2004038247A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- license
- client
- time
- software
- license management
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromJapaneseDescription
Translated fromJapanese【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明はコンピュータソフトウェアのライセンスに関し、特に、ライセンスの管理を行うサーバを用いたライセンス管理方法、ライセンス管理システム、ライセンス管理プログラムに関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
コンピュータソフトウェアの不正な複製や利用は、現在でもかなりの割合で行われている。そのため、ソフトウェアのベンダは、不正な複製や利用を防ぐために、種々の対策を講じている。
【0003】
それらの対策として、小型の装置をUSB(Universal Serial Bus)に接続し、ハードプロテクトを行うタイプや、複製が不可能なように細工されたCD(Compact Disc)でソフトウェアを配布するタイプ、また、フレキシブルディスクを用いるタイプなどがある。
【0004】
また、最近はネットワークを利用したソフトウェアのライセンスサービスも始まっている。この場合の不正防止対策として、例えばソフトウェアのベンダに設けられたサーバが、クライアントであるユーザのコンピュータのオペレーティングシステムのバージョン番号や、デバイスのID番号、ソフトウェアのバージョン番号などのクライアント情報と、ライセンスキーとをネットワークを通じて入手し、組み合わせることによってクライアントのソフトウェアを利用可能にする方法がある。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、最初に述べたハードプロテクトやフレキシブルディスクを用いる場合は、そのハードウェア自体のコストがかかるだけではなく、それらハードウェアが小型の装置であることから、紛失や破損の可能性があるとともに、USBのポートを塞ぐこともあるため使い勝手が良くない。また、複製が不可能なCDの作成にはコストがかかる。
【0006】
また、ネットワークを用いた不正防止対策であるが、最近のインターネットに関する調査結果によると、個人情報やユーザのコンピュータ独自の情報を含むパソコンの固有情報の流出や濫用を懸念する傾向が最も多い。そのため、個々のパソコンに関する情報に基づきライセンスの管理を行うコンピュータにさえも、その情報を提供することに抵抗があるユーザが多い。
【0007】
本発明は、このような問題点に鑑み、ハードウェアを用いたりCDに細工したりせずに不正な複製や利用を防ぐとともに、パソコンの情報に基づきライセンスの管理を行うコンピュータに対して情報を提供しても、個人情報やコンピュータ独自の情報である固有情報の流出や乱用を防ぐことを可能とするライセンス管理方法、ライセンス管理システム、ライセンス管理プログラムを提供することを目的とする。
【0008】
【課題を解決するための手段】
請求項1に記載の発明は、ソフトウェアのライセンスを管理するライセンス管理サーバと、該ライセンス管理サーバにネットワークを介して接続するクライアントを有するライセンス管理システムにおけるライセンス管理方法であって、前記ライセンス管理サーバは、前記クライアントから暗号化された該クライアント固有情報である暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス要求を受信した際に、該暗号化固有情報を登録するとともに、該クライアントが正しいか否かを判断して、ライセンスを付与するライセンス付与ステップと、クライアントから任意または定期的に行われる暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス更新要求を受信した際に、該クライアントの前記暗号化固有情報が正しいか否かの確認を行うステップと、該暗号化固有情報が正しい場合はクライアントに許諾信号を付与する更新ステップとを有し、前記クライアントは、最初にソフトウェアのライセンスを要求時に使用許諾され付与されるライセンスとライセンス付与時のライセンス許諾時刻を最新更新時刻とし、該最新更新時刻とクライアント固有情報を記録する初期情報記録ステップと、前記ソフトウェアの使用の際に、記録した前記ライセンスが正しいことと、記録した前記クライアント固有情報が正しいことと、記録した前記最新更新時刻より一定期間以内であることとを判断して前記ソフトウェアを起動させる起動判断ステップと、記録した前記最新更新時刻より任意または定期的に前記ライセンス管理サーバにライセンスの確認を行い、ライセンスの更新を行なう確認更新ステップとを有することを特徴とする。
【0009】
請求項1によれば、ハードウェアを用いたりCDに細工したりせずに不正な複製や利用を防ぐとともに、パソコンの情報に基づきライセンスの管理を行うコンピュータに対して情報を提供しても、個人情報やコンピュータ独自の情報である固有情報の流出や乱用を防ぐことを可能とするライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0010】
請求項2に記載の発明は、前記ライセンス管理サーバは、前記ライセンス付与ステップにおいて、ライセンス付与時の前記ライセンス管理サーバの最新更新時刻を更に付与し、前記クライアントは、前記確認更新ステップにおいて、前記許諾信号に前記ライセンス管理サーバの最新更新時刻を含み、前記初期情報記録ステップにおいて、付与された前記最新更新時刻をライセンス許諾時刻である最新更新時刻として記録することを特徴とする。
【0011】
請求項2によれば、ライセンスにライセンス管理サーバの最新更新時刻を付与したライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0012】
請求項3に記載の発明は、ソフトウェアのライセンスを管理するライセンス管理サーバから、ライセンスを受信するライセンス受信クライアントにおけるライセンス管理方法であって、前記ソフトウェアのライセンスを要求時に使用許諾に対応し付与されるライセンスとライセンス付与時のライセンス許諾時刻とクライアント固有情報とを記録する初期情報記録ステップと、前記クライアント固有情報を暗号化した暗号化固有情報を、前記ライセンス管理サーバへ送信する暗号化固有情報送信ステップと、前記ソフトウェアの使用の際に、記録した前記ライセンスが正しいことと、記録した前記固有情報が正しいことと、記録した前記最新更新時刻より一定期間以内であることとを判断して前記ソフトウェアを起動させる起動判断ステップと、記録した更新時間より任意または定期的に前記ライセンス管理サーバにライセンスの確認を行い、ライセンスの更新を行なう確認更新ステップとを有することを特徴とする。
【0013】
請求項3によれば、ハードウェアを用いたりCDに細工したりせずに不正な複製や利用を防ぐとともに、パソコンの情報に基づきライセンスの管理を行うコンピュータに対して情報を提供しても、個人情報やコンピュータ独自の情報である固有情報の流出や乱用を防ぐことを可能とするライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0014】
請求項4に記載の発明は、前記サーバにライセンスの返還要求をするステップと、前記クライアント情報を消去するステップとを有することを特徴とする。
【0015】
請求項4によれば、ライセンスが必要なくなった場合に、ライセンスを返還することができるため、特定のコンピュータにライセンスが固定されることのないライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0016】
請求項5に記載の発明は、前記起動判断ステップにおいて、前記クライアントの時間が過去に戻された時に前記ソフトウェアを起動させないことを特徴とする。
【0017】
請求項5によれば、時間が過去に戻されるなどの改竄があった場合は、ソフトウェアを起動することのないライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0018】
請求項6に記載の発明は、前記初期情報記録ステップ、或いは前記確認更新ステップにおいて、ライセンス、ライセンス許諾時刻、クライアント固有情報とをファイル、レジストリの2つのファイルに記録することを特徴とする。
【0019】
請求項6によれば、ライセンス、ライセンス許諾時刻、クライアント固有情報の記録場所としてファイルやレジストリを用いるライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0020】
請求項7に記載の発明は、前記ライセンスの確認と更新とを行うための更新メニューにより、前記確認更新ステップは、任意で行われることを特徴とする。
【0021】
請求項7によれば、ライセンスの更新を任意で行うことが可能となるため、ユーザの都合に合わせて更新処理を行うことを可能とするライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0022】
請求項8に記載の発明は、ネットワークを介してクライアントのソフトウェアの管理を行うライセンス管理サーバにおけるソフトウェア管理方法であって、前記クライアントから暗号化された該クライアント固有情報である暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス要求を受信した際に、該暗号化固有情報を登録するとともに、該クライアントが正しいか否かを判断して、前記ライセンス管理サーバの最新更新時刻を前記クライアントに付与するために許諾信号に前記ライセンス管理サーバの最新更新時刻を含む前記ライセンスを付与するライセンス付与ステップと、前記クライアントから任意または定期的に行われる暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス更新要求を受信した際に、該クライアントの前記暗号化固有情報を確認する確認ステップと、該暗号化固有情報が正しい場合は前記クライアントに許諾信号を付与する更新ステップとを有することを特徴とする。
【0023】
請求項8によれば、ハードウェアを用いたりCDに細工したりせずに不正な複製や利用を防ぐとともに、パソコンの情報に基づきライセンスの管理を行うコンピュータに対して情報を提供しても、個人情報やコンピュータ独自の情報である固有情報の流出や乱用を防ぐことを可能とするライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0024】
請求項9に記載の発明は、前記ライセンスの返還要求を受信する返還要求受信ステップと、返還された前記ライセンスを初期化する初期化ステップとを有することを特徴とする。
【0025】
請求項9によれば、ライセンスが必要なくなった場合に、ライセンスを返還することができるため、特定のコンピュータにライセンスが固定されることのないライセンス管理方法を提供できる。
【0026】
請求項10に記載の発明は、ソフトウェアのライセンスを管理するライセンス管理サーバと、該ライセンス管理サーバに接続するクライアントを有するライセンス管理システムであって、前記ライセンス管理サーバは、前記クライアントから暗号化された該クライアント固有情報である暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス要求を受信した際に、該暗号化固有情報を登録するとともに、該クライアントが正しいか否かを判断して、ライセンスを付与するライセンス付与手段と、クライアントからの任意または定期的に行われる暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス更新要求を受信した際に、該クライアントの前記暗号化固有情報が正しいか否かの確認を行う手段と、該暗号化固有情報が正しい場合はクライアントに許諾信号を付与する更新手段とを有し、前記クライアントは、最初にソフトウェアのライセンスを要求時に使用許諾され付与されるライセンスとライセンス付与時のライセンス許諾時刻を最新更新時刻とし、該最新更新時刻とクライアント固有情報を記録する初期情報記録手段と、前記ソフトウェアの使用の際に、記録した前記ライセンスが正しいことと、記録した前記クライアント固有情報が正しいことと、記録した前記最新更新時刻より一定期間以内であることとを判断して前記ソフトウェアを起動させる起動判断手段と、記録した前記最新更新時刻より任意または定期的に前記ライセンス管理サーバにライセンスの確認に行い、ライセンスの更新を行なう確認更新手段とを有することを特徴とする。
【0027】
請求項10によれば、ハードウェアを用いたりCDに細工したりせずに不正な複製や利用を防ぐとともに、パソコンの情報に基づきライセンスの管理を行うコンピュータに対して情報を提供しても、個人情報やコンピュータ独自の情報である固有情報の流出や乱用を防ぐことを可能とするライセンス管理システムを提供できる。
【0028】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面に基づいて説明する。
【0029】
本発明の実施の形態における全体構成図を図1に示す。図1に示されるように、本実施の形態におけるライセンス管理システムは、ライセンス管理サーバ10と、ソフトベンダーサーバ(ダウンロードサーバ)12と、A社のパソコンである16a、16b、16cとそれらが接続するインターネット14と、ソフトウェアが記録された記録媒体18a、18bで構成される。
【0030】
ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ソフトウェアのライセンスの管理を行うサーバである。ソフトベンダーサーバ12は、ソフトウェアをインターネット14を通じて他のパソコンに供給するサーバである。パソコン16a、16b、16cはソフトウェアがインストールされたパソコンである。
【0031】
このインストールは、ソフトウェアの使用に先立ち予め行っておく形態となっており、そのインストール方法は、記録媒体18a、18bを用いても良いし、ソフトベンダーサーバ12を用いても良い。
【0032】
ちなみに、図1の場合は、パソコン16aは記録媒体18aから、パソコン16bは記録媒体18bから、パソコン16cは、ソフトベンダーサーバ12からそれぞれソフトウェアがインストールされている。
【0033】
また、図1におけるライセンス管理サーバ10は、A社用のライセンスを1つ発行可能であり、図1は、そのライセンスがパソコン16aに与えられているために、他のパソコンは使用できない状況を示している。
【0034】
次に、上述したライセンス管理サーバ10、ソフトベンダーサーバ12や、パソコン16などのコンピュータのハードウェア構成図を図2に示す。なお、パソコン16とは、パソコン16a、16b、16cのいずれにも共通する処理などを説明する場合に用いる表現とする。
【0035】
図2に示されるハードウェア構成は、それぞれバスBで相互に接続されている入力装置22と,表示装置23と,ドライブ装置24と,記録媒体25と,補助記憶装置26と,メモリ装置27と,演算処理装置20と,インターフェース装置21とを含むように構成される。
【0036】
入力装置22は、コンピュータシステムの利用者が操作するキーボード及びマウスなどで構成され、コンピュータシステムに各種操作信号を入力するために用いられる。表示装置23は、コンピュータシステムを操作するのに必要な各種ウインドウやデータ等を表示する。インターフェース装置21は、コンピュータシステムをネットワークに接続する為のインターフェースであり、例えばNIC(Network Interface Card)やモデム等で構成される。
【0037】
そして、上記コンピュータシステムを動作させるためのプログラムは、CD−ROM等の記録媒体25によって提供されるか、ネットワークを通じてダウンロードされる。また、記録媒体25は、ドライブ装置24にセットされ、データやプログラムが記録媒体25からドライブ装置24を介して補助記憶装置26にインストールされる。
【0038】
補助記憶装置26は、データやプログラムを格納すると共に、必要なファイル等を格納する。メモリ装置27は、コンピュータシステムの起動時に補助記憶装置26からプログラムを読み出して格納する。演算処理装置20は、メモリ装置27に読み出され格納されたプログラムに従って処理を実行する。
【0039】
次に、図3を用いて、ライセンス管理システムにおける全体の流れを説明する。まずステップS101で、パソコン16にソフトウェアがインストールされる。次に、ステップS102で、パソコン16は、後述する暗号化固有情報をライセンス管理サーバ10に送信することでライセンス管理サーバ10からキーを取得し、情報の設定を行う。この情報は、ファイル32や、各種の環境設定やドライバの指定、アプリケーションの関連付けなどの情報を保存するファイルであるレジストリ34に設定される。また、それら設定される情報は、PC固有情報36と、時間情報38と、キー情報40で構成される。このうち、PC固有情報は、パソコンのMAC(Media Access Control)アドレス、コンピュータ名、プロセッサ情報、HD(Hard Disk)ボリュームシリアルNO.、そしてOS(Operating System)名、及びバージョン、ソフトウェアのプログラムがインストールされたフォルダの生成日時で構成される。
【0040】
また、時間情報38は、複数の日時情報で構成される。それらはサーバタイムスタンプと、前回のライセンス更新時間を示す最終タイムと、PCタイムスタンプとなっており、サーバタイムスタンプは、ライセンス管理サーバ10の最新更新時刻を利用している。次のキー情報40は、ライセンス管理サーバ10から取得したシリアル番号で構成される。このキー情報40は、図に示されるように、ライセンス管理サーバ10のキーBANK30で管理されている。
【0041】
これらの情報は、ライセンスを受信した時に、一緒に受信したサーバタイムスタンプと、サーバに更新確認を行う時間間隔を指定する「一定期間」とともに、クライアント情報として設定される。そして、これらの情報は、ステップS103で示されるようなソフトウェアの起動時及び終了時、そしてステップS104のライセンス更新時、さらにステップS105のキー返還時に参照または更新、或いは削除される。
【0042】
また、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、さらに図4に示されるソフトウェア別更新間隔データベースと、図5に示されるライセンス管理データベースを有する。ソフトウェア別更新間隔データベースは、ライセンスの更新間隔をソフトウェア別に記したデータベースであり、例えばソフトAは、10日ごとにライセンスを更新しなければならないことを示している。
【0043】
ライセンス管理データベースは、ユーザごとにライセンスを管理するデータベースであり、ユーザ名とそれに対応したID番号、パスワード、ソフト名、ライセンス番号、最新更新時間、暗号化固有情報で構成される。ID番号は、ユーザのID番号であり、パスワードは、ユーザの認証に用いられ、ソフト名は、使用するソフトウェアの名前である。また、最新更新時間は、更新を行った最新の時間を表している。そして、暗号化固有情報は、パソコン16のPC固有情報を暗号化した情報であり、その詳細な説明は、次のフローチャートの説明で行われる。
【0044】
図6のフローチャートは、図3のステップS102に対応する処理であるキー情報の取得と情報設定時の処理を示している。
【0045】
最初にステップS201で、パソコン16は、上述したPC固有情報を取得する。次に、ステップS202で、パソコン16は、PC固有情報を暗号化する。この暗号化の目的は二つあり、一つは、ネットワークおよびライセンス管理サーバ10に対し、パソコン16のPC固有情報を隠蔽することである。もう一つの目的は、ライセンス管理サーバ10がパソコンのPC固有情報に変化があったことを検出することである。
【0046】
最初の目的であるPC固有情報の隠蔽によって、パソコン16のPC固有情報がネットワークおよびライセンス管理サーバ10に、そのままのデータとして流出することがなく、PC固有情報の流出や濫用を懸念するユーザも安心して利用することができる。また、二つ目の目的であるPC固有情報の変化の検出であるが、この検出により、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、他のパソコンとパソコン16とを区別することができ、ライセンスを持たない他のパソコンがソフトウェアを使用するなどの不正な利用も防止することができる。また、パソコン16のPC固有情報が改竄されたことも検出することが可能となる。
【0047】
このように、ここでの暗号化の方式は、一般的な暗号化の方式に限らず、生成された情報から、もとのPC固有情報が特定できず、PC固有情報の変化が検出可能な方式であれば良い。したがって、ここでの暗号化は、PC固有情報自体を暗号化してもよいし、PC固有情報のハッシュ値(メッセージ認証子)を生成してもよい。また、暗号化の目的が暗号通信ではないため、暗号化するためのアルゴリズムは、パソコン16が任意に定めることができる。もっとも、ライセンス管理サーバ10を管理する管理会社が、暗号化を行うプログラムを、サービスを受けるパソコン16などに予め提供するようにしても良い。なお、以下の説明においても、PC固有情報の暗号化とは、上述した暗号化を示すこととする。
【0048】
以上で暗号化に関する説明を終え、再びフローチャートの説明を行う。パソコン16は、ステップS203で、図に示されるように、ライセンス管理サーバ10内のキーBANK30に接続し、事前にライセンス管理サーバ10に登録されているソフトウェアユーザのID(IDentification)、PW(Pass Word)、ソフトウェアの情報であるソフト情報、暗号化したPC固有情報である暗号化固有情報とをライセンス管理サーバ10に送信する。
【0049】
なお、ライセンスキーも、既にライセンス管理サーバに登録してあるものとして説明するが、ユーザで事前に利用するソフトウェアのライセンス数だけを定めてあり、ユーザからの要求時に生成するようにしても良い。
【0050】
これらの情報を受信したライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS204でキーBANK30を参照して認証処理を行う。そして、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、認証処理の結果、キーの発行を行えない場合は、パソコン16に、その旨を送信し、パソコン16は、ステップS206で、キーの発行が行えないことを示す取得不可表示を行い、処理を終了する。
【0051】
ステップS205の判断処理で、IDとPWとソフトウェア情報を用いた認証処理の結果、キーの発行を行っても良い場合、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS207で、キーが既に発行されていないかどうかチェックする。このチェックは、最新の更新時刻が西暦0000年00月00日00時00分と一致するかどうかのチェックである。一致した場合、発行していることになり、キーの発行はできないため、パソコン16に、その旨を送信し、パソコン16は、ステップS206で、キーの発行が行えないことを示す取得不可表示を行い、処理を終了する。
【0052】
最新の更新時間が西暦0000年00月00日00時00分と一致していない場合、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS208で、キーの発行を行う際に、発行するキーに該当するキーBANK30(図5参照)の最新更新時刻に現在の時刻を設定し、キーとサーバタイムスタンプをパソコン16に送信する。また、受信した暗号化固有情報をライセンス管理データベース(図5参照)へ登録する。
【0053】
なお、ステップS207のキー返還のチェック処理は、ライセンス管理サーバ10が、最新更新時刻を持たなくても可能であり、この場合、ライセンス管理データベース(図5参照)の最新更新時刻も不要となる。
【0054】
キー情報とサーバタイムスタンプとを受信したパソコン16は、ステップS209でファイル32及びレジストリ34の2ヶ所に対し、キー情報の設定を行う。次に、パソコン16は、ステップS210で、サーバタイムスタンプと最終タイムとPCタイムスタンプと一定期間からなる時間情報の設定をファイル32とレジストリ34に対して行う。このとき、時間情報内の最終タイムに、先ほど受信したサーバタイムスタンプを代入する。そして、ステップS211で、パソコン16は、ファイル32とレジストリ34に対し、プログラムフォルダ生成日時の設定を行う。次に、パソコン16は、ステップS212で、ファイル32とレジストリ34に対し、PC固有情報の書き込みを行い、キー情報の取得と情報設定時の処理を終了する。
【0055】
次に、図7のフローチャートを用いて、ソフトウェア起動時の処理について説明する。まず、パソコン16は、ステップS301で、自らのPC固有情報を取得する。次に、ステップS302で、パソコン16は、取得したPC固有情報を暗号化する。以降、比較時には復号化して利用しているが省略する。これは、安全性は少し落ちるが暗号化せずに使用しても構わない。そして、パソコン16は、ステップS303でPC固有情報36が記録されているファイル32とレジストリ34とで、先ほど取得したPC固有情報の照査を行う。その結果、取得したPC固有情報と、ファイル32とレジストリ34にそれぞれある2つのPC固有情報36の計3者が一致した場合、次のステップS304へ処理を進める。一致しなかった場合、パソコン16は、ステップS313へ処理を進め、エラーメッセージを表示し、処理を終了する。
【0056】
PC固有情報の照査が終わると、次に、パソコン16は、ステップS305で、ファイル32とレジストリ34とを用いて、キー情報の照査を行う。その結果、パソコン16は、キー情報のうち、ファイル32とレジストリ34からなる2者が一致した場合、次のステップS307へ処理を進める。一致しなかった場合、パソコン16は、ステップS313へ処理を進め、エラーメッセージを表示し、処理を終了する。
【0057】
キー情報の照査が終わると、次に、パソコン16は、ステップS307で、現在の日時情報であるPCタイムの取得を行う。このPCタイムとは、パソコン16の内蔵時計の時刻を示している。パソコン16は、ステップS308で、レジストリ34に記録されている最終タイムと、PCタイムの比較を行う。この場合の最終タイムは、ライセンス管理サーバ10から受信した日時情報または最後にソフトウェアが使用された日時情報を表している。
【0058】
PCタイムと最終タイムとを比較した結果、ステップS309で、PCタイムが最終タイムより大きい場合、次のステップS310へ処理を進める。PCタイムが最終タイム以下の場合、現在の時刻と、最後にソフトウェアを使用した時刻とが矛盾するため、パソコン16は、ステップS313へ処理を進め、エラーメッセージを表示し、処理を終了する。
【0059】
次に、パソコン16は、ステップS310で、レジストリ34の最終タイムを、先ほど取得したPCタイムに更新する。そして、パソコン16は、ステップS311で、フォルダの生成時間と、ファイル32と、レジストリ34からフォルダ情報を取得する。次のステップS312で、フォルダ、ファイル、レジストリのうちの3者が一致しなかった場合、パソコン16は、ステップS313でエラーメッセージを表示する。3者が一致した場合、パソコン16は、ステップS314へ処理を進め、現在時刻であるPCタイムより、指定期間とサーバタイムスタンプを足した値が小さい場合に、ステップS317でソフトウェアを起動する。
【0060】
この処理の具体例を説明する。上記処理は、サーバタイムスタンプが、例えば4月1日の0時0分となっており、指定期間が5日である場合、4月1日の0時0分の5日後である4月6日の0時0分よりもPCタイムが前の時刻であれば、指定期間内であるのでソフトウェアを使用することができるという処理である。
【0061】
また、ステップS314で、PCタイムが例えば4月7日であるような、指定期間を過ぎている場合、そのままでは、ソフトウェアを使用することはできないため、パソコン16は、ステップS315で、ライセンスの更新処理(図8参照)を行う。
【0062】
次に、パソコン16は、ライセンスの更新処理によるライセンス管理サーバ10からの応答が、正常戻り値であるかどうかで処理を分岐する。
【0063】
ライセンス管理サーバ10からの応答が正常戻り値であった場合、パソコン16は、ステップS318でソフトウェアを起動する。ステップS316での戻り値が、正常戻り値でなかった場合、パソコン16は、ステップS317へ処理を進める。
【0064】
ステップS317の処理は、指定期間が過ぎても、さらに期間βが経過するまでは、ステップS318でソフトウェアを起動し、期間βが経過した後はソフトウェアを起動せずにそのまま終了させる処理である。
【0065】
以上でソフトウェア起動時の説明を終え、次に、図8を用いて定期的に行われるライセンスの更新処理について説明する。ステップS401で、パソコン16は、自らのPC固有情報を取得する。次に、ステップS402で、パソコン16は、取得したPC固有情報を暗号化する。
【0066】
次に、パソコン16は、ステップS403で、ライセンス管理サーバ10内のキーBANK30に接続できる場合は、ステップS405に進み、接続できない場合は、ステップS404でキーBANK接続不可表示を行い、処理を終了する。
【0067】
ステップS405で、パソコン16は、ソフトウェアユーザのID、PW、ソフト情報、キー、暗号化固有情報をライセンス管理サーバ10に送信する。
【0068】
ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS406で、キーBANK30を参照して認証処理を行う。そして、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS407で、ID、PW、キーが同じであれば、ステップS409へ処理を進め、異なっていればパソコン16にその旨を送信し、パソコン16は、ステップS408で、キーの更新が行えないことを示す更新不可表示を行い、処理を終了する。
【0069】
次に、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS407で、キーが返還されていないかどうかチェックする。このチェックは、前回の更新時間が西暦0000年00月00日00時00分と一致するかどうかのチェックである。一致した場合、返還していることになり、キーの更新はできないため、パソコン16に、その旨を送信し、パソコン16は、ステップS408で、キーの更新が行えないことを示す更新不可表示を行い、処理を終了する。
【0070】
前回の更新時間が西暦0000年00月00日00時00分と一致していない場合、次に、ステップS408で、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、受信した暗号化固有情報が、ライセンス管理データベース(図5参照)に登録されている暗号化固有情報と一致しない場合、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、キーの更新ができないため、パソコン16に、その旨を送信し、パソコン16は、ステップS406で、キーの更新が行えないことを示す更新不可表示を行い、処理を終了する。
【0071】
なお、ステップS407のキー返還のチェック処理は、ライセンス管理サーバ10が、最新更新時刻を持たなくても可能であり、この場合、ライセンス管理データベース(図5参照)の最新更新時刻も不要となる。
【0072】
