CN217488974U - An extension and flexion gap combined measuring device - Google Patents
An extension and flexion gap combined measuring deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN217488974U CN217488974UCN202122457510.XUCN202122457510UCN217488974UCN 217488974 UCN217488974 UCN 217488974UCN 202122457510 UCN202122457510 UCN 202122457510UCN 217488974 UCN217488974 UCN 217488974U
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- osteotomy
- place ahead
- pointer
- femur
- cut
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Prostheses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本实用新型涉及一种伸直、屈曲间隙结合的测量器,属于医疗设备技术领域。The utility model relates to a measuring device combined with straightening and flexion gaps, belonging to the technical field of medical equipment.
背景技术Background technique
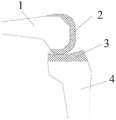
目前,随着人口老龄化的出现,许多人会产生膝关节骨关节炎的病症,使得患者出现膝关节酸痛,无法站立,或者站立不稳等症状,而膝关节表面置换是治疗膝关节骨关节炎的最终手段,需要医生将与胫骨4的关节面3连接的那些坏死或磨损的股骨1进行切除,如图1所示,并安装人工关节假体2,使得患者能够重新站立以及正常走路。At present, with the aging of the population, many people will develop knee osteoarthritis, which makes the patient suffer from knee joint pain, inability to stand, or stand instability. Knee joint resurfacing is a treatment for knee joint bone The final measure of inflammation requires the doctor to remove those necrotic or
在膝关节骨表面置换时,伸直间隙、屈曲间隙的平衡是手术操作的关键,伸直间隙优先是截骨操作的最常用的方法。现有的骨外科医生在给患者进行切除手术时,先在屈曲的股骨1上纵向切除一个截面,形成第一切面3,完成伸直间隙截骨,如图2所示,再通过间隙检测器使得伸直间隙、屈曲间隙平衡,然后根据股骨以及人工关节假体的大小,并通过间隙测量器得到最接近股骨尺寸的人工关节假体2的数据,最后通过截骨器依次进行股骨1上第二切面1-5、第三切面1-4、第四切面1-2、第五切面1-1的切除,其中,第五切面1-1的高度决定人工关节假体2的大小。切骨完成后将人工关节假体2套在股骨1的切面上。In knee resurfacing, the balance of extension gap and flexion gap is the key to surgical operation, and extension gap priority is the most common method of osteotomy. When an existing orthopedic surgeon performs a resection operation on a patient, he first cuts a section longitudinally on the
但是,目前的测量器在使用时,仅仅是通过测量器测量截骨器在第五切面1-1时的高度,从而得到使用什么尺寸的人工关节假体2,如果测量得到的尺寸与人工关节假体的尺寸相差太大,需要重新进行切割并测量;如果测量得到的尺寸位于两个不同人工关节假体的尺寸之间,那么也只能使用小尺寸的人工关节假体,但是这种小尺寸的人工关节假体与股骨之间并不是完全贴合,可能导致患者站立不稳等不良影响。However, the current measuring device only measures the height of the osteotomy device at the fifth cutting plane 1-1 through the measuring device, so as to obtain the
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本实用新型要解决的技术问题是:如何使得股骨截骨后能与相应的人工关节假体精确匹配。The technical problem to be solved by the utility model is: how to make the femur can be accurately matched with the corresponding artificial joint prosthesis after osteotomy.
为了解决上述技术问题,本实用新型的技术方案是提供了一种伸直、屈曲间隙结合的测量器,其特征在于,包括前方截骨板和测量股骨前后径的指针,前方截骨板内设有用于水平切屈曲股骨顶部的截骨口,截骨口贯穿前方截骨板,前方截骨板的一侧固定有固定座,固定座与连接杆连接,连接杆的顶端固定有指针。In order to solve the above-mentioned technical problems, the technical solution of the present utility model is to provide a measuring device for straightening and flexion gap combination, which is characterized in that it includes a front osteotomy plate and a pointer for measuring the anterior and posterior diameter of the femur, and the anterior osteotomy plate is internally provided with There is an osteotomy opening for horizontally cutting and flexing the top of the femur, the osteotomy opening penetrates the front osteotomy plate, one side of the front osteotomy plate is fixed with a fixing seat, the fixing seat is connected with a connecting rod, and a pointer is fixed on the top of the connecting rod.
优选地,所述的连接杆为螺杆,螺杆设于固定座内,固定座内设有与螺杆上外螺纹匹配的内螺纹。Preferably, the connecting rod is a screw rod, the screw rod is arranged in the fixing seat, and the inner thread matching the outer thread on the screw rod is arranged in the fixing seat.
优选地,所述的指针的一端为折弯结构。Preferably, one end of the pointer is a bending structure.
与现有技术相比,本实用新型的测量器结构简单、精确率高,节省了原有结构复杂的测量器,通过将现有截骨器顶部的前方截骨板分离,并将其与指针结合,通过指针测量得到股骨前后径大小,同时调整前方截骨板的位置,使得通过前方截骨板上截骨口切割股骨后的尺寸与人工关节假体完全相匹配,提高手术成功率以及操作效率。Compared with the prior art, the measuring device of the present invention has the advantages of simple structure and high accuracy, saving the original measuring device with complex structure. Combined, the anteroposterior diameter of the femur is measured by the pointer, and the position of the anterior osteotomy plate is adjusted at the same time, so that the size of the femur after cutting the femur through the osteotomy opening on the anterior osteotomy plate completely matches the artificial joint prosthesis, which improves the success rate of surgery and operation. efficiency.
通过本实用新型的测量器,在完成屈曲间隙截骨的同时,测量股骨前后径大小,还可完成股骨整体截骨。The measuring device of the utility model can measure the anteroposterior diameter of the femur while completing the osteotomy of the flexion gap, and can also complete the overall osteotomy of the femur.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为膝关节骨表面置换人工关节假体后的示意图;Fig. 1 is the schematic diagram after knee joint bone surface replacement artificial joint prosthesis;
图2为股骨切除后的示意图;Fig. 2 is the schematic diagram after femur resection;
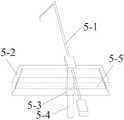
图3为一种伸直、屈曲间隙结合的测量器的立体图;Figure 3 is a perspective view of a measuring device combined with straightening and flexion gaps;
图4为一种伸直、屈曲间隙结合的测量器的侧视图;Figure 4 is a side view of a measuring device combined with straightening and flexion gaps;
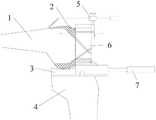
图5为一种伸直、屈曲间隙结合的测量器与截骨器结合使用的示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of the combined use of a measuring device combined with an extension and flexion gap and an osteotomy device;
图6为一种伸直、屈曲间隙结合的测量器的使用示意图;6 is a schematic diagram of the use of a measuring device combined with a straightening and flexion gap;
图7为图6的侧向俯视图。FIG. 7 is a side plan view of FIG. 6 .
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本实用新型更明显易懂,兹以优选实施例,并配合附图作详细说明如下。In order to make the present utility model more obvious and easy to understand, the preferred embodiments are described in detail as follows in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
实施例1Example 1
本实用新型提供了一种伸直、屈曲间隙结合的测量器,如图3、图4所示,其包括前方截骨板5-2和测量股骨前后径的指针5-1,前方截骨板5-2内设有用于水平切屈曲股骨顶部的截骨口5-5,截骨口5-5贯穿前方截骨板5-2,前方截骨板5-2的一侧固定有固定座5-3,固定座5-3内设有螺杆5-4,固定座5-3内设有与螺杆5-4上外螺纹匹配的内螺纹,螺杆5-4的顶端固定有指针5-1,通过指针5-1一端顶在屈曲股骨顶部,螺杆5-4的底端穿过固定座5-3,用于连接截骨器6,通过转动螺杆5-4,调节前方截骨板5-2在螺杆5-4上的位置,从而通过螺杆5-4上的指示得到使用何种尺寸的人工关节假体2。指针5-1的一端为折弯结构,折弯结构的端部用于顶在屈曲股骨顶部。指针5-1与截骨口5-5平行。The utility model provides a measuring device combined with straightening and flexion gaps, as shown in Figures 3 and 4, which includes a front osteotomy plate 5-2 and a pointer 5-1 for measuring the anteroposterior diameter of the femur, the front osteotomy plate 5-1. 5-2 is provided with an osteotomy opening 5-5 for horizontally cutting and flexing the top of the femur, the osteotomy opening 5-5 penetrates the front osteotomy plate 5-2, and one side of the front osteotomy plate 5-2 is fixed with a fixing seat 5 -3, a screw 5-4 is arranged in the fixing seat 5-3, an inner thread matching the outer thread on the screw 5-4 is arranged in the fixing seat 5-3, and a pointer 5-1 is fixed on the top of the screw 5-4, One end of the pointer 5-1 is pressed against the top of the flexed femur, and the bottom end of the screw 5-4 is passed through the fixing seat 5-3 for connecting the
其中,屈曲间隙为股骨屈曲时与胫骨上关节面之间的距离;伸直间隙为股骨伸直时与胫骨上关节面之间的距离。Among them, the flexion gap is the distance between the femur and the upper articular surface of the tibia when the femur is flexed; the extension gap is the distance between the femur and the upper articular surface of the tibia when the femur is straightened.
如图5-图7所示,本实用新型的使用过程如下:As shown in Figure 5-Figure 7, the use process of the present utility model is as follows:
在基于伸直间隙截骨完成的基础上,并通过检测器7将截骨器6的位置确定,并将截骨器6上本实用新型的测量器5固定在截骨器6顶部,通过测量器5上的指针5-1测量股骨前后径大小,随后根据股骨前后径大小确定人工关节假体2尺寸,根据人工关节假体2的尺寸确定前方截骨板5-2上截骨口5-5的位置,随后进行股骨上各个位置的切除操作,最后将人工关节假体2套在截骨后的股骨上,即完成膝关节骨表面置换的手术。On the basis of the completion of the osteotomy based on the extension gap, the position of the
实施例2Example 2
本实施例中,将实施例1中的固定座5-3与螺杆5-4的螺纹连接改为固定连接,并在使用本实用新型的测量器5时,可在截骨器6与本实用新型的测量器5之间设置调节器,从而调节测量器5的高度位置。In this embodiment, the threaded connection between the fixing seat 5-3 and the screw 5-4 in
其他与实施例1相同。Others are the same as in Example 1.
Claims (3)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202122457510.XUCN217488974U (en) | 2021-10-12 | 2021-10-12 | An extension and flexion gap combined measuring device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202122457510.XUCN217488974U (en) | 2021-10-12 | 2021-10-12 | An extension and flexion gap combined measuring device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN217488974Utrue CN217488974U (en) | 2022-09-27 |
Family
ID=83336466
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202122457510.XUActiveCN217488974U (en) | 2021-10-12 | 2021-10-12 | An extension and flexion gap combined measuring device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN217488974U (en) |
- 2021
- 2021-10-12CNCN202122457510.XUpatent/CN217488974U/enactiveActive
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN100581490C (en) | Knee-joint prosthesis implantation process, osteotomy module thereof and device thereof | |
| CN107343817B (en) | Computer-aided design of integrated guide for orthopedic osteotomy and orthopaedic fixation and its manufacturing method | |
| Jeffery et al. | Coronal alignment after total knee replacement | |
| CN104758028B (en) | Individualized osteotomy positioning guide device for distal femur and tibial plateau and use method | |
| JP2012500667A (en) | Force sensing method for partial and total knee arthroplasty | |
| CN110613469A (en) | Automatic leg bone and lower limb force line detection method and device | |
| Milner et al. | A comparison of four in vivo methods of measuring tibial torsion | |
| Tammachote et al. | Comparison of customized cutting block and conventional cutting instrument in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial | |
| CN204909559U (en) | Individuation knee joint thighbone distal end cuts bone conduction board | |
| CN203506854U (en) | Line of force alignment assist device for external positioning of tibia marrow | |
| Larsen | The value of individual joints for radiologic assessment of rheumatoid arthritis | |
| CN217488974U (en) | An extension and flexion gap combined measuring device | |
| CN115778476A (en) | Complete set of device for adjusting osteotomy on femoral side in knee joint replacement | |
| CN207734193U (en) | A kind of femur osteotomy rule | |
| CN114469252A (en) | Femoral medial posterior condylar osteotomy measurement positioning system | |
| WO2025081729A1 (en) | System for determining angle of osteotomy | |
| CN113855346B (en) | Knee joint bone surface replacement device | |
| CN118453111A (en) | Intraoperative knee joint space adjustment device and knee joint surgery equipment | |
| SIMONS et al. | The microsurgical dissection of a stillborn fetal clubfoot. | |
| CN115153834B (en) | A method and system for intelligent osteotomy and correction of lower limbs before 3D surgery | |
| CN211381607U (en) | Anterior femoral condyle osteotomy guide device for total knee arthroplasty | |
| CN204655037U (en) | Individualized osteotomy positioning and guiding device for distal femur and tibial plateau | |
| CN110801265A (en) | Anterior femoral condyle osteotomy guide device for total knee arthroplasty | |
| Jakobsen | Operative Treatment of Lateral Tibial Condyle Fractures: A follow-up study of 68 cases | |
| Gong et al. | Correlation between surface area ratio of medial to lateral tibial plateau and knee alignment in adults |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |