CN219148776U - Magnetic Fully Implantable IV Port - Google Patents
Magnetic Fully Implantable IV PortDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN219148776U CN219148776UCN202222190689.1UCN202222190689UCN219148776UCN 219148776 UCN219148776 UCN 219148776UCN 202222190689 UCN202222190689 UCN 202222190689UCN 219148776 UCN219148776 UCN 219148776U
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- magnetic
- magnet
- port
- port body
- positioning ring
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
- Y02A50/30—Against vector-borne diseases, e.g. mosquito-borne, fly-borne, tick-borne or waterborne diseases whose impact is exacerbated by climate change
Landscapes
- Infusion, Injection, And Reservoir Apparatuses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于医疗器械技术领域,特别涉及一种磁性完全植入式静脉输液港。The invention belongs to the technical field of medical devices, in particular to a magnetic completely implantable venous infusion port.
背景技术Background technique
完全植入式静脉输液港(total implantable venous access port,TIVAP)是一种可皮下植入并长期留置的静脉输液装置,利用该装置可将药物直接输送到中心静脉,避免了高浓度、刺激性强药物造成的外周血管硬化、栓塞及静脉炎,也可有效防止化疗时药物对血管壁的损伤,为需要长期输液治疗及恶性肿瘤患者的化疗提供可靠的、长久的静脉通路。TIVAP具有可减少反复穿刺、减轻患者痛苦、留置时间长、提高患者生活质量等优点而在临床上被逐渐推广应用,尤其适用于需要长期、反复静脉输液及肿瘤化疗的患者。TIVAP优点非常突出,但在具体使用时也会出现一些不便,根据公开的文献报道[Civetta G,Lombardi L,Lanotte A,et al.Needle Insertion Difficulty Algorithm(NIDA):Anovel pilot study to predict Huber needle insertion difficulty in totallyimplanted devices[J].J Vasc Access,2021Aug 18:11297298211040343.doi:10.1177/11297298211040343.Epub ahead of print.PMID:34405754],对175例患者研究结果显示港针一次性插入成功率仅为36%,如何提高港针一次插入成功率是临床护理中面临的一个难点。Total implantable venous access port (TIVAP) is a kind of intravenous infusion device that can be implanted subcutaneously and left in place for a long time. With this device, the drug can be directly delivered to the central vein, avoiding high concentration and irritation. Peripheral vascular sclerosis, embolism and phlebitis caused by strong drugs can also effectively prevent drug damage to blood vessel walls during chemotherapy, and provide reliable and long-term venous access for chemotherapy in patients requiring long-term infusion therapy and malignant tumors. TIVAP has the advantages of reducing repeated punctures, relieving patients' pain, long indwelling time, and improving the quality of life of patients, so it has been gradually popularized and applied clinically. It is especially suitable for patients who need long-term, repeated intravenous infusion and tumor chemotherapy. The advantages of TIVAP are very prominent, but there are also some inconveniences in specific use. According to published literature reports [Civetta G, Lombardi L, Lanotte A, et al. Needle Insertion Difficulty Algorithm (NIDA): Anovel pilot study to predict Huber needle insertion difficulty in totally implanted devices[J].J Vasc Access,2021Aug 18:11297298211040343.doi:10.1177/11297298211040343.Epub ahead of print.PMID:34405754], the results of a study on 175 patients showed that the Hong Kong needle was successfully inserted at one time Rate is only 36 %, how to improve the one-time insertion success rate of Hong Kong needle is a difficult point in clinical nursing.
同样根据上述文献,显示导致TIVAP港针插入失败的原因包括患者体重的改变、装置的类型、植入时间以及操作者技术水平等。因此,目前临床中常通过加强医护人员的技术培训来提高港针一次性插入的成功率,尚未见针对TIVAP装置本身的有效优化设计。临床上在港针插入过程中,操作人员常常需要使用拇指、食指和中指来触摸并固定皮下植入的港体,然后选择皮肤凸起的中央部位进针。这种操作方法对于体型较瘦或皮肤比较松弛的患者而言容易完成,然而当TIVAP植入过深、植入时间较久或者患者皮肤松弛度较差时,操作者难以准确定位TIVAP中央的硅胶隔膜,导致实施时需要多次试探后方能将港针插入。Also according to the above-mentioned literature, the reasons for the failure of TIVAP port needle insertion include changes in patient weight, device type, implantation time, and operator skill level. Therefore, at present, the success rate of one-time insertion of the Hong Kong needle is often improved by strengthening the technical training of medical staff in clinical practice, and there is no effective optimal design for the TIVAP device itself. Clinically, during the needle insertion process, the operator often needs to use the thumb, index finger, and middle finger to touch and fix the subcutaneously implanted port body, and then select the central part of the raised skin to insert the needle. This operation method is easy to complete for patients with thin body or loose skin. However, when the TIVAP is implanted too deeply, for a long time or the patient has poor skin relaxation, it is difficult for the operator to accurately position the silicone in the center of the TIVAP. Diaphragm, resulting in the need for multiple trials before the Hong Kong needle can be inserted.
发明内容Contents of the invention
为了克服上述现有技术的缺点,本发明的目的在于提供一种磁性完全植入式静脉输液港,以期解决现有TIVAP装置在使用过程中存在的港针一次性插入成功率低的问题。In order to overcome the above-mentioned shortcomings of the prior art, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a magnetic fully implantable venous infusion port, in order to solve the problem of low success rate of one-time insertion of the port needle existing in the use of the existing TIVAP device.
为了实现上述目的,本发明采用的技术方案是:In order to achieve the above object, the technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
一种磁性完全植入式静脉输液港,包括磁性港体装置和磁性定位装置;所述磁性港体装置包括带有储液槽的港体,所述储液槽是港体中下部的空间部分,所述储液槽的上部以硅胶隔膜封装,所述港体内设置有靶磁体;所述磁性定位装置包括定位环,所述定位环内设置锚定磁体,所述靶磁体的顶端磁极与所述锚定磁体的底端磁极极性相反,所述定位环底端的形状大小与所述港体顶端的形状大小满足:在靶磁体与锚定磁体相吸后,硅胶隔膜处于定位环的内孔投影中。A magnetic completely implantable intravenous infusion port, comprising a magnetic port body device and a magnetic positioning device; the magnetic port body device includes a port body with a liquid storage tank, and the liquid storage tank is a space part in the middle and lower part of the port body , the upper part of the liquid storage tank is sealed with a silica gel diaphragm, and a target magnet is arranged in the port; the magnetic positioning device includes a positioning ring, and an anchor magnet is arranged in the positioning ring, and the top magnetic pole of the target magnet is aligned with the The polarity of the bottom end of the anchoring magnet is opposite, and the shape and size of the bottom end of the positioning ring meet the shape and size of the top of the port body: after the target magnet and the anchoring magnet are attracted, the silicone diaphragm is in the inner hole of the positioning ring Projecting.
在一个实施例中,所述储液槽接通有连接导管,所述连接导管连通储液槽和中心静脉。In one embodiment, the fluid storage tank is connected with a connecting conduit, and the connecting conduit communicates with the fluid storage tank and the central vein.
在一个实施例中,所述港体顶端为环形,所述硅胶隔膜置于内孔中,封装所述储液槽的上部。In one embodiment, the top of the port body is ring-shaped, and the silicone diaphragm is placed in the inner hole to encapsulate the upper part of the liquid storage tank.
在一个实施例中,所述靶磁体为环形,内嵌设置于港体的侧壁;所述锚定磁体为环形,内嵌设置于定位环的侧壁;所述靶磁体与锚定磁体的尺寸相同,中心对应。In one embodiment, the target magnet is ring-shaped, embedded in the side wall of the port body; the anchor magnet is ring-shaped, embedded in the side wall of the positioning ring; the target magnet and the anchor magnet Same size, center corresponding.
在一个实施例中,所述靶磁体对应位于硅胶隔膜的外周。In one embodiment, the target magnets are correspondingly located on the outer periphery of the silicone membrane.
在一个实施例中,所述港体的外侧下部设置有若干固定孔。In one embodiment, the outer lower part of the port body is provided with several fixing holes.
在一个实施例中,所述定位环带有手柄,所述手柄沿远离所述定位环的方向向上翘起。In one embodiment, the positioning ring has a handle, and the handle is tilted upward in a direction away from the positioning ring.
在一个实施例中,所述定位环沿纵向开有一个缺口,相应地,所述锚定磁体沿纵向亦开有相同缺口,所述缺口作为港针的出针口。In one embodiment, the positioning ring has a notch along the longitudinal direction, and correspondingly, the anchor magnet also has the same notch along the longitudinal direction, and the notch is used as the needle outlet of the port needle.
在一个实施例中,所述靶磁体为N个呈环形阵列分布的磁极方向相同的磁体块一;所述锚定磁体为N个呈环形阵列分布的磁极方向相同的磁体块二;各磁体块一分别与一个磁体块二对应相吸,实现磁性港体装置和磁性定位装置的组合。In one embodiment, the target magnet is
在一个实施例中,所述硅胶隔膜的顶端面与所述港体的顶端面平齐,底端面边沿向外延伸嵌入所述港体的侧壁中。In one embodiment, the top surface of the silicone membrane is flush with the top surface of the port body, and the edge of the bottom end surface extends outwards and is embedded in the side wall of the port body.
与现有技术相比,本发明在港体上端嵌入有靶磁体,磁性定位装置头端为定位环,其内嵌入有锚定磁体。靶磁体和锚定磁体的N-S极相互配对并能够准确对位相吸。本发明通过离体实验验证了该装置定位穿刺的便捷性。通过在离体动物皮肤组织下植入磁性完全植入式静脉输液港模型,模拟港针插入操作显示该装置一次穿刺成功率可达100%。因此,本发明磁性完全植入式静脉输液港设计巧妙、加工简单、成本低、使用便捷,能够显著提高穿刺成功率,具有临床转化潜力。Compared with the prior art, in the present invention, a target magnet is embedded in the upper end of the port body, and the head end of the magnetic positioning device is a positioning ring, in which an anchoring magnet is embedded. The N-S poles of the target magnet and the anchor magnet are paired with each other and can attract each other accurately. The present invention verifies the convenience of positioning and puncturing of the device through in vitro experiments. By implanting a magnetic fully implanted venous infusion port model under the skin tissue of an isolated animal, the simulated port needle insertion operation shows that the success rate of one-time puncture of the device can reach 100%. Therefore, the magnetic fully implantable venous infusion port of the present invention is ingenious in design, simple in processing, low in cost, convenient in use, can significantly improve the success rate of puncture, and has the potential of clinical transformation.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明磁性港体整体结构示意图。Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the magnetic port body of the present invention.
图2是本发明磁性港体剖面结构示意图。Fig. 2 is a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of the magnetic port body of the present invention.
图3是本发明磁性港体中的靶磁体结构示意图。Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the target magnet in the magnetic port body of the present invention.
图4是本发明磁性定位装置整体结构示意图。Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of the magnetic positioning device of the present invention.
图5是本发明磁性定位装置剖面结构示意图。Fig. 5 is a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of the magnetic positioning device of the present invention.
图6是本发明磁性定位装置中的锚定磁体结构示意图。Fig. 6 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the anchoring magnet in the magnetic positioning device of the present invention.
1-硅胶隔膜;2-港体;3-连接导管;4-固定孔;5-靶磁体;6-储液槽;7-手柄;8-定位环;9-出针口。1-silicone diaphragm; 2-port body; 3-connecting catheter; 4-fixing hole; 5-target magnet; 6-reservoir; 7-handle; 8-positioning ring; 9-needle outlet.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和实施例详细说明本发明的实施方式。The implementation of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the drawings and examples.
如前所述,由于完全植入式静脉输液港在皮下植入并长期留置,由于TIVAP植入过深、植入时间较久或者患者皮肤松弛度较差等原因,使得定位困难,港针的一次性插入成功率较低。为此,如果能提高对硅胶隔膜的定位能力,将极大提高港针的一次性插入成功率。As mentioned above, since the fully implanted venous port is implanted subcutaneously and left in place for a long time, the TIVAP implantation is too deep, the implantation time is long, or the patient’s skin laxity is poor, making positioning difficult. The one-time insertion success rate is low. For this reason, if the positioning ability of the silicone diaphragm can be improved, the success rate of one-time insertion of the Hong Kong needle will be greatly improved.
磁外科(Magnetosurgery/Magnetic Surgery,MS)是利用特殊设计的磁性医疗器械或设备,将磁性物质间“非接触性”磁场力转化为临床诊疗中能够发挥特定功能的力,从而完成组织压榨、器官锚定、管腔导航、间隙扩张、可控示踪、定向驱动等功能的新兴综合性技术学科。磁锚定技术(magnetic anchor technique,MAT)是磁外科重要临床应用技术之一,MAT是利用磁体与磁体,或磁体与顺磁性物质之间的磁场吸引力使锚定磁体(anchormagnet,AM)对靶磁体(target magnet,TM)进行非接触性空间锚定的技术。目前基于磁锚定技术原理设计的磁性医疗器械多用于胸腔镜肺楔形切除、腹腔镜减戳孔手术及磁锚定辅助内镜黏膜下剥离术等,主要目的在于进一步减少创伤、优化手术操作。Magnetic surgery (Magnetosurgery/Magnetic Surgery, MS) is the use of specially designed magnetic medical devices or equipment to convert the "non-contact" magnetic field force between magnetic substances into a force that can perform specific functions in clinical diagnosis and treatment, thereby completing tissue crushing, organ surgery, etc. An emerging comprehensive technical discipline with functions such as anchoring, lumen navigation, gap expansion, controllable tracking, and directional drive. Magnetic anchor technique (MAT) is one of the important clinical application techniques of magnetic surgery. MAT uses the magnetic field attraction between magnets or magnets and paramagnetic substances to make anchor magnets (anchormagnet, AM) The technology of non-contact space anchoring by target magnet (TM). At present, magnetic medical devices designed based on the principle of magnetic anchoring technology are mostly used in thoracoscopic lung wedge resection, laparoscopic poke reduction surgery, and magnetic anchor-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection. The main purpose is to further reduce trauma and optimize surgical operations.
根据磁锚定技术基本原理,本发明首次提出了基于磁锚定技术的磁性完全植入式静脉输液港(magnetic total implantable venous access port,MTIVAP)的设计方案,现介绍如下。According to the basic principle of magnetic anchoring technology, the present invention proposes the design scheme of magnetic total implantable venous access port (MTIVAP) based on magnetic anchoring technology for the first time, which is introduced as follows.
本发明的磁性完全植入式静脉输液港,主要包括磁性港体装置和磁性定位装置,或者可称为仅由磁性港体装置和磁性定位装置组成。The magnetic completely implantable venous infusion port of the present invention mainly includes a magnetic port body device and a magnetic positioning device, or may be called only composed of a magnetic port body device and a magnetic positioning device.
参考图1、图2和图3,磁性港体装置的主体为港体2,港体2内部有储液槽6,示例地,港体2的中部有一个孔结构,该结构的底部封闭,顶部以硅胶隔膜1封装,硅胶隔膜1与该孔结构底部之间的空间部分即为储液槽6,使用时,当港针刺穿硅胶隔膜1,则能够与储液槽6连通。本发明在港体2内设置有靶磁体5。Referring to Fig. 1, Fig. 2 and Fig. 3, the main body of the magnetic port device is a
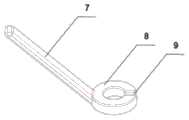
参考图4、图5和图6,磁性定位装置的主体为定位环8,定位环8内设置锚定磁体10。锚定磁体的底端磁极与靶磁体的顶端磁极的极性相反,以使得二者能够相吸。Referring to FIG. 4 , FIG. 5 and FIG. 6 , the main body of the magnetic positioning device is a
并且,定位环8底端的形状大小与港体2顶端的形状大小应能够满足:在靶磁体5与锚定磁体10相吸后,硅胶隔膜1处于定位环8的内孔投影中,以此实现硅胶隔膜1的定位,即实现港针能够一次性插入储液槽6中。由于储液槽6通过连接导管3连通中心静脉,因此能够通过港针-储液槽6-连接导管3向中心静脉输液。Moreover, the shape and size of the bottom end of the
在本发明的一个实施例中,港体2顶端设置为环形,硅胶隔膜1置于其内孔中。为操作便利和安全考虑,硅胶隔膜1的顶端面与港体2的顶端面平齐,其底端面边沿可向外延伸嵌入港体2的侧壁中,使得封装更加紧密可靠。港体2的外形可为梯台形状,其外侧下部可设置有若干固定孔4,以便于港体固定于皮下组织中。In one embodiment of the present invention, the top of the
在本发明的一个实施例中,靶磁体5被设置为环形,内嵌设置于港体2的侧壁,并优选对应环绕于硅胶隔膜1的外周。相应地,锚定磁体10也为环形,内嵌设置于定位环8的侧壁。靶磁体5与锚定磁体10的尺寸相同,且中心对应。以实现可靠的相吸定位。示例地,靶磁体5和锚定磁体10为N-S极相互配对并能够准确对位相吸的钕铁硼磁环。In one embodiment of the present invention, the
在本发明的另一个实施例中,靶磁体5被设置为N个呈环形阵列分布的磁极方向相同的磁体块一,其形状优选为扇形块,内嵌设置于港体2的侧壁。锚定磁体10则被配置为N个呈环形阵列分布的磁极方向相同的磁体块二,其形状同样优选为扇形块,并内嵌设置于定位环8的侧壁。各磁体块一分别与一个磁体块二对应相吸,实现磁性港体装置和磁性定位装置的组合。In another embodiment of the present invention, the
在本发明的其它实施例中,靶磁体5可被配置为若干扇形块,而锚定磁体10则被配置为环形,或者,锚定磁体10可被配置为若干扇形块,而靶磁体5则被配置为环形。无论如何配置,靶磁体5与锚定磁体10的内径以及外径等尺寸仍需一致,且中心处于同一中轴线上,以实现可靠的相吸定位。In other embodiments of the present invention, the
在本发明的一个实施例中,为了操作便利,定位环8带有至少一个手柄7,手柄7可水平连接于定位环8的侧壁,也可沿远离定位环8的方向向上翘起。当选择后者时,操作的便利性更强。In one embodiment of the present invention, for convenient operation, the
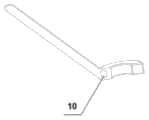
在本发明的一个实施例中,为了更方便地取下磁性定位装置,可在定位环8上沿纵向开有一个缺口,此时,相应地,锚定磁体10沿纵向亦开有相同缺口,该缺口作为港针的出针口9,沿此缺口平移,即可取出磁性定位装置。In one embodiment of the present invention, in order to remove the magnetic positioning device more conveniently, a notch can be provided in the longitudinal direction on the
本发明的工作原理:Working principle of the present invention:
由于港体2上端的靶磁体5与定位环8中的锚定磁体10的N-S极相对应,在使用时当定位环8靠近患者静脉输液港表面的皮肤时,锚定磁体10与靶磁体5可自动对位相吸,此时定位环8中间的皮肤区域与港体2的硅胶隔膜1所在区域的皮肤上下重叠一致,在定位环8中央所在区域插入港针即可精准对应硅胶隔膜1上方的皮肤,从而确保港针插入的精准性。当设置出针口9时,港针插入后水平滑动磁性定位装置,可使港针从定位环8的出针口9移出。Because the
根据磁锚定技术原理同时结合3D打印技术成功制作出本发明的磁性完全植入式静脉输液港样品。在该样品中靶磁体5为外径16.8mm、内径12mm、高6mm的磁环,采用N45烧结钕铁硼精加工而成,表面氮化钛镀层处理,轴向饱和充磁,磁体质量4.44g,磁感应强度4350GS(1T=10000Gs)。锚定磁体10为外径16.8mm、内径12mm、高3mm的磁环,所用磁性材料及表面改性方案同靶磁体,磁体质量2.20g,磁感应强度3760GS。According to the principle of magnetic anchoring technology and combined with 3D printing technology, the magnetic fully implantable venous infusion port sample of the present invention was successfully produced. In this sample, the
利用电子万能试验机(型号UTM6202,深圳三思纵横科技股份有限公司)对锚定磁体10和靶磁体5的磁力学性能进行测试,结果显示锚定磁体与靶磁体的磁力与二者之间位移成反比,随着位移的增加,磁力逐渐减弱。锚定磁体和靶磁体在零距离时的磁性吸引力大小为36.87N,5mm间距时为2.17N,其磁力-位移曲线见表1所示。Utilize the electronic universal testing machine (model UTM6202, Shenzhen Sansi Zongheng Technology Co., Ltd.) to test the magnetic mechanical properties of the
表1锚定磁体与靶磁体磁力-位移曲线Table 1 Magnetic force-displacement curves of anchor magnet and target magnet
以3D打印的磁性完全植入式静脉输液港为模拟操作对象,将其植入离体实验猪皮下建立静脉输液港植入模型。分别在有、无磁性定位装置辅助下完成港针插入操作。由10名测试人员(中年资护士)在两种情况下港针插入操作。结果显示无磁性定位装置时,港针一次性插入成功率为60%,有磁性定位装置辅助时港针一次性插入成功率为100%,且操作简单,易于掌握。Taking the 3D-printed magnetic fully implanted venous port as the simulated operation object, it was implanted under the skin of isolated experimental pigs to establish a venous port implantation model. The needle insertion operation was completed with or without the assistance of a magnetic positioning device. 10 testers (middle-aged nurses) performed needle insertion operations under two conditions. The results showed that the one-time insertion success rate of the Hong Kong needle was 60% without the magnetic positioning device, and 100% with the assistance of the magnetic positioning device, and the operation was simple and easy to master.
由此可见,本发明具有以下特点:(1)结构设计巧妙、加工工艺简单。从设计理念上来讲,通过在港体的上端设置环形靶磁体且将硅胶隔膜完全包围其中,与静脉港配套使用的磁性定位装置则有与之相匹配的环形锚定磁体。使用时锚定磁体和靶磁体能够隔着皮肤对位吸合,此时定位环内区域与静脉港硅胶隔膜所在区域相对应,即为港针插入区域,极大提高了港针穿刺的精准性。从加工工艺上来看,在港体内嵌入环形靶磁体是完全可以实现的。(2)勺状的磁性定位装置可方便操作时拿取和固定,定位环采用非整环结构设计,以便港针在插入后能够经出针口顺利撤出磁性定位装置。(3)钕铁硼永磁材料具有极佳的磁学性能,以烧结型钕铁硼为原料可尽可能在小尺寸的情况下实现磁力最大化。It can be seen that the present invention has the following characteristics: (1) ingenious structural design and simple processing technology. In terms of design concept, by setting a ring-shaped target magnet on the upper end of the port body and completely surrounding the silicone diaphragm, the magnetic positioning device used in conjunction with the vein port has a matching ring-shaped anchoring magnet. When in use, the anchoring magnet and the target magnet can be aligned across the skin. At this time, the area inside the positioning ring corresponds to the area where the silicone diaphragm of the vein port is located, which is the insertion area of the port needle, which greatly improves the accuracy of port needle puncture. . From the perspective of processing technology, it is completely achievable to embed ring-shaped target magnets in the port. (2) The spoon-shaped magnetic positioning device can be easily taken and fixed during operation. The positioning ring adopts a non-integral ring structure design so that the needle can be smoothly withdrawn from the magnetic positioning device through the needle outlet after insertion. (3) NdFeB permanent magnet materials have excellent magnetic properties. Using sintered NdFeB as raw materials can maximize the magnetic force in a small size as much as possible.
然而,值得说明的是,本发明基于磁锚定技术原理设计的磁性完全植入式静脉输液港也有其自身的固有缺陷。第一,在植入期间,患者需远离强磁场环境,且不能进行磁共振检查,因此临床上应尽可能避免给短期内有可能行磁共振检查的患者植入磁性完全植入式静脉输液港;第二,对于体内有心脏起搏器、人工心脏等电子设备的患者而言,是否可植入磁性完全植入式静脉输液港尚需要进一步评价其安全性;第三,港体植入深度、患者皮肤松弛度等是影响港针插入的关键因素。在易插入型患者人群中,磁性完全植入式静脉输液港与常规TIVAP相比优势并不突出,但在插入困难型的患者中其优势将凸显,这也提示本发明磁性完全植入式静脉输液港有其自身的适用患者群体。However, it is worth noting that the magnetic fully implantable venous infusion port designed based on the principle of magnetic anchoring technology in the present invention also has its own inherent defects. First, during the implantation period, the patient needs to stay away from a strong magnetic field environment, and MRI examinations cannot be performed. Therefore, clinically, it should be avoided as much as possible to implant magnetic fully implantable venous infusion ports in patients who may undergo MRI examinations in the short term. ; Second, for patients with electronic devices such as cardiac pacemakers and artificial hearts, whether it can be implanted with a magnetic fully implantable venous port needs further evaluation of its safety; third, the implantation depth of the port body , Patient's skin laxity etc. are the key factors affecting Hong Kong needle insertion. In easy-to-insert patient groups, the advantages of the magnetic fully implantable venous port are not prominent compared with conventional TIVAP, but their advantages will be prominent in patients with difficult insertion, which also suggests that the magnetic fully implantable venous port of the present invention Infusion ports have their own applicable patient groups.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202222190689.1UCN219148776U (en) | 2022-08-19 | 2022-08-19 | Magnetic Fully Implantable IV Port |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202222190689.1UCN219148776U (en) | 2022-08-19 | 2022-08-19 | Magnetic Fully Implantable IV Port |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN219148776Utrue CN219148776U (en) | 2023-06-09 |
Family
ID=86639747
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202222190689.1UExpired - Fee RelatedCN219148776U (en) | 2022-08-19 | 2022-08-19 | Magnetic Fully Implantable IV Port |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN219148776U (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115317711A (en)* | 2022-08-19 | 2022-11-11 | 西安交通大学医学院第一附属医院 | Magnetic completely-implanted venous transfusion port |
- 2022
- 2022-08-19CNCN202222190689.1Upatent/CN219148776U/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115317711A (en)* | 2022-08-19 | 2022-11-11 | 西安交通大学医学院第一附属医院 | Magnetic completely-implanted venous transfusion port |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US3640269A (en) | Fluid-conducting instrument insertable in living organisms | |
| US8454690B2 (en) | Systems and methods for tissue expansion with fluid delivery and drainage system | |
| US20040199129A1 (en) | Vascular access port | |
| MX2010009360A (en) | Venous access port assembly with push surfaces. | |
| CN110339433B (en) | Triple puncture needle device and method for transthoracic epicardial intramyocardial injection under ultrasonic guidance | |
| CN206007700U (en) | A kind of full-implantation type venous transfusion port | |
| CN219148776U (en) | Magnetic Fully Implantable IV Port | |
| KR20140113597A (en) | Safety neural injection system and related methods | |
| CN115317711A (en) | Magnetic completely-implanted venous transfusion port | |
| CN108785791A (en) | The application method of two-chamber venous transfusion port and its venous transfusion, drug storage sustained release | |
| WO2007085904A2 (en) | Surgical template | |
| JPH03126438A (en) | Skin terminal | |
| CN215460909U (en) | Implantable drug delivery device | |
| JP2602109B2 (en) | Drug injection system | |
| CN212651171U (en) | Implanted transfusion port | |
| CN219645838U (en) | A magnetic positioning intraperitoneal chemotherapy device | |
| CN211188555U (en) | Subcutaneous implantation type abdominal cavity chemotherapy device | |
| Zhang et al. | A novel YZ magnetic totally implantable venous access port based on the magnetic anchor technique | |
| CN217793261U (en) | Continuous drug administration device in superficial solid tumor | |
| CN113599620A (en) | Implantable drug delivery device | |
| CN222150644U (en) | PICC catheter implanted under the skin | |
| Zhang et al. | Value of a novel YZ magnetic totally implantable venous access port in improving the success rate of one-time needle insertion | |
| CN201481897U (en) | Improved structure of artificial blood vessel injection seat | |
| CN206499707U (en) | Implanted transfusion port puncture positioning device | |
| JP4619501B2 (en) | Non-destructive needle and tissue collection device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20230609 |