次に、ステップS410で、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、受信した暗号化固有情報が、登録されている暗号化固有情報と同じで正しと判断されると、ステップS410で、ライセンスを保持するための更新処理を行う。この更新処理では、キーBANKの該当キーの前回更新時間に、現在の時間を設定する処理が行われ、パソコン16がキーを更新したことの書き込みをキーBANK30に行われるとともに、パソコン16には、サーバタイムスタンプが送信される。
【0073】
サーバタイムスタンプを受信したパソコン16は、ステップS412で、レジストリ34とファイル32に対し、サーバタイムスタンプと最終タイムとPCタイムスタンプからなる時間情報の設定を行い、処理を終了する。
【0074】
この更新処理は、図7で説明したように、ソフトウェア起動時に指定期間を過ぎている場合には自動的に行われるが、指定期間を過ぎていない場合でもユーザが更新したい場合は、当該ソフトウェア実行中の画面上で図10に示されるソフトウェアに設けられた更新メニュー41を選択することによっても更新することができる。
【0075】
この更新メニュー41をユーザが選択した場合の処理を図11のフローチャートを用いて説明する。ステップS601で、パソコン16は、ユーザの選択によるライセンスの更新メニューが選択されたことを検出する。次に、ステップS602で、パソコン16は、ライセンス更新処理を実行する。そのライセンス更新処理が正常終了であれば、パソコン16は、ステップS603の分岐により、更新処理を終了する。ライセンス更新処理が異常終了であれば、パソコン16は、ステップS603からステップS604へ処理を進め、更新処理が異常終了であることの警告を表示し、更新処理を終了する。
【0076】
このように、ユーザが任意で更新処理を行うことができるため、例えば、指定期間内は、出張のためライセンスを更新することができないときなどは、予めライセンスの更新を行っておくことが可能となる。
【0077】
次に、図9のフローチャートを用いて、ライセンスの返還処理について説明する。ステップS501で、パソコン16は、自らのPC固有情報を取得する。次に、ステップS502で、パソコン16は、取得したPC固有情報を暗号化する。
【0078】
そして、パソコン16は、ステップS503で、図に示されるように、ライセンス管理サーバ10内のキーBANK30に接続し、ソフトウェアユーザのID、PW、ソフト情報、キー、暗号化固有情報とをライセンス管理サーバ10に送信する。
【0079】
接続されたライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS504で、キーBANK30を参照して認証処理を行う。ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS505で、ID、PW、ソフト情報が同じであれば、ステップS507へ処理を進め、異なっていればパソコン16に、その旨を送信し、パソコン16は、ステップS506で、キーの返還が行えないことを示す返還不可表示を行い、処理を終了する。
【0080】
次に、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS507で、既にキーが返還されていないかどうかチェックする。このチェックは、前回の更新時間が西暦0000年00月00日00時00分と一致するかどうかのチェックである。一致した場合、既にキーを返還していることになり、キーの返還はできないため、パソコン16に、その旨を送信し、パソコン16は、ステップS506で、キーの返還が行えないことを示す返還不可表示を行い、処理を終了する。なお、返還不可表示を行った後、S510へ進んでも構わない。
【0081】
返還されていない場合、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、ステップS508へ処理を進める。そして、受信した暗号化固有情報が、ライセンス管理データベース(図5参照)に登録されている暗号化固有情報と異なる場合はキーの返還ができないため、パソコン16にその旨を送信し、パソコン16は、ステップS506で、キーの変換が行えないことを示す返還不可表示を行い処理を終了する。なお、返還不可表示を行った後、ステップS510へ進んでも構わない。
【0082】
なお、ステップS507のキー返還のチェック処理は、ライセンス管理サーバ10が、最新更新時刻を持たなくても可能であり、この場合、ライセンス管理データベース(図5参照)の最新更新時刻も不要となる。
【0083】
受信した暗号化固有情報が、登録されている暗号化固有情報と同じで正しければ、ステップS509で、ライセンス管理サーバ10は、キー返還処理を行う。このキー返還処理は、ライセンス管理データベース(図5参照)の該当する最新更新時間を西暦0000年00月00日00時00分にセットし、キーBANK30に対して、パソコン16がキーを返還したことの書き込みを行い、登録固有情報のクリアを行うとともに、認証の確認がされたことをパソコン16に送信する。
【0084】
パソコン16は、ステップS510でファイル32及びレジストリ34に対し、キー情報の消去を行う。次に、パソコン16は、ステップS511で、時間情報の消去をレジストリ34に対して行う。そして、ステップS512で、パソコン16は、ファイル32とレジストリ34に対し、プログラムフォルダ生成日時の消去を行う。次に、パソコン16は、ステップS513で、ファイル32とレジストリ34に対し、PC固有情報の消去を行い、キー情報の返還処理を終了する。
【0085】
このようにライセンスを返還することが可能なため、複数の人数が有するそれぞれのパソコンでライセンスを共有することができる。例えば、2人が1つのライセンスを共有する場合、1人がライセンスを使い終えてライセンスを返還すると、残りの1人は、その返還されたライセンスにより自分のパソコン上でソフトウェアを実行することが可能となる
また、1人の場合でも、出張などの際に、自分のデスクトップパソコンで使用しているライセンスを、一旦ライセンス管理サーバ10に返還し、出張用のノートパソコンに先ほど返還したライセンスを新たに取得して用いることが可能となるなど、ライセンスを柔軟に使用することができる。
【0086】
なお、固有情報は上記に拘らず、パソコンを特定できる情報ならばなんでも良い。一定期間後に、パソコンよりライセンスを確認するに必要な最新更新時刻、一定期間もサーバで記録せず、パソコン側で保持ようにしても良い。指定期間もサーバ持たなくても良い。
【0087】
また、上記実施の形態において、ファイルやレジストリに書き込みを行う処理は、安全性は少し落ちるが、ファイルまたはレジストリの2ヶ所への書き込みではなく、どちらか1ケ所でも構わない。
【0088】
さらに、サーバでライセンス発行の管理を最新更新時刻のみで行う例としたが、ライセンス発行の管理用にライセンス管理フラグを別に持つことでライセンス管理確認を明確にしても良い。
【0089】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、ハードウェアを用いたりCDに細工したりせずに不正な複製や利用を防ぐとともに、パソコンの情報に基づきライセンスの管理を行うコンピュータに対して情報を提供しても、個人情報やコンピュータ独自の情報である固有情報の流出や乱用を防ぐことを可能とするライセンス管理方法、ライセンス管理システムが得られる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施の形態における全体構成図である。
【図2】コンピュータのハードウェア構成図である。
【図3】全体の処理の流れを示すフローチャートである。
【図4】ソフトウェア別更新間隔データベースを示す図である。
【図5】ライセンス管理データベースを示す図である。
【図6】キー取得処理と情報設定処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図7】ソフトウェア起動時の処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図8】ライセンス更新時の処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図9】ライセンス返還時の処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図10】ソフトウェアに表示された更新メニューを示す図である。
【図11】更新メニューによる更新処理を示すフローチャートである。
【符号の説明】
10…ライセンス管理サーバ
12…ソフトベンダーサーバ
14…インターネット
16、16a、16b、16c…パソコン
18a、18b…記録媒体
20…演算処理装置
21…インターフェース装置
22…入力装置
23…表示装置
24…ドライブ装置
25…記録媒体
26…補助記憶装置
27…メモリ装置
30…キーBANK
32…ファイル
34…レジストリ
36…PC固有情報
38…時間情報
40…キー情報
41…更新メニュー[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to computer software licenses, and more particularly, to a license management method, a license management system, and a license management program using a server that manages licenses.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Unauthorized duplication and use of computer software is still significant. Therefore, software vendors take various measures to prevent unauthorized duplication and use.
[0003]
As a countermeasure, a small device is connected to a USB (Universal Serial Bus) to perform hard protection, a type that distributes software on a CD (Compact Disc) that has been crafted so that copying is not possible, There is a type using a flexible disk.
[0004]
Recently, software licensing services using networks have started. As a countermeasure against fraud in this case, for example, a server provided by a software vendor uses client information such as an operating system version number of a client computer, a device ID number, software version number, and a license key. There is a method of obtaining client software through obtaining and combining them through a network.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, when using the hard protect or flexible disk described above, not only does the cost of the hardware itself increase, but also because the hardware is a small device, there is a possibility of loss or damage, It is not convenient because it may block USB ports. Also, creating a CD that cannot be duplicated is costly.
[0006]
In addition, although it is a countermeasure for preventing fraud using a network, recent survey results on the Internet most often indicate that personal information including personal information and information unique to a user's computer is leaked or abused. Therefore, there are many users who are reluctant to provide the information even to the computer that manages the license based on the information on each personal computer.
[0007]
In view of such problems, the present invention prevents unauthorized duplication and use without using hardware or modifying a CD, and also transmits information to a computer that manages licenses based on information from a personal computer. It is an object of the present invention to provide a license management method, a license management system, and a license management program that can prevent leakage or abuse of personal information or unique information that is information unique to a computer even if provided.
[0008]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The invention according to claim 1 is a license management method in a license management system having a license management server for managing software licenses and a client connected to the license management server via a network, wherein the license management server is Upon receiving a license request having encrypted unique information that is the client unique information encrypted from the client, register the encrypted unique information and determine whether the client is correct, A license granting step of granting a license, and upon receiving a license update request having encryption unique information that is arbitrarily or periodically performed from the client, confirming whether the encryption unique information of the client is correct or not. Step and the encryption unique information is correct. Updating a license signal to the client, wherein the client first sets the license to be used and granted at the time of requesting the license of the software and the license grant time at the time of granting the license as the latest update time. An initial information recording step of recording the latest update time and client specific information; and, when using the software, the recorded license is correct; the recorded client specific information is correct; and the recorded latest update time. A boot determining step of activating the software by determining that the time is within a certain period, and arbitrarily or periodically confirming the license from the license management server from the recorded latest update time and updating the license And a confirmation update step. That.
[0009]
According to the first aspect, it is possible to prevent unauthorized duplication or use without using hardware or modifying a CD, and to provide information to a computer that manages a license based on information of a personal computer. It is possible to provide a license management method that can prevent leakage or abuse of personal information or unique information that is information unique to a computer.
[0010]
In the invention according to
[0011]
According to the second aspect, a license management method in which the latest update time of the license management server is added to the license can be provided.
[0012]
According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided a license management method for a license receiving client that receives a license from a license management server that manages a software license, wherein the license of the software is granted in response to a license upon request. An initial information recording step of recording a license, a license grant time at the time of license grant, and client unique information; and an encryption unique information transmitting step of transmitting encrypted unique information obtained by encrypting the client unique information to the license management server. When using the software, it is determined that the recorded license is correct, that the recorded unique information is correct, and that the software is within a certain period of time from the recorded latest update time, and that the software is updated. A boot decision step to boot It confirms the license to any or periodically the license management server from the recorded update time, and having a check update step of updating the license.
[0013]
According to the third aspect, it is possible to prevent unauthorized duplication or use without using hardware or modifying a CD, and to provide information to a computer that manages a license based on information of a personal computer. It is possible to provide a license management method that can prevent leakage or abuse of personal information or unique information that is information unique to a computer.
[0014]
The invention according to a fourth aspect is characterized in that the method includes a step of requesting the server to return a license and a step of deleting the client information.
[0015]
According to the fourth aspect, when the license is no longer required, the license can be returned, so that a license management method in which the license is not fixed to a specific computer can be provided.
[0016]
The invention according to claim 5 is characterized in that, in the activation determination step, the software is not activated when the time of the client is set back to the past.
[0017]
According to the fifth aspect, it is possible to provide a license management method that does not activate software when tampering such as returning time to the past has occurred.
[0018]
The invention according to claim 6 is characterized in that in the initial information recording step or the confirmation update step, a license, a license grant time, and client-specific information are recorded in two files, a file and a registry.
[0019]
According to claim 6, it is possible to provide a license management method using a file or a registry as a recording location of a license, a license grant time, and client-specific information.
[0020]
The invention according to
[0021]
According to the seventh aspect, since the license can be updated arbitrarily, it is possible to provide a license management method capable of performing the update process according to the user's convenience.
[0022]
The invention according to claim 8 is a software management method in a license management server that manages software of a client via a network, wherein the license management server has encrypted unique information that is the client unique information encrypted from the client. Upon receiving the license request, register the encryption unique information, determine whether the client is correct, and add the latest update time of the license management server to the license signal to give the client the latest update time. A license granting step of granting the license including the latest update time of the license management server; and upon receiving a license update request having encryption unique information that is arbitrarily or periodically performed from the client, the encryption of the client is performed. Confirmation steps to confirm unique information, If encrypted specific information is correct and having an update step of imparting permission signal to the client.
[0023]
According to claim 8, while preventing unauthorized duplication or use without using hardware or modifying a CD, even if information is provided to a computer that manages a license based on information of a personal computer, It is possible to provide a license management method that can prevent leakage or abuse of personal information or unique information that is information unique to a computer.
[0024]
The invention according to claim 9 is characterized in that it has a return request receiving step of receiving the license return request and an initialization step of initializing the returned license.
[0025]
According to the ninth aspect, the license can be returned when the license is no longer needed, so that a license management method can be provided in which the license is not fixed to a specific computer.
[0026]
The invention according to
[0027]
According to the tenth aspect, it is possible to prevent unauthorized duplication or use without using hardware or modifying a CD, and to provide information to a computer that manages a license based on information of a personal computer, It is possible to provide a license management system that can prevent leakage or abuse of personal information or unique information that is information unique to a computer.
[0028]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0029]
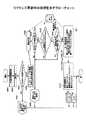
FIG. 1 shows an overall configuration diagram according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1, in the license management system according to the present embodiment, a
[0030]
The
[0031]
This installation is performed in advance before using the software, and the installation may be performed by using the
[0032]
By the way, in the case of FIG. 1, the
[0033]
Further, the
[0034]
Next, FIG. 2 shows a hardware configuration diagram of a computer such as the
[0035]
The hardware configuration shown in FIG. 2 includes an
[0036]
The
[0037]
Then, a program for operating the computer system is provided by a
[0038]
The
[0039]
Next, the overall flow of the license management system will be described with reference to FIG. First, in step S101, software is installed on the personal computer 16. Next, in step S102, the personal computer 16 obtains a key from the
[0040]
The
[0041]
These pieces of information are set as client information together with the server time stamp received together with the license and the “certain period” that specifies a time interval for performing update confirmation to the server. These pieces of information are referred to, updated, or deleted when the software is activated and terminated as shown in step S103, when the license is updated in step S104, and when the key is returned in step S105.
[0042]
The
[0043]
The license management database is a database that manages licenses for each user, and includes a user name, an ID number corresponding thereto, a password, a software name, a license number, a latest update time, and encryption unique information. The ID number is the ID number of the user, the password is used to authenticate the user, and the software name is the name of the software to be used. The latest update time indicates the latest time at which the update was performed. The encrypted unique information is information obtained by encrypting the PC unique information of the personal computer 16, and the detailed description thereof will be given in the following flowchart.
[0044]
The flowchart of FIG. 6 shows a process at the time of acquiring key information and setting information, which is a process corresponding to step S102 of FIG.
[0045]
First, in step S201, the personal computer 16 acquires the above-described PC unique information. Next, in step S202, the personal computer 16 encrypts the PC unique information. The purpose of this encryption is twofold. One is to hide the PC-specific information of the personal computer 16 from the network and the
[0046]
By concealing the PC unique information, which is the first purpose, the PC unique information of the personal computer 16 does not leak to the network and the
[0047]
As described above, the encryption method here is not limited to a general encryption method, and the original PC-specific information cannot be specified from the generated information, and a change in the PC-specific information can be detected. Any method is acceptable. Therefore, in this encryption, the PC unique information itself may be encrypted, or a hash value (message authenticator) of the PC unique information may be generated. Since the purpose of encryption is not encryption communication, the algorithm for encryption can be arbitrarily determined by the personal computer 16. However, the management company that manages the
[0048]
The explanation on the encryption has been completed above, and the flowchart will be explained again. As shown in the figure, the personal computer 16 connects to the
[0049]
Note that the license key is also described as being already registered in the license management server. However, only the number of software licenses to be used by the user is determined in advance, and the license key may be generated when requested by the user.
[0050]
The
[0051]
If it is determined in step S205 that the key can be issued as a result of the authentication process using the ID, the PW, and the software information, the
[0052]
If the latest update time does not match 00:00:00, 00/00, 0000 AD, the
[0053]
The key return check processing in step S207 can be performed even if the
[0054]
Upon receiving the key information and the server time stamp, the personal computer 16 sets the key information in the
[0055]
Next, the process at the time of starting the software will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG. First, in step S301, the personal computer 16 acquires its own PC-specific information. Next, in step S302, the personal computer 16 encrypts the acquired PC unique information. Hereinafter, the data is decrypted and used for comparison, but is omitted. This is less secure but may be used without encryption. Then, in step S303, the personal computer 16 checks the PC unique information obtained earlier with the
[0056]
After the PC-specific information is checked, the personal computer 16 checks the key information using the
[0057]
After checking the key information, the personal computer 16 acquires the PC time, which is the current date and time information, in step S307. The PC time indicates the time of the internal clock of the personal computer 16. In step S308, the personal computer 16 compares the last time recorded in the
[0058]
As a result of comparing the PC time and the final time, if it is determined in step S309 that the PC time is longer than the final time, the process proceeds to next step S310. If the PC time is less than or equal to the final time, the current time and the time at which the software was last used are inconsistent. Therefore, the personal computer 16 advances the processing to step S313, displays an error message, and ends the processing.
[0059]
Next, in step S310, the personal computer 16 updates the last time in the
[0060]
A specific example of this processing will be described. In the above processing, when the server time stamp is, for example, 0:00 on April 1 and the specified period is 5 days, April 6, which is 5 days after 00:00 on April 1 If the PC time is earlier than 0:00 on the day, it is within the designated period, and the software can be used.
[0061]
If it is determined in step S314 that the PC time has passed the designated period, for example, April 7, the software cannot be used as it is, and the personal computer 16 updates the license in step S315. The processing (see FIG. 8) is performed.
[0062]
Next, the personal computer 16 branches the processing depending on whether or not the response from the
[0063]
If the response from the
[0064]
The process of step S317 is a process in which the software is started in step S318 even after the designated period has elapsed and the period β has elapsed, and the software is terminated without starting the software after the period β has elapsed.
[0065]
The above description at the time of starting the software is completed. Next, a license update process that is periodically performed with reference to FIG. 8 will be described. In step S401, the personal computer 16 acquires its own PC-specific information. Next, in step S402, the personal computer 16 encrypts the acquired PC unique information.
[0066]
Next, in step S403, if the personal computer 16 can connect to the
[0067]
In step S405, the personal computer 16 transmits the software user ID, PW, software information, key, and encryption unique information to the
[0068]
In step S406, the
[0069]
Next, the
[0070]
If the previous update time does not match 00:00:00, 00/00, 0000 AD, then in step S408, the
[0071]
The key return check process in step S407 can be performed even if the
[0072]
Next, in step S410, when the
[0073]
In step S412, the personal computer 16 that has received the server time stamp sets time information including the server time stamp, the last time, and the PC time stamp in the
[0074]
This update process is automatically performed when the specified period has passed when the software is activated, as described with reference to FIG. 7. However, when the user wants to update even if the specified period has not passed, the software execution The update can also be performed by selecting an
[0075]
Processing when the user selects the
[0076]
As described above, since the user can arbitrarily perform the update processing, for example, when the license cannot be updated due to a business trip during the designated period, the license can be updated in advance. Become.
[0077]
Next, the license return process will be described with reference to the flowchart in FIG. In step S501, the personal computer 16 acquires its own PC-specific information. Next, in step S502, the personal computer 16 encrypts the acquired PC unique information.
[0078]
Then, in step S503, the personal computer 16 connects to the
[0079]
In step S504, the connected
[0080]
Next, the
[0081]
If the license has not been returned, the
[0082]
The key return check processing in step S507 can be performed even if the
[0083]
If the received encrypted unique information is the same as the registered encrypted unique information and is correct, in step S509, the
[0084]
The personal computer 16 deletes the key information from the
[0085]
Since the license can be returned as described above, the license can be shared by the personal computers owned by a plurality of persons. For example, if two people share one license, one can use the license and return the license, and the other can use the returned license to run the software on their personal computer Becomes
Even when one person is on a business trip, the license used on his desktop personal computer is returned to the
[0086]
Regardless of the above, the unique information may be any information that can specify the personal computer. After a certain period, the latest update time required for confirming the license from the personal computer and the certain period may not be recorded on the server but may be stored on the personal computer. It is not necessary to have a server for the designated period.
[0087]
In the above embodiment, the process of writing to a file or a registry is slightly less secure, but may be performed at one of the files or the registry instead of writing to two locations.
[0088]
Furthermore, although the example in which the server manages license issuance only at the latest update time has been described, the license management confirmation may be clarified by separately providing a license management flag for license issuance management.
[0089]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, unauthorized duplication and use can be prevented without using hardware or creating a CD, and even if information is provided to a computer that manages licenses based on personal computer information, A license management method and a license management system that can prevent leakage and abuse of information and unique information that is information unique to a computer can be obtained.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is an overall configuration diagram according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a hardware configuration diagram of a computer.
FIG. 3 is a flowchart illustrating a flow of an entire process.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a software-based update interval database.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a license management database.
FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing a key acquisition process and an information setting process.
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing processing at the time of starting software.
FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing processing at the time of license update.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing processing at the time of license return.
FIG. 10 is a diagram showing an update menu displayed on software.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart illustrating an update process using an update menu.
[Explanation of symbols]
10 License management server
12 ... Soft vendor server
14. Internet
16, 16a, 16b, 16c ... personal computer
18a, 18b ... recording medium
20 ... arithmetic processing unit
21 Interface device
22 input device
23 Display device
24 ... Drive device
25 ... recording medium
26 ... Auxiliary storage device
27 ... Memory device
30 ... Key Bank
32 ... File
34 ... Registry
36 ... PC-specific information
38… Time information
40 ... Key information
41 ... Update menu
Claims (11)
Translated fromJapanese前記ライセンス管理サーバは、前記クライアントから暗号化された該クライアント固有情報である暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス要求を受信した際に、該暗号化固有情報を登録するとともに、該クライアントが正しいか否かを判断して、ライセンスを付与するライセンス付与ステップと、
クライアントから任意または定期的に行われる暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス更新要求を受信した際に、該クライアントの前記暗号化固有情報が正しいか否かの確認を行うステップと、
該暗号化固有情報が正しい場合はクライアントに許諾信号を付与する更新ステップとを有し、
前記クライアントは、最初にソフトウェアのライセンスを要求時に使用許諾され付与されるライセンスとライセンス付与時のライセンス許諾時刻を最新更新時刻とし、該最新更新時刻とクライアント固有情報を記録する初期情報記録ステップと、
前記ソフトウェアの使用の際に、記録した前記ライセンスが正しいことと、記録した前記クライアント固有情報が正しいことと、記録した前記最新更新時刻より一定期間以内であることとを判断して前記ソフトウェアを起動させる起動判断ステップと、
記録した前記最新更新時刻より任意または定期的に前記ライセンス管理サーバにライセンスの確認を行い、ライセンスの更新を行なう確認更新ステップとを有することを特徴とするライセンス管理方法。A license management method in a license management system having a license management server for managing software licenses and a client connected to the license management server via a network,
The license management server, upon receiving a license request having the encrypted unique information that is the encrypted client unique information from the client, registers the encrypted unique information and determines whether the client is correct. A license granting step of granting a license,
Upon receiving a license update request having encryption unique information that is arbitrarily or periodically performed from the client, a step of checking whether the encryption unique information of the client is correct,
An updating step of giving a license signal to the client when the encryption unique information is correct,
An initial information recording step in which the client first sets a license used and granted at the time of requesting a software license and a license grant time at the time of granting a license as a latest update time, and records the latest update time and client-specific information;
When using the software, the software is activated upon determining that the recorded license is correct, that the recorded client-specific information is correct, and that it is within a certain period of time from the recorded latest update time. An activation determination step for causing
A license update method for checking the license with the license management server arbitrarily or periodically from the recorded latest update time, and updating the license.
前記クライアントは、前記確認更新ステップにおいて、前記許諾信号に前記ライセンス管理サーバの最新更新時刻を含み、
前記初期情報記録ステップにおいて、付与された前記最新更新時刻をライセンス許諾時刻である最新更新時刻として記録することを特徴とする請求項1に記載のライセンス管理方法。The license management server further provides, in the license granting step, a latest update time of the license management server at the time of license grant;
The client, in the confirmation update step, includes the latest update time of the license management server in the license signal,
2. The license management method according to claim 1, wherein, in the initial information recording step, the latest update time provided is recorded as a latest update time that is a license grant time.
前記ソフトウェアのライセンスを要求時に使用許諾に対応し付与されるライセンスとライセンス付与時のライセンス許諾時刻とクライアント固有情報とを記録する初期情報記録ステップと、
前記クライアント固有情報を暗号化した暗号化固有情報を、前記ライセンス管理サーバへ送信する暗号化固有情報送信ステップと、
前記ソフトウェアの使用の際に、記録した前記ライセンスが正しいことと、記録した前記固有情報が正しいことと、記録した前記最新更新時刻より一定期間以内であることとを判断して前記ソフトウェアを起動させる起動判断ステップと、記録した更新時間より任意または定期的に前記ライセンス管理サーバにライセンスの確認を行い、ライセンスの更新を行なう確認更新ステップとを有することを特徴とするライセンス管理方法。A license management method in a license receiving client that receives a license from a license management server that manages software licenses,
An initial information recording step of recording a license to be provided in accordance with the license at the time of requesting the software license, a license grant time at the time of license grant, and client-specific information;
Transmitting encrypted unique information obtained by encrypting the client unique information to the license management server;
When using the software, the software is activated upon determining that the recorded license is correct, that the recorded unique information is correct, and that it is within a certain period of time from the recorded latest update time. A license management method, comprising: a start determination step; and a confirmation update step of arbitrarily or periodically confirming a license from the license management server from the recorded update time and updating the license.
前記クライアント情報を消去するステップとを有することを特徴とする請求項3に記載のライセンス管理方法Requesting the server to return a license;
4. The method according to claim 3, further comprising the step of deleting the client information.
前記クライアントから暗号化された該クライアント固有情報である暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス要求を受信した際に、該暗号化固有情報を登録するとともに、該クライアントが正しいか否かを判断して、前記ライセンス管理サーバの最新更新時刻を前記クライアントに付与するために許諾信号に前記ライセンス管理サーバの最新更新時刻を含む前記ライセンスを付与するライセンス付与ステップと、
前記クライアントから任意または定期的に行われる暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス更新要求を受信した際に、該クライアントの前記暗号化固有情報を確認する確認ステップと、
該暗号化固有情報が正しい場合は前記クライアントに許諾信号を付与する更新ステップとを有することを特徴とするライセンス管理方法。A software management method in a license management server that manages client software via a network,
Upon receiving a license request having encrypted unique information that is the client unique information encrypted from the client, register the encrypted unique information, and determine whether the client is correct. A license granting step of granting the license including the latest update time of the license management server in a license signal to give the client the latest update time of the license management server;
When receiving a license update request having encryption unique information that is arbitrarily or periodically performed from the client, a confirmation step of checking the encryption unique information of the client,
Updating the client with a license signal if the encrypted unique information is correct.
返還された前記ライセンスを初期化する初期化ステップとを有することを特徴とする請求項8に記載のライセンス管理方法。A return request receiving step of receiving the license return request;
The license management method according to claim 8, further comprising an initialization step of initializing the returned license.
前記ライセンス管理サーバは、前記クライアントから暗号化された該クライアント固有情報である暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス要求を受信した際に、該暗号化固有情報を登録するとともに、該クライアントが正しいか否かを判断して、ライセンスを付与するライセンス付与手段と、
クライアントからの任意または定期的に行われる暗号化固有情報を有するライセンス更新要求を受信した際に、該クライアントの前記暗号化固有情報が正しいか否かの確認を行う手段と、
該暗号化固有情報が正しい場合はクライアントに許諾信号を付与する更新手段とを有し、
前記クライアントは、最初にソフトウェアのライセンスを要求時に使用許諾され付与されるライセンスとライセンス付与時のライセンス許諾時刻を最新更新時刻とし、該最新更新時刻とクライアント固有情報を記録する初期情報記録手段と、
前記ソフトウェアの使用の際に、記録した前記ライセンスが正しいことと、記録した前記クライアント固有情報が正しいことと、記録した前記最新更新時刻より一定期間以内であることとを判断して前記ソフトウェアを起動させる起動判断手段と、
記録した前記最新更新時刻より任意または定期的に前記ライセンス管理サーバにライセンスの確認に行い、ライセンスの更新を行なう確認更新手段とを有することを特徴とするライセンス管理システム。A license management system having a license management server that manages software licenses and a client connected to the license management server,
The license management server, upon receiving a license request having the encrypted unique information that is the encrypted client unique information from the client, registers the encrypted unique information and determines whether the client is correct. Licensing means for granting a license,
Upon receiving a license update request having encryption unique information that is arbitrarily or periodically performed from the client, means for checking whether the encryption unique information of the client is correct,
Update means for giving a license signal to the client when the encryption unique information is correct,
An initial information recording unit that sets a license that is initially licensed and granted at the time of requesting a software license and a license grant time at the time of granting the license as a latest update time, and records the latest update time and client-specific information;
When using the software, the software is activated upon determining that the recorded license is correct, that the recorded client-specific information is correct, and that it is within a certain period of time from the recorded latest update time. Activation determination means for causing
A license update system for arbitrarily or periodically checking the license with the license management server from the recorded latest update time, and updating the license.
ソフトウェアのライセンスを要求時に使用許諾に対応し付与されるライセンスとライセンス付与時のライセンス許諾時刻とクライアント固有情報とを記録する初期情報記録ステップと、
前記クライアント固有情報を暗号化した暗号化固有情報を、前記ライセンス管理サーバへ送信する暗号化固有情報送信ステップと、
前記ソフトウェアの使用の際に、前記書き込んであるライセンスキーが正しく、記録した前記クライアント固有情報が、正しいこと、記録した前記最新更新時刻より一定期間以内であることとならばソフトウェアを起動させる起動判断ステップと、
記録した更新時間より任意または定期的に前記ライセンス管理サーバにライセンスの確認を行い、ライセンスの更新を行なう確認更新ステップとを実行させるためのライセンス管理プログラム。On the computer,
An initial information recording step of recording a license granted in response to a license at the time of requesting a software license, a license grant time at the time of license grant, and client-specific information;
Transmitting encrypted unique information obtained by encrypting the client unique information to the license management server;
When using the software, if the written license key is correct, the recorded client-specific information is correct, and it is within a certain period of time from the recorded latest update time, a start determination to start the software Steps and
A license management program for causing the license management server to check the license arbitrarily or periodically from the recorded update time, and to execute a confirmation update step of updating the license.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002190454AJP4012771B2 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2002-06-28 | License management method, license management system, license management program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002190454AJP4012771B2 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2002-06-28 | License management method, license management system, license management program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004038247Atrue JP2004038247A (en) | 2004-02-05 |
| JP4012771B2 JP4012771B2 (en) | 2007-11-21 |
Family
ID=31700366
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002190454AExpired - Fee RelatedJP4012771B2 (en) | 2002-06-28 | 2002-06-28 | License management method, license management system, license management program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4012771B2 (en) |
Cited By (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006005557A (en)* | 2004-06-16 | 2006-01-05 | Toshiba Corp | Storage medium processing method, storage medium processing apparatus, and program |
| WO2006016619A1 (en)* | 2004-08-12 | 2006-02-16 | Nikon Corporation | Substrate processing apparatus, use state ascertaining method, and false use preventing method |
| WO2007083499A1 (en)* | 2006-01-19 | 2007-07-26 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Substrate processing device, license management program, license information provision device, license information provision program, license management system and recording medium |
| JP2007280039A (en)* | 2006-04-06 | 2007-10-25 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | User authentication system and method |
| US7467113B2 (en)* | 2006-03-24 | 2008-12-16 | Walgreen Co. | License verification system and method |
| JP2010530101A (en)* | 2007-06-08 | 2010-09-02 | サンディスク コーポレイション | MEMORY DEVICE HAVING CIRCUIT FOR IMPROVING ACCURACY OF TIME ESTIMATION USED FOR ENTITENT AUTHENTICATION AND METHOD USED IN THE DEVICE |
| US7949607B2 (en) | 2004-06-21 | 2011-05-24 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Image forming apparatus, license managing method for applications executed by image forming apparatus, program for implementing the method, and storage medium storing the program |
| US8448009B2 (en) | 2009-08-17 | 2013-05-21 | Sandisk Il Ltd. | Method and memory device for generating a time estimate |
| US20130271945A1 (en) | 2004-02-06 | 2013-10-17 | Nikon Corporation | Polarization-modulating element, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method |
| US8688924B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2014-04-01 | Sandisk Technologies Inc. | Method for improving accuracy of a time estimate from a memory device |
| US8688588B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2014-04-01 | Sandisk Technologies Inc. | Method for improving accuracy of a time estimate used in digital rights management (DRM) license validation |
| US8869288B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2014-10-21 | Sandisk Technologies Inc. | Method for using time from a trusted host device |
| JP2015118451A (en)* | 2013-12-17 | 2015-06-25 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・データ | Authentication device, authentication method, and authentication program |
| US9341954B2 (en) | 2007-10-24 | 2016-05-17 | Nikon Corporation | Optical unit, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method |
| US9423698B2 (en) | 2003-10-28 | 2016-08-23 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus and projection exposure apparatus |
| US9678437B2 (en) | 2003-04-09 | 2017-06-13 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus having distribution changing member to change light amount and polarization member to set polarization in circumference direction |
| US9678332B2 (en) | 2007-11-06 | 2017-06-13 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination apparatus, illumination method, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method |
| US9885872B2 (en) | 2003-11-20 | 2018-02-06 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method with optical integrator and polarization member that changes polarization state of light |
| US9891539B2 (en) | 2005-05-12 | 2018-02-13 | Nikon Corporation | Projection optical system, exposure apparatus, and exposure method |
| US10101666B2 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2018-10-16 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method |
- 2002
- 2002-06-28JPJP2002190454Apatent/JP4012771B2/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (37)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9885959B2 (en) | 2003-04-09 | 2018-02-06 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus having deflecting member, lens, polarization member to set polarization in circumference direction, and optical integrator |
| US9678437B2 (en) | 2003-04-09 | 2017-06-13 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus having distribution changing member to change light amount and polarization member to set polarization in circumference direction |
| US9760014B2 (en) | 2003-10-28 | 2017-09-12 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus and projection exposure apparatus |
| US9423698B2 (en) | 2003-10-28 | 2016-08-23 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus and projection exposure apparatus |
| US10281632B2 (en) | 2003-11-20 | 2019-05-07 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method with optical member with optical rotatory power to rotate linear polarization direction |
| US9885872B2 (en) | 2003-11-20 | 2018-02-06 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method with optical integrator and polarization member that changes polarization state of light |
| US20130271945A1 (en) | 2004-02-06 | 2013-10-17 | Nikon Corporation | Polarization-modulating element, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method |
| US10241417B2 (en) | 2004-02-06 | 2019-03-26 | Nikon Corporation | Polarization-modulating element, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method |
| US10234770B2 (en) | 2004-02-06 | 2019-03-19 | Nikon Corporation | Polarization-modulating element, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method |
| US10007194B2 (en) | 2004-02-06 | 2018-06-26 | Nikon Corporation | Polarization-modulating element, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and exposure method |
| US8731202B2 (en) | 2004-06-16 | 2014-05-20 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Storage-medium processing method, a storage-medium processing apparatus, and a storage-medium processing program |
| US8126150B2 (en) | 2004-06-16 | 2012-02-28 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Storage medium processing method, storage medium processing device, and program |
| JP2006005557A (en)* | 2004-06-16 | 2006-01-05 | Toshiba Corp | Storage medium processing method, storage medium processing apparatus, and program |
| US7949607B2 (en) | 2004-06-21 | 2011-05-24 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Image forming apparatus, license managing method for applications executed by image forming apparatus, program for implementing the method, and storage medium storing the program |
| WO2006016619A1 (en)* | 2004-08-12 | 2006-02-16 | Nikon Corporation | Substrate processing apparatus, use state ascertaining method, and false use preventing method |
| TWI381417B (en)* | 2004-08-12 | 2013-01-01 | 尼康股份有限公司 | A substrate processing device, a usage confirmation method, and an improper use prevention method |
| JPWO2006016619A1 (en)* | 2004-08-12 | 2008-05-01 | 株式会社ニコン | Substrate processing apparatus, usage status confirmation method, and unauthorized use prevention method |
| US8996422B2 (en) | 2004-08-12 | 2015-03-31 | Nikon Corporation | Substrate processing system, method of confirmation of its state of use, and method of prevention of illicit use |
| JP4705034B2 (en)* | 2004-08-12 | 2011-06-22 | 株式会社ニコン | Substrate processing equipment, usage status confirmation method |
| AU2005272460B2 (en)* | 2004-08-12 | 2012-03-22 | Nikon Corporation | Substrate Processing System, Method Of Confirmation Of Its State Of Use, And Method Of Prevention Of Illicit Use |
| US9891539B2 (en) | 2005-05-12 | 2018-02-13 | Nikon Corporation | Projection optical system, exposure apparatus, and exposure method |
| WO2007083499A1 (en)* | 2006-01-19 | 2007-07-26 | Tokyo Electron Limited | Substrate processing device, license management program, license information provision device, license information provision program, license management system and recording medium |
| KR100946810B1 (en)* | 2006-01-19 | 2010-03-09 | 도쿄엘렉트론가부시키가이샤 | Board processing apparatus, license information providing apparatus, license management system, and recording medium |
| US8103596B1 (en) | 2006-03-24 | 2012-01-24 | Walgreen Co. | License verification system and method |
| US7467113B2 (en)* | 2006-03-24 | 2008-12-16 | Walgreen Co. | License verification system and method |
| JP2007280039A (en)* | 2006-04-06 | 2007-10-25 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | User authentication system and method |
| US8688588B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2014-04-01 | Sandisk Technologies Inc. | Method for improving accuracy of a time estimate used in digital rights management (DRM) license validation |
| JP2010530101A (en)* | 2007-06-08 | 2010-09-02 | サンディスク コーポレイション | MEMORY DEVICE HAVING CIRCUIT FOR IMPROVING ACCURACY OF TIME ESTIMATION USED FOR ENTITENT AUTHENTICATION AND METHOD USED IN THE DEVICE |
| US8869288B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2014-10-21 | Sandisk Technologies Inc. | Method for using time from a trusted host device |
| US8688924B2 (en) | 2007-06-08 | 2014-04-01 | Sandisk Technologies Inc. | Method for improving accuracy of a time estimate from a memory device |
| US10101666B2 (en) | 2007-10-12 | 2018-10-16 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method |
| US9857599B2 (en) | 2007-10-24 | 2018-01-02 | Nikon Corporation | Optical unit, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method |
| US9341954B2 (en) | 2007-10-24 | 2016-05-17 | Nikon Corporation | Optical unit, illumination optical apparatus, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method |
| US9678332B2 (en) | 2007-11-06 | 2017-06-13 | Nikon Corporation | Illumination apparatus, illumination method, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method |
| US8751855B2 (en) | 2009-08-17 | 2014-06-10 | Sandisk Il Ltd. | Method and memory device for generating a time estimate |
| US8448009B2 (en) | 2009-08-17 | 2013-05-21 | Sandisk Il Ltd. | Method and memory device for generating a time estimate |
| JP2015118451A (en)* | 2013-12-17 | 2015-06-25 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・データ | Authentication device, authentication method, and authentication program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP4012771B2 (en) | 2007-11-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4012771B2 (en) | License management method, license management system, license management program | |
| KR101219819B1 (en) | Flexible licensing architecture for licensing digital application | |
| US6857067B2 (en) | System and method for preventing unauthorized access to electronic data | |
| JP4278327B2 (en) | Computer platform and operation method thereof | |
| TWI492085B (en) | Method, device and computer storage medium for enhancing product functionality based on user identifier | |
| US8443455B2 (en) | Apparatus, method, and computer program for controlling use of a content | |
| US20080027742A1 (en) | Information processing method, information processing apparatus, computer program and storage medium | |
| WO2004075092A1 (en) | Software-management system, recording medium, and information-processing device | |
| JP2003500722A (en) | Information protection method and device | |
| JP2002373029A (en) | How to prevent unauthorized copying of software using IC tags | |
| MX2012000077A (en) | Method for remotely controlling and monitoring the data produced on desktop on desktop software. | |
| JPH11194937A (en) | Rent control system for electronic computer program | |
| JPWO2006004130A1 (en) | Data management method, program thereof, and program recording medium | |
| JP3993036B2 (en) | License management method, license management system, license management program | |
| US20050177823A1 (en) | License management | |
| WO2005050436A1 (en) | Information processing device, information processing system, and program | |
| JP2007065850A (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program | |
| JP4588991B2 (en) | File management system | |
| JP4017149B2 (en) | Processor with function for preventing unauthorized execution of programs | |
| JP4765459B2 (en) | License authentication device | |
| JP2004213057A (en) | Software unauthorized use prevention system | |
| JPH11238038A (en) | Network license management system and recording medium | |
| JP2001357156A (en) | Identifier management apparatus and method in software distribution system | |
| JP2003029863A (en) | Software license management system | |
| JP5372843B2 (en) | Content utilization apparatus and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date:20040107 | |
| A977 | Report on retrieval | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date:20060811 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20060829 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20061027 | |
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date:20070717 | |
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date:20070809 | |
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date:20070904 | |
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date:20070910 | |
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model | Ref document number:4012771 Country of ref document:JP Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100914 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100914 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313532 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100914 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100914 Year of fee payment:3 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130914 Year of fee payment:6 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) | Free format text:PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160914 Year of fee payment:9 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 | |
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 | |
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees | Free format text:JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 | |
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |