DE102010044551A1 - Anode and their use in an alkaline electroplating bath - Google Patents
Anode and their use in an alkaline electroplating bathDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- DE102010044551A1 DE102010044551A1DE201010044551DE102010044551ADE102010044551A1DE 102010044551 A1DE102010044551 A1DE 102010044551A1DE 201010044551DE201010044551DE 201010044551DE 102010044551 ADE102010044551 ADE 102010044551ADE 102010044551 A1DE102010044551 A1DE 102010044551A1
- Authority
- DE
- Germany
- Prior art keywords
- anode
- exchange membrane
- zinc
- anolyte
- anion exchange
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
- 238000009713electroplatingMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription15
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium hydroxideChemical compound[OH-].[Na+]HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsabstractdescription91
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription60
- 239000011701zincSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription20
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-NZincChemical group[Zn]HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 229910052725zincInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 229910000831SteelInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 239000010959steelSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 229910001297Zn alloyInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-MPotassium hydroxideChemical compound[OH-].[K+]KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 230000008021depositionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 239000003011anion exchange membraneSubstances0.000claimsdescription28
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-NNickelChemical compound[Ni]PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription14
- 239000004033plasticSubstances0.000claimsdescription14
- 239000003014ion exchange membraneSubstances0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000012670alkaline solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000000151depositionMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 229910052759nickelInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000004696Poly ether ether ketoneSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000004744fabricSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 229920002530polyetherether ketonePolymers0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000007747platingMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- QELJHCBNGDEXLD-UHFFFAOYSA-Nnickel zincChemical compound[Ni].[Zn]QELJHCBNGDEXLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description29
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000description28
- 235000011121sodium hydroxideNutrition0.000description28
- 210000004379membraneAnatomy0.000description23
- XFXPMWWXUTWYJX-UHFFFAOYSA-NCyanideChemical compoundN#[C-]XFXPMWWXUTWYJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description12
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description12
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-NSulfuric acidChemical compoundOS(O)(=O)=OQAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description11
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description9
- 238000005341cation exchangeMethods0.000description6
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description6
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description6
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description6
- 239000011734sodiumSubstances0.000description6
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description5
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description5
- 238000010790dilutionMethods0.000description5
- 239000012895dilutionSubstances0.000description5
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description5
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description5
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-LSodium CarbonateChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=OCDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description4
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-LSulfateChemical compound[O-]S([O-])(=O)=OQAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description4
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description4
- -1hydroxide ionsChemical class0.000description4
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description4
- 230000003647oxidationEffects0.000description4
- 238000007254oxidation reactionMethods0.000description4
- 230000001681protective effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000000354decomposition reactionMethods0.000description3
- 230000018044dehydrationEffects0.000description3
- 238000006297dehydration reactionMethods0.000description3
- 238000001465metallisationMethods0.000description3
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description3
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description3
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-LCarbonateChemical compound[O-]C([O-])=OBVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description2
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-NTitaniumChemical compound[Ti]RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000002253acidSubstances0.000description2
- 150000001450anionsChemical class0.000description2
- 239000010405anode materialSubstances0.000description2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncarbonic acidChemical compoundOC(O)=OBVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description2
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description2
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description2
- 239000007857degradation productSubstances0.000description2
- 238000011038discontinuous diafiltration by volume reductionMethods0.000description2
- 238000004070electrodepositionMethods0.000description2
- 238000005246galvanizingMethods0.000description2
- LELOWRISYMNNSU-UHFFFAOYSA-Nhydrogen cyanideChemical compoundN#CLELOWRISYMNNSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 238000006386neutralization reactionMethods0.000description2
- 230000003204osmotic effectEffects0.000description2
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description2
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000003973paintSubstances0.000description2
- 229920001643poly(ether ketone)Polymers0.000description2
- 230000008929regenerationEffects0.000description2
- 238000011069regeneration methodMethods0.000description2
- 229910000029sodium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description2
- BUHVIAUBTBOHAG-FOYDDCNASA-N(2r,3r,4s,5r)-2-[6-[[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(2-methylphenyl)ethyl]amino]purin-9-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diolChemical compoundCOC1=CC(OC)=CC(C(CNC=2C=3N=CN(C=3N=CN=2)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)C=2C(=CC=CC=2)C)=C1BUHVIAUBTBOHAG-FOYDDCNASA-N0.000description1
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-NCalciumChemical compound[Ca]OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910000990Ni alloyInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000004743PolypropyleneSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003513alkaliSubstances0.000description1
- 229910045601alloyInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000000956alloySubstances0.000description1
- 150000001412aminesChemical class0.000description1
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description1
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-Lcalcium carbonateSubstances[Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=OVTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 229910000019calcium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000000969carrierSubstances0.000description1
- 239000008139complexing agentSubstances0.000description1
- 239000012141concentrateSubstances0.000description1
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000description1
- 238000012937correctionMethods0.000description1
- 238000007405data analysisMethods0.000description1
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000description1
- 238000007872degassingMethods0.000description1
- 230000001419dependent effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000006866deteriorationEffects0.000description1
- 238000004512die castingMethods0.000description1
- 238000003618dip coatingMethods0.000description1
- 238000005265energy consumptionMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 230000002349favourable effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000011049fillingMethods0.000description1
- 238000011086high cleaningMethods0.000description1
- 239000001257hydrogenSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052739hydrogenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 125000004435hydrogen atomChemical class[H]*0.000description1
- 230000007062hydrolysisEffects0.000description1
- 238000006460hydrolysis reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000002401inhibitory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000977initiatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000002452interceptive effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000009533lab testMethods0.000description1
- 230000000670limiting effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description1
- ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-Lmagnesium carbonateChemical compound[Mg+2].[O-]C([O-])=OZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 239000001095magnesium carbonateSubstances0.000description1
- 229910000021magnesium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 235000019341magnesium sulphateNutrition0.000description1
- 230000008018meltingEffects0.000description1
- 238000002844meltingMethods0.000description1
- LGQLOGILCSXPEA-UHFFFAOYSA-Lnickel sulfateChemical compound[Ni+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=OLGQLOGILCSXPEA-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 229910000363nickel(II) sulfateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000006259organic additiveSubstances0.000description1
- 150000002894organic compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000006864oxidative decomposition reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000007591painting processMethods0.000description1
- 230000002093peripheral effectEffects0.000description1
- 229920001155polypropylenePolymers0.000description1
- 238000001556precipitationMethods0.000description1
- 230000002829reductive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001105regulatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 150000003839saltsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000000926separation methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000007086side reactionMethods0.000description1
- ZNCPFRVNHGOPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-Lsodium oxalateChemical compound[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)C([O-])=OZNCPFRVNHGOPAG-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 229940039790sodium oxalateDrugs0.000description1
- 239000001117sulphuric acidSubstances0.000description1
- 230000000153supplemental effectEffects0.000description1
- JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-NtellanylidenegermaniumChemical compound[Te]=[Ge]JBQYATWDVHIOAR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229920001169thermoplasticPolymers0.000description1
- 239000004416thermosoftening plasticSubstances0.000description1
- 239000010936titaniumSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052719titaniumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 231100000331toxicToxicity0.000description1
- 230000002588toxic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000012546transferMethods0.000description1
- 238000004065wastewater treatmentMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C25—ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D—PROCESSES FOR THE ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PRODUCTION OF COATINGS; ELECTROFORMING; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D17/00—Constructional parts, or assemblies thereof, of cells for electrolytic coating
- C25D17/02—Tanks; Installations therefor
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C25—ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D—PROCESSES FOR THE ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PRODUCTION OF COATINGS; ELECTROFORMING; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D17/00—Constructional parts, or assemblies thereof, of cells for electrolytic coating
- C25D17/002—Cell separation, e.g. membranes, diaphragms
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C25—ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D—PROCESSES FOR THE ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PRODUCTION OF COATINGS; ELECTROFORMING; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D17/00—Constructional parts, or assemblies thereof, of cells for electrolytic coating
- C25D17/10—Electrodes, e.g. composition, counter electrode
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C25—ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D—PROCESSES FOR THE ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PRODUCTION OF COATINGS; ELECTROFORMING; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D3/00—Electroplating: Baths therefor
- C25D3/02—Electroplating: Baths therefor from solutions
- C25D3/22—Electroplating: Baths therefor from solutions of zinc
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C25—ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PROCESSES; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D—PROCESSES FOR THE ELECTROLYTIC OR ELECTROPHORETIC PRODUCTION OF COATINGS; ELECTROFORMING; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C25D3/00—Electroplating: Baths therefor
- C25D3/02—Electroplating: Baths therefor from solutions
- C25D3/56—Electroplating: Baths therefor from solutions of alloys
- C25D3/565—Electroplating: Baths therefor from solutions of alloys containing more than 50% by weight of zinc
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Electrolytic Production Of Metals (AREA)
- Electroplating And Plating Baths Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromGermanDescription
Translated fromGermanDie Erfindung betrifft eine Anode sowie deren Verwendung in einem alkalischen Galvanikbad. Diese Anode ist in der galvanotechnischen Anwendung für den Einsatz in stark alkalischen, galvanischen Elektrolyten auf Basis von Natriumhydroxid oder Kaliumhydroxid zum Abscheiden von Zink und Zinklegierungen auf Substraten von Stahl und Zink-Druckguss geeignet.The invention relates to an anode and its use in an alkaline electroplating bath. This anode is suitable in electroplating applications for use in strongly alkaline, galvanic electrolytes based on sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide for the deposition of zinc and zinc alloys on substrates of steel and zinc die-casting.
Nach dem Stand der Technik werden in der Funktion ähnliche Membrananoden auf dem Gebiet der kataphoretischen Tauchlackierung eingesetzt, um störende Anionen, die während des elektrophoretischen Lackierprozesses im wasserbasierten Lackierbad entstehen, über spezielle Anionenaustauschmembranen in einen verdünnten Säureanolyten zu überführen und somit aus dem Lackierbad zu entfernen.According to the state of the art, similar membrane anodes are used in the field of cataphoretic dip coating in order to transfer interfering anions, which are formed during the electrophoretic painting process in the water-based paint bath, via special anion exchange membranes into a dilute acid anolyte and thus to remove it from the paint bath.
Das Funktionsprinzip der Anionenaustauschmembran bei der Anwendung in der Galvanotechnik zur Metallabscheidung ist analog zu betrachten, jedoch müssen Besonderheiten wie:
- – Art der Membran
- – Querschnitte der stromleitenden Teile
- – chemische Beständigkeit der Materialien
- - Type of membrane
- - Cross sections of the current-conducting parts
- - chemical resistance of the materials
Stand der Technik ist weiterhin, in alkalischen Verzinkungselektrolyten am häufigsten Anoden aus Stahl, Edelstahl oder vernickeltem Stahl einzusetzen. Dabei werden verschiedene geometrische Formen gewählt, z. B. Platten in rechteckiger Form, Streckmetall in Rechteckform oder zylindrischer Form, Rundstäbe, Rohre und andere.The state of the art continues to be the most common use of anodes made of steel, stainless steel or nickel-plated steel in alkaline galvanizing electrolytes. In this case, different geometric shapes are chosen, for. As plates in rectangular shape, expanded metal in a rectangular or cylindrical shape, rods, tubes and others.
Stark alkalische galvanische Verzinkungselektrolyte neigen, je nach Elektrolytzusammensetzung, nach relativ kurzer Betriebszeit von einigen Wochen zu teilweise starken Ablagerungen auf den Anodenoberflächen. Das hat den Nachteil der allmählichen Verschlechterung der kathodischen Stromausbeute und somit der Effizienz des galvanischen Prozesses sowie der galvanischen Anlage. Die Kosten an Elektroenergie pro beschichteter Oberflächengröße steigen an.Strongly alkaline galvanic electrolytic electrolytes tend, depending on the electrolyte composition, after a relatively short operating time of a few weeks to partially strong deposits on the anode surfaces. This has the disadvantage of the gradual deterioration of the cathodic current efficiency and thus the efficiency of the galvanic process and the galvanic plant. The cost of electrical energy per coated surface area increases.
Diese Ablagerungen bestehen bei Natriumhydroxid basierten Elektrolyten zu großen Anteilen aus Natriumkarbonat und Natriumoxalat infolge der Oxidation an der Anodenoberfläche. Zusätzlich verändern organische Abbauprodukte die Ausgangseigenschaften der galvanischen Elektrolyte.These deposits are large proportions of sodium carbonate and sodium oxalate due to oxidation at the anode surface in sodium hydroxide based electrolytes. In addition, organic degradation products alter the initial properties of the galvanic electrolytes.
Ein regelmäßiger, teilweise hoher Reinigungsaufwand an den Anoden sowie den Behältern ist notwendig. Der Karbonatgehalt solcher Elektrolyte muss oft mit Kristallisatoren unter zusätzlichem Elektroenergieverbrauch gesenkt werden. Alternativ werden die galvanischen Bäder neu angesetzt. Die verbrauchten Elektrolyte werden entsorgt und erzeugen zusätzliche Chemikalien-, Entsorgungs- und Abwasserbehandlungskosten sowie Anlagenausfallzeiten.A regular, sometimes high cleaning effort on the anodes and the containers is necessary. The carbonate content of such electrolytes often has to be lowered with crystallizers with additional electric energy consumption. Alternatively, the galvanic baths are recalculated. The spent electrolytes are disposed of and generate additional chemicals, disposal and wastewater treatment costs, as well as equipment downtime.
Die in der
- – platiniertes Titan als Anodenwerkstoff
- – perfluorierte Kationenaustauscher-Membran sehr kostenintensiv in der Beschaffung und werden deshalb auch ausschließlich für alkalische Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyte verwendet. Der Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyt (Katholyt) wird hierbei durch eine Kationenaustauscher-Membran von der Anode getrennt. Als Anolyt wird verdünnte Schwefelsäure verwendet.
- - Platinized titanium as the anode material
- - Perfluorinated cation exchange membrane very costly in the procurement and are therefore used exclusively for alkaline zinc-nickel electrolytes. The zinc-nickel electrolyte (catholyte) is separated from the anode by a cation exchange membrane. The anolyte used is dilute sulfuric acid.
Als Nachteile der großtechnischen Anwendung der
- a. Verdünnung des Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten während des galvanischen Prozesses infolge Neutralisation des Natriumhydroxides durch Protonen des Schwefelsäure-Anolyten, die über die Kationenaustauscher-Membran „transportiert” werden und mit Hydroxidionen zu Wasser reagieren:
H+Anolyt + OH–Katholyt → H2OKatholyt - b. Volumenanstieg des Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten: Die in Punkt a) beschriebene Verdünnung und die daraus resultierende, notwendige Zugabe von Natriumhydroxid zur Wiederherstellung der für die Legierungsabscheidung erforderlichen Natriumhydroxidkonzentration im Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten führt zu einem kontinuierlichen Volumenanstieg des Elektrolyten. Durch Wassertransport vom Schwefelsäure-Anolyten über die Kationenaustauschmembran in den Katholyten (Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten) infolge osmotischer Druckunterschiede wird dieser Effekt verstärkt.
- c. Aus a) und b) folgend wird ein zusätzlicher, erheblicher technischer und energetischer Aufwand betrieben, um den permanent entstehenden, schwach verdünnten Elektrolyt-Volumenüberhang mittels Vakuumverdampfer aufzukonzentrieren und diskontinuierlich wieder in den Prozess zurückzuführen.
- a. Dilution of the zinc-nickel electrolyte during the galvanic process due to neutralization of the sodium hydroxide by protons of the sulfuric acid anolyte, which are "transported" through the cation exchange membrane and react with hydroxide ions to form water:
H+anolyte + OH-catholyte → H2 Ocatholyte - b. Volume increase of the zinc-nickel electrolyte: The dilution described in point a) and the resulting necessary addition of sodium hydroxide to restore the sodium hydroxide concentration in the zinc-nickel electrolyte required for the alloy deposition leads to a continuous increase in the volume of the electrolyte. Water transport from the sulfuric acid anolyte via the cation exchange membrane into the catholyte (zinc-nickel electrolyte) due to osmotic pressure differences enhances this effect.
- c. From a) and b) following, an additional, considerable technical and energetic effort is operated to concentrate the permanently formed, weakly diluted electrolyte volume excess by means of a vacuum evaporator and discontinuously fed back into the process.
Ausgehend hiervon ist es Aufgabe der Erfindung, eine kostengünstige Anode zur Verfügung zu stellen, die in stark alkalischen Elektrolyten die Bildung von Abbauprodukten minimiert, gebrauchte, mit herkömmlichen Anoden betriebene Zinkelektrolyte regeneriert und leistungsfähiger macht sowie neu angesetzte Elektrolyte auf konstant hohem Leistungsniveau hält.Proceeding from this, it is the object of the invention to provide a low-cost anode which minimizes the formation of decomposition products in strongly alkaline electrolytes, regenerates used zinc electrolytes operated with conventional anodes and makes them more efficient, and keeps new electrolytes at a constantly high level of performance.
Diese Aufgabe wird durch die Anode mit den Merkmalen des Anspruchs 1 gelöst. Anspruch 11 betrifft ein alkalisches Galvanikbad und Anspruch 15 die Verwendung der Anode. Weitere vorteilhafte Ausführungsformen sind in den abhängigen Ansprüchen enthalten.This object is achieved by the anode with the features of
Erfindungsgemäß wird eine Anode mit Ionenaustauschermembran für ein alkalisches Galvanikbad zur Abscheidung von Zink und/oder Zinklegierungen vorgeschlagen, wobei die Anode zumindest bereichsweise von der Ionenaustauschermembran umgeben ist, durch die die Anode von einem alkalischen Elektrolyten und der Kathode trennbar ist. Die erfindungsgemäße Anode zeichnet sich dadurch aus, dass die Ionenaustauschermembran eine Anionenaustauschermembran ist.According to the invention, an anode with an ion exchange membrane for an alkaline electroplating bath for depositing zinc and / or zinc alloys is proposed, wherein the anode is at least partially surrounded by the ion exchange membrane, by which the anode is separable from an alkaline electrolyte and the cathode. The anode according to the invention is characterized in that the ion exchange membrane is an anion exchange membrane.
Durch eine Anionenaustauschmembran wird der galvanische Zinkelektrolyt von der Anode getrennt, um unerwünschte Nebenreaktionen wie Oxidation der organischen Zusätze mit Bildung von Ablagerungen auf den Anodenoberflächen zu verhindern.An anion exchange membrane separates the galvanic zinc electrolyte from the anode to prevent undesired side reactions such as oxidation of the organic additives with formation of deposits on the anode surfaces.
Gealterte Elektrolyte, die Abbauprodukte enthalten, können bei Anwendung der erfindungsgemäßen Anode regeneriert und dadurch wieder leistungsfähiger werden. Folglich kann auf diese Weise auch die Standzeit verlängert werden, bevor ein neues Galvanikbad anzusetzen ist.Aged electrolytes containing decomposition products can be regenerated when using the anode according to the invention and thus become more efficient again. Consequently, in this way, the life can be extended before a new galvanic bath is to be set.
Dabei besteht die Anionenaustauschermembran bevorzugt aus Polyetheretherketon oder enthält dieses.In this case, the anion exchange membrane preferably consists of polyetheretherketone or contains this.
Polyetheretherketon gehört zur Gruppe der Polyetherketone. Diese zeichnen sich dadurch aus, dass sie hochtemperaturbeständige thermoplastische Kunststoffe sind. Der wichtigste Vertreter dieser Gruppe ist das Polyetheretherketon, dessen Schmelztemperatur 335°C beträgt. Polyetherketone sind gegen fast alle organischen und anorganischen Chemikalien beständig. Weiterhin sind sie bis etwa 280°C beständig gegen Hydrolyse.Polyetheretherketone belongs to the group of polyetherketones. These are characterized by the fact that they are high temperature resistant thermoplastics. The most important member of this group is the polyetheretherketone, whose melting point is 335 ° C. Polyether ketones are resistant to almost all organic and inorganic chemicals. Furthermore, they are resistant to hydrolysis up to about 280 ° C.
Bevorzugt weist die Anionenaustauschermembran der erfindungsgemäßen Anode eine Dicke von 0,1 mm bis 0,13 mm auf.Preferably, the anion exchange membrane of the anode according to the invention has a thickness of 0.1 mm to 0.13 mm.
Weiterhin weist die Anionenaustauschermembran bevorzugt einen spezifischen Widerstand von < 1 Ω/cm auf.Furthermore, the anion exchange membrane preferably has a specific resistance of <1 Ω / cm.
Eine weitere Variante der Anionenaustauschermembran ist ein mehrschichtiger Aufbau.Another variant of the anion exchange membrane is a multilayer structure.
Die Anode kann aus Stahl, Edelstahl, Nickel und/oder vernickeltem Stahl bestehen oder dieses enthalten. Weiterhin kann auch ein Streckmetall aus den vorgenannten Materialien in zylindrischer Form mit Schraubverschluss und Befestigungsvorrichtung an einer Anodenschiene eingesetzt werden.The anode can be made of steel, stainless steel, nickel and / or nickel-plated steel or contain this. Furthermore, an expanded metal of the aforementioned materials in cylindrical form with screw and fastening device can be used on an anode rail.
Die Anode kann rechteckig, rund, zylinderförmig oder rohrförmig sein. Weiterhin kann die Anode von Kunststoff, insbesondere in Form eines Kunststoffgewebes, Kunststoffwänden oder einem Kunststoffboden umgeben sein. Darüberhinaus kann die Anode starr oder flexibel sein.The anode may be rectangular, round, cylindrical or tubular. Furthermore, the anode may be surrounded by plastic, in particular in the form of a plastic fabric, plastic walls or a plastic floor. Moreover, the anode can be rigid or flexible.
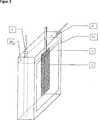
Beispielsweise kann eine runde Anode zylindermantelförmig von einem inneren Stützgitterrohr, einer Anionenaustauschermembran sowie einem Schutzstrumpf, der z. B. aus Kunststoffgewebe bzw. einem Kunststoffgitter besteht, umgeben sein. Dabei sind bevorzugt der Schutzstrumpf, die Anionenaustauschermembran und das innere Stützgitterrohr schichtartig miteinander verbunden.For example, a round anode cylinder jacket of an inner support grid tube, an anion exchange membrane and a protective sock, the z. B. plastic fabric or a Plastic mesh is to be surrounded. In this case, the protective sock, the anion exchange membrane and the inner support grid tube are preferably connected to one another in a layered manner.
In einer kastenförmigen, bevorzugten Ausführungsvariante sind der Anolytzulauf und der Anolytablauf zueinander senkrecht angeordnet, wobei der Anolytzulauf an der Oberseite des Anodenkastens und der Anolytablauf an der Rückseite des Anodenkastens angeordnet ist. Dabei kann die Anode aus Steckmetall sein.In a box-shaped, preferred embodiment variant, the anolyte inlet and the anolyte outlet are arranged perpendicular to one another, the anolyte inlet being arranged on the upper side of the anode box and the anolyte outlet being arranged on the rear side of the anode box. In this case, the anode may be made of plug metal.
Gemäß einer weiteren Variante ist es bevorzugt, dass die Anode gewinkelt aufgebaut ist. Im Falle einer rohrförmigen, gewinkelten Variante kann die Anode beispielsweise als Spirale, die gegebenenfalls flexible ist, ausgeführt sein.According to a further variant, it is preferred that the anode is constructed angled. In the case of a tubular, angled variant, the anode may be designed, for example, as a spiral, which may be flexible.
Weiterhin verfügt jede in einem galvanischen Elektrolyten eingesetzte Anode bevorzugt über je einen Anolytzulauf und einen Anolytrücklauf, so dass alle Anoden über die gleichen Funktions- und Reaktionsbedingungen verfügen.Furthermore, each anode used in a galvanic electrolyte preferably has in each case one anolyte feed and one anolyte return, so that all the anodes have the same functional and reaction conditions.
Bei der Anwendung von Zink-Nickel-Legierungs-Elektrolyten hat sich teilweise der Einsatz von speziellen Anoden auf der Grundlage der
Anders als bei Anwendung von Kationenaustausch-Membrananoden, wie in der
Erfindungsgemäß ist ein alkalisches Galvanikbad zur Abscheidung von Zink und/oder Zinklegierung mit einer Anode und einer Kathode vorgesehen, wobei die Anode von einem alkalischen Elektrolyten durch eine Ionenaustauschermembran getrennt ist. Erfindungsgemäß ist die Ionenaustauschermembran dabei eine Anionenaustauschermembran.According to the invention, an alkaline electroplating bath is provided for depositing zinc and / or zinc alloy with an anode and a cathode, wherein the anode is separated from an alkaline electrolyte by an ion exchange membrane. According to the invention, the ion exchange membrane is an anion exchange membrane.
Bevorzugt enthält das Galvanikbad eine alkalische Lösung als Anolyt. Dies hat den Vorteil, dass, im Fall von Membrandefekten, keine Säure den alkalischen Zink- oder Zinklegierungselektrolyten neutralisiert und im Extremfall unbrauchbar macht.The electroplating bath preferably contains an alkaline solution as anolyte. This has the advantage that, in the case of membrane defects, no acid neutralizes the alkaline zinc or zinc alloy electrolyte and, in extreme cases, renders it unusable.
Als Membran wird für diese Erfindung bevorzugt eine alkalibeständige Anionenaustauschmembran verwendet.As the membrane, an alkali-resistant anion exchange membrane is preferably used for this invention.
Bevorzugt ist die alkalische Lösung im Galvanikbad eine Natriumhydroxidlösung und/oder eine Kaliumhydroxidlösung.Preferably, the alkaline solution in the electroplating bath is a sodium hydroxide solution and / or a potassium hydroxide solution.
Dabei ist es bevorzugt, dass die alkalische Lösung einen pH-Wert im Bereich von 10 bis > 14 aufweist.It is preferred that the alkaline solution has a pH in the range of 10 to> 14.
Wird in der erfindungsgemäßen Anode die Anionenaustauschmembran durch eine Kationenaustauschmembran ersetzt und Schwefelsäure als Anolyt verwendet, kann die Regenerationsfunktion für bisher konventionell genutzte Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyte nicht erfüllt werden, da durch den Kontakt von Protonen aus dem Anolyt (Schwefelsäure) mit Cyanid-Ionen aus dem Katholyt (Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyt) an der Membran-Kathodenseite die Gefahr der Bildung von hochgiftiger Blausäure gegeben ist.If in the anode of the invention, the anion exchange membrane replaced by a cation exchange membrane and sulfuric acid used as the anolyte, the regeneration function for previously conventionally used zinc-nickel electrolytes can not be met, as by the contact of protons from the anolyte (sulfuric acid) with cyanide ions the catholyte (zinc-nickel electrolyte) on the membrane cathode side the risk of the formation of highly toxic hydrogen cyanide is given.
Erfindungsgemäß ist auch die Verwendung der beschriebenen Anode in einem Galvanikbad.The use of the described anode in a galvanic bath is also according to the invention.
Die bei der galvanischen Metallabscheidung an der Kathode verbrauchte negative Ladungsmenge entspricht der äquivalenten positiven Ladungsmenge, die in Form von einfach positiv geladenen Hydroxidionen an der Anode verbraucht werden und dabei Wasser und Sauerstoff bilden.The amount of negative charge consumed in the electrodeposition at the cathode corresponds to the equivalent amount of positive charge consumed in the form of simply positively charged hydroxide ions at the anode, thereby forming water and oxygen.
Anode:Anode:
4OH– – 4e → 2H2O + O2 (I)4OH- - 4e → 2H2 O + O2 (I)
Kathode: Cathode:
Zn2+ + 2e → 2Zn (Metallabscheidung) (II)Zn2+ + 2e → 2Zn (metal deposition) (II) 2H+ + 2e → H2 (Wasserstoffabscheidung) (III)2H+ + 2e → H2 (hydrogen separation) (III)
Die Reaktion (III) als Co-Reaktion zur Metallabscheidung (II) ist bei Verwendung von Membrananoden stark gebremst.The reaction (III) as co-reaction to the metal deposition (II) is greatly slowed down when using membrane anodes.
Daraus ergibt sich, dass ein gleichmäßiger Verbrauch von Hydroxidionen im Zink bzw. Zinklegierungselektrolyten sowie im Anolyten erfolgt, der mit Volumenverringerung einhergeht. Die Volumenverringerung wird im galvanischen Praxisbetrieb durch die notwendigen Ergänzungschemikalien teilweise kompensiert und je nach Volumenausschleppung mit der galvanisierten Ware und deren Warenträgern wird nach Erfordernis zusätzlich mit Wasser aufgefüllt.It follows that a uniform consumption of hydroxide ions takes place in the zinc or zinc alloy electrolyte and in the anolyte, which is accompanied by volume reduction. The volume reduction is partially compensated in the galvanic practice by the necessary supplemental chemicals and depending on volume carryover with the galvanized goods and their goods carriers is additionally filled with water if required.
Es wird somit kein kontinuierlicher Volumenzuwachs im galvanischen Elektrolyten infolge von Verdünnungseffekten erzeugt.Thus, no continuous increase in volume in the galvanic electrolyte due to dilution effects is produced.
Osmoseeffekte durch Wasserentzug aus dem Anolyten während Anlagenstillstandszeiten werden verhindert, indem der Anolyt auf eine höhere Natriumhydroxidkonzentration eingestellt wird als der Katholyt (Zinkelektrolyt).Osmosis effects from dehydration from the anolyte during plant downtime are prevented by adjusting the anolyte to a higher sodium hydroxide concentration than the catholyte (zinc electrolyte).
Aus den Labor- und Pilotversuchen hat sich bei einem Natriumhydroxidgehalt von 120 g/l im Zinkelektrolyten, eine Natriumhydroxidkonzentration von 150–160 g/l im Anolyten als günstig erwiesen.From the laboratory and pilot experiments, a sodium hydroxide concentration of 150-160 g / l in the anolyte was found to be favorable at a sodium hydroxide content of 120 g / l in the zinc electrolyte.
Bei zu hoher Konzentration von Natriumhydroxid im Anolyten erfolgt im stromlosen Zustand Osmose in entgegengesetzter Richtung, d. h. Verdünnung des Anolyten durch Wasser aus dem Katholyten mit Volumenanstieg des Anolyten bis zum Ausgleich der Ionenaktivitäten von Anolyt und Katholyt.At too high a concentration of sodium hydroxide in the anolyte in the de-energized state osmosis takes place in the opposite direction, d. H. Dilution of the anolyte by water from the catholyte with volume increase of the anolyte to balance the ionic activities of anolyte and catholyte.
Dieser Zustand ist unkritisch, da der Volumenzuwachs im Anolyten in den Katholyten zurückgeführt werden kann (in der Praxis hingegen kann der Anolyt aus den Membrananoden „überlaufen”).This condition is uncritical, since the volume increase in the anolyte can be traced back to the catholyte (in practice, however, the anolyte can "overflow" from the membrane anodes).
Die Volumenbilanz von Anolyt und Katholyt bleibt dabei ausgeglichen.The volume balance of anolyte and catholyte remains balanced.
Die Verwendung von Membrananoden mit Anionenaustauschmembran in gebrauchten Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten ermöglicht eine Regenerierung derselben, indem Cyanid-Ionen, die bei konventionellem Betreiben von Zink-Nickel-Bädern (ohne Membrantechnik) durch chemische Umsetzung an der Anode gebildet werden und die kathodische Stromausbeute senken, auf Grund ihrer negativen elektrischen Ladung in den Anolyten gelangen und mit diesem gezielt entsorgt werden können.The use of membrane anodes with anion exchange membrane in used zinc-nickel electrolytes enables regeneration thereof by cyanide ions formed by conventional zinc-nickel baths (without membrane technology) by chemical reaction at the anode and lowering the cathodic current efficiency , due to their negative electrical charge in the anolyte and can be disposed of with this targeted.
Weiterhin werden, wenn auch in geringem Umfang, Karbonat- und Sulfationen, welche ebenfalls den galvanischen Abscheideprozess verlangsamen, aus dem Zink- bzw. Zinklegierungselektrolyten über die Anionenaustauschmembran in den Anolyten überführt und können systematisch entfernt werden.Furthermore, although to a lesser extent, carbonate and sulfate ions, which also slow the electrodeposition process, are transferred from the zinc or zinc alloy electrolyte via the anion exchange membrane to the anolyte and can be systematically removed.
Anhand der folgenden
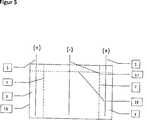
In
In
In
In
Beispiel 1:Example 1:
Technische Voraussetzungen:Technical requirements:
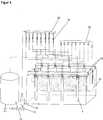
- Versuchsanordnung: siehe
5 Experimental arrangement: see5
Labor-Membran-Anode:
Versuchsdurchführung:Experimental procedure:
- a) Der Zink-Nickelelektrolyt wurde mit 30 Ah/l belastet, d. h. drei Tage ca. je 8 Stunden mit der beschriebenen Strombelastung.a) The zinc-nickel electrolyte was loaded with 30 Ah / l, i. H. three days approx. 8 hours each with the described current load.
- b) Die chemische Zusammensetzung hinsichtlich Natriumhydroxid (NaOH), Nickel (Ni), Zink (Zn) wurde regelmäßig analytisch überprüft und durch Zugaben von Nickellösung, Natronlauge sowie Auflösen von Zinkmetall konstant gehalten.b) The chemical composition with regard to sodium hydroxide (NaOH), nickel (Ni), zinc (Zn) was regularly checked analytically and kept constant by adding nickel solution, sodium hydroxide and dissolving zinc metal.
- c) Die Kathodenbleche wurden im Zyklus von einer Stunde entnommen und die Schichtdicke der Zink-Nickel-Schicht vermessen.c) The cathode sheets were removed in the cycle of one hour and measured the layer thickness of the zinc-nickel layer.
Versuchsergebnisse: Test results:
- a) Zu Beginn der Versuche wurde auf dem Kathodenblech eine durchschnittliche abgeschiedene Schichtdicke von 9 μm gemessen. Das entspricht einer kathodischen Stromausbeute von ca. 30%.a) At the beginning of the experiments, an average deposited layer thickness of 9 μm was measured on the cathode plate. This corresponds to a cathodic current efficiency of approx. 30%.
- b) Nach einer Strombelastung des Elektrolyten von ca. 20 Ah/l wurde eine Farbveränderung von braun nach weinrot beobachtet. Dies deutete qualitativ darauf hin, dass durch den Galvanisierprozess keine neuen Abbauprodukte durch anodische Oxidation entstehen konnten. Zum Vergleich: Ein neu angesetzter Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyt ist von violetter Farbe und zeigt nach geringer Strombelastung eine weinrote Färbung.b) After a current load of the electrolyte of about 20 Ah / l, a color change from brown to burgundy was observed. This indicated qualitatively that the plating process did not lead to any new decomposition products due to anodic oxidation.For comparison, a newly prepared zinc-nickel electrolyte is of violet color and shows a burgundy color after a low current load.
- c) Mit dem Farbwechsel konnte ein deutlicher Anstieg der kathodischen Stromausbeute gemessen werden: Nach einer Beschichtungszeit von einer Stunde wurde eine durchschnittliche Schichtdicke von 15 μm gemessen. Dies entspricht einer kathodischen Stromausbeute von ca. 50%.c) With the color change, a significant increase in the cathodic current efficiency was measured: After a coating time of one hour, an average layer thickness of 15 μm was measured. This corresponds to a cathodic current efficiency of about 50%.
- d) Nach den täglichen Stillstandszeiten ohne Strombelastung (ca. 12–14 Stunden) mit Verbleib der mit Anolyt gefüllten Membranröhren im Zink-Nickel-Bad wurde nach dem ersten Tag festgestellt, dass das Anolytvolumen in beiden Membranröhren um ca. 25% gesunken war und unterhalb des Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyt-Niveaus lag. Die Natriumhydroxidkonzentration des verbliebenen Anolyten hatte sich auf 150 g/l erhöht. Die Ursache ist mit osmotischen Druckunterschieden zwischen Anolyt und Katholyt (Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyt) erklärbar.d) After the daily downtime without current load (about 12-14 hours) with the fate of anolyte filled membrane tubes in the zinc-nickel bath was found after the first day that the anolyte volume in both membrane tubes had fallen by about 25%, and below the zinc-nickel electrolyte level.The sodium hydroxide concentration of the remaining anolyte had increased to 150 g / l. The cause can be explained by osmotic pressure differences between anolyte and catholyte (zinc-nickel electrolyte).
- e) Eine Erhöhung der Natriumhydroxidkonzentration auf 150 g/l und Auffüllen des Anolytvolumens in den Membranröhren mit demineralisiertem Wasser führte nach dem zweiten Tag zu keinem Wasserentzug im Anolyten.e) Increasing the sodium hydroxide concentration to 150 g / l and filling the anolyte volume in the membrane tubes with demineralized water resulted in no dehydration in the anolyte after the second day.
- f) Eine Erhöhung der Natriumhydroxidkonzentration auf 180 g/l im Anolyten am dritten Tag zeigte nach der Stillstandszeit einen Volumenanstieg des Anolyten in den Membranröhren über das Elektrolytniveau des Zink-Nickel-Bades bis zum Überlaufen. Durch Wasserentzug (Osmose) aus dem Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten hatte sich eine Natriumhydroxidkonzentration von 155 g/l im Anolyten eingestellt.f) Increasing the sodium hydroxide concentration to 180 g / L in the anolyte on the third day after the downtime showed an increase in the volume of the anolyte in the membrane tubes above the electrolyte level of the zinc-nickel bath until overflowing.By dehydration (osmosis) from the zinc-nickel electrolyte, a sodium hydroxide concentration of 155 g / l had set in the anolyte.
- g) Nach einer Strombelastung des Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten von 30 Ah/l (dritter Tag) konnte eine weitere Leistungssteigerung des Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten nachgewiesen werden: Die durchschnittliche gemessene Schichtdicke nach einer Stunde Beschichtungszeit betrug nunmehr 19 μm. Das entspricht einer kathodischen Stromausbeute von ca. 60%.g) After a current load of the zinc-nickel electrolyte of 30 Ah / l (third day), a further increase in performance of the zinc-nickel electrolyte could be detected: The average measured layer thickness after one hour of coating time was now 19 microns. This corresponds to a cathodic current efficiency of approx. 60%.
- h) Folgende Analysenwerte wurden nach 30 Ah/l Strombelastung ermittelt (Verlust durch durch übergelaufenen Anolyt infolge Osmose nicht berücksichtigt):h) The following analysis values were determined after 30 Ah / l current load (loss due to overflowing anolyte due to osmosis not taken into account):
Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyt:
Versuchsauswertung: Data analysis:
- a) Die Versuche zeigten ein deutliches Absinken der Zyanidkonzentration im Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten infolge Entfernung über die Anionenaustauschmembran, wobei die absolute Menge an Zyanid im Anolyten nicht wieder gefunden wurde. Dies kann auf oxidative Zersetzung von Zyanid im Anolyten zurückzuführen sein.a) The experiments showed a significant decrease in the cyanide concentration in the zinc-nickel electrolyte due to removal via the anion exchange membrane, wherein the absolute amount of cyanide in the anolyte was not found again. This may be due to oxidative decomposition of cyanide in the anolyte.
- b) Da die Neuentstehung von Zyanid durch die Anionenaustauschmembran verhindert wurde, verringerte sich kontinuierlich die Konzentration von Zyanid im Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten.b) Since the formation of cyanide by the anion exchange membrane was prevented, the concentration of cyanide in the zinc-nickel electrolyte continuously decreased.
- c) In der Folge sinkender Zyanid-Konzentration erfolgten eine Farbänderung des Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten sowie eine deutlich messbare Steigerung der kathodischen Stromausbeute.c) As a result of decreasing cyanide concentration, a color change of the zinc-nickel electrolyte and a clearly measurable increase in the cathodic current yield took place.
- d) Karbonat- und Sulfat-Ionen wurden in geringem Umfang aus dem Zink-Nickel-Elektrolyten entfernt. Dies trägt ebenfalls zur Steigerung der kathodischen Stromausbeute bei.d) Carbonate and sulfate ions have been slightly removed from the zinc-nickel electrolyte. This also contributes to the increase in the cathodic current efficiency.
- e) Um Ausfällungen und Ablagerungen von Kalzium- oder Magnesiumkarbonat und -sulfat zu vermeiden, da diese Salze die Membranfunktion stark beeinträchtigen oder zum Totalausfall führen können, muss der Anolyt unbedingt mit voll entsalztem Wasser angesetzt und ergänzt werden.e) In order to avoid precipitation and deposits of calcium or magnesium carbonate and sulfate, since these salts can severely impair membrane function or lead to total failure, the anolyte must always be prepared and supplemented with demineralized water.
Der Test einer in
ZITATE ENTHALTEN IN DER BESCHREIBUNG QUOTES INCLUDE IN THE DESCRIPTION
Diese Liste der vom Anmelder aufgeführten Dokumente wurde automatisiert erzeugt und ist ausschließlich zur besseren Information des Lesers aufgenommen. Die Liste ist nicht Bestandteil der deutschen Patent- bzw. Gebrauchsmusteranmeldung. Das DPMA übernimmt keinerlei Haftung für etwaige Fehler oder Auslassungen.This list of the documents listed by the applicant has been generated automatically and is included solely for the better information of the reader. The list is not part of the German patent or utility model application. The DPMA assumes no liability for any errors or omissions.
Zitierte PatentliteraturCited patent literature
- EP 1344850 A1[0008, 0009, 0026, 0027]EP 1344850 A1[0008, 0009, 0026, 0027]
Claims (15)
Translated fromGermanPriority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE201010044551DE102010044551A1 (en) | 2010-09-07 | 2010-09-07 | Anode and their use in an alkaline electroplating bath |
| PCT/EP2011/004511WO2012031753A1 (en) | 2010-09-07 | 2011-09-07 | Anode and use thereof in an alkaline electroplating bath |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE201010044551DE102010044551A1 (en) | 2010-09-07 | 2010-09-07 | Anode and their use in an alkaline electroplating bath |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| DE102010044551A1true DE102010044551A1 (en) | 2012-03-08 |
Family
ID=44645656
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE201010044551CeasedDE102010044551A1 (en) | 2010-09-07 | 2010-09-07 | Anode and their use in an alkaline electroplating bath |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| DE (1) | DE102010044551A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2012031753A1 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3042985A4 (en)* | 2015-07-22 | 2016-08-17 | Dipsol Chem | Zinc alloy plating method |
| WO2016150793A3 (en)* | 2015-03-25 | 2016-11-10 | Coventya International Gmbh | Two-chamber electrodialysis cell with anion and cation exchange membrane for use as an anode in alkaline zinc electrolytes and zinc alloy electrolytes for the purpose of deposition of metal in electroplating systems |
| DE102016008333A1 (en)* | 2015-11-12 | 2017-05-18 | Liebherr-Aerospace Lindenberg Gmbh | Process for the low-hydrogen zinc-nickel coating of a high-strength tempered steel |
| EP3042984B1 (en)* | 2015-07-22 | 2019-04-03 | Dipsol Chemicals Co., Ltd. | Zinc alloy plating method |
| CN113383118A (en)* | 2019-01-24 | 2021-09-10 | 德国艾托特克公司 | Membrane anode system for electrolytic zinc-nickel alloy deposition |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL2016000638A1 (en)* | 2016-03-18 | 2016-07-01 | Transducto S A | Tubular electrochemical apparatus for electro obtaining metal from solutions, consisting of a cover and a pair of non-conductive material end caps with anolyte and catholyte inlets and outlets, and separate internal concentric layers composed of electrodes and an ion exchange membrane between they. |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2001092604A2 (en)* | 2000-05-31 | 2001-12-06 | De Nora Elettrodi S.P.A. | Electrolysis cell for restoring the concentration of metal ions in processes of electroplating |
| EP1344850A1 (en) | 1998-07-30 | 2003-09-17 | Walter Hillebrand GmbH & Co. Galvanotechnik | Alkaline zinc-nickel bath |
| DE60023190T2 (en)* | 2000-06-15 | 2006-07-13 | Taskem Inc., Brooklyn Hts. | ZINC-NICKEL-electroplating |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2764337B2 (en)* | 1990-05-10 | 1998-06-11 | 新日本製鐵株式会社 | Ni or Ni-Zn alloy or Ni-Zn-Co alloy plating method |
| US5162079A (en)* | 1991-01-28 | 1992-11-10 | Eco-Tec Limited | Process and apparatus for control of electroplating bath composition |
| US20060157355A1 (en)* | 2000-03-21 | 2006-07-20 | Semitool, Inc. | Electrolytic process using anion permeable barrier |
| EP1639155B1 (en)* | 2003-06-03 | 2016-11-02 | Coventya, Inc. | Zinc and zinc-alloy electroplating |
| US7442286B2 (en)* | 2004-02-26 | 2008-10-28 | Atotech Deutschland Gmbh | Articles with electroplated zinc-nickel ternary and higher alloys, electroplating baths, processes and systems for electroplating such alloys |
| DE102008032398A1 (en)* | 2008-07-10 | 2010-01-14 | Umicore Galvanotechnik Gmbh | Improved copper-tin electrolyte and process for depositing bronze layers |
- 2010
- 2010-09-07DEDE201010044551patent/DE102010044551A1/ennot_activeCeased
- 2011
- 2011-09-07WOPCT/EP2011/004511patent/WO2012031753A1/enactiveApplication Filing
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1344850A1 (en) | 1998-07-30 | 2003-09-17 | Walter Hillebrand GmbH & Co. Galvanotechnik | Alkaline zinc-nickel bath |
| WO2001092604A2 (en)* | 2000-05-31 | 2001-12-06 | De Nora Elettrodi S.P.A. | Electrolysis cell for restoring the concentration of metal ions in processes of electroplating |
| DE60023190T2 (en)* | 2000-06-15 | 2006-07-13 | Taskem Inc., Brooklyn Hts. | ZINC-NICKEL-electroplating |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2016150793A3 (en)* | 2015-03-25 | 2016-11-10 | Coventya International Gmbh | Two-chamber electrodialysis cell with anion and cation exchange membrane for use as an anode in alkaline zinc electrolytes and zinc alloy electrolytes for the purpose of deposition of metal in electroplating systems |
| US10738391B2 (en) | 2015-03-25 | 2020-08-11 | Coventya International Gmbh | Two-chamber electrodialysis cell with anion and cation exchange membrane for use as an anode in alkaline zinc electrolytes and zinc alloy electrolytes for the purpose of deposition of metal in electroplating systems |
| EP3042985A4 (en)* | 2015-07-22 | 2016-08-17 | Dipsol Chem | Zinc alloy plating method |
| CN106550606A (en)* | 2015-07-22 | 2017-03-29 | 迪普索股份公司 | Kirsite method for plating |
| US10156020B2 (en) | 2015-07-22 | 2018-12-18 | Dipsol Chemicals Co., Ltd. | Zinc alloy plating method |
| EP3042984B1 (en)* | 2015-07-22 | 2019-04-03 | Dipsol Chemicals Co., Ltd. | Zinc alloy plating method |
| CN106550606B (en)* | 2015-07-22 | 2019-04-26 | 迪普索股份公司 | Kirsite method for plating |
| DE102016008333A1 (en)* | 2015-11-12 | 2017-05-18 | Liebherr-Aerospace Lindenberg Gmbh | Process for the low-hydrogen zinc-nickel coating of a high-strength tempered steel |
| CN113383118A (en)* | 2019-01-24 | 2021-09-10 | 德国艾托特克公司 | Membrane anode system for electrolytic zinc-nickel alloy deposition |
| US20220119978A1 (en)* | 2019-01-24 | 2022-04-21 | Atotech Deutschland Gmbh | Membrane anode system for electrolytic zinc-nickel alloy deposition |
| US12320027B2 (en)* | 2019-01-24 | 2025-06-03 | Atotech Deutschland Gmbh | Membrane anode system for electrolytic zinc-nickel alloy deposition |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2012031753A1 (en) | 2012-03-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0878561B1 (en) | Process and apparatus for the regeneration of tin plating solutions | |
| DE69317315T2 (en) | Method and device for nickel electroplating | |
| DE102010044551A1 (en) | Anode and their use in an alkaline electroplating bath | |
| WO2000006807A2 (en) | Alkali zinc nickel bath | |
| DE102010015361A1 (en) | Membrane electrolysis stack, this containing electrodialysis device and method for regenerating a stromloslos working bath for metal deposition | |
| EP1717353B1 (en) | Alkaline galvanizing bath comprising a filtration membrane | |
| DE10112075C1 (en) | Method and device for recovering metals, also in combination with anodic coupling processes | |
| DE4023444A1 (en) | Cyanide-free copper plating process - where a portion of the plating bath is electrolysed by an independently-controlled insol. anode to reduce bath impurities | |
| EP3274489B1 (en) | Two-chamber electrodialysis cell with anion and cation exchange membrane for use as an anode in alkaline zinc electrolytes and zinc alloy electrolytes for the purpose of deposition of metal in electroplating systems | |
| EP2184384B1 (en) | Galvanic bath and method for deposition of zinc-containing layers | |
| EP3000918B1 (en) | Method and device for the galvanic application of a surface coating | |
| DE102007040005A1 (en) | Depositing functional layers from electroplating bath, circulates zinc-nickel electrolyte between bath and regeneration unit providing ozone- and ultraviolet light treatment | |
| EP0801692A2 (en) | Electroplating plant | |
| DE602004009218T2 (en) | METHOD FOR THE DISPOSAL OF ZINC OR ZINC ALLOYS | |
| DE102014001799B3 (en) | Plant for coating objects | |
| EP3415665B1 (en) | Method for the galvanic deposition of zinc-nickel alloy layers from an alkaline zinc-nickel alloy bath with reduced degradation of additives | |
| DE2929305C2 (en) | Process and device for the continuous electrodeposition of manganese on steel | |
| WO2022229175A1 (en) | Device and method for coating a component or semi-finished product with a chromium layer | |
| DE102011085967A1 (en) | Process for the neutralization of negatively charged contaminants in aqueous media | |
| DE102009004155A1 (en) | Process and apparatus for regenerating peroxodisulfate pickling solutions | |
| DE102008031003B4 (en) | A method of producing a CNT-containing layer of an ionic liquid | |
| DE102004038693B4 (en) | Apparatus and method for removing foreign matter from process solutions and process for regenerating a cation exchanger | |
| DE102014005755A1 (en) | Process for the electrolytic production of high-purity copper with very low sulfur contents | |
| DE10322120A1 (en) | Methods and devices for extending the service life of a process solution for chemical-reductive metal coating | |
| DE202008014947U1 (en) | Galvanic bath for the separation of zinciferous layers |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| R002 | Refusal decision in examination/registration proceedings | ||
| R003 | Refusal decision now final | Effective date:20131105 |