EP2264721A1 - Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage - Google Patents
Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltageDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2264721A1 EP2264721A1EP09251587AEP09251587AEP2264721A1EP 2264721 A1EP2264721 A1EP 2264721A1EP 09251587 AEP09251587 AEP 09251587AEP 09251587 AEP09251587 AEP 09251587AEP 2264721 A1EP2264721 A1EP 2264721A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- power
- driving coil
- electromagnetic
- excitation
- voltage
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 230000005284excitationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription46
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription32
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- 239000003990capacitorSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000007787solidSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000012530fluidSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000020169heat generationEffects0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000004804windingMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000004146energy storageMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000005674electromagnetic inductionEffects0.000claims1
- 230000006698inductionEffects0.000claims1
- 230000001939inductive effectEffects0.000description2
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F7/00—Magnets
- H01F7/06—Electromagnets; Actuators including electromagnets
- H01F7/08—Electromagnets; Actuators including electromagnets with armatures
- H01F7/18—Circuit arrangements for obtaining desired operating characteristics, e.g. for slow operation, for sequential energisation of windings, for high-speed energisation of windings
- H01F7/1805—Circuit arrangements for holding the operation of electromagnets or for holding the armature in attracted position with reduced energising current
Definitions
- the present inventionis mainly related to the electromagnetic actuating device installed with a DC or AC driving coil being electrified to produce electromagnetic actuating effect, wherein the power source device with variable output voltage being operatively controlled by the switching device to electrify the driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device by higher voltage power input, wherein after electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device is further operatively controlled by the switching device to be switched to provide lower voltage power to the driving coil thereby holding electrification for excitation thus reducing total current passing through the driving coil while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
- the present inventiondiscloses an electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage, wherein the DC or AC driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device is operatively controlled by the switching device, wherein it includes applications for normal close or normal open type electromagnetic brakes, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic clutches, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic switches,
- the power source device with variable output voltageis operatively controlled by the switching device to electrify the driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device by higher voltage power input to produce a larger electromagnetic actuating force on the electromagnetic actuating device, wherein after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device is further operatively controlled by the switching device to be switched to provide lower voltage power to the driving coil thereby holding electrification for excitation thus reducing total current passing through the driving coil while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
- an electromagnetic actuating device with a DC or AC driving coilis operatively controlled by the switching device, wherein it includes applications for normal close or normal open type electromagnetic brakes, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic clutches, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic switches, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic relays, normal close or normal open type solenoid valves, etc.
- the power source device with variable output voltageis operatively controlled by the switching device to electrify the driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device by higher voltage power input to produce a larger electromagnetic actuating force on the electromagnetic actuating device, wherein after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device is further operatively controlled by the switching device to be switched to provide lower voltage power to the driving coil thereby holding electrification for excitation thus reducing total current passing through the driving coil while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
- the switching device (101)For the electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by lower voltage, after the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device (102) is electrified for excitation by high voltage DC or AC power (VH) input, DC or AC power output from the power source device with variable output voltage (100) being operatively controlled by the switching device (101) is switched to lower voltage DC or AC power(VL) output for supplying input to the driving coil (102') to hold electrification for excitation, wherein the switching methods include:
- the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating devicebeing supplied by higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) input to be electrically actuated for excitation is switched to supply lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102') thereby hold electrification for excitation, wherein the switching method is further shown in Fig.
- FIG. 4which is a circuit-block schematic view showing that the electromagnetic actuating device is installed with a position detector device to operatively control the excitation power to the driving coil; wherein the position detector device (105) is installed at a stable position after relative actuation between the rotor and the stator of the electromagnetic actuating device or at a selected position in the stroke of actuation, so that the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device (102) being supplied by higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) to be driven to the stable position or the selected position in the stroke of actuation is through the position detector device (105) to directly switch the power source device with variable output voltage (100) to provide lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) output to the driving coil (102') thereby holding electrification for excitation; or the driving coil (102') being supplied by higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) to be driven to a stable position or a selected position in the stroke of actuation is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) being operatively controlled by the position
- the position detector device (105)can be constituted by pressure sensing type electromechanical switching devices or pressure-actuating spring leaf type switches, or can be constituted by optical, electromagnetic inducing type, capacitive inducing type or other conventional position sensing devices, wherein this device can be optionally installed or not installed as required.
- the electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by lower voltagecan be through the power source device with variable output voltage (100) being operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to provide higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) to electrify the driving coil (102') for excitation so as to obtain the larger electromagnetic effective force on the electromagnetic actuating device, wherein it is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) after actuation to be switched to allow the power source device with variable output voltage (100) to provide lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102') thus holding electrification for excitation thereby reducing total current passing through the driving coil (102'), while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device can still be satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
- VHDC or AC power
- the inventionalso provides an electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and electrification being held by low voltage by a power source device with variable output voltage being operatively controlled by a switching device to provide higher voltage power to a driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device so as to produce a larger electromagnetic effective force on the electromagnetic actuating device; wherein, after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device is further operatively controlled by the switching device to be switched to provide lower voltage power to the driving coil, thereby holding electrification for excitation thus reducing the total current passing through the driving coil, while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force, thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss; it essentially comprises:
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Relay Circuits (AREA)
- Direct Current Feeding And Distribution (AREA)
- Electromagnets (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- The present invention is mainly related to the electromagnetic actuating device installed with a DC or AC driving coil being electrified to produce electromagnetic actuating effect, wherein the power source device with variable output voltage being operatively controlled by the switching device to electrify the driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device by higher voltage power input, wherein after electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device is further operatively controlled by the switching device to be switched to provide lower voltage power to the driving coil thereby holding electrification for excitation thus reducing total current passing through the driving coil while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
- For conventional electromagnetic actuating devices driven by supplying DC or AC power to driving coils for producing electromagnetic actuating effect, if the coil electrification power remains unchanged when the electrification status is actuated and held, the current for holding electrification is larger, therefore it has the disadvantages of high heat loss and wasting electric energy.
- The present invention discloses an electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage, wherein the DC or AC driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device is operatively controlled by the switching device, wherein it includes applications for normal close or normal open type electromagnetic brakes, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic clutches, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic switches,
- normal close or normal open type electromagnetic relays, normal close or normal open type solenoid valves, etc. as well as electromagnets, electromagnetic locks, spiral tube windings or other electromagnetic actuating devices with driving coils for electromagnetic driving effects, or operating type electromagnetic actuating devices which can be driven by driving coils or operated by numerous manual or mechanical power methods; wherein the power source device with variable output voltage is operatively controlled by the switching device to electrify the driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device by higher voltage power input to produce a larger electromagnetic actuating force on the electromagnetic actuating device, wherein after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device is further operatively controlled by the switching device to be switched to provide lower voltage power to the driving coil thereby holding electrification for excitation thus reducing total current passing through the driving coil while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
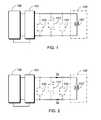
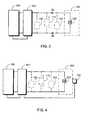
Fig. 1 is a circuit-block schematic view of the embodiment of the present invention showing that the electromagnetic actuating device with a driving coil is actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage.Fig. 2 is a circuit schematic view showing the electrification by higher voltage DC or AC power input in the embodiment ofFig. 1 .Fig. 3 is a circuit schematic view showing that lower voltage DC or AC power input is supplied to the driving coil for holding electrification in the embodiment ofFig. 1 .Fig. 4 is a circuit-block schematic view showing that the electromagnetic actuating device is installed with a position detector device to operatively control the excitation power to the driving coil.- 100 :
- Power source device with variable output voltage
- 101 :
- Switching device
- 102 :
- Electromagnetic actuating device
- 103 :
- AC surge absorption device
- 105 :
- Position detector device
- 113 :
- DC surge absorption device
- 123 :
- General type surge absorption device
- 102' :
- Driving coil
- Ia :
- Larger excited current
- Ib :
- Smaller holding current
- VH :
- Higher voltage DC or AC power
- VIN :
- DC or AC voltage
- VL :
- Lower voltage DC or AC power
- The present invention discloses that an electromagnetic actuating device with a DC or AC driving coil is operatively controlled by the switching device, wherein it includes applications for normal close or normal open type electromagnetic brakes, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic clutches, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic switches, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic relays, normal close or normal open type solenoid valves, etc. as well as electromagnets, electromagnetic locks, spiral tube windings or other electromagnetic actuating devices with driving coils for electromagnetic driving effects, or operating type electromagnetic actuating devices which can be driven by driving coils or operated by numerous manual or mechanical power methods; wherein the power source device with variable output voltage is operatively controlled by the switching device to electrify the driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device by higher voltage power input to produce a larger electromagnetic actuating force on the electromagnetic actuating device, wherein after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device is further operatively controlled by the switching device to be switched to provide lower voltage power to the driving coil thereby holding electrification for excitation thus reducing total current passing through the driving coil while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
- The embodiments of the electromagnetic actuating device with a driving coil are described in the following:
Fig. 1 is a circuit-block schematic view of the embodiment of the present invention showing that the electromagnetic actuating device with a driving coil is actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage, wherein it mainly comprises:- A power source device with variable output voltage (100): related to a power source supply device (100) with variable output voltage constituted by electrical machineries, electronic components, or power source supply devices containing microprocessor and relevant software with relevant power supply functions as well as voltage and current control functions, wherein its input end is for receiving DC or AC power (VIN) to be operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to provide higher voltage DC or AC power output (VH), or lower voltage DC or AC power output (VL), or DC power output of semi-wave or full waved or chopped wave, etc., wherein the voltage relationships between DC or AC input voltage (VIN) at input end of the power source device (100) with variable output voltage, higher voltage DC or AC power output (VH) and lower voltage DC or AC power output (VL) include:
- (1) VIN>VH > VL; or
- (2) VH > VIN > VL; or
- (3) VH > VL > VIN; or
- (4) VIN = VH > VL; or
- (5) VH > VIN = VL;
- A switching device (101): It is constituted by an electromechanical switch, an electric relay, an electromagnetic switch or a solid state switching device, etc. operable by the manual, mechanical, fluid or electrical power being operated by the manual, mechanical, fluid or electrical power for supply DC or AC power to the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device (102) to provide the switching function for electrification and power cut-off, or it is through the switchover operation by the switching device (101) to electrify the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device by higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) from the power source device (100) thereby allowing the larger excited current (Ia) to pass through the driving coil.
Fig. 2 is a circuit schematic view showing the electrification by higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) input in the embodiment ofFig. 1 , wherein the driving coil (102') being actuated for excitation by higher voltage DC or AC power input is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to be switched to allow the power source device of variable output voltage (100) to supply lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input to the driving coil (102') thus allowing smaller excited current (Ib) to pass through the driving coil (102') thereby holding electrification for excitation.Fig. 3 is a circuit schematic view showing that lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input is supplied to the driving coil for holding electrification in the embodiment ofFig. 1 , wherein when lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input is supplied to the driving coil (102') for holding electrification, total current on the driving coil is reduced, while operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device is still ensured by the electromagnetic effective force, thereby saving electric power and reducing heat generation in the electromagnetic actuating device.
- A power source device with variable output voltage (100): related to a power source supply device (100) with variable output voltage constituted by electrical machineries, electronic components, or power source supply devices containing microprocessor and relevant software with relevant power supply functions as well as voltage and current control functions, wherein its input end is for receiving DC or AC power (VIN) to be operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to provide higher voltage DC or AC power output (VH), or lower voltage DC or AC power output (VL), or DC power output of semi-wave or full waved or chopped wave, etc., wherein the voltage relationships between DC or AC input voltage (VIN) at input end of the power source device (100) with variable output voltage, higher voltage DC or AC power output (VH) and lower voltage DC or AC power output (VL) include:
- For the electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by lower voltage, after the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device (102) is electrified for excitation by high voltage DC or AC power (VH) input, DC or AC power output from the power source device with variable output voltage (100) being operatively controlled by the switching device (101) is switched to lower voltage DC or AC power(VL) output for supplying input to the driving coil (102') to hold electrification for excitation, wherein the switching methods include:
- (1) The power of the power source device with variable output voltage (100) for supplying to the driving coil (102') being operatively controlled by a manual-sequential operating switching device (101) is switched from providing higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) input to electrically actuate the driving coil for excitation to lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input thereby holding electrification for excitation; or
- (2) The power of the power source device with variable output voltage (100) for supplying to the driving coil (102') being operatively controlled by the switching device (101) is switched with a time delay function from providing higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) input to electrically actuate the driving coil for excitation to lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input thereby holding electrification for excitation after a time delay; or
- (3) By detecting the current value passing through the switching device (101) to the driving coil (102'), when the excited current value of the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device (102) to be electrically actuated by the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) output of the power source device with variable output voltage (100) ≥ the setting current value, or ≥ the status of setting current value exceeding over the setting time, the switching device (101) being driven to operatively control the power of the power source device (100) with variable output voltage for supplying to the driving coil (102') is switched to lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) output for supplying to the driving coil (102') thereby holding electrification for excitation; or
- (4) The switching device (101) is operatively controlled by two or more than two methods of the above said (1)(2)(3);
- The electromagnetic actuating devices (102): It is the device installed with an AC or DC powered driving coil (102') including conventional normal close or normal open type electromagnetic brakes, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic clutches, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic switches, normal close or normal open type electromagnetic relays, normal close or normal open type solenoid valves, etc. as well as electromagnets, electromagnetic locks, spiral tube windings or other electromagnetic actuating devices with driving coils for electromagnetic driving effects, or operating type electromagnetic actuating devices which can be driven by driving coils or operated by numerous manual or mechanical power methods; wherein the power source device with variable output voltage (100) is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to electrify the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device (102) by higher voltage power (VH) input, wherein after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device with variable output voltage (100) is further switched to provide lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102') thereby holding electrification for excitation thereby saving power and reducing heat generation; while when the driving coil (102') of electromagnetic actuating device (102) is supplied by lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input to hold electrification for excitation, required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss;
- The AC surge absorption device (103), DC surge absorption device (113), general type surge absorption device (123): The AC surge absorption device (103), DC surge absorption device (113) or general type surge absorption device (123) being optionally installed to parallel connect with the driving coil based on input power types to electromagnetic actuating device (102) is used to help absorbing the produced inductance of counter-electric potential in the driving coil (102'), when the driving coil (102') is operated by the switching device (101) to open or close, or to receive higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) for electrifying the driving coil (102'), or to be switched to provide lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) output to the driving coil (102') for holding excitation, wherein AC or DC power input to the driving coil (102') can be respectively matchingly optionally connected with the AC surge absorption device (103), DC surge absorption device (113), or general type surge absorption device (123); wherein the surge absorption device is optionally constituted by the following: (1) When the driving coil (102') is powered by AC power, the AC surge absorption device (103) is installed, such as that it can be constituted by a bipolar solid state varistor, or constituted by at least two kinds of components of the resistors, inductors, bipolar capacitors, etc. in series connection, parallel connection, or series-parallel connection, or constituted by the bipolar capacitor alone, or constituted by other conventional AC surge absorption circuit devices; (2) When the driving coil (102') is powered by DC power, the DC surge absorption device (113) is installed, such as that it can be constituted by reverse polarity diodes in parallel connection to appear a flywheel diode with energy storage effect, or constituted by at least two kinds of components of the resistors, inductors, uni-polar or bipolar capacitors in series connection, parallel connection, or series-parallel connection, or constituted by the uni-polar or bipolar capacitor alone, or constituted by the solid state varistor or other conventional DC surge absorption devices; (3) When the driving coil (102') is powered by mixture of AC and DC power, the general type surge absorption device (123) capable of absorbing either AC surge power or DC surge power is installed, such as that it can be constituted by at least two kinds of components of the resistors, inductors or bipolar capacitors in series connection, parallel connection, or series-parallel conneciton, or constituted by the bipolar capacitor alone, or constituted by bipolar solid state varistor or other conventional general type surge absorption devices; wherein this device can be optionally installed or not installed as required.
- For the electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage, the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device being supplied by higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) input to be electrically actuated for excitation is switched to supply lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102') thereby hold electrification for excitation, wherein the switching method is further shown in
Fig. 4 which is a circuit-block schematic view showing that the electromagnetic actuating device is installed with a position detector device to operatively control the excitation power to the driving coil; wherein the position detector device (105) is installed at a stable position after relative actuation between the rotor and the stator of the electromagnetic actuating device or at a selected position in the stroke of actuation, so that the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device (102) being supplied by higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) to be driven to the stable position or the selected position in the stroke of actuation is through the position detector device (105) to directly switch the power source device with variable output voltage (100) to provide lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) output to the driving coil (102') thereby holding electrification for excitation; or the driving coil (102') being supplied by higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) to be driven to a stable position or a selected position in the stroke of actuation is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) being operatively controlled by the position detector device (105) to be switched to allow the power source device with variable output voltage (100) to provide lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102') thereby holding electrification for excitation; - The position detector device (105) can be constituted by pressure sensing type electromechanical switching devices or pressure-actuating spring leaf type switches, or can be constituted by optical, electromagnetic inducing type, capacitive inducing type or other conventional position sensing devices, wherein this device can be optionally installed or not installed as required.
- As summarized from the above descriptions, the electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by lower voltage can be through the power source device with variable output voltage (100) being operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to provide higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) to electrify the driving coil (102') for excitation so as to obtain the larger electromagnetic effective force on the electromagnetic actuating device, wherein it is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) after actuation to be switched to allow the power source device with variable output voltage (100) to provide lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102') thus holding electrification for excitation thereby reducing total current passing through the driving coil (102'), while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device can still be satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
- The invention also provides an electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and electrification being held by low voltage by a power source device with variable output voltage being operatively controlled by a switching device to provide higher voltage power to a driving coil installed in the electromagnetic actuating device so as to produce a larger electromagnetic effective force on the electromagnetic actuating device; wherein, after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device is further operatively controlled by the switching device to be switched to provide lower voltage power to the driving coil, thereby holding electrification for excitation thus reducing the total current passing through the driving coil, while required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force, thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss; it essentially comprises:
- a power source device with variable output voltage (100) constituted by electrical machineries, electronic components, or power source supply devices containing a microprocessor and relevant software with relevant power supply functions as well as voltage and current control functions, wherein its input end is for receiving DC or AC power (VIN) to be operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to provide higher voltage DC or AC power output, or lower voltage DC or AC power output (VL), or DC power output of semi-wave or full waved or chopped wave, wherein the voltage relationships between the DC or AC input voltage (VIN) at input end of the power source device (100), the higher voltage DC or AC power output (VH) and the lower voltage DC or AC power output (VL) include:
- (1) (VIN) > (VH) > (VL); or
- (2) (VH) > (VL); or
- (3) (VH) > (VL) > (VIN); or
- (4) (VIN) = (VH) > (VL); or
- (5) (VH) > (VIN) = (VL);
the electromagnetic actuating device (102) is installed with an AC-powered or a DC-powered driving coil (102') for electromagnetic driving effects, or an operational electromagnetic actuating device which can be driven by driving coils or operated by manual or mechanical power methods; wherein the power source device (100) is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to electrify the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device (102) by the higher voltage power (VH) input; wherein, after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device (100) is further switched to provide the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102') thereby holding electrification for excitation and saving power and reducing heat generation; while, when the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device (102) is supplied by the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input to hold electrification for excitation, the required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
Claims (11)
- An electromagnetic actuator comprising a power source device (100) having a variable output voltage, a switching device (101) for controlling the power source device, and an electromagnetic actuating device (102) provided with a powered driving coil (102'), wherein the power source device is operatively controlled by the switching device to provide a higher voltage power to the driving coil so as to produce a larger electromagnetic effective force, or to provide a lower voltage output to the driving coil thereby passing a smaller current through the driving coil and holding electrification for excitation, while ensuring that predetermined operating characteristics of the electromagnetic actuating device are maintained.
- An actuator as claimed in claim 1, wherein the power source device is constituted by electrical machineries, electronic components, or power source supply devices containing a microprocessor and relevant software with relevant power supply functions, as well as voltage and current control functions, wherein its input end is for receiving DC or AC power (VIN) to be operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to provide a higher voltage DC or AC power output (VH), or a lower voltage DC or AC power output(VL), or a DC power output of semi-wave or full waved or chopped wave wherein the voltage relationships between DC or AC input voltage (VIN) at the input end of the power source device (100), the higher voltage DC or AC power output (VH) and the lower voltage DC or AC power output (VL) include:(1) (VIN) > (VH) > (VL); or(2) (VH) > (VIN) > (VL); or(3) (VH) > (VL) > (VIN); or(4) (VIN) = (VH) > (VL); or(5) (VH) > (VIN) = (VL);
- An actuator as claimed in claim 2, wherein the switchover operation of the switching device (101) is such as to electrify the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device by the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) from the power source device (100), thereby allowing a larger excited current (Ia) to pass through the driving coil; wherein the driving coil (102') is actuated for
excitation by the higher voltage DC or AC power input and is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to be switched to allow the power source device (100) to supply the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input to the driving coil (102'), thus allowing a smaller excited current (Ib) to pass through the driving coil (102'), thereby holding electrification for excitation; whereby, when the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input is supplied to the driving coil (102') for holding electrification, the total current through the driving coil is reduced, while the operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are ensured by the electromagnetic effective force, thereby saving electric power and reducing heat generation in the electromagnetic actuating device. - An actuator as claimed in claim 2 or claim 3, wherein the switching device (101) is constituted by an electromechanical switch, an electric relay, an electromagnetic switch or a solid state switching device operable by manual, mechanical, fluid or electrical power being operated by manual, mechanical, fluid or electrical power for supplying DC or AC power to the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device (102) to provide a switching function for electrification and power cut-off.
- An actuator as claimed in any one of claims 2 to 4, wherein the electromagnetic actuating device (102) is a device installed with an AC-powered or DC-powered driving coil (102') for electromagnetic driving effects, or an operational electromagnetic actuating device which can be driven by driving coils or operated by manual or mechanical power methods; wherein the power source device (100) is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to electrify the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device (102) by the higher voltage power (VH) input; wherein, after the electromagnetic actuating device is actuated, the power source device (100) is further switched to provide the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102'), thereby holding electrification for excitation and saving power and reducing heat generation; while, when the driving coil (102') is supplied by the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input to hold electrification for excitation, the required operating characteristics of the electrified electromagnetic actuating device are still satisfied by the electromagnetic effective force, thereby saving electric power and reducing heat loss.
- An actuator as claimed in any one of claims 2 to 5, wherein when after the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device (102) is electrified for excitation by the high voltage DC or AC power (VH) input, the DC or AC power output from the power source device (100) is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to switch to the lower voltage DC or AC power(VL) output for supplying input to the driving coil (102') to hold electrification for excitation, wherein the switching methods include:(1) the power of the power source device (100) is operatively controlled by a manual-sequential operating switching device (101) to switch from providing the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) input for electrically actuating the driving coil for excitation to the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input, thereby holding electrification for excitation; or(2) the power of the power source device (100) is operatively controlled by the switching device (101) to switch, with a time delay function, from providing the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) input for electrically actuating the driving coil for excitation, to the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) input, thereby holding electrification for excitation after a time delay; or(3) by detecting the current value passing through the switching device (101) to the driving coil (102'), when the excited current value of the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device (102) to be electrically actuated by the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) output of the power source device, (100) ≥ the setting current value, or ≥ the status of setting current value exceeding the setting time, the switching device (101) is driven operatively to control the power of the power source device (100) for supplying to the driving coil (102') is switched to the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) output for supplying to the driving coil (102'), thereby holding electrification for excitation; or(4) the switching device (101) is operatively controlled by two or more than two methods of the above methods (1)(2)(3).
- An actuator as claimed in any one of claims 2 to 6, wherein the driving coil (102') of the electromagnetic actuating device being supplied by the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) input to be electrically actuated for excitation is switched to supply the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102'), thereby holding electrification for excitation, wherein the switching methods further include a position detector device (105) installed at a stable position after relative actuation between a rotor and a stator of the electromagnetic actuating device, or at a selected position in the stroke of actuation, so that the driving coil (102') installed in the electromagnetic actuating device (102) being supplied by the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) to be driven to the stable position or the selected position in the stroke of actuation, is switched by the position detector device (105) directly to switch the power source device (100) to provide the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) output to the driving coil (102'), thereby holding electrification for excitation; or the driving coil (102') being supplied by the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) to be driven to a stable position, or a selected position in the stroke of actuation, is operatively controlled by the switching device (101), being operatively controlled by the position detector device (105), to be switched to allow the power source device (100) to provide the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) to the driving coil (102'), thereby holding electrification for excitation.
- An actuator as claimed in claim 7, wherein the position detector device (105) is constituted by a pressure-sensing electromechanical switching device, a pressure-actuating spring leaf switch, or by an optical, an electromagnetic induction, a capacitive induction or another conventional position sensing device.
- An actuator as claimed in any one of claims 2 to 8, wherein an AC surge absorption device (103), a DC surge absorption device (113) or a general surge absorption device (123) is installed to parallel connect with the driving coil (102') based on input power types of the electromagnetic actuating device (102) to help absorb the produced inductance of the counter-electric potential in the driving coil (102'), when the driving coil (102') is operated by the switching device (101) to open or close, or to receive the higher voltage DC or AC power (VH) for electrifying the driving coil (102'), or to be switched to provide the lower voltage DC or AC power (VL) output to the driving coil (102') for holding excitation, wherein the AC or DC power input to the driving coil (102') can be connected with the AC surge absorption device (103), the DC surge absorption device (113), or the general surge absorption device (123).
- An actuator as claimed in claim 9, wherein the surge absorption device is constituted by the following:(1) when the driving coil (102') is powered by AC power, the AC surge absorption device (103) is installed, and is constituted by a bipolar solid state varistor, or by at least two kinds of components such as resistors, inductors, bipolar capacitors in series connection, parallel connection, or series-parallel connection, or constituted by a bipolar capacitor alone, or constituted by other conventional AC surge absorption circuit devices; or(2) when the driving coil (102') is powered by DC power, the DC surge absorption device (113) is installed, and is constituted by reverse polarity diodes in parallel connection to constitute a flywheel diode with energy storage effect, or is constituted by at least two kinds of components such as resistors, inductors, uni-polar or bipolar capacitors in series connection, parallel connection, or series-parallel connection, or is constituted by a uni-polar or bipolar capacitor alone, or is constituted by a solid state varistor or other conventional DC surge absorption device; or(3) when the driving coil (102') is powered by a mixture of AC and DC power, the general surge absorption device (123) capable of absorbing either AC surge power or DC surge power is installed, and is constituted by at least two kinds of components such as resistors, inductors or bipolar capacitors in series connection, parallel connection, or series-parallel connection, or is constituted by a bipolar capacitor alone, or is constituted by a bipolar solid state varistor or other conventional general type surge absorption device.
- An actuator as claimed in any one of claims 1 to 10, wherein the electromagnetic actuating device (102) includes applications for normally-closed or normally-open electromagnetic brakes, normally-closed or normally-open electromagnetic clutches, normally-closed or normally-open electromagnetic switches, normally-closed or normally-open electromagnetic relays, normally-closed or normally-open solenoid valves as well as electromagnets, electromagnetic locks, spiral tube windings or other electromagnetic actuating devices with driving coils for electromagnetic driving effects, or operational electromagnetic actuating devices which can be driven by driving coils or operated by manual or mechanical power methods.
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910134338.5ACN101866737A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-04-14 | Electromagnetic actuating device for high-voltage starting and low-voltage power-on maintaining |
| TW098120350ATW201101361A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | The electromagnetic actuating device capable of partially holding electrification after being actuated in parallel connection |
| TW098120354ATW201100680A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage |
| TW098120351ATW201101350A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | Electromagnetic actuating device with coils capable of holding electrification in series connection after being actuated in parallel connection |
| EP09251587AEP2264721A1 (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage |
| JP2009157866AJP2011015542A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-07-02 | Electromagnetic starter |
| JP2009158855AJP2011015573A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-07-03 | Electromagnetic starter |
Applications Claiming Priority (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910134338.5ACN101866737A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-04-14 | Electromagnetic actuating device for high-voltage starting and low-voltage power-on maintaining |
| TW098120350ATW201101361A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | The electromagnetic actuating device capable of partially holding electrification after being actuated in parallel connection |
| TW098120354ATW201100680A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage |
| TW098120351ATW201101350A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | Electromagnetic actuating device with coils capable of holding electrification in series connection after being actuated in parallel connection |
| EP09251587AEP2264721A1 (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage |
| JP2009157866AJP2011015542A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-07-02 | Electromagnetic starter |
| JP2009158855AJP2011015573A (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-07-03 | Electromagnetic starter |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2264721A1true EP2264721A1 (en) | 2010-12-22 |
Family
ID=51019541
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP09251587AWithdrawnEP2264721A1 (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2009-06-18 | Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2264721A1 (en) |
| JP (2) | JP2011015542A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101866737A (en) |
| TW (3) | TW201101350A (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI488207B (en)* | 2012-08-17 | 2015-06-11 | Lite On Electronics Guangzhou | Relay driving device and driving method thereof |
| CN111021842B (en)* | 2019-12-31 | 2022-01-21 | 常州瓦良格电气有限公司 | Series-parallel automatic switching control system for improving reliability of electromagnetic lock |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1074754B (en)* | 1960-02-04 | Siemens-Schuckertwerke Aktiengesellschaft, Berlin Und Erlangen | Circuit arrangement for supplying direct current train magnets from an alternating voltage source | |
| DE4332995C1 (en)* | 1993-09-28 | 1994-10-20 | Siemens Ag | Method for driving relays which are arranged in parallel |
| US5422780A (en)* | 1992-12-22 | 1995-06-06 | The Lee Company | Solenoid drive circuit |
| DE19723931A1 (en)* | 1997-06-06 | 1998-12-10 | Siemens Ag | Device for controlling an electromechanical actuator |
| EP2071602A1 (en)* | 2007-12-14 | 2009-06-17 | Yang, Tai-Her | Electrically excited load full voltage actuation reduced voltage sustaining driving circuit |
- 2009
- 2009-04-14CNCN200910134338.5Apatent/CN101866737A/enactivePending
- 2009-06-18TWTW098120351Apatent/TW201101350A/enunknown
- 2009-06-18EPEP09251587Apatent/EP2264721A1/ennot_activeWithdrawn
- 2009-06-18TWTW098120354Apatent/TW201100680A/enunknown
- 2009-06-18TWTW098120350Apatent/TW201101361A/enunknown
- 2009-07-02JPJP2009157866Apatent/JP2011015542A/enactivePending
- 2009-07-03JPJP2009158855Apatent/JP2011015573A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1074754B (en)* | 1960-02-04 | Siemens-Schuckertwerke Aktiengesellschaft, Berlin Und Erlangen | Circuit arrangement for supplying direct current train magnets from an alternating voltage source | |
| US5422780A (en)* | 1992-12-22 | 1995-06-06 | The Lee Company | Solenoid drive circuit |
| DE4332995C1 (en)* | 1993-09-28 | 1994-10-20 | Siemens Ag | Method for driving relays which are arranged in parallel |
| DE19723931A1 (en)* | 1997-06-06 | 1998-12-10 | Siemens Ag | Device for controlling an electromechanical actuator |
| EP2071602A1 (en)* | 2007-12-14 | 2009-06-17 | Yang, Tai-Her | Electrically excited load full voltage actuation reduced voltage sustaining driving circuit |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011015573A (en) | 2011-01-20 |
| JP2011015542A (en) | 2011-01-20 |
| CN101866737A (en) | 2010-10-20 |
| TW201101350A (en) | 2011-01-01 |
| TW201101361A (en) | 2011-01-01 |
| TW201100680A (en) | 2011-01-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2264722A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by AC power and held by DC power | |
| US7706118B2 (en) | Operative control circuit of multiple electromagnetic actuating devices in series and parallel connection | |
| JP4392555B2 (en) | Single-coil solenoid with a permanent magnet and a permanent magnet, its manufacturing method, non-magnetic switch for single-coil solenoid, single-coil solenoid kit | |
| CA2927144A1 (en) | Constant-current controller for an inductive load | |
| CN104364859B (en) | Electronically controlled solenoid | |
| US20090262479A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage | |
| US20080074823A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuator parallel actuation serial sustaining driving circuit | |
| EP2264721A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuating device being actuated by high voltage and held electrification by low voltage | |
| CA2626645A1 (en) | Electrically excited load full voltage actuation reduced voltage sustaining driving circuit | |
| US20090262480A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuating device with coils capable of holding electrification in series connection after being actuated in parallel connection | |
| US20090260944A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuating device with driving and holding tapped coil | |
| EP2264723A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuating device with coils capable of holding electrification in series connection after being actuated in parallel connection | |
| EP2264724A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuating device capable of partially holding electrification after being actuated in parallel connection | |
| EP2071602A1 (en) | Electrically excited load full voltage actuation reduced voltage sustaining driving circuit | |
| EP2264720A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuating device with driving and holding tapped coil | |
| CN100505511C (en) | Apparatus for driving electromagnets especially for operating pumps | |
| EP2071595A1 (en) | Electromagnetic actuator parallel actuation serial sustaining driving circuit | |
| AU2008201387A1 (en) | Operative control circuit of multiple electromagnetic actuating devices in series and parallel connection | |
| CN214099429U (en) | Electromagnetic driver | |
| KR20090102062A (en) | Electrically excited load full voltage actuation reduced voltage sustaining driving circuit | |
| JPS62260308A (en) | Method and apparatus for driving multi-electromagnet apparatus | |
| CN1755860A (en) | Energy-saving material-saving environment-friendly AC contactor | |
| JPH11311360A (en) | Display circuit of direct current solenoid valve |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase | Free format text:ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 | |
| AK | Designated contracting states | Kind code of ref document:A1 Designated state(s):AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK TR | |
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent | Extension state:AL BA RS | |
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent | Free format text:STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN | |
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn | Effective date:20110625 |