DE102015001247A1 - Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding area of a motor vehicle and system - Google Patents
Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding area of a motor vehicle and systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- DE102015001247A1 DE102015001247A1DE102015001247.9ADE102015001247ADE102015001247A1DE 102015001247 A1DE102015001247 A1DE 102015001247A1DE 102015001247 ADE102015001247 ADE 102015001247ADE 102015001247 A1DE102015001247 A1DE 102015001247A1
- Authority
- DE
- Germany
- Prior art keywords
- geographical position
- information
- motor vehicle
- roundabout
- surrounding area
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription25
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000004422calculation algorithmMethods0.000description8
- 230000004927fusionEffects0.000description8
- 230000003044adaptive effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000description4
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description4
- 230000001419dependent effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000013178mathematical modelMethods0.000description2
- BUHVIAUBTBOHAG-FOYDDCNASA-N(2r,3r,4s,5r)-2-[6-[[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(2-methylphenyl)ethyl]amino]purin-9-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diolChemical compoundCOC1=CC(OC)=CC(C(CNC=2C=3N=CN(C=3N=CN=2)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)C=2C(=CC=CC=2)C)=C1BUHVIAUBTBOHAG-FOYDDCNASA-N0.000description1
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000description1
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 230000002596correlated effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000875corresponding effectEffects0.000description1
- 125000004122cyclic groupChemical group0.000description1
- 230000005484gravityEffects0.000description1
- 238000007620mathematical functionMethods0.000description1
- 238000012805post-processingMethods0.000description1
- 238000007781pre-processingMethods0.000description1
- 230000011218segmentationEffects0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000002604ultrasonographyMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/88—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G01S13/93—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes
- G01S13/931—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01C—MEASURING DISTANCES, LEVELS OR BEARINGS; SURVEYING; NAVIGATION; GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS; PHOTOGRAMMETRY OR VIDEOGRAMMETRY
- G01C21/00—Navigation; Navigational instruments not provided for in groups G01C1/00 - G01C19/00
- G01C21/38—Electronic maps specially adapted for navigation; Updating thereof
- G01C21/3804—Creation or updating of map data
- G01C21/3833—Creation or updating of map data characterised by the source of data
- G01C21/3844—Data obtained from position sensors only, e.g. from inertial navigation
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/86—Combinations of radar systems with non-radar systems, e.g. sonar, direction finder
- G01S13/867—Combination of radar systems with cameras
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/88—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/88—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G01S13/93—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes
- G01S13/931—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles
- G01S2013/932—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles using own vehicle data, e.g. ground speed, steering wheel direction
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/88—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G01S13/93—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes
- G01S13/931—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles
- G01S2013/9327—Sensor installation details
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/01—Detecting movement of traffic to be counted or controlled
- G08G1/0104—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions
- G08G1/0108—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions based on the source of data
- G08G1/0112—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions based on the source of data from the vehicle, e.g. floating car data [FCD]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromGermanDescription
Translated fromGermanDie Erfindung betrifft ein Verfahren zur Bereitstellung von Information über zumindest ein Objekt in einem Umgebungsbereich eines Kraftfahrzeugs einer Fahrzeugflotte, bei dem die Information im Kraftfahrzeug erfasst und zusammen mit Positionsdaten des Kraftfahrzeugs an eine Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung übertragen und bereitgestellt wird. Die Erfindung betrifft außerdem ein System mit zumindest einem Kraftfahrzeug einer Fahrzeugflotte und einer Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung.The invention relates to a method for providing information about at least one object in an environmental region of a motor vehicle of a vehicle fleet, in which the information is detected in the motor vehicle and transmitted together with position data of the motor vehicle to a traffic information collecting device and provided. The invention also relates to a system comprising at least one motor vehicle of a vehicle fleet and a traffic information collecting device.
Verfahren zur Bereitstellung von Information über zumindest ein Objekt in einem Umgebungsbereich eines Kraftfahrzeugs einer Fahrzeugflotte sind aus dem Stand der Technik bekannt. So ist in der
Nachteilig an dem genannten Stand der Technik ist, dass die Information durch das Umfeldmodell nur trivial modelliert wird.A disadvantage of the cited prior art is that the information is modeled only trivially by the environment model.
Es ist Aufgabe der Erfindung, ein Verfahren sowie ein System bereitzustellen, mit welchem beziehungsweise bei welchem die Information über das zumindest eine Objekt in dem Umgebungsbereich des Kraftfahrzeugs effektiv durch eine Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung bereitgestellt werden kann.It is an object of the invention to provide a method and a system, with which or in which the information about the at least one object in the surrounding area of the motor vehicle can be effectively provided by a traffic information collecting device.
Diese Aufgabe wird erfindungsgemäß durch ein Verfahren sowie durch ein System mit den Merkmalen gemäß den jeweiligen unabhängigen Ansprüchen gelöst.This object is achieved by a method and by a system having the features according to the respective independent claims.
Bei einem erfindungsgemäßen Verfahren wird Information über zumindest ein Objekt in einem Umgebungsbereich eines Kraftfahrzeugs einer Fahrzeugflotte bereitgestellt. Die Information wird im Kraftfahrzeug erfasst und zusammen mit Positionsdaten des Kraftfahrzeugs an eine Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung übertragen und durch die Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung bereitgestellt. Ein wesentlicher Gedanke der Erfindung ist, dass die Information mit zumindest einer ersten geographischen Position des Objekts und einer zweiten geographischen Position des Objekts bereitgestellt wird, und die zweite geographische Position abhängig von der ersten geographischen Position bestimmt und bereitgestellt wird.In a method according to the invention, information about at least one object in an environmental region of a motor vehicle of a vehicle fleet is provided. The information is detected in the motor vehicle and transmitted together with position data of the motor vehicle to a traffic information collecting device and provided by the traffic information collecting device. An essential idea of the invention is that the information is provided with at least a first geographical position of the object and a second geographical position of the object, and the second geographical position is determined and provided depending on the first geographical position.
Durch das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren wird es möglich, die Information über das Objekt in dem Umgebungsbereich effektiv bereitzustellen.By the method according to the invention, it becomes possible to effectively provide the information about the object in the surrounding area.
Möglich wird das, weil die zweite geographische Position abhängig von der ersten geographischen Position bestimmt wird. Das bedeutet, dass die zweite geographische Position angepasst wird, falls sich die erste geographische Position ändert. Die erste geographische Position und die zweite geographische Position können beispielsweise als Geokoordinate ausgebildet sein. Die Geokoordinate kann beispielsweise eine Position in einem erdfesten Koordinatensystem wie einem UTM-Koordinatensystem (Universal Transverse Mercator) beschreiben. Die Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung umfasst vorzugsweise eine Datenbank. Die erste geographische Position ist insbesondere ein Primärattribut, während die zweite geographische Position insbesondere ein Sekundärattribut ist. So wird das Sekundärattribut beispielsweise angepasst, falls sich das Primärattribut ändert. Das Objekt ist insbesondere eine komplexe Landmarke, wie beispielsweise ein Kreisverkehr. Die komplexe Landmarke umfasst punktgenaue beziehungsweise punktförmige Landmarken, wie beispielsweise die erste geographische Position und/oder die zweite geographische Position. Insbesondere wird das Objekt mit einem Graphen parametrisch beschrieben. Das bedeutet, die Information über das Objekt wird durch den Graphen modelliert. Die parametrische Beschreibung des Objekts umfasst Attribute beziehungsweise Parameter, wie beispielsweise die erste geographische Position und die zweite geographische Position. Die Attribute werden durch die Information bereitgestellt und mittels des Graphen modelliert beziehungsweise zusammenhängend beschrieben. Der Graph ist in der Graphentheorie eine abstrakte Struktur, die eine Menge von Attributen zusammen mit den zwischen diesen Attributen bestehenden Verbindungen repräsentiert. Die mathematischen Abstraktionen der Attribute werden dabei Knoten des Graphen genannt. Die paarweisen Verbindungen zwischen Knoten heißen Kanten. Die Kanten können gerichtet oder ungerichtet sein. Vorliegend wird vorzugsweise ein kreisfreier gerichteter Graph genutzt, um die Information zu beschreiben beziehungsweise die Attribute der Information des Objekts miteinander verknüpft beziehungsweise abhängig voneinander bereitzustellen. Die Attribute, wie die erste geographische Position und die zweite geographische Position, werden durch die Knoten des Graphen repräsentiert. Die Kanten des Graphen zeigen somit insbesondere eine Korrelation der an die jeweiligen Kanten angebundenen Attribute. So ist die erste geographische Position insbesondere ein Startknoten des Graphen, während ein Sekundärattribut, wie beispielsweise die zweite geographische Position ein Zielknoten des Graphen ist. Der Graph weist insbesondere keine Zyklen auf.This is possible because the second geographical position is determined depending on the first geographical position. This means that the second geographic position will be adjusted if the first geographic position changes. The first geographical position and the second geographical position may be designed as geo-coordinates, for example. For example, the geocoordinate may describe a position in a ground-based coordinate system, such as a Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinate system. The traffic information collecting device preferably comprises a database. In particular, the first geographical position is a primary attribute, while the second geographical position is in particular a secondary attribute. For example, the secondary attribute is adjusted if the primary attribute changes. The object is in particular a complex landmark, such as a roundabout. The complex landmark comprises punctiform landmarks such as the first geographic location and / or the second geographic location. In particular, the object is parametrically described with a graph. This means that the information about the object is modeled by the graph. The parametric description of the object includes attributes or parameters, such as the first geographic location and the second geographic location. The attributes are provided by the information and modeled by means of the graph or described coherently. The graph is an abstract structure in graph theory that represents a set of attributes along with the connections between those attributes. The mathematical abstractions of the attributes are called nodes of the graph. The pairwise connections between nodes are called edges. The edges can be directional or undirected. In the present case, preferably a circle-free directed graph is used in order to describe the information or to link the attributes of the information of the object with one another or to make them dependent on one another. The attributes, such as the first geographical position and the second geographical position, are represented by the nodes of the graph. The edges of the graph thus show in particular a correlation of the attributes bound to the respective edges. In particular, the first geographic location is a starting node of the graph, while a secondary attribute, such as the second geographic location, is a destination node of the graph. In particular, the graph has no cycles.
Es ist insbesondere mehr beabsichtigt, als lediglich absolute und relative Koordinaten bereitzustellen. Durch den Graphen kann eine effektivere Verwaltung der Information und eine effektivere Bereitstellung der Information erfolgen, als wenn die erste geographische Position lediglich absolut angegeben ist und die zweite geographische Position lediglich relativ zu der ersten geographischen Position angegeben ist. Durch den Graphen kann ein funktioneller Zusammenhang, in Form eines mathematischen Modells, zwischen der ersten geographischen Position und der zweiten geographischen Position beschrieben werden. Somit kann durch den Graphen eine effektive und komplexe Korrelation zwischen der ersten geographischen Position und der zweiten geographischen Position beschrieben werden.In particular, it is intended to be more than merely providing absolute and relative coordinates. The graph may provide more effective management of the information and more effective provision of the information than if the first geographic location is only absolute and the second geographic location is only relative to the first geographic location. Through the graph, a functional relationship, in the form of a mathematical model, between the first geographical position and the second geographical position can be described. Thus, the graph may describe an effective and complex correlation between the first geographic position and the second geographic position.
So kann das Objekt beispielsweise als ein Kreisverkehr in dem Umgebungsbereich ausgebildet sein. Die erste geographische Position kann dann beispielsweise ein Mittelpunkt des Kreisverkehrs sein. Die zweite geographische Position kann dann beispielsweise ein Hilfspunkt sein, welcher für die Konstruktion eines Teils des Kreisverkehrs benötigt wird. Ändert sich also die erste geographische Position, so ändert sich insbesondere auch die zweite geographische Position abhängig von dem der Abhängigkeit zugrundeliegenden Graphen beziehungsweise mathematischen Modells.For example, the object may be designed as a roundabout in the surrounding area. The first geographical position may then be, for example, a center of the roundabout. The second geographical position may then be, for example, an auxiliary point needed for the construction of part of the roundabout. If, therefore, the first geographical position changes, the second geographic position in particular also changes depending on the graph or mathematical model underlying the dependency.
Vorzugsweise ist vorgesehen, dass die erste geographische Position unabhängig von der zweiten geographischen Position bestimmt wird. Somit hängt die erste geographische Position also insbesondere nicht von der zweiten geographischen Position ab. Es ist also insbesondere vorgesehen, dass die erste geographische Position geändert wird und somit die zweite geographische Position angepasst wird. Ferner ist es insbesondere nicht vorgesehen, dass die zweite geographische Position geändert wird und dadurch die erste geographische Position angepasst wird. Dies entspricht insbesondere dem Modell des gerichteten Graphen. Durch den gerichteten Graphen wird eine Richtung vorgegeben, in welcher die Knoten des Graphen durchlaufen werden können. Vorteilhaft ist also eine effektive und fehlereinflussreduzierte Bereitstellung der Information durch den gerichteten Graphen.It is preferably provided that the first geographical position is determined independently of the second geographical position. Thus, in particular, the first geographical position does not depend on the second geographical position. It is therefore provided in particular that the first geographical position is changed and thus the second geographical position is adjusted. Furthermore, it is not provided in particular that the second geographical position is changed and thereby the first geographical position is adjusted. This corresponds in particular to the model of the directed graph. The directed graph specifies a direction in which the nodes of the graph can be traversed. Thus, an effective and error-reduced provision of information by the directed graph is advantageous.
Weiterhin ist vorzugsweise vorgesehen, dass die Information mit einer dritten geographischen Position bereitgestellt wird, und die dritte geographische Position abhängig von der ersten geographischen Position bestimmt wird. Die dritte geographische Position ist insbesondere analog zu der zweiten geographischen Position ebenfalls vorzugsweise ein Sekundärattribut, welches von dem Primärattribut, insbesondere der ersten geographischen Position, abhängt. Vorteilhaft ist also, dass die Modellierung der Information besonders vielfältig möglich ist und mit der zweiten geographischen Position und der dritten geographischen Position mehrere Sekundärattribute von dem Primärattribut abhängen können. Die Beschreibung des Objekts beziehungsweise die Modellierung der Information des Objekts kann somit vielfältig erfolgen und die Information kann effektiv durch insbesondere die Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung bereitgestellt werden.Furthermore, it is preferably provided that the information is provided with a third geographical position, and the third geographical position is determined depending on the first geographical position. The third geographical position is also, analogously to the second geographical position, preferably also a secondary attribute, which depends on the primary attribute, in particular the first geographical position. It is therefore advantageous that the modeling of the information is possible in a particularly versatile manner and that with the second geographical position and the third geographical position, a plurality of secondary attributes can depend on the primary attribute. The description of the object or the modeling of the information of the object can thus be varied and the information can be effectively provided by, in particular, the traffic information collecting device.
In einer Ausführungsform ist es vorzugsweise vorgesehen, dass die erste geographische Position durch einen Mittelpunkt des Objekts beschrieben wird. Ebenso kann die erste geographische Position beispielsweise durch einen Schwerpunkt des Objekts beschrieben werden. Insbesondere ist vorgesehen, dass die erste geographische Position durch den Mittelpunkt eindeutig zuzuordnen ist. Somit kann die Anordnung des Objekts in beispielsweise einem erdfesten Koordinatensystem präzise erfolgen. Der Mittelpunkt des Objekts kann sich beispielsweise aber auch auf Mittelpunkte von Teilobjekten des Objekts beziehen. Insbesondere ist jedoch vorgesehen, dass der Mittelpunkt ein eindeutig zuordenbarer Referenzpunkt des Objekts ist.In one embodiment, it is preferably provided that the first geographical position is described by a center point of the object. Likewise, the first geographical position can be described, for example, by a center of gravity of the object. In particular, it is provided that the first geographical position can be unambiguously assigned by the center. Thus, the arrangement of the object can be done precisely in, for example, a ground-based coordinate system. The center of the object may, however, also refer, for example, to centers of sub-objects of the object. In particular, however, it is provided that the center is a clearly assignable reference point of the object.
In einer weiteren Ausführungsform ist es vorzugsweise vorgesehen, dass durch die zweite geographische Position ein Hilfspunkt für die Konstruktion eines Teilobjekts des Objekts beschrieben wird. So kann der Hilfspunkt beispielsweise genutzt werden, um eine vollständige Geometrie, wie beispielsweise komplexe Konturen von Teilobjekten des Objekts zu beschreiben. So ist ein Kreis beispielsweise durch den Mittelpunkt des Kreises und einen Radius definiert. Wird die geometrische Form des Objekts jedoch komplexer, so wird für die Konstruktion des komplexen Objekts üblicherweise auf Hilfspunkte zurückgegriffen. Die komplexen Erweiterungen des Objekts werden vorliegend beispielsweise als die Teilobjekte beschrieben. So kann das Objekt beispielsweise als Kreisverkehr vorliegen und das Teilobjekt kann beispielsweise eine Auffahrt des Kreisverkehrs sein. Der Vorteil des Hilfspunkts ist also, dass komplexere Objekte beschrieben und somit letztendlich eindeutig konstruiert werden können.In a further embodiment, it is preferably provided that an auxiliary point for the construction of a sub-object of the object by the second geographical position is described. For example, the auxiliary point can be used to describe a complete geometry, such as complex contours of subobjects of the object. For example, a circle is defined by the center of the circle and a radius. However, if the geometric shape of the object becomes more complex, auxiliary points are usually used for the construction of the complex object. The complex extensions of the object are described herein as, for example, the sub-objects. For example, the object can be present as a roundabout and the subobject can be, for example, a driveway of the roundabout. The advantage of the auxiliary point is therefore that more complex objects can be described and thus ultimately clearly constructed.
In einer weiteren Ausführungsform kann es vorgesehen sein, dass durch den Hilfspunkt ein Radius eines Konturbereichs des Teilobjekts beschrieben wird. So kann der Hilfspunkt beispielsweise angeben, von welcher Position aus der Radius des Konturbereichs des Teilobjekts konstruiert werden soll. Der Konturverlauf des Teilobjekts kann somit eindeutig definiert werden. Durch das eindeutige Definieren des Teilobjekts kann die Information effektiv bereitgestellt werden.In a further embodiment it can be provided that a radius of a contour region of the sub-object is described by the auxiliary point. For example, the auxiliary point can specify from which position the radius of the contour area of the sub-object is to be constructed. The contour of the subobject can thus be clearly defined. By uniquely defining the sub-object, the information can be effectively provided.
Insbesondere ist vorgesehen, dass das Objekt als ein kraftfahrzeugexternes Verkehrsinfrastrukturelement, insbesondere als ein Kreisverkehr, in dem Umgebungsbereich beschrieben wird. Das Verkehrsinfrastrukturelement kann beispielsweise als Ampel und/oder Verkehrszeichen und/oder Verkehrsinsel und/oder Kreisverkehr und/oder Kreuzung und/oder Spurmarkierung ausgebildet sein. Vorteilhaft ist also, dass vielfältige Verkehrsinfrastrukturelemente die Information bereitstellen können, welche modelliert, in der Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung gespeichert und schließlich effektiv bereitgestellt werden kann.In particular, it is provided that the object is described as a motor vehicle-external traffic infrastructure element, in particular as a roundabout, in the surrounding area. The traffic infrastructure element can be designed, for example, as a traffic light and / or traffic sign and / or traffic island and / or roundabout and / or intersection and / or lane marking. It is therefore advantageous that various traffic infrastructure elements can provide the information that can be modeled, stored in the traffic information collecting device and finally effectively provided.
In einer weiteren Ausführungsform ist es vorzugsweise vorgesehen, dass durch das Teilobjekt eine Auffahrt des Kreisverkehrs und/oder eine Abfahrt des Kreisverkehrs beschrieben wird. Die Auffahrt des Kreisverkehrs ist also beispielsweise der Teil der Fahrbahn des Kreisverkehrs, auf welchem die Fahrzeuge in den Kreisverkehr einfahren. Die Abfahrt des Kreisverkehrs beschreibt somit den Teil der Fahrbahn des Kreisverkehrs, auf welchem die Fahrzeuge von dem Kreisverkehr abfahren. Das Teilobjekt ermöglicht also eine genaue Beschreibung des Objekts und somit ein effektives Bereitstellen der Information.In a further embodiment, it is preferably provided that a driveway of the roundabout and / or a descent of the roundabout is described by the subobject. The driveway of the roundabout is thus, for example, the part of the roadway of the roundabout on which the vehicles enter the roundabout. The departure of the roundabout thus describes the part of the carriageway of the roundabout on which the vehicles leave the roundabout. The subobject thus enables a precise description of the object and thus an effective provision of the information.
Weiterhin ist es vorzugsweise vorgesehen, dass der Umgebungsbereich in Teilumgebungsbereiche unterteilt wird, und die Information durch die Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung abhängig von den Teilumgebungsbereichen bereitgestellt wird. Hierdurch kann ein Verfahren mit eingeschränkter Lokalität bereitgestellt werden. Das bedeutet insbesondere, dass die Information nur für einen Teilbereich des Objekts bereitgestellt wird, und beispielsweise angrenzende Teilbereiche genutzt werden, um die Information, welche von dem Objekt innerhalb des Teilbereichs bereitgestellt wird, anzupassen. Die Unterteilung der Teilbereiche des Objekts erfolgt insbesondere durch die Teilumgebungsbereiche. So kann beispielsweise ein Raster auf der Erdoberfläche angelegt werden, wobei jeder der Teilumgebungsbereiche einem Feld des Rasters entspricht. Vorteilhaft an der Unterteilung des Umgebungsbereichs in Teilumgebungsbereiche ist die Reduzierung der Datenmenge für das Verarbeiten der Information in der Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung. Somit kann die Information in der Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung effektiver verarbeitet werden und effektiver bereitgestellt werden. Vorzugsweise werden die Teilumgebungsbereiche, welche für das Bereitstellen der Information genutzt werden, anhand einer Achternachbarschaft bestimmt. Das bedeutet, dass beispielsweise ein viereckiger Teilumgebungsbereich zusammen mit seinen acht nachbarschaftlich angrenzenden viereckigen Teilumgebungsbereichen bearbeitet wird.Furthermore, it is preferably provided that the surrounding area is subdivided into sub-surrounding areas, and the information is provided by the traffic information collecting device depending on the sub-surrounding areas. As a result, a method with limited locality can be provided. This means in particular that the information is provided only for a subarea of the object, and, for example, adjacent subareas are used to adapt the information provided by the object within the subarea. The subdivision of the subareas of the object takes place, in particular, through the subareas. For example, a grid may be applied to the earth's surface, with each of the sub-environment areas corresponding to one field of the grid. An advantage of the subdivision of the surrounding area into sub-surrounding areas is the reduction of the amount of data for the processing of the information in the traffic information collecting device. Thus, the information in the traffic information collection device can be processed more effectively and provided more effectively. Preferably, the sub-environment areas used for providing the information are determined on the basis of an eighth-neighbor. This means, for example, that a quadrilateral subarea is handled along with its eight neighbor adjacent quadrilateral subareas.
Die Erfindung betrifft auch ein System mit zumindest einem Kraftfahrzeug einer Fahrzeugflotte und einer Verkehrsinformations-Sammeleinrichtung, wobei das System dazu ausgelegt ist, ein erfindungsgemäßes Verfahren oder eine vorteilhafte Ausführung davon auszuführen.The invention also relates to a system comprising at least one motor vehicle of a vehicle fleet and a traffic information collecting device, the system being designed to carry out a method according to the invention or an advantageous embodiment thereof.
Die mit Bezug auf das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren vorgestellten bevorzugten Ausführungsformen und deren Vorteile geltend entsprechend für das erfindungsgemäße System.The preferred embodiments presented with reference to the method according to the invention and their advantages apply correspondingly to the system according to the invention.
Weitere Merkmale der Erfindung ergeben sich aus den Ansprüchen, den Figuren und der Figurenbeschreibung. Alle vorstehend in der Beschreibung genannten Merkmale und Merkmalskombinationen sowie die nachfolgend in der Figurenbeschreibung genannten und/oder in den Figuren alleine gezeigten Merkmale und Merkmalskombinationen sind nicht nur in der jeweils angegeben Kombination, sondern auch in anderen Kombinationen oder aber in Alleinstellung verwendbar, ohne den Rahmen der Erfindung zu verlassen. Es sind somit auch Ausführungen von der Erfindung als umfasst und offenbart anzusehen, die in der Figur nicht explizit gezeigt und erläutert sind, jedoch durch separierte Merkmalskombinationen aus den erläuterten Ausführungen hervorgehen und erzeugbar sind. Es sind auch Ausführungen und Merkmalskombinationen als offenbart anzusehen, die somit nicht alle Merkmale eines ursprünglich formulierten unabhängigen Anspruchs aufweisen.Further features of the invention will become apparent from the claims, the figures and the description of the figures. All the features and feature combinations mentioned above in the description as well as the features and feature combinations mentioned below in the figure description and / or shown alone in the figures can be used not only in the respective specified combination but also in other combinations or alone, without the frame to leave the invention. There are therefore also embodiments of the invention as encompassed and disclosed, which are not explicitly shown and explained in the figure, however, emerge and can be generated by separate feature combinations of the described embodiments. Embodiments and combinations of features are also to be regarded as disclosed, which thus do not have all the features of an originally formulated independent claim.
Ausführungsbeispiele der Erfindung werden nachfolgend anhand schematischer Zeichnungen näher erläutert.Embodiments of the invention are explained in more detail below with reference to schematic drawings.
Dabei zeigen:Showing:
In
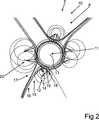
Eine Information
So wird gemäß
Der kraftfahrzeugseitige Sensor
Die Abhängigkeit der zweiten geographischen Position
Ein Startknoten des Graphen wird insbesondere durch das Primärattribut repräsentiert, während ein Zielknoten des Graphen durch ein Sekundärattribut der Attribute repräsentiert wird. Somit kann eine kreisfreie beziehungsweise zyklenfreie und gerichtete Abhängigkeit von Attributen, wie beispielsweise der ersten geographischen Position
Gemäß
Gemäß dem Ausführungsbeispiel werden die Attribute der Information
Weiterhin kann durch den kreisfreien gerichteten Graphen eine Berücksichtigung von dynamisch vielen Sekundärattributen für jedes Objekt
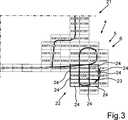
Durch das Unterteilen des Umgebungsbereichs
Die adaptive Unterteilung von Arealen beziehungsweise des Umgebungsbereichs
Durch die adaptive Unterteilung wird insbesondere eine parallele Verarbeitung und dadurch eine effektivere Verarbeitung der Information
ZITATE ENTHALTEN IN DER BESCHREIBUNG QUOTES INCLUDE IN THE DESCRIPTION
Diese Liste der vom Anmelder aufgeführten Dokumente wurde automatisiert erzeugt und ist ausschließlich zur besseren Information des Lesers aufgenommen. Die Liste ist nicht Bestandteil der deutschen Patent- bzw. Gebrauchsmusteranmeldung. Das DPMA übernimmt keinerlei Haftung für etwaige Fehler oder Auslassungen.This list of the documents listed by the applicant has been generated automatically and is included solely for the better information of the reader. The list is not part of the German patent or utility model application. The DPMA assumes no liability for any errors or omissions.
Zitierte PatentliteraturCited patent literature
- DE 102013205392 A1[0002]DE 102013205392 A1[0002]
Claims (10)
Translated fromGermanPriority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102015001247.9ADE102015001247A1 (en) | 2015-01-31 | 2015-01-31 | Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding area of a motor vehicle and system |
| US15/521,545US9983307B2 (en) | 2015-01-31 | 2016-01-20 | Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding region of a motor vehicle and system |
| CN201680003236.8ACN107077784B (en) | 2015-01-31 | 2016-01-20 | Method and system for providing information on at least one object in an environmental region of a motor vehicle |
| PCT/EP2016/000091WO2016120001A1 (en) | 2015-01-31 | 2016-01-20 | Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding region of a motor vehicle and system |
| EP16701725.0AEP3158295B1 (en) | 2015-01-31 | 2016-01-20 | Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding region of a motor vehicle and system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102015001247.9ADE102015001247A1 (en) | 2015-01-31 | 2015-01-31 | Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding area of a motor vehicle and system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| DE102015001247A1true DE102015001247A1 (en) | 2016-08-04 |
Family
ID=55237624
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102015001247.9AWithdrawnDE102015001247A1 (en) | 2015-01-31 | 2015-01-31 | Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding area of a motor vehicle and system |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9983307B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP3158295B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN107077784B (en) |
| DE (1) | DE102015001247A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2016120001A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6321532B2 (en)* | 2014-11-28 | 2018-05-09 | 株式会社デンソー | Vehicle travel control device |
| US11144855B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2021-10-12 | Conduent Business Services, Llc | System and method for managing coverage of parking enforcement for a neighborhood with the aid of a digital computer |
| US10817814B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2020-10-27 | Conduent Business Services, Llc | System and method for coordinating parking enforcement officer patrol in real time with the aid of a digital computer |
| US11062241B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2021-07-13 | Conduent Business Services, Llc | System and method for facilitating parking enforcement officer dispatching in real time with the aid of a digital computer |
| US11120375B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2021-09-14 | Conduent Business Services, Llc | System and method for monitoring parking enforcement officer performance in real time with the aid of a digital computer |
| US11151494B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2021-10-19 | Palo Alto Research Center Incorporated | System and method for visualizing parking enforcement officer movement in real time with the aid of a digital computer |
| US11126942B2 (en)* | 2016-08-26 | 2021-09-21 | Conduent Business Services, Llc | System and method for facilitating parking enforcement officer performance in real time with the aid of a digital computer |
| US11157860B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2021-10-26 | Conduent Business Services, Llc | System and method for motivating parking enforcement officer performance with the aid of a digital computer |
| US11068813B2 (en) | 2016-08-26 | 2021-07-20 | Palo Alto Research Center Incorporated | System and method for providing conditional autonomous messaging to parking enforcement officers with the aid of a digital computer |
| DE102018108538B4 (en)* | 2018-04-11 | 2024-07-18 | Audi Ag | Procedure for determining traffic information |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102009008745A1 (en)* | 2009-02-12 | 2010-08-19 | Volkswagen Ag | Method for automatic traffic routing of motor vehicle, involves transmitting traffic routing data from surrounding field model to corresponding road user for traffic routing by central control unit |
| DE102013001308A1 (en)* | 2013-01-26 | 2014-07-31 | Audi Ag | Method and navigation device for providing information about a parking space |
| DE102013205392A1 (en) | 2013-03-27 | 2014-10-02 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Backend for driver assistance systems |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7899616B2 (en)* | 1997-10-22 | 2011-03-01 | Intelligent Technologies International, Inc. | Method for obtaining information about objects outside of a vehicle |
| US6385539B1 (en)* | 1999-08-13 | 2002-05-07 | Daimlerchrysler Ag | Method and system for autonomously developing or augmenting geographical databases by mining uncoordinated probe data |
| JP2006507483A (en)* | 2002-09-20 | 2006-03-02 | エム7 ビジュアル インテリジェンス,エルピー | Data collection and processing system by mobile body |
| CA2531662C (en)* | 2003-07-07 | 2016-04-26 | Sensomatix Ltd. | Traffic information system |
| DE102006052482A1 (en) | 2006-11-07 | 2008-05-08 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Method for updating a database |
| DE102008012654A1 (en) | 2007-08-29 | 2009-03-05 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Online creation of a digital map |
| US8294594B2 (en)* | 2008-03-10 | 2012-10-23 | Nissan North America, Inc. | On-board vehicle warning system and vehicle driver warning method |
| US20100082564A1 (en)* | 2008-10-01 | 2010-04-01 | Navteq North America, Llc | Spatial Index for Locating Geographic Data Parcels Stored on Physical Storage Media |
| WO2010129192A1 (en)* | 2009-05-04 | 2010-11-11 | Tele Atlas North America Inc. | Methods and systems for creating digital transportation networks |
| JP5661782B2 (en) | 2009-10-22 | 2015-01-28 | トムトム ジャーマニー ゲーエムベーハー ウント コー. カーゲーTomtom Germany Gmbh & Co. Kg | Additional map generation, refinement and expansion using GPS trajectories |
| WO2011127226A1 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2011-10-13 | Tomtom North America, Inc. | A method of resolving a location from data representative thereof |
| US8618951B2 (en)* | 2010-09-17 | 2013-12-31 | Honda Motor Co., Ltd. | Traffic control database and distribution system |
| US9140792B2 (en)* | 2011-06-01 | 2015-09-22 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | System and method for sensor based environmental model construction |
| CN102706291B (en)* | 2012-05-18 | 2014-12-24 | 长安大学 | Method for automatically measuring road curvature radius |
| JP6027365B2 (en)* | 2012-07-30 | 2016-11-16 | 富士通テン株式会社 | Radar apparatus, vehicle control system, and signal processing method |
| JP2013011612A (en)* | 2012-08-31 | 2013-01-17 | Yupiteru Corp | Target object notification device, and program |
| SE537621C2 (en)* | 2013-09-10 | 2015-08-11 | Scania Cv Ab | Detection of objects using a 3D camera and a radar |
| CA2891051C (en)* | 2014-01-06 | 2016-05-10 | Geodigital International Inc. | Determining portions of a roadway model requiring updating |
| US9721471B2 (en)* | 2014-12-16 | 2017-08-01 | Here Global B.V. | Learning lanes from radar data |
- 2015
- 2015-01-31DEDE102015001247.9Apatent/DE102015001247A1/ennot_activeWithdrawn
- 2016
- 2016-01-20WOPCT/EP2016/000091patent/WO2016120001A1/enactiveApplication Filing
- 2016-01-20EPEP16701725.0Apatent/EP3158295B1/enactiveActive
- 2016-01-20CNCN201680003236.8Apatent/CN107077784B/enactiveActive
- 2016-01-20USUS15/521,545patent/US9983307B2/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102009008745A1 (en)* | 2009-02-12 | 2010-08-19 | Volkswagen Ag | Method for automatic traffic routing of motor vehicle, involves transmitting traffic routing data from surrounding field model to corresponding road user for traffic routing by central control unit |
| DE102013001308A1 (en)* | 2013-01-26 | 2014-07-31 | Audi Ag | Method and navigation device for providing information about a parking space |
| DE102013205392A1 (en) | 2013-03-27 | 2014-10-02 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Backend for driver assistance systems |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3158295B1 (en) | 2017-10-04 |
| US20170307754A1 (en) | 2017-10-26 |
| EP3158295A1 (en) | 2017-04-26 |
| US9983307B2 (en) | 2018-05-29 |
| CN107077784A (en) | 2017-08-18 |
| CN107077784B (en) | 2020-08-14 |
| WO2016120001A1 (en) | 2016-08-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3158295B1 (en) | Method for providing information about at least one object in a surrounding region of a motor vehicle and system | |
| DE102010006828B4 (en) | Method for the automatic creation of a model of the surroundings of a vehicle as well as driver assistance system and vehicle | |
| DE102013208521B4 (en) | Collective learning of a highly accurate road model | |
| EP3385673B1 (en) | Method and device for the reducing the number of intermediate nodes in a route | |
| EP3436782B1 (en) | Updating an electronic map | |
| DE102016212587A1 (en) | Method and system for generating map information | |
| DE112016003567T5 (en) | Control method for a moving body, moving body, and a moving body control system | |
| EP2641061B1 (en) | Method for automatically determining a boundary of a partial area of a total area | |
| DE102016213817A1 (en) | A method, apparatus and computer readable storage medium having instructions for determining the lateral position of a vehicle relative to the lanes of a lane | |
| DE102015000399A1 (en) | Mapping of lanes using vehicle fleet data | |
| DE102017208509A1 (en) | Method for generating a road model during a journey of a motor vehicle and control device and motor vehicle | |
| DE102020105250A1 (en) | Determining the course of a lane delimitation | |
| DE102010001700A1 (en) | Method for determination utilization of e.g. roads, for driver of vehicle, has repeating detection of utilization of route section and increase of degree of utilization of route section, where degree of utilization is increased again | |
| DE102019213403A1 (en) | Method for the sensor-based localization of a host vehicle, host vehicle and a computer program | |
| EP3504100B1 (en) | Method for creating a digital track plan for a track system | |
| DE102013217060A1 (en) | Accurate positioning of a vehicle | |
| DE102021214763A1 (en) | Method and control device for controlling an automated vehicle | |
| DE102019204260A1 (en) | Controlling a motor vehicle | |
| DE102017011982A1 (en) | Method for route forecasting | |
| DE102021006166A1 (en) | Procedure for data transfer between two digital road maps | |
| DE102021207528A1 (en) | Detection of connection patterns based on trajectory data | |
| DE102018210681A1 (en) | Process for optimizing map data | |
| DE102018115895A1 (en) | Obstacle detection method and system | |
| DE102022003749A1 (en) | Method for determining lanes for vehicles, in particular for creating a digital map | |
| DE102024201714A1 (en) | Method for creating a digital map of the surroundings of a vehicle using a mapping system, and mapping system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| R012 | Request for examination validly filed | ||
| R016 | Response to examination communication | ||
| R120 | Application withdrawn or ip right abandoned |