CN211911903U - A ureteral stent for inhibiting recurrent stenotic irritation and calculi - Google Patents
A ureteral stent for inhibiting recurrent stenotic irritation and calculiDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN211911903U CN211911903UCN201922058677.1UCN201922058677UCN211911903UCN 211911903 UCN211911903 UCN 211911903UCN 201922058677 UCN201922058677 UCN 201922058677UCN 211911903 UCN211911903 UCN 211911903U
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- stent
- coating
- release drug
- ureteral
- sustained
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000000306recurrent effectEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription15
- 230000002401inhibitory effectEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription9
- 230000007794irritationEffects0.000titleabstractdescription7
- 230000002966stenotic effectEffects0.000titledescription3
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription57
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription55
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription53
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000claimsabstractdescription50
- 208000031481Pathologic ConstrictionDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription34
- 208000037804stenosisDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription29
- 238000013268sustained releaseMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription28
- 239000012730sustained-release formSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription28
- 230000002272anti-calculusEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-NCopperChemical compound[Cu]RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription17
- 229910052802copperInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription17
- 239000010949copperSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription17
- 239000011664nicotinic acidSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 239000004575stoneSubstances0.000abstractdescription13
- 230000036262stenosisEffects0.000abstractdescription12
- 238000002513implantationMethods0.000abstractdescription7
- 230000005764inhibitory processEffects0.000abstractdescription4
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 208000032984Intraoperative ComplicationsDiseases0.000abstract1
- 230000001154acute effectEffects0.000abstract1
- 230000002045lasting effectEffects0.000abstract1
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description20
- 229920000669heparinPolymers0.000description12
- 208000037803restenosisDiseases0.000description11
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description9
- 238000005507sprayingMethods0.000description9
- HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-NHeparinChemical compoundOC1C(NC(=O)C)C(O)OC(COS(O)(=O)=O)C1OC1C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C(O)C(OC2C(C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C(OC3C(C(O)C(O)C(O3)C(O)=O)OS(O)(=O)=O)C(CO)O2)NS(O)(=O)=O)C(C(O)=O)O1HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description7
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-NacetoneSubstancesCC(C)=OCSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description7
- 238000000889atomisationMethods0.000description7
- 229960002897heparinDrugs0.000description7
- 230000003592biomimetic effectEffects0.000description6
- ORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-Lcopper(II) chlorideChemical compoundCl[Cu]ClORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description6
- VYFYYTLLBUKUHU-UHFFFAOYSA-NdopamineChemical compoundNCCC1=CC=C(O)C(O)=C1VYFYYTLLBUKUHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- ZFGMDIBRIDKWMY-PASTXAENSA-NheparinChemical compoundCC(O)=N[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](COS(O)(=O)=O)O[C@@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](C(O)=O)O[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](OS(O)(=O)=O)[C@@H](O[C@@H]3[C@@H](OC(O)[C@H](OS(O)(=O)=O)[C@H]3O)C(O)=O)O[C@@H]2O)CS(O)(=O)=O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1OZFGMDIBRIDKWMY-PASTXAENSA-N0.000description5
- 229920001661ChitosanPolymers0.000description4
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description4
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description4
- 229920000747poly(lactic acid)Polymers0.000description4
- 239000004626polylactic acidSubstances0.000description4
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-NDichloromethaneChemical compoundClCClYMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthyl acetateChemical compoundCCOC(C)=OXEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 229960003638dopamineDrugs0.000description3
- 229960001008heparin sodiumDrugs0.000description3
- 210000003734kidneyAnatomy0.000description3
- 239000002504physiological saline solutionSubstances0.000description3
- 229920001610polycaprolactonePolymers0.000description3
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-NChloroformChemical compoundClC(Cl)ClHEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- CTENFNNZBMHDDG-UHFFFAOYSA-NDopamine hydrochlorideChemical compoundCl.NCCC1=CC=C(O)C(O)=C1CTENFNNZBMHDDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-NHydrochloric acidChemical compoundClVEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 229930012538PaclitaxelNatural products0.000description2
- 229960003280cupric chlorideDrugs0.000description2
- 229920006237degradable polymerPolymers0.000description2
- 229960001149dopamine hydrochlorideDrugs0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 229960001592paclitaxelDrugs0.000description2
- 229920001606poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)Polymers0.000description2
- 239000004632polycaprolactoneSubstances0.000description2
- 230000002980postoperative effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000description2
- RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-NtaxolChemical compoundO([C@@H]1[C@@]2(C[C@@H](C(C)=C(C2(C)C)[C@H](C([C@]2(C)[C@@H](O)C[C@H]3OC[C@]3([C@H]21)OC(C)=O)=O)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(=O)C=1C=CC=CC=1)C=1C=CC=CC=1)O)C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1RCINICONZNJXQF-MZXODVADSA-N0.000description2
- 210000002700urineAnatomy0.000description2
- AEMRFAOFKBGASW-UHFFFAOYSA-NGlycolic acidPolymersOCC(O)=OAEMRFAOFKBGASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 101000691618Homo sapiens Inactive phospholipase C-like protein 1Proteins0.000description1
- 102100026207Inactive phospholipase C-like protein 1Human genes0.000description1
- 229920002732PolyanhydridePolymers0.000description1
- 229920000954PolyglycolidePolymers0.000description1
- 206010046405Ureteric injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 230000001028anti-proliverative effectEffects0.000description1
- 229910000365copper sulfateInorganic materials0.000description1
- ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-Lcopper(II) sulfateChemical compound[Cu+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-]ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description1
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000description1
- 230000010339dilationEffects0.000description1
- 238000003618dip coatingMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 150000002148estersChemical class0.000description1
- 238000001727in vivoMethods0.000description1
- 230000001939inductive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009545invasionEffects0.000description1
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000012046mixed solventSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 239000003960organic solventSubstances0.000description1
- 229920000848poly(L-lactide-ε-caprolactone)Polymers0.000description1
- 229920000515polycarbonatePolymers0.000description1
- 239000004417polycarbonateSubstances0.000description1
- 229920001690polydopaminePolymers0.000description1
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000description1
- -1polytrimethylenePolymers0.000description1
- 239000000843powderSubstances0.000description1
- 231100000241scarToxicity0.000description1
- 239000002904solventSubstances0.000description1
- 238000004528spin coatingMethods0.000description1
- 230000004936stimulating effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000description1
- 230000000451tissue damageEffects0.000description1
- 231100000827tissue damageToxicity0.000description1
- 230000017423tissue regenerationEffects0.000description1
- 238000011282treatmentMethods0.000description1
- 210000000626ureterAnatomy0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M27/00—Drainage appliance for wounds or the like, i.e. wound drains, implanted drains
- A61M27/002—Implant devices for drainage of body fluids from one part of the body to another
- A61M27/008—Implant devices for drainage of body fluids from one part of the body to another pre-shaped, for use in the urethral or ureteral tract
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Otolaryngology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Anesthesiology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
- Media Introduction/Drainage Providing Device (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本实用新型涉及医疗器械技术领域,具体地指一种抑制复发性狭窄刺激症状及结石的输尿管支架。The utility model relates to the technical field of medical devices, in particular to a ureteral stent for inhibiting recurrent stenosis irritation symptoms and calculi.
背景技术Background technique
输尿管狭窄患者术中须先利用球囊扩张狭窄部位,再将双猪尾支架植入输尿管中。球囊扩张对输尿管组织产生的刺激效应是诱发术后再狭窄的原因之一。碎石等手术采用的输尿管镜侵入造成的输尿管组织损伤也是引起术后再狭窄的重要原因。患者植入双猪尾支架后的组织修复初期阶段和支架有效服役期内往往无法抑制瘢痕组织形成,使得复发性狭窄高发。同时,双猪尾支架两端分别置于肾脏和膀胱中,长时间与尿液接触故而易形成结石。结石堵塞输尿管支架及由结石引发的疼痛也是影响支架使用寿命的重要原因。实用新型专利CN204033851U“预防输尿管狭窄的支架”给出了表面涂有缓释抗组织增生药物层的输尿管支架,该种支架在植入前期对预防狭窄具有一定作用,但一旦药物完全释放,便无抑制能力,且无法保证药物释放期间支架端头无结石堵塞情况。因此,需设计一种抑制复发性狭窄刺激症状及结石的输尿管支架。In patients with ureteral stenosis, a balloon must be used to dilate the stenotic site, and then a double pigtail stent is implanted into the ureter. The stimulating effect of balloon dilation on ureteral tissue is one of the reasons for inducing postoperative restenosis. The ureteral tissue damage caused by the invasion of ureteroscopes used in lithotripsy and other operations is also an important cause of postoperative restenosis. In the initial stage of tissue repair after implantation of double pigtail stents and the effective service period of stents, the formation of scar tissue is often unable to be inhibited, resulting in a high incidence of recurrent stenosis. At the same time, the two ends of the double pigtail stent are placed in the kidney and the bladder, respectively, and it is easy to form stones in contact with urine for a long time. Stone blockage of ureteral stents and pain caused by stones are also important factors affecting the service life of stents. The utility model patent CN204033851U "Stand for preventing ureteral stenosis" provides a ureteral stent coated with a slow-release anti-proliferative drug layer on the surface. This stent has a certain effect on preventing stenosis in the early stage of implantation, but once the drug is completely released, there is no Inhibition ability, and there is no guarantee that the stent tip will not be blocked by stones during drug release. Therefore, it is necessary to design a ureteral stent that suppresses the symptoms of recurrent stenotic irritation and calculi.
实用新型内容Utility model content
针对上述现有技术存在的缺陷,本实用新型提供了一种持续抑制复发性狭窄和结石的输尿管支架。Aiming at the above-mentioned defects of the prior art, the present invention provides a ureteral stent that continuously suppresses recurrent stenosis and calculi.
本实用新型的技术方案是:The technical scheme of the present utility model is:
一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架,包括支架本体;所述支架本体外依次由内至外设置有载铜仿生涂层和缓释药物层;所述缓释药物层包括缓释药物抗结石涂层和缓释药物抗狭窄涂层;A stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end calculi, comprising a stent body; the stent body is provided with a copper-loaded bionic coating and a sustained-release drug layer in sequence from the inside to the outside; the sustained-release drug layer includes a sustained-release drug Anti-calculus coating and slow-release drug anti-stenosis coating;
所述支架本体分为端部、重叠部及中间部,中间部位于支架本体的中间位置,端部位于支架本体的两端位置,重叠部位于端部与中间部之间;其中,端部设置缓释药物抗结石涂层,重叠部设置缓释药物抗结石涂层和缓释药物抗狭窄涂层,中间部设置缓释药物抗狭窄涂层。The bracket body is divided into an end part, an overlapping part and a middle part, the middle part is located at the middle position of the bracket body, the end part is located at the two ends of the bracket body, and the overlapping part is located between the end part and the middle part; A sustained-release drug anti-calculus coating is provided, the overlapping portion is provided with a sustained-release drug anti-calculus coating and a sustained-release drug anti-stenosis coating, and the intermediate portion is provided with a sustained-release drug anti-stenosis coating.
端部为环形结构。The end is a ring structure.
所述重叠部的长度为1-5厘米。The length of the overlapping portion is 1-5 cm.
缓释药物抗狭窄涂层和缓释药物抗结石涂层由内至外依次设置重叠部上。The slow-release drug anti-stenosis coating and the slow-release drug anti-calculus coating are sequentially arranged on the overlapping portion from the inside to the outside.
所述缓释药物层厚度为10-30μm。The thickness of the slow-release drug layer is 10-30 μm.
所述载铜仿生涂层是不可降解的,是通过将支架本体在盐酸多巴胺溶液中反应后得到载有聚多巴胺的支架,再与浓度为0.5-5wt.%的氯化铜或硫酸铜溶液接枝反应得到载有铜的仿生涂层结构。The copper-loaded bionic coating is non-degradable, and is obtained by reacting the stent body in a dopamine hydrochloride solution to obtain a polydopamine-loaded stent, and then connecting it with a copper chloride or copper sulfate solution with a concentration of 0.5-5wt.%. The branch reaction resulted in a copper-loaded biomimetic coating structure.
优选地,将肝素钠溶于生理盐水中,得到含有肝素的药物溶液,将载有仿生涂层结构的支架两端环状部位与肝素溶液反应,得到端部载有肝素的抗结石支架结构。Preferably, sodium heparin is dissolved in physiological saline to obtain a drug solution containing heparin, and the annular parts at both ends of the stent carrying the biomimetic coating structure are reacted with the heparin solution to obtain an anti-calculus stent structure carrying heparin at the ends.
进一步优选地,将肝素-壳聚糖溶于有机溶剂中,所述肝素-壳聚糖浓度为1-3wt.%;所述肝素与壳聚糖比例为1:5-1:1;采用超声雾化喷涂法制备端部载有肝素的抗结石支架结构。Further preferably, heparin-chitosan is dissolved in an organic solvent, and the concentration of heparin-chitosan is 1-3 wt.%; the ratio of heparin and chitosan is 1:5-1:1; ultrasonic waves are used. Heparin-loaded anti-calculus scaffolds were prepared by atomization spraying.
所述制备缓释药物抗狭窄涂层溶液是紫杉醇-聚乳酸-丙酮,所述紫杉醇-聚乳酸浓度为0.5-5wt.%;所述紫杉醇与聚乳酸比例为1:5-1:1。The anti-stenosis coating solution for preparing a sustained-release drug is paclitaxel-polylactic acid-acetone, and the concentration of the paclitaxel-polylactic acid is 0.5-5 wt.%; the ratio of the paclitaxel and the polylactic acid is 1:5-1:1.
所述可降解聚合物包括但不限于聚乳酸PLA、聚己内酯PCL、聚丙交酯-聚乙交酯共聚物PLGA、聚丙交酯-聚己内酯共聚物PLCL、聚三亚甲基聚碳酸酯PTMC、聚酸酐中的一种或几种混合物。The degradable polymers include but are not limited to polylactic acid PLA, polycaprolactone PCL, polylactide-polyglycolide copolymer PLGA, polylactide-polycaprolactone copolymer PLCL, polytrimethylene polycarbonate One or several mixtures of ester PTMC and polyanhydride.
所述溶剂为丙酮或丙酮与二氯甲烷、氯仿等混合溶剂。The solvent is acetone or a mixed solvent of acetone and dichloromethane, chloroform and the like.
所述可降解聚合物溶液涂覆方法包括但不限于超声雾化喷涂,表面浸涂法,旋转涂覆法中的一种或几种。The degradable polymer solution coating method includes, but is not limited to, one or more of ultrasonic atomization spraying, surface dip coating, and spin coating.
所述涂层制备方法超声雾化喷涂法,溶液质量浓度为0.5-5.0%,温度为室温,环境湿度为20-70%,溶液流速0.01-1.0mL/min,超声功率0.6-1W。The coating preparation method is an ultrasonic atomization spraying method, the mass concentration of the solution is 0.5-5.0%, the temperature is room temperature, the ambient humidity is 20-70%, the solution flow rate is 0.01-1.0mL/min, and the ultrasonic power is 0.6-1W.
所述输尿管支架本体为金属输尿管支架或高分子输尿管支架。The ureteral stent body is a metal ureteral stent or a polymer ureteral stent.
本实用新型的优点和效果在于延长临床中输尿管支架的服役寿命,减少输尿管植入引发的相关刺激症状,尤其针对输尿管狭窄患者或手术中由器械损伤引发的输尿管损伤患者。通过药物控制支架植入初期的复发性狭窄和药物释放完全后载铜涂层长期抑制复发性狭窄从而实现支架植入后刺激症状减少。同时,支架的两个端头置于肾脏和膀胱中,长期与尿液接触,是结石形成的高发部位,肝素涂层和载铜仿生涂层共同作用可有效地减少结石形成。支架端部环状结构与中间段交界位置在体内与肾脏和膀胱频繁摩擦,输尿管支架对周围组织产生的刺激也易引发结石形成,因此,在交界部位须进行肝素涂层与抗狭窄涂层的重叠处理,以减少不同刺激症状。The advantages and effects of the utility model lie in prolonging the service life of the ureteral stent in clinical practice and reducing the related irritation symptoms caused by ureteral implantation, especially for patients with ureteral stenosis or ureteral injury caused by instrument damage during surgery. By controlling the recurrent stenosis at the initial stage of stent implantation with drugs and the long-term inhibition of recurrent stenosis by the copper-loaded coating after complete drug release, the irritation symptoms after stent implantation can be reduced. At the same time, the two ends of the stent are placed in the kidney and bladder, which are in contact with urine for a long time, and are the high-incidence sites of stone formation. The combination of heparin coating and copper-loaded bionic coating can effectively reduce stone formation. The junction between the annular structure at the end of the stent and the middle segment frequently rubs against the kidneys and bladder in vivo, and the stimulation of the surrounding tissue by the ureteral stent can also easily lead to stone formation. Therefore, heparin coating and anti-stenosis coating must be applied at the junction. Overlap treatments to reduce symptoms of different irritations.
附图说明Description of drawings
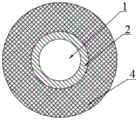
图1为本实用新型端部结构层示意图。Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the end structure layer of the present invention.
图2为本实用新型重叠部结构层示意图。FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the structure layer of the overlapping portion of the present invention.
图3为本实用新型中间部结构层示意图。FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of the structure layer of the middle part of the present invention.
图4为本实用新型支架架构示意图。FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of the structure of the bracket of the present invention.
附图标记:支架本体-1;端部-11;重叠部-12;中间部-13;载铜仿生涂层-2;缓释药物抗结石涂层-3;缓释药物抗狭窄涂层-4。Reference numerals: stent body-1; end part-11; overlapping part-12; middle part-13; copper-loaded biomimetic coating-2; sustained-release drug anti-calculus coating-3; sustained-release drug anti-stenosis coating- 4.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
结合附图1-4和具体实施例进一步说明本实用新型。The present utility model is further described with reference to the accompanying drawings 1-4 and specific embodiments.
实施例1:Example 1:
一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架制备:称取20mg盐酸多巴胺,溶于10ml配制好的pH=6.0的PBS溶液中,获得浓度为2mg/ml的多巴胺溶液。称取1mg氯化铜粉末溶于10ml生理盐水中,获得氯化铜质量浓度为1mg/ml的溶液,并用盐酸将其调至pH=5.0。将输尿管支架本体1材料与多巴胺溶液于4℃条件下,避光反应24h。再将所得支架本体1与氯化铜溶液反应1h后得到有载铜仿生涂层2的输尿管支架。Preparation of a stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end stones: weigh 20 mg of dopamine hydrochloride, dissolve it in 10 ml of a prepared PBS solution with pH=6.0, and obtain a dopamine solution with a concentration of 2 mg/ml. 1 mg of cupric chloride powder was weighed and dissolved in 10 ml of physiological saline to obtain a solution with a mass concentration of cupric chloride of 1 mg/ml, which was adjusted to pH=5.0 with hydrochloric acid. The ureteral stent body 1 material and the dopamine solution were reacted at 4°C in the dark for 24h. The obtained stent body 1 is then reacted with a copper chloride solution for 1 hour to obtain a ureteral stent with a copper-loaded bionic coating 2 .
具体地,一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架,包括支架本体1,所述支架本体1外设置有载铜仿生涂层2。Specifically, a stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end stones includes a stent body 1, and a copper-loaded bionic coating 2 is provided on the outside of the stent body 1.
实施例2:Example 2:
一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架制备:载铜仿生涂层2制备方法同实施例1。Preparation of a stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end stones: the preparation method of copper-loaded biomimetic coating 2 is the same as that of Example 1.
依照实施例1配制浓度为2mg/ml的多巴胺溶液。称取9mg肝素钠溶于10ml生理盐水中,pH值调为7.0,获得肝素钠质量浓度为1mg/ml的溶液。将载有载铜仿生涂层的输尿管支架的两个端部11分别浸入肝素钠溶液中5cm,在37℃恒温箱中反应1h,得到有缓释药物抗结石涂层3的输尿管支架。Dopamine solution at a concentration of 2 mg/ml was prepared according to Example 1. 9 mg of heparin sodium was weighed and dissolved in 10 ml of physiological saline, and the pH value was adjusted to 7.0 to obtain a solution with a mass concentration of heparin sodium of 1 mg/ml. The two
具体地,一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架,包括支架本体1,所述支架本体外设置有载铜仿生涂层2。所述支架本体1分为端部11及中间部13,端部11位于支架本体1的两端位置,且设置缓释药物抗结石涂层3。Specifically, a stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end stones includes a stent body 1, and a copper-loaded bionic coating 2 is provided on the outside of the stent body. The stent body 1 is divided into an
实施例3:Example 3:
一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架制备:载铜仿生涂层2制备方法同实施例1。Preparation of a stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end stones: the preparation method of copper-loaded biomimetic coating 2 is the same as that of Example 1.
称取0.3g壳聚糖和0.15g肝素钠,搅拌溶于10ml乙酸乙酯中,所得溶液采用超声雾化法喷涂于内层输尿管支架两端环状结构处,喷涂位置分别距端部3cm处。超声雾化喷涂参数为:溶液流速0.08ml/min,超声功率0.8W,喷涂环境湿度50%,得到有缓释药物抗结石涂层3的输尿管支架。Weigh 0.3 g of chitosan and 0.15 g of sodium heparin, stir and dissolve in 10 ml of ethyl acetate, and the obtained solution is sprayed on the annular structures at both ends of the inner ureteral stent by ultrasonic atomization, and the spraying positions are respectively 3 cm away from the ends. . The parameters of ultrasonic atomization spraying are: solution flow rate 0.08ml/min, ultrasonic power 0.8W, spraying environment humidity 50%, to obtain a ureteral stent with slow-release drug
具体地,一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架,包括支架本体1,所述支架本体1外设置有载铜仿生涂层2。所述支架本体1分为端部11及中间部13,端部11位于支架本体1的两端位置,且设置缓释药物抗结石涂层3。Specifically, a stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end calculi includes a stent body 1 , and a copper-loaded bionic coating 2 is provided outside the stent body 1 . The stent body 1 is divided into an
实施例4:Example 4:
一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架制备:载铜仿生涂层2制备方法及缓释药物抗结石涂层3制备方法同实施例3。Preparation of a stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end calculi: the preparation method of the copper-loaded bionic coating 2 and the preparation method of the sustained-release
称取0.15gPLGA和0.15g紫杉醇,搅拌溶于10ml丙酮中,所得溶液采用超声雾化法喷涂于中层输尿管支架中间段处表面,喷涂距离为距两端2cm处。超声雾化喷涂参数为:溶液流速0.05ml/min,超声功率0.78W,喷涂环境湿度30%,得到有缓释药物抗结石涂层3和缓释药物抗狭窄涂层4的输尿管支架。Weigh 0.15g PLGA and 0.15g paclitaxel, stir and dissolve in 10ml acetone, and the obtained solution is sprayed on the surface of the middle section of the middle ureteral stent by ultrasonic atomization, and the spraying distance is 2cm from both ends. The parameters of ultrasonic atomization spraying are: solution flow rate 0.05ml/min, ultrasonic power 0.78W, spraying environment humidity 30%, to obtain ureteral stent with slow-release
具体地,一种预防输尿管再狭窄及端部结石的支架,包括支架本体1,所述支架本体1外依次由内至外设置有载铜仿生涂层2和缓释药物层;所述缓释药物层包括缓释药物抗结石涂层3和缓释药物抗狭窄涂层4;Specifically, a stent for preventing ureteral restenosis and end calculi includes a stent body 1, and the stent body 1 is provided with a copper-loaded bionic coating 2 and a sustained-release drug layer sequentially from the inside to the outside; the sustained-release The drug layer includes a sustained-release
所述支架本体1分为端部11、重叠部12及中间部13,中间部13位于支架本体1的中心位置,端部11位于支架本体1的两端位置,重叠部12位于端部11与中间部13之间;其中,端部11设置缓释药物抗结石涂层3,重叠部12设置缓释药物抗结石涂层3和缓释药物抗狭窄涂层4,中间部13设置缓释药物抗狭窄涂层4。The bracket body 1 is divided into an
端部11为支架本体1两端为外侧的环形结构。The
所述重叠部12的长度为1-5厘米。The length of the overlapping
缓释药物抗狭窄涂层4和缓释药物抗结石涂层3由内至外依次设置重叠部12上。The sustained-release
本实用新型未尽事宜为公知技术。Matters not covered in the present invention are known in the art.
上述实施例只为说明本实用新型的技术构思及特点,其目的在于让熟悉此项技术的人士能够了解本实用新型的内容并据以实施,并不能以此限制本实用新型的保护范围。凡根据本实用新型精神实质所作的等效变化或修饰,都应涵盖在本实用新型的保护范围之内。The above-mentioned embodiments are only to illustrate the technical concept and characteristics of the present invention, and the purpose thereof is to enable those who are familiar with the technology to understand the content of the present invention and implement accordingly, and cannot limit the protection scope of the present invention with this. All equivalent changes or modifications made according to the spirit of the present invention shall be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201922058677.1UCN211911903U (en) | 2019-11-26 | 2019-11-26 | A ureteral stent for inhibiting recurrent stenotic irritation and calculi |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201922058677.1UCN211911903U (en) | 2019-11-26 | 2019-11-26 | A ureteral stent for inhibiting recurrent stenotic irritation and calculi |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN211911903Utrue CN211911903U (en) | 2020-11-13 |
Family
ID=73319447
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201922058677.1UActiveCN211911903U (en) | 2019-11-26 | 2019-11-26 | A ureteral stent for inhibiting recurrent stenotic irritation and calculi |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN211911903U (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113081416A (en)* | 2021-02-25 | 2021-07-09 | 中国人民解放军北部战区总医院 | Urinary system support |
| CN115970069A (en)* | 2022-12-13 | 2023-04-18 | 南通大学附属医院 | Preparation method of ureteral stent tube carrying pirfenidone nanoparticle composite coating |
- 2019
- 2019-11-26CNCN201922058677.1Upatent/CN211911903U/enactiveActive
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113081416A (en)* | 2021-02-25 | 2021-07-09 | 中国人民解放军北部战区总医院 | Urinary system support |
| CN115970069A (en)* | 2022-12-13 | 2023-04-18 | 南通大学附属医院 | Preparation method of ureteral stent tube carrying pirfenidone nanoparticle composite coating |
| CN115970069B (en)* | 2022-12-13 | 2024-09-24 | 南通大学附属医院 | Preparation method of composite coating ureteral stent tube carrying pirfenidone nanoparticles |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Ghimire et al. | Initial evidence for the return of coronary vasoreactivity following the absorption of bioabsorbable magnesium alloy coronary stents | |
| US5980566A (en) | Vascular and endoluminal stents with iridium oxide coating | |
| CN103316382B (en) | Protection-sleeve-carrying paclitaxel drug balloon and preparation method thereof | |
| JP4371653B2 (en) | Implantable medical device | |
| US9468746B2 (en) | Systems and methods for local bioactive material delivery | |
| TW200404527A (en) | Method and apparatus for treating vulnerable coronary plaques using drug-eluting stents | |
| CN101862233A (en) | The method of drug-delivery endovascular stent and treatment restenosis | |
| JP5329435B2 (en) | Coronary stent with asymmetric drug release controlled coating | |
| CN102048602B (en) | Preparation method of meshy degradable blood vessel stent | |
| US8709465B2 (en) | Diazeniumdiolated phosphorylcholine polymers for nitric oxide release | |
| CN105833358B (en) | A kind of intracranial drug-eluting stent system and preparation method thereof | |
| CN211911903U (en) | A ureteral stent for inhibiting recurrent stenotic irritation and calculi | |
| CN108742959A (en) | Blood vessel saccule, saccule support drug release device and drug release method thereof | |
| CN105457105A (en) | Novel developable magnesium alloy intravascular stent | |
| WO2004064910A1 (en) | Indwelling stent | |
| Park et al. | Bioreducible polymer–delivered siRNA targeting MMP-9: suppression of granulation tissue formation after bare metallic stent placement in a rat urethral model | |
| CN101239216A (en) | Novel sacculus dilating catheter | |
| US20150335794A1 (en) | Smart coating for implantable devices | |
| US20150209483A1 (en) | Bioabsorbable medical devices and methods of use thereof | |
| CN106890368A (en) | For the ureter bracket and preparation method of tumour targeted therapy | |
| WO2018059207A1 (en) | New use of amlexanox | |
| JP2015154925A (en) | Stent excellent in corrosion resistance | |
| CN100435880C (en) | Medicament elution interventional medical apparatus and preparing method thereof | |
| US20120121682A1 (en) | cRGD PEPTIDE DERIVATIVE AND ITS MANUFACTURE, AND IMPLANT HAVING A COATING CONTAINING A cRGD PEPTIDE DERIVATIVE | |
| CN205459229U (en) | Drug coating metal air flue support |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |